- United States
- English English

Research leading blockchain use cases
Be inspired by how innovators are transforming their businesses through use cases built on the ibm blockchain platform. you can join an existing blockchain network or work with us to create your own..
Join an existing network Co-create a network with us
Driving auto supply chains forward with blockchain

Until recently, the only way automakers could keep track of the supply chain was through databases and paper trails. That all changed when Renault moved its documentation to blockchain, and invited the rest of the auto industry to join in the digital transformation.
Read the case study
AI and Blockchain help discover and transact IP

IPwe helps companies make better use of their intellectual property. Yet the IP transaction platform saw inefficiencies and a lack of transparency in the ecosystem. With IBM Blockchain and AI, it created a suite of products to increase visibility and flexibility within the patent marketplace.
Sonoco and IBM: Safeguarding the efficacy of lifesaving medications with blockchain

Transporting temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals is no easy task, especially with the global distribution of COVID-19 vaccines. With IBM Blockchain Transparent Supply, the many supply chain partners can communicate and gather reliable data.
Watch video (03:11)
IBM and eProvenance: Preserving the quality and integrity of wine with blockchain

Ensuring the wine you bought in Europe is the exactly what you’re getting in the US. VinAssure is a blockchain-powered platform that supports wine quality and safety, unlocks the supply chain and enhances trust in the cold chain.
Watch video (03:07)
Blockchain use cases
Solution area All Food Trust Platform Services Blockchain Transparent Supply
Industry All Banking & Financial Markets Consumer Cross Border Payments Government Healthcare Insurance Media and Advertising Services Supply Chain Manufacturing Cross Industry
Sort by Default Most Recent Oldest

supply, blockchain-transparent-supply, , , eProvenance, wine,integrity
Watch the video (03:07)

supply,healthcare
supply,healthcare, blockchain-transparent-supply, , , Sonoco, vaccine,medication
Watch the video (03:11)

cross-industry
cross-industry, platform,services, , , IPwe, digital assets,intellectual property,AI,patent
Learn more

manufacturing,supply
manufacturing,supply, platform,services, , , Renault, automotive

banking,supply
Blockchain for invoice reconciliation and dispute resolution
banking,supply, platform,services, , , ibm,
Read the post

Reopening venues with contactless blockchain digital ticketing
media, platform,services, , , True Tickets, ticketing,arsht

How IBM Blockchain technology powers IBM Digital Health Pass
healthcare, platform,services, , , ibm, healthcare,vaccine,watson

Improving the letter of guarantee banking process with blockchain
banking, platform,services, , , ibm, letter-of-guarantee,bank-guarantee,bci,lygon

AAIS: Enabling regulatory compliance and increased data access using blockchain
insurance, platform,services, , , AAIS,
Watch the video (02:00)

ANZ Bank partners with a consortium to transform financial guarantees using IBM Blockchain
banking, platform, , , ANZ Bank,
Watch the video (01:58)

supply,consumer
Farmer Connect and IBM - Connecting coffee growers and consumers with blockchain
supply,consumer, food-trust, , , Farmer Connect, food-supply-chain,traceability
Watch the video (03:03)

supply,government,insurance,services
Coordinating disaster recovery efforts with blockchain
supply,government,insurance,services, platform,services, , , ,

UBS: we.trade offers fast, simple and secure trade transactions based on IBM Blockchain
banking, platform, , , UBS,we.Trade,
Watch the video (02:19)

Protect Pharmaceutical Product Integrity with the Pharmaceutical Utility Network
supply, platform, , , Walmart,Merck,KPMG, drug-supply-chain-security-act

The Vertrax Blockchain is reshaping the oil and gas supply chain with the first multi-cloud deployment of IBM Blockchain Platform
supply, platform,services, , , Vertrax, multi-cloud
Read the case study (629 KB)

Food Trust and Raw Seafoods: Connecting seafood suppliers and distributors with blockchain
supply,consumer, food-trust, , , Raw Seafoods, food-supply-chain,traceability
Watch the video (02:28)

Blockchain helps trace responsibly produced raw materials
supply, platform, , , RCS Global,

TradeLens and Blockchain Technology Supply Chain Demo
supply, platform, , , Tradelens,
Watch the video (03:32)

Diamonds are forever with a secure blockchain - The Everledger story
supply,consumer, platform, , , Everledger,
Watch the video (01:17)

Plastic Bank: Enabling plastic recycling and financial inclusion with IBM Blockchain
banking, platform,services, , , Plastic Bank,
Watch the video (02:06)

Nuarca transforms proxy voting using blockchain
government, platform,services, , , Nuarca, voting

INBLOCK: Improving cryptocurrency security with Blockchain and LinuxONE
banking, platform, , , INBLOCK, security
Watch the video (02:03)

Marsh: Transforming proof of insurance with blockchain
insurance, platform,services, , , Marsh,
Watch the video (01:50)

Helping companies trade seamlessly with IBM Blockchain
banking, platform,services, , , we.Trade,

Carrefour sales boosted by blockchain tracking
supply,consumer, food-trust, , , Carrefour, food-supply-chain,traceability
Learn more (link resides outside ibm.com)

Blockchain for advertising: The new black for media buying
media, platform, , , Mediaocean,

Albertsons Joins IBM Food Trust Blockchain Network To Track Romaine Lettuce From Farm To Store
supply,consumer, food-trust, , , Albertson, food-supply-chain,traceability

IBM and Twiga Foods Introduce Blockchain-Based MicroFinancing for Food Kiosk Owners in Kenya
banking, platform, , , Twiga,

Transform healthcare outcomes with the simplicity of IBM Blockchain
healthcare, platform,services, infographic, , ibm,
See the infographic (188 KB)

insurance,banking
Blockchain in insurance: Five reasons why openIDL will succeed
insurance,banking, platform, , , AAIS,AIG,Standard Charter,Marsh,
Watch the video (04:11)

Building trust and transparency in insurance policies with blockchain
insurance, platform,services, , , AIG,
Watch the video (02:57)

healthcare,government
CDC leverages IBM Blockchain technology for Electronic Health Records
healthcare,government, workshop, video, , CDC,
Watch the video (01:39)

Banks team with IBM for blockchain powered trade finance
banking, platform,services, , , we.trade,
Watch the video (02:44)
No use case match your criteria
What will we solve together?
Join an existing network and take advantage of innovation in your industry or use established networks to build your own. Either way, we have resources ready to help you.
Contact us to learn more
Co-create a network with us
Blockchain technology in financial services: a comprehensive review of the literature
Purpose The purpose of this study is to thoroughly review studies that have used blockchain technology in financial services. This study will help provide a holistic framework that would highlight the current state and challenges of the blockchain in the financial services sector. Design/methodology/approach The objective of this study is to systematically examine and organize the current body of research literature that either quantitatively or qualitatively explored the use of blockchain technology in financial services. The study uses PRISMA-guided systematic review along with bibliometric analysis to achieve the purpose. Findings This study contributes to the existing literature by exploring and analyzing systematic studies available on blockchain with special reference to financial services sector. With blockchain based on five principles, namely, computational logic, peer-to-peer transmission, irreversibility of records, distributed database and transparency with pseudonym has immense potential to unleash and transform the financial service industry. With increasing blockchain-based operations of decentralized banking, insurance, trade finance, financial markets and cryptocurrency market, the subject is rapidly growing and seeking considerable contribution from scholars from around the world. Research limitations/implications This study uses systematic literature review approach, which has its own demerits. Like other studies based on Systematic Literature Review, this study also suffers from a certain bias such as sample selection bias, publication bias, data interpretation and the combination of quantitative and qualitative studies in the population. Further, the adoption and resultant benefits of blockchain have not been empirically tested. Practical implications This study can help policymakers and institutions in determining their future course of action, as it highlights the state of research in the area of blockchain technology and financial services. Originality/value Very few studies have done a comprehensive review of literature on blockchain in financial services.
- Related Documents
The state of play of blockchain technology in the financial services sector: A systematic literature review
Fifa – highlighting the links between global banking and international money laundering.
PurposeThis paper uses the recent (August 2015) FIFA arrests to provide an example of how illicit financial flows are occurring through the formal banking and financial services sector. The purpose of this paper is to explore which elements of anti-money laundering (AML) compliance need to be addressed to strengthen the banking response and reduce the impact of IFFs within the banking sector.Design/methodology/approachThe paper is based on the indictment document currently prepared for the FIFA arrests and the District Court case of Chuck Blazer the FIFA Whistleblower. It uses the banking examples identified in the indictment as typologies of money laundering and wire fraud. Corresponding industry reports on AML compliance are included to determine where the major weaknesses and gaps are across the financial service.FindingsThe main findings from the analysis are that banks still have weak areas within AML compliance. Even recognised red flag areas such as off shore havens, large wire transfers and front companies are still being used. The largest gaps still appear to be due diligence and beneficial ownership information.Research limitations/implicationsThe research topic is very new and emerging topic; therefore, analysis papers and other academic writing on this topic are limited.Practical implicationsThe research paper has identified a number of implications for the banking sector, addressing AML deficiencies, especially the need to consider the source of funds and the need for further enhanced due diligence systems for politically exposed and influential people and the importance of beneficial ownership information.Social implicationsThis paper has implications for the international development and the global banking sector. It will also influence approaches to AML regulation, risk assessment and audit within the broader financial services sector.Originality/valueThe originality of this paper is the link between the emerging issues associated with allegations of bribery and corruption within FIFA and the illicit financial flow implications across the banking sector.
Enhancing brand value using corporate social responsibility initiatives
Purpose This study aims to investigate employees’ perceptions of socially responsible financial services brands in Saudi Arabia. The study also identifies the motives and challenges for Islamic banks for higher involvement in social responsibility initiatives to enhance their brand values. Design/methodology/approach An inductive approach was used in this study to identify the motives and challenges related to corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities. The research design uses a qualitative approach where in-depth interviews were carried out among the employees in the financial services sector in Saudi Arabia. Findings Findings provide insights about how CSR initiatives for financial services brands in a developing and Islamic country are perceived. Results show that the focus of CSR activities is on the attribute of CSR, the magnitude of CSR and attitude towards CSR. Results show two main motives to engage in CSR activities, which are instrumental and ethical motives. The main challenges are related to the government, business, charitable organisations and customers and society. Practical implications Implications exist for how CSR is perceived in a new context and in the financial services industry. Understanding the current perception of CSR from a financial service brand perspective helps policymakers to develop appropriate platforms for financial service providers to become more socially involved. Originality/value The major contribution of this study lies in investigating the CSR perception among the key stakeholder (i.e. the employees) from a brand management perspective in the Saudi Arabian financial services sector. Further, this study shows the main motives and challenges, which local financial service brands face to become socially responsible. The categories of attributes, magnitude and attitudes can be used to enhance brand value in one of the economically advanced countries in the Arabic world, Saudi Arabia. In the first category “attribute”, the perception of socially responsible banks are highlighted, while the elements of CSR, including its dimensions, are emphasised in the second category “magnitude”. The third category “attitude” shows two themes, including stakeholders’ issues and business-related issues.
Association between performance measurement systems and organisational effectiveness
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to investigate the role of performance measurement systems in organisational effectiveness in the context of the financial services sector within a developing country. Design/methodology/approach – Using the mail survey method data were collected from 69 financial institutions operating in Nepal. Multivariate analysis, in particular multiple regression analysis was employed to test the hypotheses. Findings – The results suggest that non-financial measures and feedback are tightly intertwined with organisational effectiveness. While institutions are focused on using the performance measures concerning internal business process perspective, less emphasis is placed on using customer and employee-related performance measures because they are considered less significant to organisational effectiveness. The findings also reveal that strategy-related feedback is considered more critical by management, as opposed to performance and staff. The study also provides evidence that 40.58 per cent of the financial institutions in Nepal had implemented the Balanced Scorecard, which is considered to be high when compared with other developing countries. Practical implications – The findings provide managers with valuable insights pertaining to the role of non-financial performance measures and the importance of feedback in improving organisational effectiveness, which could assist them in (re) aligning their performance measurement practices. Originality/value – The findings of this study contributes to the limited management accounting literature on performance measurement and the impact on organisational effectiveness by providing evidence from the financial services sector within the context of a developing country.

Systematic Literature Review on Application of Blockchain Technology in E-Finance and Financial Services
China's rural middle class will boost consumption.
Subject Household consumption in China. Significance China is the world's second-largest consumer market. The country's middle class possesses significant discretionary spending power and rising incomes have given access to a much more varied shopping basket than ever before, generating profound adjustments in the pattern of consumer demand. Impacts The rural market will be an increasingly important source of consumer demand, even amid accelerated urbanisation. As a rural middle class emerges, rural consumer spending will surge and will also become more sophisticated. Consumption will grow fastest in the services sector. New ways of paying for consumption spending will enable rapid growth of the financial services sector. New geographical drivers of consumption will emerge as lower-tier cities account for more and more of China’s affluent consumers.
Knowledge management: does gender matter? A systematic review of literature
Purpose This paper aims to review for the first time existing research literature about the role of gender in creating, sharing and using knowledge in organizations and proposes a conceptual framework to guide future research directions. Design/methodology/approach Based on the systematic literature review method this study collects, synthesizes and analyses articles related to knowledge management (KM) and gender published in online databases by following a pre-defined review protocol. The paper analyses 41 papers published in peer-reviewed journals. Findings The role of gender in KM has been rarely addressed in KM journals and journals with specific emphasis on gender. The existing literature is fragmented, but existing research suggests that knowledge sharing might be influenced by gender. Based on the analysis and synthesis, a conceptual framework is proposed to guide further research on determining if gender matters in KM. Research limitations/implications Academic researchers should aim to include gender-related variables into their KM research to further explore if gender matters in KM. Practical implications The practical implication suggests that managers and knowledge managers should raise awareness about how stereotypes and gendered expectations about role behaviour affect how knowledge and experiences are created and shared within the organization. Social implications The authors believe that a better understanding of knowledge handling and gendered role expectations at the workplace could also have an impact beyond organizational boundaries. Originality/value The paper presents the first comprehensive systematic literature review of the article published on knowledge creation, sharing and usage and gender and provides a conceptual framework for future research.
Diffusion of blockchain in logistics and transportation industry: an analysis through the synthesis of academic and trade literature
Purpose Blockchain technology has fascinated researchers and industry professionals. Since its birth, the attention for blockchain has been exponentially increasing, however, most of the industries are still skeptical in adoption for value creation. The purpose of this study is to analyze the actual level of implementation and diffusion of blockchain technology within the logistics and transportation industry by comparing and using the collective intelligence of academic literature and industry practices of implementation of blockchain in this domain. Design/methodology/approach This study uses the methodology of systematic literature review along with inductive reasoning. The systematic literature review of academic and industry frontiers together has brought a bigger and real picture into consideration. Findings The results highlight that, within the transportation sector, currently there is a very low diffusion of blockchain, although applications show immense promises for the future. The various application where blockchain technology can make a significant impact are also identified. Research limitations/implications Due to the early stage of experimentation with blockchain technology, high-quality data which is relevant to the optimized usage of this technology in the logistics and transportation industry is not available. Practical implications The study will help the practitioners in identifying additional avenues in which they could implement blockchain for the effectiveness, efficiency and growth of the logistics and transportation industry. Originality/value The analysis of mixed sources of information for undertaking systematic literature review by assessing academic and trade publications is a novelty of this study.
Blockchain as a mean to secure Internet of Things ecosystems – a systematic literature review
PurposeBlockchain is evolving to become a platform for securing Internet of things (IoT) ecosystems. Still, challenges remain. The purpose of this literature review is to highlight the applicability of blockchain as a medium to secure IoT ecosystems. A two-dimensional framework anchored on (1) IoT layers and (2) security goals is used to organize the existent IoT security threats and their corresponding countermeasures identified in the reviewed literature. The framework helped in mapping the IoT security threats with the inherent features of blockchain and accentuate their prominence to IoT security.Design/methodology/approachAn approach integrating computerized natural language processing (NLP) with a systematic literature review methodology was adopted. A large corpus of 2,303 titles and abstracts of blockchain articles was programmatically analyzed in order to identify the relevant literature. The identified literature was subjected to a systematic review guided by a well-established method in IS research.FindingsThe literature evidently highlights the prominence of blockchain as a mean to IoT security due to the distinctive features it encompasses. The authors’ investigation revealed that numerous existent threats are better addressed with blockchain than conventional mechanisms. Nevertheless, blockchain consumes resources such as electricity, time, bandwidth and disk space at a rate that is not yet easily accessible to common IoT ecosystems.Research limitations/implicationsResults suggest that a configurational approach that aligns IoT security requirements with the resource requirements of different blockchain features is necessary in order to realize the proper balance between security, efficiency and feasibility.Practical implicationsPractitioners can make use of the classified lists of convention security mechanisms and the IoT threats they address. The framework can help underline the countermeasures that best achieve their security goals. Practitioners can also use the framework to identify the most important features to seek for in a blockchain technology that can help them achieve their security goals.Originality/valueThis study proposes a novel framework that can help classify IoT threats based on the IoT layer impacted and the security goal at risk. Moreover, it applies a combined man-machine approach to systematically analyze the literature.
SEC charges private fund administrator with gatekeeping failures
Purpose To explain a set of recent US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) administrative settlements targeting fund administrators and to alert fund administrators and other financial service providers to their growing “gatekeeper” obligations. Design/methodology/approach This article explores the factual and legal contours of SEC administrative settlements with a fund administrator, as well as related enforcement actions against investment managers, to better understand the affirmative steps the SEC is expecting financial service providers to take to help root out fraud and misappropriation in the financial services sector. Findings The SEC’s administrative settlements with this fund administrator illustrate the SEC’s expanding focus on the “gatekeeper” function and signal the intent of the SEC to impute culpability for wrongdoing to fund administrators and other financial service providers simply for not doing enough to root out fraud and misappropriation in the financial services sector. Originality/value This article contains valuable information about recent SEC enforcement activity and practical guidance from experienced white collar, securities, and investment management lawyers.
Export Citation Format
Share document.
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access Only $1 for 4 weeks
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital.
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- Videos & Podcasts
- FT App on Android & iOS
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Premium newsletters
- Weekday Print Edition
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Everything in Print
- Everything in Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition
7 Blockchain Case Studies from Different Industries in 2024
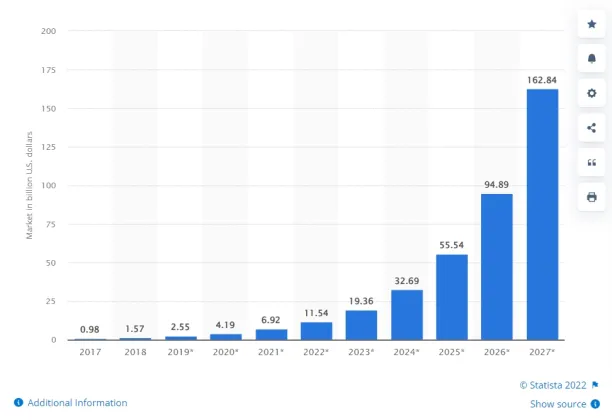
Global investment in blockchain technology is skyrocketing (see Figure 1) because blockchain can enhance data exchange in multi-party processes thanks to:
- Enhanced transparency
- Increased speed
- Reduced transfer costs.
Blockchain pioneers have a chance to acquire a competitive edge . However, executives have many investment alternatives and maturity of some blockchain based solutions is low. Therefore, executives need to make smart decisions to invest in an optimal manner in blockchain based solutions.
In this article, we present 7 blockchain case studies. Real-world examples can help executives identify solution areas that are mature enough for investment.
Figure 1: Blockchain market size in billion US dollars
Procurement
1. blockchain ease supplier master data management: trust your supplier.
Business challenge:
Trust Your Supplier saw an opportunity to reduce costs and effort when it came to finding and onboarding a reputable supplier. Supply chain interruptions and quality expectations to comply with regulations or stakeholders’ environmental and social concerns , are two important risk aspects that firms must deal with. Finding a suitable supplier is a time-consuming and expensive process for businesses because verifying and obtaining data from providers is difficult since companies do not want to share their data openly.
Initiative:
Trust Your Supplier collaborated with IBM to create an open source blockchain platform that allows businesses to securely and effectively share data with permissioned partners. Platform allows businesses to have their data confirmed by third-party verifiers such as:
- Dun & Bradstreet (business data).
- Eco Vadis (ESG data).
- Rapid Ratings (finance data).
Once your company’s data is confirmed, a blockchain-based corporate digital passport is created, allowing:
- Enhanced compliance.
- Enhanced risk management.
- Reduced onboarding duration of suppliers.
- Reduce supplier onboarding duration more than 70%.
- Lessen the cost for data verification to work with a suitable supplier 50%.
- Improve compliance by almost instantaneously checking international quality certificates of other parties like GRI, ISO, SASB etc.
2. Blockchain eases trade finance: Marco Polo Network
For both exporters and importers, international trading can be risky. When an importer pays in advance for goods, the exporter may collect the cash without sending the goods. However, if the exporter agrees to receive payment after delivery, the importer may refuse to pay after receiving the products. To overcome this problem, traders collaborate with third parties such as banks that employ instruments like letters of credit , which guarantee payment once goods are delivered to the importer.
Marco Polo Network utilizes blockchain technology to provide a platform for exporters and importers to transparently share delivery data by integrating with supply chain ERP systems and creating an irrevocable contract for parties that guarantees the exchange of money and goods under specified conditions (e.g. money transferred when goods receives the importer).
Initiative potentially eliminates the need for third party existence that solves “trust issue”. However, third parties also involve and benefit while they are using Marco Polo Network’ solution since the platform increases transparency.
- Enhances working capital cycle for both buyer and seller.
- Automates transaction settlement process.
- Reduced complexity by digitizing documents.
Supply chain
3. blockchain improves compliance: renault .
The automotive sector is highly regulated . Renault, for example, deals with 6,000 regulatory and quality characteristics relating to:
- Safety regulations
- Geometric features
- Material quality
- Environmental concerns
A vehicle must meet certain internal and external compliance criteria in order to be offered on the market. A change in regulations needs to be communicated downstream to suppliers and suppliers of suppliers to ensure that they all build according to the new specifications. Therefore, Renault needed a platform throughout the ecosystem in a transparent manner to ensure compliance.
Renault and IBM collaborated to create the automotive industry’s first extended compliance end-to-end distributed blockchain platform for the traceability of components internal and external regulatory compliance.
- Reduces expense of non-compliance by half.
- The initiative reduces the cost of managing non-quality/non-compliance by 10%.
- Renault wants to invest more in blockchain technology for the visibility of product carbon footprints and recycling operations as a result of the initiative’s success, aligning with the company’s ESG and circular economy ambitions.
4. Blockchain authenticates infant products quality: Nestle
After 300,000 newborns were sickened with melamine from powdered milk products in 2008, Chinese parents ‘ trust in infant nourishment products was damaged. Nestle was looking for ways to reassure Chinese parents about the quality of their newborn nourishment product NAN A2 to penetrate the market effectively.
Nestle teamed up with Techrock , a Chinese technology firm, to create a public blockchain platform that integrates with a mobile app . As a result, parents can verify the NAN A2’s following characteristics using their phone:
- Ingredients
- Place the ingredients sourced from
- Origin of production
- Packaging details including the photos.
- Due to the transparency provided by blockchain, Nestle held the largest market share in China’s infant nourishment sector.
5. Blockchain ensures instant claims processing: Etherisc
Etherisc is an insurtech startup that was looking for ways to speed up the claims processing. Traditional claims processing comprises five processes, as shown in Figure 2. Though the time it takes to settle a claim varies by insurance company and type, it usually takes weeks. However, according to EY , nearly 90% of insureds choose an insurer based on the quality and speed of claims processing.
Figure 2: Steps of Claims Processing
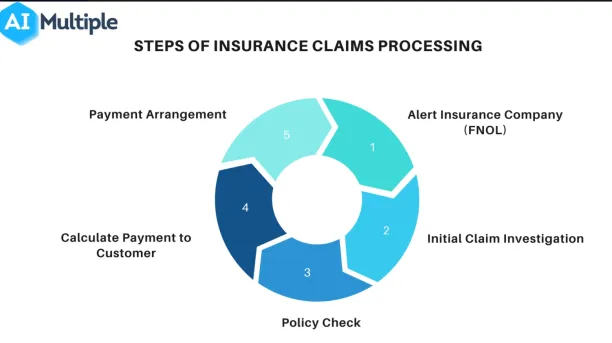
To automate claims processing Etherisc uses blockchain technology which enables smart contracts that enforce the agreement when the certain conditions specified on the contract are met.
Etherisc employed third-party data providers to determine if the payment arrangement’s terms were met or not (see Figure 3). Therefore, after alerting the insurance provider, Etherisc evaluates the initial claim investigation and policy check processes in real time, increasing its claims processing efficiency.
Figure 3: Claims processing with blockchain
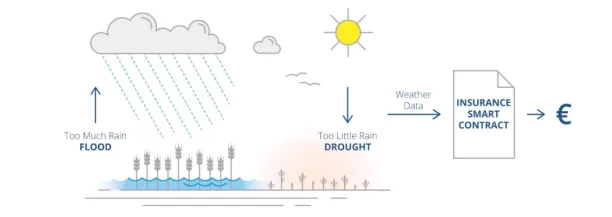
- Reduces the time needed for claims settlement.
- Automatically investigates probable fraud using data from third parties ( IoT devices or reputable databases).
6. Blockchain optimizes the power grid: Tennet
TenneT , situated in the Netherlands and Germany, is an energy transmission operator. Because energy demand and supply are not always in balance, electricity distribution is difficult. Energy productivity of sustainable energy supplies varies instantly depending on the state of the weather. Wind turbine electricity generation, for example, differs depending on the wind conditions of the day. Similarly electricity demand varies within the day. Thus, optimizing electricity distribution becomes a challenging issue.
To optimize the power grid Tennet cooperated with IBM and Sonnen. IBM deployed blockchain Sonnen, producer of home energy storage systems provides an opportunity for interaction with minor energy producers and consumers.
Energy storage systems linked to the TenneT’s power grid database via blockchain. Thanks to blockchain’s distributed ledger, inaccuracies in the demand and supply of electricity are transparently shared with a variety of stakeholders. Initiative enables the connected energy storage units to collect or release additional electricity as needed in a couple of moments, reducing grid transmission inefficiencies.
- Elevated curtailment and re-routing operations became unnecessary so the initiative saves millions of dollars.
- A significant step toward the transformation towards renewable energy sources has been taken. Because initiative provides a way of management for the significant supply volatility of renewable energy sources.
- Support local energy producers like home owners or farmers who deploy solar plants or wind turbines and lower their electricity expenses as well carbon footprint’s .
7. Blockchain assists the tracking of intellectual property (IP): IPwe
Many businesses do not have the opportunity to present the true value of their assets to potential investors so some companies are undervalued. IPwe intended to transform the inefficient old IP system, in which patent holders, lawyers, corporations, intermediaries, and global patent offices lack communication for a variety of reasons, including the inability to transfer information from one source to another transparently.
IPwe teamed up with IBM to create a blockchain that allows IP to be tokenized and stored in the cloud. As a result, traders have easy access to IP and can invest in it based on clear data. IPwe also provides a place for businesses to fairly advertise their intellectual property.
- IPwe’s blockchain database has 80% of global patents.
If you think blockchain could help your company, use our data-driven lists to compare the best blockchain platforms and services .
If you have further questions regarding blockchain you can contact us:
This article was drafted by former AIMultiple industry analyst Görkem Gençer.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month. Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider , Forbes, Washington Post , global firms like Deloitte , HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission . You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple. Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization. He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider . Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Next to Read
12 blockchain in supply chain case study in 2024, process mining blockchain in 2024: top 4 use cases & case studies.
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
Related research
3 Ways Blockchain Will Transform Insurance Operations in 2024

Smart Contracts: What Are They & Why They Matter in 2024
- SMB Technology
- Mobile Productivity
- Mobile Security
- Computing & Monitors
- Memory & Storage
- Digital Signage
- Trending Tech
- Hospitality
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Food & Beverage
- Live Events & Sports
- Spectaculars & DOOH
- Gaming & Esports
- White Papers
- Infographics
- Assessments & Calculators
- Case Studies
- About Samsung Insights
- Our Experts
Subscribe to Insights
Get the latest insights from Samsung delivered right to your inbox.
See our Privacy Policy
Samsung Business Insights

Featured posts in

Why Galaxy Z Fold5 is an ideal solution for wealth managers

How financial services can turn to tech-first solutions to support sustainability

How insurance claims adjusters can boost efficiency with mobile tech
How samsung knox suite enables best-in-class security and device management for financial services.
Security and compliance are common concerns for IT leaders in the financial services industry — but over the last few years, they’ve become top priorities, with businesses facing a significant spike in cybersecurity threats.
Given the rise of the hybrid workplace, mobile devices and tablets allow employees to stay connected, whether they are in the office, out in the field or meeting with customers. However, financial services companies are subject to a range of regulatory requirements around data protection and security on their devices. This puts extra pressure on financial firms to secure their data, enforce IT policies and protect those devices against malicious actors and threats.
Still, research shows that about 25% of malware attacks target financial services companies. In 2023, 64% of IT and cybersecurity professionals in the financial industry were hit by ransomware . With many financial workers now splitting their working days between the office, home and client visits, IT leaders and their teams are facing increased pressure to secure mobile devices regardless of where they are.
Samsung Knox , which is built into Samsung Galaxy mobile devices , tablets and wearables, protects business data for financial services and other regulated industries with government-grade protection. Samsung Knox offers mobile security, unified endpoint management, and fraud and theft protection to businesses. The platform is trusted for robust, government-grade security, with its defense starting at the hardware level and continuing to protect against the most advanced security threats.
Shop special offers
Find out about offers on the latest Samsung technology.
Speak to a solutions expert
Get expert advice from a solutions consultant.
Who are you buying for?
I'm buying for myself
I'm buying for a small business
I'm buying for a large enterprise
Secure, deploy and manage data with Samsung Knox
IT leaders can use Samsung Knox Suite to manage various devices from a central location and a single user interface. The powerful enterprise mobility solutions enable teams to secure, deploy, manage and analyze data from corporate devices throughout the enterprise mobility lifecycle.
- Secure: Take advantage of advanced security management features that help businesses comply with stringent security requirements, offering advanced encryption technologies and government-grade protection.
- Deploy: Enjoy easier enrollment, with the ability to enroll corporate devices in enterprise mobility management (EMM) systems automatically and securely, right out of the box.
- Manage: Manage devices easily with remote support, intuitive onboarding, a seamless user experience and tools that fit both the office and the field.
- Analyze: Remotely gain insight into device health and data control, no matter where your employees use their devices.
Knox’s unified endpoint management effectively saves IT teams time and resources. They can deploy thousands of devices simultaneously, push updates, gather data analytics, and track, monitor and support field workers in a remote setting.
For mobile security, regulated industries like healthcare are equipped with Samsung Knox Suite and use devices like Samsung Galaxy Tab S9+ to remotely access electronic health records in locations such as client homes. Samsung Knox Configure can help these organizations protect against internal threats and better manage their fleet of devices.
Unique benefits of Samsung Knox for financial services
Samsung Knox protects the financial services workforce that is increasingly going mobile, whether that’s a financial advisor meeting with a client in their home using a Galaxy Z Fold5 , an insurance claims adjuster out in the field working off a Galaxy Tab Active5 or a bank associate on a branch floor receiving alerts on their Galaxy Watch6 . With its latest devices — including Galaxy S24 and Galaxy Z Fold5 — Samsung has leveled up its device protection with a secure processor dedicated to protecting your PIN, password, pattern and blockchain private key.
What's next for the future of finance?

Samsung surveyed 1,000 finance professionals about the future of mobile tech. Here's what they said. Download Now
While on the go and working remotely, it’s common for finance employees to want to run apps and store content for personal use in addition to accessing business applications and data. Instead of device use policies that prohibit or limit employees’ use of particular apps and content, Knox Platform for Enterprise offers features that isolate and encrypt business apps and data in containers to help protect from employee behavior. For example, by deploying a separate enterprise container, administrators can ensure enterprise data is protected against malicious apps inadvertently downloaded from third-party marketplaces and reduce the risk of data leakage. If an employee leaves the organization, the managed Work Profile allows remote wipe tools to erase the business partition, while leaving personal content and apps untouched. Devices with enterprise data can also be remotely wiped if lost or stolen.
Remote device health attestation lets you check device integrity across your fleet and detect rooting, device ID tampering and more. Advanced encryption technologies such as DualDAR , Sensitive Data Protection (SDP) and one-click Common Criteria Mode provide extra security against threats. Data in transit is protected by advanced network security features with Knox VPN, an on-demand firewall and a secure browser.
With Knox, financial services companies can:
- Secure devices throughout the EMM journey.
- Streamline deployment to set up thousands of devices with ease.
- Simplify device management with Samsung Knox and Android Enterprise.
The ultimate pair for productivity and protection
Samsung and Android work closely together to provide enterprises with the most reliable and secure mobile experience possible. Since joining forces over a decade ago, the partnership has addressed the most pressing challenges businesses face today: maintaining productivity, protecting the workforce and offering flexibility.
Specifically, over the past several years, Samsung and Android have partnered to:
- Harmonize Android Enterprise and Samsung Knox Platform for Enterprise to offer a seamless experience for Android customers seeking Samsung’s advanced security and device management capabilities.
- Synchronize mobile device enrollment services (Android zero-touch enrollment and Knox Mobile Enrollment ) to offer a variety of services that help streamline the employee onboarding experience and re-deployment of devices.
Android’s core security foundation, combined with Samsung Knox’s hardware-based protection and advanced real-time protection, addresses today’s most demanding security challenges — especially in an industry like financial services. The flexible platform and comprehensive set of Android Enterprise management APIs address every device use case, from locked down to open use. Admins can also enjoy granular controls of devices in this highly regulated industry. With Samsung Knox, IT teams can easily enroll devices, build the required profiles, manage applications and support employees through remote access sessions.
For a full overview of all Samsung technology solutions for the Finance industry, please visit this page . And sign up for a Samsung Business Account to get exclusive offers, including volume pricing discounts, on our Rugged devices , as well as our newest devices like Galaxy S24 Series and Galaxy Z Fold5 .

Jeannine DeFoe
Jeannine DeFoe is an experienced financial writer, specializing in wealth management. fintech and personal finance, and how technology helps financial firms. A former reporter, she now creates articles, case studies and more for numerous leading wealth firms and fintechs.
- Finance Transformation
- Galaxy Tab Active
- Galaxy Tab S9+
- Galaxy Z Fold5
- Knox Configure
- Knox Platform for Enterprise
- Samsung Knox
Related Posts
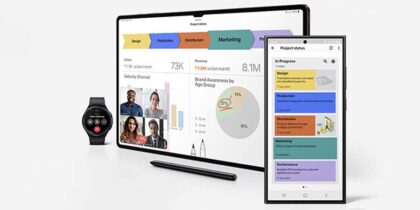
From the office to the commute and beyond: How Samsung and Android power the needs of modern financial services
Samsung devices help financial employees working in the office or remotely improve their productivity while offering the information security you need.

5 compliance challenges for financial institutions and how to solve them
Learn how Samsung's suite of mobile devices and platforms can help financial institutions handle five of their most critical compliance challenges.

How digital tools help banks enhance employee and customer experience
Learn how one piece of mobile technology can help retail bank branch associates serve clients in a changing industry.
Featured Posts

Working in wealth management has always been a balancing act between tasks like financial planning, providing investment advisory services and monitoring portfolios. As client

Financial firms can make sustainable changes by reassessing the technology and digital solutions they use.

Samsung's portable yet powerful mobile technology lets claims adjusters juggle the multitasking and travel required in their jobs.
How can we help you?
I'm buying for myself
I'm buying for a small business
I'm buying for a large enterprise
Our solutions architects are ready to collaborate with you to address your biggest business challenges.
- Mobile Phones
- Laptops/2-in-1
- Business Services
- Displays & Digital Signage
- Hospitality TVs
- Wireless Networks
- Public Safety

A member of our solutions architect team will be in touch with you soon.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's a look at 10 blockchain use cases in the financial industry that showcase the promise and potential of the technology. 1. Faster, cheaper, and more secure financial services - and at larger scale. Because blockchain enables immutable transactions effectively in real time, experts credit it with offering a faster, more secure and highly ...
The advantage of Blockchain is that financial transactions may be quickly validated, cleared, and settled without the need for a central authority. Blockchain technology will significantly affect capital markets and other financial services. Blockchain will change the financial sector in the following years.
This study will help provide a holistic framework that would highlight the current state and challenges of the blockchain in the financial services sector.,The objective of this study is to systematically examine and organize the current body of research literature that either quantitatively or qualitatively explored the use of blockchain ...
This qualitative study provided insights into the top 17 blockchain use cases identified by Financial Services leaders in 2018 and how much progress (or lack of progress) has been made in 2020 ...
Our study presents and intensifies the opportunities and constraints of the implementation of blockchain technology in finance around the world. The article presents the results of a systematic literature review on blockchain technology, as advanced in articles published between 2017 and 2021. In the course of reviewing the articles, we found ...
Blockchain is undoubtedly considered one of the most innovative technologies in financial services from the past decade. Interests in blockchain technology continue to grow on a daily basis, while many promising blockchain-enabled applications and services continue to draw financial interest in the industrial sector and the broader financial services communities.
The Ethereum blockchain enables more open, inclusive, and secure business networks, shared operating models, more efficient processes, reduced costs, and new products and services in banking and finance. It enables digital securities to be issued within shorter periods of time, at lower unit costs, with greater levels of customization.
Blogs: Blockchain for financial services Blockchain is disrupting the financial services sector worldwide — across industries, financial institutions and organizations. Banking technology solutions See solutions that are agile, trusted and transformative. Explore the future of banking technology on the hybrid cloud with IBM. Blockchain use cases
The purpose of this paper is to study the actual cases of Blockchain applied in Korea in 2017, so that a vision of business model innovation of financial institutions can be drawn.,The financial institutions in Korea are in the technology verification stage to introduce Blockchain technology.
The study draws information from academic and non-academic sources, utilizing qualitative analysis. Through informative articles, the paper examines the blockchain and cryptocurrency markets, providing readers with up-to-date developments. Numerous ongoing studies and financial use cases demonstrate the numerous advantages of blockchain technology.
1. Introduction. Blockchain technology is a financial technology (FinTech) which is first developed as the distributed ledgers for bitcoin. For some time, blockchain technology was overshadowed by the bitcoin phenomenon, but in current years it has started to attract attention in its own right and is becoming a core technology in the FinTech family (Du, Pan, Dorothy, Leidner, & Yinga, 2019).
Learn the practical applications of blockchain technology and take advantage of the potential to disrupt your industry. ... Read the case study . ... ANZ Bank partners with a consortium to transform financial guarantees using IBM Blockchain. banking, platform, , , ANZ Bank, 2020-03-19. Watch the video (01:58)
PwC sees considerable potential for blockchain in financial services. Our risk assurance team of experienced business, technology and regulatory experts can assist in multiple facets of ensuring that blockchain can benefit your organisation and drive business forward. Research and knowledge services Operational risk.
Blockchain technology, often hailed as the backbone of digital currency, has steadily evolved to become a disruptive force in the financial services industry. As a secure, decentralized and ...
The study looks at how blockchain affects several financial services like lending, trade finance, and payments and remittances. ... Policymakers, financial institutions, and other stakeholders who want to use blockchain technology to enhance financial services and advance financial inclusion should take note of the study's conclusions ...
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force in the financial industry, offering the potential to streamline and enhance financial markets' clearing and settlement processes. This paper explores the application of blockchain technology in these critical areas. We examine traditional clearing and settlement procedures, the challenges they pose, and how blockchain can address ...
The financial industry offers a valuable case study. This story has been excerpted from the STAT Report, "STAT's guide to blockchain in health care.". N ot long ago, blockchain technology ...
Purpose The purpose of this study is to thoroughly review studies that have used blockchain technology in financial services. This study will help provide a holistic framework that would highlight the current state and challenges of the blockchain in the financial services sector. Design/methodology/approach The objective of this study is to ...
A number of high-profile blockchain experiments in banking and finance have ended in failure this year, undermining the case for the technology's future in financial services. The biggest ...
Global investment in blockchain technology is skyrocketing (see Figure 1) because blockchain can enhance data exchange in multi-party processes thanks to:. Enhanced transparency; Increased speed; Reduced transfer costs. Blockchain pioneers have a chance to acquire a competitive edge.However, executives have many investment alternatives and maturity of some blockchain based solutions is low.
Over the course of the last crypto bull market (approximately 2020-2022), many large financial services firms announced various projects and products based on blockchain technology.
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) is the main blockchain application in finance in 2024. The 2021 survey lists "digital currency" as the most likely blockchain application in financial services ...
6.1 Blockchain - The Technology for Document Management. This section showcases how blockchain revolutionizes document management, ensuring transparency, security, and traceability of digital assets in an immutable ledger. This case study illustrates the power of blockchain in enhancing data integrity and trust in document handling.
The purpose of this study is to thoroughly review studies that have used blockchain technology in financial services. This study will help provide a holistic framework that would highlight the current state and challenges of the blockchain in the financial services sector.,The objective of this study is to systematically examine and organize the current body of research literature that either ...
2024 Digital Transformation & Next-Gen Technology Study ... Financial services companies have made big strides in digital transformation in recent years. Firms are investing heavily through the economic cycle, modernizing their core IT platforms to support continuous innovation and adopt next-gen technologies, such as AI and blockchain ...
Cloud Cybersecurity Data & Artificial Intelligence Digital Engineering & Manufacturing Emerging Technology Enterprise Platforms Finance & Risk Management Learning Marketing & Experience Metaverse Private Equity Sales & Commerce Strategic Managed Services Strategy Supply Chain Sustainability Talent & Organization Technology Transformation
Jeannine DeFoe is an experienced financial writer, specializing in wealth management. fintech and personal finance, and how technology helps financial firms. A former reporter, she now creates articles, case studies and more for numerous leading wealth firms and fintechs. View more posts by Jeannine DeFoe
Salama, R., Cacciagrano, D., Al-Turjman, F. (2024). Blockchain and Financial Services a Study of the Applications of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) in Financial Services. In: Barolli, L. (eds) Advanced Information Networking and Applications. AINA 2024. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 204.
The "zero-knowledge" (ZK) bit of Jolt refers to a form of cryptographic trickery that powers a16z's VM under the hood - allowing the virtual computer to process and verify data while adhering to ...
Eastman isn't stopping with AI. The company is continuing to develop its broader technical experience to drive one of its highest priorities: sustainability. Noseda says Eastman is building plants that will create recycled plastic and textile products. It will use blockchain to track and record from where feedstock comes, allowing customers ...