80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples
Have some suggestions and questions about nature vs nurture? On this page, find research and essay topics to explore a particular aspect of the discussion.

📑 Aspects to Cover in a Nature vs Nurture Essay
🏆 best nature vs nurture essay topics & essay examples, 📌 most interesting nurture vs nature topics to write about, 👍 good nature vs nurture topics, ❓ questions about nature vs nurture.
What affects human development: nature or nurture? Are gender roles and differences come naturally, or does society impose them? What can be argued about the personalities of identical twins? Explore any of the issues with us! Our IvyPnada team has prepared nurture vs nature topics to write about. Check essay examples via the links as well.
At first glance, a nature vs nurture essay seems to be easy. However, a limited view of the subject matter may cost you marks, which is why it is crucial to offer a well-rounded account of the debate. Here are some of the aspects that you might want to include in your essay on nature vs nurture.
- The importance of the topic. The debate on what influences one’s personality, intelligence, and character is among the most prominent ones in psychology and other social sciences. Your task is to reflect this and to attempt to justify why the debate is so important. What could be done if it were resolved one day? How does the dispute affect other subject fields and topics in psychology? How would the resolution help the study of psychology and human behavior to move forward? Would it help to prove certain theories or refute the others, and what would be the effect on professional practice?
- The origins of the debate. While you explore the first aspect, you might stumble upon the history of the nature vs nurture debate. Covering this theme in your essay could also earn you some extra marks. Merely summarizing historical facts is not enough, though, because your tutor is probably aware of them already. Instead, you should focus on why the debate started. Were there any developments in psychology that prompted it?
- Prominent views. It is hard to omit the opinions expressed by famous scholars while writing an essay on this subject. John Locke, John B. Watson, Calvin Hall, and other authors had all shared ideas on the issue. If you need more names, try searching sample essays on nature and nurture online since most of them point out the key names. This might also help you to identify possible nature vs nurture essay titles.
- Results of research studies. Research evidence is among the key nature vs nurture essay topics because there were many attempts to prove one or the other view. Examples of such studies may be cited in your textbook, so it should be the first point of your research. Your school’s library and Google Scholar might also give you more information. If you find any sources online, make sure that they are of academic quality, or you might lose marks.
- Your personal experience and thoughts. Because the controversy is so prominent, nearly all people who study psychology or social studies have an opinion on it. If the instructions don’t prevent you from doing this, you should share your thoughts on the debate between nature and nurture. Support your opinion with credible research evidence and link it to the work of other scholars. If you believe that the environment is more important than genes, why is that? What other theorists supported this view, and why did they? Your opinion, supported by relevant facts and views, may become an excellent nature vs nurture essay thesis.
- Suggestions for further research. Try to think about what could be done to resolve the debate once and for all. What are the main gaps in studies on nature vs nurture and how could they be addressed by scholars?
Covering all of the themes above will help you to produce an outstanding essay. Make sure to check our website for a nature vs nurture essay prompt, titles, and other useful materials!
- Nature vs. Nurture In most cases, nature determines the physical characteristics which in effect influence the behavior of an individual. These are traits which largely determined by the socio-cultural environmental factors or the way the individuals are socialized […]
- Nature vs. Nurture: “In Cold Blood” by Truman Capote Thus, by contrasting Dick’s nurturing in love and affection and the conditions of his blissful childhood and adolescence with the details of a horrible crime committed by him and his attitude to it, the author […]
- As Nature Made Him: Summary and Analysis As aforementioned, the author of this book provides useful analysis of this aspect of personality. One of the greatest questions that readers get answer from this book is the question of nature vs.nurture in sexuality […]
- Human Development: Nature or Nurture? With studies and theories carried out to examine the impact of nature on the personal development and personality traits, heredity is an important factor in the development.
- “Nature” Versus “Nurture”: Effects on Child Development Consequently, a child’s behavior cannot be viewed as solely attributable to the genetic composition of the parents and the hereditary characteristics.
- Physical and Mental Wellbeing: Nature Versus Nurture In conclusion, the debates on nature versus nurture reveal that both innate health conditions and external factors shape the outcomes for physical and mental wellbeing of an individual.
- Nature vs. Nurture: New Science Stirs Debate How Behavior Is Shaped A prime example of this nature of debates is the debate on whether nature or nurture has a greater bearing on the development of the diverse individual behavioral differences that exist.
- Alcoholism-Nature vs. Nurture Debate The analysis on physiological physiology regarding alcohol shows that, alcohol displays feelings of superiority and fearless behavior and also, it reduces an individual’s fear.
- Nature Versus Nurture and Learning Among Children Of much concern among modern researchers is the determination of the degree of influence of nature and nurture on the development of a child and the provision of learning experiences.
- The Relationship Between Nature and Nurture on the Intelligence
- The Controversies Surrounding the Topic of Nature Versus Nurture
- The Nurture Side of the Dichotomy Nature Versus Nurture
- The Formula For Fruition: The Age Old Debate of Nature Versus Nurture by Kendra Cherry
- The Meaning of Nature and Nurture in Psychology
- The Role of Nature vs. Nurture in Violent Behavior
- Influence of Nature Versus Nurture on Child Development
- The Role of Nature and Nurture: Adolescence Eating Disorders
- The Nature vs. Nurture Debate in Learning More About Alcoholism
- The Psychological Argument Between Nature vs. Nurture
- The Role of Nature and Nurture in Human Development
- The Influence of Nature Versus Nurture on an Individual Human Behavior
- Use of Nature and Nurture Based Studies on Epigenetics
- The Impact of Nature and Nurture on Huck’s and Finn’s Personality and Behavior in the Adventure of Huckleberry Finn by Mark Twain
- The Correlation Between Nature and Nurture in the Personal Development
- Role of Nature and Nurture in Language Development
- Personality, Behavior, and the Significance of Nature vs. Nurture
- The Disputes Concerning the Popular Nature vs. Nurture Argument
- Understanding the Role of Nature Versus Nurture in Alcohol Addiction
- Wild Child vs. Nature and Nurture
- The Importance of Nature Verses Nurture in Shaping Behavior and Personality
- The Differences Between Boys and Girls from Combination Between Nature and Nurture
- The Role of Nature and Nurture in Human Homosexuality
- The Nature Versus Nurture Debate in the Blasphemy of Talking Politics During Bach Year, an Article by Susan McClary
- What Roles Do Nature and Nurture Play on Children’s
- What Differentiates the Entrepreneurs From Non-Entrepreneurs on Nature and Nurture
- The Source of Violence: Nature vs. Nurture
- Gender and Socialization: Nature or Nurture
- How Nature and Nurture Affects the Pies in Adolescence and Adulthood
- The Debate Between Criminal Nature and Criminal Nurture: William Sheldon Theory
- The Nurture and Care From Nature and the Damage Caused by Humans to Our Environment
- The Evolutionary Theory of Nature vs. Nurture
- The Personality and Biology Differences in Nature Versus Nurture and Man Versus Woman Situations in Daily Life
- The Importance of Twin Studies in the Nature Versus Nurture Debate
- The Scientific and Cultural Debate of Nature vs. Nurture
- The Issue of Nature Versus Nurture in the Development of Serial Killers
- The Role of Nature vs. Nurture, Culture and Gender, and Family
- What Makes a Monster Nature vs. Nurture in Mary Shelleys Frankenstein
- The Theme of Nature Versus Nurture in Shelly’s Frankenstein
- The Psychology Field of Study About Nature and Nurture
- How Children Develop and the Interplay of Nature vs. Nurture?
- How Nature vs. Nurture Affect Human Development?
- Homosexuality: Nature vs. Nurture?
- How Do Nature vs. Nurture Work Together Example?
- How Does Nature vs. Nurture Affect Human Behavior?
- Why Is Nature vs. Nurture Called a False Debate?
- Nature vs. Nurture: Do Our Genes Affect Our Personalities?
- Nature vs. Nurture: Which Has a More Significant Influence on Child Development?
- How Do You Argue Nature vs. Nurture?
- Nature vs. Nurture: Who’s to Blame for Acts of Violence?
- How Does Nature vs. Nurture Affect Intelligence?
- Nature vs. Nurture: Which Is the Origin of Virtue?
- How Does Shelley Represent the Nature vs. Nurture Debate?
- Nature vs. Nurture: Which Determines Personality?
- What Are Examples of Nature vs. Nurture?
- Nature vs. Nurture: What Does Matter More?
- What Is Stronger Nurture vs. Nature?
- Why Nurture Is Better Than Nature?
- How Does the Nature vs. Nurture Debate in May Affect the Physical?
- What Is Nature vs. Nurture in Child Development?
- How Nature vs. Nurture Influence Substance Abuse?
- Twin Studies: What Can They Tell Us About Nature vs. Nurture?
- How Does Nature vs. Nurture Affect the Development of Social-Emotion Attributes?
- Who Won Nature vs. Nurture?
- How Nature vs. Nurture Apply the Principles of Life?
- What Is the Difference Between Nature vs. Nurture in Child Development?
- What Is the Main Idea of Nature vs. Nurture?
- Is Nature vs. Nurture Misleading?
- Nature vs. Nurture: What Impacts a Child’s IQ?
- How Does Nature vs. Nurture Affect Human Development?
- Literacy Development Titles
- Personality Development Ideas
- Social Development Essay Topics
- Human Nature Essay Titles
- Academic Achievements Research Topics
- Bioethics Titles
- Emotional Intelligence Paper Topics
- Genetics Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/nature-vs-nurture-essay-examples/
"80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/nature-vs-nurture-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/nature-vs-nurture-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/nature-vs-nurture-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "80 Nature vs Nurture Essay Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/nature-vs-nurture-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Affective Science
- Biological Foundations of Psychology
- Clinical Psychology: Disorders and Therapies
- Cognitive Psychology/Neuroscience
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational/School Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Individual Differences
- Methods and Approaches in Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational and Institutional Psychology
- Personality
- Psychology and Other Disciplines
- Social Psychology
- Sports Psychology
- Share Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Nature and nurture as an enduring tension in the history of psychology.
- Hunter Honeycutt Hunter Honeycutt Bridgewater College, Department of Psychology
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.518
- Published online: 30 September 2019
Nature–nurture is a dichotomous way of thinking about the origins of human (and animal) behavior and development, where “nature” refers to native, inborn, causal factors that function independently of, or prior to, the experiences (“nurture”) of the organism. In psychology during the 19th century, nature-nurture debates were voiced in the language of instinct versus learning. In the first decades of the 20th century, it was widely assumed that that humans and animals entered the world with a fixed set of inborn instincts. But in the 1920s and again in the 1950s, the validity of instinct as a scientific construct was challenged on conceptual and empirical grounds. As a result, most psychologists abandoned using the term instinct but they did not abandon the validity of distinguishing between nature versus nurture. In place of instinct, many psychologists made a semantic shift to using terms like innate knowledge, biological maturation, and/or hereditary/genetic effects on development, all of which extend well into the 21st century. Still, for some psychologists, the earlier critiques of the instinct concept remain just as relevant to these more modern usages.
The tension in nature-nurture debates is commonly eased by claiming that explanations of behavior must involve reference to both nature-based and nurture-based causes. However, for some psychologists there is a growing pressure to see the nature–nurture dichotomy as oversimplifying the development of behavior patterns. The division is seen as both arbitrary and counterproductive. Rather than treat nature and nurture as separable causal factors operating on development, they treat nature-nurture as a distinction between product (nature) versus process (nurture). Thus there has been a longstanding tension about how to define, separate, and balance the effects of nature and nurture.
- nature–nurture
- development
- nativism–empiricism
- innate–learned
- behavioral genetics
- epigenetics
Nature and Nurture in Development
The oldest and most persistent ways to frame explanations about the behavioral and mental development of individuals is to distinguish between two separate sources of developmental causation: (a) intrinsic, preformed, or predetermined causes (“nature”) versus (b) extrinsic, experiential, or environmental causes (“nurture”). Inputs from these two sources are thought to add their own contribution to development (see Figure 1 ).
Figure 1. The traditional view of nature and nurture as separate causes of development. In the traditional view, nature and nurture are treated as independent causal influences that combine during development to generate outcomes. Note that, during development, the effects of nature and nurture (shown in horizontal crossing lines) remain independent so that their effects on outcomes are theoretically separable.
Because some traits seem to derive more from one source than the other, much of the tension associated with the nature–nurture division deals with disagreements about how to balance the roles of nature and nurture in the development of a trait.
Evidence of Nature in Development
Evidence to support the nature–nurture division usually derives from patterns of behavior that suggest a limited role of environmental causation, thus implying some effect of nature by default. Table 1 depicts some common descriptors and conditions used to infer that some preference, knowledge, or skill is nature based.
Table 1. Common Descriptors and Associated Conditions for Inferring the Effects of Nature on Development
It is important to reiterate that nature-based causation (e.g., genetic determination) is inferred from these observations. Such inferences can generate tension because each of the observations listed here can be explained by nurture-based (environmental) factors. Confusion can also arise when evidence of one descriptor (e.g., being hereditary) is erroneously used to justify a different usage (e.g., that the trait is unlearned).
The Origins of Nature Versus Nurture
For much of recorded history, the distinction between nature and nurture was a temporal divide between what a person is innately endowed with at birth, prior to experience (nature), and what happens thereafter (nurture). It was not until the 19th century that the temporal division was transformed into a material division of causal influences (Keller, 2010 ). New views about heredity and Darwinian evolution justified distinguishing between native traits and genetic causes from acquired traits and environmental causes. More so than before, the terms nature and nurture were often juxtaposed in an opposition famously described by Sir Francis Galton ( 1869 ) as that between “nature versus nurture.”
Galton began writing about heredity in the mid-1860s. He believed we would discover laws governing the transmission of mental as well as physical qualities. Galton’s take on mental heredity, however, was forged by his desire to improve the human race in a science he would later call “eugenics.” In the mid- 19th century , British liberals assumed humans were equivalent at birth. Their social reform efforts were geared to enhancing educational opportunities and improving living conditions. Galton, a political conservative, opposed the notion of natural equality, arguing instead that people were inherently different at birth (Cowan, 2016 ), and that these inherited mental and behavioral inequalities were transmitted through lineages like physical qualities. Because Galton opposed the widely held Lamarckian idea that the qualities acquired in one’s lifetime could modify the inherited potential of subsequent generations, he believed long-lasting improvement of the human stock would only come by controlling breeding practices.
To explain the biological mechanisms of inheritance, Galton joined a growing trend in the 1870s to understand inheritance as involving the transmission of (hypothetical) determinative, germinal substances across generations. Foreshadowing a view that would later become scientific orthodoxy, Galton believed these germinal substances to be uninfluenced by the experiences of the organism. His theory of inheritance, however, was speculative. Realizing he was not equipped to fully explicate his theory of biological inheritance, Galton abandoned this line of inquiry by the end of that decade and refocused his efforts on identifying statistical laws of heredity of individual differences (Renwick, 2011 ).
Historians generally agree that Galton was the first to treat nature (as heredity) and nurture (everything else) as separate causal forces (Keller, 2010 ), but the schism gained biological legitimacy through the work of the German cytologist Auguste Weismann in the 1880s. Whereas Galton’s theory was motivated by his political agenda, Weismann was motivated by a scientific, theoretical agenda. Namely, Weismann opposed Lamarckian inheritance and promoted a view of evolution driven almost entirely by natural selection.
Drawing upon contemporary cytological and embryological research, Weismann made the case that the determinative substances found in the germ cells of plants and animals (called the “germ-plasm”) that are transmitted across generations were physically sequestered very early in embryogenesis and remained buffered from the other cells of the body (“somato-plasm”). This so-called, Weismann’s barrier meant that alterations in the soma that develop in the lifetime of the organism through the use or disuse of body parts would not affect the germinal substances transmitted during reproduction (see Winther, 2001 , for review). On this view, Lamarckian-style inheritance of acquired characteristics was not biologically possible.
Galton and Weismann’s influence on the life sciences cannot be overstated. Their work convinced many to draw unusually sharp distinctions between the inherited (nature) and the acquired (nurture). Although their theories were met with much resistance and generated significant tension in the life sciences from cytology to psychology, their efforts helped stage a new epistemic space through which to appreciate Mendel’s soon to be rediscovered breeding studies and usher in genetics (Muller-Wille & Rheinberger, 2012 ).
Ever since, psychology has teetered between nature-biased and nurture-biased positions. With the rise of genetics, the wedge between nature–nurture was deepened in the early to mid- 20th century , creating fields of study that focused exclusively on the effects of either nature or nurture.
The “Middle Ground” Perspective on Nature–Nurture
Twenty-first-century psychology textbooks often state that the nature–nurture debates have been resolved, and the tension relaxed, because we have moved on from emphasizing nature or nurture to appreciating that development necessarily involves both nature and nurture. In this middle-ground position, one asks how nature and nurture interact. For example, how do biological (or genetic) predispositions for behaviors or innate knowledge bias early learning experiences? Or how might environmental factors influence the biologically determined (maturational) unfolding of bodily form and behaviors?
Rejection of the Nature–Nurture Divide
For some, the “middle-ground” resolution is as problematic as “either/or” views and does not resolve a deeper source of tension inherent in the dichotomy. On this view, the nature–nurture divide is neither a legitimate nor a constructive way of thinking about development. Instead, developmental analysis reveals that the terms commonly associated with nature (e.g., innate, genetic, hereditary, or instinctual) and nurture (environmental or learned) are so entwined and confounded (and often arbitrary) that their independent effects cannot be meaningfully discussed. The nature–nurture division oversimplifies developmental processes, takes too much for granted, and ultimately hinders scientific progress. Thus not only is there a lingering tension about how to balance the effects of nature and nurture in the middle-ground view, but there is also a growing tension to move beyond the dichotomous nature–nurture framework.
Nativism in Behavior: Instincts
Definitions of instinct can vary tremendously, but many contrast (a) instinct with reason (or intellect, thought, will), which is related to but separable from contrasting (b) instinct with learning (or experience or habit).
Instinct in the Age of Enlightenment
Early usages of the instinct concept, following Aristotle, treated instinct as a mental, estimative faculty ( vis aestimativa or aestimativa naturalis ) in humans and animals that allowed for the judgments of objects in the world (e.g., seeing a predator) to be deemed beneficial or harmful in a way that transcends immediate sensory experience but does not involve the use of reason (Diamond, 1971 ). In many of the early usages, the “natural instinct” of animals even included subrational forms of learning.
The modern usage of instincts as unlearned behaviors took shape in the 17th century . By that point it was widely believed that nature or God had implanted in animals and humans innate behaviors and predispositions (“instincts”) to promote the survival of the individual and the propagation of the species. Disagreements arose as to whether instincts derived from innate mental images or were mindlessly and mechanically (physiologically) generated from innately specified bodily organization (Richards, 1987 ).
Anti-Instinct Movement in the Age of Enlightenment
Challenges to the instinct concept can be found in the 16th century (see Diamond, 1971 ), but they were most fully developed by empiricist philosophers of the French Sensationalist tradition in the 18th century (Richards, 1987 ). Sensationalists asserted that animals behaved rationally and all of the so-called instincts displayed by animals could be seen as intelligently acquired habits.
For Sensationalists, instincts, as traditionally understood, did not exist. Species-specificity in behavior patterns could be explained by commonalities in physiological organization, needs, and environmental conditions. Even those instinctual behaviors seen at birth (e.g., that newly hatched chicks peck and eat grain) might eventually be explained by the animal’s prenatal experiences. Erasmus Darwin ( 1731–1802 ), for example, speculated that the movements and swallowing experiences in ovo could account for the pecking and eating of grain by young chicks. The anti-instinct sentiment was clearly expressed by the Sensationalist Jean Antoine Guer ( 1713–1764 ), who warned that instinct was an “infantile idea” that could only be held by those who are ignorant of philosophy, that traditional appeals to instincts in animals not only explained nothing but served to hinder scientific explanations, and that nothing could be more superficial than to explain behavior than appealing to so-called instincts (Richards, 1987 ).
The traditional instinct concept survived. For most people, the complex, adaptive, species-specific behaviors displayed by naïve animals (e.g., caterpillars building cocoons; infant suckling behaviors) appeared to be predetermined and unlearned. Arguably as important, however, was the resistance to the theological implications of Sensationalist philosophy.
One of the strongest reactions to Sensationalism was put forward in Germany by Herman Samuel Reimarus ( 1694–1768 ). As a natural theologian, Reimarus, sought evidence of a God in the natural world, and the species-specific, complex, and adaptive instincts of animals seemed to stand as the best evidence of God’s work. More so than any other, Reimarus extensively catalogued instincts in humans and animals. Rather than treat instincts as behaviors, he defined instincts as natural impulses (inner drives) to act that were expressed perfectly, without reflection or practice, and served adaptive goals (Richards, 1987 ). He even proposed instincts for learning, a proposal that would resurface in the mid- 20th century , as would his drive theory of instinct (Jaynes & Woodward, 1974 ).
Partly as a result of Reimarus’ efforts, the instinct concept survived going into the 19th century . But many issues surrounding the instinct concept were left unsettled. How do instincts differ from reflexive behaviors? What role does learning play in the expression of instincts, if any? Do humans have more or fewer instincts than animals? These questions would persist well into the first decades of the 20th century and ultimately fuel another anti-instinct movement.
Instinct in the 19th Century
In the 19th century , the tension about the nature and nurture of instincts in the lifetime of animals led to debates about the nature and nurture of instincts across generations . These debates dealt with whether instincts should be viewed as “inherited habits” from previous generations or whether they result from the natural selection. Debating the relative roles of neo-Lamarckian use-inheritance versus neo-Darwinian natural selection in the transmutation of species became a significant source of tension in the latter half of the 19th century . Although the neo-Lamarckian notion of instincts as being inherited habits was rejected in the 20th century , it has resurged in recent years (e.g., see Robinson & Barron, 2017 ).
Darwinian evolutionary theory required drawing distinctions between native and acquired behaviors, and, perhaps more so than before, behaviors were categorized along a continuum from the purely instinctive (unlearned), to the partially instinctive (requiring some learning), to the purely learned. Still, it was widely assumed that a purely instinctive response would be modified by experience after its first occurrence. As a result, instinct and habit were very much entangled in the lifetime of the organism. The notion of instincts as fixed and unmodifiable would not be widely advanced until after the rise of Weismann’s germ-plasm theory in the late 19thcentury .
Given their importance in evolutionary theory, there was greater interest in more objectively identifying pure instincts beyond anecdotal reports. Some of the most compelling evidence was reported by Douglas Spalding ( 1844–1877 ) in the early 1870s (see Gray, 1967 ). Spalding documented numerous instances of how naïve animals showed coordinated, seemingly adaptive responses (e.g., hiding) to objects (e.g., sight of predators) upon their first encounter, and he helped pioneer the use of the deprivation experiment to identify instinctive behaviors. This technique involved selectively depriving young animals of seemingly critical learning experiences or sensory stimulation. Should animals display some species-typical action following deprivation, then, presumably, the behavior could be labeled as unlearned or innate. In all, these studies seemed to show that animals displayed numerous adaptive responses at the very start, prior to any relevant experience. In a variety of ways, Spalding’s work anticipated 20th-century studies of innate behavior. Not only would the deprivation experiment be used as the primary means of detecting native tendencies by European zoologists and ethologists, but Spalding also showed evidence of what would later be called imprinting, critical period effects and evidence of behavioral maturation.
Reports of pure instinct did not go unchallenged. Lloyd Morgan ( 1896 ) questioned the accuracy of these reports in his own experimental work with young animals. In some cases, he failed to replicate the results and in other cases he found that instinctive behaviors were not as finely tuned to objects in the environment as had been claimed. Morgan’s research pointed to taking greater precision in identifying learned and instinctive components of behavior, but, like most at the turn of the 20th century , he did not question that animal behavior involved both learned and instinctive elements.
A focus on instinctive behaviors intensified in the 1890s as Weismann’s germ-plasm theory grew in popularity. More so than before, a sharp distinction was drawn between native and acquired characteristics, including behavior (Johnston, 1995 ). Although some psychologists continued to maintain neo-Lamarckian notions, most German (Burnham, 1972 ) and American (Cravens & Burnham, 1971 ) psychologists were quick to adopt Weismann’s theory. They envisioned a new natural science of psychology that would experimentally identify the germinally determined, invariable set of native psychological traits in species and their underlying physiological (neural) basis. However, whereas English-speaking psychologists tended to focus on how this view impacted our understanding of social institutions and its social implications, German psychologists were more interested in the longstanding philosophical implications of Weismann’s doctrine as it related to the differences (if any) between man and beast (Burnham, 1972 ).
Some anthropologists and sociologists, however, interpreted Weismann’s theory quite differently and used it elevate sociology as its own scientific discipline. In the 1890s, the French sociologist Emil Durkheim, for example, interpreted Weismann’s germinal determinants as a generic force on human behavior that influenced the development of general predispositions that are molded by the circumstances of life (Meloni, 2016 ). American anthropologists reached similar conclusions in the early 20th century (Cravens & Burnham, 1971 ). Because Weismann’s theory divorced biological inheritance from social inheritance, and because heredity was treated as a generic force, sociologists felt free to study social (eventually, “cultural”) phenomena without reference to biological or psychological concerns.
Anti-Instinct Movement in the 1920s
Despite their differences, in the first two decades of the 20th century both psychologists and sociologists generally assumed that humans and animals had some native tendencies or instincts. Concerns were even voiced that instinct had not received enough attention in psychology. Disagreements about instincts continued to focus on (the now centuries old debates of) how to conceptualize them. Were they complex reflexes, impulses, or motives to act, or should instinct be a mental faculty (like intuition), separate from reasoning and reflex (Herrnstein, 1972 )?
In America, the instinct concept came under fire following a brief paper in 1919 by Knight Dunlap titled “Are There Any Instincts?” His primary concern dealt with teleological definitions of instincts in which an instinct referred to all the activities involved in obtaining some end-state (e.g., instincts of crying, playing, feeding, reproduction, war, curiosity, or pugnacity). Defined in this way, human instincts were simply labels for human activities, but how these activities were defined was arbitrarily imposed by the researchers. Is feeding, for instance, an instinct, or is it composed of more basic instincts (like chewing and swallowing)? The arbitrariness of classifying human behavior had led to tremendous inconsistencies and confusion among psychologists.
Not all of the challenges to instinct dealt with its teleological usage. Some of the strongest criticisms were voiced by Zing-Yang Kuo throughout the 1920s. Kuo was a Chinese animal psychologist who studied under Charles Tolman at the University of California, Berkeley. Although Kuo’s attacks on instinct changed throughout the 1920s (see Honeycutt, 2011 ), he ultimately argued that all behaviors develop in experience-dependent ways and that appeals to instinct were statements of ignorance about how behaviors develop. Like Dunlap, he warned that instincts were labels with no explanatory value. To illustrate, after returning to China, he showed how the so-called rodent-killing instinct in cats often cited by instinct theorists is not found in kittens that are reared with rodents (Kuo, 1930 ). These kittens, instead, became attached to the rodents, and they resisted attempts to train rodent-killing. Echoing the point made by Guer, Kuo claimed that appeals to instinct served to stunt scientific inquiry into the developmental origins of behavior.
But Kuo did not just challenge the instinct concept. He also argued against labeling behaviors as “learned.” After all, whether an animal “learns” depends on the surrounding environmental conditions, the physiological and developmental status of the animal, and, especially, the developmental (or experiential) history of that animal. Understanding learning also required developmental analysis. Thus Kuo targeted the basic distinction between nature and nurture, and he was not alone in doing so (e.g., see Carmichael, 1925 ), but his call to reject it did not spread to mainstream American psychologists.
By the 1930s, the term instinct had fallen into disrepute in psychology, but experimental psychologists (including behaviorists) remained committed to a separation of native from acquired traits. If anything, the dividing line between native and acquired behaviors became more sharply drawn than before (Logan & Johnston, 2007 ). For some psychologists, instinct was simply rebranded in the less contentious (but still problematic) language of biological drives or motives (Herrnstein, 1972 ). Many other psychologists simply turned to describing native traits as due to “maturation” and/or “heredity” rather than “instinct.”
Fixed Action Patterns
The hereditarian instinct concept received a reboot in Europe in the 1930s with the rise of ethology led by Konrad Lorenz, Niko Tinbergen, and others. Just as animals inherit organs that perform specific functions, ethologists believed animals inherit behaviors that evolved to serve adaptive functions as well. Instincts were described as unlearned (inherited), blind, stereotyped, adaptive, fixed action patterns, impervious to change that are initiated (released) by specific stimuli in the environment.
Ethologists in 1930s and 1940s were united under the banner of innateness. They were increasingly critical of the trend by American psychologists (i.e., behaviorists) to focus on studying on how a limited number of domesticated species (e.g., white rat) responded to training in artificial settings (Burkhardt, 2005 ). Ethologists instead began with rich descriptions of animal behavior in more natural environments along with detailed analyses of the stimulus conditions that released the fixed action patterns. To test whether behavioral components were innate, ethologists relied primarily on the deprivation experiment popularized by Spalding in the 19th century . Using these methods (and others), ethologists identified numerous fascinating examples of instinctive behaviors, which captured mainstream attention.
In the early 1950s, shortly after ethology had gained professional status (Burkhardt, 2005 ), a series of challenges regarding instinct and innateness were put forth by a small cadre of North American behavioral scientists (e.g., T. C. Schneirla, Donald Hebb, Frank Beach). Arguably the most influential critique was voiced by comparative psychologist Daniel Lehrman ( 1953 ), who presented a detailed and damning critique of deprivation experiments on empirical and logical grounds. Lehrman explained that deprivation experiments isolate the animal from some but not all experiences. Thus deprivation experiments simply change what an animal experiences rather than eliminating experience altogether, and so they cannot possibly determine whether a behavior is innate (independent of experience). Instead, these experiments show what environmental conditions do not matter in the development of a behavior but do not speak to what conditions do matter .
Lehrman went on to argue that the whole endeavor to identify instinctive or innate behavior was misguided from the start. All behavior, according to Lehrman, develops from a history of interactions between an organism and its environment. If a behavior is found to develop in the absence of certain experiences, the researcher should not stop and label it as innate. Rather, research should continue to identify the conditions under which the behavior comes about. In line with Kuo, Lehrman repeated the warning that to label something as instinctive (or inherited or maturational) is a statement of ignorance about how that behavior develops and does more to stunt than promote research.
Lehrman’s critique created significant turmoil among ethologists. As a result, ethologists took greater care in using the term innate , and it led to new attempts to synthesize or re-envision learning and instinct .
Some of these attempts focused on an increased role for learning and experience in the ontogeny of species-typical behaviors. These efforts spawned significant cross-talk between ethologists and comparative psychologists to more thoroughly investigate behavioral development under natural conditions. Traditional appeals to instinct and learning (as classical and operant conditioning) were both found to be inadequate for explaining animal behavior. In their stead, these researchers focused more closely on how anatomical, physiological, experiential, and environmental conditions influenced the development of species-typical behaviors.
Tinbergen ( 1963 ) was among those ethologists who urged for greater developmental analysis of species-typical behaviors, and he included it as one of his four problems in the biological study of organisms, along with causation (mechanism), survival value (function), and evolution. Of these four problems, Tinbergen believed ethologists were especially well suited to study survival value, which he felt had been seriously neglected (Burkhardt, 2005 ).
The questions of survival value coupled with models of population genetics would gain significant momentum in the 1960s and 1970s in England and the United States with the rise of behavioral ecology and sociobiology (Griffiths, 2008 ). But because these new fields seemed to promote some kind of genetic determinism in behavioral development, they were met with much resistance and reignited a new round of nature–nurture debates in the 1970s (see Segerstrale, 2000 ).
However, not all ethologists abandoned the instinct concept. Lorenz, in particular, continued to defend the division between nature and nurture. Rather than speaking of native and acquired behaviors, Lorenz later spoke of two different sources of information for behavior (innate/genetic vs. acquired/environmental), which was more a subtle shift in language than it was an actual change in theory, as Lehrman later pointed out.
Some ethologists followed Lorenz’s lead and continued to maintain more of a traditional delineation between instinct and learning. Their alternative synthesis viewed learning as instinctive (Gould & Marler, 1987 ). They proposed that animals have evolved domain-specific “instincts to learn” that result from the its genetic predispositions and innate knowledge. To support the idea of instincts for learning, ethologists pointed to traditional ethological findings (on imprinting and birdsong learning), but they also drew from the growing body of work in experimental psychology that seemed to indicate certain types of biological effects on learning.
Biological Constraints and Preparedness
While ethology was spreading in Europe in the 1930s–1950s, behaviorism reigned in the United States. Just as ethologists were confronted with including a greater role of nurture in their studies, behaviorists were challenged to consider a greater role of nature.
Behaviorists assumed there to be some behavioral innateness (e.g., fixed action patterns, unconditioned reflexes, primary reinforcers and drives). But because behaviorists focused on learning, they tended to study animals in laboratory settings using biologically (or ecologically) irrelevant stimuli and responses to minimize any role of instinct (Johnston, 1981 ). It was widely assumed that these studies would identify general laws of learning that applied to all species regardless of the specific cues, reinforcers, and responses involved.
Challenges to the generality assumption began to accumulate in the 1960s. Some studies pointed to failures that occurred during conditioning procedures. Breland and Breland ( 1961 ), for example, reported that some complex behaviors formed through operant conditioning would eventually become “displaced” by conditioned fixed action patterns in a phenomenon they called “instinctive drift.” Studies of taste-aversion learning (e.g., Garcia & Koelling, 1966 ) also reported the failure of rats to associate certain events (e.g., flavors with shock or audiovisual stimuli with toxicosis).
Other studies were pointing to enhanced learning. In particular, it was found that rats could form strong conditioned taste aversions after only a single pairing between a novel flavor and illness. (This rapid “one trial learning” was a major focus in the research from Niko Tinbergen’s ethological laboratory.) Animals, it seemed, had evolved innate predispositions to form (or not form) certain associations.
In humans, studies of biological constraints on learning were mostly limited to fear conditioning. Evidence indicated that humans conditioned differently to (biologically or evolutionarily) fear-relevant stimuli like pictures of spiders or snakes than to fear-irrelevant stimuli like pictures of mushrooms or flowers (Ohman, Fredrikson, Hugdahl, & Rimmö, 1976 ).
These findings and others were treated as a major problem in learning theory and led to calls for a new framework to study learning from a more biologically oriented perspective that integrated the evolutionary history and innate predispositions of the species. These predispositions were described as biological “constraints” on, “preparedness,” or “adaptive specializations” for learning, all of which were consistent with the “instincts to learn” framework proposed by ethologists.
By the 1980s it was becoming clear that the biological preparedness/constraint view of learning suffered some limitations. For example, what constraints count as “biological” was questioned. It was well established that there were general constraints on learning associated with the intensity, novelty, and timing of stimuli. But, arbitrarily it seemed, these constraints were not classified as “biological” (Domjan & Galef, 1983 ). Other studies of “biological constraints” found that 5- and 10-day old rats readily learned to associated a flavor with shock (unlike in adults), but (like in adults) such conditioning was not found in 15-day-old rats (Hoffman & Spear, 1988 ). In other words, the constraint on learning was not present in young rats but developed later in life, suggesting a possible role of experience in bringing about the adult-like pattern.
Attempts to synthesize these alternatives led to numerous calls for more ecologically oriented approaches to learning not unlike the synthesis between ethology and comparative psychology in the 1960s. All ecological approaches to learning proposed that learning should be studied in the context of “natural” (recurrent and species-typical) problems that animals encounter (and have evolved to encounter) using ecologically meaningful stimuli and responses. Some argued (e.g., Johnston, 1981 ) that studies of learning should take place within the larger context of studying how animals develop and adapt to their surround. Others (Domjan & Galef, 1983 ) pointed to more of a comparative approach in studying animal learning in line with behavioral ecology that takes into account how learning can be influenced by the possible selective pressures faced by each species. Still, how to synthesize biological constraints (and evolutionary explanations) on learning with a general process approach remains a source of tension in experimental psychology.
Nativism in Mind: Innate Ideas
Nativism and empiricism in philosophy.
In the philosophy of mind, nature–nurture debates are voiced as debates between nativists and empiricists. Nativism is a philosophical position that holds that our minds have some innate (a priori to experience) knowledge, concepts, or structure at the very start of life. Empiricism, in contrast, holds that all knowledge derives from our experiences in the world.
However, rarely (if ever) were there pure nativist or empiricist positions, but the positions bespeak a persistent tension. Empiricists tended to eschew innateness and promote a view of the mental content that is built by general mechanisms (e.g., association) operating on sensory experiences, whereas nativists tend to promote a view of mind that contains domain-specific, innate processes and/or content (Simpson, Carruthers, Laurence, & Stich, 2005 ). Although the tension about mental innateness would loosen as empiricism gained prominence in philosophy and science, the strain never went away and would intensify again in the 20th century .
Nativism in 20th Century Psychology: The Case of Language Development
In the first half of the 20th century , psychologists generally assumed that knowledge was gained or constructed through experience with the world. This is not to say that psychologists did not assume some innate knowledge. The Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget, for example, believed infants enter the world with some innate knowledge structures, particularly as they relate to early sensory and motor functioning (see Piaget, 1971 ). But the bulk of his work dealt with the construction of conceptual knowledge as children adapt to their worlds. By and large, there were no research programs in psychology that sought to identify innate factors in human knowledge and cognition until the 1950s (Samet & Zaitchick, 2017 )
An interest in psychological nativism was instigated in large part by Noam Chomsky’s ( 1959 ) critique of B. F. Skinner’s book on language. To explain the complexity of language, he argued, we must view language as the knowledge and application of grammatical rules. He went on to claim that the acquisition of these rules could not be attributed to any general-purpose, learning process (e.g., reinforcement). Indeed, language acquisition occurs despite very little explicit instruction. Moreover, language is special in terms of its complexity, ease, and speed of acquisition by children and in its uniqueness to humans. Instead, he claimed that our minds innately contain some language-specific knowledge that kick-starts and promotes language acquisition. He later claimed this knowledge can be considered some sort of specialized mental faculty or module he called the “language acquisition device” (Chomsky, 1965 ) or what Pinker ( 1995 ) later called the “language instinct.”
To support the idea of linguistic nativism, Chomsky and others appealed to the poverty of the stimulus argument. In short, this argument holds that our experiences in life are insufficient to explain our knowledge and abilities. When applied to language acquisition, this argument holds children’s knowledge of language (grammar) goes far beyond the limited, and sometimes broken, linguistic events that children directly encounter. Additional evidence for nativism drew upon the apparent maturational quality of language development. Despite wide variations in languages and child-rearing practices across the world, the major milestones in language development appear to unfold in children in a universal sequence and timeline, and some evidence suggested a critical period for language acquisition.
Nativist claims about language sparked intense rebuttals by empiricist-minded psychologists and philosophers. Some of these retorts tackled the logical limitations of the poverty of stimulus argument. Others pointed to the importance of learning and social interaction in driving language development, and still others showed that language (grammatical knowledge) may not be uniquely human (see Tomasello, 1995 , for review). Nativists, in due course, provided their own rebuttals to these challenges, creating a persistent tension in psychology.
Extending Nativism Beyond Language Development
In the decades that followed, nativist arguments expanded beyond language to include cognitive domains that dealt with understanding the physical, psychological, and social worlds. Developmental psychologists were finding that infants appeared to be much more knowledgeable in cognitive tasks (e.g., on understanding object permanence) and skillful (e.g., in imitating others) than had previously been thought, and at much younger ages. Infants also showed a variety of perceptual biases (e.g., preference for face-like stimuli over equally complex non-face-like stimuli) from very early on. Following the standard poverty of the stimulus argument, these findings were taken as evidence that infants enter the world with some sort of primitive, innate, representational knowledge (or domain-specific neural mechanisms) that constrains and promotes subsequent cognitive development. The nature of this knowledge (e.g., as theories or as core knowledge), however, continues to be debated (Spelke & Kinzler, 2007 ).
Empiricist-minded developmental psychologists responded by demonstrating shortcomings in the research used to support nativist claims. For example, in studies of infants’ object knowledge, the behavior of infants (looking time) in nativist studies could be attributed to relatively simple perceptual processes rather than to the infants’ conceptual knowledge (Heyes, 2014 ). Likewise, reports of human neonatal imitation not only suffered from failures to replicate but could be explained by simpler mechanisms (e.g., arousal) than true imitation (Jones, 2017 ). Finally, studies of perceptual preferences found in young infants, like newborn preferences for face-like stimuli, may not be specific preferences for faces per se but instead may reflect simpler, nonspecific perceptual biases (e.g., preferences for top-heavy visual configurations and congruency; Simion & Di Giorgio, 2015 ).
Other arguments from empiricist-minded developmental psychologists focused on the larger rationale for inferring innateness. Even if it is conceded that young infants, like two-month-olds, or even two-day-olds, display signs of conceptual knowledge, there is no good evidence to presume the knowledge is innate. Their knowledgeable behaviors could still be seen as resulting from their experiences (many of which may be nonobvious to researchers) leading up to the age of testing (Spencer et al., 2009 ).
In the 21st century , there is still no consensus about the reality, extensiveness, or quality of mental innateness. If there is innate knowledge, can experience add new knowledge or only expand the initial knowledge? Can the doctrine of innate knowledge be falsified? There are no agreed-upon answers to these questions. The recurring arguments for and against mental nativism continue to confound developmental psychologists.
Maturation Theory
The emergence of bodily changes and basic behavioral skills sometimes occurs in an invariant, predictable, and orderly sequence in a species despite wide variations in rearing conditions. These observations are often attributed to the operation of an inferred, internally driven, maturational process. Indeed, 21st-century textbooks in psychology commonly associate “nature” with “maturation,” where maturation is defined as the predetermined unfolding of the individual from a biological or genetic blueprint. Environmental factors play a necessary, but fundamentally supportive, role in the unfolding of form.
Preformationism Versus Epigenesis in the Generation of Form
The embryological generation of bodily form was debated in antiquity but received renewed interest in the 17th century . Following Aristotle, some claimed that embryological development involved “epigenesis,” defined as the successive emergence of form from a formless state. Epigenesists, however, struggled to explain what orchestrated development without appealing to Aristotelean souls. Attempts were made to invoke to natural causes like physical and chemical forces, but, despite their best efforts, the epigenesists were forced to appeal to the power of presumed, quasi-mystical, vitalistic forces (entelechies) that directed development.
The primary alternative to epigenesis was “preformationism,” which held that development involved the growth of pre-existing form from a tiny miniature (homunculus) that formed immediately after conception or was preformed in the egg or sperm. Although it seems reasonable to guess that the invention and widespread use of the microscope would immediately lay to rest any claim of homuncular preformationism, this was not the case. To the contrary, some early microscopists claimed to see signs of miniature organisms in sperm or eggs, and failures to find these miniatures were explained away (e.g., the homunculus was transparent or deflated to the point of being unrecognizable). But as microscopes improved and more detailed observations of embryological development were reported in the late 18th and 19th centuries , homuncular preformationism was finally refuted.
From Preformationism to Predeterminism
Despite the rejection of homuncular preformationism, preformationist appeals can be found throughout the 19th century . One of the most popular preformationist theories of embryological development was put forth by Ernst Haeckel in the 1860s (Gottlieb, 1992 ). He promoted a recapitulation theory (not original to Haeckel) that maintained that the development of the individual embryo passes through all the ancestral forms of its species. Ontogeny was thought to be a rapid, condensed replay of phylogeny. Indeed, for Haeckel, phylogenesis was the mechanical cause of ontogenesis. The phylogenetic evolution of the species created the maturational unfolding of embryonic form. Exactly how this unfolding takes place was less important than its phylogenetic basis.
Most embryologists were not impressed with recapitulation theory. After all, the great embryologist Karl Ernst von Baer ( 1792–1876 ) had refuted strict recapitulation decades earlier. Instead, there was greater interest in how best to explain the mechanical causes of development ushering in a new “experimental embryology.” Many experimental embryologists followed the earlier epigenesists by discussing vitalistic forces operating on the unorganized zygote. But it soon became clear that the zygote was structured, and many people believed the zygote contained special (unknown) substances that specified development. Epigenesis-minded experimental embryologists soon warned that the old homuncular preformationism was being transformed into a new predetermined preformationism.
As a result, the debates between preformationism and epigenesis were reignited in experimental embryology, but the focus of these debates shifted to the various roles of nature and nurture during development. More specifically, research focused on the extent to which early cellular differentiation was predetermined by factors internal to cells like chromosomes or cytoplasm (preformationism, nature) or involved factors (e.g., location) outside of the cell (epigenesis, nurture). The former emphasized reductionism and developmental programming, whereas the latter emphasized some sort of holistic, regulatory system responsive to internal and external conditions. The tension between viewing development as predetermined or “epigenetic” persists into the 21st century .
Preformationism gained momentum in the 20th century following the rediscovery of Mendel’s studies of heredity and the rapid rise of genetics, but not because of embryological research on the causes of early differentiation. Instead, preformationism prevailed because it seemed embryological research on the mechanisms of development could be ignored in studies of hereditary patterns.
The initial split between heredity and development can be found in Galton’s speculations but is usually attributed to Weismann’s germ-plasm theory. Weismann’s barrier seemed to posit that the germinal determinants present at conception would be the same, unaltered determinants transmitted during reproduction. This position, later dubbed as “Weismannism,” was ironically not one promoted by Weismann. Like nearly all theorists in the 19th century , he viewed the origins of variation and heredity as developmental phenomena (Amundson, 2005 ), and he claimed that the germ-plasm could be directly modified in the lifetime of the organism by environmental (e.g., climactic and dietary) conditions (Winther, 2001 ). Still, Weismann’s theory treated development as a largely predetermined affair driven by inherited, germinal determinants buffered from most developmental events. As such, it helped set the stage for a more formal divorce between heredity and development with the rise of Mendelism in the early 20th century .
Mendel’s theory of heredity was exceptional in how it split development from heredity (Amundson, 2005 ). More so than in Weismann’s theory, Mendel’s theory assumed that the internal factors that determine form and are transmitted across generations remain unaltered in the lifetime of the organism. To predict offspring outcomes, one need only know the combination of internal factors present at conception and their dominance relations. Exactly how these internal factors determined form could be disregarded. The laws of hereditary transmission of the internal factors (e.g., segregation) did not depend on the development or experiences of the organism or the experiences the organism’s ancestors. Thus the experimental study of heredity (i.e., breeding) could proceed without reference to ancestral records or embryological concerns (Amundson, 2000 ). By the mid-1920s, the Mendelian factors (now commonly called “genes”) were found to be structurally arranged on chromosomes, and the empirical study of heredity (transmission genetics) was officially divorced from studies of development.
The splitting of heredity and development found in Mendel’s and Weismann’s work met with much resistance. Neo-Lamarckian scientists, especially in the United States (Cook, 1999 ) and France (Loison, 2011 ), sought unsuccessfully to experimentally demonstrate the inheritance of acquired characteristics into the 1930s.
In Germany during the 1920s and 1930s, resistance to Mendelism dealt with the chromosomal view of Mendelian heredity championed by American geneticists who were narrowly focused on studying transmission genetics at the expense of developmental genetics. German biologists, in contrast, were much more interested in the broader roles of genes in development (and evolution). In trying to understand how genes influence development, particularly of traits of interest to embryologists, they found the Mendelian theory to be lacking. In the decades between the world wars, German biologists proposed various expanded views of heredity that included some form of cytoplasmic inheritance (Harwood, 1985 ).
Embryologists resisted the preformationist view of development throughout the early to mid- 20th century , often maintaining no divide between heredity and development, but their objections were overshadowed by genetics and its eventual synthesis with evolutionary theory. Consequently, embryological development was treated by geneticists and evolutionary biologists as a predetermined, maturational process driven by internal, “genetic” factors buffered from environmental influence.
Maturation Theory in Psychology
Maturation theory was applied to behavioral development in the 19th century in the application of Haeckel’s recapitulation theory. Some psychologists believed that the mental growth of children recapitulated the history of the human race (from savage brute to civilized human). With this in mind, many people began to more carefully document child development. Recapitulationist notions were found in the ideas of many notable psychologists in the 19th and early 20th centuries (e.g., G. S. Hall), and, as such, the concept played an important role in the origins of developmental psychology (Koops, 2015 ). But for present purposes what is most important is that children’s mental and behavioral development was thought to unfold via a predetermined, maturational process.
With the growth of genetics, maturational explanations were increasingly invoked to explain nearly all native and hereditary traits. As the instinct concept lost value in the 1920s, maturation theory gained currency, although the shift was largely a matter of semantics. For many psychologists, the language simply shifted from “instinct versus learning” to “maturation versus practice/experience” (Witty & Lehman, 1933 ).
Initial lines of evidence for maturational explanations of behavior were often the same as those that justified instinct and native traits, but new embryological research presented in the mid-1920s converged to show support for strict maturational explanations of behavioral development. In these experiments (see Wyman, 2005 , for review), spanning multiple laboratories, amphibians (salamanders and frogs) were exposed to drugs that acted as anesthetics and/or paralytics throughout the early stages of development, thus reducing sensory experience and/or motor practice. Despite the reduced sensory experiences and being unable to move, these animals showed no delays in the onset of motor development once the drugs wore off.
This maturational account of motor development in amphibians fit well with contemporaneous studies of motor development in humans. The orderly, invariant, and predictable (age-related) sequential appearance of motor skills documented in infants reared under different circumstances (in different countries and across different decades) was seen as strong evidence for a maturational account. Additional evidence was reported by Arnold Gessell and Myrtle McGraw, who independently presented evidence in the 1920s to show that the pace and sequence of motor development in infancy were not altered by special training experiences. Although the theories of these maturation theorists were more sophisticated when applied to cognitive development, their work promoted a view in which development was primarily driven by neural maturation rather than experience (Thelen, 2000 ).
Critical and Sensitive Periods
As the maturation account of behavioral development gained ground, it became clear that environmental input played a more informative role than had previously been thought. Environmental factors were found to either disrupt or induce maturational changes at specific times during development. Embryological research suggested that there were well-delineated time periods of heightened sensitivity in which specific experimental manipulations (e.g., tissue transplantations) could induce irreversible developmental changes, but the same manipulation would have no effect outside of that critical period.
In the 1950s–1960s a flurry of critical period effects were reported in birds and mammals across a range of behaviors including imprinting, attachment, socialization, sensory development, bird song learning, and language development (Michel & Tyler, 2005 ). Even though these findings highlighted an important role of experience in behavioral development, evidence of critical periods was usually taken to imply some rigid form of biological determinism (Oyama, 1979 ).
As additional studies were conducted on critical period effects, it became clear that many of the reported effects were more gradual, variable, experience-dependent, and not necessarily as reversible as was previously assumed. In light of these reports, there was a push in the 1970s (e.g., Connolly, 1972 ) to substitute “sensitive period” for “critical period” to avoid the predeterminist connotations associated with the latter and to better appreciate that these periods simply describe (not explain) certain temporal aspects of behavioral development. As a result, a consensus emerged that behaviors should not be attributed to “time” or “age” but to the developmental history and status of the animal under investigation (Michel & Tyler, 2005 ).
Heredity and Genetics
In the decades leading up to and following the start of the 20th century , it was widely assumed that many psychological traits (not just instincts) were inherited or “due to heredity,” although the underlying mechanisms were unknown. Differences in intelligence, personality, and criminality within and between races and sexes were largely assumed to be hereditary and unalterable by environmental intervention (Gould, 1996 ). The evidence to support these views in humans was often derived from statistical analyses of how various traits tended to run in families. But all too frequently, explanations of data were clouded by pre-existing, hereditarian assumptions.
Human Behavioral Genetics
The statistical study of inherited human (physical, mental, and behavioral) differences was pioneered by Galton ( 1869 ). Although at times Galton wrote that nature and nurture were so intertwined as to be inseparable, he nevertheless devised statistical methods to separate their effects. In the 1860s and 1870s, Galton published reports purporting to show how similarities in intellect (genius, talent, character, and eminence) in European lineages appeared to be a function of degree of relatedness. Galton considered, but dismissed, environmental explanations of his data, leading him to confirm his belief that nature was stronger than nurture.
Galton also introduced the use of twin studies to tease apart the relative impact of nature versus nurture, but the twin method he used was markedly different from later twin studies used by behavioral geneticists. Galton tracked the life history of twins who were judged to be very similar or very dissimilar near birth (i.e., by nature) to test the power of various postnatal environments (nurture) that might make them more or less similar over time. Here again, Galton concluded that nature overpowers nurture.
Similar pedigree (e.g., the Kallikak study; see Zenderland, 2001 ) and twin studies appeared in the early 1900s, but the first adoption study and the modern twin method (which compares monozygotic to dizygotic twin pairs) did not appear until the 1920s (Rende, Plomin, & Vandenberg, 1990 ). These reports led to a flurry of additional work on the inheritance of mental and behavioral traits over the next decade.
Behavioral genetic research peaked in the 1930s but rapidly lost prominence due in large part to its association with the eugenics movement (spearheaded by Galton) but also because of the rise and eventual hegemony of behaviorism and the social sciences in the United States. Behavioral genetics resurged in the 1960s with the rising tide of nativism in psychology, and returned to its 1930s-level prominence in the 1970s (McGue & Gottesman, 2015 ).
The resurgence brought with a new statistical tool: the heritability statistic. The origins of heritability trace back to early attempts to synthesize Mendelian genetics with biometrics by Ronald Fisher and others. This synthesis ushered in a new field of quantitative genetics and it marked a new way of thinking about nature and nurture. The shift was to no longer think about nature and nurture as causes of traits in individuals but as causes of variation in traits between populations of individuals. Eventually, heritability came to refer to the amount of variance in a population sample that could be statistically attributed to genetic variation in that sample. Kinship (especially twin) studies provided seemingly straightforward ways of partitioning variation in population trait attributes into genetic versus environmental sources.
Into the early 21st century , hundreds of behavioral genetic studies of personality, intelligence, and psychopathology were reported. With rare exceptions, these studies converge to argue for a pervasive influence of genetics on human psychological variation.
These studies have also fueled much controversy. Citing in part behavioral genetic research, the educational psychologist Arthur Jensen ( 1969 ) claimed that the differences in intelligence and educational achievement in the United States between black and white students appeared to have a strong genetic basis. He went on to assume that because these racial differences appeared hereditary, they were likely impervious to environmental (educational) intervention. His article fanned the embers of past eugenics practices and ignited fiery responses (e.g., Hirsch, 1975 ). The ensuing debates not only spawned a rethinking of intelligence and how to measure it, but they ushered in a more critical look at the methods and assumptions of behavioral genetics.
Challenges to Behavioral Genetics
Many of the early critiques of behavioral genetics centered on interpreting the heritability statistic commonly calculated in kinship (family, twin, and adoption) studies. Perhaps more so than any other statistic, heritability has been persistently misinterpreted by academics and laypersons alike (Lerner, 2002 ). Contrary to popular belief, heritability tells us nothing about the relative impact of genetic and environmental factors on the development of traits in individuals. It deals with accounting for trait variation between people, not the causes of traits within people. As a result, a high heritability does not indicate anything about the fixity of traits or their imperviousness to environmental influence (contra Jensen), and a low heritability does not indicate an absence of genetic influence on trait development. Worse still, heritability does not even indicate anything about the role of genetics in generating the differences between people.
Other challenges to heritability focused not on its interpretation but on its underlying computational assumptions. Most notably, heritability analyses assume that genetic and environmental contributions to trait differences are independent and additive. The interaction between genetic and environmental factors were dismissed a priori in these analyses. Studies of development, however, show that no factor (genes, hormones, parenting, schooling) operates independently, making it impossible to quantify how much of a given trait in a person is due to any causal factor. Thus heritability analyses are bound to be misleading because they are based on biologically implausible and logically indefensible assumptions about development (Gottlieb, 2003 ).
Aside from heritability, kinship studies have been criticized for not being able to disentangle genetic and environmental effects on variation. It had long been known that that in family (pedigree) studies, environmental and genetic factors are confounded. Twin and adoption studies seemed to provide unique opportunities to statistically disentangle these effects, but these studies are also deeply problematic in assumptions and methodology. There are numerous plausible environmental reasons for why monozygotic twin pairs could resemble each other more than dizygotic twin pairs or why adoptive children might more closely resemble their biological than their adoptive parents (Joseph & Ratner, 2013 ).
A more recent challenge to behavioral genetics came from an unlikely source. Advances in genomic scanning in the 21st century made it possible in a single study to correlate thousands of genetic polymorphisms with variation in the psychological profiles (e.g., intelligence, memory, temperament, psychopathology) of thousands of people. These “genome-wide association” studies seemed to have the power and precision to finally identify genetic contributions to heritability at the level of single nucleotides. Yet, these studies consistently found only very small effects.
The failure to find large effects came to be known as the “missing heritability” problem (Maher, 2008 ). To account for the missing heritability, some behavioral geneticists and molecular biologists asserted that important genetic polymorphisms remain unknown, they may be too rare to detect, and/or that current studies are just not well equipped to handle gene–gene interactions. These studies were also insensitive to epigenetic profiles (see the section on Behavioral Epigenetics), which deal with differences in gene expression. Even when people share genes, they may differ in whether those genes get expressed in their lifetimes.
But genome-wide association studies faced an even more problematic issue: Many of these studies failed to replicate (Lickliter & Honeycutt, 2015 ). For those who viewed heritability analyses as biologically implausible, the small effect sizes and failures to replicate in genome-wide association studies were not that surprising. The search for independent genetic effects was bound to fail, because genes simply do not operate independently during development.
Behavioral Epigenetics
Epigenetics was a term coined in the 1940s by the developmental biologist Conrad Waddington to refer to a new field of study that would examine how genetic factors interact with local environmental conditions to bring about the embryological development of traits. By the end of the 20th century , epigenetics came to refer to the study of how nongenetic, molecular mechanisms physically regulate gene expression patterns in cells and across cell lineages. The most-studied mechanisms involve organic compounds (e.g., methyl-groups) that physically bind to DNA or the surrounding proteins that package DNA. The addition or removal of these compounds can activate or silence gene transcription. Different cell types have different, stable epigenetic markings, and these markings are recreated during cell division so that cells so marked give rise to similar types of cells. Epigenetic changes were known to occur during developmental periods of cellular differentiation (e.g., during embryogenesis), but not until 2004 was it discovered that these changes can occur at other periods in the life, including after birth (Roth, 2013 )
Of interest to psychologists were reports that different behavioral and physiological profiles (e.g., stress reactivity) of animals were associated with different epigenetic patterns in the nervous system (Moore, 2015 ). Furthermore, these different epigenetic patterns could be established or modified by environmental factors (e.g., caregiving practices, training regimes, or environmental enrichment), and, under certain conditions, they remain stable over long periods of time (from infancy to adulthood).
Because epigenetic research investigates the physical interface between genes and environment, it represents an exciting advance in understanding the interaction of nature and nurture. Despite some warnings that the excitement over behavioral epigenetic research may be premature (e.g., Miller, 2010 ), for many psychologists, epigenetics underscores how development involves both nature and nurture.
For others, what is equally exciting is the additional evidence epigenetics provides to show that the genome is an interactive and regulated system. Once viewed as the static director of development buffered from environment influence, the genome is better described as a developing resource of the cell (Moore, 2015 ). More broadly, epigenetics also points to how development is not a genetically (or biologically) predetermined affair. Instead, epigenetics provides additional evidence that development is a probabilistic process, contingent upon factors internal and external to the organism. In this sense, epigenetics is well positioned to help dissolve the nature–nurture dichotomy.
Beyond Nature–Nurture
In the final decades of the 20th century , a position was articulated to move beyond the dichotomous nature–nurture framework. The middle-ground position on nature–nurture did not seem up to the task of explaining the origins of form, and it brought about more confusion than clarity. The back-and-forth (or balanced) pendulum between nature- and nurture-based positions throughout history had only gone in circles. Moving forward would require moving beyond such dichotomous thinking (Johnston, 1987 ).
The anti-dichotomy position, referred to as the Developmentalist tradition, was expressed in a variety of systems-based, metatheoretical approaches to studying development, all of which extended the arguments against nature–nurture expressed earlier by Kuo and Lehrman. The central problem with all nativist claims according to Developmentalists is a reliance on preformationism (or predeterminism).
The problem with preformationism, they argue, besides issues of evidence, is that it is an anti-developmental mindset. It presumes the existence of the very thing(s) one wishes to explain and, consequently, discourages developmental analyses. To claim that some knowledge is innate effectively shuts down research on the developmental origins of that knowledge. After all, why look for the origins of conceptual knowledge if that knowledge is there all along? Or why search for any experiential contributions to innate behaviors if those behaviors by definition develop independently of experience? In the words of Developmentalists Thelen and Adolph ( 1992 ), nativism “leads to a static science, with no principles for understanding change or for confronting the ultimate challenge of development, the source of new forms in structure and function” (p. 378).
A commitment to maturational theory is likely one of the reasons why studies of motor development remained relatively dormant for decades following its heyday in the 1930–1940s (Thelen, 2000 ). Likewise, a commitment to maturational theory also helps explain the delay in neuroscience to examine how the brain physically changes in response to environmental conditions, a line of inquiry that only began in the 1960s.
In addition to the theoretical pitfalls of nativism, Developmentalists point to numerous studies that show how some seemingly native behaviors and innate constraints on learning are driven by the experiences of animals. For example, the comparative psychologist Gilbert Gottlieb ( 1971 ) showed that newly hatched ducklings display a naïve preference for a duck maternal call over a (similarly novel) chicken maternal call (Gottlieb, 1971 ), even when duck embryos were repeatedly exposed to the chicken call prior to hatching (Gottlieb, 1991 ). It would be easy to conclude that ducklings have an innate preference to approach their own species call and that they are biologically constrained (contraprepared) in learning a chicken call. However, Gottlieb found that the naïve preference for the duck call stemmed from exposure to the duck embryos’ own (or other) vocalizations in the days before hatching (Gottlieb, 1971 ). Exposure to these vocalizations not only made duck maternal calls more attractive, but it hindered the establishment of a preference for heterospecific calls. When duck embryos were reared in the absence of the embryonic vocalizations (by devocalizing embryos in ovo ) and exposed instead to chicken maternal calls, the newly hatched ducklings preferred chicken over duck calls (Gottlieb, 1991 ). These studies clearly showed how seemingly innate, biologically based preferences and constraints on learning derived from prenatal sensory experiences.
For Developmentalists, findings like these suggest that nativist explanations of any given behavior are statements of ignorance about how that behavior actually develops. As Kuo and Lehrman made clear, nativist terms are labels, not explanations. Although such appeals are couched in respectable, scientific language (e.g., “X is due to maturation, genes, or heredity”), they argue it would be more accurate simply to say that “We don’t know what causes X” or that “X is not due to A, B, or C.” Indeed, for Developmentalists, the more we unpack the complex dynamics about how traits develop, the less likely we are to use labels like nature or nurture (Blumberg, 2005 ).
On the other hand, Developmentalists recognize that labeling a behavior as “learned” also falls short as an explanatory construct. The empiricist position that knowledge or behavior is learned does not adequately take into account that what is learned and how easily something is learned depends on (a) the physiological and developmental status of the person, (b) the nature of the surrounding physical and social context in which learning takes place, and the (c) experiential history of the person. The empiricist tendency to say “X is learned or acquired through experience” can also short-circuit developmental analyses in the same way as nativist claims.
Still, Developmentalists appreciate that classifying behaviors can be useful. For example, the development of some behaviors may be more robust, reliably emerging across a range of environments and/or remaining relatively resistant to change, whereas others are more context-specific and malleable. Some preferences for stimuli require direct experience with those stimuli. Other preferences require less obvious (indirect) types of experiences. Likewise, it can still be useful to describe some behaviors in the ways shown in Table 1 . Developmentalists simply urge psychologists to resist the temptation to treat these behavioral classifications as implying different kinds of explanations (Johnston, 1987 ).
Rather than treat nature and nurture as separate developmental sources of causation (see Figure 1 ), Developmentalists argue that a more productive way of thinking about nature–nurture is to reframe the division as that between product and process (Lickliter & Honeycutt, 2015 ). The phenotype or structure (one’s genetic, epigenetic, anatomical, physiological, behavioral, and mental profile) of an individual at any given time can be considered one’s “nature.” “Nurture” then refers to the set of processes that generate, maintain, and transform one’s nature (Figure 2 ). These processes involve the dynamic interplay between phenotypes and environments.
Figure 2. The developmentalist alternative view of nature–nurture as product–process. Developmentalists view nature and nurture not as separate sources of causation in development (see Figure 1 ) but as a distinction between process (nurture) and product (nature).
It is hard to imagine any set of findings that will end debates about the roles of nature and nurture in human development. Why? First, more so than other assumptions about human development, the nature–nurture dichotomy is deeply entrenched in popular culture and the life sciences. Second, throughout history, the differing positions on nature and nurture were often driven by other ideological, philosophical, and sociopolitical commitments. Thus the essential source of tension in debates about nature–nurture is not as much about research agendas or evidence as about basic differences in metatheoretical positions (epistemological and ontological assumptions) about human behavior and development (Overton, 2006 ).
- Amundson, R. (2000). Embryology and evolution 1920–1960: Worlds apart? History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences , 22 , 335–352.
- Amundson, R. (2005). The changing role of the embryo in evolutionary thought: Roots of evo-devo . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Blumberg, M. S. (2005). Basic instinct: The genesis of novel behavior . New York, NY: Thunder’s Mouth Press.
- Breland, K. , & Breland, M. (1961). The misbehavior of organisms. American Psychologist , 16 , 681–684.
- Burkhardt, R. (2005). Patterns of behavior: Konrad Lorenz, Niko Tinbergen and the founding of ethology . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Burnham, J. C. (1972). Instinct theory and the German reaction to Weismannism. Journal of the History of Biology , 5 , 321–326.
- Carmichael, L. (1925). Heredity and environment: Are they antithetical? The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 20 (3), 245–260.
- Chomsky, N. (1959). A review of B. F. Skinner’s verbal behavior. Language , 35 , 26–57.
- Chomsky, N. (1965). Aspects of the theory of syntax . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Connolly, K. (1972). Learning and the concept of critical periods in infancy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology , 14 (6), 705–714.
- Cook, G. M. (1999). Neo-Lamarckian experimentalism in America: Origins and consequences. Quarterly Review of Biology , 74 , 417–437.
- Cowan, R. S. C. (2016). Commentary: Before Weismann and germplasm there was Galton and eugenics: The biological and political meaning of the inheritance of acquired characteristics in the late 19th century . International Journal of Epidemiology , 45 , 15–20.
- Cravens, H. , & Burnham, J. C. (1971). Psychology and evolutionary naturalism in American thought, 1890–1940. American Quarterly , 23 , 635–657.
- Diamond, S. (1971). Gestation of the instinct concept. History of the Behavioral Sciences , 7 (4), 323–336.
- Domjan, M. , & Galef, B. G. (1983). Biological constraints on instrumental and classical conditioning: Retrospect and prospect. Animal Learning & Behavior , 11 (2), 151–161.
- Dunlap, K. (1919). Are there any instincts? Journal of Abnormal Psychology , 14 , 307–311.
- Galton, F. (1869). Hereditary genius . London, U.K.: Macmillan.
- Garcia, J. , & Koelling, R. A. (1966). Relation of cue to consequence in avoidance learning. Psychonomics , 4 (1), 123–124.
- Gottlieb, G. (1971). Development of species identification in birds . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Gottlieb, G. (1991). Experiential canalization of behavioral development: Results. Developmental Psychology , 27 (1), 35–39.
- Gottlieb, G. (1992). Individual development and evolution: The genesis of novel behavior . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Gottlieb, G. (2003). On making behavioral genetics truly developmental. Human Development , 46 , 337–355.
- Gould, J. L. , & Marler, P. (1987). Learning by instinct. Scientific American , 256 (1), 74–85.
- Gould, S. J. (1996). The mismeasure of man (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Norton.
- Gray, P. H. (1967). Spalding and his influence on research in developmental behavior. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences , 3 , 168–179.
- Griffiths, P. E. (2008). Ethology, sociobiology, and evolutionary psychology. In S. Sarkar & A. Plutnsky (Eds.), A companion to the philosophy of biology (pp. 393–414). New York, NY: Blackwell.
- Harwood, J. (1985). Geneticists and the evolutionary synthesis in interwar Germany. Annals of Science , 42 , 279–301.
- Herrnstein, R. J. (1972). Nature as nurture: Behaviorism and the instinct doctrine. Behaviorism , 1 (1), 23–52.
- Heyes, C. (2014). False belief in infancy: A fresh look. Developmental Science , 17 (5), 647–659.
- Hirsch, J. (1975). Jensenism: The bankruptcy of “science” without scholarship. Educational Theory , 25 , 3–27.
- Hoffman, H. , & Spear, N. E. (1988). Ontogenetic differences in conditioning of an aversion to a gustatory CS with a peripheral US. Behavioral and Neural Biology , 50 , 16–23.
- Honeycutt, H. (2011). The “enduring mission” of Zing-Yang Kuo to eliminate the nature–nurture dichotomy in psychology. Developmental Psychobiology , 53 (4), 331–342.
- Jaynes, J. , & Woodward, W. (1974). In the shadow of the enlightenment. II. Reimarus and his theory of drives. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences , 10 , 144–159.
- Jensen, A. (1969). How much can we boost IQ and scholastic achievement. Harvard Educational Review , 39 , 1–123.
- Johnston, T. (1981). Contrasting approaches to a theory of learning. Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 4 , 125–173.
- Johnston, T. (1987). The persistence of dichotomies in the study of behavior. Developmental Review , 7 , 149–172.
- Johnston, T. (1995). The influence of Weismann’s germ-plasm theory on the distinction between learned and innate behavior. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences , 31 , 115–128.
- Jones, S. (2017). Can newborn infants imitate? Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science , 8 , e1410.
- Joseph, J. , & Ratner, C. (2013). The fruitless search for genes in psychiatry and psychology: Time to reexamine a paradigm. In S. Krimsky & J. Gruber (Eds.), Genetic explanations: Sense and nonsense (pp. 94–106). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Keller, E. F. (2010). The mirage of space between nature and nurture . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Koops, W. (2015). No developmental psychology without recapitulation theory . European Journal of Developmental Psychology , 12 (6), 630–639.
- Kuo, Z. Y. (1930). The genesis of the cat’s response to the rat. Journal of Comparative Psychology , 11 , 1–36.
- Lehrman, D. S. (1953). A critique of Konrad Lorenz’s theory of instinctive behavior. Quarterly Review of Biology , 28 , 337–363.
- Lerner, R. (2002). Concepts and theories of human development (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Lickliter, R. , & Honeycutt, H. (2015). Biology, development and human systems . In W. Overton & P. C. M. Molenaar (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology and developmental science . Vol. 1: Theory and method (7th ed., pp. 162–207). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Logan, C. A. , & Johnston, T. D. (2007). Synthesis and separation in the history of “nature” and “nurture.” Developmental Psychobiology , 49 (8), 758–769.
- Loison, L. (2011). French roots of French neo-Lamarckisms,1879–1985 . Journal of the History of Biology , 44 , 713–744.
- Maher, B. (2008). Personal genomes: The case of the missing heritability . Nature , 456 , 18–21.
- McGue, M. , & Gottesman, I. I. (2015). Behavior genetics . In R. L. Cautin & S. O. Lilienfeld (Eds.), The encyclopedia of clinical psychology (Vol. 1). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley Blackwell.
- Meloni, M. (2016). The transcendence of the social: Durkheim, Weismann and the purification of sociology . Frontiers in Sociology , 1 , 1–13.
- Michel, G. F. , & Tyler, A. N. (2005). Critical period: A history of transition of questions of when, to what, to how . Developmental Psychobiology , 46 (3), 156–162.
- Miller, G. (2010).The seductive allure of behavioral epigenetics. Science , 329 (5987), 24–27.
- Moore, D. S. (2015). The developing genome. An introduction to behavioral epigenetics . New York, NY: Oxford University Press
- Morgan, C. L. (1896). Habit and instinct . New York, NY: Edward Arnold.
- Muller-Wille, S. , & Rheinberger, H.-J. (2012). A cultural history of heredity . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Ohman, A. , Fredrikson, M. , Hugdahl, K. , & Rimmö, P.A. (1976). The premise of equipotentiality in human classical conditioning: Conditioned electrodermal responses to potentially phobic stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 105 (4), 313–337.
- Overton, W. F. (2006). Developmental psychology: Philosophy, concepts, methodology. In R. Lerner (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 1. Theoretical models of human development (pp. 18–88). New York, NY: Wiley.
- Oyama, S. (1979). The concept of the sensitive period in developmental studies. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly , 25 (2), 83–103.
- Piaget, J. (1971). Biology and knowledge: An essay on the relation between organic regulations and cognitive processes . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Pinker, S. (1995). The language instinct: How the mind creates language . London, U.K.: Penguin.
- Rende, R. D. , Plomin, R. , & Vandenberg, S. G. (1990). Who discovered the twin method? Behavioral Genetics , 20 (2), 277–285.
- Renwick, C. (2011). From political economy to sociology: Francis Galton and the social-scientific origins of eugenics . British Journal for the History of Science , 44 , 343–369.
- Richards, R. J. (1987). Darwin and the emergence of evolutionary theories of mind and behavior . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Robinson, G. E. , & Barron, A. B. (2017). Epigenetics and the evolution of instincts. Science , 356 (6333), 26–27.
- Roth, T. L. (2013). Epigenetic mechanisms in the development of behavior: Advances, challenges, and future promises of a new field . Development and Psychopathology , 25 , 1279–1291.
- Samet, J. , & Zaitchick, D. (2017). Innateness and contemporary theories of cognition . In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy . Stanford, CA: Stanford University.
- Segerstrale, U. (2000). Defenders of the truth: The battle for science in the sociobiology debate and beyond . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Simion, F. , & Di Giorgio, E. (2015). Face perception and processing in early infancy: Inborn predispositions and developmental changes . Frontiers in Psychology , 6 , 969.
- Simpson, T. , Carruthers, P. , Laurence, S. , & Stich, S. (2005). Introduction: Nativism past and present . In P. Carruthers , S. Laurence , & S. Stich (Eds.), The innate mind: Structure and contents (pp. 3–19). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Spelke, E. , & Kinzler, K. D. (2007). Core knowledge . Developmental Science , 10 (1), 89–96.
- Spencer, J. P. , Samuelson, L. K. , Blumberg, M. S. , McMurray, R. , Robinson, S. R. , & Tomblin, J. B. (2009). Seeing the world through a third eye: Developmental systems theory looks beyond the nativist-empiricist debate. Child Development Perspectives , 3 , 103–105.
- Thelen, E. (2000). Motor development as foundation and future of developmental psychology. International Journal of Behavioral Development , 24 (4), 385–397.
- Thelen, E. , & Adolph, K. E. (1992). Arnold L. Gesell: The paradox of nature and nurture. Developmental Psychology , 28 (3), 368–380.
- Tinbergen, N. (1963). On the aims and methods of ethology. Zeitschrift für Tierpsychologie , 20 , 410–433.
- Tomasello, M. T. (1995). Language is not an instinct. Cognitive Development , 10 , 131–156.
- Winther, R. G. (2001). Weismann on germ-plasm variation. Journal of the History of Biology , 34 , 517–555.
- Witty, P. A. , & Lehman, H. C. (1933). The instinct hypothesis versus the maturation hypothesis. Psychological Review , 40 (1), 33–59.
- Wyman, R. J. (2005). Experimental analysis of nature–nurture. Journal of Experimental Zoology , 303 , 415–421.
- Zenderland, L. (2001). Measuring minds. Henry Herbert Goddard and the origins of American intelligence testing . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Psychology. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 30 October 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|91.193.111.216]
- 91.193.111.216
Character limit 500 /500
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Neuroscience and Nervous System Disorders. From Molecules to Minds: Challenges for the 21st Century: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2008.

From Molecules to Minds: Challenges for the 21st Century: Workshop Summary.
- Hardcopy Version at National Academies Press
Grand Challenge: Nature Versus Nurture: How Does the Interplay of Biology and Experience Shape Our Brains and Make Us Who We Are?
Nature vs. nurture is one of the oldest questions in science. The answer is not an either/or, but rather it is both nature and nurture, acting in various degrees.
As summarized below in greater detail, many workshop participants—including Hyman, Marder, and Michael Greenberg, chair of the Department of Neurobiology at Harvard Medical School—chose to highlight the nature versus nurture question as one of the Grand Challenges of the field, but in so doing, they put a twist on the question, asking: How does the interplay of biology and experience shape our brains and make us who we are?
The key word there is “interplay.” “Interplay” suggests, and modern research in neuroscience demands, that there is a back and forth pattern between nature and nurture, a dynamic system that involves a continuous feedback loop shaping the physical structure of our brains.
- Brain Plasticity
Thirty years ago, the working assumption in neuroscience was this: People are born with a set number of neurons, hardwired in a certain way, and brain function is essentially all downhill from there. We spend our lifetimes losing connections and neurons—the brain slowly falling apart until we die.
Except it is not true. In 1998, Fred “Rusty” Gage, working out of the Laboratory of Genetics at the Salk Institute, showed that the human brain can and does produce new nerve cells into adulthood ( Eriksson et al., 1998 ). In mice, he showed that exercise could increase the rate of neurogenesis, showing that the system is not fixed, but responds itself to experience and the outside world. The discovery of neurogenesis and an improved understanding of neuroplasticity—the ability of the brain to shape, form, eliminate, and strengthen new connections throughout life—has completely recast the question of nature versus nurture.
“Neurons can change their connectivity,” explained Blakemore. “They can change the strength of their connections. They can change the morphology of their connections. They can do it not necessarily just in early stages of life, although that is especially exaggerated, but probably throughout life responding to new environments and experiences.”
New research shows, for instance, that the number and strength of connections we have in the brain is determined by how often those connections are stimulated. The brain, if you will, has a “use it or lose it” approach to neurological maintenance.
Genetic programming also plays a key role. In most cases, the initial formation of a synapse occurs independent of stimulation. But if that synapse is not used, the brain will “prune” or eliminate it. Conversely, the more often a connection is used, the stronger it becomes in a physical sense, with more dendritic spines connecting to one another and a stronger net connection over time.
On the developmental side, researchers now understand the critical role that sensory input plays in shaping the wiring of the brain from the earliest days. Blakemore discussed work in his lab on the development of neural wiring in mice. Researchers have known since the 1960s that the neurons connected to the ultrasensitive whiskers of mice align themselves in a format called “barrel fields.” Each of these barrel fields is connected to a single whisker, although how or why they influence function is unknown. Blakemore showed that if you removed a clump of whiskers at an early age, the segment of the brain linked to that area never develops the barrel structure.
Similar research has shown in mice that if you tape one eye shut from birth, the mouse never gains the ability to see from that eye—it needs the stimulation to develop. However, if you tape shut the eye of an adult mouse for a similar period of time, vision is not affected.
All this seems to point the finger toward experience, but of course, the system really works as a complete feedback loop.
“We used to think . . . that the capacity of the brain to change its connections was an entirely independent process from the genetic regulation of structure,” said Blakemore. “But, of course, that cannot be the case. If adaptive change is possible, that must be the consequence of having molecular mechanisms that mediate those changes. Plasticity is a characteristic that has been selected for, so there must be genes for plasticity.”
In the case of barrel fields, Blakemore’s lab and other investigators have identified a number of molecules and genes that appear to be involved in mediating between incoming information for the whiskers and the anatomical changes necessary to produce the barrel field.
Understanding how this interplay works has huge implications for understanding how our brain develops and changes over time, and raises a number of interesting questions. Marder, for instance, asked how the brain can be so plastic and yet still retain memories over time.
Plasticity, however, is just one half of the equation; the underlying genetics are critically important, and new techniques and technologies make this a particularly interesting time to address these questions. For instance, modern, high-throughput gene-profiling technologies allow researchers to figure out all of the underlying transcriptions in a neuron, and see how these are manifest in the body.
Understanding the interplay of biology and experience on learning and development will surely require understanding the biological processes that cause changes in individual neurons and synapses. But this is only part of the puzzle. We must also understand the control of learning processes at a system-wide level in the brain. How does the brain orchestrate the right set of neural synaptic updates based on training experiences we encounter over our lifetime? Given the tremendous number of synapses in the brain, it is unlikely that a purely bottom-up approach will suffice to answer this question.
A complementary approach to studying experience-based learning at a system level relies on machine learning algorithms that have been developed to allow robots to learn from experience, described Mitchell. One intriguing study has shown that temporal-difference learning algorithms, which enable robots successfully to learn control strategies such as how to fly helicopters autonomously, can be used to predict the neural activity of dopamine-based systems in the human brain that are involved in reward-based learning ( Schultz et al., 1997 ; Seymour et al., 2004 ; Doya, 2008 ). The integration of such system-level computational models alongside new research into synaptic plasticity offers an opportunity to examine the interplay of biology and experience on learning and development from multiple perspectives.
New tools will allow researchers to understand how variability between different genes and neurons and neuronal activity could influence behavior and capabilities across different people, the researchers said. Who we are is not only influenced by the yes/no expression of genes, but also the specific levels of expression among different genes, which in turn influences neuronal activity.
- Gene-Environment Interactions
Nature and nurture are not simply additive interactions that result in a particular behavior, but rather a complex interplay of many factors. Nature includes not only the usual factors—parents, homes, what people learn—but also many other factors that individuals are exposed to routinely in their daily environments. As Marder emphasized, we cannot simply assume that gene X produces behavior Y. Instead as Bialek described, there are often many additional factors that directly and indirectly interact with gene X and ultimately influence variants in behavior. These variants define individuality.
As previously described, it has been known for almost 50 years that experience from the outside environment shapes our brain. This comes initially from the original work of Nobel Laureates David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel who studied how information is sensed and processed in the part of the brain responsible for vision. As Greenberg commented, the field is now at a point where we could in the next 10 years attain a significant mechanistic understanding of how the environment impinges directly on our genes to give rise to a malleable organ that allows us to adapt and change.
- Huge Clinical Importance
Multiple participants at the workshop—including Nora Volkow, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse; Joseph Takahashi, investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Northwestern University; Lichtman; and Coyle—highlighted the role of genetics in shaping the brain as one of the fundamental challenges for neuroscience, both for its basic scientific interest and for its practical applications: Understanding how genes and experience come together to impact the brain could significantly alter how we think about treating neurological disease. Many of the most common neurological and mental health disorders—schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease—are complex genetic disorders that are influenced by environmental factors.
Alcino Silva, professor in the Departments of Neurobiology, Psychiatry and Psychology at the University of California, Los Angeles, showcased research from his lab showing he could treat and reverse developmental disorders in adult mice. This finding is worth repeating because it is so contrary to our general thinking on developmental disorders: Scientists working out of Silva’s lab have been able to reverse the impacts of the developmental disorder NF-1 (Neurofibromatosis type 1), which is caused by genetic malfunction, by treating the pathology of the disease in adult mice. These mice, which have obvious cognitive deficits, regain mental function when treated; Silva has advanced the study into human clinical trials.
The applications of this vein of study extend beyond developmental disorders. A growing body of evidence is revealing a massive feedback loop among genetics, neurological structure, experience, and disease. You are three times more likely to die from a heart attack if you are depressed than if you are not, for instance, and depression has a huge impact on diabetes as well, stated Coyle.
Taking a step backward, clinical data also show that people who experience multiple stressful episodes in their lives tend to suffer from clinical depression. But there is tremendous variation: Some people are resistant to stress and others are not.
“It turns out that the pattern is correlated with a polymorphic variation in one particular gene, the gene for the transporter for serotonin, a transmitter which is known to be involved in regulating mood,” explained Blakemore.
How do genes work in the brain to determine our resilience to stress, and how can those capabilities be monitored and modulated for better health?
- The Way Forward
Asking these kinds of questions was not realistic 10 or even 5 years ago. The advent of high-throughput gene profiling and the growing sophistication of our ability to manipulate genes in animal models lets us, for the first time, explore the role that genes play in both creating and modulating our neural structures. At the same time, new imaging techniques and technologies like channel rhodopsin “light switches” let us better characterize neural systems and their response to the world around us, and to begin to plumb the tremendous feedback loop among genes, experience, and the physical activity in the brain.
Until quite recently, these have remained philosophical questions, commented Marder. However, the field of neuroscience is now in a position—through all the molecular, connectomics, and technological advances—to put these questions on firm mechanistic, biological bases, and to attack them scientifically.
- Cite this Page Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Neuroscience and Nervous System Disorders. From Molecules to Minds: Challenges for the 21st Century: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2008. Grand Challenge: Nature Versus Nurture: How Does the Interplay of Biology and Experience Shape Our Brains and Make Us Who We Are?
- PDF version of this title (527K)
In this Page
Other titles in this collection.
- The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health
Recent Activity
- Grand Challenge: Nature Versus Nurture: How Does the Interplay of Biology and Ex... Grand Challenge: Nature Versus Nurture: How Does the Interplay of Biology and Experience Shape Our Brains and Make Us Who We Are? - From Molecules to Minds
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Nature vs. Nurture Debate In Psychology
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
The nature vs. nurture debate in psychology concerns the relative importance of an individual’s innate qualities (nature) versus personal experiences (nurture) in determining or causing individual differences in physical and behavioral traits. While early theories favored one factor over the other, contemporary views recognize a complex interplay between genes and environment in shaping behavior and development.
Key Takeaways
- Nature is what we think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors.
- Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception, e.g., the product of exposure, life experiences, and learning on an individual.
- Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture concerning specific psychological traits.
- Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact in a host of qualitatively different ways.
- For example, epigenetics is an emerging area of research that shows how environmental influences affect the expression of genes.
The nature-nurture debate is concerned with the relative contribution that both influences make to human behavior, such as personality, cognitive traits, temperament and psychopathology.
Examples of Nature vs. Nurture
Nature vs. nurture in child development.
In child development, the nature vs. nurture debate is evident in the study of language acquisition . Researchers like Chomsky (1957) argue that humans are born with an innate capacity for language (nature), known as universal grammar, suggesting that genetics play a significant role in language development.
Conversely, the behaviorist perspective, exemplified by Skinner (1957), emphasizes the role of environmental reinforcement and learning (nurture) in language acquisition.
Twin studies have provided valuable insights into this debate, demonstrating that identical twins raised apart may share linguistic similarities despite different environments, suggesting a strong genetic influence (Bouchard, 1979).
However, environmental factors, such as exposure to language-rich environments, also play a crucial role in language development, highlighting the intricate interplay between nature and nurture in child development.
Nature vs. Nurture in Personality Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in personality psychology centers on the origins of personality traits. Twin studies have shown that identical twins reared apart tend to have more similar personalities than fraternal twins, indicating a genetic component to personality (Bouchard, 1994).
However, environmental factors, such as parenting styles, cultural influences, and life experiences, also shape personality.
For example, research by Caspi et al. (2003) demonstrated that a particular gene (MAOA) can interact with childhood maltreatment to increase the risk of aggressive behavior in adulthood.
This highlights that genetic predispositions and environmental factors contribute to personality development, and their interaction is complex and multifaceted.
Nature vs. Nurture in Mental Illness Development
The nature vs. nurture debate in mental health explores the etiology of depression. Genetic studies have identified specific genes associated with an increased vulnerability to depression, indicating a genetic component (Sullivan et al., 2000).
However, environmental factors, such as adverse life events and chronic stress during childhood, also play a significant role in the development of depressive disorders (Dube et al.., 2002; Keller et al., 2007)
The diathesis-stress model posits that individuals inherit a genetic predisposition (diathesis) to a disorder, which is then activated or exacerbated by environmental stressors (Monroe & Simons, 1991).
This model illustrates how nature and nurture interact to influence mental health outcomes.
Nature vs. Nurture of Intelligence
The nature vs. nurture debate in intelligence examines the relative contributions of genetic and environmental factors to cognitive abilities.
Intelligence is highly heritable, with about 50% of the variance in IQ attributed to genetic factors, based on studies of twins, adoptees, and families (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Heritability of intelligence increases with age, from about 20% in infancy to as high as 80% in adulthood, suggesting amplifying effects of genes over time.
However, environmental influences, such as access to quality education and stimulating environments, also significantly impact intelligence.
Shared environmental influences like family background are more influential in childhood, whereas non-shared experiences are more important later in life.
Research by Flynn (1987) showed that average IQ scores have increased over generations, suggesting that environmental improvements, known as the Flynn effect , can lead to substantial gains in cognitive abilities.
Molecular genetics provides tools to identify specific genes and understand their pathways and interactions. However, progress has been slow for complex traits like intelligence. Identified genes have small effect sizes (Plomin & Spinath, 2004).
Overall, intelligence results from a complex interplay between genes and environment over development. Molecular genetics offers promise to clarify these mechanisms. The nature vs nurture debate is outdated – both play key roles.
Nativism (Extreme Nature Position)
It has long been known that certain physical characteristics are biologically determined by genetic inheritance.
Color of eyes, straight or curly hair, pigmentation of the skin, and certain diseases (such as Huntingdon’s chorea) are all a function of the genes we inherit.
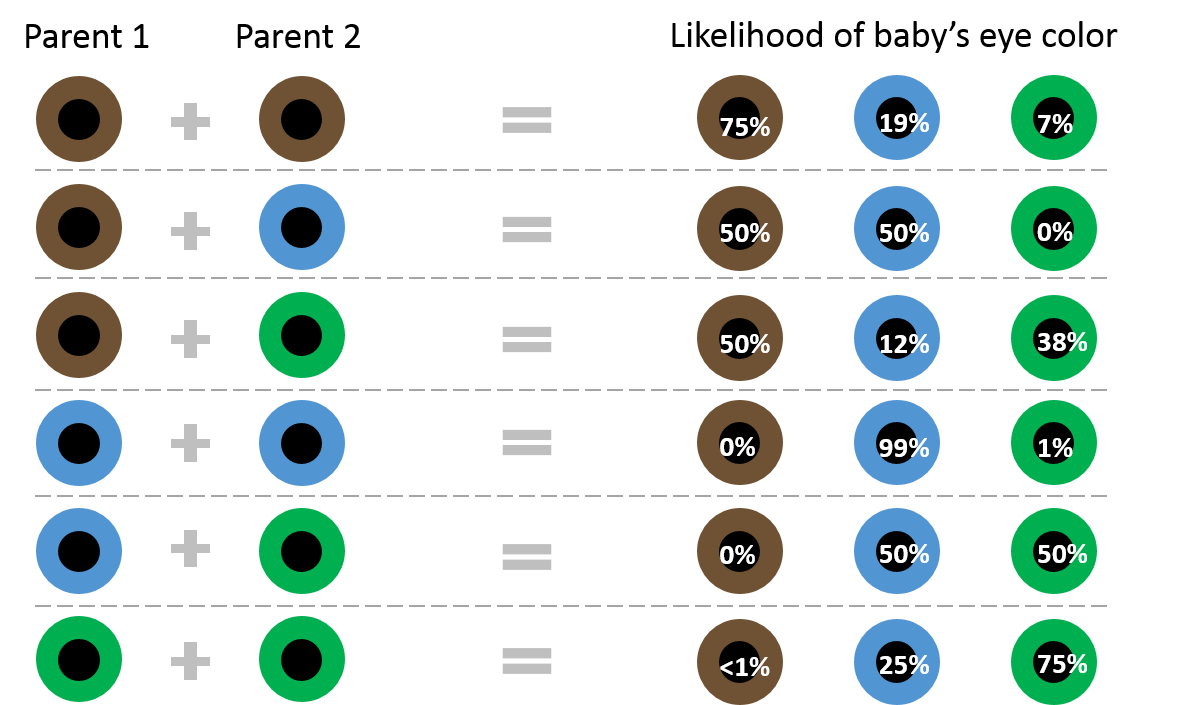
These facts have led many to speculate as to whether psychological characteristics such as behavioral tendencies, personality attributes, and mental abilities are also “wired in” before we are even born.
Those who adopt an extreme hereditary position are known as nativists. Their basic assumption is that the characteristics of the human species as a whole are a product of evolution and that individual differences are due to each person’s unique genetic code.
In general, the earlier a particular ability appears, the more likely it is to be under the influence of genetic factors. Estimates of genetic influence are called heritability.
Examples of extreme nature positions in psychology include Chomsky (1965), who proposed language is gained through the use of an innate language acquisition device. Another example of nature is Freud’s theory of aggression as being an innate drive (called Thanatos).
Characteristics and differences that are not observable at birth, but which emerge later in life, are regarded as the product of maturation. That is to say, we all have an inner “biological clock” which switches on (or off) types of behavior in a pre-programmed way.
The classic example of the way this affects our physical development is the bodily changes that occur in early adolescence at puberty.
However, nativists also argue that maturation governs the emergence of attachment in infancy , language acquisition , and even cognitive development .

Empiricism (Extreme Nurture Position)
At the other end of the spectrum are the environmentalists – also known as empiricists (not to be confused with the other empirical/scientific approach ).
Their basic assumption is that at birth, the human mind is a tabula rasa (a blank slate) and that this is gradually “filled” as a result of experience (e.g., behaviorism ).
From this point of view, psychological characteristics and behavioral differences that emerge through infancy and childhood are the results of learning. It is how you are brought up (nurture) that governs the psychologically significant aspects of child development and the concept of maturation applies only to the biological.
For example, Bandura’s (1977) social learning theory states that aggression is learned from the environment through observation and imitation. This is seen in his famous Bobo doll experiment (Bandura, 1961).

Also, Skinner (1957) believed that language is learned from other people via behavior-shaping techniques.
Evidence for Nature
- Biological Approach
- Biology of Gender
- Medical Model
Freud (1905) stated that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality.
He thought that parenting is of primary importance to a child’s development , and the family as the most important feature of nurture was a common theme throughout twentieth-century psychology (which was dominated by environmentalists’ theories).
Behavioral Genetics
Researchers in the field of behavioral genetics study variation in behavior as it is affected by genes, which are the units of heredity passed down from parents to offspring.
“We now know that DNA differences are the major systematic source of psychological differences between us. Environmental effects are important but what we have learned in recent years is that they are mostly random – unsystematic and unstable – which means that we cannot do much about them.” Plomin (2018, xii)
Behavioral genetics has enabled psychology to quantify the relative contribution of nature and nurture with regard to specific psychological traits. One way to do this is to study relatives who share the same genes (nature) but a different environment (nurture). Adoption acts as a natural experiment which allows researchers to do this.
Empirical studies have consistently shown that adoptive children show greater resemblance to their biological parents, rather than their adoptive, or environmental parents (Plomin & DeFries, 1983; 1985).
Another way of studying heredity is by comparing the behavior of twins, who can either be identical (sharing the same genes) or non-identical (sharing 50% of genes). Like adoption studies, twin studies support the first rule of behavior genetics; that psychological traits are extremely heritable, about 50% on average.
The Twins in Early Development Study (TEDS) revealed correlations between twins on a range of behavioral traits, such as personality (empathy and hyperactivity), and components of reading such as phonetics (Haworth, Davis, Plomin, 2013; Oliver & Plomin, 2007; Trouton, Spinath, & Plomin, 2002).
Implications
Jenson (1969) found that the average I.Q. scores of black Americans were significantly lower than whites he went on to argue that genetic factors were mainly responsible – even going so far as to suggest that intelligence is 80% inherited.
The storm of controversy that developed around Jenson’s claims was not mainly due to logical and empirical weaknesses in his argument. It had more to do with the social and political implications that are often drawn from research that claims to demonstrate natural inequalities between social groups.
For many environmentalists, there is a barely disguised right-wing agenda behind the work of behavioral geneticists. In their view, part of the difference in the I.Q. scores of different ethnic groups is due to inbuilt biases in the methods of testing.
More fundamentally, they believe that differences in intellectual ability are a product of social inequalities in access to material resources and opportunities. To put it simply children brought up in the ghetto tend to score lower on tests because they are denied the same life chances as more privileged members of society.
Now we can see why the nature-nurture debate has become such a hotly contested issue. What begins as an attempt to understand the causes of behavioral differences often develops into a politically motivated dispute about distributive justice and power in society.
What’s more, this doesn’t only apply to the debate over I.Q. It is equally relevant to the psychology of sex and gender , where the question of how much of the (alleged) differences in male and female behavior are due to biology and how much to culture is just as controversial.
Polygenic Inheritance
Rather than the presence or absence of single genes being the determining factor that accounts for psychological traits, behavioral genetics has demonstrated that multiple genes – often thousands, collectively contribute to specific behaviors.
Thus, psychological traits follow a polygenic mode of inheritance (as opposed to being determined by a single gene). Depression is a good example of a polygenic trait, which is thought to be influenced by around 1000 genes (Plomin, 2018).
This means a person with a lower number of these genes (under 500) would have a lower risk of experiencing depression than someone with a higher number.
While still limited in predictive power, polygenic risk scores provide a way to quantify innate genetic risk, allowing researchers to study how this interacts with environmental factors to influence outcomes.
The high polygenicity of psychiatric disorders (many genes each contributing small effects) revealed by genetic architecture studies shows that there isn’t a simple genetic determinism for most psychiatric conditions.
This complexity is further increased when you consider how these genes might interact with each other (epistasis) and with environmental factors. The same genetic profile might lead to different outcomes in different environments.
The Nature of Nurture
Nurture assumes that correlations between environmental factors and psychological outcomes are caused environmentally. For example, how much parents read with their children and how well children learn to read appear to be related. Other examples include environmental stress and its effect on depression.
However, behavioral genetics argues that what looks like environmental effects are to a large extent a reflection of genetic differences (Plomin & Bergeman, 1991).
People select, modify, and create environments correlated with their genetic disposition. This means that what sometimes appears to be an environmental influence (nurture) is a genetic influence (nature).
So, children genetically predisposed to be competent readers will be happy to listen to their parents read them stories, and be more likely to encourage this interaction.
Interaction Effects
However, in recent years there has been a growing realization that the question of “how much” behavior is due to heredity and “how much” to the environment may itself be the wrong question.
Take intelligence as an example. Like almost all types of human behavior, it is a complex, many-sided phenomenon that reveals itself (or not!) in a great variety of ways.
The “how much” question assumes that psychological traits can all be expressed numerically and that the issue can be resolved in a quantitative manner.
Heritability statistics revealed by behavioral genetic studies have been criticized as meaningless, mainly because biologists have established that genes cannot influence development independently of environmental factors; genetic and nongenetic factors always cooperate to build traits.
The reality is that nature and culture interact in a myriad of qualitatively different ways (Gottlieb, 2007; Johnston & Edwards, 2002).
Instead of defending extreme nativist or nurturist views, most psychological researchers are now interested in investigating how nature and nurture interact.
For example, in psychopathology , this means that both a genetic predisposition and an appropriate environmental trigger are required for a mental disorder to develop.
This concept, known as the diathesis-stress model, suggests that individuals may inherit a vulnerability to certain mental health conditions, but the actual manifestation of these disorders frequently depends on exposure to specific environmental stressors.
- Diathesis : Some individuals have a genetic vulnerability (predisposition) to certain mental disorders.
- Stress : Environmental factors or life events act as triggers.
- Interaction : The combination of genetic vulnerability and environmental stress leads to the manifestation of a disorder.
For instance, a person might carry genes associated with depression, but may not develop the disorder unless exposed to significant life stressors, trauma, or adverse experiences.
Furthermore, the emerging field of epigenetics provides additional insight into this complex relationship.
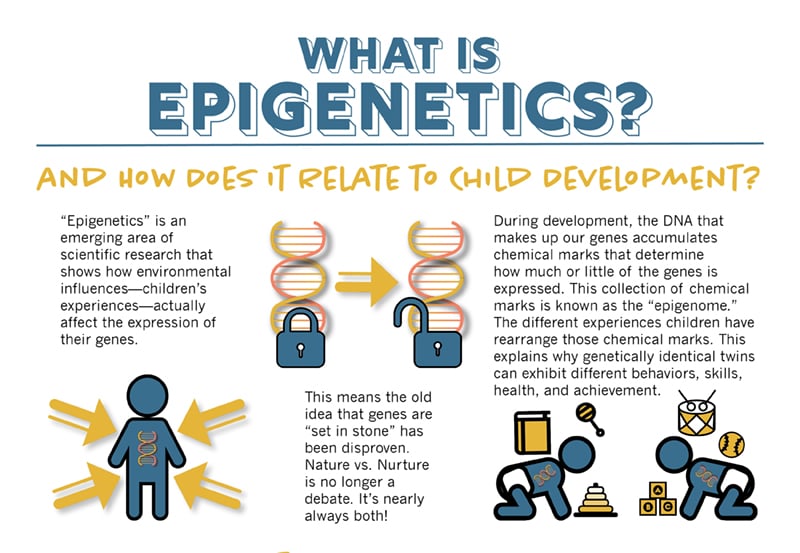
What is Epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the term used to describe inheritance by mechanisms other than through the DNA sequence of genes. For example, features of a person’s physical and social environment can effect which genes are switched-on, or “expressed”, rather than the DNA sequence of the genes themselves.
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that don’t involve alterations to the DNA sequence itself. Instead, these changes affect how genes are read and translated into proteins.
Basic Explanation
Imagine your DNA as a huge instruction manual for your body. Epigenetics is like highlighters and sticky notes added to this manual.
These markers don’t change the actual text (your DNA), but they can make certain instructions easier or harder to read. Things in your environment, like what you eat, how stressed you are, or even your experiences, can add or remove these markers.
This process can turn genes “on” or “off,” affecting how your body works. Sometimes, these changes can even be passed down to your kids, kind of like inherited highlighter marks in the manual.
Mechanisms of Epigenetic Modification
Epigenetic modifications provide a direct biological mechanism by which environmental experiences (nurture) can alter how our genes (nature) function. This challenges the idea of genes as a fixed, unchangeable blueprint.
Epigenetic changes can occur throughout life, but certain periods (like early development or adolescence) may be particularly sensitive to these modifications.
There are several ways epigenetic changes can occur:
- DNA methylation : Adding methyl groups to DNA, typically suppressing gene expression.
- Histone modification : Changes to the proteins that DNA wraps around, affecting how tightly or loosely genes are packaged.
- Non-coding RNA : RNA molecules that can regulate gene expression.
These epigenetic changes can be temporary or long-lasting, and in some cases, may even be heritable.
Example : Early life stress has been shown to cause epigenetic changes in genes related to stress response, potentially increasing vulnerability to stress-related disorders later in life.
Environmental Stressors
Environmental stressors have been shown to induce epigenetic changes, with substantial evidence from both animal and human studies (Klengel et al., 2016).
These stressors can include malnutrition, exposure to toxins, extreme stress, or trauma, leading to alterations in DNA methylation patterns, histone modifications, and changes in non-coding RNA expression (Bale, 2015).
For instance, research has demonstrated that early life stress can result in long-lasting epigenetic modifications of genes involved in stress response pathways, potentially increasing vulnerability to stress-related disorders later in life (McGowan et al., 2009).
Maternal care in rats has been linked to epigenetic changes in offspring, affecting their stress reactivity (Weaver et al., 2004).
In humans, studies of Holocaust survivors and their descendants have revealed epigenetic alterations associated with trauma exposure, suggesting potential transgenerational effects (Yehuda et al., 2016).
These findings underscore the profound impact of environmental factors on gene expression and highlight the plasticity of our epigenome in response to external influences (Szyf, 2011).
Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance
Some epigenetic modifications may be passed down to future generations, suggesting that environmental influences on one generation could affect the genetic expression of subsequent generations.
One such example is what is known as the Dutch Hunger Winter, during last year of the Second World War. What they found was that children who were in the womb during the famine experienced a life-long increase in their chances of developing various health problems compared to children conceived after the famine.
Epigenetic effects can sometimes be passed from one generation to the next, although the effects only seem to last for a few generations. There is some evidence that the effects of the Dutch Hunger Winter affected grandchildren of women who were pregnant during the famine.
Therefore, it makes more sense to say that the difference between two people’s behavior is mostly due to hereditary factors or mostly due to environmental factors.
This realization is especially important given the recent advances in genetics, such as polygenic testing. The Human Genome Project, for example, has stimulated enormous interest in tracing types of behavior to particular strands of DNA located on specific chromosomes.
If these advances are not to be abused, then there will need to be a more general understanding of the fact that biology interacts with both the cultural context and the personal choices that people make about how they want to live their lives.
There is no neat and simple way of unraveling these qualitatively different and reciprocal influences on human behavior.
The Concept of “Memories” Being Passed Down
While there’s evidence that environmental stressors can induce epigenetic changes that might affect future generations, the concept of specific “memories” being passed down is not supported by current scientific evidence.
This concept often stems from misinterpretation of studies showing behavioral or physiological changes in offspring related to parental experiences.
Some animal studies have demonstrated that offspring of stressed parents exhibit altered stress responses or behavioral changes.
For example, Dias and Ressler (2014) showed in mice that fear responses to specific odors can be passed down to subsequent generations. However, these are not “memories” in the conventional sense, but rather alterations in stress response systems or sensory sensitivities.
Human studies in this area are much more complex and limited. Research has examined children of trauma survivors (e.g., Holocaust survivors, 9/11 survivors) and found differences in stress hormone levels or risk for PTSD (Yehuda et al., 2016).
However, these studies face significant challenges in separating genetic, epigenetic, and social/cultural factors.
The challenges in interpreting human studies are substantial. Humans have complex social structures and cultural transmission of information, making it often impossible to separate the effects of biological inheritance from social learning and shared environments (Heard & Martienssen, 2014).
The longer lifespan and generation time in humans also make it challenging to study transgenerational effects. What’s often observed is not the transmission of specific memories, but rather altered predispositions or sensitivities.
For example, children of trauma survivors might have an altered stress response system, making them more sensitive to stress, but they don’t inherit specific memories of the trauma (Bowers & Yehuda, 2016).
While specific memories aren’t passed down, changes in gene expression related to stress response systems could potentially be inherited. These could affect how future generations respond to stress or process sensory information (Zannas et al., 2015).
Epigenetics: Licking Rat Pups
Michael Meaney and his colleagues at McGill University in Montreal, Canada conducted the landmark epigenetic study on mother rats licking and grooming their pups.
This research found that the amount of licking and grooming received by rat pups during their early life could alter their epigenetic marks and influence their stress responses in adulthood.
Pups that received high levels of maternal care (i.e., more licking and grooming) had a reduced stress response compared to those that received low levels of maternal care.
Meaney’s work with rat maternal behavior and its epigenetic effects has provided significant insights into the understanding of early-life experiences, gene expression, and adult behavior.
It underscores the importance of the early-life environment and its long-term impacts on an individual’s mental health and stress resilience.
Epigenetics: The Agouti Mouse Study
Waterland and Jirtle’s 2003 study on the Agouti mouse is another foundational work in the field of epigenetics that demonstrated how nutritional factors during early development can result in epigenetic changes that have long-lasting effects on phenotype.
In this study, they focused on a specific gene in mice called the Agouti viable yellow (A^vy) gene. Mice with this gene can express a range of coat colors, from yellow to mottled to brown.
This variation in coat color is related to the methylation status of the A^vy gene: higher methylation is associated with the brown coat, and lower methylation with the yellow coat.
Importantly, the coat color is also associated with health outcomes, with yellow mice being more prone to obesity, diabetes, and tumorigenesis compared to brown mice.
Waterland and Jirtle set out to investigate whether maternal diet, specifically supplementation with methyl donors like folic acid, choline, betaine, and vitamin B12, during pregnancy could influence the methylation status of the A^vy gene in offspring.
Key findings from the study include:
Dietary Influence : When pregnant mice were fed a diet supplemented with methyl donors, their offspring had an increased likelihood of having the brown coat color. This indicated that the supplemented diet led to an increased methylation of the A^vy gene.
Health Outcomes : Along with the coat color change, these mice also had reduced risks of obesity and other health issues associated with the yellow phenotype.
Transgenerational Effects : The study showed that nutritional interventions could have effects that extend beyond the individual, affecting the phenotype of the offspring.
The implications of this research are profound. It highlights how maternal nutrition during critical developmental periods can have lasting effects on offspring through epigenetic modifications, potentially affecting health outcomes much later in life.
The study also offers insights into how dietary and environmental factors might contribute to disease susceptibility in humans.
Challenges in Epigenetic Research:
- Epigenetic changes can be tissue-specific, making it challenging to study in the living human brain
- The causal direction (whether epigenetic changes cause disorders or result from them) is often unclear
- The complexity of interactions between multiple epigenetic mechanisms and genetic variants
Bale, T. L. (2015). Epigenetic and transgenerational reprogramming of brain development. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16 (6), 332-344.
Bandura, A. Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through the imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 63, 575-582
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bouchard, T. J. (1994). Genes, Environment, and Personality. Science, 264 (5166), 1700-1701.
Bowers, M. E., & Yehuda, R. (2016). Intergenerational transmission of stress in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41 (1), 232-244.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment. Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Loss . New York: Basic Books.
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., … & Poulton, R. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science , 301 (5631), 386-389.
Chomsky, N. (1957). Syntactic structures. Mouton de Gruyter.
Chomsky, N. (1965). Aspects of the theory of syntax . MIT Press.
Dias, B. G., & Ressler, K. J. (2014). Parental olfactory experience influences behavior and neural structure in subsequent generations. Nature neuroscience, 17( 1), 89-96.
Dube, S. R., Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Edwards, V. J., & Croft, J. B. (2002). Adverse childhood experiences and personal alcohol abuse as an adult. Addictive Behaviors , 27 (5), 713-725.
Flynn, J. R. (1987). Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: What IQ tests really measure. Psychological Bulletin , 101 (2), 171.
Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality . Se, 7.
Galton, F. (1883). Inquiries into human faculty and its development . London: J.M. Dent & Co.
Gottlieb, G. (2007). Probabilistic epigenesis. Developmental Science, 10 , 1–11.
Haworth, C. M., Davis, O. S., & Plomin, R. (2013). Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): a genetically sensitive investigation of cognitive and behavioral development from childhood to young adulthood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 16(1) , 117-125.
Heard, E., & Martienssen, R. A. (2014). Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: myths and mechanisms. Cell, 157 (1), 95-109.
Horsthemke, B. (2018). A critical view on transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in humans. Nature communications, 9 (1), 1-4.
Jensen, A. R. (1969). How much can we boost I.Q. and scholastic achievement? Harvard Educational Review, 33 , 1-123.
Johnston, T. D., & Edwards, L. (2002). Genes, interactions, and the development of behavior . Psychological Review , 109, 26–34.
Keller, M. C., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2007). Association of different adverse life events with distinct patterns of depressive symptoms. American Journal of Psychiatry , 164 (10), 1521-1529.
Klengel, T., Dias, B. G., & Ressler, K. J. (2016). Models of intergenerational and transgenerational transmission of risk for psychopathology in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41 (1), 219-231.
McGowan, P. O., Sasaki, A., D’Alessio, A. C., Dymov, S., Labonté, B., Szyf, M., … & Meaney, M. J. (2009). Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nature Neuroscience, 12(3), 342-348.
Meaney, M. J. (2010). Epigenetics and the biological definition of gene× environment interactions. Child development, 81 (1), 41-79.
Monroe, S. M., & Simons, A. D. (1991). Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: implications for the depressive disorders. Psychological Bulletin , 110 (3), 406.
Oliver, B. R., & Plomin, R. (2007). Twins” Early Development Study (TEDS): A multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems from childhood through adolescence . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 10(1) , 96-105.
Petrill, S. A., Plomin, R., Berg, S., Johansson, B., Pedersen, N. L., Ahern, F., & McClearn, G. E. (1998). The genetic and environmental relationship between general and specific cognitive abilities in twins age 80 and older. Psychological Science , 9 (3), 183-189.
Plomin, R., & Petrill, S. A. (1997). Genetics and intelligence: What’s new?. Intelligence , 24 (1), 53-77.
Plomin, R. (2018). Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . MIT Press.
Plomin, R., & Bergeman, C. S. (1991). The nature of nurture: Genetic influence on “environmental” measures. behavioral and Brain Sciences, 14(3) , 373-386.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1983). The Colorado adoption project. Child Development , 276-289.
Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1985). The origins of individual differences in infancy; the Colorado adoption project. Science, 230 , 1369-1371.
Plomin, R., & Spinath, F. M. (2004). Intelligence: genetics, genes, and genomics. Journal of personality and social psychology , 86 (1), 112.
Plomin, R., & Von Stumm, S. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence. Nature Reviews Genetics , 19 (3), 148-159.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal behavior . Acton, MA: Copley Publishing Group.
Sullivan, P. F., Neale, M. C., & Kendler, K. S. (2000). Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry , 157 (10), 1552-1562.
Szyf, M., Weaver, I. C., Champagne, F. A., Diorio, J., & Meaney, M. J. (2005). Maternal programming of steroid receptor expression and phenotype through DNA methylation in the rat . Frontiers in neuroendocrinology , 26 (3-4), 139-162.
Trouton, A., Spinath, F. M., & Plomin, R. (2002). Twins early development study (TEDS): a multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems in childhood . Twin Research and Human Genetics, 5(5) , 444-448.
Waterland, R. A., & Jirtle, R. L. (2003). Transposable elements: targets for early nutritional effects on epigenetic gene regulation . Molecular and cellular biology, 23 (15), 5293-5300.
Weaver, I. C., Cervoni, N., Champagne, F. A., D’Alessio, A. C., Sharma, S., Seckl, J. R., … & Meaney, M. J. (2004). Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nature Neuroscience, 7(8), 847-854.
Yehuda, R., Daskalakis, N. P., Bierer, L. M., Bader, H. N., Klengel, T., Holsboer, F., & Binder, E. B. (2016). Holocaust exposure induced intergenerational effects on FKBP5 methylation. Biological psychiatry, 80(5), 372-380.
Zannas, A. S., Wiechmann, T., Gassen, N. C., & Binder, E. B. (2016). Gene–stress–epigenetic regulation of FKBP5: clinical and translational implications. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41 (1), 261-274.
Further Information
- Genetic & Environmental Influences on Human Psychological Differences
Evidence for Nurture
- Classical Conditioning
- Little Albert Experiment
- Operant Conditioning
- Behaviorism
- Social Learning Theory
- Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
- Social Roles
- Attachment Styles
- The Hidden Links Between Mental Disorders
- Visual Cliff Experiment
- Behavioral Genetics, Genetics, and Epigenetics
- Epigenetics
- Is Epigenetics Inherited?
- Physiological Psychology
- Bowlby’s Maternal Deprivation Hypothesis
- So is it nature not nurture after all?
Evidence for an Interaction
- Genes, Interactions, and the Development of Behavior
- Agouti Mouse Study
- Biological Psychology
What does nature refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nature” refers to the influence of genetics, innate qualities, and biological factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of hereditary factors in shaping who we are.
What does nurture refer to in the nature vs. nurture debate?
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nurture” refers to the influence of the environment, upbringing, experiences, and social factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of external factors in shaping who we are.
Why is it important to determine the contribution of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture) in human development?
Determining the contribution of heredity and environment in human development is crucial for understanding the complex interplay between genetic factors and environmental influences. It helps identify the relative significance of each factor, informing interventions, policies, and strategies to optimize human potential and address developmental challenges.
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
Introduction, general overviews.
- Conceptual Problems
- Biological Constraints, Predispositions, and Preparedness in Learning
- Critical Periods
- Innate Knowledge
- Heritability
- Behavioral Epigenetics
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Life-Span Development
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Executive Functions in Childhood
- Remote Work
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology by Hunter Honeycutt LAST REVIEWED: 12 January 2023 LAST MODIFIED: 12 January 2023 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0305
The nature-nurture dichotomy is a long-standing and pervasive framework for thinking about the causal influences believed to be operating during individual development. In this dichotomy, nature refers to factors (e.g., genes, genetic programs, and/or biological blueprints) or forces (e.g., heredity and/or maturation) inherent to the individual that predetermine the development of form and function. Nurture generally refers to all the remaining, typically “external,” causal factors (e.g., physical and social conditions) and processes (e.g., learning and experience) that influence development. The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture. It is commonly stated that psychologists have moved on from asking whether traits (or variation in traits) develop from nature or nurture, to recognize instead that both nature and nurture work together or “interact” to produce outcomes, although exactly how to view the interaction is a matter of much debate. While acknowledging the interaction of nature and nurture, one’s theoretical models and research focus might emphasize the prominence of one over the other. Thus, nativists focus more on the importance of innate factors or forces operating on development, whereas empiricists focus more on experiential or environmental factors. However, not everyone finds value in thinking about development in terms of nature and nurture. By the middle of the twentieth century, some psychologists, biologists, and philosophers began to view nature-nurture as a conceptually deficient and biologically implausible dichotomy that oversimplifies the dynamics of behavior and development. Such people espouse some variant of “developmental systems theory” and seek to eliminate or otherwise fuse the nature-nurture division.
The works in this section are mostly trade books that provide general introductions to the nature-nurture debate across a variety of topical areas in psychology, all of which would be suitable for use in classes with undergraduate students at all levels. Goldhaber 2012 contrasts four popular perspectives on the nature-nurture issue and would be a good place to start for anyone unfamiliar with the nature-nurture debate in psychology. Nativist perspectives are represented by Pinker 2002 , Plomin 2018 , and Vallortigara 2021 . An empiricist-leaning position on behavior development is put forth in Schneider 2012 . Developmental systems theory is promoted in Blumberg 2005 and Moore 2002 . Two edited books are included and both are better suited for advanced undergraduate- or graduate-level students. The first edited book, Coll, et al. 2013 , focuses on the nature-nurture issue across a range of topics and perspectives in psychology. The other, Mayes and Lewis 2012 , presents empiricist (or environmentalist) perspectives on child development.
Bateson, P. 2017. Behaviour, development and evolution . Cambridge, UK: OpenBook Publishers.
DOI: 10.11647/OBP.0097
Written by a distinguished ethologist who draws extensively from his work on animal behavior, this book argues that the nature-nurture division is neither valid nor helpful in capturing the complex system of factors that influence behavioral development. Topics include imprinting and attachment, parent-offspring relations, the influence of early-life experiences on later-life outcomes, problems with genetic determinism, and the role of behavior in evolutionary change.
Blumberg, M. S. 2005. Basic instinct: The genesis of novel behavior . New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press.
Consistent with developmental systems theory, Blumberg presents an overview of the conceptual and empirical limitations of nativism in explanations of behavioral and neural development in animals and cognitive development in humans.
Coll, C. G., E. L. Bearer, and R. M. Lerner, eds. 2013. Nature-nurture: The complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences on human behavior and development . New York: Psychology Press.
The contents of this edited volume are almost entirely original works with commentary that span multiple disciplines (psychology, biology, economics, philosophy) and multiple perspectives (behavioral genetics and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue.
Goldhaber, D. 2012. The nature-nurture debates: Bridging the gap . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
DOI: 10.1017/CBO9781139022583
Goldhaber reviews four major perspectives (behavior genetics, environmentalism, evolutionary psychology, and developmental systems theory) on the nature-nurture issue. He argues we should reject reductionist views based on either genetic determinism or environmental determinism in favor of more holistic, interactionist approaches.
Mayes, L. C., and M. Lewis, eds. 2012. The Cambridge handbook of environment in human development . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
This handbook explores a wide variety of ways in which the environment influences child development. Chapters cover conceptual frameworks and methodological issues in thinking about and studying environmental influences as well reviewing ways in which environmental contexts and systems influence specific aspects of child development.
Moore, D. S. 2002. The dependent gene: The fallacy of nature vs. nurture . New York: Henry Holt.
This book provides an introduction to the developmental systems theory take on the nature-nurture issue particularly as it relates to genetic determinism, heritability and heredity.
Pinker, S. 2002. The blank slate: The modern denial of human nature . New York: Viking.
In this best-selling book, Pinker draws on evidence from behavioral genetics, evolutionary psychology, and cognitive psychology to argue for a nativist position concerning human nature.
Plomin, R. 2018. Blueprint: How DNA makes us who we are . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Plomin reviews traditional and more modern evidence from behavioral genetics to argue that genes are the primary factor in bringing about psychological differences between people. Moreover, he argues that many “environmental” factors operating on development are themselves strongly influenced by genetic differences.
Schneider, S. M. 2012. The science of consequences: How they affect genes, change the brain, and impact our world . Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
Schneider presents a view grounded in behavior analysis to argue for the critical role that the consequences of genetic activity, neural activity, and behavioral activity play in individual development. While emphasizing environmental (or experiential) factors influencing development, this book also highlights the systemic and interactive nature of developmental systems across multiple levels of analysis.
Vallortigara, G. 2021. Born knowing: Imprinting and the origins of knowledge . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
DOI: 10.7551/mitpress/14091.001.0001
Drawing upon research in comparative cognition and comparative neuroscience, much of it his own, Vallortigara argues that animals, including humans, enter the world with a set of unlearned, innate or instinctive behaviors and neural circuits that bias or predispose subsequent learning and development.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Action Research
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Effect Size
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- Heuristics and Biases
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Item Response Theory
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Mediation Analysis
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Meta-Analysis
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Older Workers
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Path Models
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Person-Centered and Experiential Psychotherapies: From Car...
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Protocol Analysis
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Situational Strength
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|91.193.111.216]
- 91.193.111.216
Nature Versus Nurture
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2021
- pp 5347–5349
- Cite this reference work entry

- Piper Harris 3 , 4 &
- Rebeca Mireles-Rios 3
127 Accesses
1 Citations
Behavioral genetics ; Biology versus environment ; Maturation versus enculturation
Nature versus nurture is the debate regarding the influence of genetics/biology and environment on human development and behavioral characteristics.
Introduction
Are humans inherently good or bad and intelligent or unintelligent? Are humans born with certain traits, characteristics, and knowledge, or are these developed through experiences? These questions are at the center of the nature versus nurture debate, stemming back as far as 400 B.C.E. Nature versus nurture is the dispute regarding the contributions of biological and environmental factors on human development. Nature encompasses genetic, biological, and hereditary factors that are innately present in humans, whereas nurture refers to those external, environmental factors that influence human development after conception, including childhood experiences and social relationships. Francis Galton, who coined the phrase nature ...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Galton, F. (1874). English men of science: Their nature and nurture . London: Macmillan.
Google Scholar
Gordon, I., & Slater, A. (1998). Nativism and empiricism: The history of two ideas. In A. M. Slater (Ed.), Perceptual development: Visual, auditory and speech perception in infancy (pp. 73–103). East Sussex, UK: Psychology Press.
Lock, M., & Palsson, G. (2016). Can science resolve the 199 nature/nurture debate? Malden, MA: Polity Press.
Pun, A., Birch, S. A., & Baron, A. S. (2016). Infants use relative numerical group size to infer social dominance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 201514879. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1514879113 .
Sheridan, M. A., Fox, N. A., Zeanah, C. H., McLaughlin, K. A., & Nelson, C. A. (2012). Variation in neural development as a result of exposure to institutionalization early in childhood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 109 (32), 12927–12932. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200041109 .
Article Google Scholar
Spelke, E. S. (1998). Nativism, empiricism, and the origins of knowledge. Infant Behavior and Development, 21 (2), 181–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0163-6383(98)90002-9 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA
Piper Harris & Rebeca Mireles-Rios
University of California – Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Piper Harris
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rebeca Mireles-Rios .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Oakland University, Rochester, MI, USA
Todd K Shackelford
Viviana A Weekes-Shackelford
Section Editor information
Penn State Worthington Scranton, Scranton, USA
Douglas Sellers
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Harris, P., Mireles-Rios, R. (2021). Nature Versus Nurture. In: Shackelford, T.K., Weekes-Shackelford, V.A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Psychological Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19650-3_1301
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19650-3_1301
Published : 22 April 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-19649-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-19650-3
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

COMMENTS
Looking for nurture vs nature topics to write about? Our list is for you! Check some 80 nature vs nurture essay examples find original ideas for your paper.
In The Nature-Nurture Debates, Goldhaber reviews the four major perspectives on the issue – behavior genetics, environment, evolutionary psychology, and developmental systems theory – and ...
The Origins of Nature Versus Nurture. For much of recorded history, the distinction between nature and nurture was a temporal divide between what a person is innately endowed with at birth, prior to experience (nature), and what happens thereafter (nurture).
The discovery of neurogenesis and an improved understanding of neuroplasticity—the ability of the brain to shape, form, eliminate, and strengthen new connections throughout life—has completely recast the question of nature versus nurture. “Neurons can change their connectivity,” explained Blakemore.
Though we recognize the highly varied content of research in basic and applied domains, we focus this article on the central issue of nature and nurture causation of sex differences and similarities in traits, abilities, behavioral tendencies, and attitudes and beliefs.
In the nature vs. nurture debate, “nature” refers to the influence of genetics, innate qualities, and biological factors on human development, behavior, and traits. It emphasizes the role of hereditary factors in shaping who we are.
The nature versus nurture debate represents one of the oldest issues in the research of human behavior dealing with the question whether inherited traits or life experiences (e.g., upbringing) play a greater role in shaping, for example, our personality.
Given that genes are often taken to represent “nature,” it is especially important to understand the way genes interact with “nurture”—the surrounding environment or cultural context—to make advances in research on human psychology.
The nature versus nurture debate in psychology deals with disagreements about the extent to which the development of traits in humans and animals reflects the relative influence of nature and nurture.
Nature encompasses genetic, biological, and hereditary factors that are innately present in humans, whereas nurture refers to those external, environmental factors that influence human development after conception, including childhood experiences and social relationships.