Advertisement

A conceptual framework for zero waste management in Bangladesh
- Original Paper
- Published: 06 April 2022
- Volume 20 , pages 1887–1904, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- F. Ahmed ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8737-8142 1 ,
- S. Hasan 2 ,
- M. S. Rana 3 &
- N. Sharmin 4
1471 Accesses
12 Citations
Explore all metrics
The rapid expansion of industrialization, urbanization, and the influx of migrant citizens into the cities has become a cause of concern for huge waste generation in Bangladesh. These wastes include solid, and liquid contaminated with chemicals, food waste, ago-waste etc. generated from multiple sources have been frequently dumped in open landfills, causing environmental degradation in the urban areas. This indiscriminate dumping of waste in the open places reveals the poor waste management capability of the city’s authorities. Thus soil, air and water pollution is common phenomena in the most of the cities in Bangladesh. The main challenge is the severe land scarcity. It has dense highly population which causing more than 7000 metric ton waste generating per day only from the Capital Dhaka city. Therefore, this study aims to formulate a conceptual framework to facilitate a zero-waste management initiative in Bangladesh through analyzing an extensive existing study available in the research domain. It is expected that the application of the proposed waste management framework will inspire a number of entrepreneurs to involve themselves in waste recycling initiatives with the direct interference of the municipalities and the government’s concerned ministries. Lastly this research amplifies the policy recommendations for the policymakers of Bangladesh which will enable them to manage zero waste management in Bangladesh. However, this type of research not done before in Bangladesh that can be helpful for existing literatures for further research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
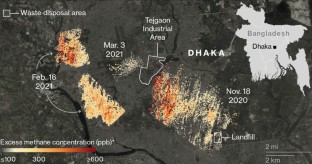
Source: GHGS at; Satellite Image via Bing Maps; Bloomberg)
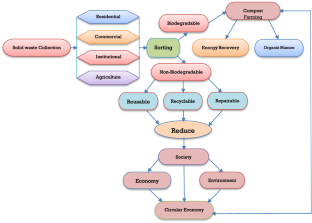
Source: Authors)

Source: Waste Concern 2014
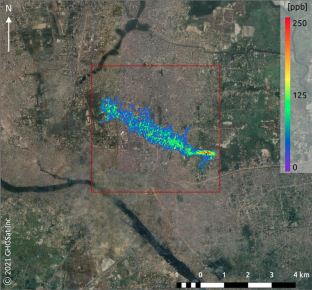
Source: Google Maps; GHGSat Inc.; Bloomberg)
Similar content being viewed by others

Municipal Waste Management in India: A Critical Review of Disposal System and Model Implementation
Addressing sustainability through waste management: a perspective from higher education institutions in Southeast Asia

Understanding Waste Flow in Malaysian Cities for Sustainable Waste Management
Abbas II, Nai’ya R, Arigbede YA (2011) Use of remote sensing and GIS in effective and efficient solid waste management planning (a case study of Samaru, Zaria, Nigeria). Res J Earth Planet Stud 1(2):046–052
Google Scholar
Abedin MA, Jahiruddin M (2015) Waste generation and management in Bangladesh: an overview. Asian J Med Biol Res 1(1):114–120
Article Google Scholar
Ahsan A, Alamgir M, El-Sergany MM, Shams S, Rowshon MK, Daud NN (2014) Assessment of municipal solid waste management system in a developing country. Chin J Eng 2014(12a):1–11
Alam MNI, Ahmed W, Badhon SM (2018) Feasibility of waste to energy conversion in Bangladesh (Doctoral dissertation)
Aliani HA (2012) Pro Poor solid waste management-For secondary cities and small towns in Asia and Pacific. Sustainable Urban Development Unit, ESCAP
Ashikuzzaman M, Howlader MH (2020) Sustainable solid waste management in bangladesh: issues and challenges. In: Pariatamby A, Hamid FS, Bhatti MS (eds) Sustainable waste management challenges in developing countries. IGI Global, pp 35–55
Chapter Google Scholar
Statistics B (2018) Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) Statistics and informatics division, ministry of planning. www.bbs.gov.bd . (Accessed 9 November 2019).
Balasubramanian D, Kamaraj S, Krishnamoorthy R (2020) Synthesis of biodiesel from waste cooking oil by alkali doped calcinated waste egg shell powder catalyst and optimization of process parameters to improve biodiesel conversion (No. 2020-01-0341). SAE Technical Paper
Barrett J, Scott K (2012) Link between climate change mitigation and resource efficiency: a UK case study. Glob Environ Chang 22(1):299–307
Bartl A (2011) Barriers towards achieving a zero waste society. Waste Manage 12(31):2369–2370
Baul TK, Sarker A, Nath TK (2021) Restaurants’ waste in Chittagong city, Bangladesh: current management, awareness on environmental hazard and perception towards potential uses. J Clean Prod 292:126073
BBS (Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics) (2017) Bangladesh Economic Review. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Dhaka
Bhuiyan SH (2010) A crisis in governance: Urban solid waste management in Bangladesh. Habitat Int 34(1):125–133
Cheng H, Hu Y (2010) Municipal solid waste (MSW) as a renewable source of energy: current and future practices in China. Biores Technol 101(11):3816–3824
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chiemchaisri C, Visvanathan C (2008) Greenhouse gas emission potential of the municipal solid waste disposal sites in Thailand. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 58(5):629–635
Concern W (2014) Bangladesh waste database 2014. Dhaka: Waste Concern. Retrieved June, 29, 2019
Connett P (2013) The zero waste solution: untrashing the planet one community at a time. Chelsea Green Publishing
Concern W (2016) Prospects of plastics waste recycling in Bangladesh. Prospects of Plastics Waste Recycling in Bangladesh
Cristina G, Camelin E, Pugliese M, Tommasi T, Fino D (2019) Evaluation of anaerobic digestates from sewage sludge as a potential solution for improvement of soil fertility. Waste Manage 99:122–134
Curran T, Williams ID (2012) A zero waste vision for industrial networks in Europe. J Hazard Mater 207:3–7
Enayetullah I, Sinha AHMM (2000) A study on resource recovery from solid waste in Khulna City. The World Bank, Dhaka, Waste and Sanitation Program in South Asia
Franco-García ML, Carpio-Aguilar JC, Bressers H (2019) Towards zero waste, circular economy boost: waste to resources. In: Franco-García ML, Carpio-Aguilar JC, Bressers H (eds) Towards zero waste. Springer, Cham, pp 1–8
Franks DM, Boger DV, Côte CM, Mulligan DR (2011) Sustainable development principles for the disposal of mining and mineral processing wastes. Resour Policy 36(2):114–122
Gharfalkar M, Court R, Campbell C, Ali Z, Hillier G (2015) Analysis of waste hierarchy in the European waste directive 2008/98/EC. Waste Manage 39:305–313
Ghinea C, Gavrilescu M (2019) Solid waste management for circular economy: challenges and opportunities in Romania-the case study of Iasi County. In: Franco-García ML, Carpio-Aguilar JC, Bressers H (eds) Towards zero waste. Springer, Cham, pp 25–60
Greyson J (2007) An economic instrument for zero waste, economic growth and sustainability. J Clean Prod 15(13–14):1382–1390
Halder PK, Paul N, Hoque ME, Hoque AM, Parvez MS, Rahman MH, Ali M (2014) Municipal solid waste and its management in Rajshahi City, Bangladesh: a source of energy. Int J Renew Energy Res 4(1):168–175
Hoang NH, Fogarassy C (2020) Sustainability evaluation of municipal solid waste management system for Hanoi (Vietnam)—Why to choose the ‘Waste-to-Energy’ concept. Sustainability 12(3):1085
Hoornweg D, Sugar L, Trejos Gómez CL (2011) Cities and greenhouse gas emissions: moving forward. Environ Urban 23(1):207–227
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P, Kennedy C (2015) Peak waste: When is it likely to occur? J Ind Ecol 19(1):117–128
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2012) What a waste: a global review of solid waste management
Hossain ABMS, Boyce AN, Salleh A, Chandran S (2010) Impacts of alcohol type, ratio and stirring time on the biodiesel production from waste canola oil. Afr J Agric Res 5(14):1851–1859
Islam KN (2017) Greenhouse gas footprint and the carbon flow associated with different solid waste management strategy for urban metabolism in Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 580:755–769
Islam R, Nazifa TH, Yuniarto A, Uddin AS, Salmiati S, Shahid S (2019) An empirical study of construction and demolition waste generation and implication of recycling. Waste Manage 95:10–21
Jamal T, Zahid M, Martins JM, Mata MN, Rahman HU, Mata PN (2021) Perceived green human resource management practices and corporate sustainability: multigroup Analysis and major industries perspectives. Sustainability 13(6):3045
Jin J, Wang Z, Ran S (2006) Solid waste management in Macao: practices and challenges. Waste Manage 26(9):1045–1051
Johari A, Ahmed SI, Hashim H, Alkali H, Ramli M (2012a) Economic and environmental benefits of landfill gas from municipal solid waste in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(5):2907–2912
Johari A, Hashim H, Mat R, Alias H, Hassim M, Rozzainee M (2012b) Generalization, formulation and heat contents of simulated MSW with high moisture content. J Eng Sci Technol 7(6):701–710
Kabir MR (2015) Municipal solid waste management system: a study on Dhaka north and South City corporations. J Bangladesh Inst Plan ISSN 2075:9363
Kassim SM, Ali M (2006) Solid waste collection by the private sector: Households’ perspective—findings from a study in Dar es Salaam city, Tanzania. Habitat Int 30(4):769–780
Kaza S, Yao L, Bhada-Tata P, Van Woerden F (2018) What a waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. World Bank Publications
Khan KS, Joergensen RG (2009) Changes in microbial biomass and P fractions in biogenic household waste compost amended with inorganic P fertilizers. Biores Technol 100(1):303–309
Kormoker T, Proshad R, Khan MM (2017) Analysis of water quality in urban water supply system of Bangladesh. J Env Analyt Toxicol 7(4):2161–2525
Malav LC, Yadav KK, Gupta N, Kumar S, Sharma GK, Krishnan S, Bach QV (2020) A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. J Clean Prod 277:123227
Matete N, Trois C (2008) Towards zero waste in emerging countries–a South African experience. Waste Manage 28(8):1480–1492
Mohammedshum AA, Gebresilassiea MA, Rulindaa CM, Kahsaya GH, Tesfay MS (2014) Application of GIS and Remote Sensing in effective solid waste disposal site selection in Wukro town, Tigray, Ethiopia. Int Arch Photogram Rem Sens Spatial Inform Sci 2:115–119
Moniruzzaman SM, Bari QH, Fukuhara T (2011) Recycling practices of solid waste in Khulna city, Bangladesh. J Solid Waste Technol Manag 37(1):1–15
Mujeri MK, Chowdhury TT, Shahana S (2013) Energy Subsidies in Bangladesh: a profile of groups vulnerable to reform. Bangladesh Institute of Development Studies
Murphy S, Pincetl S (2013) Zero waste in Los Angeles: Is the emperor wearing any clothes? Resour Conserv Recycl 81:40–51
Nasrin F (2016) Waste management in Bangladesh: current situation and suggestions for action. Int Res J Soc Sci 5(10):36–42
Nizar M, Munir E, Munawar E (2018) Implementation of zero waste concept in waste management of Banda Aceh City. J Phys Conf Series 1116(5):052045
Pfammatter R, Schertenleib R (1996) Non-Governmental refuse collection in low–income urban areas Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science and Technology. SANDEC. 96pp
Phillips PS, Tudor T, Bird H, Bates M (2011) A critical review of a key waste strategy initiative in England: zero waste places projects 2008–2009. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(3):335–343
Saji A, Shahana S, Subahan S, Thasneem A, Basheerudheen A (2019) Cost effective residential building using plastic bottles-a home for the future
Scarlat N, Motola V, Dallemand JF, Monforti-Ferrario F, Mofor L (2015) Evaluation of energy potential of municipal solid waste from African urban areas. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 50:1269–1286
Sewak A, Kim J, Rundle-Thiele S, Deshpande S (2021b) Influencing household-level waste-sorting and composting behaviour: What works? A systematic review (1995–2020) of waste management interventions. Waste Manag Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X20985608
Shahbazi S, Wiktorsson M, Kurdve M, Jönsson C, Bjelkemyr M (2016) Material efficiency in manufacturing: Swedish evidence on potential, barriers and strategies. J Clean Prod 127:438–450
Shams S, Sahu JN, Rahman SS, Ahsan A (2017) Sustainable waste management policy in Bangladesh for reduction of greenhouse gases. Sustain Cities Soc 33:18–26
Shum PL, Kok HK, Maingard J, Schembri M, Bañez RMF, Van Damme V, Asadi H (2020) Environmental sustainability in neurointerventional procedures: a waste audit. J Neurointerventional Surg 12(11):1053–1057
Song Q, Li J, Zeng X (2015) Minimizing the increasing solid waste through zero waste strategy. J Clean Prod 104:199–210
Sultana A, Alam MM, Middya TR, Mandal D (2018) A pyroelectric generator as a self-powered temperature sensor for sustainable thermal energy harvesting from waste heat and human body heat. Appl Energy 221:299–307
Tsheleza V, Nakin MD, Ndhleve S, Kabiti HM, Musampa CM (2019) Vulnerability of growing cities to solid waste-related environmental hazards: the case of Mthatha, South Africa. Jàmbá J Disaster Risk Stud 11(1):1–10
Van Ewijk S, Stegemann JA (2016) Limitations of the waste hierarchy for achieving absolute reductions in material throughput. J Clean Prod 132:122–128
Yasmin S, Rahman MI (2017) A review of solid waste management practice in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Int J Environ Prot Policy 5(2):19–25
Zaman AU (2014) Measuring waste management performance using the ‘Zero Waste Index’: the case of Adelaide, Australia. J Clean Prod 66:407–419
Zaman AU (2015) A comprehensive review of the development of zero waste management: lessons learned and guidelines. J Clean Prod 91:12–25
Zaman AU (2016) A comprehensive study of the environmental and economic benefits of resource recovery from global waste management systems. J Clean Prod 124:41–50
Zaman AU, Lehmann S (2013) The zero waste index: a performance measurement tool for waste management systems in a ‘zero waste city.’ J Clean Prod 50:123–132
Zaman A, Ahsan T (2019) Zero-Waste Strategy
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Environmental Science, IUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Department of Civil Engineering, IUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Department of Business Policy and Strategy, Faculty of Business and Accountancy, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Department of Chemistry, IUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Corresponding author
Correspondence to F. Ahmed .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
This manuscript doesn’t carry any conflict of interest. It is not involving with any funding project. This is solely self-generated project targeting publication.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: SUNIL Kumar.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ahmed, F., Hasan, S., Rana, M.S. et al. A conceptual framework for zero waste management in Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20 , 1887–1904 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04127-6
Download citation
Received : 30 August 2021
Revised : 12 January 2022
Accepted : 15 March 2022
Published : 06 April 2022
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04127-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Zero-waste management
- Conceptual framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Zero Waste Management Research Paper
Zero Waste management is a program designed to reduce waste in our society. Zero Waste lifestyle is a mission to save the world from waste and recyclable materials.
This lifestyle is an important subject for discussion, which is why Collin Beavan used the subject of Zero Waste lifestyle to facilitate in his re-election in the senate. This way of life has circulated over many regions in the recent times (Colin, 2012). Zero Waste lifestyle has a target of reaching out to people all over the world. The objective of a zero waste lifestyle is to reduce waste on the environment.
Whether rich or poor, zero waste lifestyle will reduce hazards in our enviroment. Some communities have adopted the idea and they are reaping the benefits. San Francisco came all out in 2008 to declare her intentions of having a healthy environment. Authorities at the state level enacted an act to address the issues with waste disposal. The high in the society and lower class citizens were all included in the policy.
Florida also formulate a policy of zero waste lifestyle. The government instituted a committee that looked at various factors that could hinder the success of a zero waste lifestyle. They finally came up with a blueprint, which introduced incentives to residents that adopted a zero waste lifestyle.
There was a massive turnout from all social classes in Florida. The high social class adopted the way of life as they were well informed of the need to have a safe environment. The low-class citizens objected a bit, but were motivated to tag along because of the incentives given to people who accepted with the policy. Today, Florida has an exceptional record for keeping her environment safe. Every social economic class in Florida has adopted the zero waste lifestyle (Khan, Prior, & Islam, 2008).
Zero Waste lifestyle is beneficial to all the socioeconomic classes. Although the rich in the society do not agree with a Zero Waste management, there seems to be headway in achieving a Zero Waste lifestyle. The rich argued that there is little significance in the economy if they adopt a Zero Waste lifestyle. Until the recycle and reuse of products is enforced, a Zero Waste lifestyle will not get the desired recognition.
People from the middle socioeconomic class will adopt a Zero Waste lifestyle because it will help them save cost in every aspect of life. It introduces the technology of re-designing every resource so that it will have an extended lifespan. The ability to use a commodity and then reuse it for another purpose will save them some money.
The San Francisco compact act is a land law set aside by the local authorities in San Francisco to protect the environment from non-degradable waste. The law requires that every resident of San Francisco should manage his/her waste as stipulated by the waste ordinance.
The government in San Francisco has propagated a Zero Waste lifestyle. This has helped in reducing the risk of having waste cover on our environment. They have introduced an incentive policy according to which people would receive cash for recycling their waste products (Lean, 2006). Today, San Francisco is rated 67% of its waste recycle program. Zero waste lifestyle is suitable for every socio- economic class; it requires an individual properly to manage his/her waste. Thus, it is beneficial to every person.
People with high socioeconomic status may accept a Zero Waste lifestyle in that they believe that they could help change the world. There has been an increasing concern with the risks of an unsafe environment. A research survey of US environmental agency projects serious damage to the country’s water supply due to negative effects on the environment.
This means that all the efforts must be done to avert a major crisis in the region. The high social economic class can really influence the society to accept a Zero Waste lifestyle. It is more viable for the high socio-economic class as it members are capable of adopting it (Lean, 2006).
On the other hand, people from low social economic class may not agree with some aspects of a Zero Waste lifestyle due to their economic status. Their low life conditions may really affect while accepting this plan. However, the key to this program is to enact a law that would mandate the entire region on the need to manage the waste.
Just as the authorities of San Francisco and India have formulated a law that stipulates the recycle of waste resources, many other countries can follow their example (Zero waste home, 2010). Zero Waste lifestyle is a practical plan, and its benefit can be seen in our everyday activities.
Finally, many other organizations have a similar program and may believe in the same objectives of a Zero Waste lifestyle. They can come together in facilitating the recycle of every product from the day it was manufactured. Remember that Zero Waste plans imply that any product that does not have an alternative use should not be created in the first place.
Colin,B. (2012) No Impact man: My Speech at Green Party National Convention . Web.
Cooper, E. (2010). The Alternative Kitchen Garden: An A-Z . Hampshire: Permanent Publications.
Dhir, R., Newlands, M. D., & Dyer, T. D. (2003). Sustainable Waste Management . Reston, VA: Thomas Telford.
Lean, G. (2006). Disappearing World: Global Warming Claims Tropical Island . Web.
Zero waste home . (2010). Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 9). Zero Waste Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zero-waste/
"Zero Waste Management." IvyPanda , 9 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/zero-waste/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Zero Waste Management'. 9 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Zero Waste Management." January 9, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zero-waste/.
1. IvyPanda . "Zero Waste Management." January 9, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zero-waste/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Zero Waste Management." January 9, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/zero-waste/.
- Wastewater Reuse in the United Arab Emirates
- Software Reuse Strategies
- Direct and Indirect Potable Reuse
- To Use or not to Reuse: A Case for Recycling
- Living a Zero Waste Lifestyle
- Dell’s Initiative to Recycle Ocean-Bound Plastics
- Zero Waste Principles Applied by Humans
- The Importance of Zero Waste Management
- Building Reuse and Its Environmental Value
- Garbage Sorting in San Francisco - Environmental Study
- Summary and Comparison of Articles; “Hiding in Plain Sight” by Heather Rogers and, “On Dumpster Diving” by Lans Eighner
- Possible Solutions to the Problem of Solid Waste Management Basing on the Comparison of the Situation in the USA and the European Countries
- Identifying of Hazardous Waste and How to Manage It
- Garbage Pollution
- E-Waste Disposal in US

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this context, "all researchers agreed that, the "Zero-Waste" concept is one of the promising and an effective way to solve the waste management & recycling issues. Zero waste approach is to inspire the reshape of resource supply chain, as a result that entire products or by-product (resource materials) can be reused & recycled, and the ...
Zero waste manag ement means the holistic concept of waste management whic h recognizes waste as a. resource produced during the interim phase of the process of resource consumption. Zer o waste ...
This Special Issue aims to gather research papers regarding recent developments and innovation in applying the 'Zero waste' concept to achieve sustainable waste management. ... This research aims to provide a global perspective regarding scientific research on zero-waste management and sustainable consumption by identifying years of ...
The growth of waste generation is a global problem. Developing effective waste management methods is challenging for companies and the government. This research aims to provide a global perspective regarding scientific research on zero-waste management and sustainable consumption by identifying years of evolution, the most relevant and influential keywords, articles, journals, universities ...
In this paper, a qualitative research method was used to analyse previous studies on zero waste. ... Zero waste management should promote economic activities by creating job opportunities and a circular economic society (Lee et al., 2014). Producers play key roles along with waste management service providers in the ZW management system.
waste management In 1973, the 'Zero Waste' term was firstly introduced by Dr Paul Palmer as approach for recovering resources from chemicals (Song et al., 2015). The Zero Waste concept is a prominent sys- ... Brazilian pulp and paper sector. Waste Management & Research 12: 1193-1194. Song Q, Li J and Zeng X (2015) Minimizing the ...
Oliveira A, Navia R (2017) Zero waste bio-refineries: The example of Brazilian pulp and paper sector. Waste Management & Research 12: 1193-1194. Crossref. Google Scholar. Song Q, Li J, Zeng X (2015) Minimizing the increasing solid waste through zero waste strategy.
Solid waste generation has been significantly accelerated by the rapid growth of economy and population worldwide. The traditional waste management focusing on waste utilization and disposal is unable to unravel the continuous depletion of finite natural resources. "Zero waste" as an integrated waste management method to promote waste reduction through a pack of strategies such as cleaner ...
The conservation of natural resources, reduction in waste, and minimization of energy consumption are now the primary focuses of zero waste management. Thus, this study examined the direct impact of green technology on zero waste management. We also explored the significant mediation role of the green supply chain (GSC) in links between green technology and zero waste management. Moreover, we ...
Europe, 2019). The most desirable strategy for achieving zero waste, according to the US EPA materials management hierarchy and the EU Zero Waste Hierarchy, is source reduction and reuse, which requires addressing the system of production and consumption. "Zero Waste" Strategies by Cities and Companies
In this context, " all researchers. agreed that, the "Zero-Waste" concept is one of the promising and an effective way to solve the. waste management & recycling issues. Zero waste approach ...
The solid waste management (SWM) approach for the protection of resources known as "zero waste" (ZW) has become popular in recent years. Waste characterization is the first step to pursuing a comprehensive and sustainable SWM strategy. The aim of this study is to determine the waste characterization and recycling potential of the Istanbul Technical University (Türkiye) Ayazağa Campus ...
With this scope and objectives in mind, this manuscript is organized as follows: Section 1 presents the introduction of this research, followed by Section 2 with a theoretical framework about the concepts or topics: zero-waste management, sustainable consumption, development, and previous bibliometrics analysis.
3.1. Kebijakan Persampahan Nasional dan Banda Aceh. The percentage of organic waste, paper and plastic produced by Banda Aceh were 89.1%; 2.5%; 0.74%. The weight of garbage produced by Banda Aceh City is 86057,64 ton / month and produce carbon emission of 83726,6 ton / month.
It has dense highly population which causing more than 7000 metric ton waste generating per day only from the Capital Dhaka city. Therefore, this study aims to formulate a conceptual framework to facilitate a zero-waste management initiative in Bangladesh through analyzing an extensive existing study available in the research domain.
Table of contents for Waste Management & Research: The Journal for a Sustainable Circular Economy, 41, 3, Mar 01, ... SUBMIT PAPER. Waste Management & Research: The Journal for a Sustainable Circular Economy. ... A zero valent iron (ZVI) enhanced Peroxone process (ZVI/Peroxone) was used to treat biologically treated landfill leachate (BTL). ...
Zero Waste concept is an effective and prominent system to address the solid waste problem and system to motivate the reforming of resource supply chain away from an obsolete style, so that whole products or by-product materials are recycled or reused ( Awasthi et al., 2021 ). For example, by using the Complex Value Optimisation of Resource ...
Global waste continues to grow exponentially, but the "Zero Waste" concept has emerged as one innovative counter-strategy. Japanese waste management relies mostly on incineration, but rural ...
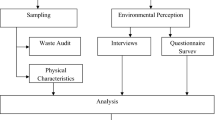
such as Research Papers, Annual Reports, Websites, Journals, Government Websites, Newspapers and an observation of the study area is made to interpret about the various problem and major causes and effect of the waste management. Discussion- Waste management must be accomplished by both waste diversion and commodity reuse. They
Zero Waste Management Research Paper. Exclusively available on IvyPanda. Updated: Jan 9th, 2024. Zero Waste management is a program designed to reduce waste in our society. Zero Waste lifestyle is a mission to save the world from waste and recyclable materials. We will write a custom essay on your topic. 809 writers online.
This article is the first quantitative study focused on contributing a complete overview of the progress of zero-waste management and sustainable consumption, providing a collaborative network of ...
Smart Waste Management (SWM) discusses the waste management process for different types of waste while introducing an intelligent approach to controlling the amount of waste. This paper introduces SWM4.0, which applies Industry4.0 (I4.0) technologies in various related events. First, the paper presents a systematic literature review on the role of I4.0 technologies in SWM activities regarding ...
1.0 Zero Waste. Zero waste is defined here as a concerted effort to minimize waste disposal with an. ultimate goal to avoid it completely. Although it is not possible to a chieve zero waste ...