- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 14 December 2021

Bullying at school and mental health problems among adolescents: a repeated cross-sectional study
- Håkan Källmén 1 &
- Mats Hallgren ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0599-2403 2
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health volume 15 , Article number: 74 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
95k Accesses
13 Citations
37 Altmetric
Metrics details
To examine recent trends in bullying and mental health problems among adolescents and the association between them.
A questionnaire measuring mental health problems, bullying at school, socio-economic status, and the school environment was distributed to all secondary school students aged 15 (school-year 9) and 18 (school-year 11) in Stockholm during 2014, 2018, and 2020 (n = 32,722). Associations between bullying and mental health problems were assessed using logistic regression analyses adjusting for relevant demographic, socio-economic, and school-related factors.
The prevalence of bullying remained stable and was highest among girls in year 9; range = 4.9% to 16.9%. Mental health problems increased; range = + 1.2% (year 9 boys) to + 4.6% (year 11 girls) and were consistently higher among girls (17.2% in year 11, 2020). In adjusted models, having been bullied was detrimentally associated with mental health (OR = 2.57 [2.24–2.96]). Reports of mental health problems were four times higher among boys who had been bullied compared to those not bullied. The corresponding figure for girls was 2.4 times higher.
Conclusions
Exposure to bullying at school was associated with higher odds of mental health problems. Boys appear to be more vulnerable to the deleterious effects of bullying than girls.
Introduction
Bullying involves repeated hurtful actions between peers where an imbalance of power exists [ 1 ]. Arseneault et al. [ 2 ] conducted a review of the mental health consequences of bullying for children and adolescents and found that bullying is associated with severe symptoms of mental health problems, including self-harm and suicidality. Bullying was shown to have detrimental effects that persist into late adolescence and contribute independently to mental health problems. Updated reviews have presented evidence indicating that bullying is causative of mental illness in many adolescents [ 3 , 4 ].
There are indications that mental health problems are increasing among adolescents in some Nordic countries. Hagquist et al. [ 5 ] examined trends in mental health among Scandinavian adolescents (n = 116, 531) aged 11–15 years between 1993 and 2014. Mental health problems were operationalized as difficulty concentrating, sleep disorders, headache, stomach pain, feeling tense, sad and/or dizzy. The study revealed increasing rates of adolescent mental health problems in all four counties (Finland, Sweden, Norway, and Denmark), with Sweden experiencing the sharpest increase among older adolescents, particularly girls. Worsening adolescent mental health has also been reported in the United Kingdom. A study of 28,100 school-aged adolescents in England found that two out of five young people scored above thresholds for emotional problems, conduct problems or hyperactivity [ 6 ]. Female gender, deprivation, high needs status (educational/social), ethnic background, and older age were all associated with higher odds of experiencing mental health difficulties.
Bullying is shown to increase the risk of poor mental health and may partly explain these detrimental changes. Le et al. [ 7 ] reported an inverse association between bullying and mental health among 11–16-year-olds in Vietnam. They also found that poor mental health can make some children and adolescents more vulnerable to bullying at school. Bayer et al. [ 8 ] examined links between bullying at school and mental health among 8–9-year-old children in Australia. Those who experienced bullying more than once a week had poorer mental health than children who experienced bullying less frequently. Friendships moderated this association, such that children with more friends experienced fewer mental health problems (protective effect). Hysing et al. [ 9 ] investigated the association between experiences of bullying (as a victim or perpetrator) and mental health, sleep disorders, and school performance among 16–19 year olds from Norway (n = 10,200). Participants were categorized as victims, bullies, or bully-victims (that is, victims who also bullied others). All three categories were associated with worse mental health, school performance, and sleeping difficulties. Those who had been bullied also reported more emotional problems, while those who bullied others reported more conduct disorders [ 9 ].
As most adolescents spend a considerable amount of time at school, the school environment has been a major focus of mental health research [ 10 , 11 ]. In a recent review, Saminathen et al. [ 12 ] concluded that school is a potential protective factor against mental health problems, as it provides a socially supportive context and prepares students for higher education and employment. However, it may also be the primary setting for protracted bullying and stress [ 13 ]. Another factor associated with adolescent mental health is parental socio-economic status (SES) [ 14 ]. A systematic review indicated that lower parental SES is associated with poorer adolescent mental health [ 15 ]. However, no previous studies have examined whether SES modifies or attenuates the association between bullying and mental health. Similarly, it remains unclear whether school related factors, such as school grades and the school environment, influence the relationship between bullying and mental health. This information could help to identify those adolescents most at risk of harm from bullying.
To address these issues, we investigated the prevalence of bullying at school and mental health problems among Swedish adolescents aged 15–18 years between 2014 and 2020 using a population-based school survey. We also examined associations between bullying at school and mental health problems adjusting for relevant demographic, socioeconomic, and school-related factors. We hypothesized that: (1) bullying and adolescent mental health problems have increased over time; (2) There is an association between bullying victimization and mental health, so that mental health problems are more prevalent among those who have been victims of bullying; and (3) that school-related factors would attenuate the association between bullying and mental health.
Participants
The Stockholm school survey is completed every other year by students in lower secondary school (year 9—compulsory) and upper secondary school (year 11). The survey is mandatory for public schools, but voluntary for private schools. The purpose of the survey is to help inform decision making by local authorities that will ultimately improve students’ wellbeing. The questions relate to life circumstances, including SES, schoolwork, bullying, drug use, health, and crime. Non-completers are those who were absent from school when the survey was completed (< 5%). Response rates vary from year to year but are typically around 75%. For the current study data were available for 2014, 2018 and 2020. In 2014; 5235 boys and 5761 girls responded, in 2018; 5017 boys and 5211 girls responded, and in 2020; 5633 boys and 5865 girls responded (total n = 32,722). Data for the exposure variable, bullied at school, were missing for 4159 students, leaving 28,563 participants in the crude model. The fully adjusted model (described below) included 15,985 participants. The mean age in grade 9 was 15.3 years (SD = 0.51) and in grade 11, 17.3 years (SD = 0.61). As the data are completely anonymous, the study was exempt from ethical approval according to an earlier decision from the Ethical Review Board in Stockholm (2010-241 31-5). Details of the survey are available via a website [ 16 ], and are described in a previous paper [ 17 ].
Students completed the questionnaire during a school lesson, placed it in a sealed envelope and handed it to their teacher. Student were permitted the entire lesson (about 40 min) to complete the questionnaire and were informed that participation was voluntary (and that they were free to cancel their participation at any time without consequences). Students were also informed that the Origo Group was responsible for collection of the data on behalf of the City of Stockholm.
Study outcome
Mental health problems were assessed by using a modified version of the Psychosomatic Problem Scale [ 18 ] shown to be appropriate for children and adolescents and invariant across gender and years. The scale was later modified [ 19 ]. In the modified version, items about difficulty concentrating and feeling giddy were deleted and an item about ‘life being great to live’ was added. Seven different symptoms or problems, such as headaches, depression, feeling fear, stomach problems, difficulty sleeping, believing it’s great to live (coded negatively as seldom or rarely) and poor appetite were used. Students who responded (on a 5-point scale) that any of these problems typically occurs ‘at least once a week’ were considered as having indicators of a mental health problem. Cronbach alpha was 0.69 across the whole sample. Adding these problem areas, a total index was created from 0 to 7 mental health symptoms. Those who scored between 0 and 4 points on the total symptoms index were considered to have a low indication of mental health problems (coded as 0); those who scored between 5 and 7 symptoms were considered as likely having mental health problems (coded as 1).
Primary exposure
Experiences of bullying were measured by the following two questions: Have you felt bullied or harassed during the past school year? Have you been involved in bullying or harassing other students during this school year? Alternatives for the first question were: yes or no with several options describing how the bullying had taken place (if yes). Alternatives indicating emotional bullying were feelings of being mocked, ridiculed, socially excluded, or teased. Alternatives indicating physical bullying were being beaten, kicked, forced to do something against their will, robbed, or locked away somewhere. The response alternatives for the second question gave an estimation of how often the respondent had participated in bullying others (from once to several times a week). Combining the answers to these two questions, five different categories of bullying were identified: (1) never been bullied and never bully others; (2) victims of emotional (verbal) bullying who have never bullied others; (3) victims of physical bullying who have never bullied others; (4) victims of bullying who have also bullied others; and (5) perpetrators of bullying, but not victims. As the number of positive cases in the last three categories was low (range = 3–15 cases) bully categories 2–4 were combined into one primary exposure variable: ‘bullied at school’.
Assessment year was operationalized as the year when data was collected: 2014, 2018, and 2020. Age was operationalized as school grade 9 (15–16 years) or 11 (17–18 years). Gender was self-reported (boy or girl). The school situation To assess experiences of the school situation, students responded to 18 statements about well-being in school, participation in important school matters, perceptions of their teachers, and teaching quality. Responses were given on a four-point Likert scale ranging from ‘do not agree at all’ to ‘fully agree’. To reduce the 18-items down to their essential factors, we performed a principal axis factor analysis. Results showed that the 18 statements formed five factors which, according to the Kaiser criterion (eigen values > 1) explained 56% of the covariance in the student’s experience of the school situation. The five factors identified were: (1) Participation in school; (2) Interesting and meaningful work; (3) Feeling well at school; (4) Structured school lessons; and (5) Praise for achievements. For each factor, an index was created that was dichotomised (poor versus good circumstance) using the median-split and dummy coded with ‘good circumstance’ as reference. A description of the items included in each factor is available as Additional file 1 . Socio-economic status (SES) was assessed with three questions about the education level of the student’s mother and father (dichotomized as university degree versus not), and the amount of spending money the student typically received for entertainment each month (> SEK 1000 [approximately $120] versus less). Higher parental education and more spending money were used as reference categories. School grades in Swedish, English, and mathematics were measured separately on a 7-point scale and dichotomized as high (grades A, B, and C) versus low (grades D, E, and F). High school grades were used as the reference category.
Statistical analyses
The prevalence of mental health problems and bullying at school are presented using descriptive statistics, stratified by survey year (2014, 2018, 2020), gender, and school year (9 versus 11). As noted, we reduced the 18-item questionnaire assessing school function down to five essential factors by conducting a principal axis factor analysis (see Additional file 1 ). We then calculated the association between bullying at school (defined above) and mental health problems using multivariable logistic regression. Results are presented as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (Cis). To assess the contribution of SES and school-related factors to this association, three models are presented: Crude, Model 1 adjusted for demographic factors: age, gender, and assessment year; Model 2 adjusted for Model 1 plus SES (parental education and student spending money), and Model 3 adjusted for Model 2 plus school-related factors (school grades and the five factors identified in the principal factor analysis). These covariates were entered into the regression models in three blocks, where the final model represents the fully adjusted analyses. In all models, the category ‘not bullied at school’ was used as the reference. Pseudo R-square was calculated to estimate what proportion of the variance in mental health problems was explained by each model. Unlike the R-square statistic derived from linear regression, the Pseudo R-square statistic derived from logistic regression gives an indicator of the explained variance, as opposed to an exact estimate, and is considered informative in identifying the relative contribution of each model to the outcome [ 20 ]. All analyses were performed using SPSS v. 26.0.
Prevalence of bullying at school and mental health problems
Estimates of the prevalence of bullying at school and mental health problems across the 12 strata of data (3 years × 2 school grades × 2 genders) are shown in Table 1 . The prevalence of bullying at school increased minimally (< 1%) between 2014 and 2020, except among girls in grade 11 (2.5% increase). Mental health problems increased between 2014 and 2020 (range = 1.2% [boys in year 11] to 4.6% [girls in year 11]); were three to four times more prevalent among girls (range = 11.6% to 17.2%) compared to boys (range = 2.6% to 4.9%); and were more prevalent among older adolescents compared to younger adolescents (range = 1% to 3.1% higher). Pooling all data, reports of mental health problems were four times more prevalent among boys who had been victims of bullying compared to those who reported no experiences with bullying. The corresponding figure for girls was two and a half times as prevalent.
Associations between bullying at school and mental health problems
Table 2 shows the association between bullying at school and mental health problems after adjustment for relevant covariates. Demographic factors, including female gender (OR = 3.87; CI 3.48–4.29), older age (OR = 1.38, CI 1.26–1.50), and more recent assessment year (OR = 1.18, CI 1.13–1.25) were associated with higher odds of mental health problems. In Model 2, none of the included SES variables (parental education and student spending money) were associated with mental health problems. In Model 3 (fully adjusted), the following school-related factors were associated with higher odds of mental health problems: lower grades in Swedish (OR = 1.42, CI 1.22–1.67); uninteresting or meaningless schoolwork (OR = 2.44, CI 2.13–2.78); feeling unwell at school (OR = 1.64, CI 1.34–1.85); unstructured school lessons (OR = 1.31, CI = 1.16–1.47); and no praise for achievements (OR = 1.19, CI 1.06–1.34). After adjustment for all covariates, being bullied at school remained associated with higher odds of mental health problems (OR = 2.57; CI 2.24–2.96). Demographic and school-related factors explained 12% and 6% of the variance in mental health problems, respectively (Pseudo R-Square). The inclusion of socioeconomic factors did not alter the variance explained.
Our findings indicate that mental health problems increased among Swedish adolescents between 2014 and 2020, while the prevalence of bullying at school remained stable (< 1% increase), except among girls in year 11, where the prevalence increased by 2.5%. As previously reported [ 5 , 6 ], mental health problems were more common among girls and older adolescents. These findings align with previous studies showing that adolescents who are bullied at school are more likely to experience mental health problems compared to those who are not bullied [ 3 , 4 , 9 ]. This detrimental relationship was observed after adjustment for school-related factors shown to be associated with adolescent mental health [ 10 ].
A novel finding was that boys who had been bullied at school reported a four-times higher prevalence of mental health problems compared to non-bullied boys. The corresponding figure for girls was 2.5 times higher for those who were bullied compared to non-bullied girls, which could indicate that boys are more vulnerable to the deleterious effects of bullying than girls. Alternatively, it may indicate that boys are (on average) bullied more frequently or more intensely than girls, leading to worse mental health. Social support could also play a role; adolescent girls often have stronger social networks than boys and could be more inclined to voice concerns about bullying to significant others, who in turn may offer supports which are protective [ 21 ]. Related studies partly confirm this speculative explanation. An Estonian study involving 2048 children and adolescents aged 10–16 years found that, compared to girls, boys who had been bullied were more likely to report severe distress, measured by poor mental health and feelings of hopelessness [ 22 ].
Other studies suggest that heritable traits, such as the tendency to internalize problems and having low self-esteem are associated with being a bully-victim [ 23 ]. Genetics are understood to explain a large proportion of bullying-related behaviors among adolescents. A study from the Netherlands involving 8215 primary school children found that genetics explained approximately 65% of the risk of being a bully-victim [ 24 ]. This proportion was similar for boys and girls. Higher than average body mass index (BMI) is another recognized risk factor [ 25 ]. A recent Australian trial involving 13 schools and 1087 students (mean age = 13 years) targeted adolescents with high-risk personality traits (hopelessness, anxiety sensitivity, impulsivity, sensation seeking) to reduce bullying at school; both as victims and perpetrators [ 26 ]. There was no significant intervention effect for bullying victimization or perpetration in the total sample. In a secondary analysis, compared to the control schools, intervention school students showed greater reductions in victimization, suicidal ideation, and emotional symptoms. These findings potentially support targeting high-risk personality traits in bullying prevention [ 26 ].
The relative stability of bullying at school between 2014 and 2020 suggests that other factors may better explain the increase in mental health problems seen here. Many factors could be contributing to these changes, including the increasingly competitive labour market, higher demands for education, and the rapid expansion of social media [ 19 , 27 , 28 ]. A recent Swedish study involving 29,199 students aged between 11 and 16 years found that the effects of school stress on psychosomatic symptoms have become stronger over time (1993–2017) and have increased more among girls than among boys [ 10 ]. Research is needed examining possible gender differences in perceived school stress and how these differences moderate associations between bullying and mental health.
Strengths and limitations
Strengths of the current study include the large participant sample from diverse schools; public and private, theoretical and practical orientations. The survey included items measuring diverse aspects of the school environment; factors previously linked to adolescent mental health but rarely included as covariates in studies of bullying and mental health. Some limitations are also acknowledged. These data are cross-sectional which means that the direction of the associations cannot be determined. Moreover, all the variables measured were self-reported. Previous studies indicate that students tend to under-report bullying and mental health problems [ 29 ]; thus, our results may underestimate the prevalence of these behaviors.
In conclusion, consistent with our stated hypotheses, we observed an increase in self-reported mental health problems among Swedish adolescents, and a detrimental association between bullying at school and mental health problems. Although bullying at school does not appear to be the primary explanation for these changes, bullying was detrimentally associated with mental health after adjustment for relevant demographic, socio-economic, and school-related factors, confirming our third hypothesis. The finding that boys are potentially more vulnerable than girls to the deleterious effects of bullying should be replicated in future studies, and the mechanisms investigated. Future studies should examine the longitudinal association between bullying and mental health, including which factors mediate/moderate this relationship. Epigenetic studies are also required to better understand the complex interaction between environmental and biological risk factors for adolescent mental health [ 24 ].
Availability of data and materials
Data requests will be considered on a case-by-case basis; please email the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Olweus D. School bullying: development and some important challenges. Ann Rev Clin Psychol. 2013;9(9):751–80. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185516 .
Article Google Scholar
Arseneault L, Bowes L, Shakoor S. Bullying victimization in youths and mental health problems: “Much ado about nothing”? Psychol Med. 2010;40(5):717–29. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291709991383 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Arseneault L. The long-term impact of bullying victimization on mental health. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):27–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20399 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Moore SE, Norman RE, Suetani S, Thomas HJ, Sly PD, Scott JG. Consequences of bullying victimization in childhood and adolescence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Psychiatry. 2017;7(1):60–76. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v7.i1.60 .
Hagquist C, Due P, Torsheim T, Valimaa R. Cross-country comparisons of trends in adolescent psychosomatic symptoms—a Rasch analysis of HBSC data from four Nordic countries. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019;17(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-019-1097-x .
Deighton J, Lereya ST, Casey P, Patalay P, Humphrey N, Wolpert M. Prevalence of mental health problems in schools: poverty and other risk factors among 28 000 adolescents in England. Br J Psychiatry. 2019;215(3):565–7. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2019.19 .
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Le HTH, Tran N, Campbell MA, Gatton ML, Nguyen HT, Dunne MP. Mental health problems both precede and follow bullying among adolescents and the effects differ by gender: a cross-lagged panel analysis of school-based longitudinal data in Vietnam. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-019-0291-x .
Bayer JK, Mundy L, Stokes I, Hearps S, Allen N, Patton G. Bullying, mental health and friendship in Australian primary school children. Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2018;23(4):334–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/camh.12261 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hysing M, Askeland KG, La Greca AM, Solberg ME, Breivik K, Sivertsen B. Bullying involvement in adolescence: implications for sleep, mental health, and academic outcomes. J Interpers Violence. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260519853409 .
Hogberg B, Strandh M, Hagquist C. Gender and secular trends in adolescent mental health over 24 years—the role of school-related stress. Soc Sci Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.112890 .
Kidger J, Araya R, Donovan J, Gunnell D. The effect of the school environment on the emotional health of adolescents: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2012;129(5):925–49. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2248 .
Saminathen MG, Låftman SB, Modin B. En fungerande skola för alla: skolmiljön som skyddsfaktor för ungas psykiska välbefinnande. [A functioning school for all: the school environment as a protective factor for young people’s mental well-being]. Socialmedicinsk tidskrift [Soc Med]. 2020;97(5–6):804–16.
Google Scholar
Bibou-Nakou I, Tsiantis J, Assimopoulos H, Chatzilambou P, Giannakopoulou D. School factors related to bullying: a qualitative study of early adolescent students. Soc Psychol Educ. 2012;15(2):125–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-012-9179-1 .
Vukojevic M, Zovko A, Talic I, Tanovic M, Resic B, Vrdoljak I, Splavski B. Parental socioeconomic status as a predictor of physical and mental health outcomes in children—literature review. Acta Clin Croat. 2017;56(4):742–8. https://doi.org/10.20471/acc.2017.56.04.23 .
Reiss F. Socioeconomic inequalities and mental health problems in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2013;90:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.04.026 .
Stockholm City. Stockholmsenkät (The Stockholm Student Survey). 2021. https://start.stockholm/aktuellt/nyheter/2020/09/presstraff-stockholmsenkaten-2020/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2021.
Zeebari Z, Lundin A, Dickman PW, Hallgren M. Are changes in alcohol consumption among swedish youth really occurring “in concert”? A new perspective using quantile regression. Alc Alcohol. 2017;52(4):487–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agx020 .
Hagquist C. Psychometric properties of the PsychoSomatic Problems Scale: a Rasch analysis on adolescent data. Social Indicat Res. 2008;86(3):511–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-007-9186-3 .
Hagquist C. Ungas psykiska hälsa i Sverige–komplexa trender och stora kunskapsluckor [Young people’s mental health in Sweden—complex trends and large knowledge gaps]. Socialmedicinsk tidskrift [Soc Med]. 2013;90(5):671–83.
Wu W, West SG. Detecting misspecification in mean structures for growth curve models: performance of pseudo R(2)s and concordance correlation coefficients. Struct Equ Model. 2013;20(3):455–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2013.797829 .
Holt MK, Espelage DL. Perceived social support among bullies, victims, and bully-victims. J Youth Adolscence. 2007;36(8):984–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-006-9153-3 .
Mark L, Varnik A, Sisask M. Who suffers most from being involved in bullying-bully, victim, or bully-victim? J Sch Health. 2019;89(2):136–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/josh.12720 .
Tsaousis I. The relationship of self-esteem to bullying perpetration and peer victimization among schoolchildren and adolescents: a meta-analytic review. Aggress Violent Behav. 2016;31:186–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2016.09.005 .
Veldkamp SAM, Boomsma DI, de Zeeuw EL, van Beijsterveldt CEM, Bartels M, Dolan CV, van Bergen E. Genetic and environmental influences on different forms of bullying perpetration, bullying victimization, and their co-occurrence. Behav Genet. 2019;49(5):432–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-019-09968-5 .
Janssen I, Craig WM, Boyce WF, Pickett W. Associations between overweight and obesity with bullying behaviors in school-aged children. Pediatrics. 2004;113(5):1187–94. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.113.5.1187 .
Kelly EV, Newton NC, Stapinski LA, Conrod PJ, Barrett EL, Champion KE, Teesson M. A novel approach to tackling bullying in schools: personality-targeted intervention for adolescent victims and bullies in Australia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(4):508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2019.04.010 .
Gunnell D, Kidger J, Elvidge H. Adolescent mental health in crisis. BMJ. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2608 .
O’Reilly M, Dogra N, Whiteman N, Hughes J, Eruyar S, Reilly P. Is social media bad for mental health and wellbeing? Exploring the perspectives of adolescents. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;23:601–13.
Unnever JD, Cornell DG. Middle school victims of bullying: who reports being bullied? Aggr Behav. 2004;30(5):373–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20030 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Department for Social Affairs, Stockholm, for permission to use data from the Stockholm School Survey.
Open access funding provided by Karolinska Institute. None to declare.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stockholm Prevents Alcohol and Drug Problems (STAD), Center for Addiction Research and Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden
Håkan Källmén
Epidemiology of Psychiatric Conditions, Substance Use and Social Environment (EPiCSS), Department of Global Public Health, Karolinska Institutet, Level 6, Solnavägen 1e, Solna, Sweden
Mats Hallgren
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HK conceived the study and analyzed the data (with input from MH). HK and MH interpreted the data and jointly wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mats Hallgren .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
As the data are completely anonymous, the study was exempt from ethical approval according to an earlier decision from the Ethical Review Board in Stockholm (2010-241 31-5).
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Principal factor analysis description.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Källmén, H., Hallgren, M. Bullying at school and mental health problems among adolescents: a repeated cross-sectional study. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health 15 , 74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-021-00425-y
Download citation
Received : 05 October 2021
Accepted : 23 November 2021
Published : 14 December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-021-00425-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
- Adolescents
- School-related factors
- Gender differences
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health
ISSN: 1753-2000
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
Advertisement
Bullying: issues and challenges in prevention and intervention
- Published: 12 August 2023
- Volume 43 , pages 9270–9279, ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Muhammad Waseem ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8720-955X 1 , 2 , 3 &
- Amanda B. Nickerson 4
891 Accesses
2 Citations
68 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Bullying is a public health issue that persists and occurs across several contexts. In this narrative review, we highlight issues and challenges in addressing bullying prevention. Specifically, we discuss issues related to defining, measuring, and screening for bullying. These include discrepancies in the interpretation and measurement of power imbalance, repetition of behavior, and perceptions of the reporter. The contexts of bullying, both within and outside of the school setting (including the online environment), are raised as an important issue relevant for identification and prevention. The role of medical professionals in screening for bullying is also noted. Prevention and intervention approaches are reviewed, and we highlight the need and evidence for social architectural interventions that involve multiple stakeholders, including parents, in these efforts. Areas in need are identified, such as understanding and intervening in cyberbullying, working more specifically with perpetrators as a heterogeneous group, and providing more intensive interventions for the most vulnerable youth who remain at risk despite universal prevention efforts.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Updated Perspectives on Linking School Bullying and Related Youth Violence Research to Effective Prevention Strategies

Bullying and Cyberbullying Throughout Adolescence

Data availability
This manuscript does not involve patient data. This is a review based on the published literature.
Allen, K. P. (2010a). A bullying intervention system in high school: A two-year school-wide follow-up. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 36 (3), 83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2011.01.002
Article Google Scholar
Allen, K. P. (2010b). A bullying intervention system: Reducing risk and creating support for aggressive students. Preventing School Failure, 54 (3), 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/10459880903496289
American Educational Research Association (2013). Prevention of bullying in schools, colleges, and universities: Research report and recommendations . https://www.aera.net/Education-Research/Issues-and-Initiatives/Bullying-Prevention-and-School-Safety/Bullying-Prevention
Axford, N., Bjornstad, G., Clarkson, S., Ukoumunne, O. C., Wrigley, Z., Matthews, J., Berry, V., & Hutchings, J. (2020). The effectiveness of the KiVa bullying prevention program in Wales, UK: Results from a pragmatic cluster randomized controlled trial. Prevention Science, 21 (5), 615–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-020-01103-9
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Baldry, A. C., & Farrington, D. P. (2007). Effectiveness of programs to prevent school bullying. Victims & Offenders, 2 (2), 183–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/15564880701263155
Barboza, G. E., Schiamberg, L. B., Oehmke, J., Korzeniewski, S. J., Post, L. A., & Heraux, C. G. (2009). Individual characteristics and the multiple contexts of adolescent bullying: An ecological perspective. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 38 (1), 101–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-008-9271-1
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bauman, S. (2016). Do we need more measures of bullying? The Journal of Adolescent Health, 59 (5), 487–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.08.021
Bear, G. G., Mantz, L. S., Glutting, J. J., Yang, C., & Boyer, D. E. (2015). Differences in bullying victimization between students with and without disabilities. School Psychology Review, 44 (1), 98–116. https://doi.org/10.17105/SPR44-1.98-116
Blake, J. J., Lund, E. M., Zhou, Q., Kwok, O. M., & Benz, M. R. (2012). National prevalence rates of bully victimization among students with disabilities in the United States. School Psychology Quarterly, 27 (4), 210–222. https://doi.org/10.1037/spq0000008
Borgen, N. T., Olweus, D., Kirkebøen, L. J., Breivik, K., Solberg, M. E., Frønes, I., Cross, D., & Raaum, O. (2021). The potential of anti-bullying efforts to prevent academic failure and youth crime. A case using the Olweus bullying prevention program (OBPP). Prevention Science, 22 , 1147–1158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-021-01254-3
Bostic, J. Q., & Brunt, C. C. (2011). Cornered: An approach to school bullying and cyberbullying, and forensic implications. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 20 (3), 447–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2011.03.004
Bradshaw, C. P. (2015). Translating research to practice in bullying prevention. American Psychologist, 70 (4), 322–332. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039114
Camodeca, M., & Nava, E. (2022). The long-term effects of bullying, victimization, and bystander behavior on emotion regulation and its physiological correlates. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 37 (3–4), NP2056–NP2075. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260520934438
Carter, S. (2011). Bullies and power: A look at the research. Issues in Comprehensive Pediatric Nursing, 34 (2), 97–102. https://doi.org/10.3109/01460862.2011.574455
Cascardi, M., Brown, C., Iannarone, M., & Cardona, N. (2014). The problem with overly broad definitions of bullying: Implications for the schoolhouse, the statehouse, and the ivory tower. Journal of School Violence, 13 (3), 253–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/15388220.2013.846861
Chen, Q., Zhu, Y., & Chui, W. H. (2021). A meta-analysis on the effects of parenting programs on bullying prevention. Trauma, Violence & Abuse, 22 (5), 1209–1220. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838020915619
Cheng, Y. Y., Chen, L. M., Ho, H. C., & Cheng, C. L. (2011). Definitions of school bullying in Taiwan: A comparison of multiple perspectives. School Psychology International, 32 (3), 227–243. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034313479694
Cook, C. R., Williams, K. R., Guerra, N. G., Kim, T. E., & Sadek, S. (2010). Predictors of bullying and victimization in childhood and adolescence: A meta-analytic investigation. School Psychology Quarterly, 25 (2), 65–83. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020149
Cosgrove, H., & Nickerson, A. B. (2015). Anti-bullying/harassment legislation and educator perceptions of severity, effectiveness, and school climate: A cross-sectional analysis. Educational Policy, 31 (4), 518–545. https://doi.org/10.1177/0895904815604217
Dale, J., Russell, R., & Wolke, D. (2014). Intervening in primary care against childhood bullying: An increasingly pressing public health need. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 107 (6), 219–223. https://doi.org/10.1177/0141076814525071
Deshmukh, P., & Kaplan, S. (2018). Bullying as a risk factor for inpatient hospitalization: Let’s change it! Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 57 (10), S260–S260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2018.09.397
Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R. P., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students' social and emotional learning: A meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82 (1), 405–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01564.x
Espelage, D. L., & Swearer, S. M. (2003). Research on school bullying and victimization: What have we learned and where do we go from here? School Psychology Review, 32 (3), 365–383. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.2003.12086206
Espelage, D. L., Low, S., Polanin, J. R., & Brown, E. C. (2013). The impact of a middle school program to reduce aggression, victimization, and sexual violence. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 53 (2), 180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.02.021
Espelage, D. L., Low, S., Van Ryzin, M. J., & Polanin, J. R. (2015). Clinical trial of second step middle school program: Impact on bullying, cyberbullying, homophobic teasing, and sexual harassment perpetration. School Psychology Review, 44 (4), 464–479. https://doi.org/10.17105/spr-15-0052.1
Farrington, D. P., & Ttofi, M. M. (2009). School-based programs to reduce bullying and victimization. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 5 (1), 148. https://doi.org/10.4073/csr.2009.6
Farrington, D. P., & Ttofi, M. M. (2011). Bullying as a predictor of offending, violence and later life outcomes. Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 21 (2), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbm.801
Felix, E. D., Sharkey, J. D., Green, J. G., Furlong, M. J., & Tanigawa, D. (2011). Getting precise and pragmatic about the assessment of bullying: The development of the California bullying victimization scale. Aggressive Behavior, 37 (3), 234–247. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20389
Fredrick, S. S., Nickerson, A. B., & Livingston, J. A. (2021). Family cohesion and the relations among peer victimization and depression: A random intercepts cross-lagged model. Development and Psychopathology, 34 (4), 1429–1446. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095457942100016X
Frey, K. S., Hirschstein, M. K., Snell, J. L., Edstrom, L. V., MacKenzie, E. P., & Broderick, C. J. (2005). Reducing playground bullying and supporting beliefs: An experimental trial of the steps to respect program. Developmental Psychology, 41 (3), 479–490. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.41.3.479
Frey, K. S., Hirschstein, M. K., Edstrom, L. V., & Snell, J. L. (2009). Observed reductions in school bullying, nonbullying aggression and destructive bystander behavior: A longitudinal evaluation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101 (2), 466–481. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013839
Gaffney, H., Farrington, D. P., Espelage, D. L., & Ttofi, M. M. (2019a). Are cyberbullying intervention and prevention programs effective? A systematic and meta-analytical review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 45 , 134–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2018.07.002
Gaffney, H., Ttofi, M., & Farrington, D. (2019b). Evaluating the effectiveness of school-bullying prevention programs: An updated meta-analytical review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 45 , 111–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2018.07.001
Garandeau, C. F., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2014). Tackling acute cases of school bullying in the KiVa anti-bullying program: A comparison of two approaches. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 42 (6), 981–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-014-9861-1
Garandeau, C. F., Vartio, A., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2016). School bullies' intention to change behavior following teacher interventions: Effects of empathy arousal, condemning of bullying, and blaming of the perpetrator. Prevention Science, 17 (8), 1034–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0712-x
Garandeau, C. F., Lee, I. A., & Salmivalli, C. (2018). Decreases in the proportion of bullying victims in the classroom: Effects on the adjustment of remaining victims. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 42 (1), 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025416667492
Gladden, R. M., Vivolo-Kantor, A. M., Hamburger, M. E., & Lumpkin, C. D. (2014). Bullying surveillance among youths: Uniform definitions for public health and recommended data elements, version 1.0 . National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved October 23, 2021, from https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/bullying-definitions-final-a.pdf
Gómez Baya, D., Rubio Gónzalez, A., & Gaspar de Matos, M. (2018). Online communication, peer relationships and school victimisation: A one-year longitudinal study during middle adolescence. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 24 (2), 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673843.2018.1509793
Good, C. P., McIntosh, K., & Gietz, C. (2011). Integrating bullying prevention into schoolwide positive behavior support. Teaching Exceptional Children, 244 , 48–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/004005991104400106
Hagan, J. F., Shaw, J. S., & Duncan, P. M. (Eds.) (2017). Bright futures: Guidelines for health supervision of infants, children, and adolescents (4th Ed) . American Academy of Pediatrics. https://brightfutures.aap.org/Bright%20Futures%20Documents/BF4_Introduction.pdf
Hall, W. (2017). The effectiveness of policy interventions for school bullying: A systematic review. Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research, 8 (1), 45–69. https://doi.org/10.1086/690565
Hatzenbuehler, M. L., Schwab-Reese, L., Ranapurwala, S. I., Hertz, M. F., & Ramirez, M. R. (2015). Associations between antibullying policies and bullying in 25 states. JAMA Pediatrics, 169 (10), e152411. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.2411
Hensley, V. (2015). Childhood bullying: Assessment practices and predictive factors associated with assessing for bullying by health care providers . University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved October 23, 2021 from https://uknowledge.uky.edu/nursing_etds/25
Hinduja, S., & Patchin, J. W. (2015). Bullying beyond the schoolyard: Preventing and responding to cyberbullying (2nd ed.). Sage Publications.
Google Scholar
Hong, J. S., & Espelage, D. L. (2012). A review of research on bullying and peer victimization in school: An ecological system analysis. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 17 (4), 311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2012.03.003
Huang, Y., Espelage, D. L., Polanin, J. R., & Hong, J. S. (2019). A meta-analytic review of school-based anti-bullying programs with a parent component. International Journal of Bullying Prevention, 1 (1), 32–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-018-0002-1
Huitsing, G., Lodder, G. M. A., Browne, W. J., Oldenburg, B., Van der Ploeg, R., & Veenstra, R. (2020). A large-scale replication of the effectiveness of the KiVa Antibullying program: A randomized controlled trial in the Netherlands. Prevention Science, 21 (5), 627–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-020-01116-4
Hutson, E., Melnyk, B., Hensley, V., & Sinnott, L. T. (2019). Childhood bullying: Screening and intervening practices of pediatric primary care providers. Journal of Pediatric Health Care, 33 (6), e39–e45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedhc.2019.07.003
Ireland, J. L. (2000). "bullying" among prisoners: A review of research. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 5 (2), 201–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-1789(98)00031-7
Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Poskiparta, E., Alanen, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2011). Going to scale: A nonrandomized nationwide trial of the KiVa antibullying program for grades 1–9. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 79 , 796–805. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025740
Kert, A. S., Codding, R. S., Tryon, G. S., & Shiyko, M. (2010). Impact of the word “bully” on the reported rate of bullying behavior. Psychology in the Schools, 47 (2), 193–204. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20464
Kowalski, R. M., Giumetti, G. W., Schroeder, A. N., & Lattanner, M. R. (2014). Bullying in the digital age: A critical review and meta-analysis of cyberbullying research among youth. Psychological Bulletin, 140 (4), 1073–1137. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035618
Koyanagi, A., Oh, H., Carvalho, A. F., Smith, L., Haro, J. M., Vancampfort, D., Stubbs, B., & DeVylder, J. E. (2019). Bullying victimization and suicide attempt among adolescents aged 12-15 years from 48 countries. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 58 (9), 907–918.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2018.10.018
Lereya, S. T., Copeland, W. E., Costello, E. J., & Wolke, D. (2015). Adult mental health consequences of peer bullying and maltreatment in childhood: Two cohorts in two countries. The Lancet Psychiatry, 2 (6), 524–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00165-0
Lund, E. M., & Ross, S. W. (2017). Bullying perpetration, victimization, and demographic differences in college students: A review of the literature. Trauma, Violence & Abuse, 18 (3), 348–360. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838015620818
Merrell, K. W., Gueldner, B. A., Ross, S. W., & Isava, D. M. (2008). How effective are school bullying intervention programs? A meta-analysis of intervention research. School Psychology Quarterly, 23 (1), 26–42. https://doi.org/10.1037/1045-3830.23.1.26
Mishna, F. (2004). A qualitative study of bullying from multiple perspectives. Children & Schools, 26 (4), 234–247. https://doi.org/10.1093/cs/26.4.234
Mishna, F., Pepler, D., & Wiener, J. (2006). Factors associated with perceptions and responses to bullying situations by children, parents, teachers, and principals. Victims & Offenders, 1 (3), 255–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/15564880600626163
Monks, C. P., Smith, P. K., Naylor, P., Barter, C., Ireland, J. L., & Coyne, I. (2009). Bullying in different contexts: Commonalities, differences, and the role of theory. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 14 , 146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2009.01.004
Morcillo, C., Ramos-Olazagasti, M. A., Blanco, C., Sala, R., Canino, G., Bird, H., & Duarte, C. S. (2015). Socio-cultural context and bullying others in childhood. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24 (8), 2241–2249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0026-1
Moreno, M. A., Suthamjariya, N., & Selkie, E. (2018). Stakeholder perceptions of cyberbullying cases: Application of the uniform definition of bullying. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 62 (4), 444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2017.11.289
Musu, L., Zhang, A., Wang, K., Zhang, J., & Oudekerk, B. A. (2019). Indicators of school crime and safety: 2018 (NCES 2019–047/NCJ 252571). National Center for Education Statistics, U.S. Department of Education, and Bureau of Justice Statistics, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice. https://nces.ed.gov/pubs2019/2019047.pdf
Nelson, H. J., Burns, S. K., Kendall, G. E., & Schonert-Reichl, K. A. (2019). Preadolescent children's perception of power imbalance in bullying: A thematic analysis. PLoS One, 14 (3), e0211124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211124
Nickerson, A. B. (2019). Preventing and intervening with bullying in schools: A framework for evidence-based practice. School Mental Health, 11 (4), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-017-9221-8
Nickerson, A. B., Fredrick, S. S., Allen, K. P., & Jenkins, L. N. (2019). Social emotional learning (SEL) practices in schools: Effects on perceptions of bullying victimization. Journal of School Psychology, 73 , 74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2019.03.002
Nocentini, A., & Menesini, E. (2016). KiVa anti-bullying program in Italy: Evidence of effectiveness in a randomized control trial. Prevention Science, 17 (8), 1012–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0690-z
Office of the Surgeon General (2023). Social media and youth mental health: The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/sg-youth-mental-health-social-media-advisory.pdf
Olweus, D. (1993). Bullying at school: What we know and what we can do . Blackwell Publishing.
Olweus, D., & Limber, S. P. (2018). Some problems with cyberbullying research. Current Opinion in Psychology, 19 , 139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.04.012
Peeters, M., Cillessen, A. H., & Scholte, R. H. (2010). Clueless or powerful? Identifying subtypes of bullies in adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39 (9), 1041–1052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-009-9478-9
Pepler, D. J. (2006). Bullying interventions: A binocular perspective. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 15 (1), 16–20.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pepler, D., Jiang, D., Craig, W., & Connolly, J. (2008). Developmental trajectories of bullying and associated factors. Child Development, 79 (2), 325–338. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01128.x
Perren, S., & Gutzwiller-Helfenfinger, E. (2012). Cyberbullying and traditional bullying in adolescence: Differential roles of moral disengagement, moral emotions, and moral values. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 9 (2), 195–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2011.643168
Petrosino, A., Guckenburg, S., DeVoe, J., & Hanson, T. (2010). What characteristics of bullying, bullying victims, and schools are associated with increased reporting of bullying to school officials? (Issues & Answers Report, REL 2010–No. 092). U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Regional Educational Laboratory Northeast and Islands. August 2010. https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/edlabs/regions/northeast/pdf/REL_2010092_sum.pdf
Polanin, J. R., Espelage, D. L., & Pigott, T. D. (2012). A meta-analysis of school-based bullying prevention programs’ effects on bystander intervention behavior. School Psychology Review, 41 (1), 47–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.2012.12087375
Polanin, J. R., Espelage, D. L., Grotpeter, J. K., Ingram, K., Michaelson, L., Spinney, E., Valido, A., Sheikh, A. E., Torgal, C., & Robinson, L. (2022). A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventions to decrease cyberbullying perpetration and victimization. Prevention Science, 23 (3), 439–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-021-01259-y
Raman, S., Muhammad, T., Goldhagen, J., Seth, R., Kadir, A., Bennett, S., D'Annunzio, D., Spencer, N. J., Bhutta, Z. A., & Gerbaka, B. (2021). Ending violence against children: What can global agencies do in partnership? Child Abuse & Neglect, 119 (Pt 1), 104733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104733
Rettew, D. C., & Pawlowski, S. (2016). Bullying. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 25 (2), 235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2015.12.002
Rideout, V. (2017). The Common-sense census: Media use by tweens and teens . Common Sense Media. https://www.commonsensemedia.org/sites/default/files/uploads/research/census_researchreport.pdf .
Rideout, V., & Robb, M. B. (2019). Social media, social life: Teens reveal their experiences . Common Sense Media. https://www.commonsensemedia.org/sites/default/files/uploads/research/2019-census-8-to-18-key-findings-updated.pdf .
Rodkin, P. C., Espelage, D. L., & Hanish, L. D. (2015). A relational framework for understanding bullying: Developmental antecedents and outcomes. American Psychologist, 70 (4), 311–321. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038658
Ross, S. W., Horner, R. H., & Higbee, T. (2009). Bully prevention in positive behavior support. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 42 (4), 747–759. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2009.42-747
Sabia, J. J., & Bass, B. (2017). Do anti-bullying laws work? New evidence on school safety and youth violence. Journal of Population Economics, 30 (2), 473–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00148-016-0622-z
Salmivalli, C. (2010). Bullying and the peer group: A review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 15 (2), 112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2009.08.007
Singham, T., Viding, E., Schoeler, T., Arseneault, L., Ronald, A., Cecil, C. M., McCrory, E., Rijsdijk, F., & Pingault, J. B. (2017). Concurrent and longitudinal contribution of exposure to bullying in childhood to mental health: The role of vulnerability and resilience. JAMA Psychiatry, 74 (11), 1112–1119. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.2678
Smith, P. K., Singer, M., Hoel, H., & Cooper, C. L. (2003). Victimization in the school and the workplace: Are there any links? British Journal of Psychology, 94 (2), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.1348/000712603321661868
Smith, J. D., Schneider, B., Smith, P. K., & Ananiadou, K. (2004). The effectiveness of whole-school anti-bullying programs: A synthesis of evaluation research. School Psychology Review, 33 (4), 548–561. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.2004.12086267
Solberg, M., & Olweus, D. (2003). Prevalence estimation of school bullying with the Olweus/bully victim questionnaire. Aggressive Behavior, 29 (3), 239–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.10047
Srabstein, J. C., & Leventhal, B. L. (2010). Prevention of bullying-related morbidity and mortality: A call for public health policies. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 88 (6), 403. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.10.077123
Stopbullying.gov. (2021). Laws, policies, and regulations . https://www.stopbullying.gov/resources/laws
Sullivan, T. N., Farrell, A. D., Sutherland, K. S., Behrhorst, K. L., Garthe, R. C., & Greene, A. (2023). Evaluation of the Olweus bullying prevention program in US urban middle schools using a multiple baseline experimental design. Prevention Science, 22 (8), 1134–1146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-021-01244-5
Swearer, S. M., Wang, C., Maag, J. W., Siebecker, A. B., & Frerichs, L. J. (2012). Understanding the bullying dynamic among students in special and general education. Journal of School Psychology, 50 (4), 503–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2012.04.001
Thornberg, R. (2015). The social dynamics of school bullying: The necessary dialogue between the blind men around the elephant and the possible meeting point at the social ecological square. Confero: Essays on Education, Philosophy and Politics, 3 (1), 161–203. https://doi.org/10.3384/confero.2001-4562.1506245
Tiiri, E., Luntamo, T., Mishina, K., Sillanmäki, L., Brunstein Klomek, A., & Sourander, A. (2020). Did bullying victimization decrease after nationwide school-based antibullying program? A time-trend study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 59 (4), 531–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2019.03.023
Troop-Gordon, W. (2017). Peer victimization in adolescence: The nature, progression, and consequences of being bullied within a developmental context. Journal of Adolescence, 55 , 116–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.12.012
Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., & Lösel, F. (2012). School bullying as a predictor of violence later in life: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective longitudinal studies. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 17 (5), 405–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2012.05.002
Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., Lösel, F., Crago, R. V., & Theodorakis, N. (2016). School bullying and drug use later in life: A meta-analytic investigation. School Psychology Quarterly, 31 (1), 8–27. https://doi.org/10.1037/spq0000120
Vaillancourt, T., McDougall, P., Hymel, S., Krygsman, A., Miller, J., Stiver, K., & Davis, C. (2008). Bullying: Are researchers and children/youth talking about the same thing? International Journal of Behavioral Development, 32 (6), 486–495. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025408095553
Volk, A. A., Dane, A. V., & Marini, Z. A. (2014). What is bullying? A theoretical redefinition. Developmental Review, 34 (4), 327–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2014.09.001
Waasdorp, T. E., Bradshaw, C. P., & Leaf, P. J. (2012). The impact of schoolwide positive behavioral interventions and supports on bullying and peer rejection: A randomized controlled effectiveness trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 166 (2), 149–156. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.755
Waseem, M., Paul, A., Schwartz, G., Pauzé, D., Eakin, P., Barata, I., Holtzman, D., Benjamin, L. S., Wright, J. L., Nickerson, A. B., & Joseph, M. (2017). Role of pediatric emergency physicians in identifying bullying. The Journal of Emergency Medicine, 52 (2), 246–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2016.07.107
Williford, A., Boulton, A., Noland, B., Little, T. D., Kärnä, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2012). Effects of the KiVa anti-bullying program on adolescents’ depression, anxiety, and perception of peers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40 , 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-011-9562-y
Winding, T. N., Skouenborg, L. A., Mortensen, V. L., & Anderson, J. H. (2020). Is bullying in adolescence associated with the development of depressive symptoms in adulthood?: A longitudinal cohort study. BMC Psychology, 8 , 122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-020-00491-5
Xu, M., Macrynikola, N., Waseem, M., & Miranda, R. (2020). Racial and ethnic differences in bullying: Review and implications for intervention. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 50 , 101340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2019.101340
Ybarra, M. L., Boyd, D., Korchmaros, J. D., & Oppenheim, J. K. (2012). Defining and measuring cyberbullying within the larger context of bullying victimization. Journal of Adolescent Health, 51 (1), 53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.12.031
Yeager, D. S., Fong, C., Lee, H., & Espelage, D. (2015). Declines in efficacy or anti-bullying programs among older adolescents: Theory and a three-level meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 37 (1), 36–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2014.11.005
Zhang, Q., Cao, Y., & Tian, J. (2021). Effects of violent video games on aggressive cognition and aggressive behavior. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 24 (1), 5–10. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-139260/v1
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Lincoln Medical Center, 234 East 149th Street, Bronx, NY, 10451, USA
Muhammad Waseem
Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
New York Medical College, Valhalla, NY, USA
Alberti Center for Bullying Abuse Prevention, University at Buffalo, The State University of New York, 428 Baldy Hall, Buffalo, NY, 14260-1000, USA
Amanda B. Nickerson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Muhammad Waseem .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
We do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
N/A (It is a literature review).
Informed consent
N/A (it does not involve any patient involvement).
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Waseem, M., Nickerson, A.B. Bullying: issues and challenges in prevention and intervention. Curr Psychol 43 , 9270–9279 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05083-1
Download citation
Accepted : 02 August 2023
Published : 12 August 2023
Issue Date : March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05083-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Intervention
- Cyberbullying
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Bullying and the Brain
Who this is for:.
Pick up your favorite young adult novel or start watching the latest teen drama on your favorite streaming app, and chances are, one of the major plot points will involve bullying. While such stories may lead you to believe that bullying, defined by the American Psychological Association as “a form of aggressive behavior in which someone intentionally and repeatedly causes another person injury or discomfort,” is just a childhood rite of passage, many studies show it can have long-term effects on an individual’s health and well-being. Research studies looking at links between bullying and the brain have demonstrated it also can have significant cognitive and emotional consequences, much like other adverse childhood experiences such as neglect or family violence. The results are so striking that bullying is now seen as a global public health problem with impacts on child, adolescent, and adult health.
What Is an Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE)?
An ACE is a negative or potentially traumatic event that occurs in childhood. ACEs can include physical, psychological, or sexual abuse, or neglect. It’s any prolonged or repeated experience that might undermine a child’s sense of safety and stability and, in doing so, lead to increased feelings of stress and social isolation.
The landmark ACEs study, a 1998 epidemiological review that looked at how childhood trauma can affect health later in adulthood, demonstrated that ACEs are directly correlated with mental health issues, substance abuse disorders, and chronic health problems such as obesity and cardiovascular disease.
Chronic bullying , or persistent physical or psychological abuse that may come from a family member or a friend, is considered an ACE. Like other ACEs, it can lead to overwhelming feelings of stress and isolation. Children who are bullied can develop anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues later in life, studies show. Bullying has also been linked to self-harm behaviors and even suicide. It’s a problem that scientists and public health experts now understand has a powerful impact on health, social, and emotional well-being.
How Common Is Bullying?
Between 15 and 22 percent of students between the ages of 12 and 18 experience some form of bullying, according to federal programs including the Department of Education’s 2022 Indicators of School Crime and Safety and the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s 2021 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System . It is a problem widespread enough that the CDC, as well as a variety of mental health advocacy organizations , have called for more programs to prevent it from happening in schools across the US.
Are There Different Types of Bullying?
Bullying can come in many different forms. The most common types of bullying involve being the subject of rumors or lies, being consistently belittled, or called names. Some people may also be bullied physically, by being pushed or shoved, for example, or having their property taken or destroyed.
Another form, known as cyberbullying, is a relatively new type of bullying that takes place digitally. People can be bullied over the internet, whether it’s by receiving negative emails, text messages, or online comments—or having rumors or lies spread to others via social media. Regardless of the type of bullying, it is something to take seriously, especially when the person being bullied is experiencing increased stress or negative feelings in response.
How Does Bullying Affect the Brain?
Since the first ACEs study was published, researchers have tried to understand why experiences like bullying can lead to such negative health consequences. Those studies have led to new insights into how bullying can lead to changes to the brain .
For example, the IMAGEN project—a European research consortium studying adolescent brain development—looked at the effects of bullying on young adults. About 30 percent of participants in the study said they had experienced chronic bullying, and they reported higher levels of anxiety than those who hadn’t been bullied. When the researchers looked at fMRI scans of the bullied individuals, they discovered structural differences in the brain in areas like the putamen and caudate, both linked to anxiety disorders. Other studies have shown that chronic bullying is also linked to white matter changes in the brain , which may make the person more susceptible to depression.
A more recent review of studies found an expanded range of impact—with changes noted in a variety of brain areas implicated in emotional processing, including the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. The review authors also hypothesize, given the wide range of areas affected, that bullying likely affects the way these different regions interact with one another, making it more difficult for victims of bullying to understand emotional cues and regulate their emotions.
Other studies, using animal models and human participants, suggest that chronic bullying leads to an increased release of stress hormones, like cortisol, especially in brain areas involved with reward-processing. Not only do those chemicals make you more reactive to stress, in general, but over time, they can change the circuitry in the reward centers, which can put people at higher risk of developing a substance use disorder after trying alcohol, cigarettes, or other drugs.
Finally, the stress hormones released during bullying can also affect the immune system. Those hormones can lead to increased inflammation, which has been linked to both depression and anxiety disorders, as well as medical conditions such as hypertension and obesity. When you put it all together, the chronic stress involved with the experience of persistent bullying can lead to structural and functional brain changes that increase the risk of developing both mental and physical health problems into adulthood.
Are the Cognitive Changes Permanent?
The good news is that the brain is “plastic”—the networks and circuits in everyone’s brains have the ability to change over time in response to their environment. Even if you have experienced bullying at one point or another in your life, that doesn’t mean you will necessarily develop ACE-related health problems. That said, if you are experiencing depression, anxiety, or are using drugs or alcohol in an unhealthy way, it’s important to reach out to your primary care provider or a mental health professional. They can help.
Does Bullying Harm the Bully?
Studies with animals demonstrate that those who are bullied tend to show increased levels of stress hormones, and over time, those bullied animals tend to be more aggressive toward younger, smaller animals. In addition to that, a 2013 JAMA Psychiatry study in people found both bullies and their victims showed a higher prevalence of childhood psychiatric disorders, including anxiety and depression. The study also showed that bullies—and not their targets—were at a higher risk for developing antisocial personality disorder later in life. That said, it is hard to be sure, because the vast majority of children who end up bullying others have been bullied themselves. It is a vicious cycle.
What to Do If You or Someone You Know Is Being Bullied
If you are being bullied, talk to an adult you trust : a parent, teacher, coach, or other important person in your life. Most bullying happens where other people can’t see it, so when you can shine a light on it by talking about it, you can do your part to help prevent it from happening again. Mental Health America also offers recommendations on how to respond in situations where bullying is taking place, whether it’s in person or online. For example, tell bullies to stop in a calm, clear voice; try to keep yourself surrounded by other people in situations where you are likely to be bullied; and never respond to online bullies. Your specific plan for managing the problem will likely depend on the type of bullying you or someone you care about might be experiencing.
Remember: Bullying isn’t something everyone goes through, or just a “normal” part of childhood. It can and does have lasting consequences. Whenever you can prevent it from happening, you’re helping prevent the development of bullying-related mental and physical health issues, too.
*Updated March 2024
Get update on topics, grants, and upcoming events.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Campbell Syst Rev
- v.17(2); 2021 Jun

Effectiveness of school‐based programs to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization: An updated systematic review and meta‐analysis
Hannah gaffney.
1 Institute of Criminology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge UK
Maria M. Ttofi
David p. farrington, executive summary/abstract.
Bullying first emerged as an important topic of research in the 1980s in Norway (Olweus), and a recent meta‐analysis shows that these forms of aggression remain prevalent among young people globally (Modecki et al.). Prominent researchers in the field have defined bullying as any aggressive behavior that incorporates three key elements, namely: (1) an intention to harm, (2) repetitive in nature, and (3) a clear power imbalance between perpetrator and victim (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Farrington). There are many negative outcomes associated with bullying perpetration, such as: suicidal ideation (Holt et al.), weapon carrying (Valdebenito et al.), drug use (Ttofi et al.), and violence and offending in later life (Ttofi et al.). Bullying victimization too is associated with negative outcomes such as: suicidal ideation (Holt et al.), anxiety, low self‐esteem and loneliness (Hawker& Boulton). Therefore, school bullying is an important target for effective intervention, and should be considered a matter of public health concern.
The objective of this review is to establish whether or not existing school‐based antibullying programs are effective in reducing school‐bullyng behaviors. This report also updates a previous meta‐analysis conducted by Farrington and Ttofi. This earlier review found that antibullying programs are effective in reducing bullying perpetration and victimization and a primary objective of the current report is to update the earlier analysis of 53 evaluations by conducting new searches for evaluations conducted and published since 2009.
Search Methods
Systematic searches were conducted using Boolean combinations of the following keywords: bully*; victim*; bully‐victim; school; intervention; prevention; program*; evaluation; effect*; and anti‐bullying . Searches were conducted on several online databases including, Web of Science, PscyhINFO, EMBASE, EMBASE, DARE, ERIC, Google Scholar, and Scopus. Databases of unpublished reports, such as masters' and doctoral theses (e.g., Proquest) were also searched.
Selection Criteria
Results from systematic searches were screened thoroughly against the following inclusion criteria. To be included in this review, a study must have: (1) described an evaluation of a school‐based antibullying program implemented with school‐age participants; (2) utilized an operational definition of school‐bullying that coincides with existing definitions; (3) measured school‐bullying perpetration and/or victimization using quantitative measures, such as, self‐, peer‐, or teacher‐report questionnaires; and (4) used an experimental or quasi‐experimental design, with one group receiving the intervention and another not receiving the intervention.
Data Collection and Analysis
Of the 19,877 search results, 474 were retained for further screening. The majority of these were excluded, and after multiple waves of screening, 100 evaluations were included in our meta‐analysis. A total of 103 independent effect sizes were estimated and each effect size was corrected for the impact of including clusters in evaluation designs. Included evaluations were conducted using both randomized ( n = 45; i.e., randomized controlled trials/RCTs) and nonrandomized ( n = 44; i.e., quasi‐experimental designs with before/after measures; BA/EC) methodologies. All of these studies included measures of bullying outcomes before and after implementation of an intervention. The remaining 14 effect sizes were estimated from evaluations that used age cohort designs. Two models of meta‐analysis are used to report results in our report. All mean effects computed are presented using both the multivariance adjustment model (MVA) and random effects model (RE). The MVA model assigns weights to primary studies in direct proportion to study level sampling error as with the fixed effects model but adjusts the meta‐analytic standard error and confidence intervals for study heterogeneity. The RE model incorporates between‐study heterogeneity into the formula for assigning weights to primary studies. The differences and strengths/limitations of both approaches are discussed in the context of the present data.
Our meta‐analysis identified that bullying programs significantly reduce bullying perpetration (RE: odds ratio [OR] = 1.309; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.24–1.38; z = 9.88; p < .001) and bullying victimization (RE: OR = 1.244; 95% CI: 1.19–1.31; z = 8.92; p < .001), under a random effects model of meta‐analysis. Mean effects were similar across both models of meta‐analysis for bullying perpetration (i.e., MVA: OR = 1,324; 95% CI: 1.27–1.38; z = 13.4; p < .001) and bullying victimization (i.e., MVA: OR = 1.248; 95% CI: 1.21–1.29; z = 12.06; p < .001). Under both computational models, primary studies were more effective in reducing bullying perpetration than victimization overall. Effect sizes varied across studies, with significant heterogeneity between studies for both bullying perpetration ( Q = 323.392; df = 85; p < .001; I 2 = 73.716) and bullying victimization ( Q = 387.255; df = 87; p < .001; I 2 = 77.534) outcomes. Analyses suggest that publication bias is unlikely. Between‐study heterogeneity was expected, given the large number of studies included, and thus, the number of different programs, methods, measures and samples used.
Authors' Conclusions
We conclude that overall, school‐based antibullying programs are effective in reducing bullying perpetration and bullying victimization, although effect sizes are modest. The impact of evaluation methodology on effect size appears to be weak and does not adequately explain the significant heterogeneity between primary studies. Moreover, the issue of the under‐/over‐estimation of the true treatment effect by different experimental designs and use of self‐reported measures is reviewed. The potential explanations for this are discussed, along with recommendations for future primary evaluations. Avenues for future research are discussed, including the need further explain differences across programs by correlating individual effect sizes with varying program components and varying methodological elements available across these 100 evaluations. Initial findings in the variability of effect sizes across different methodological moderators provide some understanding on the issue of heterogeneity, but future analyses based on further moderator variables are needed.
1. PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARY
1.1. interventions to reduce school bullying perpetration and victimization are effective.
Bullying is a ubiquitous form of aggression in schools worldwide. Intervention and prevention programs targeting school bullying perpetration and victimization are effective, yet more research is needed to understand variability in effectiveness.
The main findings of our review are that bullying programs were effective in reducing bullying perpetration outcomes by roughly 18–19% and bullying victimization by roughly 15–16%. There are substantial variations in effects, and the reasons for these variations require further research.
1.2. What is this review about?
Bullying is defined as aggressive behaviors that occur repeatedly over time between two or more individuals. Typically, there is a clear power imbalance between victims and bullies, either socially or physically. Furthermore, bullying behaviors are those that are committed intentionally to harm the victim.
What is the aim of this review?
The aim of this review is to summarise findings from studies of the effectiveness of school‐based antibullying programs in reducing both bullying perpetration and victimization will be reported. The review summarizes 100 studies, with the largest number being from the United States.
1.3. What studies are included?
To be included in this review, primary studies must have evaluated a specific intervention program that targeted bullying perpetration and/or victimization outcomes in school‐aged children, that is, typically between four and 18 years old. Studies must have used two experimental groups of children, one that received the intervention, and one that did not, and applied quantitative measures of bullying behavior (perpetration and/or victimization) that coincided with our operational definition of bullying.
Our final meta‐analytic review includes 100 studies of the effectiveness of antibullying programs. The largest number of studies came from the United States, with most other studies from Canada and Europe.
1.4. What are the findings of this review?
Antibullying programs are effective in reducing bullying perpetration outcomes by roughly 18–19% and bullying victimization by roughly 15–16%.
Variability in the effectiveness of antibullying programs was associated with differences in methodological designs, types of programs and geographical regions. Interventions evaluated using age cohort designs collectively gave the largest overall effect for both bullying perpetration and bullying victimization.
Limitations of the results are similar to those of previous reviews; for example, the reliance of self‐reported measurements of bullying may suggest the change is in reports of bullying perpetration/victimization and not behavioral change.
1.5. What do the findings of this review mean?
The findings indicate that school‐based bullying intervention and prevention programs can be effective in reducing both bullying perpetration and victimization, although the effect is, overall, modest.
The effectiveness of antibullying programs is an important finding with implications for public health and educational policy. However, our review did identify that there are variations in the effectiveness of intervention programs. Future research is needed to explore the reasons for these variations.
1.6. How up‐to‐date is this review?
This report forms an update of an earlier review (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ). The review authors searched for studies published up to December 2016.
2. BACKGROUND
Bullying first emerged as an important topic of research in the 1980s, following the tragic suicides of young boys in Norway, the reason for which was attributed to bullying victimization (Olweus, 1993 ). Today, this form of aggressive behavior remains a prevalent problem among young people globally. For example, a recent meta‐analysis of 80 international studies discovered prevalence levels of 34.5% and 36% for bullying perpetration and bullying victimization respectively (Modecki et al., 2014 ).
Notably, bullying is a matter of public health, impacting the life outcomes of both bullies and victims, in varying ways (Arseneault et al., 2010 ; Masiello & Schroeder, 2014 ; Ttofi et al., 2012 ). Given its long‐term effects, it is imperative that effective intervention efforts are put in place in order to alleviate this troubling school phenomenon (Ttofi, 2015 ).
2.1. Defining school bullying
In order to adequately determine which interventions will effectively reduce bullying behaviors, it is important that researchers and educators start by accurately assessing the prevalence of involvement in school bullying (Swearer et al., 2010 ). There remains some degree of disagreement in relation to definitive cut‐off points for involvement in bullying (Solberg & Olweus, 2003 ; Swearer et al., 2010 ) and methods utilized for the assessment of bullying (Smith et al., 2002 ; Swearer et al., 2010 ). However, there is better agreement in regard to the defining criteria for school bullying.
Prominent researchers in the field have defined bullying as any aggressive behavior that incorporates three core elements, namely: (1) an intention to harm, (2) repetitive in nature, and (3) a clear power imbalance between perpetration and victim (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014 ; Farrington, 1993 ; Olweus, 1993 ). In other words, bullies are individuals who intend to cause harm to their victims through their actions, over a long period of time. Furthermore, victims of bullying are typically less powerful than bullies, or groups of bullies, and feel that they cannot easily defend themselves. This may be due to a physical or social power imbalance.
There are many forms of bullying, for example, school‐bullying, workplace bullying, sibling bullying and, most recently, cyberbullying. The present review is concerned only with face‐to‐face school‐bullying, namely, bullying that occurs in schools between individuals, usually aged between 4 and 18 years old. In the school context, bullying is a complex social phenomenon, that often does not happen between the bully and victim in isolation (Salmivalli, 2010 ). For example, individuals can be involved in bullying, not only as bullies, victims, or bully‐victims, but also as bystanders, defenders, or reinforcers (Zych et al., 2017 ).
Cyberbullying is another form of aggressive behaviors that may occur within a school community, and previous research has found a significant overlap between offline (i.e., school‐bullying or face‐to‐face bullying) and online bullying (Baldry et al., 2017 ). There is currently very little information about the effectiveness of intervention programs designed to reduce cyberbullying or whether school‐based programs that also target face‐to‐face bullying can impact online bullying concurrently.
2.2. The importance of addressing school bullying
School‐bullying is a strong risk marker for several negative behavioral, health, social, and/or emotional problems. A recent comprehensive review of systematic reviews highlighted that the impact of school‐bullying can occur concurrently with perpetration and/or victimization, but also later in life (Zych et al., 2015 ). Previous studies have found that bullying victimization is often followed by negative mental health outcomes such as: increased suicidal ideation (e.g., Holt et al., 2015 ); generalized or social anxiety, low self‐esteem and loneliness (e.g., Hawker & Boulton, 2000 ); psychotic symptoms (e.g., van Dam et al., 2012 ); depression (e.g., Ttofi et al., 2011a , 2011b ); sleeping problems (Geel et al., 2016 ); and other psychosomatic symptoms (Gini & Pozzoli, 2013 ).
Bullying perpetration, on the other hand, has been linked to several negative outcomes such as: suicidal ideation and suicidal attempts (Holt et al., 2015 ); weapon carrying (Valdebenito et al., 2018 ); drug use (Ttofi et al., 2016 ); and violence and offending in later life (Ttofi et al., 2011b , 2012 ). Although involvement in school bullying is not necessarily a causal factor for undesirable life outcomes, research has found that there is an apparent association. It may be the case that the experience of school bullying functions as a stepping stone toward undesirable life outcomes (Arseneault et al., 2010 ).
Moreover, involvement in school bullying, as either a bully or a victim, has been found to correlate with factors such as low academic achievement (Strøm et al., 2013 ), truancy from school (Gastic, 2008 ), and drug use (Valdebenito et al., 2015 ). Such factors are common risk factors for youth offending and delinquency (Farrington & Welsh, 2008 ). Therefore, a bullying prevention program could serve as a crime prevention program, as well as a form of promoting public health.
3. OBJECTIVES
It is clear that school bullying is an important target for effective intervention and prevention. Bullying is an ethical problem as well as a developmental one: targeting school bullying facilitates the process of optimal psychological development but it also addresses the question of human rights, especially the rights of the child (Sercombe & Donnelly, 2013 ). The aim of this paper is to provide an up‐to‐date systematic and meta‐analytical exploration of the effectiveness of school‐based antibullying programs. As such, the present report updates an earlier systematic and meta‐analytic review (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ; Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ), by including evidence from an earlier report, and all available evaluations of antibullying programs since 2009.
It is hoped that this new evidence base will assist policy‐makers and practitioners working in the field of bullying prevention. Farrington and Ttofi's ( 2009 ) review concluded that school‐based antibullying programs are effective in reducing both bullying perpetration (OR = 1.36; 95% CI: 1.26–1.47; z = 7.86; p < .0001) and bullying victimization (OR = 1.29; 95% CI: 1.18–1.42; z = 5.61; p < .0001). Their review had a major impact on the field of bullying intervention and prevention, and in the 9 years that have passed since its publication there has been a wealth of new research.
Therefore, the aim of the present report is to conduct systematic searches for new evaluations of antibullying programs, and also update earlier analysis by including their 53 evaluations.
The initial stage of any meta‐analysis involves conducting a thorough and systematic search of all the existing and relevant literature (Lipsey & Wilson, 2001 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Using predetermined keywords and strict inclusion/exclusion criteria, a systematic review aims to identify, screen, appraise, and synthesize all relevant empirical studies (Zych et al., 2017 ). In this way, systematic bias is avoided.
4.1. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
To be included in the present systematic review, a set of strict inclusion and exclusion criteria were employed to guide searches. These criteria were identical to those used in the previous meta‐analysis (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ). Specifically, to be included, primary studies must:
- (1) Describe an evaluation of a school‐based antibullying program implemented with school‐age participants (depending on the site of evaluation, ages may vary between 4 and 18 years of age);
- (2) Utilize an operational definition of school‐bullying that coincides with existing definitions (e.g., CDC, 2014 ; Farrington, 1993 ; Olweus, 1993 );
- (3) Measure school‐bullying perpetration and/or victimization using quantitative measures, such as, self‐, peer‐, or teacher‐report questionnaires; and
- (4) Use an experimental or quasi‐experimental design, with one group receiving the intervention and another (control group) not receiving the intervention. Nonrandomized studies had to measure outcomes before and after the intervention.
As a result, the present systematic review excludes studies that evaluate the effectiveness of intervention programs targeting alternative forms of bullying, such as cyber‐bullying (e.g., Del Rey et al., 2015 ), general aggression (e.g., Leff et al., 2010 ), and school violence (e.g., Giesbrecht et al., 2011 ). Other studies were excluded because they measured bullying‐related nonbehavioral outcomes, for example, “attitudes towards bullying” (e.g., Earhart, 2011 ), or coping strategies for dealing with victimization (e.g., Watson et al., 2010 ).
In addition, studies conducted with special needs, delinquent, or psychiatric populations were excluded (e.g., Espelage et al., 2015 ), so that results could be generalizable to the wider mainstream school population. Studies using qualitative measures of effectiveness, such as participant perceptions of the effectiveness of the program (e.g., Fletcher et al., 2015 ), were also excluded.
4.2. Searches 1
In order to identify potentially includable studies, Boolean searches were conducted using multiple combinations of the following keywords: bully*; victim*; bully‐victim; school; intervention; prevention; program*; evaluation; effect*; and anti‐bullying . A full description of the syntax used is provided in Appendix A.
Searches were conducted on several online databases, including, but not limited to: Web of Science, 2 PsychINFO, EMBASE, DARE, ERIC, and Scopus. Google scholar ( www.scholar.google.co.uk ) was also searched. A full list of databases searched is provided in Table 1 . EBSCOhost was used as a platform to search multiple databases concurrently and such databases are indicated in Table 1 .
Online platforms and databases manually searched
Note: EBSCOhost was used as a platform to search multiple databases concurrently. Such databases are marked with an *.
Databases of unpublished reports (e.g., ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Solutions) were also searched to include gray literature in our review. This should help to minimize potential publication bias linked to larger or significant effect sizes (Easterbrook et al., 1991 ; McAuley et al., 2000 ). In addition, evaluation studies included by previous systematic reviews were scanned, based on the name of each program, for additional‐updated evaluation results (i.e., Cantone et al., 2015 ; Chalamandaris & Piette, 2015 ; Evans et al., 2014 ; Jiménez‐Barbero et al., 2012 , 2016 ).
Studies included in the previous review (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ; Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ), were also included in the present systematic review. Searches for the present review were conducted up to the end of December 2016, 3 for empirical studies published during and since 2009.
4.3. Screening
Our searches of the literature produced approximately 19,877 reports that were screened for eligibility. Based on the title and abstract, a total of 474 primary studies were identified as relevant, were obtained and subjected to further screening. Studies were allocated to six categories based on their relevance to the current meta‐analysis. A description of each category is provided in Table 2 . Screening was undertaken by the first author (H. G.), under the supervision of the second author (M. T.), in a collaborative format. H. G. reviewed eligible studies, and any queries were settled in discussion with M. T.
Relevance scale categories used in screening
The initial wave of screening excluded 258 of these primary studies. At this stage, studies were excluded because they: (1) did not evaluate a specific antibullying program (Category 1; n = 107); (2) reviewed several different antibullying programs (Category 2; n = 108); or (3) did not report empirical quantitative data from an evaluation of a specific antibullying program (Category 3; n = 43).
A second wave of screening excluded a further 133 studies (Category 4; see Table 3 ). Primary studies were excluded at this stage because they: (1) reported irrelevant outcomes; (2) did not have an adequate control group; or (3) did not meet specified methodological criteria. The screening process is described in detail in Figure 1 . In total, 83 studies published since 2009 were included in our updated systematic review (Category 5).
Descriptions of category four studies

Screening of studies
In addition, five studies were identified during searches conducted for a meta‐analytical review of cyberbullying prevention programs (Gaffney et al., 2018 ). These studies were missed during systematic searches for the current review (i.e., Kaljee et al., 2017 ; Ortega‐Ruiz et al., 2012 ; Ostrov et al., 2015 ; Silva et al., 2016 ; Solomontos‐Kountouri et al., 2016 ). One of these studies (i.e., Kaljee et al., 2017 ) has a publication date outside of the range of our searches. However, it was included because it was available online in 2016.
To provide the most up‐to‐date analysis of school‐based bullying prevention and intervention programs, therefore, a total of 88 newly identified studies are included in the present systematic review.
5. DATA EXTRACTION
After identifying studies eligible for inclusion in the present systematic and meta‐analytical review detailed information about the antibullying programs, sample involved, and evaluation design were extracted from primary studies. The following chapter outlines the coding framework applied in greater detail.
Table 4 also outlines each piece of information extracted. Information was extracted from primary studies under four main headings: (1) Descriptives, (2) Design, (3) Program, and (4) Outcomes. Additionally, the following section outlines information extracted from primary studies in order to create a risk of bias index. Table 5 outlines the items utilized to assess risk of bias for each of the methodological designs included in the present report. Details of the risk of bias results for each study is provided in Appendix B.
Coding framework
Abbreviations: BA/EC, quasi‐experiments with before and after measures of bullying (nonrandomized); exp, experimental group; OBPP, Olweus Bullying Prevention Program; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
Risk of bias tool
Abbreviations: AC, age cohort design; BA/EC, quasi‐experimental design with before and after measures of bullying; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
This procedure was carried out by the first author in consultation with the second and third authors. 4 There were a number of studies from the previous Campbell Collaboration report (i.e., Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ) for which full texts were unavailable and thus, were excluded from several of the moderator analyses.
5.1. Descriptive
Various pieces of descriptive information were extracted from each of the 100 evaluations included in the present report. Information specific to the evaluation, such as the location or the start/end date, were recorded along with detailed information concerning the sample.
The total sample size and also the n of the relevant experimental and control groups were recorded. Age was extracted in two ways. First, where studies reported the mean age, or the age range (i.e., 8–10 years old) of participants this was recorded. Second, some studies did not report the age in years of participants, but we were able to record the school grade of included samples (i.e., Grades 4–6). Where reported, the % of females and males included in the sample was extracted.
We also coded descriptive information about the publication of the evaluation. Specifically, the type of publication and the publication year was recorded. The former represents a categorical moderator reflected whether or not the evaluation was published via the following channels, in order of hypothesized negative correlation with bias: (1) peer‐reviewed journal article; (2) chapter in an edited book/book; (3) governmental report or similar; (4) correspondence; and (5) unpublished masters or doctoral theses.
Correspondence was included to reflect data obtained from multiple evaluations of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program (OBPP) sent to the second (M. M. T.) and third (D. P. F.) authors in preparation of their earlier Campbell review. Where evaluation data had been published in multiple formats, we favored the category associated with the least potential bias. For example, Domino ( 2011 ) reported the results of an evaluation of Take the LEAD program in a doctoral dissertation, but later published these results in a peer‐reviewed journal (i.e., Domino, 2013 ). In this scenario, the included study was coded as “article.”
5.2. Design
Included studies were further categorized according to several aspects of the research design used. We coded information regarding both the measures (i.e., instruments to measure bullying behaviors) and research design.
In relation to measurements of bullying, we recorded the timeframe (i.e., past 3 months or “ever”) in which participants were asked to report on experiences of bullying, the type of report used (i.e., self‐, peer‐, or teacher‐report), and data collection points (i.e., baseline, postintervention, 3‐month follow‐up, etc.). We also noted whether the measure was a continuous scale or a global item and whether bullying perpetration, victimization, or both, outcomes were measured.
As for the research design, we recorded information regarding the unit of allocation (or unit of randomization for RCTs; see below), the number of “clusters” included, whether groups were matched at baseline, and the number of experimental or control groups. For example, Elledge et al. ( 2010 ) included multiple control groups: matched controls and nonmatched controls.
Information about the evaluation methodology was also extracted from primary reports. The types of evaluation methodologies included in the present report are now described in further detail.
5.2.1. Evaluation methodology
In order to optimize the comparability of effect sizes, primary studies included in a meta‐analysis should use the same, or at least conceptually similar, research designs (Wilson, 2010 ). Following Farrington and Ttofi's ( 2009 ) criteria, we searched for evaluations using any of the following four research designs:
- (1) Randomized controlled trials (RCTs);
- (2) Before‐after/quasi‐experimental‐control designs (BA/EC);
- (3) Other quasi‐experimental designs; and
- (4) Age cohort designs.
Each of these methodologies varied on four key elements: as randomization of participants (or clusters of participants); use of experimental and control groups; and administration of quantitative bullying measures before and after intervention.
For example, all studies coded as RCT had to include random assignment to experimental conditions (i.e., intervention and control groups) but did not have to use before and after measures of bullying outcomes. RCTs are considered to be the “gold standard” of experimental evaluations (Weisburd et al., 2001 ). Random assignment of a large number of units is used as a way in which evaluators can also randomize possible confounding variables between groups. As a result, we can infer that any observed differences result from the experimental manipulation (Farrington, 1983 ). The assumption is that randomization ensures that both observed and unobserved variables that may impact the results of an evaluation are also randomly distributed between groups. However, problems may arise if the unit‐of‐allocation, the unit‐of‐randomization, and the unit‐of‐analysis do not align.
Before‐after/quasi‐experimental‐control (BA/EC) designs, are conceptually similar to RCTs, but they do not involve random assignment to experimental conditions. Instead, participants or clusters of participants may be assigned to the intervention or control group on a self‐selected basis (e.g., Menesini et al., 2012 ), for convenience (e.g., Sapouna et al., 2010 ), or based on a greater need for intervention (e.g., Losey, 2009 ). Thus, BA/EC designs may be subject to selection biases (Farrington & Petrosino, 2001 ) that may reduce the validity of the results. These can be controlled if outcomes are measured before and after the intervention. Studies coded as BA/EC in the present report all used experimental and control groups but did not randomly assign participants to conditions. They also had to measure bullying outcomes before and after implementation of the intervention.
In contrast, studies categorized in the current review as using “other quasi‐experimental” designs utilized experimental and control conditions, without random assignment, but did not measure bullying behaviors before the intervention. Bullying outcomes were only measured after the implementation of an intervention in these studies. Therefore, selection bias is may be a threat to the internal validity of the results in such designs, which could have possibly attributed to pre‐existing differences between the groups (Farrington, 2003 ). For this reason, a decision was made to omit these designs from this updated meta‐analysis. Thus, relevant evaluations identified in the earlier Campbell Review and any new evaluations (since 2009) using this methodological design were excluded from the new meta‐analyses (see later).
In an age cohort design, students of a particular age X are initially assessed in the 1st year and serve as the control group for the evaluation of an intervention. Then, all students receive the intervention, and different students of the same age X (in the same school, in the 2nd year) serve as the experimental group (see Kärnä et al., 2013 ). This design, which is largely used in evaluations of the OBPP, deals with some selection effects, since it ensures that experimental and control children are matched on age and school, and it deals with some threats to internal validity (e.g., ageing and maturation). However, this design may be influenced by period and testing effects, and the experimental and control groups may differ on other uncontrolled variables.
Studies employing RCTs, BA/EC, and age cohort designs were included in the present systematic and meta‐analytic review. Because of the potential threat to internal validity, we excluded studies ( n = 9) in the other quasi‐experimental design category because they are poorly controlled and vulnerable to selection effects. Additionally, the four studies included in the earlier review that used an “other quasi‐experimental” design were excluded from the present systematic review.
5.3. Program
Using a socio‐ecological systems theory framework (Bronfenbrenner, 1979 ) and the previous meta‐analysis (i.e., Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ) as guidelines, information about the specific intervention program was recorded. General details about the intervention, such as the name of the program (where relevant) and the aim of the intervention (e.g., Silva et al., 2016 ) were noted along with more detailed information about the antibullying programs.
Intervention components at multiple levels of the socio‐ecological model (i.e., individual, peer, parent, and teacher, etc.) were recorded, such as work with peers, parental involvement, teacher training and whole‐school‐approach. Therefore, a brief description of each antibullying program based on this information is provided in Table 6 .
Systematic review results
In addition to specific program elements included in interventions, we also coded for possible sources of bias in evaluations and intervention development. Conflict of interest (COI) has previously been reported to impact evaluation results of many interventions and is a growing area of interest (COI; Eisner & Humphreys, 2012 ) with studies identified as having higher COI associated with larger overall effect sizes. Eisner and Humphreys outline many other possible sources of COI, such as financial gain to the evaluator, but this information was difficult to obtain for antibullying programs. Thus, a simple indication of potential COI was utilized.
We primarily focused on the overlap between individuals included as author/coauthor on the evaluation study, is also included on previous evaluations of the same program (e.g., NoTrap!; Menesini et al., 2012 ; Palladino et al., 2012 , 2016 ), or is in fact referenced as the developer of that particular program (e.g., Tsiantis et al., 2013 ). If no reference to a publication relating to the specific program was included, we concluded that the author had developed the program, and thus, the evaluation was deemed high risk.
Program specificity refers to whether the intervention program was specifically targeting bullying outcomes, or if many other outcomes were also included. Targeted programs are suggested to be more effective than generalized programs that aim to reduce many different behaviors in one intervention. Highly specific programs (i.e., those that only included bullying outcomes and very few others) were coded as “high.” Thus, programs that were less specific and included many other outcomes in addition to bullying measures were considered “low.” A third category was created (i.e., “medium”) to include studies that did multiple other outcomes in addition to bullying outcomes, but these additional variables were bullying‐related.
5.4. Outcomes
We also extracted several pieces of statistical information from primary studies that was required for the estimation of effect sizes. Statistics for bullying behaviors, for example, means and standard deviations or sample sizes and percentage of bullies and/or victims, were extracted for experimental and control groups at baseline and immediately postintervention timepoints.
We also coded bullying data for additional follow‐up timepoints where this information was reported by primary studies. Data was extracted and recorded separately for independent samples (i.e., female and male, Palladino et al., 2016 ; older and younger, Baldry & Farrington, 2001) and different measures. For example, data for both self‐ and peer‐report measures were extracted from Beery and Hunt (2009) and for different forms of bullying (e.g., Frey et al., 2005 ).
5.5. Risk of bias
As per the Campbell Collaboration reporting guidelines, a risk of bias index was created for the purpose of the present report. The EPOC tool was utilized to assess the risk category of each study on several items relating to the methodological quality of evaluations. Following earlier Campbell review (e.g., Valdebenito et al., 2018 ) this tool was also used for nonrandomized studies as other risk of bias measurement instruments were considered inappropriate for nonscientific or medical trials.
The following section describes the procedure for addressing risk of bias in the present meta‐analysis. Each primary evaluation was measured on the following items: (1) allocation sequence (AS); (2) Allocation concealment (AC); (3) Baseline equivalence on outcomes (BE); (4) Baseline equivalence on participant characteristics (BC); (5) Incomplete outcome data (ID); (6) Contamination protection (CP); and (7) Selective outcome reporting (SOR). The applicability of these categories for each of the methodological designs included in the present report is outlined in Table 5 . Each study was categorized as being high, low, or unclear (if insufficient information was available) risk on each of these EPOC items.
6. INCLUDED INTERVENTIONS
In total, 67 different school‐based antibullying programs were evaluated by primary studies included in our updated meta‐analysis. Descriptions of each of these interventions is provided in the following section of this report. These narrative reviews of included antibullying programs are based on the best available information provided by the primary studies. Twenty‐one of the evaluated antibullying programs were included (only) in the previous meta‐analysis (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ). A number of popular school‐based antibullying programs (n = 7; i.e., Bully Proofing Your School [BPYS], Friendly Schools, KiVa, OBPP, Steps to Respect, ViSC, and Youth Matters) had been re‐evaluated or additional publications since 2009. Hence, the majority of programs evaluated in our updated meta‐analysis ( n = 40) are new bullying prevention and intervention programs.
The following sections provides detailed summaries of each antibullying program included in our systematic review. Descriptions marked with an * were taken from the previous review (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ). To provide the reader with a detailed overview of existing antibullying programs studies subsequently excluded from the meta‐analysis are also included here.
6.1. *Antibullying intervention in Australian secondary schools
This antibullying intervention consisted of several activities that aimed to increase awareness and identification of bullying, to promote empathy for targets of bullying and to provide students with strategies to cope with bullying (Hunt, 2007 , p. 22). The intervention was based on an educational antibullying program, which was delivered by teachers. There was no specific training for teachers. Information about bullying was provided at parent and teacher meetings. Teacher meetings were held in conjunction with regular staff meetings while parent meetings were held after hours. A summary of the information covered at parent meetings was also published in the school newsletter in an attempt to target the wider parent population. Finally, the program includes a 2‐h classroom‐based discussion of bullying (offered by teachers) using activities from an antibullying workbook written by Murphy and Lewers ( 2000 ).
6.2. Anti‐Bullying Pledge Scheme (ABPS)
The ABPS describes a number of local antibullying schemes implemented in UK schools as a result of government recommendations and guidance (Pryce & Frederickson, 2013 ). Schools adopted a declaration of commitment, and intervention components followed a theoretical framework guided by the Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991 ).
The ABPS is a universal prevention program, that aims to reduce the prevalence of bullying perpetration and victimization in schools and increase students' perceptions of safety and support within the school environment (Pryce & Frederickson, 2013 ). Participating schools were assigned a facilitator, referred to as a “pledge supporter,” and a detailed intervention manual. The manual outlined the stages involved in implementing the ABPS program. The stages are as follows:
- Initial meeting with school management and the pledge supporter
- Intervention planning meeting
- School representatives make a declaration of commitment to the intervention
- Staff, student, and parent surveys are circulated
- Results from the surveys were collated and used to tailor intervention components to the individual schools' needs
- Ongoing visits and support from the pledge supporter throughout implementation.
6.3. *Be‐prox program
The Be‐Prox program was specifically designed to tackle bullying and victimization among kindergarten students. According to Alsaker and Valkanover ( 2001 , pp. 177–178), the somewhat higher adult‐children ratio, the interest of preschool teachers in socialization, the greater flexibility as to scheduling and teaching, and the admiration of many preschoolers for their teachers are ideal conditions for the implementation of preventive programs against bully/victim problems. The basic principle of Be‐Prox was to enhance preschool teachers' capacity to handle bully/victim problems (Alsaker, 2004 , p. 291). The program engaged teachers in an intensive focused supervision for approximately 4 months. Central features of Be‐Prox were the emphasis on group discussions, mutual support and co‐operation between consultants and teachers and between teachers and parents (Alsaker, 2004 , pp. 292–293).
The teacher training was provided in six steps (Alsaker, 2004 ; fig. 15.1, p. 292). Initially, teachers were given information about victimization (step 1) and the implications of this information was discussed (step 2). During the third step, specific implementation tasks were introduced and the teachers worked in groups in preparation for the practical implementation (step 4). After this preparation, teachers implemented specific preventive elements in the classroom (step 5) for a specific period of time. After that, teachers met and discussed their experiences of the implementation of the preventive measures (step 6).
In eight meetings over a 4‐month period, issues related to the prevention of bullying were addressed. The main purpose of the first meeting was sensitization. Teachers were asked to describe any possible bully/victim problems in their schools and were then given information about bullying and other types of aggressive behavior. They were also presented with the main principles of the program. The importance of contact between kindergarten teachers and children's parents was also emphasized and teachers were advised to consider the possibility of organizing a meeting with parents. In the second meeting, the importance of setting limits and rules to preschool children was discussed. Teachers were invited to elaborate some behavior codes in their classroom in collaboration with the children and to be ready to present them during the third meeting. Also, as a second homework task, teachers were asked to organize a parent meeting.
During the third meeting, teachers discussed their experiences of implementing classroom rules against bullying. The main focus of this meeting was the need for consistent teacher behavior, the difference between positive and negative sanctioning and the use of basic learning principles in the classroom. The main focus of the fourth session was on the role and responsibility of children who were not involved in bullying and of bystanders in the prevention of victimization. Teachers were asked to draw some kind of personality profiles of passive and aggressive victims and of bullies and to present them to the rest of the group. After this task, teachers were presented with research findings regarding the characteristics of children who were or were not involved in bullying. As a homework task for the next meeting, teachers were asked to systematically observe noninvolved children and to develop some means of involving them in the prevention of victimization.
During the fifth meeting, research‐based information about motor development and body awareness among preschool children was presented to teachers. A discussion between teachers and program researchers of children's self‐perceptions of strength, of peers' perceptions of strengths of victims of bullies, and other motor characteristics of children, aimed to yield important insights. The overall discussion and exchange of information among teachers aimed to promote teachers' understanding about how to change these perceptions within the classroom setting. Specific goals to be achieved within the classroom were clearly set, such as training in empathy and body awareness among children, participation and involvement of noninvolved children and talks with all the children about the situation in their kindergarten. During the sixth meeting, time was given to reflect on the goals formulated at the beginning of the prevention program. Teachers were also given time to discuss their experiences with implementing the goals of the fifth meeting within the classroom settings. The last two meetings followed a similar format, with time given for reflection on goals achieved, problems dealt with, and an overall evaluation of the program.
6.4. *Befriending intervention
Befriending intervention was an antibullying program that relied mainly on a peer support model. The overall aims of the program were: (a) to reduce bullying episodes through developing in bullies an awareness of their own and others' behavior; (b) to enhance children's capacity to offer support to the victims of bullying; (c) to enhance responsibility and involvement on the part of bystanders; and (d) to improve the quality of interpersonal relationships in the class group (Menesini et al., 2003 , p. 1).
The antibullying intervention was offered in five steps (Menesini et al., 2003 , p. 5). During the first phase, which targeted the class level (class intervention), several activities were offered aiming to increase children's awareness of prosocial and helping behaviors and to promote positive attitudes toward others. Through work at the class level, the school authorities sensitized and prepared the whole school population for the new service that the school unit was about to implement. In this way, another goal was achieved, namely developing values and attitudes toward “peer support activities” in the whole school population.
During the second phase of the program, the “peer supporters” were selected. Approximately three to four supporters were allocated in each classroom and were selected based on a combination of techniques, such as self‐ and peer‐nominations. These children were then trained in special full‐day sessions or in regular meetings during school time (phase three) so that they knew how to deal with other children and how to facilitate interactions among other children. Teachers and other professionals (psychologists and social workers) took part in these sessions as well. The overall aim of this phase of the antibullying program was to help peer supporters to enhance their listening and communication skills since they would be the mediators in the interactions among children.
During the fourth phase of the program, peer supporters worked in their classes with the assistance and close monitoring of their teachers. The teachers in each class organized “circle meetings” during which the needs of specific children involved in bullying (target children) were identified. Target children were contacted and, after their consent and cooperation, were offered help by the peer supporters. Peer supporters were not only assigned to specific tasks involving the target children but were also supervised by the teachers so that they were given constant feedback on their on‐going work in the class.
During the final phase of the Befriending Intervention, the leading group of peer supporters were involved in training other children in the class, so that more children could be involved in the program (in the transmission of training and passing on the roles).
6.5. *Behavioral program for bullying boys
This program targeted male youth, from a low socio‐economic area, predominately inhabited by individuals of color, involved in bullying. The program was based on the findings of an in‐depth needs assessment within three schools and targeted a specific number of male students aged sixteen who (based on the results of the questionnaire that had been administered) were “considered to be a serious threat to the harmonious functioning of everyday school life” (Meyer & Lesch, 2000 , p. 59). The theoretical basis of the program could be found in the Social Interactional Model for the development of aggression (Meyer & Lesch, 2000 , p. 61) and involved a behavioral approach for tackling the problem of bullying. The program was implemented by psychology students for ten nonconsecutive weeks, with 20‐h‐long sessions held twice weekly at the school, during school hours.
The components of the 17‐session behavioral program included homework tasks, modeling, self‐observation, role‐plays, and a token economy system for reinforcing positive behaviors. According to the program designers “the chief contingency for behavioral change was the token economy system, using Wonderland Games tokens, chocolates and cinema tickets as reward for non‐bullying behavior” (Meyer & Lesch, 2000 , p. 62). Each participant was monitored by himself and by a “buddy” who was selected in each session prior to the monitoring. Each session included an opportunity for feedback on the students' progress in the week, a discussion of a relevant applied topic, role‐playing, games, and drawing. The program designers pointed out the limitations of the intervention strategy. As they indicate (Meyer & Lesch, 2000 , p. 67) “the program was too short and structured to address the issues that were disclosed in sessions, as the severity of the nature of the aggression in the schools and vast social problems was seriously underestimated.”
6.6. Beyond the Hurt
Sutherland ( 2010 ) implemented the Beyond the Hurt program, a peer‐led school‐based bullying intervention and prevention program, developed by the Red Cross. Beyond the Hurt is a high school program and emphasizes education, prevention and intervention to reduce prevalence of bullying perpetration and victimization. Sutherland ( 2010 , p. 84) describes the four key components of the intervention: (1) education and training of peer facilitators, (2) in‐class presentations given by peer facilitators, (3) teacher workshops, and (4) online training material for teachers and community members.
This peer‐led program trains and educates select peer facilitators, who become the implementers of the intervention program within participating schools. These students are guided by a teacher and Red Cross professional throughout training and implementation of class presentations highlighting several bullying‐related issues. The overarching aim of the Beyond the Hurt program is to create a positive school and class climate in which students are encouraged to develop and maintain healthy prosocial relationships, and bullying perpetration and victimization are not supported. The program aims to promote antibullying attitudes among participants and encourage empathy and prosocial support for victims of bullying.
6.7. *Bulli and Pupe
Bulli and Pupe was an intervention program concerned with bullying and family violence. The program, developed by Baldry (2001), was “directed towards the individual and peer group, and aimed to enhance awareness about violence and its negative effects” (Baldry & Farrington, 2004 , p. 3). The intervention package consisted of three videos and a booklet divided into three parts; each video was linked to one part of the booklet. Each part of the booklet was meant to take the form of an interactive lesson where professionals, experienced in school and juvenile processes, discussed three issues according to the structure of the manual.
The first part of the booklet, entitled “Bullying among peers,” emphasized teen violence among peers. The booklet presented vignettes and graphics that reported research findings on bullying in an attempt to raise students' awareness of this issue. The corresponding video showed teenagers talking about bullying based on their own experiences and judgments. The second part of the booklet, entitled “Children witnessing domestic violence,” analyzed the effects of domestic violence on children and the repercussions for school achievement and peer relations. In the accompanying video, children in a shelter for battered women were presented, talking about their personal experiences and emotions. Finally, the third part of the booklet, entitled “Cycle of violence,” dealt with the long‐term effects of violence on adults who were victims of violence in their childhood. The corresponding video consisted of an interview conducted with a 19‐year old boy who had a violent father.
The program was in the first place delivered in 3 days by experts who, together with teachers, discussed about bullying, read the booklet and analyzed its content. The program was taken over by teachers who once a week created a facilitation group and allowed children to discuss any problems they encountered with their peers. The program was more effective with secondary students because it required its participants to have good interpersonal and cognitive skills (Baldry & Farrington, 2004 , p. 4).
6.8. The Bully Prevention Challenge Course Curriculum (BPCCC)
Battey ( 2009 ) implemented the BPCCC (Haggas, 2006 ) to students over two 45 min classes, on 4 days of one school week. The program was implemented by trained facilitators, whom included the schools' physical education/health teacher. The program commenced by providing participants with name tags and organizing some warm‐up physical activities. Next, the physical education/health teacher provided participants with information about bullying, such as, identifying and addressing bullying, who to talk to and where to seek support. Subsequent group discussions focused on empathy and understanding each other's differences. Audience participation activities also required the students to engage to represent the number of students whom had been a victim or bully.
6.9. Bully Proofing Your School
“Bully‐Proofing Your School” was a comprehensive, school‐based intervention program for the prevention of bullying (Menard & Grotpeter, 2014 ; Menard et al., 2008 ; Toner, 2010 ). The program involved three major components: (1) heightened awareness of the problem of bullying, involving a questionnaire to measure the extent of bullying and the creation of classroom rules related to zero tolerance for bullying; (2) teaching students protective skills for dealing with bullying, resistance to victimization and providing assistance to potential victims by teaching assertiveness skills; and (3) creation of a positive school climate where students were encouraged to work as positive and supportive bystanders (Menard et al., 2008 , p. 7).
The primary targets of BPYS were elementary and middle school students. School staff were involved as both secondary targets of intervention (since changes in their behavior was a requirement for the construction of a positive antibullying school environment) and as agents delivering the intervention to students. Teachers were given information and strategies to help them recognize bullying incidents among their students and how to effectively deal with these behaviors (Menard & Grotpeter, 2014 ).
The intervention in the classes consisted of a classroom curriculum, which included seven sessions of approximately 30–40 min. Each session was delivered by a teacher or by mental health staff. After completion of the classroom curriculum materials, teachers were encouraged to hold weekly classroom meetings during which students could be helped to reflect on their behaviors. Parents were offered information through newsletters. Individual parents of students involved in bullying as either perpetrators or victims were given consultation (Menard & Grotpeter, 2014 ).
6.10. Chinese antibullying intervention
Ju et al. ( 2009 ) implemented an antibullying program in a Chinese primary school employing an action research framework. There were two main aims of this intervention program. First, the program aimed to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization both on students' way to, and from, school. Second, the study aimed to investigate practical intervention elements that could be applied nationwide to Chinese primary school children (Ju et al., 2009 ).
The initial step in this intervention was the training of teachers on the fundamental principles of action research. This training program targeted the following components of educational research: (1) research methodology in education; (2) knowledge of school bullying; (3) components of action research; and (4) intervention skills, such as brainstorming and role‐playing. Second, a 5‐week intervention program was designed and implemented by teachers in classrooms. Components that targeted both victims and bullies specifically were also incorporated into the intervention.
6.11. The Confident Kids program
The Confident Kids program is an antibullying intervention designed for early adolescent males who were experiencing anxiety as a result of being bullied at school (Berry & Hunt, 2009 ). The foundations of the program lie in cognitive‐behavioral therapy, employing both anxiety management techniques and antibullying elements. Based on the “Cool Kids Program” (Lyneham et al., 2003), this intervention program aims to reduce bullying victimization by targeting factors that increase the likelihood of victimization. Therefore, this program focuses primarily on issues such as: self‐esteem, coping strategies; social skills; emotional regulation; and internalizing behaviors.
The program was implemented over a period of 8 weeks, and included student and parent involvement. Students participated in weekly group sessions led by a team of assistant and qualified clinical psychologists. These sessions incorporated a combination of tasks including: skill demonstration; role‐playing; and group discussion. Homework was allocated after each session and participants were encouraged to apply skills acquired in real‐life settings between each session.
Sessions covered a variety of issues, including both cognitive‐behavioral anxiety management techniques and antibullying information. Seven core sessions focused on the following topics: psycho‐education; cognitive restructuring (2 sessions); graded exposure; adaptive coping strategies; improving social skills; and self‐esteem. A final session targeted relapse prevention and provided a general overview of the skills learned throughout the program. Parents participated in sessions that ran parallel to the student program. Group discussions targeted the strategies being taught to student participants and also possible parent factors that could influence effectiveness of intervention for their children, for example, parental anxiety.
6.12. Cyberprogram 2.0
Cyberprogram 2.0 is a cyberbullying intervention program that also incorporates elements on school bullying (Garaigordobil & Martínez‐Valderrey, 2015 ). The intervention is delivered over 19 sessions, and outlines the following four main goals:
- To outline and conceptualize bullying and cyberbullying, including identifying the different roles involved (e.g., bullies, victims, and bystanders).
- To illustrate the consequences of bullying and cyberbullying for all those involved
- To develop coping strategies in order to reduce bullying and cyberbullying behaviors.
- Developing positive social and emotional skills, such as empathy, active listening, anger management, conflict resolution strategies, and diversity tolerance.
A wide range of activities and techniques are used, such as, role‐playing, brainstorming, case studies, and guided discussion. The Cyberprogram 2.0 intervention followed a specific methodological framework, employing four key components for implementation. They are as follows: (1) inter‐session constancy: intervention was delivered in weekly 1‐h sessions; (2) spatial‐temporal constancy: intervention was delivered in the same place and at the same time each week; (3) constancy of adult facilitator: intervention was implemented by the same adult, who same psycho‐pedagogical training, each week; and (4) constancy in the session structure: sessions being with group instruction and activities. There is then a following reflection phase that is led by the adult.
6.13. Daphne III
Daphne III was an international antibullying initiative implemented and developed in association with numerous organizations. In this study (Papacosta et al., 2014), school antibullying programs were coordinated in Cyprus by the Association for the Psychosocial Health of Children and Adolescents (APHCA). Other influential “partners” included the Cyprus Ministry of Health, mental health services, Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Ministry of Education and Culture, and Educational Psychology services. Organizations from other European countries included: Child Line [ Vsi Vaiku Linija ], in Lithuania, and Nicolaus Copericus University, in Poland, were also involved.
The overarching aim of this initiative was to educate 5th and 6th grade primary school students about bullying, and the many different forms it can take (Papacosta et al., 2014). Teachers implemented the program in their classrooms, and were trained by psychology and mental health professionals. There were eleven workshops involved in the program that followed a structured curriculum manual. This manual also provided schools with suggestions and recommendations on ways in with they could prevent, and intervene in, bullying situations.
6.14. *Dare to Care: BPYS program
“Dare to Care; Bully Proofing Your School” was a modification of the “Bully Proofing Your School” program (Beran et al., 2004 , p. 103), which in turn was modeled on the Olweus Program. This antibullying program placed emphasis on clinical support to victims and perpetrators of bullying in the form of individual and group counseling. It also enabled collaboration with community services. The essence of the program was to encourage accountability for creating solutions among all parties involved in the education system (Beran et al., 2004 , p. 104).
The program included several steps. Program facilitators provided to school personnel information and training on issues related to bullying in schools (in a full‐day professional development workshop). This workshop aimed to ensure that the program principles would be reflected in the overall curriculum and would be sustained over time. Information was also given to parents. Then, students, parents and school staff collaborated in the development of a school antibullying policy. This policy had the aim of identifying caring and aggressive behaviors and consequences of those behaviors, but with a focus on reparation rather than punishment. The antibullying policy was posted throughout the school. Finally, the program involved the implementation, on behalf of the teachers, of a classroom curriculum that educated children about the nature of bullying and strategies to avoid victimization. The curriculum included discussion, role‐plays, artwork, books, videos and skits presented to school staff, parents, and other children.
6.15. Defeat Bullying
The Defeat Bullying program is a curriculum‐based antibullying program that was published by the National Society for prevention of Cruelty to Children (NSPCC, UK) in 2007 (Herrick, 2012 ). The program materials were available to download online, as part of a nationwide campaign to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization in UK schools. The overarching aim of the Defect Bullying program is to raise awareness and improve attitudes toward bullying, educate about bullying‐related feelings and emotions, and to develop effective intervention and conflict resolution strategies (Herrick, 2012 , p. 85). Based on social identity theory (Tajfel & Turner, 1979 ), the program aims to establish an in‐class antibullying norm, so that students will be encouraged to adopt this norm, and thus, reduce levels of bullying perpetration and victimization.
There are five key lessons implemented throughout the program, and each incorporates a range of individual, class and group activities (Herrick, 2012 ). The lessons cover the following five themes: (1) understanding attitudes and values toward bullying; (2) educating about the feelings that occur as a result of bullying; (3) embracing diversity; (4) safety awareness; and (5) encouraging bystanders to get involved in antibullying strategies. The available intervention materials were also reviewed by groups of teachers, and any necessary amendments were incorporated. For example, Herrick ( 2012 ) describes that following teacher discussion groups, homework assignments relating to each lesson were developed and implemented. Parents of participating students were also invited to attend an antibullying workshop led by the researcher.
6.16. *Dutch antibullying program
The antibullying initiative in the Netherlands was inspired by the Olweus program (Fekkes et al., 2006 , p. 639). The program was specifically designed to tackle bullying behavior by involving teachers, parents and students. It offered a 2‐day training session for teachers in order to inform them about bullying behavior and to instruct them about how to deal with bullying incidents in schools. During the intervention period, teachers had access to the training staff for additional advice. Intervention schools were supported by an external organization named KPC, which specialized in training school staff and in assisting schools in setting up new curricula and guidelines. The core intervention program included: (1) antibullying training for teachers, (2) a bullying survey, (3) antibullying rules and a written antibullying school policy, (4) increased intensity of surveillance, and (5) information meetings or parents.
During the intervention, there was careful dissemination of the antibullying program to intervention schools. Also, the researchers provided information about the number of intervention and control schools, which have used the above‐mentioned elements of intervention. Finally, intervention schools were supplied with the booklet “Bullying in schools: how to deal with it” and with a “Bullying Test,” a computerized questionnaire that children could complete anonymously in the classroom.
6.17. Dutch Skills for Life
The Skills for Life program is a Dutch universal school‐based behavioral and health prevention program for adolescents aged 13–16 years old (Diekstra, 1996 ; Gravesteijn & Diekstra, 2013 ). The program targets prosocial behavior, self‐awareness, social awareness, self‐control, interpersonal skills, and ethical decision making to reduce behavioral and health problems (Fekkes et al., 2016 ). The program is based on social learning theory and Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy. As a result, the program aims to reduce bullying by enabling students to learn from each other in a classroom setting through behavioral modeling.
The program is implemented by teachers, who attend two 3‐day training workshops prior to implementation and receive “booster” training sessions throughout the intervention (Fekkes et al., 2016 ). The intervention is comprised of 25 lessons that are delivered over the course of two academic years. First, four lessons address awareness and handling of thoughts and feelings. Skills such as interpersonal problem solving, emotional regulation, and critical thinking are targeted. There are twelve additional lessons in the 1st year, and nine more lessons in the 2nd year of implementation. These generally focus on skills that are applicable to particular behavioral or health experiences. For example, lessons are aimed at: dealing with bullying; setting and respecting boundaries; substance use; norms and values; friendships; sexuality; suicidal ideation; and conflicts with peers and/or teachers. Various activities are utilized throughout the program, including, active enactment, DVDs, role play, discussion and feedback.
6.18. Dynamic Approach to School Improvement (DASI)
The DASI (Kyriakides, Creemers, Papastylianou, et al., 2014 ; Kyriakides, Creemers, Muijs, et al., 2014 ) was a whole‐school approach to bullying prevention implemented in several European countries, such as: Cyprus, Greece, UK, Belgium and the Netherlands. This approach draws factors from the educational effectiveness model (Creemers & Kyriakides, 2008 , 2012 ). The intervention targets specific school factors, that is, (1) school teaching policy, (2) school learning environment, and (3) school evaluation. This framework was previously found to improve academic achievement (e.g., Kyriakides, 2008 ).
At the beginning of the intervention, the research team held training for participating school staff. The theoretical framework was introduced, and a detailed manual was provided. The aim of the handbook was to facilitate school stakeholders to develop strategies and action plans that were specific to the schools' needs (Kyriakides, Creemers, Papastylianou, et al., 2014 ). Support was offered to each school by the research team throughout the process.
Teacher surveys were distributed prior to implementation in order to highlight specific areas that needed improvement. The next phase of the intervention involved school stakeholders coming together to form cooperative committees with representatives of parents, students, and teachers. These committees then collaborated to develop action plans and strategies to address specific problems in their schools. Committees formulated plans to implement particular intervention components that best suited their specific needs. Therefore, the schools participating did not necessarily implement the same intervention components or activities. Schools were required to retain log books of activities undertaken.
Kyriakides, Creemers, and Papastylianou, et al. ( 2014 ) provide an outline of the intervention components implemented in one experimental school involved in their trial. For example, the following are identified as essential elements implemented in order to reduce bullying:
- “Student behavior outside the classroom”—involves developing clear and efficient antibullying policy, increased teacher vigilance in bullying “hot spots” and effective supervision of students.
- Improved school learning environment
- “Rewarding good behavior”—enforcing a system that acts as a nonpunitive approach to antibullying, by motivating students to behave in a prosocial manner.
- “Collaboration and interaction between teachers”—encouraging teachers to work together and communicate effectively about bullying issues in their schools.
- Other intervention components, including, encouraging and supporting peer bystanders; identifying and support “at risk” and vulnerable students; and creating student‐made videos about bullying issues.
6.19. *Ecological antibullying program
The Ecological antibullying program examined peer group and school environment processes “utilizing a systemic interactional model with evaluations at each level of intervention” (Rahey & Craig, 2002 , p. 283). The overall aim of the program was the creation of a supportive and safe school environment in which firm limits against bullying were established. The specific goals of the program included raising awareness of the problem of bullying, increasing empathy, encouraging peers to speak against bullying and formulating clear rules against bullying.
The 12‐week program was based on the “Bully Proofing Your School” program which was designed to increase the understanding of bullying and decrease the incidence of bullying (Rahey & Craig, 2002 , p. 285). The program elements included a psycho‐educational component implemented within each classroom, a peer mediation component and specialized groups for children involved in bullying.
At the school‐wide level, the psycho‐educational program was implemented by psychology students who received training sessions and manuals prior to intervention. Prior to the program, at a school assembly the program was introduced to students. The assembly signaled the formal beginning of the intervention. The classroom programs involved interactive educational approaches such as role playing and puppet techniques. The topics addressed were bullying and victimization, conflict resolution, empathy, listening skills and individual differences (Rahey & Craig, 2002 , p. 286).
Individual programs for children involved in bullying were also part of the intervention. The relevant sessions consisted of social skills, listening, empathy training and supportive counseling. Each weekly session lasted 45 min. The program also included intervention at the teacher level. Teacher programs consisted of meetings with teachers to discuss bullying, intervention approaches, and student support for those directly involved in bullying. During the intervention, the program coordinators met with principals and teachers to offer support.
6.20. Emotional Literacy Intervention
Knowler and Frederickson ( 2013 ) evaluated the effectiveness of an emotional literacy intervention targeted on bullying behaviors to reduce bullying victimization in UK schools. Selected schools were previously implementing the Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning (SEAL; Department for Education and Skills, 2005 ) program. One of the themes included in the SEAL program is “Say no to bullying” (Knowler & Frederickson, 2013 ), however the overall program aims to improve students' social relationships, motivation, learning strategies, and holistic school improvement.
The specific emotional literacy intervention implemented and evaluated by Knowler and Frederickson ( 2013 ) involved teaching emotional literacy skills to small groups of students (Faupel, 2003 ). In the current evaluation, the intervention was delivered to groups of “low emotional literacy” and “high emotional literacy” groups distinguished by scores above, or below, median scores on the Emotional Literacy assessment‐pupil form (ELA‐PF; Faupel, 2003 ). The intervention program employed 12 weekly lessons and was implemented by trained teaching aids (Knowler & Frederickson, 2013 ). The program consisted of four main concepts: (1) self‐awareness, (2) self‐regulation, (3) empathy, and (4) social skills. Lessons employed a variation of behavioral and cognitive‐behavioral elements (Faupel, 2003 ).
6.21. Empathy training program
This intervention program was developed for children identified as bullies and aimed to increase their empathetic skills in order to reduce their bullying behaviors (Şahin, 2012 ). The empathy training program was implemented over eleven 75‐min sessions that were based on a curriculum lesson plan developed by the author. Several cognitive techniques were utilized throughout the program, such as: recognizing, evaluating and naming feelings; diadtic, experimental, modeling and role‐playing, in order to improve the students' cognitive abilities in relation to empathy. Each lesson required the students to work together to develop a slogan that emulated the content of the session. The following is an outline of the first 4 weekly lessons, and the associated slogan developed, (for a full outline see: Şahin, 2012 , p. 1327; Table 2 ).
Slogan: Be kind, loving and forgiving to each other to lead a happy life .
Slogan: Living without the awareness of feelings is like driving a car with its brakes on .
Slogan: One who claims to know everything about the universe but nothing about himself, actually knows nothing .
Slogan: We can look at the same thing but view it differently .
6.22. *Expect respect
Expect Respect was a school‐based program that aimed to promote awareness and effective responses to bullying and sexual harassment. The project was developed by Safe Place, the sole provider of comprehensive sexual and domestic violence prevention and intervention services in Austin, Texas (Rosenbluth et al., 2004 , p. 211). The program targeted the involvement of all members of the school community in recognizing and responding to bullying and sexual harassment. The overall project design was inspired by the work of Olweus (Rosenbluth et al., 2004 , p. 212). Expect Respect consisted of five core program components, namely a classroom curriculum, staff training, policy development, parent education and support services.
The classroom curriculum was based on 12 weekly sessions adapted from a specific manual called “Bullyproof: a teachers” guide on teasing and bullying for use with fourth and fifth grade students' (Whitaker et al., 2004 , p. 330). The Bullyproof curriculum was designed to be taught in conjunction with literature typically read by fourth and fifth graders. Although the antibullying curriculum was designed to be implemented by teachers, within the framework of the Expect Respect program, it was jointly led by Safe Place Staff and teachers or school counselors (Whitaker et al., 2004 , p. 331). The curriculum aimed to increase the ability and willingness of bystanders to intervene in bullying situations, thus reducing the social acceptability of bullying and sexual harassment. The Bullyproof lessons included writing assignments, role‐plays of how to intervene in bullying situations, class discussions and so on.
With regard to the staff training, a 6‐h training was provided to project staff, counselors, and fifth grade teachers. The training was given by the author of the specific manual and aimed to prepare school personnel to respond effectively to bullying incidents. In addition, 3‐h training sessions were provided once per semester for all personnel, including bus drivers, cafeteria workers, hall monitors and office staff. The training presentation included research on bullying and sexual harassment; strategies to enhance mutual respect among students; practice in using lessons from the curriculum; and methods for integrating the lessons into other subject areas including language arts and health.
School administrators were encouraged to develop an antibullying policy (policy development) in their school to ensure consistent responses by all staff members to incidents of bullying and sexual harassment. Principals were expected to present the policy to school staff, students and parents. In order to facilitate the overall procedure of policy development, Expect Respect staff provided an initial policy template to school administrators (Whitaker et al., 2004 , p. 332) and each school was encouraged to expand this initial policy in accordance with the specific needs of their unit.
The Expect Respect program also included parent training. Educational presentations were offered to parents, twice a year, providing information about the project. The information given to parents through these meetings (as well as through parent newsletters sent home) was aimed at enhancing parents' strategies to help children involved in bullying as bullies, victims, bully‐victims, or bystanders.
Further support services were provided such as continuous assistance of school counselors by Safe Place staff. School counselors were given a specialized session on how to deal with students who were repeatedly involved in bullying as either perpetrators or victims. They were also provided with a comprehensive resource manual containing reading and resource materials on bullying, sexual harassment and domestic violence.
6.23. fairplayer.manual
The fairplayer.manual is a structured, curriculum‐based antibullying program for Grade 7–9 students (Bull et al., 2009 ; Wölfer & Scheithauer, 2014 ). The overarching aim of the intervention is to reduce bullying and relational aggression by improving students' social and moral competencies. The program focuses on raising awareness, changing attitudes, and encouraging bystander intervention.
The program is implemented over 15‐weekly 90 min lessons, and can be delivered either by trained teachers (Bull et al., 2009 ), or psychologists (Wölfer & Scheithauer, 2014 ). Intervention lessons employ cognitive‐behavioral techniques and target nine specific topics. The first introductory lesson introduces the program to students, and class antibullying rules are developed. Two following lessons are concerned with raising awareness about bullying‐related issues, such as, the various forms of bullying and the consequences associated with perpetration and victimization. One lesson subsequently focuses on improving students' understanding of their own and peers' feelings. A further two lessons highlight the numerous participant roles involved in bullying, for example, bullies, victims, outsiders (i.e., noninvolved), assistants, and re‐inforcers (Wölfer & Scheithauer, 2014 ). The latter roles describe different forms of bystanders, those who witness bullying and allow it to happen and those who reinforce bullying behaviors. Social dynamics in the classroom is also addressed in one intervention session. By addressing the different dynamics, networks and norms socially in the class, this lesson aims to improve the classroom climate and encourage co‐operation among students. Another intervention lesson models and promotes bystander intervention in order to encourage noninvolved children to become actively engaged with intervening in bullying situations that they may witness.
Following these core awareness‐raising and knowledge‐improving lessons, participating students undertake five social skill‐training session s. These lessons focus on developing social, emotional, and moral skills of participants, in order to combat bullying. Perspective taking, empathy, and moral dilemmas are just some of the issues that are included. Diversity is the topic addressed in one of the following lessons, where students learn to respect and appreciate diversity. Finally, a concluding lesson brings together all of the issues covered by the intervention and demonstrates ways in which participants can utilize skills and knowledge in their everyday lives.
6.24. FearNot!
The FearNot! (Fun with Empathetic Agents to achieve Novel Outcomes in Teaching; Sapouna et al., 2010 ) was an immersive learning intervention that aimed to reduce bullying victimization. Students from British and German primary schools participated in the virtual learning program for weekly 30‐min sessions over the course of three consecutive weeks. Participating schools were required to have adequate computer facilities in order to be able to run the program.
During intervention sessions bullying scenarios were enacted by male and female 3D animated characters. The content of these scenarios reflected the characters' genders, for example, scenarios involving male characters included more incidents of physical bullying, whereas female characters demonstrated more relational bullying. Following each of the bullying episodes, participants were asked to interact and provide the animated victim of bullying with a suitable coping strategy to prevent future victimization. The program then enabled students to see the outcomes of their suggested strategy. In some circumstances, the animated victim of bullying responded that they did not feel emotionally adequate enough to carry out the suggested coping strategy (e.g., not strong enough to stand up to the bully).
Based on previous research (e.g., Kochenderfer & Ladd, 2000 ), students were then provided with an indication of how successful their proposed coping mechanism would be in real‐world bullying scenarios. For example, students were provided with a score on a scale of zero (never successful) to ten (always successful; Sapouna et al., 2010 ). In addition to the computerized program, teachers in intervention schools were provided with a detailed intervention manual. However, during the FearNot! program, teachers were instructed only to assist students with issues of comprehension, and not to guide them on suitable responses to the bullying scenarios.
6.25. Fourth R
The Fourth R: Strategies for Healthy Youth Relationships is a dating violence prevention program that targeted bullying perpetration and victimization as secondary outcomes (Cissner & Ayoub, 2014 ). This curriculum‐based intervention program was based on social learning theory (Bandura, 1978 ), and was implemented in classrooms by trained teachers during health and physical education classes. Participating teachers completed an intensive 1‐day training session that provided them with the skills to implement the program effectively. Detailed manuals and lesson outlines/materials were provided, and the Fourth R curriculum was integrated into existing health and physical education curricula.
The Fourth R was designed as a 21‐lesson curriculum that incorporates a variety of activities and lessons. Role‐playing, individual, pair and group work, and detailed examples/scenarios of conflict are examples of Fourth R‐style tasks. Program lessons were categorized into the following 3 units: (1) Personal Safety and Injury Prevention; (2) Healthy Growth and Sexuality; and (3) Substance Use and Abuse. Each unit consisted of seven 45‐min lessons. The Fourth R was also designed to be implemented in either gender‐segregated or co‐ed classrooms.
6.26. *Friendly Schools Project
“Friendly Schools” was a theoretically grounded program. Its educational techniques (e.g., role modeling, drama activities, skills training, etc.) were based on notions derived from Social Cognitive theory, the Health Belief Model and Problem Behavior theory (Cross et al., 2004 , 2011 ). An interesting aspect of this program is that it was based on the results of a systematic review (Cross et al., 2004 , p. 187), which provided a set of key elements to be included in the final intervention strategy. The program targeted bullying at three levels: (a) the whole‐school community, (b) the students' families, and (c) the fourth and fifth grade students and their teachers.
With regard to the whole‐school intervention component, in each school, a Friendly Schools Committee was organized with key individuals (e.g., a parent representative, a school psychologist, a school nurse, teaching staff) who could co‐ordinate and successfully sustain the antibullying initiative. Each committee was provided with a 4‐h training, designed to build members' capacity to address bullying. Each member was provided with a specific strategy manual. The manual was a step‐by‐step guide on how to implement the antibullying initiative. It included among others the Pikas “Method of Shared Concern” and the “No Blame” approach (Cross et al., 2011 ; Pikas, 2002 ).
With regard to the family intervention component, this included home activities linked to each classroom‐learning activity. Parents were also provided with 16 skills‐based newsletter items (eight for each year of the intervention) that aimed to provide research information on bullying as well as advice to parents on what to do if their child was a perpetrator or a victim of bullying behavior.
Moving on to the Grade 4 and 5 classroom curricula, the Friendly Schools curriculum consisted of nine learning activities per year. The curriculum was offered by trained teachers in three blocks of three 60‐min lessons, over a three‐school‐term period. The learning activities aimed to promote awareness of what was bullying behavior; to help students to become assertive and talk about bullying with teachers and parents; and to promote peer and adult discouragement of bullying behavior.
Finally, the Friendly Schools program offered manuals to teachers. The teacher manuals were designed to be entirely self‐contained so as to maximize the likelihood of teacher implementation. Friendly Schools project staff also provided teacher training (a 6‐h course) for all intervention teachers.
6.27. *Granada antibullying program
This program was a pilot antibullying program with the following aims: (a) to establish children's involvement in bullying within different participant roles/categories; (b) to reduce the number of students involved in the phenomenon as bullies, victims and bully‐victims; (c) to increase the number of students who are categorized as noninvolved in bullying, through the enhancement of prosocial skills; and (d) to identify the threats to fidelity of the program and establish the validity of the pilot program with the possibility of replicating it in future (Martin et al., 2005 , p. 376). Forty‐nine sixth graders from one Spanish primary school in Granada participated in the program.
The program designers gathered information about the social, educational and economic background of the school, of the students' families and the community in general. That was done during 3 meetings/seminars of 3 h each. Parents, teachers and members of the educational team attended those meetings. Through these meetings, it was established that the program should target interpersonal relationships of the children. It was decided that the program would be curriculum‐based as part of the normal program of the school. It was decided that the program would be implemented by one of the researchers because the teachers did not have enough qualifications to do it and because of lack of time and resources for teacher training. Parents and teachers were provided with information about bullying (a dossier/file) that they could use to discuss the problem of bullying with children. Also, teachers could attend the intervention program so that later they would be able to implement it by themselves. Parents were invited to attend some talks on bullying that would be given by the implementation team so that the program could be continued outside the school. The program was implemented for 5 months at the classroom level (30 sessions; 3 sessions per week with one tutor, i.e., one of the evaluators).
During the first 5 sessions, the tutor informed the children about peer bullying. Topics covered in the first 5 sessions involved issues such as concept of bullying, types of bullying, how to identify it, individual and group differences in bullying, and classroom rules against bullying. From the 6th to the 21st sessions, the program emphasis was on the emotional and social abilities of the children. Several topics were covered such as: identification and expression of emotions during bullying situations; communication abilities; ability to pose questions; ability of children to give and receive complements and complaints; ability to say no in life; ability to ask for a change of behavior; and ability to solve interpersonal problems. From the 17th to the 21st sessions, the program placed emphasis on mediation.
From the 22nd to the 25th sessions, the program emphasis was on human rights. Several topics were covered such as: freedom and equality, respect of private life, respect for other people's belongings, and respect for others' opinions. Similarly, from the 26th to 30th sessions, the emphasis was on moral education. During the whole program (sessions 1–30), there was also an emphasis on the inhibition of impulsivity and enhancement of reflexivity. For the enhancement of reflexivity, the program designers used a specific program called “Programa de Intervencion para Aumentar la Attention y la Reflixividad” [PIAAR] developed by Gargallo (2000) (see Martin et al., 2005 , p. 378). This focuses on cognitive techniques that aim to inhibit impulsivity and enhance self‐control. The program also included role‐playing, peer mediation, guided discussion, brainstorming, and drawings.
The authors acknowledge several problems with the implementation of the program such as: little involvement by parents and teachers; implementation of the program lessons during recess time or during the physical education program; lack of time to cover all the topics; no second follow‐up because of difficulties of following the children; problems with the size and selection of the sample; the instrument they used; and possible contamination of results because of the way they categorized the children (Martin et al., 2005 , p. 382). These pitfalls could easily be spotted. For example, the evaluators indicate that they implemented the program with the most aggressive sixth graders who had the worst interpersonal problems (Martin et al., 2005 , p. 738). This made it difficult to know whether any changes in bullying in the experimental condition were attributable to the effectiveness of the program or to regression to the mean. Also, even though they distributed a self‐report questionnaire, they categorized children based on those questionnaires only after teachers' suggestions.
6.28. *Greek antibullying program (1)
The Greek antibullying initiative was a 4‐week intervention program that aimed to minimize both bullying and victimization. The conceptual framework of the Greek antibullying program was based on the theoretical model proposed by Salmivalli in 1999 (Andreou et al., 2007 , p. 696), according to which changing an individual's behavior (e.g., the bully's behavior) entailed motivating not only the particular person but also the rest of the group members (participant roles' approach).
The program was embedded within the wider curriculum of the fourth‐, fifth‐, and sixth‐grade classrooms and consisted of eight instructional hours, each hour corresponding to one curricular activity. The curricular activities were presented to students by their classroom teachers who received training beforehand. The teacher training consisted of five 4‐h meetings and aimed to increase awareness of the bullying problem and its seriousness as well as to raise teachers' self‐efficacy in implementing the program (Andreou et al., 2007 , p. 697).
The Greek antibullying curriculum was divided into three parts in accordance with the three main theoretical axes proposed by Salmivalli in 1999, namely: (1) awareness‐raising; (2) self‐reflection; and (3) commitment to new behaviors (Andreou et al., 2007 , pp. 697–698).
In line with the first axis (awareness‐raising), small‐group and whole‐class discussions were conducted (over three instructional hours) that aimed to increase students' awareness of the bullying problem. Corresponding materials included a real snap‐shot from the playground, a story entitled “A new friend” and students' own drawings. In line with the second theoretical axis (self‐reflection), two instructional hours involving classroom discussions were conducted. These discussions placed emphasis on the participant roles that students took in the bullying process. Corresponding materials involved each students' completion of open‐ended sentences. Through this activity students were intended to reflect on critical issues around the causes, benefits, feelings, and consequences of adopting different roles. In line with the final axis (commitment to new behaviors), three instructional hours of small‐group and whole‐class discussions were conducted concerning different ways of approaching or solving the peer‐conflict situation and the formulation of class rules. Corresponding materials involved an open‐ended comic‐strip for group completion to find a solution to the bullying situation presented in the relevant story.
6.29. Greek antibullying program (2)
This antibullying program was implemented in Greek elementary schools during the academic year 2011/2012 (Tsiantis et al., 2013 ). The school‐based program incorporated many elements and was implemented by teachers. Participating teachers attended a 2‐day training seminar before implementation began. A teacher's manual (Tsiantis, 2011 ) was also provided and outlined the detailed and systematic procedures involved in the intervention. Throughout the program teachers were provided with additional support from two mental health professionals whom acted as program co‐ordinators.
The program comprised of 11 weekly workshops that were implemented for two 45‐min class periods (90‐min in total). Class activities included group discussions, games and the formation and signing of class antibullying rules (Tsiantis et al., 2013 ). Parent meetings were also organized to increase parent participation with the intervention. The first meeting provided parents with information about the intervention program and bullying issues. During the second parent session, students presented the achievements they had made during the intervention.
6.30. Inclusive
The INCLUSIVE program is a whole‐school restorative approach to bullying prevention and intervention (Bonnell et al., 2015 ). The program involves creating an “action group” within each participating school in order to combat bullying. These groups are comprised of a minimum of six students and six members of staff, with at least one representative from senior management, teaching, support, and pastoral staff. Each action group is appointed an external expert facilitator for the duration of the intervention. It is the facilitators' role to provide ongoing support and training to each member of the action group. Action groups were required to meet regularly throughout the intervention year, approximately once every half term.
The INCLUSIVE intervention was designed to include several core standardized intervention components, including staff training in restorative practices, and a student social and emotional skills curriculum. However, the program also allows for schools to adapt the intervention according to school‐specific needs. These needs were established using a needs assessment survey distributed to year 8 students prior to commencement of the intervention. This survey aimed to establish student views on bullying and aggression in their schools, while providing information regarding school engagement and connectedness, perceptions of safety/risks, social support and social skills, relationships, and teaching in personal, social and health (PSHE) classes. Results of the needs assessment survey were then employed by the action group to tailor the INCLUSIVE intervention to target specific needs. The action groups also utilized this information to review and improve schools' existing policies, procedures and schemes (e.g., peer mediation and “buddying” schemes).
In relation to the core components of the INCLUSIVE intervention, all school staff were provided with introductory training in restorative practices by their affiliated expert facilitator. A minimum of twenty school staff were also required to attend intensive training provided by a specialist training provider. Restorative practices, such as “Circle Time,” were taught to staff to improve school climate and student‐staff communication. This technique involves teachers and staff sitting together in a circle discussing various emotional, social, and curricular issues. Each member of the circle is considered a valued contributor, and all inputs are treated equally. Circle time aims to support student communication and promote positive relationships. Another restorative technique used in the INCLUSIVE program was “formal conferencing,” which aimed to deal with serious bullying and aggressive incidents directly. Formal conferencing involves bringing together teachers, parents and students to establish appropriate punishment and ways in which the harm caused can be repaired. This approach emphasizes a nonjudgmental and inclusive environment so that both victims and perpetrators of bullying and/or aggression are involved.
Year 8 students also completed 5–10 h of social and emotional skills training throughout the process of the INCLUSIVE intervention. These lessons were based on the Gatehouse Project curriculum and could be delivered as either stand‐alone modules or integrated into existing academic curriculums. Modules covered included: (1) Establishing respectful relationships; (2) Emotion management; (3) Understanding and creating trusting relationships; (4) Exploring others' needs and avoiding conflict; and (5) Maintaining and repairing relationships.
6.31. *KiVa
The name of this project is an acronym of the expression “Kiusaamista Vastaan” which means “against bullying.” The word “kiva” in Finnish means “nice” and this is why this acronym was chosen for the specific antibullying initiative in Finland. Regarding the overall perspective of the program, the KiVa project included a universal and an indicated intervention (Kärnä et al., 2011a , 2011b , 2013 ; Nocentini & Menesini, 2016; Salmivalli et al., 2007). The universal intervention referred to efforts made to influence the group norms while the indicated intervention referred to the way in which specific cases were handled in schools through individual and group discussions between the teacher and the students involved (Salmivalli et al., 2007, p. 6).
The KiVa program included a large variety of concrete materials for students, teachers, and parents. It also utilized the Internet and virtual learning environments (e.g., computer games against bullying) aiming in this way to enhance students' attitudes against bullying. Also, students received their own personal user ID, which they could use as a password before the completion of each web‐based questionnaire on bullying. KiVa included 20‐h student lessons, which were carried out by student teachers. The lessons involved discussions, group work, short films about bullying, and role‐playing exercises. After each lesson, a class rule was adopted, based on the central theme of the lesson.
A unique feature of the KiVa program was the use of an antibullying computer game. The game involved five levels and the teacher always activated the next level of the game after the relevant lesson was completed. Students were able to begin using the game after the third lesson; the second level of the program was played after the fifth lesson, and so on until the end of the school year. Each level of the computer game included three components that were named as “I know,” “I can,” and “I do.” In the first component, students were informed about basic facts on bullying. In the second component, the “I can”‐component, students moved around in the virtual school and faced different challenging bullying incidents. Finally, the third component was used to encourage students to make use of their knowledge and skills in real life situations.
Another important element of the KiVa project was the teacher training. Teachers were also provided with vests that they could use during playtime while supervising the school yard. This simple technique aimed to enhance teachers' visibility in the schoolyard and to signal that bullying was taken seriously in the school. Also, all teachers carrying out the KiVa program could seek advice from a web‐based discussion forum, where they could share experiences and ideas about bullying with other colleagues.
Within the school framework, the program also facilitated the use of a peer support group for victims of bullying. The classroom teacher was expected to arrange a group with 2–4 classmates—those who were pro‐social and had high status in the class—who were expected to provide support to victimized students, thus sustaining healthy peer relationships. An interesting element in the KiVa program is that it incorporated both punitive and nonblame approaches when dealing with perpetrators of bullying. Half of the school teams were instructed to use more punitive approaches (e.g., what you have done is wrong and it has to stop right now) while the rest of the school teams were instructed to use no‐blame approaches in their discussions with children (e.g., “your classmate is also having a hard time and this is why he behaves like that; what could we do to help him?”). There was also co‐operative group work among experts when dealing with children involved in bullying.
Finally, the KiVa program involved parents. A parents' guide was sent to the home and provided information about bullying and advice on how parents could be involved to reduce this problem. Information nights for parents were also organized and provided.
6.32. Lead Peace Intervention
The Lead Peace intervention is based on a resiliency conceptual framework (Resnik, 2000 ), thus, aims to reduce youth problem behaviors using an assets‐based approach (Harpin, 2011 ; Sieving & Widome, 2008 ). The intervention was developed as a school‐based “service learning and health education” program to reduce risk of violence and school failure in middle school students (Sieving, 2006). Developed from the Points of Light Youth Leadership curriculum for 9th to 12th grade students (Sieving, 2006), the program was adapted for use with Grade 6–8 students (Harpin, 2011 ).
The core curriculum targets factors on three levels: (1) environmental (e.g., adult resources and supports, family norms and behaviors, peer norms and behaviors, school/community opportunities and social connectedness); (2) personal (e.g., attitudes, beliefs, perceived norms, emotional distress); and (3) behavioral (e.g., social and emotional skills, coping behaviors, school performance). The program aims to reduce risky health and social behaviors (e.g., interpersonal aggression, physical fighting, bullying) in order to promote positive and reduce risky behaviors. The curriculum is implemented for 3 years, and can be delivered in two “doses”: (1) Lead Peace program (basic)—includes 15–20 intervention lessons each year; or (2) Lead Peace plus program—includes 30 intervention lessons, 15–20 additional community service hours, and health education and family outreach activities.
6.33. Lunch Buddy Mentoring program
The Lunch Buddy mentoring program was a school‐based antibullying program that aimed to reduce bullying victimization in elementary school children (Elledge et al., 2010 ). The program was based on previous research that suggests youth mentoring can be utilized as an effective prevention technique (Dortch, 2000). In comparison to peer‐mentoring antibullying program, the Lunch Buddy program employed college student mentors based on prior success of college student mentoring aggressive children (Cavell & Hughes, 2000 ).
Mentors were provided with training prior to implementation of the program and participated in weekly meetings throughout the program. Children were identified as potential participants using a self‐ and teacher‐report victimization index. The self‐report School Experiences Questionnaire (Kochenderfer & Ladd, 2000 ) and teacher ratings of child victimization due to physical, verbal and relational aggressive were combined to create this index. School principals also collaborated with counselors to identify potentially suitable candidates. Eligible participants were then matched with same‐sex college student mentors, based on the availability of mentors during the mentees scheduled lunchtimes. Mentors visited the mentees twice a week, over the course of 5–6 months. During these visits mentors were required to sit with their mentee and their peers during lunchtime. Each mentor was also required to complete a log sheet after each visit.
6.34. Media Heroes
Chaux et al. ( 2016 ) evaluated the effectiveness of the cyberbullying prevention program “Media Heroes” [ Medienhelden ] on reports of traditional school bullying. The Media Heroes program is based theoretically on the Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991 ) and the social context of participant roles in bullying (Salmivalli, 2010 ). The program aims to reduce cyberbullying perpetration by enhancing empathy, increasing awareness and knowledge about what constitutes cyberbullying, the safety risks associated with Internet activity, and by providing assertive and useful methods in which bystanders can intervene in cyberbullying (Chaux et al., 2016 ).
There are two versions of Media Heroes: (1) a short version implemented over four 90‐min lessons that take place in one school day; and (2) a long version that is implemented over 15‐weekly 45‐min lessons (Schultze‐Krumbholz et al., 2012 ). Intervention activities include, role‐playing, class debates, news and film content, group learning and student‐parent presentations (Chaux et al., 2016 ). Measures of both traditional‐ and cyber‐bullying were implemented in this evaluation, due to the significant overlap in the prevalence of these behaviors.
6.35. NoTrap!
Noncadiamointrappola (Let's Not Fall into a Trap), or NoTrap!, is a web‐based antibullying program that has been developed, implemented and refined over several studies (Menesini et al., 2012 ; Palladino et al., 2012 , 2016 ). Initially implemented in two Italian schools in 2008, the program involves students actively engaging in the development of a website promoting antibullying (Menesini et al., 2012 ). A selected number of students per school are provided with training and enroll as online peer‐educators. These students acted as online moderators of an antibullying forum, regulating discussion threads and responding to users' questions and concerns (Menesini et al., 2012 ). In addition, peer‐educators also conducted face‐to‐face awareness raising workshops and meetings with their classmates, to highlight the key issues surrounding traditional‐ and cyber‐bullying (Palladino et al., 2016 ).
Subsequent editions of the NoTrap! program incorporated additional elements based on findings from previous evaluations. For example, Palladino et al. ( 2012 ) placed more emphasis on: (1) victims' roles and victim support, (2) involving bystanders, (3) greater involvement of teachers in antibullying activities, and (3) creation of a Facebook group to supplement online materials. The third revision of the NoTrap! program incorporated standardization of the face‐to‐face antibullying activities led by peer educators (Palladino et al., 2016 ). New peer‐led activities involved group work that targeted empathy and problem‐solving skills (Palladino et al., 2016 ).
6.36. *Olweus Bullying Prevention Program
The OBPP was a multilevel program aiming at targeting the individual, the school, the classroom and the community level. Apart from marked mass‐media publicity, the program started with a 1‐day school conference during which the problem of bullying was addressed between school staff, students, and parents. This signaled the formal commencement of the intervention. Two different types of materials were produced: a handbook or manual for teachers (entitled “Olweus” core program against bullying and antisocial behavior') and a folder with information for parents and families. The program also included: (1) CD‐program that was used for assessing and analyzing the data obtained at the pre‐test period, so that school‐specific interventions could then be implemented; (2) a video on bullying; (3) the Revised Olweus Bully/Victim Questionnaire and (4) the book “Bullying at school: what we know and what we can do.”
The antibullying measures mainly targeted three different levels of intervention: the school, the classroom and the individual. At the school level, the intervention included:
- Meetings among teachers to discuss ways of improving peer‐relations; staff discussion groups.
- Parent/teacher meetings to discuss the issue of bullying.
- Increased supervision during recess and lunchtime.
- Improvement of playground facilities so that children have better places to play during recess time.
- Questionnaire surveys.
- The formation of a coordinating group.
At the classroom level the intervention included:
- Students were given information about the issue of bullying and were actively involved in devising class rules against bullying.
- Classroom activities for students included role‐playing situations that could help students learn how to deal better with bullying.
- Class rules against bullying.
- Class meetings with students.
- Meetings with the parents of the class.
At the individual level the intervention included:
- Talks with bullies and their parents and enforcement of nonhostile, nonphysical sanctions.
- Talks with victims, providing support and providing assertiveness skills training to help them learn how to successfully deal with bullying; also, talks with the parents of victims.
- Talks with children not involved to make them become effective helpers.
An interesting feature of the OBPP is that it offered guided information about what schools should do at both the intervention and the maintenance period. The Olweus program demands significant commitment from the school during the 'introductory period' which covers a period of about 18 months. Later the methodology acquired by the staff and the routines decided by the school may be maintained using less resources … Yet, even for the maintenance period, the program offers a point by point description of what the school should do to continue its work against bullying in accordance with Olweus methodology (Olweus, 2004c, p. 1). Also, at the school level training was offered to the whole school staff, with additional training provided to the coordinators and key personnel. These were responsible for coordinating the overall antibullying initiative in their school. The program also included cooperation among experts and teachers (e.g., psychologists) who worked with children involved in bullying.
6.37. Positive Action program
The Positive Action Program is a generalized school‐based “well‐being” program (Lewis et al., 2013 ). The program targets both distal (e.g., school climate and teacher classroom management) and proximal (e.g., students' thoughts, feelings, and self‐efficacy) facets are targeted in order to impact a range of health‐ and behavioral‐related outcomes (Li et al., 2011 ). The program is based on three core elements.
First, the Positive Action philosophy. Based on the theory of self‐concept (Combs, 1962 ; Purkey, 1970 ; Purkey & Novak, 1996 ) and a Positive Psychology (Frederickson, 2000; Seligman & Csikszentmihalyi, 2000 ) approach, the philosophy emphasizes positive feelings about the self, to encourage positive behaviors toward others (Flay & Allerd, 2010 ). Second, the Thoughts‐Actions‐Feelings Circle concept is used throughout the program to illustrate the reinforcing cycle of thoughts, feelings and actions. This is delivered to outline that positive thoughts lead to positive actions, positive actions in turn lead to positive feelings, which then reinforce positive thoughts. Third, a strict six‐unit curriculum that involves daily lessons, interactive learning and social‐emotional skill development.
The PA curriculum is designed to be adapted for kindergarten to Grade 12 students, and is based on six key concepts: (1) self‐concept; (2) social and emotional positive actions for managing oneself responsibly; (3) positive actions relating to a healthy body and mind; (4) honesty with oneself; (5) getting along with others; and (6) continuous self‐improvement (Lewis et al., 2013 ). The intervention program also involves teacher, parent/family and community training. Schools implementing the PA program receive support from developers throughout implementation by training, manuals, school‐wide climate development, counselors, family classes, and individual consultations for staff with a PA implementation coordinator.
6.38. Preventure and Adventure CBT
The Preventure and Adventure intervention programs were part of two 2 year longitudinal projects that targeted adolescent alcohol use and bullying behaviors (Topper, 2011 ). Intervention components were primarily personality‐targeted cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for “high risk” students. Participants were screened prior to taking part in the intervention for four individual personality domains: (1) hopelessness; (2) anxiety‐sensitivity; (3) sensation seeking; and (4) impulsivity. Students who were classified as being “high risk” on any of the four domains were invited to participate, and assigned to one of four potential intervention workshops. These intervention sessions were CBT‐based and were aimed at each of the four personality domains. Thus, a student who scored highly on the impulsivity measure was assigned to the impulsivity‐focused CBT session. For participants that scored above the mean on multiple measures, they were assigned to the session that corresponded to the personality domain that they deviated the most from standardized scores.
High risk students in each school were randomly assigned to either the intervention or control condition, as were “low risk” students, for comparison. The Preventure study took place between 2005 and 2007, and either a chartered counseling psychology, an experienced special needs teacher, or a master‐level research assistant implemented intervention workshops. In comparison, the Adventure study took place between 2007 and 2009, and although the intervention sessions followed the same procedure, they were implemented by trained teachers in each school.
6.39. *Pro‐ACT+E program
Pro‐ACT+E was a universal, multidimensional program that aimed to prevent bullying in secondary schools (Sprober et al., 2006). It involved a cognitive‐behavioral approach to the problem of bullying and victimization by building up prosocial behavior. The program was universal: it did not involve specific work with perpetrators or victims of bullying. However, it included both teacher and parent training and a 2‐h classroom discussion with students about violence problems. The program offered curriculum materials that aimed to increase awareness in relation to the problem of bullying and placed emphasis on specific issues such as classroom management and classroom rules against bullying.
6.40. *Progetto Pontassieve
The program was delivered in a period of 3 years, and it consisted of two main parts. During the 1st two years it was delivered more at the school level whereas the 3rd year was more at the class and individual level (Ciucci & Smorti, 1998 ). During the 1st year a training course for teachers took place addressing psychosocial risks for children and bully‐victim problems. At the end of the training, a study was conducted to reveal how serious was the problem of bullying and what were its characteristics. The 2nd year of the intervention included a counseling service for each individual who was affected by bullying.
The intervention took place in the 3rd year and was based on the use of two different methods: Quality Circles, where pupils had to cooperate to find practical solutions to their problems, with the use of the Interpersonal Process Recall which consisted of the recording of one Quality Circle and discussion about it. The other method used was Role Playing conducted in small groups with subsequent class discussions, which helped students to examine possible strategies to face and overtake bullying problems. The aims of both of these methods were to make students aware that they could intervene in an efficient way to reduce bullying.
6.41. *Project Ploughshares for Peace
Project Ploughshares Puppets for Peace (P4 program) was an antibullying program that aimed to educate elementary school students about bullying and conflict resolution (Beran & Shapiro, 2005 , p. 703). The P4 program used puppets and a 30‐min script. Using three‐feet, hand‐and‐rod puppets, two puppeteers enacted a story that involved direct and indirect bullying, as well as a successful resolution to this scenario. These behaviors occurred among two female puppets and a male puppet friend.
After watching the play, students were invited to identify the bullying behaviors. During the discussion, four main strategies—presented as “4 Footsteps”—to deal with bullying were suggested to pupils: (1) ignore, (2) say stop, (3) walk away, and (4) get help. The show took approximately 45 min and aimed to increase children's awareness about which behaviors could be categorized as bullying and to show various strategies that children who were bullied and/or who witnessed bullying could use to discourage it (Beran & Shapiro, 2005 , p. 703).
6.42. Rational Emotive Behavioral Education (REBE) and ViSC
Trip et al. ( 2015 ) implemented a dual program consisting of REBE (Trip & Bora, 2010 ) and ViSC social competence (Strohmeier et al., 2012 ) elements. These components were combined to address both social and emotional factors involved in bullying and positive youth development (PYD). This program approaches bullying from a sociological perspective, including factors on the individual, family, peer, classroom, and school levels (Espelage & Horne, 2008 ; Swearer & Espelage, 2011 ).
ViSC social competence program is a systemic approach to antibullying that targets students, teachers and parents (Strohmeier et al., 2012 ). Implemented by teachers in the classroom, the program comprises several intervention units that aim to: (1) foster empathy and perspective training, (2) enhance responsibility, and (3) improve students' behavioral responses to bullying (Trip et al., 2015 , p. 733).
REBE elements employed by Trip et al. ( 2015 ) on the other hand, target specific elements of aggression that are lacking in the ViSC units. Based on the theory of Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (Ellis, 1962 ), the REBE elements of the intervention program target the difference between desire and reality (Trip & Bora, 2010 ) and anger. The REBE program activities target specific elements of anger, specifically, anger triggers, personal experiences of anger and the consequences of anger (Trip et al., 2015 ).
6.43. Restorative Whole‐school Approach (RWsA)
The RWsA (Hopkins, 2004 ; Morrison, 2002 ) was a school‐based antibullying initiative that employs a restorative justice inspired philosophy. Hence, the program focuses on creating a positive school environment to prevent bullying in the long‐term, rather than a short‐term disciplinary and punishment approach (Wong et al., 2011 ). The program had three core goals: (1) to create a positive and harmonious school learning environment; (2) implement an interactive classroom curriculum; and (3) encourage an effective partnership between teachers, students, parents and relevant professionals.
A whole‐school antibullying nonpunitive ethos and policy is implemented as the core of the intervention (Wong et al., 2011 ). This policy aims to establish a positive school environment in order to combat bullying‐related risk factors. The curriculum lessons incorporated elements on various issues, including, empathy, assertiveness, coping, problem‐solving, and conflict resolution.
6.44. Resourceful Adolescent Program (RAP)
The RAP is a classroom‐based CBT intervention designed for adolescents aged 12–15 years of age (Stallard et al., 2013 ). The program is a depression prevention program, however, bullying problems were included as secondary outcomes. The program incorporates a detailed manual and student workbooks, and was implemented over nine sessions, of approximately 50–60 min each. The core components include: psycho‐education, helpful thinking, identifying personal strengths, keeping calm, problem solving, support networks, and keeping the peace. The program was designed to flexible and adaptable to participating schools' varying busy timetables.
6.45. *S.S. Grin
The Social Skills Group Intervention (S.S. GRIN) was a school‐based program that aimed to help children enhance their social skills. S.S. GRIN was designed as a social‐skills training intervention for peer‐rejected, victimized, and socially anxious children. It could be applied to an array of problems that are social in nature (e.g., aggression, low self‐esteem, depression, social anxiety, social withdrawal) not just bullying (DeRosier & Marcus, 2005 , p. 140). The authors argued that the program went beyond the most common social‐skills training (De Rosier & Marcus, 2005, p. 141) by emphasizing the cognitive aspects of relations and emotions. That is, children were not only taught prosocial skills, but they were also taught, on the cognitive level, how to identify negative perceptions and behaviors in an effort to help children to regulate their own emotions as well as enhance their coping skills.
Overall, the program was a combination of social‐learning and cognitive‐behavioral techniques, used to help children build social skills and positive relationships with peers. It was a highly structured, manualized program (DeRosier, 2004 , p. 197) with a number of sessions containing scripts and activities to undertake. Each session included didactic instruction combined with active practice such as role‐playing, modeling and hands‐on activities (De Rosier, 2004, p. 197). The children participated in group sessions for eight consecutive weeks. Each session lasted approximately an hour. The groups were led by each school's counselor and an intern, who were trained and supervised by one of the program instructors (De Rosier & Marcus, 2005, p. 143).
6.46. School‐based Drama program
This school‐based antibullying program was based on drama (Owens & Barber, 1998 ) and social cognitive theories (Bandura, 1978 ). The main aim of this project was to design and implement a drama‐based program to improve social relationships and social/emotional well‐being in children, which in turn may help to reduce bullying (Joronen et al., 2011 ). Targeted concepts included: empathy; social competence; student‐teacher interaction; child–parent interaction; and recognition of values/emotions.
This program was developed by the combined efforts of researchers, drama experts and teachers. It was implemented in‐class by trained teachers and school nurses over a period of 6 months. Teachers and school nurses attended a 2‐day seminar and received two drama handbooks, however, there was no manual or fixed program outline provided. Support was provided through email communication between teachers and researchers for the duration of program implementation. Teachers conducted one drama session per month with their class. These sessions covered a variety of topics, including, bullying, friendship, loss of a friend, supporting a bullied peer, tolerance, and child abuse.
6.47. School‐wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (SWPBIS)
SWPBIS was a universal behavioral intervention program that targets school‐level factors in order to improve school climate and promote positive student and staff behaviors (Waasdorp et al., 2012 ). Instead of following a specific antibullying curriculum, SWPBIS aimed to reduce bullying by targeting schools' discipline and behavioral management strategies. A SWPBIS team in each school organized and facilitated the intervention implementation.
These teams were responsible for developing a set of “positive expectations” for the school. These were a number of statements that outlined what the school expected in relation to student and staff behavior, for example, “be responsible, respectful, and ready to learn” (Waasdorp et al., 2012 , p. 150). Posters highlighting the expectation statements were then displayed all around participating schools, both in classrooms and outside of classrooms, and are positively reinforced using reward systems. Furthermore, data from student surveys and discipline referrals were employed throughout the intervention to inform teachers of potential bullying “hot spots” that require increased supervision and monitoring. School staff also received training on classroom management and how to respond consistently and effectively to bullying. Additionally, students identified as being “high risk” or vulnerable to bullying behaviors or victimization were provided with selective intensive intervention.
6.48. School bus antibullying intervention
This intervention program was a universal antibullying program designed to reduce the prevalence of bullying behaviors on school buses (Krueger, 2010 ). The program was purposefully developed and utilizes materials and content from the “Take a Stand, Lend a Hand, Stop Bullying Now!” tools that are available free of charge.
The intervention was implemented with elementary school children over five consecutive days, during the final 20‐min of the school day. Lessons were delivered by the school's social worker and principal to two groups (kindergarten to 2nd grade students, and 3rd to 5th grade students) of participants. The program followed this format from days 2–5, however, on day 1, all participants completed the introductory lesson together. The school‐bus antibullying program primarily utilized DVD materials from the “Take a Stand” content. These video clips depicted cartoon characters engaging in different bullying scenarios.
On day 1 (i.e., the introductory lesson) an overview of school bullying and related issues, including bystander intervention, was provided to participants. The associated DVD clip depicted a male character physically bullying another child in the playground while other students watched. Participants then discussed the clip in groups, and were introduced to the “Three Steps to Stop Bullying Chart.” This technique involves three steps, Stop, Help , and Tell , that bystanders can take if they witness bullying.
On each subsequent day, a new DVD clip was shown to participants and the Stop, Help , and Tell concepts were revisited. The school's social worker or principal led discussion groups by posing questions to the students concerning the feelings and emotions experienced by the victim of bullying, potential coping strategies that the victim could use, and possible bystander behaviors. Participants also shared their previous experiences with similar situations. Furthermore, using the Stop, Help , and Tell paradigm, participants brainstormed potential ways to tell a bully to stop behaving in a certain manner, ways to help the victim and appropriate trusted adults that they can tell about the situation.
6.49. Second Step
The Second Step: Student Success Through Prevention is a middle school Social‐Emotional Learning (SEL) program that aims to reduce bullying, peer victimization, physical aggression, homophobic name‐calling and sexual violence (Espelage et al., 2013 , 2015 ). The intervention curriculum is taught in‐class by trained teachers. Lessons are interactive and engaging, requiring students to take part in whole‐class, small group and individual work. A take home task is also given after each lesson to reinforce skills learned. DVDs are also used to accompany and enrich lesson content.
The 6th grade Second Step curriculum involves 15 weekly lessons on various social and emotional skills and bullying‐related topics. The following outlines the curriculum: (1) empathy and communication—five lessons; (2) bullying—two lessons; (3) emotion regulation (e.g., coping with stress)—three lessons; (4) problem‐solving—two lessons; and (5) substance abuse prevention—four lessons.
Each lesson has clearly outlined learning objectives to reduce problem behaviors and increase prosocial behaviors. For example, lessons on bullying target the peer context by increasing knowledge, improving attitudes, and encouraging bystander intervention in order to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization. Students are educated about the differences between types of bullying, importance and responsibilities of bystanders in preventing bullying and a number of positive bystander behaviors are modeled. The 7th grade Second Step curriculum involves a similar lesson structure, with some slight changes. The intervention is delivered over 13 weekly lessons, and cyber‐bullying and sexual harassment issues are incorporated into bullying modules.
6.50. Shared Concern
Wurf ( 2012 ) assessed the effectiveness of the whole‐school approach to bullying intervention and prevention, with a particular emphasis on Pikas' ( 2002 ) nonpunitive method of shared concern. The Pikas method of Shared Concern is a teacher, or counselor, implemented intervention, that is divided into five key stages. First, the intervener identifies the students involved in bullying and talks with them individually. These discussions aim to provide nonpunitive and constructive options for both bullies and victims (Wurf, 2012 ). The second and third stages involve providing empathy and ongoing support to the victims of bullying. Finally, the fourth stage incorporates a mediation session between bullies and victim(s). A conflict resolution approach to prevent bullying is agreed upon and implemented by all involved. The fifth and final stage occurs during the follow‐up period, whereby the teacher or counselor monitors the involved students to ensure that the bullying has stopped.
6.51. *Short Intensive Intervention in Czechoslovakia
The antibullying intervention in Czechoslovakia was inspired by the OBPP and borrowed elements from it, such as the Olweus videocassette on bullying (Rican et al., 1996 , p. 399). The Olweus bullying questionnaire was used to measure several aspects of bullying within the schools. A peer nomination technique was also used to identify bully and victim scores. The relevant results from both measurement scales were presented to teachers in the intervention schools to increase awareness of the problem of bullying. The program researchers discussed with the teachers “possibilities of an individual approach to the bullies as well as to the victims” (Rican et al., 1996 , p. 399).
As another intervention element, teachers were instructed to introduce relevant ethical aspects into the curriculum where possible: the ideal of knighthood was suggested for history classes and the ideal of consideration for the weak was introduced in sentences used for dictation and analysis (Rican et al., 1996 , p. 400). Another element of the intervention involved the use of a method called “class charter.” Specifically, children were asked to indicate how they would like their teachers and other classmates to behave toward them as well as how students should behave toward teachers and among themselves. The final aim of this classroom activity was the construction of a set of rules and principles, which was then signed by all pupils in the classroom and placed there in a visible position. Finally, the Olweus video‐cassette on bullying was shown to children and was used as a means of promoting the antibullying idea in the school.
6.52. *Short Video Intervention
This antibullying strategy, involved a single viewing of an antibullying video, entitled Sticks and Stones, and aimed to examine its effects on secondary school students' views of, and involvement in, bullying. The program aimed to examine both attitudes toward bullying and the actual behavior since “it would not be unreasonable to propose that these attitudes will influence actual behavior” (Boulton & Flemington, 1996 , p. 334). The program involved only one school that had no prior antibullying policy.
The video presented pupils (either in groups or on their own) talking about bullying, their views about this phenomenon and their personal experiences of bullying. The video also involved a number of bullying scenes (see Boulton & Flemington, 1996 , p. 337 for examples).
6.53. Social and Emotional Training (SET) intervention
This intervention program was a school‐based SET mental health program for Swedish school children (Kimber et al., 2008 ). The SET program was primarily focused on mental health, but also targeted other aspects of participants' lives, such as bullying. Both internalizing and externalizing aspects of child mental health are addressed.
Trained teachers delivered the program over the course of two academic years. Intensity of program implementation varied according to the age of students. Junior students (i.e., grades 1–5) received the program in 45‐min sessions twice a week, while senior students (i.e., grades 6–9) completed one 45‐min session per week. Program developers provided each participating teacher with detail manuals for implementing the program with each grade and grade‐specific student workbooks. Role‐playing and modeling tasks covered many themes, including: social problem solving; conflict management; dealing with strong emotions; and resisting peer pressure. Teachers were also supervised once a month during the 1st year of implementation, and students were encouraged to practice skills both at school and at home.
6.54. Social Norms Project
Lishak ( 2011 ) implemented an antibullying program based on social norms theory (Perkins, 2003 ) with middle school students. The program was implemented over a period of 12 weeks and was developed based on student responses to an anonymous web‐based survey and student discipline and suspension reports (Lishak, 2011 ). Student surveys collected information regarding perceptions of bullying in the school and results were then relayed to participants via weekly lessons, assemblies, posters, and media content throughout the school. Data from school discipline, suspension and visitation logs were collated to estimate the prevalence of bullying and school violence.

6.55. *Social Skills Training (STT) program
STT was a program specifically designed to support “chronic victims” of bullying (Fox & Boulton, 2003 , p. 237). The general aim of the program was to help children improve their social skills, therefore reducing a child's individual risk of victimization (Fox & Boulton, 2003 , p. 234). The program involved an 8‐week course during which children learnt how to use both problem‐solving and relaxation skills, how to think positively, how to modify their nonverbal behavior and how to use some verbal strategies such as “fogging” and “mirroring” (Fox & Boulton, 2003 , p. 235).
During the program, victims of bullying were gathered in groups of five to ten and were exposed to the aims of the program for 1 h/week. Two trainers delivered the 1‐h sessions throughout the program. The 1st week was dedicated to children introducing each other and listening each other's problem. The next two sessions dealt with issues of friendship and aimed to help children form strong friendships (e.g., having conversations; asking to join in), while the fourth session dealt with issues of body language: teaching children how to modify their nonverbal behavior in a way that would protect them from being victimized. During the fifth session children learned how to be assertive while in the next two sessions children were taught how to deal with the bully. The eighth session signaled the end of the program.
6.56. *SPC and CAPSLE program
This evaluation compared the effects of two intervention packages with a treatment‐as‐usual condition (Fonagy et al., 2009 ). Nine schools were randomly allocated to the two experimental and one control (treatment‐as‐usual) conditions after a stratified allocation procedure, which was used to stratify schools based on the percentage of low‐income students (indicated by students' free‐ and reduced‐lunch status). In the experimental conditions, the full intervention was offered for 2 years (the efficacy phase) with a limited 3rd year of intervention (the maintenance phase).
The first experimental condition involved a “School Psychiatric Consultation” (SPC), a manualized protocol that aims to address mental health issues of children with disruptive behavioral problems, internalizing problems, or poor academic performance. SPC was a school‐level intervention focused on individual children. Three child psychiatry residents, supervised biweekly by a senior child psychiatrist, delivered mental health consultation following the SPC manual for 4 h/week. The psychiatric residents attended weekly school resource meetings and consulted directly with teachers, parents and other school personnel, through classroom observations and meetings, providing 140 consultations for 65 students in year 1 and 97 consultations for 45 students in year 2.
The second experimental condition involved the implementation of CAPSLE (“Creating a Peaceful School Learning Environment”), a manualized psychodynamic approach addressing the cocreated relationship between bullies, victims and bystanders. In contrast to SPC, CAPSLE represents a whole‐school intervention approach. It aimed to modify the educational and disciplinary school climate. A CAPSLE team drawn from school staff in the pilot project led implementation in the two intervention years using a training manual. In year 1, teachers received a day of group training, students received nine sessions of self‐defense training, and the CAPSLE team consulted with school staff monthly. Year 2 started with a school‐wide half‐day refresher self‐defense course, and consultation continued with counselors, teachers and adult/peer mentor programs. In year 3 (the maintenance phase), self‐defense training continued as in year 2.
CAPSLE includes several antibullying materials that can be used by teachers such as a Teacher Discipline Manual (used in the teacher training), a Student Workbook, Buttons and Magnets and Patches (used as a way of reinforcing of desirable student behavior), Parent Warning Notes (notifying parents about specific problem behavior of the child) as well as antibullying videos that can be used during the physical education lessons (and videos that can be used by parents). CAPSLE also includes the Gentle Warrior Program, a 12‐week curriculum specifically designed for physical education teachers. For CAPSLE, intervention fidelity was assessed using a teacher self‐report measure that required teachers to state the frequency with which various CAPSLE program components were implemented.
6.57. Standard CBT and CBT plus media program
This intervention program combined elements of standardized CBT and DVD bullying‐related materials in order to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization among elementary school children (McLaughlin, 2009 ). The standardized CBT lessons were delivered by a trained counselor, and focused on bullying and aggression relation issues. Two experimental groups were employed, one of which received only the CBT lessons, and the other completed the CBT lessons and were shown the bullying DVDs.
The program was implemented over 4 weekly lessons that followed a strict outline. In week 1, the lesson focused on defining bullying, identifying bullying roles and different forms of bullying, and exploring the possible characteristics of bullies, victims, and bystanders. Week 2's lesson was concerned with establishing the consequences of bullying for all those involved, including the bully, victim and bystanders. Empathy for victims of bullying was also developed. Activities included creating feeling lists, and participating in role plays. Lesson three aimed to promote bystander intervention by developing awareness and knowledge of appropriate responses to bullying, suitable ways to intervene, and promoting assertiveness. Classes are taught using educational and informative posters. The final lesson, in week 4, aimed to outline the gender differences in bullying, why these occur, and ways to combat gender‐specific forms of bullying. In their classes, students establish class antibullying rules and are taught about the support available in school to stop bullying.
In addition, students in the CBT + media experimental group watched three DVDs that highlighted the issues outlined in the weekly lessons. The DVDs that were shown are as follow: (1) Let's Get Real , which shows young people talking about their personal experiences of bullying; (2) The Deepest Hurt , that depicts girls role‐playing various scenarios of relational aggression; and (3) The Broken Toy , a dramatization of the damage bullying can cause. Following the videos, students engaged in group discussions led by the counselor about the issues illustrated in each DVD.
6.58. *Stare bene a scuola: Progetto di prevensione del bullismo
This intervention was based on the curriculum activities and the whole school approach because it tried to involve all people in a school (Gini et al., 2003 ). The program was delivered to 6 schools and included several activities. Teachers were first trained in 3 days on “cooperative learning” and in particular on the Jigsaw technique. Teachers then had an on‐going supervision once every 15 days. The intervention in the class lasted 4 months with two meetings a week. The intervention was directed toward the following areas: (1) awareness of the body and what it feels; (2) emotional awareness; and (3) bullying awareness. These areas were dealt with in each of the sessions, starting from the first one. For each thematic area, several activities were conducted and several methods were used.
6.59. Start Strong
“Start Strong: Building Healthy Teen Relationships” was a school‐based curriculum focused teen dating‐violence prevention program (Williams et al., 2015 ). The program was implemented over 2 years in four experimental schools (that implemented the program) and four comparison schools (that did not implement the program). Schools were matched based on: school size, percentage of students eligible for free school lunches, race/ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. The effectiveness of the program was measured for outcomes that included the perpetration and victimization of teen dating‐violence, bullying and sexual harassment.
6.60. *Steps to Respect
The Step to Respect program aimed to tackle bullying by: (1) increasing staff awareness; (2) fostering socially responsible beliefs; and (3) teaching social‐emotional skills so as to promote healthy relationships (Frey et al., 2005 , p. 481). The program included staff and family training manuals, a program guide and lesson‐based curricula for third‐ through sixth‐grade classrooms (Hirschstein & Frey, 2007 , p. 7).
Components at a whole school level consisted of an antibullying policy and procedures, staff training and parent meetings, all aiming at sharing understanding of bullying and its consequences and increasing adult awareness, monitoring, and involvement. At the classroom level, the proposed activities consisted of teaching friendship skills, emotion regulation skills, identifying types of bullying, teaching prevention strategies and peer group discussion. The aim was to improve peer relations and reduce the risk of victimization, assess level of safety and recognize, report and refuse bullying. At the individual level, students involved in bullying were approached and coached based on the “Four‐A Responses”: affirm behavior, ask questions, assess immediate safety and act.
The S to R training manual consisted of an instructional session for all school staff and two in‐depth training sessions for counselors, administrators, and teachers. There were also videos accompanying the program. With regard to staff training, there were two levels of training: all school staff received an overview of the program goals and principal aspects of the program (program guide). Teachers, counselors, and administrators received additional training in how to coach students involved in bullying, based on behavioral skills training, cooperative learning and role‐playing.
The student curriculum comprised skills and literature‐based lessons delivered by third‐ through sixth‐grade teachers during a 12–14‐week period. The intervention consisted of 10 semi‐scripted skills lessons with topics such as joining groups, distinguishing reporting from tattling and being a responsible bystander.
Finally, with regard to the parent intervention, administrators informed parents about the program and the school's antibullying policy and procedures. Parents could also benefit from other resources such as letters provided to them and newsletters describing whole‐school antibullying activities undertaken at school.
6.61. Strengths in Motion (SIM)
The SIM (Rawana et al., 2011 ) program was a strength‐based whole school antibullying intervention. There were several components involved in the program, all of which centered around a strength‐based approach. This technique involves highlighting and enhancing individuals' strengths in order to develop positive mental health (Duckworth et al., 2005 ). In the context of the present evaluation, Rawana et al. ( 2011 ) requested that each participating school allocated one room as a designated intervention resource room. In the first instance, this room acted as a “Good Start Centre” (p. 287) where new students to the school were provided with two half‐day orientation sessions prior to starting school. Part of these orientation sessions was individualized strength assessments. It was predicted that by providing new students with guidance on how to best use their strengths to integrate successfully into school life the likelihood of future bullying and victimization would be reduced.
The second use of the intervention room was as a “Cool Down & Prevention,” where students experiencing behavioral or emotional problems could go to calm down. Staff were on hand to prevent the behaviors from escalating and offer helpful advice. The room also acted as an alternative to suspension from school, whereby students could be mandated to spend a certain number of days in the “Good Choices Room.” An ambassador's club for students identified as being at high risk for bullying perpetration or victimization was also held in the resource room. Finally, mental health professionals provided student and parent workshops and staff received tailored training on the strength‐based approach to bullying prevention and intervention.
6.62. Take the LEAD (TTL)
The TTL (Domino, 2011 , 2013 ) program was designed to increase the social competencies of participants in order to reduce bullying behaviors. The intervention is based on SEL and PYD theories.
Various social and emotional skills are targeted during the 16‐weekly lesson curriculum, including: (1) Self‐awareness; (2) Self‐management; (3) Social‐awareness; (4) Relationship skills; (5) Decision making; (6) Problem solving; and (7) Leadership. Trained teachers taught TTL lessons during normal class periods on a weekly basis. Participating teachers were trained on the skill‐based curriculum by the developers of the TTL program. During training, teachers were taught about specific learning objectives and goals of the intervention program, and also about the lesson plans and activities involved in “Take the LEAD.” Information evenings for parent were also held as part of the TTL intervention and aimed to raise parents' awareness of key social‐emotional issues.
Each of the sixteen TTL lessons involved specific learning objectives and goals. Lessons involved a combination of knowledge and skill development and an application component, so that participants were given the opportunity to apply skills in real‐world settings. For example, the “Communication skills” lesson aimed to “explore elements of communication that enhance interpersonal skills and foster positive relationships (Domino, 2013 , p. 432). During this lesson students brainstormed ideas about effective and positive communication techniques and were then required to practice these skills (e.g., eye contact, active listening and showing empathy) in pairs. Finally, participants were required to practice these techniques in an interview with a classmate, and later with a parent.
6.63. *Toronto antibullying program
The Toronto antibullying program was inspired by the OBPP (Pepler et al., 2004 , p. 125). It was based on the understanding that bullying is a problem that extends far beyond the individual children; it involved the peer group and the teachers, as well as the parents of children (Pepler et al., 2004 , p. 127). The program included several preventive elements implemented at the school, parent, and classroom levels, as well as additional work with specific students involved in bullying as perpetrators or victims.
The level of implementation of the program varied across the intervention schools. However, in all intervention schools three critical elements were found: staff training, codes of behavior and improved playground supervision. At the school level an emphasis was placed on developing a positive code of behavior among students, engaging teachers, and promoting positive playground interactions. At the parent level, information nights were held during which parents were informed about the problem of bullying in their school. Also, information about the program and its objectives was sent home. At the classroom level, children were involved in developing classroom rules against bullying. Further classroom activities aimed to change students' attitudes and to promote healthy relationships among peers. At the individual level, children involved in bullying as perpetrators or victims received specialized intervention through consultation and though engaging their parents. Follow‐up monitoring of these cases helped school authorities to establish that bullying incidents were terminated or discontinued.
6.64. *Transtheoretical‐based Tailored antibullying program
This antibullying initiative involved “transtheoretical‐based tailored programs that provided individualized and interactive computer interventions to populations of middle and high school students involved in bullying as bullies, victims and/or passive bystanders” (Evers et al., 2007 , p. 398). The intervention involved only three 30‐min computer sessions during the school year for the students and a 10‐page manual for staff and parents with optional activities. According to the program designers, the transtheoretical model is “a theory of behavior change that applies particular change processes like decision‐making and reinforcement to help individuals progress at particular stages of change” (Evers et al., 2007 , p. 398).
Intervention materials included the “Build Respect, Stop Bullying” program, which is a multicomponent, internet‐based computer system (Evers et al., 2007 , p. 402). Students initiated the program by running a multimedia CD which brought them to the program website. Students could use the program by creating a login name based on personal information and a password. Once the students registered for the program, logged in and consented to be involved in the intervention study, they were given instructions on how to proceed. This multi‐media program also included short movies (videos) of students giving testimonials about bullying (Evers et al., 2007 , p. 403).
Other elements of the program included: (1) a 10‐page family guide, sent to children's homes, which provided brief information about the multi‐media program and its relation to the antibullying initiative; and (2) a 10‐page staff guide, which included general information about bullying and how to support student change, classroom activities and information on how to work with parents. Teachers were not provided with any training.
6.65. Utrecht Healthy Schools
The Utrecht Healthy Schools program was a comprehensive educational program that targeted adolescent health behaviors (Busch et al., 2013 ). The integrated program aims to improve various different health‐related behaviors exhibited by Dutch secondary school students, such as, nutrition, exercise, sexual health, substance and alcohol use, smoking behaviors, bullying, and excessive use of television, gaming and Internet use. The program was implemented as a whole‐school approach and consisted of five key components.
First, participating schools implemented a “healthy school” policy outlining a zero‐tolerance attitude toward risky or violent behaviors, such as alcohol use, smoking or bullying. Second, the program aimed to create a healthy school environment by offering healthy options in the canteen, removing vending machines, ensuring proper sports facilities, hosting alcohol‐free school parties and implementing a smoke‐free school yard. In the third instance, the program aimed to involve parents in intervention activities by providing parent workshops and/or take‐home activities for students. Finally, curriculum materials focused on personal skill development and the program aimed to incorporate public health services into the intervention program.
6.66. *Viennese Social Competence Training program (ViSC)
The ViSC aimed to provide students “with systematic theoretically‐based guidance in becoming responsible and competent actors in conflict situations” (Atria & Spiel, 2007 ; Yanagida et al., 2019 ). It was specifically designed for disadvantaged adolescents aged fifteen to nineteen who were considered at risk for future problems (Atria & Spiel, 2007 , p. 179). The theoretical basis of the programs drew its main ideas from social information processing theory and from research that approached the problem of bullying as a group phenomenon (Gollwitzer et al., 2006 , p. 126).
The ViSC program consisted of thirteen lessons which were divided into three phases: (1) impulses and group dynamics; (2) reflection; and (3) action. The first phase, entitled “impulses and group dynamics,” consisted of six lessons and the main aim was to enhance students' competence in dealing with critical situations by teaching them how to look at social situations from different perspectives using vignette stories, discussions and role‐plays. The second phase, reflection , involved one lesson during which pupils reflected on what had been learned in the first phase of the program.
The last phase, action , consisted of six lessons during which the trainer asked students to define how they wanted to benefit from the remaining lessons. The trainer collected students' individual ideas, evaluated them and—along with the students—put them in practice in alignment with the global goal of the program: enhancing pupils' social competence. The third phase of the program was flexible and it could involve several projects suggested by pupils such as a movie production, a work of art, the organization of a party, and so on. This flexibility was allowed and was, in fact, a main feature of ViSC because organizing such projects “involves a variety of critical situations, in which alternative, nonaggressive response options can be probed, rehearsed, and evaluated for success” (Gollwitzer et al., 2006 , p. 126).
Based on the design of the program, the training of students was conducted by specialist trainers, not their teachers. The trainers participated in instruction workshops and were also supervised during the training by the ViSC developers' team at the University of Vienna (Gollwitzer et al., 2006 , p. 127). According to the principles of the program, it was essential for the trainer to avoid receiving any information about individual students offered by teachers; students' assessments should be based on standardized diagnostic measures (Atria & Spiel, 2007 , p. 184). Moreover, the training was conducted during regular class time and teachers were advised to attend the lessons, so that the program was taken seriously by the students. ViSC has been implemented and evaluated three times: by Gollwitzer (2005), by Atria and Spiel ( 2007 ) and by Gollwitzer et al. ( 2006 ).
6.67. Youth‐led program
The Youth‐led program (YLP; Connolly et al., 2015 ) was a generalized middle school violence prevention program. This program was developed by a community agency, and involved training high school students to lead violence prevention workshops with middle school students in order to increase the latter's knowledge and attitudes of peer aggression and victimization.
Experienced mental health professionals were employed to select and supervise male and female high school students that would become “youth leaders.” These students received training in afterschool sessions on skills and knowledge of peer aggression. Topics covered included bullying perpetration and victimization, but also peer aggression, violence, and harassment.
The final sessions of this training required the youth leaders to create two individualized presentations; one covering bullying and the other discussing general aggression. Mixed gender pairs of youth leaders then conducted these presentations in middle school classrooms under the supervision of a mental health worker. These presentations lasted for approximately 45 min each.
6.68. *Youth Matters
The Youth Matters program used “a curricular and a modified systemic approach to bullying prevention” (Jenson & Dieterich, 2007 , p. 287). The aim of the curriculum was to strengthen peer and school norms against antisocial behaviors by addressing critical issues (issue modules) such as the difference between teasing and bullying, building empathy, risks and norms surrounding aggression and so on. The curriculum also aimed to promote skills (skill modules; structured skills training sessions) that students could use in order to stay safe at school, cope with bullying, enhance their social skills and improve their peer relationships. To address systemic issues associated with bullying, curriculum modules terminated with the development of classroom or school‐wide projects, which placed emphasis on the negative consequences of bullying for students.
The curriculum consisted of 10‐session modules. Each module included a 30–40‐page story, the content of which was directly linked to the structured skills training sessions. When looking at the implementation of the program, all curriculum materials were “language sensitive”: translated into Spanish for use in the three Spanish‐speaking classrooms included in the evaluation. Youth Matters curriculum modules were offered to fourth and fifth graders. According to Jenson and Dieterich ( 2007 , p. 287), grades 4 and 5 were selected “based on an appropriate fit between developmental ability and curricula.”
The Youth Matters program was based on a theoretically grounded curriculum. The curriculum was based on theoretical constructs derived from the Social Development Model. The latter integrated perspectives from three theories (i.e., social control theory, social learning theory and differential association theory) and proposed that four factors inhibit the development of antisocial development in children. These were: (1) bonding or attachment to family, schools and positive peers; (2) belief in the shared values or norms of the above‐mentioned social units; (3) external constraints or consistent standards against antisocial behavior; and (4) social, cognitive and emotional skills that can be seen as protective tools for children to solve problems and perform adequately in social situations. The Youth Matters curriculum addressed each of these four core areas.
6.69. Zero program
The Zero antibullying program is based on the idea that bullying is predominately a version of proactive aggression (Roland et al., 2010 ). The program aims to create a school environment that prevents these forms of proactive aggression. The intervention places the majority of responsibility for bullying prevention and intervention with the adults within the school environment (Roland et al., 2010 ). School staff were required to define clear standards of positive prosocial behavior among the students and to ensure that these standards are met. Thus, the adults within the school context adhere to a “zero tolerance” policy toward bullying. Another key feature of the intervention is that students are instructed to treat all school property appropriately and respectfully and the intervention philosophy is carried into classroom activities and standards also.
During the intervention, class teachers engage their respective classes in active discussions about issues relating to bullying in adherence with the intervention guidelines. The preventative function of the Zero program takes both a direct and indirect approach (Roland & Galloway, 2004 ). Teachers are also expected to be vigilant and visible in school corridors and playgrounds during nonclass time and follow intervention procedures when dealing with specific instances of bullying (Roland et al., 2010 ). When particular instances of bullying are identified, the victim is first approached and takes part in a few sessions with trained staff being comforted and assured. Parental involvement also occurs at this point. Finally, the perpetrators are invited to attend meetings and conflict resolution occurs under a restorative justice model.
6.70. Zippy's Friends
Zippy's Friends is a universal school‐based program for children aged 6–8 years old (Holen et al., 2013 ; Mishara & Ystgaard, 2006 ). The overarching aim of the program is to develop and improve participants' coping strategies in order to reduce and prevent psychological problems. Zippy' Friends has been funded by the global suicide prevention organization “Befrienders International,” and is now distributed internationally by the nonprofit group “Partnership for Children.”
The intervention is delivered over the course of 24 weekly lessons, that are implemented by classroom teachers. The program is based around six stories of the imaginary character “Zippy,” three children, and their families and friends. A structured curriculum outline for each lesson allows participants to engage and discuss the various themes that emerge in each of the stories. Themes that are incorporated include: emotions; communication; friendships; conflict resolution; loss and change.
Teachers are provided with a detailed manual for the program and are required to guide their classrooms through the intervention while also encouraging active engagement with the content. Typical activities that are involved in the Zippy's friends program include: drawing, role‐playing, performing exercises, play and dialogue.
7. RESULTS OF SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
In addition to the newly identified studies ( n = 88), primary evaluations ( n = 53) discovered by Farrington and Ttofi ( 2009 ) are also included in the present systematic review, giving a total of 141 studies. However, this updated systematic review has excluded evaluations that used an “other” experimental‐control design ( n = 13). Next, a detailed explanation is provided about studies which were excluded from the current review and justifications for this decision.
7.1. Studies excluded because of missing information
A certain amount of statistical information is needed in order to produce meaningful effect sizes in a meta‐analysis. We estimated an antibullying program's effectiveness as the difference between the experimental and control groups on bullying outcomes, either measured as the percentage of bullies/nonbullies or victims/nonvictims or based on mean scores on measurement instruments before and after implementation of the intervention.
However, 21 studies identified by our systematic review did not present sufficient effect size information, and so the primary authors of these publications were contacted. We were able to obtain relevant information for the majority of these studies, but three authors were unable to provide required statistics and seven did not respond to our email communication.
Thus, 10 studies had to be excluded from our meta‐analysis because of a lack of information regarding quantitative outcomes. These relate to: Gradinger et al. ( 2015 ); Harpin ( 2011 ); Kyriakides et al. ( 2014 ); Lewis et al. ( 2013 ); Lishak ( 2011 ); Low and Van Ryzin ( 2014 ); van der Ploeg et al. ( 2016 ); Sahin (2012); Schroeder et al. ( 2012 ); and Wurf (2010). In the previous review by Farrington and Ttofi ( 2009 ), 44 out of 53 evaluations provided sufficient information on quantitative outcomes.
7.2. Studies excluded because of nonindependent samples
One further stipulation of a meta‐analysis is that the final samples must be independent of one another (Borenstein et al., 2009 ; Ellis, 2010 ). Overlapping samples are statistically dependent, and thus the variance of the summary effect size produced by the meta‐analysis would be under‐estimated (Wilson, 2010 ). Therefore, before conducting our meta‐analysis we ensured that all samples were independent of one another.
This issue of nonindependent samples was particularly relevant for the multiple evaluations of the KiVa antibullying program. Our thorough systematic searches identified 16 potentially includable studies presenting evaluation data from implementation of the KiVa program (i.e., Ahtola et al., 2012 , 2013 ; Garandeau, Lee, et al., 2014 , Garandeau, Poskiparta, et al., 2014 ; Haataja et al., 2014 ; Hutchings & Clarkson, 2015 ; Kärnä et al., 2011a , 2011b , 2013 ; Nocentini & Menesini, 2015 ; Noland, 2011 ; Sainio et al., 2012 ; Salmivalli et al., 2012 ; Williford et al., 2012 , 2013 ; Yang & Salmivalli, 2015 ). For a description of each of these studies, see Table 7 .
Description of KiVa studies
* Included in meta‐analysis.
However, following further screening, only four of the aforementioned studies were subsequently included in the systematic and meta‐analytic review (i.e., Kärnä et al., 2011a , 2011b , 2013 ; Nocentini & Menesini, 2016). These four studies presented independent results of the KiVa program from the initial nationwide evaluation in Finland. Kärnä et al. ( 2011a ) used an age cohort design with adjacent cohorts and reported the initial results from the nationwide implementation in Finland. Second, Kärnä et al. ( 2011b ) reported the results from the RCT with Finnish students in grades 4–6, and Kärnä et al. ( 2013 ) reported results for students in grades 1–3 and 7–9. In addition, Nocentini and Menesini (2016) reported the results of the implementation and evaluation of KiVa in Italian schools. The remaining 12 publications relating to the KiVa program utilized data from the RCT evaluation in Finland (i.e., Kärnä et al., 2013 or Kärnä et al., 2011b ) but explored different facets of the program's effectiveness.
Four studies identified in our systematic searches replaced evaluations included in the earlier review. For example: (1) Menard and Grotpeter ( 2014 ) was a continuation of the Menard et al. ( 2008 ) evaluation; (2) Cross et al. ( 2011 ) was a republication of the Cross et al. ( 2004 ) evaluation included in the previous review; (3) Jenson et al. ( 2013 ) and Jenson et al. ( 2010 ) presented data from additional follow‐up points to the Jenson et al. ( 2007 ) evaluation; and (4) Frey et al. ( 2009 ) used an age cohort design to evaluate follow‐up effects from the earlier Frey et al. ( 2005 ) study. In cases such as these, the most recent publication, or the publication with the most statistical information, was included in the meta‐analysis.
Ten studies (published both before and since 2009) were identified as reporting the effectiveness of an antibullying program from the same sample, or were repeat publications of earlier studies (e.g., DeRosier, 2004 and DeRosier & Marcus, 2005 ; Domino, 2011 and Domino, 2013 ; Espelage et al., 2013 and Espelage et al., 2015 ; Jenson et al., 2013 and Jenson et al., 2010 ; and Menesini et al., 2012 ; Study 2 and Palladino et al., 2012 ). In these instances, the most recent publications were selected, and as a result, five studies were excluded from the meta‐analysis.
7.3. Included studies
Therefore, 128 studies are included. Table 5 summarizes the intervention programs and methodological components of the 79 newly identified studies that are included in the present systematic review. For details of the remaining 49 studies please refer to Farrington and Ttofi ( 2009 ).
7.4. Moderator analysis
The following moderators were selected a priori for further analysis, under the descriptive label (i.e., location of intervention, publication type, publication year), design label (i.e., evaluation method and unit of allocation/randomization), and the program heading (i.e., name of intervention, COI, and program specificity). Results of these moderator analyses analogous to the analysis of variance (ANOVA) are presented in Sections 8.5.1 to 8.5.7 of the present report.
7.4.1. Evaluation method
The primary moderator chosen for further analysis was evaluation method. Specifically, whether the evaluation was conducted using a RCT, quasi‐experimental with before and after measures (BA/EC) or age cohort (AC) design.
Overall, in relation to bullying perpetration outcomes, 36 evaluations used RCT designs, 31 used BA/EC designs and 14 used age cohort designs. However, due to some evaluations reporting data for multiple independent samples, a total of 40 effect sizes were estimated for bullying perpetration outcomes from RCT designs. A further 36 were estimated from BA/EC designs and 14 effect sizes came from evaluations using age cohort designs.
For bullying victimization outcomes, overall, 33 evaluations used RCT designs that gave 37 independent effect sizes for bullying victimization and 37 evaluations used BA/EC designs and gave 42 independent effect sizes. Similar to perpetration outcomes, 14 evaluations used age cohort designs to evaluate the effect of antibullying programs on bullying victimization outcomes.
7.4.2. Location of intervention
Evaluations included in the present analysis were conducted in many different countries around the world. However, there were only a few countries in which multiple evaluations of antibullying programs had been published.
Specifically, in the following countries only one evaluation was included in the present report: Austria (i.e., Yanagida et al., 2019 ); Brazil (i.e., Silva et al., 2016 ); China (i.e., Ju et al., 2009); Czechoslovakia (modern day Czech Republic and Solvakia; i.e., Rican et al., 1996 ); Hong Kong (i.e., Wong et al., 2011 ); Ireland (O'Moore and Milton, 2004 ); Malaysia (i.e., Yaakub et al., 2010 ); Romania (i.e., Trip et al., 2015 ); Sweden (i.e., Kimber et al., 2008 ); Switzerland (Alsaker & Valkanover, 2001 ); South Africa (Meyer & Lesch, 2000 ); and Zambia (Kaljee et al., 2017 ).
If these evaluations were to be included in further moderator analysis, we would be examining the differences based on only one sample and effect size. Therefore, moderator analysis was conducted only between locations in which multiple evaluations of antibullying programs had been conducted.
So, of the 100 evaluations included in our meta‐analysis of school‐based antibullying programs, the majority (80 for perpetration, 84 for victimization) were conducted in one of 12 different countries. With respect to bullying perpetration outcomes, these countries were as follows: Australia ( n = 2); Canada ( n = 6); Cyprus ( n = 3); Finland ( n = 6); Germany ( n = 5); Greece ( n = 2); Italy ( n = 11); Netherlands ( n = 3); Norway ( n = 8); Spain ( n = 3); UK ( n = 4); and United States ( n = 26). With respect to bullying victimization outcomes, these countries were as follows: Australia ( n = 3); Canada ( n = 7); Cyprus ( n = 3); Finland ( n = 6); Germany ( n = 4); Greece ( n = 2); Italy ( n = 10); the Netherlands ( n = 3); Norway ( n = 7); Spain ( n = 3); UK ( n = 6); and United States ( n = 28).
7.4.3. Publication type and year
Overall, the majority of evaluations were published in peer‐reviewed journal articles, for both bullying perpetration ( n = 67) and bullying victimization ( n = 72) outcomes. Two evaluations were published in chapters of edited books and both reported effects of a program on both bullying victimization and perpetration. No evaluations identified were published as entire books. Moreover, 12 unpublished dissertations were identified that published evaluation data for bullying perpetration and bullying victimization outcomes. Data was also retrieved for both outcomes from three governmental reports. Four of the effect sizes included in the present report were estimated from data emailed to authors (M. M. T. and D. P. F.) in preparation of the previous Campbell report (i.e., Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ).
We also categorized included evaluations according to whether they were included in the previous report (i.e., “2009” studies), or only included in the present report (i.e., “2016” studies). In relation to bullying perpetration outcomes, 37 studies were coded as 2009 studies and 53 studies were coded as 2016 studies. Similarly, more studies were coded as 2016 ( n = 54) studies in comparison to 2009 ( n = 39) studies for bullying victimization outcomes.
7.4.4. Intervention program
We found that very few specific antibullying programs had been implemented and evaluated more than once using independent samples. Sixty‐five different school‐based bullying intervention and prevention programs were included in our meta‐analysis, but only eight were repeatedly evaluated. Moderator analysis with respect to the specific intervention program therefore, focused on programs that had been repeatedly evaluated.
In relation to reducing bullying perpetration outcomes the intervention programs thus included in our moderator analysis were: BPYS ( n = 3; e.g., Menard & Grotpeter, 2014 ); fairplayer.manual ( n = 2; e.g., Bull et al., 2009 ); KiVa ( n = 6; Kärnä et al., 2011b ); NoTrap! ( n = 4; e.g., Menesini et al., 2012 ); Second Step ( n = 3; e.g., Espelage et al., 2015 ); Steps to Respect ( n = 2; e.g., Frey et al., 2005 ); ViSC ( n = 5; e.g., Yanagida et al., 2019 ).
Similarly, these interventions were included in our moderator analysis in relation to bullying victimization outcomes with the exception of the fairplayer.manual program. This intervention was evaluated twice only in relation to bullying perpetration outcomes.
Additionally, multiple evaluations of the OBPP were included in our meta‐analysis. Overall, 12 independent evaluations of this intervention were included in our analysis in relation to bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes. These are included in our moderator analysis as a collective subgroup and also as further subgroups. Evaluations of the OBPP conducted in the United States (perpetration n = 6; victimization n = 7) and those conducted in Norway (perpetration n = 5; victimization n = 5) were included in the moderator analysis separately. There was one evaluation of the OBPP conducted in Malaysia is included in the overall category ( n = 12).
7.4.5. Unit of allocation/randomization
Systematic review findings showed that one consistent issue with included intervention programs was that the unit of allocation of participants, or clusters of participants, was different to the unit of analysis in most evaluations. Age cohort designs were omitted from this moderator analysis as the unit of allocation was largely unclear due to the logistics of this experimental design.
The majority of RCT and BA/EC evaluations assigned schools to experimental conditions (perpetration n = 44; victimization n = 47) yet the unit of analysis was individual students. A number of evaluations (perpetration n = 19; victimization n = 15) assigned classes to experimental conditions yet the unit of analysis was individual students. Less than 10 evaluations (perpetration n = 7; victimization n = 9) included assigned students to experimental and control conditions. One study randomly assigned districts to experimental conditions, and information was not available for five studies in relation to bullying perpetration outcomes and four studies in relation to bullying victimization.
7.4.6. Conflict of interest
In the present report, 40 studies were categorized as high COI. A large number of studies (perpetration n = 36; victimization n = 39) were considered low COI, and 14 were categorized as possible COI. Information concerning COI was unavailable for 4 evaluations in relation to bullying perpetration outcomes.
7.4.7. Program specificity
Overall, a small number ( n = 11) of studies included in our analysis were coded as low on the program specificity variable. The vast majority of evaluations were considered highly specific (i.e., were mostly concerned with only bullying behavioral outcomes; n = 59). Additionally, 18 studies were categorized as medium in relation to specificity, where extra outcome variables were measured but these variables were related to bullying (e.g., school climate).
7.5. Risk of bias analysis
Figure 2 presents the results of the risk of bias analysis for each of the items on the EPOC tool and the additional items we included. The following section describes each of these categories in more detail, with examples of high‐ and low‐risk studies included. The main limitation in assessing risk of bias was the lack of information reported by primary studies. Thus, while the best effort was made to categorize each primary evaluation as being high or low risk, a large number of studies were recorded as “unclear” risk.

Risk of bias analysis results. AC, allocation concealment; AS, allocation sequence; BC, baseline equivalence on participant characteristics; BE, baseline equivalence on outcomes; BOA, blind outcome assessment; COI, conflict of interest; CP, contamination protection; ID, incomplete outcome data; SOR, selected outcome reporting
As seen in Figure 2 , the fewest studies were considered unclear risk on CP and selected outcome reporting. Furthermore, a large number of studies were considered low risk on these items.
For the purpose of analysis, the categories high, unclear, and low risk were transformed into scores of 3, 2, and 0 respectively. A continuous “risk of bias” variable was then estimated as the sum total of scores on each of the EPOC items. As such, the lowest possible score a study could be given was zero and the maximum score was 24.
Descriptive statistical analysis identified that risk of bias scores ranged from 0 to 17, with a mean score of 9.62. Meta‐regression analysis was conducted to assess the relationship between risk of bias and effect sizes. The result of this analysis is included in Section 7 of this report. The following sections provide more detail about each of the risk categories.
7.5.1. Allocation sequence
AS refers to the way in which participants, or clusters of participants, were assigned to experimental conditions. For example, low‐risk studies were those where a random number generator or another randomization software was used. In total, 30 studies were categorized as high risk on the AS item. Moreover, 29 studies were low risk and 32 were unclear risk.
7.5.2. Allocation concealment
AC item refers to whether the method of allocation was concealed from participants or not. In total, 36 studies were categorized as high risk on the AC item. A further 19 studies were considered low risk, and 34 were unclear risk.
7.5.3. Baseline equivalence: Outcome
Baseline equivalence refers to the comparability of experimental and control participants before the intervention has taken place. This item specifically refers to equivalence on relevant outcomes, in this case, school bullying perpetration and victimization. When experimental and control participants are not statistically significant at baseline then we can be more certain that any changes are a result of the intervention. Overall, 14 studies were categorized as high risk on the baseline equivalence on bullying outcomes item. A total of 54 studies were low risk and 21 were unclear risk.
7.5.4. Baseline equivalence: Characteristics
Similarly, baseline equivalence on participant characteristics increases the chance that any change is a result of the intervention, and not a confounding variable such as differential participant characteristics at baseline. Overall, 15 studies were categorized as high risk on the baseline equivalence in participant characteristics item, 64 studies were low risk, and 11 were unclear risk.
7.5.5. Incomplete outcome data
Included evaluations were required to incorporate pre‐ and post‐intervention measures of bullying (except if randomization was used). However, because of this, it is likely that there will be some attrition in primary studies. The incomplete outcome data item referred to the risk associated with differential attrition between experimental groups and/or ways in which attrition and missing cases were dealt with by primary studies. Twelve studies were categorized as high risk on the incomplete outcome data item. Additionally, 48 studies were low risk and 29 were unclear risk.
7.5.6. Blind outcome assessment
This item assesses the risk associated with any bias which may arise if outcome measurements are not conducted blindly. In other words, if the individual, or individuals, who administer and collect the measurement instruments are aware of the experimental conditions of participants at the time of measurement. Overall, 27 studies were categorized as high risk on the BOA item. Twenty studies were low risk and 43 were unclear risk.
7.5.7. Contamination protection
Risk of contamination occurs when there is a possibility that experimental and control participants may interact or encounter one another during the course of the evaluation. Thus, the effects of the intervention may “spill over” to control students and impact the results of the evaluation. In our analysis, 35 studies were categorized as high risk on the CP item, 47 studies were low risk, and 9 were unclear risk.
7.5.8. Selective outcome reporting
SOR occurs when the outcomes reported in an evaluation study differ from the outcomes of interest proposed originally. For example, if a trial protocol proposed different outcomes than those actually reported in the publication of the trial results. Two studies were categorized as high risk on the SOR item. Eighty‐four studies were low risk, and three were unclear risk.
8. META‐ANALYSIS
After accounting for missing information, studies excluded because of their methodology (i.e., “other experimental‐control” designs), and studies with overlapping samples, a total of 41 studies were excluded from the meta‐analysis. Thus, a total of 100 studies were eligible for inclusion in our meta‐analysis. Table 8 outlines the raw data from these studies used to estimate effect sizes. The Comprehensive Meta‐Analysis (CMA) software was used to estimate all summary effect sizes in the present meta‐analysis.
Raw data from included evaluations
Abbreviations: A, after; B, before; C, control; E, experimental; M , mean; N , sample size; n , group sample size.
8.1. Effect sizes
A meta‐analysis aims to estimate comparable effect sizes from multiple primary studies. The choice of effect size depends on how statistical information is reported by primary studies (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). In meta‐analyses such as this one, the data is largely presented in continuous (e.g., means, standard deviations, sample sizes) or dichotomous (e.g., prevalence or percentages) forms (Wilson, 2010 ). Thus, primary effect sizes estimated were Cohen's d and Odds Ratios.
As previously mentioned, we aimed to estimate one effect size for each independent sample included in primary studies. Therefore, where studies reported results separately for male and female participants, or primary and secondary school students, one effect size was calculated for each group.
For primary studies that presented results as percentages or frequencies of participants identifying as either bullies or victims, the odds ratio (OR) effect size was estimated. The ORs for before and after intervention time‐points were calculated independently. The CMA™ software that we used to analyze effect sizes in the present report did not allow us to enter raw data for before and after time‐points for primary studies that reported dichotomous outcomes separately. Thus, we were unable to use this software to calculate a pre‐post intervention estimate for these studies. Hence, these calculations were carried out manually, 5 by the first author, using the method outlined by Farrington and Ttofi ( 2009 ).
Cohen's d was estimated for primary studies when results were reported in the form of continuous data. Cohen's d is estimated as the difference between experimental and control means divided by the pooled standard deviation (Wilson, 2010 , p. 184). Effects were assigned a positive direction in cases where bullying was less in the experimental group compared to the control group or where the reduction in bullying outcomes was larger in the experimental group in comparison to the change in the control group. Following this logic, a negative effect was found when there was: (1) a larger reduction in the control group compared to the experimental group; or (2) there was no change or increase in bullying perpetration/victimization in the experimental group but a reduction or smaller increase in the control group.
For comparability, all effect sizes were converted to ODs. Summary mean effects for bullying perpetration, bullying victimization, and for each of the moderator subgroup are thus reported as odds ratios. In the present review, odds ratios greater than one represent a positive, or desirable, intervention effect. Namely, a reduction of bullying in the experimental group, that is comparably larger than the change in bullying in the control group. Therefore, the change is attributed to have occurred because of the intervention program. Similarly, odds ratios less than one represent a negative, or undesirable, intervention effect and odds ratios that equal one represents a null effect.
8.2. Corrections for clustering
As the present review aims to evaluate the effectiveness of school‐based antibullying programs, cluster‐randomized trials were included. Clustering is a common phenomenon in educational evaluations (Donner & Klar, 2002 ), and occurs when “clusters,” not individuals, are randomly assigned to experimental conditions (Higgins et al., 2011 ). In other words, primary studies sometimes assigned classes or schools to intervention and control conditions, rather than individual students.
Often this approach is utilized in evaluation studies to reduce treatment contamination and increase administrative convenience (Donner et al., 2001 ). However, one of the main issues with incorporating cluster‐randomized trials in a meta‐analysis is that participants within a cluster are likely to be more homogeneous than participants in another cluster (Higgins et al., 2011 ). Thus, the variance of estimates of treatment effectiveness will be under‐estimated (Donner & Klar, 2002 , p. 2974). Clustering could occur for several reasons in studies included in the present report. For example: (1) classes of children, not individual children, were e randomized to intervention or control condition; (2) the intervention was implemented at the classroom level (i.e., to a class or group of children at one time); or (3) the intervention was targeted at teachers, who were trained to implement the intervention in their respective classrooms.
Therefore, effect sizes in the present meta‐analysis were corrected for the inclusion of clusters in primary studies. This is achieved by estimating a design effect:
where M represents the mean cluster size in each study (e.g., the mean number of students per classroom 6 ) and the ICC is the intraclass correlation coefficient.
The ICC is rarely reported by primary studies (Higgins et al., 2011 ; Valdebenito et al., 2018 ). Based on Murray and Blitse ( 2003 ), and subsequently the strategy followed by Farrington and Ttofi ( 2009 ), an ICC of 0.025 was assumed in the current meta‐analysis. The variances of effect sizes were then multiplied by this design effect estimated for each study. In the present meta‐analysis, there were only four studies where corrections for clustering were not required. Three studies (i.e., Berry & Hunt, 2009 ; Knowler & Frederickson, 2013 ; Meyer & Lesch, 2000 ) randomly assigned participants to experimental conditions, and Elledge et al. ( 2010 ) described an intervention that was not implemented in a classroom (i.e., the intervention occurred in one‐on‐one sessions with victims of bullying).
8.3. Computational models
The results of our meta‐analysis are presented using two different models. First, we will report the results as estimated using a random effects model that weights studies, largely in proportion to the between‐study variance and accounting for sampling error, thus allowing for the natural variation that occurs between primary studies (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). We also present the results under the MVA model (Jones, 2005; Farrington & Welsh, 2013 ). which uses the same estimation of a mean effect size as the fixed effects model in that it assigns greater weight to larger evaluations, but also accounts for the between‐study heterogeneity. The MVA model takes account of the heterogeneity of effect sizes to fit the data exactly and yields the same mean effect size as a fixed effect model, but with and increased confidence interval. 7
Farrington and Welsh ( 2013 ) have argued that larger evaluations should be given more weight, and that adding to the variance of effect sizes in order to reduce the heterogeneity is not an optimal method of estimating the weighted mean effect size. When there is considerable heterogeneity in effect sizes, all studies tend to be given much the same weighting in a random effects model. Therefore, several effect sizes from independent samples in one study (e.g., a multisite evaluation) will have a greater weight in the random effects model than in the fixed effects model.
Comparing six models of estimating mean effect sizes for the impact on CCTV on crime rate, Farrington and Welsh ( 2013 ) found that five of the six models produced very similar mean odds ratio effect sizes, with the exception of the random effects model. In this case the random effects model estimated a much higher mean odds ratio (Farrington & Welsh, 2013 , p. 11).
The MVA model is suggested as an alternative approach that overcomes the issues of the random effects model. This technique can be seen as an adjustment to the fixed effects model and combines both the strengths of the fixed effects model (i.e., larger studies = larger weights) and the random effects model (i.e., adjusting for highly probable between‐study variance), and has been used in several meta‐analyses from both the behavioral sciences (e.g., Portnoy & Farrington, 2015 ; Ttofi et al., 2016 ; Zych, Baldry, et al., 2019 ; Zych, Viejo, et al., 2019 ) and medical sciences, where this is known as the “Shore adjustment” (e.g., Ayieko et al., 2014 ; Carlos‐Wallace et al., 2016 ; Erren et al., 2009 ; Steinmaus et al., 2008 ).
A full review of the strengths and limitations of this model is beyond the scope of the current review. Therefore, in our current meta‐analysis we report mean effect sizes for the impact of antibullying programs on bullying perpetration and bullying victimization using both the random effects model and the MVA model. In later sections, we discuss the differences in the weighted mean effect sizes according to the model chosen.
8.4. Moderator analysis
In traditional empirical research when one wishes to compare two mean values to evaluate the difference between two participants, or two groups of participants, a t test is the standard statistical test. In meta‐analysis, we want to compare subgroups of studies rather than sub‐groups of individuals, so the analysis is slightly different. We followed guidelines provided by noted meta‐analysts for this type of analysis (Borenstein et al., 2009 ; Lipsey & Wilson, 2001 ).
Our approach involved two steps: (1) computing the mean effect and variance for each subgroup; and (2) comparing the mean effects between subgroups (Borenstein et al., 2009 , p. 152). This approach has been used previously by researchers to conduct similar analyses (e.g., Kaminski et al., 2008 ; Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ).
Comparing the mean effect sizes for subgroups involves a method that is analogous to a one‐way ANOVA in primary research (Hedges, 1982 ; Lipsey & Wilson, 2001 ; Wilson, 2002). The meta‐analyst creates mutually exclusive categories of primary studies and then compares the between‐studies ( Q B ) and the within‐studies ( Q W ) variance.
The between‐studies heterogeneity is the value used to evaluate whether the difference between subgroups is statistically significant (i.e., whether the difference in weighted mean effect sizes for subgroups is, at least partially, explained by the relevant intervention component). Similar to a one‐way analysis of variance, this approach partitions the variance and compares the variability between‐groups. The following formula is used to estimate the Q B :
The degrees of freedom for the between‐studies heterogeneity is estimated as j − 1 and the statistical significance is determined using a χ 2 distribution. As Q B is estimated using the weights assigned to observed effect sizes, the value will vary between the fixed effects model and the random effects model. Q B is not reported for comparisons of subgroups with very unequal numbers of studies (e.g., location of the evaluation). Under the MVA model, the heterogeneity between groups is estimated by dividing the fixed effects Q B by Q/df . The present report presents results from moderator analysis under both the random effects and MVA models.
8.5. Meta‐regression analysis
CMA™ version 3 software was used to conduct meta‐regression analysis to explore the relationship between continuous moderator variables and perpetration and victimization outcomes. Weighted regression analysis (Lipsey & Wilson, 2001 ) were used to explore which moderators were independently related to school bullying perpetration and victimization. Meta‐regression analyses were only conducted for continuous moderator variables.
Meta‐regression analyses were computed under a fixed effects model, and the standard error of regression coefficients were adjusted using the MVA model. The Q and df of Q for the mean summary effect sizes for subgroups were used to adjust the standard error to reflect between‐study variance.
9. RESULTS OF META‐ANALYSIS
In total, 100 studies were included in our meta‐analysis of the effectiveness of school‐based antibullying programs. From these evaluations, we were able to estimate 103 independent effect sizes. These are presented for bullying perpetration and bullying victimization outcomes in Tables 8 and 9 , respectively. The majority of these effect sizes were estimated from studies that used RCT designs ( n = 45 effect sizes) or BA/EC designs ( n = 44 effect sizes). We estimated the remaining 14 effect sizes from age cohort designs.
Meta‐analysis results: School‐bullying perpetration outcomes
Abbreviations: BA/EC, before‐after/experimental control designs; CI, confidence intervals; MVA, multiplicative variance adjustment; OR, odds ratio; RCT, randomized controlled trial; Sig, statistically significant.
9.1. School‐bullying perpetration outcomes
Overall, we found that antibullying programs significantly reduced bullying perpetration under both computational models of meta‐analysis. The effect sizes for each evaluation are presented in Table 9 . The mean summary effect sizes were similar under both the multivariance adjustment model (MVA: OR = 1.324; 95% CI 1.27–1.38; z = 13.4; p < .001; I 2 = 81.42) and the random effects model (RE: OR = 1.309; 95% CI: 1.24–1.38; z = 9.88; p < 0.001; τ 2 = 0.044).
This result indicates that participants in primary studies who received an antibullying intervention were less likely to report engaging in bullying others after completing the program in comparison to control students who did not partake in the program.
Analysis of the funnel plot (Figure 3 ) suggests that publication bias is not present, as studies are symmetrically distributed around the mean effect size. In addition, point estimates did not vary using Duval and Tweedie's trim and fill procedure under a random effects model (in both cases: OR = 1.308; 95% CI 1.240–1.380). Based on these results, it was reasonable to assume that publication bias was not likely.

Publication bias analysis: school‐bullying perpetration
9.2. School‐bullying victimization outcomes
Overall, we found that antibullying programs significantly reduced bullying victimization under both computational models of meta‐analysis. The effect sizes for each evaluation are presented in Table 10 . The mean summary effect sizes were very similar under both the multivariance adjustment model (MVA: OR = 1.248; 95% CI 1.21–1.29; z = 12.06; p < .001; I 2 = 78.327) and the random effects model (RE: OR = 1.244; 95% CI: 1.19–1.31; z = 8.92; p < 0.001; τ 2 = 0.032).
Meta‐analysis results: School‐bullying victimization outcomes
This result suggests that students who participated in an antibullying program were significantly less likely to report being bullied by others after receiving the intervention in comparison to students who did not receive the intervention.
The funnel plot in Figure 4 indicates that no publication bias is present in analysis of bullying victimization effect sizes, as the studies fall symmetrically around the mean effect size. Duval and Tweedie's trim and fill procedure highlighted some minor differences between observed effect sizes (OR = 1.245; 95% CI 1.186–1.306; Q = 460.97) and adjusted effect sizes (OR = 1.241; 95% CI 1.182–1.303; Q = 473.43). However, this difference is negligible. Based on these results, it was reasonable to assume that publication bias was not likely.

Publication bias analysis: school‐bullying victimization
9.3. Analysis of heterogeneity
In a meta‐analysis, heterogeneity ( Q ) is the between‐study spurious variance that occurs partly because of true variation in effect sizes, but also as a result of random error (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). Heterogeneity is estimated as the excess variation that exists when we compare the total amount of between‐study variance and within‐study random error.
In the present meta‐analysis, there was significant heterogeneity between studies for both bullying perpetration ( Q = 323.392; df = 85; p < 0.001; I 2 = 73.716) and bullying victimization ( Q = 387.255; df = 87; p < 0.001; I 2 = 77.534) outcomes. Multiple moderator analyses were conducted to explore possible explanations for this heterogeneity.
9.4. Risk of bias analysis
Scores on each of the risk of bias items were summed to estimate a total risk of bias score. This continuous variable was then used to examine the relationship between effectiveness and risk of bias in meta‐regression models.
For perpetration outcomes, risk of bias was not associated with effect size under a random effects model of meta‐regression ( b = 0.003; SE = 0.006; z = 0.50; p = .621) or under the MVA model ( b = 0.014; SE = 0.014; z = 1.01; p = .156). Similarly, risk of bias scores did not significantly predict bullying victimization effect sizes under a random effects meta‐regression ( b = 0.007; SE = 0.005; z = 1.30; p = .195) or the MVA model ( b = 0.012; SE = 0.012; z = 1.006; p = .157).
9.5. Moderator analyses 8
9.5.1. evaluation method.
Our meta‐analysis further investigated the effectiveness of antibullying programs in relation to the methodological designs used by evaluation studies. The breakdown of results by methodological design is also shown in Tables 9 and 10 for bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes respectively.
Primary studies employing age cohort designs associated with the largest effect sizes for both bullying perpetration (OR = 1.474; 95% CI, 1.39–1.56; p < .001) and bullying victimization (OR = 1.302; 95% CI, 1.230–1.378; p < .001) under a random effects model. Similarly, AC studies were associated with the largest effect sizes under the MVA model also (perpetration OR = 1.422; 95% CI, 1.36–1.46; p < .001) and victimization OR = 1.289; 95% CI, 1.29–1.35; p < .001).
Under the MVA model of meta‐analysis, mean effect sizes were the same for RCT evaluations (OR = 1.171; 95% CI, 1.08–1.27; p < .001) and BA/EC evaluations (OR = 1.170; 95% CI, 1.05–1.31; p = .005) for bullying perpetration outcomes. Moreover, the differences between RCT evaluations (OR = 1.117; 95% CI, 1.03–1.22; p = .01) and BA/EC evaluations (OR = 1.188; 95% CI, 1.07–1.33; p = .002) were marginal for bullying victimization outcomes under the MVA model.
In relation to bullying victimization outcomes, before‐after/experimental‐control designs gave the second largest mean effect size (OR = 1.225; 95% CI, 1.085–1.383; p = 0.001), followed by RCTs (OR = 1.210; 95% CI, 1.091–1.342; p < .001) under a random effects model. However, the result was the opposite for bullying perpetration outcomes under a random effects model (RCT: OR = 1.244; 95% CI, 1.123–1.379; p < .001; BA/EC: OR = 1.187; 95% CI, 1.044–1.350; p = 0.009).
Due to the marginal differences and lack of clear pattern in which method was associated with the largest effect sizes (between RCT and BA/EC) further moderator analysis was not conducted.
9.5.2. Location of intervention
Mean effects for bullying perpetration and bullying victimization outcomes are presented graphically in Figures 5 and 6 , respectively. Table 11 outlines the mean effects for each of the 12 countries for both bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes under both the MVA model and the random effects model.

Forest plot of effect size by location: school‐bullying perpetration

Forest plot of effect sizes by location: school‐bullying victimization
Moderator analyses results: Location of evaluation
Evaluations conducted in Greece were associated with the largest effect sizes for bullying perpetration outcomes, followed by Norway, Italy, United States, and Finland under the MVA model of meta‐analysis. Evaluations conducted in Italy were associated with the largest mean effect sizes in relation to bullying victimization, followed by Spain, Norway, United States, and Finland under the MVA model of meta‐analysis. Additionally, evaluations conducted in Germany and the UK gave significant mean effects when computed using the MVA model.
Under the random effects model, Greek evaluations were similarly associated with the largest effect sizes for bullying perpetration, followed by Spanish and Norwegian evaluations. Evaluations conducted in Italy and the United States were also associated with significant mean effects for reductions in bullying perpetration. In relation to bullying victimization, evaluations conducted in Spain and Italy were associated with very similar mean effect sizes and were the largest of the 12 effect sizes, followed by evaluations conducted in Norway. Evaluations conducted in Australia were also associated with significant mean effects in reducing bullying victimization ( p < .05) and evaluations conducted in Finland and the United States were nearly statistically significant ( p = .05 and p = .06, respectively) under the random effects model.
Due to the large number of different countries and the unequal number of studies in each location, further subgroup analyses were not conducted.
9.5.3. Publication type and year
Table 12 outlines the mean summary effect sizes for each of the publication type moderators for bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes. Evaluations for which data was received via email correspondence from evaluators gave the largest mean effect sizes for both bullying perpetration and bullying victimization. Differences in the mean effect sizes for evaluations reported via unpublished dissertations, either masters or doctoral theses, gave the smallest mean effect sizes for both bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes. Subgroup analysis was not conducted further using these categorizations due to the imbalance in numbers of evaluations in each category (i.e., evaluations were overwhelmingly published in peer‐reviewed journal article format).
Moderator analyses results: Publication type
However, additional analysis was conducted to examine any potential differences between peer reviewed and nonpeer reviewed evaluations. Therefore, the above categories were collapsed, and evaluations reported by dissertation, chapter, correspondence and governmental reports (perpetration n = 23; victimization n = 21) were compared to evaluations published via peer‐reviewed journal article.
Under the MVA model, non‐peer‐reviewed evaluations gave a larger (OR = 1.493; 95% CI, 1.266–1.761; p < .001) mean effect size than peer‐reviewed evaluations (see Table 11 ). Moreover, moderator analysis indicated that the difference was statistically significant ( Q B = 12.861; df = 1; p < .001). However, under the random effects model, both groups gave similar effect sizes for bullying perpetration outcomes, and the difference between peer‐reviewed (see Table 11 ) and non‐peer‐reviewed (OR = 1.309; 95% CI, 1.137–1.508; p < .001) was not statistically significant ( Q B = 0.595; df = 1; p = .441).
For bullying victimization outcomes, similar results were obtained. Under the MVA model, non‐peer‐reviewed evaluations gave statistically significant larger mean effect sizes (OR = 1.403; 95% CI, 1.262 1.560; p < .001) than peer‐reviewed evaluations (see Table 11 ; Q B = 27.197; df = 1; p < .001). Yet, there was a marginal difference under the random effects model between peer‐reviewed (see Table 11 ) and non‐peer‐reviewed (OR = 1.231; 95% CI, 1.059–1.431; p = .007) and the difference was not statistically significant ( Q B = 0.048; df = 1; p = .827).
The mean summary effect size for “2009” studies on the year of publication moderator was OR = 1.487 (95% CI, 1.430–1.546; p < .001) under the MVA model and OR = 1.411 (95% CI, 1.315–1.513; p < .001) under the random effects model for bullying perpetration outcomes. Across both computational models these summary effects were larger than those for studies labeled “2016” on bullying perpetration for the MVA model (OR = 1.243; 95% CI, 1.667–1.324; p < .001) and the RE model (OR = 1.184; 95% CI, 1.087–1.289; p < .001). Moderator analysis analogous to the ANOVA showed that this difference was statistically significant ( Q B = 76.412; df = 1; p < .001) under fixed effects and mixed effects analysis ( Q B = 9.676; df = 1; p = .002).
In relation to bullying victimization, the mean summary effect size for studies labeled “2009” was larger (OR = 1.322; 95% CI, 1.220–1.432; p < .001) under the MVA model than the mean summary effect size for studies labeled “2016” (OR = 1.229; 95% CI, 1.175–1.285; p < .001). Moderator analysis analogous to the ANOVA found that this difference was statistically significant ( Q B = 10.115; df = 1; p = .001) but the difference between odds ratios was marginal. However, under the random effects model the minimal difference between the “2009” studies (OR = 1.215; 95% CI, 1.094–1.350; p < .001) was not statistically different to the mean summary effect size for “2019” studies (OR = 1.223; 95% CI, 1.139–1.313; p < .001; Q B = 0.010; df = 1; p = .920).
9.5.4. Intervention program
The mean summary effect sizes for 10 different intervention programs in relation to reducing bullying perpetration behaviors and 9 different intervention programs in relation to reducing bullying victimization behaviors. Table 13 outlines the effectiveness of specific antibullying programs in reducing both school‐bullying perpetration and victimization. The effectiveness of these programs varied greatly.
Moderator analyses results: Intervention program
In relation to school‐bullying perpetration outcomes, the OBPP was associated with the largest mean effect sizes. In addition, evaluations of the OBPP in Norway were associated with larger summary effect sizes than evaluations of OBPP conducted in the United States. However, the difference was not statistically significant for school‐bullying perpetration outcomes when moderator analysis analogous to the ANOVA was conducted ( Q b = 3.65; df = 1; p = 0.06).
Other programs were significantly effective in reducing school‐bullying perpetration behaviors, for example KiVa, Second Step, and Steps to Respect. Positive effect sizes (i.e., OR > 1) were also observed for the BPYS and NoTrap! programs but these effects were not statistically significant in relation to reduction in bullying perpetration outcomes. Negative effects were found for two antibullying programs, the fairplayer manual and ViSC, although these effects were not statistically significant.
In relation to school‐bullying victimization outcomes, NoTrap! was associated with the largest mean effect size, followed by the BPYS Program, and then the OBPP. Our analysis identified that other antibullying programs were also significantly effective in reducing school‐bullying victimization, for example, Steps to Respect and KiVa.
Again, effect sizes for the OBPP varied between evaluations conducted in Norway and evaluations conducted in the United States for bullying victimization outcomes. Moreover, our analysis found that the difference in the magnitude of these effect sizes was statistically significant ( Q b = 74.95; df = 1; p < 0.001). Our analysis also identified negative effects of the Second Step program in relation to bullying victimization outcomes. Evaluations of the ViSC program also had a negative effect on bullying victimization, although this effect was not statistically significant.
9.5.5. Unit of allocation/randomization
Table 14 outlines the mean effects for subgroups of studies according to how participants were allocated to experimental or control groups. Results are presented for bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes for all studies that allocated studies in classes, schools, or individual students. The mean effects for RCT and BAEC for each allocation unit are also presented separately.
Moderator analyses results: Unit of allocation/randomization
In relation to bullying perpetration outcomes, under the MVA model, studies that assigned participants in classes were associated with the largest effect sizes. However, the difference between the mean effect for all evaluations that used classes or schools as the unit of allocation were verging on statistically significance ( Q b = 3.705, df = 1, p = .054). Under the random effects model, evaluations that assigned students to experimental conditions were associated with the largest effect size for bullying perpetration outcomes when all designs were included, and for RCT evaluations and BA/EC evaluations individually. However, the mean effect size for many of the subgroups were not collectively statistically significant overall under the random effects model.
Similarly, under the MVA model, evaluations conducted using a RCT design, and assigned classes to conditions, were associated with the largest effect size for bullying perpetration, although the mean group for this subgroup was not statistically significant. Moreover, moderator analysis analogous to the ANOVA found that the difference in the mean effect size for RCT designs that assigned classes to experimental and control conditions were not statistically different to RCT designs that assigned schools to experimental and control conditions ( Q b = 1.140, df = 1, p = .286 ) .
In relation to BAEC designs, evaluations that assigned students to experimental conditions were associated with the largest mean effect size, although the effect was not statistically significant. However, the difference between the mean effect for BAEC evaluations that assigned classes and those that assigned schools to conditions was statistically significant under the MVA model ( Q b = 4.551, df = 1, p = .033).
For bullying victimization outcomes, studies where the unit of allocation was classes of participants were associated with the largest effect sizes, followed by schools and individual students under the MVA model. The difference between studies that allocated classes and studies that allocated schools was statistically significant ( Q b = 12.450, df = 1, p < .001). This pattern was observed when all designs were included, and for the subgroup of RCT evaluations and the subgroup of BA/EC evaluations. Thus, when participants were assigned in classes the mean effect size for these RCT evaluations were significantly associated with larger effect sizes ( Q b = 13.590, df = 1, p < .001) for reductions in bullying victimization than RCT evaluations that assigned schools. Yet the difference between the mean effect sizes for BA/EC evaluations that assigned classes were not statistically significant ( Q b = 3.359, df = 1, p = .067) than BA/EC evaluations that assigned schools to experimental conditions.
9.5.6. Conflict of interest
COI was a categorical moderator variable with three levels: high‐risk (H), low‐risk (L), and possible‐risk (P). Moderator analysis analogous to the ANOVA was conducted so as to assess the differences between evaluations on each level. Studies categorized as possible‐risk on COI variable were excluded from subgroup comparisons to establish the differences between evaluations that were clearly high‐risk and evaluations that were clearly low‐risk. Table 15 outlines the mean summary effects for each group for both bullying perpetration and bullying victimization outcomes.
Moderator analyses results: Conflict of interest
Note : Four studies and six studies were excluded from the present moderator analysis for perpetration and victimization outcome respectively as not enough information was available.
Moderator analyses found that the difference between high‐risk and low‐risk studies on COI variable was statistically significant for bullying perpetration outcomes under both the MVA model ( Q B = 50.129; df = 1; p < .001) and the random effects model ( Q B = 4.900; df = 1; p = .027). This suggests that evaluations considered to have high COI were associated with larger overall effect sizes for bullying perpetration. Similarly, high‐risk COI studies were significantly associated with slightly larger effect sizes for bullying victimization in comparison to low‐risk COI studies when compared under both the MVA model ( Q B = 16.127; df = 1; p < .001) and the random effects model ( Q B = 4.449; df = 1; p = .035).
9.5.7. Program specificity
The majority of evaluations included in our meta‐analysis were of highly specific intervention programs, that is, those that targeted bullying behaviors and no other outcomes. Consistently across computational model and both perpetration and victimization outcomes these subgroups were associated with the largest mean effect sizes. These results are presented in Table 16 . Additionally, highly specific programs were the only subgroup of evaluations that gave a statistically significant mean summary effect under both the MVA model and the random effects model for bullying victimization outcomes. In relation to bullying perpetration outcomes, the subgroup of evaluations that were coded as “medium” on the program specificity moderator were associated with a statistically significant mean effect size under the MVA model ( p < .001) and the random effects model ( p = .036).
Moderator analyses results: Program specificity
10. DISCUSSION
10.1. summary of main findings.
Overall, our updated meta‐analysis found that school‐based antibullying programs are effective in reducing both school‐bullying perpetration and victimization. For school‐bullying perpetration the weighted mean OR = 1.324 under the MVA model, or OR = 1.309 under a random‐effects model (RE) were associated with reductions of approximately 19–20%. 9 In comparison, the weighted mean ORs for bullying victimization outcomes were 1.248 and 1.242 under the MVA model and the random effects model respectively. These mean effect sizes correspond to an approximate reduction in bullying victimization of 15–16%. These results suggest that the included interventions were slightly more effective at reducing school‐bullying perpetration than school‐bullying victimization.
The results of this meta‐analysis are consistent with findings from most of previous reviews that indicate that antibullying programs have a small but significant effect, with some variations in overall results being attributable to methodological differences in inclusion and exclusion criteria (Ttofi et al., 2014 ). Our mean effect sizes are also consistent with the earlier review (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ; Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ), although the differences further outline that moderator variables such as methodological design may be responsible for variability. For example, the weighted mean effect sizes for both bullying perpetration and bullying victimization outcomes estimated in the earlier Campbell report were larger than those estimated in the present report.
Yet, we included publication year as a categorical moderator variable in the present analysis. We found that more recent studies (i.e., those that were not included by Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ) were significantly different to studies that were included in the earlier review. Namely, recent studies were actually associated with significantly larger effect sizes for both bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes (see Section 8.5.3).
Therefore, as we excluded studies considered to have utilized less scientifically rigorous methodological designs this may explain the differences in the weighted mean effect sizes. Specifically, we excluded evaluations conducted using “other experimental‐control designs,” described in the earlier review as evaluations in which participants were assigned to experimental and control conditions but bullying outcomes were only measured after implementation of the intervention. Thus, attributing any change in behaviors to the intervention is potentially risky because there may be other reasons why a positive effect of the intervention was observed. For example, the experimental and control groups were not comparable at baseline, but this remains unknown as no measure of bullying was obtained.
Thus, the inclusion of these less methodologically rigorous evaluations may explain why the weighted mean effects sizes reported in the earlier review were larger than those reported in the current report, but our moderator analysis found a contradictory pattern. The following sections of this report will aim to discuss the findings obtained by our moderator analyses and also the strengths and limitations of the current analysis and potential avenues for future research. The heterogeneity in this meta‐analysis was very large for both bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes. This may suggest that there was a wide range of effects across programs and we may not be able to explain differences using moderator analysis.
10.2. Moderator analyses
10.2.1. evaluation method.
Under both the MVA and random effects models, evaluations conducted using age cohort designs were identified to be, collectively, the most effective, or at least associated with the largest mean effect sizes. This is consistent with Farrington and Ttofi's ( 2009 ) review. This methodological design was first introduced as an evaluation design for the OBPP (Olweus, 1991 ). This approach has been criticized for the potential threats to internal validity, history and testing effects (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 , p. 15). It has been suggested that this design avoids the threats of aging and maturation effects, as individuals within the same school act as a control group for same‐aged experimental participants (Olweus, 2005a ). However, this design is vulnerable to cross‐contamination between experimental and control participants which would impact the overall effectiveness. Notably, intervention researchers have tested the OBPP with other methodological designs (e.g., Bauer et al., 2007 ) which resulted in smaller effects.
Interestingly, the pattern between RCTs and BA/EC designs was less clear. In relation to bullying victimization outcomes, evaluations using BA/EC designs appear to be more effective than evaluations using RCT designs. However, for bullying perpetration outcomes, evaluations using RCT designs appear to be more effective than evaluations that utilized BA/EC designs. Further research is needed to understand these effects. However, the nature of these analyses is correlational and the differences between effect sizes are marginal. Thus, no concrete conclusion can be drawn in relation to the association between randomized and nonrandomized quasi experimental designs and effect size in the present context.
10.2.2. Unit of allocation/randomization
In theory, RCTs are the best method of evaluation of interventions because random allocation ensures that any observed differences between experimental and control groups occurs as a result of experimental manipulation, thus giving the best possible internal validity (Farrington, 1983 , 2003 ). However, the unit of random allocation can have an impact on internal validity. For example, we assume that individuals are randomly assigned to experimental and control conditions, so that RCT designs adequately account for the random variation that occurs in real‐world research (Weisburd, 2003 ).
However, in practice, evaluations of antibullying programs may be more likely to assign groups of individuals, for example in terms of classrooms or schools, to experimental conditions rather than individual students. This is true for both randomized (e.g., classrooms, Chaux et al., 2016 ; or schools, Espelage et al., 2015 ) and nonrandomized (e.g., classrooms, Ortega‐Ruiz et al., 2012 ; or schools, Rawana et al., 2011 ) methodologies. When this is the case, we need larger numbers to ensure adequate statistical conclusion validity and avoid issues of selection effects and differential attrition (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ; Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ). There was a lot of variation in the unit of allocation in our primary studies, which may explain why we did not find that one methodological design was more effective than another.
Moreover, the majority of included evaluations did not use the same unit for allocation and analysis, thus, posing a threat to our results. We approach the results therefore with caution, favouring more conservative estimates. Furthermore, the relationship between the unit of randomization/allocation moderator variable and the effect sizes for bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes was unclear. Whether or not the differences between subgroups of evaluations that assigned classes or schools to experimental conditions were statistically significant or not depended on the computational model used and the bullying outcome in question. For bullying perpetration, the differences between studies based on unit of allocation were not statistically significant for randomized and nonrandomized studies. For bullying victimization outcomes, studies where classes were the unit of allocation were associated with the largest effect sizes when all designs where included and for randomized evaluations, but not for nonrandomized evaluations, separately.
Risk of bias analysis also found that a large number of RCT studies were categorized as being high risk for allocation‐related items on the EPOC tool. Therefore, the differences observed between primary evaluations in our meta‐analysis may be due to the observation that largely the unit of allocation and the unit of analysis were not the same in primary studies. However, further analysis and investigation is needed to better understand these results.
10.2.3. Location of intervention
Overall, the results of our meta‐analysis are consistent with previous findings and show that school‐based antibullying programs have a modest but significant effect in reducing bullying behaviors. However, our meta‐analysis included evaluations of antibullying programs from a wide range of countries and specific intervention programs, far more than previous meta‐analyses (e.g., Cantone et al., 2015 ; Chalamandaris & Piette, 2015 ; Evans et al., 2014 ; Jiménez‐Barbero et al., 2012 , 2016 ). As a result, the results of this meta‐analysis are robust and have implications for bullying research globally.
Our analysis identifies that antibullying programs worldwide are effective in reducing school‐bullying perpetration and victimization by significant amounts. Moreover, evaluations in different countries appear to vary in effectiveness. In Greece, where evaluations included in our meta‐analysis were associated with the largest effect sizes, school‐bullying perpetration behaviors were reduced by approximately 40%. Evaluations conducted in the Norway, Italy and the United States were also effective in reducing bullying perpetration by approximately 21–25%.
Antibullying programs implemented and evaluated in Italy were associated with the largest reduction in school‐bullying victimization in our meta‐analysis, with the odds ratio effect size corresponding to an approximate reduction of 31%. Moreover, evaluations conducted in Spain and Norway reduced school‐bullying victimization by approximately 28% and 23%, respectively. Evaluations conducted in Finland, Germany and the UK were also significantly effective, although less so, reducing school‐bullying victimization by approximately 8–12%.
There are many potential explanations for the differences in effectiveness observed between countries. For example, definitions of school‐bullying, and behaviors that constitute bullying, differ between countries. Previous research conducted by Smith et al. (2000) showed that school‐bullying is perceived differently across different countries and cultures and this may explain variability in bullying reporting. Definitions of school bullying, and behaviors that constitute bullying, differ between countries. For example, Smith et al. ( 2016 ) showed that school bullying in Eastern cultures manifests more often as exclusion or isolation of an individual victim. In comparison, school bullying in Western cultures comprises a wider range of physical, verbal and relational forms of aggression.
Our meta‐analysis included several examples of cases where the same intervention program was evaluated in different countries (e.g., KiVa program in Finland (Kärnä et al., 2013 ) and in Italy (Nocentini & Menesini, 2016)). While societal practices, educational systems, and individual lifestyles may differ greatly, some argue that there may be some support for the cross‐national applicability of specific intervention programs. However, there is a current lack of existing research comparing the effectiveness of specific interventions in specific countries.
Previous research has indicated that are also cultural differences in bullying behaviors among adolescents (e.g., Smith et al., 2016 ). As such, an antibullying program to reduce these behaviors may be impacted by these differences. This is particularly evident when we observe the variations in effect sizes for the OBPP (Olweus, 1993 ) and the KiVa antibullying program. These programs may be the most well‐known antibullying programs that are commercially available, and as such as the only examples in our review of interventions evaluated in completely different locations.
The OBPP program was originally designed and implemented in Norway, and it is therefore not surprising that the OBPP program appears to be effective in reducing both school‐bullying perpetration and victimization when evaluated in Norway, compared to evaluations in the United States (see Table 13 ). While the program was still significantly effective in the United States, the percentage decrease in school‐bullying perpetration was roughly 25% and in school‐bullying victimization was roughly 11%. These figures are lesser in comparison to the decreases in bullying behaviors seen in Norwegian evaluations (35% perpetration; 29% victimization). These differences could be attributed to different evaluation methodologies (see Gaffney et al., 2019), however, they most likely reflect cultural and societal differences between youth in Norway and youth in the United States.
Interestingly, the opposite is observed with the KiVa program. When KiVa was evaluated in Finnish samples, the program was effective in reducing school‐bullying perpetration by approximately 4–5% and school‐bullying victimization by approximately 6% (Kärnä et al., 2011a , 2011b , 2013 ). However, when evaluated in Italian primary and secondary schools, the effect sizes were much larger. Nocentini and Mensini (2016) found that KiVa was effective in reducing school‐bullying perpetration by approximately 15–20% and school‐bullying victimization by approximately 25%.
In the case of KiVa, each of the evaluations used the same methodology (i.e., RCT), but varied greatly in the sample size. Thus, further research is needed to explain why some interventions (e.g., OBPP or KiVa) appear to be more effective in some samples compared to others. The programs are still effective, but the variation in effect size could be attributable to a number of different methodological and implementation factors that warrant further exploration.
10.2.4. Intervention program
Following this logic, we also explored the effectiveness of the specific antibullying programs. Out of the four most widely disseminated antibullying programs included in our review (i.e., KiVA, NoTrap!, OBPP, ViSC), the OBPP was collectively the most effective in reducing school bullying perpetration of these. Across 11 evaluations, the OBPP reduced bullying perpetration by approximately 26%, which was larger than any other widely disseminated program.
In relation to school‐bullying victimization outcomes, the NoTrap! program was the most effective, reducing victimization by around 37%. NoTrap! also reduced bullying perpetration by a considerable amount, approximately 22%, but this effect was not statistically significant. The KiVA program, significantly reduced school bullying perpetration by approximately 9% and school bullying victimization by approximately 11%. The ViSC program was the only program to increase bullying perpetration (by roughly 4%) and bullying victimization (by roughly 4%) although these effects were not statistically significant.
Another moderator we used to code differences between included evaluations was the specificity of the intervention program. In other words, we evaluated each intervention program on how specific it related to bullying behaviors. Unsurprisingly, our findings suggest that antibullying programs gave the largest overall effect sizes. While the significance of the differences between subgroups was not computed due to the large discrepancies between the numbers of evaluations included in each subgroup.
However, our inclusion criteria for the current report was strictly concerned with school‐bullying intervention programs and behavioral outcomes of bullying. As such, we may have overlooked effective programs that only included nonbehavioral outcomes of bullying (e.g., attitudes toward bullying, awareness of bullying) or other problem behaviors (e.g., peer aggression or victimization, mental health issues, juvenile delinquency, etc.) that occur among young people in schools. Changes in these behaviors may also impact bullying, either directly or indirectly, yet, more research is needed to understand this potential effect. Most obvious in the present report is how programs that target specifically school‐bullying may impact cyber‐bullying, and vice versa, given the significant overlap in the prevalence of these behaviors (Baldry et al., 2017 ).
Further research is also needed to better understand specifically “what works” in these “specific interventions.” In the previous review, (Farrington and Ttofi 2009 ; Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ) conducted detailed coding of interventions and evaluations and analyzed how effect sizes varied between components and features of primary studies. For example, parent training, playground supervision, and more intense and longer programs were significantly correlated with larger reductions in bullying perpetration (Ttofi & Farrington, 2011 ). Moreover, several intervention components were associated with larger reductions in bullying victimization (e.g., videos, disciplinary methods, co‐operative group work and more intense and longer programs). Therefore, an important avenue for future research is to assess the differences in effectiveness of antibullying programs according to specific intervention components across the 100 evaluations included in our meta‐analysis. Such research would have important implications for policy and the development of future antibullying programs.
Additionally, it appears that since 2009 several large‐scale antibullying programs have been implemented and evaluated (e.g., KiVa; Kärnä et al., 2013 ; NoTrap!; Menesini et al., 2012 ; Palladino et al., 2016 ). Because there is typically more information available on the specific components of these programs, we may be able to code more specific details in future analyses. For example, many studies may fit the criteria for “parent training,” but there is a significant difference between the intensity of parental involvement. For example, some studies may include parents merely by sending letters home with participant children (e.g., Brown et al., 2011 ), while others include parents more actively by holding information evenings or requiring children to complete take‐home tasks with parental involvement (e.g., Berry & Hunt, 2009 ; Domino, 2013 ).
Earlier research highlighted how varying levels of implementation of each intervention component may explain variability in intervention outcomes (Bloom et al., 2003 ). Interestingly, a narrative review by Smith et al. ( 2003 ) reported that although 14 whole‐school antibullying programs obtained modest effects overall, those that monitored implementation obtained twice the mean effects on self‐reported rates of bullying and victimization than those that did not monitor implementation. Thus, additional analyses are required to better understand specifically what works in existing antibullying programs and the underlying mechanisms of behavioral change
10.2.5. COI and publication type
Possibly the most conclusive results from our moderator analyses were observed in relation to COI and publication type. First, across both computational models and outcomes, studies that were categorized as being high‐risk for COI were associated with significantly larger reductions in bullying perpetration and victimization. Second, under the MVA model of meta‐analysis, non‐peer‐reviewed evaluations were associated with significantly larger reductions in both bullying perpetration and victimization outcomes. However, the same results were not observed under the random effects.
We examined COI in terms of the involvement of the program developer in the evaluation. Our results may indicate possible sources of biases. For example, it may be that when the individual, or team, that are credited with developing an antibullying program are also involved in the evaluation of said intervention, biases such as confirmation bias may impact the results. However, it may not be a perceivably “negative” source of bias. Perhaps, when the program developer is involved in the implementation of the program, the intervention is simply delivered better and more effectively. There are a number of other factors that could also be affected and in turn impact the effect size, such as teacher and staff efficacy and motivation to participate the in the program.
There are more sophisticated measures of COI (e.g., Eisner et al., 2012 ) that include elements such as whether or not the evaluator could potentially benefit financially from the intervention program. Further indicators of COI are thus needed to better understand the impact on evaluation results. For example, our findings in relation to COI and larger effect sizes may be explained as: evaluations in which the program developer was included appear to be more effective because of the expertise and intricate knowledge of the developer. Therefore, the results may reflect differences in the quality of program implementation rather than troublesome biases. Additional research is needed.
10.3. Limitations and avenues for future research
Like most meta‐analyses, the current report is largely limited by the lack of understanding as to what is the “true effect.” When comparing mean effect sizes between moderators for example, it is difficult to determine the validity of the result. Throughout our discussion of result we discuss that one subgroup of studies was associated with larger or smaller effect sizes than another, and the statistical significance of these differences. Thus, we avoid saying studies in subgroup A (e.g., evaluations conducted in Greece) are more effective than studies in subgroup B (e.g., evaluations conducted in Italy). Due to the correlational nature of our moderator analyses we cannot make causal inferences. In addition to this limitation, and those previously discussed (Section 9.2 ), the following section of this report discusses some further limitations.
10.3.1. Measurement of bullying
Experts in the area of school‐bullying research have outlined how there still remain issues of comparability in the assessment of school‐bullying perpetration and victimization (Volk et al., 2017 ). Studies included in the present meta‐analysis used a wide variety of quantitative measures of school‐bullying behaviors, including self‐report measures (e.g., the Revised Olweus Bully/Victim Questionnaire—Olweus, 1986 , 1996 ), or peer‐report measures (e.g., the Participant Role Questionnaire—Salmivalli et al., 1996 ). One issue that arises is that the timeframe within which participants are required to indicate the frequency of bullying can vary greatly. One scale may ask about bullying experiences within the last 3 months, while another may ask about ever having experienced, or participated in, school‐bullying. Moreover, included studies utilized a mixture of continuous or dichotomous measures of school‐bullying, and the cut‐off points used to categorize someone as either a bully, victim, or not‐involved also varied.
Furthermore, the majority of evaluations included in our analysis reported bullying outcomes at different time points, largely, before implementation, after implementation, with a possible additional follow‐up time point. However, we computed effect sizes using measures of bullying taken before implementation and immediately post implementation of the intervention. Therefore, we cannot generalize results to the long‐term effectiveness of antibullying programs, or any potential influence of dose‐response effect. Future research should aim to examine the longitudinal effectiveness of interventions to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization in the long‐term.
When conducting our systematic searches for the present review, we did not set restrictions based on measurement issues, other than including quantitative measures of school‐bullying behaviors. However, types of reports, for example, could influence the overall effectiveness effect size. This may possibly explain why our meta‐analysis found that programs are more effective in reducing bullying perpetration outcomes. For example, if programs are concerned with raising awareness about bullying and the associated negative impact on victims, participants who reported bullying perpetration before the intervention may be less likely to self‐report bullying behaviors after completing the program. As a result, the intervention may be perceived as being effective, but the change in reports of bullying may have been a result of social desirability responding (He et al., 2015 ; Rigby & Johnson, 2006 ). Conversely, raising awareness on the negative impact of school bullying may lead to increased reporting of victimization due to sensitization effects (Stevens et al., 2000 ). Notably, sensitization effects due to raised awareness may affect not only self‐report data but also peer nomination data and teacher reports (Smith et al., 2003 , p. 597). Therefore, future research could aim to examine whether the style of report used, differing cut‐off points and varying timeframes affect estimations of intervention effectiveness.
10.3.2. Cyberbullying behaviors
Another key limitation of the present review is the omission of cyberbullying behaviors. Prominent researchers in the area have argued that cyberbullying behaviors do not warrant a completely separate line of study, because of the significant overlap between offline and online bullying (Olweus & Limber, 2017 ). A recent meta‐analysis of cyberbullying intervention and prevention programs found that, out of studies assessing various facets of cyberbullying, a large number were concerned with this overlap (Gaffney et al., 2019). The Gaffney et al. (2019) meta‐analysis concluded that anticyberbullying programs were effective in reducing cyberbullying perpetration by roughly 9–15% and cyberbullying victimization by roughly 14–15%. As illustrated in that other review, there is a need for future research to assess the effectiveness of intervention programs that target both online and offline bullying concurrently. As a result of the significant overlap (e.g., Waasdorp & Bradshaw, 2015), it is important for policy makers, researchers, and program developers to know whether or not these forms of aggressive behaviors should be targeted together or individually. Future research should aim to examine the effectiveness of programs designed to reduce school‐bullying on cyberbullying outcomes, and vice versa. Additional analysis to examine the differences between programs that target offline and online behaviors concurrently in terms of effectiveness to reduce both school‐ and cyber‐bullying is also needed.
10.3.3. Models of meta‐analyses
The current report presents findings using two computational models of meta‐analyses: the random effects model and the multiplicative variance adjustment model. While, the random effects model is often suggested as the preferred model for meta‐analyses in social sciences, for reasons already discussed (Section 7.3 ), this approach is also limited. However, even though many meta‐analyses in medical sciences (e.g., Ayieko et al., 2014 ; Dorjee et al., 2018 ; Woolf‐King et al., 2013 ) have used the MVA model as an alternative method of accounting for between‐study heterogeneity in weighted mean effect sizes, this model is yet to be widely accepted in behavioral sciences. A number of recent publications (e.g., Portnoy & Farrington, 2015 ; Zych et al., 2019 ) have begun to use the MVA model.
It is evident in the current report that the results are influenced by the computational model used. The overall mean effect sizes for bullying perpetration and victimization were not that different under both models but the results of moderator analyses were greatly influenced by how we accounted for the between‐study heterogeneity. Further research is needed in order to examine the reasons for this and also evaluate how best to choose an appropriate computational model when conducting a meta‐analysis.
10.4. Concluding remarks
This report presents an updated systematic and meta‐analytical review of the effectiveness of school‐bullying intervention and prevention programs. Overall, our review found that school‐based antibullying programs are effective in reducing both bullying perpetration and bullying victimization, and that effect sizes can vary according to several moderator variables. However, further research is needed to better understand the reasons for variation in observed effect sizes. Research is needed to investigate the specific components of antibullying programs that work best to reduce bullying behaviors. The results of our meta‐analysis have important implications for policy and the development of future antibullying programs, but future research should aim to better understand the effective mechanisms in bullying intervention and prevention.
11. TECHNICAL APPENDICES
11.1. calculating the before‐after intervention effect.
Williams et al. ( 2015 ) evaluated the effectiveness of the Start Strong program based on students' self‐reported experiences of bullying victimization. The primary study found that, at baseline, 23% of participants in the experimental group ( N = 717) reported bullying victimization, while 23% of participants in the control group ( N = 800) also reported bullying victimization at baseline. Hence, the baseline OR was calculated as follows (Table 17 ):
Data used to estimate baseline odds ratio
Thus, the OR before = 0.999, Ln OR before = −0.002, and var Ln OR before = 0.015. Williams et al. ( 2015 ) report that after implementation of the Start Strong program, bullying victimization was reported by 28% of experimental participants and 34% of control participants. Accordingly, the posttest OR was calculated as follows (Table 18 ):
Data used to estimate postintervention odds ratio
Thus, the OR after = 1.323; Ln OR after = 0.28; and var Ln OR after = 0.013. Employing these figures, the ln OR for the intervention effect of the Start Strong program was calculated as:
The ln OR change is computed as the difference between the before and after effect size and the variance of this new estimate is adjusted by multiplying the sum of the variances of before and after variances by 0.75. This is an approximation of the assumed correlation between before and after effect sizes. The ln OR change and the SE of ln OR change were then entered into CMA as an estimation of the intervention effect.
11.2. Multiplicative variance adjustment
In the present meta‐analysis, the summary effect size estimated for bullying perpetration was OR = 1.324 with 95% confidence intervals of 1.298–1.351 under a fixed effects model. The effect size in the MVA model is the same as the effect size in the fixed effects model. The variance of the effect size in the MVA model is calculated as follows:
Therefore, in the above example of the summary effect size for bullying perpetration outcomes, the FE var is 0.000104. Therefore, with Q = 458.555 and df = 109, the MVA adjustment for fixed effects is 0.02098, calculated as:
Therefore, the adjusted standard error is 0.0209. In this example thus, the MVA fixed effect is OR = 1.324, and the 95% confidence intervals are 1.271–1.380.
11.3. Odds ratio to percentage conversion
The conversion from weighted mean odds ratio to percentage value is also described in the previous Campbell report (see Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ). The formula involves assuming equal allocation of participants to experimental and control conditions and that the % of bullies and/or victims was lesser in the experimental condition than in the control condition (as supported by our overall positive mean effect size).
For example, if there are 200 participants in each experimental condition and approximately 30% of participants report bullying victimization in the control condition and 25% victims in the experimental condition, the numbers of victims and nonvictims would be as follows: (Table 19 ).
Data used to convert odds ratio to percentage
Therefore using the previously described formula for estimating an odds ratio, the following data would correspond to an odds ratio of 1.286 (i.e., [150 × 60]/[140 × 50]). Moreover, the percentage decrease would be approximately 16.67% (i.e., (10/60) × 100).
Using this basic formula, we can manipulate the % and number of victims in each experimental condition in order to achieve a odds ratio that corresponds to our weighted mean effect size (i.e., MVA: OR = 1.324 and RE: OR = 1.309 for bullying perpetration; MVA: OR = 1.248 and RE: OR = 1.242 for bullying victimization). Using the n values that give the closest possible mean effect size we can thus estimate the corresponding percentage reduction in either bullying perpetration or victimization outcomes.
APPENDIX A.
Appendix: full search syntax, database: web of science.
Bully* AND Intervention AND Evaluation
Anti‐Bullying AND School AND Program* AND Evaluation
Anti‐Bully* AND Program* AND Outcome
Bully‐victim AND Prevention AND Evaluation
Bully* AND School AND Intervention
Bully* AND School AND Prevention
Database: Scopus
Bully* AND School AND Program*
Bully* AND School AND Evaluation
Bully* AND School AND Intervention AND Evaluation
Bully* AND School AND Prevention AND Evaluation
Anti‐bullying AND Program* AND Evaluation
Database: National Criminal Justice Reference Service
Bully* AND Prevention AND Evaluation
Anti‐bullying AND Program* AND Effect*
Database: PsycINFO
Bully* AND Intervention AND Program* AND Evaluation
Bully* AND Prevention AND Program* AND Effect*
Database: Cochrane Controlled Trials Register
Bully* AND Intervention AND Program*
Bully* AND Prevention AND Program AND Evaluation
Database: British Education Index
Bully* AND Prevention AND Program* AND Evaluation
Bully* AND Intervention AND Program* AND Effect*
Database: Embase
Database: medline, database: eric & criminal justice abstracts.
www.scholar.google.co.uk
APPENDIX B.
Appendix: risk of bias results for included studies.
Note : H, hig risk, score 3; L, low risk, score 0; U, unclear risk, score 2. Risk of bias score is estimated as sum of scores on individual risk of bias items.
Abbreviations: AC, Allocation concealment; AS, Allocation sequence; BC, Baseline Equivalence on Characteristics; BE, Baseline Equivalence of Outcome; BOA, Blind Outcome Assessment; CP, Contamination Protection; ID, Incomplete Data; SOR, Selected Outcome Reporting.
Gaffney, H., Ttofi, M. M., & Farrington, D. P. (2021). Effectiveness of school‐based programs to reduce bullying perpetration and victimization: An updated systematic review and meta‐analysis . Campbell Systematic Reviews , 17 , e1143. 10.1002/cl2.1143 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Systematic review
Plain language summary on the Campbell website
1 The authors regret that more detailed information concerning specific combinations of keywords and databases searched as per the Campbell MECCIR reporting standards. This information is held on restricted access computers and due to COVID‐19 pandemic, the closure of University buildings, this data could not be retrieved.
2 Web of Science Core Collection database.
3 Unfortunately detailed information about the datas of searches cannot be provided for this review, contrary to MECCIR R35.
4 We were unable to double code in this review. However, as some studies were included in the present review and an earlier review (Farrington & Ttofi, 2009 ), a proportion of the studies were double‐coded.
5 A worked example is provided in Technical Appendix 10.1.
6 Calculated as: total number of students/number of classrooms.
7 A worked example of this adjustment is provided in Technical Appendix 10.2.
8 Moderator analyses under the MVA model will be greatly affected by the presence of very large studies in the meta‐analysis. Unfortunately, we were not able to follow recommendations made by the methods editor to windsorize weights or conduct sensitivity analyses by removing these large studies. Due to the COVID‐19 pandemic the software to carry out these tests was not available to us. Thus, the reader should consider the impact of large studies when interepting the results of moderator analyses under the MVA model.
9 The procedure used to estimate approximate percentage values for weighted mean odds ratios is provided in Technical Appendix 10.3.
REFERENCES TO INCLUDED STUDIES
- Alsaker, F. D. (2004). Bernese program against victimization to kindergarten and elementary schools. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 289–306). Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alsaker, F. D., & Valkanover, S. (2001). Early diagnosis and prevention of victimization in kindergarten. In Juvonen J. & Graham S. (Eds.), Peer harassment in school (pp. 175–195). Guilford. [ Google Scholar ]
- Andreou, E., Didaskalou, E., & Vlachou, A. (2007). Evaluating the effectiveness of a curriculum‐based anti‐bullying intervention program in Greek primary schools . Educational Psychology , 27 , 693–711. [ Google Scholar ]
- Avşar, F., & Alkaya, S. A. (2017). The effectiveness of assertiveness training for school‐aged children on bullying and assertiveness level . Journal of Pediatric Nursing , 36 , 186–190. 10.1016/j.pedn.2017.06.020 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baldry, A. C., & Farrington, D. P. (2004). Evaluation of an intervention program for the reduction of bullying and victimization in schools . Aggressive Behavior , 30 , 1–15. 10.1002/ab.20000 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Battey, G.J.L. (2009). Can bullies become buddies? Evaluation of and theoretical support for an experiential education bully prevention curriculum with seventh grade students (Doctoral dissertation). Available from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses (UMI No. 3348633).
- Bauer, N. S., Lozano, P., & Rivara, F. P. (2007). The effectiveness of the Olweus bullying prevention program in public middle schools: A controlled trial . Journal of Adolescent Health , 40 , 266–274. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beran, T., & Shapiro, B. (2005). Evaluation of an anti‐bullying program: Student reports of knowledge and confidence to manage bullying . Canadian Journal of Education , 28 ( 4 ), 700–717. [ Google Scholar ]
- Beran, T., Tutty, L., & Steinrath, G. (2004). An evaluation of a bullying prevention program for elementary schools . Canadian Journal of School Psychology , 19 ( 1/2 ), 99–116. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berry, K., & Hunt, C. J. (2009). Evaluation of an intervention program for anxious adolescent boys who are bullied at school . Journal of Adolescent Health , 45 , 376–382. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.04.023 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bonell, C., Fletcher, A., Fitzgerald‐Yau, N., Hale, D., Allen, E., Elbourne, D., Jones, R., Bond, L., Wiggins, M., Miners, A., Legood, R., Scott, S., Christie, D., & Viner, R. (2015). Initiating change locally in bullying and aggression through the school environment (INCLUSIVE): A pilot randomised controlled trial . Health Technology Assessment , 19 ( 53 ), 1–110. 10.3310/hta19530 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boulton, M. J., & Flemington, I. (1996). The effects of a short video intervention on secondary school pupils' involvement in definitions of and attitudes towards bullying . School Psychology International , 17 , 331–345. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown, E. C., Low, S., Smith, B. H., & Haggerty, K. P. (2011). Outcomes from a school‐randomized controlled trial of Steps to Respect: A bullying prevention program . School Psychology Review , 40 ( 3 ), 423–443. 10.1037/e734362011-045 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bull, H. D., Schultze, M., & Scheithauer, H. (2009). School‐based prevention of bullying and relational aggression: The fairplayer.manual . European Journal of Developmental Science , 3 ( 3 ), 312–317. [ Google Scholar ]
- Busch, V., De Leeuw, R. J. J., & Schrijvers, A. J. P. (2013). Results of a multibehavioral health‐promoting school pilot intervention in a Dutch secondary school . Journal of Adolescent Health , 52 ( 4 ), 400–406. 10.1016/j.adohealth.2012.07.008 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chaux, E., Velásquez, A. M., Schultze‐Krumbholz, A., & Scheithauer, H. (2016). Effects of the cyberbullying prevention program Media Heroes ( Medienhelden ) on traditional bullying . Aggressive Behavior , 42 ( 2 ), 157–165. 10.1002/ab.21637 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cissner, A. B., & Ayoub, L. H. (2014). Building healthy teen relationships: An evaluation of the Fourth R curriculum with middle school students in the Bronx . U.S.A: Center for Court Innovation. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ciucci, E., & Smorti, A. (1998). Il fenomeno delle pretonenze nella scuola: Problemi e prospettive di intervention [The phenomenon of bullying in school: Problems and prospects for intervention] . Psichiatria dell'infanzia e dell'adolescenza , 65 , 147–157. [ Google Scholar ]
- Connolly, J., Josephson, W., Schnoll, J., Simkins‐Strong, E., Pepler, D., MacPherson, A., Weiser, J., Moran, M., & Jiang, D. (2015). Evaluation of a youth‐led program for preventing bullying, sexual harassment, and dating aggression in middle schools . Journal of Early Adolescence , 35 ( 3 ), 403–434. 10.1177/0272431614535090 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cross, D., Hall, M., Hamilton, G., Pintabona, Y., & Erceg, E. (2004). Australia: The friendly schools project. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 187–210). Cambridge University Press. 10.1017/CB09780511584466.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cross, D., Monks, H., Hall, M., Shaw, T., Pintabona, Y., Erceg, E., Hamilton, G., Roberts, C., Waters, S., & Lester, L. (2011). Three‐year results of the Friendly School whole‐of‐school intervention on children's bullying behaviour . British Educational Research Journal , 37 ( 1 ), 105–129. 10.1080/01411920903420024 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DeRosier, M. E. (2004). Building relationships and combating bullying: Effectiveness of a school‐based social skills group intervention . Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology , 33 ( 1 ), 196–201. 10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_18 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DeRosier, M. E., & Marcus, S. R. (2005). Building friendships and combating bullying: Effectiveness of S.S. GRIN at one‐year follow‐up . Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology , 34 ( 1 ), 140–150. 10.1207/s15374424jccp3401_13 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Domino, M. (2011). The impact of Take the LEAD on school bullying among middle school youth (Doctoral Dissertation). Available from ProQuest Dissertation and Theses database (UMI No. 3434870).
- Domino, M. (2013). Measuring the impact of an alternative approach to school bullying . Journal of School Health , 83 ( 6 ), 430–437. 10.1111/josh.12047 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elledge, L. C., Cavell, T. A., Ogle, N. T., & Newgent, R. A. (2010). School‐based mentoring as selective prevention for bullied children: A preliminary test . Journal of Primary Prevention , 31 , 171–187. 10.1007/s10935-010-0215-7 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ertesvag, S. K., & Vaaland, G. S. (2007). Prevention and reduction of behavioural problems in school: An evaluation of the Respect program . Educational Psychology , 27 , 713–736. [ Google Scholar ]
- Espelage, D. L., Low, S., Polanin, J. R., & Brown, E. C. (2013). The impact of a middle school program to reduce aggression, victimization, and sexual violence . Journal of Adolescent Health , 53 ( 2 ), 180–186. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.02.021 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Espelage, D. L., Low, S., Polanin, J. R., & Brown, E. C. (2015). Clinical trial of Second Step© middle‐school program: Impact on aggression & victimization . Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology , 37 , 52–63. 10.1016/j.appdev.2014.11.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Evers, K. E., Poskiparta, J. O., van Marter, D. F., Johnson, J. L., & Prochaska, J. M. (2007). Transtheoretical‐based bullying prevention effectiveness trials in middle schools and high schools . Educational Research , 49 , 397–414. [ Google Scholar ]
- Farmer, V. L., Williams, S. M., Mann, J. I., Schofield, G., McPhee, J. C., & Taylor, R. W. (2017). Change of school playground environment on bullying: A randomized controlled trial . Pediatrics , 139 ( 5 ), e20163072. 10.1542/peds.2016-3072 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fekkes, M., Pijpers, F. I. M., & Verloove‐Vanhorick, P. (2006). Effects of antibullying school program on bullying and health complaints . Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine , 160 ( 6 ), 638–644. 10.1001/archpedi.160.6.638 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fekkes, M., van de Sande, M. C. E., Gravesteijn, J. C., Pannebakker, F. D., Buijs, G. J., Diekstra, R. F. W., & Kocken, P. L. (2016). Effects of the Dutch Skills for Life program on the health behaviour, bullying, and suicidal ideation of secondary school students . Health Education , 116 ( 1 ), 2–15. 10.1108/HE-05-2014-0068 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Finn, K.O'K. (2009). An evaluation of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program . Retrieved from ProQuest Dissertations Publishing (3343406).
- Fonagy, P., Twemlow, S. W., Vernberg, E. M., Nelson, J. M., Dill, E. J., Little, T. D., & Sargent, J. A. (2009). A cluster randomized controlled trial of child‐focused psychiatric consultation and a school systems‐focused intervention to reduce aggression . The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 50 ( 5 ), 607–616. 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.02025.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fox, C., & Boulton, M. (2003). Evaluating the effectiveness of a social skills training (SST) program for victims of bullying . Educational Research , 45 , 231–247. [ Google Scholar ]
- Frey, K., Hirschstein, M. K., Snell, J. L., van Schoiack Edstrom, L., MacKenzie, E. P., & Broderick, C. J. (2005). Reducing playground bullying and supporting beliefs: An experimental trial of the Steps to Respect program . Developmental Psychology , 41 , 479–491. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garaigordobil, M., & Martínez‐Valderrey, V. (2015). Effects of Cyberprogram 2.0 on “face‐to‐face” bullying, cyberbullying and empathy . Psciothema , 27 ( 1 ), 45–51. 10.7334/psciotherma2014.78 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gini, G., Belli, B., & Casagrande, M. (2003). Le prepotenze a scuola: Una esperienza di ricerca‐intervento antibullisimo [Bullying at school: An experience of research‐intervention against bullying] . Eta Evolutiva , 76 , 33–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gollwitzer, M., Eisenbach, K., Atria, M., Strohmeier, D., & Banse, R. (2006). Evaluation of aggression‐reducing effects of the “Viennese Social Competence Training” . Swiss Journal of Psychology , 65 , 125–135. [ Google Scholar ]
- Herrick, C. (2012). An investigation into the effectiveness of an anti‐bullying campaign (Doctoral Dissertation). University of Nottingham, UK.
- Holen, S., Waaktaar, T., Lervåg, A., & Ystgaard, M. (2013). Implementing a universal stress management program for young school children: Are there classroom climate or academic effects? Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research , 57 ( 4 ), 420–444. 10.1080/00313831.2012.656320 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hunt, C. (2007). The effect of an education program on attitudes and beliefs about bullying and bullying behaviour in junior secondary school students . Child and Adolescent Mental Health , 12 ( 1 ), 21–26. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jenson, J. M., Brisson, D., Bender, K. A., & Williford, A. P. (2013). Effects of the Youth Matters prevention program on patterns of bullying and victimization in elementary and middle school . Social Work Research , 37 ( 4 ), 361–372. 10.1093/swr/svt030 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jenson, J. M., & Dieterich, W. A. (2007). Effects of a skill‐based prevention program on bullying and bully victimization among elementary school children . Prevention Science , 8 , 285–296. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jenson, J. M., Dieterich, W. A., Brisson, D., Bender, K. A., & Powell, A. (2010). Preventing childhood bullying: Findings and lessons from the Denver Public Schools trial . Research on Social Work Practice , 20 ( 5 ), 509–517. 10.1177/1049731509359186 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joronen, K., Konu, A., Rankin, H. S., & Astedt‐Kurki, P. (2011). An evaluation of a drama program to enhance social relationships and anti‐bullying at elementary school: A controlled study . Health Promotion International , 27 ( 1 ), 5–14. 10.1093/heapro/dar012 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ju, Y., Shuqiong, W., & Wenxin, Z. (2009). Intervention research on school bullying in primary schools . Frontiers of Education in China , 4 , 111–122. 10.1007/s11516-009-0007-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaljee, L., Zhang, L., Langhaug, L., Munjile, K., Tembo, S., Menon, A., Stanton, B., Li, X., & Malungo, J. (2017). A randomized‐controlled trial for the teachers' diploma programme on psychosocial care, support and protection in Zambian government primary schools . Psychology, Health, and Medicine , 22 ( 4 ), 381–392. 10.1080/13548503.2016.1153682 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Alanen, E., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2013). Effectiveness of the KiVa Antibullying Program: Grades 1–3 and 7–9 . Journal of Educational Psychology , 105 ( 2 ), 535–551. 10.1037/a0030417 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Poskiparta, E., Alanen, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2011a). Going to scale: A nonrandomized nationwide trial of the KiVa antibullying Program for Grades 1–9 . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 79 ( 6 ), 796–805. 10.1037/a0025740 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Poskiparta, E., Kaljonen, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2011b). A large‐scale evaluation of the KiVa antibullying program: Grades 4–6 . Child Development , 82 ( 1 ), 311–330. 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01.557.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kimber, B., Sandell, R., & Bremberg, S. (2008). Social and emotional training in Swedish classrooms for the promotion of mental health: Results from an effectiveness study in Sweden . Health Promotion International , 23 ( 2 ), 134–143. 10.1093/heapro/dam046 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Knowler, C., & Frederickson, N. (2013). Effects of an emotional literacy intervention for students identified with bullying behaviour . Educational Psychology , 33 ( 7 ), 862–883. 10.1080/01443410.2013.785052 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krueger, L. M. (2010). The implementation of an anti‐bullying program to reduce bullying behaviours on elementary school buses (Doctoral dissertation). D'Youville College, Buffalo, NY (UMI 3441874).
- Li, K. K., Washburn, I., DuBois, D. L., Vuchinich, S., Ji, P., Brechling, V., Day, J., Beets, M. W., Acock, A. C., Berbaum, M., Snyder, F., & Flay, B. R. (2011). Effects of the Positive Action programme on problem behaviours in elementary school students: A matched‐pair randomised control trial in Chicago . Psychology and Health , 26 ( 2 ), 187–204. 10.1080/08870446.2011.531574 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Losey, R. A. (2009). An evaluation of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program's effectiveness in a high school setting (Doctoral dissertation). University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH.
- Low, S., & Van Ryzin, M. (2014). The moderating effects of school climate on bullying prevention efforts . School Psychology Quarterly , 29 ( 3 ), 306–319. 10.1037/spq0000073 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Martin, F. D. F., Martinez, M., del, C. P. , & Tirado, J. L. A. (2005). Design, implementation and evaluation of a bullying prevention pilot program. [Spanish: Diseno, aplicacion y evaluacion de un Programa Piloto para la Prevencion del Maltrato entre companeros] . Revista Mexicana de Psicologia , 22 , 375–384. [ Google Scholar ]
- McLaughlin, L. P. (2009). The effect of cognitive behavioral therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy plus media on the reduction of bullying and victimization and the increase of empathy and bystander response in a bully prevention program for urban sixth‐grade students (Doctoral Dissertation). University of Toledo.
- Melton, G. B., Limber, S. P., Flerx, V., Nation, M., Osgood, W., Chambers, J., Henggeler, S., Cunningham, P., & Olweus, D. (1998). Violence among rural youth, Final report to the Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, Washington, DC.
- Menard, S., & Grotpeter, J. K. (2014). Evaluation of Bully‐Proofing Your School as an elementary school antibullying intervention . Journal of School Violence , 13 ( 2 ), 188–209. 10.1080/15388220.2013.840641 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Menard, S., Grotpeter, J., Gianola, D., & O'Neal, M. (2008). Evaluation of Bully Proofing your school: Final report . Downloaded from the NCJRS http://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/221078.pdf
- Menesini, E., Codescasa, E., Benelli, B., & Cowie, H. (2003). Enhancing children's responsibility to take action against bullying: Evaluation of a befriending intervention in Italian middle schools . Aggressive Behavior , 29 , 1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- Menesini, E., Nocentini, A., & Palladino, B. E. (2012). Empowering students against bullying and cyberbullying: Evaluation of an Italian peer‐led model . International Journal of Conflict and Violence , 6 ( 2 ), 314–320. [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyer, N., & Lesch, E. (2000). An analysis of the limitations of a behavioural programme for bullying boys from a sub‐economic environment . Southern African Journal of Child and Adolescent Mental Health , 12 ( 1 ), 59–69. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nocentini, A., & Menesini, E. (2015). KiVa antibullying program in Italy: Evidence of effectiveness in a randomized control trial . Prevention Science , 17 ( 8 ), 1012–1023. 10.1007/s11121-016-0690-z [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1992). Bullying among school children: Intervention and prevention. In Peters R. D., McMahon R. J. & Quinsey V. L. (Eds.), Aggression and violence throughout the lifespan (pp. 100–125). Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1993). Bully/victim problems among school children: Long‐term consequences and an effective intervention program. In Hodgins S. (Ed.), Mental disorder and crime (pp. 317–349). Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1994a). Bullying at school: Basic facts and effects of a school based intervention program . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 35 , 1171–1190. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1994b). Bullying at school: Basic facts and an effective intervention programme . Promotion and Education , 1 , 27–31. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1994c). Bullying at school: Long‐term outcome for the victims and an effective school‐based intervention program. In Huesmann L. R. (Ed.), Aggressive behavior: Current perspectives (pp. 97–130). Plenum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1995). Peer abuse or bullying at school: Basic facts and a school‐based intervention programme . Prospects , 25 ( 1 ), 133–139. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1996a). Bullying or peer abuse in school: Intervention and prevention. In Davies G., Lloyd‐Bostock S., McMurran M. & Wilson C. (Eds.), Psychology, law, and criminal justice: International developments in research and practice (pp. 248–267). Walter de Gruyter. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1996b). Bullying at school: Knowledge base and effective intervention . Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences , 784 , 265–276. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1996c). Bully/victim problems at school: Facts and effective intervention . Reclaiming Children and Youth: Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Problems , 5 ( 1 ), 15–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1997a). Bully/victim problems in school: Knowledge base and an effective intervention project . Irish Journal of Psychology , 18 , 170–190. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1997b). Bully/victim problems in schools: Facts and intervention . European Journal of Psychology of Education , 12 , 495–510. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1997c). Tackling peer victimization with a school‐based intervention program. In Fry D. P. & Bjorkqvist K. (Eds.), Cultural variation in conflict resolution: Alternatives to violence (pp. 215–232). Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (2004a). The Olweus Bullying Prevention Programme: Design and implementation issues and a new national initiative in Norway. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 13–36). Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (2004b). Bullying at school: Prevalence estimation, a useful evaluation design, and a new national initiative in Norway . Association for Child Psychology and Psychiatry Occasional Papers , 23 , 5–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (2005a). A useful evaluation design, and the effects of the Olweus bullying prevention program . Psychology, Crime and Law , 11 , 389–402. [ Google Scholar ]
- O'Moore, A. M., & Milton, S. J. (2004). Ireland: The Donegal primary school antibullying project. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 275–288). Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortega‐Ruiz, R., Del Rey, R., & Casas, J. A. (2012). Knowing, building and living together on Internet and social networks: The ConRed cyberbullying prevention program . International Journal of Conflict and Violence , 6 ( 2 ), 303–313. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ostrov, J. M., Godleski, S. A., Kamper‐DeMarco, K. E., Blakely‐McClure, S. J., & Celenza, L. (2015). Replication and extension of the early childhood friendship project: Effects on physical and relational bullying . School Pyschology Review , 44 ( 4 ), 445–463. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pagliocca, P. M., Limber, S. P., & Hashima, P. (2007). Evaluation report for the Chula Vista Olweus Bullying Prevention Program . Final report prepared for the Chula Vista Police Department.
- Palladino, B. E., Nocentini, A., & Menesini, E. (2012). Online and offline peer led models against bullying and cyberbullying . Psicothema , 24 ( 4 ), 634–639. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palladino, B. E., Nocentini, A., & Menesini, E. (2016). Evidence‐based intervention against bullying and cyberbullying: Evaluation of the NoTrap! program in two independent trials . Aggressive Behavior , 42 ( 2 ), 194–206. 10.1002/ab.21636 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pepler, D. J., Craig, W. M., O'Connell, P., Atlas, R., & Charach, A. (2004). Making a difference in bullying: Evaluation of a systemic school‐based program in Canada. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 125–140). Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Polanin, M.K. (2015). Effects of cultural awareness training in conjunction with an established bullying prevention program (Doctoral Dissertation). Loyola University Chicago.
- Pryce, S., & Frederickson, N. (2013). Bullying behaviour, intentions and classroom ecology . Learning Environment Research , 16 , 183–199. 10.1007/s10984-013-9137-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rahey, L., & Craig, W. M. (2002). Evaluation of an ecological program to reduce bullying in schools . Canadian Journal of Counselling , 36 , 281–295. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rawana, J. S., Norwood, S. J., & Whitley, J. (2011). A mixed‐method evaluation of a strength‐based bullying prevention program . Canadian Journal of School Psychology , 26 ( 4 ), 283–300. 10.1177/0829573511423741 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rican, P., Ondrova, K., & Svatos, J. (1996). The effect of a short, intensive intervention upon bullying in four classes in a Czech town . Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences , 794 , 399–400. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roland, E., Bru, E., Midthassel, U. V., & Vaaland, G. S. (2010). The Zero programme against bullying: Effects of the programme in the context of the Norwegian manifesto against bullying . Social Psychology of Education , 13 , 41–55. 10.1007/s11218-009-9096-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenbluth, B., Whitaker, D. J., Sanchez, E., & Valle, L. A. (2004). The Expect Respect Project: Preventing bullying and sexual harassment in US elementary schools. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 211–233). Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Salmivalli, C., Kaukiainen, A., & Voeten, M. (2005). Anti‐bullying intervention: Implementation and outcome . British Journal of Educational Psychology , 75 , 465–487. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salmivalli, C., Kaukiainen, A., Voeten, M., & Sinisammal, M. (2004). Targeting the group as a whole: The Finnish anti‐bullying intervention. In Smith P. K., Pepler D. & Rigby K. (Eds.), Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? (pp. 251–275). Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sapouna, M., Wolke, D., Vannini, N., Watson, S., Woods, S., Schneider, W., Enz, S., Hall, L., Paiva, A., André, E., Dautenhahn, K., & Aylett, R. (2010). Virtual learning intervention to reduce bullying victimization in primary school: A controlled trial . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 51 ( 1 ), 104–112. 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02137.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- da Silva, J., de Oliveira, W., Braga, I., Farias, M., da Silva Lizzi, E., Gonçalves, M., Pereira, B., & Silva, M. (2016). The effects of a skill‐based intervention for victims of bullying in Brazil . International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 13 , 1042. 10.3390/ijerph13111042 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Solomontos‐Kountouri, O., Gradinger, P., Yanagida, T., & Strohmeier, D. (2016). The implementation and evaluation of the ViSC program in Cyprus: Challenges of cross‐national dissemination and evaluation results . European Journal of Developmental Psychology , 13 ( 6 ), 737–755. 10.1080/17405629.2015.1136618 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spröber, N., Schlottke, P. F., & Hautzinger, M. (2006). ProACT + E: Ein Programm zur Pravention von “bullying” an Schulen und zur Forderung der positiven Entwicklung von Schulern: Evalation eines schulbasierten, universalen, primar‐praventiven Programms fur weiterfuhrende Schulen unter Einbeziehung von Lehrern, Schulern und Eltern. [German: ProACT + E: A programme to prevent bullying in schools and to increase the positive development of students. Evaluation of a school‐based, universal, primary preventive programme for secondary schools that includes teachers, students, and parents] . Zeitschrift fur Klinische Psychologie und Psychotherapie: Forschung und Praxis , 35 , 140–150. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stallard, P., Phillips, R., Montgomery, A., Spears, M., Anderson, R., Taylor, J., Araya, R., Lewis, G., Ukoumunne, O., Millings, A., Georgiou, L., Cook, E., & Sayal, K. (2013). A cluster randomised controlled trial to determine the clinical effectiveness and cost‐effectiveness of classroom‐based cognitive–behavioural therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in high‐risk adolescents . Health Technology Assessment , 17 ( 47 ). 10.3310/hta17470 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Strohmeier, D., Hoffmann, C., Schiller, E., Stefanek, E., & Spiel, C. (2012). ViSC Social Competence Program . New Directions for Youth Development , 133 , 71–84. 10.1002/yd.20008 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sutherland, A. E. (2010). The roles of school climate and peers in bullying (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Queen's University, Canada.
- Toner, B. K. (2010). The implementation of the bully prevention program: Bully Proofing Your School and its effect on bullying and school climate on sixth grade suburban Students (Doctoral dissertation). Available from the ProQuest Dissertation and Theses database (UMI No. 3414552).
- Topper, L. R. (2011). Bullying victimisation and alcohol‐misuse in adolescence: Investigating the functional relationship and new prevention strategies (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). King's College London, UK.
- Trip, S., Bora, C., Sipos‐Gug, S., Tocai, I., Gradinger, P., Yanagida, T., & Strohmeier, D. (2015). Bullying prevention in schools by targeting cognitions, emotions, and behavior: Evaluating the effectiveness of the REBE‐ViSC program . Journal of Counselling Psychology , 62 ( 4 ), 732–740. 10.1037/cou0000084 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tsiantis, A. C. J., Beratis, I. N., Syngelaki, E. M., Stefanakou, A., Asimopolous, C., Sideridis, G. D., & Tsiantis, J. (2013). The effects of a clinical prevention program on bullying, victimization, and attitudes toward school of elementary school students . Behavioral Disorders , 38 ( 4 ), 243–257. [ Google Scholar ]
- Waasdorp, T. E., Bradshaw, C. P., & Leaf, P. J. (2012). The impact of schoolwide positive behavioural interventions and supports on bullying and peer rejection . Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine , 166 ( 2 ), 149–156. 10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.755 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, C., & Goldberg, T. S. (2017). Using children's literature to decrease moral disengagement and victimization among elementary school students . Psychology in the Schools , 54 , 918–931. 10.1002/pits.22042 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitaker, D. J., Rosenbluth, B., Valle, L. A., & Sanchez, E. (2004). Expect respect: A school‐based intervention to promote awareness and effective responses to bullying and sexual harassment. In Espelage D. L. & Swearer S. M. (Eds.), Bullying in American schools: A social‐ecological perspective on prevention and intervention (pp. 327–350). Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitney, I., Rivers, I., Smith, P. K., & Sharp, S. (1994). The Sheffield Project: Methodology and findings. In Smith P. K. & Sharp S. (Eds.), School bullying: Insights and perspectives (pp. 20–56). Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams, J., Miller, S., Cutbush, S., Gibbs, D., Clinton‐Sherrod, M., & Jones, S. (2015). A latent transition model of the effects of a teen dating violence prevention initiative . Journal of Adolescent Health , 56 , S27–S32. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.08.019 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yaakub, N. F., Haron, F., & Leong, G. C. (2010). Examining the efficacy of the Olweus prevention programme in reducing bullying: The Malaysian experience . Procedia–Social and Behavioral Sciences , 5 , 595–598. 10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.07.148 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yanagida, T., Strohmeier, D., & Spiel, C. (2019). Dynamic change of aggressive behavior and victimization among adolescents: Effectiveness of the ViSC program . Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology , 48 , S90–S104. 10.1080/15374416.2016.1233498 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
REFERENCES TO EXCLUDED STUDIES
- Ahtola, A., Haataja, A., Kärnä, A., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2013). Implementation of anti‐bullying lessons in primary classrooms: How important is head teacher support? Educational Research , 55 ( 4 ), 376–392. 10.1080/00131881.2013.844941 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahtola, A., Haataja, A., Kärnä, A., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2012). For children only? Effects of the KiVa antibullying program on teachers . Teaching and Teacher Education , 28 , 851–859. 10.1016/j.tate.2012.03.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DeSmet, A., Bastiaensens, S., Van Cleemput, K., Poels, K., Vandebosch, H., Deboutte, G., Herrewijn, L., Malliet, S., Pabian, S., Van Broeckhoven, F., De Troyer, O., Deglorie, G., Van Hoecke, S., Samyn, K., & De Bourdeaudhuij, I. (2018). The efficacy of the Friendly Attac serious digitial game to promote prosocial bystander behavior in cyberbullying among young adolescents: A cluster‐randomized controlled trial . Computers in Human Behavior , 78 , 336–347. 10.1016/j.chb.2017.10.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Del Rey, R., Casas, J. A., & Ortega, R. (2015). The impacts of the ConRed program on different cyberbullying roles . Aggressive Behavior , 42 ( 2 ), 123–135. 10.1002/ab.21608 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Earhart, J. A., Jr. (2011). Promoting positive peer relationships among youths: A study examining the effects of a class‐wide bullying prevention program (Doctoral dissertation). University of California, Santa Barbara. Retrieved from: ProQuest dissertations publishing (no. 3481964).
- Espelage, D. L., Rose, C. H., & Polanin, J. R. (2015). Social‐emotional learning program to reduce bullying, fighting, and victimization among middle school students with disabilities . Remedial and Special Education , 36 , 1–13. 10.1177/0741932514564564 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fletcher, A., Fitzgerald‐Yau, N., Wiggins, M., Viner, R. M., & Bonell, C. (2015). Involving young people in changing their school environment to make it safer: Findings from a process evaluation in English secondary schools . Health Education , 115 ( 3‐4 ), 322–338. 10.1108/HE-04-2014-0063 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Frey, K. S., Hirschstein, M. K., Edstrom, L. V., & Snell, J. L. (2009). Observed reductions in school bullying, nonbullying aggression, and destructive bystander behavior: A longitudinal evaluation . Journal of Educational Psychology , 101 ( 2 ), 466–481. 10.1037/a0013839 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garandeau, C. F., Lee, I. A., & Salmivalli, C. (2014). Differential effects of the KiVa anti‐bullying program on popular and unpopular bullies . Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology , 35 ( 1 ), 44–50. 10.1016/j.appdev.2013.10.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garandeau, C. F., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2014). Tackling acute cases of school bullying in the KiVa anti‐bullying program: A comparison of two approaches . Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology , 42 , 981–991. 10.1007/s10802-014-9861-1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giesbrecht, G. F., Leadbeater, B. J., & MacDonald, S. W. S. (2011). Child and context characteristics in trajectories of physical and relational victimization among early elementary school children . Development and Psychopathology , 23 , 239–252. 10.1017/S09545739410000763 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gradinger, P., Yanagida, T., Strohmeier, D., & Spiel, C. (2015). Prevention of cyberbullying and cyber victimization: Evaluation of the ViSC Social Competence program . Journal of School Violence , 14 ( 1 ), 87–110. 10.1080/15388220.2014.96323 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haataja, A., Voeten, M., Boulton, A. J., Ahtola, A., Poskiparta, E., & Samlivalli, C. (2014). The KiVa antibullying curriculum and outcome: Does fidelity matter? Journal of School Psychology , 52 , 479–493. 10.1016/j.jsp.2014.07.001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harpin, S. B. (2011). Missingness in longitudinal research: Attrition analysis and imputation approaches in a school‐based study of young adolescents (Doctoral Dissertation). University of Minnesota.
- Hutchings, J., & Clarkson, S. (2015). Introducing and piloting the KiVa bullying prevention programme in the UK . Educational and Child Psychology , 32 ( 1 ), 49–61. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kyriakides, L., Creemers, B. P. M., Muijs, D., Rekers‐Mombarg, L., van Petegem, P., & Pearson, D. (2014). Using the dynamic model of educational effectiveness to design strategies and actions to face bullying . School Effectiveness and School Improvement , 25 ( 1 ), 83–104. 10.1080/09243453.2013.771686 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leff, S. S., Waasdorp, T. E., Paskewich, B., Gullan, R. L., Jawad, A. F., Paquette MacEvoy, J., Feinberg, B. E., & Power, T. J. (2010). The Preventing Relational Aggression in School Everyday program: A preliminary evaluation of acceptability and impact . School Psychology Review , 39 ( 4 ), 569–587. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lewis, K. M., Schure, M. B., Bavarian, N., DuBois, D. L., Day, J., Ji, P., Silverthorn, N., Acock, A., Vuchinich, S., & Flay, B. R. (2013). Problem behavior and urban, low‐income youth: A randomized controlled trial of Positive Action in Chicago . American Journal of Preventive Medicine , 44 ( 6 ), 622–630. 10.1016/j.amepre.2013.01.030 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lishak, N. (2011). Examination of bullying behaviours and the implementation of a social norms project in a middle school (Doctoral Dissertation). Walden University. (UMI 3454156).
- Low, S., Van Ryzin, M. J., Brown, E. C., Smith, B. H., & Haggerty, K. P. (2014). Engagement matters: Lessons from assessing classroom implementation of Steps to Respect: A bullying prevention program over a one‐year period . Prevention Science , 15 , 165–176. 10.1007/s11121-012-0359-1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Noland, B. (2011). Effects of the KiVa anti‐bullying program on adolescents' perceptions of peers, depression, and anxiety (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Kansas: University of Kansas.
- van der Ploeg, R., Steglich, C., & Veenstra, R. (2016). The support group approach in the Dutch KiVa anti‐bullying programme: Effects on victimization, defending and well‐being at school . Educational Research , 58 ( 3 ), 221–236. 10.1080/00131881.2016.1884949 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Şahin, M. (2012). An investigation into the efficiency of empathy training program on preventing bullying in primary schools . Children and Youth Services Review , 34 , 1325–1330. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2012.03.013 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sainio, M., Veenstra, R., Huitsing, G., & Salmivalli, C. (2012). Same‐ and other‐sex victimization: Are the risk factors similar? Aggressive Behavior , 38 , 422–455. 10.1002/ab.21445 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salmivalli, C., Kärnä, A., & Poskiparta, E. (2012). Counteracting bullying in Finland: The KiVa program and its effects on different forms of being bullied . International Journal of Behavioral Development , 35 ( 5 ), 405–411. 10.1177/0165025411407457 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schroeder, B. A., Messina, A., Schroeder, D., Good, K., Barto, S., Saylor, J., & Masiello, M. (2012). The implementation of a statewide bullying prevention program: Preliminary findings from the field and the importance of coalitions . Health promotion practice , 13 ( 4 ), 49–495. 10.1177/1524839910386887 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stevens, V., de Bourdeaudhuij, I., & van Oost, P. (2000). Bullying in Flemish schools: An evaluation of anti‐bullying intervention in primary and secondary schools . British Journal of Educational Psychology , 70 , 195–210. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson, S. E. J., Vannini, N., Woods, S., Dautenhahn, K., Sapouna, M., Enz, S., Schneider, W., Wolke, D., Hall, L., Paiva, A., André, E., & Aylett, R. (2010). Inter‐cultural differences in response to a computer‐based anti‐bullying intervention . Educational Research , 52 ( 1 ), 61–80. 10.1080/001318811003588261 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Williford, A., Boulton, A., Noland, B., Little, T. D., Kärnä, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2012). Effects of the KiVa anti‐bullying program on adolescents' depression, anxiety, and perception of peers . Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology , 40 , 289–300. 10.1007/s10802-011-9551-1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Williford, A., Elledge, L. C., Boulton, A. J., DePaolis, K. J., Little, T. D., & Salmivalli, C. (2013). Effects of the KiVa anti‐bullying program on cyberbullying and cybervictimization frequency among Finnish youth . Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology , 42 ( 6 ), 820–833. 10.1080/15374416.2013.787623 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wölfer, R., & Scheithauer, H. (2014). Social influence and bullying behavior: Intervention‐based network dynamics of the fairplayer.manual bullying prevention program . Aggressive Behavior , 40 , 309–319. 10.1002/ab.21524 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wong, D. S. W., Cheng, C. H. K., Ngan, R. M. H., & Ma, S. K. (2011). Program effectiveness of a restorative whole‐school approach for tackling school bullying in Hong Kong . International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology , 55 ( 6 ), 846–862. 10.1177/0306624X10374638 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wurf, G. (2012). High school anti‐bullying interventions: An evaluation of curriculum approaches and the method of Shared Concern in four Hong Kong international schools . Australian Journal of Guidance and Counselling , 22 ( 1 ), 139–149. 10.1017/jgc.2012.2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2015). Effectiveness of the KiVa antibullying programme on bully‐victims, bullies and victims . Educational Research , 57 ( 1 ), 80–90. 10.1080/00131881.2014.983724 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
ADDITIONAL REFERENCES
- Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behaviour . Organisational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes , 50 , 179–211. [ Google Scholar ]
- Altinay, D. (2003). Psycho‐dramatic group therapy . Istanbul: System Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arseneault, L., Bowes, L., & Shakoor, S. (2010). Bullying victimization in youths and mental health problems: ‘Much ado about nothing'? Psychological Medicine , 40 ( 5 ), 717–729. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Atria, M., & Spiel, C. (2007). Viennese Social Competence (ViSC) training for students: Program and Evaluation. In Maher C. A., Zins J. & Elias M. (Eds.), Bullying, Victimization, and Peer Harassment: A Handbook of Prevention and Intervention (pp. 179–197). Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ayieko, J., Abuogi, L., Simchowitz, B., Bukusi, E. A., Smith, A. H., & Reingold, A. (2014). Efficacy of isoniazid prophylactic therapy in prevention of tuberculosis in children: A meta‐analysis . BMC Infectious Diseases , 14 ( 1 ), 91. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baldry, A. C., Farrington, D. P., & Sorrentino, A. (2017). School bullying and cyberbullying among boys and girls: Roles and overlap . Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment, & Trauma , 26 ( 9 ), 937–951. 10.1080/10926771.2017.1330793 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baldry, A. C., Sorrentino, A., & Farrington, D. P. (2019). Cyberbullying and cybervictimization versus parental supervision, monitoring and control of adolescents' online activities . Children and Youth Services Review , 96 , 302–307. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.11.058 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura, A. (1978). Social learning theory of aggression . Journal of Communication , 28 ( 3 ), 12–29. 10.1111/j.1460-2466.1978.tb01621.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloom, H. S., Hill, C. J., & Riccio, J. A. (2003). Linking program implementation and effectiveness: Lessons from a pooled sample of welfare‐to‐work experiments . Journal of Policy Analysis and Management , 22 ( 4 ), 551–575. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brighi, A., Ortega, R., Pyzalski, J., Scheithauer, H., Smith, P.K., Tsormpatzoudis, C., Barkoukis, V., Del Rey, R., & Thompson, J. (2012). European Cyberbullying Intervention Project Questionnaire (ECIPQ) . Unpublished manuscript. Bologna, Italy: University of Bologna.
- Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta‐analysis . Wiley Ltd. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). Ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design . Harvard University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cantone, E., Piras, A. P., Vellante, M., Preti, A., Daníelsdóttir, S., D'Aloja, E., Lesinskiene, S., Angermeyer, M. C., Carta, M. G., & Bhugra, D. (2015). Interventions on bullying and cyberbullying in schools: A systematic review . Clinical Practice & Epidiology in Mental Health , 11 ( Suppl 1 M4 ), 58–76. 10.2174/174501791511010058 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carlos‐Wallace, F. M., Zhang, L., Smith, M. T., Rader, G., & Steinmaus, C. (2016). Parental, in utero, and early‐life exposure to benzene and the risk of childhood leukaemia: A meta‐analysis . American Journal of Epidemiology , 183 ( 1 ), 1–14. 10.1093/aje/kwv120 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cavell, T. A., & Hughes, J. N. (2000). Secondary prevention as context for assessing change processes in aggressive children . Journal of School Psychology , 38 , 199–236. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chalamandaris, A., & Piette, D. (2015). School‐based anti‐bullying interventions: Systematic review of the methodology to assess their effectiveness . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 24 , 131–174. 10.1016/j.avb.2015.04.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . (2014). Bullying surveillance among school‐ aged children: Uniform definitions and recommended data elements . Washington, DC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). [ Google Scholar ]
- Combs, A. (1962). The self in chaos . PsycCRITIQUES , 7 ( 2 ), 53–54. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creemers, B. P. M., & Kyriakides, L. (2008). The dynamics of educational effectiveness: A contribution to policy, practice and theory in contemporary schools . Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creemers, B. P. M., & Kyriakides, L. (2012). Improving quality in education: Dynamic approaches to school improvement . Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- van Dam, D. S., van der Ven, E., Velthorst, E., Selten, J. P., Morgan, C., & de Haan, L. (2012). Childhood bullying and the association with psychosis in non‐clinical and clinical samples: A review and meta‐analysis . Psychological Medicine , 42 , 2463–2474. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Department for Education and Skills . (2005). Excellence and enjoyment: Social and emotional aspects of learning . London: Author. [ Google Scholar ]
- Diekstra, R. F. W. (1996). Keerpunten: Naar een preventief jeugbeleid (Turning Points: Towards preventive youth policy) . Municipal Authority Greater City of Rotterdam (GCD) .
- Donner, A., & Klar, N. (2002). Issues in meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials . Statistics in Medicine , 21 , 2971–2980. 10.1002/sim.1301 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Donner, A., Piaggio, G., & Villar, J. (2001). Statistical methods for the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials . Statistical Methods in Medical Research , 10 , 325–338. 10.1191/096228001680678322 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dorjee, K., Choden, T., Baxi, S. M., Steinmaus, C., & Reingold, A. L. (2018). Risk of cardiovasculat disease associated with exposure to abacavir among individuals with HIV: A systematic review and meta‐analyses of results from 17 epidemiological studies . International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents , 52 , 541–553. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Duckworth, A. L., Steen, T. A., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2005). Positive psychology in clinical practice . Annual Review of Clinical Psychology , 1 , 629–651. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Easterbrook, P. J., Gopalan, R., Berlin, J. A., & Matthews, D. R. (1991). Publication bias in clinical research . The Lancet , 337 ( 8746 ), 867–872. 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90201-Y [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eisner, M., & Humphreys, D. (2012). Measuring conflict of interest in prevention and intervention research: A feasibility study. In T. Bliesener, A. Beelmann, & M. Stemmler (Eds.), Antisocial Behavior and Crime , (pp. 165 – 180). Hogrefe.
- Ellis, A. (1962). Reason and emotion in psychotherapy . Stuart. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellis, P. D. (2010). The Essential Guide to Effect sizes: Statistical power, Meta‐analysis, and the interpretation of research results . Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Erren, T. C., Glende, C. B., Morfeld, P., & Piekarski, C. (2009). Is exposure to silica associated with lung cancer in the absence of silicosis? A meta‐analytical approach to an important public health question . International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health , 82 ( 8 ), 997–1004. 10.1007/s00420-008-0381-0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Espelage, D., & Horne, A. (2008). School violence and bullying prevention: From research based explanations to empirically based solutions. In Brown S. & Lent R. (Eds.), Handbook of Counselling psychology (4 th edition, pp. 588–606). Wiley and Sons. [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans, C. B. R., Fraser, M. W., & Cotter, K. L. (2014). The effectiveness of school‐based bullying prevention programs: A systematic review . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 19 ( 5 ), 532–544. 10.1016/j.avb.2014.07.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P. (1983). Randomized experiments on crime and justice . Crime and Justice , 4 , 257–308. [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P. (1993). Understanding and preventing bullying . Crime and Justice: A Review of Research , 17 , 381–458. [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P. (2003). Methodological quality standards for evaluation research . The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 587 ( 1 ), 49–68. [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P., Lösel, F., Ttofi, M. M., & Theodorakis, N. (2012). School bullying, depression and offending behavior later in life: An updated systematic review of longitudinal studies . Stockholm: Swedish National Council for Crime Prevention. [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P., & Petrosino, A. (2001). The Campbell Collaboration crime and justice group . ANNALS of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 578 ( 1 ), 35–49. 10.1177/000271620157800103 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P., & Ttofi, M. M. (2009). School‐based programs to reduce bullying and victimization . Campbell Systematic Reviews , 6 , 1–148. 10.4073/csr.2009.6 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P., & Welsh, B. C. (2008). Saving children from a life of crime: Early risk factors and effective interventions . Oxford University press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrington, D. P., & Welsh, B. C. (2013). Measuring effect size in meta‐analysis, with special reference to area‐based crime prevention programs and the effects of closed‐circuit television on crime. In Kuhn A., Schwarzenegger C., Margot P., Donatsch A., Aebi M. & Jositsch D. (Eds.), Criminology, criminal policy and criminal law from an international perspective (pp. 75–89). Stampfli. [ Google Scholar ]
- Faupel, A. (2003). Emotional literacy assessment and intervention ages 7‐11 . NFER Nelson.
- Ferguson, C. J., Miguel, C. S., Kilburn, J. C., & Sanchez, P. (2007). The effectiveness of school‐based anti‐bullying programmes: A meta‐analytic review . Criminal Justice Review , 32 , 401–414. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flay, B. R., & Allred, C. G. (2010). The Positive Action program: Improving academics, behavior, and character by teaching comprehensive skills for successful learning and living. In Lovat T., Toomey R. & Clement N. (Eds.), International Research Handbook on Values Education and Student Wellbeing (pp. 471–501). Springer. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gaffney, H., Farrington, D. P., Espelage, D. L., & Ttofi, M. M. (2018). Are cyberbullying intervention and prevention programs effective? A systematic and meta‐analytical review . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 45 , 134–153. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gaffney, H., Ttofi, M. M., & Farrington, D. P. (2018). Evaluating the effectiveness of school‐bullying prevention programs: An updated meta‐analytical review . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 45 , 111–133. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gastic, B. (2008). School truancy and the disciplinary problems of bullying victims . Educational Review , 60 ( 4 ), 391–404. 10.1080/00131910802393423 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geel, M., , van Goemans, A. , & Vedder, P. H. (2016). The relation between peer victimization and sleeping problems: A meta‐analysis . Sleep medicine reviews , 27 , 89–95. 10.1016/j.smrv.2015.05.004 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geel, M., , van Vedder, P. , & Tanilon, J. (2014). Bullying and weapon carrying: A meta‐analysis . JAMA Pediatrics , 168 , 714–720. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gini, G., & Pozzoli, T. (2013). Bullied children and psychosomatic problems: A meta‐analysis . Pediatrics , 132 , 720–729. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gini, G., Pozzoli, T., Lenzi, M., & Vieno, A. (2014). Bullying victimization at school and headache: A meta‐analysis of observational studies . Headache , 54 , 976–986. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gravesteijn, J. C., & Diekstra, R. F. W. (2013). Skills for Life, docentenhandleiding, teachers manual . EduActief. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haggas, L. S. (2006). A bully prevention challenge course curriculum (Unpublished master's professional project). Western Oregon University.
- Hawker, D. S. J., & Boulton, M. J. (2000). Twenty years' research on peer victimization and psychosocial maladjustment: A meta‐analytic review of cross‐sectional studies . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 41 , 441–455. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- He, J., Van de Vijver, F. J., Dominguez Espinosa, A., Abubakar, A., Dimitrova, R., Adams, B. G., & Fischer, R. (2015). Socially desirable responding: Enhancement and denial in 20 countries, Cross‐Cultural Research ( 49 , pp. 227–249. 3 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Hedges, L. V. (1982). Estimation and testing for differences in effect size: Comment on Hsu . Psychological Bulletin , 91 , 391–393. [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins, J. P. T., Deeks, J. J., & Altman, D. G. (2011). Special topics in statistics. In Higgins J. P. T. & Green S. (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 481–530). John Wiley & Sons Ltd. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirschstein, M. K., & Frey, K. S. (2007). Promoting behaviors and beliefs that reduce bullying. The Steps to Respect program. In Jimerson S. R. & Furlong M. J. (Eds.), The handbook of school violence and school safety: From research to practice . Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Holt, M. K., Vivolo‐Kantor, A. M., Polanin, J. R., Holland, K. M., DeGue, S., Matjasko, J. L., Wolfe, M., & Reid, G. (2015). Bullying and suicidal ideation and behaviors: A meta‐analysis . Pediatrics , 135 ( 2 ), e496–e509. 10.1542/peds.2014-1864 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hopkins, B. (2004). Just Schools: A whole school approach to restorative justice . Jessica Kingsley. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jiménez‐Barbero, J. A., Ruiz Hernández, J. A., Llor‐Esteban, B., & Pérez‐García, M. (2012). Effectiveness of antibullying school programmes: A systematic review by evidence levels . Children and Youth Services Review , 34 ( 9 ), 1646–1658. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2012.04.025 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jiménez‐Barbero, J. A., Ruiz‐Hernández, J. A., Llor‐Zaragoza, L., Pérez‐García, M., & Llor‐Esteban, B. (2016). Effectiveness of anti‐bullying school programs: A meta‐analsysis . Children and Youth Services Review , 61 , 165–175. 10.1016/j.childyouth.2015.12.015 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaminski, J. W., Valle, L. A., Filene, J. H., & Boyle, C. L. (2008). A meta‐analytic review of components associated with parent training program effectiveness . Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology , 36 , 567–589. 10.1007/s10802-007-9201-9 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kochenderfer, B. J., & Ladd, G. W. (2000). Victimized children's responses to peers’ aggression: Behaviors associated with reduced versus continued victimization . Development and Psychopathology , 9 , 59–73. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kyriakides, L. (2008). Testing the validity of the comprehensive model of educational effectiveness: A step towards the development of a dynamic model of effectiveness . School Effectiveness and School Improvement , 19 ( 4 ), 429–446. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kyriakides, L., Creemers, B. P. M., Papastylianou, D., & Papadatou‐Pastou, M. (2014). Improving the school learning environment to reduce bullying: An experimental study . Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research , 58 ( 4 ), 453–478. 10.1080/00313831.2013.773556 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (2001). Practical meta‐analysis . Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Littell, J. H., Corcoran, J., & Pillai, V. (2008). Systematic reviews and meta‐analysis . Oxford University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Masiello, M. G., & Schroeder, D. (2014). A public health approach to bullying prevention . APHA Press. 10.2105/9780875530413 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McAuley, L., Tugwell, P., & Moher, D. (2000). Does the inclusion of grey literature influence estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta‐analysis? The Lancet , 356 ( 9237 ), 1228–1231. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mishara, B. L., & Ystgaard, M. (2006). Effectiveness of a mental health promotion program to improve coping skills in young children: “Zippy's Friends” . Early Childhood Research Quarterly , 21 ( 1 ), 110–123. [ Google Scholar ]
- Modecki, K. L., Minchin, J., Harbaugh, A. G., Guerra, N. G., & Runions, K. C. (2014). Bullying prevalence across contexts: A meta‐analysis measuring cyber and traditional bullying . Journal of Adolescent Health , 55 , 602–611. 10.1016/j.adohealth.2014.06.007 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrison, B. (2002). Bullying and victimization in schools: A restorative justice approach . Australian Institute of Criminology: Trends and Issues , 219 , 1–6. [ Google Scholar ]
- Murray, D. M., & Blitstein, J. L. (2003). Methods to reduce the impact of intraclass correlation in group‐randomized trials . Evaluation Review , 27 , 79–103. 10.1177/0193841x02239019 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murphy, E., & Lewers, R. (2000). The hidden hurt . Wizard Books. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1986). The Olweus bully/victim questionnaire . University of Bergen. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1991). Bully/victim problems among school children: Basic facts and effects of a school‐based intervention program . In Pepler D. J. & Rubin K. H. (Eds.), The Development and Treatment of Childhood Aggression, (pp. 411–448) . Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D. (1996). The revised Olweus bully/victim questionnaire . Mimeo. Bergen, Norway: Research Center for Health Promotion (HEMIL Center), University of Bergen. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olweus, D., & Limber, S. P. (2017). Some problems with cyberbullying research . Current Opinion in Psychology , 19 , 139–143. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ostrov, J. M., & Kamper, K. E. (2015). Future directions for research on the development of relational and physical peer victimization . Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology , 44 , 509–519. 10.1080/15374416.2015.1012733 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Owens, A., & Barber, K. (1998). Draama toimii , [Dramaworks]. Helsinki, Finland: JB‐kustannus. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perkins, W. H. (2003). The social norms approach to preventing school and college age substance abuse . Jossey‐Bass. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pikas, A. (2002). New developments of the Shared Concern method . School Psychology International , 23 ( 3 ), 307–326. [ Google Scholar ]
- Piquero, A. R., Jennings, W. G., Diamond, B., Farrington, D. P., Tremblay, R. E., Welsh, B. C., & Reingle Gonzalez, J. M. (2016). A meta‐analysis update on the effects of early family/parent training programs on antisocial behaviour and delinquency . Journal of Experimental Criminology , 12 , 229–248. 10.1007/s11292-016-9256-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Portnoy, J., & Farrington, D. P. (2015). Resting heart rate and antisocial behavior: An updated systematic review and meta‐analysis . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 22 , 33–45. 10.1016/j.avb.2015.02.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Purkey, W. W. (1970). Self concept and school achievement . Prentice Hall. [ Google Scholar ]
- Purkey, W. W., & Novak, J. M. (1996). Inviting school success: A self‐concept approach to teaching, learning, and democratic practice . Wadsworth. [ Google Scholar ]
- Resnik, M. D. (2000). Protective factors, resiliency, and healthy youth development . Adolescent medicine: State of the art reviews , 11 ( 1 ), 157–164. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rigby, K., & Johnson, B. (2006). Expressed readiness of Australian schoolchildren to act as bystanders in support of children who are being bullied . Educational psychology , 26 ( 3 ), 425–440. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roland, E., & Galloway, D. (2004). Professional cultures in schools with high and low rates of bullying . School effectiveness and school improvement , 15 ( 3‐4 ), 241–260. 10.1080/09243450512331383202 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salmivalli, C. (2010). Bullying and the peer group: A review . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 15 ( 2 ), 112–120. 10.1016/j.avb.2015.10.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salmivalli, C., Lagerspertz, K., Björkqvist, K., Österman, K., & Kaukiainen, A. (1996). Bullying as a group process: Participant roles and their relations to social status within the group . Aggressive Behavior , 22 , 1–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schultze‐Krumbholz, A., Wölfer, R., Jäkel, A., Zagorscak, P., & Scheithauer, H. (2012). Effective prevention of cyberbullying in Germany: The Medienhelden program. Paper presented at the 10 th ISRA World Meeting, Luxembourg.
- Seligman, M. E., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2000). Positive psychology . American Psychologist , 55 ( 1 ), 5–14. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sercombe, H., & Donnelly, B. (2013). Bullying and agency: Definition, intervention and ethics . Journal of Youth Studies , 16 ( 4 ), 491–502. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sieving, R. E., & Widome, R. (2008). Toward preventing youth violence: Engaging urban middle‐school students in community service learning . CURA Reporter , 38 ( 1 ), 12–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sismani, E., Paradeisioti, A., & Lazarou, C. (2014). Bullying phenomenon and preventive programs in Cyprus's school system . International Journal of Mental Health Promotion , 16 ( 1 ), 67–80. 10.1080/14623730.2014.888894 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith, P. K., Ananiadou, K., & Cowie, H. (2003). Interventions to reduce school bullying . The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry , 48 ( 9 ), 591–599. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith, P. K., Cowie, H., Olafsson, R. F., & Liefooghe, A. P. (2002). Definitions of bullying: A comparison of terms used, and age and gender differences, in a Fourteen–Country international comparison . Child Development , 73 ( 4 ), 1119–1133. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith, J. D., Schneider, B. H., Smith, P. K., & Ananiadou, K. (2004). The effectiveness of whole‐school antibullying programs: A synthesis of evaluation research . School psychology review , 33 , 547–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith, P. K., Kwak, K., & Toda, Y. (2016). School bullying in different cultures: Eastern and Western perspectives . Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Solberg, M. E., & Olweus, D. (2003). Prevalence estimation of school bullying with the Olweus Bully/Victim Questionnaire . Aggressive Behavior , 29 ( 3 ), 239–268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Steinmaus, C., Smith, A. H., Jones, R. M., & Smith, M. T. (2008). Meta‐analysis of benzene exposure and non‐Hodgkin lymphoma: Biases could mask an important association . Occupational & Environmental Medicine , 65 ( 6 ), 371–378. 10.1136/oem.2007.036913 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Strøm, I. F., Thoresen, S., Wentzel‐Larsen, T., & Dyb, G. (2013). Violence, bullying and academic achievement: A study of 15‐year‐old adolescents and their school environment . Child Abuse & Neglect , 37 ( 4 ), 243–251. 10.1016/j.chiabu.2012.10.010 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swearer, S. M., & Espelage, D. L. (2011). A social‐ecological framework of bullying among youth. Bullying in North American schools . Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swearer, S., Siebecker, A. B., Johnsen‐Frerichs, L. A., & Wang, C. (2010). Assessment of bullying/victimization: The problem of comparability across studies and methodologies. In Jimerson S. R., Swearer S. M. & Espelage D. L. (Eds.), Handbook of bullying in schools: An international perspective (pp. 305–327). Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. (1979). An integrative theory of intergroup conflict. In Austin W. G. & Worschel S. (Eds.), The social psychology of intergroup relations . Brooks/Cole Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trip, S., & Bora, C. (2010). Educatie rational‐emotiva si comportamentala. Program de preventive primara si secundara pentru clasele V‐VIII [Rational‐emotive and behavioral education. Primary and secondary prevention program for V‐VIII grades]/Oradea, Romania: Editura Universitati din Oradea.
- Tsiantis, J. (Ed.). (2011). Bullying prevention and coping workshops: Class activities with students . A.P.H.C.A. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M. (2015). Adolescent bullying linked to depression in early adulthood: Evidence supports early intervention . British Medical Journal , 350 , h2694. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M., & Farrington, D. P. (2011). Effectiveness of school‐based programs to reduce bullying: A systematic and meta‐analytic review . Journal of Experimental Criminology , 7 , 27–56. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., Lösel, F., & Loeber, R. (2011a). Do victims of school bullies tend to become depressed later in life? A systematic review and meta‐analysis of longitudinal studies . Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research , 3 ( 2 ), 63–73. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., Lösel, F., & Loeber, R. (2011b). The predictive efficiency of school bullying versus later offending: A systematic/meta‐analytic review of longitudinal studies . Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health , 21 , 80–89. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., & Lösel, F. (2012). School bullying as a predictor of violence later in life: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of prospective longitudinal studies . Aggression and Violent Behaviour , 17 , 405–418. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M., Eisner, M., & Bradshaw, C. P. (2014). Bullying prevention: Assessing existing meta‐evaluations. In Bruinsma G. & Weisburd D. (Eds.), Encyclopaedia of criminology and criminal justice (pp. 231–242). Springer. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., Lösel, F., Crago, R. V., & Theodorakis, N. (2016). School bullying and drug use later in life: A meta‐analytic investigation . School Pscyhology Quarterly , 31 ( 1 ), 8–27. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valdebenito, S., Eisner, M., Farrington, D. P., Ttofi, M. M., & Sutherland, A. (2018). School‐based interventions for reducing disciplinary school exclusion: A systematic review . Campbell Systematic Reviews , 2018 , 1. 10.4073/csr.2018.1 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valdebenito, S., Ttofi, M., & Eisner, M. (2015). Prevalence rates of drug use among school bullies and victims: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of cross‐sectional studies . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 23 , 137–146. 10.1016/j.avb.2015.05.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valdebenito, S., Ttofi, M. M., Eisner, M., & Gaffney, H. (2018). Weapon carrying in and out of school among pure bullies, pure victims and bully‐victims: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of cross‐sectional and longitudinal studies . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 33 , 62–77. [ Google Scholar ]
- Volk, A. A., Veenstra, R., & Espelage, D. L. (2017). So you want to study bullying? Recommendations to enhance the validity, transparency, and comparability of bullying research . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 36 , 34–43. [ Google Scholar ]
- Vreeman, R. C., & Carroll, A. E. (2007). A systematic review of school‐based interventions to prevent bullying . Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine , 161 , 78–88. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weisburd, D. (2003). Ethical practice and evaluation of interventions in crime and justice: The moral imperative for randomized trials . Evaluation Review , 27 ( 3 ), 336–354. 10.1177/0193841X03027003007 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weisburd, D., Lum, C. M., & Petrosino, A. (2001). Does research design affect study outcomes in criminal justice? ANNALS of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 578 ( 1 ), 50–70. 10.1177/000271620157800104 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson, D. B. (2010). Meta‐analysis. In Piquero A. R. & Weisburd D. (Eds.), Handbook of quantitative criminology (pp. 181–208). Springer. [ Google Scholar ]
- Woolf‐King, S. E., Steinmaus, C. M., Reingold, A. L., & Hahn, J. A. (2013). An update on alcohol use and risk of HIV infection in sub‐Saharan Africa: Meta‐analysis and future research directions . International Journal of Alcohol and Drug Research , 2 ( 1 ), 99–110. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zych, I., Baldry, A. C., Farrington, D. P., & Llorent, V. J. (2019). Are children involved in cyberbullying low on empathy? A systematic review and meta‐analysis of research on empathy versus different cyberbullying roles . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 45 , 83–97. 10.1016/j.avb.2018.03.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zych, I., Farrington, D. P., Llorent, V. J., & Ttofi, M. M. (2017). Protecting children against bullying and its consequences: SpringerBriefs in behavioral criminology . Springer International Publishing. 10.1007/978-3-319-53028-4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zych, I., Ortega‐Ruiz, R., & del Rey, R. (2015). Systematic review of theoretical studies on bullying and cyberbullying: Facts, knowledge, prevention, and intervention . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 23 , 1–21. 10.1016/j.avb.2015.10.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zych, I., Viejo, C., Vila, E., & Farrington, D. P. (2019). School bullying and dating violence in adolescents: A systematic review and meta‐analysis . Trauma, Violence, & Abuse , 152483801985446. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Europe PMC requires Javascript to function effectively.
Either your web browser doesn't support Javascript or it is currently turned off. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page.
Search life-sciences literature (43,989,266 articles, preprints and more)
- Free full text
- Citations & impact
- Similar Articles
Identifying and Addressing Bullying
Author information, affiliations.
- Nickerson AB 2
Study Guide from StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) , 20 Jul 2017 PMID: 28722959
Books & documents Free full text in Europe PMC
Abstract
Free full text .
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Muhammad Waseem ; Amanda B. Nickerson .
Last Update: December 13, 2023 .
Continuing Education Activity
Bullying is a serious and widespread global problem with detrimental consequences for the physical and mental well-being of children. It is a repeated and deliberate pattern of aggressive or hurtful behavior targeting individuals perceived as less powerful. Bullying manifests in various forms, such as physical, verbal, social/relational, and cyberbullying, each with unique characteristics. Vulnerable youth at greater risk of being bullied are individuals who are perceived as "different," including those belonging to racial and ethnic minorities, immigrants, refugees, individuals with notable physical features or disabilities, and younger and defenseless children.
Healthcare professionals are uniquely positioned to identify and prevent bullying and intervene to mitigate its mental and physical health consequences. This activity reviews issues of particular importance to clinicians. It gives them practical tips to increase their awareness of bullying, enabling early recognition and effective management of this complex issue. Bullying is a problem that affects both the victims and the perpetrators, and this course equips learners with the knowledge and skills to positively impact the lives of the youth it affects.
Objectives:
- Identify signs and symptoms of bullying behavior, recognizing overt and subtle indications of victimization.
- Differentiate between various forms of bullying, including physical, verbal, social, and cyberbullying, to tailor appropriate intervention strategies.
- Assess the underlying causes of bullying behavior, including social and psychological factors, to develop prevention and intervention strategies.
- Collaborate with interprofessional team members to select appropriate therapeutic interventions and resources for victims and perpetrators of bullying.
Introduction
Bullying is a significant and pervasive yet preventable public health problem with detrimental consequences for children's physical and mental well-being. Bullying is a repeated and deliberate pattern of aggressive or hurtful behavior targeting individuals perceived as less powerful. [1] The CDC's formal and somewhat unwieldy definition is "any unwanted aggressive behavior by another youth or group of youths who are not siblings or current dating partners that involves an observed or perceived power imbalance and is repeated multiple times or is highly likely to be repeated."[CDC. Fast Facts: Preventing Bullying ] In Australia, the National Center Against Bullying defines bullying as an "ongoing and deliberate misuse of power in relationships through repeated verbal, physical or social behavior that intends to cause physical, social, or psychological harm." This activity focuses on children and youth younger than 18 and does not address adult or workplace bullying.
Historically, bullying has been seen as a "rite of passage" in childhood, and even today, there often is a tacit acceptance of bullying behavior. Many healthcare professionals struggle to accept bullying as a public health issue. An increased awareness of the long-term consequences on physical and mental health necessitates a shift in these attitudes.[Campbell, Kristin. Bullying and Victimization . AAP] Populations at greater risk are those perceived as "different," including racial, religious, and ethnic minorities, immigrants, refugees, individuals with notable physical features or disabilities, and younger or more vulnerable children. Bullying episodes are usually unprovoked and deliberate, and bullies often seek visibility and prestige through their actions.
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in preventing and identifying bullying and assisting with mitigating its mental and physical health consequences. This overview provides clinicians with the knowledge and tools to increase their awareness of bullying, enabling early recognition and effective intervention. Bullying is a problem that affects victims, perpetrators, and bystanders, and this overview equips clinicians with the skills to improve the lives of affected youth.
Bullying can happen anywhere, although it is most common in and around schools. Bullying usually occurs in relatively unstructured situations and minimally supervised areas such as playgrounds, cafeterias, hallways, bus stops, and buses. Bullying manifests in various forms, such as physical, verbal, social/relational, and cyberbullying, each having unique characteristics. Verbal bullying, including name-calling and taunting, is the most frequent.
Cyberbullying has received much attention in the past few years, as children and teens now have easy access to digital devices and social media sites. Cyberbullying manifests as text messages, social media posts, emails, online forums, and other platforms, and the risk increases considerably with the duration of a child's online activity. The term was first coined in the 1990s but has only become a significant concern in the 21st century as rates have risen, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic when electronic media use soared during lockdowns. Name-calling occurs most frequently, but 15% of youth bullied online describe being scared. Teens also report receiving unsolicited and explicit images meant to intimidate them.[Vogels, Emily. Teens and Cyberbullying 2022 ]
Artificial intelligence (AI) has complicated this issue. The Wall Street Journal wrote about a group of high school boys who used an online tool powered by AI to create nude photographs of female classmates, which they spread electronically. Although this might have been an isolated event, these fake nude likenesses will persist in cyberspace indefinitely and are likely to cause irreparable adverse effects.[WSJ. Nov 4-5, 2023, p1] Despite these growing concerns, only 11% of teens talk with their parents or caregivers about their cyberbullying experiences.[Security.org. Cyberbullying ] Identifying this form of bullying is challenging because the episodes may be less repetitive than typical verbal or physical bullying. [2] In many instances, perpetrators remain anonymous, allowing them to engage in behavior they might not display face-to-face with their victims. Because online content is easily preserved and disseminated, cyberbullying results in ongoing suffering, especially when hurtful messages "go viral." Cyberbullying differs from traditional bullying as it does not rely on physical proximity or a specific location and can occur at any time of day or night. Traditional bullying at school usually does not extend to the home setting, but victims of cyberbullying may feel they cannot escape since their electronic devices are turned on 24/7. Like traditional bullying, cyberbullying can cause profound adverse psychological effects.
Relational or social bullying occurs when the aggressor manipulates social relationships to harm or control the victim. Unlike physical and verbal bullying, which involve direct acts of aggression, relational bullying is more subtle. The aggressors often rely on tactics such as spreading rumors, excluding victims from social groups, and manipulating social dynamics to damage reputations or relationships. In social bullying, the bully aims to isolate, hurt, or control the victim emotionally, which can result in psychological and emotional sequelae. Social bullying is no longer restricted to the schoolyard but frequently takes the form of cyberbullying.
Clinicians play a crucial role in identifying bullying and treating the children it impacts. They screen patients for risk factors, educate families about coping skills, and advocate in their communities and local schools. School anti-bullying measures can help prevent bullying and empower youth to intervene when they are bystanders. This overview describes how clinicians can address bullying in an outpatient setting to improve child well-being and reduce its physical, psychological, social, and educational harms.
What creates a bully? Bullying results from a complex combination of individual, social, and environmental factors, and many youths who engage in it have specific backgrounds and qualities. Likewise, victims often share similar traits.
Exposure to adverse childhood events increases the likelihood of becoming a bully. Associated characteristics include aggression, frustration, lack of empathy, poor impulse control, a tendency to blame others for their problems, an inability to accept responsibility for one's actions, a desire for power, the perception that others are hostile, and having friends who are bullies. Bullies have also been noted to exhibit more antisocial behaviors and use more marijuana and alcohol than their peers. [3] Bullies do not always need to be physically stronger than their victims. The perceived power imbalance is derived from many factors, including popularity, socioeconomic status, peer group, and cognitive ability. Bullies frequently use their behavior to gain social status within their peer group. [4] Some perpetrators may not consciously consider themselves bullies, especially those previously victimized.
Bullying affects all socioeconomic groups, and lower socioeconomic status (SES) has been associated with higher rates of victimization. Still, higher SES does not necessarily prevent an individual from being targeted. [5] [6] Children from dysfunctional families or those exposed to violence at home are more vulnerable. However, protective factors include being connected with a supportive family or caring adult, strong peer relationships, and having close friends. [7] [Bass, P and Scholar, S. How to Identify and Treat Bullying . Contemporary PEDS Journal] Empowering children with skills to cope with their feelings has been shown to shield them somewhat from bullying's negative effects. [8]
Children perceived as "different" from their peers are more likely to experience bullying. [9] This includes youth from racial and ethnic minorities, who may also be disproportionately impacted by other factors associated with bullying, such as adverse community and school environments. A strong ethnic identity and positive cultural and family values, however, may protect these children from the hurtful effects of bullying. [10] Likewise, youth from religious minorities or immigrant and refugee groups are targeted more often than their peers. Other examples include children with noticeable physical features, such as birthmarks, tall or short stature, disabilities, and chronic medical conditions, including severe acne, seizures, neurofibromatosis, autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit disorder (ADHD), and obesity. [11] Teens with obesity are twice as likely to be bullied as their normal-weight peers. [12] Children who are socially isolated, unpopular, lacking in interpersonal skills, or those with few friends are vulnerable as well.
Bullying frequently serves to enforce perceived social norms within adolescent peer groups, such as heterosexual relationships and traditional gender roles. Students who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or queer (LGBTQ) often find themselves the targets of bias-based bullying, with a reported incidence nearly twice that of other students. They experience higher rates of verbal bullying, physical bullying, and cyberbullying, leading to injuries, emotional distress, and even suicide.[Earnshaw et al. LBGTQ Bullying . AAP]
Some individuals who engage in bullying behavior may have experienced bullying or victimization themselves. These "bully victims" are at even higher risk of psychosomatic and behavioral problems than their uninvolved peers and report increased rates of suicidal ideation and attempts.[Flannery et al. Bullying and School Violence. Pediatrics Clinics of North America ]
Epidemiology
According to the National Center for Educational Statistics' School Crime Supplement (2019), 22% of students aged 12 to 18 report being bullied at school. Teachers and academic administrators consider it a frequent disciplinary problem, with 14% saying they deal with it daily or at least weekly. The types of bullying reported include being the subject of rumors (15%), verbal taunting (14%), exclusion from activities (6%), being pushed, shoved, tripped, or spit on (5%), physical threats (4%), and coercion for students to do things they did not want to or the destruction of their possessions. (2%)
The CDC (Preventing Bullying, 2023) reports that about 20% of US high school students report being bullied at school, with 17% overall and as many as 30% of girls reporting cyberbullying. Half say that cyberbullying is a "major problem."[Vogels, Emily. Teens and Cyberbullying 2022 ]
About 40% of children report witnessing bullying at their school. [13] This is a global issue, with cited rates internationally ranging from 5% to 45%. [14] Most studies report a greater prevalence among boys than girls, especially among middle school children. For boys, physical and verbal bullying is typical, but girls experience more verbal and social bullying. [15] Traditional bullying peaks around age 12 and then gradually declines. Recent research suggests that social and cyberbullying continue to increase during adolescence. [15] [16] Racial, religious, and ethnic minority youth are disproportionately influenced by bullying, and Black teens experience bullying more than other groups. [17] [18] They are twice as likely as Hispanic or White teens to report they feel their race made them a target of cyberbullying.[Vogels, Emily. Teens and Cyberbullying 2022 ]
Approximately 40% of high school students who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or unsure of their sexual identity report being bullied, while 22% of bisexual high school students report being targeted. LGBTQ students are bullied twice as often as their heterosexual and cisgender peers and are less likely to report it. [19] [20]
History and Physical
Bullying may be the chief complaint for an appointment in a clinical setting. However, many children do not disclose they are targets of bullying, and clinicians should be suspicious when the review of systems is positive for somatic complaints and nonspecific symptoms or warning signs appear in the social history. Bullied children can present with insomnia, nightmares, bedwetting, appetite changes, headaches, and stomachaches. When asked, they may endorse mood swings, feelings of helplessness, poor self-esteem, or suicidal thoughts. Children who are bullied may exhibit psychosomatic symptoms or have previously been diagnosed with anxiety or depression. [21] [22] Social history clues include school absenteeism, declining grades, loss of friends, and lost or damaged belongings such as school books and clothing.
Recognizing at-risk children early may avert long-term consequences. Identifying risk factors can help prevent bullying, and early detection is the first step in intervention. Clinicians who screen for bullying can support affected families and direct them to appropriate resources. They can utilize validated screening tools such as the HEADDS (Home, Education/employment, Activities, Drugs, Sexuality, Suicide/depression) assessment [23] or the Bright Futures questionnaires from the American Academy of Pediatrics.[Hagen et al. Bright Futures. AAP] The Bullying, Cyberbullying, and Social Media Use Pediatric Checklist is available online from the Massachusetts Aggression Reduction Center (www.MARCcenter.org) and is free for clinicians. Identifying victims can be tricky since many children do not readily disclose their involvement in bullying. Clinicians should, therefore, foster an inclusive and affirming healthcare environment where youth feel safe discussing their identities and experiences. [24] This is especially important for LGBTQ patients who may not view their homes or schools as supportive.
About 70% of victims do not want to admit it to an adult, and indirect questioning during the medical history-taking may yield additional information. Inquiring about how school is going or if kids have friends to sit with at lunch may provide insight into how bullying might be a problem. [25]
Physical examination is usually unremarkable, but weight gain or loss alerts clinicians to possible appetite issues, and unexplained bruises or cuts may indicate physical altercations or self-inflicted injuries, necessitating further evaluation.
Primary care clinicians are often asked to evaluate children for learning or behavior problems, including possible ADHD. An example is a teen boy who previously was a strong student, active in sports, and a musician in the school band who presents with declining grades. The teacher questions attention issues since he no longer completes his homework and says he "forgets to do it." Further questioning reveals that a classmate has been confronting him daily after school, grabbing his backpack and dumping its contents. Therefore, he leaves his bag in his locker to avoid these unpleasant encounters and no longer finishes or turns in his assignments. He will not require an educational or psychiatric evaluation for ADHD once the clinician identifies that bullying is the underlying cause of his declining grades.
Another example is a teen immigrant girl with weight loss whose mother is concerned she does not like American school lunches. However, a thorough history and physical examination reveal she has been feeling isolated, and she reports that kids tease her incessantly about her lack of English language skills. No one will sit with her at lunchtime, so she avoids the cafeteria. She admits to mood swings, and the physical examination is notable for self-inflicted cutting scars on her forearms. The clinician must elicit further information to determine if she is at risk of suicidal ideation or behavior before developing a management plan and arranging follow-up.
Bullying belongs to the spectrum of recurrent traumatic experiences of childhood, with similar physiologic, psychologic, social, and cognitive outcomes as child maltreatment or family violence.[Campbell, Kristin. Bullying and Victimization . AAP] According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), trauma-informed care is medical care that recognizes the results of traumatic stress on children and their families. Clinicians are often the first professionals who interact with those affected by trauma and have the opportunity and obligation to respond sensitively. They can ensure a patient's safety and confidentiality, use respectful language, and support autonomy. [26] A trauma-informed physical examination serves to establish trust and reduce feelings of vulnerability or potential triggers of prior traumatic events. [27] [28] In the case of the teen with cutting scars, this may be the first occasion anyone has seen her skin lesions that are usually covered by her clothing. Performing the examination calmly and privately will foster confidence and encourage the girl to relate further relevant details about her unfortunate experiences.
When bullying is suspected or confirmed, the clinician should first speak with the child directly and privately to assess the severity of the problem. Because this may be the first time sharing such sensitive information, the clinician should create a safe space for the child to feel comfortable, using open-ended questions, active listening, and empathy, and ensuring confidentiality unless a situation mandates reporting to authorities.
A simple approach is to ask these three questions:
- Are you being bullied?
- How often does this happen?
- How long has this been going on? [29]
Understanding the nature and extent of the episodes is essential for effective intervention. The clinician must differentiate between physical, verbal, social, and cyberbullying, as each requires a unique approach. Assessing the severity of the incidents helps prioritize support and resources and determine if a child's welfare is threatened and if reporting to child protective services is mandated. Clinicians should also inquire about other forms of victimization, such as child maltreatment and domestic violence, during the confidential interview.
Further evaluation usually co-occurs with treatment and management, as presented in the next section.
Treatment / Management
How can clinicians manage bullying? When bullying is suspected or confirmed, they should gather additional information about the circumstances and context from the patient, caregivers, and teachers if indicated. Next, they must decide whether to provide anticipatory guidance, direct families to helpful resources, refer them to a mental health specialist, or contact the school or appropriate law enforcement authorities. [8] In all cases, clinicians should first ensure the child's safety. Most cases of bullying are not emergencies, but at times, a child is in imminent danger, has been the victim of physical or sexual abuse, or has expressed thoughts of suicidal ideation. Clinicians must know when to elevate the level of care and facilitate transporting such children to the nearest emergency facility for evaluation. [8]
When clinicians treat victims of bullying in an outpatient setting, they must first ensure that children feel safe and realize that they are not at fault. Clinicians can teach them skills to use when confronted by bullies. Children should tell the bully to stop, then walk away and notify a trusted adult. They must inform another adult if they have already reported the circumstances and nothing was done. Clinicians can participate in brief role-playing activities with their patients and encourage parents and caregivers to rehearse successful, assertive behaviors at home with their children. Many parents do not know where to start when their child is a target of bullying and appreciate information from trusted clinicians about the signs and effects of bullying and how to convey their concerns to teachers and counselors. Caregivers can be directed to valuable resources such as stopbullying.org and marccenter.org and encouraged to promote youth activities that build self-esteem, such as sports and hobbies. Clinicians can advise parents and caregivers not to call the bully's parents or try to retaliate but allow the school to investigate. Parents may also benefit from training to discuss bullying and other issues with their children. [25] They must monitor children's online activity, discuss the possible consequences of their media use, and ask if they have experienced any problems online. Clinicians can recommend never forwarding or responding to hurtful messages and advise keeping evidence of inappropriate digital media, blocking cyberbullies, and always informing a trusted adult about inappropriate content. Clinicians can arrange counseling and mental health services when indicated and work with schools and other agencies as applicable to protect victims from further harm.
Most structured bullying interventions occur in academic settings, and clinicians should know about local programs when caregivers and schools seek their expertise in addressing bullying. All states in the US require schools to develop anti-bullying policies and procedures, and similar initiatives exist in many other countries. [14] Clinicians should understand their community's statutes and develop step-by-step strategies to investigate reports when necessary. [30] School-based initiatives vary, but successful programs promote empathy for victims, strengthen coping and socialization skills, educate staff and families, and foster a schoolwide anti-bullying culture. [31] Schools can empower bystanders to intervene when they witness bullying. In one study, 57% of episodes ceased within ten seconds when an onlooker spoke up, but they only did so 15-20% of the time. [32] .[Salmivalli, C. Bullying and the Peer Group . Aggression and Violent Behavior.] On the other hand, bystanders who actively support or encourage bullies can empower them to continue their aggressive behavior. Multidisciplinary interventions targeting peer groups rather than individuals involving families, schools, and communities may have the most impact. [33] [34] Unfortunately, such multifaceted programs are costly, and the effects are difficult to measure. [35] A meta-analysis of such school initiatives reported a mean decrease of approximately 20% in bullying rates, demonstrating room for improvement. [36]
Outside their practices, clinicians can advocate locally, in their states, and nationally to support anti-bullying initiatives. They can work to improve community education and services and lobby to strengthen anti-bullying laws and evidence-based policies that prohibit bullying based on racial, ethnic, or sexual stereotypes.
Clinicians are also likely to care for the perpetrators of bullying. It is essential to denounce the behavior but not the child. Bullies themselves may well have been victims and need to tell their stories. Clinicians should listen without interrupting, remain nonconfrontational, and express concern for the victim. They can set boundaries for acceptable behavior, ask the patient to describe their actions, and suggest ways to improve. Effective clinicians communicate that bullying is always inappropriate and will not be tolerated, but also seek to appreciate the underlying causes or circumstances. They can recommend consistent disciplinary consequences, such as removing privileges or making reparations. They can connect with the child's school and advocate for penalties such as mandated community service rather than suspension or expulsion, which should be reserved for youth exhibiting severely disruptive or aggressive behavior. Overly harsh policies often ignore the underlying social and behavioral issues contributing to bullying and may lead students to abandon formal education early. Bullies should be assessed for psychosocial problems and offered mental health counseling if indicated. Some children may even cease bullying when they become aware of the hurt they have caused others and learn alternative coping methods for their feelings.
Differential Diagnosis
Clinicians can usually elicit a history of bullying if they take the time to ask relevant questions and listen carefully to the patient's responses. However, symptoms frequently associated with bullying may be nonspecific and result from other concerning circumstances, such as peer conflict, dating violence, family dysfunction, harassment, or hazing. [37] These issues must be addressed and treated accordingly. When bullying is identified as the problem, clinicians should evaluate victims for mental health consequences, including posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation, understanding that the presence of multiple coexisting issues may worsen the patient's physical and emotional health.
In the medical model, prognosis predicts disease outcomes, such as recovery, recurrence, and death. Bullying, however, is not a disease, and the focus centers on consequences and complications rather than prognosis. In general use, however, the word prognosis forecasts a likely outcome. The medical and educational literature indicates that unless effective prevention and intervention measures are adopted, the prognosis for bullying is grim, and it will continue to take its toll on children and youth around the globe.
Complications
Bullying is associated with short and long-term adverse physical and mental health outcomes. [38] [39] Even when adequately treated, some physical injuries may cause lingering disabilities. Victims often experience academic difficulties, such as worsening grades, absenteeism, and concentration problems. In recent years, unfavorable consequences have been increasingly recognized for both victims and bullies, including social isolation, anxiety, depression, suicidality, and illicit substance use. [40] [41] These sequelae often continue into adulthood. Stigma-based bullying has been even more strongly associated with health problems than bullying in general. [24]
Victims of severe bullying may feel threatened and depressed and are at risk of developing post-traumatic stress disorder. As adults, they are more likely to carry weapons and have higher rates of suicide attempts and poor psychosocial adjustment. [42] [43] In one study, victims of bullying in grade 5 used more tobacco, marijuana, and alcohol in grade 10. [44] The self-medication hypothesis suggests these substances are consumed to cope with painful emotions related to psychological trauma. [44] Depression, anxiety, relationship problems, poor health, failing academic performance, suicidal ideation and attempts, and sleep problems have all been associated with being bullied. [45] [46] Another study demonstrated homophobic name-calling by nonfriends was linked with increased psychological distress among LGBTQ students, and LGBTQ youth who commit suicide are nearly five times as likely to have been bullied compared with their non-LGBTQ peers who take their own lives. [47] [May 26, 2020. 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0940] LGBTQ bullying is also associated with increased rates of adolescent substance use, including tobacco, alcohol, marijuana, and illicit drugs [48]
Teens who have been physically threatened or in a fight are more likely to bring a weapon to school than other bullying victims or nonvictims. They are also more inclined to display violent behaviors at school, contributing to an unsafe academic environment.[Pham et al. Weapon Carrying Among Victims of Bullying . AAP]
Youth who bully often exhibit a negative attitude towards school and may leave before graduating, especially if they are punished by expulsion. Long-term associated consequences include criminal activities and arrests, intimate partner violence, delinquency, and antisocial behavior. [49] ]
Youth who are "bully victims" may experience even worse outcomes than their peers. They have been reported to have higher rates of child mental health issues, more thoughts of self-harm and suicidality, and increased substance use. [50] [51] [52] Supportive adults at home and school may serve to buffer youth from the effects of bullying on future substance use. Still, controlled studies are lacking because it is difficult to separate bullying from other issues contributing to substance use, such as anxiety or other significant traumatic childhood events.
Consultations
Several school and community bullying prevention centers provide resources and specialized support to counter bullying. In addition, helplines for bullying and cyberbullying are available in many countries.
The following resources are confidential, free, and available 24/7:
Stop Bullying Now Hotline
- 1-800-273-8255 or www.stopbullying.gov
- Established by the US Department of Health and Human Services
- Available to adults and children
The Massachusetts Aggression Reduction Center
www.MARCcenter.org Bullying And Cyberbullying Prevention and Advocacy Collaborative (BACPAC) at Children's Hospital Boston: www.childrenshospital.org/BACPAC
Childline
- 0800 1111 (United Kingdom)
- Available to children under 18 years
- Offers advice and counseling to young people in distress or abusive situations
Kids Helpline
- 1-800-55-1800 (Australia)
- Provides advice to children, parents, and schools
Deterrence and Patient Education
Bullying prevention programs, usually found in school systems, may deter bullying and its effects. Few randomized controlled trials evaluate their efficacy, and it is unlikely that one approach will work in every school or community.[Flnnery et al. Bullying and School Violence. Pediatrics Clinics of North America ] Successful strategies include an academic culture that does not tolerate bullying, involves bystanders, encourages classroom discussions with role-playing, improves supervision in less-structured areas like playgrounds, and offers educational programs for parents and caregivers. Isolated curriculum interventions are less effective than multidisciplinary programs that allow teachers and all school ancillary staff to participate, including cafeteria workers, administrators, custodians, and bus drivers. [53] Some schools use focus groups to guide program content and strategize to understand children's perspectives. [54]
Schools with gay-straight alliance clubs demonstrate increased well-being among LGBTQ students. An example of a statewide effort is the Massachusetts Safe Schools Program for LGBTQ Students, a joint initiative between the Department of Elementary and Secondary Education and the Massachusetts Commission on LGBTQ Youth. It includes classroom instruction, student activities, teacher proficiency workshops, and opportunities for policy development. [24] [55] Clinicians can recommend that communities and schools use ideas from this and similar programs as models when developing their guidelines.
Pearls and Other Issues
Bullying is not primarily a law enforcement issue, but all 50 states in the US have enacted school anti-bullying legislation or policies. Bullying may also appear in the criminal code related to other crimes, such as aggravated harassment or stalking, and may apply to juveniles, depending upon the locale. Clinicians should be informed about the laws in their communities, report incidents when legally required to do so, and continue to advocate for their young patients.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
How can the interprofessional team come together to prevent and intervene with bullying? Pediatricians and other primary care clinicians who care for children are the team leaders for identifying and treating youth affected by bullying. They are experts in advocating for their patients and working with medical specialists, nurses, mental health professionals, teachers, school administrators, parents, and other caregivers.
The first step is to routinely screen youth for bullying exposure and identify subtle indicators when patients do not readily disclose they are victims. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends violence prevention counseling for school-age children and screening at well-child visits beginning at age 6. [56] Clinicians and nurses identify and assess victims and perpetrators of bullying and counsel youth and their caregivers about practical actions. Next, clinicians decide when a referral to a mental health provider or social worker is indicated and arrange appropriate and timely follow-up after the initial consultation. [57]
Clinicians and mental health specialists teach parents and caregivers communication skills and positive discipline strategies since it is known that children from supportive families are more resistant to bullying and less likely to become perpetrators. Family therapists work on reducing anger and improving interpersonal relationships in dysfunctional families since bullying is often only one symptom of maladjustment in the home.
Clinicians advocate for children at school and assist parents and caregivers in connecting with teachers and administrators. They advise schools on the mental and physical health consequences of bullying and serve as a resource when schools establish and promote policies and academic environments that condemn bullying. These programs teach children who are bystanders to intervene and potentially dissuade bullies, who may feel pressure to conform to the behavior of the majority. [58] [59] [57] Schools that foster a culture of empathy and encourage students to report bullying may be more successful in reducing its prevalence and consequences. Teachers, administrators, and school nurses often are firsthand witnesses who communicate their concerns to primary care clinicians who assess children for physical and mental health sequelae. The interprofessional team supporting children's welfare includes child protection agencies and law enforcement officials. Clinicians engage with them to coordinate care when necessary to safeguard at-risk children.
In summary, identifying and addressing bullying takes an interprofessional team led by primary care clinicians, including medical, mental health, educational, law enforcement, and community specialists, who work together to achieve optimal health outcomes for youth experiencing this all-too-frequent public health problem.
Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Muhammad Waseem declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Amanda Nickerson declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
Citations & impact
This article has not been cited yet.
Impact metrics
Alternative metrics.

Similar Articles
To arrive at the top five similar articles we use a word-weighted algorithm to compare words from the Title and Abstract of each citation.
Suicidal Ideation
Harmer B , Lee S , Duong TVH , Saadabadi A
StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) , 23 Dec 2020
Cited by: 0 articles | PMID: 33351435
Florida Domestic Violence
Houseman B , Semien G
StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) , 10 Apr 2018
Cited by: 0 articles | PMID: 29630246
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks
Preuss CV , Kalava A , King KC
StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) , 07 Feb 2019
Cited by: 0 articles | PMID: 30726003
Bullying in children: impact on child health.
BMJ Paediatr Open , 5(1):e000939, 11 Mar 2021
Cited by: 22 articles | PMID: 33782656 | PMCID: PMC7957129
Cyberbullying: Review of an Old Problem Gone Viral.
Aboujaoude E , Savage MW , Starcevic V , Salame WO
J Adolesc Health , 57(1):10-18, 01 Jul 2015
Cited by: 90 articles | PMID: 26095405
Europe PMC is part of the ELIXIR infrastructure
- Brain Development
- Childhood & Adolescence
- Diet & Lifestyle
- Emotions, Stress & Anxiety
- Learning & Memory
- Thinking & Awareness
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Childhood Disorders
- Immune System Disorders
- Mental Health
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Infectious Disease
- Neurological Disorders A-Z
- Body Systems
- Cells & Circuits
- Genes & Molecules
- The Arts & the Brain
- Law, Economics & Ethics
Neuroscience in the News
- Supporting Research
- Tech & the Brain
- Animals in Research
- BRAIN Initiative
- Meet the Researcher
- Neuro-technologies
- Tools & Techniques
- Core Concepts
- For Educators
- Ask an Expert
- The Brain Facts Book

Bullying and the Brain
- Published 30 Apr 2015
- Reviewed 30 Apr 2015
- Author Mary Bates
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
Brain research is revealing that bullying is more than just an unfortunate part of growing up. It can cause long-term changes to the brain that leads to cognitive and emotional deficits as serious as the harm done by child abuse.
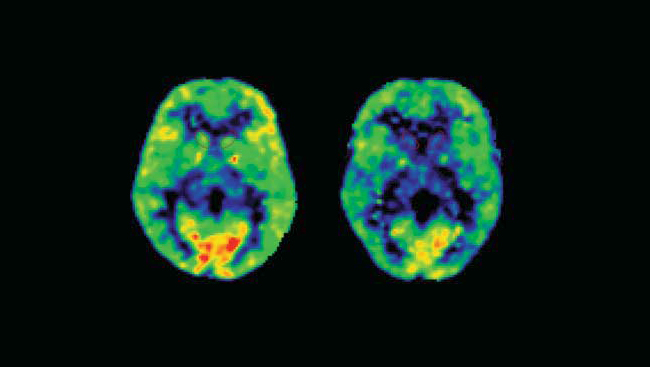
Being bullied is a stressful experience. Victims of bullying often struggle with anxiety, depression , poor self-esteem, and drug abuse — during the bullying and well into adulthood.
It turns out that long-term changes to the brain may be behind these behavioral issues. Bullying can leave a lasting mark on the developing brain, and brain science is starting to show how devastating and persistent the scars of bullying can be.
Stressed Out
Bullying can alter levels of stress hormones, and research in animals and people shows how this can affect brain function.
Chronic stress in humans is a known risk factor for drug abuse, and scientists want to know if being a victim of bullying poses a similar risk. To study this, scientists like Klaus Miczek , a psychologist at Tufts University, model bullying in rodents, often by putting an older, more aggressive rat or mouse in the cage of a juvenile animal. The dominant animal pushes the younger one around, maybe even biting it to show it who’s boss.
Miczek has found that bullied animals have higher amounts of the stress hormone corticosterone in areas of the brain that process rewarding stimuli, like drugs of abuse. He also saw that too much of the hormone can remain in these brain areas long after the stress has ended, possibly leading to a propensity to abuse drugs. When given access to drugs like cocaine and alcohol , Miczek’s bullied rodents took more of the drugs than non-bullied animals, even months later when they were adults.
The most interesting aspect of this research, Miczek says, is how little social stress it takes to lead to a persistent, long-lasting effect. "In rats, it only requires four episodes of social stress, which are five minutes long each," he says. "And the effects of that are seen into adulthood."
Bullying can also alter stress hormones in humans. In a long-term study of teenagers, Tracy Vaillancourt , a psychologist at the University of Ottawa, found that bullied boys and girls have abnormal levels of cortisol compared to their non-bullied peers. Abnormal cortisol levels can weaken the immune system and can even kill nerve cells in the hippocampus , a brain region involved in memory. In fact, Vaillancourt has found that bullied teens perform more poorly on memory tests designed to examine hippocampal functioning compared to their non-bullied peers, suggesting that their abnormal cortisol levels might be affecting their brains.
Immune to Stress
Social stress also has a dramatic effect on immune system functioning, which in turn can negatively affect brain function.
When exposed to stress, our bodies produce more white blood cells, which in turn produce and release more pro-inflammatory substances that normally function to help the body fight off infection. In the case of chronic stress, scientists think the body produces too many white blood cells, resulting in sustained production and release of pro-inflammatory substances.
"When you experience chronic social stress, you have the immune response, but it doesn't turn off properly," says Scott Russo , a neuroscientist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. "The immune system ramps up and doesn't shut down, and that then causes damage such as nerve cell death. In vulnerable individuals, these changes can last for months following the stress."
However, Russo found that some animals are resilient in the face of social stress. When exposed to an aggressive adult, these individuals had fewer white blood cells and pro-inflammatory substances. Russo thinks there is some mechanism by which resilient individuals dampen negative inflammatory responses to stress.
To illustrate the connection between the immune system and behavioral resilience, Russo and his colleagues took immune system cells from resilient mice and injected them into stressed mice. They found that, following the injections, stressed mice showed less social avoidance and anhedonia, the inability to feel pleasure. In effect, the stressed animals received the benefits of the resilient animal's immune system.
The results show that social stress can lead to a heightened immune response which, in turn, can lead to changes in behavior. Russo’s research suggests that dysregulation of the immune system, like that linked to chronic social stress, can lead to psychiatric disorders , such as depression and anxiety.
A Vicious Circle
Not only do victims of bullying experience heightened stress and immune responses, but research in animals suggests that they might also be more likely to become bullies themselves.
Researchers at the University of Texas at Austin studied social stress in hamsters and found that juvenile hamsters who were bullied by an adult became more aggressive toward smaller animals, while being fearful and subordinate with hamsters of similar size or larger.
"Basically, a bully victim becomes a victimizer," says Yvon Delville , who led the study.
Delville also examined the hamsters' brains and found that socially-stressed hamsters showed changes in the levels of the neurotransmitters vasopressin and serotonin. In people, high levels of vasopressin are associated with increased aggression, while serotonin is known to inhibit aggression.
Bullied hamsters had lower levels of vasopressin and higher levels of serotonin than their non-bullied littermates. Delville is currently determining how these changes in neurotransmitter levels lead to enhanced aggression, and he suspects the aggression is secondary to changes in brain areas that govern more general features of behavior, such as impulse control.
Delville's results suggest adolescence may be a sensitive period for the development of aggressive behavior in adulthood, with chronic social stress making it more likely that victims will become bullies themselves. He says his results support what is often observed in humans: where you have violence against children, you'll find children becoming violent.
"People argue that bullying is a rite of passage or it builds character, but that idea is so misguided," Vaillancourt says. "Our work supports the idea that bullying is actually a seriously harmful event in a child's life. It's a public health issue, because it affects so many children adversely and the biological evidence supports that it confers a risk for future health problems."
Not all bullied kids have long-term damage to their brains or changes in their behavior, but those who do may carry these neurological scars for a lifetime. Brain research is helping to recast bullying as a serious form of childhood trauma with the potential to cause long-term chemical and structural damage to the brain.
About the Author

Mary Bates is a freelance science writer interested in the brains and behavior of humans and other animals. For her graduate degree in psychology, she studied the echolocation abilities of big brown bats. She has written for Psychology Today, Scientific American's Mind Matters blog, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and other print and online publications.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
Burke AR, Miczek KA. Stress in adolescence and drugs of abuse in rodent models: role of dopamine, CRF, and HPA axis. Pschopharmacology 231(8): 1557-1580 (2014).
Christoffel DJ, Golden SA, Russo SJ. Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 22(5): 535-549 (2011).
Delville Y, Melloni RH Jr., Ferris CF. Behavioral and neurobiological consequences of social subjugation during puberty in golden hamsters. The Journal of Neuroscience. 18: 2667-2672 (1998).
Norman KJ, Seiden JA, Klickstein JA, Han X, Hwa LS, et al. Social stress and escalated drug self-administration in mice I. Alcohol and corticosterone. Psychopharmacology. 232(6): 991-1001 (2015).
Russo SJ, Murrough J, Han MH, Charney DS, Nestler EJ. Neurobiology of resilience. Nature Neuroscience. 15(11): 1475-1484 (2012).
Vaillancourt T, Duku E, Becker S, Schmidt L, Nicol J, et al. Peer victimization, depressive symptoms, and high salivary cortisol predict poor memory in children. Brain and Cognition. 77: 191-199 (2011).
Vaillancourt T, Duku E, deCatanzaro D, MacMillan H, Muir C, et al. Variation in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity among bullied and non-bullied children. Aggressive Behavior. 34: 294-305 (2008).
Vaillancourt T, Hymel S, McDougall P. The biological underpinnings of peer victimization: Understanding why and how the effects of bullying can last a lifetime. Theory into Practice. 52: 241-248 (2013).
Also In Childhood & Adolescence

Popular articles on BrainFacts.org

Check out the latest news from the field.
Educator Resources
Explain the brain to your students with a variety of teaching tools and resources.
BrainFacts Book
Download a copy of the newest edition of the book, Brain Facts: A Primer on the Brain and Nervous System.

SUPPORTING PARTNERS
- Privacy Policy
- Accessibility Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Manage Cookies
Some pages on this website provide links that require Adobe Reader to view.

Why Are Bullies Popular? Brain Science Can Explain
Research documents the way brains can harness empathy for cruelty..
Posted February 16, 2024 | Reviewed by Monica Vilhauer
- How to Handle Bullying
- Find counselling to support kids or teens
- Brain science has learned the key role empathy plays in abusive behaviors.
- We think our empathy should stop us from bullying, but it can facilitate maltreatment.
- Bullies and abusers use empathy to bond with community, while at the same time targeting victims with cruelty.
- Research shows empathy manifests in two opposing ways that impact our conduct, making it caring or cruel.
Brains harnessing empathy for cruelty is counter-intuitive. In fact, we usually think of someone who is empathic as utterly unable to bully others. Empathy is our innate capacity to recognize what others are thinking, feeling, and intending. Dr. Helen Reiss explains we are born wired for empathy: studies have shown that infants will imitate facial expressions very early as they are mirroring those caring for them.

Researchers have seen that animals who identify the distress or pain of another in their species will halt aggressive behaviour in response. Primatologist Jules Masserman and colleagues conducted research in 1964 that showed rhesus monkeys would not pull a chain to access food when they learned it meant other monkeys would get an electric shock as a result. They chose not to have the food if it caused others to suffer. That is empathy at work.
Empathy is our capacity to walk in someone else’s shoes, see the world from their point of view, feel their pain. Our empathy is critical to our social interactions and our chance of safety and survival by living in community. Bullying is the opposite: it causes pain; it divides people; it shames and conveys the message to the targets that they don’t belong. Bullying does not acknowledge our essential human bond; instead, it dehumanizes.
Bullies are often well-liked in their communities
This is why it’s perplexing that individuals who bully and abuse are also well-liked in the community. They’re often popular, charismatic , and sometimes even have cult-followings. Even children who bully seem able to turn off and turn on their cruel conduct so that only victims are targeted, while other children are treated with kindness. Even children who bully can cover up their harmful behaviour when adults are present.
With adults who bully and abuse, it is more sophisticated. As is extensively documented, they are adept at grooming higher-ups in the workplace, masquerading as the pillar of the community in social circles, as well as virtue-signalling to ensure they are not identified as abusive. This dual personality — one that exudes respectable kindness and the other that defaults to maltreatment of victims — frequently acts as an effective cover-up, even from the law.
Individuals in recent media scandals such as Harvey Weinstein, Larry Nassar, and Bill Cosby are classic examples of abusive individuals who are well-established and honoured in their communities. Their abuse goes on for decades by being systemically ignored as if it is not possible that such respected, powerful, prestigious people could also be extremely harmful to targets. One minute the person is kind and caring, the next minute he’s humiliating someone. How can this person be a “bully-empath”? How can someone be both empathic and abusive?
Empathy is not one brain system, but two
A chilling answer to the bully-empath split is provided in the research and work of neuroscientist Dr. Simon Baron-Cohen. He and his colleagues refer to those who do harm to others as “Zero-Negative” on the empathy spectrum. Those who are Zero-Negative can include individuals who are diagnosed as borderline, narcissistic , and psychopathic . What these individuals have in common from a neuroscience perspective is a severely underactive empathy circuit. Their brains behave in atypical ways when examining the ten interactive regions of the empathy circuit. When researchers look separately at the two empathy systems within the circuit, those who harm others have only one empathy system that is intact and the other that is eroded.
Baron-Cohen’s research offers an answer to the confusing fact that those who bully and abuse also appear to have empathy. A psychopath has “intact cognitive empathy but reduced affective empathy.” In other words, a psychopath who lies, maltreats, abuses, harms others in a variety of ways, and doesn’t care at all about it, has a brain with eroded affective empathy. Our affective empathy is how we feel someone else’s pain. We can see their pain, hear it, and actually experience it. If you see someone cut their hand, you are likely to physically react, recoil, wince.
The psychopath does not feel someone else’s pain. They lack affective empathy. However, they still have access to cognitive empathy. This gives them the advantage of being able to read others. In a cold, calculating way, they can think very adeptly about what someone thinks, what emotions they have, and what intentions they plan. The psychopath – without affective reactions like remorse, guilt , anguish – uses their cognitive insights to create a following and to destroy targets.

When the bullying or abusive individual is reported on or confronted with the harm they are causing, they deny it, and call upon their followers (those they treat with kindness and offer advantages to) in order to vouch for them. The bully or abuser is aware that they are causing harm and they are motivated to cover it up.
Textbook case of Zero-Negative empathy
A textbook example of this is nurse Lucy Letby in the U.K. who doctors reported as suspiciously involved in far too many infant deaths. She accused them of bullying her. The doctors had to issue an apology and this allowed her to continue as a serial killer of babies. Ultimately she was charged and convicted. While Letby was killing the babies, she was also comforting the devastated parents who were thankful for her care and kindness.
Nurse Letby has cognitive empathy. While she did not hesitate to kill seven babies and tried to kill six more, she knew how to manipulate doctors and administrators, and most tragically, she knew how to read grieving parents. If Letby’s brain was studied by Baron-Cohen and his team of neuroscientists, it would show atypical, eroded affective empathy.
Baron-Cohen asserts at the end of his book The Science of Evil that empathy “is the most valuable resource in our world” and he expresses profound concern that it is not the cornerstone of education . He’d like to see empathy prioritized in parenting and policing and especially politics . The erosion of empathy is complex, but environment plays an outsized role. Abuse begets abuse. The neglected, harmed, verbally put down child is far more likely to have atypical affective empathy which can lead to bullying and abusive behaviours. Knowing how critical our two empathy systems (affective and cognitive) are for all individuals, communities, and the world makes us realize how much we need to invest in it.
Baron-Cohen, S. (2011). The Science of Evil. New York: Hachette.

Jennifer Fraser, Ph.D., is an award-winning educator and bestselling author. Her latest book, The Bullied Brain: Heal Your Scars and Restore Your Health , hit shelves and airwaves in April 2022.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Q&A: How and why we studied teens and cyberbullying
Roughly six-in-ten U.S. teens have been bullied or harassed online, according to a new Pew Research Center report that explores teens’ experiences with cyberbullying and their views about it. Senior Researcher Monica Anderson discusses the methods and meaning behind the data.
Bullying has been around for decades, centuries even. Cyberbullying is a newer manifestation of bullying. How did you define cyberbullying for this research?
We’re aware that cyberbullying can be a very nuanced issue. Our own research has shown that what might be harassment to one person might not be considered harassment by another.
At the same time, other studies may use different measures to assess the prevalence of cyberbullying. For this project, we measured six specific incidents that teens might face online or on their cellphone: offensive name-calling, rumor-spreading, being sent explicit images without their consent, having explicit images of themselves shared without their consent, having someone other than a parent constantly asking where they are, what they’re doing or who they’re with, and physical threats. If a teen said they ever had one or more of those experiences, they were considered a target of cyberbullying.
Our definition was designed to show that these experiences can range from less severe forms of harassment – like name-calling that teens may shrug off – to more severe forms of online abuse that includes stalking or physical threats.
Could you explain how surveying teens can be different and, in some ways, more difficult than surveying adults?
One big challenge with surveying teens is that you first have to get consent from a parent. If we’re doing a study of adults, we can call them directly or use our American Trends Panel . Surveying teens requires a second level of contact, and the more times you have to contact respondents, the more difficult it can be.
One of the consistent things we’ve found is that teens have a lot of thoughtful and engaging things to say about their own experiences and what’s going on in the world around them. Monica Anderson
As far as the content of our research, one of the consistent things we’ve found is that teens have a lot of thoughtful and engaging things to say about their own experiences and what’s going on in the world around them. People sometimes wonder if we alter questions so that teens can better understand. At times, we do alter them. We might use phrases like “spreading drama” or “going viral” that have special relevance for teens. But for most of our technology-centered surveys we’re polling teens in the same way we poll adults.
What do you think is a standout finding from the research?
One key finding in our research of adults is that women are more likely than men to face sexualized forms of online harassment – and we see a similar finding in our work dealing with teens as well. For instance, teenage girls are more likely than boys to say they’ve received explicit images they did not ask for. That’s especially true for older teen girls: 35% of girls ages 15 to 17 have received unwanted explicit images.
Your previous research has shown that 41% of U.S. adults have personally experienced online harassment. In this report, we learn that 59% of U.S. teens have been bullied or harassed online. Can you talk about the differences between these two results?
For starters, we are looking at two different groups of people in these surveys, so we’d expect that their experiences might vary. But there are also striking similarities in the findings if you compare young adults and the teens. It’s clear that harassment is incredibly common for both groups: A majority of 18- to 29-year-olds say they’ve experienced some type of harassment online.
Teenage girls are more likely than boys to say they’ve received explicit images they did not ask for. That’s especially true for older teen girls: 35% of girls ages 15 to 17 have received unwanted explicit images. Monica Anderson
We also tailored some questions in an effort to capture the lived experiences of adults and young people. For example, we use slightly different questions to measure online harassment in our surveys of teens and adults. When we conducted focus groups with teens, they often mentioned how easy it is for people to spread rumors or lies about others via texting and social media. So, we explicitly include “spreading false rumors” in our surveys of teens.
But although some questions differ, there are consistencies in the overall findings. For example, name-calling is the most common form of online harassment for both teens and adults. And as noted above, adult women and teenage girls are more likely to experience sexualized forms of online harassment when compared with their male counterparts.
While the report is mainly based on teens’ experiences with cyberbullying, it also addresses parents’ views of the issue and discusses how teens rate certain groups, including parents and teachers, when it comes to addressing cyberbullying. What were some of the findings related to these other groups?
In general, parents are quite confident in their ability to teach their children about what they should and shouldn’t share online. It’s also very clear that both teens and parents see this as an important issue: About six-in-ten teens say that cyberbullying is a major problem for people their age, and a similar share of parents say they worry about their teen being harassed or bullied online. In fact, parents are one of the few groups that teens give relatively high marks when asked how they are doing at addressing cyberbullying.
Cyberbullying is becoming more present in people’s minds due to the recent research, documentaries and news stories about it. How do you think this contributes to the Center’s work, as well as to broader research on technology and its impact on society?
The issue of cyberbullying has been front and center in the public consciousness lately, with a number of lawmakers and first lady Melania Trump taking a stand on the subject. A number of states have enacted legislation on the topic, and school districts across the country are looking for ways to deal with the issue. We hope this research helps to shed light on the extent to which harassment and bullying have become a common feature of teen life and brings teens’ own voices and experiences to the broader debate.
Cyberbullying will inevitably change as technology does. Looking forward, are there ways that your team would like to expand the research?
One of the biggest policy questions surrounding this topic is how the public reconciles the desire for people being able to speak their mind freely, while simultaneously ensuring that people can still feel welcome and safe online. Our research with adults has found that Americans are divided on this question, and they can struggle to find consensus on what sorts of behaviors cross the line into outright harassment. There is a lot of work to be done to unpack public perceptions of these deeper issues that often underscore debates about online harassment.
In addition, our teens survey shows that young people generally have a negative assessment of how key groups (with the exception of their parents) are tackling cyberbullying. It would be worth understanding why teens feel this way and hearing their thoughts on what – if anything – can be done to curtail bad online behavior.
- Methodological Research
- Online Harassment & Bullying
- Online Privacy & Security
- Platforms & Services
- Privacy Rights
- Teens & Tech
- Teens & Youth

A.W. Geiger is a former associate digital producer and writer for Pew Research Center
Online opt-in polls can produce misleading results, especially for young people and Hispanic adults
Who are you the art and science of measuring identity, q&a: how we used large language models to identify guests on popular podcasts, q&a: how – and why – we’re changing the way we study tech adoption, state of the news media methodology, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

COMMENTS
Introduction. With its negative consequences for wellbeing, bullying is a major public health concern affecting the lives of many children and adolescents (Holt et al. 2014; Liu et al. 2014 ). Bullying can take many different forms and include aggressive behaviours that are physical, verbal or psychological in nature (Wang, Iannotti, and Nansel ...
Objective To examine recent trends in bullying and mental health problems among adolescents and the association between them. Method A questionnaire measuring mental health problems, bullying at school, socio-economic status, and the school environment was distributed to all secondary school students aged 15 (school-year 9) and 18 (school-year 11) in Stockholm during 2014, 2018, and 2020 (n ...
Abstract. During the school years, bullying is one of the most common expressions of violence in the peer context. Research on bullying started more than forty years ago, when the phenomenon was defined as 'aggressive, intentional acts carried out by a group or an individual repeatedly and over time against a victim who cannot easily defend him- or herself'.
Bullying involvement is associated with feelings of being unsafe, poor relationships and social support, poor academic outcomes, and an increased risk of depression and other mental health issues. Friends (64%) followed by parents or guardians (57%) and then teachers and other staff members (46%) are the people students most commonly turn to ...
Although attention to bullying has increased markedly among researchers, policy makers, and the media since the late 1990s, bullying and cyberbullying research is underdeveloped and uneven. Despite a growing literature on bullying in the United States, a reliable estimate for the number of children who are bullied in the United States today still eludes the field (Kowalski et al., 2012; Olweus ...
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand U.S. children's experiences with bullying, both online and in person. Findings are based on surveys conducted by the Center, as well as data from the Bureau of Justice Statistics, the National Center for Education Statistics and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Bullying is a prevalent concern, with approximately 20% of youth in the United States reporting being victimized by this significant social stressor (Musu et al., 2019).Although prevention efforts have improved knowledge, attitudes, and self-perceptions about bullying, most programs demonstrate less significant change in actual bullying behaviors (Rettew & Pawlowski, 2016; Yeager et al., 2015).
WASHINGTON — A special issue of American Psychologist® provides a comprehensive review of over 40 years of research on bullying among school age youth, documenting the current understanding of the complexity of the issue and suggesting directions for future research. "The lore of bullies has long permeated literature and popular culture.
Key points. Bullying is seen as a moral issue, but a meta-analysis of research shows it's a medical issue. Bullying, along with child maltreatment, can do physical damage to important brain regions.
Defining and Contextualising Bullying. While certain individuals are more likely to bully (psychological dimension), the structures in which they exist (sociological dimension) can also contribute towards an environment (educational dimension) where bullying is more acceptable.Furthermore, social media and other online spaces (technological dimension) are now extending the nature and scope of ...
Bullying behavior is a serious problem among school-age children and adolescents; it has short- and long-term effects on the individual who is bullied, the individual who bullies, the individual who is bullied and bullies others, and the bystander present during the bullying event. In this chapter, the committee presents the consequences of bullying behavior for children and youth. As ...
Research studies looking at links between bullying and the brain have demonstrated it also can have significant cognitive and emotional consequences, much like other adverse childhood experiences such as neglect or family violence. The results are so striking that bullying is now seen as a global public health problem with impacts on child ...
Bullying. Bullying is a form of aggressive behavior in which someone intentionally and repeatedly causes another person injury or discomfort. Bullying can take the form of physical contact, words, or more subtle actions. The bullied individual typically has trouble defending him or herself and does nothing to "cause" the bullying.
1. Psychological: Being a victim of bullying was associated with increased depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Victims of bullying reported more suicidal thinking and engaged in greater self ...
Bullying first emerged as an important topic of research in the 1980s, following the tragic suicides of young boys in Norway, the reason for which was attributed to bullying victimization (Olweus, 1993). Today, this form of aggressive behavior remains a prevalent problem among young people globally.
Continuing Education Activity. Bullying is a serious and widespread global problem with detrimental consequences for the physical and mental well-being of children. It is a repeated and deliberate pattern of aggressive or hurtful behavior targeting individuals perceived as less powerful. Bullying manifests in various forms, such as physical ...
Brain research is revealing that bullying is more than just an unfortunate part of growing up. It can cause long-term changes to the brain that leads to cognitive and emotional deficits as serious as the harm done by child abuse. The stress caused by bullying can negatively affect the developing brain. Stressed animals can show increased levels ...
Brain science has learned the key role empathy plays in abusive behaviors. We think our empathy should stop us from bullying, but it can facilitate maltreatment. Bullies and abusers use empathy to ...
Bullying is aggressive behavior that is intentional and involves an imbalance of power or strength. It is a repeated behavior and can be physical, verbal, or relational. While boys may bully others using more physical means, girls often bully others by social exclusion. Bullying has been part of school, and even workplaces, for years.
Abstract. Bullying is a severe problem that is experienced, especially in schools. Children belong to the same social group, but some feel powerful than others and therefore take advantage of them ...
Research. Topic 1: Bullying in schools; Research Title: Consequences of bullying in schools; Research objectives: Students can understand what bullying is. Students understand how bullying works. Students know that bullying may contribute to later difficulties with health and well-being. Students know the consequences of bullying in school ...
Research shows that this age-old saying simply isn't true. Often, the physical impact of bullying (the "sticks and stones") is easy to recognize, such as a child getting up after being pushed, damaged personal items, or having torn clothing. However, bullying often impacts our children in ways that aren't so obvious.
Roughly six-in-ten U.S. teens have been bullied or harassed online, according to a new Pew Research Center report that explores teens' experiences with cyberbullying and their views about it. Senior Researcher Monica Anderson discusses the methods and meaning behind the data. Bullying has been around for decades, centuries even.
3. Sexual bullying: this refers to use dirty words, touch, or threat of doing. 4. Psychological bullying: harassment, threats and intimidation, humiliation and rejection from the group. 5. Bullying in social relations: preventing some individuals from exercising certain activities or reject their friendship or spreading rumors about others. 6.