What Is a Doctorate Degree?
A doctorate is usually the most advanced degree someone can get in an academic discipline, higher education experts say.

What Is a Doctorate?

Getty Images
It's unwise to apply to a doctoral program if you don't have a clear idea of how you might use a doctorate in your career.
In many academic disciplines, the most advanced degree one can earn is a doctorate. Doctorate degree-holders are typically regarded as authorities in their fields, and many note that a major reason for pursuing a doctorate is to increase professional credibility.
"If someone wants to be respected as an expert in their chosen field, and also wants to have a wider array of options in research, writing, publishing, teaching, administration, management, and/or private practice, a doctorate is most definitely worth considering," Don Martin, who has a Ph.D. in higher education administration , wrote in an email.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say.
Earning a doctorate usually requires at least four years of effort and may entail eight years, depending on the complexity of a program's graduation requirements. It also typically requires a dissertation, a lengthy academic paper based on original research that must be vetted and approved by a panel of professors and later successfully defended before them for the doctorate to be granted.
Some jobs require a doctorate, such as certain college professor positions, says Eric Endlich, founder of Top College Consultants, an admissions consulting firm that helps neurodivergent students navigate undergraduate and graduate school admissions.
Endlich earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree, commonly known as a Ph.D., from Boston University in Massachusetts. He focused on psychology and notes that a doctoral degree is generally required to be a licensed psychologist.
"Since a Ph.D. is a research-focused degree, it can be advantageous to those seeking high-level research positions in scientific fields such as astrophysics or biotechnology," he says.

How Long it Takes to Get a Doctorate Degree
Martin, founder and CEO of Grad School Road Map, an organization that helps grad school applicants navigate the admissions process, says obtaining a doctorate is often a lengthy endeavor.
"Typically it can take between four and six years to complete any doctoral program," he says. "If comprehensive examinations and a dissertation are part of the graduation requirements, it may take a year or two longer. There is no standard amount of time – some students take seven to 10 years to finish."
Endlich says doctoral degree hopefuls should be aware that completing a dissertation may take a long time, especially if unexpected hurdles arise.
"My dissertation, for example, involved recruiting college students to complete questionnaires, and it took much longer than I anticipated to recruit enough subjects for my study," he says.
The standards for a dissertation, which include the proposal and research, are rigorous and usually involve a review and approval by a faculty committee, says Hala Madanat, vice president for research and innovation at San Diego State University in California.
"As part of dissertation requirements, some programs will require publication of the research in high-impact peer-reviewed journals," Madanat wrote in an email.
Types of Doctoral Degree Programs
According to professors and administrators of doctoral programs, there are two types of doctorates.
Doctor of Philosophy
A doctor of philosophy degree is designed to prepare people for research careers at a university or in industry, and teach students how to discover new knowledge within their academic discipline. Ph.D. degrees are offered in a wide range of academic subjects, including highly technical fields like biology , physics, math and engineering; social sciences like sociology and economics; and humanities disciplines like philosophy.
A Ph.D. is the most common degree type among tenure-track college and university faculty, who are typically expected to have a doctorate. But academia is not the only path for someone who pursues a Ph.D. It's common for individuals with biology doctorates to work as researchers in the pharmaceutical industry, and many government expert positions also require a Ph.D.
Professional or clinical doctorates
These are designed to give people the practical skills necessary to be influential leaders within a specific industry or employment setting, such as business, psychology , education or nursing . Examples of professional doctoral degrees include a Doctor of Business Administration degree, typically known as a DBA; a Doctor of Education degree, or Ed.D.; and a Doctor of Nursing Practice degree, or DNP.
A law degree, known as a juris doctor or J.D., as well as a Doctor of Medicine degree, or M.D., are also considered professional doctorates.
How to Get a Doctorate
Getting a doctorate is challenging. It ordinarily requires a series of rigorous classes in a field of study and then passage of a qualification exam in order to begin work on a dissertation, which is the final project.
Dissertations are difficult to write, says David Harpool, vice president of graduate and online programs at Newberry College in South Carolina. Some research indicates that only about half of doctoral students go on to finish their degree, and a main reason is that many never finish and successfully defend their dissertation
"Many of them are in programs that permit them to earn a master’s on the way to a doctorate," Harpool, who earned a Ph.D. from Saint Louis University in Missouri and a J.D. from the University of Missouri , wrote in an email. "The transition from mastering a discipline to creating new knowledge (or at least applying new knowledge in a different way), is difficult, even for outstanding students."
Learn about how M.D.-Ph.D. programs
There is a often a "huge shift in culture" at doctoral programs compared to undergraduate or master's level programs, says Angela Warfield, who earned a Ph.D. in English from the University of Iowa.
Doctoral professors and students have more of a collaborative relationship where they function as colleagues, she says. And there's pressure on each student to produce "significant and original research."
Many full-time doctoral students work for the school as researchers or teaching assistants throughout their program, so time management is crucial to avoid burnout. However, the dissertation "is by far the biggest battle," she says. The goal is to avoid an "ABD," she says, meaning "all but dissertation."
"In my writing group, we had two motivational slogans: 'ABD is not a degree,' and 'a good dissertation is a done dissertation,'" Warfield, now the principal consultant and founder of admissions consulting firm Compass Academics, wrote in an email.
How Are Doctorate Admissions Decisions Made?
Admissions standards for doctoral programs vary depending on the type of doctorate, experts say.
The quality of a candidate's research is a distinguishing factor in admissions decisions, Madanat says. Meanwhile, leaders of clinical and professional doctorate programs say that the quality of a prospective student's work experience matters most.
Doctoral programs typically expect students to have a strong undergraduate transcript , excellent letters of recommendation and, in some cases, high scores on the Graduate Record Examination , or GRE, Endlich says.
"The size of the programs may be relatively small, and universities need to be sure that applicants will be able to handle the demands of their programs," he says.
Because professional doctorates often require students to come up with effective solutions to systemic problems, eligibility for these doctorates is often restricted to applicants with extensive first-hand work experience with these problems, according to recipients of professional doctorates.
In contrast, it's common for Ph.D. students to begin their programs immediately after receiving an undergraduate degree. The admissions criteria at Ph.D. programs emphasize undergraduate grades, standardized test scores and research projects , and these programs don't necessarily require work experience.
Admissions decisions may also depend on available funding, says Madanat, who works with doctoral students to provide funding, workshops and faculty support to help their research.
Who Is a Good Fit for a Doctoral Program?
Doctoral degree hopefuls "should be interested in making a deep impact on their field, open-minded, eager to learn, curious, adaptable and self-motivated," Madanat says. "Doctoral programs are best suited for those whose goals are to transform and change the fields they are studying and want to make a difference in the way the world is."
Someone who loves to study a subject in great depth, can work alone or in teams, is highly motivated and wants to develop research skills may be a good candidate for a doctoral program, Endlich says.
Because of the tremendous effort and time investment involved in earning a doctorate, experts say it's foolish to apply to a doctoral program if it's unclear how you might use a doctorate in your career.
"The students are being trained with depth of knowledge in the discipline to prepare them for critical thinking beyond the current state of the field," Madanat says. "Students should consider the reasons that they are pursuing a doctoral degree and whether or not it aligns with their future professional goals, their family circumstances and finances."
Rachel D. Miller, a licensed marriage and family therapist who completed a Ph.D. degree in couples and family therapy at Adler University in Illinois in 2023, says pursuing a doctorate required her to make significant personal sacrifices because she had to take on large student loans and she needed to devote a lot of time and energy to her program. Miller says balancing work, home life and health issues with the demands of a Ph.D. program was difficult.
For some students, the financial component may be hard to overlook, Warfield notes.
"Student debt is no joke, and students pursuing graduate work are likely only compounding undergraduate debt," she says. "They need to really consider the payoff potential of the time and money sacrifice."
To offset costs, some programs are fully funded, waiving tuition and fees and providing an annual stipend. Some offer health insurance and other benefits. Students can also earn money by teaching at the university or through fellowships, but those adding more to their plate should possess strong time management skills, experts say.
"Graduate school, and higher education in general, can be brutal on your physical and mental health," Miller wrote in an email.
But Miller says the time and effort invested in her doctoral program paid off by allowing her to conduct meaningful research into the best way to provide therapy to children affected by high-conflict divorce and domestic violence. She now owns a therapy practice in Chicago.
Miller urges prospective doctoral students to reflect on whether getting a doctorate is necessary for them to achieve their dream job. "Really know yourself. Know your purpose for pursuing it, because that's what's going to help carry you through."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
30 Fully Funded Ph.D. Programs

Tags: graduate schools , education , students , academics
You May Also Like
Coping with death as a future doctor.
Kathleen Franco, M.D., M.S. Nov. 5, 2024

Weighing LSAT Test Prep Options
Gabriel Kuris Nov. 4, 2024

Graduate School with Student Loan Debt
A.R. Cabral Oct. 31, 2024

Finding Scholarships for Grad School
Sarah Wood Oct. 30, 2024

Decide Whether to Retake the GMAT
Anna Fiorino Oct. 21, 2024

Law School Applicants and Volunteering
Gabriel Kuris Oct. 21, 2024

Weighing Accelerated B.A.-J.D. Programs
Gabriel Kuris Sept. 30, 2024

What Is a Good GMAT Score?
Cole Claybourn Sept. 30, 2024

Why Law School Location Matters
Gabriel Kuris Sept. 23, 2024

How to Become a Doctor
Jarek Rutz Sept. 23, 2024


The PhD student experience – What is it really like for PhDs?
Are you curious about what it’s really like to be a PhD student, navigating the world of academia and research?
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the lesser-known aspects of the PhD journey, from the profound impact of your supervisor to the competitive environment you’ll face.
Discover the truth about the importance of publishing papers and the realities of funding and job security in academia.
We’ll also give you a glimpse into the daily life of a PhD student, and explore the highs and lows of this challenging yet rewarding experience.
So, buckle up and join us as we uncover the secrets of the PhD student experience that no one else will tell you!
The little known-facts that you need to know about the PhD experience,
This is what no one else will tell you!
What does the daily life of a PhD student look like?
Embarking on a PhD journey can be a thrilling yet demanding experience, as a doctoral student is constantly immersed in:
- academic responsibilities,
- and professional development.
From the early morning, the life of a PhD student begins with checking emails, planning the day, and setting priorities.
A typical day usually involves conducting experiments or research in the laboratory, analyzing data, and reading scientific literature to stay up-to-date with their field.
PhD students often participate in regular meetings with their supervisors, who provide guidance and advice on their research projects.
These meetings are crucial for maintaining momentum and ensuring a productive working relationship.
A typical daily schedule for a PhD student might look like this:
7:00 AM – Wake up, morning routine, breakfast
7:45 AM – Check emails, plan the day, and set priorities
8:30 AM – Arrive at the laboratory, set up experiments or research tasks
9:30 AM – Attend a class or seminar (if applicable)
11:00 AM – Conduct experiments or research in the laboratory
12:30 PM – Lunch break, socialize with fellow graduate students
1:30 PM – Analyze data and read scientific literature relevant to the research project
3:00 PM – Meeting with supervisor to discuss research progress and receive guidance
4:30 PM – Continue working on experiments, data analysis, or literature review
6:00 PM – Dinner break
8:00 PM – Draft or edit thesis, work on conference presentations or publications
10:00 PM – Wind down and engage in a hobby or leisure activity for mental health and work-life balance
11:00 PM – Bedtime routine, sleep
In addition to their primary research, many PhD students assist and mentor undergraduate students, contributing to a diverse and dynamic academic community.
Balancing the demands of coursework, research projects, and administrative responsibilities can make for long working hours, which is why it’s important for doctoral students to maintain their mental health and work-life balance.
Attending conferences, participating in social events, and engaging in professional development opportunities are important aspects of the PhD experience.
Given the commitment and dedication required, full-time PhD students often rely on funded positions to support their education and living expenses.
Despite the inherent difficulties, the experience equips students with a range of new skills and expertise, setting them on a path to contribute significantly to academia and the world beyond.
How stressful is being a PhD student?
Being a PhD student can be quite stressful due to the unique challenges and demands of the program.
It varies from person to person and the supervisor will have a huge impact on how stressful a PhD will be for a student.
Here is a case study of the highs and lows of a PhD from a PhDs student’s perspective:
This PhD student experienced frustration with experiments not working or yielding results, leading to feelings of imposter syndrome and demotivation. A lack of progress was a significant source of stress during this time, as well as comparing oneself to peers who seemed to be achieving more success.
However, there were also numerous highlights throughout the PhD experience. Attending conferences and presenting research offered opportunities to gain feedback, collaborate with others, and even travel. Engaging in scientific discussions and exploring the significance of one’s work provided a sense of purpose and satisfaction.
Furthermore, working with cutting-edge equipment, such as advanced microscopes, allowed the student to appreciate the unique and privileged nature of their research.
The pressure to produce significant contributions to one’s field and the uncertainty of achieving results within a limited time frame can induce anxiety.
For instance, many students find themselves constantly juggling various responsibilities, such as conducting experiments, analysing data, attending meetings with their supervisor, and writing their thesis or papers.
Aside from academic pressure, managing work-life balance can be difficult as well. It’s not uncommon for PhD students to work long hours, often sacrificing personal time and relationships.
The lack of a structured schedule and the need for self-motivation can add to the stress and the competitive environment in academia and the constant pursuit of funding can further exacerbate stress levels.
PhD student workloads and holidays
The life of a PhD student is often characterized by heavy workloads and limited opportunities for holidays.
In a typical PhD program, students juggle numerous responsibilities, including research projects, coursework, and professional development activities, such as attending conferences and training.
This is particularly true for funded PhD students, who are expected to adhere to strict timelines set by their supervisors and the university’s academic calendar.
In the science field, the workload can be even more demanding due to the nature of research, which often involves conducting experiments that can take months or years to complete.
This commitment means that even during holidays, PhD students may feel the need to work in order to meet deadlines, leading to burnout and stress.
Later Stage PhD ( Doctorate Candidates )
When PhD students reach the later stages of their doctorate program, they become PhDs preparing to complete their research project and thesis.
This stage comes with an intense academic workload, with high demand for researcher-level skills and scientific knowledge.
A typical day for a PhD at this stage involves conducting research, analysing data, and editing their findings to complete their thesis.
In my experience it is WRITING, WRITING and more WRITING…with a touch of editing.
There are deadlines to meet, and students may face pressure, but the reward of completing a doctorate degree is worth it.
At this point, a PhD is expected to demonstrate their ability to conduct independent research and contribute to their field of study.
The latter stages of the doctorate program offer a rigorous and rewarding challenge for students who want to pursue a career in science, education, and research.
Wrapping up – PhD and Doctoral Student experience
The PhD student experience is a complex and multifaceted journey that offers a unique blend of challenges and triumphs.
As we have explored in this blog, the road to obtaining a PhD is filled with personal growth, professional development, and numerous hurdles to overcome.
But, for those who persevere, the rewards can be immense, leading to a sense of accomplishment, increased expertise, and the potential to make a significant impact in their chosen field.
In navigating this adventure, it is essential for PhD students to maintain a healthy work-life balance and develop strong support networks to help them manage stress and maintain motivation.
The journey may be demanding, but with the right mindset and guidance, the experience can be truly transformative.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

EXPLORE SMU
Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies
How to choose a phd program and compare offers.

You’ve been patiently waiting for your decision letters to roll in. Now you have the results, and you couldn’t be happier — you’ve been admitted to multiple PhD programs! But with so many great options, how do you know which one to choose?
If you need some help comparing PhD offers, read below for some tips on how to select the right PhD program when you’re admitted to multiple schools.
If acceptance status isn’t the only thing standing in your way of choosing the right program, we can help. In this short video, we walk you through each step of the program search — making the whole process simple and straightforward.
Know the Program Deadlines
Fall admission decision letters are generally issued in early spring so students have time to evaluate their offers. Many schools abide by the April 15th Resolution , which says that students aren’t obligated to respond to offers of financial support before that date. This agreement primarily applies to offers that include funding, like fellowships, scholarships, or assistantships, but some institutions may extend this deadline to all types of decisions.
What to do if you haven’t heard from all your PhD programs in time
If you’re accepted to a program without a funding offer, there’s a chance they’ll want your decision sooner. If this happens and you need to make a decision before you’ve heard back from your other schools, it may be possible to get an extension. Call the department and explain your situation — there’s no guarantee they’ll give you an extension, but it shows that you’re strongly interested in their offer.
Whatever you do, don’t use one school’s deadline to pressure another department for a decision before they’re ready. Highly competitive programs receive hundreds of applications. They may have a more involved process that takes longer to complete. Try to be patient, but if you’re truly concerned about the timing of your decision, you can contact the Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies to inquire about an approximate timeline for decisions politely.
Understanding Your Degree Funding Offers
If you’re offered funding, take time to consider the full package. Don’t just consider a program’s strengths — you should also consider the cost of living and other day-to-day expenses you might have to cover during your studies. What seems like a small stipend may be the better offer because of other benefits, while a larger stipend might not be enough if you still have to pay a high amount of tuition and fees. You’ll also want to look into what future funding opportunities might be available as you mature through the program.
Some students wonder if they should disclose the offers they’ve received from other institutions to help them possibly negotiate a better deal with their top choice school. The decision is up to you. Sharing that information might encourage a department to increase your award, but some programs may not be able to compete financially with your other offers. It doesn’t hurt to ask for more support but remember to be respectful when asking about additional funding and don’t take it personally if they cannot provide you with more assistance.
Comparing Lifestyle Compatibility
You might have a good idea of what the program and faculty are like, but what about the city you’ll be living in?
- Do you know if there’s accessible public transportation or if you’ll need a car?
- Do you enjoy the climate year round?
- Is there an airport nearby so you can travel home on the breaks?
This place could potentially be your home for the next several years. If you’re not from the area, do a little research to find out what you might need to prepare before moving there.
The best way to understand what it’s like to be a student is to ask one. If the department offers a chance to visit the campus, take advantage of it if you haven’t been before. Talk to current students to learn what the graduate student community is like — they’re your best source of advice on accessible housing, how to get around and where to hang out and shop.
If you can’t make it to campus, don’t hesitate to reach out to your department or the Graduate Admissions Office with your questions, or see if your institution has a student life website with links to local resources.
Picking a PhD Program
For those programs whose offers you are declining, pay them a courtesy by submitting your decision in the format that they’ve requested, whether it’s logging into an application portal or returning a contract by email. This gives the most accurate information to the department and lets them know they can open up your spot to another deserving student.
When you’re ready to accept the offer that best meets your needs, follow the department’s instructions and reply by the deadline to ensure your spot is secure. Then celebrate — because you’re officially a PhD student!
Still in the application process? Check out "How to Get a PhD: A Guide to Choosing and Applying to PhD Programs".

Request more
Information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information
Published On
More articles, recommended articles for you, what does fully funded actually mean.
You may have heard that many PhD programs are fully funded — universities pay doctoral students to...
Is Getting a PhD Worth It?
Perhaps you’re finishing up a bachelor’s or master’s degree, or maybe you’ve hit a wall in your...
How to Compare History PhD Programs
So, you've set your sights on pursuing a PhD in History. As a prospective History PhD student, you...
Browse articles by topic
Subscribe to.
Which program are you applying to?

Accepted Admissions Blog
Everything you need to know to get Accepted

April 10, 2024
Applying to PhD Programs: When, Where, How, and Why?

So, you are thinking you might want to pursue a PhD. That’s great! However, it can sometimes be difficult to decide whether to really go for it. Maybe you are weighing the time commitment required or the prospect of leaving a job you love. Maybe you are wondering whether you are prepared for such an undertaking or whether you’d even have a shot at getting in. When considering such an important move, it’s good to adopt a methodical approach to the decision-making process.
This article is designed to help you think through some key factors in making important decisions about graduate school. You might ask yourself the following key questions:
- When should I apply?
- Where should I apply?
- How do I get in?
- Why do I want to go?
Let’s consider these questions one at a time.

Question 1: “When should I apply?”
The right time to apply to graduate school is when your personal, academic, and professional experiences have aligned such that you know for certain you want to further your knowledge and skills in a specific field. Read on for some signs that these experiences are, in fact, aligned.
In your personal life
Think about when you were first introduced to your field of study. What made you want to keep learning about it? Is that drive to know more about your field of study still there? If the answer is yes, then you might be personally ready for graduate study. Memorable personal experiences – and the lessons you have learned from them – can also make you personally ready for graduate study.
For example, perhaps you were diagnosed with a condition and have spent the past decade managing it. The psychological strain of this experience has made you highly empathic toward patients suffering from chronic conditions. You’re now committed to studying the effectiveness of various approaches to promoting mental health among this population.
Or maybe one of your fondest childhood memories is birdwatching with your dad, who taught you all about various species and their migration patterns. This experience led you to pursue ornithology, and you still get excited about learning about birds.
Something doesn’t have to be profound to others for it to be deeply meaningful to you.
In your academic life
You’ve demonstrated – via high grades or assignments on which you went above and beyond the basic requirements – that you have a strong grasp of the technical aspects of your intended field. You’ve done more than memorize core concepts and theories; you’ve contemplated how they relate to the broader aims of the field. You’ve taken more advanced classwork, completed an independent project, or did professional work that involved innovation and research. And you now want to apply those theories and concepts in graduate school and your career.
Let’s say you majored in civil engineering. You’ve excelled in all your engineering courses, as well as in chemistry, math, and physics. In the process, you’ve learned how to apply the core principles of each field to design resilient infrastructure that does not fail in extraordinary events and is socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable.
In your professional life
Whether you’ve worked/volunteered in a relevant setting for six months or six years, you’ve learned about and contributed to the rigorous research process. Ideally, you’ve taken on multiple roles, each one more demanding than the previous one. But at every stage, you’ve taken your responsibilities seriously, because you understand that each task, no matter how seemingly trivial, must be performed diligently, lest you risk compromising the data and ultimately the findings of the entire study.
As an undergraduate research assistant, you might have begun with basic responsibilities, such as data entry and cleaning in Excel. After demonstrating that you are reliable and diligent, you were able to help conduct studies and maybe even run some of your own analyses using the data.
Then, by the time you entered your current role (the one you’re in when you apply to PhD programs), you are able to not only evaluate all the variables being assessed but also identify other variables that aren’t being measured and articulate why they should be included in future research. At this point, you’re able to generate your own research questions, formulate testable hypotheses, and even design a hypothetical study in which the findings are interesting regardless of whether your hypotheses are supported.
When you’ve identified these signs in your personal, academic, and professional experiences, you’re ready to apply.
Question 2: “Where should I apply?”
To identify the right program(s) to apply to, it is crucial to look beyond the school’s ranking or reputation . The “2024-2025 Best National University Rankings” by U.S. News & World Report should not be your primary source for one simple reason: PhD programs are very idiosyncratic. Even if you have chosen a field of study (ideally, the field in which you received your undergraduate and/or master’s degree), there are likely many research areas within that field and even more specific topics within each area. The right research area for you will depend on your previous research experience, as well as on the specific topic(s) you want to investigate.
For example, within the field of psychology , there are many areas, including clinical psychology, cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, health psychology, evolutionary psychology, personality psychology, and social psychology. Then, within, say, social psychology, there’s a vast array of specific topics, such as attitudes, aggression, decision-making, emotion, prejudice, and prosocial behavior, to name a few. As you can imagine, these topics are not mutually exclusive. In fact, combining topics can generate unique findings. Therefore, when thinking about where to apply, you might prioritize programs where the faculty are studying combinations of topics you find particularly interesting.
Another factor to consider is that programs differ as a function of the research methods they employ. Thus, when thinking about where to apply, in addition to identifying programs where the faculty are researching the specific topics you are most interested in, it’s necessary to consider whether those faculty members are using methods that you would like to apply in your future career. Do you want to master advanced statistical techniques? Do you want to work with state-of-the-art technologies? Do you want to interact with people? Do you want to observe phenomena in the “real world” or in experimental settings? It’s not only about what you’re researching; it’s also about how you’re researching it.
Once you’ve identified programs based on those considerations, it’s time to identify prospective faculty advisors within your chosen programs . After all, you’re not just applying to PhD programs; you’re applying to work with specific faculty members, and they are the ones who will be reviewing your application and deciding whether to accept you. Based on the faculty members’ professional biographies (which you can usually find on the program’s website), you’ll probably be able to identify the professors whose interests are most like your own.
But it is not enough to be confident that you want to work with a given faculty member. Next, you’ll want to familiarize yourself with that professor’s recent work by reading research papers they’ve published in the past couple years. As you’re reading, ask yourself whether this faculty member writes and thinks clearly and presents arguments and evidence in a compelling manner. You will be mentored by this person for five years (or more!), so it’s crucial that you find someone you admire and are motivated to learn from.
In sum, the steps in deciding where to apply for PhD study are as follows:
- Choose your field of study.
- Identify your preferred area(s) within that field.
- Discover the specific topics you find most fascinating.
- Consider what methods you want to employ.
- Evaluate the merits of prospective faculty advisors.
Question 3: “How do I get in?”
Once you’ve determined that you’re ready to apply, and you know where you want to apply , the focus shifts to whether you’ll be accepted. Getting into a PhD program is largely a matter of fit . The faculty members who evaluate your application want to know what insights you can offer to their current and future research studies, how your interpersonal style will contribute to their lab or research hub dynamics, and whether you are committed to extending their research in a meaningful way after you obtain your doctorate. You can convey all this crucial information in your statement of purpose.
It’s difficult to overstate the importance of your statement of purpose. You might have an exceptional CV, but if your statement of purpose is lackluster and fails to convey to your prospective faculty advisor that you are the right fit, then you are unlikely to be accepted. Conversely, you might have a modest CV, or even a weakness, such as a low GPA, but nevertheless be accepted if you convey in your statement that (1) you have taken (and will continue to take) concrete steps to become more prepared for PhD training, and (2) you possess unique skills and knowledge that are highly relevant to your prospective advisor’s research area but that might not be reflected in traditional metrics of achievement (e.g., your CV, GPA).
To write a compelling statement of purpose , you need to articulate everything relevant to Question 1: “When should I apply?” You have already reflected on how your personal, academic, and professional experiences have aligned such that you know that you are ready to apply. But it is not enough for you to know that you are ready. You need to convince your prospective advisor that you are.
This is where Accepted can help . The most valuable service we offer is essay consulting. We can teach you how to craft a narrative about your journey that is coherent, authentic, and distinctive. During each consultation, we will challenge you to think more deeply and clearly than you ever have about where you’ve been and where you’re going. You will learn how to identify and effectively convey the reasons your prospective advisor should accept you.
Question 4: “Why do I want to go?”
A PhD is an academic degree that prepares you to conduct original research, perform advanced statistical analyses, interpret empirical results, and evaluate competing theories. You will be trained to become an academic – that is, a university professor who directs a research lab and teaches students the nuances of a specific field. The skills you acquire during your doctoral training can be applied to industry, governmental, and nonprofit settings; however, doing so should not be your primary goal. Your prospective advisor will want to know that you are committed to the work of an academic. It is great if your research has important implications for those other sectors, so long as you are still committed first and foremost to the production and dissemination of knowledge in your field. The thought of conducting original research in a university setting should make you excited to get started.
Thus, the best reasons to pursue a PhD are intrinsic. After all, a PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy . You get a PhD because you are passionately drawn to the philosophy of your chosen field. You can’t help but think about it in your everyday life, because you see it everywhere. It is a lens through which life makes sense. Discovering its guiding principles, subject matter, and potential applications allows you to identify patterns in the world around you – and sometimes within yourself as well. So why should you pursue a PhD? Because you can’t not .

Vanessa Febo has ten years of experience teaching academic and professional writing at UCLA, with a special certification in teaching writing techniques. She has drawn on this expertise to guide clients to placements at top institutions, including Harvard, Stanford, and USC. Before joining Accepted, Vanessa coached UCLA students through the application process for graduate programs, major grants, fellowships, and scholarships, including the Fulbright, Stanford Knight-Hennessey, and the Ford Foundation Fellowship. Additionally, Vanessa has extensive experience successfully guiding clients through applications for a diverse range of programs, including those in business, humanities, social sciences, and STEM fields. Want Vanessa to help you get accepted? Click here to get in touch!
Related Resources
- Get Accepted to PhD Programs in the Humanities , podcast Episode 568
- How to Apply Successfully to STEM PhD Programs , podcast Episode 566
- Graduate School in Psychology: PsyD or Psy Phd, Which Is Right for You?
About Us Press Room Contact Us Podcast Accepted Blog Privacy Policy Website Terms of Use Disclaimer Client Terms of Service
Accepted 1171 S. Robertson Blvd. #140 Los Angeles CA 90035 +1 (310) 815-9553 © 2022 Accepted


- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How to Choose a PhD Program
Successfully completing a doctoral program requires commitment and perseverance. the most important step in this process is to consider whether academic life is right for you and what kind of doctoral program — from discipline to environment — will be the best fit for your goals and preferences., we asked our current students and faculty, “what is key to making this decision” following are some questions they suggested you ask yourself, and answer, in order to select the appropriate program..
First, a basic description of a doctoral program:
As a doctoral student, you will spend the first two years of your program exploring areas of interest through coursework. In the two to three years that follow, you will select and pursue your own research topic, one which will make an original contribution to the existing body of knowledge in your field. Your original research culminates in an extensive written document known as the doctoral dissertation.
General Questions
If you are considering your career options, answering these questions will help you clarify your goals and ambitions — and determine if a doctoral program is the right decision for you.
- Am I the type of person who is suited for a career in academia? Am I independently motivated to answer questions that I find interesting?
- Do I want to spend the rest of my career doing research, as well as reading and talking about it?
- Do I have a strong enough academic background in order to apply and be accepted by the program?
- Is now the time for me to pursue a PhD?
- What are my goals after completing the PhD?
Program Questions
If you know you want to pursue a doctoral degree, answers to these questions will help you select the right program for you.
- How many faculty are working with students?
- How many faculty members are doing research in areas related to my own interests?
- What opportunities are there to work with a variety of faculty and to be exposed to different approaches in research (modeling, work with data, experiment design)?
- Am I technically prepared to learn to do research in this field?
- Most PhD students change their vision of research and many change their intended concentration area after joining the program and being exposed to a variety of research styles. Does my program of choice offer flexibility needed to do so?
- Is there financial support for students to attend academic conferences to present their own research?
- What opportunities are there for students to participate in colloquia, both as an attendee and as a presenter?
- What is the department’s placement record? What types of jobs do graduates take and where?
- Finally, how well do graduates of the program perform in the long term (contributing to the field through publication, practice of management and earning tenure)?
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
From undergrad to phd, the diverse skill set you need to become a professor, what brought this cdc researcher to wharton's phd program.
EXPLORE SMU
Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies
How to get a ph.d.:, a guide to choosing and applying to ph.d. programs.
DOWNLOAD THE GUIDE
Here at SMU, we know that the decision to pursue a Ph.D. in any field can be difficult — it’s a significant investment of your time and resources, with several unknowns along the way. When students are just starting their search, here are some common questions we have received:
- How do you prepare a strong application?
- How do you select a program that fits your area of interest?
- Will you get in?
- What are the years in a Ph.D. program actually like?
In this resource, we offer you the insider information you need to choose a program, apply successfully, and thrive during your years of graduate study. You’ll get answers to common questions, tips for putting together your application, and testimonies from students who made it through the application process and are now pursuing a Ph.D.
What’s in the Guide
Common Reasons for Getting a Ph.D.
Jump to Section
How to Pick a Ph.D. Program
You’ve Decided to Go for It! Take the First Steps to Getting A Ph.D.
Ph.D. FAQs: How to Choose a Doctoral Program That’s Right for You
Applying to Ph.D. Programs: What Do Ph.D. Programs Look For?
How to Apply for a Ph.D. Program: The Ph.D. Application Process
Understanding How to Finance Your Ph.D. Program
Advice from Current Ph.D. Students: How to Choose a Ph.D. Program
How Many Years For a Doctorate? Our Advice for Thriving Every Step of the Way
Ph.D. Programs at SMU: A Look at Your Options Across the Disciplines
Want to Learn More?
COMMON REASONS for
Getting a ph.d..
WHAT PH.D. STUDENTS LIKED MOST
PH.D. AS AN INTERNATIONAL STUDENT GUIDE
HOW TO PICK A PH.D. PROGRAM
Do you find yourself wondering, what would motivate someone to earn a Ph.D.? Only about two percent of adults over 25 hold a doctoral degree, according to a 2022 study by the U.S. Census Bureau . But what drives this group of elite learners?
A 2019 survey of more than 6,000 Ph.D. students asked a wide array of questions on topics ranging from life in a Ph.D. program to students’ satisfaction with their program.
Here's what Ph.D students liked the most about their doctoral program:
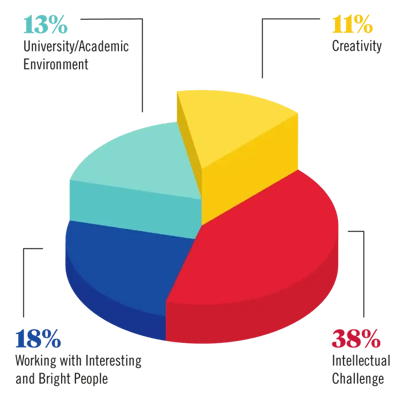
Additionally, although earning a Ph.D. is a large commitment of time and energy, 75% of respondents reported being happy with their decision to pursue a Ph.D. saying they were somewhat satisfied or very satisfied with their decision.
75% of respondents reported being happy with their decision to pursue a Ph.D.
When you start exploring earning a Ph.D., you may encounter some setbacks and deterrence. However, if you have a genuine love for the subject and wish to become a thought leader in your area of expertise, don’t let this discourage you.
Perhaps you’re thinking that a Ph.D. in a STEM field makes sense, but don’t see how to justify your degree in Anthropology or History? In the STEM academic track, the return on investment (ROI) of a graduate degree may seem more clear than in the humanities.
Never fear. Love of the subject, not monetary gain, is what truly motivates students to journey through graduate school. A Ph.D. in any field is a feat in research, critical thought, and dedication, and these skills are extremely valuable even in disciplines with less obvious market value.
-min.png?width=300&height=400&name=How%20to%20Get%20a%20PhD%20Guide%20Cover%20(1)-min.png)
Download the Full Guide
How to pick, a ph.d. program.
WATCH THE VIDEO
So, you know what you want to study, but now you’re faced with the task of finding the right school. It can be easy to become overwhelmed by all of the options. The process of selecting which Ph.D. program is the right fit doesn’t have to be difficult or stressful, you just need an organized plan to help you sort through the factors you need to be looking for.
Not sure what you should be looking for? We can help you with that! In this short video, we walk you through each step of selecting the right Ph.D. program — making it simple and straightforward.
you've decided to go for it
Take the first steps to getting a ph.d..
STEM VS. HUMANITIES
MOODY SCHOOL GUIDE
Ready to take the leap and begin your Ph.D. career? We’re here to help you take the first steps. To determine what program could be right for you, it’s best to begin your research early, and to consider the following things when analyzing and comparing Ph.D. programs:

Before we dive into application requirements, most graduate programs require the GRE for students and the TOEFL or IELTS for international students. Getting a good score on these tests does not ensure your entrance into a program, but it does help. If you struggle with standardized tests, consider signing up for a tutoring service in order to feel better equipped and more prepared.
PH.D. FAQS:
How to choose a doctoral program, that's right for you .
STEM VS HUMANITIES
MOODY SCHOOL GUIDE
Not always, it depends on your program. Some programs will allow you to move straight from an undergraduate degree into a doctoral program that includes graduate coursework. Other programs will require a master’s degree before beginning a Ph.D.
It generally takes five to seven years to complete a Ph.D. program, but make sure to contact your program to learn about the specifics. For more information and an overview of the Ph.D. timeline, check out our article: The Ph.D. Timeline – What Can You Expect From Your Program?
While it is tempting to apply to several Ph.D. programs to enhance your chances of being accepted, this is one example where “quality over quantity” holds particularly true. Ph.D. programs generally accept students based on how closely their research interests align with the work of their professors.
Rather than applying to a dozen programs, pick 4-6 that are truly great matches for your interests and spend the time necessary to make your application stand out as one of the best.
We wrote a resource that covers this exact question!
Read — Comparing Admission Offers and Selecting Your School — to learn how to pick the Ph.D. program that is right for you!
STEM vs. Humanities: Key Differences

- Research proposal often determined in conjunction with departmental research
- Typically higher stipends
- Conducting experiments and then analyzing the resulting data

- Research proposal is self-directed
- Often lower stipends, but more likely to obtain a job in academia
- Analysis of texts and concepts to expound upon in your dissertation

Learn More About the Moody School
DOWNLOAD NOW
applying to Ph.D. programs:
What do ph.d. programs look for.
PERSONAL STATEMENTS
TRANSCRIPTS
LETTERS OF RECOMMENDATION
When starting the application process, you should review the Ph.D program application requirements and contact the school to ask any of your remaining questions. Starting with this step will help you stay focused as you gather the assets you need and will keep you from wasting time on things that are not required.
Applicant questions usually fall into one of two categories: questions about the substance of the program (e.g. Is there an opportunity to do research as a first-year?), and questions about the logistics of the application (e.g. What is the school code for sending you my GRE scores?).
Don’t hesitate to contact faculty directly to ask questions pertaining to the substance of the program. They love talking with prospective students about what they do, and they will be able to provide much more detail than the admissions office. On the other hand, admissions or graduate office staff should be able to give you prompt guidance on logistical questions pertaining to your application (faculty are not as familiar with these topics).

Personal Statements
A student with a clear research direction can write a very compelling personal statement. You don’t need to have your exact dissertation topic worked out yet, but it’s important to have a good sense of the following:
- Your general area of interest;
- The faculty in the department you’d want to work with;
- The resources at the university that would help with your work.
Hitting these points in your personal statements tells the faculty not only that you are prepared for the work, but that this particular university is a good home for you. An applicant can be impressive, but if the faculty don’t see you as a good fit for the school’s program, they won’t be inclined to admit you.
Transcripts
When you order copies of your undergraduate and graduate school transcripts, as well as any test scores you may need, leave plenty of time to meet the deadline so that these documents do not hold up your application. Frequently, schools will accept unofficial transcripts for the initial application, but a final, official transcript will be necessary if you are accepted and decide to attend.

Letters of Recommendation
The hallmark of a Ph.D. program is that it is research-based. Success at the undergraduate level is an important factor, but a better indication of success is research experience. The strongest letter of recommendation is from a professor who knows you not just as a student in their classroom, but as a researcher. Choose someone who can speak to your work in the lab or the archive, making a contribution to the discipline rather than simply absorbing content from a lecture.
Discover some tips from our admissions professionals on securing the best letters of recommendation
how to apply for a Ph.D.
Application process.
DELIVERABLE LINKS
GUIDE TO GRADUATE ADMISSIONS AT SMU
In addition to the items in the section above, make sure to check off this list (or edit it to include your specific requirements).
Be sure to check your department’s website for additional requirements, such as minimum test score requirements and writing sample prompts. Not all departments will ask for additional items, but for those that do, make sure you’re prepared in advance.
Application Form and Fee
Get Application Advice
GRE and TOEFL/IELTS Test Scores for non-native English speakers
How to Ace the TOEFL/IELTS
Statement and Purpose
Statement of Purpose FAQs
Letters of Recommendation (typically 3 required)
Get Our Tips for Your Best Recommendations
Undergraduate and Graduate Transcripts
Should You Earn a Master's or Ph.D.?
Curriculum Vitae (CV) / Resume
How to Craft a Clear CV/Resume
After all these elements of your application are submitted and reviewed by the department, they may conduct a graduate school interview with the candidates who are moving forward.
Applications for Ph.D. programs are often reviewed on a rolling basis, but some do have hard deadlines. It’s hard to say exactly when you will hear back, as it depends on the individual department, but generally, you should not expect a response before February of your expected enrollment year.
As your offers of admission begin to roll in, you’ll need to discern how to compare Ph.D. programs and ultimately choose the best one for you.
Pro-tip: If you are applying to a Ph.D. program as an international student, we’ve developed a full resource for you!

Guide to Graduate Admissions at SMU
ACCESS THE GUIDE
Understanding
Finance your ph.d. program.
FIND STEM GRANTS AND FELLOWSHIPS
HOW A PH.D. WILL BENEFIT YOUR FINANCES
Here’s some sage advice: when it comes to funding your Ph.D. program , it should be funded by the university as a tuition scholarship and a stipend. If you are not offered any funding, it may be an indication that you are not a good fit for that program.
Your stipend offer depends on the university, but the general range for a Ph.D. stipend is $15,000-$35,000.
SMU currently has 55 Moody School funded Ph.D. students and offers a wide range of fellowships, stipends, grants , and health insurance to financially support students in our doctoral programs. SMU offers the following fellowships:

In some cases, the stipend is contingent upon the student holding a research or teaching assistantship.
Research assistantships: Typically research assistantships are funded through faculty members’ research grants from outside organizations. Faculty members determine who and how many research assistants they need in order to get their critical research done.
Teaching assistantships: Typically teaching assistantships are arranged through the university. This arrangement helps graduate students get experience in the classroom and helps institutions balance out the cost of graduate student stipends.
Fellowships beyond your university are also good opportunities for additional financial support during your years of graduate work.
Explore how to find grants and fellowships for your STEM research or check out fellowship listings like this one dedicated for women across disciplines.
How will a ph.d. benefit your finances.
Although the price tag of a Ph.D. can look steep, the reality is that the vast majority of doctoral students receive full, or significant, funding for their program. This means that you’ll spend 5-7 years earning your degree, but will likely graduate without additional tuition debt, ready to step into your career field as a trained expert.
But what do the numbers say? Here’s the real story on the financial impact of pursuing a Ph.D. according to research conducted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics . The truth is, people who have earned a doctoral degree are looking at a significant increase in overall lifetime earnings.

[Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics ]
Advice from current
Ph.d. students.
AMILA NANAYAKKARA
APRIL SIMPSON
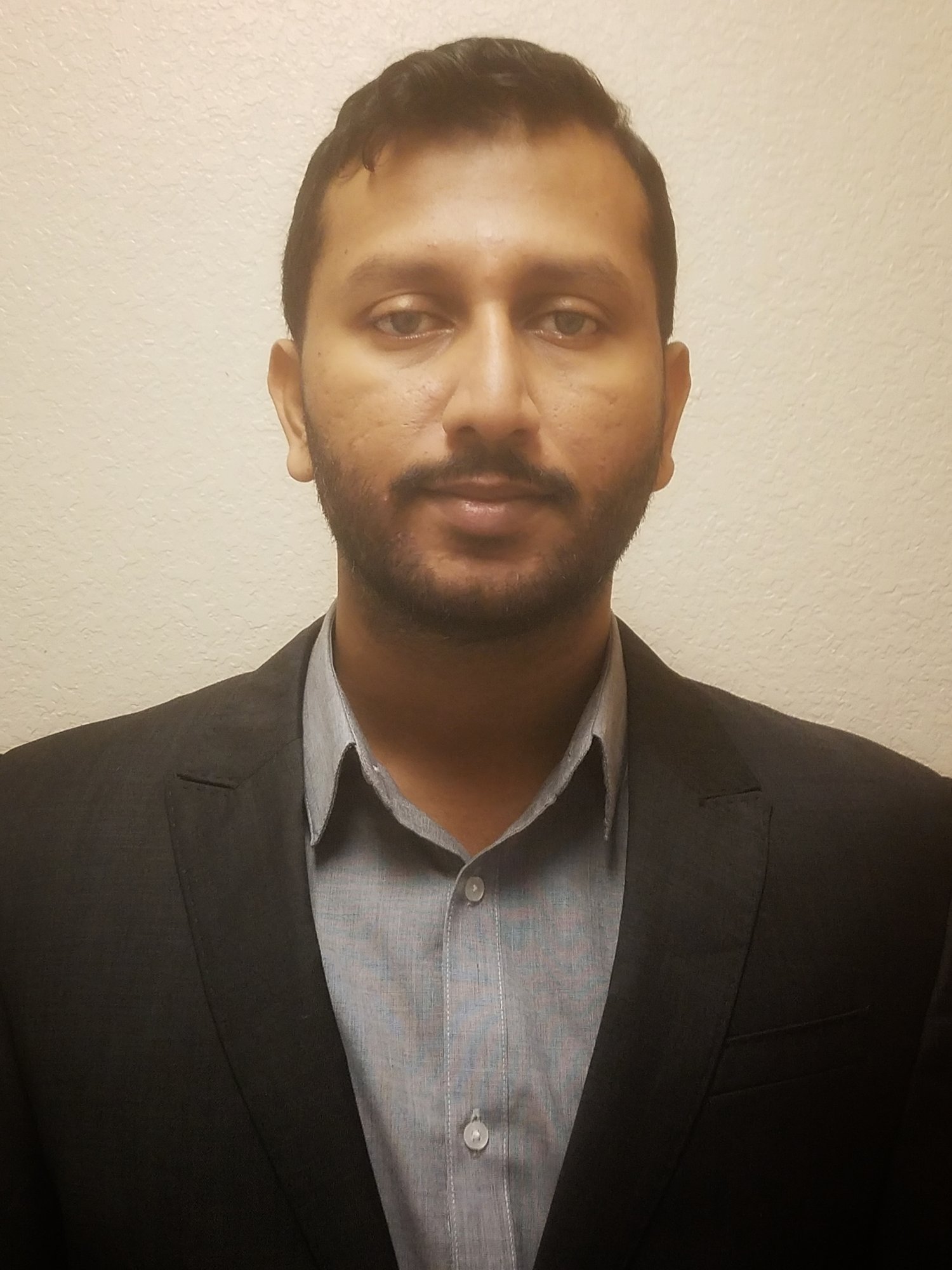

Amila Nanayakkara
I am Amila Nanayakkara from Sri Lanka. I did my undergrad in University of Colombo. After that I [worked] as a research assistant for 2 years at the Industrial Technology Institute in Sri Lanka.
Now I am in my 5 th year pf my Ph.D. program, studying biology. To be specific, we study multi-drug resistant cancers and how to reverse the drug resistance.
Yes, [I did encounter some doubts during my decision process] especially about the future, or what should I do after the Ph.D. It takes 5-6 years [to complete] which is like the best part of your life. I had my doubts [about] investing this much time on the Ph.D.
But I [realized] that there are other options rather than being an academic after [getting] a Ph.D. Also, I was pretty sure that I wanted to do research, wanted to do new things always. I hated routine work. I had a short time job in a bank and I realized that I do not like office work at all [so the Ph.D. became very appealing].
I liked the research [happening at] SMU. I liked to work in cancer biology specifically, and I knew Dr. Vogel and Dr. Wise’s lab [would be] a place I would like to work. Also I think the PI (Principal Investigator, the lead researcher for a grant project) plays a huge part in your lab [experience]. So I wanted to join a lab where you are given freedom and not micromanaged. When I talked to Pia Vogel and Wise I realized this is the best place for me. The whole Biology department seemed like a very friendly place too. Also, I really liked the environment of SMU as a whole as well.
April Simpson
I am originally from Chattanooga, Tenn. In 2009, I earned a Bachelor of Arts in Religious Studies (with minors in Math and World Languages) at Gardner-Webb University. I also completed two master’s degrees at Gardner-Webb between 2010 and 2014: Master of Arts in Religious Studies (concentration in Biblical Studies) and Master of Divinity. From the start of my master’s program, I knew I planned to pursue a Ph.D.
I am now in my third year at SMU. I am a student in the Graduate Program in Religious Studies (Dedman College), and my field of study is New Testament. I have completed all my coursework as well as my comprehensive field exams, and I am in the process of writing my dissertation proposal this fall; I expect to be admitted into candidacy sometime in the next few months.
There were three major factors that could have inhibited my pursuit of the Ph.D.: highly selective admissions processes, cost, and rigor of the Ph.D..
I knew long before I applied that elite programs are highly selective due to funding limitations and high standards. At times I wondered whether I would be able to stand out enough to be selected. My response was to do my part—to work as hard as I could reasonably work—to make myself a desirable candidate for admission. I maintained an excellent GPA, prepared intensely for the GRE, gained teaching experience, involved myself in the Society of Biblical Literature (an important professional organization in my field), and sought out references who could speak to my academic and professional abilities and work ethic. I decided that, while the application and selection process was not totally within my control (you cannot make them pick you), I would foster my own drive to work hard and excel in an attempt to accomplish what was in my own control.
Another factor was cost. I knew that, without tuition funding and stipendiary support, I would not be able to afford pursuit of the Ph.D., nor is it advised in my field to take out loans at this level. Fortunately, most elite programs are fully funded, including a stipend that helps cover living expenses (and unfortunately, this means those programs have even more competitive admission, as I already noted). I decided to apply only to fully funded, widely respected programs so that, if admitted, I would be able to afford a Ph.D. program. And, again, I worked hard to make myself the best applicant I could be.
Finally, I knew that the Ph.D. is a rigorous degree. At times I worried that I would not be cut out for this level of work. Interestingly, these worries tend to manifest themselves not only among aspiring students but also among current Ph.D. students, something we refer to as “imposter syndrome.” At any rate, I listened to and trusted faculty mentors who told me I was, indeed, able to complete a Ph.D.; I listened to my own inner voice that told me to keep at it and to give it my best. And, again, I worked hard.
I did a great deal of selection before ever applying to Ph.D. programs, so that I only applied to programs I was fairly confident I would be willing to attend. Despite some overlap in the application process, each program application is different in some way, and it takes time and resources to apply to schools. As I prepared to apply, I looked for well-respected/highly rated schools that had the following qualities (this list is not ranked): (1) full funding, (2) faculty and program structure that would support my research/career interests and goals, (3) generally, an environment of collaboration rather than of antagonistic competition, (4) high academic standards, (5) a professional atmosphere, (6) a clear commitment to the success of students enrolled in the program, and (7) an interest in professional development not only in terms of research and general professionalism but also—and importantly—in terms of teaching.
When I visited SMU, I was very impressed with the faculty (both their achievements and their willingness to work with me and support my work), the Graduate Program in Religious Studies students (including other newly admitted students), the facilities (including SMU’s beautiful campus and especially Bridwell Library), and the funding. I could envision myself as part of the community here. It became even clearer to me that enrolling in the Graduate Program in Religious Studies (Ph.D.) at SMU was such a great opportunity, one that I could not pass up. Although this meant that my husband and I would be moving far away from family and friends and that we would be adjusting to life in a new city, we embraced this opportunity.

Download our Guide to Getting Your Ph.D. as an International Student
How many years for a doctorate, our advice for thriving every step of the way.
PH.D. TIMELINE
WRITING YOUR DISSERTATION
You’ve applied, been accepted, and decided to attend your Ph.D. program. In the flurry of excitement around your decision, the reality of what the next 5-7 years will look like may have eluded you. What does life as a Ph.D. student really look like? And how long does it take to get a Ph.D.?
Your time in your Ph.D. program is both exciting and challenging and, depending on your school and program, the next 5-7 years will look a little different for everyone. Here’s what you can generally expect in your Ph.D. program:
Ph.D. timeline
In the first year, your department should offer you guidance about what classes to take and requirements to fulfill. It’s tempting to jump right into research, but make sure you pace yourself and take advantage of networking opportunities, such as program and college events, graduate associations, and additional lectures. Each of these will expose you to the field and help you to make meaningful connections that will serve you throughout your doctoral program.
Read more: 4 Tactics to Help You Build a Professional Network While Getting Your Ph.D.
Much the same as year one, your focus will be attending seminars and honing in your dissertation topic. Continue to network and get to know your professors. Usually, sometime in the second or third year you will take your qualifying exams and be admitted to candidacy, formally moving into the dissertation research and writing phase.
In the beginning of Year 2, (if you have not already done so) you’ll want to begin reaching out to faculty mentors and building relationships with them. As you progress through your Ph.D. your faculty mentor, or dissertation advisor, will become one of your most important connections.
Read more: 3 Tips for Graduate Students to Consider When Choosing a Faculty Mentor
This year may be used to complete any remaining seminars, language requirements, qualifying exams, or to focus on perfecting your experiments and solidifying research. If you have not already been admitted to candidacy you will do so here.
At this point in your doctoral program, teaching and writing is your primary aim. You’ll work closely with your dissertation advisor, and establish a good rhythm of going back and forth regarding your progress. This stage of your Ph.D. will take incredible dedication and patience.
Read more: 5 Common Myths About Ph.D. Programs — Setting the Record Straight
In your final year, you’ve hopefully completed drafting your dissertation and will prepare for your defense. If all goes well, you’ll graduate with flying colors!
Typically, course requirements for your Ph.D. will be completed after the first two years, but this can vary depending on the discipline and program. Keep in mind that some programs have average durations far longer than five years. For example, anthropologists usually do fieldwork for their Ph.D. degrees, which extends the program by several years compared to STEM programs.
Read more: The Ph.D. Timeline – What Can You Expect From Your Program?
The Final Step: Writing Your Dissertation
The most general statement that can be made about writing your dissertation would describe the process as: do research, propose a prospectus, and then write about it! Writing is a skill perfected by regular practice, so be sure you are consciously honing this skill during your years of coursework and seeking out feedback about how you could improve.

Read more: Get a sense of what it takes to complete your Ph.D. Here are 5 tips for writing your Ph.D. dissertation
However, the particulars vary a lot by discipline. In some cases, you will research and write as you go (more often in the humanities); whereas in the sciences, you’ll generally perform research over many years and compile your findings in a dissertation over one to two semesters. In some cases, you are publishing articles throughout your 5 years, and those articles can provide the basis or rough outline for a dissertation.
As you think about your dissertation, it might seem overwhelming to imagine finding something new or interesting enough to write about it and be deemed an expert. Often your first years in a Ph.D. program, taking coursework and working more directly under faculty, will help you find your research niche that will then become your dissertation. A good Ph.D. program will help you grow and develop as you prepare to work independently as a scholar.
In almost all cases, dissertation research and writing are self-driven. After you are admitted to candidacy, it is up to YOU to decide what you need to do, when you are going to do it, and what your final product will be. This is where a good advisor, who can provide guidance and help you implement a system to stay on track, is crucial. In addition to having good research, one of the biggest keys to success in writing your dissertation is to be organized.
Ph.D. programs at SMU:
A look at your options, across the disciplines .
FULL LIST OF GRAD PROGRAMS
SMU is a distinguished center for global research with a liberal arts tradition, and our graduate programs are known for their rigor and commitment to research. Here at the Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies, we are proud to offer 32 Ph.D. programs that are the backbone of the high caliber research taking place at the University.
Check out a full list of our graduate programs.
Learn more about some of the ph.d. programs offered at smu.

Electrical and Computer Engineering
Download the Resource

Statistical Science
![775781_[Shannon] [SMU] CEE Guide_MockUp_082120-1 775781_[Shannon] [SMU] CEE Guide_MockUp_082120-1](https://grad.smu.edu/hs-fs/hubfs/775781_%5BShannon%5D%20%5BSMU%5D%20CEE%20Guide_MockUp_082120-1.png?width=242&height=242&name=775781_%5BShannon%5D%20%5BSMU%5D%20CEE%20Guide_MockUp_082120-1.png)
Civil and Environmental Engineering

Computational and Theoretical Chemistry

Earth Sciences

International Applicants

Access Our Full Resource Library
Want to learn more?
REQUEST MORE INFO
USEFUL LINKS
If your interest is piqued and you’d like to learn more about choosing, applying for, and thriving in a Ph.D. program, you can explore the following resources below. You can also reach out to the Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies — we would be happy to assist you.
REQUEST MORE
Information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information
Useful Links
Doctoral Programs
Master's Programs
Graduate School Blog
Graduate Student Funding
Begin Application
- Guide to Applying for Graduate School
The process of preparing for and applying to a PhD program can be overwhelming. The University of Pennsylvania has created this webpage to help prospective PhD students think through the process so you can put together a strong application.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest degree one may obtain within a particular field of study. This ranges from studies in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) fields; Social Science fields such as Education, Economics, Political Science, and Sociology; as well as Humanities fields such as English, History, Music, Philosophy, and more. The PhD degree aims to prepare people to think critically, develop research, and produce scholarship that may be used for further research or implementation . The PhD historically prepared students to take on faculty roles in colleges and universities, and that is still the goal for many students pursuing the PhD. However, today the PhD is a sought-after degree in many other industries including pharmaceutical research, arts organizations and other nonprofits, publishing, government policy, big tech, finance, and more.
- Who can apply to a PhD program? PhD education is available to people from various educational, occupational, socioeconomic, and demographic backgrounds.
- Who should get a PhD? People interested in uncovering new ideas, solutions, or processes within a specific area of study through conducting independent research.
- Why is it important for diverse candidates to become PhD holders? Our world thrives on heterogeneous ideas and experiences, which is why it is indispensable to include students with diverse perspectives in our PhD programs. These students will generate important and original research.
Most PhD programs are fully funded, meaning that for a specific number of years, the program will pay for your tuition and fees and health insurance, as well as provide you with a stipend for living expenses . The structure of this funding varies by field. Below is an outline of general funding information as well as trends according to field of study.
- Teaching Assistantships or Research Assistantships: Part-time service that provides teaching and research training opportunities within your area of study.
- Funding packages provided through faculty research grants: Many STEM fields fund students through research grants awarded to faculty. In these cases, students perform research alongside the faculty.
- Fellowships: Internal or external merit-based funding. Some fellowships require an application while others are given via nomination. Educational institutions typically have a resource listing fellowship opportunities. Winning a competitive fellowship looks good on your resume.
- Grants: Requires an application with supporting materials of either your grades, scholarly work, and/or anticipated research. These are available through internal and external means. Grants greatly vary so be sure to always understand the requirements. Educational institutions typically have a resource listing grant opportunities. Winning a competitive grant looks good on your resume.
- Employment: For example, serving as a residential advisor, on-campus jobs, etc. Some PhD programs restrict additional employment, so be sure to check before applying for jobs.
- The funding opportunities described here often can be combined.
Choosing a school or program that provides the most potential funding may be a challenging decision. The value of the same amount of funding will differ depending on the cost of living in different geographic locations. Admitted applicants should investigate cost-of-living tools (available on the web) and be sure to understand how their funding will be structured. Ask questions when you are admitted, such as:
- Could you share more about your program’s funding mechanism?
- For how long is funding guaranteed? How does that compare to the average time-to-completion? Historically, what percentage of students have received funding beyond the guaranteed funding package?
- Does funding cover tuition, fees, books, health insurance?
- Does the funding rely on teaching, research, or other service? How much and for how long?
Choosing a program for your studies is a personal decision that should reflect not only your research interests, but your work style, and interests outside of the classroom. Here we have identified five key tips to consider when selecting schools.
- Ask about which programs are strong in your area of interest, which have high completion rates, and which have career outcomes that align with your goals.
- Explore the websites of the professional academic associations in the field(s) that interest you. Many will have a directory of doctoral programs and other resources for graduate students. For example, see the American Economic Association’s list of graduate programs and their preparing for graduate school page .
- Conduct a general internet search with terms related to your research interest.
- Determine your geographic and personal preferences. Does the area meet your community needs? Is it important that the university aligns with your sociopolitical values? Do you prefer a large city or a smaller/college town? Is there a particular region(s) that has better access to resources needed to conduct your research?
- Access your current or former university career center. These services are often still available for former students!
- As you narrow your choices, try to identify at least 3 faculty in the programs of interest with whom you’d like to study. Also note how many of them have tenure. If relevant, research which of those faculty are taking on advisees in your year of matriculation.
- Read articles from faculty with similar research interests.
- Note the number of awards, publications, and service activities of faculty.
- Identify research opportunities funded by both your program and university at large.
- Connect with current and former students in the program for informational interviews.
- Connect with campus Diversity Offices.
- Whenever possible, before submitting your applications, make an appointment to visit the campuses and department(s) that interest you.
- Use LinkedIn to see what graduates of your program are doing and how they are involved in their communities.
- Estimate your feasible cost of living by geographic location and compare to the funding package offered.
- Consider availability of health insurance, childcare, housing, transportation, and other fringe benefits.
- Connect with a local bank or your prospective university’s financial services office for budgeting, savings, and other financial wellness advice.
- Research the career outcomes for PhD graduates from the institutions that interest you in your specific field.
- Your First Year in a Ph.D. Program
- What Does Academic Success Mean and How to Achieve it? (STEM)
- Pathways to Science (STEM)
- 7 Advantages PhDs Have Over Other Job Candidates (Industry)
- During your undergraduate/master’s education, you should pursue coursework and/or research that will prepare you for the higher expectations of a PhD program; for example, taking a research methods course, pursuing a summer research experience, or conducting research with a professor at your home institution.
- Identify instructors who could write a letter of recommendation. Share with those instructors your interest in doctoral studies; faculty can be excellent resources for advice as well as recommendations!
- Experiences outside of higher education can also strengthen your PhD application. These may range from project management to volunteer work.
- Develop soft or hard skills. A soft skill that is most useful from the first day of your PhD program is networking. This is necessary not only for meeting other students but also to find collaborators with similar research interests and selecting faculty for your dissertation committee. Learning how to negotiate will also serve you well when approaching collaborative projects. Hard skills related to your field might include learning statistical analysis software, economic theory, a foreign language, or search engine optimization. In short, identify a few soft and hard skills that you can familiarize yourself with prior to your program’s start date.
- Finally, prepare by identifying leading researchers and practitioners in your field , exploring peer-reviewed literature and/or publications, and gain familiarity with research methods.
- Typically, PhD applications are due 10-12 months in advance of the program’s start date (i.e. apply in November to start the following September). A good rule of thumb is to begin your application process 6 months before the deadline.
- The availability of reduced application fees or fee waivers varies and sometimes depends on financial status and/or experiences (AmeriCorps, National Society of Black Engineers, attending certain conferences, etc.). If you are interested in a reduced fee or waiver, reach out to the program coordinator for details.
- Be sure to address all the specific questions/topics in the statement prompt.
- Clearly state why you want to pursue a PhD.
- Propose your research interest.
- Identify the faculty you’d like to study under.
- Discuss the unique qualities/experiences you offer to the program/school.
- Outline what you hope to do with your degree.
- Ask for recommendation letters early in the process, at least 2-4 weeks before the deadline. A good letter takes time to write!
- Provide recommenders with your resume, information about the program, your statement of purpose and/or information about your research interests and research goals.
- Consider your current/former instructors, supervisors, colleagues. These should be people who can speak to your work ethic, academic abilities, and research interests.
- Test scores (i.e. TOEFL, GRE, GMAT, etc.) may or may not be required.
- All transcripts including those for coursework completed abroad and transfer credits. Some programs require official transcripts, which take longer to procure.
- Resume/Curriculum Vitae (CV)
- Writing sample (field dependent): Include a graduate-level sample and update any statements, statistics, etc. as needed. It is highly encouraged that you edit your previous work.
- Diversity statement: Many institutions offer an optional short statement where students can expand on their diverse backgrounds and experiences that may contribute to the diversity interests/efforts of the school.
- Dress professionally, even if the interview is virtual. You don’t necessarily need to wear a suit but dress pants/skirt and a blouse/button down shirt would be appropriate.
- Develop an engaging elevator pitch, a 30-60 second summary of your research interests and what you hope to gain by becoming a student at that particular university. Practice your pitch with a career counselor, faculty advisor, or friends, and ask for honest feedback.
- Prepare 2-3 questions to ask during the interview. These could include questions about program expectations, the experience and success of their PhD students, and (academic/financial/mental health) support for PhD students.
- Some interview programs will include multiple activities including a social event. Be sure to maintain a professional attitude: do not drink too much and keep conversation on academic/professional topics.
- This is also your opportunity to decide whether this campus is a good fit for you.
- Academia Insider is a good resource.
Unlike undergraduate and master’s level education, coursework is just one component of the degree. A PhD comes with additional expectations: you must independently conduct scholarly research in your field of study, train in specific activities such as teaching or lab/field research, pass “milestone” requirements along the way, such as comprehensive exams, and complete the process by writing a dissertation. Furthermore, some fields require you to write multiple articles (number varies by field/program) for conference presentation and/or peer-reviewed publication.
There are other important elements as well:
- Student/Advisor relationship. This is one of the most valuable relationships you can have as a PhD student. Your faculty advisor not only assists you with learning how to approach your research topic, but also typically serves as the lead supervisor of your dissertation research and writing, and ideally mentors you throughout the PhD experience. The selection process of choosing your advisor varies so be sure to know what is expected of you as a student and what is expected of the faculty member. Whenever possible, it is important to align your personality and work style with that of your faculty advisor. Many universities publish expectations for the PhD student/faculty advisor relationship; AMP’ed is Penn’s guide.
- Other relationships: Your faculty advisor is far from the only important person during your PhD career. Other faculty members will also serve on your dissertation committee and be potential mentors. Students in your program can also provide good advice and guidance along the way.
- Coursework: Most programs have a number of required courses all students must take regardless of research interests. Once you have finished this requirement, the classes you choose should closely align with your research topic. Choose courses that will help you learn more about your dissertation topic and research methods. It is a good idea to discuss elective course selection with your advisor.
- The dissertation is a large-scale, written document that explores a narrow research topic of your choice. It is the final step before receiving your degree and must be presented and “defended” to your dissertation committee (made up of faculty members) for approval. Defending means that you have to answer in-depth questions about your topic. While this might sound daunting, the dissertation is simply a demonstration of all the knowledge and expertise you have acquired through your PhD education.
- Networking comes in many forms and includes connections with your fellow classmates, faculty members, and scholarly community. Formal networking events typically take place at academic conferences, where scholars and students present research. Increasing your academic circle will not only allow you to have study buddies, but offer you the opportunity to collaborate on articles or even gain employment. Your school’s career center can provide best practices for effective networking.
Explore graduate programs at the University of Pennsylvania and click on the programs that interest you to learn more about admissions and academic requirements.
Upcoming Penn information sessions and recruitment events include:
- Fontaine Fellows Recruitment Dinner (by invitation only): every March
- Summer Virtual Series for undergraduates thinking about graduate school: June-July, 2024
- DEEPenn STEM (Diversity Equity Engagement at Penn in STEM): October 11-13, 2024. Application deadline is May 24, 2024.
- DivE In Weekend (Diversity & Equity Initiative for Mind Research): October 18-20, 2024. Application due May 30, 2024.
- IDDEAS@Wharton (Introduction to Diversity in Doctoral Education and Scholarship): April 2025. Application opens in November 2024.
National conferences to explore:
- The Leadership Alliance supports students into research careers
- McNair Scholar Conferences
- SACNAS , the largest multidisciplinary and multicultural STEM diversity event in the U.S.
- ABRCMS , the annual biomedical research conference for minoritized scientists
- The PhD Project for students interested in business PhD programs
From Proposal to Defense: What Does a PhD Journey Look Like?

Embarking on a journey towards a PhD is not merely an academic pursuit but a transformative experience that demands dedication, perseverance, and intellectual rigor. From the initial stages of developing a research proposal to the culmination in defending a dissertation, the path to earning a doctoral degree is marked by distinct stages, each presenting its own challenges and milestones. In this blog post, we’ll explore what a PhD journey typically entails, highlight key stages, discuss common obstacles, and provide strategies for navigating them effectively.
Stage 1: Developing a Research Proposal
The journey towards a PhD begins with crafting a compelling research proposal. This document outlines the research topic, objectives, methodology, and significance of the proposed study. Key steps in this stage include:
- Choosing a Research Topic : Identifying a research gap or problem that warrants investigation within your field of study.
- Literature Review : Conducting a thorough review of existing literature to build a theoretical framework and justify the research’s importance.
- Formulating Research Questions : Articulating clear and focused research questions or hypotheses that will guide the study.
- Drafting the Proposal : Writing a coherent and persuasive document that outlines the proposed research design, methods, and expected outcomes.
Challenges : Narrowing down a research topic, navigating the literature review process, and ensuring feasibility within time and resource constraints.
Strategies : Seek guidance from mentors and peers, attend workshops on proposal writing, and be prepared to revise and refine your proposal based on feedback.
Stage 2: Conducting Research and Writing
Once the research proposal is approved, PhD candidates proceed to conduct their research and begin drafting their dissertation. This stage involves:
- Data Collection and Analysis : Implementing the research plan, collecting data through experiments, surveys, interviews, or archival research, and analyzing findings.
- Writing Chapters : Structuring the dissertation into chapters that typically include introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Continuous Feedback : Engaging with advisors and committee members for feedback on draft chapters and refining the research based on their input.
Challenges : Managing time effectively, maintaining motivation during the lengthy writing process, and addressing unforeseen methodological or logistical issues.
Strategies : Establishing a realistic timeline, breaking down tasks into manageable chunks, and joining writing groups or seeking support from fellow candidates.
Stage 3: Dissertation Defense Preparation
As the dissertation nears completion, PhD candidates prepare for their defense, a rigorous oral examination where they present and defend their research findings before a committee of experts. Key activities in this stage include:
- Finalizing the Dissertation : Incorporating feedback from advisors and polishing the manuscript for submission.
- Preparing the Defense Presentation : Creating a clear and concise presentation that outlines the study’s objectives, methodology, findings, and implications.
- Mock Defense Sessions : Participating in mock defense sessions to practice answering questions and addressing critiques.
Challenges : Overcoming nerves and anxiety about presenting and defending years of research, addressing committee critiques effectively, and ensuring thorough preparation.
Strategies : Rehearsing the defense presentation multiple times, anticipating potential questions, and seeking advice from peers who have successfully defended their dissertations.

In conclusion, the journey to earning a PhD is a demanding yet rewarding endeavor that requires dedication, resilience, and intellectual curiosity. Each stage—from developing a research proposal to defending the dissertation—presents unique challenges that test the candidate’s skills and determination. At ValidGrad, we recognize the significance of this achievement and offer high-quality replica PhD certificates that accurately reflect your hard-earned accomplishment. Whether you need a replacement certificate or wish to commemorate your achievement with a replica, ValidGrad provides a convenient, reliable service with fast shipping and competitive pricing. Celebrate your academic journey with ValidGrad and showcase your success with pride.
By navigating the stages of the PhD journey effectively and leveraging support from mentors, peers, and resources like ValidGrad , aspiring doctoral candidates can overcome challenges and achieve their academic and professional goals.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What is a PhD? Advice for PhD students
How long does it take to get a doctorate degree how do you get into grad school are you qualified to do a phd answers to these questions and more.
What is a PhD?
A PhD, which stands for “doctor of philosophy”, is the most advanced academic degree. It’s earned through extensive research on a specific topic, demonstrating expertise and contributing new knowledge to the field.
What does “PhD” mean?
The term “PhD” is often used as a synonym for any doctoral-level qualification. Doctorate degrees can often be split into two categories: MPhil and PhD.

Download your Study Abroad Guide for FREE!
An MPhil is similar to a PhD as it includes a research element (which is usually shorter and less in-depth than a PhD thesis, and often more akin to a dissertation undertaken at undergraduate or master’s level).
MPhil students focus more on interpreting existing knowledge and theory and critically evaluating other people’s work rather than producing their own research. The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries.
A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as “candidates”, to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
PhD requirements vary significantly among countries and institutions. The PhD, once completed, grants the successful candidate the title of “doctor of philosophy”, also called PhD or DPhil.
What is a professional doctorate?
A professional doctorate is a kind of degree that helps people become experts in their fields. Instead of focusing mainly on theory and research like a regular PhD, a professional doctorate is all about practical skills and knowledge.
This kind of doctorate is great for students who want to get better at their jobs in areas like teaching, healthcare, business, law or psychology. The courses and projects in these programmes are designed to tackle real problems you might face at work.
For example, you might have heard of the doctor of education (EdD), doctor of business administration (DBA), doctor of psychology (PsyD) or doctor of nursing practice (DNP). These programmes combine learning, hands-on projects and sometimes a thesis paper or essay to show you’re skilled at solving on-the-job challenges.
How long does it take to study a PhD?
The time required to complete a PhD can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, a full-time PhD programme takes around three to six years to finish. However, it’s important to take into account individual circumstances and the nature of the research involved.
1. Full-time vs. part-time: If you’re studying full-time, dedicating most of your time to your studies, it usually takes about three to four years to complete a PhD. However, studying part-time while managing other commitments might extend the duration. Part-time PhDs can take around six to eight years, and sometimes even longer.
2. Nature of research: The complexity of your research proposal can influence the time required. Certain research questions may involve intricate experiments, extensive data collection or in-depth analysis, potentially leading to a longer completion timeline.
3. Field of study: The subject area you’re researching can also affect the necessary time. Some fields, such as sciences or engineering, might involve more hands-on work, while theoretical subjects might require more time for literature review and analysis.
4. Supervision and support: The guidance and availability of your academic supervisor can affect the pace of your research progress. Regular meetings and effective communication can help keep your studies on track.
5. Thesis writing: While the research phase is crucial, the stage of writing your thesis is equally significant. Organising and presenting your research findings in a clear and cohesive manner can take several months.
6. External commitments: Personal commitments, such as work, family or health-related factors, can influence your study time. Some students need to balance these alongside their PhD studies, potentially extending the duration.
7. External Funding: The availability of funding can also affect your study duration. Some funding might be linked to specific project timelines or research objectives.
So, although a PhD usually takes between three and six years of full-time study, with potential variations based on research complexity, enrolment as part-time or full-time, field of study and personal circumstances. It’s vital to have a realistic understanding of these factors when planning your PhD journey.
How long is a PhD in the UK?
In the UK, the length of a PhD programme typically ranges from three to four years of full-time study. As explained above, there are many factors to consider.
How long is a PhD in the US?
Similarly to the UK, in the United States, the duration of a PhD programme can vary widely depending on the field of study, research topic and individual circumstances. On average, a full-time PhD programme in the US typically takes between five and six years to complete.
Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US?
PhD programmes generally take longer to complete in the US than in the UK due to various factors in the education systems and programme structures of each country:
1. Programme structure: UK PhD programmes often emphasise early, focused research from the first year, leading to shorter completion times. In contrast, US programmes commonly include more initial coursework in your first and second year and broader foundational training, which can extend the overall duration.
2. Course work requirements: Many US PhD programmes require a lot of course work, which can lengthen the time needed to finish. UK programmes tend to have fewer or no course work demands, allowing students to concentrate primarily on research skills.
3. Research funding: In the UK, PhD funding is often awarded with specific timeframes in mind, motivating completion of the research degree in the agreed duration. In the US, funding approaches can vary, requiring students to secure funding from multiple sources, potentially affecting their progress and completion time.
4. Teaching responsibilities: Some US PhD students take on teaching roles as part of their funding, dividing their time and potentially prolonging their studies.
5. Research approach: Differences in research methodologies and project scopes can affect the time needed for data collection, experimentation and analysis.
6. Academic culture: The US education system values a well-rounded education, including coursework and comprehensive exams. This can extend the time before full-time research begins. UK PhD programmes often prioritise independent research early on.
7. Part-time and work commitments: US PhD candidates might have more flexibility for part-time work or other commitments, which can affect research progress.
8. Dissertation requirements: US PhD programmes generally include a longer and more comprehensive dissertation, involving more chapters and a broader exploration of the research topic.
These variations in programme structures, funding models and academic cultures contribute to the differing completion times between the two countries.
What qualifications do you need for a PhD?
To be eligible for a PhD programme, certain educational qualifications are generally expected by universities. These qualifications serve as indicators of your readiness to engage in advanced research and contribute to the academic community.
First, an undergraduate or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field is typically the most common requirement. This degree provides you with a foundational understanding of the subject and introduces you to basic research methodologies. It serves as a starting point for your academic journey.
Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme?
In addition to an undergraduate degree, many PhD programmes also require candidates to hold postgraduate or master’s degrees, often in fields related to the intended PhD research. A master’s degree offers a deeper exploration of the subject matter and enhances your research skills. Possessing a master’s degree signifies a higher level of expertise and specialisation.
The combination of both undergraduate and postgraduate degrees demonstrates a solid academic background. This background is crucial before you engage in doctoral study because pursuing a PhD involves more than just knowledge; it requires advanced research abilities, critical thinking and the capacity to provide an original contribution and new insights into the chosen field of study.
While these qualifications are usually requested, there are exceptions. Some institutions offer direct-entry programmes that encompass bachelor’s, master’s and PhD degrees in a streamlined structure. This approach is often seen in scientific and engineering disciplines rather than humanities.
In exceptional cases, outstanding performance during undergraduate studies, coupled with a well-defined research proposal, might lead to direct entry into a PhD programme without requiring a master’s degree.
Admission requirements can vary between universities and programmes. Some institutions might have more flexible prerequisites, while others could have more stringent criteria. Make sure that you thoroughly research all admission requirements of the PhD programmes you’re interested in to ensure you provide the right information.
Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries?
PhD entry requirements in Canada and Australia can be somewhat similar to those in the UK and the US, but there are also some differences. Just like in the UK and the US, having a bachelor’s degree followed by a master’s degree is a common way to qualify for a PhD in Canada and Australia. However, the exact rules can vary, such as how much research experience you need or the grades you should have.
In Canada and Australia, as in the UK and the US, international students usually need to show their English language skills through tests like IELTS or TOEFL. And, like in other places, you might need to give a research proposal to explain what you want to study for your PhD.
But remember, even though there are some similarities, each country has its own rules.
PhD diary: Preparing for a PhD Nine things to know before doing a PhD Women in STEM: undertaking PhD research in cancer Studying for a part-time PhD: the challenges and the benefits Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student? Looking for PhD tips? Why not check Twitter PhD diary: Where do I begin? How to do a PhD on a budget
How much does it cost to study a PhD?
The cost of pursuing a PhD can vary significantly between international and home (domestic) students, and it depends on the country, university and programme you choose.
United Kingdom (UK)
Home students in the UK often pay lower tuition fees compared with international students. Home students might also have access to government funding or subsidised tuition rates.
International students typically pay higher tuition fees, which can vary widely depending on the university and programme. Fees can range from around £10,000 to £25,000 or more per year.
United States (US)
PhD programme costs in the US can be quite high, especially for international students. Public universities often have lower tuition rates for in-state residents compared with out-of-state residents and international students.
Private universities in the US generally have higher tuition fees, and international students might be charged higher rates than domestic students.
Canadian universities often charge higher tuition fees for international students compared with domestic students.
Some universities offer funding packages that include tuition waivers and stipends for both domestic and international doctoral students.
In Australia, domestic students (Australian citizens and permanent residents) usually pay lower tuition fees than international students.
International students in Australia might have higher tuition fees, and costs can vary based on the university and programme.
Apart from tuition fees, other aspects play a role in the overall financial consideration:
PhD studentship: Many universities offer PhD studentships that provide financial support to research students, covering both tuition fees and a stipend for living expenses.
Stipend and housing: Stipends are designed to cover living expenses. Stipend amounts can vary depending on the university and location. If you’re studying in London in the UK, stipends might be higher to account for the higher living costs in the city. Some universities also offer subsidised or affordable housing options for doctoral students.
Tuition and stipend packages: Some PhD programmes provide funding packages that include both tuition waivers and stipends. These packages are to help relieve the financial burden on students during their doctoral studies.
Research the financial support options provided by the universities you’re interested in to make an informed decision about the cost of your PhD journey.
What funding options are available for PhD candidates?
PhD candidates have various funding options available to support their studies and research journeys. Some of these options include:
PhD scholarships: Scholarships are a common form of financial aid for PhD candidates. They are awarded based on academic merit, research potential or other specific criteria. Scholarships can cover tuition fees and provide a stipend for living expenses.
Bursaries: Bursaries are another form of financial assistance offered to students, including PhD candidates, based on financial need. They can help cover tuition fees or provide additional financial support.
In the UK, specific funding options are available:
Regional consortium: Some regions have research consortiums that offer funding opportunities for doctoral candidates. These collaborations can provide financial support for research projects aligned with specific regional needs.
UK research institute: Research councils in the UK often offer stipends to PhD candidates. These stipends cover living expenses and support research work.
University-based studentship: Many UK universities offer studentships. You can read more about these above.
In the USA, there are also funding options available:
Research assistantships (RAs): Many universities offer research assistantships where PhD candidates work on research projects under the guidance of faculty members. In exchange, they receive stipends and often have their tuition waived.
Teaching assistantships (TA): Teaching assistantships involve assisting professors in teaching undergraduate courses. In return, PhD candidates receive stipends and sometimes tuition remission.
Fellowships: Fellowships are competitive awards that provide financial support for PhD candidates. They can come from universities, government agencies, private foundations and other institutions. Fellowships can cover tuition, provide stipends and offer research or travel funds.
Graduate assistantships: Graduate assistantships include a range of roles, from research and teaching to administrative support. These positions often come with stipends and sometimes include tuition benefits.
External grants and fellowships: PhD candidates can apply for grants and fellowships from external organisations and foundations that support research careers in specific fields. Examples include the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Fulbright Programme.
Employer sponsorship: In some cases, employers might sponsor employees to pursue PhDs, especially if the research aligns with the company’s interests.
You can read about the current available scholarships for international students of all education levels on our website .
What does a PhD Involve?
How does a PhD work?
A PhD includes thorough academic research and significant contributions to your chosen field of study. The timeline for completing a PhD can significantly vary based on the country, college or university you attend and the specific subject you study.
The duration of a PhD programme can vary based on factors such as the institution’s requirements and the academic discipline you’re pursuing. For instance, the timeline for a PhD in a science-related field might differ from that of a humanities discipline.
UK PhD timeline example
Looking at a typical PhD degree in a London higher education institution, we can consider this example timeline.
In the initial year of your PhD, you’ll collaborate closely with your designated academic supervisor. This collaboration involves refining and solidifying your research proposal, which lays the foundation for your entire doctoral journey.
This is also the time to establish a comprehensive plan, complete with well-defined milestones and deadlines. A crucial aspect of this year is conducting an extensive literature review, immersing yourself in existing academic works to understand the landscape of your chosen research area. It’s important to make sure that your research idea is original and distinct from prior studies.
As you begin the second year, you’ll actively collect data and gather information related to your research topic. Simultaneously, you’ll initiate the process of crafting your thesis. This involves combining your research findings and analysis into sections of your thesis document.
This is also the phase where you might have opportunities to share your research insights at academic meetings, conferences or workshops. Depending on the programme, you might even engage in teaching activities. Some PhD candidates also begin contributing to academic journals or books, showcasing their findings to a broader audience.
The third year of a PhD programme often marks the final stage of your research efforts. This is when you dedicate substantial time to writing and finalising your complete thesis. Once your thesis is completed to the highest standard, you’ll submit it for thorough evaluation.
A significant milestone in the third year is the viva voce, an oral examination where you’ll defend your thesis before a panel of experts in your field. The viva voce is an opportunity to showcase your deep understanding of your research and defend your findings.
Why should you do a PhD?
For many people, acquiring a doctorate degree is the pinnacle of academic achievement, the culmination of years of commitment to higher education.
However, the act of pursuing a PhD can be a complex, frustrating, expensive and time-consuming exercise. But with the right preparation, some sound advice and a thorough understanding of the task at hand, your years as a doctoral student can be some of the most rewarding of your life.
People choose to work towards a doctorate for many reasons. If you are looking to pursue an academic position, such as university lecturer or researcher, then a PhD is usually required.
Many people obtain a PhD as part of a partnership with an employer, particularly in scientific fields such as engineering, where their research can prove useful for companies.
In some cases, however, PhDs are simply down to an individual’s love of a subject and their desire to learn more about their field.
What are some benefits of studying a PhD?
Pursuing a PhD can have many benefits that extend beyond academic achievement, encompassing personal growth, professional advancement and meaningful contributions to knowledge.
One of the most notable benefits of a PhD is the potential for tenure in academia. Attaining tenure provides a level of job security that allows you to delve into long-term research projects and make enduring contributions to your field. It signifies a stage where you can explore innovative ideas and pursue in-depth research, fostering your academic legacy.
While not obligatory, the opportunity to collaborate on research projects with your supervisor is another valuable aspect of a PhD pursuit. These collaborations might even come with financial compensation, offering real-world experience, skill development and practical applications of your research. Engaging in such collaborations can enrich your research portfolio and refine your research methodologies.
A pivotal aspect of a PhD journey is the chance to publish your original research findings. By disseminating your work in academic journals or presenting it at conferences, you contribute to the expansion of knowledge within your field. These publications establish your expertise and reputation among peers and researchers worldwide, leaving a lasting impact.
The pursuit of a PhD can provide a unique platform to build a diverse network of colleagues, mentors and collaborators. Engaging with fellow researchers, attending conferences and participating in academic events offer opportunities to make valuable connections. This network can lead to collaborations, expose you to a spectrum of perspectives and pave the way for future research endeavours.
What is a PhD thesis? And what is a PhD viva?
A PhD thesis will be produced with help from an academic supervisor, usually one with expertise in your particular field of study. This thesis is the backbone of a PhD, and is the candidate’s opportunity to communicate their original research to others in their field (and a wider audience). PhD students also have to explain their research project and defend their thesis in front of a panel of academics. This part of the process is often the most challenging, since writing a thesis is a major part of many undergraduate or master’s degrees, but having to defend it from criticism in real time is arguably more daunting. This questioning is known as a “viva”, and examiners will pay particular attention to a PhD’s weaknesses either in terms of methodology or findings. Candidates will be expected to have a strong understanding of their subject areas and be able to justify specific elements of their research quickly and succinctly.
In rare cases, students going for a PhD may instead be awarded an MPhil if the academic standard of their work is not considered fully up to par but still strong enough to be deserving of a qualification.
Can you do a PhD part time?
Many PhD and MPhil candidates choose to pursue their qualification part time, in order to allow time to work and earn while studying. This is especially true of older students, who might be returning to academia after working for a few years.
When applying, you should always speak to the admissions team at your university to ensure this is possible and then continue to work with your supervisor to balance all your commitments.
Can I do a PhD through distance learning?
This is something else that you will need to check with your university. Some institutions offer this option, depending on the nature of your research.
You will need to be clear how many times you will need to travel to your university to meet with your supervisor throughout your PhD.
Your PhD supervisor
Choosing the right PhD supervisor is essential if you want to get the most out of your PhD. Do your research into the faculty at the institution and ensure that you meet with your proposed supervisor (either virtually or in person) before fully committing.
You need to know that not only do they have the right expertise and understanding of your research but also that your personalities won’t clash throughout your PhD.
Remember, to complete your PhD, you will need a strong support network in place, and your supervisor is a key part of that network.
Coping with PhD stress
If you do decide to embark on a doctorate, you may well encounter stress and anxiety. The work involved is often carried out alone, the hours can be long and many students can suffer from the pressure they feel is on their shoulders.
Ensuring that you check in regularly with your emotions and your workload is crucial to avoid burnout. If you have other commitments, such as a job or a family, then learning to balance these can feel overwhelming at times.
Give yourself regular breaks, speak to your supervisor and ensure that you know what university resources and support systems are available to you in case you need to access them.
Post-doctorate: what happens after you finish your PhD?
Many PhD graduates pursue a career in academia, while others will work in industry. Some might take time out, if they can afford to, to recover from the efforts of PhD study.
Whatever you choose to do, undertaking a PhD is a huge task that can open up a range of doors professionally. Just remember to take some time out to celebrate your achievement.
How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential?
How much does a professor with a PhD make a year?
Professors with PhDs can earn different amounts depending on where they work and their experience. In the UK, a professor might make around £50,000 to £100,000 or more each year. In the US, it's between about $60,000 and $200,000 or even higher. The exact salary depends on things like the place they work, if they have tenure, and what they teach.
How much does a PhD add to salary?
Having a PhD can make your salary higher than if you had a lower degree. But exactly how much more you earn can change. On average, people with PhDs earn more than those with bachelor’s or master’s degrees. The increase in salary is influenced by many things, such as the job you do, where you work and what field you’re in.
In fields such as research, healthcare, technology and finance, your knowledge and skills from your PhD can potentially help you secure a higher salary position.
In the end, having a PhD can boost your earning potential and open doors to well-paying jobs, including professorships and special roles in different areas. But the exact effect on your salary is influenced by many things, so ensure you weigh the cost against the benefit.
How to choose a PhD programme?
Choosing a PhD programme involves defining your research interest, researching supervisors and programme reputation, evaluating funding options, reviewing programme structure, considering available resources, assessing networking opportunities, factoring in location and career outcomes, visiting the campus if possible and trusting your instincts.
How can I find available PhD programmes?
You can find available PhD programmes by visiting university websites, using online directories such as “FindAPhD”, checking professional associations, networking with professors and students, following universities on social media, attending career fairs and conferences, contacting universities directly and exploring research institutes’ websites.
How to apply for a PhD programme?
To apply for a PhD programme:
Research and select universities aligned with your interests.
Contact potential supervisors, sharing your proposal, CV and references.
Prepare application materials: research proposal, CV, recommendation letters and a writing sample.
Ensure you meet academic and language-proficiency requirements.
Complete an online application through the university’s portal.
Pay any required application fees.
Write a statement of purpose explaining your motivations.
Provide official transcripts of your academic records.
Submit standardised test scores if needed.
Some programmes may require an interview.
The admissions committee reviews applications and decides.
Apply for scholarships or assistantships.
Upon acceptance, review and respond to the offer letter.
Plan travel, accommodation and logistics accordingly.
Remember to research and follow each university’s specific application guidelines and deadlines.
How to apply for a PhD as an international student?
Many stages of the PhD application process are the same for international students as domestic students. However, there are sometimes some additional steps:
International students should apply for a student visa.
Take language proficiency tests such as TOEFL or IELTS if required.
Provide certificates if needed to validate your previous degrees.
Show evidence of sufficient funds for tuition and living expenses.
Check if you need health insurance for your chosen destination.
Translate and authenticate academic transcripts if necessary.
Attend orientation sessions for cultural adaptation.
Apply for university housing or explore off-campus options.
Familiarise yourself with international student support services.
Ben Osborne, the postgraduate student recruitment manager at the University of Sussex explains in detail how to apply for a PhD in the UK .
Giulia Evolvi, a lecturer in media and communication at Erasmus University, Rotterdam explains how to apply for a PhD in the US .
Finally, Samiul Hossain explores the question Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student?
Q. What is a PhD? A. A PhD is the highest level of academic degree awarded by universities, involving in-depth research and a substantial thesis.
Q. What does “PhD” mean? A. “PhD” stands for doctor of philosophy, recognising expertise in a field.
Q. What is a professional doctorate? A. A professional doctorate emphasises practical application in fields such as education or healthcare.
Q. How long does it take to study a PhD? A. It takes between three and six years to study a full-time PhD programme.
Q. How long is a PhD in the UK? A. It takes around three to four years to study a full-time UK PhD.
Q. How long is a PhD in the US? A. It takes approximately five to six years to complete a full-time US PhD.
Q. Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US? A. US programmes often include more course work and broader training.
Q. What qualifications do you need for a PhD? A. You usually need an undergraduate degree as a minimum requirement, although a master’s might be preferred.
Q. Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme? A. Master’s degrees are preferred but not always required.
Q. Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries? A. Entry requirements are similar in many countries, but there may be additional requirements. Make sure to check the university website for specific details.
Q. How much does it cost to study a PhD? A. The cost of PhD programmes vary by country and university.
Q. What funding options are available for PhD candidates? A. Scholarships, assistantships, fellowships, grants, stipends are all funding options for PhD candidates.
Q. What does a PhD involve? A. PhDs involve research, seminars, thesis, literature review, data analysis and a PhD viva.
Q. Why should you do a PhD? A. There are many reasons to study a PhD including personal growth, research skills, contributions to academia and professional development.
Q. What are some benefits of studying a PhD? A. Benefits of graduating with a PhD include achieving tenure, collaborations with colleagues, publication of your work, and networking opportunities.
Q. What is a PhD thesis? A. A PhD thesis is a comprehensive document that showcases the original research conducted by a PhD candidate.
Q. What is a PhD viva? A. A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce or oral examination, is the final evaluation of a PhD candidate’s research and thesis where the panel asks questions, engages in discussions and assesses the depth of the candidate’s understanding and expertise.
Q. Can you do a PhD part-time? A. Yes, part-time options are available for PhDs.
Q. Can I do a PhD through distance learning? A. Some universities offer online PhDs; you can find out more on their websites.
Q. How to choose a PhD programme? A. You can find PhD programmes through research, by contacting faculty, checking resources and considering location.
Q. How can I find available PhD programme? A. You can find available PhD programmes on university sites, through directories and by networking.
Q. How to apply for a PhD programme A. To apply for a PhD programme, research suitable universities and programmes, get in touch with potential supervisors, gather required documents like transcripts and reference letters, complete the online application, pay any necessary fees and submit a statement of purpose and research proposal. If needed, meet language-proficiency criteria and attend interviews. After acceptance, explore funding choices, confirm your spot and get ready for the programme’s start.
Q. How to apply for a PhD as an international student A. To apply for a PhD as an international student, follow similar steps to domestic students, but you need to include securing a student visa and passing language requirements.
Q. What is a PhD dropout rate? A. The dropout rate from PhDs varies but is approximately 30-40 per cent.
Q. How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential? A. A PhD can boost earning potential, especially in research, technology, healthcare and academia. Impact varies by job, industry and location. Experience, skills and demand also influence salary.
Q. How to address a person with a PhD? A. When addressing someone with a PhD, it’s respectful to use “Dr”, followed by their last name, whether they have a PhD in an academic field or a professional doctorate. For instance, “Dr. Smith”.
Q. Is there a difference between a PhD and a doctorate? A. The terms “PhD” and “doctorate” are often used interchangeably, though a PhD is a specific type of doctorate focused on original research. A doctorate can refer more broadly to any doctoral-level degree, including professional doctorates with practical applications.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and an MD? A. A PhD is a doctor of philosophy, awarded for academic research, while an MD is a doctor of medicine, focusing on medical practice. They lead to different career paths and involve distinct areas of study.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and a professional doctorate? A. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree, while a professional doctorate emphasises applying research to practical fields such as education or business. PhDs often involve original research, while professional doctorates focus on real-world application.
Q. What is the difference between UK and US PhDs? A. The difference between UK and US PhDs lies mainly in structure and duration. UK PhDs often have shorter durations and a stronger emphasis on independent research from an early stage. US PhDs typically include more initial coursework and broader foundational training before full-time research begins.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD student and a candidate? A. A PhD student is actively studying and researching in a doctoral programme, while a PhD candidate has completed programme requirements except for the dissertation and is close to completion.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an EdD? A. A PhD and an EdD (doctor of education) differ in focus. A PhD emphasises research and academic contributions, while an EdD focuses on applying research to practical educational issues.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a DBA? A. A PhD and a DBA (doctor of business administration) differ in purpose. A PhD emphasises theoretical research and academia, while a DBA is practice-oriented, aimed at solving real business problems.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a PsyD? A. A PhD and a PsyD (doctor of psychology) differ in emphasis. A PhD focuses on research and academia, while a PsyD emphasises clinical practice and applying psychological knowledge.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an LLD? A. A PhD and an LLD (doctor of laws or Legum doctor) are distinct. A PhD is awarded in various disciplines, while an LLD is usually an honorary degree for significant contributions to law.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an MD-PhD? A. A PhD and an MD-PhD differ. An MD-PhD is a dual degree combining medical training (MD) with research training (PhD).
Q. What is the Cambridge PhD? A. A Cambridge PhD involves original research guided by a supervisor, resulting in a thesis. It’s offered at the University of Cambridge .
Q. What is the Oxford DPhil? A. An Oxford DPhil is equivalent to a PhD and involves independent research leading to a thesis. The term “DPhil” is unique to the University of Oxford .
Q. What is the PhD programme acceptance rate? A. PhD acceptance rates vary by university, field and competition. Prestigious universities and competitive fields often have lower acceptance rates.
Q. What is a PhD supervisor? A. A PhD supervisor guides and supports a student’s research journey, providing expertise and feedback.
Q. What is a PhD panel? A. A PhD panel evaluates a candidate’s research, thesis and oral defence. It consists of experts in the field.
Q. What is a PhD stipend? A. A PhD stipend is a regular payment supporting living expenses during research, often tied to teaching or research assistant roles.
Q. What is a PhD progression assessment? A. A PhD progression assessment evaluates a student’s progress, often confirming their continuation in the programme.
Q. What is a PhD defence? A. A PhD defence, or viva, is the final oral examination where a candidate presents and defends their research findings and thesis before experts.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Pursuing a PhD in neuroscience
Luis Humberto Eudave Ramos

Why study a PhD in English literature?
John Francis Davies

8 habits to help you get through your PhD
Shabana Khan
Register free and enjoy extra benefits

What is a PhD?
- Types of Doctorates
- A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest globally recognized postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award.
- PhDs are awarded to candidates who undertake original and extensive research in a particular field of study.
- Full time PhD programmes typically last three to four years, whilst part time PhD programmes typically last six to seven years.
- A PhD can lead to an academia teaching role or a career in research. A PhD can also equip you with skills suitable for a wide range of jobs unrelated to your research topic or academia.
Definition of a PhD – A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD , Ph.D or a DPhil ) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible.
PhDs differ from undergraduate and master’s degrees in that PhDs are entirely research-based rather than involving taught modules (although doctoral training centres (DTCs) offer programmes that start with a year of lecture-based teaching to help develop your research skills prior to starting your project).
In most English-speaking countries, those that complete a PhD use the title “Doctor” (typically abbreviated to Dr) in front of their names and are referred to as such within academic and/or research settings. Those that work in fields outside of academia may decide not to use the formal doctor title but use post-nominal letters (e.g. John Smith PhD); it’s unusual though for someone to use both the Doctor title and post-nominal letters in their name.
PhD vs Doctorate
A PhD and a professional doctorate are both research-based terminal degrees.
However, where a PhD focuses on original research mostly around theoretical concepts, a professional doctorate focuses on examining existing knowledge to solve real-life, practical problems.
While there is much crossover between the two, a PhD is generally better suited for an individual to wants to advance the knowledge and understanding in their field, and a professional doctorate degree is better suited to a working professional who wants to better be able to apply knowledge and understanding to their field.
What Are the Entry Requirements for a PhD?
To be accepted on to a PhD programme, students usually need to hold at least a high ( 2:1 and above ) undergraduate degree that is related to the field of research that they want to pursue. A PhD candidate may also be expected to hold a Master’s degree , however, this does not mean you must have one, as it is still possible to enrol into a PhD without a Master’s .
Self-funded courses may sometimes be more relaxed in relation to entry requirements . It may be possible to be accepted onto a self-funded PhD programme with lower grades, though these students typically demonstrate their suitability for the role through professional work experience.
Whilst a distance learning project is possible , most PhD candidates will carry out their research over at least three years based at their university, with regular contact with two academic supervisors (primary and secondary). This is particularly the case for lab-based projects, however, some PhD projects require spending time on-site away from university (e.g. at a specialist research lab or at a collaborating institution abroad).
How Long Does a PhD Take?
Typically, full-time PhDs last 3-4 years and part-time PhDs last 6-7 years. However, at the discretion of the university, the thesis writing-up period can be extended by up to four years.
Although most doctoral programmes start in September or October, they are generally much more flexible than taught-courses and can start at any time of the year.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?
Tuition fees for UK and EU students vary between £3,000 and £6,000 per year, with the average tuition fee of £4,712 per year for 2023/24 programmes.
Tuition fees increase considerably for international students, varying between £16,000 to £25,000 per year, with an average tuition fee of £19,600 per year .
Nonetheless, most students will secure PhD funding in the form of studentships, scholarships and bursaries to help pay for these fees. These funding opportunities can either be partial, which cover tuition fees only, or full, which cover both tuition fees and living expenses.
UK national students can also apply for Doctoral Loans from Student Finance England if they are unable to secure funding.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Does a PhD Involve?
To be awarded a PhD, a doctoral student is required to produce a substantial body of work that adds new knowledge to their chosen field.
A PhD programme will typically involve four key stages:
Stage 1: Literature Review
The first year of a PhD involves attending regular meetings with your supervisors and carrying out a search on previously published work in your subject area. This search will be used to produce a literature review which should set the context of the project by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within the field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. In most cases, this will be an extension of your research proposal should you have produced one as part of your application. The literature review should conclude by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project. This stage of setting achievable goals which are original and contribute to the field of research is an essential first step in a successful PhD.
The supervisor is the main point of contact through the duration of a PhD – but remember: they are there to mentor, not to teach, or do it for you . It will be your responsibility to plan, execute and monitor your own work as well as to identify gaps in your own knowledge and address them.
Stage 2: Research
The second year (and prehapse some of your third year) is when you work on your research. Having identified novel research questions from your review of the literature, this is where you collect your data to help answer these questions. How you do this will depend on the nature of your doctoral research: for example, you may design and run experiments in a lab alongside other PhD students or visit excavation sites in remote regions of the world. You should check in regularly with your supervisors to update them and run any ideas or issues past them.
Have the structure and chapters of your thesis in mind as you develop and tackle your research questions. Working with a view of publishing your work will be very valuable later on.
Stage 3: Write up of Thesis
The next key stage of a PhD is writing a doctoral thesis , which typically takes from anywhere between three months to one year. A thesis is a substantial body of work that describes the work and outcomes of the research over the previous two to three years. It should tell a detailed story of the PhD project – focusing on:
- The motivations for the research questions identified from the literature review.
- The methodologies used, results obtained, and a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the findings.
- A detailed discussion of the key findings with an emphasis on the original contributions made to your field of research and how this has been impactful.
There is no universal rule for the length of a PhD thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 80,000 to 100,000 words.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available.
Stage 4: Attending the Viva
A viva voce , most commonly referred to as just a ‘ viva ‘, is an interview-style examination where the PhD student is required to engage in a critical appraisal of their work and defend their thesis against at least two examiners. The examiners will ask questions to check the PhD student has an in-depth understanding of the ideas and theories proposed in their thesis, and whether they have developed the research skills that would be expected of them.
The viva is one of the final steps in achieving a PhD, and typically lasts at least two hours, but this duration can vary depending on the examiners, the university and the PhD project itself.
Once you have done the viva – you’re on the home stretch. You will typically be asked to make some amendments to your thesis based on the examiner’s feedback. You are then ready to submit your final thesis for either:
- PhD – If you pass the requirements you will be awarded a PhD degree (most common outcome),
- MPhil – If you failed to meet requirements for a PhD, you may be downgraded to an MPhil degree (uncommon outcome),
- Fail – No award is given, typically for cases of plagiarism (extremely uncommon outcome).
What Is It Like to Undertake a PhD?
We’re often asked what it is like to undertake a PhD study. Unfortunately, this isn’t a simple answer to this question as every research project is different.
To help give insight into the life of a PhD student, we’ve interviewed PhD students at various stages of their programmes and put together a series of PhD Student Interviews . Check out the link to find out what a PhD is like and what advice they have to offer you.
What Are the Benefits of A PhD?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and independent research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but sets you up with invaluable skills and traits.
Career Opportunities
First, a PhD prepares you for a career in academia if you wish to continue in this area. This takes form as a career in the Higher Education sector, typically as a lecturer working their way to becoming a professor leading research on the subject you’ve studied and trained in.
Second, a PhD also enables the opportunity for landing a job in a research & development role outside of the academic environment. Examples of this include laboratory work for a private or third sector company, a governmental role and research for commercial and industrial applications.
Transferable Skills
Finally, in possessing a PhD degree, you can show to employers that you have vital skills that make you an asset to any company. Three examples of the transferable skills that you gain through a PhD are effective communication, time management, and report writing.
- Communication – presenting your work in written and oral forms using journal papers and podium presentations, shows your ability to share complex ideas effectively and to those with less background knowledge than you. Communication is key in the professional environment, regardless of the job.
- Time management – The ability to prioritise and organise tasks is a tremendous asset in the professional industry. A PhD holder can use their qualification to demonstrate that they are able to manage their time, arrange and follow a plan, and stick to deadlines.
- Report writing – Condensing three years of work into a thesis demonstrates your ability to filter through massive amounts of information, identify the key points, and get these points across to the reader. The ability to ‘cut out the waffle’ or ‘get to the point’ is a huge asset in the professional industry.
Aside from the above, you also get to refer to yourself as a Doctor and add fancy initials after your name!
What Can I Do After a PhD?
One of the most desirable postdoctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on a R&D position.
It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only opens the door for an academic career such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD opens these doors, the opportunities extend far beyond educational roles. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles . This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
How Do I Find a PhD?
We appreciate that finding a PhD programme to undertake can be a relatively daunting process. According to Higher Education Student Statistics , over 22,000 PhDs were awarded in 2016/17 within the United Kingdom alone. Clearly there are a huge number of PhD programmes available. This can sometimes be confusing for prospective doctorates, particularly when different programmes are advertised in different places. Often, it is difficult to know where to look or where to even start. We’ve put together a list of useful sources to find the latest PhD programmes:
- A great place to start is with our comprehensive and up-to-date database of available PhD positions .
- Assuming you are still at university, speak to an existing PhD supervisor within your department.
- Attend as many postgraduate open days as you can. Whilst there, speak to current PhD students and career advisors to get an awareness of what PhDs are on offer.
- Visit the postgraduate section of university websites and the PhD Research Council section of the UKRI website.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Log in
- Site search
What is a PhD?
As the highest degree level achievable, completing a PhD shows that you've made a meaningful new contribution to your research field
PhDs at a glance
- Involves three or four years of full-time study, or up to seven part time.
- Typically undertaken after achieving a Masters degree.
- Can either be funded or self-funded.
- Assessed through a written thesis and oral exam.
- Many Doctoral graduates choose to pursue an academic or research career.
What does PhD stand for?
The term PhD or Doctorate of Philosophy is an abbreviation of the Latin phrase 'philosophiae doctor'.
A PhD degree typically involves students independently conducting original and significant research in a specific field or subject, before producing a publication-worthy thesis.
While some Doctorates include taught components, PhD students are almost always assessed on the quality and originality of the argument presented in their independent research project.
What are the most popular PhD subjects?
- clinical psychology
- creative writing
- computer science
- engineering.
How long does a Doctorate degree take?
Full-time PhDs usually last for three or four years, while part-time PhDs can take up to six or seven. However, the thesis deadline can be extended by up to four years at the institution's discretion. Indeed, many students who enrol on three-year PhDs only finish their thesis in their fourth year.
While most PhD studentships begin in September or October, both funded and self-funded PhDs can be undertaken at any point during the year.
Do I need a Masters to do a PhD?
The majority of institutions require PhD candidates to possess a Masters degree , plus a Bachelors degree at 2:1 or above. However, some universities demand only the latter, while self-funded PhD students or those with significant professional experience may also be accepted with lower grades.
You may need to initially register for a one or two-year Master of Philosophy (MPhil) or Master of Research (MRes) degree rather than a PhD. If you make sufficient progress, you and your work will then be 'upgraded' to a PhD programme. If not, you may be able to graduate with a Masters degree.
If you need an MPhil or MRes before enrolling on your PhD, search Masters degrees .
What does a PhD involve?
A standard PhD by thesis degree is typically split into three stages. A three-year PhD may follow this pattern:
- First year - You'll meet with your supervisor to discuss your research proposal and agree an action plan with deadlines. You'll then complete your literature review, in which you'll evaluate and critique existing works to inform the direction of your project and ensure that your research will be original.
- Second year - Your focus will shift to gathering results and developing your thesis, and potentially begin writing chapters of your thesis. You may also present your results and ideas at academic conferences, gain teaching experience, collaborate with other students on similar projects, communicate the benefits of your research to the general public through workshops, lectures and presentations, or submit work for publication in an academic journal or book.
- Third year - Primarily involves writing your thesis, though your research may still be in progress. After your supervisor gives their approval, you'll submit your thesis before undertaking a one to three-hour oral exam ( viva voce ) in which you'll discuss and defend your thesis in the presence of at least one internal and external examiner.
How do I find a PhD?
As a PhD is different to other degrees, you're committing to more than simply an advanced qualification. You've chosen to engage in a large-scale independent research project and so you'll need to take into account a range of factors that will drive your search.
A methodical approach to the process is required and you'll need to consider the subject you're interested in carrying out research in and the type of Doctorate you're looking for, making sure this is the right project for you. Only when you're fully prepared and have a good idea of your research proposal should you search for PhD opportunities .
What other types of Doctorate are there?
Alternative types of PhD include:
- Higher Doctorate - These are usually granted on the recommendation of a committee of internal and external examiners, which assesses a portfolio of published, peer-reviewed research you've undertaken over the course of many years. This type of Doctorate is usually for those with several years of academic experience. Common award titles include the Doctor of Civil Law (DCL), Doctor of Divinity (DD), Doctor of Literature/Letters (DLit/DLitt/LitD/LittD), Doctor of Music (DMus/MusD), Doctor of Science (DS/SD/DSc/ScD) and Doctor of Law (LLD).
- Integrated/New Route PhD - This four-year PhD course is offered by over 30 universities and involves taking a one-year MRes before studying a three-year PhD. It combines taught elements with independent research, allowing students to learn different methodologies while building their transferable skills.
- Professional Doctorate - Geared towards students of vocational subjects such as medicine, education and engineering, professional Doctorates are focused on teaching and so normally involve smaller research projects and thesis component. They're often favoured by those aiming for a career outside of academia and are usually supported by employers.
Read more about the different PhD pathways at 5 routes to getting a Doctorate .
How much does a PhD cost?
Tuition fees vary, but usually fall between £3,000 and £6,000 per year for UK students and those from the European Union (EU) with settled status. UK Research Councils pay universities £4,786 per year (from 2024/25) on behalf of each funded PhD student, so this gives a good indication of the average figure.
For EU students looking to pursue a Doctorate in 2024/25, you'll need to have gained settled or pre-settled status to be eligible for student finance - see PhD loans .
Non-EU students may pay considerably more for their tuition fees.
Despite this, many PhD students are now part or fully funded - scholarships and bursaries are widely available, and particular attention should be paid to Research Council grants .
PhD studentships and assistantships involving a mixture of research and teaching are also common, with scientific studentships usually paid at a higher rate.
Read more about funding postgraduate study .
How do I apply for a PhD?
Some students propose their own research area and apply for funding, while in some cases a supervisor may already have funding for a project and advertise it like a job. When making a PhD application, you'll typically be asked to submit:
- an academic CV
- your academic transcripts
- two or three academic references
- a personal statement
- a research proposal.
International students without settled UK status looking to study certain courses in medicine, mathematics, engineering and material sciences are required to comply with the Academic Technology Approval Scheme (ATAS) .
This involves undergoing a security clearance process with the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office. International students may also have to prove their English proficiency.
Can I study a PhD abroad?
As the aim of postdoctoral research is to stretch the boundaries of understanding within your chosen field, you may find that the best place to begin your research lies overseas.
According to the Higher Education Student Statistics: UK, 2021/22 , 113,000 postgraduate research students are based in the UK, with 46,350 of these identified as international PhD candidates.
While studying in the UK has proved a strong draw for foreign PhD students, a number of other countries have also proved themselves to be research-orientated nations.
The following 15 countries all feature within the top 100 of the QS World University Rankings 2024 :
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Switzerland
If you're interested in studying a PhD abroad, explore our country profiles .
What can I do next?
Your ability to critically analyse, display intellectual maturity, and research independently and honestly is highly valued within academia and the workplace.
Many students who undertake a PhD get an academic job or become an industry researcher, possibly following the PhD with postdoctoral study, then a fellowship or lectureship.
Other career options will depend on your study area. For instance, according to HESA's Graduate Outcomes 2020/21 data, a significant number of PhD graduates went on to work in teaching, natural and social science, therapy, and business, research and administrative careers.
Consider what else a PhD degree can lead to at your PhD, what next?
Find out more
- Get help with choosing your PhD supervisor .
- Discover 5 challenges faced by PhD students .
- Explore professional qualifications .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Gross Stipend/Salary. Right away your eye might be drawn to a phrase like "Your total financial aid package is worth…" and some huge number like $50,000 or $90,000. Don't be distracted by it! You need to know what your actual pay will be - what is usually referred to as your stipend. The letter should delineate between your stipend ...
9. There are no real breaks. In a stereotypical "9-to-5" job, when the workday is over or the weekend arrives, you can generally forget about your work. And a vacation provides an even longer respite. But in a PhD program, your schedule becomes "whenever you find time to get your work done."
7 stages of the PhD journey. A PhD has a few landmark milestones along the way. The three to four years you'll spend doing a PhD can be divided into these seven stages. Preparing a research proposal. Carrying out a literature review. Conducting research and collecting results. Completing the MPhil to PhD upgrade.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say ...
What does the daily life of a PhD student look like? Embarking on a PhD journey can be a thrilling yet demanding experience, as a doctoral student is constantly immersed in: research, academic responsibilities, and professional development. From the early morning, the life of a PhD student begins with checking emails, planning the day, and ...
Written by Mark Bennett. A PhD is a doctoral research degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve. A PhD involves students taking on independent and significant research culminating in a publishing-worthy thesis. The degree normally takes between three and four years of full-time work towards an original contribution ...
Picking a PhD Program. For those programs whose offers you are declining, pay them a courtesy by submitting your decision in the format that they've requested, whether it's logging into an application portal or returning a contract by email. This gives the most accurate information to the department and lets them know they can open up your ...
A Ph.D. is a research degree that involves the production of original knowledge and scholarship. Doctoral degrees have traditionally been regarded as training programs for academics. As such, a Ph.D. program differs from undergraduate or Master's studies. Most Ph.D. programs involve some initial coursework (specific requirements for ...
In sum, the steps in deciding where to apply for PhD study are as follows: Choose your field of study. Identify your preferred area (s) within that field. Discover the specific topics you find most fascinating. Consider what methods you want to employ. Evaluate the merits of prospective faculty advisors.
As mentioned, the progress of a PhD is entirely reliant on the student. You will be in charge of your research and how you present it. If you find gaps in your knowledge or skills then it's up to you to fill them. You will also be expected to involve yourself in external activities, such as conferences or publishing research papers.
Successfully completing a doctoral program requires commitment and perseverance. The most important step in this process is to consider whether academic life is right for you and what kind of doctoral program — from discipline to environment — will be the best fit for your goals and preferences. We asked our current students and faculty ...
What does life as a Ph.D. student really look like? And how long does it take to get a Ph.D.? Your time in your Ph.D. program is both exciting and challenging and, depending on your school and program, the next 5-7 years will look a little different for everyone. Here's what you can generally expect in your Ph.D. program: Ph.D. timeline
The PhD historically prepared students to take on faculty roles in colleges and universities, and that is still the goal for many students pursuing the PhD. However, today the PhD is a sought-after degree in many other industries including pharmaceutical research, arts organizations and other nonprofits, publishing, government policy, big tech ...
Ph.D. programs emphasize research and include more coursework in research methods and statistics. Students typically have more research-based opportunities during the program, and graduates may pursue careers in research or academia. The Psy.D. takes 4-5 years to complete, including an internship year.
In conclusion, the journey to earning a PhD is a demanding yet rewarding endeavor that requires dedication, resilience, and intellectual curiosity. Each stage—from developing a research proposal to defending the dissertation—presents unique challenges that test the candidate's skills and determination.
The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries. A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as "candidates", to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
Think of this section as your PhD crystal ball! From an overview of the PhD journey and an insight into working with a supervisor to what you can expect from the PhD thesis and the final viva voce exam, we've covered the rhythms and routines of PhD research.
A PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy. In answer to the question, "Is a PhD a doctor," the answer is yes. Both a PhD and a professional doctorate like an EdD earn you the title of "doctor.". But there are differences between the types of doctoral degrees. Learn more about a PhD vs. a professional doctorate below.
Definition of a PhD - A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD, Ph.D or a DPhil) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible. PhDs differ from undergraduate and master's degrees in that PhDs are ...
The term PhD or Doctorate of Philosophy is an abbreviation of the Latin phrase 'philosophiae doctor'. A PhD degree typically involves students independently conducting original and significant research in a specific field or subject, before producing a publication-worthy thesis. While some Doctorates include taught components, PhD students are ...