- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking

How to Write a Debate Speech
Last Updated: April 12, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,494,685 times.
So, you've joined debate, and it's time to write a debate speech. There are some tried and true methods to writing an effective debate speech. If you understand them, and the components that make up a standard debate speech, you will increase your chances of success.
Sample Speeches

Preparing for the Debate Speech

- You may be asked to stand affirmative or negative. In LD (Lincoln-Douglas debate), the first affirmative speech will be at most 7 minutes long, and the first negative speech will be at most 6 minutes. [1] X Research source
- The speakers then present arguments against the earlier affirmative or negative speech that was just read. Speakers must listen carefully and be able to counter arguments. There are two segments involving cross-examination (CX), in which the debaters are allowed to ask questions and openly debate the topic. This is most often called cross-examination, or cx for short, and occurs after the first affirmative speech, and the first negative speech.
- The best thing you can do to better understand LD/PF/Policy debate is practice and research.

- Brainstorm the topic, and research it before you sit down to write. Write out a list of key components for both sides of the issue. If you are on a debate team, do this together. Each member could discuss the key component list, in order to figure out which issues you want to cover in each speech.
- Spend some time at the library or on the Internet using credible sources to research the key reasons that seem strongest. Use books, scholarly journals, credible newspapers, and the like. Be very cautious about unverified information bandied about on the Internet.
- You will also want prepare to deal with the strongest arguments your opponent(s) might make. Ignoring the other side’s best arguments can weaken your rhetorical appeal.

- A basic debate outline should contain six parts: An attention-getter, your stated stance (aff or neg)/ restatement of the resolution, your definitions, your value, criterion, and contentions.
- You can break each of those six parts into subcategories. It’s often a good idea to write the contentions last, focusing on the value and criterion to hold it up first.
Writing the Debate Speech

- You should address the jury or audience with formal salutations. For example, you could say something like, “Good morning, ladies and gentlemen.” Debates are very formal in tone.
- Making a good first impression with the judges is very important. This leads judges to assume the debater is persuasive. One technique to write a strong introduction is to contextualize the topic, especially in relation to real world events. [6] X Trustworthy Source American Bar Association Leading professional organization of lawyers and law students Go to source
- Introductions can also focus on prominent examples, quotations, or on a personal anecdote that can help establish a rapport with the audience and judges. Be careful using humor; it involves risks and can lead to awkward silences if not done right. Find a relevant specific that illustrates the underlying point.

- Don’t muddle your position. It needs to be extremely clear whether you affirm or negate the resolution, so don’t hem and haw and contradict yourself. The audience also should not have to wait until the end to find out. Make your stance very clear, and do it early on
- For example, you could say, “my partner and I firmly negate (or affirm) the resolution which states that unilateral military force by the United States is justified to prevent nuclear proliferation.” [7] X Research source

- A good rule of thumb is to back up your position with 3-4 strong points of supporting argumentation. You definitely need to have more than 1 or 2 key points to back up the stance you have taken.
- The body of the speech – the key points and their development – should be, by far, the longest part of the debate speech (perhaps 3 ½ minutes to 30 seconds for an opening and for a conclusion, depending on the rules of the debate you are doing).

- Focus on the causes of the problem, the effects of the problem, expert opinion, examples, statistics, and present a solution. Try to use visual images, not just generic terms – show don’t tell, and illustrate a point with details.
- Appeal to the motives and emotions of the listener with a light touch. Appeal to their sense of fair play, desire to save, to be helpful, to care about community, etc. Ground examples in how people are affected.
- Try using rhetorical questions, which make your opponents consider the validity of their point; irony, which undermines their point and makes you seem more mature and intelligent; simile, which gives them something to relate to; humor, which gets the audience on your side when done well; and repetition, which reinforces your point.

- Aristotle believed that speakers were more persuasive if they combined elements of logos (persuasion by reasoning) with pathos (having an element of emotional appeal) and ethos (an appeal based on the character of the speaker) - for example, that they seem intelligent or of good will.
- There are two ways to use logic – inductive (which makes the case with measurable evidence like statistics or a specific anecdote or example) and deductive (which makes the case by outlining a general principle that is related to the specific topic to infer a conclusion from it - as in, I oppose all wars except those involving imminent self defense; thus, I must oppose this one because it's a war that was not in imminent self defense, and here's why). Or the reverse.
- You should use pathos sparingly. Emotional appeal on its own can be dangerous. Logos - the appeal to reason - should be at the core. However, logical appeal without any pathos at all can render a speech dry and dull. Consider what you are trying to make your audience feel. Explaining how a topic affects real people is one way to use pathos well.
Concluding the Debate Speech

- One strong way to conclude a debate speech is to bookend the conclusion with the opening, by referring back to the introduction and tying the conclusion into the same theme.
- Quotations can be a good way to end a speech. You can also end with a brief summation of the key arguments of the speech to ensure they remain fresh in judges’ minds.

- Use a clear, loud voice, and be careful to watch pacing. You don’t want to speak too loud or too slowly. Remember that confidence goes a long way toward persuasion.
Expert Q&A

Reader Videos
- Never add new points in your speech because you still have time, as you might not present it in the best way. When you are nervous, you might even say an argument in favor of the other side and you don't want that. Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 2
- Never degrade your topic. Thanks Helpful 32 Not Helpful 3
- Don't use all your points in your debate- in an actual debate, it is sometimes useful to have other information to cite if the argument starts going their way Thanks Helpful 29 Not Helpful 3
Tips from our Readers
- You can make a sample opening and closing speech beforehand so you can focus more time on developing your arguments during the actual debate.
- Make sure to include rebuttals in your speech, as they are just as important as your main arguments.
- Practice as much as possible — it will make you more confident and help you maintain eye contact.
- Imagine you're just practicing with a friend rather than performing in front of an audience.
- Take deep breaths before starting to ease nerves.

- Remember, just because you can write a debate speech, it doesn't mean you can say a debate speech effectively. Practice! Thanks Helpful 22 Not Helpful 5
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.learndebating.com/english/DEBATING.pdf
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/research/faq/reliable
- ↑ Patrick Muñoz. Voice & Speech Coach. Expert Interview. 12 November 2019.
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/oralcommunication/guides/how-to-outline-a-speech
- ↑ https://www.americanbar.org/groups/litigation/resources/newsletters/trial-evidence/five-tips-engaging-opening-statements/
- ↑ http://www.oxfordsd.org/Page/5582
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/argument/
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/persuasive-speaking
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/speech-anxiety
About This Article

To write a debate speech, start by researching the topic thoroughly with credible and scholarly sources, and make an outline of your argument including an introduction, thesis argument, key points, and conclusion. Write the thesis argument and develop 3-4 strong points of argumentation. Be sure to clearly state your stance, and utilize expert opinions, statistics, and examples to support your opinion. To finish the speech, write an interesting introduction that incorporates your thesis and a brief conclusion that summarizes your main points. If you want to learn more, such as how to make your debate speech persuasive, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Kaveesha Pathiranahewa
Dec 1, 2021
Payton Ayoardi
Jul 25, 2021
David Williams
Nov 21, 2017
Luyanda Nondalo
Feb 6, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

How to Write a Winning Debate Speech
What is a Debate?
A classroom debate involves students delivering persuasive speeches to present and support their opinions on a given subject. This activity helps develop critical thinking and communication skills, enabling students to gain a more comprehensive grasp of various topics.
Debate speeches are written according to a set of rules so a moderator can assess their effectiveness and allow others to question or challenge their statements within a formal debate.
A classroom debate is not an unruly fight or pointless argument but a structured formal conversation on a chosen topic in which two teams argue for or against it to convince the neutral moderator that they hold the stronger position.
Debating is a form of persuasive communication, and while we will be sticking to the fundamentals of how to write a debating speech, we also have a great guide to persuasive essay writing that elaborates on specific persuasive techniques.
Complete Teaching Unit on Class Debating

This unit will guide your students to write excellent DEBATE SPEECHES and craft well-researched, constructed ARGU MENTS ready for critique from their classmates.
Furthermore, this EDITABLE UNIT will provide the TOOLS and STRATEGIES for running highly engaging CLASSROOM DEBATES.
How To Run A Classroom Debate
Before jumping in headfirst to write your debating speech, ensure you understand how a debate is run to maximise your strategy and impact when it counts.
Debates occur in many different contexts, such as public meetings, election campaigns, legislative assemblies, and as entertainment on television shows. These contexts determine the specific structure the debate will follow.
This guide provides a basic step-by-step debate structure we can comfortably run with students in a classroom. By familiarizing students with this structure, they will effortlessly transition to other debate frameworks.
Running a classroom debate can be an engaging and educational activity that helps students develop critical thinking, communication, and research skills. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to organize and facilitate a successful classroom debate:
1. Choose a Topic For Your Debate.
Also called a resolution or a motion , the topic is sometimes chosen to debate. This is usually the case in a school activity to practice debating skills.
The resolution or motion is usually centered around a true or false statement or a proposal to change the current situation. Often, the motion starts, ”This House believes that….”
Select a topic relevant to your curriculum and the students’ interests. Ensure that it is debatable and has multiple perspectives. Further down this article, you can find a list of popular classroom debating topics.
2. Form Two Debating Teams
Two teams of three speakers each are formed. These are referred to as ‘ The House for the Motion ’ or the ‘ Affirmative ’ team and ‘The House Against the Motion ’ or the ‘ Negative ’ team.
Preparation is an essential aspect of debating. The speech and debate team members will need time to research their arguments, collaborate, and organize themselves and their respective roles in the upcoming debate.
They’ll also need time to write and rehearse their speeches. The better prepared and coordinated they are as a team, the greater their chances of success in the debate.
3. Assign Roles to Students.
Each team member should have a specific role, such as speaker, researcher , or rebuttal specialist . This encourages teamwork and ensures that each student is actively involved.
4. Research and Preparation:
- Allocate time for teams to research and prepare their arguments. Encourage students to use multiple sources, including books, articles, and reputable websites. Make sure you read our complete guide to powerful student research strategies.
5. Set Debate Format:
- Define the debate format, including the structure of each round. Common formats include opening statements, cross-examination, rebuttals, and closing statements.
6. Establish Rules:
- Set ground rules for the debate, such as time limits for each speaker, etiquette, guidelines for respectful communication, and consequences for rule violations.
7. Conduct a Practice Debate:
- Before the actual debate, conduct a practice round. This helps students become familiar with the format and allows you to provide feedback on their arguments and presentation skills.
- On the day of the debate, set up the classroom to accommodate the format. Ensure that each round has a clear structure, and designate a timekeeper to keep the debate on schedule.
9. Facilitate Q&A Sessions:
- After each team presents their arguments, allow time for questions and cross-examination. This encourages critical thinking and engagement among the students.
10. Evaluate and Debrief:
- After the debate, provide constructive feedback to each team. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of their arguments, presentation skills, and teamwork. Also, please encourage students to reflect on what they learned from the experience.
- Have a class discussion about the debate, exploring different perspectives and opinions. This can deepen students’ understanding of the topic and enhance their critical thinking skills.
Consider integrating the debate topic into future lessons or assignments. This reinforces the learning experience and allows students to delve deeper into the subject matter.
Remember to create a supportive and respectful environment throughout the debate, emphasizing the importance of listening to opposing views and engaging in constructive dialogue.
Each speaker takes a turn making their speech, alternating between the House for the Motion, who goes first, and the House Against the Motion. Each speaker speaks for a pre-agreed amount of time.
Ensure your debate is held in front of an audience (in this case, the class), and occasionally, the audience is given time to ask questions after all the speeches have been made.
Finally, the debate is judged either by moderators or by an audience vote.

Download our Debate Organizer
Stay fousssed with this handy template to keep all your ideas organized.
How To Write A Debate
How to start a debate speech.
In highly competitive speech and debate tournaments, students are only provided the topic on the day, and limited time is allowed for preparation, but this is not recommended for beginners.
Regardless of the stakes of your classroom debate, the speechwriting process always begins with research. Thorough research will provide students with both the arguments and the supporting evidence for their position on a topic and generate forward-thinking about what their opponents might use against them.
Writing Your Introduction
The purpose of the introduction in a debate speech is to achieve several things:
- Grab the attention of the audience,
- Introduce the topic
- Provide a thesis statement
- Preview some of the main arguments.
Grab The Attention Of Your Audience With Strong Hooks
Securing the audience’s attention is crucial, and failure to do this will have a strong, negative impact on how the team’s efforts will be scored as a whole. Let’s explore three proven strategies to hook your audience and align their thinking to yours.
Introduce Your Topic With Efficiency and Effectiveness
Once the audience’s attention has been firmly grasped, it’s time to introduce the topic or the motion. This should be done straightforwardly and transparently to ensure the audience understands the topic of the debate and the position you are approaching it from.
For example, if the topic of the debate was school uniforms, the topic may be introduced with:
Provide Your Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a concise declaration summarizing the points and arguments of your debating speech.
- It presents a clear stance on a topic and guides the reader on what to expect in the content.
- A good thesis statement is debatable and allows for opposing viewpoints and discussion.
- It serves as a roadmap for the writer, ensuring coherence and focus in the piece.
- It helps the audience understand the purpose and direction of the work from the beginning.
The thesis statement should express the student’s or the team’s position on the motion. Clearly explaining the speaker’s side of the debate. An example can be seen here.
Provide A Preview Of Your Arguments
The final part of the introduction section of a debate speech involves previewing the main points of the speech for the audience.
There is no need to go into detail with each argument here; that’s what the body of the speech is for. It is enough to provide a general thesis statement for each argument or ‘claims’ – (more on this to follow).
Previewing the arguments in a speech is especially important as the audience and judges only get one listen to a speech – unlike a text, which can be reread as frequently as the reader likes.
debate introduction examples for students
Attention grabbers task.
After explaining the different types of attention grabbers and the format for the rest of the introduction to your students, challenge them to write an example of each type of opening for a specific debate topic.
When they’ve finished writing these speech openings, discuss with the students which one best fits their chosen topic. Then, they can continue by completing the rest of the introduction for their speech using the format described above.
You might like to try a simple topic like “Homework should be banned.” you can choose from our collection further in this article.
Writing T he Body of the Speech
The body paragraphs are the real meat of the speech. They contain the in-depth arguments that make up the substance of the debate, and How well these arguments are made will determine how the judges will assess each speaker’s performance, so it’s essential to get the structure of these arguments just right.
Let’s take a look at how to do that.
How to structure an Argument
With the introduction out of the way, it’s time for the student to get down to the nitty-gritty of the debate – that is, making compelling arguments to support their case.
There are three main aspects to an argument in a debate speech. They are:
- The Warrant
Following this structure carefully enables our students to build coherent and robust arguments. Ttake a look at these elements in action in the example below.
Brainstorming Arguments
Present your students with a topic and, as a class, brainstorm some arguments for and against the motion.
Then, ask students to choose one argument and, using the Claim-Warrant-Impact format, take a few moments to write down a well-structured argument that’s up to debate standard.
Students can then present their arguments to the class.
Or, you could also divide the class along pro/con lines and host a mini-debate!
Concluding a Debate Speech
The conclusion of a speech or a debate is the final chance for the speaker to convey their message to the audience. In a formal debate that has a set time limit, the conclusion is crucial as it demonstrates the speaker’s ability to cover all their material within the given time frame.
Avoid introducing new information and focus on reinforcing the strength of your position for a compelling and memorable conclusion.
A good conclusion should refer back to the introduction and restate the main position of the speaker, followed by a summary of the key arguments presented. Finally, the speaker should end the speech with a powerful image that will leave a lasting impression on the audience and judges.

Examples of strong debate Conclusions
The Burden of the Rejoinder
In formal debates, the burden of the rejoinder means that any time an opponent makes a point for their side, it’s incumbent upon the student/team to address that point directly.
Failing to do so will automatically be seen as accepting the truth of the point made by the opponent.
For example, if the opposing side argues that all grass is pink, despite how ridiculous that statement is, failing to refute that point directly means that, for the debate, all grass is pink.
Our students must understand the burden of the rejoinder and ensure that any points the opposing team makes are fully addressed during the debate.
The Devils Advocate
When preparing to write their speech, students should spend a significant proportion of their team collaborating as a team.
One good way to practice the burden of the rejoinder concept is to use the concept of Devil’s Advocate, whereby one team member acts as a member of the opposing team, posing arguments from the other side for the speaker to counter, sharpening up their refutation skills in the process.
20 Great Debating Topics for Students
- Should cell phones be allowed in schools?
- Is climate change primarily caused by human activities?
- Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
- Is social media more harmful than beneficial to society?
- Should genetically modified organisms (GMOs) be embraced or rejected?
- Is the death penalty an effective crime deterrent?
- Should schools implement mandatory drug testing for students?
- Is animal testing necessary for scientific and medical advancements?
- Should school uniforms be mandatory?
- Is censorship justified in certain circumstances?
- Should the use of performance-enhancing drugs be allowed in sports?
- Is homeschooling more beneficial than traditional schooling?
- Should the use of plastic bags be banned?
- Is nuclear energy a viable solution to the world’s energy needs?
- Should the government regulate the fast food industry?
- Is social inequality a result of systemic factors or individual choices?
- Should the consumption of meat be reduced for environmental reasons?
- Is online learning more effective than traditional classroom learning?
- Should the use of drones in warfare be banned?
- Is the legalization of marijuana beneficial for society?
These topics cover a range of subjects and offer students the opportunity to engage in thought-provoking debates on relevant and impactful issues.
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO DEBATING

The Ultimate Guide to Opinion Writing for Students and Teachers

Top 5 Persuasive Writing Techniques for Students

5 Top Persuasive Writing Lesson Plans for Students and Teachers

23 Persuasive writing Topics for High School students

How to Write Perfect Persuasive Essays in 5 Simple Steps
Debating strategies for students.
Research and preparation are essential to ensure good performance in a debate. Students should spend as much time as possible drafting and redrafting their speeches to maximize their chances of winning. However, a debate is a dynamic activity, and victory cannot be assured by pre-writing alone.
Students must understand that the key to securing victory lies in also being able to think, write (often in the form of notes), and respond instantly amid the turmoil of the verbal battle. To do this, students must understand the following keys to victory.
When we think of winning a debate, we often think of blinding the enemy with the brilliance of our verbal eloquence. We think of impressing the audience and the judges alike with our outstanding oratory.
What we don’t often picture when we imagine what a debate winner looks like is a quiet figure sitting and listening intently. But being a good listener is one of our students’ most critical debating skills.
If students don’t listen to the other side, whether by researching opposing arguments or during the thrust of the actual debate, they won’t know the arguments the other side is making. Without this knowledge, they cannot effectively refute the opposition’s claims.
Read the Audience
In terms of the writing that happens before the debate takes place, this means knowing your audience.
Students should learn that how they present their arguments may change according to the demographics of the audience and/or judges to whom they will be making their speech.
An audience of retired school teachers and an audience of teen students may have very different responses to the same arguments.
This applies during the actual debate itself too. If the student making their speech reads resistance in the faces of the listeners, they should be prepared to adapt their approach accordingly in mid-speech.
Practice, Practice, Practice
The student must practice their speech before the debate. There’s no need to learn it entirely by heart. There isn’t usually an expectation to memorize a speech entirely, and doing so can lead to the speaker losing some of their spontaneity and power in their delivery. At the same time, students shouldn’t spend the whole speech bent over a sheet of paper reading word by word.
Ideally, students should familiarize themselves with the content and be prepared to deliver their speech using flashcards as prompts when necessary.
Another important element for students to focus on when practising their speech is making their body language, facial expressions, and hand gestures coherent with the verbal content of their speech. One excellent way to achieve this is for the student to practice delivering their speech in a mirror.
And Finally…
Debating is a lot of fun to teach and partake in, but it also offers students a valuable opportunity to pick up some powerful life skills.
It helps students develop a knack for distinguishing fact from opinion and an ability to assess whether a source is credible or not. It also helps to encourage them to think about the other side of the argument.
Debating helps our students understand others, even when disagreeing with them. An important skill in these challenging times, without a doubt.
Debating Teaching Strategies
Clearly Define Debate Roles and Structure when running speech and debate events: Clearly define the roles of speakers, timekeepers, moderators, and audience members. Establish a structured format with specific time limits for speeches, rebuttals, and audience participation. This ensures a well-organized and engaging debate.
- Provide Topic Selection and Preparation Time: Offer students a range of debate topics, allowing them to select a subject they are passionate about. Allocate ample time for research and preparation, encouraging students to gather evidence, develop strong arguments, and anticipate counterarguments.
- Incorporate Scaffolded Debating Skills Practice: Before the actual debate, engage students in scaffolded activities that build their debating skills. This can include small group discussions, mock debates, or persuasive writing exercises. Provide feedback and guidance to help students refine their arguments and delivery.
- Encourage Active Listening and Note-taking during speech and debate competitions: Emphasize the importance of active listening during the debate. Encourage students to take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and persuasive techniques used by speakers. This cultivates critical thinking skills and prepares them for thoughtful responses during rebuttals.
- Facilitate Post-Debate Reflection and Discussion: After the debate, facilitate a reflection session where students can share their thoughts, lessons learned, and insights gained. Encourage them to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of their arguments and engage in constructive dialogue. This promotes metacognitive skills and encourages continuous improvement.
By following these tips, teachers can create a vibrant and educational debate experience for their students. Through structured preparation, active engagement, and reflective discussions, students develop valuable literacy and critical thinking skills that extend beyond the boundaries of the debate itself.
A COMPLETE UNIT FOR TEACHING OPINION WRITING
Teach your students to write EXCELLENT PERSUASIVE ESSAYS and master INFLUENTIAL WRITING SKILLS using PROVEN TEACHING STRATEGIES with this 140-PAGE UNIT.
ALL RESOURCES AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS INCLUDED – NO PREP REQUIRED.
30+ 5-star Ratings ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Debate Writing
Debate Speech

A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing and Delivering A Debate Speech
Published on: Mar 9, 2022
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
20+ Thought Provoking Debate Examples: Including Tips
Interesting and Great Debate Topics (2024)
Learn All About Different Types of Debate - Complete Guide
10 Expert Debate Tips for Improving Your Debate Skills
Learn the Art of Debate Writing: Proven Techniques for Convincing Arguments
Share this article
Whether you are a student, a policymaker, or a business leader, the ability to debate effectively can be a game-changer.
Debate speeches are important for anyone wanting to persuade others. However, writing and delivering a debate speech isn’t easy, especially if you are new to the process.
This guide explains simple steps on how to write and deliver an excellent debate speech. It covers everything from preparing your arguments to delivering your speech with confidence and conviction.
So dive in to learn!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Debate Speech?
A debate speech is a structured argument on a specific topic that is presented in a formal setting.
The main purpose of debate speech is to:
- Express your point of view persuasively and effectively
- Convince the opposition that you are right.
- Change the peopleâs point of view on a particular topic.
In a debate speech, the speaker presents their argument in a clear, concise, and convincing manner. Debate speeches have a set time limit, and the speaker must use their time effectively to make their case and address counterarguments.
Preparing for a Debate Speech
You can only win your debate if you have spent time preparing it well. Follow the steps below to be prepared for your next debate speech.
Understanding the Debate Format
It's essential to understand the format of the debate in which you want to participate. Different debate formats have specific rules and guidelines that you need to follow to succeed.
Some popular types of debates include parliamentary, Lincoln-Douglas, and policy debates.
- Parliamentary debate is a format where two teams of two or three members argue for or against a motion. It is presided over by a moderator. In this format, debaters have limited preparation time to gather information and construct their arguments.
- Lincoln-Douglas debate is a one-on-one debate where debaters argue for their positions on a specific topic. This format usually involves a value system and a criterion that the debaters must uphold and defend.
- Policy debate is a format where two teams of two members argue for or against a specific policy proposal. This format requires in-depth research and analysis of the policy and its potential implications.
Selecting a Position
Choose a topic that you are passionate about and that you feel strongly about. Once you have chosen a topic, narrow it down to a specific aspect that you can argue for or against.
The clearer your position, the easier it will be to research and prepare your arguments.
Need some good debate topic ideas to get started? Check out our list of interesting and engaging debate topics to help you out!
Researching and Gathering Information
Once you have selected your topic, research it thoroughly. Gather as much information as you can from credible sources such as academic journals, news articles, and government reports.
Take detailed notes, and make sure to record the sources you use so that you can reference them later.
Understanding Both Sides of the Argument
To write a persuasive debate speech, it is important to understand both sides of the argument.
Consider the arguments that your opponents might make and anticipate counterarguments. This will help you to strengthen your own arguments and address potential weaknesses in your position.
Organizing Your Arguments
Once you have gathered all of the information you need, organize your arguments in a clear and logical way.
Start by outlining the main points you want to make and then add supporting evidence to each point. Make sure that your arguments flow logically and build on each other.
Practicing Your Delivery
Finally, practice your delivery. Read your speech out loud several times to get a feel for how it flows.
Time yourself to make sure that you can fit all of your arguments into the allotted time. Consider practicing in front of a friend or family member to get feedback on your delivery.

Paper due? Why Suffer? That's our job
How to Present a Debate Speech?
This type of speech requires some essential components. Here are the major components you need to present an effective debate speech.
1. Catchy Introduction
The first important step is starting the debate with a compelling introduction. You can begin with a question, a quote, or a statistic related to the topic.
Moreover, your introduction should state your stance on the topic and provides a preview of your arguments.
2. State the Problem & Define Key Terms
Define key terms in your speech that are important to your argument. This helps to ensure that your audience understands the meaning of the words you use.
3. Present Your Arguments
Present your arguments in a clear and logical order. Start with your strongest argument and provide evidence to support it. Then, move on to the weaker arguments and provide evidence for each one.
A good argument often follows the PEE structure, which means âPoint, Evidence, Explanation (PEE)â.
- Point or Reason: This is where you state your main idea or argument, providing a concise and clear statement of your position. The point should be specific, focused, and relevant to the topic at hand. It serves as the foundation for your argument
- Evidence: Here, you provide supporting evidence to bolster your argument. This can take the form of examples, statistics, or any other relevant information that helps illustrate your point.
- Explanation: In this part, you elaborate on how the evidence you provided supports your point. This is where you explain the relationship between your point and the evidence, highlighting its significance
4. Rebuttals
Address counterarguments by acknowledging the opposing viewpoints and refuting them with evidence. This is called a rebuttal.
It shows that you have considered both sides of the argument and strengthens your own position. Addressing counterarguments through rebuttals is a vital aspect of constructing a well-rounded and persuasive argument.
Rebuttals involve presenting evidence that challenges the opposing counter-arguments and weakens their validity. Additionally, it is crucial to explain the flaws or fallacies in the opposing arguments during the process of rebuttal.
5. Conclusion
End your speech with a strong conclusion that summarizes your arguments and restates your stance on the topic. You can also end with a call to action, encouraging your audience to take action based on your argument.
Tips for Presenting a Debate Speech Effectively
The above steps will help you prepare and present an acceptable speech, but you can improve it even more with the tips below.
- Use Clear and Concise Language
Speak clearly and use language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or complex words that might confuse your audience.
- Emphasize Key Points
Highlight the key points of your argument by using vocal inflection and tone. Emphasize important words or phrases to help your audience remember your key arguments.
- Use Body Language and Gestures
Body language and gestures can help to reinforce your arguments and make your speech more engaging. Use hand gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your posture and movement to keep your audience interested.
- Maintain Eye Contact
Maintain eye contact with your audience throughout your speech. This will help to establish a connection with them and make them feel more engaged with your argument.
- Use Vocal Variety and Tone
Vary your vocal tone and pace to add interest and emphasis to your speech. Use pauses and changes in pace to emphasize important points, and vary your volume to make your arguments more impactful.
- Use the Debate Speech Checklist
Here is a checklist that can help you evaluate your debate.
- Does your speech cover your opinion about the topic?
- Does your speech start with a catchy hook?
- Does your speech cover all the main points?
- Does your speech provide sufficient counterarguments?
- Does your speech contain enough evidence?
- Does your speech provide a call to action to the conclusion?
Debate Speech Examples
Here are some examples to help you prepare and present your debate speech better.
Debate Speech Structure
Debate Speech Template
Debate Speech Sample
Writing and delivering a successful debate speech requires careful planning, research, and effective communication skills.
By following the steps and tips provided above, you can persuade your audience effectively and make a lasting impact. Remember to practice, rehearse, and be confident in your abilities.
Still need expert help in writing your speech? Weâve got you covered!
CollegeEssay.org is here to assist you. We are an expert speech writing service with a team of experienced professionals.
Our AI essay writing tools can help you at every step of the speech-writing process, from selecting a topic to gathering evidence.
We provide customized, high-quality writing services at an affordable price. You can also take advantage from our AI essay writer tool to improve your writing skills.
So why wait? Contact our professional essay writing service and impress your audience with an amazing speech!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 types of debate.
The four main types of debate are:
- Parliamentary Debate
- Lincoln-Douglas Debate
- Cross-Examination Debate
- Academic Debate
What are the 2 sides of a debate called?
The opposition and proposition are the two sides of a debate.
Caleb S. (Literature, Marketing)
Caleb S. has extensive experience in writing and holds a Masters from Oxford University. He takes great satisfaction in helping students exceed their academic goals. Caleb always puts the needs of his clients first and is dedicated to providing quality service.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

How to Write a Debate Speech in English | Format, and Examples
Every student has to write a debate at some point in school, college, or university and if you don’t know about the methods and steps to write a debate speech, you won’t write an effective debate speech to increase your chance of success. Following a proper structure and format in debate writing is essential for a good debate to convenience the audience. There are some tips and methods to write an effective debate speech and by setting a tone and correct words choice and sentences, you can grab the judge’s and the audience’s attention. So, are you searching for pro tips on how to write a debate speech in English? Let’s dive into this article and get complete knowledge about debate writing.
Before diving into the steps of debate writing, it’s necessary to understand debate speech definition and debate speech format.
Debate Speech Definition
A debate speech is a formal discussion on a specific topic between two opposing sides or groups. One side discusses in a favor of the given topic or title, while the other side speaks against it or disagrees with the first side. The main purpose of a debate speech is to convince the judges and audience that your opinion is right. In debate speech, you need to express your views in a specific format and make your opponents impress by good debate writing skills.
Debate Speech Format
You can follow the following pattern for a debate speech.
Opening Statements and Explanation
This section consists of the opening sentences by using three arguments with explaining questions.
- Pro Tema – Up to 5 minutes
- Con Team – Up to 2 minutes
- Con Team – Up to 5 minutes
- Pro Team – Up to 2 minutes
Rebuttals (No new Arguments Here)
In this section, the debaters repeat the deponent arguments and evaluate what is wrong with his/her position.
- Pro Team – Up to 3 minutes
- Con Team – Up to 3 minutes
Debate Summary
In the summary, debates summarize their positions after detailed arguments and discussions with the opponents. In addition, the debaters also say why their position is the best.
Finally, each group will be assumed to answer the questions up to 20 minutes long session. For instance, you can look at the following debate speech template to get an idea of the debate speech structure.
Debate Speech Format PDF
How to Write a Debate (6 Steps)
Structuring and writing your debate correctly will increase your chance of success. By following the 6 easy steps below will help you win the debate competition. Without further ado let’s dive into the following steps.
- Begin With a Strong Opening Lines
- Define the Topic
- Signposting
Step #1: Begin With a Strong Opening Lines
Every good speech and discussion starts with a strong sentence. Remember the first impression is the last impression, hence start your debate with a strong opening line that can help you impress the audience and the judge immediately. For example, you can start your debate by asking an open-ended question, tell a story, state an amazing fact or say a powerful quotation.
Step #2: Define the Topic
When you started your debate with a strong sentence and catch the audience’s attention, in the next step you need to make the subject clear to your listeners. You need to state the topic and your group’s position on the topic to help the audience comprehend the side you are going to argue about.
For Example:
“Ladies and gentlemen, today I would like to talk to you about the education system. The education system that we have followed in our country has been reformed many times. Computer literacy at the age of 13 can help in the child’s future studies. Here, I will argue that the problem is the pandemic, besides being stressful, are indecisive in assessing student learning.”
Step #3: Signposting
Signposting may seem irritating and avoidable. If you are word-addict it can even seem like it’s confusing the flow of your otherwise clear and lyrical speech. However, it’s totally important in the format of a good debate speech. You might think that you write a good debate speech, but remember the audience isn’t you to judge. They don’t how much idea about the topic as you have and they might get bored for a few moments in your introduction and then get completely lost. This is why signposting is necessary for debate.
This is a good way to remind your audience of what you are discussing and where you are up to in your speech. Hence, after your introduction add a few points that tell the audience that how many points you are going to deliver and in what order you are delivering them.
Also Read : Essential Transition Words and Phrases for Writing
Step #4: Rebuttal
Have you heard that sometimes the best offense is a good defense? In a professional debate, the most compelling part is usually when one side takes one of the arguments of the opponent and then cuts it to pieces. Indeed, it’s the most difficult part of any debate speech to finish correctly. In a debate speech Rebutting arguments forces you to think thoroughly on the spot. You have a little time like 30 to 40 seconds to take arguments that your opponent has spent a lot of time researching and edging and convincingly oppose it.
There are some approaches that you can use while rebutting in a debate speech and make the challenge a little less dismay. These include the following:
- Pre-research thoroughly
- What’s the point
- Economic Challanges
- Say your own arguments
Step #5: Arguments
The argument is the most significant part of a debate speech. To make it clear for you, we have divided this down into four simple subtopics.
1. Decide what to argue:
If you have researched the topics and have good information, then a lot of arguments will come to your mind. It always requires good research to come up with talking points. Consider the issue. You can research online, read books and novels for good ideas. When you have good knowledge of the topic then the right arguments will come to your mind no matter how strong your position is.
2. The Layout :
Writing an argument is the same as writing a body paragraph for an essay. You can start each argument by signposting for instance, “Initially, I want to argue….” and then follow up with a sentence shortly. After this, you need to talk in detail about the topic by giving some facts and statics to constitute what you are saying, and then at the end link neatly back to the title of the debate to make clear to the audience that you are not only giving a passionate rant but instead making a carefully calculated point that related in with a general thesis statement.
3. Find Evidence:
Embedding the right evidence into your debate speech makes you more conceivable, but using the wrong and irrelevant evidence from a wrong source leaves you vulnerable to be attacked by the opposition. Hence, it’s necessary to search beforehand and find the right evidence.
4. Persuasive Strategies:
Remember you can be as persuasive and colorful in debate as you write a persuasive piece. Don’t use harsh words or insult your opponents and don’t use the sense of humor where it’s not important, but other than the obvious limitation you can use as many persuasive strategies as you can.
Step #6: How to Conclude
The conclusion is the result of your writing and is one of the most important parts of a debate speech. It should sum the points you have written in the whole parts of your writing, and by delivering the conclusion of your debate the listeners or readers should feel as if they have gained the result of whatever you have written in the body.
Writing a conclusion for a debate speech is the same as writing a conclusion for an essay. In the link below you can read more about how to conclude a debate.
- How to Write the Best Concluding Paragraph
Debate Speech Sample in English
Download PDF
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Scripts for 6th december finland independence day, the 5 best ways to understand what you hear in english, how to get tax benefits on a personal loan for education, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Debate Writing
Debate Writing - A Comprehensive Writing Guide
14 min read

People also read
Interesting Debate Topics and Ideas for Students
Debate Speech - Ultimate Writing Guide for Students
Types of Debate - A Complete Overview & Examples
Free Debate Examples for All Academic Levels
Best Debate Tips for Students
Advanced Debating Techniques for Students
Have you ever found yourself at a loss for words when it comes to articulating your thoughts in a debate?
The inability to formulate your thoughts in a debate can be a significant obstacle, hindering your ability to express yourself effectively. But don’t worry!
If you’re someone who’s wandering around trying to find the secrets to craft an outstanding debate speech, we’ve got your back.
In this blog, we’ll introduce you to debate writing, types, format, some tips, and debate examples, so you can understand how to pen down the perfect debate.
Let’s get going!
- 1. What is Debate Writing?
- 2. Types of Debate
- 3. Debate Writing Format
- 4. How to Write a Debate?
- 5. How to End the Debate?
- 6. Debate Writing Tips and Tricks
- 7. Advanced Techniques for Debate Writing
- 8. Debate Writing Examples
- 9. Debate Writing Topics for Students
What is Debate Writing?
A debate is a formal contest of argumentation where two opposing teams defend and attack a given resolution. Similarly, it is also a persuasive manner of speaking to convert one’s opinion into your viewpoint.
Here, the speaker either speaks for or against a particular topic being discussed. Moreover, it is the process of preparing and writing the debate before its formal presentation.
Features of Debate Writing
The following are the main features of debate writing.
- Informative - A good debate must provide complete information and facts. It is supposed to inform and educate people with the help of logical reasoning.
- Well-reasoned - The arguments discussed in a debate must be logical, relevant, competent, and well-explained.
- Persuasive - A debate must emphasize strong arguments to convince the people.
- Orderly - A debate must present the facts in a structured and organized form. It should also follow a specific format.
- Dynamic - In a debate, two teams present opposing arguments. Similarly, all the important points must be questioned and answered by each team member.
Types of Debate
The following is a detailed description of common debating types that are practiced on various occasions.
- Team Policy Debate - It consists of two teams, each with two debaters. The main aim is to present a huge amount of data coherently.
- Cross-examination Debate - It is considered a period between speeches. Here, the opponents ask each other to clarify and understand the points based on evidence.
- Lincoln-Douglas Debate - It is a one-on-one and an open-style debate. Here, the debaters focus on arguing for or against a topic persuasively and logically.
- Spontaneous Argumentation - Includes two teams that argue on a specific idea, but it does not require much research work. Similarly, this debate focuses more on presentation than content.
- Public Forum Debate - It includes arguments on controversial topics. Moreover, these are used to test the argumentation, cross-examination, and refutation skills of the debaters.
- Parliamentary Debate - It consists of two teams, one called the government and the other called the opposition team. The Government team proposes a motion, and the Opposition team argues against it.
If you want to learn more about the different debating types, head to over comprehensive blog on types of debates.
Debate Writing Format
The debate writing for middle or high school follows the same format structure. Here, we have mentioned a detailed format for you to get an idea of the parts of a debate.
Check out the given debate writing template to get help with structuring your debate.
Debate Writing Template

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Start a Debate?
When starting the debate writing process, the question “ How to write a debate introduction?… ” could come off as a daunting one, but don’t worry.
Here are some easy steps for you to write a compelling debate introduction.

1. Impressive greeting and strong opening sentence:
Greet your audience with enthusiasm, capturing their attention with a compelling opening statement that sets the tone for your debate.
2. Tell a personal story:
Connect emotionally by sharing a relevant personal anecdote that humanizes the topic, making it relatable and engaging.
3. State an amazing Fact:
Introduce a surprising or impressive fact related to your debate topic to pique interest and establish credibility.
4. Use a powerful quotation:
Incorporate a thought-provoking quote that aligns with your argument, adding depth and authority to your speech.
5. Ask a rhetorical question:
Pose a rhetorical question to stimulate critical thinking among your audience, encouraging them to ponder the issue at hand.
6. State a problem:
Clearly articulate the problem or challenge associated with your debate topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
7. Share your opinion about the topic:
Express your stance on the matter, providing a concise preview of your argument and setting the stage for the forthcoming points in your debate speech.
How to Write a Debate?
Following are the steps you can stick to for writing a debate speech that lets you stand out from the competition:
1. Understand the Debate
The first of many steps in debate writing is understanding its nature. Here, both teams will be given a topic, and they will choose an affirmative or negative stance.
2. Research the Topic Thoroughly
Brainstorm and research the topic thoroughly to understand all the aspects of the debate. Make a list of critical points and use credible sources to cover them in your key arguments.
3. Develop a Debate Outline
Develop a basic debate speech outline that consists of three main sections. It includes an introduction, body, and conclusion that are discussed below in detail.
It is the first section of the outline that includes an attention grabber. Introduce your topic and present the context with the help of a thesis statement . Also, provide a brief overview of the students’ arguments to understand the direction of the debate.
It is the main section of the debate that discusses the key arguments in detail. Moreover, it further includes logical reasoning and evidence to support the thesis.
The conclusion is the last chance to demonstrate significant ideas. It summarizes the main body by adding emotion and drama to the words and includes a strong closing sentence.
4. Writing the Debate
Start writing the final draft of your debate. Mention the crucial elements of persuasion, which are ethos, pathos, and logos. These are used to explain the effects of the resolution in the real world.
Also, use transition words to maintain a logical flow between paragraphs. Lastly, edit and proofread your work to avoid plagiarism, grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
Here is a great example of a well-written debate introduction:
If you’re thinking, “ How to write a debate greeting? ”, take a thorough look at the detailed steps below:
If you have the question, “ How to write a debate against the motion? ” in mind, look at this step-by-step procedure below:
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to End the Debate?
End the debate by making sure that you have included the following elements. It will help you assess the credibility of your debate.
- Does your debate start with an interesting greeting?
- Does it provide original content, personal experience, and a call to action?
- Does the debate follow a proper format structure?
- Does it include the correct sentence structure?
- Does it maintain logical transitions to flow ideas from one paragraph to another?
- Have you proofread or revised it for common mistakes such as spelling, grammar, and punctuation?
- Does the debate mention your opinion about the given topic?
- Does the debate end with a powerful conclusion sentence to leave a lasting impact on the audience?
Debate Writing Tips and Tricks
Here are some amazing debate tips and tricks for you to write a perfect debate:
- It is better to know and prepare for a debate before starting it
- Conduct thorough research work to collect relevant data and draft creative arguments about the topic
- A writer should think relatively to identify the validity of significant claims
- Try to understand the formal debate through a variety of personal experiences
- Support the arguments with examples and evidence to make them more credible and authentic
- Also, consider the perspective of the judges and audience while making a critical argument
- Always structure your speech while keeping the time limits in mind
- Do not always disagree with the opponent’s arguments. Instead, you should take notes and think logically
- Build your case by keeping in mind all the possible objections that others can raise
- Never make the mistake of introducing new arguments in your closing section
Advanced Techniques for Debate Writing
Below are some easy debating techniques to write a primary and high school debate.
- Introduce the topic at the beginning of the debate and form an opinion about it.
- Know your audience to adjust your argument according to them.
- Assign the two sides as affirmatives and negatives.
- Take enough time to research the case and the vocabulary used for it.
- Organize your opinion and present supporting facts to persuade the audience.
- Follow a basic debate structure that includes the following period.
- Get an idea about the opponent’s arguments and advance your research by weakening them.
- Make a judgment based on the audience’s votes and your opinion about the arguments.
- Connect to the audience emotionally by presenting examples, evidence, and personal experiences.
- Incorporate simple, well-timed humor to engage and emphasize your argument effectively
Debate Writing Examples
Check out the following examples of debate writing to get a better idea of the concept.
Debate Example for Ks2
Debate Writing Class 6
Debate Writing Class 7
Debate Writing Class 8
Debate Writing Class 9
Debate Writing Class 11 PDF
Debate Writing Class 12
Debate Writing Example on Online Classes
If you want inspiration from more examples on various debate topics, visit our comprehensive debate examples blog!
Debate Writing Topics for Students
The following are some impressive debate writing prompts for students to get started.
- All schools should conduct compulsory drug testing on their students
- Middle and high schools must ban sex education
- Is it ethical to move in before getting married?
- Academic institutes should ban smoking on college premises
- Peer pressure is harmful to students
- High schools should provide daycare services to students who have children
- The government should develop nuclear energy for commercial use
- Celebrities can get away with crime more easily than non-celebrities
- Cell phones should not be used in classrooms
- Money motivates people more than any other factor in the workplace
Head over to our list of debate topics to choose from a wide range of unique debate writing ideas.
To sum it up, This comprehensive guide to debate writing will help you write a perfect one for your high school or college. We’ve covered all the essential details one would need to craft a winning debate.
However, if you think that you could use a helping hand to perfect your debate writing game, we’ve got you covered.
You can get help from our speech writing service to solve your debate writing worries. Our writing experts will deliver you comprehensive and well-composed debates at rates that won’t break the bank.
Simply reach out to our reliable essay writing service , and we’ll take care of all your writing-related problems.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Reading Groups: Everything You Need to Know
Product review of the ultenic p30 grooming kit, reading anxiety in children: everything you need to know, iep meetings and parent-teacher conferences: everything you need to know, college disability services and accommodations: everything you need to know, spam vs. phishing: how are these unwanted messages different, how to charge your iphone properly, encouraging your teenager to read: everything you need to know, 8 ways to service an air conditioner, 3 ways to stop a baby from vomiting, how to write a debate speech: 10 steps.

A well-crafted debate speech can effectively persuade an audience and make a lasting impact. By following these ten steps, you’ll be on your way to creating a powerful and engaging debate speech.
1. Understand the topic: Begin by thoroughly researching the topic of debate. Understand various viewpoints, facts, and statistics to develop a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Familiarize yourself with common arguments for and against the issue.
2. Analyze your audience: Before crafting your speech, spend some time considering who your audience is. What do they already know about the issue? What are their concerns, values, or interests? Tailor your speech to resonate with them.
3. Define your position : Clearly state your stance on the issue at hand. Your position should be strong, specific, and concise – bold statements will keep your audience engaged in the debate.
4. Develop your main arguments: Identify 2-3 compelling arguments supporting your position. These should form the backbone of your debate speech. Be sure to provide evidence, examples, or anecdotes that support each argument.
5. Prepare counterarguments: Anticipate objections from opponents and address these in your speech. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and providing a persuasive rebuttal, you’ll strengthen your overall argument.
6. Organize your speech: Structure is crucial in presenting an effective debate speech. Begin with a captivating introduction that grabs the attention of the audience, followed by a clear thesis statement outlining your key points. Present each argument (along with its evidence) as separate supporting points before addressing counterarguments.
7. Maintain logic and consistency: Ensure that all elements of your speech are logically connected and coherently presented throughout. Avoid contradicting yourself or presenting irrelevant information.
8. Use persuasive language techniques: Employ rhetorical devices like metaphors, analogies, or hyperbole to enhance the impact of your arguments. Encourage emotional responses from your audience by appealing to values, beliefs, or fears.
9. Write an engaging conclusion: Wrap up your speech by summarizing your main arguments and highlighting their significance. End on a strong note that encourages action or emphasizes the importance of the issue.
10. Practice, practice, practice: Finally, rehearse your speech multiple times to perfect your delivery. This will not only boost your confidence but also help you identify any errors or areas of the speech that need improvement.
By following these ten steps, you’ll be well on your way to writing a persuasive and memorable debate speech that effectively communicates your position and leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
How to Make a Compass: 8 Steps
4 ways to read and speak like ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

How to Make Olive Juice: 15 Steps
How to Boot from an External Hard Drive

3 Ways to Google a Person

How to Trap Rats

How to Be a Good Citizen
How to Braid Garlic: 14 Steps
The Most Powerful Debate Speech Strategy And Topic Ideas
Hrideep barot.
- Speech Topics

Welcome to the exciting world of debate speech and topics! Forget the fancy jargon; let’s talk about how debates aren’t just about winning arguments. Picture it as a journey where we explore ideas and connect. We’re not just tossing words around; we’re diving into the core of what makes us tick.
Think of debates as more than just convincing speeches. They’re like a doorway to understanding and connecting with people. It all begins with a strong start – our introduction. It’s not just about capturing attention; it’s about inviting everyone into a space where ideas clash and minds expand.
In this space, words aren’t just tools; they’re the architects of who we are becoming. Our journey is more than winning debates; it’s about developing critical thinking, becoming great communicators, and understanding each other better. So, let’s kick off this adventure together, where the magic of debate isn’t just in the words we say but in how they shape us along the way.
11 Greatest Debate Topics Of All Time.
- How To Write a Debate Speech?
Ways In which Debate Helps Shape Overall Personality.
10 powerful debate strategies which can never go wrong. .
- Conclusion.
1. The Existence of a Higher Power: God vs. Atheism
Theological Arguments: Explore philosophical and theological arguments for the existence of God, such as the cosmological, teleological, and moral arguments.
Scientific Perspectives: Consider scientific perspectives that challenge traditional religious beliefs, including evolutionary theory and the Big Bang theory.
Personal Beliefs: Discuss the role of personal experiences and beliefs in shaping one’s stance on the existence of a higher power.
2. Freedom of Speech vs. Hate Speech Laws
Importance of Free Expression: Discuss the fundamental value of free expression in a democratic society and its role in fostering diversity of thought.
Harm Principle: Explore the harm principle as a criterion for limiting speech and the ethical considerations in regulating hate speech.
Balancing Rights: Consider the challenges in striking a balance between protecting individual rights and preventing harm to marginalized communities.
3. Legalization of Recreational Drugs: Pros and Cons
Individual Liberty: Discuss the argument for individual liberty, asserting that adults should have the autonomy to make choices about their bodies.
Public Health Concerns: Explore the potential negative impacts of drug legalization on public health and societal well-being.
Economic Implications: Consider the economic implications, including potential tax revenue and job creation, associated with the legalization of recreational drugs.
4. Climate Change: Human-Made vs. Natural Causes
Scientific Consensus: Examine the overwhelming scientific consensus supporting the idea that human activities contribute significantly to climate change.
Skeptic Perspectives: Discuss skeptical views that challenge the extent of human impact on climate change, considering natural climate variations.
Policy Implications: Explore the policy implications of different perspectives, including the urgency for mitigation and adaptation measures.
5. Capital Punishment: Morality and Deterrence
Retribution and Justice: Discuss the concept of retribution and whether capital punishment serves as a just response to heinous crimes.
Deterrence Effect: Examine the debate over the deterrent effect of capital punishment on potential criminals.
Risk of Wrongful Execution: Consider the ethical implications of the potential for wrongful executions and the irreversible nature of the death penalty.
6. Immigration Policies: Open Borders vs. Strict Control
Economic Contributions: Discuss the economic benefits of immigration, including contributions to the labor force and entrepreneurship.
National Security Concerns: Explore concerns related to national security, public resources, and the potential strain on social services.
Humanitarian Considerations: Consider the moral and humanitarian aspects of providing refuge to those fleeing violence or seeking a better life.
7. Assisted Suicide: Right to Die vs. Sanctity of Life
Autonomy and Dignity: Discuss the principle of autonomy and an individual’s right to make decisions about their own life, including the choice of assisted suicide.
Ethical and Religious Perspectives: Examine ethical and religious perspectives that emphasize the sanctity of life and the moral implications of assisted suicide.
Legal Implications: Consider the legal frameworks and ethical guidelines surrounding assisted suicide in different jurisdictions.
8. Privacy in the Digital Age: Security vs. Individual Rights
Surveillance Technologies: Explore the capabilities and implications of modern surveillance technologies, including mass data collection and facial recognition.
National Security Justifications: Discuss arguments that support increased surveillance for national security purposes, especially in the context of preventing terrorism.
Individual Privacy Concerns: Examine concerns related to the erosion of individual privacy rights, data breaches, and the potential for abuse of surveillance powers.
9. Universal Basic Income: Reducing Inequality vs. Economic Sustainability
Poverty Alleviation: Discuss the potential of a universal basic income (UBI) to alleviate poverty and provide financial stability to all citizens.
Economic Viability: Explore concerns about the economic feasibility and sustainability of implementing UBI, including potential impacts on workforce participation.
Social and Economic Equity: Consider how UBI might address systemic inequalities and contribute to a more equitable distribution of resources.
10. Censorship in the Arts: Protecting Morality vs. Freedom of Expression
Artistic Freedom: Discuss the importance of artistic freedom as a form of expression and creativity.
Moral and Cultural Sensitivities: Explore the need for censorship to protect societal values, moral standards, and cultural sensitivities.
Role of Cultural Context: Consider how cultural context and shifting societal norms influence the boundaries of artistic expression.
11. Animal Testing: Scientific Advancement vs. Animal Rights
Scientific Progress: Discuss the contributions of animal testing to scientific and medical advancements, including the development of new treatments and pharmaceuticals.
Ethical Treatment of Animals: Examine the ethical considerations surrounding the use of animals in research, focusing on animal rights, welfare, and alternatives to testing.
Balancing Interests: Explore the challenge of balancing scientific progress with the ethical treatment of animals, seeking common ground that respects both human and animal interests.
These elaborations provide a more in-depth understanding of each controversial debate topic, touching on various perspectives, considerations, and implications associated with each issue. Each topic reflects a complex interplay of values, ethics, and practical considerations that make them enduring subjects of discussion and debate.
How To Write A Debate Speech ?
Introduction: grabbing attention.
Begin your debate speech with a captivating introduction to immediately capture the audience’s interest. Consider using a powerful quote, a relevant anecdote, or a surprising fact related to your topic. The goal is to create an immediate connection with your listeners and set the stage for the discussion that follows. Make it clear why the topic is important and worthy of their attention. You might also include a brief overview of the main points you will cover to provide a roadmap for your audience.
Thesis Statement: Clearly State Your Position
Craft a concise and compelling thesis statement that communicates your stance on the topic. This statement should serve as the central point around which your entire speech revolves. Take the opportunity to highlight the significance of your position and why it is the most rational or ethical perspective. Additionally, consider briefly acknowledging the existence of opposing views to demonstrate your awareness of the complexity of the issue.
Main Arguments: Develop Strong Points
For each main argument, delve into detailed explanations supported by robust evidence. This evidence could include relevant research findings, real-life examples, or historical precedents. Be sure to explain the logical connections between your points and the overall thesis. Use persuasive language to underscore the importance of each argument, making it clear why the audience should find your perspective compelling.
Addressing Counter Arguments: Anticipate and Refute
Demonstrate a thorough understanding of the opposing viewpoint by anticipating counterarguments. Acknowledge these counterarguments respectfully before providing well-reasoned and persuasive refutations. This not only strengthens your position but also shows intellectual honesty and a willingness to engage with diverse perspectives. Use facts, logic, and reasoning to effectively dismantle counterarguments, leaving your audience with a sense of the robustness of your position.
Emphasize Impact: Appeal to Emotions and Values
While presenting your arguments, strategically incorporate emotional appeals to resonate with your audience. Share relatable stories, connect your points to shared values, and use language that evokes an emotional response. This not only adds depth to your speech but also helps create a memorable and impactful impression. A balance between logic and emotion can make your arguments more persuasive and relatable.
Use Persuasive Language: Enhance Convincing Power
Employ a variety of rhetorical devices and persuasive language techniques to enhance the power of your speech. Metaphors, analogies, and vivid language can make complex ideas more accessible and memorable. Consider using repetition to emphasize key points and create a rhythmic flow in your speech. Aim for clarity and precision in your language to ensure that your audience easily grasps the nuances of your arguments.
Maintain Clarity and Organization: Structured Delivery
Organize your speech in a clear and logical structure to facilitate easy comprehension. Begin with a strong introduction, followed by a clear progression of main points. Use transitions between ideas to maintain coherence and guide your audience through the flow of your arguments. A well-structured speech not only aids understanding but also enhances the overall impact of your message.
Engage the Audience: Foster Connection
Encourage active engagement by incorporating rhetorical questions, interactive elements, or moments of audience participation. Foster a sense of connection by speaking directly to the concerns and interests of your listeners. Consider using relatable examples of anecdotes that resonate with the experiences of your audience. Engaging your listeners in this way can create a more dynamic and memorable speech.
Conclusion: Reinforce Your Message
In your conclusion, re-emphasize the key points of your speech and restate your thesis with conviction. Summarize the main arguments in a way that reinforces your overall message. Conclude with a powerful and memorable statement that leaves a lasting impression on your audience. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion; instead, focus on leaving a strong and final impact that reinforces the significance of your position.
Q&A Preparation: Be Ready for Questions
Anticipate potential questions that may arise from your audience and prepare thoughtful and well-reasoned responses. Demonstrating a thorough understanding of your topic and the ability to address inquiries with confidence adds credibility to your overall presentation. Consider practicing responses to common questions to refine your ability to articulate your position effectively. During the Q&A session, maintain composure and be open to constructive dialogue, further showcasing your expertise and conviction.
Remember, the key to a successful debate speech lies not only in the strength of your arguments but also in your ability to connect with and persuade your audience. Regular practice, feedback, and a genuine passion for your topic will contribute to a compelling and influential presentation.
Check this out to learn about public speaking and debate differences.
Critical Thinking Skills:
Engaging in debates cultivates critical thinking by training individuals to analyze information rigorously. Debaters learn to identify key arguments, evaluate evidence, and discern logical connections. This process enhances their ability to approach complex issues with a discerning and analytical mindset.
Effective Communication:
Debate serves as a powerful platform for honing effective communication skills. Participants develop the art of articulation, mastering the ability to express ideas clearly and persuasively. Regular exposure to public speaking opportunities not only boosts confidence but also refines the delivery of compelling messages.
Check this out to learn how to deliver a memorable speech:
Research and Information Retrieval:
Debates foster strong research skills as individuals delve into diverse topics, evaluate sources, and synthesize information effectively. This process not only enhances information literacy but also teaches valuable skills in data analysis and interpretation.
Empathy and Understanding:
The nature of debates, where participants engage with a variety of viewpoints, promotes empathy and a deeper understanding of different perspectives. Exposure to diverse opinions encourages individuals to appreciate cultural nuances and fosters a more inclusive worldview.
Conflict Resolution Skills:
Debates contribute to the development of conflict resolution skills by emphasizing constructive dialogue and negotiation. Participants learn to navigate differences of opinion, seek common ground, and work towards resolutions collaboratively.
Leadership Qualities:
Active participation in debates fosters leadership qualities such as confidence and initiative. Debaters often take charge of researching, organizing arguments, and leading team efforts, contributing to the development of effective leadership skills.
Time Management:
The time constraints inherent in debates teach individuals to prioritize information effectively. Participants learn to cover multiple points within a structured timeframe, enhancing their ability to manage time efficiently.
Check this out to learn how to ace a 2-minute speech:
Teamwork and Collaboration:
Debating frequently occurs in team settings, fostering teamwork and collaboration. Participants develop skills in effective communication within teams, resolving conflicts, and achieving collective goals.
Debate, as a structured and disciplined form of discourse, provides a platform for personal growth and the development of a well-rounded personality. It not only enhances cognitive and communication skills but also nurtures qualities such as empathy, adaptability, and ethical decision-making, contributing to the holistic development of individuals.
1. Solid Research And Preparation: The Foundation Of Success
In-Depth Understanding: Devote time to thoroughly understand the nuances of your chosen topic. Conduct extensive research to be well-informed on various aspects of the issue.
Counterargument Anticipation: Anticipate potential counterarguments that opponents might present. This allows you to proactively address opposing views and strengthen your position.
Factual Support: Arm yourself with concrete evidence, facts, and statistics. This not only bolsters your credibility but also adds weight to your arguments.
2. Clear And Concise Communication: Precision Matters
Clarity of Expression: Express your ideas in a straightforward and easy-to-understand manner. Avoid unnecessary complexity that might confuse the audience and dilute your message.
Key Message Emphasis: Emphasize key points with precision. Clearly articulate your thesis and ensure that each supporting argument aligns with and reinforces your central message.
Memorable Language: Use language that is both concise and memorable. Craft statements that leave a lasting impression, making it easier for the audience to recall your key arguments.
3. Active Listening: Addressing Counterarguments Effectively
Attentiveness: Actively listen to your opponents during the debate. Paying close attention allows you to respond effectively and demonstrate respect for differing viewpoints.
Acknowledgment of Valid Points: Acknowledge valid points made by the opposition. This not only showcases your fairness but also allows you to engage in a more constructive and nuanced debate.
Strategic Response: Respond thoughtfully to counterarguments. Be prepared to address opposing views with well-reasoned and compelling rebuttals.
4. Adaptability: Flexibility In The Face Of Challenges
Responsive Approach: Be prepared to adapt your strategy based on the flow of the debate. Flexibility allows you to navigate unexpected turns and respond effectively to evolving circumstances.
Open-Mindedness: Demonstrate an open-minded approach to new information. If presented with compelling evidence, be willing to adjust your stance accordingly.
Strategic Agility: Develop the ability to think on your feet and adjust your arguments and responses as the debate unfolds.
5. Emotional Intelligence: Connecting With Your Audience
Understanding Audience Emotions: Consider the emotions and values of your audience. Tailor your arguments to resonate with the experiences and concerns of the people you are addressing.
Emotional Appeals: Incorporate emotional appeals strategically. Connecting with the audience on an emotional level makes your arguments more relatable and persuasive.
Empathy in Communication: Use empathy to establish a genuine connection. Demonstrate an understanding of the perspectives and emotions of your audience.
6. Confidence And Body Language: Projecting Authority
Confident Posture: Maintain a confident and upright posture throughout the debate. Projecting confidence through body language contributes to your perceived authority.
Eye Contact: Make deliberate and consistent eye contact with the audience and opponents. This not only conveys confidence but also fosters a sense of connection.
Vocal Presence: Ensure a strong and clear vocal presence. Speak with conviction and avoid vocal patterns that may suggest uncertainty.
7. Strategic Use of Time: Maximize Impact
Time Allocation: Strategically allocate your time to cover all key points without rushing. Prioritize high-impact arguments and allocate sufficient time for their presentation.
Strategic Pauses: Use strategic pauses for emphasis. Pauses allow the audience to absorb your points and can add weight to your arguments.
Time Management Skills: Develop effective time management skills to ensure that your speech is well-paced and impactful.
8. Consistency in Messaging: Reinforce Your Core Points
Unified Message: Maintain consistency in your messaging throughout the debate. Reinforce your core arguments and thesis to create a cohesive and unified presentation.
Avoiding Contradictions: Be vigilant about avoiding contradictions in your arguments. Inconsistencies can weaken your overall position and undermine your credibility.
Repetition for Emphasis: Repetition can be used strategically to emphasize key points and ensure that your central message is reinforced.
9. Engage the Audience: Foster Connection and Interest
Relatable Examples: Connect with the audience by using relatable examples and anecdotes. Grounding your arguments in real-life situations makes your message more accessible.
Interactive Elements: Encourage audience engagement through rhetorical questions or interactive elements. Active participation fosters a sense of involvement and interest.
Addressing Audience Concerns: Speak directly to the concerns and interests of your audience. Tailor your arguments to resonate with the experiences and values of those you are addressing.
10. Grace Under Pressure: Navigate Challenges with Composure
Calm Demeanor: Remain calm and composed, especially when faced with challenging questions or counterarguments. A composed demeanor enhances your perceived competence and confidence.
Professionalism: Handle pressure with grace and professionalism. Maintain focus on the substance of your arguments rather than getting derailed by external pressures.
Effective Problem-Solving: Develop effective problem-solving skills to address unexpected challenges. Navigating pressure with composure demonstrates resilience and adaptability.
By incorporating these elaborated strategies into your debating approach, you can enhance your effectiveness, build credibility, and leave a lasting impression on your audience. Continuous practice and refinement will contribute to your growth as a skilled and persuasive debater.
In summary, the world of debate is a transformative journey that extends beyond the exchange of arguments. Crafting a debate speech is more than an exercise in persuasion; it’s an opportunity to refine our ability to connect with others. Exploring profound topics in debates prompts introspection and broadens our understanding of the world.
Powerful debate strategies go beyond winning; they teach us adaptability and the importance of emotional intelligence. It’s not just about presenting arguments; it’s about becoming individuals who can navigate life’s challenges with resilience and grace. Debate shapes our personality in multifaceted ways. It cultivates critical thinking, enhances communication skills, and instills empathy. Engaging with diverse perspectives fosters a more nuanced worldview, contributing to a well-rounded personality.
In essence, the debate is a dynamic and evolving process that leaves an unerasable mark on our character. It’s a journey that molds us into individuals capable of not only articulating ideas persuasively but also of connecting with others on a deeper level. Through debate, we become architects of our growth, equipped with the skills and perspectives needed to thrive in the ever-changing landscape of life.
Dive into this captivating resource! Uncover secrets, gain insights, and embark on a knowledge-packed journey. Your gateway to discovery awaits!
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

10 Hand Gestures That Will Make You More Confident and Efficient

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Complete Guide to Debating: How to Improve your Debating Skills
August 1, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
Debating can look intimidating from the sidelines, with speakers appearing confident, passionate and unwavering, but it consists of skills that anybody can learn. Debating may not be something that you encounter in your everyday work but these skills can be incredibly valuable. In this article we provide a guide to the basics of debating.
What is debating?
A debate is a structured contest over an issue or policy. There are two sides – one supporting, one opposing.
Benefits of debating include:
- Allowing you to think about aspects and perspectives you may not have considered.
- Encourages you to speak strategically.
- Improving public speaking skills .
- Learning how to create a persuasive argument.
- When you have to argue against your personal view you realise that there are two sides to the argument.
Debating examples
The U.K. Prime Minister, Theresa May, answers questions:
This example video shows Theresa May answering questions from MPs in the House of Commons. Notice her strong debating skills and how she answers difficult questions under pressure.
Watch the full video here: Prime Minister’s Questions: 16 May 2018
Debate structure
There are multiple formats a debate can follow, this is a basic debate structure:
- A topic is chosen for each debate – this is called a resolution or motion. It can be a statement, policy or idea. The motion is usually a policy which changes the current state of affairs or a statement which is either truth or false. The motion typically starts with “This House…”
- The Affirmative team support the statement
- The Negative team oppose the statement
- Sometimes you will be asked to take a position in the debate but in other debates you will be allocated your position.
- Teams are provided with time to prepare – usually one hour
- Each speaker presents for a set amount of time
- Speakers alternate between the teams, usually a speaker in the Affirmative team starts, followed by a Negative speaker, then the second Affirmative speaker presents, followed by the second Negative speaker etc.
- The debate is then judged.
- There may be an audience present but they are not involved in the debate
Once you have learned how to debate in one format you can easily switch to another.

Roles of the speakers
Each speaker must typically do the following:
First Affirmative
- Contextualise the debate – clearly set out your team’s interpretation of the topic and the significant issues they disagree with.
- Provide definitions if necessary.
- Outline the team line and the team split – this is where you outline your team’s case and summarise the way your arguments have been divided between your speakers.
- Provide 2-3 arguments supporting the motion.
First Negative
- Clearly state your definition
- Provide your arguments as to why this is the superior definition
- Rebut the Affirmative’s arguments supporting their definition
- Outline a team line and team split.
- Rebut the arguments made by the First Affirmative.
- Deliver 2-3 arguments against the motion.
Second Affirmative
- If needed, resolve any definitional issues.
- Rebut the First Negative’s arguments.
- Deliver 2-3 arguments supporting the motion.
Second Negative
- Rebut the arguments made by the Affirmative team up to this point, with a focus on the Second Affirmative’s arguments.
Third Affirmative
- Rebut specific issues raised by Second Negative and defend any other important attacks on your team’s case.
- Conclude your speech with a brief summary (1-2 minutes) of your team’s case. You should include the key issues which you and the Negative team disagreed on during this.
- You can introduce new material but this is interpreted as poor team planning.
Third Negative
- This is the same structure as the Third Affirmative.
There are many variations of the three against three debate, a commonly known one is Points of Information. This is used a lot in university debates . During a speech the opposition is allowed to ask a question or make a point.
They stand up and say “point of information” or “on that point” etc. The speaker can choose to accept or reject the point. If accepted, the point of information can last around 15 seconds and the speaker can ask for it to stop at any time.
Debate definitions
Younger debaters tend to waste time defining terms so you must first decide whether you need to define a term. Ask yourself: will my speech be confusing if I don’t define this term? Could the opposition misinterpret what I mean without a definition? For example, the motion could be “we should ban plastic straws”. It’s clear what “plastic straws” are but what does “ban” mean?
Two factors which determine the definition of the debate:
1. Context – what is happening in the area that relates to this issue? For example, maybe the government of a country is debating banning smoking in public buildings and you decide to define the term “passive smoking” during the debate. If a significant event related to the topic has occurred then it should be the focus of the debate, for instance, a shocking report may have recently been revealed in the media showing the widespread effects of second-hand smoking.
2. Spirit of the motion – topics are chosen for a reason so what sort of debate was imagined when the topic was chosen? Looking at the spirit of the motion will ensure that you pick a definition that will produce a well-balanced and important debate.
If the topic is vague then you will have more choice of definitions. You have a duty to pick a clear definition and one that will create a good debate. If not, this may cause a definitional challenge which will ruin the debate and frustrate the judges.
For example, the topic may be “we spend too much money on the stars”. Stars can refer to celebrities or astronomy so you need to choose a definition.
- Look at the context and see if there has been a recent significant event related to either topics – the media is the best place to look.
- Then apply second test – which definition will lead to the best debate, which will be more interesting and debatable?
If one answer passes both tests then that’s your definition. If they tie then either is a good definition.
When providing your definition explain the context used to form the definition. This is important because your understanding of the context may be different from others due to various factors, such as, religion, culture, gender etc.
Learn more about using AI to practice your debating skills .
Basic argument structure
There are various ways of dividing up cases according to groups of arguments, such as, social/economic/political etc. You could assign each speaker to handle a group.
Place the most important arguments first, for example, “The media has more influence on self-esteem than anybody else. This is true for three reasons. Firstly (most important argument)… Secondly…, Thirdly (least important argument)…”
To structure an argument follow these steps:
- Claim – present your argument in a clear statement. This claim is one reason why you’re in favour of/against the motion.
- Evidence – the evidence supporting your claim, such as, statistics, references, quotes, analogies etc.
- Impact – explain the significance of the evidence – how does this support your claim?
Arguments are weakest at the evidence stage as it’s easy to argue against, for example, the evidence may consist of isolated examples or there may be counter evidence. But it’s not a good technique because the opposition can provide more evidence or rebut your criticisms.
It’s difficult to rebut claims because they are usually reasonable but if you can attack a claim then that speaker’s whole argument falls apart. So if you think a claim is vulnerable then rebut it but you will need a strong explanation to show why it doesn’t matter.

European human rights debating for sixth form students from across London.
There are common flaws you can look for to form a rebuttal:
1. False dichotomy – this is where the speaker is trying to falsely divide the debate into two sides even though there are more alternatives than they state. It’s likely the speaker is doing this on purpose but in some cases they do not understand the debate.
2. Assertion – this is when a speaker presents a statement which isn’t actually an argument because there is no reason to believe that the statement is valid. It may just be an assumption. You can point out that there has not been enough examination to prove this validity and then give a reason why the assertion is (probably) not valid.
3. Morally flawed – arguments can be morally flawed, for example, “All criminals given a prison sentence should be given the death penalty instead, this will save the country money and space.” What has been argued is true but it’s clearly morally flawed.
4. Correlation rather than causation – a speaker may suggest a link between two events and suggest one led to the other. But the speaker may not explain how one caused the other event which can make an argument invalid.
5. Failure to deliver promises – sometimes a speaker might fail to complete a task they promised to deliver. For instance, they may state that they will provide evidence supporting a certain claim but they may lose track of what they have said and not actually do this.
6. Straw man – the opposing team introduces an argument and then rebuts it. They may use an extreme example of your proposal or perhaps they were hoping that you would make this argument.
7. Contradiction – an argument the other team presents may contradict one of their previous arguments. You must point out that the arguments cannot be true simultaneously and then explain how this reduces their case’s credibility.
8. Compare the conclusion to reality – think “what would happen if what they (the other team) are suggesting is implemented right now?” This usually shows that it’s more complicated than they have suggested and the changes can cause secondary problems.

Judges generally score the speakers looking at this criteria:
- Content / Matter – What the debaters say, their arguments and evidence, the relevance of their arguments.
- Style / Manner – How the debaters speak, including the language and tone used.
- Strategy / Method – The structure of the speech, the clarity and responding to other’s arguments.

Debating event at the Oxford Union
Important skills for debating
To meet the judges criteria you will have to develop certain skills, consider the following:
- You points must be relevant to the topic.
- Provide evidence whenever you can and not your personal opinion.
- You must put aside your personal views and remain objective when you debate so your argument remains logical. You can be passionate about a topic but interest can turn into aggression and passion can turn into upset.
- Consider the audience’s attention span – make it interesting, for example, don’t just present lots of complicated statistics.
- Ethos – the ethical appeal
- Pathos – the emotional appeal
- Logos – the logical appeal
- Use notes but keep them brief and well organised. Use a different piece of paper for rebuttals.
- Similar to looking at conclusions to create rebuttals, think comparatively by asking yourself “How does my plan compare to what’s happening now/what would happen in the world if the other team won?” You can win the debate if you can make comparative claims about why your arguments matter more than the other team.
- Only tell jokes if you’re naturally good at it otherwise this can backfire.
- Flexibility is important because you might get allocated the side of the argument you don’t agree with. You’ll have to work hard to overcome your views. Also use this insight to think of the potential arguments you might make and then plan for counter arguments.
- Speak clearly and concisely.
- You must talk fast enough to have the time to deliver your speech but slow enough so you can be understood.
- Project your voice to the back of the room.
- Incorporate dramatic pauses.
- Emphasise important words and vary your tone appropriately.
- Have a relaxed pose and posture.
- Avoid filler words.
- Know your material.
- Emphasise using gestures and avoid nervous gestures.
- Maintain eye contact with the audience.
- Keep your language simple to avoid confusion.
- Refer to the opposite side as: “My opponent”.
- When making a rebuttal say: “My opponent said…, however…”
- Don’t exaggerate – avoid the words “never” or “always” etc.
- Avoid saying that a speaker “is wrong”, instead say that “your idea is mistaken”.
What to avoid
- Falsifying, making up or altering evidence.
- Publicly disagreeing with the judges’ decision.
- Attacking a speaker rather than an idea.
- Acting aggressively or offensively towards debaters, judges, audience etc.
- Interrupting other debaters as this can suggest that your argument isn’t very strong.
- Disagreeing with facts or obvious truths.
British Parliamentary debating
British Parliamentary debating is a popular form of debating so we will briefly explain it: There are four teams made up of two speakers each. Two teams are on the government’s side and the other two teams are the opposition but all the teams are trying to win rather than one side. The motion is given 15 minutes before the debate begins and teams are assigned to positions randomly. They alternate their speeches, with the government’s side starting. Speeches are usually 5-7 minutes.
The first two speakers on the government side are called the “opening government” and the first two speakers on the opposition’s side are called the “opening opposition”. The last two speakers on the government’s and opposition’s side are called the “closing government” and “closing opposition” correspondingly.

The speakers’ roles in the opening half of the debate are similar to the roles of the first and second speakers in the three against three debate described previously. The only difference is that the second opening government and second opening opposition speakers include summaries at the end of their speeches – this is because they will also be competing with the teams in the closing half of the debate.
The closing government and closing opposition aim to move the debate on but not contradict their side’s opening team. As well as rebuttal, the majority of the third speaker’s time consists of presenting either: new material, new arguments, a new analysis from a different perspective or extending previously presented arguments. This is called an “extension” which must be something that sets their team apart and makes them unique.
The last two speeches of the closing teams are summary speeches – they summarise the debate and disagreements between the team. Their most important goal is to explain why their side has won the debate. They are not allowed to present new arguments but they can present new evidence and rebuttal.
During the speeches points of information are offered regularly. Speakers should only accept a maximum of two points of information. The first and last minute is protected time where points of information cannot be offered.
Rather than a side trying to win, all the teams are trying to win – this allows different perspectives to be explored. The teams are then ranked 1st to 4th in the debate.
Debate topics
Almost anything can be debated, here are some popular topics – these have been written as questions but they can be easily adapted into statements:
- Is animal experimentation justified?
- Should we legalise the possession of cannabis for medicinal use?
- Should we recognise Bitcoin as a legal currency?
- Is torture acceptable when used for national security?
- Should mobile phones be banned until a certain age?
- Does technology make us more lonely?
- Should guns be banned in the U.S.?
- Should we make internet companies liable for illegal content shared on their platforms?
- Will posting students’ grades publicly motivate them to perform better?
- Should animals be used for scientific testing?
- Do violent video games make people more violent?
- Should the death penalty be stopped completely?
- Should smoking in public places be completely banned?
- Should doping be allowed in professional sports?
- Should all zoos be closed?
- Should consumers must take responsibility for the plastic waste crisis?
- Is euthanasia justified?
- Is the boarding school system beneficial to children?
Debate topics for children
If you’re trying to think of debate topics for a classroom, consider the following:
- Should mobile phones be allowed at school?
- Is global warming a problem?
- Should violent video games be banned?
- Is school detention beneficial?
- Are celebrities good role models?
- Does social networking have a beneficial effect on society?
- Are single sex schools more effective than co-ed schools?
- Do celebrities get away with more crime than non-celebrities?
- Is cloning animals ethical?
- Are humans to blame for certain animal extinctions?
Debating societies
If you’re interested in debating consider searching for a society or debating events near you:
- Most universities have a debating society and their webpages usually contain lots of useful information and tips.
- Toastmasters
- Use Meetup to find debates close to you
Specific to the UK:
- Sylvans Debating Club
- The Association of Speakers Clubs
By Patrick Carpen: The Greatest Writer On Earth
How to Write a Debate
This page was first published on the 28th of November, 2016 and last updated on the 3rd of May, 2017 by Patrick Carpen.

The word “debate” comes from “de,” possibly meaning “down” or “completely,” and “battiere,” possibly meaning “fight” or “beat.” Words of similar root may include “battered” and “battle.”
A debate, in modern usage, and for the purpose of this article, is a formal argument between two groups which is performed in front of an audience. These two groups are usually two teams in a school, or two different teams from two different schools, regions, etc.
Debates are included as part of a school’s curricula to stimulate research and excitement, which ultimately contributes to learning. Because winning a debate often leads to a sense of accomplishment, glory, trophies and prizes, both sides push themselves to the limit to take home the gold.
A debate team of a school usual consist of three speakers: a first speaker, a second speaker, and a third speaker. There is also a backup speaker who stands by in case one of the three speakers is not well and falls out of the program.
When the debate is performed, it is usually done in front of an audience of students in the school’s auditorium. There is a panel of judges who listen carefully and give scores for each speaker, and there is a group of timekeepers who make sure the debaters use the specific time allotted to each of them. And this brings us to the “timings of a debate.”
When writing a debate, it must be practiced and confirmed that each debater can complete their speeches within the allotted time frame. And this brings us to:
The Time Allocation of Each Debater
The time allocation of each debater is as follows:
First Speaker – 6 minutes
Second Speaker – 5 minutes
Third Speaker – 3 minutes
The debaters must rehearse to make sure that each one of them completes their speech comfortably within the allotted time. This takes a lot of practice and rehearsals, and must be perfected. A debater loses points for finishing more than 15 seconds before the allotted time, or 15 seconds after the allotted time. During each presentation, the debater must speak fluently, use gestures, accentuate keywords, and maintain a good posture. And this brings us to the parameters for judging a debate.
The Parameters for Judging a Debate
A debate is often such a fierce competition between two rival teams that the judges often admit that they would “not like to be a judge”. However, judges can keep a level head and make unbiased assessments by using the following judging parameters:
Development of points 15
Reasoning and logic 15
Originality 10
Relevance 10
Mechanics 15
Articulation 5
Attitude to opponent 5
Development of argument 10
Interpretation of topic (moot) 5
Rebuttal 20
Below is a debate that was performed by two Caribbean Schools in Region 9 of Guyana , South America. The moot:
The Agricultural Sector is the Gateway to Guyana’s Future
St. Ignatius Secondary proposed the moot. In other words, they were arguing in favor of the moot. They were called the “proposition.”
Sandcreek Secondary opposed the moot. They were called the opposing team.
Read the debate presentation of each one of them. Who do you think won? Leave your comment in the comment box below this article to let us know what you think!
What other comments or suggestion do you have? How could the debate of each one be better? Leave your comment and let us know your thoughts.
Note the following:
In any debate, a moot must be “defined.” A moot must also be “interpreted.”
St. Ignatius Secondary’s Debate
Moot: The Agricultural Sector is the Gateway to Guyana’s future
First Speaker :
Esteemed judges, adamant opponents, fellow colleagues of the proposition, audience all. Our belief today is, beyond the shadow of a doubt, that, “The Agricultural Sector is the gateway to Guyana’s Future.” And in the next few minutes, we will explain our viewpoint to you in such a clear and straightforward manner that you will have no option but to believe. You will believe because you will realize that everything we are saying is absolutely true.
First of all, I will do the honors of explaining our moot.
The word agriculture is derived from two Latin words, and I quote ager = which means field, and cultura, which means cultivation *end of quote*.
According to Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English, the word Agriculture is defined as, and I quote* “the practice or science of farming” *end of quote*.
Sector , in this context, refers to *quote* all resources dedicated to agriculture. *unquote*
Gateway signifies the way to economic success and prosperity for Guyana.
Future means any time beyond the present, and, in this case, implies success and prosperity in those times.
For the purpose of this debate, we interpret the moot to mean, and I quote *The Agricultural Sector will lead to a vibrant and powerful economy, technological and social advancement, and a strong financial future for Guyana.* unquote
I, Ave Tony, will give an overview of the merits of Agriculture as it applies to Guyana . My second speaker, Nikala D.’Aguillar, will dive in and explore the various agricultural prospects, and my third speaker, Ayesha King, will summarize the points of our argument.
Honorable judges, you will agree with me that Guyana has a rich agricultural heritage. The initial explosive success of this great nation was grounded in agricultural practices. It is our rich, fertile soil that brought financial power to the land of many waters. It was the explosive success of sugar, rice, tomatoes, pepper, cabbages, and the myriads of other cash crops that marked our country on the world map.
Hundreds of years ago, Europeans travelling to the land of many waters in search of a golden city found something better. They found our soil. And they realized there and then, that our soil is gold. A message was sent back to the then queen of England, who immediately consented to starting an Agricultural operation which lasts to this very day and created untold wealth for centuries to come. This is the story of Guyana’s birth as a civilized nation. This is the story of Guyana’s famed sugar plantations, which harnessed the power of Guyana’s fertile soil, and which still accounts for about 15% of Guyana’s Gross National Product.
But it doesn’t stop there, rice was next. This too was a phenomenal success which created billions of dollars in foreign revenue for decades to come, and helped earn Guyana the respect of its friends and neighbors.
Combine that with the acres and acres of cash crop production which bloomed into existence, and we soon earned the title “the bread basket of the Caribbean.”
On the other side of the map, our indigenous peoples, the Amerindians, have mastered the art of cassava, plantain, peanuts, and bananas cultivation, which have further enriched and nourished our nation.
Sadly, it seems today that we have forgotten our roots, vines, and branches. Progress in the Agricultural Sector has slowed to a virtual standstill. Excessive imports, combined with a blatant lack of investment into Guyana’s very foundation, have weakened our economy almost to a point of no return. The very sector that once brought so much wealth, pride, and prestige to this great nation has now been overrun by groundless practices.
Consequently, our economy has plummeted, our dollar has nosedived to an all-time low, and our people are left groping at straws. Isn’t it time we start spinning those straws into gold?
Honorable judges, by the end of our presentation, my team and I will convince you that our soil gives us the ability to spin straws into gold, and that the Agricultural Sector really is the gateway to Guyana’s future.
We will explain how expanding our agricultural sector and exploiting our agricultural resources will open doors and windows to economic prosperity and a brighter future for all Guyanese .
We will explain how agriculture will help preserve and amplify our mineral resources, and empower our government to do greater things for our nation.
We will show you, through real life examples and proven statistics how agriculture makes nations rich and powerful by highlighting some of the greatest agricultural success stories of all time. And more importantly, we will convince you, that we should not, at any cost, be left behind.
When we extend agricultural operations across Guyana , we will provide jobs for the citizens of this country. Through increased financial security the nuclear family will more frequently hold its bonds. Parents will be better able to send their children to school, and the government will be able to supply more needs. By farming on a much larger scale, we will be able to slash productions costs down to the bone and export to foreign countries. The revenues that will be made from these increased agricultural productions will strengthen Guyana in all areas. By stepping up agriculture in Guyana , we will produce healthier citizens through increased physical activity and more nutritious foods.
Extensive agricultural productions will win the war against malnourishment, not just for Guyana , but for the world. The low carbon emissions of agricultural operations make it the environmentalist’s dream.
Our vast, rich pastures and abundant land spaces make sheep, cattle, and other animal farming an investor’s paradise.
Let us remember that a dramatic increase in agricultural productions will mean greater revenues for the country. It will mean richer and more capable citizens. It will mean lower cost of living. It will also mean higher spending power to us as a nation. And all of this ultimately spells healthier, happier, and more productive citizens.
According to information received from the Ministry of Agriculture, we as a nation have not tapped even 1/10th of our Agricultural capabilities. What are we waiting for? To be overrun by smarter nations? No. It is time to put on our thinking caps. It is time to realize that the agricultural sector will bring in the foreign exchange that will strengthen Guyana’s economy. It is Agriculture that will help us to fund our schools and universities–which in turn will contribute to the rise of our nation.
We must once again recognize the gold that we now trample under our feet. We must revive the agricultural sector and bring golden opportunities to the deserving citizens of this great nation.
SECOND SPEAKER
I stand as the second speaker in full support of the moot “The Agricultural sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future.”
According to the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, the world’s most powerful economies: USA, France, China, Australia, Canada, and Germany are all among the top ten Agricultural producers.
By investing in our agricultural sector, we will increase our exports and earn much needed foreign revenues, thereby increasing our nation’s spending power and ability to do business with the world at large.
Increased agricultural activities will help to lower our cost of living. Since we will be producing more locally, the government will be able to pay public servants more, our currency will be strengthened and local traders will be able to offer goods at cheaper prices.
I would like to point out why Agriculture is the way to go for Guyana’s development by examining the most obvious alternative: industrialization. We’ve all read articles and heard speeches by economists who suggest that industrialization is the key to a stronger economy in Guyana . But we’d like to explain that wider agricultural practices need to precede industrialization. Under the present circumstances, the importation of heavy-duty industrial machineries which cost exorbitant sums of money would put such a dent in Guyana’s financial reserves that it would cripple our country’s economy. On top of that, we do not have mechanism in place to combat the growing problem of pollution which would arise from a premature bloom of industrial activities, or the skilled labor required for such an industrialized environment. Instead, let on focus on our strong points: an abundant labor force, rich fertile soil, and a ready international market waiting to scramble our produce.
Agriculture will pave the way for, and strengthen the process of, industrialization in Guyana . The revenue from our agricultural exports will enable us to gear ourselves for advancement in the industrial and manufacturing sectors. It would also empower us to educate and create capable citizens – able to pave the way for much needed industrialization. And more than that, we would have in our possession an abundance of raw materials needed to produce value-added products…when that time comes. It is agriculture that will pave the way for value added products, encourage modern packaging, and breed innovation.
Agriculture will help preserve and amplify our precious non-renewable resources.
With increased agricultural activities and increased revenue, we will no longer have the need to bleed our nation of its precious mineral wealth. Instead, we will wait for the right market prices and take advantage of it. On top of that, with help from the Agricultural sector, we will be able to put our revenues from mineral resources to much better use.
Agriculture will demolish unemployment and discourage criminal activities. It is a sad fact that unemployment in Guyana is at an all-time high. A Caribbean Development Bank Report states that Youth Unemployment in Guyana stands at 40% as of January, 2016. A study conducted by several leading universities, including the Ohio State University, have concluded a direct link between unemployment and crime. Extensive agricultural activities will give youths the ability to use their muscles wisely. It will give them something to dream about, aim for, and work towards. All in all, Agriculture will enrich the lives of our citizens, and create higher social values.
Agriculture will strengthen our citizens physically through increased physical activities. According to the World Health Organization Report, one of the greatest risk factors for chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer is and I quote “lack of physical activity.” And what is a risk factor for good health? You guessed it: agriculture.
Agriculture will hold families together by creating more jobs, money, and happiness. Families will be able to achieve their dreams, and rely on each other for financial, physical, and emotional support.
Agriculture will fund education across Guyana . This will lead to healthier and happier students, better learning environments and more equipped human resources for Guyana .
Honorable judges, esteemed opponents, audience, all, to sum all of what I have just said in simple words that even a child can understand: The Agricultural Sector is the Gateway to Guyana’s Future.
Third Speaker:
Honorable judges, members of the opposition, audience, all…. I am delighted to recap what my preceding team members have so energetically propounded. And that is:
Our soil is rich and fertile and highly suitable to agricultural practices.
Guyana possesses a strong, capable and ready labor force, able to supply the needs of extensive agricultural projects.
There is a hungry international market looking to purchase high quality agricultural produce at reasonable prices.
Agricultural projects are not only highly profitable, but also are low-carbon emission and therefore friendly to the environment.
Increased agricultural productions will strengthen our economy by cutting imports and increasing exports.
Increased Agricultural productions will lower the cost of living.
Agriculture is superior to industrialization at Guyana’s present stage of development.
Agriculture will pave the way for, and strengthen the process of, industrialization in Guyana .
Agriculture will pave the way for value added products, encourage modern packaging, and breed innovation.
Extensive agricultural operations will demolish unemployment.
Increased agricultural operations will help us win the fight against malnourishment by providing us with a surplus of fresh, natural foods rich in vitamins.
Greater investments into the Agricultural sector will help to reduce crime and criminal activities
Increasing and accelerating agricultural activities across Guyana will strengthen our citizens physically through increased physical activities.
More agricultural opportunities will hold families together by creating more jobs, money, and happiness.
The income from extensive agricultural productions will fund education across Guyana .
Extending agricultural activities will lead to healthier and happier citizens of Guyana .
The income from Agricultural exports will finance better learning environments and enhance and equip Guyana’s most precious resource: its human resources.
Agriculture will provide occupation for the youths and citizens in general.
The most successful world economies are the highest agricultural producers.
Furthermore, there is a growing food shortage around the globe, and by equipping our nation, we can fulfill this crucial need for the world and become richer than our wildest dreams. We will also gain the respect of the international community for our wisdom, strength, and innovation.
Honorable judges, members of the opposition, colleagues of the proposition, audience all, thank you for giving us the opportunity to express our viewpoints which we so dearly cherish. We are sure that by now you see eye-to-eye with us through our crystal clear lens and that you now totally agree with us that, as we stated from the very start, “The Agricultural Sector is the gateway to Guyana’s Future.”
Sandcreek Secondary’s Debate
First Speaker
Distinguished judges, accurate time keeper, fellow debaters, and audience all, I Sabrina Cyril stand to refute the moot that, “The Agriculture sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future.” I shall begin our argument by explaining how gold, at present, is more crucial to Guyana’s growth than agriculture. Our second speaker …..will continue our argument with her findings on how the oil sector will have the greatest impact on Guyana’s future. Our third speaker, Loree Edwin, shall conclude our argument by explaining how the sugar industry is a burden to Guyana’s future and how education is the true gateway to a prosperous future for Guyana .
Before I go on, let me first restate the moot and define a few key terms to ensure we all have a definite understanding of the argument.
The moot reads, “The Agricultural sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future.”
“Agriculture” – Can be defined as: the rearing of animals and the cultivation of crops.
“Sector” can be defined as: a single section of industry that contributes to a country’s GDP.
“Gateway,” defined by the Cambridge Complete Dictionary is, “A way of achieving something.”
“The” – a small but operative word in this argument refers to “only and solely.”
This indicates that is is the proposition’s belief that Guyana’s future is solely reliant on the performance of the agriculture sector.
The moot now reads, “The Section of Industry that Comprises the Rearing of Livestock and Cultivation of Crops is THE Only Path to Achieving Something in Guyana in Time to Come.”
It should also be noted that the use of “gateway” with its definition allows us to derive that the moot entails that the “agriculture sector is one and only gateway” to a future that sees success in achieving its goals. This is the point which we will refute.
Gold is the element on which most global monetary systems are based. The price of this infamous metal is, time and time again, used as the true indicator of a country’s growth, banking reserves, and wealth. With such prowess, it is obvious that such a mineral can be of influence in Guyana , especially when you consider how abundant it is throughout the nation and its high demand worldwide.
In recent years, the number of gold mines has been on the rise. Why? It’s because gold is proving to be an extremely profitable industry. Communities across Guyana are becoming reliant on the gold industry to fuel its economy, for example, A BBC report found that “Port Kaituma’s reliance on mining is replicated across Guyana – gold accounts for nearly half of the country’s total exports, which were some $218m (USD) in the first quarter of 2011.” This is compounded by the government’s budget highlights for this year, which show that the mining and quarrying sectors grew by 9 percent with gold exports growing by 16.4 percent this financial year.
So mining is a growing industry that already accounts for more than half of Guyana’s exports! Can you not see how gold is already proving a gateway to Guyana’s future? It provides job and prosperity when so many other sectors are faltering. In 2010, sugar, rice, and timber combined contributed 34.4% to the value of Guyana’s exports, whereas Gold by itself totaled 37.6%. This figure will rise to 50% if we include other minerals such as bauxite and diamond. These figures are all provided courtesy of the Guyana Geology & Mines Commission working in partnership with both the Bank of Guyana and the Bureau of Statistics in Guyana . And I must say, the findings are convincing, are they not?
It is only fair for us to also address the negatives surrounding the mining of this precious metal; that using some current methods, some deforestation has unfortunately taken place. Yes, this is a consequence of gold mining, but the majority is due to reckless, profit driven decisions by corporations. However, with greater state involvement and regulation, this can be rectified, resulting in a sustainable, growing and most importantly, a profitable industry that will continue to pave the gateway to Guyana’s future.
In summary, gold is already a huge part of Guyana’s present, and with its proven year on year growth, it will be an even bigger part of its future. Gateway, again, means “a way of achieving something,” and the gold sector is unquestionably already achieving something as it shapes Guyana’s future with economic improvements, job creation, and strengthening international trade.
So it an be argued that the Agriculture Sector is not THE gateway; it can be considered A gateway.
Thank you for your attention.
Second Speaker
Honorable judges, trustworthy timekeeper, fellow debaters and my captive audience, a pleasant good morning to you. My name is ___________ and I will continue our argument that “The Agricultural sector is NOT the gateway to Guyana’s future,” due to the economic power of Guyana’s plentiful supply of oil.
You heard from our first speaker about the success the mining industry is experiencing in this mineral-rich nation. Now, let me open your eyes to the true wealth of resource that our rich and vibrant land has at the near reach of its fingertips: OIL.
Current estimations by various professional sources all agree that Guyana has an undeniably huge reserve of oil, up to 1.4 BILLION barrels of petroleum. This figure is just for the wells that we have already identified around Guyana , and there are many more that are anticipated due to geological findings and continued research.
Even off-shore, Guyana contains this treasure waiting to be tapped. In a report by the US Geological Survey it is stated that, and I quote “the Guyana-Suriname Basin has the second largest unexplored oil potential in the world after Greenland.” End of quote. Coupled with the fact that in 2015, a brand new off-shore reserve was discovered, showing that Guyana has both on and off-shore potential. Exxon has been allotted a total area of 26,806 square kilometers of water off-shore for exploration, making the economic future of Guyana very promising indeed.
In August of this year, Ralph Ramkarran, a prominent Guyanese told Stabroek News how the true value of Guyana’s oil could turn around its economy. I quote:
“If Guyana’s production is in the vicinity of 500,000 barrels a day, as it should be, at a value of about 80 US Dollars per barrel, this will bring in 14.6 Billion US Dollars of which Guyana’s take at the usual 40 percent will be 5.5 billion US Dollars a year.” End of Quote.
“With increasing exploration activities, if anything close to the lower figure of 15 billion barrels are discovered, for most Guyanese the future would be beyond contemplation. With reserves of only between 800 million and 1.4 billion barrels, poverty would be diminished in a short period and Guyana per capita income of 3600 US dollars would rise rapidly.” How much you ask? I quote from the end of this report, “Guyana’s per capita will move to about 14000 US dollars in the early 2020s” purely on the back of the oil production profits and its taxation.
With that in mind, how can you possibly argue, my dear proposition, that the Agricultural Sector is THE gateway to Guyana’s future, when oil has unequivocally the greatest potential impact on the economy? Even if the full reserves aren’t tapped, the effects on Guyana’s economy will be tremendous. No other resource of sector can multiply GDP fourfold by the end of this decade, as oil alone can.
Our government is wisely taking its time in deciding on its course of action for the potential wealth it sits upon because its use will shape the next century of Guyana’s history. It is likely that when the oil revenues are re-invested that it shall be oil which will in fact be the gateway for the success of agriculture as this will provide the funds Guyana desperately needs to upgrade the sector.
My dear proposition, to claim that, “The Agricultural Sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future” is ludicrous especially after listening to me and our first speaker. Gold mining is a growing industry that is increasingly profitable. Guyana’s agriculture sector is neither of these. Oil will raise Guyana to be one of the wealthiest nations in South America and the Caribbean, while its reliance on the agriculture sector will not. Now members of the proposition, do you really believe that, “the Agricultural Sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future?” I really don’t think so.
The Agriculture sector may have the potential of being the gateway, but as of now, it is simply not!
I rest my case.
Ladies and gentlemen, thank you.
Third Speaker
You give a man a fish and you feed him for the day; you teach a man to fish and he can feed himself for the rest of his life.
My name is Loreen Edwin. I stand here to conclude our argument that, “the Agricultural Sector is NOT “THE gateway to Guyana’s future.” The first speaker went at great length to show you how the gold and mining industries are having a significant impact on Guyana’s future. The second speaker explained the impact oil will have on Guyana’s future. They have provided you with solid evidence, don’t you agree? So how can you honestly say that the agricultural sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future? Perhaps it could be Guyana’s future demise. Agriculture was indeed once Guyana’s champion of economics and growth back when sugar and rice production were cheap enough to compete with the international markets. But now, due to a lack of reinvestment and neglect of assets, the industry is in disrepair and year on, year out, it has resulted in a decreased output and falling profitability on a very sad level.
It’s not me just saying this. An article by Kaieteur News on the 11th of this month stated that, and I quote, “The Guyana Sugar Corporation (GuySuCo) cannot be sustained.” The estimated operating losses are more than $10B annually. $10 Billion down the pan! My dear proposition, you are trying to convince us that is what the gateway to Guyana’s future looks like? Dr. Clive Thomas, chairman of GuySuCo, who in a Kaieteur News report on the 11th of his very month, stated and I quote, “the assets of the industry are “rundown.” Dr. Clive also notes that it would cost the state over US$60M or $12B Guyana dollars) to repair the infamous 200 million dollar Skeldon factory alone.
This year alone, the industry had to be given 11 billion dollars. It is projected that this will continue with 18b to 20b needed as bailouts JUST to keep the business afloat and ensure its workers are paid. So esteemed proposition, how can you say that “the Agricultural Sector is the gateway to Guyana’s future” when its primary pillar, sugar, is crumbling to the extent of collapse?
Now, do you know what the most important resource of any nation is? Its people; human resource. This brings me back to my opening statement: that successfully educating a person results in the empowerment of that person. You teach that individual and they learn to be self-reliant, to be independent, to be resourceful. Knowledge is power. Education is power. And education builds a nation.
It goes without question that the education sector is significant to Guyana’s future. How can Guyana move forward if its populace is uneducated? The importance of education is reflected in the 2016 national budget where 40 Billion dollars was allocated to the education sector alone; whereas a mere 20 Billion was allocated to the agricultural sector. Improving education improves the capabilities of the future generation. With a richer knowledge base, they create, innovate, and develop new ideas that will drive our industries, bringing in a superior source of income to this country, more than we could ever hope to get from agriculture alone.
It is clear as daylight that the education sector of any country is the main gateway to its development . And for Guyana , it is no different.
So you see, learning proposition, the agricultural sector is NOT the gateway to Guyana’s future; it is an old path that will just lead to degradation and despair. In the past, it has indeed been the gateway to the future, but that future is gone, and we need a new direction; be it in education, mining or in oil. These surely are the gateway to Guyana’s future. Agriculture? No I don’t think so.
Thank you for listening.
Editor’s Note: Sandcreek was lauded for having used more statistics and factual evidences.
Related Posts:

Instant Debate Speech Maker Online
Debates are an excellent opportunity to develop many personal skills, become a more open-minded person, and learn new information. Through this activity, students improve critical thinking, public speaking, teamwork skills, increase their self-esteem, and learn to disagree with others.
Preparing for a debate can take a lot of time, which is why our team has created this tool and guide for you. With our debate speech maker, you no longer have to sit for hours and think about how to formulate your argument correctly! Also, on this page you will learn many useful facts about debates and get tips for preparing for them.
- 📢 Introduction to the Tool
🗣️ What Is a Debate?
👍 debate maker benefits, ✏️ how to write a debate speech, 🔗 references, 📢 debate script maker: an introduction.
If you’ve decided to participate in a debate, you probably know that this activity requires a lot of preparation. Sometimes, you may receive the topic of your debate in advance so that you have time to prepare thoroughly for it. But also, you may be given the subject on the day of the debate, and then you’ll have much less time to prepare. In either case, our debate maker will be an indispensable assistant!
When comparing AI vs human writers, artificial intelligence excels in the speed of content creation, although it loses in creativity. Unlike when using other AI chat bots, you don't have to bother with creating successful prompts. Using this tool is simple - to instantly make a speech, you’ll need to take these four steps:
- Type in the topic of the debate.
- State your position and audience.
- Indicate whether you are replying to an opponent.
- Click “Generate” and get your result!
A debate is a structured and formalized argumentative exchange between two or more opposing sides . While this practice is usually associated with the election season , it can also be often found in schools or colleges. Participants, categorized as either the “pro” or “con” side, systematically present and defend their perspectives on a given topic. They use evidence to back up their claims and. Each side takes turns articulating arguments and responding to their opponent's points.
The primary objective of a debate is persuasion - convincing the opposition and the audience. Although debates often lack a declared winner, they may conclude with a vote or judgment from adjudicators in formal settings. Informal debates can persist until one side concedes.
Debate Terminology Examples for Students
Here, you can become familiar with the basic terms. It’ll be beneficial for you to learn them to make it easier to grasp the debate structure further.
- Adjudicator - An impartial observer who evaluates the debate. Such moderators provide feedback on the quality of arguments and overall performance. Also, they can contribute to determining the winner in formal debates.
- An affirmative - A team or speaker supporting the motion in a debate. Affirmatives present arguments in favor of the proposition. They aim to convince the audience or adjudicators of the motion's validity.
- Motion - The central topic, idea, or statement being debated. The motion frames the discussion and determines the stances of the affirmative and opposition sides. Debaters construct arguments either in support or against this subject.
- Chairperson - The person responsible for moderating and overseeing the debate. Their goal is to maintain order and ensure adherence to the rules. The chairperson may introduce speakers and the motion.
- Card - A card is a paragraph or several paragraphs taken from an authoritative journalistic or scholarly source that proves the validity of a particular argument. It should be a verbatim quotation without additions or paraphrasing. It is important to explain the quote and how it relates to the argument.
- Floor - The general audience or participants who are not actively engaged in the debate but may have the opportunity to pose questions. They can make contributions during designated segments. The floor adds an interactive element to the discussion.
- Opposition/a Negative - A team or speaker taking an opposing stance on the core topic. The opposition presents arguments countering the proposition. Such arguments should demonstrate flaws in the affirmative's position and persuade the audience that the motion is unsupported.
- The first speaker - The initial speaker of a team. They introduce and establish the main arguments supporting or opposing the motion. Their speech should set the tone for the team's position and outline the critical points to be developed by subsequent speakers.
- The second speaker - The second speaker introduces additional evidence and reinforces the team's position. They aim to strengthen their affirmative/opposing case and respond to the arguments from the other team.
- The third speaker - The last speaker should summarize the team's key points. They may also respond to opposition’s reasons raised during the debate. The goal is to leave a lasting impression on the adjudicators before the discussion concludes.
- Reply speeches - Reply speeches are the concluding words from both the affirmative and opposition sides. These speeches are often shorter, not more than three minutes. Such speeches are the last chance to influence the overall impression, so they should strongly support your ideas.
What Does the Maker of the Argument Do in a Debate?
In a debate, the first speaker, whether on the affirmative or opposition side, should:
- Formulate a clear and concise stance on the motion.
- Organize arguments logically, presenting a structured case.
- Support points with relevant facts and examples.
- Convince adjudicators and the audience of the credibility of their position.
The Structure of a Debate
Whether an academic debate or a parliamentary one, the structure and ground rules essentially remain the same.
In this section, we'll briefly explain how your proceedings are going to look like:
- Gathering the sides . At this stage, you should determine the teams and their participants. They are divided into affirmative and negative sides. As a rule, the debates should include three speakers , who will take turns and, at each stage, strengthen their position. All participants should meet 15 minutes before the start to prepare materials .
- Starting the debate . Participants should determine the debate’s time limit, as speeches cannot last nonstop. Usually, each speaker is given a maximum of 3 minutes for their presentation. At the beginning, the speakers should introduce themselves. The duration of the answer is regulated by the timekeeper , who should give a bell 30 seconds before the end of the speaker's time to start summarizing.
- Debating the topic . The core of the debate involves a structured exchange between the sides. The first speaker for the affirmative introduces the motion, presenting key arguments. The opposition's first speaker responds, presenting counterarguments. This pattern continues with subsequent speakers building upon and responding to the points raised. The debate format could also include cross-examination or questioning segments.
- Finishing the debate . Both sides deliver final counter-speeches summarizing key arguments. The adjudicators then assess the overall performance of each side. The persuasiveness of the arguments presented assists in the audience’s decision-making. Participants may engage in discussions and receive feedback . After the debate, each team is given the opportunity to thank everyone in attendance.
As you've probably already realized, getting ready for such a significant event will take a lot of time. You'll need to gather your thoughts, stay level-headed, and be assertive in your stance. This preparation process can be quite overwhelming. That's why our debate script maker is the perfect solution!
This debate writer has many advantages:
Our tool is a great way to save time and get that initial burst of inspiration for your debate. However, that is just the beginning. You will still need to edit and finalize this speech. Additionally, you may find it helpful to learn how to write one yourself.
The following steps will show you how to improve your speech and prepare you for your future debates:
- Compelling beginning . The opening of your speech is of the utmost significance. Your task is to captivate the audience and create the overall atmosphere of the speech. We suggest using a hook at the very beginning. It can be a question or a fact intended to capture the attention of your opposition and the audience. You could also use a quote from a famous person, an interesting statistic, a rhetorical question, or even a relevant personal anecdote.
- Presenting your arguments . This is the time to talk about your position on the topic. Be sure to formulate a concise thesis statement . After that, you should provide the arguments that support it. Explain each point clearly to avoid misunderstanding among the audience.
- Explaining the position . Follow a structure where each of your arguments is followed by evidence and then justification. Proof builds credibility and engages the listeners. Ensure that you have data only from relevant and reliable sources.
- Summarizing . In the concluding part of your persuasive speech, you should reiterate your thesis and essential arguments. Emphasize the value of your position. It’s your last opportunity to impress the judge and the listeners. Round it off by offering a provocative question, a recommendation, or talking about your predictions for the future of the subject.
- Confidence and consistency . After writing your speech, you should refine its structure so that you have smooth transitions from one idea to the next. Use connecting words to tie your arguments together. Afterward, practice your speech and make sure it's clear . Your gestures, facial expressions, and intonation are ways to communicate with listeners. Be convincing but not pushy, and use a moderate pace.
We wish you good luck in your debates! And if you need to create a different kind of speech, try our informative speech generator .
Updated: Jan 26th, 2024
- What is a debate? – Vanesa Velkova, European Commission
- How debating works – Law Society of Scotland
- Debating: A Brief Introduction for Beginners – Debating SA Incorporated
- Debate Timing & Structure - Debating Matters
- How do you structure your debate speech to capture the attention and interest of your audience? - LinkedIn
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
Our debate speech maker tool is the perfect solution for those who wish to deliver the perfect response to their opponents. Easily generate a speech on any topic and wow the audience with your eloquence. Additionally, learn all about debates, their structure, and find useful tips.
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
How to Write a 4 Minute Speech Correctly
Tammy dahlvang.

The ability to clearly communicate ideas to others will serve to advance you both professionally and socially. Knowing that you can communicate well generates self-confidence in your ability to lead groups and conduct meetings. Grasping the fundamentals of effective communication will improve your conflict management skills and afford you the ability to have more productive conversations with your friends, your significant other, and your children. Communicating clearly is an easy skill to master once you understand the basic process for public speaking.

Think about your audience before you actually write down anything. This is a crucial aspect of public speaking, whether you plan to speak for four minutes or for forty minutes. Ask yourself what images from their lives you can use while speaking that will interest them. Monitor any jokes that you plan to tell to make sure they will not be offensive. Ask yourself what kind of speech will earn their attention and respect. Attention from any group is extremely hard to earn. If you do not make the effort to think through how your audience will perceive your speech, you may fail to write a speech that will communicate with them.

Research your topic well. You might have to go to the library, or you may be able to research the subject online. After you speak, you might also be asked questions. If you appear to be unprepared to answer those questions, or if you demonstrate only a shallow knowledge of the topic, you will lose credibility.

Summarize your research in three sentences or less, and write the sentences down. These are your main points. Most people cannot remember more than three points. If you must make more than three points, provide a handout that your audience can follow as you speak. Your main ideas should be in bold print.

Outline your talk. Traditional speeches have three parts: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Use your introduction to entice people to listen, and to establish rapport with your audience. Consider thanking them for giving you the opportunity to talk. Your introduction should take less than a minute of your talk. For the next two or three minutes, develop the ideas you summarized earlier. This will be the body of your talk. In the last thirty seconds or so, wrap up your talk by briefly reiterating what you have said, and why it matters.
It takes most people between four to five minutes to read two pages of double-spaced twelve point font, so if your entire talk is a little shy of two full pages, you should be on track. Many people write one paragraph for their introduction, and one paragraph for their conclusion. Allow one full paragraph per idea in the body of your speech.

Decide how extemporaneous you will be. Just because you have written a speech does not mean you have to read it. You can read your speech, you can write notes on index cards and unobtrusively use them. or you can memorize your introduction, body and conclusion. All three methods have their merits, so weigh your options.

Practice your speech in front of a friendly, but honest, audience. Ask for constructive criticism and suggestions. When first beginning to speak in public, many people have annoying mannerisms of which they are not conscious. Such distracting habits include throat clearing, saying "ummm..." in between sentences, speaking too quickly, or involuntary body movements. It may also be helpful for you to practice in front of a mirror. If there is something you need to avoid saying or doing, write a reminder to yourself at the top of the pages of your speech.
- It's a good idea to look in the mirror before you give your speech. You probably don't have lettuce stuck in your teeth, but any misgivings about how you look will make you less self-confident.
- Try to avoid taking a glass of water up to the podium with you for a four-minute speech. If you have to pause during your speech to take a drink some people will begin to daydream.
- Make sure that you are dressed appropriately.
About the Author
Tammy Dahlvang began writing professionally in 1997. She has contributed "Across the Pastor's Desk" articles to the "Albert Lea Tribune" in Albert Lea, Minn. She graduated Phi Beta Kappa from Northwestern University in 1993, and in 1997 earned a Master of Divinity from Luther Seminary in St. Paul, Minn.
Related Articles

How to Give a Good 8th-Grade Speech

How to Do a Good English Oral Presentation

How to Make an Informative Speech Longer

How to Give Good Speech Presentations in College

How to Deliver a Beautiful Eulogy for a Loved One

How to Write a Good Speech

How to Speak English With Confidence

How to Pass a Speech Class

How to Write a Speech for a 7th-Grade Class President

How to create a Toastmasters speech in 30 minutes

The Proper Etiquette at a Catholic Wake

How to Make a Handout

How to Become a Christian Women's Speaker

How to Write an Argumentative Speech

How to Maintain Composure at a Funeral

How to Greet a Friend When They Have a Loss in Their...

Steps for How to Prepare an Effective Oral Presentation

How to Tell My Boyfriend I Don't Have Any Feelings...

How to Write a Short Speech for a Junior High Student...

How to Write a Persuasive Speech in the Sixth Grade
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .

How to Write an Effective Persuasive Speech Outline: 5 Key Elements
- The Speaker Lab
- April 14, 2024
Table of Contents
If you’re a speaker, you are probably well familiar with the path from initial speech drafts to the day you actually present. By its nature, speech delivery is a journey filled with obstacles, yet it’s simultaneously an adventure in persuasion. With a well-crafted persuasive speech outline , you can do more than just present facts and figures to your audience. You can weave them into a narrative that captivates, convinces, and converts.
A meticulously planned persuasive speech outline isn’t just helpful; it’s essential. Crafting this blueprint carefully lets you deliver your message more effectively, making sure each point lands with the impact you’re aiming for. To help you achieve this impact, we have some tips and tricks for you to try.
Writing an Effective Persuasive Speech Outline
When we talk about persuasive speeches , we’re diving into the art of convincing others to see things from a certain point of view. Your speech is your one shot to grab attention, build your case, and inspire action. Your secret weapon for achieving this is your speech outline. In your speech outline, you want to touch on several key elements.
- Pick your fight: Start by zeroing in on what you really want to change or influence with this speech.
- Support your claim with evidence: Identify those key points that back up your stance to appeal to your audience’s rational side .
- The emotional hook: Weave in stories or facts that hit home emotionally .
- Avoid the kitchen sink approach: Don’t throw everything at them hoping something sticks. Be selective and strategic with the info you share.
- Nail that closer: Your conclusion isn’t just goodbye; it’s where you charge your audience with a call to action.
These elements form the backbone of your persuasive speech. By including these in your talk’s outline, you can’t go wrong.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Establishing Your Main Objective and Structuring Your Points
Now that you have a general idea of what goes into a persuasive speech outline, let’s break a couple of these pieces down and look at them a little more closely.
Identifying the Purpose of Your Persuasive Speech
When writing your speech, you first need to nail down why you’re doing this in the first place. In other words, identify your main objective. After all, choosing to speak up isn’t merely about the desire to express oneself; it’s deeply rooted in understanding the effect you hope your discourse will unleash. Do you hope to sway opinions towards the belief that animal experimentation is a relic of the past? Or perhaps persuade them that social media does more good than harm? Whatever your cause, identifying your main objective will help keep you on track and avoid rambling.
Organizing Key Points for Maximum Impact
Once you’ve determined what you want to persuade your audience of, you can start building your argument. Specifically, you can determine your key points. Key points support your position on a topic, proving to your audience that you have actual reasons for taking your position.
To pack the most punch, arrange these key points in a logical order. Consider how you might connect your key points. Are there some that can be grouped together? The flow of your argument matters just as much as the argument itself, and a disjointed argument won’t do anyone any favors. As you organize your key points, consider these tips:
- Lead with strength, but don’t throw all your cards out at once.
- Build upon each point; important transitions between them can make or break audience engagement.
- Finish strong by tying back everything to the emotional chord you struck at the beginning.
Nailing these steps will ensure that when you speak, your message doesn’t just echo—it resonates.
Selecting Compelling Topics for Your Persuasive Speeches
Let’s face it, picking the right topic for your persuasive speech outline is half the battle. But what makes a topic not just good, but great? First off, it needs to spark interest, both yours and your audience’s. If you’re not fired up about it, chances are they won’t be either. Second, make sure the topic is something relevant. It should resonate with your listeners’ experiences or touch on their concerns and aspirations. Lastly, your topic has to be something you can research and back up with solid facts and expert opinions.
For ideas to get you started, check out a variety of speech topics here .
Enhancing Persuasion Through Rhetorical Appeals
The art of persuasion is something that’s been studied since ancient Greece. Back then, Greek philosopher Aristotle came up with the three rhetorical appeals . Each one described a different way of convincing your audience of your position. Together, these appeals help you form a rock-strong argument, making them worth learning.
Building Credibility with Ethos
To get people on your side, you first need to win their trust. That’s where ethos comes into play. Demonstrating to your listeners that you’re both trustworthy and deserving of their attention hinges on transparency about your qualifications, genuine self, and the wisdom gained from occasional setbacks. Letting folks know why they should listen can make all the difference.
Connecting with the Audience Through Pathos
At some point, we’ve all been moved by a story or an ad because it hit right in the feels. That sort of emotional appeal is called pathos , and it’s powerful stuff. If you want people really invested in what you’re saying, then be sure to use this appeal in your presentation. To harness the power of pathos, try telling a story , especially one your audience can relate to. The key is authenticity—sharing true experiences resonates more than anything fabricated ever could.
Strengthening Arguments with Logos
Last but not least, we have logos, our logical appeal. Oftentimes, this logical appeal entails facts and data points, which are used to back up what you’re selling, turning skeptics into believers. But just because you’re listing facts and figures doesn’t mean this part has to be boring. To keep your audience engaged, craft persuasive narratives and then ground them in robust proof. Giving your story to go with your numbers doesn’t just help keep them engaged, it also helps the information stick.
The Importance of Supporting Evidence and Counterarguments
In your persuasive speech outline, you need to note compelling evidence for each key point. In addition, you’ll want to address opposing views.
Gathering and Presenting Convincing Evidence
No matter how trustworthy you seem, or how compelling your stories are, most people need tangible proof. That’s where concrete evidence steps into the spotlight. To fortify your argument and boost its believability, sprinkle in a mix of hard data, customer stories, numerical evidence, and endorsements from authorities. To illustrate this data for your audience, you may find it helpful to create a slideshow . Supporting every assertion with research is an essential part of any persuasive speech. Without it, arguments inevitably sound flimsy and unconvincing.
Addressing Opposing Views Effectively
Although it may seem counterintuitive, address counter-arguments head-on in your persuasive speech outline. It might feel like walking into enemy territory but it actually strengthens your own argument. By acknowledging opposing views, you’re showing that not only do you know what they are, but also that they don’t scare you.
When you address these counter-arguments, demonstrate your understanding. Again, this is where your good research skills are going to come in handy. Present the facts, and ditch biased explanations. In other words, don’t mock or belittle the other side’s viewpoint or you’ll undermine your own trustworthiness. Instead, explain opposing viewpoints with neutrality.
Adopting this strategy not only neutralizes possible objections but also enhances your stance. Plus, this makes for an engaging dialogue between both sides of any debate, which keeps audience members hooked from start to finish.
In essence, tackling counter-arguments is less about winning over naysayers and more about enriching discussions around hot-button issues. At its core, persuasion isn’t just convincing folks; it’s sparking conversations worth having.
Crafting a Captivating Introduction and Conclusion
Now that you have the body of your persuasive speech outline, it’s time to talk beginning and end. To really hit your message home, you want to grab your audience’s attention at the beginning and call them to action at the end.
Creating an Engaging Hook to Capture Attention
The opening of your speech is where you need a good first impression. To hook your audience, consider starting with an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or even a short story related to your topic. Whatever route you choose, keep it interesting and concise, so that you can transition into the rest of your persuasive speech outline.
Concluding with a Strong Call to Action
Crafting strong conclusions is about leaving your readers feeling pumped and ready to jump into action. After all, if you’ve argued convincingly enough, your audience should be ready to act. To channel this energy, urge listeners towards specific actions. Here are some strategies:
- Suggest clear next steps: Don’t leave your audience hanging wondering what’s next. Give them concrete steps they can take immediately after reading.
- Create urgency: Why wait? Let folks know why now is the perfect time to act.
- Show benefits: Paint vivid pictures of how taking action will positively impact their lives or solve their problems.
With that captivating hook and a decisive call-to-action, you are one step closer to presenting an unforgettable speech.
Utilizing Monroe’s Motivated Sequence for Persuasive Structure
As you finish off your persuasive speech outline, you may be wondering how best to structure your speech. If that’s you, then Purdue University professor Alan H. Monroe has some answers. In his book “Monroe’s Principles of Speech,” the professor outlines Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, the best structure for persuasive speeches. Each step is broken down below.
Attention: Grabbing the Audience’s Focus
You’ve got something important to say. But first, you need them to listen. Start with a bang. Throwing out a shocking truth, posing a thought-provoking query, or sharing an enthralling tale could work magic in grabbing their attention. It’s all about making heads turn and ears perk up.
Need: Highlighting the Issue at Hand
Now that they’re listening, show them there’s a gaping hole in their lives that only your message can fill. Paint a vivid picture of the problem your speech addresses.
Satisfaction: Proposing a Solution
This is where you come in as the hero with a plan. Introduce your solution clearly and convincingly. How does it patch things up? Why does it outshine merely applying quick fixes to deep-rooted issues? Give your audience hope.
Visualization: Helping the Audience Visualize Benefits
Show them life on the other side of adopting your idea or product—brighter, easier, better. Use vivid imagery and relatable scenarios so they can see themselves reaping those benefits firsthand.
Action: Encouraging Audience Action
Last step: nudge them from “maybe” to “yes.” Make this part irresistible by being clear about what action they should take next—and why now’s the time to act. Whether signing up, voting, or changing behavior, make sure they know how easy taking that first step can be.
Learn more about Monroe’s Motivated Sequence here .
What Type Of Speaker Are You?
Click below to discover your Speaker Archetype and how to start getting booked and paid to speak!
Overcoming Public Speaking Fears for Effective Delivery
Let’s face it, the thought of public speaking can turn even the most confident folks into a bundle of nerves. But hey, you’ve got this. Dive into these expert strategies and you’ll find yourself delivering speeches like a seasoned orator in no time.
Techniques to Build Confidence in Public Speaking
If you’re feeling nervous on the big day, these three techniques are perfect for you. Take a look!
- Breathe: Deep breathing is your secret weapon against those pesky nerves. It tells your brain that everything is going to be okay.
- Pose like a superhero: Stand tall and strike a power pose before you go on stage. This isn’t just fun; science backs it up as a confidence booster .
- Kick perfectionism to the curb: Aim for connection with your audience, not perfection. Mistakes make you human and more relatable.
The goal here is to calm yourself enough to be able to deliver your persuasive speech outline with confidence. Even if you still feel a little nervous, you can still present an awesome speech. You just don’t want those nerves running the show.
Practicing Your Speech for Perfect Execution
If you know that you tend to get nervous when public speaking, then you don’t want to be running through you speech for the first time on the big day. Instead, practice beforehand using these techniques.
- The mirror is your friend: Practice in front of a mirror to catch any odd gestures or facial expressions.
- Vary your voice: As you deliver your speech, let your voice rise and fall to match what you’re sharing. Avoid speaking in a monotone.
- Say no to memorization: Rather than memorizing every word, learn key points by heart. You want to sound natural out there.
Remembering these steps won’t just help you tackle public speaking fear, but will also polish those all-important public speaking skills .
Once you’ve honed the skills you need to write a persuasive speech outline, the only thing left to do is to get out there and practice them. So take the rhetorical appeals—ethos, logos, and pathos—and practice weaving each element into your speech. Or take Monroe’s Motivated Sequence and work on structuring your outline accordingly.
Prepare well and when you hit the stage, you have not just a well-prepared persuasive speech outline, but also the power to alter perspectives, challenge the status quo, or even change lives.
- Last Updated: April 11, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- Sign up For Free
LD and PF Club Team registration for the 2022-2023 debate season is now open!
- Join Our Newsletter
- Schedule a Private Call

101: Introduction to LD
What is Lincoln-Douglas (LD)
How to win a LD Debate Round
How to Judge a LD Debate Round
LD Speech Format
First Affirmative Constructive (1AC)
Cross examinations, first negative constructive (1nc), first affirmative rebuttal (1ar), second negative rebuttal (2nr), second affirmative rebuttal (2ar), 102: beyond the basics.
Constructing a Case
Framework vs. Contentions
Mastering the Constructives
Mastering the Rebuttals
Final Speeches
Lincoln-Douglas (LD) Debate Format
The following table details the speech names, lengths, and the side responsible for giving the speech.
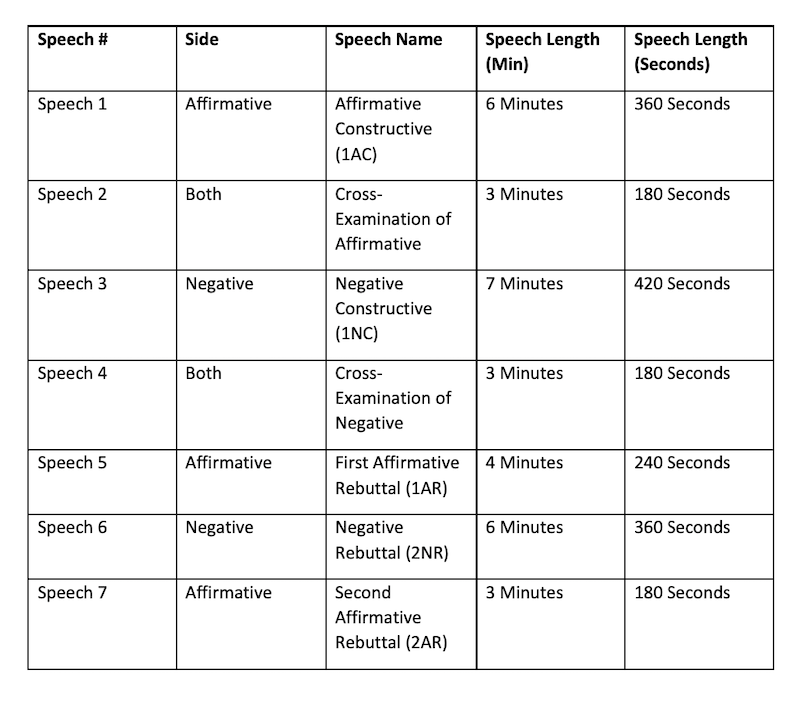
This is the first speech of the debate and is known as the “AC” or “1AC.” Here, the Affirmative (Aff) will present their prewritten case for 6 minutes. They will have a “Framework” (setting up a philosophical way to view the round) and “Contentions” (arguments about the topic that connect back to their framework).
There are two cross-examinations in a debate. The Neg cross-examines the Aff after the 1AC, while the Aff cross-examines the Neg after the 1NC. Each cross-examination is 3 minutes long.
Following the Neg’s cross-examination, the Neg gives their First Negative Constructive (also known as the “NC” or “1NC.” The speech is 7 minutes. Here’s the Neg has two jobs – presenting their own case and answering the Aff’s case. For their own case, in a traditional round the Neg will present their own Framework and their own Contention(s) before moving onto the Aff’s case. In a more “circuit” round, however, the Neg might read multiple “off-case” positions, such as Kritiks, Counterplans, Disads, and Procedurals. They are then reading multiple cases, in essence. In dealing with the Aff’s case, the Neg will want to have a combination of offense and defense, seeking to defeat the Aff’s contentions. They also might contest the Aff’s Framework, if the two teams have read different Framework arguments.
The First Affirmative Rebuttal (1AR) is 4 minutes long. Since it has to cover the long 1NC, it is the hardest speech in the debate. The Aff has two jobs – rebuilding (“extending”) their case and attacking the Neg’s positions. The Aff will typically spend around 2 minutes on their case and 2 minutes on their opponent’s positions. Given the short speech, the Aff has to be efficient. An argument not addressed by the 1AR is known as “dropped” and cannot be brought back in the Second Affirmative Rebuttal.
This is the Second Negative Rebuttal (“2NR” or “NR). It is 6 minutes long. Here, the Neg needs to defeat the 1AR, rebuild their own positions, and also crystallize the round for the judge (it is their final speech). Given how much the Neg needs to accomplish, the Neg will often “collapse” down to one core position and spend time explaining a couple of central arguments. They will also consolidate down to a couple of core attacks on the Aff’s case. The 2NR is not allowed to make new arguments – if the argument was not in the 1NC, it cannot be made in the 2NR, although there is leeway in answering new 1AR arguments.
The Second Affirmative Rebuttal, or 2AR, is 3 minutes long. It is the final speech of the debate. Here, the 2AR must reply to the 2NR and summarize the round. Judges typically apply a strict standard of new-ness to the 2AR – arguments not in the 1AR are strictly forbidden in the 2AR, since the Neg does not get a 3NR to reply. The Aff will give “voting issues” often (reasons why the Aff wins) and make sure to rebuild their case and answer the 2NR.

Judging Speech

Speech Round Overview
Choose a tab below for more info.
- Before a Speech Round
- During a Speech Round
- After a Speech Round
Review Your Ballot
- You will receive a paper or electronic ballot.
- The ballot lists the speakers in order, has a place for you to enter results, and typically includes space for feedback about each competitor.
- The ballot will also tell you which room you are assigned.
- A typical round will include six different contestants, although this number can fluctuate depending on how many students are signed up.
Prepare to Judge
- You will watch the entirety of the round, which typically lasts for about one hour.
- Silence your notifications so that the speakers can have your full attention!
- Bring a computer or notepad so you can take notes on each speech.
- Have a cell phone or stopwatch with you so you can time each speech.
Understand Tournament Policy
- As the judge, you will ask competitors to perform one at a time in the order that is listed on your ballot.
- In speech, it is common for competitors to enter in more than one event at the tournament; this is called being cross-entered.
- Students who are cross-entered may ask to speak out of order because they have another event to attend.
- You may also notice that you do not have all of your competitors in the room when the round is supposed to start. This is often because a student that is competing in your room is cross-entered and has gone to speak in a different room first.
- Find out whether cross-entry is allowed at the tournament you’re judging, and ask the coach of your school or a tournament official if there is a recommendation on how to handle it! Typically, tournaments will ask you to begin with the first speaker who is present, even if they are not the first one on your ballot. Tournaments with cross-entry typically do not allow judges to penalize students for entering the room late.
Invite the Speakers to Begin
- When you reach the time the round is supposed to begin, ask the first speaker who is listed on your ballot to begin their speech. Competitors will speak in the order listed on your ballot.
- After each speech, simply thank the competitor and invite the next speaker to begin.
Time Each Performance
- Using your phone or an electronic stopwatch, time each student from when they begin speaking to when they stop.
- Make note of the amount of time each speech lasted.
- Each speech event has a time limit and a 30-second grace period. If a student’s speech goes beyond the time limit and 30-second grace period, that student cannot be ranked the best in the round.
- There is no further penalty for going over time, and there is no penalty for being under time.
Time Signals
- Students will occasionally ask for time signals because you are timing their speeches, and it is up to you whether or not you would like to honor that request.
- Time signals let competitors know how much of their time limit they have left in the speech.
- The most common time signals are to alert the student when they have one and two minutes remaining by holding one or two fingers in the air.
- Take notes during each speech. Write down anything that stood out to you about each speech—the best moments, the parts of the speech that could be improved, and ideas for how the student can make their speech better.
- Many judges find it is easiest to record this feedback during the speech instead of waiting until all performers have finished.
Be Attentive
- Minimize anything that could be distracting for the performers like cell phone notifications and make it clear that you are giving the competitors your full attention.
- Perception can be reality for performers. For example, if you are judging online, you may be fully attentive while your camera is off, but the competitors cannot tell!
Evaluate the Speakers
- When the last speaker has finished their speech, thank all of the competitors and dismiss them from the room.
- Review your notes and, if needed, review resources related to the event you are judging so you know what factors in the speeches to consider.
Complete Your Ballot
- Rank the students from best to worst in the round.
- The best performance will receive a ranking of 1, the second best will receive a ranking of 2, and so on.
- Depending on the tournament, you may also be asked to assign competitors speaker points. These points help further differentiate the excellence of each speaker.
- Typically, points are awarded on a scale of 80-100, with 100 being outstanding.
Write Feedback
- In the comment section on the ballot, record your thoughts about each performance, suggestions for improvement, and general feedback for the performer.
- The students and their coaches receive this feedback at the end of the tournament and use it to improve!
Turn in Your Ballot
- After the rankings are complete, judges should return their ballots to the tournament organizer in person or electronically, depending on the tournament’s procedures.
- Congratulations on completing the round, and thank you for judging!
Speech Judging Resources
There are several different events that fall within the category of “speech.” Some of these events are partner events, some are self-written, some are memorized, and some of them are longer than others.
Select an event from the table to find resources specific to judging that particular event!
- Duo Interpretation (DUO)
- Humorous Interpretation (HI)
- Dramatic Interpretation (DI)
- Program Oral Interpretation (POI)
- Extemporaneous Speaking (IX and USX)
- Original Oratory (OO)
- Informative Speaking (INF)
- Prose (PRO)
- Poetry (POE)
- Pro Con Challenge (PCC)
- Original Spoken Word Poetry (SW)
- Impromptu (IMP)
- Declamation (DEC)
- Expository (EXP)
- Extemporaneous Commentary (EXC)
- Storytelling (STO)
Choose an Event
Declamation is a memorized event. There is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Declamation
- Save this one-page overview of how to judge Declamation
- Review a sample Declamation ballot with written feedback
- Check out a video on how to judge Impromptu
Humorous Interpretation (HI) is a memorized event, and there is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Humorous Interpretation
- Review a sample HI ballot with written feedback
- Check out a video on how to judge the cutting, blocking, and characterization of an Interpretation performance
Dramatic Interpretation (DI) is a memorized event, and there is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Dramatic Interpretation
- Review a sample DI ballot with written feedback
Program Oral Interpretation (POI) performances require that the speaker uses a binder or booklet. There is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Program Oral Interpretation
- Save this one-page overview of how to judge POI
- Review a sample POI ballot with written feedback
- Check out a video on how to judge Program Oral Interpretation
There are often two different categories of Extemporaneous Speaking: International Extemp (IX) and United States Extemp (USX). These two events function the same way, but IX features topics that are international in nature, and USX features topics about the United States. Extemp speakers will report to the “prep room” 30 minutes before their round begins to select a topic, prepare a speech, memorize it, and come to the room to perform it for you! You should expect speakers to join your room one at a time with a few minutes in between each speech. Extemp speeches in both IX and USX are memorized with a time limit of 7-minutes and a grace period of 30-seconds.
- Learn more about International Extemp and United States Extemp
- Review a sample Extemp ballot with written feedback
- Check out a video on how to judge Extemporaneous Speaking
Resource package subscribers can practice using a real round ! Review a video of a full Extemp round and corresponding ballots from a panel of real Extemp judges.
Original Oratory (OO) is a memorized event meant to persuade you. There is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Original Oratory
- Review a sample Original Oratory ballot with written feedback
- Check out a video on how to judge Original Oratory
Informative Speaking (INF) is a memorized event meant to educate you. Students may or may not choose to use visual aids. There is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Informative Speaking
- Review a sample Informative ballot with written feedback
- Save this one-page overview of how to judge Informative
- Check out a video on how to judge Informative Speaking
Prose (PRO) performances require that the speaker uses a binder or booklet. The time limits for Prose differ in many states, so check with your tournament director! At the high school level for the NSDA National Tournament, there is a 5-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period. At the middle school level for NSDA tournaments, there is a 7-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Prose
- Review a sample Prose ballot with written feedback
Poetry (POE) performances require that the speaker uses a binder or booklet. The time limits for Poetry differ in many states, so check with your tournament director! At the high school level for the NSDA National Tournament, there is a 5-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period. At the middle school level for NSDA tournaments, there is a 7-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Poetry
Review a sample Poetry ballot with written feedback
Pro Con Challenge (PCC) is typically an online event. It features a pro and a con speech performed within a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period. The performance should not be memorized.
- Learn more about Pro Con Challenge
- Review a sample Pro Con Challenge ballot
- Check out this video on how to judge Pro Con Challenge online.
In Impromptu (IMP), students have 7 minutes to select a topic, write a speech, memorize the speech, and deliver it. Students typically draw their Impromptu topic from an envelope that the judge receives before they go to their room. Students may prepare for 2 minutes and speak for 5, prepare for 4 minutes and speak for 3, and so on.
- Learn more about Impromptu
- Save this one-page overview of how to judge Impromptu
- Review a sample Impromptu ballot with written feedback
Original Spoken Word Poetry (SW) is a memorized event. There is a 5-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Original Spoken Word Poetry
- Review a sample Original Spoken Word Poetry ballot
Expository is a memorized event. There is a 5-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Expository
Students in Extemporaneous Commentary (EXC) will report to the “prep room” 20-minutes before their round begins to select a topic, prepare a speech, memorize it, and come to the room to perform it for you! You should expect speakers to join your room one at a time with a few minutes in between each speech. Extemp Commentary speeches are memorized and delivered from a seated position behind a table or desk. There is a time limit of 5-minutes and a grace period of 30-seconds.
- Learn more about Commentary
Storytelling is a memorized event. There is a 5-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Storytelling
- Check out a video on how to judge Storytelling
Duo Interpretation (DUO) is a two-person event. The performance should be memorized, and there is a 10-minute time limit with a 30-second grace period.
- Learn more about Duo Interpretation
- Review a sample DUO ballot with written feedback
Highlights from Day 4 of Trump’s hush money trial
What to know about trump's hush money trial.
- Former President Donald Trump's hush money trial resumed today in New York City for the fourth day. Alternate jurors were selected before the court held what's known as a Sandoval hearing to discuss the scope of the prosecution's cross-examination if Trump decides to testify. Trump later told reporters he will take the stand.
- A man set himself on fire outside the courthouse this afternoon, just before the trial took a break for lunch. The man, whom police identified as Maxwell Azzarello of St. Augustine, Fla., was in the designated protest area.
- Yesterday , state Judge Juan Merchan swore in 12 jurors after dismissing two who were already selected after they raised concerns about personal information that was made public.
- Trump has pleaded not guilty to 34 counts of falsifying business records related to a $130,000 payment made to adult film actor Stormy Daniels at the end of the 2016 election cycle to keep her quiet about her allegation that she and Trump had a sexual encounter. Trump has denied the affair.
- Catch up with what you missed on Day 3 .
How Trump tried to control his first week in court
Trump emerged from a Manhattan courtroom Monday ready for a fight.
After day one of a trial that has him facing 34 counts of falsifying business records related to hush money payments to a porn star, the former president stood in front of reporters ready to unleash a grievance-laced tirade that, at times, did not totally reflect reality but guaranteed he would continue to dominate the headlines even from court.
His immediate focus was Judge Juan Merchan’s decision to not yet rule on whether Trump can attend his son Barron’s May 17 high school graduation. Merchan did not say Trump could not go, but rather he was not yet ready to rule on the matter. Specifics aside, however, it gave Trump just enough to paint the picture for his supporters of a biased judge blocking a loving father from seeing his son’s graduation.
Read the full story here .
Trump’s lawyers used jury consultant to research and help select jurors
Megan Lebowitz
Corky Siemaszko
The New Yorkers who could decide Trump's fate were vetted in real time today by the former president’s defense team.
As the potential alternate jurors were being questioned by prosecutors seeking to convict Trump of illegally paying hush money to a porn star, and by defense attorneys trying to keep him out of jail, a jury consultant hired by Trump’s legal team was watching the candidates closely for telltale signs of possible bias while simultaneously feeding the defense attorneys her impressions.
Meanwhile, a team of researchers working with the jury consultant were doing social media and other online searches to fill out the picture of every potential juror and sending that information to Trump’s lawyers in the courtroom.
Read the full story here.
Police 'emptied' fire extinguisher on man who set himself on fire, witness says
Susan Kroll
Zoë Richards
Monica Dunn
An eyewitness said he saw police empty a fire extinguisher on the man who set himself on fire outside of the courthouse this afternoon.
"He was alive and moving when they put him on the ambulance, and they got him out of here pretty quickly," freelance photojournalist Ed Quinn told NBC News in an interview.
Quinn said he was standing alongside the fence at Collect Pond Park near the courthouse when the park filled with smoke, "and then the smoke from the fire extinguisher was billowing around. People were horrified."
New York AG asks judge to void Trump’s bond in his civil fraud verdict
In a separate case, New York Attorney General Letitia James today asked that a judge void Trump's bond in his civil fraud case, questioning whether the company that issued it has the funds to back it up.
In a 26-page filing ahead of a scheduled hearing on Monday, James expressed concern about whether Knight Specialty Insurance Company could secure the $175 million bond. She also argued that the collateral put up by the former president should be under the full control of the company.
One of James’ concerns about KSIC is that the insurer “is not authorized to write business in New York and thus not regulated by the state’s insurance department.” She added that the company “had never before written a surety bond in New York or in the prior two years in any other jurisdiction, and has a total policyholder surplus of just $138 million.”
Trump arrives back at Trump Tower
The former president's motorcade returned to Trump Tower, where he waved to the crowd, shortly after 5 p.m.
Trump says he will testify in hush money trial
Alec Hernández
Alexandra Marquez is based in Washington, D.C.
On his way out of the courtroom today, Trump was asked whether he will testify in this case.
He answered simply, "Yes."
Trump previously indicated he would take the stand.
State appeals court denies Trump's request to delay trial
Katherine Koretski
Another appeals court has denied Trump's request to delay the hush money trial.
Trump's lawyers filed another appeal of the decision to not move the trial out of Manhattan.
Trump speaks to reporters, reiterates unfounded claims
Trump spoke with reporters after the court was adjourned, reiterating accusations that the trial is a "concerted witch hunt" and repeating unfounded claims that he was being targeted to hurt his campaign.
After this morning complaining to reporters that the case was keeping him stuck in court for weeks, this afternoon Trump complained that the judge was moving too quickly.
Trump also railed against the civil fraud case, also in New York, criticizing New York Attorney General Letitia James and Judge Arthur Engoron.
The former president did not answer shouted questions from reporters.
Court adjourns for the weekend
The court adjourned for the day.
Trial proceedings will resume on Monday at 9:30 a.m. ET.
Opening statements will take place on Monday, judge says
Kyla Guilfoil
Jillian Frankel
Judge Merchan said this afternoon that the trial will move to opening statements on Monday, a timeline he said he was aiming for earlier this week.
“We’re going to have opening statements on Monday morning. This trial is starting," Merchan said.
Judge says he won't consider Trump's immunity motion
Judge Merchan said that he would not consider Trump's immunity motion that was filed just before the hush money trial began.
“That matter is decided and will not be addressed any further," Merchan said.
Merchan to decide Sandoval hearing questions on Monday
Judge Merchan told attorneys that he'll have an answer on the Sandoval hearing questions on "Monday morning."
He added that he'll also need time that day "for a few matters I want to take up including pre-motion letters that have been filed."
His remarks came after the court heard arguments over what prosecutors plan to ask defendants on cross-examination in order to help them decide whether to take the stand in their own defense.
Prosecutors cited a variety of verdicts and prior judgments against Trump, among them, verdicts in a pair of lawsuits brought by writer E. Jean Carroll that found him liable for sexual abuse and defamation and a judgment in New York Attorney General Letitia James’ civil fraud lawsuit against the former president and the Trump Organization which found that he committed fraud .
Trump attorney Emil Bove argued that the civil fraud lawsuit should not be permitted for questioning, contending “these findings are very much subject to review,” and citing a partial stay of the relief in that case .
Matthew Colangelo of the DA’s office pushed back, saying it was “hard to think of something that is more squarely in the wheelhouse” for questioning, referring to the findings of “persistent and repeated fraud and illegality.”
Prosecution points out that Merchan presided over a Trump case being debated as relevant
Ginger Gibson Senior Washington Editor
In the Sandoval hearing, lawyers for both sides have ticked through the cases that prosecutors want to be able to ask Trump about if he testifies. Included in them is a case that Merchan himself presided over.
"As your honor knows as you presided over the trial, my colleagues argued extensively Mr. Trump knew about the scheme to defraud and conspiracy and falsifying business records," said prosecutor Matthew Colangelo.
"The owners of the corporation knew it and the owner was Mr Trump. The evidence at that trial showed the defendant knew and the court of appeals says the defendant can be questioned, and we don’t see any issue with the witness advocate where the attorney would be a fact witness," he added. "We only want to question the defendant about the fact and there is no plausible problem there.”
Judge lashes out at Trump attorney over redactions: 'Have a seat'
In a tense exchange over redacting certain documents, Bove told Merchan that prosecutors "have been invested in this case since 2018, and to say this is too much work is outrageous,” referring to Trump's attorneys' claim that it would be too much work to redact certain documents.
"I am not going to ask people to do that. It is absurd,” the judge told Trump's lawyer, adding, "Have a seat, I am signing the order."
Police say man who set himself on fire threw 'conspiracy theory' pamphlets
Marlene Lenthang
Maxwell Azzarello, the man identified by police as the person who set himself on fire, had thrown numerous pamphlets around a park near the courthouse, authorities said.
“The pamphlets appear to be propaganda-based, almost a conspiracy theory type of pamphlet,” NYPD Chief of Detectives Joseph Kenny told reporters. "So, a little bit of a conspiracy theory going on here."
Azzarello took out a canister from his bag containing what’s believed to be an alcohol-based accelerant, doused himself and set himself ablaze, police said.
Officers and civilians ran into the park and attempted to put out the flames using coats and fire extinguishers, NYPD Chief of Department Jeff Maddrey told reporters.
Four police officers suffered minor injuries from fire exposure, authorities said.
Trump has returned to the courtroom
Gary Grumbach
Trump is back in the courtroom as the trial resumes. Lawyers are expected to discuss his possible testimony now.
Police identify man who set himself on fire
Police identified the man who set himself on fire as Maxwell Azzarello, of St. Augustine, Florida.
He is alive, currently intubated and in critical condition at the Weill Cornell Medicine — Burn Center.
Azzarello arrived in New York sometime earlier in the week, and his car was known to be in St. Augustine on the 13th. Police said they've spoken with his family, who were unaware he was in New York.
Trump campaign comments on man who set himself on fire
The Trump campaign released a statement this afternoon offering its "condolences to the traumatized witnesses" after a man set himself on fire outside the courthouse where the former president is on trial.
“Not knowing the motivations behind this sickening situation, it’s difficult to make any definitive remarks, other than to say we are thankful that to the best of our present knowledge, nobody other than the individual in question was hurt," national press secretary Karoline Leavitt said.
She also thanked "the great first responders of the City of New York for their actions.""Today is more proof that our nation is in deep trouble," Leavitt added before using Trump's campaign slogan "Make America Great Again."
Witness: Someone shouted, 'He's going to light himself on fire'
Katherine Doyle
Ed Quinn, a freelance photojournalist who lives in the East Village, said he was facing the court when “I heard someone scream, ‘He’s going to light himself on fire.’”
“I see him dumping gasoline on his face, very deliberately,” he said. “He had gray T-shirt on. It soaked his face. It soaked his shirt. Boom, he went up.”
Quinn said it took the police about a minute to arrive. “Women were begging, screaming, put it out, put him out,” he said.
Trump on Truth Social: 'Judge Merchan is railroading me'
In a new post on his social media network Truth Social, Trump accused Merchan of "railroading" him.
“Judge Merchan is 'railroading' me, at breakneck speed, in order to completely satisfy his 'friends.' Additionally, he has 'GAGGED' me so that I cannot talk about the most important of topics," Trump said in his post.
The former president also called President Joe Biden "crooked" and described this case as "election interference."
Video shows man after setting himself on fire
A video appears to show that moments after setting himself on fire, the man lay on the ground burning. At times, he appeared to seize. Police tried to use a small fire extinguisher to put the fire out, but were unsuccessful. While still on fire, the man tried to sit up. Police then used a large extinguisher to put out the fire.
Injured man is being taken to a hospital, police say
An injured man is being placed in an ambulance in critical condition and will be transported to a hospital, the New York City Police Department said Friday afternoon following reports that a person set themselves on fire outside the courthouse.
Police said they responded at 1:37 p.m. to the vicinity of 80 Centre St. for an aided male.
The fire is out, and the investigation is ongoing, authorities added.
Police responding to the man on fire outside the building
The New York Police Department already had a heavy presence outside of the courthouse, due to the high profile of this case. As smoke emerged from the dedicated protest area, they rushed to find what looked like a fire extinguisher.

A man set himself on fire outside the trial
A man set himself on fire inside the designated protest area outside of the Trump trial in New York, a witness says.
A person in the designated protest area is on fire
Rebecca Shabad is in Washington, D.C.
There is a person who was in the designated protest area outside the courthouse who is on fire.
Potential juror excused for past social media posts against Trump
A potential juror was excused after Trump's attorneys and Merchan examined his past social media posts about Trump.
“I don’t recall posting that,” the juror said. “That’s not mine.”
Still, the juror added, “At that time, yeah I may have thought that,” before he was excused by the judge.
Jury is complete
The sixth alternate has been seated.
Potential juror said Jan. 6 was an 'insurrection'
A male prospective juror said the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the Capitol was an "insurrection" during voir dire with Trump's lawyer.
When asked if he has strong opinions and about his posts about Trump, he said, “It’s more just the negative rhetoric and bias that he speaks about which is the most harmful.”
Asked if the juror has expressed a strong dislike for Trump, he said, “Based on his rhetoric, yes.” He added that he would stay focused on “what is the law, what constitutes breaking the law?”
One juror says he thinks of Trump as 'usually awesome'
One juror, when questioned about how he views Trump, said that when he thinks of the former president, he thinks "usually awesome."
"I don’t know him personally. He’s a family man. He’s a businessman," the juror also said about Trump.
Trump gets inside look at potential voters
Laura Jarrett
Once again Trump is getting treated to a mini political focus group in this courtroom, getting an inside look at potential voters in the 2024 election.
There are some potential jurors who said they support Trump's policies and find him to be a "family man." There is also at least one juror who said he has trouble with the Republican Party's positions on religion and women’s rights to control their own bodies.
The trial continues to be a fascinating look at everyday New Yorkers for a presumptive GOP nominee thinking of how to message to voters this fall.
Trump lawyer asks prospective juror, sexual assault survivor, if she would hold Trump's background against him
A prospective juror, asked about her views of Trump, said, “His rhetoric, at times, causes people to feel enabled.”
When asked what specifically about his rhetoric, she admitted she’s not even sure what his policies are, but noted that people have cited Trump in justifying their own racist, sexist or homophobic comments.
Trump lawyer Susan Necheles then asked whether this prospective juror, an admitted survivor of sexual assault, would hold it against Trump that women — outside this case — have accused Trump of sexual assault.
Another potential juror has been excused after expressing ‘anxiety’ about the trial
Yet another potential juror has been excused from the trial after saying that she is feeling "anxiety" and self-doubt. The potential juror's voice cracked while answering questions.
The juror is now the third to be excused Friday, underscoring the difficulty the court faces for picking Trump's jury.
Juror breaks down crying during voir dire
One of the jurors being questioned, who earlier said her father is friends with former New Jersey Gov. Chris Christie, broke down crying, saying, “I have to be honest, I feel so nervous and anxious right now. I’m sorry."
She added, "I thought I could do this ... I don’t want you to feel like I’ve wasted anyone’s time.”
Merchan called her over to the judge's bench to speak before excusing her.
Prospective juror who served prison time dismissed
A prospective juror who said she served two years in prison was dismissed by the judge who commended her bravery for sharing such personal details.
Technically, she is ineligible to serve on the jury.
“What you just did is something that most people in this courtroom would not be able to do," Merchan said to the juror.
Merchan said that the mere fact that she was convicted does not preclude her from service, but that she needs a certificate of release to be qualified for service going forward and, even then, it will depend on the nature of the case.
She was then excused and cheerfully called out, “Good luck!”
Court back in session
The jury selection process is resuming.
10-minute break
The court has taken a 10-minute break before questions for the alternate juror pool.
Potential juror says he has been 'trying to find a wife' in his spare time
One potential juror answered that his hobbies included "trying to find a wife" in his spare time.
The insurance broker, who lives in Midtown East, also added that he has a few close friends who are court officers.
Trump's interest piqued by juror who watches Fox News
When a prospective juror said she is a Fox News viewer, Trump cocked his head, then quickly conferred with Blanche. The woman added she also reads The New York Times, New York Post and The Wall Street Journal.
Trump resumed looking at her as she finished responding to the questionnaire. He appears most interested in jurors whose answers offer ambiguity around their personal political views.
Potential juror says he listens to podcast, which has featured some Trump-supporting guests
Dareh Gregorian
A potential juror who works in information technology and audio said that he listens to the "Order of Man" podcast, which happens to be very Joe Rogan-esque.
The podcast has had some Trump-supporting guests on, including one man who ordered his financial company to stop doing business in New York after the fraud judgment against Trump.
Potential juror details volunteering for Hillary Clinton campaign
One juror told Merchan that he "volunteered for get out the vote for the Democratic Party during the Clinton campaign." The volunteer work would have taken place during the same election cycle when Trump beat Clinton to win the presidency.
The potential juror added that he also "attended the Women’s March.”
A potential juror mentions Citizens United
One juror, when asked by Merchan about whether they can be fair and impartial, brought up the landmark Supreme Court campaign finance case Citizens United, saying, "Citizens United is the law of the land but I do favor people who make political contributions to have the source of the contributions made public."
“There is no reason why I can’t be a fair and impartial juror,” the person added.
Potential juror says he doesn't use Facebook and only 'signed up in middle school'
One potential juror, a younger man, said that he doesn't read or watch any news and while he has a Facebook account, he doesn't go on it.
He said he "signed up when I was in middle school or whatever."
Trump already sitting with his eyes shut

The former president is sitting with his eyes shut and appears to be chewing on something as he sits at the defense table.
First potential juror dismissed after saying she has anxiety
The first potential juror questioned this morning was dismissed after saying she has anxiety and wouldn't be "able to be completely here and fair."
“I have really really bad anxiety and people have found out where I am," she said earlier.
Trump takes his seat in court
Trump just took his seat in the courtroom in between his attorneys Emil Bove and Todd Blanche. He immediately began studying some documents in front of him and conferring with Bove.
Still photographers were in for the daily photographs, several of them pressing up against the table to get close-ups. Merchan then took his seat on the bench, saying they were working on fixing the temperature in the courtroom, which was cold yesterday, before continuing jury selection.
Trump's campaign spokesman, Steven Cheung, is in the back of the courtroom with lawyer Cliff Robert, who represents the Trump parties in the civil fraud case.
All 22 prospective jurors are present.
The 12-person jury and an alternate has been seated in the criminal trial of Trump, consisting of seven men and five women. Five more alternates will need to be selected in an effort to set up opening statements as soon as next week.
Trump says the gag order imposed on him needs to be removed
As Trump entered the courthouse this morning, he said to the cameras that Merchan needs to remove the gag order against him because it's "very, very unfair."
"They've taken away my constitutional rights to speak," Trump said. "Why am I gagged about telling the truth?"
The former president repeated that he thinks the trial is "rigged" and is "coming from the White House" and said it's "very unfair" that he is required to sit in a courthouse all day instead of going to battleground states to campaign for president.
"The gag order has to come off," he said.
Trump heads to court
Jake Traylor
The former president's motorcade has departed Trump Tower and is headed to the courthouse.
Judge denies Trump co-defendants’ motions to dismiss charges in classified documents case
U.S. District Judge Aileen Cannon yesterday denied motions by two of Trump's co-defendants to dismiss charges in the classified documents case — one of the four criminal cases, along with the hush money trial, that the former president is facing.
Trump aide Walt Nauta’s lawyers asked this month for five charges against him to be dismissed, while lawyers for Carlos De Oliveira, who was the property manager at Mar-a-Lago, Trump’s Florida estate, requested that all charges against him be tossed out.
In her filing in Florida, Cannon said De Oliveira “does not meaningfully dispute that the charging document satisfies the minimum pleading standards.” She also noted that his lawyers can challenge prosecutors’ evidence during a trial, “where the Special Counsel will bear the entire burden of proof as to all essential elements of the obstruction offenses.”
Similarly, she dismissed the motion from Nauta’s lawyers, who had argued that obstruction charges against him were unconstitutionally vague .
Cannon said she was in “general agreement with the Special Counsel” that the indictment’s allegations “provide enough of a basis to deny Nauta’s request for dismissal on vagueness grounds.”
Both men had also requested bills of particulars, meaning more details about the charges against them and why they are being accused of crimes. Cannon denied those requests, as well.
“The Court cannot say that the Indictment as a whole lacks sufficient information to assist Nauta in preparing for trial, and the discovery provided in this case is exceedingly voluminous,” Cannon said about Nauta’s request.
Read the full story here
Legal experts have suggested that Trump’s hush money case is the weakest, but the Manhattan DA says it goes beyond that and has more to do with election interference in the 2016 election.
Alternate jurors and key legal arguments on tap in Trump hush money trial
Jury selection will continue — and could conclude — today in Trump ‘s historic New York criminal trial.
With a full 12-person jury and one alternate juror sworn in yesterday, Merchan has called a pool of 96 potential jurors to his Manhattan courtroom in hope of finding five more alternate jurors for the first trial of a former president , which is expected to last roughly six weeks.
In addition to those 96 potential jurors, there are 22 left over from yesterday who will be questioned, as well.
If the effort to fill the jury box is successful, opening statements could take place as soon as Monday.
The main panel of 12 is made up of seven men and five women, including two lawyers, a teacher, a retired wealth manager, a product development manager, a security engineer, a software engineer, a speech therapist and a physical therapist. The foreman — the juror who essentially acts as the leader and spokesperson for the panel — is a married man who works in sales and gets his news from The New York Times, MSNBC and Fox News.
The lone alternate selected yesterday is a woman who works as an asset manager.
Also today, Merchan is expected to hold what’s known as a Sandoval hearing , a type of hearing designed to let defendants know the scope of questions they could face from prosecutors on cross-examination so they can make informed decisions about whether to take the witness stand in their own defense.
Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg’s office disclosed in a court filing that it would like to ask Trump about several items, among them the $464 million civil judgment against him and his company for fraud , the total $88 million verdicts and liability findings for sexual abuse and defamation in lawsuits brought by writer E. Jean Carroll, and a number of other adverse court rulings over the past few years.
Trump has denied wrongdoing in all the cases and is appealing the fraud judgment and the Carroll verdicts.
Trump’s curiosity with jurors ebbs and flows during final stage of selection process. Here’s what you missed on trial Day 3.
Jury selection in Trump’s hush money trial yesterday revealed there are certain topics that are likely to capture his attention: Miami, real estate and media.
When one New Yorker talked about his decades in law enforcement, Trump raised his eyebrows. The juror, who said he holds Yankees season tickets, added that he reads the New York Post and Daily News. It was as if Trump, who moments earlier let out a yawn, was seized by an electrical current.
Later, Trump straightened his back and cocked his chin as a young lawyer, born and raised in Miami, began running through her answers to the jury questionnaire. Asked whether she had been the victim of a crime, the woman said her phone was stolen from her in Paris, and she noted that her family’s car was “incidentally burned in an arson in Italy.”
Any reprieve Trump may have hoped for from the woman soon fell away as she talked about reading The Washington Post, a newspaper he has railed against. She said that while she harbors “opinions” about Trump, she is “very comfortable that I can put those aside.” The woman described watching Fox News occasionally “just to try to see what’s going on all sides.”
Trump crossed his arms and glared at the space in front of him.
Both jurors were later dismissed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Understand how debates work. You will be given a debate topic - this is called a "resolution." Your team must take a stance either affirmative or negative to the resolution. Sometimes you will be given the stance, and sometimes you will be asked to take a position. You may be asked to stand affirmative or negative.
Here is a standard debate speech format for a 20-15 minutes long debate: Opening Statements. Affirming Side: 5 minutes. Opposing Side: 5 minutes. Rebuttals (No New Arguments) Affirming Side: 3 minutes. Opposing Side: 3 minutes. Cross-Examination. Affirming Side to Opposing Side: 3 minutes.
Step 3: Signposting. Signposting may seem annoying and unnecessary. If you're a word-enthusiast it can even seem like it's disrupting the flow of your otherwise smooth and lyrical speech. However, it's completely and totally necessary in the structure of a good debate. You may think that you've written the best and most easy-to-follow debate in ...
1. Choose a Topic For Your Debate. Also called a resolution or a motion, the topic is sometimes chosen to debate. This is usually the case in a school activity to practice debating skills. The resolution or motion is usually centered around a true or false statement or a proposal to change the current situation.
Use Vocal Variety and Tone. Vary your vocal tone and pace to add interest and emphasis to your speech. Use pauses and changes in pace to emphasize important points, and vary your volume to make your arguments more impactful. Use the Debate Speech Checklist. Here is a checklist that can help you evaluate your debate.
Debate Speech Format. You can follow the following pattern for a debate speech. Opening Statements and Explanation. This section consists of the opening sentences by using three arguments with explaining questions. Pro Tema - Up to 5 minutes. Con Team - Up to 2 minutes. Con Team - Up to 5 minutes. Pro Team - Up to 2 minutes.
1. Understand the Debate. The first of many steps in debate writing is understanding its nature. Here, both teams will be given a topic, and they will choose an affirmative or negative stance. 2. Research the Topic Thoroughly. Brainstorm and research the topic thoroughly to understand all the aspects of the debate.
Define your position: Clearly state your stance on the issue at hand. Your position should be strong, specific, and concise - bold statements will keep your audience engaged in the debate. 4. Develop your main arguments: Identify 2-3 compelling arguments supporting your position. These should form the backbone of your debate speech.
Adaptability: Flexibility In The Face Of Challenges. Responsive Approach: Be prepared to adapt your strategy based on the flow of the debate. Flexibility allows you to navigate unexpected turns and respond effectively to evolving circumstances. Open-Mindedness: Demonstrate an open-minded approach to new information.
3. Main Arguments: The Heart of Your Speech. Main arguments are the star of your speech. They serve as the backbone of your speech, providing the content that supports your position. While ...
06 DEBATE 101: Everything You Need to Know about Policy Debate: You Learned Here NATIONAL SPEECH DEBATE ASSOCIATION I. ARGUMENTS. Arguments are the building blocks of debate. Learning about making arguments the right way is the essence of being well spoken in any walk of life, whether it is in the classroom, the workplace or at the kitchen table.
Manner is how you deliver your speech. It will include anything that enhances you presentation and makes it more engaging: the tone and volume of your voice, how quickly you speak, hand gestures, eye contact, your stance, and how you use your notes (always use palm cards - NEVER an A4 sheet of paper!). Method: How you organise it.
A debate is a structured contest over an issue or policy. There are two sides - one supporting, one opposing. Benefits of debating include: Allowing you to think about aspects and perspectives you may not have considered. Encourages you to speak strategically. Improving public speaking skills. Learning how to create a persuasive argument.
shape, or form. In speech and debate this word represents one of the most popular and rigorous middle school events. In Impromptu, you are given a choice among three prompts and have seven minutes to prepare and deliver a speech about anything related to the prompt. At its core, an Impromptu speech is your statement about life, society, history ...
A debater loses points for finishing more than 15 seconds before the allotted time, or 15 seconds after the allotted time. During each presentation, the debater must speak fluently, use gestures, accentuate keywords, and maintain a good posture. And this brings us to the parameters for judging a debate.
This short video provides seven steps to assist when writing a debate. It is a follow up to the previous video 'How to run a debate'.
All participants should meet 15 minutes before the start to prepare materials. Starting the debate. Participants should determine the debate's time limit, as speeches cannot last nonstop. Usually, each speaker is given a maximum of 3 minutes for their presentation. At the beginning, the speakers should introduce themselves.
Student Format Manual. Big Questions debating format involves opposing contestants debating a topic concerning the intersection of science, philosophy, and religion. Students can compete as individuals or as a team, this means rounds can be 1 vs. 1, 2 vs. 2, or 1 vs. 2.
First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular ...
The ability to clearly communicate ideas to others will serve to advance you both professionally and socially. Knowing that you can communicate well generates self-confidence in your ability to lead groups and conduct meetings. Grasping the fundamentals of effective communication will improve your conflict management ...
In your speech outline, you want to touch on several key elements. Pick your fight: Start by zeroing in on what you really want to change or influence with this speech. Support your claim with evidence: Identify those key points that back up your stance to appeal to your audience's rational side. The emotional hook: Weave in stories or facts ...
The First Affirmative Rebuttal (1AR) is 4 minutes long. Since it has to cover the long 1NC, it is the hardest speech in the debate. The Aff has two jobs - rebuilding ("extending") their case and attacking the Neg's positions. The Aff will typically spend around 2 minutes on their case and 2 minutes on their opponent's positions.
In Impromptu (IMP), students have 7 minutes to select a topic, write a speech, memorize the speech, and deliver it. Students typically draw their Impromptu topic from an envelope that the judge receives before they go to their room. Students may prepare for 2 minutes and speak for 5, prepare for 4 minutes and speak for 3, and so on.
Step 4: Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your speech the more you'll discover which sections need reworked, which transitions should be improved, and which sentences are hard to say. You'll also find out how you're doing on length. Step 5: Update, practice, and revise your speech until it has a great flow and you feel ...
Former President Donald Trump's hush money trial resumed today in New York City for the fourth day. Alternate jurors were selected before the court held what's known as a Sandoval hearing to ...
Five of the major US television networks have banded together to draft a letter urging President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump to commit to participating in televised debates ahead ...