
waec/wassce past questions and answers for BIOLOGY-2023 including practical
Apr 24 2024 04:24:00 PM
John Elijah
WAEC/GCE/NECO

WASSCE objective, essay, and practical past questions and answer (BIOLOGY 2023)
Table of contents, wassce/waec biology (2023) questions and answers 11 - 20, wassce/waec biology (2023) question and answers 21 - 30, wassce/waec biology (2023) question and answers 31 - 40, wassce/waec biology (2023) question and answers 41 - 50, download wassce/waec biology (2023) paper 2 (essay questions and answer 1 - 5), download wassce/waec biology (2023) paper 3 (practical questions and answer 1 - 3), wassce/waec biology (2023) questions and answers 1 - 10, 1. the ability of organisms to maintain a constant internal environment is known, the diagram below is an illustration of a mango leaf drawn by a student in a biology test. the student failed the test. study it and answer question 2 and 3.

2. From the diagram above, the likely reason why the student failed the test was that the
3. which other features of the diagram, if shown, would have earned the student more marks, the diagram below are illustrations of forms in which a particular group of organisms exist. study them and answer questions 4 and 5.

4. From the diagram above, Which group of organisms is illustrated
The diagram above are illustrations of forms in which a particular group of organisms exist. study them and answer questions 4 and 5, 5. in which of the illustrated forms does the organism that causes cholera exists, 6. study the list of organisms below and use them to answer the question below, iii - snake, arrangement of the organisms in order of increasing complexity is, 7. study the list of organisms below and use them to answer the question below, the phylum of the organism labelled iv is, the diagram below is an illustration of a cell in which photosynthesis takes place. study it and answer question 8 and 9.

8. In which of the labelled parts would molecules of water and carbon (IV) oxide combining to form sugar?
9. from the diagram above, the oxygen gas formed in the cell diffuses out of the cytoplasm into the air spaces through the part labelled, 10. an example of a process that involves osmosis is the, 11. growth in animals differs from that in plants because growth in, the diagram below is an illustration of a structure in the skeletal system of humans. study it and answer questions 12.

12. The illustrated structure is a part of the
13. consider the diagram above, an individual was involved in a car accident and the illustrated structure was badly injured. which of the following structures would most likely be affected, 14. the tricuspid valve is located between the, the diagram below is an illustration of some structures used for gaseous exchange in humans. study it and answer questions 15 and 16.

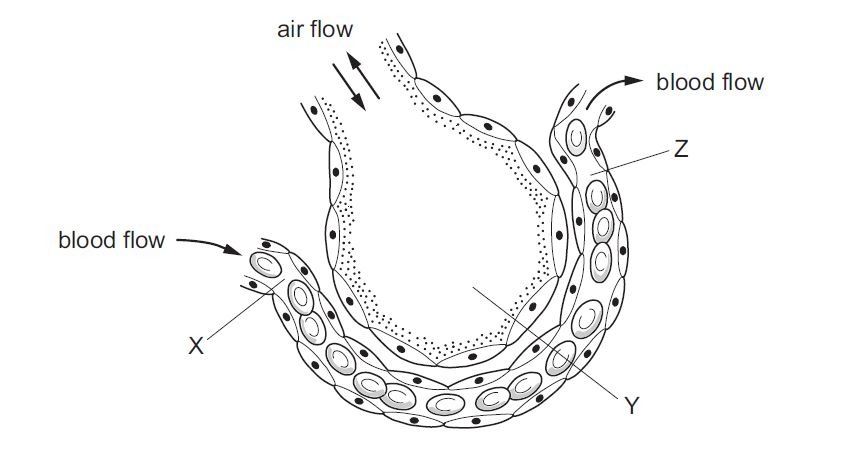
15. The part labelled I, II, III and IV respectively are
16. the part labelled iii above would be found in the, 17. which of the following hormones is wrongly paired with its secretory organ, 18. the eye defect caused by an uneven curvature of the cornea or lens or both is, 19. the androecium in a flowering plant is a collection of, 20. placentation in fruits is referred to as the, 21. which of the following processes does not occur during photosynthesis, 22. stunted growth and small yellow leaves in plants are symptoms of the deficiencies of, 23. the structure that its action could result in choking when talking and eating at the same time is, 24. the food substance that would produce the highest amount of energy is, 25. organisms that feed on dead, decaying tissues of other organisms are known as, 26. the type of nutrition in which organisms take in solid organic materials into their body is, 27. the mouthparts of a grasshoppers are adapted for, 28. a group of organisms belonging to different species that coexist in the same habitat and interact is referred to as, 29. which of the following factors is the main problem facing xerophytes, 30. fishes survive in water mainly because they possess, 31. which of the following instruments is not used in measuring abiotic factors in a habitat, 32. which of the following soil types have a high capillarity, 33. the capturing and digestion of insects by a pitcher plant is a special form of nutrition that, 34. which of the following organisms would be the producer in a food chain, 35. the rate of decomposition of dead organisms is faster in the tropical rainforest than in other biomes because, the diagram below are illustrations of organisms in a habitat study them and answer questions 36 and 37.

36. The feeding relationship between the organisms labelled III and IV in the diagram is
37. the producer in the diagram above is, 38. which of the following activities is against the conservation of natural resoures, use the information below to answer questions 39 and 40, i - making shoes from crocodile skin, ii - making tables with plastic, iii - using elephant tusk for decoration, iv - using firewood for cooking, 39. the act that should be encouraged for the conservation of wildlife and forests is, 40. in order to avoid some of the acts that would have negative effects on conservation, government should, 41. which of the following characteristics shows discontinuous variation implants, 42. a rhesus negative woman may experience stillbirth of the second child that is rhesus positive because, 43. a sudden change in the genetic composition of an organism is termed, 44. paternity disputes could be resolved accurately through, the illustration below is a genetic diagram. study it and answer questions 45 to 47.

45. What is the name of the genetic diagram?
46. what do the labels i, ii, iii, and iv respectively represent, 47. the genotypic ratio of the offspring in the genetic diagram above is, 48. what is the probability that a pregnancy would result in a male child, 49. a vestigial structure in humans is, 50. the following activities are associated with termites except, i recommend you check my article on the following:, poscholars team..
Share this post with your friends on social media if you learned something or was informed.
4 Comments on " 2023 WAEC(WASSCE) PAST QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS FOR BIOLOGY "
Kingsley yankey says:.
Mon, 27 May 2024 19:36:31 GMT
koomson Says:
Mon, 05 Aug 2024 14:03:09 GMT
Amenyoh Daniel Says:
Sun, 11 Aug 2024 02:30:44 GMT
Frimpomaa Vivienne Afia Says:
Sun, 01 Sep 2024 03:10:09 GMT
Leave a Reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts:
Stay Updated:
Quick Links

Legit WAEC GCE Biology Questions and Answers 2022/2023 ( Essay and Objectives)
The WAEC GCE Biology questions and answers for 2023 can be found here. The 2023 WAEC Biology in English Questions and Answers section welcomes you.
You will be able to find the answers to the WAEC GCE Biology Objective and Theory questions, as well as the WAEC Biology Essay 2023 and WAEC GCE 2023 Biology exams, as well as the study recommendations you need to pass your WAEC GCE Biology exam with ease.
WAEC GCE Biology Essay and Objectives Questions and Answers 2023 (Expo)
The 2023 WAEC GCE Biology expo will be posted here during the WAEC GCE Biology examination. Keep checking and reloading this page for the answers. WAEC GCE Nov/Dec. 2023 Biology Answers Loading…
FREE DOWNLOAD NOW
Today’s GCE Biology Answers:
GCE Biology OBJ: Loading…
—————————————————————————————–
Note: The answers below are the 2022 Nov/Dec answers.
i. Development and growth. After meiosis has produced a gamete, and this has fused with another gamete to form an embryo, the embryo grows using mitosis. …
ii.Cell replacement. …
iii.Asexual reproduction.
(3a) TABULATE
BIOLOGY ASSOCIATION || EXAMPLE Commensalism – Sharks and remora fish, Tigers and golden jackals
Mutualism – Bees and flowers, humans and bacteria in the gut
Parasitism – Humans and tapeworms, cows and ticks
Neutralism – Rainbow trout, and dandevon cactus and tarantulas
(3b) Pollution can be referred to as the introduction of harmful materials or substances into our environment thereby causing adverse charges.
(3ci) (i)It contributes to global warming (ii)It leaves a huge carbon footprints
(3cii) (i)it also contributes to global climate change (ii)It emits mercury which is a neurotoxin as well as carbon dioxide
(3ciii) (i)When it spills in aquatic bodies, it causes loss of aquatic lives (ii)On land, crude oil spills reduce food productivity
6a) (i) Dominance refers to the exertion of a major controlling influence of one or more species upon all other species by virtue of their number, size, productivity or related activities.
(ii) Size: Population size is the number of individual organisms in a population.
(iii) Density: This the number of living organisms per unit area or volume.
(6b) (i) Frog has lungs for breathing but also breathes through its skin. (ii) They have webbed feet, which help them to swim (iii) They have long and strong hind limbs, which help them in leaping and catching their prey.
(6c) (i) This is a mismatched blood transfusion. The blood will agglutinate which will lead to fatality. In such a situation, a reaction known as hemolytic transfusion reaction causes the patient’s body to form antibodies that attack the new blood cells.
(ii) The patient’ blood is tested and to get a matched to be transfused.
(iii) Discontinuous variation
(iv) To know the patient’s rhesus factor and blood group which are parameters necessary for a successful blood transfusion
(6di) (i) Bacteria (ii) Plants (iii) Animals
(6dii) (i) Nitrosomoners (ii) Nitrobacta (iii) Fungi
(6e) (i) Cook the food well (ii) Always cover the food (iii) Ensure the environment is always clean
More Answers Loading …
———————————————————————————————————————-
The questions below are not exactly 2022 WAEC Biology questions and answers but likely WAEC Literature likely repeated questions and answers.
These questions are strictly for practice. The 2022 WAEC GCE Biology expo will be posted on this page on the day of the WAEC GCE Biology examination. Keep checking and refreshing/reloading this page for the answers.
1. Which of the following groups of animals do not possess a nervous system? (a) Porifera (b) Cnidaria (c) Platyhelminthes (d) Nematoda
2. The structural and pointed similarities in paramecium and Euglena are in the (a) Shape of locomotory organs (b) blunt anterior and pointed posterior (c) presence of micro and mega nuclei in both. (d) presence of anterior and posterior contractile vacuoles
3. Which of the following organisms cannot exist freely on its own? (a) Chlamydomonas (b) Amoeba (c) Paramecium (d) Plasmodium
the diagram below is an illustration of an Arthropod. Study it and answer question 4
4. The Arthropod in the diagram is not an insect because it (a) has a big head that is almost equal to the “thorax. (b) has eight lets and no wings (c) does not have visible eyes on it head (d) has head, thorax and abdomen
5. Which of the following cell organelles is the site for the production of ATP? (a) Lysosome (b) Nucleus (c) Mitochondrion (d) Ribosome
6. An example of osmosis in plants is the (a) movement of water through the xylem (b) loss of water vapour from stomata (c) transaction of food through the phloem (d) absorption of water from the soil by the root.
7. The organism that can carry out both autrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition is (a) Chlamydomonas (b) Eudorina (c) Euglena (d) Spirogyra
The diagram below illustrates a part of human skeleton. Study it and answer questions 8 to 10
8. The diagram represent the bones of the (a) upper arm (b) lower arm (c) upper leg (d) lower leg
9. Which of the labeled parts articulates with the head of the trochlea to form a hinge point? (a) I (b) II (c) III (d) IV
10. The labeled part that provides surface for the attachment of the triceps is (a) I (b) II (c) III (d) IV
The diagram below illustrates
11. The transverse section of (a) dicotyledonous root (b) monocotyledonous root (c) dicotyledonous stem (d) monocotyledonous stem
12. Which of the following actions does not occur during exhalation in man? (a) Thoracic cavity decreases in volume (b) Diaphragm flattens (c) Ribs move down and in (d) Air pressure increases in the thoracic cavity
The diagram below is an illustration of the urinary tubule in a mammal. Study it and answer question 13 to 15.
13. Which of the following substances is found in part labeled II only? (a) Lipid (b) Protein (c) Salts (d) Water
14. The part which contain the lowest concentration of urea is labeled (a) I (b) II (c) III (d) IV
15. Which of the following substances is greater in concentration in the part labeled IV when compared to that of the part labeled I? (a) Lipid (b) Glucose (c) Urea (d) Uric acid
16. Deamination of amino acids in the liver produces (a) blood sugar (b) glycogen (c) bile (d) urea
17. Which of the following glands also serves as an exocrine gland? (a) Ovary (b) Pancreas (c) Adrenal (d) Thyroid
18. Which of the following sequences is the correct route of the transmission of impulses along a reflex arc?
(a) Receptor → sensory neurone → synapse intermediate neurone → synapse → motor neurone effector
(b) Receptor → motor neurone → synapse → intermediate neurone → synapse → sensory neurone → effector
(c) Effector → intermediate neurone → synapse → motor neurone → synapse →sensory neurone → receptor
(d) Effector → motor neurone → synapse → sensory neurone → synapse → intermediate neurone → receptor
Solved WAEC Mathematics Questions and Answers For 2023/2024 (Essay and Objectives)
19. when viewing an object that is close to the human eye, the (a) eye lens becomes thin. (b) ciliary muscles relax (c) suspensory ligaments become taut. (d) eye lens become fat
The diagram below is an illustration of the human sperm. Study it and answer questions 20 and 21
20. The part labeled I is the (a) acrosome (b) nucleus (c) mitochondrion (d) tail
21. The function of the part labeled II is to (a) fuse with the ovum during fertilization (b) generate the energy for the sperm to swim to the fallopian tube (c) help the sperm to swim forward (d) dissolve the membrane of the egg during fertilization.
22. Which of the following types of placentation is not common amongst syncarpous pistils? (a) Marginal (b) Axile (c) Parietal (d) Free central
23. The complex energy-rich organic matter which living organisms need for life is (a) water (b) air (c) food (d) mineral salts
24. Which of the following processes are associated with photosynthesis? I. Energy from sunlight is absorbed II Carbon dioxide is evolved III Oxygen is given off IV Glucose is synthesized.
I and II only (b) I, II and IV only (c) I, III and IV only (d) I, II, III and IV
25. Which of the following functions is associated with calcium in plants? Formation of (a) Cell wall (b) Ribosomes. (c) Proteins (d) Cell membrane
The aforementioned questions are likely WAEC GCE repeated questions and answers rather than the 2023 Biology questions and answers. These are practise questions. On the day of the WAEC GCE Biology examination, the 2023 WAEC GCE Biology questions and answers will be available on this page. Continue to check and refresh/reload this page for latest answers.
Download WAEC Timetable 2023/2024 PDF for May/June Examination
WAEC GCE Biology Essay 2023
WAEC GCE Biology Questions and Answers 2023 Loading… If you have any questions about the WAEC GCE Biology questions and answers, kindly drop your question in the comment box.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

JOIN OUR WAEC & NECO WHATSAPP SAPP GROUP

BIOLOGY-ANSWERS!
Biology-Obj 1CABAACCBCD 11DBCBABCBAC 21ACABDAADCD 31BBCBDABDBA 41ABCCBCACDA
(2a) [FILL IN THE TABLE WITH THIS]
IRON: Function: (PICK ANY ONE) -Chlorophyll formation -Electron transport in photosynthesis -Enzyme activation -Nitrogen fixation
Effects of deficiency in plants: (PICK ANY ONE) -Chlorosis (yellowing of leaves) -Stunted growth -Reduced fruit and seed production -Interference with nutrient uptake
MOLYBDENUM: Function: (PICK ANY ONE) -Nitrogen fixation -Enzymatic reactions -Iron uptake and utilization -Seed germination and growth -Chlorophyll formation
Effects of deficiency in plants: (PICK ANY ONE) -Reduced nitrogen fixation -Chlorosis (yellowing of leaves) -Impaired sulfur metabolism -Abnormal phosphorus uptake -Altered enzyme activity
POTASSIUM Function: (PICK ANY ONE) -Osmotic regulation -Enzyme activation -Protein synthesis
Effects of deficiency in plants: (PICK ANY ONE) -Stunted growth. -Leaf chlorosis. -Weak stems. -Reduced flower and fruit production. -Increased susceptibility to diseases and pests.
COPPER Function: (PICK ANY ONE) -It plays a vital role in activating various enzymes within plants -It helps to facilitate photosynthesis -It helps facilitate respiration in plants
(PICK ANY ONE) Effects of deficiency in plants: -Stunted growth -Yellowing of leaves -Death of plant tissue -Reduced fertility -Increased susceptibility to diseases
NITROGEN Function: (PICK ANY ONE) -It helps in building proteins -It is a fundamental constituent of nucleic acids and DNA -It helps in formation of chlorophyll -It helps in energy transfer and metabolism -It is an enzyme co-factor
Effects of deficiency in plants: (PICK ANY ONE) -Reduced photosynthesis -Poor protein synthesis -Leaf necrosis -Increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. -Impaired nutrient transport
(2b) (PICK ANY THREE) (i) Fruits and Vegetables (ii) Grains and Cereals (iii) Legumes and Pulses (iv) Nuts and Seeds (v) Dairy Products (vi) Meat, Poultry, and Fish
(2ci) BUCCAL CAVITY: (PICK ANY TWO) (i) The buccal cavity is the entry point for food and liquids into the digestive system. (ii) The buccal cavity is responsible for chewing or masticating food. (iii) The buccal cavity contains salivary glands that produce saliva. (iv) The buccal cavity plays a vital role in speech production.
(2cii) DUODENUM (PICK ANY TWO) (i) The duodenum receives partially digested food from the stomach and continues the process of digestion. (ii) The duodenum is involved in the absorption of nutrients from digested food. (iii) The duodenum plays a role in regulating the overall process of digestion. (iv) The duodenum secretes several important hormones that regulate various aspects of digestion.
(2ciii) STOMACH (PICK ANY TWO) (i) One of the primary roles of the stomach is to store food temporarily after it has been ingested. (ii) The stomach aids in the mechanical digestion of food through muscular contractions known as peristalsis. (iii) The stomach secretes gastric juices, primarily composed of (HCl) and enzymes such as pepsin, which play a crucial role in chemical digestion. (iv) The stomach controls the rate at which food is released into the small intestine.
(2d) Glucose and fructose
(5ai) Sense organs are the specialized organs composed of sensory neurons, which help us to perceive and respond to our surroundings.
(5aii) (i) Nose: Responds to airborne chemical substances like aroma or odors. (ii) Taste buds: Detect chemicals present in food or solution to give the perception of taste. (iii) Olfactory epithelium: Receives and detects dissolved substances in the mouth and throat, giving a sense of smell.
(5bi) (i) Male Agama (ii) Tilapia fish (iii) Male crocodile
(5bii) (i) Matured male and female Tilapia zilli (ii) Matured male and Female Clarins gariepinus (iii) Matured male and female humans
(5ci) Both have a protective covering
(5cii) TABULATE =EGG OF TOAD= (i) They do not contain the amniotic fluid (ii) The fertilised zygote are covered with membrane (iii) They are anamniotes.
=EGGS OF BIRDS= (i) Contain the amniotic fluid (ii) The fertilised zygotes are covered with shell (iii) They are amniotes.
(5d) TABULATE PLS (i) Azotobacter; Produce nitrates from free nitrogen in soil (ii) Rhizobium; Absorb atmospheric nitrogen in the soil and build up nitrates (iii) Blue green algae; Fixes atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates (iv) Nitrosomonas; Oxidises ammonium to nitrates
(5e) (i) Saprophytic nutrition; Fungi, Bacteria (ii) Symbiotic nutrition; Algae, Fungus
(1a) Classification of living things is the sorting or grouping of living things according to their common or similar characteristics
(1bi) =FUNGI= (i) It’s also employed in the production of wine. (ii) Metabolites produced by fungi are valuable commercially in the production of pharmaceuticals. (iii) Numerous food items employ fungi as a fermentation agent and a source of nutrients. (iv) It plays an important role in the release of different gases in the atmosphere.
(1bii) =PLANTS= (i) Provide food (ii) Reduce carbondioxide concentration preventing global warming (iii) Produce fuel eg charcoal (iv) Used to provide furniture
(1c) (i)Cnidaria; Hydra (ii)Nematoda; Ascaris (iii)Chordata; Dog, cat (iv)Annelida ; Earthworm, leeches (v)Mullusca; Snail, slugs, limpets

(5d&5e)

(Another 5 Version)

I’m a blogger living in Nigeria. I like to share education guides and information from various sources. I created Jambclass to serve as a platform to disseminate quality, credible and dependable information regarding various ways to excel academically. I strive to keep Nigerian youths and students informed. I started this Blog with the Vision To Inspire and Empower Young Persons; helping them Realize and Maximize their Potential.

Leave a Reply
Name (required)
Email (required, but never shared)
NOTE:- Your comment will appear after it has been approved by an admin .
Home | Recent Posts | Pages
About Jambclass
Copyright © 2022 Jambclass
Get the Most Legit Information and Guide on the Latest Jobs in Nigeria, Facebook and Education Here

NECO Biology Questions and Answers For 2023/2024 (Theory and Objectives)
Biology NECO Questions 2023. I will be showing you the NECO Biology objective and theory questions and answers for free in this post. You will also understand how NECO Biology questions are set and how to answer them.
The National Examinations Council (NECO ) is an examination body in Nigeria that conducts the Senior Secondary Certificate Examination and the General Certificate in Education in June/July and December/January respectively.
Table of Contents
NECO Biology Question and Answers Essay and OBJ (Expo)
The 2023 NECO Biology expo will be posted here today 21st July during the NECO Biology examination. Keep checking and reloading this page for the answers.
NECO 2023 Biology Answers Loading.. .
OBJ Answers:
1-10: BBEDACCAEE
11-20: DDCEABDAEC
21-30: EBBBEADBDD
31-40: EDACCCBCEA
41-50: EBBCACBAEC
51-60: DDABBDDDBE
NECO Biology Essay Answers:
The cell theory states that:
– All living organisms are made up of one or more cells.
– The cell is the basic unit of life.
– All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
– Robert Hooke, who discovered cells in 1665 and coined the term “cell”.
– Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, who proposed the cell theory in 1839-1840.
– Large, brightly colored petals that attract insects.
– Nectar-producing glands to feed the insects.
– A strong, sweet fragrance to attract the insects.
– A landing platform for the insects to rest on.
– Pollen that is sticky and easily attaches to the insects.
– Ginger: Rhizome
– Banana: Rhizome
– Sweet potato: Tuber
– The mouth mechanically breaks down the bread by chewing and mixes it with saliva, which contains enzymes that begin breaking down the carbohydrates in the bread.
– The esophagus moves the food down to the stomach, where it is mixed with stomach acid and enzymes that further break down the bread.
– The small intestine absorbs the nutrients from the bread, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, into the bloodstream.
– The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining food waste, forming feces.
– The rectum stores feces until they can be eliminated through the anus.
Amoeba —> Hydra —> Tilapia —> Toad —> Snake.
(i) Small, lightweight seeds that can be easily carried by the wind.
(ii) Hairs or wings on the fruit that increase surface area and help to catch the wind.
(iii) A dry, papery fruit that splits open easily to release the seeds.
To determine if the shoot of a plant is positively phototropic.
=Apparatus:=
A potted plant, a light source, a ruler, a marker.
=Method/Procedure:=
(i) Place the plant in a dark room for 24 hours to ensure that it is not positively or negatively phototropic.
(ii) Place the light source at a fixed distance from the plant, with the light shining directly on the plant’s shoot.
(iii) Turn on the light source and leave it on for 24 hours.
(iv) After 24 hours, measure the distance between the tip of the shoot and the light source.
(v) Mark the new position of the shoot tip on the ruler.
(vi) Repeat the experiment two more times, moving the light source to a different position each time.
=Observation:=
The shoot of the plant will grow towards them light source, bending in the direction of the light.
=Conclusion:=
The shoot of a plant is positively phototropic and grows towards a light source.
=Aerobic Respiration=
(i) Occurs in the presence of oxygen
(ii) Produces a large amount of ATP
(iii) Carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products
=Anaerobic Respiration=
(i) Occurs in the absence of oxygen
(ii) Produces a small amount of ATP
(iii) Lactic acid or ethanol is produced as a waste product.
=Complete Metamorphosis=
(i) Four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, adult.
(ii) Larva looks completely different from the adult.
=Incomplete Metamorphosis=
(i) Three stages: egg, nymph, adult.
(ii) Nymph looks similar to the adult, just smaller.
– Aim: To determine if chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis to take place.
– Apparatus: Two plants of the same species, one with leaves covered in aluminum foil, a light source, test tube, water, and a beaker.
– Method/procedure: Place one plant in a dark room and cover its leaves with aluminum foil. Place the other plant in front of a light source. After a few hours, pluck a leaf from each plant and place them in separate test tubes filled with water. Place the test tubes in a beaker and keep them in the dark.
– Observation: After a few hours, observe the test tubes to see which one has produced more oxygen bubbles.
– Conclusion: If the test tube with the leaf from the plant exposed to light produces more oxygen bubbles, then chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis to take place.
(i) Overuse of synthetic fertilizers
(ii) Overgrazing
(iii) Deforestation
(iv) Soil erosion
(i) Hearing loss
(ii) Sleep disturbance.
(i) Crop diversity: Planting different crops in the same field over time to avoid the buildup of pests and diseases.
(ii) Soil health: Planting crops that have different nutrient requirements to maintain soil fertility and prevent soil erosion.
(iii) Pest management: Planting crops that are not susceptible to the same pests and diseases in succession.
(i) Reduced leaves or spines to minimize water loss through transpiration.
(ii) Thick cuticles and waxy coatings to reduce water loss through the epidermis.
(iii) Deep roots to tap into underground water sources.
(iv) CAM photosynthesis to reduce water loss during photosynthesis.
(v) Ability to enter dormancy during drought periods.
(i) Similarity in bone structure between birds and reptiles, especially in the skull and pelvis.
(ii) Presence of scales on bird feet and legs, which are also found in reptiles.
(iii) Similarity in egg-laying and incubation between birds and reptiles.
(i) Detoxification of harmful substances in the blood.
(ii) Production of bile to aid in digestion.
(iii) Storage of glycogen, vitamins, and minerals.
(iv) Regulation of blood glucose levels.
(v) Production of blood clotting factors.
(i) Reforestation: Planting new trees in areas where forests have been cleared or degraded.
(ii) Reduced impact logging: Using sustainable logging practices that minimize damage to the forest ecosystem.
(iii) Protected areas: Establishing and maintaining protected areas for wildlife and biodiversity conservation.
(iv) Community forestry: Encouraging local communities to manage forests sustainably for their own benefit and for the benefit of future generations.

(i) Protection: the calyx protects the flower bud before it opens and the developing fruit after fertilization.
(ii) Support: the sepals of the calyx can provide support for the petals and reproductive structures.
(i) Insulin: regulates blood sugar levels.
(ii) Estrogen: regulates female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics.
(iii) Testosterone: regulates male reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics.
(iv) Adrenaline: prepares the body for “fight or flight” response to stress.
(v) Melatonin: regulates sleep-wake cycles.
(i) Gene therapy: correcting genetic disorders by introducing functional genes into the patient’s cells.
(ii) Predictive medicine: using genetic testing to identify individuals who are at risk for certain diseases and develop personalized prevention or treatment plans.
(i) Large surface area: to maximize light absorption.
(ii) Thin and flat shape: to reduce the distance that light needs to penetrate into the leaf.
(iii) Chlorophyll pigments: to absorb light energy and convert it into chemical energy.
——————————————————————————————————-
NECO Biology Questions and Answers For Practice
- NECO Igbo Language Answers
- NECO Yoruba Language Answers
- NECO Hausa Language Answers
——————————————————————————————————————
The questions below are the NECO past questions and answers that will help you in your 2023 NECO Biology Questions.
1. Plants are classified into the following classes except
(a)Bryophyte.
(b) Coelenterate.
(c) pteridophyta.
(d) thallophyta.
(e) Spermatophyte.
2. The cell wall of plants is rigid due to the presence of?
(a) Cambium
(b) cellulose
(d) chloroplast
3. The structure responsible for the transportation of mineral salt from the root to other parts of the plant is?
(a)Collenchyma
(d) sclerenchyma
4. Which of the following cell organelles traps sunlight energy in plant?
(a)Chloroplast
(b) Endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Mitochondrion
(d) Ribosome (e) Vacuole
5. The following conditions are necessary for photosynthesis except
(a) Carbon(iv)oxide.
(b) chlorophyll
(c) light energy
6. Which of the following organisms carries out photosynthesis?
(c) paramecium
(d) plasmodium
7. Which of these is an amphibian?
8. A flower with two or more fused carpels is called
(a) Apocarpous
(b) monocarpous
(c) polycarpous
(d) pistillate
(e) syncarpous
9. The response of plants to the stimulus of touch is called?
(a) Chemotropism
(b) geotropism
(c) hydrotropism
(d) phototropism
(e) thigmotropism
10. Which of the following is a bryophyte?
(a) Bladder wort
(b) Fly trap
(c) Liver wort
(d) Pitcher
11. Cellular respiration occurs in the
(a) Chloroplast
(b) endoplasmic reticulum
(c) food vacuole
(d) mitochondrion
(e) nucleus
12. In a moss plant, spores are produced in the
(a) Capsule
(c) rhizoid
13. Exoskeleton is a characteristic feature of
(b) earthworm
(d) millipede
(e) tapeworm
14. Which of the following influences growth in plants?
(a) Acetic acid
(c) Chlorophyll
(d) Ethylene
15. Land snail belongs to the phylum
(a) Annelida
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Mollusca
(e) nematode
16. The opening of the anthers and stigmas of a bisexual flower at the same time is called
(a) Cleistogamy
(b) dichogamy
(c) homogamy
(d) protandry
(e) protogyny
17. The following are the effect of auxins on plant except in
(a) Flowering
(b) fruiting without fertilization
(c) ripening of fruits
(d) root formation
(e) stem elongation

Use the diagram below to answer questions 18 and 19.
18. The diagram represents the internal structure of a
19. The part labeled I is the
(b) endodermis
(c) phloem (d) root hair (e) xylem
20. Which of these is a water soluble vitamin?
(a) A
21. The following diseases are airborne except
(a) Clolera
(b) measles
(c) meningitis
(d) pneumonia
(e) small pox.
22. The excretory organ of insects is called
(a) Contractile vacuole
(b) flame cell
(d) malphighian tubule
(e) nephridium
23. Which of these animals undergo metamorphosis
24. Villi are finger-like structures found in the
(a) Large intestine
(c) small intestine
(d) stomach
(e) tongue.
25. In mammals, sperms are formed in the
(a) Cowper’s gland
(b) scrotal sac.
(c) seminal vesicle
(d) seminiferous tubules
(e) vas deferens
26. Which of the following is not a part of the mammalian brain?
(a) Cerebellum
(b) cerebrum
(c) Olfactory lobe
(d) spinal cord
(e) Thalamus
27. In plant, Chlorosis is caused by the deficiency of
(b) magnesium
(c) nitrogen
(d) potassium
(e) Sulphur
28. Which of the following diseases is not sexually transmitted
(b) Hepatitis
(d) influenza
(e) Syphilis
29. Which of the following is not a caste in a termitarium.
(d) soldiers
(e) workers
- NECO Marketing Questions and Answers
- NECO Mathematics Questions and Answers
- NECO English Science Questions and Answers
30. The structure responsible for excretion in tape worm is called
(a) Cell membrane
(b) contractile vacuole
(c) flame cell
(d) malphigian tubule
31. The mode of nutrition of mushroom is
(a) autotrophic
(b) epiphytic
(c) parasitic
(d) saprophytic
(e) symbiotic
32. The earthworm is an example of
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Mollusca
(d) nematoda
(e) Platyhelminthes
33. Fat and oil are also known as
(b) fatty acids
(c) glycerol
(e) carbohydrates
34. Gaseous exchange in the lungs occurs at the
(a) Alveolus
(b)bronchus
(c)bronchiole
(e) trachea
35. The following are pigment except
(c) chromatophores
(d) haemoglobin
(e) melanin

Use the diagram below to answer questions 36 – 38.
36. The type of placentation shown above is found in
(a) cana lily
(d) pride of Barbados
(e) sunflower
37. the part labeled x is the
(c) placenta
38. the type of placentation represented in the diagram is
(c) free central
(d) marginal
(e) parietal
39. the growth that occurs at the tip of shoot and root is called
(a) allometric
(c) isometric
(d) primary
(e) secondary
40. carnassial teeth are found in
41. Which of the following bones is not a part of axial skeleton?
(a) Backbone
(e) Sternum
Use the diagram below to answer questions 42 and 43

42. The part labeled ii is the
(b) hyaline cartilage
(c) ligament
(d) synovial cavity
(e) synovial membrane
43. The function of the part labeled iii is to
(a) Soften the bones
(b) join bones together
(c) lubricate joints
(d) protect bones from wearing
(e) reduce friction at joints
44. The part that supplies food and oxygen to the eye is
(a) Choroids
45. The part of the male reproductive system that stores sperm is
(b) epididymis
(c) prostate gland
(d) seminal vesicle
(e) vas deferens.
46. An organ in bird that grinds its food is
(c) gizzard
47. Which of the following animals exhibit basking
48. The following are functions of the sympathetic nervous system except
(a) Dilation of pupil of eye.
(b) inhibition of saliva secretion
(c) reduction of blood pressure
(d) reduction of urine output
(e) stimulation of ejaculation
49. The following homeostatic mechanisms are carried out by mammals except
(a) Excretion
(b) osmoregulation
(c) pH regulation
(d) reproduction
(e) thermoregulation
50. Part of the brain that controls blood pressure is called
(c) corpus callosum
(d) medulla oblongata
(e) pons varolii
51. Haemorrhage is caused due to the deficiency of vitamin
52. The control method of pests using predators is called
(a) Biological
(b) chemical
(c) cultural
(d) mechanical
(e) physical
53. The following are vectors except
(a) Black fly
(b) butterfly
(c) housefly
(d) mosquito
(e) tsetse fly
54. The deficiency of proteins in a developing child result in
(a) Beri beri
(b) kwashiorkor
(c) night blindness
(d) rickets
55. The theory of “use and disuse” of body parts was propounded by
(a) Carl Linneaus
(b) Charles Darwin
(c) Gregor Mendel
(d) Jean Lamarck
(e) Robert Hooke
56. The knowledge of heredity and variation are not required in
(a) Blood transfusion
(b) crime detection
(c) determination of paternity
(d) longevity
(e) marriage
57. Which of these is not a pollutant
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Lead oxide
(c) Nitrogen gas
(d) Nitrogen oxide
(e) sulphur dioxide
58. The topmost layer of a typical soil profile is
(b) coarse sand
(c) fine sand
59. Plants that survive in marine habitats are called
(a) Halophytes
(b) hydrophytes
(c) mesophytes
(d) saprophytes
(e) xerophytes
60. The felling of trees in a forest is called
(a) Afforestation
(b) deforestation
(c) desertification
(d) forest pruning
(e) re-afforestation
Answer any three questions only
1a. State one role each of the following in photosynthesis
(i) Sunlight
(ii) Chlorophyll
b. List five types of bones found in the forearm of man
c. Mention three functions of a worker caste in termitarium
d. Define ecosystem
e. Draw a well labelled diagram (8-10cm long) of the nephron
2a. Define the following
(ii) Implantation
(iii) Species
(iv) Saprophytes
b (i) State four functions of the mammalian skeleton
(ii) Mention two muscles that bring about movement of a forearm
(iii) Name three digestive enzymes found in the small intestine and state one function of each
3a. (i) Mention three diseases of the liver
(ii) In a tabular form, state five differences between plant and animal cells
b. Using annotated diagrams only, illustrate the carbon cycle.
c. (i) List two types of supporting tissues in plant
(ii) Give two characteristics of a reptile
4a. Define the following terms
(i) Diffusion
(ii) Osmosis
(iii) plasmolysis
b (i) State four effects of overcrowding
(ii) mention two ways of conserving wildlife.
(iii) Give two examples of social animals
c (i) Define metamorphosis
(ii) List two examples of insects that undergo incomplete metamorphosis
(iii) Give two examples of a berry fruit
5a. (i) Draw a well labelled diagram (8-10cm long) of the human alimentary canal
(ii) Complete the table below
b. T T and t t are monohybrid plants representing tallness and shortness respectively
- By means of crossing, show the F1 generation
- Using punnet square method, show the F2 generation
- Give the phenotypic ratio of the F1 and F2 generations shown above
That’s all about NECO Biology Questions and Answers for 2022 (Theory and Objectives). If you have any questions, kindly drop your question in the comment box.
Last Updated on July 21, 2023 by Admin
Related posts:

92 thoughts on “NECO Biology Questions and Answers For 2023/2024 (Theory and Objectives)”
I pray to God to continue blessing you and your family members, we really appreciate it and we are so much happy.
Thank you for all the answer,but pls we need today biology answers
what time will you bring biology neco 2023 objective and theory
Please I need all science subjects question and answer
I need biology Neco 2023 really essay and objective
Please I need the Neco biology question only
I need biology question and answer for 2023 neco
Please I need answers On neco
Pls i need science subject question and answer for neco 2023
pls i need all the science subject question and answer for neco 2023
Thank u very much for the question pls i need the answer for the objective and theory
Thank for this it is really encouraging me
Please I need 2020 Biology Theory and Objective questions 2020
Thank you so much, pls I need answers
great i love you guys. showing the. rightful answer on time is best
How do I pass my jamb and waec for my 5main subjects as a science student
I need general maths answer for neco 2021
Hello please how can we get the answers in the objectives and theory for Neco 2022/2023
I trust them, general mathematics 2021answers will be uploaded before the Exam sure
reading wisely and always when you are in a good mood
Please l need biology questions and answers for neco 2022
Same too but its 2023 own i need
Please did you mean you give question before the exam And is exactly what will come out
I need general mathematics 2021 neco answers
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Biology Waec Syllabus
Below is this 2024 Waec Syllabus for Biology. Note that this syllabus is for both internal and external candidates.
Aims and Objectives
- understanding of the structure and functions of living organisms as well as appreciation of nature
- acquisition of adequate laboratory and field skills in order to carry out and evaluate experiments and projects in Biology
- acquisition of necessary scientific skills, for example, observing, classifying and interpreting biological data
- acquisition of the basic relevant knowledge in Biology needed for future advanced studies in biological sciences
- acquisition of scientific attitudes for problem-solving
- ability to apply biological principles in everyday life in matters that affect personal, social, environmental, community health and economic problems
- awareness of the existence of interrelationships between biology and other scientific disciplines
Scheme of Examination
There will be three papers: Papers 1, 2, and 3, all of which must be taken. Papers 1 and 2 will be composite papers to be taken in one sitting.
This will consist of fifty multiple-choice objective questions drawn from Section A of the syllabus (the section of the syllabus that is common to all countries). It will carry 50 marks and last for 50 minutes.
This will consist of six essay questions drawn from the entire syllabus. The paper will be put into three sections: Sections A, B and C.
Will consist of four questions drawn from Section A of the syllabus.
It will be for candidates in Ghana only and will be drawn from Section B of the syllabus (i.e., the section of the syllabus peculiar to Ghana). It will consist of short, structured questions.
It will be for candidates in Nigeria, Sierra Leone, The Gambia, and Liberia and will be drawn from Section C of the syllabus (i.e., the section of the syllabus containing material for those countries only). It will also consist of short-structured questions.
Candidates will be expected to answer two questions from Section A and all the short-structured questions from either Section B or Section C.
Each question in Section A will carry 20 marks, while the compulsory short-structured questions in Sections B and C will carry 30 marks. The total score will be 70 marks. The paper shall take 1 hour and 40 minutes.
Paper 3 will be a practical test (for school candidates) or a test of practical work (for private candidates) lasting 2 hours and consisting of three sections: Sections A, B and C.
This will consist of two compulsory questions drawn from Section A of the syllabus, each carrying 25 marks.
This will be for candidates in Ghana only. It will consist of one question drawn from Section B of the syllabus and will carry 30 marks.
This will be for candidates in Nigeria, Sierra Leone, the Gambia, and Liberia. It will consist of one question drawn from Section C of the syllabus and will carry 30 marks.
Candidates will be expected to answer all the questions in Section A and one question in either Section B or C. The paper will carry a total score of 80 marks.
Detailed Biology Syllabus
Concept of living.
- Living and non-living things
- Classification of living things into Kingdoms
- Differences between plants and animals
- cell (single-celled organisms): Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium
- Tissue: Hydra
- Organ (storage organ) bulb, rhizome and heart.
- System/Organ System: In mammals, flowering plants – reproductive system, excretory system, etc.
- Complexity of organization in higher organisms: advantages and disadvantages
- Single and free-living: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, and Chlamydomonas
- Colony: Volvox
- Filament: Spirogyra
- Part of a living organism: cheek cells, onion root tip cells, and epidermis of fleshy leaves
- Cell structure and functions of cell components
- Similarities and differences between plant and animal cells
- Physical and biophysical processes
- active transport
- Autotrophic (photosynthesis)
- Heterotrophic (holozoic)
- Aerobic respiration
- anaerobic respiration
- energy release
- Excretion in single-celled aquatic organisms. Diffusion by body surface and by the contractile vacuole
- Waste products of metabolism
- Basis of growth: cell division (mitosis), enlargement, and differentiation.
- Aspects of growth: increase in dry weight, irreversible increase in size and length, and increase in the number of cells.
- Regions of the fastest growth in plants
- Influence of growth hormones and auxins
- Growth curvatures (Tropisms)
- Development: Enlargement and differentiation
- Organelles for movement: cilia and flagella
- Types of reproduction.
- Asexual: fission, budding and vegetative propagation
- Sexual: Conjugation, formation of male and female gametes (gametogenesis), fusion of gametes fertilization)
- Biological significance
- Skeletal materials, e.g. bone, cartilage and chitin.
- Types of skeleton: exoskeleton, endoskeleton and hydrostatic skeleton
- Bones of the vertebral column, girdles and long bones of the appendicular skeleton
- Mechanisms of support in animals
- Functions of skeleton in animals: Protection, support, locomotion and respiratory movement
- Main features of supporting tissues in plants
- Functions of supporting tissues in plants: strength, rigidity (resistance against the forces of the wind and water), flexibility and resilience.
- surface area/volume ratio.
- substances have to move greater distances
- Structure of the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries
- Composition and function of blood and lymph
- Materials for transport: excretory products, gases, digested food, and other nutrients
- Uptake and movement of water and mineral salts in plants
- Translocation
- Transpiration
- Movement of water to the apex of trees and herbs
- Body surface: cutaneous, gills and lungs.
- Mechanisms of gaseous exchange in fish, toads, mammals and plants
- Types of excretory systems: Kidney, stomata and lenticels
- Kidney: Structure and functions
- Functions of the liver
- Structure and function
- Site of secretion, functions and effects of over and under-secretion
- Plant hormones
- Components of the central nervous system
- Parts of the brain and their functions; cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, hypothalamus and their functions
- Structure and function of the Spinal Cord
- Somatic Nervous System
- Autonomic nervous system
- Structure and functions of the neurone
- Classification of neurones
- The reflex arc
- Reflex and voluntary actions
- Differences between reflex and voluntary actions
- Conditioned reflex and its role in behavior
Structure and function of the:
- Structure and function of male and female reproductive systems
- Differences between male and female reproductive organs
- Structure of the gametes (sperm and ovum)
- Fertilization, development of the embryo and birth
- Birth control
- Metamorphosis in insects: life histories of butterfly and cockroach
- Comparison of reproduction in fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals
- Arrangements of floral parts of a named insect-pollinated flower and a named wind-pollinated flower
- Structure and function of the male and female parts of a flower
- Types of pollination
- Features of cross-pollinated and self-pollinated flowers
- Agents of Pollination
- Kinds of placentation: axile, marginal and parietal
- Types of fruits (classification)
- Structure of fruits
- Dispersal of fruits and seeds: Agents of dispersal
Plant and Animal Nutrition
- Process of photosynthesis and its chemical equation
- Light and dark reactions
- Materials and conditions necessary for photosynthesis
- Evidence of photosynthesis
- Mineral nutrition: Macro and micro-nutrients
- Soil and atmosphere as sources of mineral elements.
- Food substances; classes and sources
- Balanced diet and its importance
- Digestive enzymes: Classes, characteristics and functions
- Autotrophic: Photosynthesis
- Heterotrophic: holozoic, parasitic, symbiotic and saprophytic
- Alimentary tract of different animals.
- Dental Formula
- Feeding in protozoa and mammals
Basic Ecological Concepts
- Ecological components: environment, biosphere, habitat, population, biotic community and ecosystem
- Biotic and abiotic
- Ecological factors in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems
- Physical factors: Climatic, topographic and gaseous
- Edaphic factors: Chemical and physical composition, moisture content and soil texture
- Producers: autotrophs
- Consumers: heterotrophs
- Decomposers
- Food/Energy relationship in aquatic and terrestrial environments
- Pyramid of energy and Pyramid of numbers
- Decomposers: (micro and macro-decomposers)
- Gaseous products
- Role of decomposers
- Type of associations: Parasitism, symbiosis, commensalism and saprophytism
- Adaptation of organisms to habitats
- Nature, names, sources and effects of air pollutants
- Effect of noise
- Type and effects of pollutants
- Structural changes in species composition, variety or diversity and increase in numbers
- General characteristics and outcomes of succession
- Primary succession
- Succession in terrestrial and aquatic habitats
- Secondary succession, climax of the succession: characteristic of a stable ecosystem
- Factors that affect population size: natality, mortality, emigration, immigration, food shortage, predation, competition and diseases
- Preservation and storage of foods
- Weevils and cotton strainers
- Control of pests
- Carriers of microorganisms
- Beneficial effects in nature, medicine and industries
- Harmful effects of microorganisms, diseases caused by microorganisms: cholera, measles, malaria and ringworm.
- Methods of controlling harmful microorganisms: high temperature, antibiotics, antiseptics, high salinity and dehydration
- Ways of controlling the vectors
- Refuse and sewage disposal
- Immunization, vaccination and inoculation (control of diseases)
Conservation of Natural Resources
- Resources to be conserved: soil, water, wildlife, forest and minerals
- Ways of ensuring conservation
Variation in Population
- size, height and weight
- colour (skin, eye, hair coat of animals)
- fingerprints
- Ability to roll tongue
- Ability to taste
- phenylthiocarbamide (PTC)
- Blood groups (ABO) classification
Biology of Heredity (Genetics)
- Genetic Terminologies
- Hereditary variation
- Mendel’s experiments
- Mendelian traits
- Mendelian laws
- Process of transmission of hereditary characters from parents to offspring
- Probability in genetics (Hybrid formation)
- Linkage, sex determination and sex-linked characters
- Agriculture
Adaptation for survival and Evolution
- Evidence of evolution
- Theories of evolution
- Biology as a science of life
- Procedure for biological work
- Importance of Biology
- Body symmetry, sectioning and orientation
- The microscope
- Biological drawings
- Movement of substances into and out of cells: Endocytosis and Exocytosis
- Nucleic acids
- DNA structure and replication, RNA transcription
- Protein synthesis
- Amoeba, Paramecium, and Euglena
- Spirogyra and Rhizopus
- Mosses and ferns
- Characteristics of some of the orders of Class Insecta
- Identification of organisms using biological keys
- Interactions in Nature Soil
- Dissection of a small mammal
- Transport: Structure of the mammalian heart
- Cellular respiration
- Skeletal tissues
- Secondary sexual characteristics
- Prenatal/Antenatal care
- Morphology of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
- Transport: Guttation
- Reproduction: Floral formula
- Integrated water resources management
- Community Health
- Recombinant DNA Technology
- Contamination of water
- Identification of polluted water
- Wastewater treatment
- Fish stock management
- Fish farming
- Food additives
- Biology and Agriculture
- Biotechnology
- Biological fuel generation
- Cell theory
- Types of responses: taxis and nastism
- Environmental factors that evoke responses; temperature, pH etc
- Diseases of the kidney: Nephritis, kidney stone and diuresis, Their effects and remedies.
- Diseases of the liver: infective hepatitis, cancer of the liver and gallstones. Their effects and remedies
- Display e.g. peacocks
- Territoriality
- Seasonal migration associated with breeding in herrings, eels and birds.
- Metamorphosis and life history of houseflies.
- Yolk in eggs of fish, toads and birds for nourishment
- Placenta in animals
- Essential factors which affect developing embryos.
- Types of germination
- Nitrogen cycle
- autotrophic, chemosynthetic, and carnivorous plants
- Alimentary tracts of different animals
- Description and function of various parts.
- Categories: Carnivorous, herbivorous and omnivorous
- Modifications and mechanisms associated with the following habits; filter feeding, fluid feeding, feeding adaptation in insects, saprophytic feeding, parasitic feeding etc.
- Lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, niche
- Population size
- Energy loss in the ecosystem
- Solar radiation: its intake and loss at the earth’s surface
- Energy loss in the biosphere
- Process of the carbon cycle
- Importance of carbon in nature
- Importance of water cycle
- Importance of water to living organisms
- Tolerance, Minimum and maximum range
- Characteristics of habitat
- distribution of plants and animals in the habitat
- adaptive features of plants and animals in the habitat
- distribution of plants and animals in habitat
- Dynamic equilibrium population and population density
- Classification of plants based on life cycle
- Bush burning
- Herbicide/pesticide
- Different farming methods
- Microorganisms in air and water
- Groups of microorganisms: bacteria, viruses, some algae, protozoa and some fungi
- Microorganisms in our bodies and food
- Food hygiene and health organization.
Application of Variations
- Crime detection
- Blood transfusion
- Determination of paternity
- Factors that bring about competition
- Intra and Inter-species competition
- Relationship between competition and succession
- obtaining food protection and defense
- securing mates for reproduction,
- regulating body temperature
- conserving water
- Adaptive Colouration Plants and animals Colouration and their functions
Download Complete PDF
View the Biology Waec Syllabus as text below or download the syllabus as a PDF below. Please use the button below to Download offline PDF files for external or internal Waec.

Home » WAEC Biology Answers 2024 [Essay & OBJ] Questions is Out
2024 WAEC Biology Answers and Questions Released.
The Waec biology answers 2024 objective and essay questions are now available. The West African Examination Council, WAEC Biology exam paper will be written on Thursday, 23rd May 2024.
The Waec Biology 2 (Essay) paper will start by 9:30 am and will last for 1hr 40 mins while the Biology 1 (Objective) exam will commence at 11:10 am and will last for 50 mins.
WAEC Biology Answers 2024.
Section B [Essay] Answer any FOUR questions. Write your answers on the answer booklet provided.
1. a. (i) List three characteristics of living organisms.
(ii) Explain briefly the characteristics listed in 1(a) (i) above. (b) In a tabular form, state four differences between plants and animals.
(c) (i) Name one organism that exhibits both plant and animal features.
(ii) State four animal features and two plant features possessed by the organism named in 1(c)(i)
1.a (i) and (ii) Characteristics of living Organisms…
Movement; Living things change the position of the whole body/parts of the body; from one place to another; in search of food/shelter/mates, etc.
Excretion; This involves the removal/getting rid of waste products of cell metabolism; metabolic wastes are poisonous if allowed to accumulate.
Respiration; This is the breakdown/burning of food substances; by aerobic/anaerobic respiration; to release energy needed for all processes of life.
Reproduction; This is the ability of living organisms to produce new individuals of their own kind; this ensures the continuity of the species of an organism.
Irritability; Response/reaction of organisms; towards changes in the environment; to ensures survival.
Nutrition; The process involved in obtaining/manufacturing food; can be autotrophic/ heterotrophic; and utilizing it for growth and maintenance/life processes.
Growth; This is the irreversible increase; in size and weight of an organism; which leads to complexity and maturation.
Competition; Ability of organisms to struggle; for all necessity of life; to survive in their en vironment.
Adaptation; A bility of organisms to adjust; to changes in environment; for survival.
2. a. What is photosynthesis? b. List: (i) four external factors; (ii) two internal factors; that affect the rate of photosynthesis. c. (i) List the major products of the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis. (ii) State the importance of each of the products listed in 2(c) (i) above. d. (i)Explain why there are no green plants at the lower depths of some lakes. (ii) State why decomposers are important to flowering plants.
3. (a) Explain the following terms: (i) disease; (ii) symptoms of diseases (b) (i) List two physical and two chemical barriers that prevent pathogens from penetrating the body of an organism. (ii) Explain how vaccination protects the body from contracting infectious diseases. (c) Distinguish between an antibody and an antigen. (d) Name the causative agents of: (i) Malaria; (ii) Cholera; (iii) AIDS.
4. (a) (i) What is excretion? (ii) List the excretory organs in humans and name one waste product excreted by each organ. (b) How does the mammalian kidney function as an excretory organ? (c) Name the excretory organs in (i) insects; (ii) earthworms.
5. (a) (i) What is conservation? (ii) State six factors responsible for the decline of the abundance and variety of wildlife. (b) Outline six ways in which the government can improve the situation in 5(a) (ii) above. (c) (i) What is Eutrophication? (ii) State two causes of eutrophication.
6. (a) Describe the carbon cycle. (b) State the functions of: (i) nitrogen fixing bacteria; (ii) nitrifying bacteria; (iii) denitrifying bacteria; in nature. ANS: (a) Carbon occurs in the air/ atmosphere/as carbon dioxide/dissolved in the oceans /seas/ water bodies, and is circulated continuously; through the activity of microorganisms /decay bacteria/ saprophytic organisms /fungi; which decompose the dead organisms; plants /animals release carbon dioxide and water; the carbon dioxide released increases the concentration of carbon in the atmosphere /ocean/ sea /water bodies; this is further increased by respiration in plants and animals; combustion of wood/ coal/ oil/ fuel; some of the excess carbon dioxides is absorbed by the sea /water bodies and also used by plants in photosynthesis; organisms in seas /oceans /water bodies release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere/ water.
(b) Functions of – (i) Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria; Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nodules of legumes; those living freely in the soil; convert atmospheric nitrogen; into ammonia /ammonium compounds. (ii) Nitrifying Bacteria; They live freely in the soil; oxidize/breakdown the ammonium compounds; to nitrites; which are then oxidized by others/ Nitrobacter/ named bacteria; to nitrates. (iii) Denitrifying Bacteria; They live freely in the soil; these break down/ oxidize ammonium compounds; into nitrogen; and oxygen; which is released into the atmosphere.
7. (a) (i) What is a gene? (ii) Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype. (b) Explain the following terms: (i) hybrid; (ii) pure breeding; (iii) nucleotide. (c) In garden pea seeds, a smooth seed coat is dominant over a rough seed coat. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant whose parent were rough-coated.
8. (a) (i) Describe epigeal germination of a seed. (ii) In a tabular form, state three differences between epigeal germination and hypogeal germination. (b) (i) What is seed dormancy? (ii) State three ways by which dormancy in seeds can be broken. (c) State six advantages of using contraceptives in human populations.
WAEC Biology Objective Questions 2024.
Section A [Objectives] Answer ALL questions. Shade your answers on the answer booklet provided.
1. Where are most nitrogen compounds excreted from humans? A. kidneys B. liver C. rectum D skin.
2. A motor neurone transmits impulses from A muscle to the spinal cord. B receptor to muscle. C receptor to the spinal cord. D spinal cord to muscle.
3. In which order does light pass through these structures in the eye? A. cornea → aqueous humour → lens → vitreous humour → retina B. cornea → vitreous humour → lens → aqueous humour → retina C. lens → aqueous humour → cornea → vitreous humour → retina D. lens → vitreous humour → cornea → aqueous humour → retina.
4. A person with Down’s syndrome is born with 47 chromosomes in each cell, instead of 46. What could cause this? A. A mutation happened during the production of the egg cell. B. More than one sperm fused with the egg at fertilisation. C. Radiation caused a change in the structure of a gene in the father’s sperm. D. The mother was exposed to harmful chemicals while she was pregnant.
5. A red-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant. All the offspring have red flowers. What is the genotype of these offspring? A. RR and Rr B. RR only C. Rr only D. rr only.
6. A plant has flowers whose anthers mature and fall off before the stigma is fully developed. What will this prevent? A. cross-pollination B. insect-pollination C. self-pollination D. wind-pollination.
7. The cell wall of a plant cell is removed using an enzyme. What would happen if this cell is then placed in distilled water? A. It would take longer for the cell to become turgid. B. Proteins in the cytoplasm would leave through the cell membrane. C. The cell would become smaller as water passes out. D. The cell would burst as water moves into it.
8. Some organisms live at the bottom of the seas where it is very dark. To synthesise glucose, they use energy from chemicals in the very hot water that comes out of volcanoes. What is a distinguishing feature of these organisms? A. Their enzymes are easily denatured by heat. B. They do not need carbon dioxide. C. They do not need to be green. D. They obtain energy only as carnivores.
9. Under which set of conditions will the transpiration rate of a well-watered plant be fastest? A. a cool, dry, windless day B. a cool, rainy, windy day C. a hot, dry, windy day D. a hot, rainy, windy day.
10. Why is glucose found in the urine of diabetics? A. increased uptake and use of glucose by the body cells B. not enough glucose in the blood is converted to glycogen C. stored fats in the body are being oxidized D. too much glucose is absorbed by the kidney cells.
11. Which bones form a joint at the shoulder? A. humerus and scapula B. humerus and ulna C. radius and ulna D. radius and scapula.
12. Which sequence describes the flow of energy in an ecosystem? A. carnivore → herbivore → plant → Sun B. plant → herbivore → carnivore → Sun C. Sun → carnivore → herbivore → plant D. Sun → plant → herbivore → carnivore.
PS: Once again, there is nothing like the Waec biology expo. Do not fall victim to scammers online trying to obtain money from you with fake promises of having access to a live question paper before the exam. What we have on this page are likely exam questions from Waec biology past questions and answers to serve as a revision guide.
Keep following, more questions and answers will be added soon.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this article, we have carefully compiled past questions for biology WASSCE 2023 objective, practical and theory all you need to do, is go through the questions, mastering the answers, and studying the patterns.
WAEC Biology Questions and Answers 2023. I will be showing you WAEC Biology objective and theory repeated questions for free. You will also understand how WAEC Biology questions are set and many more examination details.
Find below the WASSCE Biology Question For 2023 Final Year Students – PDF. How to Download the WAEC Biology Past Question? To download the WAEC WASSCE Biology past Questions PDF, click on the Download link below.
Get Free Live 2023 WAEC GCE November/December (2nd Series) BIOLOGY (BIO) Essay & OBJ & Practical Questions and Answers for Private Candidates Free of.
Biology WAEC Questions 2023. In this post, I will provide you with free access to the WAEC Biology theory and objective questions and answers. To top it all off, you’ll learn all you need to know to ace the WAEC Biology exam.
You will be able to find the answers to the WAEC GCE Biology Objective and Theory questions, as well as the WAEC Biology Essay 2023 and WAEC GCE 2023 Biology exams, as well as the study recommendations you need to pass your WAEC GCE Biology exam with ease.
BUCCAL CAVITY: (PICK ANY TWO) (i) The buccal cavity is the entry point for food and liquids into the digestive system. (ii) The buccal cavity is responsible for chewing or masticating food. (iii) The buccal cavity contains salivary glands that produce saliva.
Biology NECO Questions 2023. I will be showing you the NECO Biology objective and theory questions and answers for free in this post. You will also understand how NECO Biology questions are set and how to answer them.
Aims and Objectives. understanding of the structure and functions of living organisms as well as appreciation of nature. acquisition of adequate laboratory and field skills in order to carry out and evaluate experiments and projects in Biology.
2024 WAEC Biology Answers and Questions Released. The Waec biology answers 2024 objective and essay questions are now available. The West African Examination Council, WAEC Biology exam paper will be written on Thursday, 23rd May 2024.