
- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.

Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
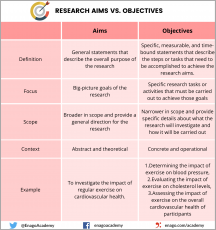
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
No internet connection.
All search filters on the page have been cleared., your search has been saved..
- Sign in to my profile My Profile
Writing Effective Research Aims and Objectives
- By: Margaret-Anne Houston , Marissa McDonagh Edited by: Margaret-Anne Houston
- Product: Sage Research Methods: Business
- Publisher: SAGE Publications Ltd
- Publication year: 2023
- Online pub date: March 21, 2023
- Discipline: Business and Management
- Methods: Research questions , Writing research , Research design
- DOI: https:// doi. org/10.4135/9781529668216
- Keywords: fuel poverty , social media Show all Show less
- Academic Level: Advanced Undergraduate Online ISBN: 9781529668216 More information Less information
The writing of effective research aims and objectives can cause confusion and concern to new and experienced researchers and learners. This step in your research journey is usually the first written method used to convey your research idea to your tutor. Therefore, aims and objectives should clearly convey your topic, academic foundation, and research design. In order to write effective research aims and objectives, researchers should consider all aspects of their proposed work. For example, the sample(s) to be approached for participation in the primary data collection. Identifying research objectives that are SMART is key to ensuring key aspects of the work are considered prior to any data collection. This includes consideration of access to samples and the ethics of researching the topic and research design. Finally, seeing your work as others will read it, can be an effective evaluation tool to ensure your own research objectives adequately capture and reflect your intended study. Therefore, this guide encourages you to consider common issues with identifying and writing research aims and objectives through consideration of examples.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this guide, readers should be able to:
- Identify the meaning and purpose of a research aim within business research
- Understand the link between an effective research aim and the wider topic and literature/secondary sources, where appropriate
- Understand how to identify and write Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timely (SMART) Research objectives, research questions, and consideration of research hypothesis
- Recognize the link between writing an effective research aim and the research design. Write own research aim and objectives
Introduction
The writing of effective research aims and objectives can cause confusion and concern to new (and experienced!) researchers and learners. Attempting to identify the scope and focus of a project within a few specific statements, can take time and consideration of all aspects of your research design. If you are still unsure of your approach to your topic, or even the boundaries of the topic itself, this uncertainty can make the framing of an effective research aim seem like an uphill task.
However, even if this is your first time trying to convey your research idea within a few concise and precise statements, there are steps to take to ensure your work clearly communicates your meaning to your audience. This how-to-guide draws on examples of business topic research aims and objectives and explores techniques for reviewing their meaning. This active learning approach will enable you to grow confidence in framing and communicating your own research.
The importance of ensuring the research aim and objectives are not only reflective of the topic choice but are also achievable can be a fluid process, which in itself, can result in anxious researchers. Seeing your work as others will read it, can be an effective evaluation tool to ensure your own research objectives adequately capture and reflect your intended study. Therefore, this guide encourages you to consider common issues with identifying and writing research aims and objectives through consideration of examples.
Identify the Meaning and Purpose of a Research Aim with Business Research
Writing an effective research aim is an integral part of the research process. A research aim is a statement of intent. It should communicate your research goal clearly and should provide a focus for your work from the offset. It is important to differentiate between a research aim and the objectives. If a research aim tells the reader what you plan to achieve, then the research objectives should state how you would reach that goal. Often the objectives will provide a road map of the steps you will take in order to meet the research aim. Therefore, a research aim in business-related topics is typically a single sentence or even two, which conveys the overall purpose of the research-the end goal!
The terminology you use when writing your research aim is important. Note the following example aims from Business related topics:
- 1. This research aims to evaluate the lasting effects of lockdown and ‘work from home’ initiatives on productiveness in the financial service industry.
- 2. This research aims to establish a link between innovations in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and recruitment processes for The Royal Bank of Scotland.
- 3. This research aims to investigate to what extent Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives can influence consumer behavior. A case study of Aldi UK.
- 4. This research aims to assess the effectiveness of technology companies’ risk management of cyber and information risks measured on the basis of supply chain resilience.
- 5. This research aims to explore the impact of Government funded initiatives to encourage social entrepreneurship in Scotland.
As evidenced above all of the aims stated contain verbs, these highlight how the research will be undertaken. Words such as to assess, to establish, to explore or to evaluate all reflect research analysis. This conveys your intention clearly to the reader and whilst it may not fully demonstrate exactly how the project will be undertaken, the verbs show what the goal is.
The objectives, which follow the aim, can help to show the exact ways the aim will be achieved, highlighting the research methods. It is important to think carefully about whether you plan to or will be to, come to a clear conclusion. Often it is not possible and this can be due to many factors such as the time or scope of the issue. For example, in the aims stated above number 2 is the only one that states it will ‘establish a link.’ This is because the aim is specific and measurable. The objectives should identify the specific processes it will examine and link to effective recruitment practices that are more effective than prior to AI being used.
However, for the other aims it is more appropriate to explore or investigate the topics, as opposed to ‘establishing’ or to ‘evidence an impact.’
Abbreviations are a useful way of shortening words or phrases and they can give writing a more coherent flow. It is worth noting that all abbreviations like AI or CSR should only be used when they are spelled out initially and if they appear frequently throughout your writing.
It is important to always check with your supervisor or course Handbook but typically, you should have a research question, a research aim, and objectives. The research question should capture what the issue is, often it will help to explain your research aim by offering a critical perspective. For example, if your research is to evaluate the effect of something then your question may be to what extent is that something works?
Finally, it is important to remember that the wording of your research aim may change slightly as your research progresses. Often students will modify the words to reflect what they are undertaking as the process develops.
Section Summary
- An effective research aim should clearly set out the goal of a project.
- Carefully consider the terminology you use at this stage, and ensure it reflects the outcome of the study.
- Remember a research aim can be fluid and the exact wording is likely to change as you progress through your research journey.
Understand the Link Between an Effective Research Aim and the Wider Topic and Literature/secondary Sources, Where Appropriate
When developing the research aim it is important to be engaged with the wider topic and associated literature and secondary sources from the offset. These sources will be crucial in helping you to tackle the topic successfully.
Identifying an idea for a research project can sometimes be a relatively simple first step in the research process. It is often narrowing the idea down to a research aim, which can be more difficult. A good way to start is to brainstorm ideas, think about what interests you the most about your studies, and note down keywords which can then be used as search terms. Researchers, at all levels of research and study, should consider information-seeking as a process through which they engage with the primary literature and secondary sources concerning their topic area. This will develop self-confidence in your ability to define the terms of reference of your work and studies. An inquiring mind and openness to a degree of flexibility of approach in these early stages of research, can be key to ensuring initial topic ideas can be molded into achievable research aims and objectives.
Research could be considered to be cyclical, not a one-off process. Therefore, in order to ensure a definable and achievable research topic, many projects use a mixture of sources. This requires a degree of confidence on the part of the researcher; to identify the relevant resources they require, a strategy for how to find them and also, a process for information management.
Many researchers will start with an online search for both academic and non-academic sources. The short-term success of this first step can be dictated by the choice of keywords and phrases. That is, those terms that the researcher believes are most relevant for, and most likely to come up with links to their research topic. However, caution should be employed in this initial task of online searching - this is an important opportunity to consider how we identify these specific keywords. A limited understanding of the area will be enhanced through further reading. It can allow the researcher to access previous studies in the same topic area and identify effective research methods. An informed research aim should be underpinned by reading and evaluating sources in relation to the research idea.
Using the research aims below as examples, note the sources required and some issues to consider for each source. By strategically linking your research aim to the wider area you will ensure your research is robust from the start.
- Reading combined with ongoing critical appraisal of associated sources can help to refine and focus your research aim and objectives.
- Think of your research as an ongoing process. Reading associated sources should be embedded in every stage of your research journey.
- Ensure you are acknowledging the wider research area and associated sources from the offset as this will help to refine and focus your research aim and objectives.
Understanding How to Identify SMART Research Objectives, Research Questions, and Consideration of Research Hypothesis
First-time final year undergraduates are normally expected to identify a research topic and research design that are realistic and achievable. Not only should they be realistic as topics but also achievable within a short time period when most learners have never undertaken such work previously. A common pitfall of many initial research topics is identifying an area that is too wide in scope. A simple step is to consider how to express and convey the work within a series of research objectives. Careful consideration of the content of these statements can help narrow the topic focus, and ensure the research design is relevant to the work to be undertaken. Therefore, writing your objectives should be viewed as a process and not a one-off exercise. Remember, they convey your work to an audience and set out the initial boundaries of the research to be undertaken.
Therefore, research aims and objectives should provide focus and direction for the research topic. Many business research methods texts will introduce the writing of research aims and objectives as a specific skill required to ensure they are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timely (SMART). By following the SMART guidelines and analyzing examples of common issues within aims and objectives, learners can build confidence and ensure their aims and objectives are strong. Together with these five criteria, the language used can convey the depth of the inquiry. By way of explanation, consider the following topic submitted for consideration as a final-year project:
The research aim is to evaluate consumer perceptions of the impact of social media advertising on their car purchasing decisions. The fieldwork will examine consumer attitudes toward social media advertising and the benefits of this approach. This will be explored through the following research objectives:
- 1. Examine relevant literature concerning advertising, and trends in social media within the car industry;
- 2. Identify the attitudes of key players and stakeholders within the advertising industry toward the use of social media;
- 3. Discuss the effects of new technology on social media and advertising trends;
- 4. Evaluate how consumers relate to new technology with a view to making recommendations for improvement in the use of social media within online advertising.
S pecific – the research objectives reflect the terminology also used within the research aim.
M easureable – this does not necessarily mean that the work will involve quantitative data. Consider that the objectives identify the issues and samples and so the target of the work.
A chievable – does the work appear to be a piece of research that could be undertaken and completed within the confines of the undergraduate program? It could be achievable on the basis that the work does not appear to require a long time period to complete and the samples should be accessible. Achievability is also a consideration of university ethical consideration processes. For example, although a researcher is able to identify a sample of participants who are experiencing fuel poverty, consideration must be given to the possible ethical issues that surround requesting their participation. It may be deemed that the research could in some manner cause harm to the participants, such as stress through talking about their lived experiences. This stress could also be felt by the researcher who may not be trained to deal with such emotional situations. In both of these examples, the university ethics process could decide this work is unachievable.
R ealistic – the issue of social media advertising is realistic within the stated industry. The samples identified also appear linked to the topic. Furthermore, the academic foundation of the work is also identified – advertising. The work also appears to be realistic in terms of the resources required to complete it. The ethical use of data gathered from social media could also be relevant to determining if this topic is realistic. As with Achievability above, issues such as how the data was originally gathered and how it will then be used by the researcher, would be scrutinized by the Ethics process. Again, the principle of ‘do no harm’ would be applied to determine if the work is realistic.
T imely – although the work does not offer a specific timeframe, the use of social media for advertising is evident within the car industry. Therefore, this could be said to be timely.
Furthermore, the terminology is important. If you choose words that are descriptive, they will convey work that is also descriptive. So, try to use words such as ‘describe,’ ‘understand,’ or ‘gain an insight into’ only where they adequately reflect that your research is not an in-depth study. Consider using terms to evidence how you will approach each objective including: evaluate; critique; critically discuss and examine. All infer the research will go beyond a surface inquiry.
Now, at this stage, consider if the research wished to study the possible relationships between variables such as the impact on consumers of exposure to social media advertising on car sales decision-making. As with the approach to the similar topic above, this could be explored using qualitative data by gathering the experiences of consumers and/or people within the car industry. However, research that specifically wishes to explore possible links between issues and/or specific variables, could sometimes be better framed using a research hypothesis. This is a statement that identifies possible c ause and effect ’ relationships between variables. Therefore, the focus of the above topic could be reconsidered to identify the impact of social media advertising within the car industry. The new research question and hypothesis could be thus:
The research question: Do consumers perceive the impact of social media advertising on their car purchasing decisions?
Null Hypothesis: There is no difference in car purchasing decisions between those consumers who are exposed to social media advertising of cars compared to those who are not.
Alternative Hypothesis: There is a relationship between whether or not a consumer has been exposed to social media advertising and their car purchasing decision.
In order to address the hypothesis, some form of statistical testing would be required which is not covered in this guide. However, as a researcher, you should always consider what it is specifically that you wish to research when framing your work. This topic consideration could identify specific issues and/or variables which you wish to explore further to test if there are statistical relationships. In this situation, you could consider including hypothesis testing within your research design. As can be viewed above, related topics may be presented in different ways, with the inclusion or exclusion of a research hypothesis. The existence of possible relationships may be explored through research that seeks perceptions of advertising. However, research which seeks statistical evidence would be best represented with hypothesis testing.
- Research aim and objectives convey to your audience the topic and possible boundaries of your work. Therefore, ensuring they are presented as SMART, allows others to assess your work in the way you intended.
- Research ethics should be considered when writing research aims and objectives, including the potential impact of participation on individuals. Research should do no harm to the individuals involved, including the sample and researchers themselves.
- Research does not always necessitate consideration of the research hypothesis. However, in some circumstances, a well-considered hypothesis could offer statistical weight to your findings.
Recognizing the Link Between Writing an Effective Research Aim and the Research Design
The research aim and objectives should be written in a way that conveys the specific area or problem to be researched. This should allow anyone reading your research aim to understand the main focus of the work. For example, your work may aim to examine the lived experiences of individuals living with fuel poverty within a specific geographic area or demographic. In this example, you can clearly identify the topic – lived experiences of fuel poverty – and the focus – individuals within the chosen geographical area/demographic . To a more experienced researcher, it can also offer insight into the research design which may be reasonably expected. So, studies of ‘lived experiences’ can involve the gathering and/or analysis of qualitative data from individuals/communities as the researcher seek to gather the first-hand experiences of participants (individuals).
Clearly written research aim and objectives should allow the reader to consider the following information:
- 1. Wider academic area(s) within which the topic falls (for example, accountancy; marketing; management);
- 2. The main areas of the literature identified within the aim and/or objectives;
- 3. The data which would be expected to be gathered to in order to meet/address the research objectives;
- 4. The data collection methods which could be deemed relevant to the research aim and,
- 5. Overall, if the research aim and objectives are SMART (see above).
Consider the wording in the example below:
The research aim of this dissertation is to examine the lived experiences of people living with fuel poverty and their attitudes towards support services within a local council area. This research aim will be addressed through the following research objectives:
- 1. Critically review previous literature and evaluate the origins and purpose of different definitions of ‘fuel poverty.’
- 2. Explore the attitudes of individuals currently experiencing fuel poverty towards support agencies and other stakeholders.
- 3. Analyze the opportunities and barriers to support agencies and related stakeholders within a local council area with specific regard to supporting those experiencing fuel poverty.
- 4. Compare and contrast the lived experiences of individuals experiencing fuel poverty with those of the support agencies to identify potential service gaps.
Looking closely at the work above, it could be reasonable to make the following assumptions about the research:
The academic area(s) within which the topic falls (for example, accountancy; marketing; management; social sciences; economics). This can be researched and explored by keyword searching the research aim. In this example, there appear to be multiple academic roots to the work:
- ‘lived experiences of people living with fuel poverty’ – this could be viewed as a social science/economics topic or even an engineering area. Either would depend on the specific view taken to investigate fuel poverty, i.e., real-world examples of lived experiences, specially such as narratives about their daily life. Alternatively, this aim could encapsulate studies within engineering areas that seek to understand the impact of construction and design decisions on the daily life of individuals.
- ‘…and their attitudes towards support services within a local council area’ – by adding a focus for the study as being specific to support services, this work is now narrowed to more reflect the social sciences area.
- If the work was indeed to study any issues such as building construction, this would be expected to appear within the research aim to convey the topic clearly and precisely.
Therefore, it could be expected that if the research draws on wider academic areas, this should be evident from the terminology within the research objectives. A consistent use of terminology ensures the academic foundation of the work is identifiable throughout. It could also be reasonably presumed that the relevant issues of each sample (individuals within fuel poverty, the support services, and stakeholders), would be refined to include specific factors to ensure the work is focused on specific issues.
Next, consider the type of data you would expect to gather to in order to meet/address the research objectives. The following options appear to be linked to the wording of the objectives:
- Secondary Data: The objectives identify the need for literature in the first stages of work in order to address objectives 1, 2, and 3. As the research is based on lived experiences, this could include not only academic work but also charity and government reports. Given that this is a real-world issue, examples could also be identified from reputable news agencies. All of these sources could help identify possible issues that may be identified by research participants during the data gathering. If these issues are not identified by the participants, they could be used to form a critical discussion around opportunities or barriers (objective 3).
- Primary Data: Given the focus on lived experiences related to support services, the research may be presumed to include a qualitative study. A qualitative study would allow participants to use their own voices and language to explain their lived experiences. Whereas a quantitative study, by its nature, could explore the issues already known to the researcher when the instrument was written, e.g., survey. Qualitative data could perhaps encourage more personal issues to be identified by the individual participants, and also offer some context for their position.
Subsequently, consider which data collection methods you would expect to be used to address the research aim.
- Quantitative data gathering tools: Could quantitative data gathering explore the lived experiences of this sample? Many areas could be effectively explored however lived experiences tend to be personal to the individual and so qualitative could offer more depth and richness to the data.
- As both the research aim and objectives identify specific samples, the research could be considered to have a boundary around those to be invited to participate. Therefore, secondary data may identify the definitions of fuel poverty and offer reasons for any differences. It could also allow the identification of the roles and remits of support services and stakeholders. However, it will not offer specific lived experience details that can come from the sample of individuals.
If specific organizational sectors or companies were identified, the use of quantitative data-gathering tools, such as a survey, may allow more specific information to be gathered. Remember, the research aim identifies that the focus is the individuals who experience fuel poverty. Therefore, a survey could address issues such as knowledge and understanding of these service providers. However, it could then miss hearing about the informal networks used by individuals for support, which could come to light during a qualitative study.
Finally, if in doubt, show your research aim and objectives to a colleague and ask them to tell you , what they think your research is about. This simple exercise will enable you to realize what other people understand from your work and so, allow you to tweak where necessary. This should ensure your research is not only accessible to different audiences but ultimately, is a fair reflection of your topic choice.
- Clearly written research aims and objectives can effectively convey information about your work. This allows a reader to consider the key aspects of your topic and sets expectations about the contents of your report/dissertation/thesis.
- Always ensure that the language used to write a research aim and objectives, adequately convey the meaning and depth of your research. It should be specific to your topic but also accessible to the intended audience(s).
- SMART research objectives can convey your understanding of research design. This should be apparent from the layering of issues and identification of relevant samples.
In conclusion, this guide has offered practical steps through example-based exercises to help you format your idea into an effective research aim and objectives. Having progressed through the exercises, you will have considered issues such as the importance of understanding how a research aim can help you refine your idea. It is also the mechanism to convey your research intention to your audience. Through exploring the importance of linking your research aim to the wider research area this will give you the confidence to develop SMART objectives. Following this, your work will reflect key areas of your research design through the use of relevant research methods terminology.
Therefore, by following the steps in this guide you should now be confident to take your idea and form it into robust research aims and objectives.
Multiple-Choice Quiz Questions
1. The purpose of a research aim is to ______.
Incorrect Answer
Feedback: This is not the correct answer. The correct answer is C.
Correct Answer
Feedback: Well done, correct answer
2. It is important to understand the link between the research aim and the wider topic because ______.
Feedback: This is not the correct answer. The correct answer is B.
3. How many research objectives are necessary to ensure a successful final-year project?
4. Research objectives reflect ______
5. Research design can be reflected in the research aim and objectives by ______.
Web Resources
Further reading, sign in to access this content, get a 30 day free trial, more like this, sage recommends.
We found other relevant content for you on other Sage platforms.
Have you created a personal profile? Login or create a profile so that you can save clips, playlists and searches
- Sign in/register
Navigating away from this page will delete your results
Please save your results to "My Self-Assessments" in your profile before navigating away from this page.
Sign in to my profile
Please sign into your institution before accessing your profile
Sign up for a free trial and experience all Sage Learning Resources have to offer.
You must have a valid academic email address to sign up.
Get off-campus access
- View or download all content my institution has access to.
Sign up for a free trial and experience all Sage Learning Resources has to offer.
- view my profile
- view my lists
21 Research Objectives Examples (Copy and Paste)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve.
These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected by the researcher to present a clear intention or course of action for his or her qualitative or quantitative study.
Research objectives are typically nested under one overarching research aim. The objectives are the steps you’ll need to take in order to achieve the aim (see the examples below, for example, which demonstrate an aim followed by 3 objectives, which is what I recommend to my research students).
Research Objectives vs Research Aims
Research aim and research objectives are fundamental constituents of any study, fitting together like two pieces of the same puzzle.
The ‘research aim’ describes the overarching goal or purpose of the study (Kumar, 2019). This is usually a broad, high-level purpose statement, summing up the central question that the research intends to answer.
Example of an Overarching Research Aim:
“The aim of this study is to explore the impact of climate change on crop productivity.”
Comparatively, ‘research objectives’ are concrete goals that underpin the research aim, providing stepwise actions to achieve the aim.
Objectives break the primary aim into manageable, focused pieces, and are usually characterized as being more specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Examples of Specific Research Objectives:
1. “To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.” 2. “To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).” 3. “To analyze the impact of changing weather patterns on crop diseases within the same timeframe.”
The distinction between these two terms, though subtle, is significant for successfully conducting a study. The research aim provides the study with direction, while the research objectives set the path to achieving this aim, thereby ensuring the study’s efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Write Research Objectives
I usually recommend to my students that they use the SMART framework to create their research objectives.
SMART is an acronym standing for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It provides a clear method of defining solid research objectives and helps students know where to start in writing their objectives (Locke & Latham, 2013).
Each element of this acronym adds a distinct dimension to the framework, aiding in the creation of comprehensive, well-delineated objectives.
Here is each step:
- Specific : We need to avoid ambiguity in our objectives. They need to be clear and precise (Doran, 1981). For instance, rather than stating the objective as “to study the effects of social media,” a more focused detail would be “to examine the effects of social media use (Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter) on the academic performance of college students.”
- Measurable: The measurable attribute provides a clear criterion to determine if the objective has been met (Locke & Latham, 2013). A quantifiable element, such as a percentage or a number, adds a measurable quality. For example, “to increase response rate to the annual customer survey by 10%,” makes it easier to ascertain achievement.
- Achievable: The achievable aspect encourages researchers to craft realistic objectives, resembling a self-check mechanism to ensure the objectives align with the scope and resources at disposal (Doran, 1981). For example, “to interview 25 participants selected randomly from a population of 100” is an attainable objective as long as the researcher has access to these participants.
- Relevance : Relevance, the fourth element, compels the researcher to tailor the objectives in alignment with overarching goals of the study (Locke & Latham, 2013). This is extremely important – each objective must help you meet your overall one-sentence ‘aim’ in your study.
- Time-Bound: Lastly, the time-bound element fosters a sense of urgency and prioritization, preventing procrastination and enhancing productivity (Doran, 1981). “To analyze the effect of laptop use in lectures on student engagement over the course of two semesters this year” expresses a clear deadline, thus serving as a motivator for timely completion.
You’re not expected to fit every single element of the SMART framework in one objective, but across your objectives, try to touch on each of the five components.
Research Objectives Examples
1. Field: Psychology
Aim: To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.
- Objective 1: To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.
- Objective 2: To investigate the relationship between class grades and reported sleep duration.
- Objective 3: To survey student perceptions and experiences on how sleep deprivation affects their cognitive capabilities.
2. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To understand the effects of urban green spaces on human well-being in a metropolitan city.
- Objective 1: To assess the physical and mental health benefits of regular exposure to urban green spaces.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the social impacts of urban green spaces on community interactions.
- Objective 3: To examine patterns of use for different types of urban green spaces.
3. Field: Technology
Aim: To investigate the influence of using social media on productivity in the workplace.
- Objective 1: To measure the amount of time spent on social media during work hours.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the perceived impact of social media use on task completion and work efficiency.
- Objective 3: To explore whether company policies on social media usage correlate with different patterns of productivity.
4. Field: Education
Aim: To examine the effectiveness of online vs traditional face-to-face learning on student engagement and achievement.
- Objective 1: To compare student grades between the groups exposed to online and traditional face-to-face learning.
- Objective 2: To assess student engagement levels in both learning environments.
- Objective 3: To collate student perceptions and preferences regarding both learning methods.
5. Field: Health
Aim: To determine the impact of a Mediterranean diet on cardiac health among adults over 50.
- Objective 1: To assess changes in cardiovascular health metrics after following a Mediterranean diet for six months.
- Objective 2: To compare these health metrics with a similar group who follow their regular diet.
- Objective 3: To document participants’ experiences and adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
6. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To analyze the impact of urban farming on community sustainability.
- Objective 1: To document the types and quantity of food produced through urban farming initiatives.
- Objective 2: To assess the effect of urban farming on local communities’ access to fresh produce.
- Objective 3: To examine the social dynamics and cooperative relationships in the creating and maintaining of urban farms.
7. Field: Sociology
Aim: To investigate the influence of home offices on work-life balance during remote work.
- Objective 1: To survey remote workers on their perceptions of work-life balance since setting up home offices.
- Objective 2: To conduct an observational study of daily work routines and family interactions in a home office setting.
- Objective 3: To assess the correlation, if any, between physical boundaries of workspaces and mental boundaries for work in the home setting.
8. Field: Economics
Aim: To evaluate the effects of minimum wage increases on small businesses.
- Objective 1: To analyze cost structures, pricing changes, and profitability of small businesses before and after minimum wage increases.
- Objective 2: To survey small business owners on the strategies they employ to navigate minimum wage increases.
- Objective 3: To examine employment trends in small businesses in response to wage increase legislation.
9. Field: Education
Aim: To explore the role of extracurricular activities in promoting soft skills among high school students.
- Objective 1: To assess the variety of soft skills developed through different types of extracurricular activities.
- Objective 2: To compare self-reported soft skills between students who participate in extracurricular activities and those who do not.
- Objective 3: To investigate the teachers’ perspectives on the contribution of extracurricular activities to students’ skill development.
10. Field: Technology
Aim: To assess the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on the tourism industry.
- Objective 1: To document the types and popularity of VR experiences available in the tourism market.
- Objective 2: To survey tourists on their interest levels and satisfaction rates with VR tourism experiences.
- Objective 3: To determine whether VR tourism experiences correlate with increased interest in real-life travel to the simulated destinations.
11. Field: Biochemistry
Aim: To examine the role of antioxidants in preventing cellular damage.
- Objective 1: To identify the types and quantities of antioxidants in common fruits and vegetables.
- Objective 2: To determine the effects of various antioxidants on free radical neutralization in controlled lab tests.
- Objective 3: To investigate potential beneficial impacts of antioxidant-rich diets on long-term cellular health.
12. Field: Linguistics
Aim: To determine the influence of early exposure to multiple languages on cognitive development in children.
- Objective 1: To assess cognitive development milestones in monolingual and multilingual children.
- Objective 2: To document the number and intensity of language exposures for each group in the study.
- Objective 3: To investigate the specific cognitive advantages, if any, enjoyed by multilingual children.
13. Field: Art History
Aim: To explore the impact of the Renaissance period on modern-day art trends.
- Objective 1: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
- Objective 2: To analyze modern art pieces for the influence of the Renaissance style.
- Objective 3: To survey modern-day artists for their inspirations and the influence of historical art movements on their work.
14. Field: Cybersecurity
Aim: To assess the effectiveness of two-factor authentication (2FA) in preventing unauthorized system access.
- Objective 1: To measure the frequency of unauthorized access attempts before and after the introduction of 2FA.
- Objective 2: To survey users about their experiences and challenges with 2FA implementation.
- Objective 3: To evaluate the efficacy of different types of 2FA (SMS-based, authenticator apps, biometrics, etc.).
15. Field: Cultural Studies
Aim: To analyze the role of music in cultural identity formation among ethnic minorities.
- Objective 1: To document the types and frequency of traditional music practices within selected ethnic minority communities.
- Objective 2: To survey community members on the role of music in their personal and communal identity.
- Objective 3: To explore the resilience and transmission of traditional music practices in contemporary society.
16. Field: Astronomy
Aim: To explore the impact of solar activity on satellite communication.
- Objective 1: To categorize different types of solar activities and their frequencies of occurrence.
- Objective 2: To ascertain how variations in solar activity may influence satellite communication.
- Objective 3: To investigate preventative and damage-control measures currently in place during periods of high solar activity.
17. Field: Literature
Aim: To examine narrative techniques in contemporary graphic novels.
- Objective 1: To identify a range of narrative techniques employed in this genre.
- Objective 2: To analyze the ways in which these narrative techniques engage readers and affect story interpretation.
- Objective 3: To compare narrative techniques in graphic novels to those found in traditional printed novels.
18. Field: Renewable Energy
Aim: To investigate the feasibility of solar energy as a primary renewable resource within urban areas.
- Objective 1: To quantify the average sunlight hours across urban areas in different climatic zones.
- Objective 2: To calculate the potential solar energy that could be harnessed within these areas.
- Objective 3: To identify barriers or challenges to widespread solar energy implementation in urban settings and potential solutions.
19. Field: Sports Science
Aim: To evaluate the role of pre-game rituals in athlete performance.
- Objective 1: To identify the variety and frequency of pre-game rituals among professional athletes in several sports.
- Objective 2: To measure the impact of pre-game rituals on individual athletes’ performance metrics.
- Objective 3: To examine the psychological mechanisms that might explain the effects (if any) of pre-game ritual on performance.
20. Field: Ecology
Aim: To investigate the effects of urban noise pollution on bird populations.
- Objective 1: To record and quantify urban noise levels in various bird habitats.
- Objective 2: To measure bird population densities in relation to noise levels.
- Objective 3: To determine any changes in bird behavior or vocalization linked to noise levels.
21. Field: Food Science
Aim: To examine the influence of cooking methods on the nutritional value of vegetables.
- Objective 1: To identify the nutrient content of various vegetables both raw and after different cooking processes.
- Objective 2: To compare the effect of various cooking methods on the nutrient retention of these vegetables.
- Objective 3: To propose cooking strategies that optimize nutrient retention.
The Importance of Research Objectives
The importance of research objectives cannot be overstated. In essence, these guideposts articulate what the researcher aims to discover, understand, or examine (Kothari, 2014).
When drafting research objectives, it’s essential to make them simple and comprehensible, specific to the point of being quantifiable where possible, achievable in a practical sense, relevant to the chosen research question, and time-constrained to ensure efficient progress (Kumar, 2019).
Remember that a good research objective is integral to the success of your project, offering a clear path forward for setting out a research design , and serving as the bedrock of your study plan. Each objective must distinctly address a different dimension of your research question or problem (Kothari, 2014). Always bear in mind that the ultimate purpose of your research objectives is to succinctly encapsulate your aims in the clearest way possible, facilitating a coherent, comprehensive and rational approach to your planned study, and furnishing a scientific roadmap for your journey into the depths of knowledge and research (Kumar, 2019).
Kothari, C.R (2014). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques . New Delhi: New Age International.
Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners .New York: SAGE Publications.
Doran, G. T. (1981). There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Management review, 70 (11), 35-36.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2013). New Developments in Goal Setting and Task Performance . New York: Routledge.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Research Aims and Objectives: The dynamic duo for successful research
Picture yourself on a road trip without a destination in mind — driving aimlessly, not knowing where you’re headed or how to get there. Similarly, your research is navigated by well-defined research aims and objectives. Research aims and objectives are the foundation of any research project. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, ensuring that you stay focused and on track throughout the process. They are your trusted navigational tools, leading you to success.
Understanding the relationship between research objectives and aims is crucial to any research project’s success, and we’re here to break it down for you in this article. Here, we’ll explore the importance of research aims and objectives, understand their differences, and delve into the impact they have on the quality of research.
Understanding the Difference between Research Aims and Objectives
In research, aims and objectives are two important components but are often used interchangeably. Though they may sound similar, they are distinct and serve different purposes.
Research Aims:
Research aims are broad statements that describe the overall purpose of your study. They provide a general direction for your study and indicate the intended achievements of your research. Aims are usually written in a general and abstract manner describing the ultimate goal of the research.
Research Objectives:
Research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. They break down the research aims into smaller, more manageable components and provide a clear picture of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it.
In the example, the objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to reach the aim. Essentially, aims provide the overall direction for the research while objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to accomplish the aims. Aims provide a broad context for the research, while the objectives provide smaller steps that the researcher must take to accomplish the overall research goals. To illustrate, when planning a road trip, your research aim is the destination you want to reach, and your research objectives are the specific routes you need to take to get there.
Aims and objectives are interconnected. Objectives play a key role in defining the research methodology, providing a roadmap for how you’ll collect and analyze data, while aim is the final destination, which represents the ultimate goal of your research. By setting specific goals, you’ll be able to design a research plan that helps you achieve your objectives and, ultimately, your research aim.
Importance of Well-defined Aims and Objectives
The impact of clear research aims and objectives on the quality of research cannot be understated. But it’s not enough to simply have aims and objectives. Well-defined research aims and objectives are important for several reasons:
- Provides direction: Clear aims and well-defined objectives provide a specific direction for your research study, ensuring that the research stays focused on a specific topic or problem. This helps to prevent the research from becoming too broad or unfocused, and ensures that the study remains relevant and meaningful.
- Guides research design: The research aim and objectives help guide the research design and methodology, ensuring that your study is designed in a way that will answer the research questions and achieve the research objectives.
- Helps with resource allocation: Clear research aims and objectives helps you to allocate resources effectively , including time, financial resources, human resources, and other required materials. With a well-defined aim and objectives, you can identify the resources required to conduct the research, and allocate them in a way that maximizes efficiency and productivity.
- Assists in evaluation: Clearly specified research aims and objectives allow for effective evaluation of your research project’s success. You can assess whether the research has achieved its objectives, and whether the aim has been met. This evaluation process can help to identify areas of the research project that may require further attention or modification.
- Enhances communication: Well-defined research aims and objectives help to enhance communication among the research team, stakeholders, funding agencies, and other interested parties. Clear aims and objectives ensure that everyone involved in your research project understands the purpose and goals of the study. This can help to foster collaboration and ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
How to Formulate Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating effective research aims and objectives involves a systematic process to ensure that they are clear, specific, achievable, and relevant. Start by asking yourself what you want to achieve through your research. What impact do you want your research to have? Once you have a clear understanding of your aims, you can then break them down into specific, achievable objectives. Here are some steps you can follow when developing research aims and objectives:
- Identify the research question : Clearly identify the questions you want to answer through your research. This will help you define the scope of your research. Understanding the characteristics of a good research question will help you generate clearer aims and objectives.
- Conduct literature review : When defining your research aim and objectives, it’s important to conduct a literature review to identify key concepts, theories, and methods related to your research problem or question. Conducting a thorough literature review can help you understand what research has been done in the area and what gaps exist in the literature.
- Identify the research aim: Develop a research aim that summarizes the overarching goal of your research. The research aim should be broad and concise.
- Develop research objectives: Based on your research questions and research aim, develop specific research objectives that outline what you intend to achieve through your research. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Use action verbs: Use action verbs such as “investigate,” “examine,” “analyze,” and “compare” to describe your research aims and objectives. This makes them more specific and measurable.
- Ensure alignment with research question: Ensure that the research aim and objectives are aligned with the research question. This helps to ensure that the research remains focused and that the objectives are specific enough to answer your research question.
- Refine and revise: Once the research aim and objectives have been developed, refine and revise them as needed. Seek feedback from your colleagues, mentors, or supervisors to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable within the given resources and timeframe.
- Communicate: After finalizing the research aim and objectives, they should be communicated to the research team, stakeholders, and other interested parties. This helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal and understands the purpose of the study.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid While Formulating Aims and Objectives
There are several common mistakes that researchers can make when writing research aims and objectives. These include:
- Being too broad or vague: Aims and objectives that are too general or unclear can lead to confusion and lack of focus. It is important to ensure that the aims and objectives are concise and clear.
- Being too narrow or specific: On the other hand, aims and objectives that are too narrow or specific may limit the scope of the research and make it difficult to draw meaningful conclusions or implications.
- Being too ambitious: While it is important to aim high, being too ambitious with the aims and objectives can lead to unrealistic expectations and can be difficult to achieve within the constraints of the research project.
- Lack of alignment: The aims and objectives should be directly linked to the research questions being investigated. Otherwise, this will lead to a lack of coherence in the research project.
- Lack of feasibility: The aims and objectives should be achievable within the constraints of the research project, including time, budget, and resources. Failing to consider feasibility may cause compromise of the research quality.
- Failing to consider ethical considerations: The aims and objectives should take into account any ethical considerations, such as ensuring the safety and well-being of study participants.
- Failing to involve all stakeholders: It’s important to involve all relevant stakeholders, such as participants, supervisors, and funding agencies, in the development of the aims and objectives to ensure they are appropriate and relevant.
To avoid these common pitfalls, it is important to be specific, clear, relevant, and realistic when writing research aims and objectives. Seek feedback from colleagues or supervisors to ensure that the aims and objectives are aligned with the research problem , questions, and methodology, and are achievable within the constraints of the research project. It’s important to continually refine your aims and objectives as you go. As you progress in your research, it’s not uncommon for research aims and objectives to evolve slightly, but it’s important that they remain consistent with the study conducted and the research topic.
In summary, research aims and objectives are the backbone of any successful research project. They give you the ability to cut through the noise and hone in on what really matters. By setting clear goals and aligning them with your research questions and methodology, you can ensure that your research is relevant, impactful, and of the highest quality. So, before you hit the road on your research journey, make sure you have a clear destination and steps to get there. Let us know in the comments section below the challenges you faced and the strategies you followed while fomulating research aims and objectives! Also, feel free to reach out to us at any stage of your research or publication by using #AskEnago and tagging @EnagoAcademy on Twitter , Facebook , and Quora . Happy researching!
This particular material has added important but overlooked concepts regarding my experiences in explaining research aims and objectives. Thank you
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Improving Research Manuscripts Using AI-Powered Insights: Enago reports for effective research communication
Language Quality Importance in Academia AI in Evaluating Language Quality Enago Language Reports Live Demo…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 5 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What factors would influence the future of open access (OA) publishing?

Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022

T he research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
41 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
This is a well researched and superbly written article for learners of research methods at all levels in the research topic from conceptualization to research findings and conclusions. I highly recommend this material to university graduate students. As an instructor of advanced research methods for PhD students, I have confirmed that I was giving the right guidelines for the degree they are undertaking.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey
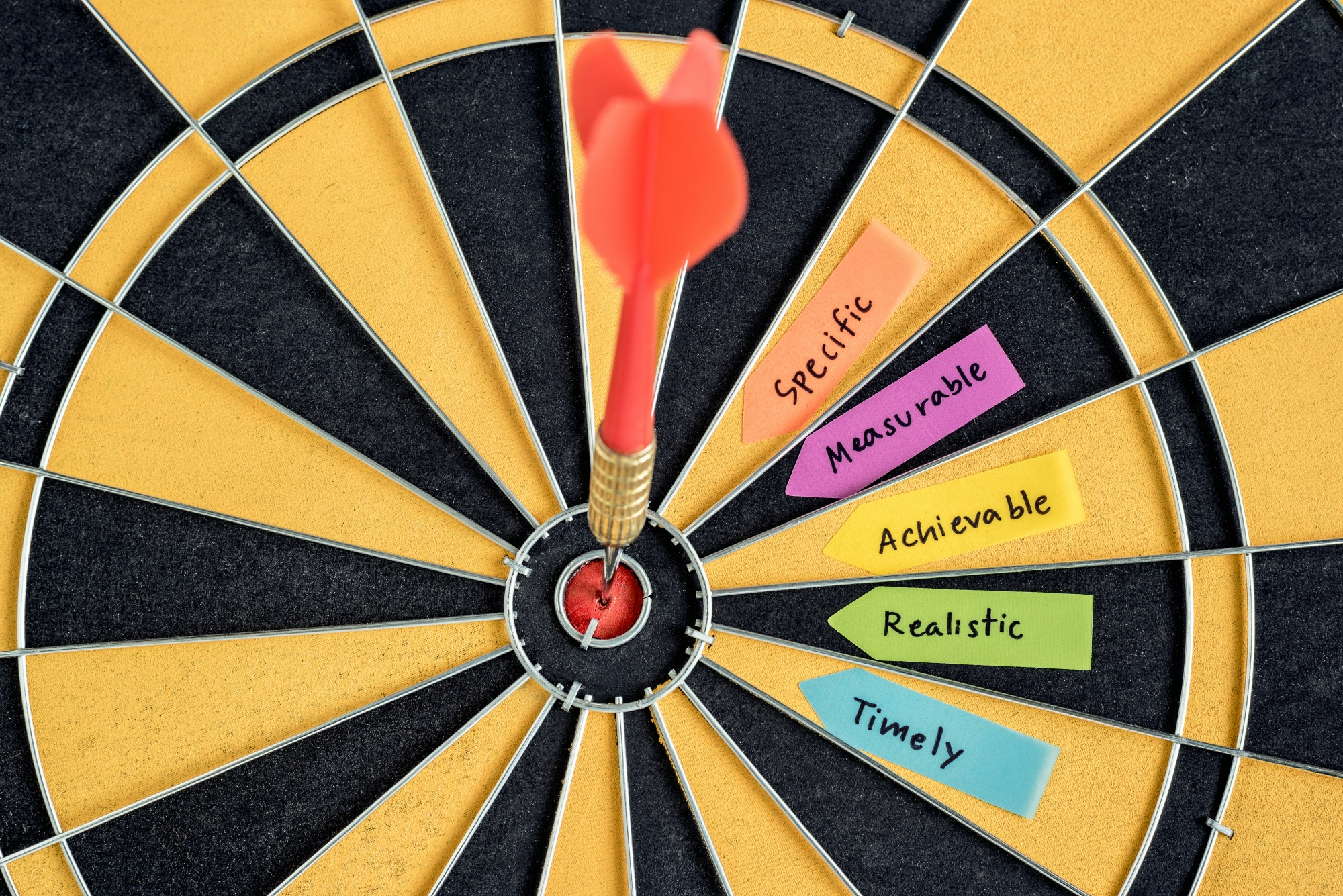

What Are Research Objectives and How to Write Them (with Examples)

Table of Contents
Introduction
Research is at the center of everything researchers do, and setting clear, well-defined research objectives plays a pivotal role in guiding scholars toward their desired outcomes. Research papers are essential instruments for researchers to effectively communicate their work. Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an active statement about how the study will answer this research question. These objectives help guide the development and design of the study and steer the research in the appropriate direction; if this is not clearly defined, a project can fail!
Research studies have a research question, research hypothesis, and one or more research objectives. A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve. The difference between these three is illustrated by the following example:
- Research question : How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
- Research hypothesis : Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
- Research objective : To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly.
What is the introduction in research papers?
Research objectives are usually included in the introduction section. This section is the first that the readers will read so it is essential that it conveys the subject matter appropriately and is well written to create a good first impression. A good introduction sets the tone of the paper and clearly outlines the contents so that the readers get a quick snapshot of what to expect.
A good introduction should aim to: 2,3
- Indicate the main subject area, its importance, and cite previous literature on the subject
- Define the gap(s) in existing research, ask a research question, and state the objectives
- Announce the present research and outline its novelty and significance
- Avoid repeating the Abstract, providing unnecessary information, and claiming novelty without accurate supporting information.
Why are research objectives important?
Objectives can help you stay focused and steer your research in the required direction. They help define and limit the scope of your research, which is important to efficiently manage your resources and time. The objectives help to create and maintain the overall structure, and specify two main things—the variables and the methods of quantifying the variables.
A good research objective:
- defines the scope of the study
- gives direction to the research
- helps maintain focus and avoid diversions from the topic
- minimizes wastage of resources like time, money, and energy
Types of research objectives
Research objectives can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives . 4 General objectives state what the research expects to achieve overall while specific objectives break this down into smaller, logically connected parts, each of which addresses various parts of the research problem. General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem.
Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Example (specific objective): To assess the influence of firm size on the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
In addition to this broad classification, research objectives can be grouped into several categories depending on the research problem, as given in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of research objectives
Characteristics of research objectives
Research objectives must start with the word “To” because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6
- A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives):
- Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
- Measurable—identifies the main variables of the study and quantifies the targets
- Achievable—attainable using the available time and resources
- Realistic—accurately addresses the scope of the problem
- Time-bound—identifies the time in which each step will be completed
- Research objectives clarify the purpose of research.
- They help understand the relationship and dissimilarities between variables.
- They provide a direction that helps the research to reach a definite conclusion.
How to write research objectives?
Research objectives can be written using the following steps: 7
- State your main research question clearly and concisely.
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study, which is similar to the research question but states the intended outcomes more definitively.
- Divide this main goal into subcategories to develop your objectives.
- Limit the number of objectives (1-2 general; 3-4 specific)
- Assess each objective using the SMART
- Start each objective with an action verb like assess, compare, determine, evaluate, etc., which makes the research appear more actionable.
- Use specific language without making the sentence data heavy.
- The most common section to add the objectives is the introduction and after the problem statement.
- Add the objectives to the abstract (if there is one).
- State the general objective first, followed by the specific objectives.
Formulating research objectives
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8
- Identify the research problem.
- Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
- Identify the research gaps the current study should cover based on your literature review. These gaps could be theoretical, methodological, or conceptual.
- Define the research question(s) based on the gaps identified.
- Revise/relate the research problem based on the defined research question and the gaps identified. This is to confirm that there is an actual need for a study on the subject based on the gaps in literature.
- Identify and write the general and specific objectives.
- Incorporate the objectives into the study.
Advantages of research objectives
Adding clear research objectives has the following advantages: 4,8
- Maintains the focus and direction of the research
- Optimizes allocation of resources with minimal wastage
- Acts as a foundation for defining appropriate research questions and hypotheses
- Provides measurable outcomes that can help evaluate the success of the research
- Determines the feasibility of the research by helping to assess the availability of required resources
- Ensures relevance of the study to the subject and its contribution to existing literature
Disadvantages of research objectives
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8
- Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process
- Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings
Key takeaways
- Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
- They define the scope and direction of the research and maintain focus.
- The objectives should be SMART—specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
- Clear research objectives help avoid collection of data or resources not required for the study.
- Well-formulated specific objectives help develop the overall research methodology, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and utilization.
- Research objectives should cover all aspects of the problem statement in a coherent way.
- They should be clearly stated using action verbs.
Frequently asked questions on research objectives
Q: what’s the difference between research objectives and aims 9.
A: Research aims are statements that reflect the broad goal(s) of the study and outline the general direction of the research. They are not specific but clearly define the focus of the study.
Example: This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.
Research objectives focus on the action to be taken to achieve the aims. They make the aims more practical and should be specific and actionable.
Example: To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation.
Q: What are the examples of research objectives, both general and specific?
A: Here are a few examples of research objectives:
- To identify the antiviral chemical constituents in Mumbukura gitoniensis (general)
- To carry out solvent extraction of dried flowers of Mumbukura gitoniensis and isolate the constituents. (specific)
- To determine the antiviral activity of each of the isolated compounds. (specific)
- To examine the extent, range, and method of coral reef rehabilitation projects in five shallow reef areas adjacent to popular tourist destinations in the Philippines.
- To investigate species richness of mammal communities in five protected areas over the past 20 years.
- To evaluate the potential application of AI techniques for estimating best-corrected visual acuity from fundus photographs with and without ancillary information.
- To investigate whether sport influences psychological parameters in the personality of asthmatic children.
Q: How do I develop research objectives?
A: Developing research objectives begins with defining the problem statement clearly, as illustrated by Figure 1. Objectives specify how the research question will be answered and they determine what is to be measured to test the hypothesis.
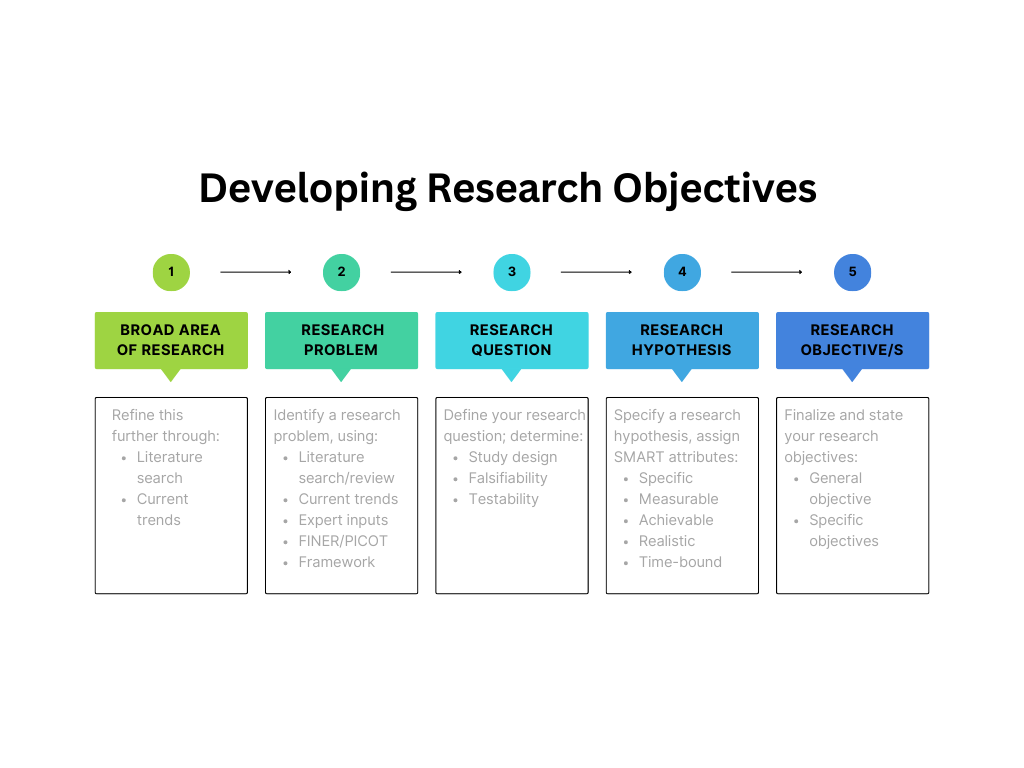
Q: Are research objectives measurable?
A: The word “measurable” implies that something is quantifiable. In terms of research objectives, this means that the source and method of collecting data are identified and that all these aspects are feasible for the research. Some metrics can be created to measure your progress toward achieving your objectives.
Q: Can research objectives change during the study?
A: Revising research objectives during the study is acceptable in situations when the selected methodology is not progressing toward achieving the objective, or if there are challenges pertaining to resources, etc. One thing to keep in mind is the time and resources you would have to complete your research after revising the objectives. Thus, as long as your problem statement and hypotheses are unchanged, minor revisions to the research objectives are acceptable.
Q: What is the difference between research questions and research objectives? 10
Q: are research objectives the same as hypotheses.
A: No, hypotheses are predictive theories that are expressed in general terms. Research objectives, which are more specific, are developed from hypotheses and aim to test them. A hypothesis can be tested using several methods and each method will have different objectives because the methodology to be used could be different. A hypothesis is developed based on observation and reasoning; it is a calculated prediction about why a particular phenomenon is occurring. To test this prediction, different research objectives are formulated. Here’s a simple example of both a research hypothesis and research objective.
Research hypothesis : Employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
Research objective : To assess whether employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
To summarize, research objectives are an important part of research studies and should be written clearly to effectively communicate your research. We hope this article has given you a brief insight into the importance of using clearly defined research objectives and how to formulate them.
- Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Can J Surg. 2010 Aug;53(4):278-81.
- Abbadia J. How to write an introduction for a research paper. Mind the Graph website. Accessed June 14, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction-for-a-research-paper/
- Writing a scientific paper: Introduction. UCI libraries website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://guides.lib.uci.edu/c.php?g=334338&p=2249903
- Research objectives—Types, examples and writing guide. Researchmethod.net website. Accessed June 17, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/research-objectives/#:~:text=They%20provide%20a%20clear%20direction,track%20and%20achieve%20their%20goals .
- Bartle P. SMART Characteristics of good objectives. Community empowerment collective website. Accessed June 16, 2023. https://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pd-smar.htm
- Research objectives. Studyprobe website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.studyprobe.in/2022/08/research-objectives.html
- Corredor F. How to write objectives in a research paper. wikiHow website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.wikihow.com/Write-Objectives-in-a-Research-Proposal
- Research objectives: Definition, types, characteristics, advantages. AccountingNest website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://www.accountingnest.com/articles/research/research-objectives
- Phair D., Shaeffer A. Research aims, objectives & questions. GradCoach website. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://gradcoach.com/research-aims-objectives-questions/
- Understanding the difference between research questions and objectives. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://board.researchersjob.com/blog/research-questions-and-objectives
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !

Related Posts

How does R Discovery Translate Complex Academic Papers Accurately

What Constitutes Good Research in Academia?

Formulating Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating research aim and objectives in an appropriate manner is one of the most important aspects of your thesis. This is because research aim and objectives determine the scope, depth and the overall direction of the research. Research question is the central question of the study that has to be answered on the basis of research findings.
Research aim emphasizes what needs to be achieved within the scope of the research, by the end of the research process. Achievement of research aim provides answer to the research question.
Research objectives divide research aim into several parts and address each part separately. Research aim specifies WHAT needs to be studied and research objectives comprise a number of steps that address HOW research aim will be achieved.
As a rule of dumb, there would be one research aim and several research objectives. Achievement of each research objective will lead to the achievement of the research aim.
Consider the following as an example:
Research title: Effects of organizational culture on business profitability: a case study of Virgin Atlantic
Research aim: To assess the effects of Virgin Atlantic organizational culture on business profitability
Following research objectives would facilitate the achievement of this aim:
- Analyzing the nature of organizational culture at Virgin Atlantic by September 1, 2022
- Identifying factors impacting Virgin Atlantic organizational culture by September 16, 2022
- Analyzing impacts of Virgin Atlantic organizational culture on employee performances by September 30, 2022
- Providing recommendations to Virgin Atlantic strategic level management in terms of increasing the level of effectiveness of organizational culture by October 5, 2022
Figure below illustrates additional examples in formulating research aims and objectives:

Formulation of research question, aim and objectives
Common mistakes in the formulation of research aim relate to the following:
1. Choosing the topic too broadly . This is the most common mistake. For example, a research title of “an analysis of leadership practices” can be classified as too broad because the title fails to answer the following questions:
a) Which aspects of leadership practices? Leadership has many aspects such as employee motivation, ethical behaviour, strategic planning, change management etc. An attempt to cover all of these aspects of organizational leadership within a single research will result in an unfocused and poor work.
b) An analysis of leadership practices in which country? Leadership practices tend to be different in various countries due to cross-cultural differences, legislations and a range of other region-specific factors. Therefore, a study of leadership practices needs to be country-specific.
c) Analysis of leadership practices in which company or industry? Similar to the point above, analysis of leadership practices needs to take into account industry-specific and/or company-specific differences, and there is no way to conduct a leadership research that relates to all industries and organizations in an equal manner.
Accordingly, as an example “a study into the impacts of ethical behaviour of a leader on the level of employee motivation in US healthcare sector” would be a more appropriate title than simply “An analysis of leadership practices”.
2. Setting an unrealistic aim . Formulation of a research aim that involves in-depth interviews with Apple strategic level management by an undergraduate level student can be specified as a bit over-ambitious. This is because securing an interview with Apple CEO Tim Cook or members of Apple Board of Directors might not be easy. This is an extreme example of course, but you got the idea. Instead, you may aim to interview the manager of your local Apple store and adopt a more feasible strategy to get your dissertation completed.
3. Choosing research methods incompatible with the timeframe available . Conducting interviews with 20 sample group members and collecting primary data through 2 focus groups when only three months left until submission of your dissertation can be very difficult, if not impossible. Accordingly, timeframe available need to be taken into account when formulating research aims and objectives and selecting research methods.
Moreover, research objectives need to be formulated according to SMART principle,
where the abbreviation stands for specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
Examples of SMART research objectives
At the conclusion part of your research project you will need to reflect on the level of achievement of research aims and objectives. In case your research aims and objectives are not fully achieved by the end of the study, you will need to discuss the reasons. These may include initial inappropriate formulation of research aims and objectives, effects of other variables that were not considered at the beginning of the research or changes in some circumstances during the research process.

John Dudovskiy
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How to Write the Dissertation Aims and Objectives – Guide & Examples
Published by Grace Graffin at January 27th, 2023 , Revised On October 9, 2023
Aims and objectives are among the essential aspects of a dissertation. If you write aims and objectives effectively, they can act as a foundation to give your research clarity and focus.
This article will provide you with all the necessary information regarding aims and objectives, their differences, writing tips , and the common mistakes you should avoid while writing them.
The aim is often a single sentence or a short paragraph that describes your dissertation’s main goal and intent. It tells what you hope to achieve at the end. You should write the aim so that it becomes identifiable when it is achieved with the completion of your dissertation .
The aim is written in a subsection of the introduction to clarify the overall purpose of the dissertation .
Example: It is often observed that employees in culturally diverse workplaces struggle to work effectively in a team. A probable cause of this issue is bullying at the workplace. This research investigates the impact of bullying on employee job satisfaction at culturally diverse workplaces and the resulting loss of employee productivity. This research will use surveys and case study analysis to analyze the impact of bullying on employees.
The objectives in a dissertation describe the ways through which you intend to achieve the research aim. They are specific statements that break down the aim into several smaller key sections of the overall research. Suitable objectives can help you stay focused and conduct research in the direction of your aim.
The number of objectives should be realistic; usually, between three to six, and each one should be possible to achieve. The following example shows the objectives for the previously-mentioned dissertation aim.
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace
The objectives of a dissertation should be SMART.
- Specific: should be precise, focused, and well-defined
- Measurable: the progress should be measurable, and you should be able to determine when you have achieved an objective.
- Achievable: you should be able to carry out the required action within your available resources
- Relevant: should be related to the dissertation aim
- Time-bound: should be possible within the available time
Differences between aims and objectives
Aims and objectives are often mixed, but there are clear differences between them.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

How to write aims and objectives?
There is no particular way or standard to write the aims and objectives. Different researchers have different writing styles, and often it can be influenced by your research supervisor. However, you should follow certain basic principles while writing aims and objectives in a dissertation.
Writing the aim statement
The aim statement should cover the following essential elements.
- Why is the research necessary? (covers the underlying problem on which the study is to be conducted)
- What is the research about? (description of the research title)
- How are you going to conduct it? (a brief statement of intended research methods)
An appropriate aim clearly defines the research purpose without confusing the reader. If you struggle to explain your research and its importance in simpler terms, you should consider refining your research to clarify it further.
Writing objectives
The objectives describe how you would achieve your research aim. You can do this through the following steps,
- The first one to two objectives can be applied to the literature review . (Verbs to be used: investigate, examine, study)
- One objective can be applied to the methodology portion. (Verbs to be used: collect, select, demonstrate, estimate)
- Two to three objectives can cover the critical evaluation or discussion chapters (Verbs to be used: analyze, compare, evaluate)
- The final objective will cover the conclusion or recommendation portion. (Verbs to be used: conclude, recommend)
Instead of writing like a paragraph, the objectives should be written as a numbered list to give them more clarity.
How many aims and objectives should be there?
It depends upon the topic of your research and mainly upon your supervisor’s requirements. Generally, a dissertation has a single broad statement as the research aim. However, it is acceptable to include a main aim along with two to three subsidiary aims.
Similarly, the number of objectives should be realistic and sufficient to measure the progress regarding the achievement of the research aim. Their number can generally vary from three to six depending upon the aim.
Common mistakes to avoid while writing research aims and objectives
- Writing a broad research aim
Writing a broad research aim is a common mistake, and it often becomes difficult to achieve. It may create a problem when you are asked to prove how you have achieved your aims during your viva defense . It would be best to narrow your study to a specific area in the early stages of the dissertation.
- Formulating overlapping research objectives
The objectives should be written such that they are measurable and distinct from each other. If they overlap, it makes it difficult to structure your dissertation properly in specific chapters.
- Setting unrealistic aims
Students often get over-ambitious while describing the research aim and face problems afterward in achieving those aims. You should avoid this mistake and be realistic about what you can achieve in the available time and resources.
Aims and objectives are the sections that require significant time and attention to avoid future hassles while conducting research and writing your dissertation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to set dissertation aims and objectives.
To set dissertation aims and objectives, define your research goals clearly. Aims state what you want to achieve, while objectives outline specific, measurable steps to reach those goals. Ensure they align with your research question and contribute to your study’s significance.
You May Also Like
This article contains information about the dissertation Gantt charts for research, features of Gantt charts, templates of Gantt charts, and their benefits.
What are the key factors influencing language development and what can do to accelerate the process of language acquisition? Here is all you need to know!
UK has many top-ranked universities in the world. Here are all the reasons why you should pursue your MBA degree in the UK.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works

Dissertation Services
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Dissertation Assistance Service
- Dissertation Consulting Service
- Buy Dissertation
- Dissertation Abstract Writing Services
- Dissertation Formatting Service
- Buy Dissertation Methodology
- Dissertation Case Study Service
- Pay For Dissertation
- Dissertation Chapter Writing Services
- Dissertation Conclusion Services
- Dissertation Data Analysis Services
- Dissertation Discussion Writing Services
- Dissertation Introduction Writing Service
- Dissertation Outline Service
- Online Dissertation Help
- Write My Dissertation
- Do My Dissertation
- Help With Thesis Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing England
- Dissertation Writing Service London
- Dissertation Writing Northern Ireland
- Dissertation Writing Scotland
- Dissertation Writing Wales
- Personal Statement Writing Service
Dissertation Subjects
- Marketing Dissertation
- Digital Marketing Dissertation
- Law Dissertation Help
- Economics Dissertation
- Accounting Dissertation
- Business Management Dissertation
- Nursing Dissertation
- Psychology Dissertation
- Social Media Marketing Dissertation
- English Literature Dissertation Help
- Finance Dissertation
- History Dissertation
- HRM Dissertation
- IT Dissertation
- Linguistics Dissertation Help
- Supply Chain Management Dissertation Help
- Health And Social Care Dissertation
Dissertation Levels
- Buy Master Dissertation
- MBA Dissertation Writing Service
- Buy PhD Dissertation
- Masters Dissertation Proposal Help
- MBA Dissertation Proposal Help
- PhD Data Collection Services
- PhD Dissertation Proposal Help
- PhD Qualitative Data Analysis Services
- Master Thesis Help
- PhD Thesis Writing Help
- PhD Dissertation Editing
- Finance Dissertation Editing
- Digital Marketing Dissertation Editing
- Accounting Dissertation Editing
- Sociology Dissertation Editing
- English Literature Dissertation Editing
- Economics Dissertation Editing
- Linguistics Dissertation Editing
- Business Management Dissertation Editing
- Psychology Dissertation Editing
- Marketing Dissertation Editing
- Academic Poster Designing Services
- Dissertation PowerPoint Presentation Service
- Dissertation Presentation Writing Services
- Literature Review Writing Service
- Primary Data Collection Service
- Qualitative Data Dissertation Services
- Research Data Collection Service
- Secondary Data Collection Help
- DISSERTATION SERVICES
- DISSERTATION SUBJECTS
- DISSERTATION LEVELS
- Buy MBA Dissertation
- PhD Dissertation Editing Services
Hire a Writer
Get an expert writer for your academic paper
Check Samples
Take a look at samples for quality assurance
Dissertation Topics
Free customised dissertation topics for your assistance
- Academic Writing Guide: Aims and…
- Accounting Dissertation Topics (8)
- Banking & Finance Dissertation Topics (10)
- Business Management Dissertation Topics (35)
- Economic Dissertation Topics (1)
- Education Dissertation Topics (12)
- Engineering Dissertation Topics (9)
- English Literature Dissertation Topics (3)
- HRM Dissertation Topics (3)
- Law Dissertation Topics (13)
- Marketing Dissertation Topics (9)
- Medical Dissertation Topics (7)
- Nursing Dissertation Topics (10)
- Other Topics (10)
- Supply Chain Dissertation Topics (2)
- Biomedical Science (1)
- Business Management Research Topics (1)
- Computer Science Research Topics (1)
- Criminology Research Topics (1)
- Economics Research Topics (1)
- Google Scholar Research Topics (1)
- HR Research Topics (1)
- Law Research Topics (1)
- Management Research Topics (1)
- Marketing Research Topics (1)
- MBA Research Topics (1)
- Medical Research Topics (1)
- How To (23)
Get a native to improve your language & writing
Enjoy quality dissertation help on any topic
Qualitative & Quantitative data analysis
Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
Date published May 19 2023 by Stella Carter
Do you find it difficult to produce an organized academic paper? Do you have a hard time coming up with worthwhile goals and objectives for your project?
In that case, whether you are a student or researcher who wishes to create a successful set of aims and objectives of education, this blog post is a priceless resource. It can guide you on how to create a strong set of goals and objectives for any project, as well as practical advice and success-boosting strategies.
Table of Contents
How “Dissertation Proposal” Can Help You!
Our top dissertation writing experts are waiting 24/7 to assist you with your university project, from critical literature reviews to a complete masters dissertation.
The Notion of Aims and Objectives
Aims and objectives are the two key elements in academic writing that aid in identifying the goal and area of concentration of a research endeavor. The importance of aims and objectives in research is crucial in describing what a researcher hopes to accomplish and acts as a roadmap for the entire research. Goals refer to the overall purposes and purpose of the research, whereas objectives are specific and measurable targets that a researcher sets out to accomplish in order to meet the broader aims.
The examples of research objectives in a research proposal show that goals and objectives aid in defining the specific research questions that must be answered. For instance, if a study’s goal is to examine how technology is affecting the education industry, one of the goals may be to evaluate how well various systems for learning use technology and the views of educators on using technology in the classroom.
You must go through the examples of research objectives that are pertinent to your research question to keep your research project on track. Moreover, they aid in bringing clarity to the reader and researcher, improving the study’s organization and comprehension.
Tips for Writing Effective Aims and Objectives
The creation of a concise and clear research proposal requires the drafting of effective objectives and aims for academic writing. If you are still confused what is aims and objectives? In fact, they define the purpose of the study, the anticipated results, and the use of methodology which aids in directing the research process.
1. Keep your aims and objectives clear and concise
Maintaining clear, and concise goals and objectives is the first piece of advice that any example of research objectives must contain. The aim of your study should include a statement outlining the general objective of your investigation.
It should be brief and to the point. On the other hand, objectives ought to be precise and measurable. They should outline your goals and your strategy for achieving them. Avoid making generalized or vague statements and speak in plain and easily understandable terms.
2. Align your aims and objectives with your research question
Another tip for writing effective aims and objectives examples is to align them with your research question. Your research question should be the driving force behind your research project, and your aims and objectives should support this question. Consider the research question as the compass that will guide your research project, and use your aims and objectives to keep you on course.
3. Make your aims and objectives realistic
When writing your aims and objectives, it’s important to make them realistic. This means setting goals that you can realistically achieve with the resources you have available such as timeframe, and budget. After all, what is aims and objectives that are not realistic? Setting unrealistic goals will only lead to frustration and disappointment.
4. Ensure your aims and objectives are relevant
Making sure that your goals and objectives are pertinent to your study topic is one of the most crucial pieces of writing advice. They should answer the primary research issue, be supported by prior work in the area, and add to the body of information at hand. You should also think about how your research will affect society and how it will help other people.
5. Review and revise your aims and objectives regularly
Subsequently, it is critical to regularly examine and adjust your goals and objectives. Some valuable aims and objectives examples show how they are modified or refined as your research project develops. Your goals and objectives will stay relevant and practical throughout your study assignment with regular review and revision.
What Are the Aims and Objectives of the Research?
Academic writing always includes research, and each research endeavor needs to have a clear set of goals. The main goal of the research is to collect pertinent data, analyze it, and draw logical conclusions from the results. It involves a methodical and structured strategy that enables researchers to address particular issues, test theories, and investigate novel concepts. Objectives are specific and measurable goals that help researchers achieve their aims.
If you go through the examples of research objectives in a research proposal, you will notice that they provide a clear direction to the research project, outline the research questions, and establish the framework for data collection and analysis. Objectives should be SMART – specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound to ensure that researchers can track progress and make adjustments to the research plan if necessary. Depending on the discipline and the particular research endeavor, the aims and objectives of the research can change.
Some studies may try to test current hypotheses, others aim to establish new ones. Regardless of the research’s nature, it’s critical to establish the aims and objectives of a project upfront. This promotes concentration, reduces interruptions, and guarantees that the investigation stays on course. Setting clear goals and objectives helps researchers to successfully complete their study project and significantly advance their subject.
What Is Research Methodology?
The methodical and logical approach a researcher takes when performing a research study is referred to as research methodology. It is a thorough framework that details the strategies and procedures that a researcher uses to do research.
The objectives of research methodology must be based on sound research techniques to get trustworthy data and develop conclusions that are true to the findings. The type of study project also influences the methods a researcher will choose. A qualitative research study, for example, necessitates a different strategy than a quantitative research effort.
Types of research methodologies:
There are two categories that highlight the separate objectives of research methodology. Primary and secondary. Primary techniques involve the gathering of new data through observations, surveys, and interviews. While secondary methods use the analysis of pre-existing data from sources including government papers, books, and other publications.
However, a strong research methodology should also describe the sample size, sampling strategy, data gathering, and data processing methods. The research design needs to be rigorous enough to remove bias and improve the likelihood of getting accurate results. A good research methodology should be replicable, allowing other researchers to verify the findings.
What Is an Example Of Aims Goals And Objectives?
Aims, goals, and objectives are integral components of academic writing. These elements help to clearly define the purpose of your work and guide the reader through your research or project. Your academic writing can be significantly improved in terms of impact and quality by having a firm grasp of these ideas.
The research aims and objectives examples declare that the main purpose of a research endeavor, for instance, is the aim. While the goal usually has a wide scope and acts as a guide for the entire research process. For instance, investigating the link between physical activity and the risk of heart disease could be the goal of a study on the impact of exercise on cardiovascular health.
Objectives, on the other hand, are more definite and quantifiable than an aim. They offer in-depth explanations of the goals you have for your research. The broad goal is broken down into small, achievable, quantifiable, and doable objectives. For instance, determining the ideal duration, intensity, and frequency of exercise required to promote heart health could be one of the study’s primary aims.
How Do You Write Aims and Objectives for Research?
Writing aims and objectives for research can be a challenging task. However, they are crucial elements of any research project as they define the purpose, scope, and direction of the study. Therefore, crafting clear and concise aims and objectives is essential so that these elements help in providing guidance for both you as the writer and your audience. So, how do you write aims and objectives that effectively communicate your research goals?
To acknowledge this importance of aims and objectives in research, the following steps can be helpful:
- The first step in writing aims and objectives is to identify the research question. This will help to define the scope of the research and what the study aims to achieve.
- The following step is to begin breaking down your general objectives into more specific aims.
- The language used to write aims and objectives should be specific and precise. This will ensure that the objectives are clear and measurable.
- Aims and objectives should be realistic and achievable as one can find in any research aims and objectives examples. This means that they should be based on what is achievable within the resources, timeframe, and budget available for the study.
- Aims and objectives should be relevant to the research question and the research topic. They should align with the research methodology and the research design.
- Aims and objectives should be concise and clear. They should be written in a way that is easy to understand and free of jargon or technical language.
- Once you’ve drafted your aims and objectives, review them carefully to ensure they are clear and concise. You may need to take dissertation abstract help to refine your wording or adjust your objectives based on feedback or further research.
Hence, writing aims and objectives for research requires careful planning and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined above, you can ensure that your aims and objectives are effective and contribute to the success of your research project.
What Is an Example of an Aim?
An aim is the overall purpose of your academic writing or research. It aids in making the purpose and course of your work more clear. For instance, an objective of a study can be to investigate how social media affects mental health.
Moreover, the aim of someone taking research proposal help for an academic essay might be to advocate a specific point of view or to analyze a topic. It is crucial that the goal is clear and doable. This means that you need to be very clear about your goals and how you plan to reach them. You will have a clear grasp of what you want to accomplish if you make sure the goal is measurable and time-bound.
How Do You Write a Good Objective?
A good objective is clear, specific, and achievable. It is critical to write objectives clearly and without unclear terminology for which you can take cheap dissertation help services. In order to track progress, it is crucial to make sure the aim is measurable. When crafting a strong aim, begin by stating the necessary action, then explain what you hope to accomplish through that action. When describing your plans, use verbs that help you to be specific.
The use of non-measurable phrases should be avoided as they could result in ambiguous goals. You can take a law dissertation writing service to see if the objective is pertinent to the main goal of your project or research. Your goal should be in line with the aims and objectives you have established. You can take into account the resources that make sure your goal is reasonable and doable given the limitations of your project and the resources you have at your disposal.
Last but not least, include a deadline in your aim to make sure it is time-bound. In this way, you will be held more responsible and the goal will be closer to being accomplished. You can establish effective objectives that will keep you concentrated on reaching your project’s overall goals if you buy MBA dissertation writing service . Always keep in mind that setting clear, detailed, quantifiable, pertinent, and reasonable goals can help you succeed.
In academic writing, aims and objectives are essential components of research papers, dissertations, and theses. The aims of the research identify the overall purpose of the study, while the objectives provide specific goals and targets.
Effective aims and objectives of education enhance the clarity, focus, and validity of the research, and enable readers to understand the scope and outcomes of the study. By following the tips outlined in this guide, academic writers can craft clear and concise aims and objectives that will add value to their research.
Consult Our Writers to Discuss Your Needs
View different varieties of dissertation topics and samples on multiple subjects for every educational level
Difference between Aim and Objectives of a Research Study
Understanding the difference between aims and objectives in research.
In the field of research, distinguishing between the terms “aim” and “objective” is crucial yet often confusing. Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they represent different aspects of the research process. This comprehensive guide will clarify the difference between aims and objectives, how to use them effectively, and why understanding this distinction is essential for successful research.
What Is the Aim of a Research Study?
The aim of a research study is a broad, overarching statement that defines the general purpose and goal of the research. It addresses the fundamental question of why the study is being conducted and what the researcher hopes to achieve. The aim provides a high-level overview and sets the direction for the entire study. A well-defined aim is crucial as it helps to frame the research questions, guides the research process, and communicates the significance of the study to stakeholders such as funding bodies, academic peers, and the public. It essentially provides the foundation upon which the research is built.
For example, if a researcher is investigating the impact of diet on cardiovascular health, the aim might be: “To explore the effects of dietary habits on the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in adults.”
What Are the Objectives of a Research Study?
Objectives are specific, detailed statements that outline the steps or actions required to achieve the aim of the study. They break down the broad aim into manageable tasks and provide a clear roadmap for conducting the research. Objectives are more detailed and measurable compared to the aim, and they help operationalize the research process.
The key functions of objectives include:
- Clarifying the Research Question: Objectives refine and specify the research question by detailing the exact aspects of the study to be investigated.
- Identifying Key Variables: They help in pinpointing the key variables and factors that need to be measured or analyzed.
- Outlining the Research Methodology : Objectives provide a structured approach to the research methodology, detailing the methods and procedures that will be employed.
- Ensuring Focus and Direction: By breaking down the aim into smaller tasks, objectives help maintain focus and direction throughout the research process.
Objectives are often framed using the SMART criteria:
– Specific: Clear and unambiguous.
– Measurable: Includes criteria to measure progress and success.
– Achievable: Feasible within the given timeframe and resources.
– Relevant: Directly related to the aim of the study.
– Time-bound: Has a defined deadline for completion.
Examples Illustrating the Difference Between Aims and Objectives
To better understand the difference between aims and objectives, consider the following examples:
– aim: to investigate the relationship between physical activity and mental health..
Objectives:
– To review existing literature on the relationship between physical activity and mental health.
– To collect data on physical activity levels and mental health indicators in a sample population.
– To analyze the data to determine the influence of physical activity on mental health .
– To draw conclusions based on the findings and make recommendations for future research or interventions.
In this example, the aim is to explore the broader relationship between physical activity and mental health. https://www.manuscriptedit.com/scholar-hangout/explore-the-social-determinants-of-mental-health/The objectives break down this aim into specific tasks, such as reviewing literature, collecting data, analyzing results, and making recommendations.
– Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness of a new teaching method for improving student performance in mathematics.
– To identify the core components and theoretical basis of the new teaching method.
– To implement the teaching method in selected classrooms.
– To collect and analyze data on student performance before and after the implementation.
– To evaluate the effectiveness of the teaching method based on the performance data.
– To provide recommendations for optimizing the teaching method and its implementation.
Here, the aim is to assess the effectiveness of a new teaching method. The objectives detail the steps required to evaluate this effectiveness , including identifying components, implementing the method, collecting data, analyzing results, and making recommendations.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters?
Recognizing the difference between aims and objectives is important for several reasons:.
- Clarity: A clear distinction helps in formulating precise research questions and hypotheses, ensuring that the research is well-structured and focused.
- Planning: Well-defined aims and objectives aid in planning the research methodology and resources, allowing for efficient allocation of time and resources.
- Communication: Clearly defined aims and objectives facilitate better communication of the research purpose and scope to stakeholders, including reviewers, funders, and collaborators.
- Evaluation: Objectives provide measurable targets that can be used to assess the progress and success of the research, aiding in evaluating the research process and outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, while the aim of a research study represents the broad goal or purpose, objectives are specific statements that outline the steps necessary to achieve that aim. Understanding the difference between aims and objectives helps in creating a clear and structured research plan, ensuring that the study remains focused and aligned with its overall purpose. By clearly defining both aims and objectives, researchers can enhance the clarity, effectiveness, and impact of their research .
For more insights and resources on research and academic writing , visit our website [ManuscriptEdit](https://www.manuscriptedit.com). If you have any queries or need assistance, feel free to contact us at [email protected].
References: “Thesis Writing.” Google Books , books.google.co.in/books?
Hirsch, E. D. “Objective Interpretation.” PMLA/Publications of the Modern Language Association of America , vol. 75, no. 4-Part1, Sept. 1960, pp. 463–79. https://doi.org/10.2307/460609 .
Elevate Your Research to Global Recognition with Manuscriptedit
Are you a dedicated doctor, PhD, or postdoc seeking to showcase your groundbreaking research in prestigious global journals? At Manuscriptedit, we specialize in transforming your research into impactful publications. Our expert services are designed to help you navigate the complexities of academic publishing and achieve recognition in top-tier journals worldwide.
Why Choose Manuscriptedit?
- Expert Guidance : Our team of seasoned professionals understands the intricacies of the publication process. From manuscript preparation to submission, we provide comprehensive support to ensure your research meets the highest standards.
- Global Reach : We have established connections with leading journals across various disciplines. Our expertise ensures your research is presented to the right audience and increases its chances of acceptance in reputed international journals.
- Tailored Services : Whether you need assistance with editing, formatting, or navigating submission guidelines, our services are customized to fit your specific needs. We handle all aspects of the publication process, allowing you to focus on your research.
- Proven Success : Our track record speaks for itself. We have successfully assisted numerous doctors, PhDs, and postdocs in publishing their research in high-impact journals, enhancing their academic and professional standing.
Our Services Include:
- Manuscript Editing : We provide detailed editing services to improve the clarity, structure, and quality of your research paper, ensuring it meets the rigorous standards of top journals.
- Formatting and Compliance : Our team ensures your manuscript adheres to the specific formatting and submission guidelines of your target journals, reducing the risk of rejection due to technical issues.
- Submission Assistance : We guide you through the submission process, including the preparation of cover letters and response to reviewer comments, to enhance your chances of successful publication.
- Personalized Support : Our dedicated consultants offer personalized support throughout the entire publication journey, from initial consultation to post-submission follow-up.
Take the Next Step in Your Academic Career register now For Free Consultation: REGISTER NOW
Publishing in renowned journals can significantly boost your academic profile and open doors to new opportunities. With Manuscriptedit, you gain a trusted partner in achieving your publication goals.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Follow Us On:

Our Services
English Editing Publication Support Writing & Rewriting Research Support Customized Services
KYOTO, JAPAN
Global Marketing Association Co. Ltd, 8th Floor, ASTEM Bldg. Kyoto Research Park, 134 Chudoji Minamimachi, Shimogyo-ku, Kyoto-city, KYOTO - 600883, JAPAN [email protected] www.manuscriptedit.jp
NC, DURHAM, USA
2530 Meridian Parkway, Suite 300, Durham, NC, 27713, United States of America
MAIDSTONE, UK
26 Kings Hill Avenue, Kings Hill, West Malling, Maidstone, ME19 4AE
BHUBANESWAR, INDIA
DCB-401,4th Floor,DLF Cyber City, Chandaka Industrial Estate,Patia, Bhubaneswar-751024, Odisha, INDIA
BANGALORE, INDIA
Level 9 Raheja Towers, 26-27 Mahatma Gandhi Road, Bangalore-560 001, INDIA
© 2024 ManuscriptEdit. All Rights Reserved.
Refund & Cancellation / Privacy Policy / Terms &--> / Service agreement
Refund & Cancellation / Privacy Policy / Terms & Conditions / Author Service agreement / Editor Service agreement
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between research aims and objectives.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Chat with us
- Email [email protected]
- Call +44 (0)20 3917 4242
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our support team is here to help you daily via chat, WhatsApp, email, or phone between 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. CET.
Our APA experts default to APA 7 for editing and formatting. For the Citation Editing Service you are able to choose between APA 6 and 7.
Yes, if your document is longer than 20,000 words, you will get a sample of approximately 2,000 words. This sample edit gives you a first impression of the editor’s editing style and a chance to ask questions and give feedback.
How does the sample edit work?
You will receive the sample edit within 24 hours after placing your order. You then have 24 hours to let us know if you’re happy with the sample or if there’s something you would like the editor to do differently.
Read more about how the sample edit works
Yes, you can upload your document in sections.
We try our best to ensure that the same editor checks all the different sections of your document. When you upload a new file, our system recognizes you as a returning customer, and we immediately contact the editor who helped you before.
However, we cannot guarantee that the same editor will be available. Your chances are higher if
- You send us your text as soon as possible and
- You can be flexible about the deadline.
Please note that the shorter your deadline is, the lower the chance that your previous editor is not available.
If your previous editor isn’t available, then we will inform you immediately and look for another qualified editor. Fear not! Every Scribbr editor follows the Scribbr Improvement Model and will deliver high-quality work.
Yes, our editors also work during the weekends and holidays.
Because we have many editors available, we can check your document 24 hours per day and 7 days per week, all year round.
If you choose a 72 hour deadline and upload your document on a Thursday evening, you’ll have your thesis back by Sunday evening!
Yes! Our editors are all native speakers, and they have lots of experience editing texts written by ESL students. They will make sure your grammar is perfect and point out any sentences that are difficult to understand. They’ll also notice your most common mistakes, and give you personal feedback to improve your writing in English.
Every Scribbr order comes with our award-winning Proofreading & Editing service , which combines two important stages of the revision process.
For a more comprehensive edit, you can add a Structure Check or Clarity Check to your order. With these building blocks, you can customize the kind of feedback you receive.
You might be familiar with a different set of editing terms. To help you understand what you can expect at Scribbr, we created this table:
View an example
When you place an order, you can specify your field of study and we’ll match you with an editor who has familiarity with this area.
However, our editors are language specialists, not academic experts in your field. Your editor’s job is not to comment on the content of your dissertation, but to improve your language and help you express your ideas as clearly and fluently as possible.
This means that your editor will understand your text well enough to give feedback on its clarity, logic and structure, but not on the accuracy or originality of its content.
Good academic writing should be understandable to a non-expert reader, and we believe that academic editing is a discipline in itself. The research, ideas and arguments are all yours – we’re here to make sure they shine!
After your document has been edited, you will receive an email with a link to download the document.
The editor has made changes to your document using ‘Track Changes’ in Word. This means that you only have to accept or ignore the changes that are made in the text one by one.
It is also possible to accept all changes at once. However, we strongly advise you not to do so for the following reasons:
- You can learn a lot by looking at the mistakes you made.
- The editors don’t only change the text – they also place comments when sentences or sometimes even entire paragraphs are unclear. You should read through these comments and take into account your editor’s tips and suggestions.
- With a final read-through, you can make sure you’re 100% happy with your text before you submit!
You choose the turnaround time when ordering. We can return your dissertation within 24 hours , 3 days or 1 week . These timescales include weekends and holidays. As soon as you’ve paid, the deadline is set, and we guarantee to meet it! We’ll notify you by text and email when your editor has completed the job.
Very large orders might not be possible to complete in 24 hours. On average, our editors can complete around 13,000 words in a day while maintaining our high quality standards. If your order is longer than this and urgent, contact us to discuss possibilities.
Always leave yourself enough time to check through the document and accept the changes before your submission deadline.
Scribbr is specialised in editing study related documents. We check:
- Graduation projects
- Dissertations
- Admissions essays
- College essays
- Application essays
- Personal statements
- Process reports
- Reflections
- Internship reports
- Academic papers
- Research proposals
- Prospectuses
Calculate the costs
The fastest turnaround time is 24 hours.
You can upload your document at any time and choose between four deadlines:
At Scribbr, we promise to make every customer 100% happy with the service we offer. Our philosophy: Your complaint is always justified – no denial, no doubts.
Our customer support team is here to find the solution that helps you the most, whether that’s a free new edit or a refund for the service.
Yes, in the order process you can indicate your preference for American, British, or Australian English .
If you don’t choose one, your editor will follow the style of English you currently use. If your editor has any questions about this, we will contact you.

Affiliate 💸
Get started free
Research Project Guide
6 Tips On How To Start A Research Project Successfully
Discover practical tips on how to start research project successfully and set yourself up for success from the very beginning!
Oct 21, 2024

Starting a research project can feel like standing at the base of a mountain, unsure where to begin the climb. Whether dealing with a tight deadline or aiming for efficiency, knowing how to start a research project is crucial. This guide will provide practical insights to help you conduct fast research and write efficiently to tackle your project confidently and quickly. One innovative tool to help you achieve these goals is Otio's AI research and writing partner, designed to streamline the research process and enhance your writing efficiency.
Table Of Contents
What is a research project, 9 best tools for research projects, tips for starting an independent research project, supercharge your researching ability with otio — try otio for free today.

A research project is a structured exploration to answer specific questions or achieve particular objectives. Picture it as a well-organized journey, with clear steps that guide you from start to finish. You’ll begin with a literature review to understand what’s already known. Then, you’ll design your study, gather and analyze data, and report your findings. These projects are crucial in addressing problems, forming hypotheses, and creating strategies based on available resources like staff and funding.
The research must include a defined problem, a solid theoretical foundation, and a data collection and analysis process, regardless of the scientific field. According to UNESCO , there are roughly 7.8 million researchers worldwide, and scientific publications have surged by 23% since 2008.
Related Reading
• How to Find Academic Sources • How to Analyze Quantitative Data • How to Start a Research Project • How to Organize a Research Paper • Argumentative Essay Topics • Research Methodology Types • How Long Does It Take to Write a Research Paper • How to Create a Research Question • Can Ai Write a Paper for Me • Methods Section of Research Paper

1. Streamline Your Research with Otio
Research today is a minefield of distractions. Content overload leaves you juggling bookmarks, notes, and read-it-later apps. Otio creates a streamlined workspace where you can gather everything from tweets to YouTube videos in one place. Its AI-generated notes transform your resources into usable information, and its chat-like interface lets you interact with your sources intuitively. Give Otio a shot and see how it speeds up your research process .
2. Finding the Right Supervisor
A good supervisor is your guide through the research process. They'll help you design your study, choose the proper methods, and interpret your data. Talk to faculty members, trusted professors, or colleagues to find your match. Once you have a list of potential advisors, email an introductory email and request a meeting.
3. Refining Your Research Topic
Once you've found a supervisor, they can help narrow down the topic. The more specific your focus, the better you can direct your research and dig deep into your subject matter. A refined topic will also save you time by keeping your scope manageable and ensuring that you're concentrating on the most relevant aspects.
4. Crafting a Strong Thesis
Your thesis is the backbone of your project, providing direction and focus. It allows you to collect and organize information more efficiently and guides your readers through your argument. A clear and concise thesis statement is essential for helping your audience understand your project's purpose.
5. Developing a Research Timeline
Creating a timeline helps you structure your project and stay on track. It ensures you're organized and accounted for every step, from research to writing to editing. A timeline can also keep you motivated and prevent you from getting sidetracked.
6. Organizing Your Research with an Outline
Outlines provide structure and clarity, allowing you to organize your thoughts logically. They serve as a roadmap for your research, keeping you focused on the critical points and helping you identify gaps in your research before you start writing.
1. Otio: Streamline Your Research Workflow
Otio provides a unified AI -powered workspace for researchers, allowing them to manage the overwhelming influx of data from bookmarks, tweets, and videos. It enables users to extract key insights and produce draft outputs swiftly .
2. Zotero: Your Research Assistant
Zotero is a tool designed to simplify research by allowing users to efficiently collect, organize, annotate, and share data. It integrates smoothly with browsers, allowing users to save articles and publications conveniently.
Pros
User-friendly interface
The free version includes all features and updates
Plugin support for popular word processors
Cons
Limited free cloud storage
No official Android app is available
3. EndNote: Automate Your Citation Process
EndNote streamlines the referencing process by automatically formatting citations and creating a bibliography as you write. It’s a cloud-based tool that enables collaboration and smooth work across devices.
Compatible with library databases
Supports various citation styles
Efficiently imports multiple references
Primarily desktop-focused with limited online features
4. elink.io: Simplify Content Curation
elink.io is a bookmarking and curation tool that helps researchers save and organize web content effortlessly. It allows users to compile and share their collections with others, enhancing collaboration.
Easy to use with quick deployment
Eye-catching graphics and custom uploads
Smooth integration with SurveyMonkey
Customer service issues reported
Inconsistent pricing
5. Grammarly: Enhance Your Writing Quality
Grammarly is an AI-powered typing assistant that identifies spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors and suggests replacements. It’s a free basic version with a premium upgrade for more advanced features.
Advanced features for fluency and consistency
User-friendly interface
Non-intrusive writing experience
Inconsistent accuracy in context-dependent cases
May unnecessarily lengthen sentences
6. Asana: Manage Your Research Projects
Asana is a task management platform that connects development, copywriting, design, research teams, and product managers. It offers many features, including time tracking and Jira integration.
Time-tracking capabilities
Securely stores information about projects
User-friendly dashboard for task management
Overwhelming for small teams or simple projects
No built-in time-tracking
7. SurveyMonkey: Create Surveys with Ease
SurveyMonkey is a leading online survey tool with millions of users. It offers hundreds of templates for researchers to set up and deploy surveys for various purposes quickly.
Easy survey creation and multimedia integration
Valuable reporting toolkit
Excellent customer service
Too many features for some users
Limited user access options
8. ProofHub: Stay Organized and Focused
ProofHub is an all-in-one project and team management application that helps research teams efficiently plan their projects. It offers features like Kanban boards, Gantt charts, and time-tracking.
Affordable for large teams
Customizable project reports
Mobile apps for iOS and Android
Limited support
Costly for individuals and new teams
9. RefnWrite: Improve Your Academic Writing

RefnWrite is a tool that helps researchers improve their academic writing with a library of phrases and templates. It uses AI to suggest phrases, cross-reference previous work, and more.
Comprehensive phrase bank and templates
Powerful paraphrasing tool
Smooth integration with Microsoft Word
The learning curve for advanced features
Limited free trial

1. Spotting the Knowledge Gap: Your Starting Line
Kick off your independent research by spotting a gap in existing knowledge. This is an underexplored area ripe for discoveries. While some might immediately see this gap, others could need to dig deeper. A thorough literature review on your topic of interest can help. Many academic papers have insights into unanswered questions in their discussion or conclusion sections, making them an excellent resource for formulating your research question. Plus, this process can help you think about methodologies to use.
2. Securing a Mentor: Your Research Sidekick
Sure, you’re going for independence in your research, but mentors are assets, not obstacles. Even if you know a lot about your topic, you’re still in learning mode. Having an expert guide you through feedback and advice can be a game-changer and might even be necessary for progress. Once you have a research question, collaborate with faculty or professionals open to supporting you. For example, in a project I did on fentanyl overdose deaths, I needed access to autopsy reports. I got the needed resources by proposing my idea to a local forensic pathologist and gaining her mentorship.
3. Shaping Your Project: Setting Goals and Plans
With your research question ready, setting your project’s goals is time. Are you aiming for publication? Developing a product? Winning a competition? With these goals in mind, outline your objectives, methods, and timeline. Check out programs that support research projects, like the Holster Scholar Program and the UConn IDEA Grant. While exploring options, be realistic about the time and resources your project will need.
4. Making the Move: Get Going!
Independent research projects allow you to explore your passions and build essential skills. While the journey can be arduous, the knowledge and skills you gain are priceless. Enjoy the ride.
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner. Try Otio for free today !
• Data Collection Tools • Title Page for Research Paper • How to Cite a Research Paper • Research Paper Abstract Example • How to Write Results in a Research Paper • How to Write a Psychology Research Paper • Best AI for Data Analysis • How to Write a Discussion in a Research Paper • Research Questions Examples • Best AI for Writing Research Papers • Ai Visualization Tools
Today, researchers and students face a storm of information. Too many settle for complex bookmarking and note-taking apps to manage their workflow, but this is not sustainable. As content creation becomes more accessible, the overload will only increase. What’s the solution? Otio offers a single AI -native workspace covering all research stages—from collecting diverse data sources to producing first drafts. Think about it: why scatter your efforts when one app can guide you through your entire research process?
A Researcher’s Best Friend: Collecting and Organizing Data
Otio is your research partner , helping you gather everything from tweets and books to videos. You don’t have to skip between different platforms, losing precious time. Otio lets you bring it all together in one place. Consider having a treasure trove of information, all neatly organized and ready to explore. This means less time hunting for data and more time connecting ideas.
Decoding the Noise: Extracting Key Takeaways
Once you have your data, you need to make sense of it. Otio uses AI to generate detailed notes on your bookmarks. Whether a YouTube video or an academic article, the platform highlights the most critical points. You can chat with your sources or entire knowledge bases, just like ChatGPT. This means you can ask questions and get answers fast. You won’t have to sift through endless content pages to find what you need.
From Reading List to Research Draft: Creating with Confidence
One of Otio’s most loved features is its ability to help you draft your work. Once you’ve collected and understood your data, the platform assists you in writing your research paper or essay. You can go from a reading list to a rough draft quickly, allowing you to focus on refining your ideas . This means you can spend less time struggling with writer’s block and more time producing meaningful work.
• Note-taking AI for Students • Zotero vs Mendeley • Logseq vs Obsidian • Milanote vs Notion • Obsidian vs Evernote • Claude AI Alternative • Milanote vs Miro • Best Chat Gpt Alternatives • Writesonic vs Jasper

Oct 23, 2024
How To Analyze Quantitative Data In 9 Simple Steps

Oct 22, 2024
How To Find Academic Sources In 4 Simple Ways
Join over 80,000 researchers changing the way they read & write

Chrome Extension
© 2024 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Join over 50,000 researchers changing the way they read & write
Join thousands of other scholars and researchers
Try Otio Free
© 2023 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Sprint for Women's Health awards aim to close gaps in women's health research
Published October 23, 2024
Biden-Harris Administration announces ARPA-H's Sprint for Women’s Health awards aimed at closing gaps in women’s health research
$110 million awarded will accelerate next generation of discoveries and create a portfolio of investments
The Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health ( ARPA-H ), an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), today announced the teams selected by its Sprint for Women’s Health to receive awards. The agency committed over $110 million to fund solutions for health conditions that uniquely or disproportionately affect women. This effort will advance the White House Initiative on Women’s Health Research and help spur the type of innovation and private sector engagement long needed to improve women’s health.
“In order to improve women’s health, we need to pursue and invest in research focused on advancements for women. This is especially true where we know far too little about how to prevent and treat a range of conditions that affect women across their lifespan,” said HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra. “The Biden-Harris Administration continues to change how health research is pursued and utilized. The groups being recognized today have picked up that challenge and are doing work that is groundbreaking and lifesaving.”
The 23 awardees range from small start-ups to global innovators and were selected based on their high-impact and novel approaches to the Sprint’s six topics . Awardees are tackling cancer, ovarian health, gynecological and endometriosis care, obstetrics, menopause, lymphatics, pain management, and neurological and cardiovascular conditions. Solutions to these health challenges include biomarker research, diagnostics, therapeutics, devices, and digital health.
“Less than 10 months ago we first launched the Sprint for Women’s Health and asked for bold and transformative women's health solutions. Now with these awardees, we are sprinting towards changing the lives of millions of women who have been left behind in research for far too long,” said ARPA-H Director Renee Wegrzyn, Ph.D . “We're pursuing not just great science, but a different way of doing business in the government. Integral to the Sprint is to catalyze and transform the market for women's health.”
Of the 23 awardees, 30% have never received government funding, 39% have fewer than 50 employees, and over 70% are led by women. Awards represent early-stage research (spark*) and later-stage development (launchpad**). If successful, launchpad efforts will move to commercialization in two years after funding, bringing health solutions directly to women in record time.
ARPA-H saw tremendous interest in the Sprint for Women’s Health, with over 1700 submissions, representing 45 states, the District of Columbia, and 34 countries. Collectively, these applicants represent more than a billion dollars of novel ideas, approaches, solutions, and discoveries in women’s health. The ARPA-H Sprint for Women’s Health is conducted in collaboration with the Investor Catalyst Hub of ARPANET-H , the agency’s nationwide health innovation network that connects people, innovators, and institutions to accelerate better health outcomes for everyone.
Awardees include:
- Aalto University School of Science* in Espoo, Finland, aims to develop a home-based labor management device that tracks maternal and fetal health data remotely, helping expectant mothers plan for delivery.
- Ancilia Biosciences Inc* in New York, aims to overcome treatment-resistant bacterial vaginosis and enable new therapies for vaginal health.
- Aspira Women’s Health Inc** based in Shelton, Conn. aims to create a first-of-a-kind non-invasive endometriosis blood test.
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Inc.** in Boston aims to develop a non-invasive imaging biomarker to evaluate brain disorders in women.
- California Institute of Technology* in Pasadena, Calif., aims to develop a novel, affordable wearable sweat sensing system to measure and map chronic pain.
- Celmatix Inc* based in New York, aims to develop a therapeutic to extend healthy ovarian function and lifespan.
- Children’s Research Institute** in Washington, D.C., aims to develop an accessible real-time assessment of chronic pain based on a woman’s eyes response to light.
- Daré Bioscience, Inc.** based in San Diego, Calif., aims to develop a first-of-a-kind early at-home HPV treatment.
- Gameto Inc** based in Austin, Texas aims to construct a novel ovarian therapy to prevent disease in menopause.
- GE Medical Systems Information Technologies, Inc.* in Niskayuna, N.Y., aims to develop a non-invasive MRI highlighting immune surveillance, brain health, and more.
- General Proximity* in San Francisco aims to create a therapeutic to an undruggable target, which may be able to target multiple cancers in women.
- Glaucus, Inc.* based in Brooklyn, N.Y., aims to develop a fast and affordable at-home sexually transmitted infections/urinary tract infections test.
- Gravidas Diagnostics, Inc* based in Los Angeles, aims to create a first-of-a-kind home-based, low-cost, fingerstick test for early detection of preeclampsia.
- Massachusetts General Hospital* in Boston, Mass., aims to develop a non-invasive wearable headband for at-home use to detect precursors of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Monash University* in Victoria, Australia, aims to develop portable, non-invasive, less-time dependent, and cost-effective approaches for treating ischemic stroke.
- Nura Health Inc* based in Los Angeles, aims to develop a personalized diagnostic and treatment platform for endometriosis.
- The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc.* in Cambridge, Mass., aims to build a model that assesses medication safety in pregnancy without putting women or babies at risk.
- The University of Iowa** in Iowa City aims to develop an ovarian cancer treatment using personalized nanoparticles and a woman’s own immune system.
- The Washington University* in St. Louis aims to develop a blood test that decodes pain and tracks symptoms to create treatments for conditions like endometriosis.
- Tufts University* in Medford, Mass., aims to develop non-invasive wearable sensors to measure biomarkers in interstitial fluid related to pain.
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill* aims to treat migraines by targeting the lymphatic system and unique female biology that increases migraine susceptibility.
- Vanderbilt University Medical Center* in Nashville, Tenn., aims to develop an at-home medication to mitigate the health risks of preterm labor.
- Wyss Institute* in Cambridge, Mass., aims to develop an implantable lymphoid organ as a cancer therapy to treat late-stage and metastasized ovarian cancer.
For more information about the awardees, visit the Sprint for Women’s Health page .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved. Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific. Research aims focus on a project's long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
This step in your research journey is usually the first written method used to convey your research idea to your tutor. Therefore, aims and objectives should clearly convey your topic, academic foundation, and research design. In order to write effective research aims and objectives, researchers should consider all aspects of their proposed work.
A research aim typically refers to a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Your research objectives are more specific than your research aim and indicate the particular focus and approach of your project.
Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve. These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected by the researcher to present a clear intention or course of action for his or her qualitative or ...
Research aims and objectives are the foundation of any research project. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, ensuring that you stay focused and on track throughout the process. They are your trusted navigational tools, leading you to success. Understanding the relationship between research objectives and aims is crucial to ...
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope (the delimitations) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can "go deep" and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity.
Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an ...
Formulating research aim and objectives in an appropriate manner is one of the most important aspects of your thesis. This is because research aim and objectives determine the scope, depth and the overall direction of the research. Research question is the central question of the study that has to be answered on the basis of research findings.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.
Summary. The importance of research aims and objectives cannot be over-stressed. It is vital to have a very clear understanding of what the research is about and what you are actually trying to achieve. You need to know this. And you need to be able to communicate it to others. Carrying out a research project is rather like going on a journey.
Research Objectives. Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research.The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying. 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace. 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees. 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace.
Aim: To understand the contribution that local governments make to national level energy policy. Objectives: Conduct a survey of local politicians to solicit responses. Conduct desk-research of local government websites to create a database of local energy policy.
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
Consider the research question as the compass that will guide your research project, and use your aims and objectives to keep you on course. 3. Make your aims and objectives realistic ... The research aims and objectives examples declare that the main purpose of a research endeavor, for instance, is the aim. While the goal usually has a wide ...
Developing research aims and objectives. 39. Research objectives. A research aim will usually be followed by a series of statements describing a project's
Conclusion. In summary, while the aim of a research study represents the broad goal or purpose, objectives are specific statements that outline the steps necessary to achieve that aim. Understanding the difference between aims and objectives helps in creating a clear and structured research plan, ensuring that the study remains focused and ...
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.
Check out programs that support research projects, like the Holster Scholar Program and the UConn IDEA Grant. While exploring options, be realistic about the time and resources your project will need. 4. Making the Move: Get Going! Independent research projects allow you to explore your passions and build essential skills.
The Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health , an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), today announced the teams selected by its Sprint for Women's Health to receive awards. The agency committed over $110 million to fund solutions for health conditions that uniquely or disproportionately affect women.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.