We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!

Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Neurology for the speech-language pathologist
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station40.cebu on January 10, 2023
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

- Medical Books
- Allied Health Professions

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: $62.65 $62.65 FREE delivery: Tuesday, April 23 Ships from: Amazon Sold by: ayvax
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Add work books and access codes to your order
Buy used: $25.94
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service we offer sellers that lets them store their products in Amazon's fulfillment centers, and we directly pack, ship, and provide customer service for these products. Something we hope you'll especially enjoy: FBA items qualify for FREE Shipping and Amazon Prime.
If you're a seller, Fulfillment by Amazon can help you grow your business. Learn more about the program.
Other Sellers on Amazon

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist 6th Edition
There is a newer edition of this item:.

Purchase options and add-ons
The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 6th Edition provides students and clinicians with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology in speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the nervous system, including: development of the nervous system, organization of the brain, protective mechanisms, descending motor and ascending sensory pathways, and cranial nerves. New content, case studies, and a strong clinical focus make this new edition essential as you move into practice.
- Case studies and clinical applications in clinically oriented chapters provide you with realistic clinical applications.
- Presents complex information clearly in a concise, easy-to-understand manner.
- Clinical emphasis throughout makes this text valuable as you move into clinical practice ― and prepare for the Praxis exam.
- Evolve companion website has vocabulary flashcards and study questions with answers so students can assess their knowledge.
- Key terms in each chapter and an end-of-text glossary give you easy access to accurate, concise definitions.
- NEW! Separate section on pediatric speech and language disorders, including a chapter on the developing brain.
- EXPANDED! Updated sections on neurodiagnostic and neuroimaging procedures, as well as childhood apraxia of speech, fluency disorders, Autism, and TBI.
- NEW! Updated discussion of the anatomy and function of the cerebellum gives you the most current information.
- UPDATED! Covers the latest neuroimaging research on anatomy, physiology, and disorders of speech-language.
- EXPANDED! Discusses the brain connectivity and the neural network underlying learning and language.
- EXPANDED! Addresses motor control for speech production so you stay in the know.
- ISBN-10 0323100279
- ISBN-13 978-0323100274
- Edition 6th
- Publisher Mosby
- Publication date April 8, 2016
- Language English
- Dimensions 8.25 x 0.25 x 10.75 inches
- Print length 336 pages
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Similar items that may ship from close to you


Product details
- Publisher : Mosby; 6th edition (April 8, 2016)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 336 pages
- ISBN-10 : 0323100279
- ISBN-13 : 978-0323100274
- Item Weight : 1.46 pounds
- Dimensions : 8.25 x 0.25 x 10.75 inches
- #21 in Audiology & Speech Pathology (Books)
- #1,102 in Professional
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
Advertisement
Speech Language Pathology in the Neurocritical Care Unit
- Published: 09 October 2023
- Volume 25 , pages 499–516, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
- Nicole Frost MA, CCC-SLP, BCS-S 1 ,
- Gavin Yuan BA 2 ,
- Julie Zhang BA 2 ,
- Amy Rickard CCC-SLP 3 ,
- Erin McGee CCC-SLP 3 ,
- Michelle DiMattia CCC-SLP 3 &
- Stephan A. Mayer MD ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1272-6277 2 , 3
284 Accesses
5 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
A Correction to this article was published on 14 November 2023
This article has been updated
Purpose of review
The aim of this study is to review the scope of practice of speech language pathologists (SLPs) in the daily practice of neurocritical care.
Recent findings
In patients with aphasia, impairment-based or function-based language interventions improve outcomes. Augmentative and alternative communication devices can help certain patients with severely impaired speech production. After tracheostomy, one-way speaking valves can be placed either in-line with a ventilator or after weaning; it has been shown that earlier placement is associated with faster decannulation. Swallow screening, bedside swallow evaluations, and instrumental swallowing evaluations such as videofluoroscopic swallow studies (VFSS) or fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) are valuable tools for diagnosing dysphagia and identifying candidates for percutaneous enteral gastrostomy. Deficit-based rehabilitation of dysphagia is centered on re-training swallowing muscles and reorganizing neural synapses involved in swallowing function, capitalizing on the principles of neuroplasticity and motor learning. Neuromodulation therapies such as pharyngeal electrical stimulation can promote functional reorganization of cortical pathways involved in swallowing and show promise to improve swallow function and reduce aspiration risk.
SLPs are essential members of the multi-disciplinary neurocritical care team, particularly with regard to the evaluation and management of communication, cognition, and swallowing dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
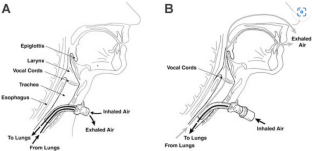
Reproduced from Elpern EH, Borkgren Okonek M, Bacon M, Gerstung C, Skrzynski M. Effect of the Passy-Muir tracheostomy speaking valve on pulmonary aspiration in adults. Heart & Lung: the journal of critical care. 2000;29(4):287–93. https://doi.org/10.1067/mhl.2000.106941 .
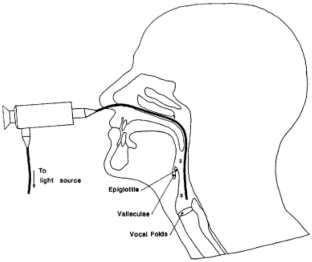
Reproduced from Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olson N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia. 1988;2:216–19.
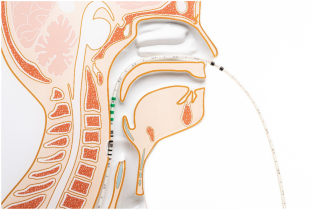
Reproduced with permission from Phagenesis, Inc. on 6/2/23.
Similar content being viewed by others

Rehabilitation of Speech, Language, and Swallowing Disorders in Clients with Acquired Brain Injury
Association between timing of speech and language therapy initiation and outcomes among post-extubation dysphagia patients: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
Takashi Hongo, Ryohei Yamamoto, … Atsunori Nakao

Speech, Language, and Swallowing Difficulties in Neurology: A Sub-Saharan African Perspective
Change history, 14 november 2023.
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-023-00777-0
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • of importance •• of major importance.
Brady MC, Kelly H, Godwin J, Enderby P, Campbell P. Speech and language therapy for aphasia following stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2016(6):CD000425. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000425.pub4 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Norman RS, Swan AA, Jenkins A, Ballard M, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Updating and refining prevalence rates of traumatic brain injury–related communication disorders among post-9/11 veterans: a chronic effects of neurotrauma consortium study. SIG 2 Neurogenic Communication Disorders. 2021:6(5):1060–72.
Johansen MC, Langton-Frost N, Gottesman RF. The role of cardiovascular disease in cognitive impairment. Curr Geri Rep. 2020:9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13670-020-00309-7 .
Takizawa C, Gemmell E, Kenworthy J, Speyer R. A systematic review of the prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke, parkinson’s disease, alzheimer’s disease, head injury, and pneumonia. Dysphagia. 2016;31(3):434–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9695-9 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
McCann MR, Hatton KW, Vsevolozhskaya OA, Fraser JF. Earlier tracheostomy and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with hemorrhagic stroke: associated factors and effects on hospitalization. J Neurosurg. 2019;132(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.7.JNS181345 .
Allareddy V, Rampa S, Nalliah RP, et al. Prevalence and predictors of gastrostomy tube and tracheostomy placement in anoxic/hypoxic ischemic encephalopathic survivors of in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the United States. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0132612. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132612 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Angstwurm K, Vidal A, Stetefeld H, et al. Early tracheostomy is associated with shorter ventilation time and duration of ICU stay in patients with myasthenic crisis-A multicenter analysis. J Intensive Care Med. 2022;37(1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066620967646 .
Dunn K, Rumbach A, Finch E. Language function in the acute phase following non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage: a prospective cohort study. J Commun Disord. 2022;96:106192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomdis.2022.106192 .
Godecke E, Hird K, Lalor EE, Rai T, Phillips MR. Very early poststroke aphasia therapy: a pilot randomized controlled efficacy trial. Int J Stroke. 2012;7(8):635–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2011.00631.x .
Godecke E, Armstrong E, Rai T, Ciccone N, Rose ML, Middleton S, et al. for the VERSE Collaborative Group. A randomized control trial of intensive aphasia therapy after acute stroke: The Very Early Rehabilitation for SpEech (VERSE) study. Int J Stroke. 2021;16(5):556–72. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493020961926 .
Vitti E, Hillis AE. Treatment of post-stroke aphasia: a narrative review for stroke neurologists. Int J Stroke. 2021;16(9):1002–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/17474930211017807 .
Shewan CM, Kertesz A. Reliability and validity characteristics of the Western Aphasia Battery (WAB). J Speech Hear Disord. 1980;45(3):308–24. https://doi.org/10.1044/jshd.4503.308 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Berube S, Nonnemacher J, Demsky C, et al. Stealing cookies in the twenty-first century: measures of spoken narrative in healthy versus speakers with aphasia. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2019;28(1S):321–9. https://doi.org/10.1044/2018_AJSLP-17-0131 .
Edmonds LA, Mammino K, Ojeda J. Effect of verb network strengthening treatment (VNeST) in persons with aphasia: extension and replication of previous findings. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014;23(2):S312–29. https://doi.org/10.1044/2014_AJSLP-13-0098 .
Efstratiadou EA, Papathanasiou I, Holland R, Archonti A, Hilari K. A systematic review of semantic feature analysis therapy studies for aphasia. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018;61(5):1261–78. https://doi.org/10.1044/2018_JSLHR-L-16-0330 .
Minkina I, Silkes JP, Bislick L, et al. The influence of phonomotor treatment on word retrieval: insights from naming errors. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2019;62(11):4080–104. https://doi.org/10.1044/2019_JSLHR-L-19-0014 .
Armour M, Brady S, Sayyad A, Krieger R. Self-reported quality of life outcomes in aphasia using life participation approach values: 1-year outcomes. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2019;1(3–4):100025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arrct.2019.100025 .
Garry J, Casey K, Cole TK, et al. A pilot study of eye-tracking devices in intensive care. Surgery. 2016;159(3):938–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2015.08.012 .
• Ju XX, Yang J, Liu XX. A systematic review on voiceless patients' willingness to adopt high-technology augmentative and alternative communication in intensive care units. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2021;63:102948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iccn.2020.102948 . This systematic review investigated the efficacy of AAC interventions in ICU patients. The final analysis included 18 studies across 914 participants. Six studies found that high-tech AAC tools facilitated ease of communication with health care staff. Six studies also found that these tools lead to decreased anxiety and depression.
Happ MB, Baumann BM, Sawicki J, Tate JA, George EL, Barnato AE. SPEACS-2: intensive care unit “communication rounds” with speech language pathology. Geriatr Nurs. 2010;31(3):170–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2010.03.004 .
Trotta RL, Hermann RM, Polomano RC, Happ MB. Improving nonvocal critical care patients’ ease of communication using a modified SPEACS-2 program. J Healthc Qual. 2020;42(1):e1–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/JHQ.0000000000000163 .
Rose L, Sutt AL, Amaral AC, Fergusson DA, Smith OM, Dale CM. Interventions to enable communication for adult patients requiring an artificial airway with or without mechanical ventilator support. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;10(10):CD013379. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013379.pub2 .
Zahari Y, Wan Hassan WMN, Hassan MH, Mohamad Zaini RH, Abdullah B. The practice, outcome and complications of tracheostomy in traumatic brain injury patients in a neurosurgical intensive care unit: surgical versus percutaneous tracheostomy and early versus late tracheostomy. Malays J Med Sci. 2022;29(3):68–79. https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2022.29.3.7 .
Mccredie VA, Alali AS, Scales DC, Adhikari NKJ, Rubenfeld GD, Cuthbertson BH, et al. Effect of early versus late tracheostomy or prolonged intubation in critically ill patients with acute brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurocrit Care. 2017;26(1):14–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-016-0297-z .
Bösel J, Niesen W, Salih F, et al. Effect of early vs standard approach to tracheostomy on functional outcome at 6 months among patients with severe stroke receiving mechanical ventilation: the SETPOINT2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327(19):1899–909. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.4798 .
• Davis S, Weyh AM, Salman SO, Madbak F, Fraker JT. Speech pathology services are integral, but underutilized in tracheostomy rehabilitation. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2021;14(2):110–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1943387520948381 . This case series examined the use of SLPs in rehabilitation of tracheostomy. The authors determined that the mean time lag from tracheostomy to first SLP encounter was 5.9 ± 8.0 days. The study also demonstrated an improvement in decannulation following SLP utilization.
Hess DR. Facilitating speech in the patient with a tracheostomy. Respir Care. 2005;50(4):519–25.
PubMed Google Scholar
Hernandez G, Pedrosa A, Ortiz R, Cruz Accuaroni MDM, Cuena R, Vaquero Collado C, et al. The effects of increasing effective airway diameter on weaning from mechanical ventilation in tracheostomized patients: a randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(6):1063–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-2870-7 .
Amathieu R, Sauvat S, Reynaud P, et al. Influence of the cuff pressure on the swallowing reflex in tracheostomized intensive care unit patients. Br J Anaesth. 2012;109(4):578–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aes210 .
Lian S, Teng L, Mao Z, Jiang H. Clinical utility and future direction of speaking valve: a review. Front Surg. 2022;9:913147. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.913147 .
Sutt AL, Caruana LR, Dunster KR, Cornwell PL, Anstey CM, Fraser JF. Speaking valves in tracheostomised ICU patients weaning off mechanical ventilation—do they facilitate lung recruitment? Crit Care. 2016;20:91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-016-1249-x .
Suiter DM, McCullough GH, Powell PW. Effects of cuff deflation and one-way tracheostomy speaking valve placement on swallow physiology. Dysphagia. 2003;18(4):284–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0022-x .
Sutt AL, Cornwell P, Mullany D, Kinneally T, Fraser JF. The use of tracheostomy speaking valves in mechanically ventilated patients results in improved communication and does not prolong ventilation time in cardiothoracic intensive care unit patients. J Crit Care. 2015;30(3):491–4.
•• Martin KA, Cole TDK, Percha CM, Asanuma N, Mattare K, Hager DN, et al. Standard versus accelerated speaking valve placement after percutaneous tracheostomy: a randomized controlled feasibility study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(10):1693–701. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.202010-1282OC . This trial compared placement of a one-way speaking valve within an accelerated (median 22, interquartile range [IQR] 21–23 hours) versus standard time frame (median 45.5, IQR 43-) hours). Patients in the early speaking valve placement had a longer tolerance of speaking valve use (median 65, IQR 45–720 vs 15, IQR 3–20 mins) overall. There were no aspiration or hypoxic events in either group. This study highlights the feasibility and safety of early speaking valve placement after tracheostomy.
Giacino JT, Sherer M, Christoforou A, et al. Behavioral recovery and early decision making in patients with prolonged disturbance in consciousness after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2020;37(2):357–65. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2019.6429 .
Hammond FM, Giacino JT, Nakase Richardson R, et al. Disorders of consciousness due to traumatic brain injury: functional status ten years post-injury. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(7):1136–46. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.5954 .
Gurin L, Evangelist M, Laverty P, et al. Early neurorehabilitation and recovery from disorders of consciousness after severe COVID-19. Neurocrit Care. 2022;36(2):357–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-021-01359-1 .
Seel RT, Douglas J, Dennison AC, Heaner S, Farris K, Rogers C. Specialized early treatment for persons with disorders of consciousness: program components and outcomes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;94(10):1908–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.11.052 .
Pape TL, Rosenow JM, Steiner M, et al. Placebo-controlled trial of familiar auditory sensory training for acute severe traumatic brain injury: a preliminary report. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2015;29(6):537–47. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968314554626 .
Moattari M, Alizadeh Shirazi F, Sharifi N, Zareh N. Effects of a sensory stimulation by nurses and families on level of cognitive function, and basic cognitive sensory recovery of comatose patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a randomized control trial. Trauma Mon. 2016;21(4):e23531. https://doi.org/10.5812/traumamon.23531 .
Fiest KM, Soo A, Hee Lee C, et al. Long-term outcomes in ICU patients with delirium: a population-based cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204(4):412–20. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202002-0320OC .
Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gélinas C, et al. Executive summary: clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of pain, agitation/sedation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disruption in adult patients in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(9):1532–48. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000003259 .
Deemer K, Zjadewicz K, Fiest K, et al. Effect of early cognitive interventions on delirium in critically ill patients: a systematic review. Can J Anaesth. 2020;67(8):1016–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12630-020-01670-z .
Rivosecchi RM, Kane-Gill SL, Svec S, Campbell S, Smithburger PL. The implementation of a nonpharmacologic protocol to prevent intensive care delirium. J Crit Care. 2016;31(1):206–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.09.031 .
•• Faustino TN, Suzart NA, Rabelo RNDS, et al. Effectiveness of combined non-pharmacological interventions in the prevention of delirium in critically ill patients: a randomized clinical trial. J Crit Care. 2022;68:114–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.12.015 . The authors found that numerous non-pharmacologic interventions (including reorientation, cognitive stimulation, and environmental management) were sufficient to significantly reduce the incidence of delirium in the ICU compared to a placebo group.
Álvarez EA, Garrido MA, Tobar EA, et al. Occupational therapy for delirium management in elderly patients without mechanical ventilation in an intensive care unit: a pilot randomized clinical trial. J Crit Care. 2017;37:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.09.002 .
Brummel NE, Girard TD, Ely EW, et al. Feasibility and safety of early combined cognitive and physical therapy for critically ill medical and surgical patients: the activity and cognitive therapy in ICU (ACT-ICU) trial. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40(3):370–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-3136-0 .
Marra A, Ely EW, Pandharipande PP, Patel MB. The ABCDEF bundle in critical care. Crit Care Clin. 2017;33(2):225–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2016.12.005 .
Skoretz SA, Flowers HL, Martino R. The incidence of dysphagia following endotracheal intubation: a systematic review. Chest. 2010;137(3):665–73. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.09-1823 .
Macht M, Wimbish T, Bodine C, Moss M. ICU-acquired swallowing disorders. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(10):2396–405. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31829caf33 .
Brodsky MB, Pandian V, Needham DM. Post-extubation dysphagia: a problem needing multidisciplinary efforts. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(1):93–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05865-x .
DePippo KL, Holas MA, Reding MJ. Validation of the 3-oz water swallow test for aspiration following stroke. Arch Neurol. 1992;49(12):1259–61. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1992.00530360057018 .
Suiter DM, Leder SB. Clinical utility of the 3-ounce water swallow test. Dysphagia. 2008;23(3):244–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9127-y .
Warner HL, Suiter DM, Nystrom KV, Poskus K, Leder SB. Comparing accuracy of the Yale swallow protocol when administered by registered nurses and speech-language pathologists. J Clin Nurs. 2014;23(13–14):1908–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.12340 .
Martino R, Silver F, Teasell R, et al. The Toronto bedside swallowing screening test (TOR-BSST): development and validation of a dysphagia screening tool for patients with stroke. Stroke. 2009;40(2):555–61. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.510370 .
Estupiñán Artiles C, Regan J, Donnellan C. Dysphagia screening in residential care settings: a scoping review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021;114:103813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103813 .
Martin-Harris B, Canon CL, Bonilha HS, Murray J, Davidson K, Lefton-Greif MA. Best practices in modified barium swallow studies. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2020;29(2S):1078–93. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_AJSLP-19-00189 .
Warnecke T, Dziewas R, Langmore S. FEES and other instrumental methods for swallowing evaluation. In: Neurogenic Dysphagia. Cham: Springer; 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42140-3_3 .
Altman KW, Richards A, Goldberg L, Frucht S, McCabe DJ. Dysphagia in stroke, neurodegenerative disease, and advanced dementia. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2013;46(6):1137–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2013.08.005 .
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344–418. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211 .
Dennis MS, Lewis SC, Warlow C, FOOD Trial Collaboration. Effect of timing and method of enteral tube feeding for dysphagic stroke patients (FOOD): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9461):764–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17983-5 .
Wilmskoetter J, Simpson AN, Simpson KN, Bonilha HS. Practice patterns of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in acute stroke: are the guidelines achievable? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25(11):2694–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.07.017 .
Wilmskoetter J, Herbert TL, Bonilha HS. Factors associated with gastrostomy tube removal in patients with dysphagia after stroke: a review of the literature. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(2):166–74.
D’Netto P, Rumbach A, Dunn K, Finch E. Clinical predictors of dysphagia recovery after stroke: a systematic review. Dysphagia. 2023;38(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10443-3 .
Panebianco M, Marchese-Ragona R, Masiero S, Restivo DA. Dysphagia in neurological diseases: a literature review. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(11):3067–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04495-2 .
Kleim JA, Jones TA. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008;51(1):S225–39. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2008/018) .
Burkhead Morgan L. Exercise-based dysphagia rehabilitation: past, present, and future. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups: SIG 13 Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia). 2017;2(13):36–43. https://doi.org/10.1044/persp2.SIG13.36 .
Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, et al. Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(5):1314–21. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.32999 .
Heslin N, Regan J. Effect of effortful swallow on pharyngeal pressures during swallowing in adults with dysphagia: a pharyngeal high-resolution manometry study. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2022;24(2):190–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/17549507.2021.1975817 .
Archer SK, Smith CH, Newham DJ. Surface electromyographic biofeedback and the effortful swallow exercise for stroke-related dysphagia and in healthy ageing. Dysphagia. 2021;36(2):281–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10129-8 .
Bahia MM, Lowell SY. A systematic review of the physiological effects of the effortful swallow maneuver in adults with normal and disordered swallowing. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2020;29(3):1655–73. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_AJSLP-19-00132 .
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Polacco RE, et al. Outcomes of tongue-pressure strength and accuracy training for dysphagia following acquired brain injury. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013;15(5):492–502. https://doi.org/10.3109/17549507.2012.752864 .
Franciotti R, Di Maria E, D'Attilio M, Aprile G, Cosentino FG, Perrotti V. Quantitative measurement of swallowing performance using iowa oral performance instrument: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2319. Published 2022 Sep 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092319 .
Park JS, Kim HJ, Oh DH. Effect of tongue strength training using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument in stroke patients with dysphagia. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(12):3631–4. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.3631 .
Adkins DL, Boychuk J, Remple MS, Kleim JA. Motor training induces experience-specific patterns of plasticity across motor cortex and spinal cord. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006;101(6):1776–82. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00515.2006 .
Athukorala RP, Jones RD, Sella O, Huckabee ML. Skill training for swallowing rehabilitation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(7):1374–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2014.03.001 .
Troche MS, Curtis JA, Sevitz JS, et al. Rehabilitating cough dysfunction in parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Mov Disord. 2023;38(2):201–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.29268 .
Benfield JK, Everton LF, Bath PM, England TJ. Does therapy with biofeedback improve swallowing in adults with dysphagia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;100(3):551–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2018.04.031 .
Perry SE, Sevitz JS, Curtis JA, Kuo SH, Troche MS. Skill training resulted in improved swallowing in a person with multiple system atrophy: an endoscopy study. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2018;5(4):451–2. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12628 .
Nordio S, Arcara G, Berta G, et al. Biofeedback as an adjunctive treatment for post-stroke dysphagia: a pilot-randomized controlled trial. Dysphagia. 2022;37(5):1207–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10385-2 .
Malandraki GA, Rajappa A, Kantarcigil C, Wagner E, Ivey C, Youse K. The intensive dysphagia rehabilitation approach applied to patients with neurogenic dysphagia: a case series design study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(4):567–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2015.11.019 .
Carnaby-Mann GD, Crary MA. McNeill dysphagia therapy program: a case-control study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91(5):743–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2010.01.013 .
Cola PC, Gatto AR, da Silva RG, et al. Taste and temperature in swallowing transit time after stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2012;2(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1159/000339888 .
Peña-Chávez RE, Schaen-Heacock NE, Hitchcock ME, et al. Effects of food and liquid properties on swallowing physiology and function in adults. Dysphagia. 2023;38(3):785–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10525-2 .
Bisch EM, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ, Lazarus CL. Pharyngeal effects of bolus volume, viscosity, and temperature in patients with dysphagia resulting from neurologic impairment and in normal subjects. J Speech Hear Res. 1994;37(5):1041–59. https://doi.org/10.1044/jshr.3705.1041 .
Suntrup S, Marian T, Schröder JB, Suttrup I, Muhle P, Oelenberg S, et al. Electrical pharyngeal stimulation for dysphagia treatment in tracheotomized stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41(9):1629–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-015-3897-8 .
Muhle P, Suntrup-Krueger S, Bittner S, et al. Increase of substance P concentration in saliva after pharyngeal electrical stimulation in severely dysphagic stroke patients—an indicator of decannulation success? Neurosignals. 2017;25(1):74–87. https://doi.org/10.1159/000482002 .
Bath PM, Woodhouse LJ, Suntrup-Krueger S, et al. Pharyngeal electrical stimulation for neurogenic dysphagia following stroke, traumatic brain injury or other causes: main results from the PHADER cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;28: 100608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100608 .
Morrell K, Hyers M, Stuchiner T, et al. Telehealth stroke dysphagia evaluation is safe and effective. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;44(3–4):225–31. https://doi.org/10.1159/000478107 .
Burns CL, Ward EC, Hill AJ, Phillips N, Porter L. Conducting real-time videofluoroscopic swallow study via telepractice: a preliminary feasibility and reliability study. Dysphagia. 2016;31(3):473–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9701-2 .
Ward EC, Burns CL, Theodoros DG, Russell TG. Impact of dysphagia severity on clinical decision making via telerehabilitation. Telemed J E Health. 2014;20(4):296–303. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2013.0198 .
Duncan S, Mcauley DF, Walshe M, Mcgaughey J, Anand R, Fallis R, et al. Interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia in acute and critical care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(7):1326–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-020-06126-y .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD, USA
Nicole Frost MA, CCC-SLP, BCS-S
New York Medical College, Valhalla, NY, USA
Gavin Yuan BA, Julie Zhang BA & Stephan A. Mayer MD
Westchester Medical Center Health Network, 100 Woods Road, Taylor Pavillion E119, Valhalla, NY, 10595, USA
Amy Rickard CCC-SLP, Erin McGee CCC-SLP, Michelle DiMattia CCC-SLP & Stephan A. Mayer MD
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stephan A. Mayer MD .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
Dr Mayer reports receiving consulting fees from Phagenesis Inc, maker of a pharyngeal electrical stimulation device. The other authors have no conflicts to report.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Frost, N., Yuan, G., Zhang, J. et al. Speech Language Pathology in the Neurocritical Care Unit. Curr Treat Options Neurol 25 , 499–516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-023-00772-5
Download citation
Accepted : 28 September 2023
Published : 09 October 2023
Issue Date : November 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-023-00772-5

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Neurology for the speech-language pathologist by Love, Russell J. Publication date 2001 ... Pdf_module_version 0.0.20 Ppi 360 Rcs_key 24143 Republisher_date 20230113125612 Republisher_operator [email protected] Republisher_time 130 Scandate ...
The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 6th Edition provides students and clinicians with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology in speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the nervous system, including: development of the nervous system ...
Description. The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 6th Edition provides students and clinicians with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology in speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the ...
The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 6th Edition provides students and clinicians with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology in speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the nervous system, including: development of the nervous system ...
Butterworth-Heinemann, Oct 22, 2013 - Health & Fitness - 326 pages. Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist presents the fundamentals in understanding the nervous system in the context of communication. The book takes into consideration the nervous anatomic systems, such as sensory pathways. The text first introduces the speech-language ...
The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 6th Edition provides students and clinicians with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology in speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the nervous system ...
Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist - E-Book Wanda Webb, Richard K. Adler Limited preview - 2016. Common terms and phrases. activity afferent agnosia alexia aphasia apraxia apraxia of speech artery association areas auditory axon basal ganglia behavior bilateral brain injury brainstem Broca area called caused cell body central ...
The speech-language pathologist must be knowledgeable in the area of neurology and neurological disease to participate in the treatment of communication disorders. The brain, spinal cord, and nerves taken together make up the central nervous system or neuraxis. The largest mass of brain tissue is identified as the cerebrum.
The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 7th Edition provides you with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology as it relates to human communication and the study of speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the nervous system, including ...
About This Book. Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist presents the fundamentals in understanding the nervous system in the context of communication. The book takes into consideration the nervous anatomic systems, such as sensory pathways. The text first introduces the speech-language neurology, and then proceeds to discussing the ...
Description. Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist presents the fundamentals in understanding the nervous system in the context of communication. The book takes into consideration the nervous anatomic systems, such as sensory pathways. The text first introduces the speech-language neurology, and then proceeds to discussing the ...
Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist. Paperback ISBN: 9780323830980 Authors. Rima Abou-Khalil, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Hearing and Speech Sciences Vanderbilt University Medical School 8334 MCE South Tower and Wanda Webb, PhD, CCC-SLP, Assistant Professor of Hearing and Speech Sciences, Vanderbilt ...
How evidence-based practice (E3BP) informs speech- language pathology for primary progressive aphasia. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2020;35:1533317520915365. Crossref
2000. TLDR. Five major areas in which disordered and normal speech can be integrated into an improved understanding of speech motor control are considered: sensory function in the regulation of speech; rhythm as a temporal substrate for the organization of speech movements; kinematics of individual movements and motor systems; neural bases of ...
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY (AJSLP) JOURNAL OF SPEECH, LANGUAGE, AND HEARING RESEARCH (JSLHR) ... PDF. Tools. Add to favorites; Download Citation; Track Citations; Share. Facebook; Twitter; Linked In " Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 3rd Edition." Perspectives on Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia ...
Description. The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 7th Edition provides you with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology as it relates to human communication and the study of speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you ...
Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist presents the fundamentals in understanding the nervous system in the context of communication. The book takes into consideration the nervous anatomic systems, such as sensory pathways. The text first introduces the speech-language neurology, and then proceeds to discussing the organization and neural function of the nervous system.
The concise, easy-to-understand Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist, 6th Edition provides students and clinicians with a practical guide for the study and understanding of neurology in speech-language pathology (SLP). Correlated with clinical syndromes and diseases seen in SLP, it gives you a solid understanding of the nervous system, including: development of the nervous system ...
This article is not intended to diminish the critical importance of the role of the neurologist, nor is it designed to make neurologists of speech-language pathologists. It is intended to aid the speech-language pathologist in gaining the knowledge necessary to recognize important neurological indicators that necessitate medical intervention. I.
Speech language pathologists (SLPs) specialize in the domains of communication, cognition, and swallowing. In the neurocritical care unit (NCCU), SLPs provide evaluation and a wide range of treatments for patients that experience difficulties in one or more of these domains as a result of their underlying neurological condition (Table 1).The prevalence of aphasia in patients in the NCCU ranges ...
speech, language, and cognition that are affected by neurological-based diseases, trauma, and disorders. Medical imaging including CT scan, MRI, and other imaging procedures are discussed. Course Prerequistes : This course is designed for graduate students in speech-language pathology.
Libro- Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist-Mosby (Wanda Webb-2016).pdf - Free ebook download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read book online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
CAS is a neurological speech disorder that impairs a child's ability to plan, coordinate, produce, and sequence the temporal and spa-tial aspects of speech. Although the severity of CAS var- ies from child to child, children with CAS demonstrate ... Three licensed speech-language pathologists with experience in the assessment of pediatric ...
A clear, concise, and approachable writing style helps students understand neurology in the context of speech-language pathology. Supplemented by a wealth of new illustrations and learning features for students, this new edition helps to demystify this often-daunting subject matter. The 5th edition also introduces a new author, Dr. Richard Adler, who brings a fresh perspective and an ...
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY (AJSLP) JOURNAL OF SPEECH, LANGUAGE, AND HEARING RESEARCH (JSLHR) ... PDF. Tools. Add to favorites; Download Citation; Track Citations; Share. Facebook; Twitter; ... Brief measures of health-related quality of life for clinical research in neurology. Neurology, 78(23), 1860-1867. https://doi.org ...
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is one of the chronic and neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system (CNS). It generally affects motor, sensory, cerebellar, cognitive, and language functions. It is thought that identifying MS speech disorders using quantitative methods will make a significant contribution to physicians in the diagnosis and follow-up of MS patients.
Method: Twelve children with Down syndrome (M age = 40.82 months) and their biological parents participated in the current study.We collected separate mother-child and father-child dyadic interactions and one family choice interaction (i.e., both caregivers present and occasionally siblings) in families' homes.