Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
- Qualitative studies
- Research design
- Get an email alert for Qualitative studies
- Get the RSS feed for Qualitative studies
Showing 1 - 13 of 1,134
View by: Cover Page List Articles
Sort by: Recent Popular

From code to care: Clinician and researcher perspectives on an optimal therapeutic web portal for acute myeloid leukemia
Terese Knoppers, Cassandra E. Haley, [ ... ], Ma’n H. Zawati
Research on the generative logic and configuration effects of the policy implementation environment in China’s grassroots digital construction: Traceability based on grounded theory and the validation of the csQCA method
Junjie Li, Bangfan Liu
Experiences on health-related quality of life of Jordanian patients living with heart failure: A qualitative study
Ahmad Rajeh Saifan, Haneen Abu Hayeah, [ ... ], Mohannad Eid AbuRuz
“They must have seen it, you know.” Body talk, extension talk, and action talk: A qualitative study on how palliative care patients and their significant others express experiencing these nonverbal cues
Charlotta Öhrling, Elisabet Sernbo, [ ... ], Stina Nyblom
Developing feasible and acceptable strategies for integrating the use of patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) in gender-affirming care: An implementation study
Rakhshan Kamran, Liam Jackman, [ ... ], Jeremy Rodrigues
Nursing Staff Presenteeism Scale: Development and psychometric test
Shiao-Pei Hung, Jin-Lain Ming, [ ... ], Chii Jeng
Research on an innovative design and evaluation method of Chinese tea sets based on GT-AHP-FCE
YanXiao Zhao, Basyarah Hamat, [ ... ], Leah Ling Li Pang
A qualitative study on the adoption of the new duty hour regulations among medical residents and faculty in Korea
Eui-Ryoung Han, Eun-Kyung Chung
PREHAB FAI- Prehabilitation for patients undergoing arthroscopic hip surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome -Protocol for an assessor blinded randomised controlled feasibility study
Anuj Punnoose, Leica Claydon-Mueller, Alison Rushton, Vikas Khanduja
Nurses’ perception of uncertainty regarding suspected pain in people with dementia: A qualitative descriptive study
Mohammad Rababa, Raghad Tawalbeh, Tala Abu-Zahra
beedi workers in Mysore District, India: A mixed-methods study protocol">Occupational exposures among women beedi workers in Mysore District, India: A mixed-methods study protocol
Priyanka Ravi, Kiranmayee Muralidhar, [ ... ], Lynn B. Gerald
“It’s what mothers do.” A qualitative exploration of mothers’ experiences of supporting their daughter to be physically active
Carol Brennan, Grainne O’Donoghue, [ ... ], James Matthews
Key dimensions of women’s and their partners’ experiences of childbirth: A systematic review of reviews of qualitative studies
Yael Benyamini, Amy Delicate, [ ... ], Claudia Maria Limmer
Connect with Us
- PLOS ONE on Twitter
- PLOS on Facebook
Qualitative Research Journal
Issue(s) available: 59 – From Volume: 6 Issue: 1 , to Volume: 24 Issue: 2

- Issue 2 2024 When intercultural communication meets translation studies: divergent experiences in qualitative inquiries
- Issue 1 2024 Methodological entanglements – public pedagogy research
- Issue 5 2023
- Issue 4 2023
- Issue 3 2023
- Issue 2 2023
- Issue 1 2023
- Issue 4 2022
- Issue 3 2022
- Issue 2 2022
- Issue 1 2022 Critically Exploring Co-production
- Issue 4 2021
- Issue 3 2021
- Issue 2 2021
- Issue 1 2021
- Issue 4 2020 Research and Methodology in times of Crisis and Emergency
- Issue 3 2020 The Practice of Qualitative Research in Migration Studies: Ethical Issues as a Methodological Challenge
- Issue 2 2020
- Issue 1 2020
- Issue 4 2019 Creative approaches to researching further, higher and adult education
- Issue 3 2019
- Issue 2 2019
- Issue 1 2019 Journeys in and through sound
- Issue 4 2018
- Issue 3 2018
- Issue 2 2018 Revisiting ‘Can the Subaltern Speak?’: 30 years later
- Issue 1 2018
- Issue 4 2017
- Issue 3 2017 Bordering, exclusions and necropolitics
- Issue 2 2017
- Issue 1 2017
- Issue 4 2016
- Issue 3 2016 Auto-, duo- and collaborative- ethnographies:
- Issue 2 2016
- Issue 1 2016
- Issue 4 2015 Art practice as methodological innovation
- Issue 3 2015
- Issue 2 2015 Sub-prime scholarship
- Issue 1 2015
- Issue 3 2014
- Issue 2 2014
- Issue 1 2014 Approaches to Researching Masculinities
- Issue 3 2013
- Issue 2 2013 Selected papers from the 2012 Association of Qualitative ResearchDiscourse, Power and Resistance Conference
- Issue 1 2013
- Issue 2 2012
- Issue 1 2012
- Issue 2 2011
- Issue 1 2011
- Issue 2 2010
- Issue 1 2010
- Issue 2 2009
- Issue 1 2009
- Issue 2 2008
- Issue 1 2008
- Issue 2 2007
- Issue 1 2007
- Issue 2 2006
- Issue 1 2006
Outside the field, inside the home: lessons learned from adapting qualitative research strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic
This collaborative paper presents three case studies on four scholars' experiences with remote data collection. The authors highlight the challenges and strengths of online…
Incorporating pragmatism in a behaviour change-led climate adaptation project: a collaborative reflection
This article argues the value of integrating pragmatism in applying behavioural science to complex challenges. We describe a behaviour change-led knowledge co-production process…
Harnessing the potential of translanguaging in Tanzanian secondary education
This study aims to explore motives behind teachers' and students' use of translanguaging and how they use it in Tanzanian public secondary school classrooms.
Negotiating with technology: advancing the virtual in qualitative research methods
This study aims to describe key elements that are critical to virtual qualitative research especially while working with practitioners as participants.
Using data as poetry and text in case study research – poetic representations of adult learner experiences in neighbourhood houses
We argue this method of inquiry better represents the participants' learning, lives and experiences in the formal neoliberal education system prioritising performativity…
Conducting collage elicitation research online: what happens when we remove the scissors and glue?
This autoethnographic article presents the adaptation of collage—an arts-based method traditionally used in face-to-face settings—into an online research tool. It emphasizes the…
“But our worlds are different!”: reflexivity as a tool to negotiate insider–outsider dilemmas
In ethnographic research, negotiating insider–outsider perspectives is essential in order to get closer to the participants’ lives. By highlighting the importance of empathy and…
“Online group discussion was challenging but we enjoyed it!” an exploratory practice in extensive reading
While many works have reported adopting exploratory practice (EP) principles in language teaching research, only a few studies have explored the enactment of EP in an online…
Free association and qualitative research interviewing: perspectives and applications
This paper contributes to a dialogue about the psychoanalytic concept of free association and its application in the context of qualitative research interviewing. In doing so, it…
Opportunities and challenges facing LGBTQ+ people in employment in rural England post-pandemic: a thematic analysis
The following study aimed to better understand rural dwelling LGBTQ+ adults’ experiences of the challenges and opportunities facing their working lives in England.
Tell me about your trauma: an empathetic approach-based protocol for interviewing school leaders who have experienced a crisis
In this study, we illuminate how techniques can be incorporated into interview protocols when conducting research with educational leaders who are being asked to discuss their…
Advancing women to leadership in academia: does personal branding matter?
Personal branding is a strategic tool of marketing and communication to define success in organisations. While it constitutes a conscious attempt to commodify self and audit self…
Reflections on a cross-cultural interview study
The aim of this article is to address some aspects of a cross-cultural interview study conducted in a PhD research project. This is done by reflecting on and discussing the…
Translanguaging approaches and perceptions of Iranian EGP teachers in bi/multilingual educational spaces: a qualitative inquiry
This study aims to analyze translanguaging practices and beliefs of Iranian English for General Purposes (EGP) teachers and find discrepancies between the practice and perception…
Women leaders' lived experiences of bravery in leadership
The research aims to understand the stories of women leaders who have demonstrated bravery in leadership. By analyzing their lived experiences through storytelling and narratives…
Listening to children's voices: reflections on methods, practices and ethics in researching with children using zoom video interviews
The purpose of this research was to reflect on the enablers, challenges and ethical considerations in conducting qualitative research with young children using online methods. The…
Using teacher narratives to map policy effects in the Victorian Government International Baccalaureate Primary Years Programme (IB-PYP) context
Government primary schools in Australia increasingly take up the International Baccalaureate's Primary Years Programme (IB-PYP) to supplement government-mandated curriculum and…
The use of digital technologies in the co-creation process of photo elicitation
This article approaches the possibilities of photo elicitation as a technique for social research in the landscape of technology-mediated instantaneous interpersonal communication.
Culturally responsive and communicative teaching for multicultural integration: qualitative analysis from public secondary school
The aim of this paper is to examine the strategic approach of culturally responsive and communicative teaching (CRCT) through a critical assessment of interracial teachers in…
Unraveling the challenges of education for sustainable development: a compelling case study
Education for sustainable development (ESD) has gained significant attention, but integrating ESD into existing education systems is challenging. The study aims to explore the…
Children's voices through play-based practice: listening, intensities and critique
This paper offers a reflection of a research process aimed at listening to young children's voices in their everyday school life through a play-based context in a Scottish school…
Handle with care; considerations of Braun and Clarke's approach to thematic analysis
The purpose of this paper is to support potential users of thematic analysis (as outlined by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke). Researchers with the intention of applying…
Problem areas of determining the sample size in qualitative research: a model proposal
The lack of a definite standard for determining the sample size in qualitative research leaves the research process to the initiative of the researcher, and this situation…
Operationalising critical realism for case study research
Critical realism is an increasingly popular “lens” through which complex events, entities and phenomena can be studied. Yet detailed operationalisations of critical realism are at…
Language, educational inequalities and epistemic access: crafting alternative pathways for Fiji
The goal of this article is two-fold. The first is to contribute new insights to inform education policies for addressing the underlying educational inequalities and injustices…
Behind my pet's shadow: exploring the motives underlying the tendency of socially excluded consumers to anthropomorphize their pets
Social exclusion is a complicated psychological phenomenon with behavioral ramifications that influences consumers' lifestyles and behaviors. In contrast, anthropomorphism is a…
Street vendors and power relations among actors: process of place making in Borobudur food and craft market
Existing literature shows conflicting views regarding street vendors in a place. They are considered both positive and negative. Their existence has rarely been examined from a…
Visual tools for supporting interviews in qualitative research: new approaches
This study aims to describe and evaluate various visual and creative tools for supporting the in-depth biographical interview aimed at analyzing educational communities and their…
Illuminating the path: a methodological exploration of grounded theory in doctoral theses
This article explores challenges faced by doctoral candidates using grounded theory (GT) in their theses, focusing on coding, theory development and time constraints. It also…
The experience of hurt in the deepest part of self; a phenomenological study in young people with non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI)
What is happening in the perceived world of young people who have non-suicidal self-injury? The answer to this question explains many quantitative research findings in the field…
Living with the scepticism for qualitative research: a phenomenological polyethnography
This paper aims to explore how an academic researcher and a practitioner experience scepticism for their qualitative research.
It's too late – the post has gone viral already: a novel methodological stance to explore K-12 teachers' lived experiences of adult cyber abuse
The purpose of this scoping rapid review was to identify and analyse existing qualitative methodologies that have been used to investigate K-12 teachers' lived experiences of…
“A balancing act of keeping the faith and maintaining wellbeing”: perspectives from Australian faith communities during the pandemic
The pandemic presented many new challenges is all spheres of life including faith communities. Around the globe, lockdowns took pace at various stages with varying restrictions…
How to build rapport in online space: using online chat emoticons for qualitative interviewing in feminist research
This study draws on the author's experiences building rapport through online chat for data collection for the author's doctoral dissertation. The author contacted ten Korean women…
Online date, start – end:
Copyright holder:, open access:.
- Dr Mark Vicars
Further Information
- About the journal (opens new window)
- Purchase information (opens new window)
- Editorial team (opens new window)
- Write for this journal (opens new window)

We’re listening — tell us what you think
Something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
International Journal of Qualitative Methods
Preview this book.
- Description
- Aims and Scope
- Editorial Board
- Abstracting / Indexing
- Submission Guidelines
Journal Highlights
- Impact Factor: 5.4 Ranked 5/110 in Social Sciences, Interdisciplinary – SSCI
- Indexed In: Clarivate Analytics: Social Science Citation Index, the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), and Scopus
- Launched In: 2002
- Publication is subject to payment of an article processing charge (APC)
- Submit here
International Journal of Qualitative Methods (IJQM) is a peer-reviewed open access journal which focuses on methodological advances, innovations, and insights in qualitative or mixed methods studies. Please see the Aims and Scope tab for further information.
This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) . Submission Information
Submit your manuscript today at https://sage.atyponrex.com/journal/ijq .
Please see the Submission Guidelines tab for more information on how to submit your article to the journal. Open access article processing charge (APC) information
Publication in the journal is subject to payment of an article processing charge (APC). The APC serves to support the journal and ensures that articles are freely accessible online in perpetuity under a Creative Commons license .
The APC for this journal is currently 2650 USD for regular articles and 1750 USD for qualitative study protocols.
Students are eligible for a special rate of 75% off the current APC as long as they are the first and corresponding author. Validation of status is required after submission.
The International Institute for Qualitative Methodology (IIQM) members will receive a 25% discount on the APC.
The article processing charge (APC) is payable when a manuscript is accepted after peer review, before it is published. The APC is subject to taxes where applicable. Please see further details here .
Please direct any queries to [email protected] .
Useful Links
- Submission Page
- SAGE Open Access Main Page
- SAGE Open Access FAQs
- Contact the Editor: [email protected]
The International Journal of Qualitative Methods is the peer-reviewed interdisciplinary open access journal of the International Institute for Qualitative Methodology (IIQM) at the University of Alberta, Canada.
The journal was established in 2002 as an eclectic and international forum for papers reporting original methodological insights, study design innovations, and funded-project proposals using qualitative or mixed methods research that are useful to the global research community.
- Clarivate Analytics: Social Science Citation Index
- Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ)
This Journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics .
This Journal recommends that authors follow the Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals formulated by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE).
Please read the guidelines below then visit the journal’s submission site https://sage.atyponrex.com/journal/ijq to upload your manuscript. Please note that manuscripts not conforming to these guidelines may be returned. Remember you can log in to the submission site at any time to check on the progress of your paper through the peer review process.
Only manuscripts of sufficient quality that meet the aims and scope of IJQM will be reviewed.
As part of the submission process you will be required to warrant that you are submitting your original work, that you have the rights in the work, that you are submitting the work for first publication in the Journal and that it is not being considered for publication elsewhere and has not already been published elsewhere, and that you have obtained and can supply all necessary permissions for the reproduction of any copyright works not owned by you.
The International Journal of Qualitative Methods is the peer-reviewed interdisciplinary open access journal of the Institute of Qualitative Methodology (IIQM) at the University of Alberta, Canada.
The journal was established in 2002 as an eclectic and international forum for papers reporting original methodological insights, study design innovations, and funded-project proposals using qualitative or mixed methods research that are useful to the global research community.
Please Read the Manuscript Submission Guidelines below before submitting your manuscript here: SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- Open Access
- Article processing charge (APC)
- W hat do we publish? 3.1 Aims & scope 3.2 Article types 3.2.1 Regular Articles: Methodological Insights, Advantages and Innovations 3.2.2 Qualitative Study Protocols 3.3 Writing your paper 3.3.1 Making your article discoverable
- Editorial policies 4.1 Peer Review Policy 4.2 Authorship 4.3 Acknowledgements 4.3.1 Writing assistance 4.4 Funding 4.5 Declaration of conflicting interests 4.6 Research ethics and patient consent 4.7 Clinical Trials 4.8 Reporting guidelines
- Publishing policies 5.1 Publication ethics 5.2 Contributor's publishing agreement
- Preparing your manuscript 6.1 Word processing formats 6.2 Artwork, figures and other graphics 6.3 Supplementary material 6.4 Reference style 6.5 English language editing services
- Submitting your manuscript 7.1 H ow to submit your manuscript 7.2 Title, keywords and abstracts 7.3 Information required for completing your submission 7.4 ORCID 7.5 Permissions
- On acceptance and publication 8.1 Sage Production 8.2 Continuous publication 8.3 Promoting your article
- Further information
1. Open Access
International Journal of Qualitative Methods (IJQM) is an open access, peer-reviewed journal. Each article accepted by peer review is made freely available online immediately upon publication, is published under a Creative Commons license and will be hosted online in perpetuity. Publication costs of the journal are covered by the collection of article processing charges which are paid by the funder, institution or author of each manuscript upon acceptance. There is no charge for submitting a paper to the journal.
For general information on open access at Sage please visit the Open Access page or view our OpenAccess FAQs .
Back to top
2. Article processing charge (APC)
If, after peer review, your manuscript is accepted for publication, a one-time article processing charge (APC) is payable. This APC covers the cost of publication and ensures that your article will be freely available online in perpetuity under a Creative Commons license.
The APC for this journal iS $2650 USD for regular articles.
Students are eligible for a special rate of 75% off the current APC as long as they are the first and corresponding author. Validation of status is required after submission.
3. What do we publish?
For information on preparing and formatting your manuscript, please see this section .
3.1 Aims & scope
Before submitting your manuscript to IJQM , please ensure you have read the Aims & Scope.
3.2 Article types
3.2.1 Regular Articles: Methodological Insights, Advantages and Innovations
These articles must clearly report a methodological insight, advance and/or innovation in qualitative or mixed methods research likely to be of interest, benefit or relevance to the global community of researchers interested in these methods. Papers should be intelligible across disciplines and expertise levels.
Submissions must focus substantially on methodological not substantive results. What the paper adds to existing methodological knowledge must be clearly stated in the manuscript.
Please limit your title to 30 words or less.
Articles should be no longer than is necessary to contextualize and convey methodological insights, advances or innovations. Articles should fall between 3,500 and 7,500 words excluding references and abstract.
Provide an abstract, which effectively summarizes the content of your article, in particular its methodological insight, innovation or advance. Your abstract should be 200-300 words.
3.2.2 Qualitative Study Protocols
Many journals are now publishing study protocols. To further the development of qualitative methods, IJQM now accepts nationally funded study protocols for qualitative or mixed methods studies for inclusion in the journal.
These types of papers can help researchers:
- Share methodological ideas, insights, and practices
- Develop insights from cutting-edge and highly creative studies
- Contribute to the future advancement of qualitativemethods
- Raise the profile of both the study and theresearcher(s)
All protocols accepted by IJQM will feature as full indexed papers in the journal.
Focus of protocols Study protocols should not normally exceed 5000 words (excluding references). Protocols should be submitted in English according to the author guidelines of the journal and should include the following sections:
Background / Study justification / Summary of pilot work Give a persuasive overview to justify your study based on past research and theory, followed by details of any pilot work done to date.
Explanation and justification of method Give a clear, comprehensive, and detailed overview of which method you used, what you did, and why.
Sampling / Recruitment Give a clear, comprehensive, and detailed overview of the people involved in the study, what you did to recruit them, and why.
Data Handling / Analysis Give a clear, comprehensive, and detailed overview of how you handled and analysed your data, including how you will handle disagreements and/or team analysis.
Ethics Provide a summary of the main ethical issues raised by the study and how these are to be addressed.
Rigor Discuss the approach to qualitative rigor to be adopted and the steps to be used to maintain rigor.
Full copies of interview schedules/ Focus group schedules / Fieldwork plans Include full schedules if possible.
Criteria for review Protocols must detail empirical qualitative studies or mixed method studies with a substantial qualitative component (e.g., not quantitative studies / reviews) that have received peerreviewed state / provincial / federal / national funding; such studies would not be subject to further peer review prior to publication, but will still undergo review for final approval. Protocols which raise substantial ethical concerns may be subject to full peer review as per normal IJQM procedures.
Student proposals / non-funded / locally-funded studies will not be considered.
3.3 Writing your paper
The Sage Author Gateway has some general advice and on how to get published , plus links to further resources.
3.3.1 Making your article discoverable
When writing up your paper, think about how you can make it discoverable. The title, keywords and abstract are key to ensuring readers find your article through search engines such as Google. For information and guidance on how best to title your article, write your abstract and select your keywords, have a look at this page on the Gateway: How to Help Readers Find Your Article Online
4. Editorial policies
4.1 Peer review policy
Following a preliminary triage to eliminate submissions unsuitable for IJQM all papers are sent out for review. The covering letter is important. To help the Editor in their preliminary evaluation, please indicate why you think the paper suitable for publication.
The journal’s policy is to have manuscripts reviewed by a minimum of two expert reviewers. IJQM utilizes a double-anonymized peer review process in which the reviewer and authors’ names and information are withheld from the other. Reviewers may at their own discretion opt to reveal their names to the author in their review but our standard policy practice is for their identities to remain concealed. All manuscripts are reviewed as rapidly as possible, while maintaining rigor. Reviewers make comments to the author and recommendations to the Editor-in-Chief who then makes the final decision.
The Editor or members of the Editorial Board may occasionally submit their own manuscripts for possible publication in the journal. In these cases, the peer review process will be managed by alternative members of the Board and the submitting Editor/Board member will have no involvement in the decision-making process.
4.2 Authorship
Papers should only be submitted for consideration once consent is given by all contributing authors. Those submitting papers should carefully check that all those whose work contributed to the paper are acknowledged as contributing authors. The list of authors should include all those who can legitimately claim authorship. This is all those who:
(i) Made a substantial contribution to the concept or design of the work; or acquisition, analysis or interpretation of data, (ii) Drafted the article or revised it critically for important intellectual content, (iii) Approved the version to be published, (iv) Each author should have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content.
Authors should meet the conditions of all of the points above. Each author should have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content.
When a large, multicentre group has conducted the work, the group should identify the individuals who accept direct responsibility for the manuscript. These individuals should fully meet the criteria for authorship.
Acquisition of funding, collection of data, or general supervision of the research group alone does not constitute authorship, although all contributors who do not meet the criteria for authorship should be listed in the Acknowledgments section. Please refer to the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) authorship guidelines for more information on authorship.
All parties who have made a substantive contribution to the article should be listed as authors. Principal authorship, authorship order, and other publication credits should be based on the relative scientific or professional contributions of the individuals involved, regardless of their status. A student is usually listed as principal author on any multiple-authored publication that substantially derives from the student’s dissertation or thesis.
Please note that AI chatbots, for example ChatGPT, should not be listed as authors. For more information see the policy on Use of ChatGPT and generative AI tools .
4.3 Acknowledgements
All contributors who do not meet the criteria for authorship should be listed in an Acknowledgements section. Examples of those who might be acknowledged include a person who provided purely technical help, or a department chair who provided only general support.
4.3.1 Third party submissions Where an individual who is not listed as an author submits a manuscript on behalf of the author(s), a statement must be included in the Acknowledgements section of the manuscript and in the accompanying cover letter. The statements must:
Disclose this type of editorial assistance – including the individual’s name, company and level of input Identify any entities that paid for this assistance Confirm that the listed authors have authorized the submission of their manuscript via third party and approved any statements or declarations, e.g. conflicting interests, funding, etc. Where appropriate, Sage reserves the right to deny consideration to manuscripts submitted by a third party rather than by the authors themselves.
4.3.2 Writing assistance
Individuals who provided writing assistance, e.g. from a specialist communications company, do not qualify as authors and so should be included in the Acknowledgements section. Authors must disclose any writing assistance – including the individual’s name, company and level of input – and identify the entity that paid for this assistance. It is not necessary to disclose use of language polishing services.
Please supply any personal acknowledgements separately to the main text to facilitate anonymous peer review.
4.4 Funding
IJQM requires all authors to acknowledge their funding in a consistent fashion under a separate heading. Please visit the Funding Acknowledgements page on the Sage Journal Author Gateway to confirm the format of the acknowledgment text in the event of funding, or state that: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or notfor-profit sectors.
4.5 Declaration of conflicting interests
It is the policy of IJQM to require a declaration of conflicting interests from all authors enabling a statement to be carried within the paginated pages of all published articles.
Please ensure that a ‘Declaration of Conflicting Interests’ statement is included at the end of your manuscript, after any acknowledgements and prior to the references. If no conflict exists, please state that ‘The Author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest’.
For guidance on conflict of interest statements, please see the ICMJE recommendations .
4.6 Research ethics and patient consent
Medical research involving human subjects must be conducted according to the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki .
Submitted manuscripts should conform to the ICMJE Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals, and all papers reporting animal and/or human studies must state in the methods section that the relevant Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Board provided (or waived) approval. Please ensure that you have provided the full name and institution of the review committee, in addition to the approval number.
For research articles, authors are also required to state in the methods section whether participants provided informed consent and whether the consent was written or verbal.
Information on informed consent to report individual cases or case series should be included in the manuscript text. A statement is required regarding whether written informed consent for patient information and images to be published was provided by the patient(s) or a legally authorized representative.
Please also refer to the ICMJE Recommendations for the Protection of Research Participants .
All research involving animals submitted for publication must be approved by an ethics committee with oversight of the facility in which the studies were conducted. The Journal has adopted the ARRIVE guidelines.
4.7 Clinical trials
IJQM conforms to the ICMJE requirement that clinical trials are registered in a WHO-approved public trials registry at or before the time of first patient enrolment as a condition of consideration for publication. The trial registry name and URL, and registration number must be included at the end of the abstract.
4.8 Reporting guidelines
The relevant EQUATOR Network reporting guidelines should be followed depending on the type of study. For example, all randomized controlled trials submitted for publication should include a completed CONSORT flow chart as a cited figure and the completed CONSORT checklist should be uploaded with your submission as a supplementary file. Systematic reviews and metaanalyses should include the completed PRISMA flow chart as a cited figure and the completed PRISMA checklist should be uploaded with your submission as a supplementary file. The EQUATOR wizard can help you identify the appropriate guideline.
Other resources can be found at NLM’s Research Reporting Guidelines and Initiatives .
5. Publishing policies
5.1 Publication ethics
Sage is committed to upholding the integrity of the academic record. We encourage authors to refer to the Committee on Publication Ethics’ International Standards for Authors and view the Publication Ethics page on the Sage Author Gateway .
5.1.1 Plagiarism
IJQM and Sage take issues of copyright infringement, plagiarism or other breaches of best practice in publication very seriously. We seek to protect the rights of our authors and we always investigate claims of plagiarism or misuse of published articles. Equally, we seek to protect the reputation of the journal against malpractice. Submitted articles may be checked with duplication-checking software. Where an article, for example, is found to have plagiarized other work or included third-party copyright material without permission or with insufficient acknowledgement, or where the authorship of the article is contested, we reserve the right to take action including, but not limited to: publishing an erratum or corrigendum (correction); retracting the article; taking up the matter with the head of department or dean of the author's institution and/or relevant academic bodies or societies; or taking appropriate legal action.
5.1.2 Prior publication
If material has been previously published, it is not generally acceptable for publication in a Sage journal. However, there are certain circumstances where previously published material can be considered for publication. Please refer to the guidance on the Sage Author Gateway or if in doubt, contact the Editor at the address given below.
5.2 Contributor's publishing agreement
Before publication Sage requires the author as the rights holder to sign a Journal Contributor’s Publishing Agreement. IJQM publishes manuscripts under Creative Commons licenses . The standard license for the journal is Creative Commons by Attribution Non-Commercial (CC BYNC), which allows others to re-use the work without permission as long as the work is properly referenced and the use is non-commercial. For more information, you are advised to visit Sage's OA licenses page .
Alternative license arrangements are available, for example, to meet particular funder mandates, made at the author’s request.
6. Preparing your manuscript
6.1 Word processing formats
The preferred formats for your manuscript are Word, RTF, XLS. LaTeX files are also accepted. Word and (La)Tex templates are available on the Manuscript Submission Guidelines page of our Author Gateway.
The text should be double-spaced throughout with a minimum of 3cm for left and right margins and 5cm at head and foot. Text should be standard 12 point.
6.2 Artwork, figures and other graphics
For guidance on the preparation of illustrations, pictures and graphs in electronic format, please visit Sage’s Manuscript Submission Guidelines .
Figures supplied in color will appear in color online.
6.3 Supplementary material
This journal is able to host additional materials online (e.g. datasets, podcasts, videos, images etc) alongside the full-text of the article. These will be subjected to peer-review alongside the article. For more information please refer to our guidelines on submitting supplementary files, which can be found within our Manuscript Submission Guidelines page.
6.4 Reference style
IJQM adheres to the APA reference style. Please review the guidelines on APA to ensure your manuscript conforms to this reference style.
6.5 English language editing services
Authors seeking assistance with English language editing, translation, or figure and manuscript formatting to fit the journal’s specifications should consider using Sage Language Services. Visit Sage Language Services on our Journal Author Gateway for further information.
7. Submitting your manuscript
7.1 How to submit your manuscript
International Journal of Qualitative Methods – to submit a new article , please go to our new submission site, Sage Journals Submission: https://sage.atyponrex.com/journal/amd . From this site you can create submissions and revisions and track the status of your manuscripts. Please note, you will need to create a new CONNECT account on the Sage Journals Submission site the first time you use it, your Sage Track account will not work on this submission system.
IMPORTANT: To submit a revision for a manuscript that was submitted to International Journal of Qualitative Methods via Sage Track prior to 17th October 2023 , please submit your revision in Sage Track, not via Sage Journals Submission. All transfers into International Journal of Qualitative Methods will also need to be submitted via Sage Track. Please reference the email you received after approving the transfer or reach out to our Transfer Support Team for assistance.
7.2 Title, keywords and abstracts
Please add a title page to your submission. This page will not be a part of the document sent out for peer review, but it is needed for Editorial purposes. The title page should include: a) Title b) List of authors, and their affiliations c) Corresponding author and their details d) Acknowledgement e) Funding Information f) Conflict of Interest.
Please supply a title, short title, an abstract and keywords to accompany your article. The title, keywords and abstract are key to ensuring readers find your article online through online search engines such as Google. Please refer to the information and guidance on how best to title your article, write your abstract and select your keywords by visiting the Sage Journal Author Gateway for guidelines on How to Help Readers Find Your Article Online .
7.3 Information required for completing your submission
Provide full contact details for the corresponding author including email, mailing address and telephone numbers. Academic affiliations are required for all co-authors. These details should be presented separately to the main text of the article to facilitate anonymous peer review.
You will be asked to provide contact details and academic affiliations for all co-authors via the submission system and identify who is to be the corresponding author. These details must match what appears on your manuscript. At this stage please ensure you have included all the required statements and declarations and uploaded any additional supplementary files (including reporting guidelines where relevant).
As part of our commitment to ensuring an ethical, transparent and fair peer review process Sage is a supporting member of ORCID, the Open Researcher and Contributor ID . ORCID provides a unique and persistent digital identifier that distinguishes researchers from every other researcher, even those who share the same name, and, through integration in key research workflows such as manuscript and grant submission, supports automated linkages between researchers and their professional activities, ensuring that their work is recognized.
The collection of ORCID iDs from corresponding authors is now part of the submission process of this journal. If you already have an ORCID iD you will be asked to associate that to your submission during the online submission process. We also strongly encourage all co-authors to link their ORCID ID to their accounts in our online peer review platforms. It takes seconds to do: click the link when prompted, sign into your ORCID account and our systems are automatically updated. Your ORCID iD will become part of your accepted publication’s metadata, making your work attributable to you and only you. Your ORCID iD is published with your article so that fellow researchers reading your work can link to your ORCID profile and from there link to your other publications.
If you do not already have an ORCID iD please follow this link to create one or visit our ORCID homepage to learn more.
7.5 Permissions
Authors are responsible for obtaining permission from copyright holders for reproducing any illustrations, tables, figures or lengthy quotations previously published elsewhere. For further information including guidance on fair dealing for criticism and review, please visit our Frequently Asked Questions on the Sage Journal Author Gateway .
8. On acceptance and publication
If your paper is accepted for publication after peer review, you will first be asked to complete the contributor’s publishing agreement. Once your manuscript files have been check for Sage Production, the corresponding author will be asked to pay the article processing charge (APC) via a payment link. Once the APC has been processed, your article will be prepared for publication and can appear online within an average of 30 days. Please note that no production work will occur on your paper until the APC has been received.
8.1 Sage Production
Your Sage Production Editor will keep you informed as to your article’s progress throughout the production process. Proofs will be sent by PDF to the corresponding author and should be returned promptly. Authors are reminded to check their proofs carefully to confirm that all author information, including names, affiliations, sequence and contact details are correct, and that Funding and Conflict of Interest statements, if any, are accurate.
8.2 Online publication
One of the many benefits of publishing your research in an open access journal is the speed to publication. With no page count constraints, your article will be published online in a fully citable form with a DOI number as soon as it has completed the production process. At this time it will be completely free to view and download for all. Articles are batch every year and are then available in the Archive.
8.3 Promoting your article
Publication is not the end of the process! You can help disseminate your paper and ensure it is as widely read and cited as possible. The Sage Author Gateway has numerous resources to help you promote your work. Visit the Promote Your Article page on the Gateway for tips and advice.
9. Further information
Any correspondence, queries or additional requests for information on the Manuscript Submission process should be sent to the International Journal of Qualitative Methods editorial office as follows:
- Advertising
- Current Issue
- Email Alert
- Foreign rights
- Permissions
- Read Online
- Reprints and sponsorship
Founding Editor:
Michael W. Firmin , Cedarville University
Wayne A. Babchuk, University of Nebraska--Lincoln
Yuchun Zhou, Ohio University
Managing Editor:
Alexis Chavez , University of Nebraska--Lincoln
Associate Editors:
Mark A. Giesler , Saginaw Valley State University
Debbie Miller , University of Nebraska--Lincoln
Bernadro Pohl, University of Houston - Downtown
Tiffany Young, Doane University
Copy Editor:
Paige Hespe , University of Nebraska--Lincoln
Editorial Board:
Kimberly Acquaviva , George Washington University
Kimberly Baker, University of Northern Iowa
Andrea Bingham , University of Colorado
Jessika Boles , Vanderbilt University
Eileen Boswell, University of Nebraska-Lincoln
L. Ebony Boulware , Johns Hopkins University
Huan Chen , University of Florida
Megan Powell Cuzzolino, Harvard University
Elizabeth Dore , Radford University
Jazlin Ebenezer , Wayne State University
Kassandra Engfer, Hawaii Pacific University
Jennifer Esposito , Georgia State University
Cecilia Fernandez , University of Michigan
Priva Fischweicher , Barry University
Abe Flanigan , Georgia Southern University
Janice Fournillier , Georgia State University
Kathleen Gilbert , Indiana University
Robin Goldberg-Glen , Widener University
Petter Grahl Johnstad , Hordaland County Municipality
Lauren Gulbas , Dartmouth College
Jennifer Hall , University of Lynchburg
Suejung Han , Illinois State University
Anne Hornak , Central Michigan University
Nancy Hornberger , University of Pennsylvania
Joseph Hruby , Baldwin-Wallace College
Lee Humphreys , Cornell University
Robert S. Isherwood , Slippery Rock
Suzie Jones , Utah State University
Christina Kim, Cedarville University
Effie Kritikos , Northeastern Illinois University
Maria E. Lozano , Columbia University
Tiffani N. Luethke , University of Nebraska at Kearney
Jose Martinez, Seymour Community Schools (Indiana)
Judy Meloy , Castleton State College
James Morton , University of Alaska Fairbanks
James L. Olive-Liebhart, University of Dayton
Laura Parson , North Dakota State University
Erin Partridge , Notre Dame de Namur University
Analay Perez , University of Nebraska - Lincoln
Robin Phelps-Ward , Clemson University
Lubomir Popov , Bowling Green State University
Tobin Richardson , KSM Consulting
Mary Romero , Arizona State University
Carolyn Rouse , Princeton University
Diane Ryndak , University of Florida
Kennedy Saldanha, Eastern Michigan University
Rachel M. Schmitz, Oklahoma State University
Hong-Chi Shiau , Shih-Hsin University (Taiwan)
Ruslan Slutsky , University of Toledo
Maureen V. Spelman , North Central University
Deborah Skinstad, Stellenbosch University
William Stevens , University of Chicago
Tony L. Talbert , Baylor University
Herb L. Thompson III , University of Nebraska at Omaha
Ashley Thrasher , Western Carolina University
Dorothy Valcarcel Craig , Middle Tennessee State University
Mark Warren , Harvard University
Leah E. Wickersham , Texas A & M University
Lindy B. Williams , Cornell University
Chelsea Wooding , National University
Victoria Zascavage , Xavier University
Journal of Ethnographic & Qualitative Research (JEQR) is a quarterly, peer-reviewed periodical, publishing scholarly articles that address topics relating directly to empirical qualitative research and conceptual articles addressing topics related to qualitative. The journal has been assigned ISSN #1935-3308. It is indexed with ERIC and EBSCO (H.W. Wilson, Social Science Full Text, Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, SocINDEX, and Academic Search Complete). Additionally, we intend to pursue abstract indexing with PsychInfo and other indexing organizations. An example of a published JEQR article is Researching Violence: Conducting Risky Fieldwork in Dangerous Spaces Across Latin America and the Caribbean .
JEQR is a printed journal available for subscription at university libraries. Inquiries, including permission for reprints, should be sent to [email protected] . The journal (ISSN 1935-3308) accepts unsolicited manuscripts from all scholars, with prompt feedback regarding their status for potential publication.
Beyond typical fair-use federal guidelines, permission is granted for the photocopying of single articles for use by university faculty in non-profit contexts, including library reserve use or reading packets. This assumes that no profit is made from the copying and permission has been obtained from the article's respective lead author. PDF files of JEQR articles are provided to authors which reasonably may be shared at their discretion for teaching and limited scholarly purposes, provided the non-profit parameters indicated above. JEQR articles may not be reprinted elsewhere without express consent from the journal's executive editor.
JEQR gratefully acknowledges peer-review assistance from the Editorial Board. In the spirit of open academic inquiry, views expressed in the articles represent the respective authors and are not necessarily endorsed by the editors or related universities .
Among other quality research conferences, potential JEQR authors are encouraged to first present their papers at the Ethnographic & Qualitative Research Conference. EQRC began at the University of Massachusetts (Amherst), moving to Teachers College, Columbia University in New York City. Subsequent sponsors included Duquesne University (Pittsburgh), State University of New York (Albany), and Cedarville University (Greater Dayton area, Ohio). EQRC possesses a long and rich tradition as a forum for dissemination of scholarly ideas in the qualitative research tradition. The conference is usually held in February, with the call for papers issued in fall semester. Visit www.eqrc.net for details.
In addition to EQRC, the journal also publishes juried papers from a number of other quality conferences, following independent peer-review by JEQR staff and its review board members. Please notify the JEQR editor if you are aware of other qualitative research conferences that may desire affiliation with the journal.
JEQR also welcomes submissions of all manuscripts that have not been presented at conferences. Although authors often benefit from the feedback received through conference presentation, it is not an explicit or implicit requirement for JEQR publication and the editorial staff welcome all original manuscripts that are not simultaneously under other journal publication consideration or review .
About Journal
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes qualitative research articles from a number of social science disciplines such as psychology, health science, sociology, criminology, education, political science, and administrative studies. The journal is an international and interdisciplinary focus and greatly welcomes papers from all countries. The journal offers an intellectual platform for researchers, practitioners, administrators, and policymakers to contribute and promote qualitative research and analysis.
ISSN: 2576-2141
Call for Papers- American Journal of Qualitative Research
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) welcomes original research articles and book reviews for its next issue. The AJQR is a quarterly and peer-reviewed journal published in February, May, August, and November.
We are seeking submissions for a forthcoming issue published in February 2024. The paper should be written in professional English. The length of 6000-10000 words is preferred. All manuscripts should be prepared in MS Word format and submitted online: https://www.editorialpark.com/ajqr
For any further information about the journal, please visit its website: https://www.ajqr.org
Submission Deadline: November 15, 2023
Announcement
Dear AJQR Readers,
Due to the high volume of submissions in the American Journal of Qualitative Research , the editorial board decided to publish quarterly since 2023.
Volume 8, Issue 2
Current issue - in progress.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted and exacerbated the difficult juggling act women in the U.S. have to do between parenting their children and working outside the home. The pandemic has also led to a decline in maternal mental health, particularly among mothers with young children, mothers of color, and those with previous mental health issues. The authors noted these experiences in their own lives as mothers with children and observed them in the lives of the women around them. These observations informed the design of this narrative inquiry study, in which we used semi-structured interviews to explore mothers’ shifting ideas and experiences of mothering, work, and family life during a global pandemic. We used creative analytic practice (CAP) to compose reflexive researcher conversations around the interview data that enabled us to highlight nuances in the data, show more transparently our meaning-making, make visible our researcher subjectivities, show uncertainties about aspects of data interpretation, and create a more accessible data representation.
Keywords: Mothering, COVID-19 pandemic, U.S. women, Narrative inquiry, Creative analytic practice.
The COVID-19 pandemic put France’s healthcare system under extreme tension and led to significant levels of stress among healthcare professionals in general and nurses in particular. Research has shown how these elements affected nurses’ physical and psychological health and manifested as insomnia, anxiety, and depressive syndromes. The present qualitative study aimed to explore the lived experiences of France’s nurses as a function of their level of exposure to the virus and whether they worked in the hospital sector or practiced privately in the community during the pandemic’s first wave. It also sought to describe the resources nurses used to maintain their overall health. We administered 19 qualitative interviews to 19 nurses in the autumn of 2021. The present study revealed that nurses were subjected to significant stress during the pandemic. Our data analysis enabled us to draw out three principal themes: 1) Being on the edge in stormy period ; 2) Personal impact on several levels and 3) Floating together and learning. There were no significant differences between the groups that were subjected to different levels of exposure to COVID-19. All the groups were affected by the pandemic that struck a healthcare system that was already systematically fragile. Nurses were severely tested by the COVID-19 pandemic, but their consciousness of the importance of their role grew, despite questioning what meaning there was to their profession, perhaps even to their lives . The trauma still felt fresh 18 months later, during the interviews, and this cannot be ignored in future healthcare policymaking .
Keywords: COVID-19, nurses, salutogenesis, stressors, health resources.
Annual mammography screening is recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and American Cancer Society (ACS) to reduce mortality through early detection of breast cancer. In rural Appalachia, rates of later-stage breast cancer incidence and mortality are higher than national averages. We explored the ways that providers and staff at breast cancer screening facilities employed novel approaches to overcome patient- and facility-level barriers to access to breast cancer screening in the Appalachian region. We conducted 23 semi-structured interviews with 28 clinical providers and staff of breast health facilities in Appalachia. Themes reflect how limiting features of breast screening facilities influenced access to care; the way patient-level barriers presented challenges to access to breast screening; and that external and regulatory forces presented obstacles to access to care. In addition, the unique geographical and geographical attributes of the Appalachian region shaped access and adherence to mammography screening recommendations. Thematic findings highlight that facilities implemented patient-centered strategies to overcome access-related barriers. Results may inform the ways breast cancer screening facilities address suboptimal access to breast health screening. They may also inform future resource allocations to enable facilities to reach breast cancer screening performance goals.
Keywords: rural health, breast cancer, preventive health care, women’s health.
Paternal parenting affects child development; hence, the father’s absence has a deleterious effect on the male child. The literature on parenting shows limited focus on how parenting impacts children by gender. This qualitative hermeneutic phenomenological study investigated the key question, “How does a father’s absence during childhood influence a man’s subsequent parenting of his son(s)?” An integrated theoretical framework was used to guide the study: Parenting Style Theory, Social-Cognitive Theory, and Bioecological Systems Theory. Nine Trinidadian males aged 20 to 35 years who were parenting sons were recruited to participate using snowball sampling. Data on men’s adverse childhood experiences were gathered using semi-structured interviews. Content and thematic analyses were done using DELVE software. Key findings include the influence of stereotypical cultural constructs, the church’s critical role in addressing childhood trauma, the transmission of father absence across generations, and the relationship between neurodevelopment and adverse childhood experiences. Implications of these findings will benefit child and adolescent advocacy, inform policymaking, aid professional intervention in mental health and education, and strengthen familial systems and ecclesiastical contexts. Future research should explore the lived experiences of men who crave emotional connection with their sons yet struggle with the stereotypical cultural perception of manhood.
Keywords: father absence, brain development, childhood trauma, intergenerational, the transmission of behavior.
The purpose of this qualitative transcendental phenomenological study was to understand the essence of the shared lived experiences of undergraduate college students with anxiety disorders at two universities in the Southeastern United States. Ellis’s cognitive theory, rational emotive behavior therapy, guided the study which took place at a mid-sized, public nonsectarian university and a small, private liberal arts college. The central research question elicited rich data regarding the shared lived experiences of the study participants. The four research sub-questions address participants’ perceptions regarding the impact of their disorders on their lifestyles and academic performance. A purposeful criterion sample was used to select the participants who completed a questionnaire, open-ended individual interviews, a single focus group interview, and participant journals. Phenomenological reduction was used to create a composite integration of meaning and the essence of the lived experience of the participants. Data results identified five themes: (a) social fears, (b) stressor issues, (c) generational issues, (d) academic performance barriers, and (e) institutional education and accommodation preferences.
Keywords: Alexithymia, anxiety, disorder, qualitative, stressors
School shootings are traumatic events that can lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder among students who experience these events. It is important to find effective strategies to help students cope with their return to school, as well as their anxiety and stress levels while on campus. There exists a gap in the literature on the effects of therapy dogs on students who have witnessed a school shooting. This current study used a retrospective mixed-methods survey that was sent to recent graduates of Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School (located in Parkland, Florida) who witnessed the February 2018 shooting. Data were collected to assess how the therapy dogs affected students' willingness to return to school and their stress/anxiety levels while on campus. Identified themes indicated that the therapy dogs helped with anxiety levels, stress levels, and overall moods of Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School students. These findings provide important implications for community leaders and school administrators who want to promote healing and well-being in a community that has experienced violence.
Keywords: Therapy dog, school shooting, community violence.
Identifying the relation between the processes of programming and foreign language writing may lead to new directions for programming language and natural language focused instructional design. The present qualitative case study supported by quantitative data investigated foreign language writing experiences of computer engineering students taking an object-oriented programming course. Forty-five sophomores learning programming and academic English simultaneously in a foundation university in Ankara, Turkey, were selected purposefully for the case study. There were two data sources (students’ opinions and documents) and three data collection tools (a semi-structured interview, a short diary, and a composition. In terms of the findings of the research, four themes were obtained; however, only the use of metacognitive strategies will be explained in detail due to the length of the study. Participants stated that they feel the positive effects of programming experience on the use of self-evaluation strategy and that there are similarities and differences between the processes of programming and foreign language writing. Participants’ views on the effect of programming on foreign language writing did not differ according to their writing and programming performance scores. Participants stated that programming experience may have an effect on the use of metacognitive language learning strategies in the writing process. Upon analyzing participants’ comments, it is understood that programming experience does not hinder the use of metacognitive strategies but has a role in supporting and reinforcing their use. It is suggested that multiple case studies be done for similar views on the effects of programming and that each finding be proven by quantitative studies.
Keywords: programming, foreign language writing, metacognitive strategies.
The significance of participatory decision-making in educational institutions is widely acknowledged as essential in school management and administration. This study aimed to determine how involved teachers are in making decisions in their schools and what role they think they play in shaping different parts of school policies and procedures. It also looked at their perspectives on how decisions made by others are carried out in schools. Semi-structured interviews with 10 secondary school teachers focused on teachers' role in decision-making related to their routine school tasks, strategic decision-making, participatory role in making school decisions, and their willingness to participate in decision-making. This study showed that teachers' low participation is attributed to their shared desire to be involved in school management and administration-related decisions. Teachers expressed that participatory school-based decision-making can promote collaboration and collectivism among the school staff, and it plays a significant role in shaping their work satisfaction and motivation. By gaining insights into teachers' perspectives, this study aims to contribute to the broader understanding of participatory school decision-making in the Rwandan secondary education system and communicate potential improvements for fostering a more collaborative and inclusive educational environment.
Keywords: teachers’ perceptions, qualitative research, decision-making, secondary schools.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Prev Med
Qualitative Methods in Health Care Research
Vishnu renjith.
School of Nursing and Midwifery, Royal College of Surgeons Ireland - Bahrain (RCSI Bahrain), Al Sayh Muharraq Governorate, Bahrain
Renjulal Yesodharan
1 Department of Mental Health Nursing, Manipal College of Nursing Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Judith A. Noronha
2 Department of OBG Nursing, Manipal College of Nursing Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Elissa Ladd
3 School of Nursing, MGH Institute of Health Professions, Boston, USA
Anice George
4 Department of Child Health Nursing, Manipal College of Nursing Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Healthcare research is a systematic inquiry intended to generate robust evidence about important issues in the fields of medicine and healthcare. Qualitative research has ample possibilities within the arena of healthcare research. This article aims to inform healthcare professionals regarding qualitative research, its significance, and applicability in the field of healthcare. A wide variety of phenomena that cannot be explained using the quantitative approach can be explored and conveyed using a qualitative method. The major types of qualitative research designs are narrative research, phenomenological research, grounded theory research, ethnographic research, historical research, and case study research. The greatest strength of the qualitative research approach lies in the richness and depth of the healthcare exploration and description it makes. In health research, these methods are considered as the most humanistic and person-centered way of discovering and uncovering thoughts and actions of human beings.
Introduction
Healthcare research is a systematic inquiry intended to generate trustworthy evidence about issues in the field of medicine and healthcare. The three principal approaches to health research are the quantitative, the qualitative, and the mixed methods approach. The quantitative research method uses data, which are measures of values and counts and are often described using statistical methods which in turn aids the researcher to draw inferences. Qualitative research incorporates the recording, interpreting, and analyzing of non-numeric data with an attempt to uncover the deeper meanings of human experiences and behaviors. Mixed methods research, the third methodological approach, involves collection and analysis of both qualitative and quantitative information with an objective to solve different but related questions, or at times the same questions.[ 1 , 2 ]
In healthcare, qualitative research is widely used to understand patterns of health behaviors, describe lived experiences, develop behavioral theories, explore healthcare needs, and design interventions.[ 1 , 2 , 3 ] Because of its ample applications in healthcare, there has been a tremendous increase in the number of health research studies undertaken using qualitative methodology.[ 4 , 5 ] This article discusses qualitative research methods, their significance, and applicability in the arena of healthcare.
Qualitative Research
Diverse academic and non-academic disciplines utilize qualitative research as a method of inquiry to understand human behavior and experiences.[ 6 , 7 ] According to Munhall, “Qualitative research involves broadly stated questions about human experiences and realities, studied through sustained contact with the individual in their natural environments and producing rich, descriptive data that will help us to understand those individual's experiences.”[ 8 ]
Significance of Qualitative Research
The qualitative method of inquiry examines the 'how' and 'why' of decision making, rather than the 'when,' 'what,' and 'where.'[ 7 ] Unlike quantitative methods, the objective of qualitative inquiry is to explore, narrate, and explain the phenomena and make sense of the complex reality. Health interventions, explanatory health models, and medical-social theories could be developed as an outcome of qualitative research.[ 9 ] Understanding the richness and complexity of human behavior is the crux of qualitative research.
Differences between Quantitative and Qualitative Research
The quantitative and qualitative forms of inquiry vary based on their underlying objectives. They are in no way opposed to each other; instead, these two methods are like two sides of a coin. The critical differences between quantitative and qualitative research are summarized in Table 1 .[ 1 , 10 , 11 ]
Differences between quantitative and qualitative research
Qualitative Research Questions and Purpose Statements
Qualitative questions are exploratory and are open-ended. A well-formulated study question forms the basis for developing a protocol, guides the selection of design, and data collection methods. Qualitative research questions generally involve two parts, a central question and related subquestions. The central question is directed towards the primary phenomenon under study, whereas the subquestions explore the subareas of focus. It is advised not to have more than five to seven subquestions. A commonly used framework for designing a qualitative research question is the 'PCO framework' wherein, P stands for the population under study, C stands for the context of exploration, and O stands for the outcome/s of interest.[ 12 ] The PCO framework guides researchers in crafting a focused study question.
Example: In the question, “What are the experiences of mothers on parenting children with Thalassemia?”, the population is “mothers of children with Thalassemia,” the context is “parenting children with Thalassemia,” and the outcome of interest is “experiences.”
The purpose statement specifies the broad focus of the study, identifies the approach, and provides direction for the overall goal of the study. The major components of a purpose statement include the central phenomenon under investigation, the study design and the population of interest. Qualitative research does not require a-priori hypothesis.[ 13 , 14 , 15 ]
Example: Borimnejad et al . undertook a qualitative research on the lived experiences of women suffering from vitiligo. The purpose of this study was, “to explore lived experiences of women suffering from vitiligo using a hermeneutic phenomenological approach.” [ 16 ]
Review of the Literature
In quantitative research, the researchers do an extensive review of scientific literature prior to the commencement of the study. However, in qualitative research, only a minimal literature search is conducted at the beginning of the study. This is to ensure that the researcher is not influenced by the existing understanding of the phenomenon under the study. The minimal literature review will help the researchers to avoid the conceptual pollution of the phenomenon being studied. Nonetheless, an extensive review of the literature is conducted after data collection and analysis.[ 15 ]
Reflexivity
Reflexivity refers to critical self-appraisal about one's own biases, values, preferences, and preconceptions about the phenomenon under investigation. Maintaining a reflexive diary/journal is a widely recognized way to foster reflexivity. According to Creswell, “Reflexivity increases the credibility of the study by enhancing more neutral interpretations.”[ 7 ]
Types of Qualitative Research Designs
The qualitative research approach encompasses a wide array of research designs. The words such as types, traditions, designs, strategies of inquiry, varieties, and methods are used interchangeably. The major types of qualitative research designs are narrative research, phenomenological research, grounded theory research, ethnographic research, historical research, and case study research.[ 1 , 7 , 10 ]
Narrative research
Narrative research focuses on exploring the life of an individual and is ideally suited to tell the stories of individual experiences.[ 17 ] The purpose of narrative research is to utilize 'story telling' as a method in communicating an individual's experience to a larger audience.[ 18 ] The roots of narrative inquiry extend to humanities including anthropology, literature, psychology, education, history, and sociology. Narrative research encompasses the study of individual experiences and learning the significance of those experiences. The data collection procedures include mainly interviews, field notes, letters, photographs, diaries, and documents collected from one or more individuals. Data analysis involves the analysis of the stories or experiences through “re-storying of stories” and developing themes usually in chronological order of events. Rolls and Payne argued that narrative research is a valuable approach in health care research, to gain deeper insight into patient's experiences.[ 19 ]
Example: Karlsson et al . undertook a narrative inquiry to “explore how people with Alzheimer's disease present their life story.” Data were collected from nine participants. They were asked to describe about their life experiences from childhood to adulthood, then to current life and their views about the future life. [ 20 ]
Phenomenological research
Phenomenology is a philosophical tradition developed by German philosopher Edmond Husserl. His student Martin Heidegger did further developments in this methodology. It defines the 'essence' of individual's experiences regarding a certain phenomenon.[ 1 ] The methodology has its origin from philosophy, psychology, and education. The purpose of qualitative research is to understand the people's everyday life experiences and reduce it into the central meaning or the 'essence of the experience'.[ 21 , 22 ] The unit of analysis of phenomenology is the individuals who have had similar experiences of the phenomenon. Interviews with individuals are mainly considered for the data collection, though, documents and observations are also useful. Data analysis includes identification of significant meaning elements, textural description (what was experienced), structural description (how was it experienced), and description of 'essence' of experience.[ 1 , 7 , 21 ] The phenomenological approach is further divided into descriptive and interpretive phenomenology. Descriptive phenomenology focuses on the understanding of the essence of experiences and is best suited in situations that need to describe the lived phenomenon. Hermeneutic phenomenology or Interpretive phenomenology moves beyond the description to uncover the meanings that are not explicitly evident. The researcher tries to interpret the phenomenon, based on their judgment rather than just describing it.[ 7 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ]
Example: A phenomenological study conducted by Cornelio et al . aimed at describing the lived experiences of mothers in parenting children with leukemia. Data from ten mothers were collected using in-depth semi-structured interviews and were analyzed using Husserl's method of phenomenology. Themes such as “pivotal moment in life”, “the experience of being with a seriously ill child”, “having to keep distance with the relatives”, “overcoming the financial and social commitments”, “responding to challenges”, “experience of faith as being key to survival”, “health concerns of the present and future”, and “optimism” were derived. The researchers reported the essence of the study as “chronic illness such as leukemia in children results in a negative impact on the child and on the mother.” [ 25 ]
Grounded Theory Research
Grounded theory has its base in sociology and propagated by two sociologists, Barney Glaser, and Anselm Strauss.[ 26 ] The primary purpose of grounded theory is to discover or generate theory in the context of the social process being studied. The major difference between grounded theory and other approaches lies in its emphasis on theory generation and development. The name grounded theory comes from its ability to induce a theory grounded in the reality of study participants.[ 7 , 27 ] Data collection in grounded theory research involves recording interviews from many individuals until data saturation. Constant comparative analysis, theoretical sampling, theoretical coding, and theoretical saturation are unique features of grounded theory research.[ 26 , 27 , 28 ] Data analysis includes analyzing data through 'open coding,' 'axial coding,' and 'selective coding.'[ 1 , 7 ] Open coding is the first level of abstraction, and it refers to the creation of a broad initial range of categories, axial coding is the procedure of understanding connections between the open codes, whereas selective coding relates to the process of connecting the axial codes to formulate a theory.[ 1 , 7 ] Results of the grounded theory analysis are supplemented with a visual representation of major constructs usually in the form of flow charts or framework diagrams. Quotations from the participants are used in a supportive capacity to substantiate the findings. Strauss and Corbin highlights that “the value of the grounded theory lies not only in its ability to generate a theory but also to ground that theory in the data.”[ 27 ]
Example: Williams et al . conducted a grounded theory research to explore the nature of relationship between the sense of self and the eating disorders. Data were collected form 11 women with a lifetime history of Anorexia Nervosa and were analyzed using the grounded theory methodology. Analysis led to the development of a theoretical framework on the nature of the relationship between the self and Anorexia Nervosa. [ 29 ]
Ethnographic research
Ethnography has its base in anthropology, where the anthropologists used it for understanding the culture-specific knowledge and behaviors. In health sciences research, ethnography focuses on narrating and interpreting the health behaviors of a culture-sharing group. 'Culture-sharing group' in an ethnography represents any 'group of people who share common meanings, customs or experiences.' In health research, it could be a group of physicians working in rural care, a group of medical students, or it could be a group of patients who receive home-based rehabilitation. To understand the cultural patterns, researchers primarily observe the individuals or group of individuals for a prolonged period of time.[ 1 , 7 , 30 ] The scope of ethnography can be broad or narrow depending on the aim. The study of more general cultural groups is termed as macro-ethnography, whereas micro-ethnography focuses on more narrowly defined cultures. Ethnography is usually conducted in a single setting. Ethnographers collect data using a variety of methods such as observation, interviews, audio-video records, and document reviews. A written report includes a detailed description of the culture sharing group with emic and etic perspectives. When the researcher reports the views of the participants it is called emic perspectives and when the researcher reports his or her views about the culture, the term is called etic.[ 7 ]
Example: The aim of the ethnographic study by LeBaron et al . was to explore the barriers to opioid availability and cancer pain management in India. The researchers collected data from fifty-nine participants using in-depth semi-structured interviews, participant observation, and document review. The researchers identified significant barriers by open coding and thematic analysis of the formal interview. [ 31 ]
Historical research
Historical research is the “systematic collection, critical evaluation, and interpretation of historical evidence”.[ 1 ] The purpose of historical research is to gain insights from the past and involves interpreting past events in the light of the present. The data for historical research are usually collected from primary and secondary sources. The primary source mainly includes diaries, first hand information, and writings. The secondary sources are textbooks, newspapers, second or third-hand accounts of historical events and medical/legal documents. The data gathered from these various sources are synthesized and reported as biographical narratives or developmental perspectives in chronological order. The ideas are interpreted in terms of the historical context and significance. The written report describes 'what happened', 'how it happened', 'why it happened', and its significance and implications to current clinical practice.[ 1 , 10 ]
Example: Lubold (2019) analyzed the breastfeeding trends in three countries (Sweden, Ireland, and the United States) using a historical qualitative method. Through analysis of historical data, the researcher found that strong family policies, adherence to international recommendations and adoption of baby-friendly hospital initiative could greatly enhance the breastfeeding rates. [ 32 ]
Case study research
Case study research focuses on the description and in-depth analysis of the case(s) or issues illustrated by the case(s). The design has its origin from psychology, law, and medicine. Case studies are best suited for the understanding of case(s), thus reducing the unit of analysis into studying an event, a program, an activity or an illness. Observations, one to one interviews, artifacts, and documents are used for collecting the data, and the analysis is done through the description of the case. From this, themes and cross-case themes are derived. A written case study report includes a detailed description of one or more cases.[ 7 , 10 ]
Example: Perceptions of poststroke sexuality in a woman of childbearing age was explored using a qualitative case study approach by Beal and Millenbrunch. Semi structured interview was conducted with a 36- year mother of two children with a history of Acute ischemic stroke. The data were analyzed using an inductive approach. The authors concluded that “stroke during childbearing years may affect a woman's perception of herself as a sexual being and her ability to carry out gender roles”. [ 33 ]
Sampling in Qualitative Research
Qualitative researchers widely use non-probability sampling techniques such as purposive sampling, convenience sampling, quota sampling, snowball sampling, homogeneous sampling, maximum variation sampling, extreme (deviant) case sampling, typical case sampling, and intensity sampling. The selection of a sampling technique depends on the nature and needs of the study.[ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ] The four widely used sampling techniques are convenience sampling, purposive sampling, snowball sampling, and intensity sampling.
Convenience sampling
It is otherwise called accidental sampling, where the researchers collect data from the subjects who are selected based on accessibility, geographical proximity, ease, speed, and or low cost.[ 34 ] Convenience sampling offers a significant benefit of convenience but often accompanies the issues of sample representation.
Purposive sampling
Purposive or purposeful sampling is a widely used sampling technique.[ 35 ] It involves identifying a population based on already established sampling criteria and then selecting subjects who fulfill that criteria to increase the credibility. However, choosing information-rich cases is the key to determine the power and logic of purposive sampling in a qualitative study.[ 1 ]
Snowball sampling
The method is also known as 'chain referral sampling' or 'network sampling.' The sampling starts by having a few initial participants, and the researcher relies on these early participants to identify additional study participants. It is best adopted when the researcher wishes to study the stigmatized group, or in cases, where findings of participants are likely to be difficult by ordinary means. Respondent ridden sampling is an improvised version of snowball sampling used to find out the participant from a hard-to-find or hard-to-study population.[ 37 , 38 ]
Intensity sampling
The process of identifying information-rich cases that manifest the phenomenon of interest is referred to as intensity sampling. It requires prior information, and considerable judgment about the phenomenon of interest and the researcher should do some preliminary investigations to determine the nature of the variation. Intensity sampling will be done once the researcher identifies the variation across the cases (extreme, average and intense) and picks the intense cases from them.[ 40 ]
Deciding the Sample Size
A-priori sample size calculation is not undertaken in the case of qualitative research. Researchers collect the data from as many participants as possible until they reach the point of data saturation. Data saturation or the point of redundancy is the stage where the researcher no longer sees or hears any new information. Data saturation gives the idea that the researcher has captured all possible information about the phenomenon of interest. Since no further information is being uncovered as redundancy is achieved, at this point the data collection can be stopped. The objective here is to get an overall picture of the chronicle of the phenomenon under the study rather than generalization.[ 1 , 7 , 41 ]
Data Collection in Qualitative Research
The various strategies used for data collection in qualitative research includes in-depth interviews (individual or group), focus group discussions (FGDs), participant observation, narrative life history, document analysis, audio materials, videos or video footage, text analysis, and simple observation. Among all these, the three popular methods are the FGDs, one to one in-depth interviews and the participant observation.
FGDs are useful in eliciting data from a group of individuals. They are normally built around a specific topic and are considered as the best approach to gather data on an entire range of responses to a topic.[ 42 Group size in an FGD ranges from 6 to 12. Depending upon the nature of participants, FGDs could be homogeneous or heterogeneous.[ 1 , 14 ] One to one in-depth interviews are best suited to obtain individuals' life histories, lived experiences, perceptions, and views, particularly while exporting topics of sensitive nature. In-depth interviews can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. However, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research. Participant observations are suitable for gathering data regarding naturally occurring behaviors.[ 1 ]
Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Various strategies are employed by researchers to analyze data in qualitative research. Data analytic strategies differ according to the type of inquiry. A general content analysis approach is described herewith. Data analysis begins by transcription of the interview data. The researcher carefully reads data and gets a sense of the whole. Once the researcher is familiarized with the data, the researcher strives to identify small meaning units called the 'codes.' The codes are then grouped based on their shared concepts to form the primary categories. Based on the relationship between the primary categories, they are then clustered into secondary categories. The next step involves the identification of themes and interpretation to make meaning out of data. In the results section of the manuscript, the researcher describes the key findings/themes that emerged. The themes can be supported by participants' quotes. The analytical framework used should be explained in sufficient detail, and the analytic framework must be well referenced. The study findings are usually represented in a schematic form for better conceptualization.[ 1 , 7 ] Even though the overall analytical process remains the same across different qualitative designs, each design such as phenomenology, ethnography, and grounded theory has design specific analytical procedures, the details of which are out of the scope of this article.
Computer-Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software (CAQDAS)
Until recently, qualitative analysis was done either manually or with the help of a spreadsheet application. Currently, there are various software programs available which aid researchers to manage qualitative data. CAQDAS is basically data management tools and cannot analyze the qualitative data as it lacks the ability to think, reflect, and conceptualize. Nonetheless, CAQDAS helps researchers to manage, shape, and make sense of unstructured information. Open Code, MAXQDA, NVivo, Atlas.ti, and Hyper Research are some of the widely used qualitative data analysis software.[ 14 , 43 ]
Reporting Guidelines
Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) is the widely used reporting guideline for qualitative research. This 32-item checklist assists researchers in reporting all the major aspects related to the study. The three major domains of COREQ are the 'research team and reflexivity', 'study design', and 'analysis and findings'.[ 44 , 45 ]
Critical Appraisal of Qualitative Research
Various scales are available to critical appraisal of qualitative research. The widely used one is the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) Qualitative Checklist developed by CASP network, UK. This 10-item checklist evaluates the quality of the study under areas such as aims, methodology, research design, ethical considerations, data collection, data analysis, and findings.[ 46 ]
Ethical Issues in Qualitative Research
A qualitative study must be undertaken by grounding it in the principles of bioethics such as beneficence, non-maleficence, autonomy, and justice. Protecting the participants is of utmost importance, and the greatest care has to be taken while collecting data from a vulnerable research population. The researcher must respect individuals, families, and communities and must make sure that the participants are not identifiable by their quotations that the researchers include when publishing the data. Consent for audio/video recordings must be obtained. Approval to be in FGDs must be obtained from the participants. Researchers must ensure the confidentiality and anonymity of the transcripts/audio-video records/photographs/other data collected as a part of the study. The researchers must confirm their role as advocates and proceed in the best interest of all participants.[ 42 , 47 , 48 ]
Rigor in Qualitative Research
The demonstration of rigor or quality in the conduct of the study is essential for every research method. However, the criteria used to evaluate the rigor of quantitative studies are not be appropriate for qualitative methods. Lincoln and Guba (1985) first outlined the criteria for evaluating the qualitative research often referred to as “standards of trustworthiness of qualitative research”.[ 49 ] The four components of the criteria are credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability.
Credibility refers to confidence in the 'truth value' of the data and its interpretation. It is used to establish that the findings are true, credible and believable. Credibility is similar to the internal validity in quantitative research.[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] The second criterion to establish the trustworthiness of the qualitative research is transferability, Transferability refers to the degree to which the qualitative results are applicability to other settings, population or contexts. This is analogous to the external validity in quantitative research.[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] Lincoln and Guba recommend authors provide enough details so that the users will be able to evaluate the applicability of data in other contexts.[ 49 ] The criterion of dependability refers to the assumption of repeatability or replicability of the study findings and is similar to that of reliability in quantitative research. The dependability question is 'Whether the study findings be repeated of the study is replicated with the same (similar) cohort of participants, data coders, and context?'[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] Confirmability, the fourth criteria is analogous to the objectivity of the study and refers the degree to which the study findings could be confirmed or corroborated by others. To ensure confirmability the data should directly reflect the participants' experiences and not the bias, motivations, or imaginations of the inquirer.[ 1 , 50 , 51 ] Qualitative researchers should ensure that the study is conducted with enough rigor and should report the measures undertaken to enhance the trustworthiness of the study.
Conclusions
Qualitative research studies are being widely acknowledged and recognized in health care practice. This overview illustrates various qualitative methods and shows how these methods can be used to generate evidence that informs clinical practice. Qualitative research helps to understand the patterns of health behaviors, describe illness experiences, design health interventions, and develop healthcare theories. The ultimate strength of the qualitative research approach lies in the richness of the data and the descriptions and depth of exploration it makes. Hence, qualitative methods are considered as the most humanistic and person-centered way of discovering and uncovering thoughts and actions of human beings.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
About the Journal
- Journal Name : Qualitative Research
- Publisher Name : Sara Delamont and Paul Atkinson
- ISSN: 1468-7941
- Impact Factor : 3.096
- Nature : Print and Online
Make a Submission
Information.
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians


web of science

- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
Breaking down barriers to mental healthcare access in prison: a qualitative interview study with incarcerated males in Norway
- Line Elisabeth Solbakken 1 , 2 ,
- Svein Bergvik 3 &
- Rolf Wynn 1 , 4
BMC Psychiatry volume 24 , Article number: 292 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
384 Accesses
Metrics details
Mental health problems are highly prevalent in prison populations. Incarcerated persons generally come from disadvantaged backgrounds and are living under extraordinary conditions while in prison. Their healthcare needs are complex compared to the general population. Studies have found that incarcerated individuals are reluctant to seek help and that they experience challenges in accessing mental healthcare services. To some extent, seeking treatment depends on the degree of fit between potential users and health services, and actual use might be a better indication of accessibility than the fact that services are available. This study aimed to explore individual and systemic facilitators and barriers to accessing mental healthcare in a prison context.
An analytical approach drawing on elements of constructivist Grounded theory was the methodological basis of this study. Fifteen male participants were recruited from three prisons in Northern Norway. Data was collected through in-depth interviews on topics such as help-seeking experiences, perceived access to services and availability of health information.
We found that distrust in the system, challenges with the referral routines, worries about negative consequences, and perceived limited access to mental healthcare were barriers to help-seeking among incarcerated individuals. How prison officers, and healthcare personnel respond to incarcerated persons reporting mental distress could also be critical for their future willingness to seek help. Providing information about mental health and available services, initiating outreaching mental health services, and integrating mental health interventions into treatment programs are examples of efforts that might reduce barriers to accessing services.
Conclusions
Facilitating access to mental health services is crucial to accommodate the mental health needs of those incarcerated. This study provides insights into the complex interplay of individual, social and systemic factors that may contribute to the utilization of mental health care among incarcerated persons. We suggest that correctional and healthcare systems review their practices to facilitate access to healthcare for people in prison.
Peer Review reports
Mental health of people in prison
The rates of mental disorders are considerably higher among incarcerated individuals than in the general population [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Co-morbidities are common, and around 20% of incarcerated individuals have concurrent mental and substance use disorders [ 5 ]. They are at increased risk for all-cause mortality, self-harm, violence, and victimization, and suicide rates are about 3–6 times higher among incarcerated males relative to males in the broader population [ 6 ]. Adverse life experiences and disadvantaged living conditions from an early age may explain the observed accumulation of mental health problems in prison populations worldwide [ 7 , 8 ]. Genetic predispositions combined with environmental stressors are implicated in the development of mental disorders [ 9 , 10 ]. People in prison generally experience low educational achievements, low income, and unstable housing. Thus, the poor mental health of prison populations is caused by a complex interplay of social, environmental, and genetic factors [ 7 , 11 ]. In addition to the pre-existing burdens, incarcerated individuals are facing prison–specific challenges such as loss of autonomy, social isolation, bullying and violence that may exacerbate mental health issues [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. Considering the elevated rates of mental health problems in prison, facilitating access to mental health services is crucial to accommodate the needs of those incarcerated.
Access to mental health services
The treatment gap refers to the proportion of individuals with mental health problems within a specific community that require treatment without receiving it [ 16 ]. Variable access to mental healthcare and high levels of unmet mental health needs are universal challenges in communities across the world [ 17 , 18 ]. Even when health services are available, individual and systemic barriers may hinder their use. In a narrow sense, access to healthcare may be considered equivalent to available services. However, some argue that a more meaningful way to define access is the “degree of fit” between the potential users and health services [ 19 ]. For instance, if services are accessible in terms of transportation and treatment costs and whether they are compatible with potential users’ personal attitudes, beliefs and preferences. “Having access” can be understood as the potential for using available mental health services. “Gaining access”, is the individual process of choosing to use those services [ 20 ]. Within this frame of reference, access to services is more precisely defined by the actual use of services.
Mental health help-seeking
Across settings and populations, the majority of those suffering from mental health problems do not seek treatment [ 21 , 22 , 23 ]. The literature on help-seeking gives insight into the intrapersonal factors involved in accessing mental health care. Within this context, help-seeking has been defined as: " an adaptive coping process that is the attempt to obtain external assistance to deal with a mental health concern” [ 24 ]. The process of seeking help involves becoming aware of a mental health problem that may require intervention; articulating the psychological challenges in a way that can be understood by others; awareness of help sources that are available and accessible; and a willingness to talk about the mental health problem to available help sources [ 25 ]. Throughout the help-seeking process, personal thoughts and feelings become increasingly interpersonal as an individual confides in and seeks support from others. It is not uncommon to share mental health concerns with informal sources of support such as friends and family prior to, or even instead of, seeking professional help [ 26 ]. Moreover, informal networks are found to facilitate but may also discourage professional formal help-seeking for mental health problems [ 27 , 28 ].
The theory of planned behavior (TPB), a well-known model within behavior change research, may also provide a framework for understanding how personal attitudes and social influences are implicated in accessing healthcare. Subjective norms, attitudes, and perceived behavioral control are elements of TPB that are particularly important for understanding the help-seeking process [ 29 ]. In this context, subjective norms refer to a person’s beliefs about other peoples’ practice or approval of help-seeking and are related to expectations of social support in pursuing professional help. Attitudes refer to appraisals of seeking professional mental help as beneficial or harmful and a judgement of whether help-seeking would be constructive compared to alternative behaviors. Perceived behavioral control can be divided into self-efficacy (the confidence that one can seek help), and controllability (the extent of personal control in the help-seeking process). A recent review found that attitudes and perceived behavioral control predict help-seeking intentions across different population groups and cultures [ 30 ].
Access to mental health services in prison
Equity is essential in healthcare to ensure that the health system meets the needs of different groups of people and individuals [ 20 ]. “The principle of equivalence” is a widely endorsed standard for healthcare in correctional settings [ 31 ]. This principle is laid down in the United Nations´ Nelson Mandela Rules. Rule number 24 states that: “Prisoners should enjoy the same standards of health care that are available in the community, and should have access to necessary health-care services free of charge without discrimination on the grounds of their legal status” [ 32 ] (p.8) However, some argue that equal standards are not sufficient to meet the complex needs of incarcerated individuals and that mental healthcare in prison must be more intensive and integrative than services provided in the community [ 33 , 34 , 35 ]. In reality there are several reports of shortcomings in the delivery of mental healthcare in prison in many countries across the world, as mental disorders in incarcerated persons are underdiagnosed and undertreated [ 6 , 34 ]. Studies from Canada, the US, and the UK indicate that a significant proportion of incarcerated people with mental health problems have not received adequate treatment [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 ]. Suggested explanations for unmet needs are underfunding, failure in screening procedures and quality at reception, demand for more mental health knowledge among prison staff, and possible underrating of the severity of mental health problems by the prison administrations to reduce treatment costs [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ]. Taken together these reports suggest that mental health services do not fit the complex needs of incarcerated persons in high-income countries. There is less knowledge about the situation in low- and middle-income countries. However, the elevated rates of mental disorders in these countries suggest that unmet needs among incarcerated persons are a widespread challenge [ 1 ].
Mental health help-seeking in prison
Evidence suggests that the immense burden of mental disorders among people in prison is not matched by a proportional use of mental healthcare [ 41 ]. Several reports from various correctional settings have documented that incarcerated persons are reluctant to seek help for mental health problems [ 41 ]. Among the reported barriers to help-seeking in prison are confidentiality concerns [ 42 ], fear of stigma associated with a diagnosis [ 43 ], a preference for self-management or informal support [ 44 ], lack of knowledge of psychological services [ 42 , 44 ] and distrust in the system [ 45 ]. In addition, systemic factors may influence access to healthcare in prison. The culture in all-male prisons typically demands that those imprisoned mask their vulnerabilities by adopting a tough and dominant demeanor [ 46 ]. Experiencing mental illness and receiving professional mental health treatment is also associated with an increased risk of victimization in incarcerated individuals [ 47 ].
Mental health literacy (MHL) is a concept that includes the knowledge and attitudes that influence how people manage their mental health needs [ 48 ]. Having sufficient knowledge and access to information about mental health and mental health services can be a prerequisite for seeking professional help [ 49 ]. For people living in the community, seeking online information and advice is an important strategy for gaining knowledge about how to cope with mental health challenges [ 50 , 51 , 52 ]. For security reasons, access to the Internet is typically severely limited for those imprisoned [ 53 , 54 ]. Hence, this essential mental health information source is largely unavailable to them. Accordingly, incarcerated individuals are reliant on finding mental health information through information pamphlets, books, TV programs, newspapers or consulting healthcare professionals [ 55 ]. Some argue that limited access to online information and digital health services may have consequences for the well-being and successful rehabilitation of those incarcerated [ 53 , 56 , 57 ]. Thus, there are reasons to believe that restricted access to mental health information may also affect help-seeking and access to healthcare for incarcerated individuals.
The rationale for the current study
Fostering health-promoting environments and adequate access to mental healthcare within prisons is a public health imperative increasingly acknowledged in the literature [ 33 ]. Moreover, the mental health of incarcerated persons is a matter of public safety since untreated severe mental disorders are associated with a higher risk of recidivism [ 58 , 59 ]. People in prison retain their right to health services, and in principle, incarcerated persons have access to mental health services. A vital question, however, is how incarcerated persons experience gaining access and how this affects their actual use of services. Existing research on the provision of mental healthcare in prisons, particularly within a Scandinavian context, is sparse, leaving significant knowledge gaps. The question of access to health information for incarcerated persons is similarly understudied. This study aimed to investigate how incarcerated persons experience individual and systemic factors that facilitate or impede access to mental healthcare in prison.
The Helsinki Declaration of Medical Research involving human subjects and services laid the basis of the ethical considerations of this study [ 60 ]. The study was approved by the Data Protection Officer of the University Hospital of North Norway (No. 02415). The Norwegian Correctional system, which is responsible for the welfare of incarcerated individuals, approved of the study (Ref. 200900463-347). The Regional Health Research Ethics Committee concluded that the project was outside their mandate (Ref. 40,701).
The principles of voluntariness and informed consent are central to human subject research. Individuals in prison are considered vulnerable due to their restricted freedom and autonomy, poor health status, higher incidence of learning disabilities, and lower literacy levels. Consequently, additional precautions are required to ensure that research with incarcerated participants is conducted ethically [ 61 ]. User participation in designing research that includes vulnerable groups is crucial to achieving this objective [ 61 , 62 ]. Measures in accordance with recommendations were taken to ensure consent information that is complete, relevant, and understandable [ 63 ]. A user representative from Way-Back, an organization that supports incarcerated persons with reentry to their communities, contributed to the project’s planning. The user representative provided input on information about the study, research questions, the interview guide and how to conduct the interviews. The input was used to tailor information and for conducting the interviews in accordance with the constraints of the prison contexts and the needs of the incarcerated individuals. The choice of whether to reimburse participants in prison studies is debated. Because of the relative deprivation of prison life, some argue that even small incentives could potentially result in undue influence for participation in research [ 64 ]. For this reason, we chose to abstain from offering reimbursement for the participants in this study.
Study context
At any given time, about 3000 persons are serving a sentence in Norway, of which 5.6% are women and 26.2% are non-Norwegian citizens [ 65 ]. A recent study found that almost 60% of incarcerated persons in Norway had a diagnosed mental disorder, together with a 33% rise in the one-year prevalence of mental disorders between the years 2010–2019 [ 66 ]. Thus, the proportion of people with mental disorders entering prison has been increasing. In Norway, access to necessary healthcare is considered a basic human right and is legislated in the Patient’s Rights Act section 2 [ 67 ]. Healthcare is primarily tax-funded, with a nominal service fee and a relatively low cap on yearly individual costs [ 68 ]. Norway has committed to “the principle of equivalence” meaning that those imprisoned retain their right to healthcare equal to that of the general population [ 31 ]. Prison health services serve incarcerated persons with milder mental health problems and are accessible by self-referral through a paper-based request system. The prison health services can refer those who experience moderate to severe mental disorders to specialist mental health services, and treatment is often provided in prison by mental health professionals from local hospitals For people imprisoned in Norway, healthcare and medications are free of charge [ 69 ], eliminating one significant barrier to mental healthcare access [ 70 ]. Furthermore, as the municipalities and local hospitals provide health services - the importation of services promotes equity and that services are independent of the correctional system, thereby strengthening the rights of people in prison [ 71 ].
A study found that incarcerated persons in Norway were reluctant to seek help for mental health problems from prison health services unless they had concurrent sleep or substance use problems [ 72 ]. A survey by Bjørngaard et al. [ 73 ] found lower patient satisfaction with prison health services compared to people using community health services and that those with mental health problems were less satisfied compared to incarcerated patients with other health challenges. A survey representative of the Norwegian prison population found that 20% of incarcerated males sample reported that they had received mental health services, while 25% reported that they had been in need of mental health services in prison but had not received any [ 11 ]. More recent reports suggest that mental health services are insufficient to meet the needs of those imprisoned in Norway and that incarcerated individuals referred due to their severe mental illness may not be admitted to specialist services for in-patient assessment and treatment [ 74 , 75 ]. These reports indicate that mental health services do not fit the complex needs of incarcerated persons in Norway and that there are potential obstacles in their access to mental healthcare.
Study design
This study was underpinned by relativist epistemology which is based on the assumption of multiple individual realities that allow for different understandings of the same phenomenon [ 76 ]. The study design was suitable for exploring and explaining commonly experienced individual, social, cultural and structural factors that influence help-seeking and access to mental healthcare for incarcerated individuals. The study incorporates vital Grounded Theory (GT) components, including initial coding, categorizing data, constant comparative methods involving inductive and abductive reasoning, and memoing [ 77 ]. The use of theoretical sampling, which is rare in prison research due to ethical and practical constraints [ 78 ], was not employed in this study. Data collection concluded once additional data no longer contributed new insights or further elaborated the developed categories.
Preconceptions
The first author, a clinical community psychologist and a PhD student, worked part-time as a prison officer for two years during her psychology education. This experience gave her an insider’s view of the correctional system, inevitably influencing her initial perceptions. Before conducting the interviews, she held a somewhat optimistic view of the correctional system’s capacity to support and enhance the mental health of those incarcerated. However, this perspective was challenged through the narratives of the study participants, who conveyed powerful personal accounts that highlighted substantial barriers to obtaining mental health services within the prison environment. The other two authors, serving as supervisors, are also researchers and mental health professionals with considerable clinical experience. Their diverse backgrounds contributed to a supervisory dynamic that adresssed the research topic’s complexities. Throughout the study, the authors engaged in a process of collaborative reflection, concerned with maintaining a balance between engaging with participant stories and sustaining a critical stance towards the data. These discussions were essential in helping the first author navigate an empathetic understanding of the participant’s experiences with the necessary analytical objectivity required for rigorous qualitative research.
Participants and study settings
Fifteen males serving a prison sentence were recruited from three prisons in Northern Norway. Thirteen of the participants served a sentence at a high security level, while two served at lower security. The participants’ age ranged from the early twenties to the late sixties (M: 43.6 years). Two participants had other nationalities, while the rest were Norwegian citizens. Further details about the participants must be withheld to preserve their privacy. When citing individual participants, they are anonymized by using pseudonyms.
Recruitment
Participants were recruited through posters in the prison ward that conveyed basic information, including the fact that the interviews were confidential and would be recorded. The posters encouraged those interested in participating to approach a contact person for more information. A prison officer, a social worker or a reintegration coordinator were assigned the role as contact persons in the selected prisons. Those who actively approached the contact person were given more comprehensive written information about the study. Requiring an active choice by incarcerated individuals was done to enhance their experience of self-determination and autonomy in their decision to participate. The contact person scheduled appointments with the participants, and the interviewer had no prior knowledge of the participants other than what they presented in the interviews. One potential participant cancelled the interview appointment due to health issues on the interview day and withdrew from the study.
The first author conducted face-to-face, in-depth interviews. The interviews took place in prison visitation rooms or in an office in the health wards. Before the interview, the participants were given information about the study and their rights as research participants and signed a written consent form. The interviewer was alone with the participants during the interview and had a personal alarm as a safety precaution. The interview guide covered topics on knowledge of mental health and available services, help-seeking experiences, and access to mental health information (sample questions provided in Table 1 ). The participants were asked open-ended questions and were invited to speak freely on these topics. Thus, the order and framing of questions varied depending on where they fit into the participants’ narratives. This allowed for following up on the participants’ experiences and may have given the participants an increased sense of control in the interview. The first author who conducted the interviews was attentive to signs of emotional discomfort in participants and avoided pressure on sensitive topics. After the interviews, the participants were encouraged to ask questions and comment on their experience and reminded of their right to withdraw from the study. Nearly all the participants expressed that the experience of participating in the study was positive and that they appreciated the chance to contribute to the research project.
The first author transcribed the audio-recorded interviews in Norwegian, ensuring a verbatim account of the participants’ narratives. The initial eight interviews were transcribed before initiating data analysis. This early examination of the data facilitated a refinement of the interview guide, which was then applied to the subsequent seven interviews to deepen the inquiry. Data collection and analysis were concurrent as the study progressed from the ninth interview, which allowed for immediate integration of new data into the evolving analytical framework. The data was examined using the NVivo 12 software, which supported the systematic organization and analysis of the data. The data was analyzed line-by-line, searching for incidents in the form of recurring beliefs, actions, experiences, and explanations [ 79 ]. The constant comparison method was applied throughout the analysis. In the initial coding phase, incidents were compared to incidents, and through this process underlying recurring concepts and similarities were identified and assigned codes. Subsequently, codes were then compared to codes, and related codes were organized into conceptual categories, reflecting both common features and divergent viewpoints [ 77 ]. In the intermediate coding phase, the data was abstracted into categories which were compared to each other, and relationships between categories were developed and refined. The authors engaged in a collaborative and reflective dialogue throughout this process, meeting regularly to deliberate on preconceptions, the emerging categories and their interpretations. This dynamic exchange was informed by memos that captured analytical decisions, insights, and evolving interpretations, thus guiding the reflective process. In the last stage, advanced coding, a core category which binds the other categories and sub-categories together was developed. Through a collaborative process the categories were substantiated with representative quotes, which, upon completion of the analysis, were translated from Norwegian to English for inclusion in the report. This resulted in a nuanced understanding grounded in the participants’ experiences and the researchers’ interpretative lens.
The data analysis yielded four main categories illustrating the participants’ active engagement in identifying challenges and facilitators for mental healthcare access within the prison environment. The first category, “Mental health awareness,” captures how beliefs and knowledge concerning mental health were influenced by the experiences and constraints inherent to prison life, potentially affecting the pursuit of help and access to healthcare services. The second main category reveals how systemic sub-cultural values can obstruct healthcare access, whereas, on a personal level, fellow inmates served as vital support for obtaining mental health services. The third main category, “Access to mental health care,” examines how organizational and systemic barriers impede access to mental healthcare. The final main category, “Enhancing access to services,” delineates factors that lowered the bar for mental healthcare access. The core category, “Breaking down barriers,” encapsulates the dynamic interplay between incarcerated individuals and the contextual factors that influenced their ability and willingness to access mental healthcare in prison. This central theme also recognizes the collaborative effort between participants and researchers in identifying problem areas and solutions to mental healthcare access, thereby “breaking down barriers”. An outline of these categories is presented in Table 2 .
Mental health awareness
An information void.
Seeking information can be an essential first step for recognizing symptoms of mental illness that may require intervention. Prior to imprisonment, visiting their general practitioner or using online search engines were the preferred methods for finding health information for the participants in this study. In prison, however, access to the Internet is severely limited:
Where can we get information? We do not have access to computers or anything. So, I would have to call someone on the outside to get them to print articles and send them to me by post. So, no. We don’t know our rights, we don’t know about the services available to us, as a matter of fact we know very little. There’s an information void. Stuart
A few of the participants referred to the prison library as a source of information. Some also said that they could talk to health care professionals, correctional officers, or other staff members like the priest, to get mental health information. Fellow incarcerated individuals who had experienced mental health problems and received health services were also mentioned by some participants. The common thread in all suggestions was a dependency on others to access information about mental health. Only a couple of participants had tried to find mental health information during their time in prison. However, they found it difficult to obtain:
The only choice I have is to ask the prison officers to print it [mental health information], but sometimes they don’t want to do it because they think it’s bad. And I have tried to search for psychosis and such in school [in prison], but then the teachers ask why I would seek out such a gloomy subject. It feels a bit complicated to obtain information. Larry
Participants from all three prisons also pointed out the need for more information about mental healthcare in prison:
We have a notice board on the ward (…). The information should be hung there for people to see, that there is a psychologist here, and that you can talk to her. ‘cause I’ve seen little of that sort in here. Liam
One participant underscored that information about available mental health services is particularly important for those with no experience from such services prior to imprisonment:
It [information] must tell you about your opportunities. To normalize it [seeking help] in a way. And the threshold must be low. I think many experience that it is too high. If I hadn’t been in contact with mental health services before I came here, the threshold for seeking help would have been sky high for me as well. Neil
Awareness of mental health issues
Factors in the prison context were fundamental to the participants’ explanations of mental health problems. Many participants attributed the onset or worsening of mental health problems to the shock of imprisonment and to the continuous hardships of prison life. Understanding symptoms as primarily caused by external stressors such as prison hardship may have influenced their appraisals about the need to seek help. As Frank stated:
I’ve always had good mental health. Until I came here, inside these walls. Frank
Frank reported considerable symptoms of post-traumatic stress. Understanding his symptoms as something triggered by the prison living conditions, he did not see how seeking professional help could benefit him. Like many other participants, he insisted that the correctional system needed to change and had lost hope that he could improve his own situation.
In contrast, other participants who attributed their mental health problems to external stressors concluded that they indeed needed help to cope. The suffering they experienced during their first weeks in prison motivated them to seek formal help:
I asked to talk to a psychologist in here. ‘Cause, I felt that I needed to. ‘Cause in the beginning when I came here, it all seemed dark. No matter how hard I tried to do the right thing, there was some sort of dark force that was just pushing on, and the obstacles were piling up. Travis
For some, their main motivation for seeking help was to receive professional validation from healthcare personnel regarding the negative health consequences of their prison experiences. Some also hoped that healthcare professionals could advocate for better living conditions:
And it is good that others [psychologists] can take part in these things. So that it is manifested what prisons actually do to people. Jack
Social influences on help-seeking
Prison culture and mental health stigma.
The participants described how the culture within prison influenced their willingness to talk about mental health issues. The importance of appearing strong and dominant within the prison setting was emphasized by many. According to several participants, the talk at the wards was characterized by attempts to one-up the others’ stories about criminal activities to appear tough. Many also explained that hiding vulnerabilities was critical in the prison community, and some also underlined the potential for victimization for those who were not able to conform to the prison norms:
You are wearing a prison mask. You cannot show weakness. ‘Cause then you’ll soon be a victim, a sitting duck. I have experienced inmates that have, eh mostly stayed in their cells. They have been harassed so badly that they are sitting there crying. The prison milieu can be tough. Neil
Choosing to confide in and seek advice from peers can also have negative consequences. Several of the participants said that it was wise to be careful with who you chose to share mental health related issues with:
Let’s say you talk about your personal feelings, and about your sentence and stuff, right. They can be very nice to you there and then, before they stab you in the back later on, spreading everything you’ve said to destroy you. It is a cynical game. Bobby
Bobby went on to explain that a fellow incarcerated individual could use personal information for harassing, blackmailing and threatening the family of someone who has confided in them, if a conflict should arise. Some of the participants also addressed directly how the prison climate may influence willingness to seek mental health treatment:
They do not want to go to a psychologist and talk. Because then they are seen as weak and not able to cope. Because in prison everyone should be tough. Drug lords and such. But, on the inside they are not like that. Nicky
The role of peers in accessing mental health services
Despite the clear barriers, fellow incarcerated appeared to be an important informal help source for mental health problems. Many of the participants had observed signs of emotional distress among their incarcerated peers and described how they had given them advice and encouragement. According to several participants, those imprisoned also had an essential role in recognizing mental health problems in their peers:
There is no-one who talks to us regularly to check on how we are doing. That’s not a priority here. So, unless some of the inmates take on the role of an officer or a psychologist, then there’s no-one who reports concern (…) There are many inmates who are taking on a role as a social worker, but it’s kinda wrong. They are neither paid for it, nor qualified. They do it because no-one else does. Stuart
Although none of the participants said that they themselves had been prompted to seek help by peers, they told stories of how they had pushed their peers to seek formal help:
A fellow inmate. I could tell he was struggling because he talked to me as the only person. In a way, I was his psychologist. The days when he was down in the dumps, I tried to talk to him (…) And I said, listen up. It’s for your own good. I will write a request form, and we will arrange contact with a psychologist (…) and it will help. Nicky
Experiencing fellow incarcerated people in distress appeared to be common, and participants also explained how they reported to prison officers their concerns about peers with self-harm and suicide plans:
There was a fella’ who told me that he knew exactly how to take his own life (…). “I’ll just do it like this and this and this”. And, uhm. Then he said he was going to do it. And I thought that I would have to report it, and I did. Roy
Roy went on to describe in detail how his reported concern led to a prison officer interrupting the suicide attempt by the fellow incarcerated, thereby saving his life. Several other participants shared similar stories, indicating that peers played a significant role in recognizing and getting help for mental health related problems in prison.
Access to mental healthcare
Self-referral and disempowerment.
In order to access prison healthcare, those imprisoned must write and deliver a paper-based request form. All the participants in this study were aware that this is the way to contact prison healthcare, and most of them knew that the general practitioner working at the prison could refer them to a psychologist or to a psychiatric hospital. Unfortunately, the request form system seemed to amplify the participants’ perceptions of disempowerment. Rather than seeing themselves as agents taking charge of their own situation and health, they were left passively waiting to be contacted after filling out the forms:
You are pacified when you must write a request form to talk to someone. Then you don’t know when they are coming to talk to you. And then it’s like, the problem may be swept under the rug when they finally get to you. Tommy
According to the participants, many of these request forms seemed to disappear, and it could take an exceedingly long time before they got any response to their request:
Many times, when you write a request form it disappears. Nothing happens. Those request forms are worthless most of the time. Keith
There were also several participants who voiced concern over the confidentiality of the request forms even when the forms were delivered in closed envelopes:
We can see for ourselves that they [prison officers] open and read, uhm, confidential information, [lowers his voice] and to put it mildly, uhm, breaches in confidentiality are all too common. It is alarming! Neil
One of the informants also explained that incarcerated persons who had mother tongues other than Norwegian could have problems with understanding and filling out request forms to health, and that forms that were not filled out correctly were of no value. According to Roy and other participants, the correctional system did not give sufficient information and guidance about the request forms:
They might not know how to write, or understand what it [the form] says, you know? Potentially it is severe for that guy, right. It’s garbage! Garbage, that request form. They haven’t received any request from him. Roy
The perceived availability of mental healthcare
The perceptions of accessibility of mental health care varied between the participants. A few of the participants were in active treatment with a psychologist at the time of the interviews, and they had experienced the access as unproblematic. Common for some of these participants was that they had been in treatment before they entered prison:
From sending my request and to receiving an acceptance letter it took one and a half weeks. Less than three weeks later I was in treatment. It was efficient. Much quicker than I’ve ever experienced before. Neil
However, many participants said that they could not access secondary mental health services. There were two notable sub-groups among the participants who perceived that access to specialized psychological treatment was limited. The first group shared stories about living unstructured lives at the edge of society. They seemed to have little confidence in health care and correctional services, and were less hopeful of their own potential of being rehabilitated:
I have tried for several years now, but I didn’t get help. They can say whatever they want about how easy it is to access a psychologist and prison healthcare and everything, but it is not true. Ronny
Two of the participants explained how they would have to take drastic measures such as performing violent acts or acting weird to get help for their mental health problems When Marlon was asked how he could access mental health services he responded:
You would have to either hurt yourself, or someone else, so that they end up in hospital. Marlon
The interviewer asked if it was possible to access mental health services by using less drastic measures, Marlon answered:
Uhm. Naaah. I don’t know. I do not think so. Not from my experience. Marlon
Another sub-group having difficulties accessing mental health services was those in prison for the first time. Most had led more typical lives with stable employment and housing conditions before imprisonment. When they sought mental health services, they were told that these adjustment problems were normal in prison:
I’ve been struggling for several periods here and have said that I wanted to talk to a nurse or a psychologist. And then I was referred to a psychologist. And the psychologist assessed me, and said that: “Nothing’s wrong with you, you are just having a hard time, I cannot help you”. So, you do not get anyone to talk to, unless you- I don’t know what you must have really, but I sure ain’t got it. The nurses say that they haven’t got the time, and the psychologist says that I am not ill. And then I am left to feel bad. In my case, there is no service really. Stuart
Prison officers’ role in mental healthcare and accessing services
Several participants stated that mental health problems and well-being were not high on the prison agenda. Many would have appreciated it if correctional officers on a more regular basis had asked how they were doing and believed that this would have facilitated them to open up and talk about mental health issues.
In my opinion, mental health is forgotten here in a way. Physical activity, movement, workouts, yes. Since I arrived here some months ago, only twice I’ve been asked: “Hi, how are you? Is there something you want to talk about?” Travis
Some also said that they knew people in prison who were unaware of their own need for mental health care or unable to access help, and argued that the correctional system should do more to help these people to access care:
You have the type where people do not get help because they themselves are not able to request help from the prison health services and the prison officers do not see to that they get the help they need. Neil
Some were concerned about how acute health problems were handled in the weekends and evenings when prison health services were unavailable. In these situations, prison officers were left to decide whether or not to contact emergency healthcare services. Several of the participants were not satisfied by this arrangement:
(…) they think that they can make a doctor’s judgement. That they can decide that it is not that important. It is rude. It is trespassing norms. Jack
Some participants told stories of how their peers in prison did not seem to get the help they needed even though it was apparent that they were in a bad state mentally:
I have reported concern about people, before they started cutting themselves and f***ing themselves up. But what worries me, is that even though I voiced my concern to both prison health services and prison officers, no measures were taken. Before it was too late. Stuart
Asking for help from correctional officers could also have consequences. Ronny served at a lower security level. He experienced that his requests to see a psychologist were met by suggestions of transferring him to a higher security level:
I have written request forms: “I need to speak to a psychologist. Immediately”. And then they [the prison officers] are threatening me by saying that they are going to transfer me to a higher security level. They ask if I am going to hurt myself. No, I tell them. I’m not going to hurt myself. I just need to talk to a psychologist. Ronny
Another participant described how he had sometimes cut himself by shards from plates and drinking glass to suppress mental suffering. He explained how he on one occasion used the intercom to notify the officers that they needed to come and pick up a glass that was triggering an urge to self-harm. The participant said that initially a single officer came to his cell to pick up the glass:
A few minutes later there were four officers, and they unlocked the cell door, and there were a lot of questions. I guess they were worried about my mental state, and I said that I appreciated the concern. Then I reminded them that I had asked them to pick up the glass so I would NOT cut myself, so if they were to use that against me, it would be unfair. Tommy
He reassured that the situation had been resolved with the conversation. However, he had the impression that disclosing mental distress to officers could increase the risk for being transferred to a higher security level, or to a security cell.
Enhancing access to services
The perceived advantages of seeking professional help.
There were some commonly experienced benefits of seeking mental healthcare among the participants. Coming off drugs and living under stable conditions in prison provided some participants an opportunity to reflect on their lives and to gather motivation to work on their addiction and mental health problems:
I have been thinking a lot about treatment in an institution. I know how it went the last few times I got out [of prison]. Within half an hour I was sitting there with the needle. And if I don’t do anything before I get out, the same will happen again. I’m trying to prevent it (…) I’ve had treatment for drug and alcohol use before. And back then there was a psychologist who said that, once you’ve been clean for a year, then the brain is back to normal. I can feel it, like, my mindset is already changing . Kurt
For about half of the participants, seeking professional help was related to their motivation for living a law-abiding life after prison. The participants linked substance use to both mental health problems and a criminal lifestyle, and getting treatment was seen as essential for preventing recidivism:
I have lived a rough life, and I have no-one, NO-ONE. How long am I going to live? One doesn’t know. But I’ll be fifty soon. So, I must make it now. I really have to make it now [his voice bursts]. And it depends on many psychological factors. So, I’m choosing to use all the things that I have access to in prison, like treatment for drug addiction. Roy
Although many had previous experience of treatment for their substance use, they still had hopes that treatment could help them. Liam had previously experienced that consultations with a psychologist brought up subjects that was difficult for him to talk about:
I regret that I quit, because it could have done me good. But I guess it got too personal, and it stirred up things. Liam
He also explained that at the time he was more interested in doing drugs than going to therapy. However, he still believed that treatment could help him:
I will probably contact a psychologist, now that I’m about to get treatment for my addictions. It is easier to open up when there are no substances involved. Liam
In summary, seeking professional help for mental health problems was perceived to promote in-prison coping, rehabilitation, and preparation for life outside of prison for most of the participants.
Lowering the bar for accessing mental health services .
Many of the participants expressed skepticism towards ‘the system’. They described how they had been let down and disappointed by the child welfare services, the criminal justice system, and healthcare professionals. Experiences from childhood to adult life had led to a lack of confidence that healthcare personnel and the correctional system and society had their best interest at heart. For them, it was important that healthcare professionals were perceived as genuine and “on their side”:
The experience of being believed and listened to… They do not have to relate, to say that they understand so damn much, ‘cause that’s not really important. Marlon
Several participants said that barriers for talking about mental health were reduced when healthcare personnel reached out in the prison ward. One of the prisoners described two nurses who used to visit the prison wing every day at lunch-hour. He appreciated that it was possible to request a private conversation in the cell, and that he was taken seriously:
They were highly skilled. And they listened. They listened to what you had to say, and they understood you. Tommy
Having previous positive experiences of mental health treatment and knowledge of what to expect from mental health services also seemed to reduce barriers for in-prison help-seeking from some of the participants:
I saw a psychologist on a regular basis, once a week (…). And after six consultations I was past the worst in some sense. I was provided with the tools I needed to cope. Bobby .
This participant had experience with psychological treatment outside of prison and had tried to access mental health services for months in prison. However, he believed his challenges were too mild to get help from a psychologist. He emphasized the need for available low-threshold services for those who suffer from milder mental health problems:
It should be available for everyone who wants it. It should not be embarrassing, it should not be taboo, it should be… A natural part of it, really. Bobby
In addition, when services were provided as standard procedure and a natural part of rehabilitation, they were perceived as less stigmatizing. Nicky described how he was placed on a prison ward that was specialized in substance use treatment:
And when you are placed in that ward, then you are automatically assigned to a psychologist from the substance use clinic, that you can have weekly consultations with. Nicky .
Some also suggested that the systematic screening and assessment of health and social problems also could facilitate access to mental health services and this was suggested as an integral part of healthcare and rehabilitation in prison by some of the participants. Ronny underscored the importance of proper assessment:
What is this person’s problem? Why did he come back? Is there something happening to him on the outside? Could he need help with anything? Maybe someone should ask him? Ronny
Ronny went on describing the nice brochures of the correctional system, with promises of assessment of strengths and needs of individuals, but he claimed that this did not happen in reality. This view was shared by several of the other participants, as they called for more assessment to benefit the mental health and rehabilitation of incarcerated individuals.
Mental health support from different sources
The participants had different preferences regarding where to get help. Support from friends and family was seen as important for most of the participants. However, health professionals could sometimes be preferred over informal or semi-formal sources because of their role in advocating for better living conditions in prison:
I get visits from my family, but I’d like to talk to someone here in prison, so that they could gain awareness of the actual problem. If I’m spitting venom to some random lady that is here as a volunteer with the Red Cross, it’s useless, I think. If I talk to a nurse who works here at this establishment, she could perhaps do something about some of our challenges. Stuart
The cultural competency of health care personnel could also be a key factor in promoting help-seeking and forming a therapeutic alliance with people in prison. Many incarcerated individuals have lived on the edge of society, while most health care personnel, and particularly doctors and psychologists, are from the upper middle class. These cultural differences may form an abyss between the incarcerated individuals and mental healthcare personnel:
A psychologist does not have a criminal record. Now I’m generalizing. But they have performed well in school. Have passed through the system. Highly educated. Their lives have been smooth sailing (…) They have not experienced the shadow side of life. Tommy
This participant had one prior positive experience with a psychologist, but his general impression of psychologists was that they were of no help. He did not feel a connection with any of the others and had written them off completely. He preferred talking to a representative from a user organization who have led a similar life to himself:
I know that they know exactly how I’m feeling. They have served a prison sentence. And they… They have lived experience, and then it’s much easier to listen to what they have to say, because I know it’s not knowledge that they have acquired through reading. Tommy
Prison officers can also be of help to incarcerated people who experience mental health problems. Nicky said that while he was at a lower security level, he had been to a sports event outside prison with an officer and some fellow incarcerated. He had a panic attack because of all the people who kept arriving at the venue and he had to go outside for some fresh air. The prison officer followed him and was understanding, and told Nicky that he had seen many incarcerated people with similar reactions:
He was understanding and said: It will be OK. After that day at the match, coincidently, he ended up being my primary contact officer. And to socialize me back to society he fixed it so that every weekend he was working we could go to a shopping mall, to try. Little by little, by little. (…) It helped. It did. Yes. Nicky
Although Nicky had no plan to seek help for his anxiety symptoms, he appreciated the support he received from his primary contact officer.
Bobby, on the other hand, had some informal support from fellow incarcerated and had also talked with a priest. He said that he often ruminated when he had time alone in his cell and emphasized his need for sharing his thoughts with others and receiving advice. He explained why he preferred to get help from formal sources:
So, to have someone who is an outsider. Who’s not an inmate. Who has got a sensible outlook on life, that can guide you– I think that’s important. (…) Because when you talk to a fellow inmate, then… It can go in the opposite direction, right. Because many have been through major crises, they have lost friends, they have lost family, maybe they have lost their girlfriend and wife, their children won’t speak to them, right? Bobby
Most participants also held the prison priests in high regard and appreciated the availability of the service. However, talking with a priest was not seen as a replacement for a consultation with a psychologist:
It was peculiar, when I asked for someone to talk with, the priest was offered first. For me it is alright, I go to church. But I’m thinking, if someone is not a Christian. I’m like: a priest? Or if you’re not religious. A session with the priest is more like a consultation towards God and his will. He can be a good listener [the priest], but you might not get the help you need in a mental sense. So, a psychologist, a “talking person” in prison is necessary. That could check on you sometimes.
This study’s findings demonstrate that many of the factors deciding access to mental healthcare are firmly rooted at the organizational level of the correctional and healthcare systems. Prisons in the Scandinavian countries, including Norway, are presumptuously humane compared to harsher correctional settings in other parts of the world. One could assume that these favorable conditions would be more conducive to mental healthcare access. However, the systemic barriers we found largely overlapped with challenges reported in other countries [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]. In addition, we found that individual beliefs, attitudes and aspirations also influence willingness to seek mental healthcare. Interestingly, most of these intrapersonal factors are tightly interwoven with the participant’s appraisals of how the prison conditions influence their mental health. This study also addresses an important knowledge gap in the literature, namely how restrictions on access to mental health information could influence mental health help-seeking for people in prison. The identified core category, “Breaking down barriers”, reflects an overarching focus on solutions to improving mental healthcare access based on the experiences of the participants in this study.
Access to health information
Knowledge of available services and how to access them is a prerequisite for mental health help-seeking [ 80 ]. The participants in our study claimed that information about mental health services was unsatisfactory, and lack of such information has also been noted as a barrier to help-seeking in other prison-based studies [ 44 ]. Moreover, sufficient levels of mental health literacy are positively associated with increased intentions for help-seeking from both informal and formal sources [ 81 ]. The participants in our study reported severely restricted access to their preferred sources of health information and a dependency on others to obtain such information. Since information seeking may occur before individuals are ready to share their health concerns with others, having to rely on others for accessing information is a potential barrier for recognizing mental health problems [ 25 ]. Thus, it is likely that the limited access to mental health information negatively impacts incarcerated persons capacity to manage their own mental health needs. The potential consequences of restrictions on access to health information among people in prison need more research attention. However, findings from other populations suggest that closing the apparent health information gap could be an important intervention for improving help-seeking for mental health problems [ 82 , 83 ].
The social influences on accessing mental healthcare
The participants reported that prison culture reduced their willingness to seek support from fellow incarcerated and the use of professional help for mental health problems. The TBP element “subjective norms” posits that beliefs about the opinions of others may influence the willingness to seek help [ 29 ]. Attributing mental health problems to personal weakness may reflect a stereotyped attitude involved in stigmatizing mental disorders [ 84 ]. Stigma may lead to concerns about what others might think if one were to seek help, and may delay or hinder help-seeking efforts [ 80 , 85 ]. It also seemed to be an important constraint to mental healthcare access in our study. This corresponds with findings from other studies [ 45 , 46 , 47 ] and suggests that fear of appearing weak is also a significant barrier to help-seeking in a Scandinavian prison context. Based on our findings and recommendations, we advise that focus on health education and normalization of mental health problems are measures that could decrease stigma [ 86 ], and increase willingness to seek mental health support and treatment among people in prison.
Although the culture among those incarcerated was perceived to discourage seeking support for mental health problems, fellow incarcerated also played a key role in supporting those who experienced mental health problems. They were more available than other help sources and had lived experience with distress related to imprisonment. Since information about available services was insufficient, fellow incarcerated were also perceived as an important source of information. Thus, naturally occurring peer support seemed to normalize mental health problems, possibly reducing stigma and lowering the threshold for mental health help-seeking. From the literature, we know that peer-based health interventions is effective in correctional settings [ 87 ], and formalizing peer-based health information and support could be beneficial in interventions aiming to increase the use of mental health services.
Beliefs and motivations for help-seeking
The prison environment was embedded in the participants’ beliefs: attributing the onset and worsening of mental health problems to the prison conditions was common among the participants. According to the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), attitudes about the potential benefits of help-seeking and alignment with individual goals affect the readiness and willingness to seek professional help [ 29 ]. Our data supported this notion. Some participants abstained from seeking professional help as they did not see how it might benefit them in their goal of improving their living conditions. For others, a prominent motive for seeking professional help was to receive validation and help managing their challenging life situations and the everyday stressors of prison life. A few participants also framed mental health help-seeking as a mission to document the consequences of imprisonment. By sharing their experiences with professionals, they hoped healthcare personnel could help them advocate for better conditions in prison. Obtaining sufficient knowledge about essential aspects of prison life is essential for health professionals working in a prison setting [ 88 ]. Based on our findings we propose that the ability of healthcare staff to communicate their understanding of the influence of prison living conditions on mental health is crucial for gaining trust and building an alliance with their incarcerated patients.
Another important motivator for many participants seeking help was their aspirations to live a law-abiding life after being released. It has been increasingly recognized that the relationship between mental disorders and criminal activity is complex and that integrated treatment that addresses both criminogenic factors (i.e. antisocial attitudes and behavior, substance use, criminal network, family issues and low educational/vocational engagement) and mental health issues is a must to prevent recidivism [ 89 ]. This view corresponds with the beliefs and preferences for rehabilitation and healthcare of several participants in our study. They were worried about their reintegration into society, which motivated them to seek professional help. Substance use treatment, in particular, was seen as essential to attaining rehabilitative goals. However, some participants who had served multiple sentences were less positive towards help-seeking. They had more negative experiences and seemed less hopeful that mental healthcare could improve their situation. Their low expectations for potential gain combined with a perceived lack of personal control in the help-seeking process, appeared to stall help-seeking for these participants. We suggest that implementing health services with a concurrent focus on addressing both criminogenic needs and mental disorders could be especially important for fostering healthcare utilization for people with a history of reoffending.
Organizational barriers to accessing mental healthcare
The perceived challenges with the paper-based request system were considered a significant barrier to healthcare access. TPB postulates that behavioral control and self-efficacy are important in help-seeking [ 29 ]. In a system where autonomy is limited, one could assume that a self-referral system can be empowering for those seeking help. However, the participants seemed to experience the opposite as they were left passively waiting for an answer to their request. Some also expressed confidentiality concerns, as they believed that prison officers read the request notes. Thus, the process of accessing health services seemed to diminish, rather than enhance their notions of control and self-efficacy. Improving the reliability of responses to requests and ensuring confidentiality could increase the experience of control in the self-referral process and may also empower imprisoned persons to seek help.
A barrier rooted in the interactions between the individual and the helping services was found in various expressions of skepticism towards “the system” by many participants. Earlier studies have also reported distrust in the system as a barrier to help-seeking [ 41 , 44 ]. Our results elaborate on these findings as the participants spoke of how suicides and severe self-harm by fellow incarcerated people contributed to diminished faith in the system. Some had voiced concern over the health and welfare of peers and had experienced that they were not listened to by the prison officers. According to the participants, many of their fellow incarcerated people had more severe symptoms of mental health problems and did not seem to have access to the help they needed. This confirmed their beliefs that the system took little interest in their mental health, and for some of them this led to a growing feeling of hopelessness and resentment. In addition, the high prevalence of mental disorders in prison implies that incarcerated persons witness people in severe distress regularly and for prolonged periods. This issue is largely unexplored and unrecognized in prison research, and the impact of these experiences on mental well-being and recovery should be investigated further.
Participants who experienced mental distress and adjustment problems had difficulties in accessing mental health services. They needed someone to talk to about their situation that could give them advice on how to cope, however they did not fulfil the criteria for secondary mental health services. Minor mental health problems in Norwegian prisons are to be handled by the prison healthcare services. However, according to the participants their capacity is very limited. This finding corresponds to other studies [ 90 ] documenting that access to integrated mental health services was limited for those with milder mental health problems. In the community, the establishment of low threshold services for people with mental health problems has been an important commitment as early intervention can prevent the development of more serious conditions. This may be even more important for those imprisoned, since coping strategies such as physical activity and seeking social support are less accessible [ 91 ].
Prison officer’s influence on access to mental healthcare
Prison officers were perceived to have a key role as gatekeepers to healthcare. Officers can facilitate access to healthcare by encouraging help-seeking or directly contacting healthcare services based on observations and conversations with incarcerated individuals [ 39 , 41 , 92 ]. The participants in our study pointed out the need for prison officers to take their health concerns more seriously, and that the threshold for contacting healthcare services by their request was too high. In addition, being asked directly about their psychological state by staff members was seen to ease talks about mental health by the participants. Our results support the notion that prison officers that are responsive to the mental healthcare needs of incarcerated persons could build confidence that these needs would be attended to when required [ 92 ]. Thus, ensuring sufficient mental health knowledge and awareness among prison officers of their role in mental healthcare access is an essential task for correctional systems.
Previous studies have found that the correctional systems´ procedures for managing suicidal risk is a potential obstacle for help-seeking. The fear of being moved or placed in a safety cell without personal belongings was identified as a barrier to disclosing suicidal thoughts [ 39 , 93 ]. In Norway, the risk of self-harm and suicide is ideally handled by increasing social contact, activities, monitoring and healthcare. However, in the face of acute mental crisis and severe suicide risk, placing persons in solitary confinement is not an uncommon practice [ 94 ]. Challenges with having incarcerated persons admitted and treated in specialized health care institutions, understaffing, and a lack of central guidelines for handling suicide risk may contribute to the use of solitary confinement for incarcerated persons in acute mental distress in the Norwegian correctional system [ 94 ]. The Norwegian Parliamentary Ombudsman reports that fear of solitary confinement and being placed in a security cell is a barrier to seeking help for suicidal ideations and plans [ 95 ]. In our study, participants who had asked for help when they were in acute distress experienced that the officers assumed that they intended to harm themselves. They were faced with the potential of being transferred to a higher security level or being placed in solitary confinement. Thus, how prison officers respond to incarcerated persons’ reports of acute mental distress could be of critical importance for their willingness to seek help for mental health issues in the future. However, more research on the perceived and actual consequences of disclosing mental distress and suicidal ideations in prison is needed to inform interventions to promote help-seeking.
Enhancing access to mental healthcare in prison
The participants underscore some conditions that may lower the bar mental healthcare utilization. Earlier positive experiences with mental healthcare in the community was mentioned by participants as important for their willingness to seek such services in prison, which also corresponds with findings in earlier studies [ 42 , 96 ]. In addition, the participants saw mental health services that were outreaching and integrated as positive. A few participants also highlighted mental health screening at reception to discover mental disorders that may need intervention. Screening at intake, and outreaching and integrated services are also recommended in the prison research literature [ 88 ]. Our findings show that these recommended measures may also make intuitive sense to incarcerated persons - common for all of them are that they seem to reduce stigma related to utilizing mental healthcare.
Our results indicate that incarcerated persons with both milder and more severe mental disorders experience barriers to accessing mental healthcare. These results are in line with studies from other correctional settings reporting unmet needs due to challenges with access and delivery of mental healthcare [ 37 , 38 , 39 ]. The underutilization of mental health services by incarcerated persons suggests that the ‘degree of fit’ between their needs and the available mental healthcare requires improvement. The World Health Organization (WHO) advocates for correctional systems with health and well-being as an integrated part of their core business and culture [ 33 ]. Along these lines, we found that participants called for a correctional system with mental health higher on the agenda. Some also preferred to seek help for mental health problems from other sources than mental health professionals. This finding supports the recommendation of the WHO that it is important to build mental health competency in all staff members in contact with those imprisoned. As many of the barriers to mental healthcare utilization are rooted in the wider correctional setting, we also suggest that the correctional and healthcare systems, in collaboration, should review their practices to enhance perceived efficacy in accessing healthcare.
Limitations
The data in this study are based on interviews with fifteen participants from three prisons. The participants were self-selected and may have had more knowledge, interest, and willingness to talk about mental health issues than the average person in prison. We cannot claim that the results represent a complete account of access to mental healthcare and help-seeking among incarcerated persons in Norway. However, our findings were consistent with findings from other studies from Norway and correctional settings in some other countries. We have presented details about the participants, method, data, and context to allow others to consider the potential transferability of the results. We hope our findings encourage further research on access to mental healthcare for people in prison.
Mental healthcare that is outreaching and integrated is perceived to facilitate access and decrease stigma. The correctional system should address access to health information, the referral system, and their responses to incarcerated persons who disclose distress to facilitate access to healthcare. Our results also indicate that mental healthcare extends beyond the scope of health services, suggesting that sufficient mental health knowledge and agency is needed at all levels of the correctional system.
Data availability
The data produced in the course of this research is not openly accessible owing to considerations regarding privacy. However, they can be obtained from the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Theory of planned behavior
Mental health literacy
Baranyi G, Scholl C, Fazel S, Patel V, Priebe S, Mundt AP. Severe mental illness and substance use disorders in prisoners in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence studies. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(4):e461–71.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Butler T, Andrews G, Allnutt S, Sakashita C, Smith NE, Basson J. Mental disorders in Australian prisoners: a comparison with a community sample. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2006;40(3):272–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cramer V. The prevalence of mental disorders among convicted inmates in Norwegian prisons. 2014.
Sirdifield C, Gojkovic D, Brooker C, Ferriter M. A systematic review of research on the epidemiology of mental health disorders in prison populations: a summary of findings. J Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2009;20(sup1):S78–101.
Article Google Scholar
Baranyi G, Fazel S, Langerfeldt SD, Mundt AP. The prevalence of comorbid serious mental illnesses and substance use disorders in prison populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health. 2022;7(6):e557–68.
Fazel S, Hayes AJ, Bartellas K, Clerici M, Trestman R. Mental health of prisoners: prevalence, adverse outcomes, and interventions. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3(9):871–81.
Ford K, Bellis MA, Hughes K, Barton ER, Newbury A. Adverse childhood experiences: a retrospective study to understand their associations with lifetime mental health diagnosis, self-harm or suicide attempt, and current low mental wellbeing in a male Welsh prison population. Health Justice. 2020;8(1):13.
Schnittker J, Massoglia M, Uggen C. Out and down: Incarceration and Psychiatric disorders. J Health Soc Behav. 2012;53(4):448–64.
Mahgoub M, Monteggia LM. Epigenetics Psychiatry Neurother. 2013;10(4):734–41.
CAS Google Scholar
Ray M, Wallace MK, Grayson SC, Cummings MH, Davis JA, Scott J, et al. Epigenomic Links between Social Determinants of Health and symptoms: a scoping review. Biol Res Nurs. 2023;25(3):404–16.
Revold MK. Innsattes levekår 2014 Før, under Og etter soning. Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistics Norway; 2015. Report No. 47.
Google Scholar
De Viggiani N. Unhealthy prisons: exploring structural determinants of prison health. Sociol Health Illn. 2007;29:115–35.
Goomany A, Dickinson T. The influence of prison climate on the mental health of adult prisoners: a literature review. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2015;22(6):413–22.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Nurse J, Woodcock P, Ormsby J. Influence of environmental factors on mental health within prisons: focus group study. BMJ. 2003;327(7413):480.
Solbakken LE, Bergvik S, Wynn R. Beliefs about mental health in incarcerated males: a qualitative interview study. Front Psychiatry [Internet]. 2023;14. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/ https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1242756
Kohn R, Saxena S, Levav I, Saraceno B. The treatment gap in mental health care. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82(11):858–66.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pathare S, Brazinova A, Levav I. Care gap: a comprehensive measure to quantify unmet needs in mental health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27(5):463–7.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wang PS, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Borges G, Bromet EJ, et al. Use of mental health services for anxiety, mood, and substance disorders in 17 countries in the WHO world mental health surveys. Lancet. 2007;370(9590):841–50.
Penchansky R, Thomas JW. The Concept of Access: definition and relationship to consumer satisfaction. Med Care. 1981;19(2):127–40.
Gulliford M, Figueroa-Munoz J, Morgan M, Hughes D, Gibson B, Beech R, et al. What does ‘access to health care’ mean? J Health Serv Res Policy. 2002;7(3):186–8.
Alonso J, Liu Z, Evans-Lacko S, Sadikova E, Sampson N, Chatterji S, et al. Treatment gap for anxiety disorders is global: results of the World Mental Health Surveys in 21 countries. Depress Anxiety. 2018;35(3):195–208.
Doll CM, Michel C, Rosen M, Osman N, Schimmelmann BG, Schultze-Lutter F. Predictors of help-seeking behaviour in people with mental health problems: a 3-year prospective community study. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):432.
Thornicroft G. Most people with mental illness are not treated. Lancet. 2007;370(9590):807–8.
Rickwood D, Thomas K. Conceptual measurement framework for help-seeking for mental health problems. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2012;5:173–83.
Rickwood D, Deane FP, Wilson CJ, Ciarrochi J. Young people’s help-seeking for mental health problems. Aust E-J Adv Ment Health. 2005;4(3):218–51.
Jorm AF. Mental health literacy: empowering the community to take action for better mental health. Am Psychol. 2012;67(3):231–43.
Lui JC, Sagar-Ouriaghli I, Brown JSL. Barriers and facilitators to help-seeking for common mental disorders among university students: a systematic review. J Am Coll Health. 2022;1–9.
Lynch L, Moorhead A, Long M, Hawthorne-Steele I. The role of Informal sources of help in Young people’s Access to, Engagement with, and maintenance in Professional Mental Health Care—A Scoping Review. J Child Fam Stud. 2023;32(11):3350–65.
Tomczyk S, Schomerus G, Stolzenburg S, Muehlan H, Schmidt S, Ready. Willing and able? An investigation of the theory of Planned Behaviour in help-seeking for a community sample with current untreated depressive symptoms. Prev Sci. 2020;21(6):749–60.
Adams C, Gringart E, Strobel N. Explaining adults’ mental health help-seeking through the lens of the theory of planned behavior: a scoping review. Syst Rev. 2022;11(1):160.
Niveau G. Relevance and limits of the principle of ‘equivalence of care’ in prison medicine. J Med Ethics. 2007;33(10):610–3.
The United Nations Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners [Internet]. United Nations Office On Drugs and Crime. 2015. https://www.unodc.org/documents/justice-and-prison-reform/Nelson_Mandela_Rules-E-ebook.pdf
Durcan G, Zwemstra JCZ. Mental health in prison. In: Enggist S, Møller L, Gauden G, Udesen C, editors. Prisons and Health [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014. pp. 87–94. https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/249188/Prisons-and-Health.pdf
Forrester A, Till A, Simpson A, Shaw J. Mental illness and the provision of mental health services in prisons. Br Med Bull. 2018;127(1):101–9.
Lines R. From equivalence of standards to equivalence of objectives: the entitlement of prisoners to health care standards higher than those outside prisons. Int J Prison Health. 2006;2(4):269–80.
Simpson AIF, McMaster JJ, Cohen SN. Challenges for Canada in meeting the needs of persons with serious mental illness in prison. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2013;41(4):501–9.
PubMed Google Scholar
Reingle Gonzalez JM, Connell NM. Mental Health of prisoners: identifying barriers to Mental Health Treatment and Medication Continuity. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(12):2328–33.
Patel R, Harvey J, Forrester A. Systemic limitations in the delivery of mental health care in prisons in England. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2018;60:17–25.
Gilling McIntosh L, Rees C, Kelly C, Howitt S, Thomson LDG. Understanding the mental health needs of Scotland’s prison population: a health needs assessment. Front Psychiatry [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Dec 27];14. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/ https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1119228
Wright N, Jordan M, Kane E. Mental health/illness and prisons as place: Frontline clinicians׳ perspectives of mental health work in a penal setting. Health Place. 2014;29:179–85.
Byrne E, Bradshaw D, Kerin M, Pepe I. A social identity approach to mental health help-seeking behaviour in prisoners: A systematic review. J Community Appl Soc Psychol. 2023;casp.2727.
Morgan RD, Steffan J, Shaw LB, Wilson S. Needs for and Barriers to Correctional Mental Health Services: inmate perceptions. Psychiatr Serv. 2007;58(9):1181–6.
Howerton A, Byng R, Campbell J, Hess D, Owens C, Aitken P. Understanding help seeking behaviour among male offenders: qualitative interview study. BMJ. 2007;334(7588):303.
Mitchell J, Latchford G. Prisoner perspectives on mental health problems and help-seeking. J Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2010;21(5):773–88.
Kupers TA. Toxic masculinity as a barrier to mental health treatment in prison. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61(6):713–24.
De Viggiani N. Trying to be something you are not: masculine performances within a prison setting. Men Masculinities. 2012;15(3):271–91.
Daquin JC, Daigle LE. Mental disorder and victimisation in prison: examining the role of mental health treatment: Mental Disorder, treatment, and victimisation. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2018;28(2):141–51.
Jorm AF, Korten AE, Jacomb PA, Christensen H, Rodgers B, Pollitt P. Mental health literacy: a survey of the public’s ability to recognise mental disorders and their beliefs about the effectiveness of treatment. Med J Aust. 1997;166(4).
Picco L, Abdin E, Pang S, Vaingankar JA, Jeyagurunathan A, Chong SA, et al. Association between recognition and help-seeking preferences and stigma towards people with mental illness. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27(1):84–93.
Marco-Ruiz L, Wynn R, Oyeyemi SO, Budrionis A, Yigzaw KY, Bellika JG. Impact of illness on Electronic Health Use (the Seventh Tromsø Study - Part 2): Population-based Questionnaire Study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(3):e13116.
Pretorius C, Chambers D, Coyle D. Young people’s Online help-seeking and Mental Health difficulties: systematic narrative review. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(11):e13873.
Reavley NJ, Cvetkovski S, Jorm AF. Sources of information about mental health and links to help seeking: findings from the 2007 Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2011;46(12):1267–74.
Rantanen T, Järveläinen E, Leppälahti T. Prisoners as Users of Digital Health Care and Social Welfare Services: a Finnish attitude survey. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(11):5528.
Smith PS. Imprisonment and Internet-Access; Human rights, the Principle of normalization and the question of prisoners Access to Digital Communications Technology. Nord J Hum Rights. 2013;30(04):454–82.
Novisky MA, Schnellinger RP, Adams RE, Williams B. Health Information seeking behaviors in prison: results from the U.S. PIAAC Survey. J Correct Health Care. 2022;28(2):90–9.
Toreld EM, Haugli KO, Svalastog AL. Maintaining normality when serving a prison sentence in the digital society. Croat Med J. 2018;59(6):335–9.
Zivanai E, Mahlangu G. Digital prison rehabilitation and successful re-entry into a digital society: a systematic literature review on the new reality on prison rehabilitation. Cogent Soc Sci. 2022;8(1):2116809.
Baillargeon J, Contreras S, Grady JJ, Black SA, Murray O. Compliance with antidepressant medication among prison inmates with depressive disorders. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(11):1444–6.
Wallace D, Wang X. Does in-prison physical and mental health impact recidivism? SSM -. Popul Health. 2020;11:100569.
The World Medical Association-WMA Declaration of Helsinki– Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2022 Mar 14]. https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/
Gostin LO, Vanchieri C, Pope A, editors. Ethical Considerations for Research Involving Prisoners. [Internet]. Washington (DC): Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Ethical Considerations for Revisions to DHHS Regulations for Protection of Prisoners Involved in Research; 2007. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK19882/
Moore LW, Miller M. Initiating research with doubly vulnerable populations. J Adv Nurs. 1999;30(5):1034–40.
Sacristán JA, Aguarón A, Avendaño-Solá C, Garrido P, Carrión J, Gutiérrez A, et al. Patient involvement in clinical research: why, when, and how. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016;10:631–40.
Christopher PP, Garcia-Sampson LG, Stein M, Johnson J, Rich J, Lidz C. Enrolling in Clinical Research while incarcerated: what influences participants’ decisions? Hastings Cent Rep. 2017;47(2):21–9.
Norway| World Prison Brief [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2024 Mar 15]. https://www.prisonstudies.org/country/norway
Bukten A, Virtanen S, Hesse M, Chang Z, Kvamme TL, Thylstrup B, et al. The prevalence and comorbidity of mental health and substance use disorders in scandinavian prisons 2010–2019: a multi-national register study. BMC Psychiatry. 2024;24:95.
Lov om pasient- og brukerrettigheter [Internet]. Section 2, LOV-1999-07-02-63 1997. https://lovdata.no/dokument/NL/lov/1999-07-02-63/KAPITTEL_2#%C2%A72-5a
Saunes IS. International Health Care System Profiles: Norway [Internet]. New York: The Commonwealth Fund; 2020 Dec. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/international-health-policy-center/countries/norway
Helsedirektoratet. Helse- og omsorgstjenester til innsatte i fengsel [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Nov 24]. https://www.helsedirektoratet.no/veiledere/helse-og-omsorgstjenester-til-innsatte-i-fengsel/Helse-%20og%20omsorgstjenester%20til%20innsatte%20i%20fengsel%20%E2%80%93%20Veileder.pdf/_/attachment/inline/54b7b100-9415-4bc0-993e-66175a4cd4c1:5537f215b0ba85ca4a0159612413ab7450b23467/Helse-%20og%20omsorgstjenester%20til%20innsatte%20i%20fengsel%20%E2%80%93%20Veileder.pdf
World Health Organization. World mental health report: Transforming mental health for all [Internet]. Geneva. 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240049338
Pont J, Enggist S, Stöver H, Williams B, Greifinger R, Wolff H. Prison Health Care Governance: guaranteeing clinical independence. Am J Public Health. 2018;108(4):472–6.
Nesset M, Rustad ÅB, Kjelsberg E, Almvik R, Bjørngaard J. Health care help seeking behaviour among prisoners in Norway. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011.
Bjørngaard JH, Rustad ÅB, Kjelsberg E. The prisoner as patient - a health services satisfaction survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9(1):176.
Magnussen SF, Tingvold L. Kartlegging av helse- og omsorgsbehov blant innsatte i fengsel [Internet]. Gjøvik: Senter for omsorgsforskning, øst; 2022 [cited 2023 Aug 8]. Report No.: 1. https://omsorgsforskning.brage.unit.no/omsorgsforskning-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2992945/Kartlegging_innsatte.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Kriminalomsorgen K. Årsrapport 2020 [Internet]. Kriminalomsorgsdirektoratet; 2021 Feb. https://www.regjeringen.no/contentassets/b04b5cf8bb32490c990a82fd90fa05a0/arsrapport_kdi_2020.pdf
Appleton J, King L. Journeying from the philosophical contemplation of constructivism to the methodological pragmatics of health service research. J Adv Nurs. 2003;40:641–8.
Birks M, Hoare K, Mills J. Grounded Theory: The FAQs. Int J Qual Methods [Internet]. 2019 Jan 1 [cited 2023 Aug 16];18. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1609406919882535
Abbott P, DiGiacomo M, Magin P, Hu W. A Scoping Review of Qualitative Research Methods Used With People in Prison. Int J Qual Methods [Internet]. 2018 Dec 1 [cited 2023 Aug 16];17(1). http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406918803824
Birks M, Mills J, Grounded Theory. A practical guide. 3rd ed. SAGE Publications, Ltd.; 2023.
Gulliver A, Griffiths KM, Christensen H. Perceived barriers and facilitators to mental health help-seeking in young people: a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2010;10:113.
Waldmann T, Staiger T, Oexle N, Rüsch N. Mental health literacy and help-seeking among unemployed people with mental health problems. J Ment Health Abingdon Engl. 2020;29(3):270–6.
Rüsch N, Evans-Lacko SE, Henderson C, Flach C, Thornicroft G. Knowledge and attitudes as predictors of intentions to seek help for and disclose a Mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2011;62(6):675–8.
Kelly CM, Jorm AF, Wright A. Improving mental health literacy as a strategy to facilitate early intervention for mental disorders. Med J Aust [Internet]. 2007 Oct [cited 2024 Mar 19];187(S7). https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.5694/j.1326-5377.2007.tb01332.x
Corrigan PW, Watson AC. Understanding the impact of stigma on people with mental illness. World Psychiatry. 2002;1(1):16–20.
Clement S, Schauman O, Graham T, Maggioni F, Evans-Lacko S, Bezborodovs N, et al. What is the impact of mental health-related stigma on help-seeking? A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative studies. Psychol Med. 2015;45(1):11–27.
Thornicroft G, Sunkel C, Alikhon Aliev A, Baker S, Brohan E, El Chammay R, et al. The Lancet Commission on ending stigma and discrimination in mental health. Lancet Lond Engl. 2022;400(10361):1438–80.
Bagnall AM, South J, Hulme C, Woodall J, Vinall-Collier K, Raine G, et al. A systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of peer education and peer support in prisons. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(1):290.
Fovet T, Mundt AP, Fazel S et al. Psychiatry in Prisons and Corrections. In: Tasman A, Riba MB, Alarcón RD, Alfonso CA, Kanba S, Ndetei DM, editors. Tasman’s Psychiatry [Internet]. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020 [cited 2024 Feb 22]. pp. 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42825-9_103-1
Morgan RD, Scanlon F, Van Horn SA. Criminogenic risk and mental health: a complicated relationship. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(2):237–44.
Durcan G. The future of prison mental health care in England: A national consultation and review [Internet]. London: Centre for Mental Health; 2021. https://www.centreformentalhealth.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/CentreforMentalHealth_TheFutureofPrisonMentalHealthCare_0.pdf
Solbakken LE, Wynn R. Barriers and opportunities to accessing social support in the transition from community to prison: a qualitative interview study with incarcerated individuals in Northern Norway. BMC Psychol. 2022;10(1):185.
Ross MW, Liebling A, Tait S. The Relationships of Prison Climate to Health Service in Correctional environments: Inmate Health Care Measurement, satisfaction and Access in prisons. Howard J Crim Justice. 2011;50(3):262–74.
Skogstad P, Deane FP, Spicer J. Barriers to Helpseeking among New Zealand prison inmates. J Offender Rehabil. 2005;42(2):1–24.
Norwegian Parliamentary Ombudsman. Special report to the Storting on solitary confinement and lack of human contact in Norwegian prisons [Internet]. Oslo: Norwegian Parliamentary Ombudsman. 2019. (4:3). https://www.sivilombudet.no/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/SOM_Særskilt-melding_ENG_WEB.pdf
Sivilombudet. Selvmord og selvmordsforsøk i fengsel. En undersøkelse under OPCAT-mandatet [Internet]. Oslo: Sivilombudet; 2023. https://www.sivilombudet.no/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Rapport_Selvmord_i_fengsel.pdf
Skogstad P, Deane FP, Spicer J. Social-cognitive determinants of help-seeking for mental health problems among prison inmates. Crim Behav Ment Health CBMH. 2006;16(1):43–59.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the study participants and the correctional facilities for their cooperation.
Open access funding provided by UiT The Arctic University of Norway (incl University Hospital of North Norway). The study was supported by a grant from the North Norway Regional Health Authority (Helse Nord RHF). The funding body had no role in study design, data collection, analysis, or writing of the manuscript. The study was supported by the Publication Fund of UiT The Arctic University of Norway.
Open access funding provided by UiT The Arctic University of Norway (incl University Hospital of North Norway)
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Clinical Medicine, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, N-9038, Norway
Line Elisabeth Solbakken & Rolf Wynn
Division of Mental Health and Substance Use, University Hospital of North, Tromsø, Norway
Line Elisabeth Solbakken
Department of Psychology, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway
Svein Bergvik
Department of Education, ICT and Learning, Østfold University College, Tromsø, Norway
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. LES conducted the interviews and their transcription. All authors analyzed the data. LES drafted the manuscript. All authors participated in revising the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rolf Wynn .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All relevant guidelines and regulations were followed. All participants gave written informed consent. The study was approved by the Data Protection Officer of the University Hospital of North Norway. The Norwegian Correctional System, Region North, also approved the study. The study was submitted to and deemed outside the mandate of the Regional Health Research Ethics Committee of Northern Norway.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Solbakken, L.E., Bergvik, S. & Wynn, R. Breaking down barriers to mental healthcare access in prison: a qualitative interview study with incarcerated males in Norway. BMC Psychiatry 24 , 292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05736-w
Download citation
Received : 01 January 2024
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05736-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Incarcerated
- Correctional
- Mental health
- Help-seeking
- Utilization
BMC Psychiatry
ISSN: 1471-244X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Advancing the entrepreneurship ecosystem of India: A qualitative study with Chevening Fellows
- Published: 26 December 2023
Cite this article

- Kamal Gulati 1 ,
- Amrik Sohal 2 ,
- Tharaka de Vass 2 &
- Nrupal Das 3
271 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Using social cognitive theory as a guide, this research seeks to explain the perceptions of current and aspiring Indian entrepreneurs. A multiple case study approach using 19 interviews with intellectuals provided qualitative data to conduct a cross-case analysis of the two groups with the qualitative analysis software NVivo. Rare insights from current and aspiring opportunity-motivated entrepreneurial Chevening Fellowships from a predominantly necessity-motivated context offer valuable insights into entrepreneurship in India. The findings reveal what entrepreneurship means to established entrepreneurs, their motivation for embarking on the entrepreneurial journey, the skills they require to be successful, the challenges they face and their strategies to sustain are mostly different to what aspiring entrepreneurs believe how it would be. Compiled recommendations may help strengthen the entrepreneurial ecosystem, particularly in developing economy contexts, to help improve the 10% startup success rate.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
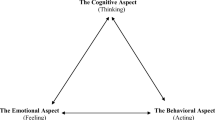
Unraveling the entrepreneurial mindset
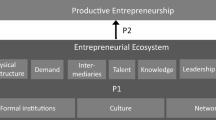
Entrepreneurial ecosystem elements
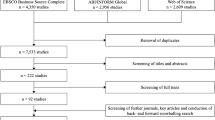
The impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and its determinants: a systematic review
Abosede, A. J., & Onakoya, A. B. (2013). Intellectual entrepreneurship: Theories, purpose and challenges. International Journal of Business Administration , 4 (5), 30.
Al Halbusi, H., Soto-Acosta, P., & Popa, S. (2022). Entrepreneurial passion, role models and self-perceived creativity as antecedents of e-entrepreneurial intention in an emerging Asian economy: The moderating effect of social media, Asia Pacific Journal of Management , 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-022-09857-2
Al-Shaikh, F. N. (2013). Opportunities and challenges of entrepreneurship in developing countries: The case of Jordan. Journal for International Business and Entrepreneurship Development, 7 (2), 163–178.
Article Google Scholar
Amit, M., Carpenter, M. K., Inokuma, M. S., Chiu, C.-P., Harris, C. P., Waknitz, M. A., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., & Thomson, J. A. (2000). Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture. Developmental Biology, 227 (2), 271–278.
Amorós, J. E., Cristi, O., & Naudé, W. (2021). Entrepreneurship and subjective well-being: Does the motivation to start-up a firm matter? Journal of Business Research, 127 , 389–398.
Atiase, V. Y. (2017). Impact of credit risk management practices on micro financing the poor for poverty alleviation in Africa: Insights from Ghana . Central University of Technology, Free State.
Google Scholar
Baron, R. A. (2013). Enhancing entrepreneurial excellence: Tools for making the possible real . Edward Elgar Publishing.
Book Google Scholar
Chevening Fellowships. (2023). Available at: https://www.chevening.org/fellowships/
De Vass, T., Nand, A. A., Bhattacharya, A., Prajogo, D., Croy, G., Sohal, A., & Rotaru, K. (2023). Transitioning to a circular economy: lessons from the wood industry. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 34 (3), 582–610.
Diandra, D., & Azmy, A. (2020). Understanding definition of entrepreneurship. International Journal of Management, Accounting and Economics, 7 (5), 235–241.
Eniola, A. A. (2021). The entrepreneur motivation and financing sources. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity , 7 (1), 25.
Frank, A. I. (2007). Entrepreneurship and enterprise skills: A missing element of planning education? Planning Practice and Research, 22 (4), 635–648.
Ghafar, A. (2020). Convergence between 21st century skills and entrepreneurship education in higher education institutes. International Journal of Higher Education, 9 (1), 218–229.
Goyal, S., Sergi, B. S., & Jaiswal, M. P. (2016). Understanding the challenges and strategic actions of social entrepreneurship at base of the pyramid. Management Decision, 54 (2), 418–440.
Hassan, A., Anwar, I., Saleem, I., Islam, K. M. B., & Hussain, S. A. (2021). Individual entrepreneurial orientation, entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurial intention: The mediating role of entrepreneurial motivations. Industry and Higher Education, 35 (4), 403–418.
Hessels, J., & Naudé, W. (2019). The intersection of the fields of entrepreneurship and development economics: A review towards a new view. Journal of Economic Surveys, 33 (2), 389–403.
Human Development Report. (2020). https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/hdr2020pdf.pdf . (Page No. 405).
IBEF. (2023). India Brand Equity Foundation 2013 . Available at: https://www.ibef.org/
Jha, S. K. (2018). Entrepreneurial ecosystem in India: Taking stock and looking ahead. IIMB Management Review, 30 (2), 179–188.
Kalyanasundaram, G. (2018). Why do startups fail? A case study based empirical analysis in Bangalore. Asian Journal of Innovation and Policy, 7 (1), 79–102.
Kapinga, A. F., & Montero, C. S. (2017). Exploring the socio-cultural challenges of food processing women entrepreneurs in Iringa, Tanzania and strategies used to tackle them. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 7 (1), 17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40497-017-0076-0
Kuratko, D. F., & Audretsch, D. B. (2009). Strategic entrepreneurship: Exploring different perspectives of an emerging concept. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 33 (1), 1–17.
Murnieks, C. Y., Klotz, A. C., & Shepherd, D. A. (2019). Entrepreneurial motivation: A review of the literature and an agenda for future research. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 41 (2), 115–143.
Naradda Gamage, S. K., Ekanayake, E. M. S., Abeyrathne, G. A. K. N. J., Prasanna, R. P. I. R., Jayasundara, J. M. S. B., & Rajapakshe, P. S. K. (2020). A review of global challenges and survival strategies of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Economies, 8 (4), 79.
Ratten, V. (2014). Encouraging collaborative entrepreneurship in developing countries: The current challenges and a research agenda. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 6 (3), 298–308.
Sariwulan, T., Suparno, S., Disman, D., Ahman, E., & Suwatno, S. (2020). Entrepreneurial performance: The role of literacy and skills. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7 (11), 269–280.
Shastri, S., Shastri, S., Pareek, A., & Sharma, R. S. (2021). Exploring women entrepreneurs’ motivations and challenges from an institutional perspective: Evidences from a patriarchal state in India. Journal of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the Global Economy, 16 (4), 653–674.
Smallbone, D., Welter, F., & Ateljevic, J. (2014). Entrepreneurship in emerging market economies: Contemporary issues and perspectives. International Small Business Journal, 32 (2), 113–116.
Stam, E., & van de Ven, A. (2021). Entrepreneurial ecosystem elements. Small Business Economics, 56 (2), 809–832.
StartupBlink. (2023). Startup Ecosystem Report 2022-2023 . Available at: https://lp.startupblink.com/report/
Sun, S. L., Shi, W., Ahlstrom, D., & Tian, L. (2020). Understanding institutions and entrepreneurship: The microfoundations lens and emerging economies. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 37 (4), 957–979.
World Bank. (2023). Ease of doing business rank 2019-2023 . Available at: https://www.worldbank.org/en/businessready
Wurth, B., Stam, E., & Spigel, B. (2022). Toward an entrepreneurial ecosystem research program. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 46 (3), 729–778.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (Vol. 5). Sage Publications.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the support of Chevening fellows who consented to participate in this study, Chevening Secretariat, Foreign Commonwealth & Development Office, Prof. Richard Briant, University of Oxford, Prof. John Hoffmaire, Chairman, Oxford Pharmaceuticals, Ms. Sarah Fallon, Regional Director, Science and Innovation, British High Commission New Delhi, Ms. Supriya Chawla, Head Chevening Scholarships India for their support.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centralized Core Research Facility, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
Kamal Gulati
Department of Management, Monash Business School, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia
Amrik Sohal & Tharaka de Vass
Paysafe, Jacksonville, FL, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Amrik Sohal .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Gulati, K., Sohal, A., de Vass, T. et al. Advancing the entrepreneurship ecosystem of India: A qualitative study with Chevening Fellows. Asia Pac J Manag (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-023-09940-2
Download citation
Accepted : 19 November 2023
Published : 26 December 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-023-09940-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Entrepreneurship
- Cross case analysis
- Motivations
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 26.4.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
Patients’ Representations of Perceived Distance and Proximity to Telehealth in France: Qualitative Study
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Amélie Loriot 1 * , MSc ;
- Fabrice Larceneux 1 * , PhD ;
- Valérie Guillard 1 * , PhD ;
- Jean-Philippe Bertocchio 2, 3 * , MD, PhD
1 Paris Dauphine–PSL (Paris Sciences & Lettres) University, Paris, France
2 Service Thyroïde – Tumeurs Endocrines, Hôpital de la Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France
3 SKEZI, Annecy, France
*all authors contributed equally
Corresponding Author:
Amélie Loriot, MSc
Paris Dauphine–PSL (Paris Sciences & Lettres) University
Place du Maréchal de Lattre de Tassigny
Paris, 75116
Phone: 33 144054405
Email: [email protected]
Background: In the last 2 decades, new technologies have emerged in health care. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of technology by both health care professionals and patients. These technologies create remote care practices that bring several benefits to the health care system: easier access to care, improved communication with physicians, and greater continuity of care. However, disparities in the acceptance and use of telehealth tools still exist among patients. These tools also disrupt conventional medical practices and prompt a new reassessment of the perceptions of distance and proximity as physical (ie, time and space dimensions) and nonphysical (ie, behavioral dimensions) concepts. The reasons why patients do or do not adopt telehealth tools for their care and therefore their perspectives on telehealth remain unanswered questions.
Objective: We explored the barriers as well as the motivations for patients to adopt telehealth tools. We specifically focused on the social representations of telehealth to establish a comprehensive conceptual framework to get a better understanding of how telehealth is perceived by patients.
Methods: This study uses a qualitative design through in-depth individual interviews. Participants were recruited using a convenience sampling method with balanced consideration of gender, age, location (urban/rural), and socioeconomic background. After collecting informed consent, interviews were transcribed and analyzed using the thematic analysis methodology.
Results: We conducted 14 interviews, with which data saturation was reached. The 2 main opposed dimensions, perceived proximity and distance, emerged as an essential structure for understanding the social representations of telehealth. A logic of engagement versus hostility emerged as the main tension in adopting telehealth, almost ideological. Interestingly, practical issues emerged regarding the adoption of telehealth: A logic of integration was opposed to a logic of constraints. Altogether, those dimensions enabled us to conceptualize a semiotic square, providing 4 categories with a coherent body of social representations. Due to the dynamic nature of these representations, we proposed 2 “paths” through which adherence to telehealth may improve.
Conclusions: Our semiotic square illustrating patients’ adherence to telehealth differentiates socially beneficial versus socially dangerous considerations and pragmatic from ideological postures. It shows how crucial it is to consider perceived distance and proximity to better understand barriers and motivations to adopting telehealth. These representations can also be considered as leverage that could be modified to encourage the step-by-step adhesion process. Even if reducing the perceived temporal distance to in-person meeting and enhancing the perceived proximity of access to care may be seen as efficient ways to adopt telehealth tools, telehealth can also be perceived as a care practice that threatens the patient-physician relationship. The patient-oriented perceived value turns out to be critical in the future development of and adherence to telehealth tools.
Introduction
Telehealth, a subset of ehealth still ongoing.
Many technologies have been developed in eHealth in recent years. Defined as the “use of information and communication technologies in support of health and health-related fields, including health care services, health monitoring, health literature, and health education, knowledge and research” [ 1 ], eHealth covers a wide range of practices. First, mobile apps and connected devices are referred to as mobile health (mHealth). Second, telehealth (ie, the practice of medicine using information and communication technologies) covers 5 practices: teleconsultation, teleexpertise, medical regulation, remote medical monitoring, and remote medical assistance.
Recent research focusing on remote care has indicated some confusion regarding the wording used to refer to health-related technologies [ 2 ]. For instance, the terms “telemedicine” and “telehealth” are often used interchangeably [ 3 ]. However, some researchers highlight a difference between these 2 concepts. Whereas telemedicine is limited to remote clinical services, telehealth is broader and refers to remote clinical services as well as remote nonclinical services, like administrative meetings [ 4 ]. Thus, telehealth has been defined as “the use of electronic information and telecommunication technologies to support and promote long-distance clinical health care, patient and professional health-related education, public health and health administration” [ 5 ].
eHealth is expected to lead to significant changes in the delivery of care and medical practices [ 6 ]. Because of (1) disparities in access to health care, (2) the aging population, and (3) budget constraints limiting public policies, the development of eHealth devices can be seen as a solution to the future challenges faced by the health system in many high-income countries [ 7 ]. Before the COVID-19 crisis, there were significant disparities in the use of eHealth tools between European countries [ 8 ]. A global shift occurred during the pandemic: The use of many eHealth tools became necessary, democratizing their use in terms of communication, monitoring, or care delivery, and the use of technology to provide health services has accelerated [ 9 , 10 ]. Telehealth may now concern everyone.
Benefits and Barriers of Telehealth
The practice of telehealth presents many benefits for patients, including (1) better access to health care services, in particular in isolated regions like rural areas; (2) improved continuity of care; (3) increased availability of health information [ 11 ]; and (4) empowerment of patients [ 12 ]. As such, telehealth is supposed to increase efficiency and quality of care [ 10 ] and favors patient-centered care by enabling better communication between patients and health care professionals [ 13 ].
However, researchers have pointed out that many barriers exist that limit health equity for all patients. Significant disparities remain regarding the access to, adherence to, and use of telehealth tools [ 14 , 15 ]. In particular, little is known about the role of digital health literacy [ 13 , 15 , 16 ] (ie, “the ability to search for, find, understand and evaluate health information from electronic sources and to apply knowledge acquired to solve a health problem” [ 17 ]). Among individuals in rural areas, low levels of education are associated with lower use of digital health tools [ 18 ]. Some scholars argue that online interactions are impersonal and dangerous because of the lack of a physical examination [ 10 ] and that telehealth may threaten the quality of the relationship between physicians and patients [ 19 ].
Studies among health care professionals have also shown a reluctance to adopt these technologies because of a fear of “dehumanization” by virtualizing patients and care [ 20 ]. This feeling of dehumanization of care could explain negative attitudes toward telehealth [ 21 ].
Patients tend to attribute significant importance to health care professionals’ physical and emotional presence [ 22 ] and direct interactions with them [ 7 ]. However, the digitalization of health is transforming these relationships [ 23 ]: Telehealth disrupts medical practices and reduces physical interactions between patients and physicians. However, it leads to reconsidering notions of distance and proximity [ 23 ], including physical and nonphysical dimensions (ie, cognitive or relational aspects that are perceived by individuals) [ 24 - 26 ]. Physical proximity and perceived proximity are not necessarily aligned. Indeed, individuals can feel themselves close to an element that is physically far but also to perceive it far when it is physically close [ 26 ]. Perceived proximity has a cognitive dimension that refers to “a mental assessment of how distant someone else seems” and an affective component, since these representations are subject to emotions rather than rational thought [ 26 , 27 ]. In health care, Talbot et al [ 28 ] investigated the perceptions French physicians may have about telehealth using the conceptual framework of proximity of Boschma [ 25 ] that includes the following 5 dimensions of proximity: cognitive, organizational, social, institutional, and geographical. However, how patients react to these changes in care delivery and the representations of these practices remain unanswered questions. Therefore, exploring patient’s representations of telehealth is important to better understand psychological mechanisms underlying the adherence to telehealth. The theory of social representations is fruitful in overcoming this limitation.
The Social Representations Theory
The theoretical background of social representations provides a framework for understanding how new concepts become common knowledge. Defined as a collective elaboration “of a social object by the community for the purpose of behaving and communicating” [ 29 ], social representations consist of a system of values, ideas, and practices that enable individuals to orient themselves in their material and social world as well as to master it and provide a code for social exchange [ 30 ]. Therefore, social representations provide people with a common frame of communication that is built in everyday interactions. More precisely, a social representation corresponds to thoughts and feelings being expressed in verbal and overt behavior of actors that constitutes an object for a social group [ 31 ].
Although social representations are commonly shared, some may be more polemical, reflecting oppositions between social groups in society [ 32 ]. In addition, social representations have a dynamic nature across and within social groups of people, and societal practices, communication, and the process of knowledge are strongly connected, particularly in the health field, which has been one of the leading research areas for this theory [ 33 - 35 ].
Interestingly, social representations constitute a structure explaining behaviors that result not only from an individual cognitive process but also from social and cultural representations and that are shared collectively [ 36 , 37 ]. Social representations have been shown to be a significant indicator of attitudes [ 38 , 39 ]. However, social representations of patients have never been studied in the context of telehealth specifically. A qualitative study is well suited to understand these representations. The objective of our qualitative research was to establish a comprehensive conceptual framework to gain a better understanding of how telehealth influences perceived proximity or distance for patients and therefore, to better apprehend their barriers as well as their motivations to adopting telehealth tools.
Study Design
A qualitative study was conducted with an interpretative approach to explore patients’ representations of telehealth and their perception of proximity toward it. We adopted an inductive, constructivist perspective, assuming that people construct their life-worlds through their representations and interpretations of telehealth as a social fact to which they attribute specific terms and meanings.
Setting and Sample
Qualitative in-depth individual interviews were set up using a semistructured thematic interview guide. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants. Variation sampling was sought [ 40 ] with consideration of gender, age, location (urban/rural), and socioeconomic background ( Multimedia Appendix 1 ). We used the saturation criterion to stop recruitment. This criterion is the point at which gathering more data about a theoretical construct reveals no new properties nor yields any further theoretical insights [ 41 ]. This saturation point is usually reached with 9 to 17 interviews [ 42 ].
Data Collection
After obtaining informed consent, patients were contacted, and an appointment for an interview was set. Interviews lasted from 45 minutes to 75 minutes and were performed directly inside the family home or conducted through the digital platform Microsoft Teams because of the geographical distance between the researcher and the participant. The study took place in May 2022. A total of 14 interviews were gathered: 8 participants were female, 6 were male, and their mean age was 52 (range 23-83) years. Of the interviews, 11 interviews were run face to face, and 4 were online.
The interview guide explored various aspects of how health and telehealth are perceived; including defining what constitutes perceived good health; understanding respondents’ relationship with their own health; examining how they seek health-related information; discussing challenges in accessing care as related to geographical, temporal, and perceived distances; and evaluating respondents’ overall and specific relationships with technology within the context of health care. This comprehensive approach aimed to gain insights into how individuals perceive telehealth and their level of engagement with it.
During each interview, we wrote down our impressions that could possibly impact the interpretation of results. Interviews were digitally audio-recorded with permission, and verbatims were transcribed.
Ethical Considerations
At the beginning of each interview, potential participants were given comprehensive information about the context, objectives, and methods of the study. The interviewees were informed that they could withdraw from this study at any time. After allowing enough time for any questions or clarification they may have required, all the participants gave their informed consent. The study design was reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Paris Dauphine–PSL (Paris Sciences & Lettres) University (20231128/01). Additionally, following national legislation, data were pseudonymized during the transcription process in a way that no participant could be directly identified: A number was assigned to each participant with no record of any directly identifying data. Participants received no compensation for participating in this research.
Data Analysis
First, we conducted a vertical analysis and read the transcripts to get an impression of the whole data set. Second, transcribed data were analyzed using a horizontal thematic analysis to develop a narrative of the findings through a categorical approach using qualitative software (NVivo Version 12). We followed the grounded theory approach to code verbatim [ 43 ]: Each transcript was coded inductively by manually marking central key words that could represent a code. The codes were then grouped under themes that emerged through the analysis process. Finally, we categorized the data by collapsing codes that conveyed similar meanings. Multimedia Appendix 2 presents an example of our analysis process.
After the first step of the analysis of social representations, which was to record all the dimensions that emerged from the participants, we used the semiotic square method to map semantic categories highlighting opposing and complementary concepts [ 44 ]. This structure enables the understanding of the tension among symbolic meanings and the elements by which meaning is being expressed [ 45 ]. The semiotic square has been often applied in consumer research [ 46 ] and specifically to explore consumers’ relationships with technology ideology [ 47 ].
First, a specific definition of telehealth emerged from the patient perspective. If researchers define telehealth broadly, the interview analysis revealed that telehealth is associated with teleconsultation for a large majority of patients and rarely with other practices. It concerns mainly remote care and is associated with questions about the quality of interactions with the physician.
Second, the content analysis revealed 4 main types of social representations of telehealth: the expected opposition between engagement and hostility and a more subtle distinction between integration and constraint.
Representations of Proximity: the Logic of Engagement
Our analysis of interviews revealed the first category of very positive social representations related to telehealth that led to a logic of engagement and adherence to this practice. This commitment is based on the idea of optimization of health services. The strong proximity with its practice is explained by a feeling of comfort and a perception of convenience. Telehealth is considered an easy, practical tool. Participant 4 (P4) mentioned:
I found it practical and comfortable.
Perceived practicality and convenience underline the actual benefits of adopting telehealth. Indeed, this practice enables a reduction of the perceived temporal distance to the consultation, leading to representations of efficiency and effectiveness (P13) on one hand and allowing reinforcement of access to care, which creates a feeling of personal usefulness (P8), on the other hand. Participant 13 (P13) mentioned:
Now that everything is overbooked in their appointments, (...), we are at about 15 days/3 weeks for getting any new appointment, both by phone or by Doctolib, in video, it is a little faster.
In addition, participant 8 (P8) said:
It is so quick, it makes everyday life easier!
From this perspective, the main issue behind social representations of proximity is related to an improvement of the functional proximity to telehealth.
Representations of Distance: the Logic of Hostility
At the opposite end to that of the first category, the second category of social representations follows a logic of hostility toward telehealth. It reveals a strong rejection of its development. Although adherence follows a view of functional proximity, rejection is explained by a lack of perceived relational proximity caused by telehealth. These representations of perceived distance reveal a profound fear of the dehumanization of medicine. Telehealth is seen as a dehumanizing practice that is destructive of human interaction by virtualizing both patients and care, as Kaplan [ 20 ] mentioned. This was confirmed by participant 6 (P6), who stated:
It kills the human contact, which is really important to me. I definitely prefer having the secretary over the phone to tell me there is an appointment in three weeks.
The major component of this category is the perceived deterioration of the relationship with the physician. Great importance is given to the human dimension in care. However, the interviews revealed these representations are based on a feeling of detachment from the caregiver caused by telehealth. This emphasizes the impersonal nature of the relationship. Participant 2 (P2) stated:
We dematerialize everything. It brings detachment from the caregiver.
From this perspective, the development of a relationship with perceived proximity and trust seems incompatible with distant and remote care. The virtual nature of this link is intrinsically considered as the opposite of human interaction. Participant 1 (P1) stated:
I do not like it. I like to see the person right in front of me.
Here, social representations of telehealth found an increase of perceived distance between the patient and physician. The perception of actual proximity to the physician tends to disappear with telehealth, which reinforces emotional and affective distance [ 48 ]. These representations finally highlight the fact that telehealth cannot replace an in-person consultation. For instance, participant 5 (P5) stated:
I would not make [a remote physician] my referring physician. There need to be a close relationship with him. I must be able to give him my trust. I am not sure that I will always have the same doctor when using teleconsultation.
Altogether, these depictions of distance nurture the perception that telehealth has a detrimental or potentially harmful impact on society, as it undermines the interpersonal nature of care.
In addition to these 2 opposite categories of representations, proximity versus distance, more nuanced types of social representations also emerged within the verbatims. We labelled them “nondistance” and “nonproximity” representations.
Representations of Nondistance: the Logic of Integration
The third category of social representations reflects “nondistance” to telehealth, as these representations are related neither to total adherence nor to rejection but rather follow a logic of integration: Participants highlighted the actual possibility to choose to use (or not) telehealth tools. Representations do not reflect a full engagement with this practice but rather a nonrejection of telehealth.
First, these representations of nondistance highlight the functional aspects of this practice. In this context, developing a relational proximity with the physician was not judged as necessary. For instance, participant 4 (P4) stated:
I felt more like I was with a teleoperator than a physician. It felt like there was a script behind it, but why not, that is not necessarily a bad thing.
This situation is not seen as a problem; the efficient and nonrelational aspect of the consultation is valued here. Thus, this representation shows a greater emphasis on the functional proximity rather than on the relational proximity [ 24 ].
The importance given to the functional aspects of telehealth was also revealed through the way specific health practices are elicited. For instance, telehealth was mainly seen as a backup or emergency solution, leading to occasional use according to the situation. Participant 5 (P5) stated:
It can be a first step to detect an emergency. For example, if you cannot get a doctor during the weekend, we have remote visits (...) So, to me, it is an emergency solution.
Because it is convenient, patients do not reject telehealth, especially when there is no need to be seen in person, for example for a prescription renewal, as suggested by participant 4 (P4):
It depends on what you are looking for in the consultation. If it is for a medication renewal, yes, I would recommend it.
Thus, these representations of nondistance do not refer to hostility nor engagement toward telehealth but rather to tolerance. The practice is adopted but not entirely accepted. Indeed, the use of telehealth should remain occasional. Participant 11 (P11) said:
If I were starting using a teleconsultation system, I would say to myself ‘no more than three times in a row.’ The fourth time, you still have to go, once every two years for a check-up, I would tend to say that.
Tolerance comes also with some reluctance about the reliability of this practice. Telehealth was perceived as less reliable than a physical consultation because there is no physical contact and no auscultation, which seems to lead to mistrust, as suggested by participants 10 (P10) and 14 (P14).
Auscultation is one of the first things you learn in medicine, like touching the patient. Try to get an auscultation from a machine, to put its hands on the belly. [P10]
When I had my operation, I had a consultation with the anesthesiologist by teleconsultation. It was silly, he told me to pull my tongue out (...) No, for me this is ridiculous! [P14]
Overall, social representations related to nondistance reveal nonrejection of telehealth under conditions of efficiency and reliability. The choice of using telehealth tools is made under specific circumstances and leads to occasional use, based on high value placed on simplicity and functional aspects.
Representations of Nonproximity: the Logic of Constraint
Within the fourth category, social representations are related to “nonproximity,” a label that reflects a logic of constraint. Whereas representations of proximity highlight engagement and active behavior toward telehealth, representations of nonproximity depict situations of the use of telehealth when there is no other choice, as participant 10 (P10) mentioned:
Is telehealth a good thing? Like everyone else, I use it because I am left with no alternative option.
Patients come to telehealth whenever they have no or few alternatives, considering telehealth as a last option, such as during a lockdown for example, as explained by participant 3 (P3):
If I had to use it, it would really be out of obligation, like during a lockdown, and because I do not have the possibility to move around.
In this perspective, telehealth tools are not really accepted and should remain a second option to physical in-person consultations, mainly because telehealth requires digital literacy. Participant 7 (P7) explained:
For the elderly, it is a problem! I have to schedule their appointments from my own mobile phone because they do not have access to the internet.
Thus, like the representations of perceived distance, the representations of nonproximity are also mostly negative. However, they do not reflect a total rejection of the practice of telehealth but rather a nonadherence as patients come to it when they have no other option.
Finally, our qualitative analysis allowed us to structure a semiotic square ( Figure 1 ) with 2 main categories of social representations of telehealth (ie, perceived proximity and perceived distance) as well as subsequent tensions in the discourse. The negation of these 2 terms forms 2 other categories illustrating 4 distinctive classes of meanings highlighting nuanced representations of perceived proximity and distance to telehealth and the opposite and complementary relationships [ 49 ]. The main components of the 4 categories are summarized in Figure 1 . Interestingly, 2 additional analyses of the semiotic square improve our vision of social representations of telehealth, one based on a vertical reading and the other based on a horizontal reading.

Telehealth: Socially Beneficial Versus Socially Dangerous
From a vertical reading of the relationships between the categories, there are 2 structuring representations of telehealth. In the left part of the semiotic square ( Figure 1 ), the complementary relationship, linking proximity and nondistance, refers to favorable representations as well as to discourse encouraging the development of telehealth. These tools are perceived as socially beneficial for all stakeholders, but there is room for improvement in generalizing their use.
Within these favorable representations of telehealth, adherence and nonrejection are based on 2 main drivers. First, trust in the physician is crucial as he or she is considered a legitimate expert, as suggested by participant 4 (P4):
I feel that doctors are experts (...), I trust them entirely because to me they seem to be experts.
Consequently, positive representations of telehealth seem to be linked to the perceived relational proximity with the health care professional. Second, these representations stem from familiarity with the tool. Being familiar with the term “telehealth” and knowing what it means generate a feeling of closeness toward it. Participant 5 (P5) stated:
I heard [about telehealth] because in my profession—I work with pharmacies—we talk about it.
In the right part of the square is the complementary relationship combining perceived distance and nonproximity. This underlines representations of hostility and skepticism toward telehealth, which are considered socially harmful or even dangerous for society. Rejection and nonadherence seem to be explained mainly by insufficient digital literacy as well as difficulties accessing the Internet and telehealth tools, as suggested by participant 9 (P9):
No, I do not use the Internet at all! (...) There are surely many things to do but I do not know how to do them...
This revealed a substantial cognitive distance to telehealth and ultimately making care practices feel more complex. The ancestral role of auscultation in medical consultation and the importance given to touching patients are noted, showing that the lack of perceived physical proximity between the patient and physician tends to reinforce the psychological distance toward telehealth and ultimately the rejection of its practice. Participant 4 (P4) said:
The ability itself of performing an actual auscultation by touching people and listening to them using a stethoscope is being lost at the expense of the care to improve the development of technology.
Telehealth: Ideological Versus Pragmatic Postures
A horizontal reading highlights the similarity of the logics of engagement and hostility, both based on ideological postures: pros and cons of the practice of telehealth depending on whether it seems to belong to the “good” versus “bad” for the society. More efficiencies appear to be pros, and less of a human relationship appears to be a con. Conversely, the logics of integration and constrain reflect pragmatic postures: how to deal with the tool and on what occasion. Sometimes, it appears to be accepted because it is convenient and adapted to specific situations, sometimes because there is no other choice. Interestingly, ideological postures tend to separate opposite groups, while the pragmatic views tend to rebuild a link between the nondistance and nonproximity groups. These nuanced, more balanced perceptions invite us to think about the practical implications, elaborating “paths” of social representations to drive patients toward less rejection of and more adherence to telehealth.
Main Findings
Using qualitative methods, our findings suggest a new conceptual framework to apprehend telehealth from patients’ perspectives based on 4 categories of social representations. First, perceived proximity was associated with social representations reflecting the idea that telehealth is intrinsically an efficient, practical, and effective solution. This logic of engagement is in line with a strong belief in progress and technological tools to face the challenges of the health care system, namely the issue of access to care. On the opposite side, social representations were more related to a feeling of distance from telehealth, enforcing an unfavorable attitude and leading to a rejection of these tools. This logic of hostility is mainly anchored in a fear of dehumanization of society. Telehealth is blamed for compromising the quality of the relations and for accelerating the loss of human contact between patients and physicians. This perceived distance from telehealth highlights a situation of exclusion, especially for patients who do not have access to digital technology or who do not have sufficient digital literacy. Aside from these 2 categories, 2 more nuanced types of representations emerged. First, from a logic of integration, social representations revealed that telehealth is appealing but showed worries and fears about its reliability. This practice can be conditionally accepted according to a situational approach. Second, a logic of constraint reflected social representations based on skepticism but leading to acceptance when there are no alternatives.
From a theoretical point of view, our results, based on a semiotic square, bring new elements to the literature of perceived proximity. We have shown that telehealth leads to reconsidering proximity through several dimensions. Although not diminishing the geographical or physical gap between the patient and the health care provider, technological tools, such as a teleconsultation from home, can enhance accessibility to health care. The relational dimension of proximity, already identified by Boschma [ 25 ], seems to also be impacted by telehealth. Indeed, many social representations have shown that this perception of proximity with the caregiver is reduced by telehealth and revealed a fear of dehumanization in the relationship. In addition, we showed that perceived functional proximity to telehealth leads to increased adherence and a favorable attitude to its development, which should encourage policymakers to strengthen this aspect in communication strategies for telehealth. These findings also constitute a societal contribution. In addition, this research has revealed 2 major oppositions embedded in the social representations. The first one consists of “good,” or a socially beneficial position, versus “bad,” or a socially dangerous position. The second one highlights the posture, rather “ideological” or “pragmatic,” leading to contributions to public policy aiming to foster adherence to eHealth tools.
Building a semiotic square also revealed potential changes in people’s representations of telehealth and thus the potential to contribute to change attitudes toward these tools. They may be adapted to patients’ concerns and aspects that patients value in the practice of consultation. Our qualitative material brings insight to how these representations can be obstacles to the adoption of telehealth, as well as elements that can foster adherence. We propose considering paths through which patients’ representations could evolve. Mobilizing the social representations along these paths could first alleviate the perception of distance to the health care professional then enable the perceived proximity to telehealth. Our analysis emphasized some risks in how telehealth is implemented. If telehealth is developed without considering representations expressing reluctancy, individuals who are subjected to the use of telehealth may remain hostile to its development, may gradually feel a distance to it, and may finally totally reject this practice (coming from nonproximity to distance). To avoid such a vicious circle, 2 paths ( Figure 2 ) may create an increased feeling of proximity to telehealth.

The first path consists of transforming representations related to a perceived nondistance into a perceived proximity to telehealth. This pathway adopts a functional approach to consultation. The challenge is to dispel fears about the technological feasibility of using digital health tools to eliminate skepticism and reinforce favorable representations. It would then be necessary to reassure patients about the importance of any human contact during medical consultations. Highlighting the regular and immediate exchanges with physicians that telehealth allows would be perceived as helpful. Developing remote auscultation solutions and increasing communication about them by highlighting the accuracy and reliability of these technologies would help to alleviate these concerns and encourage adherence to these tools. Finally, reinforcing the benefits in terms of efficiency, time optimization, and practicality would contribute to (1) reducing the perceived temporal distance of access to care and (2) increasing the perceived functional proximity to telehealth.
The second path consists of (1) transforming representations related to a perceived distance into a feeling of nonproximity and subsequently (2) fostering the perceived proximity to telehealth. This path is mainly aimed at individuals who attach great importance to the relational and human dimension of care. The first challenge would be to strengthen trust in the health care system because representations and attitudes toward telehealth are intrinsically linked to the relationship patients develop with the health care system and physicians. It is also necessary to improve access to digital technology to reduce the cognitive distance and to increase their perception of proximity. Finally, highlighting and communicating about the strengthening of relational and affective proximity, allowed by telehealth when facilitating contact between patients and physicians, could lead to favorable representations and attitudes. Therefore, conceiving a system of medical support with a health care professional in telehealth booths could be an effective solution.
Limitations and Research Avenues
This study has some limitations. First, our sample did not include patients with a broad range of diseases: Very few of them had chronic diseases. Due to the sample size, we could not cover all medical specialties: For instance, ophthalmology and the need for emergency surgery may bring specific representations of telehealth for patients. It could also be interesting to interview people from other rural areas known as “medical deserts” (ie, regions with inadequate access to health care). In addition, we interviewed patients who do not practice as health care professionals. To broaden our research findings, we could incorporate additional insights by examining the perceptions of telehealth among other groups, particularly caregivers.
The development of telehealth tools leads to new challenges in medical practice. The social representations telehealth brings go beyond the perception of proximity and distance, are multifaceted, and include postures and attitudes. The social representations revealed by the semiotic square on perceived proximity to telehealth underscore the importance of designing health care strategies based on a patient-centric approach in the implementation of digital health tools.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the participants in this study.
Data Availability
The data sets generated and analyzed during this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Authors' Contributions
This study was carried out by all authors working collaboratively. AL initiated the proposal. AL and FL conceived the study, collected the data, and performed the qualitative analysis. AL wrote the first draft of the manuscript. FL, VG, and JPB participated in data interpretation and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
JPB is a physician and works at SKEZI, a company that develops digital tools in health. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Characteristics of patients.
Example of the qualitative analysis process used in this research.
- 58th World Health assembly report. World Health Organization. 2005. URL: https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA58-REC1/english/A58_2005_REC1-en.pdf [accessed 2024-04-12]
- Queirós A, Alvarelhão J, Cerqueira M, Silva A, Santos M, Pacheco Rocha N. Remote care technology: a systematic review of reviews and meta-analyses. Technologies. Feb 10, 2018;6(1):22. [ CrossRef ]
- Fatehi F, Wootton R. Telemedicine, telehealth or e-health? A bibliometric analysis of the trends in the use of these terms. J Telemed Telecare. Dec 01, 2012;18(8):460-464. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bitar H, Alismail S. The role of eHealth, telehealth, and telemedicine for chronic disease patients during COVID-19 pandemic: A rapid systematic review. Digit Health. Apr 19, 2021;7:20552076211009396. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Telemedicine and Telehealth. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). URL: https://www.healthit.gov/topic/health-it-health-care-settings/telemedicine-and-telehealth [accessed 2024-04-12]
- Meskó B, Drobni Z, Bényei É, Gergely B, Győrffy Z. Digital health is a cultural transformation of traditional healthcare. Mhealth. Sep 2017;3:38-38. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lindberg J, Bhatt R, Ferm A. Older people and rural eHealth: perceptions of caring relations and their effects on engagement in digital primary health care. Scand J Caring Sci. Dec 14, 2021;35(4):1322-1331. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- From innovation to implementation: eHealth in the WHO European Region. World Health Organization. 2016. URL: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/326317 [accessed 2024-04-12]
- Wang W, Sun L, Liu T, Lai T. The use of E-health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a case study in China's Hubei province. Health Sociol Rev. Nov 23, 2022;31(3):215-231. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gajarawala SN, Pelkowski JN. Telehealth benefits and barriers. J Nurse Pract. Feb 2021;17(2):218-221. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gagnon M, Duplantie J, Fortin J, Landry R. Implementing telehealth to support medical practice in rural/remote regions: what are the conditions for success? Implement Sci. Aug 24, 2006;1(1):18. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Clemensen J. Patient empowerment and new citizen roles through telehealth technologies - The early stage. Proceedings of The Third International Conference on eHealth, Telemedicine, and Social Medicine. 2011.:114-119. [ FREE Full text ]
- Goodridge D, Marciniuk D. Rural and remote care: Overcoming the challenges of distance. Chron Respir Dis. May 21, 2016;13(2):192-203. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Smith B, Magnani JW. New technologies, new disparities: The intersection of electronic health and digital health literacy. Int J Cardiol. Oct 01, 2019;292:280-282. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Reiners F, Sturm J, Bouw LJ, Wouters EJ. Sociodemographic factors influencing the use of eHealth in people with chronic diseases. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Feb 21, 2019;16(4):645. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Dunn P, Hazzard E. Technology approaches to digital health literacy. Int J Cardiol. Oct 15, 2019;293:294-296. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- First meeting of WHO GCM/NCD Working Group on health education and health literacy for noncommunicable diseases. Geneva Global Health Hub. Feb 17, 2017. URL: https://g2h2.org/posts/event/first-meeting-of-who-gcmncd-working-group-on-health-education-and-health-literacy-for-noncommunicable-diseases/ [accessed 2024-04-12]
- Salemink K, Strijker D, Bosworth G. Rural development in the digital age: A systematic literature review on unequal ICT availability, adoption, and use in rural areas. Journal of Rural Studies. Aug 2017;54:360-371. [ CrossRef ]
- Hjelm NM. Benefits and drawbacks of telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. Jun 24, 2005;11(2):60-70. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kaplan B. Revisiting health information technology ethical, legal, and social issues and evaluation: telehealth/telemedicine and COVID-19. Int J Med Inform. Nov 2020;143:104239. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huryk L. Factors influencing nurses' attitudes towards healthcare information technology. J Nurs Manag. Jul 2010;18(5):606-612. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rørtveit K, Sætre Hansen B, Leiknes I, Joa I, Testad I, Severinsson E. Patients’ experiences of trust in the patient-nurse relationship—a systematic review of qualitative studies. Open Journal of Nursing. 2015;05(03):195-209. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Oudshoorn N. Physical and digital proximity: emerging ways of health care in face-to-face and telemonitoring of heart-failure patients. Sociol Health Illn. Apr 2009;31(3):390-405. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Torre A, Rallet A. Proximity and localization. Regional Studies. Feb 2005;39(1):47-59. [ CrossRef ]
- Boschma R. Proximity and innovation: a critical assessment. Regional Studies. Feb 2005;39(1):61-74. [ CrossRef ]
- Wilson JM, Boyer O'Leary M, Metiu A, Jett QR. Perceived proximity in virtual work: explaining the paradox of far-but-close. Organization Studies. May 20, 2008;29(7):979-1002. [ CrossRef ]
- van Zoonen W, Sivunen A, Rice RE, Treem JW. Organizational information and communication technologies and their influence on communication visibility and perceived proximity. International Journal of Business Communication. Oct 06, 2021;60(4):1267-1289. [ CrossRef ]
- Talbot D, Charreire Petit S, Pokrovsky A. La proximité comme perception de la distance. Le cas de la télémédecine. Rev. Fr. Gest. Nov 11, 2020;46(289):51-74. [ CrossRef ]
- Moscovici S. Attitudes and opinions. Annu Rev Psychol. Jan 1963;14(1):231-260. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Moscovici S. Foreword. In: Herzlich C, editor. Health and illness A social psychological analysis. London, England. Academic Press; 1973;IX-XIV.
- Wagner W, Duveen G, Farr R, Jovchelovitch S, Lorenzi‐Cioldi F, Marková I, et al. Theory and method of social representations. Asian J of Social Psycho. Dec 18, 2002;2(1):95-125. [ CrossRef ]
- Manuti A, Mininni G. Social representations of medically assisted fecundation a study on the discursive construction of “media texts”. Psychology. 2010;01(05):337-348. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- de Rosa AS, Wagner W. The social representations of mental illness in children and adults. In: Doise W, Moscovici S, editors. Current issues in European Social Psychology. Cambridge, United Kingdom. Cambridge University Press; 1987;47-138.
- de Rosa AS, Bocci E. Resisting cognitive polyphasia in social representations of madness. In: de Rosa AS, editor. Social Representations in the 'Social Arena'. Abingdon, United Kingdom. Routledge; 2012;310.
- de Rosa AS, Mannarini T. The “Invisible Other”: social representations of COVID-19 pandemic in media and institutional discourse. Papers on Social Representations. 2020;29(2):1-35. [ FREE Full text ]
- Moliner P, Tafani E. Attitudes and social representations: a theoretical and experimental approach. European Journal of Social Psychology. Dec 04, 1998;27(6):687-702. [ CrossRef ]
- Bidjari AF. Attitude and social representation. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011;30:1593-1597. [ CrossRef ]
- Monterrubio JC, Andriotis K. Social representations and community attitudes towards spring breakers. Tourism Geographies. Mar 03, 2014;16(2):288-302. [ CrossRef ]
- Schultes M, Kollmayer M, Mejeh M, Spiel C. Attitudes toward evaluation: An exploratory study of students' and stakeholders' social representations. Eval Program Plann. Oct 2018;70:44-50. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Patton MQ. Qualitative Research & Evaluation Methods. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications, Inc; 2002.
- Bryant A, Charmaz K. The SAGE Handbook of Grounded Theory. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications Ltd; 2007.
- Hennink M, Kaiser BN. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: A systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. Jan 2022;292:114523. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Strauss A, Corbin JM. Grounded Theory in Practice. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications, Inc; 1997.
- Greimas AJ. Structural semantics: An attempt at a method. Lincoln, NE. University of Nebraska Press; 1983.
- Signori P, Flint DJ. Revealing the unique blend of meanings in corporate identity: An application of the semiotic square. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice. Nov 20, 2019;28(1):26-42. [ CrossRef ]
- Floch J. The contribution of structural semiotics to the design of a hypermarket. International Journal of Research in Marketing. Jan 1988;4(3):233-252. [ CrossRef ]
- Kozinets RV. Technology/ideology: how ideological fields influence consumers' technology narratives. Journal of Consumer Research. 2008;34(6):865-881. [ CrossRef ]
- Fiedler K. Construal level theory as an integrative framework for behavioral decision‐making research and consumer psychology. J Consum Psychol. Jan 22, 2008;17(2):101-106. [ CrossRef ]
- Greimas AJ, Rastier F. The interaction of semiotic constraints. Yale French Studies. 1968;(41):86. [ CrossRef ]
Abbreviations
Edited by A Mavragani; submitted 13.01.23; peer-reviewed by S Tubeuf, H Yu; comments to author 13.03.23; revised version received 08.05.23; accepted 19.12.23; published 26.04.24.
©Amélie Loriot, Fabrice Larceneux, Valérie Guillard, Jean-Philippe Bertocchio. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 26.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Attitudes of black american christian church leaders toward opioid use disorder, overdoses, and harm reduction: a qualitative study.

- 1 Department of Psychiatry, Recovery Research Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
- 2 Department of Health Policy and Management, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, United States
- 3 Department of Health Services, Policy and Practice, Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, RI, United States
- 4 Department of Medicine, Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI, United States
- 5 Center for Biomedical Research Excellence (COBRE) on Opioids and Overdose, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI, United States
Introduction: Black American Christian church leaders are trusted community members and can be invaluable leaders and planners, listeners, and counselors for Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) sufferers in the opioid overdose crisis disproportionately affecting the Black community. This qualitative study examines the extent to which the knowledge, attitudes, practices, and beliefs of Black American church leaders support medical and harm reduction interventions for people with OUD.
Methods: A semi-structured interview guide was used to conduct in-depth interviews of 30 Black Rhode Island church leaders recruited by convenience and snowball sampling.
Results: Thematic analysis of the interviews identified four themes: Church leaders are empathetic and knowledgeable, believe that hopelessness and inequity are OUD risk factors, are committed to helping people flourish beyond staying alive, and welcome collaborations between church and state.
Conclusion: Black American Christian church leaders are a critical resource in providing innovative and culturally sensitive strategies in the opioid overdose crisis affecting the Black American communities. As such, their views should be carefully considered in OUD policies, collaborations, and interventions in the Black American community.
Introduction
The United States is experiencing a drug overdose crisis ( 1 ). The February 2022 Standford-Lancet Commission on opioid use in North America reported that opioid overdoses had caused more than 600,000 deaths in the United States and Canada since 1999 ( 2 ). By the end of the decade, the number of recorded deaths is projected to double ( 3 ). Near the mid 2010s, the opioid overdose crisis shifted from occurring predominantly among Whites to being essentially a crisis among Black American communities ( 4 ) due mainly to fentanyl-involved overdose deaths ( 5 ). Furthermore, over the years, while there has been a medicalization of drugs among White American communities, there has been widespread and disproportionate criminalization of drugs among Black Americans, with Black Americans 6-10 times more likely to be incarcerated for drug offenses compared to White Americans ( 6 ).
In Rhode Island, opioid overdose deaths for non-Hispanic Blacks rose from 26.4 to 49.3 per 100,000 from 2019 to 2020, the highest of any racial/ethnic group in the state ( 7 ). Rhode Island’s implementation of the first statewide program in 2016 to provide Medications for Opioid Use Disorder (MOUD) to incarcerated persons ( 8 ) with associated marked reductions in post-incarceration opioid overdose fatalities ( 9 ), was insufficient to reduce the 2019 to 2020 high opioid overdose deaths. The fentanyl contamination of the non-opioid drug supply was a contributing factor. The rate of fentanyl-involved fatal overdoses was highest among non-Hispanic Black Rhode Islanders compared to Hispanics and non-Hispanic Whites, with rates of 47.8, 20.4, and 24.8 per 100,000, respectively, in this period ( 7 ). Thus, almost all non-Hispanic Black deaths in the state associated with opioids involve fentanyl.
In response to fatal overdoses in the state, the Rhode Island government established the Governor’s Overdose and Prevention Taskforce in 2015 ( 10 ), comprising experts and community members. The Taskforce brings together professionals and community members working together to prevent overdoses and save lives ( 11 ). Additionally, the Rhode Island legislature passed, and the Governor signed a law permitting the first state-sanctioned pilot harm reduction centers in the country in July 2021 ( 12 ). To engage Black Americans and other minority populations, the Rhode Island government has adopted Connecticut’s Imani Breakthrough Recovery Intervention ( 13 ), a culturally informed approach to engaging Blacks and Latinos in substance use treatment based in churches of color.
The Black American church has been vital in disseminating other public health interventions ( 14 ), such as HIV prevention and education ( 15 ), influenza immunizations ( 16 ), and COVID-19 vaccinations ( 17 ). In addition to hosting 12-step groups like Alcoholics Anonymous ( 18 ), churches have promoted recovery from addiction efforts with Christian-based support groups, including Adult and Teen Challenge USA (a residential recovery program) and Celebrate Recovery (an evangelical Christian 12-step recovery support program) ( 19 ). While faith-based organizations could partner in expanding harm reduction services for high-risk populations, little is known about their attitudes and practices regarding OUD.
The first author interviewed Black Rhode Island Christian clergy to address the research question: What is the extent to which the knowledge, attitudes, practices, and beliefs of Black American church leaders support medical and harm reduction interventions for people with opioid use disorder (OUD)? The authors hope this study will inform and encourage church-based opioid overdose interventions, such as the Imani Breakthrough Recovery Intervention project underway in Rhode Island.
Research design overview
This qualitative research study used a semi-structured interview guide to conduct 30 interviews of Black Rhode Island church leaders recruited by convenience and snowball sampling.
Participants
Table 1 summarizes the demographic information and other characteristics of the church leaders. There were 19 (63%) male and 11 (37%) female church leader participants. The majority (63%) of participants were between 50 and 65 years. Half of them had no more than a college degree, and the other half had graduate degrees. Many were bi-vocational and had jobs besides their pastoral ministry, including a property manager, a community health worker, a chemist, clinical providers, and those serving in government agencies. Most congregants resided in Providence County of Rhode Island. Others lived in Massachusetts and Connecticut. Most congregations were Pentecostal. Others were Interdenominational, Church of God, African Methodist Episcopal, Nondenominational, American Baptist, Assemblies of God, and Evangelical. Most churches were multiracial, with a Black American predominance. Their congregant ethnicities included Caribbean, Cape Verdean, Liberian, Ghanaian, White American, and Native American. Additionally, congregation sizes ranged from nine to about 500. However, most congregations had less than 100 members.
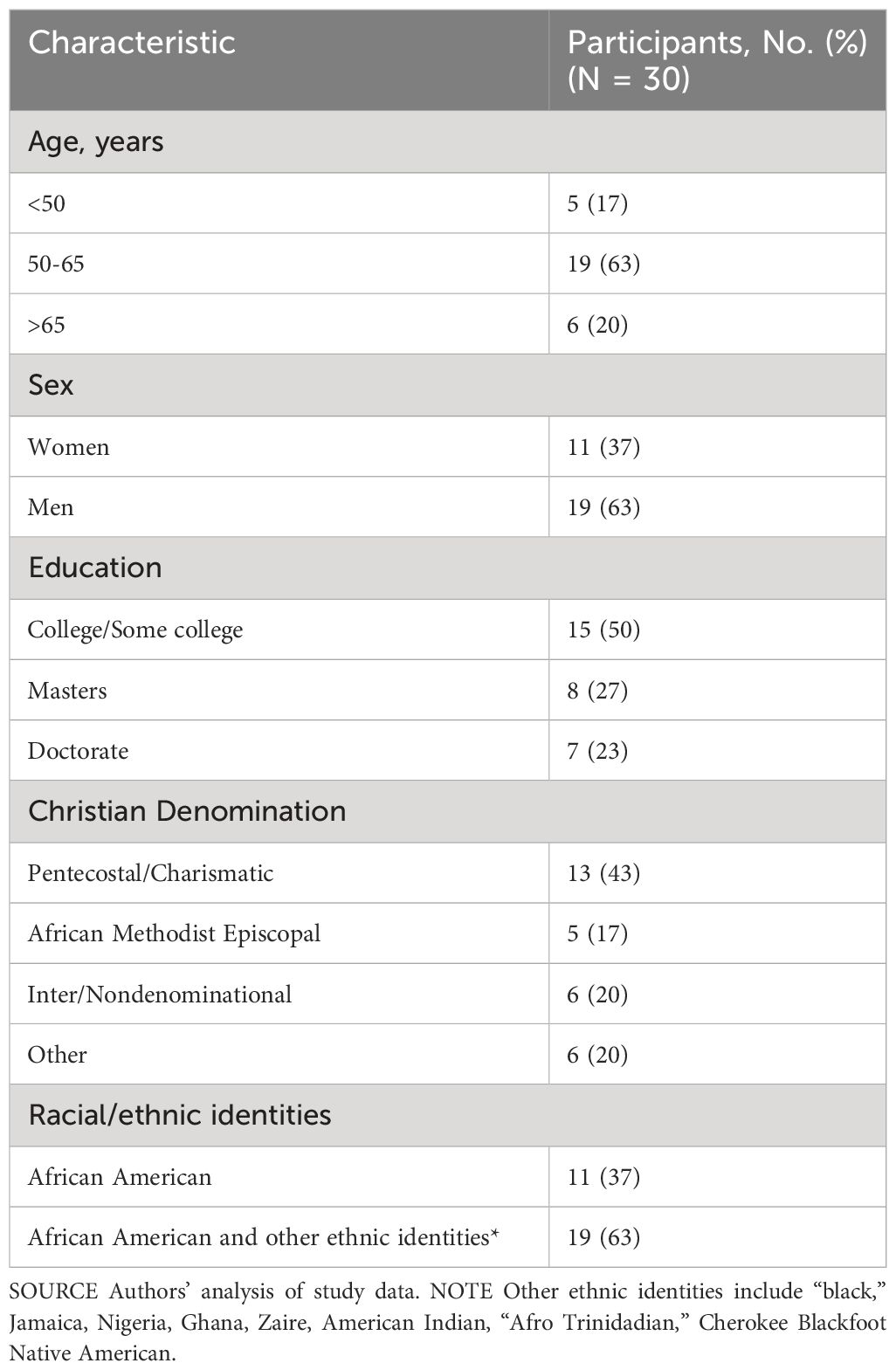
Table 1 Characteristics of Black Rhode Island clergy interviewed about their attitude toward Opioid Use Disorder and harm reduction October 2021-January 2022.
The church leaders were recruited by convenience and snowball sampling methods. For instance, at an event introducing the Imani Breakthrough Intervention to the Rhode Island public, the first author was introduced to the Ministers Alliance of Rhode Island, a multicultural collaboration of Christian pastors and ministers in the state. Soon afterward, the first author delivered a presentation about the study to the Alliance at their monthly meeting and obtained 15 participants following the presentation. Many of these participants connected the first author to their colleagues to expand the pool of participants. The first author followed up with subsequent participants via emails and phone calls.
The inclusion criteria were Black clergy in predominantly Black churches, ages 18+ years, who were pastors or in other leadership positions in Rhode Island churches. The Harvard Longwood Campus Research Protocol Institutional Review Board granted exempt status for the research protocol.
Since completing the project, the first author has outreached to some clergy participants during several monthly meetings at the Alliance for their feedback on the study outcomes, and they supported the findings.
Data collection
An introductory email to participants included a request for their availability to participate in the research interview and an attachment of the consent document with the project details. A positive email response and verbal consent before the interview sufficed because of the study’s exempt status. The authors developed a semi-structured interview guide ( Supplementary 1 ) about the OUD crisis and harm reduction by drawing from previous related studies and content area experts. The first author ran the interview guide past a qualitative research and content area expert and updated it per their feedback before administering it. The interviews were conducted via the Zoom platform and included questions for the participants on the following topics:
i. Understanding the role of the interviewee within the organization and gathering details about the organization itself.
ii. Knowledge of the OUD crisis and beliefs
iii. Knowledge of harm reduction techniques and beliefs about their efficacy and appropriateness
iv. Opinions and experience with faith-based intervention methods to mitigate the opioid use disorder crisis.
v. Demographic information of the church leaders and congregations
Data analysis
The first author followed a thematic analytic approach ( 20 ). 3Play Media ( 21 ) transcription service was employed to generate interview transcripts to aid in data familiarization and noting initial impressions. The data was managed with Dedoose qualitative analysis software ( 22 ) using an iterative analytic process with deductive codes capturing topics from the semi-structured interview guide and inductive codes derived from concepts relevant to the study, such as culturally informed approaches from the Imani Breakthrough Recovery Intervention literature. Codes and subcodes were refined iteratively by merging similar codes and associated quotes and regrouping codes and subcodes accordingly. The resulting codes were collated to identify underlying concepts and impressions to generate statements articulating themes. Further, compelling quotes were selected (see Results section) to highlight the themes.
Transparency and openness
The authors follow the journal article reporting standards for qualitative research design ( 23 ). Given how small the number of Black American clergy are in Rhode Island, study data, including recordings and interview transcripts, cannot be shared. Moreover, due to the deductive disclosure ( 24 ), it is almost impossible to de-identify the recordings and transcripts generated. As such, data sharing would breach the confidentiality implied in the participation agreement. To make this study transparent, however, the authors have included the semi-structured interview guide ( Supplementary 1 ), resulting codes and subcodes generated ( Supplementary 2 ), and thematic codes and subcodes with selected responses and associated Biblical references ( Supplementary 3 ) as Supplementary Information . This study’s design and its analysis were not pre-registered.
To minimize bias, the semi-structured interview guide questions ( Supplementary 1 ) were phrased in a neutral way to invite a conversation rather than yes-no responses. In addition, the guide used accessible language with terms defined as needed.
30 church leaders were interviewed from October 18, 2021, to January 4, 2022. The Zoom interviews lasted 70 minutes on average. All church leaders referenced Biblical texts. Supplementary 3 summarizes codes generated from the thematic analysis with selected responses and associated Biblical references ( 25 ).
The following four themes and selected related responses were identified from the analysis:
1. Church leaders are empathetic and knowledgeable about the OUD crisis in their communities. Church leaders’ knowledge, empathy, and compassion regarding the OUD crisis stem from their lived experiences. Some church leaders acknowledged the utility of Celebrate Recovery and Adult and Teen Challenge USA interventions for persons with substance use disorders. Other church leaders were involved in local church recovery support ministries and other ministries supporting social determinants of health by providing housing, education, medical care, employment opportunities, food, and clothing to the church and community.
A church leader who suffered a near-death experience with OUD and who had lost a sibling from an opioid overdose recounted how her faith contributed to her survival and subsequent recovery. Now, the majority of her congregants are persons grappling with substance use problems. As she recounted,
“I am constantly trying to remind people He (Jesus) did it for me. He can do it for you. I could not have done anything myself.”
Similarly, another church leader shared her experience of losing family members from drug overdose:
“It has even affected my own family. I’ve had three uncles die from drug overdoses.”
While a few church leaders with clinical backgrounds (including three clinical providers) were medically knowledgeable about OUD, other church leaders had contextual and historical OUD knowledge regarding the opioid overdose crisis in their communities. For many church leaders, the opioid crisis in their communities was not new:
“For the Black community, including the Black church, this is nothing new. We have been dealing with it for decades and decades and decades. Because we’re not talking about people who are out there. We’re talking about our sons and daughters. We’re talking about our fathers and mothers. We’re talking about our cousins. We’re talking about Sister So-and-so, who lives a couple of doors down.”
The church leaders understood culturally competent care. They know their community and understand what they need and are not getting. A leader’s narrative demonstrates the significance of engaging experts who can better relate to their community needs in providing OUD intervention:
“Some of these clinicians can’t relate to that. So they don’t understand. So we need those programs to help our people. But we need our people, we need the people that come from here, who knows this guy’s mother, knows this guy’s grandmother, to convince them to get involved, and help them, and wrap their arms around them, and bring it back to the way it used to be. And where do we find a lot of those people? In our churches.”
2. Church leaders believe that hopelessness and inequity are OUD risk factors . All clergy alluded to hopelessness as OUD drivers, including the trauma individuals and families experienced from the COVID-19 pandemic:
“I always believe that it’s a multifaceted issue. And with impact of the pandemic, particularly unemployment, additional stress, financial strain on families, and sense of hopelessness, it’s almost like what some might describe as the perfect storm for pushing certain people who may not have many healthier support options.”
The interviews also had many undertones of the inequity and injustice experienced in the Black American community when accessing OUD treatment facilities. For example, a church leader’s expressions suggested that some of their community members accessing OUD treatment facilities were ill-treated and not administered care with compassion, indicative of the concept of criminalization rather than the concept of medicalization:
“Black communities’ reception at these clinics and hospitals is among the poorest. When a Black person with addiction goes to the clinic for help, sometimes that is where they tend to see themselves as drug abusers, but not as people who have health problems.”
Moreover, these perceptions of poor reception when accessing OUD treatment facilities, coupled with inequity experienced by the Black community, further discourage them from accessing resources for OUD:
“First of all, as Black people, we do not really believe in a system that was not designed for us. And when you’re already disenfranchised, and you’re already down, you’re already marginalized, it’s not like you want to go and be mistreated again.”
3. Church leaders are committed to helping people flourish beyond staying alive. Generally, the church leaders appreciated the benefits of MOUDs and harm reduction methods, such as naloxone, that would set OUD individuals on a path to remission and thriving, not only keep people alive. All advocated for counseling and preventive harm reduction methods, including MOUDs. For instance, a church leader’s response to his opinion about faith-based intervention methods to mitigate the OUD crisis was:
“I will use faith to believe in God and bring professional counselors and medical experts to help folks using these drugs. I believe in the treatments, and I believe that the same God who changes and touches lives also gives us knowledge and wisdom to treat people so that people will get out of drugs. Because the thing has both physical and spiritual aspects, we need to also deal with the spiritual elements: prayer, counseling, and believing God to touch them.”
However, most of the church leaders were conflicted over those harm reduction interventions that enabled the confident utilization of opioids, such as clean syringe exchanges and fentanyl test strips and the establishment of harm reduction centers. Their teachings and convictions did not favor misusing opioids or any other substance that would jeopardize a person’s health and well-being. A church leader was almost to the point of tears sharing about her conviction:
“Would you encourage your child to use the test strip first, or are you trying to bring them to Christ? We’re supposed to bring people to do what’s godly. We can’t do that while inventing new ways to cheat.”
They were also convinced that the church establishment is critical in addressing the spiritual and deep-rooted issues of meaning, purpose, and value, allowing people to live and flourish beyond MOUDs and harm reduction methods. For instance, a church leader shared about his conviction:
“The church has a responsibility. I believe in addressing it from a holistic perspective. We are the only entity on the planet with the right and authority to deal with the whole person, the spirit, the soul, and the body, right? Because in my understanding, in my position as a spiritual leader, not every problem is spiritual. What is spiritual, you address it spiritually. What is medical, address it medically. Now, if it is a combination of both, you use both to address it.”
Further, beyond MOUDs and harm reduction methods that keep people alive, church leaders would prioritize prevention efforts such as assisting individuals with their social determinants of health needs such as safe housing and communities, better living conditions, and access to resources to enable individuals and families to flourish. A church leader with personal lived experience on the streets, now ministering to homeless persons, many of whom suffer from OUD, shared:
“I think the homeless crisis is a major start to getting some of these people out of the streets into a safe environment where they can pick up the pieces in their lives. I don’t mean put them in the projects that are already infested with drugs, somewhere where they can feel good about living, and look around, and say, OK, now I have somewhere to store my medication. I have somewhere where I can get mail, you know? I have somewhere to put on clean clothes, get up, and go to a job interview. You’re not going to get that in a shelter, you know?”
4. Church leaders welcome collaborations between church and state. While all the church leaders were pleased with the Rhode Island government’s endorsement of the Imani Recovery Breakthrough Intervention, some expressed a disconnect while engaging with the Rhode Island Governor’s Overdose and Prevention Taskforce. A church leader who was invited to a Taskforce meeting felt out of place:
“I remember the first time I went there [Governor’s Overdose and Prevention Taskforce]; I felt like I was out of the league. I wasn’t in. You know what I mean? I think it was more of the medical field, with the social workers, and with others. So I sat there for a few minutes, and I’m going, you know what, this is not what I should be part of. And I tried again, and it was still the same. So I think they would be more involved if they made faith leaders comfortable.”
Nevertheless, the church leaders are open to partnering with state authorities around the OUD crisis. They are also open to collaborating with state authorities around the OUD crisis. According to a church leader:
“Spiritual care providers or clergy and lay leaders are not in competition with professional health care providers. Our work is complementary to the work of professional healthcare providers. Fighting opioid addiction requires an intentional, integrated effort by both spiritual and secular community leaders.”
Church leaders will fully engage with state authorities and leaders in OUD intervention efforts when they are given autonomy and their values are recognized and appreciated, as elaborated by this church leader:
“Empowering the Church with additional tools and resources, including training and specific education, is a step in the right direction. The false objection based upon the concept of the separation of church and state must not be brought into the conversation. If so, the Church-Faith-Based approach will be anemic and impotent. Faith-Based and Church-Faith-Based frameworks should be seen as different approaches. The former includes the discussion of God, while the latter could involve the Head of the Church - Jesus Christ, His Word [the Biblical scriptures] and the Holy Spirit.”
This qualitative study of 30 semi-structured interviews of Black Rhode Island church leaders examined their views toward Opioid Use Disorder and harm reduction. The major finding of the study was that Black American church leaders deeply care about the health and wellbeing of people with Opioid Use Disorder. While the Black American church leaders are concerned about interventions they perceive as perpetuating use, such as fentanyl test strips or sterile syringe exchanges, they are open to many harm reduction interventions, including counseling, Medications for Opioid Use Disorder, and naloxone. The themes emerging from the interviews highlight opportunities to engage church leaders who are highly respected and influential community members to address the ongoing opioid crisis in Black communities.
The theme, Church leaders are empathetic and knowledgeable about the OUD crisis in their communities , resonates with Jerome Adams, MD, MPH, previous US Surgeon General, who appreciated the critical role of the faith community in approaching the Opioid Crisis in their communities with compassion and a sense of a call to duty. In his statement, “Keeping Faith, Bringing Hope and Healing in the Midst of the Opioid Crisis,” the Surgeon General recognized the contributions of faith communities along with social service agencies in encouraging access to MOUDs while promoting recovery services and prevention of substance misuse ( 26 ). The personal, familial, and medical close encounters with opioid overdoses by several church leaders developed empathy toward persons with OUD and provided contextual knowledge about the OUD crisis. Moreover, some church leaders in this study were involved in substance use prevention and recovery efforts locally in their congregation and through widespread Christian-based recovery ministries such as Adult and Teen Challenge USA, a residential recovery program. Adult and Teen Challenge USA employs a Bible-based curriculum to aid individuals in their recovery journey holistically (psychologically, socially, physically, and spiritually) ( 27 ). The economic benefit of faith-based residential recovery programs is significant. An impact evaluation study to assess the financial impact of a faith-based long-term residential addiction recovery intervention, the Mission, in Baltimore, Maryland, revealed that every person who participates in the Mission for a year saves the state and county governments $14, 263. These savings result from less spending on health care, social services, and criminal justice utilization ( 28 ). The study participants comprised 5,122 homeless men recovering from substance use disorder from 2006 to 2019. Surmising from this impact evaluation study, Adult and Teen Challenge USA, would be a cost-effective recovery intervention.
In addition to their lived experiences, several church leaders provided historical accounts of the OUD crisis, emphasizing that the OUD crisis was not a new epidemic in the Black American community. Historically, Black Americans accounted for the majority of the heroin use disorder crisis of the 1960s and 1970s when drug laws against this heroin-related opioid epidemic predominantly affected Black American and minority communities, resulting in a disproportionate prison population legacy ( 29 , 30 ). Relatedly, the profile of heroin users in the 1960s and 1970s were minority males ( 31 ). The disparate incarceration of minority populations persists in more recent times. For example, in 2001, 94% of imprisoned drug offenders in New York were Blacks and Hispanics compared to 5.3% Whites ( 32 ). The criminalization of minority heroin opioid users is in stark contradiction to the medicalization approach to OUD, viewing the opioid crisis as a public health problem when it is also plaguing Whites ( 33 ).
Moreover, financial restraints leading to inadequate health insurance, distrust of the medical community, and healthcare infrastructure from historical mistreatment and stigma are barriers to assessing healthcare services for OUD ( 29 ). These barriers lead to the second theme: Church leaders believe that hopelessness and inequity are OUD risk factors. Furthermore, consistent with the sentiments expressed by some church leaders, research has revealed the ethnic-discordant relationship between Blacks and health professionals, leading to Blacks disliking their experiences with their medical care compared to Whites ( 34 ).
Unfortunately, despite the shift in the focus of the epidemic from criminalizing it to treating it, the black population is still impacted disproportionately compared to their white counterparts ( 29 , 35 ). Researchers have attributed the disparity in OUD treatment outcomes for black populations to omitting them from discussions around the OUD epidemic ( 29 , 35 ) an indication that providing OUD treatments and intervention strategies to Black and other minority populations should take cultural competence into account.
All the church leaders advocated for primary prevention and recovery strategies such as counseling and role modeling to safeguard youth and families from engaging in substance misuse. They also advocated for supporting people in recovery, especially in addressing trauma and life challenges. The clergy would rather commit to providing these support strategies to enable people to flourish beyond merely keeping them alive through medical interventions. The study participants’ prevention and recovery outlook for OUD was consistent with researchers ( 36 ), who demonstrated that spiritual assistance and religious participation can help prevent misuse of substances in young adults and aid persons in addiction on their recovery journey. Their findings mirrored other studies demonstrating associations between spiritual practices and recovery from substance use disorder ( 37 ) and showing relationships between perceived spiritual support and increased self-efficacy and less cravings from substance use disorder ( 38 ). These outcomes are associated with hope. Specifically, a study investigated the association between distress tolerance and general and religious or spiritual hope for ethnic minorities, including Blacks, compared to non-Hispanic Whites, in a nationally representative adult sample (N=2875) ( 39 ). The researchers showed that ethnic minorities generally experienced lower degrees of psychological distress compared to non-Hispanic whites. Moreover, the ethnic minority groups, including Blacks, experiencing lesser degrees of psychological distress indicated higher degrees of religious or spiritual and secular hope compared to non-Hispanic Whites who are intolerant to distress.
The religious or spiritual orientation of hope by ethnic minority groups is critical in coping with challenges beyond their capacity to contain ( 40 ), including the inequities and injustices that Blacks face compared to Whites in the face of the OUD crisis. Against this backdrop is the third theme: Church leaders are committed to helping people flourish beyond staying alive. For the clergy, providing OUD treatment options and interventions alone is inadequate if they do not offer holistic care for the people. They believed that their faith and religious practices could address the deep-seated needs of people suffering from substance use disorders ( 19 ), including OUD.
Stemming from this viewpoint, most of the clergy discouraged the use of harm reduction methods they perceived as perpetuating use, including clean syringes and fentanyl test strips. This finding was congruent with an online survey of (n=133) faith leaders’ views of a needle exchange program in Illinois ( 41 ). Per the survey, the faith leaders supposed that the needle exchange program would increase drug use, though they also appreciated that the needle exchange programs would reduce blood-borne infections. This mixed response to the study findings is also captured in the present study as the “Inner Value Conflict” subcode. (Please see Supplementary 3 for more selected responses and associated Biblical references).
The overwhelming support for the church-based drug overdose intervention, the Imani Breakthrough Recovery Intervention, endorsed by the Rhode Island government, is suggestive of the fourth theme: Church leaders welcome collaborations between church and state. The Imani Breakthrough Recovery Intervention is a community-based participatory research (CBPR) approach to address the rising cases of drug overdose among Blacks and Latinos, began in partnership with the State of Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services, funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) ( 42 ). Parishioners and persons with lived experience facilitate the innovative intervention run by Black and Latino churches. The 22-week intervention is unique in addressing the effect of trauma and racism experienced by these racial minority communities relative to substance use disorder, including OUD. The intervention addresses the inequities in social determinants of health (SODH) encountered by these communities by providing wraparound support and life coaching while focusing on SAMHSA’s eight dimensions of wellness (physical, intellectual, environmental, spiritual, social, occupational, emotional, and financial health) ( 43 ) and the Citizenship Enhancement model brought about by determining the factors necessary for community reintegration by persons previously incarcerated or with mental illness. The Citizenship Enhancement model appreciates the need for access to employment opportunities, healthcare, housing, and a sense of belonging ( 44 ). A report showing 42% retention of Imani intervention participants at 12 weeks and data leading to a significant increase in Citizenship Enhancement scores from baseline to week 12, the Imani Breakthrough intervention shows promise in addressing the SODH disparities of people who use substances such as opioids in Black and Latino communities ( 42 ). The Imani Breakthrough is, thus, at the heart of the church leaders’ desire to enhance and rebuild lives to flourish and shows promise in providing culturally informed recovery intervention for Blacks and Hispanics.
These collaborations between faith-based organizations and state agencies are necessary to engage persons in addiction, their family networks, and communities in their recovery journey ( 45 ), who would otherwise be logistically unreachable by federal and state organizations. Furthermore, researchers have challenged the strict application of separation of church and state, allowing churches to use government funding to advance a social service without promoting religious activities ( 19 ). The researchers posit that this delineation between religious practices and government-funded social programs can lower the impact of faith-based interventions when the religious practices and beliefs are segregated from the intervention. Likewise, the Black church leaders in this study asserted the lower effect of faith-based initiatives not fully embracing their core beliefs.
This study adds to a growing body of knowledge showing the critical role of church leaders in addressing the OUD crisis in black and other ethnic minority communities. The church community is an intimate bridge connecting available interventions and resources to persons experiencing OUD, their families, and the community. Given that the success of OUD church-based initiatives is largely descriptive and anecdotal, more rigorous study designs, including independently cross-checking derived codes from different researchers and computing intercoder agreement, and mixed methods approach to triangulate data from different sources. Longitudinal and quantitative research methods, quantitative evaluation methods, cost-effectiveness, and economic impact assessments, should be employed to assess the public health utility of church-based interventions for OUD. Additionally, researchers should continue to include culturally centered, disparities reduction and community-engaged research approaches such as CBPR methods in interventions and study designs to empower Black and racially ethnic minority communities in discussions around the OUD crisis. These design methods can collectively provide innovative and targeted approaches for nontraditional partners to work together for high-risk groups in the fight against OUD.
Black church leaders have an affinity for primary prevention and flourishing in recovery strategies in OUD intervention efforts. Black church leaders are trusted community members and can be invaluable leaders, planners, listeners, and counselors for OUD sufferers. They are a critical resource in providing innovative and culturally sensitive strategies in the opioid overdose crisis affecting the Black American communities. Their views should be carefully considered in OUD policies, collaborations, and interventions in the Black American community.
This study’s limitations include convenience and snowball sampling recruitment methods that may be less representative of Black American clergy. While comparable to other qualitative research studies, it is worth noting that this sample was 30 clergy members and may not represent the perspectives of all Black clergy members. In addition, many of the churches were in Rhode Island’s Greater Providence community, which may have led to participants’ concerns about anonymity and confidentiality.
Data availability statement
Given how small the number of Black American clergy are in Rhode Island, study data, including recordings and interview transcripts, cannot be shared. Moreover, due to the deductive disclosure, it is almost impossible to de-identify the recordings and transcripts generated. As such, data sharing would breach the confidentiality implied in the participation agreement. To make this study transparent, however, the authors have included the semi-structured interview guide ( Supplementary 1 ), resulting codes and subcodes generated ( Supplementary 2 ), and thematic codes and subcodes with selected responses and associated Biblical references ( Supplementary 3 ) as Supplementary Information . Requests to access the datasets should be directed to AD, [email protected].
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Harvard Longwood Campus Research Protocol Institutional Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because a positive email response to an informed consent document and obtaining verbal consent before the interview sufficed due to the study’s exempt status.
Author contributions
AD: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. IW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MM: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JR: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by a fellowship award through the Recovery Research Institute, Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (R24DA051988) of the National Institutes of Health, a grant from the Center for Biomedical Research Excellence (COBRE) on Opioids and Overdose (P20GM125507), and a fellowship from the Harvard FXB Center for Health and Human rights. Dr. IW is partially supported by the Providence/Boston Center for AIDS Research (P30AI042853) and by Institutional Development Award Number U54GM115677 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health, which funds Advance Clinical and Translational Research (Advance-CTR) from the Rhode Island IDeA-CTR award. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the clergymen and clergywomen who were interviewed. Many thanks also go to Chyrell Bellamy, MSW, PhD, Professor at Yale University’s Department of Psychiatry and Co-Principal Investigator of the Imani Recovery Breakthrough Intervention, for her assistance in drafting the qualitative interview questions. For their advice in preparing this manuscript, the authors also wish to thank Emma-Louise Aveling, PhD, MPhil, a Research Scientist at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in the Department of Health Policy and Management, for her qualitative research method expertise, Howard Koh, MD, MPH, Professor of the Practice of Public Health Leadership at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health and the Harvard Kennedy School, and Co-Director of the Initiative on Health, Spirituality, and Religion at Harvard and David Heckendorn, a chaplain at Harvard University, affiliated with the InterVarsity Christian Fellowship. While this manuscript is not under review in any other publication and has not been previously published, this work is from the first author’s thesis embargoed until 4-23-2025 at the Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard ( 46 ).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Author disclaimer
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1359826/full#supplementary-material
1. Hodder SL, Feinberg J, Strathdee SA, Shoptaw S, Altice FL, Ortenzio L, et al. The opioid crisis and HIV in the USA: deadly synergies. Lancet . (2021) 397:1139–50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00391-3
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Humphreys K, Shover CL, Andrews CM, Bohnert ASB, Brandeau ML, Caulkins JP, et al. Responding to the opioid crisis in North America and beyond: recommendations of the Stanford–Lancet Commission. Lancet . (2022) 399:555–604. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02252-2
3. Howard K, Harvard TH, Chan School of Public Health. What led to the opioid crisis—and how to fix it (2022). Available online at: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/features/what-led-to-the-opioid-crisis-and-how-to-fix-it/ .
Google Scholar
4. Furr-Holden D, Milam AJ, Wang L, Sadler R. African Americans now outpace whites in opioid-involved overdose deaths: a comparison of temporal trends from 1999 to 2018. Addiction . (2021) 116:677–83. doi: 10.1111/add.15233
5. Althoff KN, Leifheit KM, Park JN, Chandran A, Sherman SG. Opioid-related overdose mortality in the era of fentanyl: Monitoring a shifting epidemic by person, place, and time. Drug Alcohol Depend . (2020) 216:108321. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108321
6. Netherland J, Hansen HB. The war on drugs that wasn’t: wasted whiteness, “Dirty doctors,” and race in media coverage of prescription opioid misuse. Cult Med Psychiatry . (2016) 40:664–86. doi: 10.1007/s11013-016-9496-5
7. Shin J, Hallowell BD, Scagos RP. Racial and ethnic disparities in accidental drug overdose deaths – Rhode Island, 2016–2020. R I Med J . (2013). 104(8):47–9.
8. Brinkley-Rubinstein L, Peterson M, Clarke J, Macmadu A, Truong A, Pognon K, et al. The benefits and implementation challenges of the first state-wide comprehensive medication for addictions program in a unified jail and prison setting. Drug Alcohol Depend . (2019) 205:107514. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.06.016
9. Green TC, Clarke J, Brinkley-Rubinstein L, Marshall BDL, Alexander-Scott N, Boss R, et al. Postincarceration fatal overdoses after implementing medications for addiction treatment in a statewide correctional system. JAMA Psychiatry . (2018) 75:405–7. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.4614
10. Marshall BDL, Yedinak JL, Goyer J, Green TC, Koziol JA, Alexander-Scott N. Development of a statewide, publicly accessible drug overdose surveillance and information system. Am J Public Health . (2017) 107:1760–3. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2017.304007
11. RI Governor’s Office, RI Department of Health (RIDOH), Behavioral Healthcare, Developmental Disabilities and Hospitals (BHDDH), Brown University. Governor’s Overdose Prevention and Intervention Task Force (2015). Available online at: https://preventoverdoseri.org/the-task-force/ .
12. RI Dept of Health. Rhode Island’s Harm Reduction Center Pilot Program (2022). Available online at: https://health.ri.gov/publications/factsheets/Harm-Reduction-Center-Pilot-Program.pdf .
13. Bellamy CD, Costa M, Wyatt J, Mathis M, Sloan A, Budge M, et al. A collaborative culturally-centered and community-driven faith-based opioid recovery initiative: the Imani Breakthrough project. Soc Work Ment Health . (2021) 19:558–67. doi: 10.1080/15332985.2021.1930329
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
14. Slade JL, Holt CL, Bowie J, Scheirer MA, Toussaint E, Saunders DR, et al. Recruitment of african american churches to participate in cancer early detection interventions: A community perspective. J Relig Health . (2018) 57:751–61. doi: 10.1007/s10943-018-0586-2
15. Derose KP, Griffin BA, Kanouse DE, Bogart LM, Williams MV, Haas AC, et al. Effects of a pilot church-based intervention to reduce HIV stigma and promote HIV testing among african americans and latinos. AIDS Behav . (2016) 20:1692–705. doi: 10.1007/s10461-015-1280-y
16. Koh HK, Coles E. Body and soul: health collaborations with faith-based organizations. Am J Public Health . (2019) 109:369–70. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2018.304920
17. Evans A, Webster J. Flores G. Partnering with the faith-based community to address disparities in COVID-19 vaccination rates and outcomes among US black and latino populations. JAMA . (2021) 326:609–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.12652
18. Woodruff A, Frakt AB. Can Churches Bring Addiction Treatment To Rural Areas? In: Health Affairs Forefront (2020). Available at: https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/forefront.20200406.943992/full/ .
19. Grim BJ, Grim ME. Belief, behavior, and belonging: how faith is indispensable in preventing and recovering from substance abuse. J Relig Health . (2019) 58:1713–50. doi: 10.1007/s10943-019-00876-w
20. Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol . (2006) 3:77–101. doi: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
21. Meet 3PlayMedia. 3Play Media (2023). Available online at: https://www.3playmedia.com/ .
22. Dedoose. Great Research Made Easy (2023). Available online at: https://www.dedoose.com/ .
23. APA. Qualitative research design (JARS–Qual) (2020). Available online at: https://apastyle.apa.org/jars/qualitative .
24. Kaiser K. Protecting respondent confidentiality in qualitative research. Qual Health Res . (2009) 19:1632–41. doi: 10.1177/1049732309350879
25. BibleGateway.com: A searchable online Bible in over 150 versions and 50 languages (2023). Available online at: https://www.biblegateway.com/ .
26. Adams J. Keeping Faith, Bringing Hope and Healing in the Midst of the Opioid Crisis. In: Federal Health & Medicine . Capital Publishing. (2018) p. 16. Available at: https://www.federalhealthmedicine.com/uploads/1/2/1/4/121472805/fhm2019.pdf .
27. Adult & Teen Challenge. Our Program (2018). Available online at: https://teenchallengeusa.org/about/ .
28. Lashley M. Economic impact of faith-based residential addiction recovery for the homeless. Public Health Nurs . (2020) 37:722–8. doi: 10.1111/phn.12779
29. James K, Jordan A. The opioid crisis in black communities. J Law Med Ethics . (2018) 46:404–21. doi: 10.1177/1073110518782949
30. Cicero TJ, Ellis MS, Surratt HL, Kurtz SP. The changing face of heroin use in the United States: A retrospective analysis of the past 50 years. JAMA Psychiatry . (2014) 71:821–6. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.366
31. Kozel NJ, Adams EH. Epidemiology of drug abuse: an overview. Science . (1986) 234(4779):970–4. doi: 10.1126/science.3490691
32. Nakdai LR. Are New York’s rockefeller drug laws killing the messenger for the sake of the message? Hofstra Law Rev . (2001) 30(2):567.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
33. Lagisetty PA, Ross R, Bohnert A, Clay M, Maust DT. Buprenorphine treatment divide by race/ethnicity and payment. JAMA Psychiatry . (2019) 76:979–81. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0876
34. Sorkin DH, Ngo-Metzger Q, De Alba I. Racial/ethnic discrimination in health care: impact on perceived quality of care. J Gen Intern Med . (2010) 25:390–6. doi: 10.1007/s11606-010-1257-5
35. Drake J, Charles C, Bourgeois JW, Daniel ES, Kwende M. Exploring the impact of the opioid epidemic in Black and Hispanic communities in the United States. Drug Science Policy Law . (2020) 6:2050324520940428. doi: 10.1177/2050324520940428
36. Johnson B, Pagano M. Can faith rewire an addict’s brain? Wall Street J . (2014). Available at: http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303779504579463251726224232.html .
37. Balboni TA, VanderWeele TJ, Doan-Soares SD, Long KNG, Ferrell BR, Fitchett G, et al. Spirituality in serious illness and health. JAMA . (2022) 328:184–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.11086
38. Lyons GCB, Deane FP, Kelly PJ. Forgiveness and purpose in life as spiritual mechanisms of recovery from substance use disorders. Addict Res Theory . (2010) 18:528–43. doi: 10.3109/16066351003660619
39. McIntosh R, Ironson G, Krause N. Keeping hope alive: Racial-ethnic disparities in distress tolerance are mitigated by religious/spiritual hope among Black Americans. J Psychosomatic Res . (2021) 144:110403. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2021.110403
40. Pargament KI. TARGET ARTICLE: the bitter and the sweet: an evaluation of the costs and benefits of religiousness. psychol Inq . (2002) 13:168–81. doi: 10.1207/S15327965PLI1303_02
41. Grundy SA, Mozelewski SR, Adjei Boakye E, Lee M, Levin BL. Faith leaders’ perceptions of needle exchange programs in the rural Illinois Delta Region: Religion as a social determinant of health. Am J Addict . (2021) 30:560–7. doi: 10.1111/ajad.13213
42. Jordan A, Costa M, Nich C, Swarbrick M, Babuscio T, Wyatt J, et al. Breaking through social determinants of health: Results from a feasibility study of Imani Breakthrough, a community developed substance use intervention for Black and Latinx people. J Subst Use Addict Treat . (2023) 153:209057. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209057
43. Swarbrick M. A wellness approach. Psychiatr Rehabil J . (2006) 29:311–4. doi: 10.2975/29.2006.311.314
44. Rowe M, Benedict P, Sells D, Dinzeo T, Garvin C, Schwab L, et al. Citizenship, community, and recovery: A group- and peer-based intervention for persons with co-occurring disorders and criminal justice histories. J Groups Addict Recovery . (2009) 4:224–44. doi: 10.1080/15560350903340874
45. White WL, Kelly JF, Roth JD. New addiction-recovery support institutions: mobilizing support beyond professional addiction treatment and recovery mutual aid. J Groups Addict Recovery . (2012) 7:297–317. doi: 10.1080/1556035X.2012.705719
46. Dankwah A. Tackling the Opioid Use Disorder crisis in Rhode Island. Attitudes of Black American Church Leaders toward Harm Reduction and Policy Implications for Intervention Models. [Doctoral dissertation] Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard. Harvard Library Office for Scholarly Communication (2022). Available at: https://dash.harvard.edu/handle/1/37371432 .
Keywords: Opioid Use Disorder, opioid overdose, Black American, qualitative, Christian, church leaders, harm reduction, clergy
Citation: Dankwah AB, Siegrist RB Jr., Wilson IB, McKenzie M and Rich JD (2024) Attitudes of Black American Christian church leaders toward Opioid Use Disorder, overdoses, and harm reduction: a qualitative study. Front. Psychiatry 15:1359826. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1359826
Received: 22 December 2023; Accepted: 11 March 2024; Published: 03 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Dankwah, Siegrist, Wilson, McKenzie and Rich. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Akosua B. Dankwah, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative Research is a peer-reviewed international journal that has been leading debates about qualitative methods for over 20 years. The journal provides a forum for the discussion and development of qualitative methods across disciplines, publishing high quality articles that contribute to the ways in which we think about and practice the craft of qualitative research.
Qualitative Research Journal (QRJ) deals comprehensively with the collection, analysis and presentation of qualitative data in the human sciences as well as theoretical and conceptual inquiry and provides an international forum for researchers and practitioners to advance knowledge and promote good qualitative research practices.
Qualitative Research was established in 2001 by Sara Delamont and Paul Atkinson. The journal was founded to offer a critical and reflective gaze on methodological approaches, understandings and engagements, and worked to counter tendencies that imagined qualitative research could become a taken for granted set of precepts and procedures.
The mission of the journal Qualitative Psychology® is to provide a forum for innovative methodological, theoretical, and empirical work that advances qualitative inquiry in psychology. The journal publishes articles that underscore the distinctive contributions that qualitative research can make to the advancement of psychological knowledge.
Browse open Calls for Papers beta. Read the latest articles of Qualitative Research Journal at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Research on an innovative design and evaluation method of Chinese tea sets based on GT-AHP-FCE. YanXiao Zhao, Basyarah Hamat, Leah Ling Li Pang. A qualitative study on the adoption of the new duty hour regulations among medical residents and faculty in Korea. Eui-Ryoung Han, Eun-Kyung Chung.
Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in the results paper given journals' word limits. Qualitative research papers are usually longer than their quantitative counterparts to allow for deep understanding and so-called "thick description". In the methods section, the focus is on ...
Journal overview. Qualitative Research in Psychology is a leading forum for qualitative researchers in all areas of psychology and seeks innovative and pioneering work that moves the field forward. The journal has published state-of-the-art debates on specific research approaches, methods and analytic techniques, such as discourse analysis ...
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
SSM - Qualitative Research in Health is a peer-reviewed, open access journal that publishes international and interdisciplinary qualitative research, methodological, and theoretical contributions related to medical care, illness, disease, health, and wellbeing from across the globe. SSM - Qualitative Research in Health is edited by Stefan Timmermans, a Senior Editor at Social Science & Medicine.
Issue 3 2020 The Practice of Qualitative Research in Migration Studies: Ethical Issues as a Methodological Challenge. Issue 2 2020. Issue 1 2020. Volume 19. Issue 4 2019 Creative approaches to researching further, higher and adult education. Issue 3 2019. Issue 2 2019. Issue 1 2019 Journeys in and through sound. Volume 18.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
The International Journal of Qualitative Methods is the peer-reviewed interdisciplinary open access journal of the International Institute for Qualitative Methodology (IIQM) at the University of Alberta, Canada.. The journal was established in 2002 as an eclectic and international forum for papers reporting original methodological insights, study design innovations, and funded-project ...
Victoria Zascavage, Xavier University. Journal of Ethnographic & Qualitative Research (JEQR) is a quarterly, peer-reviewed periodical, publishing scholarly articles that address topics relating directly to empirical qualitative research and conceptual articles addressing topics related to qualitative. The journal has been assigned ISSN #1935-3308.
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials - case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts - that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals' lives.
The journal is an international and interdisciplinary focus and greatly welcomes papers from all countries. The journal offers an intellectual platform for researchers, practitioners, administrators, and policymakers to contribute and promote qualitative research and analysis. ISSN: 2576-2141.
Qualitative research has ample possibilities within the arena of healthcare research. This article aims to inform healthcare professionals regarding qualitative research, its significance, and applicability in the field of healthcare. ... Maintaining a reflexive diary/journal is a widely recognized way to foster reflexivity. According to ...
About the Journal. Journal Name: Qualitative Research. Publisher Name : Sara Delamont and Paul Atkinson. ISSN: 1468-7941. Impact Factor : 3.096. Nature: Print and Online. Qualitative Research was established in 2001 by Sara Delamont and Paul Atkinson. The journal was founded to offer a critical and reflective gaze on methodological approaches ...
The Journal of Clinical Nursing publishes research and developments relevant to all areas of nursing practice- community, geriatric, mental health, pediatric & more. Abstract Aim To synthesise the dietary expesriences of patients with inflammatory bowel disease by reviewing relevant qualitative studies.
These discussions were essential in helping the first author navigate an empathetic understanding of the participant's experiences with the necessary analytical objectivity required for rigorous qualitative research. Participants and study settings. Fifteen males serving a prison sentence were recruited from three prisons in Northern Norway.
Using social cognitive theory as a guide, this research seeks to explain the perceptions of current and aspiring Indian entrepreneurs. A multiple case study approach using 19 interviews with intellectuals provided qualitative data to conduct a cross-case analysis of the two groups with the qualitative analysis software NVivo. Rare insights from current and aspiring opportunity-motivated ...
Qualitative research methods are increasingly recog-nized for their importance in healthcare-related research, particularly in contextualizing social and cultural realities that impact human behavior (Al-Busaidi et al., 2008; Renjith et al., 2021). There is a growing interest in and acceptance of qualitative research approaches in the health
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue: Telehealth and Telemonitoring (1499) E-Health / Health Services Research and New Models of Care (410) Clinical Communication, Electronic Consultation and Telehealth (513) Focus Groups and Qualitative Research for Human Factors Research (720) Theoretical Frameworks and Concepts (217) Theories, Models, and Frameworks in Human Factors (54 ...
Research design overview. This qualitative research study used a semi-structured interview guide to conduct 30 interviews of Black Rhode Island church leaders recruited by convenience and snowball sampling. Participants. Table 1 summarizes the demographic information and other characteristics of the church leaders. There were 19 (63%) male and ...
Qualitative Health Research (QHR) is a peer-reviewed monthly journal that provides an international, interdisciplinary forum to enhance health care and further the development and understanding of qualitative research in health-care settings.QHR is an invaluable resource for researchers and academics, administrators and others in the health and social service professions, and graduates who ...