Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
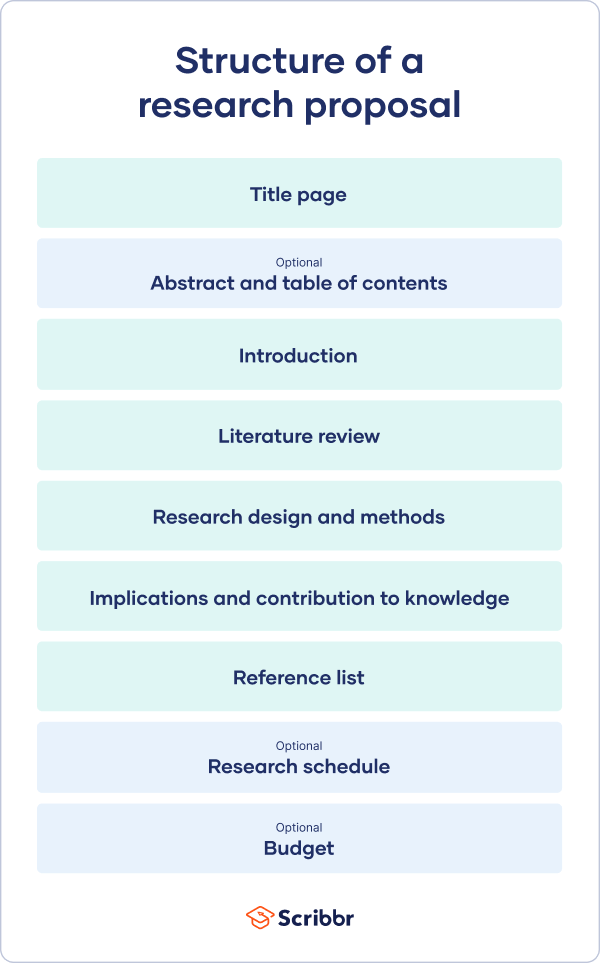
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 10 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

How to write a Research Proposal: Components of a research proposal
Components of a research proposal.
- Useful videos
- Common mistakes to avoid
- Sage Research Methods LibGuide This link opens in a new window
- Managing sources
- Request a literature search
- Research proposal - examples
- Creating a Gantt chart
- Free Apps for Research
- Academic writing
Research proposals differ in terms of their presentation depending on what each University department requires. In other words, there is no set template for a research proposal. Please contact your lecturer regarding the format you are expected to use for your research proposal.Thus, the components of a research proposal include, but are not limited to those mentioned in this guide.
1. The title
Try to come up with a title that is unique and at the same time easy to remember. It should also make a lasting impression to the reader and make them want to come back and read your proposal. The title must also capture the main concepts of the study . As the research process is lengthy, it is important that you choose a topic that you are so curious about that you remain motivated for the duration of the research process. Select a topic that you will be able to complete within the time frame that you have for your research.
3. The background
The background to the topic of your intended research must be clear and precise. It must not only include an in-depth explanation of the key points of your subject but also all the developments in the field as well as their timelines . The researcher must also explain the compelling interest in the research issue as well as the personal interest (if any) in the topic. This section must also indicate the specific area within which the topic falls in your particular field of study or subject . Aslo, how will the proposed study contribute to a particular field? In other words, the impact and the significance in a subject area must be clearly outlined. The target audience must also be clearly described.
5. Objectives of the research
It is important that the objectives are in alignment with the research questions. The objectives must indicate what the aim of the research study is. In fact, objectives give you a clear indication of the steps that you will take to achieve the aim of the research. The objectives must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
7. Literature review
Collect and present relevant literature on your topic of choice. It is important to include all the main authors or experts in a particular field. Depending on your field of study or topic, ensure that you include recent literature as well as literature that presents counterarguments to the topic. The justification for the study needs to based on existing literature. Click here for more information on how to write a literature review.
8. Limitations and delimitations of the study
The researcher must indicate the limitations of the study which are what the researcher cannot do or factors that are beyond the researcher's control, as well as delimitations that the researcher chooses not to address for the purposes of the study. Delimitations are boundaries that the researcher has set for the study. The r easons both for limitations and delimitations must be discussed in this section.
10. Work plan
Your schedule for the research must be stated clearly including the projected timelines for the various stages of your study.
11. Bibliography
All the sources that you have used for your proposal must be listed in alphabetical order using a referencing style that your lecturer has prescribed for your subject field.
Click here for more information on the various reference styles.
2. Introduction to the research
This section of the proposal must provide a broad overview of the topic. The jargon and key terms used in the particular topic must also be thoroughly explained in order to avoid confusion. The interest of the researcher in the particular topic must also be clearly outlined while at the same time mentioning, albeit briefly at this point, a critical review of the main literature that covers the topic. The researcher must also provide the aim of the research by clearly and concisely stating the problem, as well as the research questions to be dealt with. This section must also indicate what the research study will not be covering .
4. The research questions
The research questions must state clearly what your proposed study is meant to address or answer. Ensure that you use simple language that is easy to understand, while being cognisant of the level of your intended audience .
6. Research methodology / research methods
This section outlines the approach which the researcher will follow in order to address the research problem and to answer all the research questions from the researcher. The research design must be clearly defined, e.g., is the research Descriptive, Correlational, Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental, Experimental, Diagnostic or Explanatory.
State clearly
- how the research will be conducted in terms of the theoretical resources that will be used
- the theoretical framework for conducting the research, which is the theoretical approach drawn from your literature review to support your research study
- proposed research method(s)
- a comparison of the advantages, limitations and suitability of the available approaches and methods for conducting your research
- participants, instruments, procedure, analysis, etc.
Research design
Selecting the approach to use
Research approach
Research design and methodology
Importance of research
Attributes of a good research scholar
Summary of different research methodologies
9. Significance of the research
The researcher must provide justification for the need to conduct the study. What is the gap that the study will fill, and what is its contribution to the existing body of knowledge? The originality and importance of the research which will be level appropriate, must be clearly described, for instance, the required level of originality for a fourth year research project is different to that of a doctoral candidate.
The impact of the study for the subject field must be indicated. In other words, how will the research improve the field, who will it impact, how will it make changes in your industy or field etc.? Lastly, the proposed resaerch must be relatable , interesting and engaging .
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Books >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 1:02 PM
- URL: https://libguides.unisa.ac.za/research_proposal

Write a Research Proposal
Structure and content, introduction (to topic and problem), research question (or hypothesis, thesis statement, aim), proposed methodology, anticipated findings, contributions - impact and significance, tables and figures (if applicable).
- Questions for Editing and Revisions
Ask Us: Chat, email, visit or call

Video: Cite Your Sources: APA in-text citation

Get assistance
The library offers a range of helpful services. All of our appointments are free of charge and confidential.
- Book an appointment
The structure and content of a research proposal can vary depending upon the discipline, purpose, and target audience. For example, a graduate thesis proposal and a Tri-Council grant proposal will have different guidelines for length and required sections.
Before you begin writing, be sure to talk with your supervisor to gain a clear understanding of their specific expectations, and continually check in with them throughout the writing process.
- Organizing your Research Proposal - Template This 6-page fillable pdf handout provides writers with a template to begin outlining sections of their own research proposal.
This template can be used in conjunction with the sections below.
What are some keywords for your research?
- Should give a clear indication of your proposed research approach or key question
- Should be concise and descriptive
Writing Tip: When constructing your title, think about the search terms you would use to find this research online.
Important: Write this section last, after you have completed drafting the proposal. Or if you are required to draft a preliminary abstract, then remember to rewrite the abstract after you have completed drafting the entire proposal because some information may need to be revised.
The abstract should provide a brief overview of the entire proposal. Briefly state the research question (or hypothesis, thesis statement, aim), the problem and rationale, the proposed methods, and the proposed analyses or expected results.
The purpose of the introduction is to communicate the information that is essential for the reader to understand the overall area of concern. Be explicit. Outline why this research must be conducted and try to do so without unnecessary jargon or overwhelming detail.
Start with a short statement that establishes the overall area of concern. Avoid too much detail. Get to the point. Communicate only information essential for the reader’s comprehension. Avoid unnecessary technical language and jargon. Answer the question, "What is this study about?"
Questions to consider:
- What is your topic area, and what is the problem within that topic?
- What does the relevant literature say about the problem? – Be selective and focused.
- What are the critical, theoretical, or methodological issues directly related to the problem to be investigated?
- What are the reasons for undertaking the research? – This is the answer to the "so what?" question.
The following sections - listed as part of the introduction - are intended as a guide for drafting a research proposal. Most introductions include these following components. However, be sure to clarify with your advisor or carefully review the grant guidelines to be sure to comply with the proposal genre expectations of your specific discipline.
Broad topic and focus of study
- Briefly describe the broad topic of your research area, and then clearly explain the narrowed focus of your specific study.
Importance of topic/field of study
- Position your project in a current important research area.
- Address the “So what?” question directly, and as soon as possible.
- Provide context for the reader to understand the problem you are about to pose or research question you are asking.
Problem within field of study
- Identify the problem that you are investigating in your study.
Gap(s) in knowledge
- Identify something missing from the literature.
- What is unknown in this specific research area? This is what your study will explore and where you will attempt to provide new insights.
- Is there a reason this gap exists? Where does the current literature agree and where does it disagree? How you fill this gap (at least partially) with your research?
- Convince your reader that the problem has been appropriately defined and that the study is worth doing. Be explicit and detailed.
- Develop your argument logically and provide evidence.
- Explain why you are the person to do this project. Summarize any previous work or studies you may have undertaken in this field or research area.
Research question or hypothesis
- Foreshadow outcomes of your research. What is the question you are hoping to answer? What are the specific hypotheses to be tested and/or issues to be explored?
- Use questions when research is exploratory.
- Use declarative statements when existing knowledge enables predictions.
- List any secondary or subsidiary questions if applicable.
Purpose statement
- State the purpose of your research. Be succinct and simple.
- Why do you want to do this study?
- What is your research trying to find out?
Goals for proposed research
- Write a brief, broad statement of what you hope to accomplish and why (e.g., Improve something… Understand something… ). Are there specific measurable outcomes that you will accomplish in your study?
- You will have a chance to go into greater detail in the research question and methodology sections.
Background or context (or literature review)
- What does the existing research on this topic say?
- Briefly state what you already know and introduce literature most relevant to your research.
- Indicate main research findings, methodologies, and interpretations from previous related studies.
- Discuss how your question or hypothesis relates to what is already known.
- Position your research within the field’s developing body of knowledge.
- Explain and support your choice of methodology or theoretical framework.
The research question is the question you are hoping to answer in your research project. It is important to know how you should write your research question into your proposal. Some proposals include
- a research question, written as a question
- or, a hypothesis as a potential response to the research question
- or, a thesis statement as an argument that answers the research question
- or, aims and objects as accomplishment or operational statements
Foreshadow the outcomes of your research. Are you trying to improve something? Understand something? Advocate for a social responsibility?
Research question
What is the question you are hoping to answer?
Subsidiary questions (if applicable)
- Does your major research question hinge on a few smaller questions? Which will you address first?
Your hypothesis should provide one (of many) possible answers to your research question.
- What are the specific hypotheses to be tested and/or issues to be explored?
- What results do you anticipate for this experiment?
Usually a hypothesis is written to show the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Your hypothesis must be
- An expected relationship between variables
- Falsifiable
- Consistent with the existing body of knowledge
Thesis statement
Your thesis statement is a clear, concise statement of what you are arguing and why it is important. For more support on writing thesis statements, check out these following resources:
- 5 Types of Thesis Statements - Learn about five different types of thesis statements to help you choose the best type for your research.
- Templates for Writing Thesis Statements - This template provides a two-step guide for writing thesis statements.
- 5 Questions to Strengthen Your Thesis Statement - Follow these five steps to strengthen your thesis statements.
Aims and objectives
Aims are typically broader statements of what you are trying to accomplish and may or may not be measurable. Objectives are operational statements indicating specifically how you will accomplish the aims of your project.
- What are you trying to accomplish?
- How are you going to address the research question?
Be specific and make sure your aims or objectives are realistic. You want to convey that it is feasible to answer this question with the objectives you have proposed.
Make it clear that you know what you are going to do, how you are going to do it, and why it will work by relating your methodology to previous research. If there isn’t much literature on the topic, you can relate your methodology to your own preliminary research or point out how your methodology tackles something that may have been overlooked in previous studies.
Explain how you will conduct this research. Specify scope and parameters (e.g., geographic locations, demographics). Limit your inclusion of literature to only essential articles and studies.
- How will these methods produce an answer to your research question?
- How do the methods relate to the introduction and literature review?
- Have you done any previous work (or read any literature) that would inform your choices about methodology?
- Are your methods feasible and adequate? How do you know?
- What obstacles might you encounter in conducting the research, and how will you overcome them?
This section should include the following components that are relevant to your study and research methodologies:
Object(s) of study / participants / population
Provide detail about your objects of study (e.g., literary texts, swine, government policies, children, health care systems).
- Who/what are they?
- How will you find, select, or collect them?
- How feasible is it to find/select them?
- Are there any limitations to sample/data collection?
- Do you need to travel to collect samples or visit archives, etc.?
- Do you need to obtain Research Ethics Board (REB) approval to include human participants?
Theoretical frame or critical methodology
- Explain the theories or disciplinary methodologies that your research draws from or builds upon.
Materials and apparatus
- What are your survey or interview methods? (You may include a copy of questionnaires, etc.)
- Do you require any special equipment?
- How do you plan to purchase or construct or obtain this equipment?
Procedure and design
What exactly will you do? Include variables selected or manipulated, randomization, controls, the definition of coding categories, etc.
- Is it a questionnaire? Laboratory experiment? Series of interviews? Systematic review? Interpretative analysis?
- How will subjects be assigned to experimental conditions?
- What precautions will be used to control possible confounding variables?
- How long do you expect to spend on each step, and do you have a backup plan?
Data analysis and statistical procedures
- How do you plan to statistically analyze your data?
- What analyses will you conduct?
- How will the analyses contribute to the objectives?
What are the expected outcomes from your methods? Describe your expected results in relation to your hypothesis. Support these results using existing literature.
- What results would prove or disprove your hypotheses and validate your methodology, and why?
- What obstacles might you encounter in obtaining your results, and how will you deal with those obstacles?
- How will you analyze and interpret your results?
This section may be the most important part of your proposal. Make sure to emphasize how this research is significant to the related field, and how it will impact the broader community, now and in the future.
Convince your reader why this project should be funded above the other potential projects. Why is this research useful and relevant? Why is it useful to others? Answer the question “so what?”
Specific contributions
- How will your anticipated results specifically contribute to fulfilling the aims, objectives, or goals of your research?
- Will these be direct or indirect contributions? – theoretical or applied?
- How will your research contribute to the larger topic area or research discipline?
Impact and significance
- How will your research contribute to the research field of study?
- How will your research contribute to the larger topic addressed in your introduction?
- How will this research extend other work that you have done?
- How will this contribution/significance convince the reader that this research will be useful and relevant?
- Who else might find your research useful and relevant? (e.g., other research streams, policy makers, professional fields, etc.)
Provide a list of some of the most important sources that you will need to use for the introduction and background sections, plus your literature review and theoretical framework.
What are some of the most important sources that you will need to use for the intro/background/lit review/theoretical framework?
- Find out what style guide you are required to follow (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Follow the guidelines in our Cite Your Sources Libguide to format citations and create a reference list or bibliography.
Attach this list to your proposal as a separate page unless otherwise specified.
This section should include only visuals that help illustrate the preliminary results, methods, or expected results.
- What visuals will you use to help illustrate the methods or expected results?
- << Previous: Start Here
- Next: Questions for Editing and Revisions >>
- Last Updated: Jun 19, 2023 11:14 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uoguelph.ca/ResearchProposal
Suggest an edit to this guide
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 14: The Research Proposal
14.3 Components of a Research Proposal
Krathwohl (2005) suggests and describes a variety of components to include in a research proposal. The following sections – Introductions, Background and significance, Literature Review; Research design and methods, Preliminary suppositions and implications; and Conclusion present these components in a suggested template for you to follow in the preparation of your research proposal.
Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for what follows in your research proposal – treat it as the initial pitch of your idea. After reading the introduction your reader should:
- understand what it is you want to do;
- have a sense of your passion for the topic; and
- be excited about the study’s possible outcomes.
As you begin writing your research proposal, it is helpful to think of the introduction as a narrative of what it is you want to do, written in one to three paragraphs. Within those one to three paragraphs, it is important to briefly answer the following questions:
- What is the central research problem?
- How is the topic of your research proposal related to the problem?
- What methods will you utilize to analyze the research problem?
- Why is it important to undertake this research? What is the significance of your proposed research? Why are the outcomes of your proposed research important? Whom are they important?
Note : You may be asked by your instructor to include an abstract with your research proposal. In such cases, an abstract should provide an overview of what it is you plan to study, your main research question, a brief explanation of your methods to answer the research question, and your expected findings. All of this information must be carefully crafted in 150 to 250 words. A word of advice is to save the writing of your abstract until the very end of your research proposal preparation. If you are asked to provide an abstract, you should include 5 to 7 key words that are of most relevance to your study. List these in order of relevance.
Background and significance
The purpose of this section is to explain the context of your proposal and to describe, in detail, why it is important to undertake this research. Assume that the person or people who will read your research proposal know nothing or very little about the research problem. While you do not need to include all knowledge you have learned about your topic in this section, it is important to ensure that you include the most relevant material that will help to explain the goals of your research.
While there are no hard and fast rules, you should attempt to address some or all of the following key points:
- State the research problem and provide a more thorough explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction.
- Present the rationale for the proposed research study. Clearly indicate why this research is worth doing. Answer the “so what?” question.
- Describe the major issues or problems to be addressed by your research. Do not forget to explain how and in what ways your proposed research builds upon previous related research.
- Explain how you plan to go about conducting your research.
- Clearly identify the key or most relevant sources of research you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Set the boundaries of your proposed research, in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you will study, but what will be excluded from your study.
- Provide clear definitions of key concepts and terms. Since key concepts and terms often have numerous definitions, make sure you state which definition you will be utilizing in your research.
Literature review
This key component of the research proposal is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal. As described in Chapter 5 , the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting forth to investigate. Essentially, your goal in the literature review is to place your research study within the larger whole of what has been studied in the past, while demonstrating to your reader that your work is original, innovative, and adds to the larger whole.
As the literature review is information dense, it is essential that this section be intelligently structured to enable your reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your study. However, this can be easier to state and harder to do, simply due to the fact there is usually a plethora of related research to sift through. Consequently, a good strategy for writing the literature review is to break the literature into conceptual categories or themes, rather than attempting to describe various groups of literature you reviewed. Chapter 5 describes a variety of methods to help you organize the themes.
Here are some suggestions on how to approach the writing of your literature review:
- Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methods they used, what they found, and what they recommended based upon their findings.
- Do not be afraid to challenge previous related research findings and/or conclusions.
- Assess what you believe to be missing from previous research and explain how your research fills in this gap and/or extends previous research.
It is important to note that a significant challenge related to undertaking a literature review is knowing when to stop. As such, it is important to know when you have uncovered the key conceptual categories underlying your research topic. Generally, when you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations, you can have confidence that you have covered all of the significant conceptual categories in your literature review. However, it is also important to acknowledge that researchers often find themselves returning to the literature as they collect and analyze their data. For example, an unexpected finding may develop as you collect and/or analyze the data; in this case, it is important to take the time to step back and review the literature again, to ensure that no other researchers have found a similar finding. This may include looking to research outside your field.
This situation occurred with one of this textbook’s authors’ research related to community resilience. During the interviews, the researchers heard many participants discuss individual resilience factors and how they believed these individual factors helped make the community more resilient, overall. Sheppard and Williams (2016) had not discovered these individual factors in their original literature review on community and environmental resilience. However, when they returned to the literature to search for individual resilience factors, they discovered a small body of literature in the child and youth psychology field. Consequently, Sheppard and Williams had to go back and add a new section to their literature review on individual resilience factors. Interestingly, their research appeared to be the first research to link individual resilience factors with community resilience factors.
Research design and methods
The objective of this section of the research proposal is to convince the reader that your overall research design and methods of analysis will enable you to solve the research problem you have identified and also enable you to accurately and effectively interpret the results of your research. Consequently, it is critical that the research design and methods section is well-written, clear, and logically organized. This demonstrates to your reader that you know what you are going to do and how you are going to do it. Overall, you want to leave your reader feeling confident that you have what it takes to get this research study completed in a timely fashion.
Essentially, this section of the research proposal should be clearly tied to the specific objectives of your study; however, it is also important to draw upon and include examples from the literature review that relate to your design and intended methods. In other words, you must clearly demonstrate how your study utilizes and builds upon past studies, as it relates to the research design and intended methods. For example, what methods have been used by other researchers in similar studies?
While it is important to consider the methods that other researchers have employed, it is equally, if not more, important to consider what methods have not been but could be employed. Remember, the methods section is not simply a list of tasks to be undertaken. It is also an argument as to why and how the tasks you have outlined will help you investigate the research problem and answer your research question(s).
Tips for writing the research design and methods section:
Specify the methodological approaches you intend to employ to obtain information and the techniques you will use to analyze the data.
Specify the research operations you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results of those operations in relation to the research problem.
Go beyond stating what you hope to achieve through the methods you have chosen. State how you will actually implement the methods (i.e., coding interview text, running regression analysis, etc.).
Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers you may encounter when undertaking your research, and describe how you will address these barriers.
Explain where you believe you will find challenges related to data collection, including access to participants and information.

Preliminary suppositions and implications
The purpose of this section is to argue how you anticipate that your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the area of your study. Depending upon the aims and objectives of your study, you should also discuss how your anticipated findings may impact future research. For example, is it possible that your research may lead to a new policy, theoretical understanding, or method for analyzing data? How might your study influence future studies? What might your study mean for future practitioners working in the field? Who or what might benefit from your study? How might your study contribute to social, economic or environmental issues? While it is important to think about and discuss possibilities such as these, it is equally important to be realistic in stating your anticipated findings. In other words, you do not want to delve into idle speculation. Rather, the purpose here is to reflect upon gaps in the current body of literature and to describe how you anticipate your research will begin to fill in some or all of those gaps.
The conclusion reiterates the importance and significance of your research proposal, and provides a brief summary of the entire proposed study. Essentially, this section should only be one or two paragraphs in length. Here is a potential outline for your conclusion:
Discuss why the study should be done. Specifically discuss how you expect your study will advance existing knowledge and how your study is unique.
Explain the specific purpose of the study and the research questions that the study will answer.
Explain why the research design and methods chosen for this study are appropriate, and why other designs and methods were not chosen.
State the potential implications you expect to emerge from your proposed study,
Provide a sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship currently in existence, related to the research problem.
Citations and references
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your research proposal. In a research proposal, this can take two forms: a reference list or a bibliography. A reference list lists the literature you referenced in the body of your research proposal. All references in the reference list must appear in the body of the research proposal. Remember, it is not acceptable to say “as cited in …” As a researcher you must always go to the original source and check it for yourself. Many errors are made in referencing, even by top researchers, and so it is important not to perpetuate an error made by someone else. While this can be time consuming, it is the proper way to undertake a literature review.
In contrast, a bibliography , is a list of everything you used or cited in your research proposal, with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem. In other words, sources cited in your bibliography may not necessarily appear in the body of your research proposal. Make sure you check with your instructor to see which of the two you are expected to produce.
Overall, your list of citations should be a testament to the fact that you have done a sufficient level of preliminary research to ensure that your project will complement, but not duplicate, previous research efforts. For social sciences, the reference list or bibliography should be prepared in American Psychological Association (APA) referencing format. Usually, the reference list (or bibliography) is not included in the word count of the research proposal. Again, make sure you check with your instructor to confirm.
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Research Proposal

Table of Contents

In academia, especially in social and behavioral sciences, writing a research proposal is an essential first step while planning a new research project. A research proposal is an initial pitch, or theoretical framework that serves to introduce the topic and anticipated results of a project, provide an overview of the methods to be used, and convince the reader that the proposed research can be conducted successfully. It is very essential to know how to write a research proposal, whether you are a student trying to fulfill course requirements or a researcher looking for funding for scholarly research. But writing a well-structured proposal is easier said than done.
To make things simpler for you, In this article, I explained the fundamentals of a research proposal, its structure, the steps involved in writing a research proposal, and common mistakes to avoid. Continue reading to gain a thorough understanding of the concept and purpose of a research proposal. This blog will also enable you to write the research proposal quickly, reducing the likelihood of rejection.
What is a Research Proposal?
In simpler terms, A research proposal is a document written to explain and justify your chosen research topic and the necessity to carry out that particular research by addressing the research problem. Likewise, a good research proposal should carry the proposed research's results and benefits, backed by convincing evidence.
Always keep your audience in mind while writing your research proposal. Your audience expects a concise summary and a detailed research methodology from you in the research proposal.
To begin, you must understand the purpose of a research proposal in order to effectively write a research proposal and also to receive swift approvals.
What is the purpose or importance of a research proposal?

A research proposal's purpose is to provide a detailed outline of the process that will be used to answer a specific research problem. Whereas the goal of the research proposal varies from person to person. In some cases, it may be to secure funding, while in others, it may be to obtain a meager approval from the committee or the supervisor to proceed with the research project. Regardless of your research proposal's end goal, you are supposed to write a research proposal that fulfills its intended purpose of presenting the best plan for your research.
While writing a research proposal, you should demonstrate how and why your proposed research is crucial for the domain, especially if it is social and behavioral sciences. It would help if you showed how your work is necessary by addressing some key points like:
- Bridging the gaps in the existing domain of research.
- Adding new and fresh perspectives to the existing understanding of the topic.
- Undervalued data in the current stats of the domain.
Furthermore, your research proposal must demonstrate that you, as an author, are capable of conducting the research and that the results will significantly contribute to the field of knowledge. To do so, include and explain your academic background and significance along with your previous accolades to demonstrate that you and your idea have academic merit.
What is the ideal length of a research proposal?
There are no hard and fast rules about how long a research proposal should be, and it varies dramatically from different institutions and publishers. However, as a standard domain practice, a research proposal is generally between 3000- 4000 words. A majority of globally reputed institutions follow the 3000- 3500 word limit.
Since the research proposal is written well before the research is conducted, you need to outline all the necessary elements your research will entail and accomplish. Once completed, your research proposal must resemble a concise version of a thesis or dissertation without results and a discussion section.
Structure of a research proposal

When you recognize a gap in the existing books of knowledge, you will address it by developing a research problem. A research problem is a question that researchers want to answer. It is the starting point for any research project, and it can be broad or narrow, depending on your objectives. Once you have a problem, it is followed by articulating a research question. After that, you can embark on the process of writing a research proposal.
Whether your goal is to secure funding or just approval, nevertheless, your research proposal needs to follow the basic outline of a research paper, containing all the necessary sections. Therefore, the structure of a research proposal closely resembles and follows a thesis or dissertation or any research paper. It should contain the following sections:
As is well known, the first thing that catches the reader's attention is a catchy title. Therefore, you should try to come up with a catchy yet informative title for your research proposal. Additionally, it should be concise and clear to reflect enough information about your research question.
To create a good research proposal, try writing the title to induce interest and information in your readers. Pro-Tip: Avoid using phrases such as “An investigation of …” or “A review of …” etc. . These have been overused for ages and may reflect your research title as a regular entry. On the other hand, concise and well-defined titles are always something readers like and stand higher chances for a proposal approval.
2. Abstract
Write your abstract in a brief yet very informative way. It should summarize the research you intend to conduct. Put an emphasis on the research question, research hypothesis , research design and methods, and the key findings of your proposed research.
If you wish to create a detailed proposal, try including a table of contents. It will help readers navigate easily and catch a glance at your entire proposal writing. Check out this guide if you want to learn more about how to write a research abstract for your scholarly research.
3. Introduction
All papers need a striking introduction to set the context of the research question. While framing your research proposal, ensure that the introduction provides rich background and relevant information about the research question.
Your entire research proposal hinges upon your research question. Thus, fit should come out clearly in the intro. Provide a general introduction without clear explanations, and it might render your research proposal insignificant.
Start your research proposal with the research problem, engage your audience with elements that relate to the problem, and then shed some light on the research question. Then, proceed with your study's evidence-based justification, and you'll find that the audience is sticking with your proposal narrative.
While writing your research proposal, ensure that you have covered the following:
- Purpose of your study.
- Background information and significance of your study.
- Introduction to the question, followed by an introduction to the paper.
- Brief mention of the critical issues that you will focus on.
- Declaration of independent and dependent variables of the research hypothesis. (You can learn more about the variables of the research hypothesis here .)
4. Literature Review
Writing a literature review is an important part of the research process. It provides the researcher with a summary of previous studies that have been conducted on a subject, and it helps the researcher determine what areas might need additional investigation in the existing research. Guidelines for the literature review vary for different institutions.
To effectively conduct and write a literature review check this guide . You can also use tools like SciSpace Copilot , our AI research assistant that makes reading academic papers a much easier task. You can use it to get simple explanations for complex text, maths, or tables. Copilot can be particularly helpful when you’re sifting through papers as you can quickly understand the abstract, get some context around the study, and identify if the paper is relevant to your project or not.
The literature review can either be kept as a separate section or incorporated into the introduction section. A separate section is always favorable and vital in gaining the research proposal approval. Additionally, a separate section for a literature review offers in-depth background data and demonstrates the relevance of your research question by emphasizing the gaps that have remained since the previous study.
Your research proposal’s literature review must contain and serve the following:

- To provide a reference of the studies and the researchers who have previously worked in the same domain.
- To provide the build path of your research question.
- To furnish a critical examination of the previous research works.
- To present the research issues about the current investigation.
- To convince the audience about the importance of your research in the relevant domain.
Need help you with your literature review? Try SciSpace Discover and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge.
Discover millions of peer-reviewed research articles and their full-text PDFs here. The articles can be compiled in one place and saved for later use to conduct a Hassel-free literature review.
5. Research Methodology
Research design and methods is the section where you explain how you will be conducting the proposed research. Ensure that you provide and include a sufficient explanation for the chosen methods. Additionally, include some points explaining how your chosen methods will help you get the desired or expected results.
Provide ample information to the readers about your research procedures so that they can easily comprehend the methodology and its expected results. Through your research methodology, you can easily show your audience whether the results you are promising can be achieved or not.
Most importantly, make sure the methodology you choose—whether qualitative or quantitative—is the best fit for your research. You should also be able to justify your choice.
Additionally, you should properly explain both the quantitative and qualitative components of your research if they are both used. For a qualitative approach, you must offer more elaborate and in-depth theoretical-based evidence. On the other hand, for the quantitative approach, you must describe the survey or lab setup, sample size, tools, and data collection methods.
Make sure you have plenty of explanations for the research methodology to support how you approached the research problem.
6. Expected Research Results
The expected research results section is where the researcher states what they expect to find in their research. The purpose of this section is to provide a summary of the study's goals, as well as give an overview of what the researcher expects will be found out. These results must orient the reader in sync with the methodology section and provide the answers to the research questions.
7. Limitations
The limitations section of an academic research paper is a section in which the writers of the paper discuss the weaknesses of their study. They do this by identifying problems with their methods, design, and implementation. This section should also discuss any other factors that may have affected the results or accuracy of the study. This section allows readers to understand how much confidence they can place in the findings, and how applicable they are to other contexts.
Furthermore, it will also showcase your honesty and complete understanding of the topic. Your research proposal’s limitations can include:
- Reasons for the chosen sample size.
- Justifications for the availability of resources at hand.
- Any unexpected error that might occur in the course of research as well.
8. Reference and Bibliography
If you don’t want your efforts to be tagged as plagiarized, ensure that you include the reference section at the end of the research proposal and follow the appropriate citation guidelines while citing different scholarly sources and various other researchers’ work.
For references, use both the in-text and footnote citations. List all the literature you have used to gather the information. However, in the bibliography, apart from including the references you have cited, you should include the sources that you didn't cite.
Reasons why research proposals get rejected

Research proposals often get rejected due to the smallest of mistakes. To keep the chances of getting your research proposal rejection at bay or a minimum, you should be aware of what grounds committees or supervisors often decide on rejection.
Follow through to understand the common reasons why research papers get rejected:
- The proposal stated a flawed hypothesis.
- The readers or the audience don't get convinced that the expected results will be anything new or unique.
- The research methodology lacks the details and may appear unrealistic.
- The research proposal lacks coherence in the problem statement, methodology, and results.
- Inadequate literature review.
- Inaccurate interpretation of expected results from the methodology.
- Plagiarized or copied sections of the research proposal.
Common mistakes to avoid

You must stay aware of the research proposal guidelines and best writing manners. To maximize the approval chances of your research proposal, you should try to avoid some common pitfalls like:
- Making it verbose
Try explaining the various sections of the research proposal economically. Ideally, you should strive to keep your writing as a concise, brief, and to the point as possible. The more concisely you explain the purpose and goal of your research proposal, the better.
- Focusing on minor issues than tackling the core
While writing the research proposal, you may feel every issue is important, and you should provide an explanatory note for that. However, stay wiser while selecting the importance of issues. Avoid falling into the trap of trivial issues, as it may distract your readers from the core issues.
- Failure to put a strong research argument
The easiest way your readers can undermine your research proposal is by stating it is far more subjective and sounds unrealistic. A potent research argument describing the gaps in the current field, its importance, significance, and contributions to your research is the foremost requirement of a good research proposal.
Remember, even though you are proposing the objective, academic way, the goal is to persuade the audience to provide you with the required research approval.
- Not citing correctly
Understand that when you are going for some research, its outcome will contribute to the existing pool of knowledge. Therefore, always cite some landmark works of your chosen research domain and connect your proposed work with it.
Providing such intricate details will establish your research's importance, relevance, and familiarity with the domain knowledge.
Before You Go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
What Are The Elements Of A Good Research Proposal?
by Antony W
March 10, 2023

The key to writing a great research proposal for your upcoming research project is to make sure the document has the right structure.
Your paper must include all the components that your professor expects to see. So in this guide, we’ll outline all the elements of a good research proposal and explain why they’re important.
The elements of a good research proposal are the title, the introduction, literature review, aims and objectives, methodology, scope of the research, outline and timetable, and bibliography.
It’s important to include these elements in your research proposal exactly in the order in which they appear in the list above.
Why The Key Elements Of A Research Proposal Matter
The basic elements of a research proposal are important because they communicate your thought process, present the originality of your ideas, and demonstrate that you’re passionate about the subject in question.
If you structure and write your research proposal well, your paper can convince your professor that your project is feasible and you have what it takes to take your research project to the next level.
Have no time to read this guide and would rather get quick writing help? Let us write your research proposal for you!
7 Key Elements of a Research Proposal
While developing a detailed and comprehensive research proposal requires a lot of planning, attention to details, and academic writing skills , understanding the core elements of the paper is the first step to getting your proposal accepted.
So here are the elements that you should include in your research proposal.
It sounds somewhat obvious when we say that your research proposal with a title. To say the least, you already know you should.
But perhaps the most common mistake that many students make is to write general titles that lack focus.
Instead of writing a long title that’s hard to read or a short title that fails to highlight the theme of your research, write a clear and concise headline that tells your reader what your research proposal is about at a first glance.
2. Introduction
The starting paragraph to a research project is one of the elements of a good research proposal because it introduces the subject you wish to address or a research problem you wish to analyze.
Because the introduction of a research proposal is what sets the tone for the rest of the paper, it’s important to start with a hook and then organize your thoughts in a logical and organized manner.
The introduction to your research proposal should give background information and explain why you believe a research question is worth exploring. While not mandatory, you can briefly describe your methodologies in the introduction and then expand them later on.
Your introduction should be clear and concise. Make sure you include only the most relevant information in this section so you don’t make it unnecessarily too long.
3. Literature Review
Although a research proposal doesn’t include a full literature review , it’s important to include an overview of the most significant studies in your field.
The section should feature evidence and statistical data to demonstrate the significance of your research.
Through the literature review, you can easily draw your reader’s attention to existing research, identify gaps in existing studies, and make your reader understand how your proposal will contribute to the already existing research.
4. Aims and Objectives
Aims and objectives are what you wish your research proposal to accomplish. Your aims will be your overall outcome or what you want the research to achieve.
Objectives tend to be narrower and more focused. More often than not, you need to provide an explanation for each of your objectives to show how they will help to meet the aims of your study.
Unless required, you don’t really have to include a hypothesis that your research proposal looks forward to test.
5. Research Methodology
Methodologies are simply the research methods you will use to conduct your study and they must appear in your research proposal whether or not you’re conducting an experimental research.
The methodologies include analysis and sampling techniques equipment, research approaches, and ethical concerns.
Make sure your explanation for each methodology is clear and precise. It helps to justify why you’ve chosen to use a certain methodology over an alternative. This will go a long way to show that you took your time to think about your methodologies before picking them.
It’s important to explain how you will collect data, the sample size you plan to consider for your research investigation, and the techniques you consider the most appropriate to analyze the data.
6. Scope of the Research
Because you’ll be working with limited time and resource, it’s reasonable to include a section on the scope of the research in your proposal. In other words, you have to show your reader that you can start and complete your research within the constraints of these two resources.
Remember, your research will more than likely have limits, and addressing them in this section not only shows that you have given them a thought but also makes your research proposal strong and authentic.
Don’t just focus on the challenges that you’re likely to come across during your studies. You should also propose alternative solutions that you can use and why they might help.
7. Outline and Timetable
Your professor expects to see an outline and a timetable in your research proposal so it’s important that you include them in your research proposal.
The purpose of the outline is to show how you plan to structure your dissertation . Briefly note what each section will cover and explain how it all fits into the argument of your research project.
The purpose of the timetable is to show how much time you’ll need to complete your research. In particular, you need to make sure you mention exactly how long you expect each stage of your study to take.
Don’t just mention how long the research process will take. Make sure you also indicate how long you’ll take to compile your research.
Get Help with Research Proposal Writing
Knowing the elements of a good research proposal is one thing. Writing the proposal is where there’s a lot of work. If you don’t have the time to complete the work yourself, feel free to take advantage of our research proposal writing and get the paper done on time.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- {{item.title}} {{item.title}} 0" aria-label="Find options under this page" @click="mobchildshow(true, item.title)" class="more-menu">
- {{subitem.title}}
Writing a research proposal
How to write a research proposal.
For many subjects, writing a research proposal is a key part of your postgraduate research degree application. This is your opportunity to demonstrate your knowledge and how you want to contribute to the subject.
We use the proposal to match your interest with an appropriate supervisor to make sure you have the best support during your degree. We are looking for originality and relevance when assessing the overall quality of your application, including your suitability for this level of study.
We highly recommend that you explore which academic researchers are working in your subject area and contact them first with any questions, this is a good opportunity to firm up your ideas, further explore the topic and talk with others in your field.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal is a concise and coherent document, usually between 1500 – 2000 words, maximum 4 x A4 pages. You should outline your proposed research project, why it is of relevance (rationale), what research questions are you going to ask, what you hope to achieve (aims and objectives) and how you plan to carry out your research (methodology).
Step-by-step
This page is your comprehensive guide to writing a research proposal and will cover seven key elements of a proposal:
Working title
You should include a title for your thesis in the proposal.
Your title may change as you further your research, but at this stage it's important to state succinctly what your research will cover.
Introduction
Briefly identify your idea, what is your ‘research question’?
It could be the theory you want to test, or a more open question. It would be useful to give examples, 3-5 research questions from recently completed PhDs in a relevant field. You should discuss the context around your research topic, such as current debates and issues. The important thing here is that you introduce your research project with clarity and in a way that stimulates your reader’s interest.
Demonstrate the significance of your research project.
To do this, explain why your research is important, what makes it original and how it will contribute to existing knowledge within its field.
Aims and objectives
What are you hoping to achieve with your research?
Try and produce four or five bullet points of objectives for each aim, which demonstrate your understanding of how to meet your research aims. You can use the SMART acronym to support you in creating objectives, which involves making your objectives: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time specific.
Literature Review
Demonstrate your knowledge and awareness of relevant literature
A literature review is a discussion and evaluation of academic literature or a relevant body of knowledge (for practice-based research). You should use this section of your proposal to show that you are familiar with work in your chosen topic area and that your research will contribute something new and/or meaningful to it.
Methodology
Explain how you plan to carry out your research
The methodology section of your research proposal is where you explain how you plan to carry out your research. This should include the research techniques and methods you will use, why these are most appropriate and how you will implement them. You should also include a discussion of the research strategy (general approach) you will adopt, with appropriate justification, including the analytical approach. The section should also contain the range of research findings that will be gathered from the research and how you will analyse or evaluate this. For practice based research, include how will your portfolio of artefacts, code, software, compositions, computer games etc. articulate the originality of your research?
Reference all the materials you used in the preparation your proposal
You may also list references that you didn't directly draw upon, to demonstrate awareness of literature relating to your proposed material.
Support from academic staff in drafting your research proposal
Your research proposal will be read by academics with an interest in your field of research. You are therefore encouraged to contact members of academic staff informally prior to submitting your application to discuss to your research proposal. This can often speed up the applications process, as you can identify the member(s) of staff you have spoken to on your research degree application form.
Use the Huddersfield Research Portal to browse academic staff profiles and search using key words to find staff members who share your research interests.
Changing aspects of your research proposal after gaining a place as a research student
Your research proposal is your starting point, and we understand that as your idea develop s , your proposed research is likely to change. As such, you will not be obliged to adhere to the specifics of your proposal if you are offered a place as a research degree candidate at Huddersfield. However, as the proposal is the foundation of your working relationship with your supervisor(s), you will need to discuss any changes with them first.
Useful tips for writing a research proposal
- Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to be overly complicated.
- Share your proposal: Ask someone you trust (a friend, family member, tutor) to read your proposal and provide some feedback. Do they understand what your research is about? Do they think your aims and objectives are achievable? Does your research engage them?
- Align your proposal topic with University research themes: Whilst it is important to choose a research topic that you are passionate about, your proposal will be assessed (in part) on its fit with our University research themes. You therefore need to choose a topic which aligns with topics of interest to the University or academic school you hoping to work within and make it clear how your project matches up with them.
- Be realistic in your proposal: Your proposal is assessed not only on its quality, originality and fit with our research themes but also the likelihood of completion, so make sure that the scope of your research project is reasonable and realistic .
- Take your time when writing your proposal: There are a lot of elements to a high-quality research proposal, so take the time to ensure that you meet them all. At the University of Huddersfield, there are three opportunities for enrolling onto a research degree programme during the academic year (October, January, and April), meaning less time pressure when working on your proposal and application.
Once you have written your proposal, what next?
Once you have written your research proposal you will need to complete an application form. Look at our how to apply webpage for more information.

How to apply for a research degree
Our step-by-step guide will help you to make the most out of your application for a research degree

Scholarships and funding
Explore our funding options, including scholarships and Doctoral Loans.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Table of Contents

Research Proposal
Research proposal is a document that outlines a proposed research project . It is typically written by researchers, scholars, or students who intend to conduct research to address a specific research question or problem.
Types of Research Proposal
Research proposals can vary depending on the nature of the research project and the specific requirements of the funding agency, academic institution, or research program. Here are some common types of research proposals:
Academic Research Proposal
This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review , methodology , and expected outcomes.
Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is specifically designed to secure funding from external sources, such as government agencies, foundations, or private organizations. It typically includes additional sections, such as a detailed budget, project timeline, evaluation plan, and a description of the project’s alignment with the funding agency’s priorities and objectives.
Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Students pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree often need to submit a proposal outlining their intended research for their dissertation or thesis. These proposals are usually more extensive and comprehensive, including an in-depth literature review, theoretical framework, research questions or hypotheses, and a detailed methodology.
Research Project Proposal
This type of proposal is often prepared by researchers or research teams within an organization or institution. It outlines a specific research project that aims to address a particular problem, explore a specific area of interest, or provide insights for decision-making. Research project proposals may include sections on project management, collaboration, and dissemination of results.
Research Fellowship Proposal
Researchers or scholars applying for research fellowships may be required to submit a proposal outlining their proposed research project. These proposals often emphasize the novelty and significance of the research and its alignment with the goals and objectives of the fellowship program.
Collaborative Research Proposal
In cases where researchers from multiple institutions or disciplines collaborate on a research project, a collaborative research proposal is prepared. This proposal highlights the objectives, responsibilities, and contributions of each collaborator, as well as the overall research plan and coordination mechanisms.
Research Proposal Outline
A research proposal typically follows a standard outline that helps structure the document and ensure all essential components are included. While the specific headings and subheadings may vary slightly depending on the requirements of your institution or funding agency, the following outline provides a general structure for a research proposal:
- Title of the research proposal
- Name of the researcher(s) or principal investigator(s)
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of submission
- A concise summary of the research proposal, typically limited to 200-300 words.
- Briefly introduce the research problem or question, state the objectives, summarize the methodology, and highlight the expected outcomes or significance of the research.
- Provide an overview of the subject area and the specific research problem or question.
- Present relevant background information, theories, or concepts to establish the need for the research.
- Clearly state the research objectives or research questions that the study aims to address.
- Indicate the significance or potential contributions of the research.
- Summarize and analyze relevant studies, theories, or scholarly works.
- Identify research gaps or unresolved issues that your study intends to address.
- Highlight the novelty or uniqueness of your research.
- Describe the overall approach or research design that will be used (e.g., experimental, qualitative, quantitative).
- Justify the chosen approach based on the research objectives and question.
- Explain how data will be collected (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments).
- Describe the sampling strategy and sample size, if applicable.
- Address any ethical considerations related to data collection.
- Outline the data analysis techniques or statistical methods that will be applied.
- Explain how the data will be interpreted and analyzed to answer the research question(s).
- Provide a detailed schedule or timeline that outlines the various stages of the research project.
- Specify the estimated duration for each stage, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
- State the potential outcomes or results of the research.
- Discuss the potential significance or contributions of the study to the field.
- Address any potential limitations or challenges that may be encountered.
- Identify the resources required to conduct the research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- Specify any collaborations or partnerships necessary for the successful completion of the study.
- Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
———————————————————————————————–
Research Proposal Example Template
Here’s an example of a research proposal to give you an idea of how it can be structured:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being: A Mixed-Methods Study
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of social media on the well-being of adolescents. The study will employ a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews to gather comprehensive data. The research objectives include examining the relationship between social media use and mental health, exploring the role of peer influence in shaping online behaviors, and identifying strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents. The findings of this study will contribute to the understanding of the effects of social media on adolescent well-being and inform the development of targeted interventions.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background and Context:
Adolescents today are immersed in social media platforms, which have become integral to their daily lives. However, concerns have been raised about the potential negative impact of social media on their well-being, including increased rates of depression, anxiety, and body dissatisfaction. It is crucial to investigate this phenomenon further and understand the underlying mechanisms to develop effective strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents.
1.2 Research Objectives:
The main objectives of this study are:
- To examine the association between social media use and mental health outcomes among adolescents.
- To explore the influence of peer relationships and social comparison on online behaviors.
- To identify strategies and interventions to foster positive social media use and enhance adolescent well-being.
2. Literature Review
Extensive research has been conducted on the impact of social media on adolescents. Existing literature suggests that excessive social media use can contribute to negative outcomes, such as low self-esteem, cyberbullying, and addictive behaviors. However, some studies have also highlighted the positive aspects of social media, such as providing opportunities for self-expression and social support. This study will build upon this literature by incorporating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to gain a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between social media and adolescent well-being.
3. Methodology
3.1 Research Design:
This study will adopt a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. The quantitative phase will involve administering standardized questionnaires to a representative sample of adolescents to assess their social media use, mental health indicators, and perceived social support. The qualitative phase will include in-depth interviews with a subset of participants to explore their experiences, motivations, and perceptions related to social media use.
3.2 Data Collection Methods:
Quantitative data will be collected through an online survey distributed to schools in the target region. The survey will include validated scales to measure social media use, mental health outcomes, and perceived social support. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a purposive sample of participants. The interviews will be audio-recorded and transcribed for thematic analysis.
3.3 Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis to examine the relationships between variables. Qualitative data will be analyzed thematically to identify common themes and patterns within participants’ narratives. Integration of quantitative and qualitative findings will provide a comprehensive understanding of the research questions.
4. Timeline
The research project will be conducted over a period of 12 months, divided into specific phases, including literature review, study design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. A detailed timeline outlining the key milestones and activities is provided in Appendix A.
5. Expected Outcomes and Significance
This study aims to contribute to the existing literature on the impact of social media on adolescent well-being by employing a mixed-methods approach. The findings will inform the development of evidence-based interventions and guidelines to promote healthy social media use among adolescents. This research has the potential to benefit adolescents, parents, educators, and policymakers by providing insights into the complex relationship between social media and well-being and offering strategies for fostering positive online experiences.
6. Resources
The resources required for this research include access to a representative sample of adolescents, research assistants for data collection, statistical software for data analysis, and funding to cover survey administration and participant incentives. Ethical considerations will be taken into account, ensuring participant confidentiality and obtaining informed consent.
7. References
Research Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a research proposal can be a complex task, but with proper guidance and organization, you can create a compelling and well-structured proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the guidelines and requirements provided by your institution, funding agency, or program. Pay attention to formatting, page limits, specific sections or headings, and any other instructions.
- Identify your research topic: Choose a research topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the goals of your program or funding opportunity. Ensure that your topic is specific, focused, and relevant to the field of study.
- Conduct a literature review : Review existing literature and research relevant to your topic. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and findings related to your research question. This will help you establish the context, identify research gaps, and demonstrate the significance of your proposed study.
- Define your research objectives and research question(s): Clearly state the objectives you aim to achieve with your research. Formulate research questions that address the gaps identified in the literature review. Your research objectives and questions should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a research methodology: Determine the most appropriate research design and methodology for your study. Consider whether quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods approaches will best address your research question(s). Describe the data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations associated with your research.
- Create a research plan and timeline: Outline the various stages of your research project, including tasks, milestones, and deadlines. Develop a realistic timeline that considers factors such as data collection, analysis, and report writing. This plan will help you stay organized and manage your time effectively throughout the research process.
- A. Introduction: Provide background information on the research problem, highlight its significance, and introduce your research objectives and questions.
- B. Literature review: Summarize relevant literature, identify gaps, and justify the need for your proposed research.
- C . Methodology: Describe your research design, data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
- D . Expected outcomes and significance: Explain the potential outcomes, contributions, and implications of your research.
- E. Resources: Identify the resources required to conduct your research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- F . References: Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style.
- Revise and proofread: Review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for grammar and spelling errors. Seek feedback from mentors, colleagues, or advisors to refine and improve your proposal.
- Finalize and submit: Make any necessary revisions based on feedback and finalize your research proposal. Ensure that you have met all the requirements and formatting guidelines. Submit your proposal within the specified deadline.
Research Proposal Length
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. However, research proposals typically range from 1,500 to 3,000 words, excluding references and any additional supporting documents.
Purpose of Research Proposal
The purpose of a research proposal is to outline and communicate your research project to others, such as academic institutions, funding agencies, or potential collaborators. It serves several important purposes:
- Demonstrate the significance of the research: A research proposal explains the importance and relevance of your research project. It outlines the research problem or question, highlights the gaps in existing knowledge, and explains how your study will contribute to the field. By clearly articulating the significance of your research, you can convince others of its value and potential impact.
- Provide a clear research plan: A research proposal outlines the methodology, design, and approach you will use to conduct your study. It describes the research objectives, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and potential outcomes. By presenting a clear research plan, you demonstrate that your study is well-thought-out, feasible, and likely to produce meaningful results.
- Secure funding or support: For researchers seeking funding or support for their projects, a research proposal is essential. It allows you to make a persuasive case for why your research is deserving of financial resources or institutional backing. The proposal explains the budgetary requirements, resources needed, and potential benefits of the research, helping you secure the necessary funding or support.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to receive feedback and guidance from experts in your field. It allows you to engage in discussions and receive suggestions for refining your research plan, improving the methodology, or addressing any potential limitations. This feedback can enhance the quality of your study and increase its chances of success.
- Establish ethical considerations: A research proposal also addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will ensure participant confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. By demonstrating your awareness and commitment to ethical research practices, you build trust and credibility in your proposed study.
Importance of Research Proposal
The research proposal holds significant importance in the research process. Here are some key reasons why research proposals are important:
- Planning and organization: A research proposal requires careful planning and organization of your research project. It forces you to think through the research objectives, research questions, methodology, and potential outcomes before embarking on the actual study. This planning phase helps you establish a clear direction and framework for your research, ensuring that your efforts are focused and purposeful.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: A research proposal allows you to articulate the significance and relevance of your study. By providing a thorough literature review and clearly defining the research problem or question, you can showcase the gaps in existing knowledge that your research aims to address. This demonstrates to others, such as funding agencies or academic institutions, why your research is important and deserving of support.
- Obtaining funding and resources: Research proposals are often required to secure funding for your research project. Funding agencies and organizations need to evaluate the feasibility and potential impact of the proposed research before allocating resources. A well-crafted research proposal helps convince funders of the value of your research and increases the likelihood of securing financial support, grants, or scholarships.
- Receiving feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to seek feedback and guidance from experts in your field. By sharing your research plan and objectives with others, you can benefit from their insights and suggestions. This feedback can help refine your research design, strengthen your methodology, and ensure that your study is rigorous and well-informed.
- Ethical considerations: A research proposal addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will protect the rights and welfare of participants, maintain confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. This emphasis on ethical practices ensures that your research is conducted responsibly and with integrity.
- Enhancing collaboration and partnerships: A research proposal can facilitate collaborations and partnerships with other researchers, institutions, or organizations. When presenting your research plan, you may attract the interest of potential collaborators who share similar research interests or possess complementary expertise. Collaborative partnerships can enrich your study, expand your resources, and foster knowledge exchange.
- Establishing a research trajectory: A research proposal serves as a foundation for your research project. Once approved, it becomes a roadmap that guides your study’s implementation, data collection, analysis, and reporting. It helps maintain focus and ensures that your research stays on track and aligned with the initial objectives.
When to Write Research Proposal
The timing of when to write a research proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements and circumstances. However, here are a few common situations when it is appropriate to write a research proposal:
- Academic research: If you are a student pursuing a research degree, such as a Ph.D. or Master’s by research, you will typically be required to write a research proposal as part of the application process. This is usually done before starting the research program to outline your proposed study and seek approval from the academic institution.
- Funding applications: When applying for research grants, scholarships, or funding from organizations or institutions, you will often need to submit a research proposal. Funding agencies require a detailed description of your research project, including its objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. Writing a research proposal in this context is necessary to secure financial support for your study.
- Research collaborations: When collaborating with other researchers, institutions, or organizations on a research project, it is common to prepare a research proposal. This helps outline the research objectives, roles and responsibilities, and expected contributions from each party. Writing a research proposal in this case allows all collaborators to align their efforts and ensure a shared understanding of the project.
- Research project within an organization: If you are conducting research within an organization, such as a company or government agency, you may be required to write a research proposal to gain approval and support for your study. This proposal outlines the research objectives, methodology, resources needed, and expected outcomes, ensuring that the project aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Independent research projects: Even if you are not required to write a research proposal, it can still be beneficial to develop one for your independent research projects. Writing a research proposal helps you plan and structure your study, clarify your research objectives, and anticipate potential challenges or limitations. It also allows you to communicate your research plans effectively to supervisors, mentors, or collaborators.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.

Writing a Research Proposal
Parts of a research proposal, prosana model, introduction, research question, methodology.
- Structure of a Research Proposal
- Common Proposal Writing Mistakes
- Proposal Writing Resources
A research proposal's purpose is to capture the evaluator's attention, demonstrate the study's potential benefits, and prove that it is a logical and consistent approach (Van Ekelenburg, 2010). To ensure that your research proposal contains these elements, there are several aspects to include in your proposal (Al-Riyami, 2008):
- Objective(s)
- Variables (independent and dependent)
- Research Question and/or hypothesis
Details about what to include in each element are included in the boxes below. Depending on the topic of your study, some parts may not apply to your proposal. You can also watch the video below for a brief overview about writing a successful research proposal.
Van Ekelenburg (2010) uses the PROSANA Model to guide researchers in developing rationale and justification for their research projects. It is an acronym that connects the problem, solution, and benefits of a particular research project. It is an easy way to remember the critical parts of a research proposal and how they relate to one another. It includes the following letters (Van Ekelenburg, 2010):
- Problem: Describing the main problem that the researcher is trying to solve.
- Root causes: Describing what is causing the problem. Why is the topic an issue?
- fOcus: Narrowing down one of the underlying causes on which the researcher will focus for their research project.
- Solutions: Listing potential solutions or approaches to fix to the problem. There could be more than one.
- Approach: Selecting the solution that the researcher will want to focus on.
- Novelty: Describing how the solution will address or solve the problem.
- Arguments: Explaining how the proposed solution will benefit the problem.
Research proposal titles should be concise and to the point, but informative. The title of your proposal may be different from the title of your final research project, but that is completely normal! Your findings may help you come up with a title that is more fitting for the final project. Characteristics of good proposal titles are (Al-Riyami, 2008):
- Catchy: It catches the reader's attention by peaking their interest.
- Positive: It spins your project in a positive way towards the reader.
- Transparent: It identifies the independent and dependent variables.
It is also common for proposal titles to be very similar to your research question, hypothesis, or thesis statement (Locke et al., 2007).
An abstract is a brief summary (about 300 words) of the study you are proposing. It includes the following elements (Al-Riyami, 2008):
- Your primary research question(s).
- Hypothesis or main argument.
- Method you will use to complete the study. This may include the design, sample population, or measuring instruments that you plan to use.
Our guide on writing summaries may help you with this step.
- Writing a Summary by Luann Edwards Last Updated May 22, 2023 2568 views this year
The purpose of the introduction is to give readers background information about your topic. it gives the readers a basic understanding of your topic so that they can further understand the significance of your proposal. A good introduction will explain (Al-Riyami, 2008):
- How it relates to other research done on the topic
- Why your research is significant to the field
- The relevance of your study
Your research objectives are the desired outcomes that you will achieve from the research project. Depending on your research design, these may be generic or very specific. You may also have more than one objective (Al-Riyami, 2008).
- General objectives are what the research project will accomplish
- Specific objectives relate to the research questions that the researcher aims to answer through the study.
Be careful not to have too many objectives in your proposal, as having too many can make your project lose focus. Plus, it may not be possible to achieve several objectives in one study.
This section describes the different types of variables that you plan to have in your study and how you will measure them. According to Al-Riyami (2008), there are four types of research variables:
- Independent: The person, object, or idea that is manipulated by the researcher.
- Dependent: The person, object, or idea whose changes are dependent upon the independent variable. Typically, it is the item that the researcher is measuring for the study.
- Confounding/Intervening: Factors that may influence the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. These include physical and mental barriers. Not every study will have intervening variables, but they should be studied if applicable.
- Background: Factors that are relevant to the study's data and how it can be generalized. Examples include demographic information such as age, sex, and ethnicity.
Your research proposal should describe each of your variables and how they relate to one another. Depending on your study, you may not have all four types of variables present. However, there will always be an independent and dependent variable.
A research question is the main piece of your research project because it explains what your study will discover to the reader. It is the question that fuels the study, so it is important for it to be precise and unique. You do not want it to be too broad, and it should identify a relationship between two variables (an independent and a dependent) (Al-Riyami, 2008). There are six types of research questions (Academic Writer, n.d.):
- Example: "Do people get nervous before speaking in front of an audience?"
- Example: "What are the study habits of college freshmen at Tiffin University?"
- Example: "What primary traits create a successful romantic relationship?"
- Example: "Is there a relationship between a child's performance in school and their parents' socioeconomic status?"
- Example: "Are high school seniors more motivated than high school freshmen?"
- Example: "Do news media outlets impact a person's political opinions?"
For more information on the different types of research questions, you can view the "Research Questions and Hypotheses" tutorial on Academic Writer, located below. If you are unfamiliar with Academic Writer, we also have a tutorial on using the database located below.
Compose papers in pre-formatted APA templates. Manage references in forms that help craft APA citations. Learn the rules of APA style through tutorials and practice quizzes.
Academic Writer will continue to use the 6th edition guidelines until August 2020. A preview of the 7th edition is available in the footer of the resource's site. Previously known as APA Style Central.
- Academic Writer Tutorial by Pfeiffer Library Last Updated May 22, 2023 34065 views this year
If you know enough about your research topic that you believe a particular outcome may occur as a result of the study, you can include a hypothesis (thesis statement) in your proposal. A hypothesis is a prediction that you believe will be the outcome of your study. It explains what you think the relationship will be between the independent and dependent variable (Al-Riyami, 2008). It is ok if the hypothesis in your proposal turns out to be incorrect, because it is only a prediction! If you are writing a proposal in the humanities, you may be writing a thesis statement instead of a hypothesis. A thesis presents the main argument of your research project and leads to corresponding evidence to support your argument.
Hypotheses vs. Theories
Hypotheses are different from theories in that theories represent general principles and sets of rules that explain different phenomena. They typically represent large areas of study because they are applicable to anything in a particular field. Hypotheses focus on specific areas within a field and are educated guesses, meaning that they have the potential to be proven wrong (Academic Writer, n.d.). Because of this, hypotheses can also be formed from theories.
For more information on writing effective thesis statements, you can view our guide on writing thesis statements below.
- Writing Effective Thesis Statements by Luann Edwards Last Updated May 23, 2023 474 views this year
In a research proposal, you must thoroughly explain how you will conduct your study. This includes things such as (Al-Riyami, 2008):
- Research design: What research approach will your study take? Will it be quantitative or qualitative?
- Research subjects/participants: Who will be participating in your study? Does your study require human participants? How will you determine who to study?
- Sample size: How many participants will your study require? If you are not using human participants, how much of the sample will you be studying?
- Timeline: A proposed list of the general tasks and events that you plan to complete the study. This will include a time frame for each task/event and the order in which they will be completed.
- Interventions: If you plan on using anything on human participants for the study, you must include information it here. This is especially important if you plan on using any substances on human subjects.
- Ethical issues: Are there any potential ethical issues surrounding this study?
- Potential limitations: Are there any limitations that could skew the data and findings from your study?
- Appendixes: If you need to present any consent forms, interview questions, surveys, questionnaires, or other items that will be used in your study, you should include samples of each item with an appendix to reference them. If you are using a copyrighted document, you may need written permission from the original creator to use it in your study. A copy of the written permission should be included in your proposal.
- Setting: Where will you be conducting the study?
- Study instruments: What measuring tools or computer software will you be using to collect data? How will you collect the data?
- How you will analyze the data: What strategies or tools will you use to analyze the data you collect?
- Quality control: Will you have precautions in place to ensure that the study is conducted consistently and that outside factors will not skew the data?
- Budget: What type of funding will you need for your study? This will include the funds needed to afford measuring tools, software, etc.
- How you will share the study's findings: What will you plan to do with the findings?
- Significance of the study: How will your study expand on existing knowledge of the subject area?
For more information on research methodologies, you can view our guide on research methods and methodologies below.
- Research Methodologies by Pfeiffer Library Last Updated Aug 2, 2022 40625 views this year
- << Previous: Welcome
- Next: Structure of a Research Proposal >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/writingaresearchproposal
- Social Science
- Quantitative Social Research
- Research Design
RESEARCH PROPOSAL
- In book: Basic Guidelines for Research: An Introductory Approach for All Disciplines (pp.468-489)
- Edition: First
- Chapter: 11
- Publisher: Book Zone Publication, Chittagong-4203, Bangladesh

- Curtin University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Nazmunnessa Mahtab
- Shabrina Shajeen Alam
- Sabrina Shajeen Alam
- Rumana Aktar
- Tahmin Banu
- Bard Comilla
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
Research Funding Basics: What Should a Grant Proposal Include?

A grant proposal for research is like a formal request sent to an organization, asking for money to support a research project. It is a document or a group of papers that explains what the research is about and why it is important. Writing a grant proposal can be tough, especially for someone new to research. Because many funding agencies have less money to give out, and lots of researchers are asking for it, it’s crucial to write a perfect grant proposal to stand out and increase the chances of getting the needed funding.[1][2]
Elements of a grant proposal
A grant proposal has several essential elements or sections. These may go by different names depending on the guidelines of varying grant agencies, but they serve similar purposes. The cover letter acts as a polite introduction, while the executive summary provides a quick overview of the project. Organizational qualifications focus on why the applying group is suitable for the project, and a short overview offers a summary.
The statement of need explains why the project is vital by outlining the problem it addresses. The project narrative is the main part, detailing the project’s plans and methods. Finally, the budget section breaks down the requested funds, demonstrating how they will be used for the project.[1][2]
Let us examine how to write a grant proposal by taking up each of these elements.
How to Write a Grant Proposal for Research[ 1][4][7]
- Cover Letter: In a grant proposal, a cover letter is like a friendly introduction before the main request. It introduces you and your organization and aims to show that you are serious and professional about your project. The cover letter briefly talks about your project and expresses your excitement for it and gratitude for the people considering your funding request.
- Executive Summary: The executive summary is a brief, condensed overview of your proposal, addressing critical questions about the project’s purpose, need, expected outcomes, methods, success measurement, and significance. It’s usually written last, serving as a concise introduction.
- Problem Statement: The significance of your project lies in addressing a notable gap in resources, knowledge, or opportunities that genuinely requires attention. To establish the value of your project, it is crucial to define the need or problem it seeks to resolve clearly. Early in your proposal, provide background information to set the context of this problem. Importantly, emphasize how your project will have a broader, positive impact beyond simply answering an academic question.
- Project Goals and Objectives: Once you have highlighted the need for your project, it is time to detail the project itself by answering critical questions. Clearly define the goals or research questions, articulate the outcomes your project aims for, and explain the methods to achieve these objectives. Emphasize how you will measure and recognize project achievements, ensuring they align with the identified need. Establishing a realistic timeline is essential. Focusing on the impact your project will have is critical, as funders want to see clear benefits and a robust plan for verifying and assessing the project’s success.
- Budget: When seeking funding or support, it is crucial to specify exactly what you are requesting for and why you are asking for specific amounts. Budgets are often presented in tables and figures, clearly labelling each amount. Following the budget, you may need a justification statement explaining why each cost, material, and equipment is valid, reasonable, and essential for your project.
- Organizational Information: This section focuses on the organization or individual requesting the grant. When an individual is seeking a grant, all relevant personal details can be included here. This part provides essential information about the key people involved in the project, including their names, backgrounds, and positions. Additionally, it offers a comprehensive history of the organization, detailing its mission and highlighting previous projects. This section helps the grant provider understand who is behind the proposal, their qualifications, and the organization’s track record, fostering trust and confidence in the project’s potential success.
- Supporting Documents: At the end of your grant proposal, you should include various supporting materials, often in the form of appendices. These could consist of extra records, endorsements, tax status information, bios of personnel in your organization, and letters of support from allied organizations or groups involved in your project. All these documents should directly relate to your proposal and may be requested explicitly by the granting institution. Including relevant and explicit supporting materials enhances the credibility and completeness of your proposal.
References:
- Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!) – University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- How to write a grant proposal – PubMed Central
- Grant Writing – Purdue University
- Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics – University of Wisconsin – Madison
- How to Begin Developing a Statement of Need – Funding for Good – Funding for Good
- What are the critical elements of a successful grant proposal, and how do you write one? – LinkedIn
- Writing a Research Grant Proposal – University of Winnipeg
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
How to Write Dissertation Acknowledgements?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
Top 7 AI Tools for Research 2024
Maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing features, you may also like, maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a....
Watch CBS News
What is Project 2025? What to know about the conservative blueprint for a second Trump administration
By Melissa Quinn , Jacob Rosen
Updated on: July 11, 2024 / 9:40 AM EDT / CBS News
Washington — Voters in recent weeks have begun to hear the name "Project 2025" invoked more and more by President Biden and Democrats, as they seek to sound the alarm about what could be in store if former President Donald Trump wins a second term in the White House.
Overseen by the conservative Heritage Foundation, the multi-pronged initiative includes a detailed blueprint for the next Republican president to usher in a sweeping overhaul of the executive branch.
Trump and his campaign have worked to distance themselves from Project 2025, with the former president going so far as to call some of the proposals "abysmal." But Democrats have continued to tie the transition project to Trump, especially as they find themselves mired in their own controversy over whether Mr. Biden should withdraw from the 2024 presidential contest following his startling debate performance last month.
Here is what to know about Project 2025:
What is Project 2025?
Project 2025 is a proposed presidential transition project that is composed of four pillars: a policy guide for the next presidential administration; a LinkedIn-style database of personnel who could serve in the next administration; training for that pool of candidates dubbed the "Presidential Administration Academy;" and a playbook of actions to be taken within the first 180 days in office.
It is led by two former Trump administration officials: Paul Dans, who was chief of staff at the Office of Personnel Management and serves as director of the project, and Spencer Chretien, former special assistant to Trump and now the project's associate director.
Project 2025 is spearheaded by the Heritage Foundation, but includes an advisory board consisting of more than 100 conservative groups.
Much of the focus on — and criticism of — Project 2025 involves its first pillar, the nearly 900-page policy book that lays out an overhaul of the federal government. Called "Mandate for Leadership 2025: The Conservative Promise," the book builds on a "Mandate for Leadership" first published in January 1981, which sought to serve as a roadmap for Ronald Reagan's incoming administration.
The recommendations outlined in the sprawling plan reach every corner of the executive branch, from the Executive Office of the President to the Department of Homeland Security to the little-known Export-Import Bank.

The Heritage Foundation also created a "Mandate for Leadership" in 2015 ahead of Trump's first term. Two years into his presidency, it touted that Trump had instituted 64% of its policy recommendations, ranging from leaving the Paris Climate Accords, increasing military spending, and increasing off-shore drilling and developing federal lands. In July 2020, the Heritage Foundation gave its updated version of the book to then-White House Chief of Staff Mark Meadows.
The authors of many chapters are familiar names from the Trump administration, such as Russ Vought, who led the Office of Management and Budget; former acting Defense Secretary Chris Miller; and Roger Severino, who was director of the Office of Civil Rights at the Department of Health and Human Services.
Vought is the policy director for the 2024 Republican National Committee's platform committee, which released its proposed platform on Monday.
John McEntee, former director of the White House Presidential Personnel Office under Trump, is a senior advisor to the Heritage Foundation, and said that the group will "integrate a lot of our work" with the Trump campaign when the official transition efforts are announced in the next few months.
Candidates interested in applying for the Heritage Foundation's "Presidential Personnel Database" are vetted on a number of political stances, such as whether they agree or disagree with statements like "life has a right to legal protection from conception to natural death," and "the President should be able to advance his/her agenda through the bureaucracy without hindrance from unelected federal officials."
The contributions from ex-Trump administration officials have led its critics to tie Project 2025 to his reelection campaign, though the former president has attempted to distance himself from the initiative.
What are the Project 2025 plans?
Some of the policies in the Project 2025 agenda have been discussed by Republicans for years or pushed by Trump himself: less federal intervention in education and more support for school choice; work requirements for able-bodied, childless adults on food stamps; and a secure border with increased enforcement of immigration laws, mass deportations and construction of a border wall.
But others have come under scrutiny in part because of the current political landscape.
Abortion and social issues
In recommendations for the Department of Health and Human Services, the agenda calls for the Food and Drug Administration to reverse its 24-year-old approval of the widely used abortion pill mifepristone. Other proposed actions targeting medication abortion include reinstating more stringent rules for mifepristone's use, which would permit it to be taken up to seven weeks into a pregnancy, instead of the current 10 weeks, and requiring it to be dispensed in-person instead of through the mail.
The Alliance Defending Freedom, a conservative legal group that is on the Project 2025 advisory board, was involved in a legal challenge to mifepristone's 2000 approval and more recent actions from the FDA that made it easier to obtain. But the Supreme Court rejected the case brought by a group of anti-abortion rights doctors and medical associations on procedural grounds.
The policy book also recommends the Justice Department enforce the Comstock Act against providers and distributors of abortion pills. That 1873 law prohibits drugs, medicines or instruments used in abortions from being sent through the mail.

Now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade , the volume states that the Justice Department "in the next conservative administration should therefore announce its intent to enforce federal law against providers and distributors of such pills."
The guide recommends the next secretary of Health and Human Services get rid of the Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force established by the Biden administration before Roe's reversal and create a "pro-life task force to ensure that all of the department's divisions seek to use their authority to promote the life and health of women and their unborn children."
In a section titled "The Family Agenda," the proposal recommends the Health and Human Services chief "proudly state that men and women are biological realities," and that "married men and women are the ideal, natural family structure because all children have a right to be raised by the men and women who conceived them."
Further, a program within the Health and Human Services Department should "maintain a biblically based, social science-reinforced definition of marriage and family."
During his first four years in office, Trump banned transgender people from serving in the military. Mr. Biden reversed that policy , but the Project 2025 policy book calls for the ban to be reinstated.
Targeting federal agencies, employees and policies
The agenda takes aim at longstanding federal agencies, like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The agency is a component of the Commerce Department and the policy guide calls for it to be downsized.
NOAA's six offices, including the National Weather Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, "form a colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future U.S. prosperity," the guide states.
The Department of Homeland Security, established in 2002, should be dismantled and its agencies either combined with others, or moved under the purview of other departments altogether, the policy book states. For example, immigration-related entities from the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice and Health and Human Services should form a standalone, Cabinet-level border and immigration agency staffed by more than 100,000 employees, according to the agenda.

If the policy recommendations are implemented, another federal agency that could come under the knife by the next administration, with action from Congress, is the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau.
The agenda seeks to bring a push by conservatives to target diversity, equity and inclusion, or DEI, initiatives in higher education to the executive branch by wiping away a slew of DEI-related positions, policies and programs and calling for the elimination of funding for partners that promote DEI practices.
It states that U.S. Agency for International Development staff and grantees that "engage in ideological agitation on behalf of the DEI agenda" should be terminated. At the Treasury Department, the guide says the next administration should "treat the participation in any critical race theory or DEI initiative without objecting on constitutional or moral grounds, as per se grounds for termination of employment."
The Project 2025 policy book also takes aim at more innocuous functions of government. It calls for the next presidential administration to eliminate or reform the dietary guidelines that have been published by the Department of Agriculture for more than 40 years, which the authors claim have been "infiltrated" by issues like climate change and sustainability.
Immigration
Trump made immigration a cornerstone of his last two presidential runs and has continued to hammer the issue during his 2024 campaign. Project 2025's agenda not only recommends finishing the wall along the U.S.-Mexico border, but urges the next administration to "take a creative and aggressive approach" to responding to drug cartels at the border. This approach includes using active-duty military personnel and the National Guard to help with arrest operations along the southern border.
A memo from Immigration and Customs Enforcement that prohibits enforcement actions from taking place at "sensitive" places like schools, playgrounds and churches should be rolled back, the policy guide states.
When the Homeland Security secretary determines there is an "actual or anticipated mass migration of aliens" that presents "urgent circumstances" warranting a federal response, the agenda says the secretary can make rules and regulations, including through their expulsion, for as long as necessary. These rules, the guide states, aren't subject to the Administration Procedure Act, which governs the agency rule-making process.
What do Trump and his advisers say about Project 2025?
In a post to his social media platform on July 5, Trump wrote , "I know nothing about Project 2025. I have no idea who is behind it. I disagree with some of the things they're saying and some of the things they're saying are absolutely ridiculous and abysmal. Anything they do, I wish them luck, but I have nothing to do with them."
Trump's pushback to the initiative came after Heritage Foundation President Kevin Roberts said in a podcast interview that the nation is "in the process of the second American Revolution, which will remain bloodless if the left allows it to be."
The former president continued to disavow the initiative this week, writing in another social media post that he knows nothing about Project 2025.
"I have not seen it, have no idea who is in charge of it, and, unlike our very well received Republican Platform, had nothing to do with it," Trump wrote. "The Radical Left Democrats are having a field day, however, trying to hook me into whatever policies are stated or said. It is pure disinformation on their part. By now, after all of these years, everyone knows where I stand on EVERYTHING!"
While the former president said he doesn't know who is in charge of the initiative, the project's director, Dans, and associate director, Chretien, were high-ranking officials in his administration. Additionally, Ben Carson, former secretary of Housing and Urban Development under Trump; John Ratcliffe, former director of National Intelligence in the Trump administration; and Peter Navarro, who served as a top trade adviser to Trump in the White House, are listed as either authors or contributors to the policy agenda.
Still, even before Roberts' comments during "The War Room" podcast — typically hosted by conservative commentator Steve Bannon, who reported to federal prison to begin serving a four-month sentence last week — Trump's top campaign advisers have stressed that Project 2025 has no official ties to his reelection bid.
Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita, senior advisers to the Trump campaign, said in a November statement that 2024 policy announcements will be made by Trump or his campaign team.
"Any personnel lists, policy agendas, or government plans published anywhere are merely suggestions," they said.
While the efforts by outside organizations are "appreciated," Wiles and LaCivita said, "none of these groups or individuals speak for President Trump or his campaign."
In response to Trump's post last week, Project 2025 reiterated that it was separate from the Trump campaign.
"As we've been saying for more than two years now, Project 2025 does not speak for any candidate or campaign. We are a coalition of more than 110 conservative groups advocating policy & personnel recommendations for the next conservative president. But it is ultimately up to that president, who we believe will be President Trump, to decide which recommendations to implement," a statement on the project's X account said.
The initiative has also pushed back on Democrats' claims about its policy proposals and accused them of lying about what the agenda contains.
What do Democrats say?
Despite their attempts to keep some distance from Project 2025, Democrats continue to connect Trump with the transition effort. The Biden-Harris campaign frequently posts about the project on X, tying it to a second Trump term.
Mr. Biden himself accused his Republican opponent of lying about his connections to the Project 2025 agenda, saying in a statement that the agenda was written for Trump and "should scare every single American." He claimed on his campaign social media account Wednesday that Project 2025 "will destroy America."
Congressional Democrats have also begun pivoting to Project 2025 when asked in interviews about Mr. Biden's fitness for a second term following his lackluster showing at the June 27 debate, the first in which he went head-to-head with Trump.
"Trump is all about Project 2025," Pennsylvania Sen. John Fetterman told CNN on Monday. "I mean, that's what we really should be voting on right now. It's like, do we want the kind of president that is all about Project '25?"
Rep. Jim Clyburn of South Carolina, one of Mr. Biden's closest allies on Capitol Hill, told reporters Monday that the agenda for the next Republican president was the sole topic he would talk about.
"Project 2025, that's my only concern," he said. "I don't want you or my granddaughter to live under that government."
In a statement reiterating her support for Mr. Biden, Rep. Frederica Wilson of Florida called Project 2025 "MAGA Republicans' draconian 920-page plan to end U.S. democracy, give handouts to the wealthy and strip Americans of their freedoms."
What are Republicans saying about Project 2025?
Two GOP senators under consideration to serve as Trump's running mate sought to put space between the White House hopeful and Project 2025, casting it as merely the product of a think tank that puts forth ideas.
"It's the work of a think tank, of a center-right think tank, and that's what think tanks do," Florida Sen. Marco Rubio told CNN's "State of the Union" on Sunday.
He said Trump's message to voters focuses on "restoring common sense, working-class values, and making our decisions on the basis of that."
Ohio Sen. J.D. Vance raised a similar sentiment in an interview with NBC's "Meet the Press," saying organizations will have good ideas and bad ideas.
"It's a 900-page document," he said Sunday. "I guarantee there are things that Trump likes and dislikes about that 900-page document. But he is the person who will determine the agenda of the next administration."
Jaala Brown contributed to this report.
Melissa Quinn is a politics reporter for CBSNews.com. She has written for outlets including the Washington Examiner, Daily Signal and Alexandria Times. Melissa covers U.S. politics, with a focus on the Supreme Court and federal courts.
More from CBS News

Progressives look to Supreme Court to motivate voters in 2024 race

GOP effort to hold Garland in inherent contempt of Congress fails

Biden talks with Congressional Hispanic Caucus as he fights to stay in 2024 race

First Senate Democrat calls on Biden to withdraw from race

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
A research proposal outline's content typically varies in length, from 3 to 35 pages, with references (and appendices, if necessary). But like any academic activity, start the research proposal template writing process by first carefully reading the instructions. ... State the rationale of your research proposal and explain, in an engaging ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
The background to the topic of your intended research must be clear and precise. It must not only include an in-depth explanation of the key points of your subject but also all the developments in the field as well as their timelines.The researcher must also explain the compelling interest in the research issue as well as the personal interest (if any) in the topic.
The structure and content of a research proposal can vary depending upon the discipline, purpose, and target audience. For example, a graduate thesis proposal and a Tri-Council grant proposal will have different guidelines for length and required sections. ... Briefly describe the broad topic of your research area, and then clearly explain the ...
Literature review. This key component of the research proposal is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal. As described in Chapter 5, the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research.Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting ...
4. Literature Review. Writing a literature review is an important part of the research process. It provides the researcher with a summary of previous studies that have been conducted on a subject, and it helps the researcher determine what areas might need additional investigation in the existing research.
So in this guide, we'll outline all the elements of a good research proposal and explain why they're important. The elements of a good research proposal are the title, the introduction, literature review, aims and objectives, methodology, scope of the research, outline and timetable, and bibliography. It's important to include these ...
Develop an Outline. Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content. Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution. Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers ...
Useful tips for writing a research proposal. Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to ...
Academic Research Proposal. This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, and expected outcomes.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
A range of skills and expertise is needed for the task of proposal writing as well as for the research that follows a successful application. Therefore this book is intended to help those who are unfamiliar with the process of proposal writing or who want to improve their chances of success in a complex and demanding field.
A research proposal is a vital tool that can help scholars and university students complete a dissertation, receive funding for projects or fulfill course requirements. It outlines the importance of your inquiry and summarizes how you plan to investigate your research problem. Before developing a project, it's often valuable to learn some ...
Components of a Proposal. For each of the descriptions below, identify which component of the research proposal applies (title, abstract, table of contents, introduction, literature review, method ...
A research proposal's purpose is to capture the evaluator's attention, demonstrate the study's potential benefits, and prove that it is a logical and consistent approach (Van Ekelenburg, 2010). To ensure that your research proposal contains these elements, there are several aspects to include in your proposal (Al-Riyami, 2008): Title; Abstract
The structure of a research proposal includes various elements. The elements outlined below are applicable to proposals for studies situated in the humanities and those situated in STEM fields but there may be different expectations about the ordering or naming of particular sections.
A r esearch proposal is a document written by a researcher that provides a detailed description of. the pr oposed pr ogram. It is like an outline of the entire research process that gives a reader ...
A grant proposal for research is like a formal request sent to an organization, asking for money to support a research project. It is a document or a group of papers that explains what the research is about and why it is important. Writing a grant proposal can be tough, especially for someone new to research.
Here is what to know about Project 2025: What is Project 2025? Project 2025 is a proposed presidential transition project that is composed of four pillars: a policy guide for the next presidential ...
Contents move to sidebar hide (Top) 1 Background. 2 Advisory board and leadership. 3 ... Project 2025 is a collection of conservative and right-wing policy proposals from the Heritage Foundation to reshape the United States federal government and consolidate executive power ... research in climatology should receive considerably less funding in ...