Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School

This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., guide to the ap u.s. history exam.

The AP ® U.S. History exam, also known as APUSH, is a college-level exam administered every year in May upon the completion of an Advanced Placement U.S. History course taken at your high school. If you score high enough, you could earn college credit!
Check out our AP U.S. History Guide for the essential info you need about the exam:
- AP U.S. History Exam Overview
- AP U.S. History Sections & Question Types
- AP U.S. History Scoring
- How to Prepare
What's on the AP U.S. History Exam?
The College Board requires your AP teacher to cover certain topics in the AP U.S. History course. As you complete your APUSH review, make sure you are familiar with the following topics:
- Period 1 (1491–1607) : Native American Societies Before European Contact; European Exploration in the Americas; Columbian Exchange, Spanish Exploration, and Conquest; Labor, Slavery, and Caste in the Spanish Colonial System; Cultural Interactions Between Europeans, Native Americans, and Africans
- Period 2 (1607–1754) : European Colonization; The Regions of British Colonies; Transatlantic Trade; Interactions Between American Indians and Europeans; Slavery in the British Colonies; Colonial Society and Culture
- Period 3 (1754–1800) : The Seven Years’ War (The French and Indian War); Taxation Without Representation; Philosophical Foundations of the American Revolution; The American Revolution; The Influence of Revolutionary Ideals; The Articles of Confederation; The Constitutional Convention and Debates over Ratification; The Constitution; Shaping a New Republic; Developing an American Identity; Movement in the Early Republic
- Period 4 (1800–1848) : The Rise of Political Parties and the Era of Jefferson; Politics and Regional Interests; America on the World Stage; Market Revolution: Industrialization; Market Revolution: Society and Culture; Expanding Democracy; Jackson and Federal Power; The Development of an American Culture; The Second Great Awakening; An Age of Reform; African Americans in the Early Republic; The Society of the South in the Early Republic
- Period 5 (1844–1877) : Manifest Destiny; The Mexican–American War; The Compromise of 1850; Sectional Conflict: Regional Differences; Failure of Compromise; Election of 1860 and Secession; Military Conflict in the Civil War; Government Policies During the Civil War; Reconstruction; Failure of Reconstruction
- Period 6 (1865–1898) : Westward Expansion: Economic Development; Westward Expansion: Social and Cultural Development; The “New South”; Technological Innovation; The Rise of Industrial Capitalism; Labor in the Gilded Age; Immigration and Migration in the Gilded Age; Responses to Immigration in the Gilded Age; Development of the Middle Class; Reform in the Gilded Age; Controversies over the Role of Government in the Gilded Age; Politics in the Gilded Age
- Period 7 (1890–1945) : Imperialism: Debates; The Spanish–American War; The Progressives; World War I: Military and Diplomacy; World War I: Home Front; 1920s: Innovations in Communication and Technology; 1920s: Cultural and Political Controversies; The Great Depression; The New Deal; Interwar Foreign Policy; World War II: Mobilization; World War II: Military; Postwar Diplomacy
- Period 8 (1945–1980) : The Cold War from 1945 to 1980; The Red Scare; Economy after 1945; Culture after 1945; Early Steps in the Civil Rights Movement (1940s and 1950s); America as a World Power; The Vietnam War; The Great Society; The African American Civil Rights Movement (1960s); The Civil Rights Movement Expands; Youth Culture of the 1960s; The Environment and Natural Resources from 1968 to 1980; Society in Transition
- Period 9 (1980–Present): Reagan and Conservatism; The End of the Cold War; A Changing Economy; Migration and Immigration in the 1990s and 2000s; Challenges of the 21 st Century
Read More: Review for the exam with our AP U.S. History Crash Courses
Sections & Question Types
The APUSH exam takes 3 hours and 15 minutes to complete and is comprised of two sections: a multiple-choice/short answer section and a a free response section. There are two parts to each section.
APUSH Multiple Choice Questions
Questions are grouped into sets of three or four questions and based on a primary source, secondary source, or historical issue. Each set of questions is based on a different piece of source material. This section will test your ability to analyze and engage with the source materials while recalling what you already know about U.S. history.
APUSH Short Answer Questions
The three questions in this section will be tied to a primary source, historical argument, data or maps, or general propositions of U.S. history. Students are required to answer the first and second questions and then answer either the third or the fourth question. You are not required to develop and support a thesis statement, but you must describe examples of historical evidence relevant to the source or question.
APUSH Document-Based Question (DBQ)
The DBQ question requires you to answer a question based on seven primary source documents and your knowledge of the subject and time period. All the documents will pertain to a single subject. Students should develop an argument about the question and use the documents to support this argument.
APUSH Long Essay Question
For the long essay question, you’ll be given a choice of three essay options on the same theme, and you must choose one. You must develop and defend a relevant thesis, but there won’t be any documents on which you must base your response. Instead, you’ll need to draw upon your own knowledge of topics you learned in your AP U.S. History class.
For a comprehensive content review, check out our book, AP U.S. History Prep
What’s a good AP U.S. History Score?
AP scores are reported from 1 to 5. Colleges are generally looking for a 4 or 5 on the AP U.S. History exam, but some may grant credit for a 3. Here’s how students scored on the May 2020 test:
Source: College Board
How can I prepare?
AP classes are great, but for many students they’re not enough! For a thorough review of AP U.S. History content and strategy, pick the AP prep option that works best for your goals and learning style.
- AP Exams

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
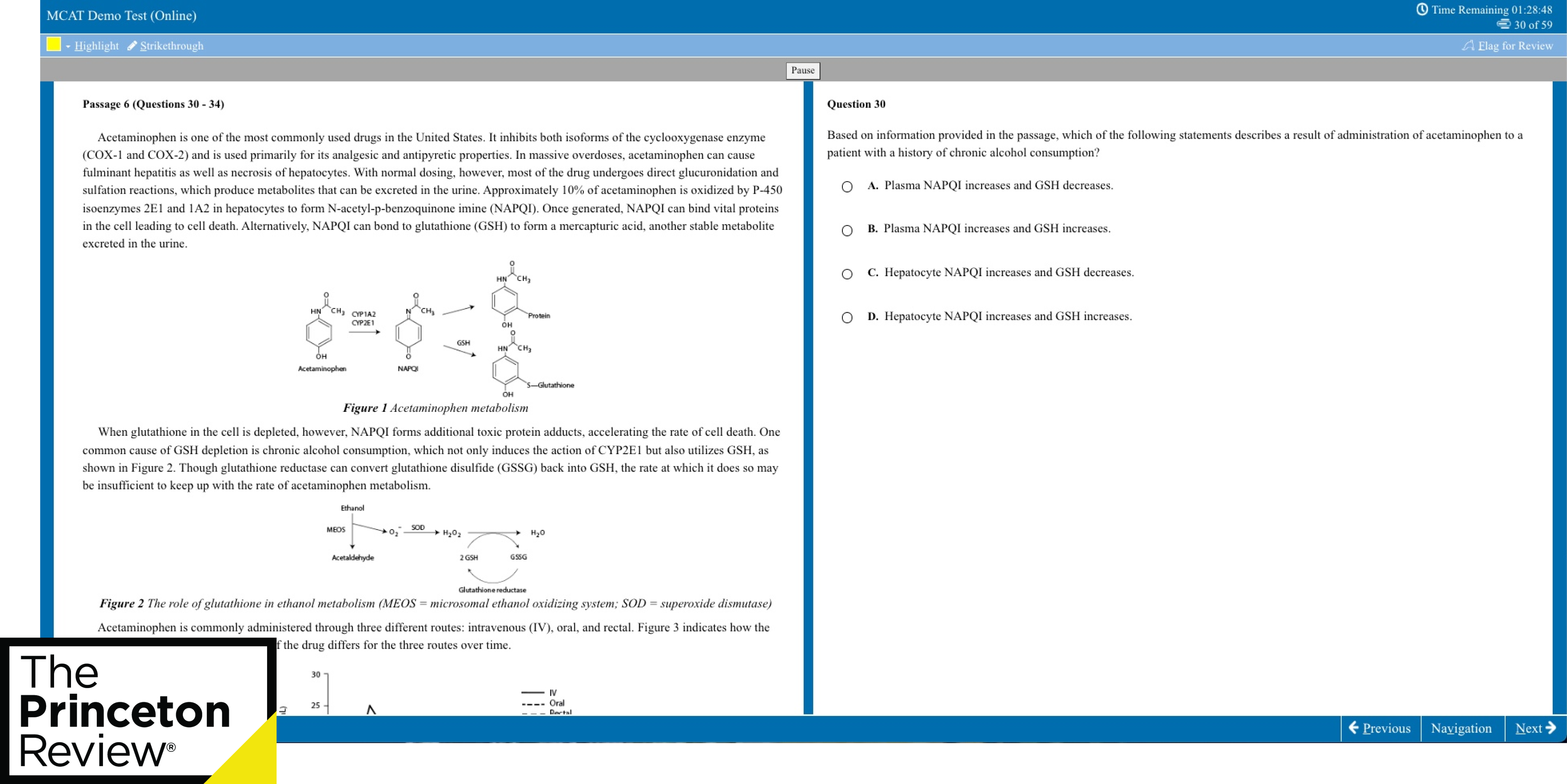
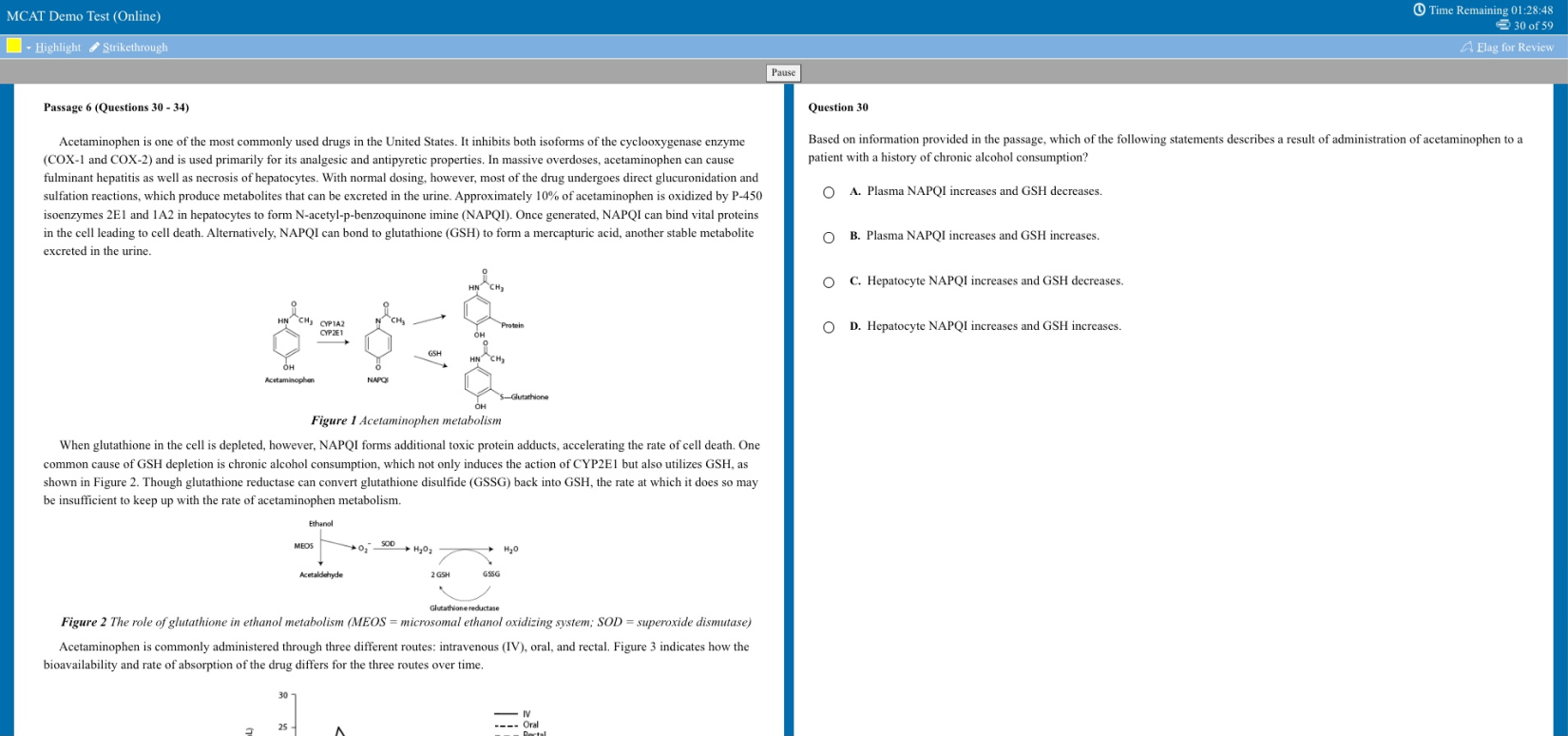
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.

MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.

APUSH Long Essay Question Example 2
Evaluate the extent to which the civil war was a turning point in the history of the united states in the period from 1800 to 1877..
- What were the major events leading up to the Civil War?
- How did the Civil War change political, economic, and social structures in the U.S.?
- What were the immediate and long-term consequences of the Civil War?
- Were there any other significant turning points during this period? How do they compare to the Civil War?
- How did the Reconstruction era that followed the Civil War further shape the nation?
- Thesis/Claim (1 point): The APUSH exam requires students to present a clear, precise, and defensible thesis in their essay. In the sample essay, the thesis is evident in the statement, “The Civil War, fought between 1861 and 1865, stands as a monumental turning point in the history of the United States.” This thesis directly addresses the prompt and sets the stage for the arguments that follow.
- Contextualization (1 point): To earn this point, students must describe a broader historical context relevant to the prompt. The essay does this by outlining the tensions between the North and the South, mentioning key events like the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850. This provides readers with a clear backdrop against which the main arguments of the essay are set.
- Evidence (2 points): The APUSH standards require students to support their thesis with specific evidence. In the sample essay, there’s a plethora of evidence cited, such as the election of Abraham Lincoln, the Emancipation Proclamation, the Homestead Act, and the Reconstruction Amendments. Each piece of evidence is directly related to the thesis and supports the argument that the Civil War was a significant turning point.
- Analysis and Reasoning (2 points): This is where students must demonstrate a deeper understanding of the topic. The essay does this in two ways. First, it analyzes the significance of each piece of evidence, explaining, for example, how the Emancipation Proclamation and the 13th Amendment changed the lives of African Americans. Second, it shows a complex understanding by comparing the impact of the Civil War to other events of the period, such as the Market Revolution and the Second Great Awakening. This comparison not only reinforces the thesis but also provides a nuanced view of the period.
When you are done reviewing this APUSH LEQ example, you can use the buttons below to proceed to our Long Essay example 3 or return to the Practice Exam main menu.
Find what you need to study
AP World Long Essay Question (LEQ) Overview
15 min read • may 10, 2022

Zaina Siddiqi
Exam simulation mode
Prep for the AP exam with questions that mimic the test!
Overview of the Long Essay Question (LEQ)
Section II of the AP Exam includes three Long Essay Question (LEQ) prompts. You will choose to write about just one of these.
The formatting of prompts varies somewhat between the AP Histories, though the rubric does not. In AP World History, the prompt includes a sentence that orients the writer to the time, place, and theme of the prompt topic, while prompts in AP US History and AP European History typically do not. However, the rubrics and scoring guidelines are the same for all Histories.
Your answer should include the following:
A valid thesis
A discussion of relevant historical context
Use of evidence supports your thesis
Use of a reasoning skill to organize and structure the argument
Complex understanding of the topic of the prompt
We will break down each of these aspects in the next section. For now, the gist is that you need to write an essay that answers the prompt, using evidence. You will need to structure and develop your essay using one of the course reasoning skills.
Many of the skills you need to write a successful LEQ essay are the same skills you will use on the DBQ. In fact, some of the rubric points are identical, so you can use a lot of the same strategies on both writing tasks!
You will have three choices of prompts for your LEQ. All three prompts will focus on the same reasoning skills, but the time periods will differ in each prompt. Prompt topics may span across time periods specified in the course outline, and the time period breakdowns for each prompt are as follows:
Writing time on the AP Exam includes both the Document Based Question (DBQ) and the (LEQ), but it is suggested that you spend 40 minutes completing the LEQ. You will need to plan and write your essay in that time.
A good breakdown would be 5 min. (planning) + 35 min. (writing) = 40 min.
The LEQ is scored on a rubric out of six points, and is weighted at 15% of your overall exam score. We’ll break down the rubric next.
How to Rock the LEQ: The Rubric
The LEQ is scored on a six point rubric, and each point can be earned independently. That means you can miss a point on something and still earn other points with the great parts of your essay.
Note: all of the examples in this section will be for this prompt from AP World History: Modern. You could use similar language, structure, or skills to write samples for prompts in AP US History or AP European History.
Let’s break down each rubric component...
What is it?
The thesis is a brief statement that introduces your argument or claim, and can be supported with evidence and analysis. This is where you answer the prompt.
Where do I write it?
This is the only element in the essay that has a required location. The thesis needs to be in your introduction or conclusion of your essay. It can be more than one sentence, but all of the sentences that make up your thesis must be consecutive in order to count.
How do I know if mine is good?
The most important part of your thesis is the claim , which is your answer to the prompt. The description the College-Board gives is that it should be “historically defensible,” which really means that your evidence must be plausible. On the LEQ, your thesis needs to be related topic of the prompt.
Your thesis should also establish your line of reasoning. Translation: address why or how something happened - think of this as the “because” to the implied “how/why” of the prompt. This sets up the framework for the body of your essay, since you can use the reasoning from your thesis to structure your body paragraph topics later.
The claim and reasoning are the required elements of the thesis. And if that’s all you can do, you’re in good shape to earn the point.
Going above-and-beyond to create a more complex thesis can help you in the long run, so it’s worth your time to try. One way to build in complexity to your thesis is to think about a counter-claim or alternate viewpoint that is relevant to your response. If you are using one of the course reasoning process to structure your essay (and you should!) think about using that framework for your thesis too.
In a causation essay, a complex argument addresses causes and effects.
In a comparison essay, a complex argument addresses similarities and differences.
In a continuity and change over time essay, a complex argument addresses change and continuity .
This counter-claim or alternate viewpoint can look like an “although” or “however” phrase in your thesis.
Powers in both land-based and maritime empires had to adapt their rule to accommodate diverse populations. However, in this era land-based empires were more focused on direct political control, while the maritime empires were more based on trade and economic development.
This thesis works because it clearly addresses the prompt (comparing land and maritime empires). It starts by addressing a similarity, and then specifies a clear difference with a line of reasoning to clarify the actions of the land vs. maritime empires.
Contextualization
Contextualization is a brief statement that lays out the broader historical background relevant to the prompt.
There are a lot of good metaphors out there for contextualization, including the “previously on…” at the beginning of some TV shows, or the famous text crawl at the beginning of the Star Wars movies.
Both of these examples serve the same function: they give important information about what has happened off-screen that the audience needs to know to understand what is about to happen on-screen.
In your essay, contextualization is the same. You give your reader information about what else has happened, or is happening, in history that will help them understand the specific topic and argument you are about to make.
There is no specific requirement for where contextualization must appear in your essay. The easiest place to include it, however, is in your introduction . Use context to get your reader acquainted with the time, place, and theme of your essay, then transition into your thesis.
Good contextualization doesn’t have to be long, and it doesn’t have to go into a ton of detail, but it does need to do a few very specific things.
Your contextualization needs to refer to events, developments and/or processes outside the time and place of the prompt. It could address something that occurred in an earlier era in the same region as the topic of the prompt, or it could address something happening at the same time as the prompt, but in a different place. Briefly describe this outside information.
Then, connect it to your thesis/argument. The language from the College Board is that contextualization must be “relevant to the prompt,” and in practical terms this means you have to show the connection. A transition sentence or phrase is useful here (plus, this is why contextualization makes the most sense in the introduction!)
Also, contextualization needs to be multiple consecutive sentences, so it’s all one argument (not sprinkled around in a paragraph). The introduction is the best place for contextualization, but not the only place.
Basically, choose a connected topic that “sets the stage” for your thesis, and briefly describe it in a couple sentences. Then, make a clear connection to the argument of your thesis from that outside information.
In the period 1450-1750, both European and Asian powers expanded their reach and created large empires across the world. In Asia, the trend was toward large, land-based empires which were controlled from a central capital city. Europeans built empires that stretched across oceans included territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
This contextualization works by addressing the time period of the prompt and establishing basic definitions for empire-building and the types of empires (land and maritimes.) These definitions will be valuable context for seeing the comparisons developed in the thesis and body paragraphs of this essay.
Evidence: Provide Specific Examples
For this point, the focus is simply about having evidence. Evidence is the historical detail you include in your writing. The specific facts and examples that prove your argument. In the LEQ, your evidence comes your knowledge of history.
Evidence goes in your body paragraphs. In fact, the bulk of your body paragraphs will be made up of evidence and supporting analysis or commentary that connects that evidence to other evidence and/or to the argument you are making.
Good evidence is specific, accurate, and relevant to the prompt. For this point, simply including multiple pieces of quality evidence is enough. If you’re a numbers person, a good starting point is to aim for two pieces of quality evidence in each body paragraph and go up from there.
In order for your evidence to count for this point, it needs to be really specific. Using course-specific vocabulary is a great strategy here to know that you are writing specific evidence. If you can’t remember a specific vocabulary term, describe what you mean in plain language with as much detail as possible.
Though the Ottoman Sultans were Muslims, they ruled over a population that included fellow Muslims, Christians, and Jews.
This evidence works because it includes specific and relevant details, namely the religions of both the Ottoman rulers and the diverse population they ruled over.
Evidence: Supports an Argument with Evidence
In addition to having evidence, this point is about using that evidence to support an argument in response to the prompt. Basically, connect your evidence back to your topic sentence and/or thesis.
Supporting statements go with your evidence in your body paragraph. Ideally, a connecting statement comes right before or after a piece of evidence.
This point is harder to earn than the previous evidence point, because it’s a little more difficult to explain fully.
One way to know if you are doing this at all is to look at the topic sentences of your body paragraphs. First of all, do you have one? You should. The first sentence of your body paragraph should make it clear what you are talking about in that paragraph. It should relate to some aspect of your thesis, and it should be connected to the reasoning skill you have chosen to organize your argument.
One characteristic shared by both kinds of empires was the need to adapt to diverse populations. As the Ottoman empire expanded its influence, it took over territory previously controlled by the Byzantines. Though the Ottoman Sultans were Muslims, they now ruled over a population that included fellow Muslims, Christians, and Jews. In order to keep peace within their empire, the Ottomans allowed people to continue practicing their traditional faiths. Ottoman cities such as Istanbul had areas of the cities set aside where different groups could live and worship without interference from others .
This section works because it defines the adaptation made by Ottoman rulers to effectively rule a diverse population, and elaborates on both how and why that adaptation was made.
Following your topic sentence, your body paragraph should elaborate on the idea in that topic sentence, using the evidence to prove your point. At first, you may rely on phrases like “this shows…” or “this means…,” which can get repetitive, but may also help you know when you are making the connections between evidence and argument explicit.
Analysis and Reasoning: Historical Reasoning
A good argument needs structure, and yours needs to use one of the course reasoning skills to create that structure. You can choose whichever skill works best for a particular prompt: causation , comparison , or continuity and change over time .
Strong reasoning goes throughout an essay, so this will be the overarching structure of your writing from the thesis through your body paragraphs.
The reasoning doesn’t necessarily have to be completely balanced or even in order to count, which gives you room to write about what you know best. For example, in an essay structured around continuity and change, you might spend most of your time addressing changes and relatively little time addressing continuity. And that’s ok.
The best essays do address both “sides” of the historical reasoning, and yours should too. If you created a complex thesis in your introduction, you can extend those ideas into your body paragraphs. Even if you don’t have equal sentences or paragraphs for each topic, as long as you address the reasoning process in your essay, you’re on the right track.
Analysis and Reasoning: Complexity
The second part of the Analysis and Reasoning scoring category is complexity. This is by far the most challenging part of the LEQ, and the point earned by the fewest students. It isn’t impossible, just difficult. Part of the difficulty is that it is the least concrete skill to teach and practice.
If you’re already feeling overwhelmed by the time limits of the LEQ, don’t stress about complexity. Focus on writing the best essay you can that answers the prompt. Plenty of students earn 5’s without the complexity point.
If you are ready to tackle this challenge, keep reading!
The College Board awards this point for essays that “demonstrate a complex understanding” of the topic of the prompt.
Complexity cannot be earned with a single sentence or phrase. It must show up throughout the essay.
A complex argument starts with a complex thesis. A complex thesis must address the topic of the prompt in more than one way. Including a counter-claim or alternate viewpoint in the thesis is a good way to set up a complex argument, because it builds in room within the structure of your essay to address more than one idea (provided your body paragraphs follow the structure of your thesis!)
A complex argument may include corroboration - evidence that supports or confirms the premise of the argument. Clear explanation that connects each piece of evidence to the thesis will help do this. In the LEQ, your evidence is all from your knowledge of history, so it’s up to you to fully explain how that evidence backs up your thesis. Consistent, thoughtful explanation can go a long way toward the complexity point.
A complex argument may also include qualification - evidence that limits or counters an initial claim. This isn’t the same as undoing or undermining your claim. Qualifying a claim shows that it isn’t universal. An example of this might be including continuity in an essay that is primarily about change.
A final way to introduce complexity to your argument is through modification - using evidence to change your claim or argument as it develops. Modification isn’t quite as extreme as qualification, but it shows that the initial claim may be too simple to encompass the reality of history.
Since no single sentence can demonstrate complexity on its own, it’s difficult to show examples of complex arguments. Fully discussing your claim and its line of reasoning, and fairly addressing your counter-claim or alternate view is the strongest structure to aim for a complexity point. Explain everything as you go and aim for success!
How to Rock the LEQ: The Process
Before you start writing....
It is tempting to just start writing at the beginning of your LEQ time, especially if you took extra time to write your DBQ and you’re feeling some pressure. It’s actually better to take a few minutes to analyze the prompt and plan your essay before you start writing to give yourself the best shot at success. You might surprise yourself with how quickly an essay comes together after you create a solid plan.
The very first thing you should do with any prompt is to be sure you understand the question . Misunderstanding the time period, topic, or geographic region of a prompt can kill a thoughtful and well-argued essay. When you’re practicing early in the year, go ahead and re-write the prompt as a question. Later on you can re-phrase it mentally without all the work.
As you think about the question, start thinking about which reasoning skill might apply best for this prompt: causation, comparison, or continuity and change over time.
Original prompt - Develop an argument that compares the process of empire building in land-based and maritime empires in the period 1450-1750 CE.
Revised - What were the key similarities and differences in the ways that land-based (Asian) and maritime (European) empires built their governments and power between 1450-1750?
Now that you know what you’re writing about, take a few minutes to brainstorm what you know about that topic. You can make a simple graphic organizer to help you see relationships between information (i.e. a Venn diagram, T-chart, timeline, etc.), or just jot down ideas as they come to mind.
Go back over you list and mark which ideas work best as context (generally broader and less related to the prompt) and which ideas work best as evidence (more specific.)
If you have time, brainstorm a sample thesis and/or outline for how you want to structure your ideas. This may seem like an extravagance with limited time, but it can be a great cheat sheet for you if you lose your way in the middle of a body paragraph.
When you have a plan you like, start writing!
Writing the essay
Your introduction should include your contextualization and thesis. Start with a statement that establishes your time and place in history, and follow that with a brief description of the historical situation. Connect that broader context to the theme and topic of the prompt. Then, make a claim that answers the prompt, with an overview of your reasoning and any counter-claim you plan to address.
Body paragraphs will vary in length, depending on how many documents or other pieces of evidence you include, but should follow a consistent structure. Start with a topic sentence that introduces the specific aspect of the prompt that paragraph will address. There aren’t specific points for topic sentences, but they will help you stay focused.
Follow your topic sentence with a piece of evidence and connect it back to your topic sentence and/or thesis. Continue with 1-2 pieces of evidence and more explanation until you have completed the argument of your topic sentence. Then start a new paragraph with a new topic sentence.
Each body paragraph will follow this general format, and there is no set number of paragraphs for the LEQ (minimum or maximum.) Write as many paragraphs as you need to fully answer the prompt by developing the argument (and counter-argument if applicable) from your thesis.
If you have time, you may choose to write a conclusion . It isn’t necessary, so you can drop it if you’re rushed. BUT, the conclusion is the only place where you can earn the thesis point outside the introduction, so it’s not a bad idea. You could re-state your thesis in new wording, or give any final thoughts in terms of analysis about your topic. You might solidify your complexity point in the conclusion if written well.
Since most people write the DBQ first, when you finish the LEQ you’re done with your AP Exam. Congratulations!
Sample Prompts
AP World History: Modern
In the period 1450-1750 CE, empires achieved increased scope and influence around the world, shaping and being shaped by the diverse populations they incorporated.
Develop an argument that compares the process of empire building in land-based and maritime empires in the period 1450-1750 CE.
AP US History
Evaluate the extent to which Massachusetts and Virginia differed in the ways that economic development affected their politics between 1607 and 1750.
AP European History
Evaluate the effectiveness of challenges to royal authority in Eastern Europe in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.
The LEQ Rubric (Quick Reference)
Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download free-response questions from past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected]. The ...
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. Each long essay question will ask you to "evaluate the extent" of some factor in American history. Since you are evaluating, you will need to develop an argument that addresses the prompt. Make sure to read all three prompts carefully. Think of the evidence you could use and the argument you could develop in ...
The second part of Section II of the AP exam contains three long essay questions—you must respond to one. The AP U.S. History long essay question assesses your ability to apply knowledge of history in a complex, analytical manner. In other words, you are expected to treat history and historical questions as a historian would.
The AP U.S. History exam gives students a choice between two long-essay questions. You chose ONE! A thesis statement is required. You will have 35 minutes to answer the one question you select. Makes up 15 % of final exam score. Graded on a 0-6 point scale.
AP Central is the official online home for the AP Program: apcentral.collegeboard.org. Inside: ... Visit the College Board on the web: collegeboard.org. Question 3 — Long Essay Question . Evaluate the extent to which debates over slavery in the period from 1830 to 1860 led the United States into the Civil War. Maximum Possible Points: 6 ...
3. That every inhabitant shall have a convenient proportion for a house lot, as we shall see [fit] for everyone's quality and estate. … 4.That everyone shall have a share of the meadow or planting ground…. ⭐️ Crafting a structured argument is crucial. Dive deep into the nuances of using reasoning skills to enhance your writing and ...
Video transcript. - [Voiceover] Okay, this video is about the long essay section on the AP U.S. History exam. Now you might also have heard this called the free response question or FRQ. I think it is officially called the long essay question, so that's what we're gonna go with for now. Now this is the last essay that you'll be writing on the ...
AP Central is the official online home for the AP Program: apcentral.collegeboard.org ... Question 2 — Long Essay Question . Evaluate the extent to which commercial exchange systems such as mercantilism fostered change in the British North American economy in the period from 1660 to 1775 . Maximum Possible Points: 6 . Points Rubric Notes A ...
APUSH Long Essay Question. For the long essay question, you'll be given a choice of three essay options on the same theme, and you must choose one. You must develop and defend a relevant thesis, but there won't be any documents on which you must base your response. Instead, you'll need to draw upon your own knowledge of topics you learned ...
How the Essay Earns a Perfect Score: The APUSH (Advanced Placement U.S. History) exam has specific standards and criteria for grading the Long Essay Question (LEQ). Let's analyze how the provided essay meets these standards impeccably: Thesis/Claim (1 point): The essay presents a clear and defensible thesis in the introduction.
The APUSH (Advanced Placement U.S. History) exam has specific standards and criteria for grading the Long Essay Question (LEQ). Let's break down why the provided essay meets these standards perfectly: Thesis/Claim (1 point): The APUSH exam requires students to present a clear, precise, and defensible thesis in their essay.
1750-2001. 1890-2001. 1815-2001. Writing time on the AP Exam includes both the Document Based Question (DBQ) and the (LEQ), but it is suggested that you spend 40 minutes completing the LEQ. You will need to plan and write your essay in that time. A good breakdown would be 5 min. (planning) + 35 min. (writing) = 40 min.
AP U.S. HISTORY EXAM SAMPLE QUESTIONS . Long Essay Question: Period 3 Suggested writing time: 40 minutes . Directions: In your response you should do the following: Å . Respond to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis or claim that establishes a line of reasoning. Å . Describe a broader historical context relevant to the prompt. Å
Step 2: Plan Your Response. Next, take time to plan your response. Check your plan against the long essay question require- ments. See the following sample plan that a high-scoring writer might make; scoring requirements are written in bold for reference. Step 3: Action! Write Your Response & Step 4: Proofread.
AP Central is the official online home for the AP Program: apcentral.collegeboard.org. https://collegeboard.org ... Question 2: Long Essay Question, Population Movement to British America 6 points. General Scoring Notes • Except where otherwise noted, each point of these rubrics is earned independently; for example, a student could earn a ...
During Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. Each long essay question begins with a general statement that provides context about the tested time period, and then the second sentence identifies your task, which will always entail developing an evaluative argument. Make sure to read all three prompts carefully. Think of the evidence you could use and the ...
Title. 2021 AP Exam Administration Sample Student Responses - AP U.S. History Long Essay Question 4. Author. College Board. Subject. 2021 AP Exam Administration: Student Samples and Commentary. Keywords.