- Our Mission

Helping Students Hone Their Critical Thinking Skills
Used consistently, these strategies can help middle and high school teachers guide students to improve much-needed skills.

Critical thinking skills are important in every discipline, at and beyond school. From managing money to choosing which candidates to vote for in elections to making difficult career choices, students need to be prepared to take in, synthesize, and act on new information in a world that is constantly changing.
While critical thinking might seem like an abstract idea that is tough to directly instruct, there are many engaging ways to help students strengthen these skills through active learning.
Make Time for Metacognitive Reflection
Create space for students to both reflect on their ideas and discuss the power of doing so. Show students how they can push back on their own thinking to analyze and question their assumptions. Students might ask themselves, “Why is this the best answer? What information supports my answer? What might someone with a counterargument say?”
Through this reflection, students and teachers (who can model reflecting on their own thinking) gain deeper understandings of their ideas and do a better job articulating their beliefs. In a world that is go-go-go, it is important to help students understand that it is OK to take a breath and think about their ideas before putting them out into the world. And taking time for reflection helps us more thoughtfully consider others’ ideas, too.
Teach Reasoning Skills
Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
One way to teach reasoning is to use problem-solving activities that require students to apply their skills to practical contexts. For example, give students a real problem to solve, and ask them to use reasoning skills to develop a solution. They can then present their solution and defend their reasoning to the class and engage in discussion about whether and how their thinking changed when listening to peers’ perspectives.
A great example I have seen involved students identifying an underutilized part of their school and creating a presentation about one way to redesign it. This project allowed students to feel a sense of connection to the problem and come up with creative solutions that could help others at school. For more examples, you might visit PBS’s Design Squad , a resource that brings to life real-world problem-solving.
Ask Open-Ended Questions
Moving beyond the repetition of facts, critical thinking requires students to take positions and explain their beliefs through research, evidence, and explanations of credibility.
When we pose open-ended questions, we create space for classroom discourse inclusive of diverse, perhaps opposing, ideas—grounds for rich exchanges that support deep thinking and analysis.
For example, “How would you approach the problem?” and “Where might you look to find resources to address this issue?” are two open-ended questions that position students to think less about the “right” answer and more about the variety of solutions that might already exist.
Journaling, whether digitally or physically in a notebook, is another great way to have students answer these open-ended prompts—giving them time to think and organize their thoughts before contributing to a conversation, which can ensure that more voices are heard.
Once students process in their journal, small group or whole class conversations help bring their ideas to life. Discovering similarities between answers helps reveal to students that they are not alone, which can encourage future participation in constructive civil discourse.
Teach Information Literacy
Education has moved far past the idea of “Be careful of what is on Wikipedia, because it might not be true.” With AI innovations making their way into classrooms, teachers know that informed readers must question everything.
Understanding what is and is not a reliable source and knowing how to vet information are important skills for students to build and utilize when making informed decisions. You might start by introducing the idea of bias: Articles, ads, memes, videos, and every other form of media can push an agenda that students may not see on the surface. Discuss credibility, subjectivity, and objectivity, and look at examples and nonexamples of trusted information to prepare students to be well-informed members of a democracy.
One of my favorite lessons is about the Pacific Northwest tree octopus . This project asks students to explore what appears to be a very real website that provides information on this supposedly endangered animal. It is a wonderful, albeit over-the-top, example of how something might look official even when untrue, revealing that we need critical thinking to break down “facts” and determine the validity of the information we consume.
A fun extension is to have students come up with their own website or newsletter about something going on in school that is untrue. Perhaps a change in dress code that requires everyone to wear their clothes inside out or a change to the lunch menu that will require students to eat brussels sprouts every day.
Giving students the ability to create their own falsified information can help them better identify it in other contexts. Understanding that information can be “too good to be true” can help them identify future falsehoods.
Provide Diverse Perspectives
Consider how to keep the classroom from becoming an echo chamber. If students come from the same community, they may have similar perspectives. And those who have differing perspectives may not feel comfortable sharing them in the face of an opposing majority.
To support varying viewpoints, bring diverse voices into the classroom as much as possible, especially when discussing current events. Use primary sources: videos from YouTube, essays and articles written by people who experienced current events firsthand, documentaries that dive deeply into topics that require some nuance, and any other resources that provide a varied look at topics.
I like to use the Smithsonian “OurStory” page , which shares a wide variety of stories from people in the United States. The page on Japanese American internment camps is very powerful because of its first-person perspectives.
Practice Makes Perfect
To make the above strategies and thinking routines a consistent part of your classroom, spread them out—and build upon them—over the course of the school year. You might challenge students with information and/or examples that require them to use their critical thinking skills; work these skills explicitly into lessons, projects, rubrics, and self-assessments; or have students practice identifying misinformation or unsupported arguments.
Critical thinking is not learned in isolation. It needs to be explored in English language arts, social studies, science, physical education, math. Every discipline requires students to take a careful look at something and find the best solution. Often, these skills are taken for granted, viewed as a by-product of a good education, but true critical thinking doesn’t just happen. It requires consistency and commitment.
In a moment when information and misinformation abound, and students must parse reams of information, it is imperative that we support and model critical thinking in the classroom to support the development of well-informed citizens.
- Health Science
- Business Education
- Computer Applications
- Career Readiness
- Teaching Strategies
« View All Posts
Career Readiness | Middle School | Critical Thinking
Problem Solving Lesson Plans Your Middle School Students Will Love
- Share This Article
July 11th, 2022 | 5 min. read

Print/Save as PDF
Need resources for teaching problem solving in your middle school career readiness classes?
As a career readiness curriculum developer, middle school teachers often ask if we have resources to help teach problem solving.
While our digital curriculum includes content on critical thinking, decision making, and other 21st Century skills, our solution may not be the best fit for everyone.
Our Middle School Digital Literacy & Career Exploration curriculum is designed to teach dozens of skills such as professionalism, communication, digital literacy, and more.
However, some teachers are only looking for supplemental problem solving lessons and activities to add to their existing curriculum.
To help you teach these skills, we've found four popular providers of problem solving lessons and activities for middle school:
- TeacherVision
- Ed Creative
All of these resources have both pros and cons, so looking at each one individually is key when planning your problem solving lessons!
1. TeacherVision's Problem Solving Lesson
TeacherVision is a digital resource that offers free online lesson plans, including a problem solving lesson.
This problem solving lesson has two key objectives:
- Students will be introduced to a problem-solving procedure
- Students will participate in a structured practice of resolving conflict
Along with the lesson objectives, you'll find the materials list and the procedure for completing the lesson.
That makes TeacherVision a robust resource with an easy-to-follow lesson plan for introducing students to problem solving .
On the downside, the lesson is listed as appropriate for students between first and eighth grade.
That means you may want to bulk it up a bit in order to really be relevant and engaging to your middle school students .
2. Ed Creative's Problem Solving and Critical Thinking Lesson Plans
Ed Creative is a subdivision of Education.com that collects lesson plans from other online resources.
That makes Ed Creative one of the best lesson plan databases online.
It includes a variety of lesson plans and activities to teach creativity, problem solving, and critical thinking skills.
Many of these lessons are intended for children up to eighth grade. That means you'll likely find resources that fit perfectly in your middle school classes.
In addition, some lessons overlap with other subjects you may need to teach in your career readiness classes . For example, one resource is entitled Thinking Critically About Advertising and would tie in well with lessons on media literacy .
The lesson encourages students to consider behind-the-scenes angles when presented with ads, encouraging them to think critically and logically about why the ad is what it is.
Still, these resources are a little disorganized which means it will take you time to review each option and decide if it's a good fit.
3. BrainPOP's Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Activities
BrainPOP is an educational resource provider with many teaching resources for every grade level.
In this case, their critical thinking and problem solving lesson plan is intended for any sixth to 12th grade student.
In this lesson, students will:
- Apply critical thinking, problem solving, and decision-making skills to online gameplay and writing tasks
- Analyze situations from multiple perspectives and viewpoints
- Distinguish between facts, opinions, and solutions
- Demonstrate 21st Century skills such as global awareness, information literacy, communication, and collaboration
BrainPOP lays out the procedure, materials, and everything else you’ll need for the lesson — even time approximations!
That thorough approach to detail makes it easier to plan different tasks you’ll carry out throughout the lesson each day.
Even if the lesson takes a full week, you can still plan appropriately and stay on task.
Unfortunately, BrainPOP doesn’t have many downloadable resources you can print and use in the classroom.
4. TEDEd's Resources for Teaching Problem Solving Skills
TEDEd is an active advocate of education and learning materials. That’s why they have an enormous section of their website dedicated to problem solving skills .
In this section, you’ll find videos and interactive tasks that walk students through riddles, problems, and complications to find desirable results.
Every riddle and problem has an answer, so you don’t have to worry about figuring it out yourself. Even better, you can be sure there’s a practical solution to every issue.
Best of all, you leave students with the freedom to innovate their own solutions, potentially creating a new solution that a riddle maker hadn’t considered.
The varying complexity and length of these lessons make them ideal for various grade levels. However, you can choose to filter specifically for middle school.
On the downside, these aren’t literal “lesson plans.” TEDEd provides many resources, but they’re not contextualized for a classroom.
Instead, you’ll have to build your lessons around these resources to get the best results.
This makes TEDEd an excellent catchall whenever you need problem solving materials.
You’ll just have to do a little extra work to make it classroom ready.
Which Problem Solving Lessons Are Best?
Overall, there isn't a simple "best" option for teaching problem solving in middle school. It all depends on the needs of you, your course, and your students.
Each resource we've shared could be a great addition to your career readiness curriculum.
However, if you need a curriculum that includes problem solving skills among other career readiness topics, consider looking into iCEV’s career readiness and digital literacy curriculum.
Thousands of teachers like you use the curriculum to teach career exploration , personal financial literacy , communication skills and more.
Overall, it helps you save time with planning, assessing, and grading student work all while maximizing student understanding and information retention.
Wondering if iCEV could work for your middle school classroom? Check out our Middle School digital Literacy & Career Exploration curriculum :

- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Members Newsfeed
20 Critical Thinking Activities for Middle Schoolers
- Middle School Education

Introduction:
Critical thinking is vital for middle school students, as it helps them develop problem-solving skills, make informed decisions, and understand different perspectives. Integrating critical thinking activities into classroom learning experiences can greatly enhance students’ cognitive abilities. The following are 20 engaging critical thinking activities designed for middle school students.
1. Brain Teasers: Use age-appropriate puzzles to challenge students’ cognitive abilities and encourage them to find creative solutions.
2. Socratic Circles: Divide the class into groups and encourage them to participate in a philosophical discussion on a given topic, asking questions that stimulate critical thinking and deeper understanding.
3. Compare and Contrast: Assign two similar but different texts for students to compare and contrast, analyzing similarities and differences between each author’s perspective.
4. What-If Questions: Encourage children to think critically about hypothetical scenarios by asking what-if questions, such as “What if the internet didn’t exist?”
5. Debate Club: Organize a debate club where students are encouraged to research and defend differing viewpoints on a topic.
6. Mind Mapping: Teach students how to create a mind map – a visual representation of their thoughts – to help them brainstorm complex issues effectively.
7. Mystery Bag: In small groups, give students a bag containing several random objects and ask them to invent an innovative product or story using all items in the bag.
8. Critical Thinking Journal: Have students maintain journals where they analyze their thought processes after completing activities, promoting self-reflection and metacognition.
9. Moral Dilemmas: Present students with moral dilemmas, requiring them to weigh pros and cons before making ethical decisions.
10. Fact or Opinion?: Give students various statements and ask them to differentiate between fact or opinion, helping them build critical thinking skills when handling information.
11. Research Projects: Assign project topics that require deep research from multiple sources, developing students’ abilities to sift through information and synthesize their findings.
12. Think-Pair-Share: Have students think individually about a complex question, then pair up to discuss their thoughts, and finally share with the class.
13. Art Interpretation: Display an artwork and ask students to interpret its meaning, theme, or message, pushing them to look beyond the surface.
14. Reverse Role Play: Assign roles for a scenario where students exchange positions (e.g., teacher-student, parent-child), fostering empathetic understanding and critical thinking skills.
15. Critical Evaluation of Media: Analyze news articles, commercials, or social media posts by asking questions about their purpose, target audience, and accuracy.
16. Six Thinking Hats: Teach students Edward de Bono’s “Six Thinking Hats” technique to improve critical thinking by exploring diverse perspectives when solving problems.
17. Analogy Building: Encourage students to create analogies from one concept to another, enhancing abstract thinking and problem-solving abilities.
18. Current Events Analysis: Keep track of current events and have students critically evaluate news stories or blog posts to encourage informed decision-making in real-world contexts.
19. Brainstorming Sessions: Hold group brainstorming sessions where students invent solutions for complex problems while practicing active listening and critical thinking.
20. Reflection Activities: Use reflective writing prompts at the end of lessons or activities to foster metacognition, self-awareness, and the development of critical thinking skills.
Conclusion:
Critical thinking activities are vital for middle schoolers as they foster intellectual growth and prepare them for future learning experiences. By incorporating these 20 activities into your classroom curriculum, you can help students develop essential critical thinking skills that will serve them throughout their academic careers and beyond.
Related Articles

Starting at a new school can be an exciting yet nerve-wracking experience…

Introduction: As middle schoolers transition into more independence, it's crucial that they…
1. Unpredictable Growth Spurts: Middle school teachers witness students entering their classrooms…

Pedagogue is a social media network where educators can learn and grow. It's a safe space where they can share advice, strategies, tools, hacks, resources, etc., and work together to improve their teaching skills and the academic performance of the students in their charge.
If you want to collaborate with educators from around the globe, facilitate remote learning, etc., sign up for a free account today and start making connections.
Pedagogue is Free Now, and Free Forever!
- New? Start Here
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Registration
Don't you have an account? Register Now! it's really simple and you can start enjoying all the benefits!
We just sent you an Email. Please Open it up to activate your account.
I allow this website to collect and store submitted data.
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

How the US is destroying young people’s future - Scott Galloway
Lesson duration 18:38
4,122,527 Views

This piece of paper could revolutionize human waste
Lesson duration 05:35
2,533,419 Views

Can you solve the magical maze riddle?
Lesson duration 04:51
362,455 Views

How to clear icy roads, with science
Lesson duration 06:13
192,339 Views

How to make smart decisions more easily
Lesson duration 05:16
1,165,021 Views

Can you solve a mystery before Sherlock Holmes?
Lesson duration 05:17
480,320 Views

Can you solve the secret assassin society riddle?
Lesson duration 05:01
721,495 Views

How to overcome your mistakes
Lesson duration 04:52
920,226 Views

What the fossil fuel industry doesn't want you to know - Al Gore
Lesson duration 25:45
741,984 Views

Can you solve the cursed dice riddle?
Lesson duration 04:31
717,451 Views

How the water you flush becomes the water you drink
Lesson duration 05:23
391,465 Views

The growing megafire crisis — and how to contain it - George T. Whitesides
Lesson duration 10:42
56,709 Views
Can you solve the time traveling car riddle?
Lesson duration 05:18
640,053 Views

4 epidemics that almost happened (but didn't)
Lesson duration 06:26
394,483 Views

The return of Mongolia's "wild" horses
Lesson duration 04:53
206,566 Views

Whatever happened to the hole in the ozone layer?
Lesson duration 05:13
524,757 Views

The most important century in human history
Lesson duration 05:20
339,511 Views

This one weird trick will get you infinite gold
Lesson duration 05:08
1,041,409 Views

How to quit your job — without ruining your career - Gala Jackson
107,304 Views

How to design climate-resilient buildings - Alyssa-Amor Gibbons
Lesson duration 14:12
43,512 Views

The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani
Lesson duration 19:09
80,461 Views

Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world?
771,438 Views

How college loans exploit students for profit - Sajay Samuel
Lesson duration 11:49
229,332 Views

What’s the smartest age?
1,587,442 Views

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, 5 problem-solving activities for the classroom.

Problem-solving skills are necessary in all areas of life, and classroom problem solving activities can be a great way to get students prepped and ready to solve real problems in real life scenarios. Whether in school, work or in their social relationships, the ability to critically analyze a problem, map out all its elements and then prepare a workable solution is one of the most valuable skills one can acquire in life.
Educating your students about problem solving skills from an early age in school can be facilitated through classroom problem solving activities. Such endeavors encourage cognitive as well as social development, and can equip students with the tools they’ll need to address and solve problems throughout the rest of their lives. Here are five classroom problem solving activities your students are sure to benefit from as well as enjoy doing:
1. Brainstorm bonanza
Having your students create lists related to whatever you are currently studying can be a great way to help them to enrich their understanding of a topic while learning to problem-solve. For example, if you are studying a historical, current or fictional event that did not turn out favorably, have your students brainstorm ways that the protagonist or participants could have created a different, more positive outcome. They can brainstorm on paper individually or on a chalkboard or white board in front of the class.
2. Problem-solving as a group
Have your students create and decorate a medium-sized box with a slot in the top. Label the box “The Problem-Solving Box.” Invite students to anonymously write down and submit any problem or issue they might be having at school or at home, ones that they can’t seem to figure out on their own. Once or twice a week, have a student draw one of the items from the box and read it aloud. Then have the class as a group figure out the ideal way the student can address the issue and hopefully solve it.
3. Clue me in
This fun detective game encourages problem-solving, critical thinking and cognitive development. Collect a number of items that are associated with a specific profession, social trend, place, public figure, historical event, animal, etc. Assemble actual items (or pictures of items) that are commonly associated with the target answer. Place them all in a bag (five-10 clues should be sufficient.) Then have a student reach into the bag and one by one pull out clues. Choose a minimum number of clues they must draw out before making their first guess (two- three). After this, the student must venture a guess after each clue pulled until they guess correctly. See how quickly the student is able to solve the riddle.
4. Survivor scenarios
Create a pretend scenario for students that requires them to think creatively to make it through. An example might be getting stranded on an island, knowing that help will not arrive for three days. The group has a limited amount of food and water and must create shelter from items around the island. Encourage working together as a group and hearing out every child that has an idea about how to make it through the three days as safely and comfortably as possible.
5. Moral dilemma
Create a number of possible moral dilemmas your students might encounter in life, write them down, and place each item folded up in a bowl or bag. Some of the items might include things like, “I saw a good friend of mine shoplifting. What should I do?” or “The cashier gave me an extra $1.50 in change after I bought candy at the store. What should I do?” Have each student draw an item from the bag one by one, read it aloud, then tell the class their answer on the spot as to how they would handle the situation.
Classroom problem solving activities need not be dull and routine. Ideally, the problem solving activities you give your students will engage their senses and be genuinely fun to do. The activities and lessons learned will leave an impression on each child, increasing the likelihood that they will take the lesson forward into their everyday lives.
You may also like to read
- Classroom Activities for Introverted Students
- Activities for Teaching Tolerance in the Classroom
- 5 Problem-Solving Activities for Elementary Classrooms
- 10 Ways to Motivate Students Outside the Classroom
- Motivating Introverted Students to Excel in the Classroom
- How to Engage Gifted and Talented Students in the Classroom
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Assessment Tools , Engaging Activities
- Online & Campus Doctorate (EdD) in Higher Edu...
- Degrees and Certificates for Teachers & Educa...
- Programming Teacher: Job Description and Sala...
Developing Problem-Solving Skills for Kids | Strategies & Tips

We've made teaching problem-solving skills for kids a whole lot easier! Keep reading and comment below with any other tips you have for your classroom!
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: The Real Deal
Picture this: You've carefully created an assignment for your class. The step-by-step instructions are crystal clear. During class time, you walk through all the directions, and the response is awesome. Your students are ready! It's finally time for them to start working individually and then... 8 hands shoot up with questions. You hear one student mumble in the distance, "Wait, I don't get this" followed by the dreaded, "What are we supposed to be doing again?"
When I was a new computer science teacher, I would have this exact situation happen. As a result, I would end up scrambling to help each individual student with their problems until half the class period was eaten up. I assumed that in order for my students to learn best, I needed to be there to help answer questions immediately so they could move forward and complete the assignment.
Here's what I wish I had known when I started teaching coding to elementary students - the process of grappling with an assignment's content can be more important than completing the assignment's product. That said, not every student knows how to grapple, or struggle, in order to get to the "aha!" moment and solve a problem independently. The good news is, the ability to creatively solve problems is not a fixed skill. It can be learned by students, nurtured by teachers, and practiced by everyone!
Your students are absolutely capable of navigating and solving problems on their own. Here are some strategies, tips, and resources that can help:
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: Student Strategies
These are strategies your students can use during independent work time to become creative problem solvers.
1. Go Step-By-Step Through The Problem-Solving Sequence
Post problem-solving anchor charts and references on your classroom wall or pin them to your Google Classroom - anything to make them accessible to students. When they ask for help, invite them to reference the charts first.

2. Revisit Past Problems
If a student gets stuck, they should ask themself, "Have I ever seen a problem like this before? If so, how did I solve it?" Chances are, your students have tackled something similar already and can recycle the same strategies they used before to solve the problem this time around.
3. Document What Doesn’t Work
Sometimes finding the answer to a problem requires the process of elimination. Have your students attempt to solve a problem at least two different ways before reaching out to you for help. Even better, encourage them write down their "Not-The-Answers" so you can see their thought process when you do step in to support. Cool thing is, you likely won't need to! By attempting to solve a problem in multiple different ways, students will often come across the answer on their own.
4. "3 Before Me"
Let's say your students have gone through the Problem Solving Process, revisited past problems, and documented what doesn't work. Now, they know it's time to ask someone for help. Great! But before you jump into save the day, practice "3 Before Me". This means students need to ask 3 other classmates their question before asking the teacher. By doing this, students practice helpful 21st century skills like collaboration and communication, and can usually find the info they're looking for on the way.
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: Teacher Tips
These are tips that you, the teacher, can use to support students in developing creative problem-solving skills for kids.
1. Ask Open Ended Questions
When a student asks for help, it can be tempting to give them the answer they're looking for so you can both move on. But what this actually does is prevent the student from developing the skills needed to solve the problem on their own. Instead of giving answers, try using open-ended questions and prompts. Here are some examples:

2. Encourage Grappling
Grappling is everything a student might do when faced with a problem that does not have a clear solution. As explained in this article from Edutopia , this doesn't just mean perseverance! Grappling is more than that - it includes critical thinking, asking questions, observing evidence, asking more questions, forming hypotheses, and constructing a deep understanding of an issue.

There are lots of ways to provide opportunities for grappling. Anything that includes the Engineering Design Process is a good one! Examples include:
- Engineering or Art Projects
- Design-thinking challenges
- Computer science projects
- Science experiments
3. Emphasize Process Over Product
For elementary students, reflecting on the process of solving a problem helps them develop a growth mindset . Getting an answer "wrong" doesn't need to be a bad thing! What matters most are the steps they took to get there and how they might change their approach next time. As a teacher, you can support students in learning this reflection process.

4. Model The Strategies Yourself!
As creative problem-solving skills for kids are being learned, there will likely be moments where they are frustrated or unsure. Here are some easy ways you can model what creative problem-solving looks and sounds like.
- Ask clarifying questions if you don't understand something
- Admit when don't know the correct answer
- Talk through multiple possible outcomes for different situations
- Verbalize how you’re feeling when you find a problem
Practicing these strategies with your students will help create a learning environment where grappling, failing, and growing is celebrated!
Problem-Solving Skill for Kids
Did we miss any of your favorites? Comment and share them below!
Looking to add creative problem solving to your class?
Learn more about Kodable's free educator plan or create your free account today to get your students coding!
Kodable has everything you need to teach kids to code!
In just a few minutes a day, kids can learn all about the fundamentals of Computer Science - and so much more! With lessons ranging from zero to JavaScript, Kodable equips children for a digital future.

Math Wheels for Note-taking?

5 Ways to Practice Problem Solving Skills in Middle School

If you’ve been teaching or around middle schoolers very long then it will not surprise you to hear that their brains are still developing. I’m not talking about being an on-going learner, I’m talking about the actual function of their brains is still in development. Because our middle schoolers are now “big kids” and independent, it is easy to forget that they are not done growing and developing. One area that our students are still developing is problem solving skills.
Critical thinking, analytical thinking, and deductive thinking will continue to develop over the next decade. But we don’t have to wait for our tweens to become early 20-somethings before tackling problem solving skills. We can help them begin to tap into this new level of thinking now. Whether it is problem solving in math class or helping them figure their way through middle school social drama, teaching and practicing problem solving skills is important.
Today, I’m thrilled to share with you five strategies I use with my middle schoolers to develop problem solving skills they can use in and out of the classroom.
Why Are Problem Solving Skills Important?
Life is filled with challenges, unexpected problems, and sticky situations we have to be able to think through. From a mult-step, multi-concept story problem in math class to navigating social situations, problem solving skills are key. That’s why I want to take a minute to chat about why problem solving skills can be one of the strongest tools our middle schoolers can have in their toolbox as they navigate the chaos of middle school!

If you think about it, middle school is their training ground for the real situations that take place where they might feel stuck or not motivated to keep going. It’s where they learn to juggle homework, navigate the social circus, and face unexpected challenges. In this crazy adventure called life, problem-solving skills can swoop in to save the day.
But here’s the plot twist: this isn’t just about making it through middle school, it’s about gearing up for success beyond the classroom. We know that the “real world” is full of job hunts, budgeting, time management, and adulting. What’s going to help them succeed? You’ve got it right- the ability to tackle problems like seasoned pros. Whether it’s negotiating a job offer, smoothing out conflicts, or fixing a leaky sink, those middle school honed problem solving skills guide them through the twists and turns of adulthood.
5 Problem Solving Skills for Middle Schoolers
One of the best ways for our middle schoolers to learn how to problem solve is through relevant activities or strategies. Not only relevant but also relatable. It’s that engagement and buy-in that makes them go, “Yeah, this makes total sense!” Incorporating relatable situations with you, the teacher, there to guide them through it creates a safety net for them. They get to witness the thinking process, see the actions in play, and hear the behind-the-scenes reasoning on how to tackle challenges.
1. Practice Critical Thinking Skills
Middle schoolers are like little detectives in the making, always asking all the questions before you can even get the whole scenario out! Use that to your advantage! Ask open-ended questions that get them thinking. Not every question or situation they encounter will be answered with a yes, no, or straightforward answer. They’ll need to think about the situation from different perspectives and consider various factors. Give them time to think and then {this is the hardest for most of us} wait and let them explain their thinking. Don’t just get an answer and move on. Even if there is uncomfortable silence – just wait. Give them the time to think so that you can take a deep dive into the thinking process.

We dive into scenarios, whether they are social or math-based, that require more than just a glance. For example, we will dissect word problems together or a math problem they may not have seen just yet to introduce the concept. We’ll explore various possibilities on how we could start off solving the math problem.
If a social concern about friend drama pops up, I will put a scenario together for us to work through by discussing the perspectives of who is included in the made-up scenario version. Why did they make the choices they did? What could they have done differently? Because they did one thing, what did that cause? It’s not about being in the know 100%, but more about becoming a thoughtful problem-solver.
As they navigate through these challenges, they’re not just finding solutions. They’re developing a knack for analyzing information, considering different angles, and crafting well-thought-out responses.
2. Teamwork Makes the Dream Work
Middle school is undoubtedly a social whirlwind. It’s a mix of laughter, friendship dramas, and a dash of chaotic energy. So, why not use that energy for some problem-solving skill-building? Group projects can be a great way for students to learn to work together, listen to others, and share their thoughts. They have to assimilate information, process it with understanding, and figure out how to apply the group knowledge to find a consensus.

Group projects allow you to weave in problem solving with academics with the opportunity to develop social problem solving skills too. It’s about weaving a web of skills that extend beyond the assignment. While tackling an academic problem, students will learn to listen to others and analyze what is being said. Through these group endeavors, they learn to appreciate different perspectives. They can start to understand each team member’s strengths and, most importantly, navigate the beautiful chaos of teamwork. There’s going to be disagreements and standstill, so they’ll begin to figure out how to talk through those moments.
But the magic happens when it all comes together. A group solution to an academic problem is usually arrived at after putting those social problem solving skills to the test.
3. Real-Life Problems, Real-Life Solutions
Let’s shift our gears to the world of math. One way to bring math to life is by looking at the focused math skills in real-life math challenges or scenarios. Textbooks have their charm and can be helpful with some practice problems. There’s an unmatched thrill in solving problems that sync with what is happening or what could happen in the real world. Having my students look at real-life scenarios when studying math helps them to see that math is relevant and impactful.

When the time is available, I love challenging my students with a scenario that requires their math skills to solve. Whether it’s crafting solutions for a community-based math puzzle or planning a party while staying on budget, these challenges are the heart of the adventure of mathematical problem-solving. But why stop there? Dive deeper into your scenario for even more problem-solving fun.
You can go as deep as you see fit with your students. They can brainstorm an initial solution or go further. They can then think about the resources they will need, how much those will cost, and where to get them. What about time constraints? They’ll then have to think about a timeline for them to put their hypothetical plan into action to get to their end goal. Suddenly, problem-solving isn’t a mundane task. It fills your classroom with excitement, engaged conversations, and a sense of purpose!
Resources to Help You Get Started
This practice comes in handy as students work through word problems during classwork as well! Help remind them of the strategies you worked through with a visual aid such as these problem-solving bookmarks .
And. . . if you are not sure where to start, I have some free Problem of the Week resources are the perfect starting place. All of the Problem of the Week resources are in the Free Math Resource Center. You can get access by signing up here.
4. ABC’s of Problem Solving Skills – Analyze, Brainstorm, Choose
ABC is a popular acronym that has many variations to it. You can easily make it your own, but what works in my classroom is to analyze, brainstorm, and choose. I’ll walk you through how I explain each letter in my room and how it helps my students’ problem-solving skills.
A – Analyze

The first letter of our problem-solving alphabet is A for Analyze. It’s one thing to just glance at the problem. It’s a whole other thing to dissect it and understand the ins and outs. What happened? Why did it happen? What is being asked? What do I need to figure out? All of these are questions that help students analyze a problem. This is a great first step whether you are solving a math problem or a social problem.
After presenting the problem I like to have my students share some of the questions they are asking themselves during the analyze phase. Depending on the question it might sound like this: Did a peer take your snack, because they don’t have much food at home or because they were being mean? Did your friend snap at you because they didn’t get enough sleep or because they were mad at you? Do I need all of the numbers provided in the problem or was there unnecessary extra information?
It’s so important for middle schoolers to learn to ask these analysis questions. It helps them take a more objective view of the problem. In social settings, it helps them to widen their awareness of themselves to those around them.
B – Brainstorm
Next, B for brainstorming! We brainstorm possible methods of solving the problem, reasons for why words are said or actions are taken, and possible solutions. Then, we look at possible ways actions and words from all involved could impact others. This is the time that we focus on possible solutions.
In math, that will include identifying the math skills needed to solve the problem, recalling formulas, and applying strategies. In real life, this might include how can we fix or make this situation better now and in the future.
C – Choose
The C for Choose. It’s decision time. We evaluate our all of brainstormed ideas and possible solutions. Then it is time to put them into action. During this step, students may choose different things and that is okay. But don’t miss the learning opportunity that comes with that. As students are developing problem solving skills it is important to give them time to share their thinking. Here students can learn from each other as they hear about things they didn’t think about or see situations or problems from a different perspective. This process is a fun and in-depth way to practice problem solving skills with students!
5. Power of Perseverance in Middle School
I purposely saved this one for last because, without this skill or trait, it will be tricky for your middle schoolers to do the previous four. Problem solving is hard. It can get messy before it starts smoothing out into a solution. Your students will become defensive, moan, groan, or just go off and do their own thing. In those moments, I take a step back, take a deep breath, and work with them to learn perseverance. It’s a complete mindset shift, but once it happens it changes how our students approach any situation.

I make sure my students understand that setbacks aren’t roadblocks but rather detours on the path to success or achievement. I emphasize the importance of grit and resilience. We talk about how mistakes are still good to make because it shows that they are trying. The key to those mistakes or roadblocks is to not stop but to keep trying by trying to do something different.
To drive this point home, I weave in tales of legends who faced adversity head-on and emerged victorious. Whether it’s Thomas Edison’s journey to invent the lightbulb or J.K. Rowling’s story of persistence in getting Harry Potter published, these narratives become the fuel for their perseverance engine. I share some of my own stories with them about times I have had to persevere. I then turn the table and have them reflect on times they struggled but persevered until they had succeeded. Most of the time, they surprise themselves!
Give Your Middle Schoolers Problem Solving Skills to Succeed
And there you have the ultimate toolbox of my top five problem-solving skills tailored for your middle schoolers. This toolbox of skills will never go out of style. These skills are the building blocks for shaping the future for our middle schoolers.

As they master the art of critical thinking, through academic and social challenges, they’re becoming equipped with the skills to construct creative solutions and tackle whatever hurdles the future may throw their way. These aren’t just skills for the present. They’re the transformative forces that pave the way for a future filled with confident, creative problem-solvers ready to leave their mark on the world. The adventure begins in your classroom!
Interested in problem solving skills through a math lens? Read Help Middle School Math Students Improve Problem Solving Skills to learn more!
Save for Later
Remember to save this post to your favorite math or teacher Pinterest board to return to for your middle schoolers’ problem-solving skills!
read next...

Math Wheel Questions Answered to Help You Get Started


Master 3rd Grade Math Concepts and More With Math Wheels

How To Tell If Executive Function Skills Impact Math Performance

How to Help Easily Distracted Students by Using Math Wheels

Welcome to Cognitive Cardio Math! I’m Ellie, a wife, mom, grandma, and dog ‘mom,’ and I’ve spent just about my whole life in school! With nearly 30 years in education, I’ve taught:
- All subject areas in 4 th and 5 th grades
- Math, ELA, and science in 6th grade (middle school)
I’ve been creating resources for teachers since 2012 and have worked in the elearning industry for about five years as well!
FIND IT FAST
Let's connect.

Select the image above to learn more!

Get FIVE days of free math lessons!

Terms of Use Privacy Policy
COPYRIGHT © 2022 COGNITIVE CARDIO MATH • ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. SITE DESIGN BY LAINE SUTHERLAND DESIGNS
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How to Teach Kids Problem-Solving Skills
KidStock / Blend Images / Getty Images
- Steps to Follow
- Allow Consequences
Whether your child can't find their math homework or has forgotten their lunch, good problem-solving skills are the key to helping them manage their life.
A 2010 study published in Behaviour Research and Therapy found that kids who lack problem-solving skills may be at a higher risk of depression and suicidality. Additionally, the researchers found that teaching a child problem-solving skills can improve mental health .
You can begin teaching basic problem-solving skills during preschool and help your child sharpen their skills into high school and beyond.
Why Problem-Solving Skills Matter
Kids face a variety of problems every day, ranging from academic difficulties to problems on the sports field. Yet few of them have a formula for solving those problems.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills may avoid taking action when faced with a problem.
Rather than put their energy into solving the problem, they may invest their time in avoiding the issue. That's why many kids fall behind in school or struggle to maintain friendships .
Other kids who lack problem-solving skills spring into action without recognizing their choices. A child may hit a peer who cuts in front of them in line because they are not sure what else to do.
Or, they may walk out of class when they are being teased because they can't think of any other ways to make it stop. Those impulsive choices may create even bigger problems in the long run.
The 5 Steps of Problem-Solving
Kids who feel overwhelmed or hopeless often won't attempt to address a problem. But when you give them a clear formula for solving problems, they'll feel more confident in their ability to try. Here are the steps to problem-solving:
- Identify the problem . Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
- Develop at least five possible solutions . Brainstorm possible ways to solve the problem. Emphasize that all the solutions don't necessarily need to be good ideas (at least not at this point). Help your child develop solutions if they are struggling to come up with ideas. Even a silly answer or far-fetched idea is a possible solution. The key is to help them see that with a little creativity, they can find many different potential solutions.
- Identify the pros and cons of each solution . Help your child identify potential positive and negative consequences for each potential solution they identified.
- Pick a solution. Once your child has evaluated the possible positive and negative outcomes, encourage them to pick a solution.
- Test it out . Tell them to try a solution and see what happens. If it doesn't work out, they can always try another solution from the list that they developed in step two.
Practice Solving Problems
When problems arise, don’t rush to solve your child’s problems for them. Instead, help them walk through the problem-solving steps. Offer guidance when they need assistance, but encourage them to solve problems on their own. If they are unable to come up with a solution, step in and help them think of some. But don't automatically tell them what to do.
When you encounter behavioral issues, use a problem-solving approach. Sit down together and say, "You've been having difficulty getting your homework done lately. Let's problem-solve this together." You might still need to offer a consequence for misbehavior, but make it clear that you're invested in looking for a solution so they can do better next time.
Use a problem-solving approach to help your child become more independent.
If they forgot to pack their soccer cleats for practice, ask, "What can we do to make sure this doesn't happen again?" Let them try to develop some solutions on their own.
Kids often develop creative solutions. So they might say, "I'll write a note and stick it on my door so I'll remember to pack them before I leave," or "I'll pack my bag the night before and I'll keep a checklist to remind me what needs to go in my bag."
Provide plenty of praise when your child practices their problem-solving skills.
Allow for Natural Consequences
Natural consequences may also teach problem-solving skills. So when it's appropriate, allow your child to face the natural consequences of their action. Just make sure it's safe to do so.
For example, let your teenager spend all of their money during the first 10 minutes you're at an amusement park if that's what they want. Then, let them go for the rest of the day without any spending money.
This can lead to a discussion about problem-solving to help them make a better choice next time. Consider these natural consequences as a teachable moment to help work together on problem-solving.
Becker-Weidman EG, Jacobs RH, Reinecke MA, Silva SG, March JS. Social problem-solving among adolescents treated for depression . Behav Res Ther . 2010;48(1):11-18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2009.08.006
Pakarinen E, Kiuru N, Lerkkanen M-K, Poikkeus A-M, Ahonen T, Nurmi J-E. Instructional support predicts childrens task avoidance in kindergarten . Early Child Res Q . 2011;26(3):376-386. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.11.003
Schell A, Albers L, von Kries R, Hillenbrand C, Hennemann T. Preventing behavioral disorders via supporting social and emotional competence at preschool age . Dtsch Arztebl Int . 2015;112(39):647–654. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2015.0647
Cheng SC, She HC, Huang LY. The impact of problem-solving instruction on middle school students’ physical science learning: Interplays of knowledge, reasoning, and problem solving . EJMSTE . 2018;14(3):731-743.
Vlachou A, Stavroussi P. Promoting social inclusion: A structured intervention for enhancing interpersonal problem‐solving skills in children with mild intellectual disabilities . Support Learn . 2016;31(1):27-45. doi:10.1111/1467-9604.12112
Öğülmüş S, Kargı E. The interpersonal cognitive problem solving approach for preschoolers . Turkish J Educ . 2015;4(17347):19-28. doi:10.19128/turje.181093
American Academy of Pediatrics. What's the best way to discipline my child? .
Kashani-Vahid L, Afrooz G, Shokoohi-Yekta M, Kharrazi K, Ghobari B. Can a creative interpersonal problem solving program improve creative thinking in gifted elementary students? . Think Skills Creat . 2017;24:175-185. doi:10.1016/j.tsc.2017.02.011
Shokoohi-Yekta M, Malayeri SA. Effects of advanced parenting training on children's behavioral problems and family problem solving . Procedia Soc Behav Sci . 2015;205:676-680. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.09.106
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
10 Best Problem Solving Activities For Middle School
Published on april 24, 2017 at 8:43 am by amber hewitt in lists , news.
If you’re a teacher or a parent looking to engage young students in a more interesting way, you might like this list of the best problem solving activities for middle school .
I wonder if middle schoolers could solve my life problems. Can they file my taxes or pay my rent? Those are some real problems that I have and I think they could be somewhat fun activities for middle schoolers. It’s interesting how problem-solving scenarios change as we age because I genuinely can’t identify with the struggle of theoretical problems involving trains or the alphabet, but I’m sure I enjoyed them when I was younger. I think my friends and I really used to love finding these things and solving them together, which is kind of a cute group activity.

pathdoc/Shutterstock.com
Problem solving is a great way to strengthen and train the brain for more difficult things as we age. They teach you teamwork, logic, and skill, which are all extremely important for developing minds. Even into adulthood you should continue solving theoretical problems like these because they’ll keep your brain strong and focused so your other issues like “how late can I sleep while still getting to work on time?” or “how much money will I have in my bank account if I order dinner every single night this week?” Those are obviously much more challenging than the fun problem-solving activities for preschoolers , or even this list with activities for kids in middle school.
In order to create this list, we used Concordia University and IceBreaker as some primary sources. We took the suggestions that were the highest ranked on both sources and averaged their rankings. If they were on both lists, they’re at a higher position on ours. Overall, each of these activities is well suited for middle school-aged children who need a little mental exercise.
Without further ado, let’s take a look at the best problem solving activities for middle school.

Slideshow List XFinance problem solving games for kids group problem solving scenarios Animals Problem Solving Activity short problem solving activities problem solving games for groups Laser Web Problem Solving Activity Clue Me In Problem Solving Activity creative problem solving activities problem solving activities for kids Alphabet Game Problem Solving Activity Group Drawing Problem Solving Activity Moral Dilemma Problem Solving Activity Walking The Plank Problem Solving Activity Survivor Scenarios Problem Solving Activity Brainstorm Bonanza Problem Solving Activity 18 fun problem-solving activities for preschoolers The Problem-Solving Box Activity for Middle School 10 Best Problem Solving Activities For Middle School Show more... Show less
Advertisement
The effect of a programming tool scratch on the problem-solving skills of middle school students
- Published: 16 October 2021
- Volume 27 , pages 4065–4086, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Osman Erol ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9920-5211 1 &
- Neşe Sevim Çırak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5843-6291 1
2224 Accesses
17 Citations
Explore all metrics
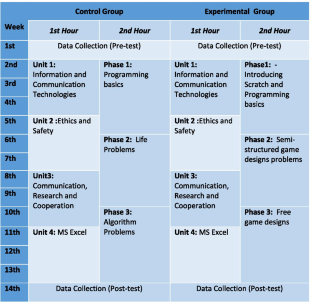
Problem-solving is one of the most important twenty-first-century skills and should be acquired at an early age. Since programming is a kind of problem-solving process, it may be seen in the context of problem-solving skills development. Hence, this study aims to identify the effectiveness of one of the most popular programming tools “Scratch” on middle school students’ problem-solving skills. For this purpose, this current study’s implementation lasted for a period of 14 weeks, based on the ‘Information Technologies and Software’ course at 2 h per week. The course curriculum was conducted for both 18 middle school students in an experimental group and 16 middle school students in a control group at least one hour per week while in the second hour, the control group worked on the activities that the coursebook included and the experimental group engaged in game design activities using Scratch. The Problem Solving Inventory for Children (PSIC) was used as a data collection tool in order to examine the participants’ self-perception with regard to their problem-solving skills. MANOVA, ANOVA, and t -tests were employed in the analysis of the obtained data. The study showed that game design activities with Scratch increased the problem-solving skills of the participants. In this context, game design activities with coding tools can be employed with children in order to help them gain problem-solving skills at an early age.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Studying the effects of teaching programming to lower secondary school students with a serious game: a case study with Python and CodeCombat
A pilot study on the effectiveness and acceptance of an educational game for teaching programming concepts to primary school students.

Introducing Coding to Children with Scratch: A Pilot Study
Akbulut, Y. (2010). Sosyal bilimlerde SPSS uygulamaları: Sık kullanılan istatistiksel analizler ve açıklamalı SPSS çözümleri [SPSS applications in social sciences: Frequently used statistical analyzes and annotated SPSS solutions] . İdeal Kültür & Yayıncılık.
Google Scholar
Anderson, J. (2009). Mathematics curriculum development and the role of problem solving. In K. School (Ed.), Proceedings of 2009 Australian curriculum studies association National Biennial Conference . Curriculum : A National Conversation (pp. 1–8). http://www.acsa.edu.au/pages/page484.asp . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Argaw, A. S., Haile, B. B., Ayalew, B. T., & Kuma, S. G. (2017). The effect of problem based learning (PBL) instruction on students’ motivation and problem solving skills of physics. Journal of mathematics science and technology education , 13 (3), 857-871. Doi: 10.12973/eurasia.2017.00647a.
Armoni, M. (2011). The nature of CS in K-12 curricula: The roots of confusion. ACM Inroads, 2 (4), 19–20. https://doi.org/10.1145/2038876.2038883
Article Google Scholar
Babori, A., Fihri Fassi, H., Hariri, A., & Bideq, M. (2016). An e-learning environment for algorithmic: Toward an active construction of skills. World journal of educational technology, 8 (2), 82-90. Doi: 10.18844/wjet.v8i2.819.
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84 (2), 191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.2.191
Baytak, A., & Land, S. M. (2011). An investigation of the artifacts and process of constructing computers games about environmental science in a fifth grade classroom. Educational Technology Research and Development, 59 (6), 765–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-010-9184-z
Brennan, K., Balch, C., & Chung, M. (2014). Creative Computing Curriculum . http://scratched.gse.harvard.edu/guide/ . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Calao, L. A., Moreno-León, J., Correa, H. E., & Robles, G. (2015). Developing mathematical thinking with scratch: An experiment with 6th-grade students. In G. Conole, T. Klobučar, C. Rensing, J. Konert, & E. Lavoué (Eds.), Design for Teaching and Learning in a networked world (pp. 17–27). Springer. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24258-3_2 .
Calder, N. (2010). Using scratch: An integrated problem-solving approach to mathematical thinking. Australian Primary Mathematics Classroom, 15 (4), 9–14.
Chu, H. C., & Hwang, G. J. (2010). Development of a project-based cooperative learning environment for computer programming courses. International Journal of Innovation and Learning, 8 (3), 256–266. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJIL.2010.035029
Clements, D. H., & Nastasi, B. K. (1999). Metacognition, learning, and educational computer environments. Information Technology in Childhood Education Annual, 1999 (1), 3–36.
Cohen, J. W. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
MATH Google Scholar
Demirer, V., & Sak, N. (2016). Programming education and new approaches around the world and in Turkey. Journal of Theory and Practice in Education , 12(3), 521–546. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/eku/issue/26697/280853
Dostál, J. (2015). Theory of problem solving. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174 , 2798–2805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.970
Dow, G. T., & Mayer, R. E. (2004). Teaching students to solve insight problems: Evidence for domain specificity in creativity training. Creativity Research Journal, 16 (4), 389–402. https://doi.org/10.1080/10400410409534550
Fessakis, G., Gouli, E., & Mavroudi, E. (2013). Problem solving by 5–6 years old kindergarten children in a computer programming environment: A case study. Computers & Education, 63 , 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.11.016
Frost, D., Verno, A., Burkhart, D., Hutton, M., North, K., Houston, I. S. D., & ES, P. P. (2009). A model curriculum for K-12 computer science: Level I objectives and outlines (pp. 2–44). Computer Science Teachers Association.
Funke, A., Geldreich, K., & Hubwieser, P. (2017). Analysis of scratch projects of an introductory programming course for primary school students. In 2017 IEEE global engineering education conference (EDUCON) (pp. 1229–1236). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/EDUCON.2017.7943005.
Gagne, R. M. (1985). The conditions of learning and theory of instruction . Holt.
Gömleksiz, M. N., & Bozpolat, E. (2012). İlköğretim 4. Ve 5. sınıf öğrencilerinin problem çözme becerilerine ilişkin görüşlerinin değerlendirilmesi [an assessment of the 4th and 5th grade primary School students’ opinions towards their problem solving skills]. Abant İzzet Baysal Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi , 12(2), 23–40. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/aibuefd/issue/1489/17987 . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Good, J. (2011). Learners at the wheel: Novice programming environments come of age. International journal of people-oriented programming , 1 (1), article 1. doi: 10.4018/ijpop.2011010101.
Heppner, P. P., & Petersen, C. H. (1982). The development and implications of a personal problem-solving inventory. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 29 (1), 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.29.1.66
Hwang, W. Y., Wang, C. Y., Hwang, G. J., Huang, Y. M., & Huang, S. (2008). A web-based programming learning environment to support cognitive development. Interacting with Computers, 20 (6), 524–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intcom.2008.07.002
Kalelioglu, F., & Gülbahar, Y. (2014). The effects of teaching programming via scratch on problem solving skills: A discussion from learners’ perspective. Informatics in Education, 13(1), 33–50. https://www.ceeol.com/search/journal-detail?id=987
Kappelman, L. C., Jones, M., Johnson, V., Mclean, E. R., & Bonnme, K. (2016). Skills for success at different stages of an IT professional’s career. Communications of the ACM, 59 (8), 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1145/2888391
Kaučič, B., & Asič, T. (2011). Improving introductory programming with scratch? In P. Biljanović, K. Skala, S. Golubić, N. Bogunović, S. Ribarić, M. Čičin-Šain, D. Čišić, Ž. Hutinski, M. Baranović, M. Mauher, & L. Ordanić (Eds.), Proceedings of the 34th international convention MIPRO (pp. 1095–1100). IEEE.
Kim, J.-R., So, I.-M., Song, E.-H., & Yi, D.-W. (2018). An evaluation of the creative problem solving ability of students by major using scratch program. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 118(19), 1915–1926. https://acadpubl.eu/jsi/2018-118-19/articles/19b/27.pdf . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Kim, S., Chung, K., & Yu, H. (2013). Enhancing digital fluency through a training program for creative problem solving using computer programming. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 47 (3), 171–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.30
Kordaki, M. (2012). Diverse categories of programming learning activities could be performed within scratch. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 46 , 1162–1166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.267
Korkmaz, Ö. (2016). The effect of Lego Mindstorms Ev3 based design activities on students’ attitudes towards learning computer programming, self-efficacy beliefs and levels of academic achievement. Baltic journal of modern computing , 4 (4), 994-1007. Doi: 10.22364/bjmc.2016.4.4.24.
Korkmaz, Ö. (2018). The effect of scratch-and Lego Mindstorms Ev3-based programming activities on academic achievement, problem-solving skills and logical-mathematical thinking skills of students. MOJES: Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Sciences, 4(3), 73–88. https://mojes.um.edu.my/article/view/12658
Korkmaz, Ö., Çakır, R., & Özden, M. Y. (2015). Bilgisayarca düşünme beceri düzeyleri ölçeğinin (BDBD) ortaokul düzeyine uyarlanması [Computational Thinking Levels Scale (Ctls) Adaptation for Secondary School Level]. Gazi Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi, 1 (2), 143–462.
Lai, A.-F., & Yang, S.-M. (2011). The learning effect of visualized programming learning on 6th graders’ problem solving and logical reasoning abilities. In international conference on electrical and control engineering (ICECE) (pp. 6940-6944). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/ICECENG.2011.6056908.
Lau, W. W., & Yuen, A. H. (2011). Modelling programming performance: Beyond the influence of learner characteristics. Computers & Education, 57 (1), 1202–1213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.01.002
Lishinski, A., Yadav, A., Enbody, R., & Good, J. (2016). The influence of problem solving abilities on students’ performance on different assessment tasks in introductory programming. In SIGCSE ‘16 (pp. 329-324). ACM. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/2839509.2844596 .
Maloney, J. H., Peppler, K., Kafai, Y., Resnick, M., & Rusk, N. (2008). Programming by choice. In proceedings of the 39th SIGCSE technical symposium on computer science education - SIGCSE ‘08 (Vol. 40, pp. 367-371). ACM. doi: 10.1145/1352135.1352260.
Maloney, J., Resnick, M., Rusk, N., Silverman, B., & Eastmond, E. (2010). The scratch programming language and environment. ACM transactions on computing education (TOCE), 10 (4), article 16. doi: 10.1145/1868358.1868363.
Marcelino, M. J., Pessoa, T., Vieira, C., Salvador, T., & Mendes, A. J. (2017). Learning computational thinking and scratch at distance. Computers in Human Behavior, 80 , 470–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.09.025
Marques, F. O., & Marques, M. T. (2012). No problem? No research, little learning... big problem! Journal of Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, 10(3), 60–62. http://www.iiisci.org/journal/sci/FullText.asp?var=&id=HRE981NS . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Mayer, R. E. (1998). Cognitive, metacognitive and motivational aspects of problem solving. Instructional Science, 26 , 49–63. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003088013286
McGehee, J. J. (2001). Developing interdisciplinary units: A strategy based on problem solving. School Science and Mathematics, 101 (7), 380–389. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1949-8594.2001.tb17972.x
MEB. (2018). Bilişim Teknolojileri ve Yazılım dersi öğretim programı (Ortaokul 5 ve 6. Sınıflar) [information technologies and software course curriculum (5th and 6th grades)] . Milli Eğitim Bakanlığı.
Miller, M., & Nunn, G. D. (2001). Using group discussion to improve social problem solving and learning. Education, 121 (3), 470–475.
Min, W., Mott, B., Park, K., Wiebe, E., Boyer, K. E., & Lester, J. (2020). Promoting computer science learning with block-based programming and narrative-centered gameplay. In proceedings of IEEE conference on games (pp. 654-657). IEEE.
Nelson, J. (2009, May 01). Celebrating scratch in libraries: The gaming life. School Library Journal. https://www.slj.com/?detailStory=celebrating-scratch-in-libraries-the-gaming-life . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Nouri, J., Zhang, L., Mannila, L., & Norén, E. (2020). Development of computational thinking, digital competence and 21st century skills when learning programming in K-9. Education Inquiry, 11 (1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/20004508.2019.1627844
Oddie, A., Hazlewood, P., Blakeway, S., & Whitfield, A. (2010). Introductory problem solving and programming: Robotics versus traditional approaches. Innovations in Teaching & Learning in Information & Computer Sciences, 9 (2), 1–11. Doi: 10.11120/ital.2010.09020011.
Oluk, A., & Saltan, F. (2015). Effects of using the scratch program in 6th grade information technologies courses on algorithm development and problem solving skills. Participatory educational research , 2 (5), 10-20. Doi: 10.17275/per.15.spi.2.2.
Papert, S. (1980). Mindstorms: Children, computers, and powerful ideas. Basic.
Pearson, E. S., & Hartley, H. O. (1958). Biometrika tables for statisticians . Cambridge University Press.
Psycharis, S., & Kallia, M. (2017). The effects of computer programming on high school students’ reasoning skills and mathematical self-efficacy and problem solving. Instructional Science, 45 , 583–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-017-9421-5
Resnick, M., Kafai, Y., Maeda, J., Rusk, N., & Maloney, J. (2003). A networked, media-rich programming environment to enhance technological fluency at after-school centers in economically-disadvantaged communities . Proposal submitted to the National Science Foundation. https://web.media.mit.edu/~mres/papers/scratch-proposal.pdf . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Resnick, M., Maloney, J., Hernández, A. M., Rusk, N., Eastmond, E., Brennan, K., Millner, A., Rosenbaum, E., Silver, J., Silverman, B., & Kafai, Y. (2009). Scratch: Programming for all. Communications of the ACM, 52 (11), 60–67. https://doi.org/10.1145/1592761.1592779
Rodríguez-Martínez, J. A., González-Calero, J. A., & Sáez-López, J. M. (2020). Computational thinking and mathematics using scratch: An experiment with sixth-grade students. Interactive Learning Environments, 28 (3), 316–327. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1612448
Romero, J. S. (2010). Library programming with Lego Mindstorms, scratch, and Pico cricket: Analysis of best practices for public libraries. Computers in Libraries, 30 (1), 16–19.
Sáez-López, J. M., Román-González, M., & Vázquez-Cano, E. (2016). Visual programming languages integrated across the curriculum in elementary school: A two year case study using “scratch” in five schools. Computers & Education, 97 , 129–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.03.003
Serin, O., Bulut Serin, N., & Saygılı, G. (2010). İlköğretim düzeyindeki çocuklar için problem çözme envanteri’nin (ÇPÇE) geliştirilmesi [developing problem solving inventory for children at the level of primary education (PSIC)]. İlköğretim Online , 9(2), 446–458. http://ilkogretim-online.org.tr/index.php/io/article/view/1774/1610
Shalihah, F., Supramono, S., & Abdullah, A. (2019). Blended learning-based media usage to practice problem solving skills. European Journal of Education Studies. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2544571
Siegle, D. (2009). Developing student programming and problem-solving skills with visual basic. Gifted child today, 32 (4), 24–29. Doi: 10.1177%2F107621750903200408.
Soykan, F., & Kanbul, S. (2018). Analysing K12 students’ self-efficacy regarding coding education. TEM Journal, 7(1), 182–187. https://dx.doi : .org/ https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM71-22
Taylor, M., Harlow, A., & Forret, M. (2010). Using a computer programming environment and an interactive whiteboard to investigate some mathematical thinking. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 8 , 561–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.12.078
Vatansever, Ö., & Göktalay, Ş. B. (2018). How does teaching programming through scratch affect problem-solving skills of 5th and 6th grade middle School students? Uluslararasi Avrasya Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 9(33), 1778–1801. http://www.ijoess.com/DergiTamDetay.aspx?ID=2223&Detay=Ozet . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Veerasamy, A. K., D’Souza, D., Lindén, R., & Laakso, M. J. (2019). Relationship between perceived problem-solving skills and academic performance of novice learners in introductory programming courses. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 35 (2), 246–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12326
Voskoglou, M. G., & Buckley, S. (2012). Problem solving and computers in a learning environment. Egyptian Computer Science Journal, 36(4), 28–46. http://ecsjournal.org/JournalArticle.aspx?articleID=336 . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
Wilson, A., Hainey, T., & Connolly, T. M. (2013). Using scratch with primary school children: An evaluation of games constructed to gauge understanding of programming concepts. International Journal of Game-Based Learning (IJGBL), 3 (1), 93–109. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijgbl.2013010107
Wilson, A., & Moffat, D. C. (2010). Evaluating scratch to introduce younger school children to programming. In J. Lawrance & R. Bellamy (Eds.), Proceedings of the 22nd annual psychology of programming interest group. PPIG.
Yildiz-Durak, H., & Guyer, T. (2019). An investigation of the opinions of gifted primary school students’ in the programming training processes [Programlama ogretim surecinde ustun yetenekli ilkokul ogrencilerinin goruslerinin incelenmesi]. Ankara University journal of Faculty of Educational Sciences, 52 (1), 107-137. Doi: 10.30964/auebfd.466922.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mehmet Akif Ersoy University, Burdur, Turkey
Osman Erol & Neşe Sevim Çırak
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Osman Erol .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Erol, O., Çırak, N.S. The effect of a programming tool scratch on the problem-solving skills of middle school students. Educ Inf Technol 27 , 4065–4086 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10776-w
Download citation
Received : 17 May 2021
Accepted : 05 October 2021
Published : 16 October 2021
Issue Date : April 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10776-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Middle school
- Problem-solving skill
- Programming education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Scenarios
Do you have kiddos who struggle with their social problem-solving skills? Teach your students the simple process of how to solve a problem along with having them review how well their solution worked or didn’t work.
Why Teach Problem Solving Skills?
Learning to problem solve is an essential skill that is used not only throughout childhood but also into adulthood. Social problem solving is the ability to change or adapt to undesirable situations that arise throughout our day.
On a daily basis, a child will encounter social problems that they will need to solve.
Anything from:
- arguing with another student
- to hurting a friend’s feelings
- to having a difficult conversation
- working with others

Start with Small Problems
Many of the “problems” children encounter are often small problems which the child may be over-reacting to, such as wanting a different coloring crayon or wanting to be first in line, however, these small problems are still very real to the child.
Practicing problem-solving with these small problems can be a great learning opportunity. Children can practice problem-solving with a small problem which can help them learn how to handle bigger problems in the future.
Problem Solving Importance
Social problem-solving skills are critical to a child’s social interactions, personal and professional relationships. A child’s ability to handle change, cope with stress, and handle challenges improves with a child’s ability to successfully solve social problems.
The ultimate goal is that the child will be able to solve social problems all on their own, but until they can independently solve a problem they will need to learn how to communicate and self-advocate to positively solve their problems.
Steps to Problem Solving
Children can be taught how to problem solve through a guided process of breaking down the problem and using simple steps to solve the problem.
Learning specific steps to problem-solving can allow children to remember how to solve a problem when they become overwhelmed or stressed.
Although learning to solve a problem independently can take some time and practice it is well worth the investment to have a child who can eventually solve most social situations in a positive manner on their own.
What we learnt about solving problems is don't freak out, if one thing doesn't work , try something else out. And work together as a team. #melthammathsweek #MELTHAMPUPILVOICE @problemsolveit pic.twitter.com/iVm1Im4Aue — yr6melthamce (@yr6melthamce) February 4, 2019
Problem Solving Form
Teach your students the 4 steps to becoming a social problem-solver.
- Identify the problem. For instance, start by having your student identify the social problem.
- Create three solutions. Also, have your student come up with three different solutions that they could use to solve the problem that they identified.
- Identify the consequences. Then, identify the consequence for each individual solution.
- Pick the best solution. Lastly, have your student identify which of their three solutions is the best choice Then have your student put into words why they think that solution is the best solution.
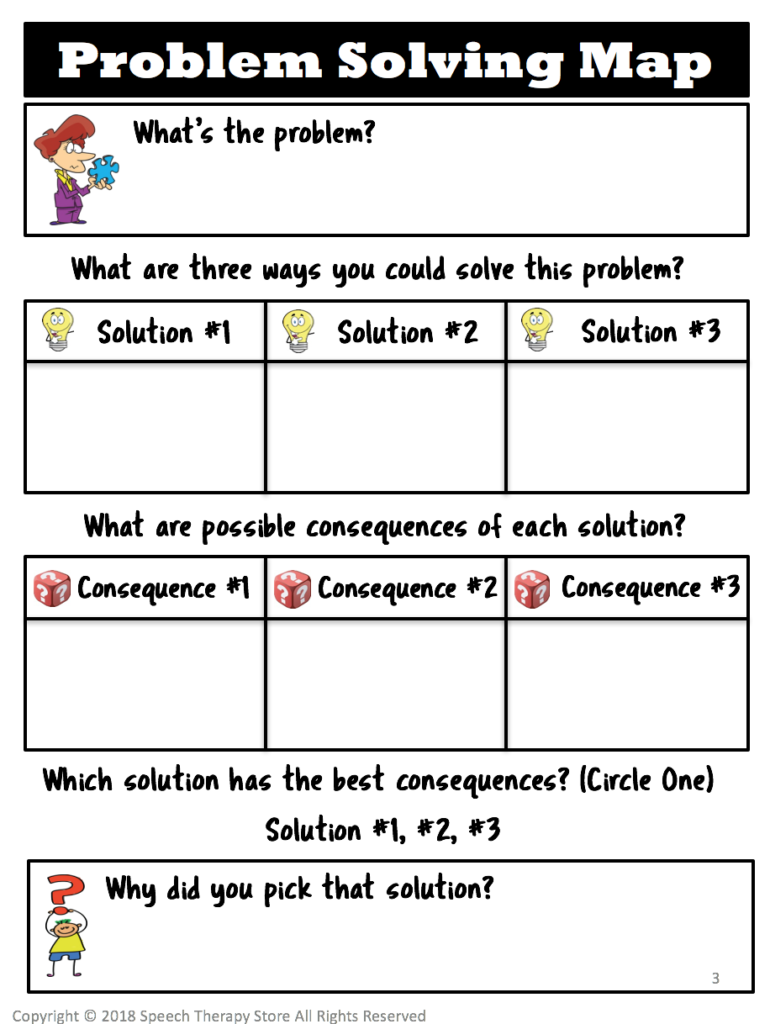
Problem Solving Review Form
After your students go through the social problem-solver have them use the social problem-solving review form.
- What happened. For instance, after your student tried their solution have them explain what happened next.
- Review the results. Also, have your student identify whether or not their solution got them the results they wanted.
- Use this solution again. Furthermore, have your student identify whether or not they would use this solution again in the future to solve the same or similar problem.
- What would you do differently? Finally, have your student explain what they would do differently if they didn’t get the results they wanted or if they wouldn’t use that solution again in the future.
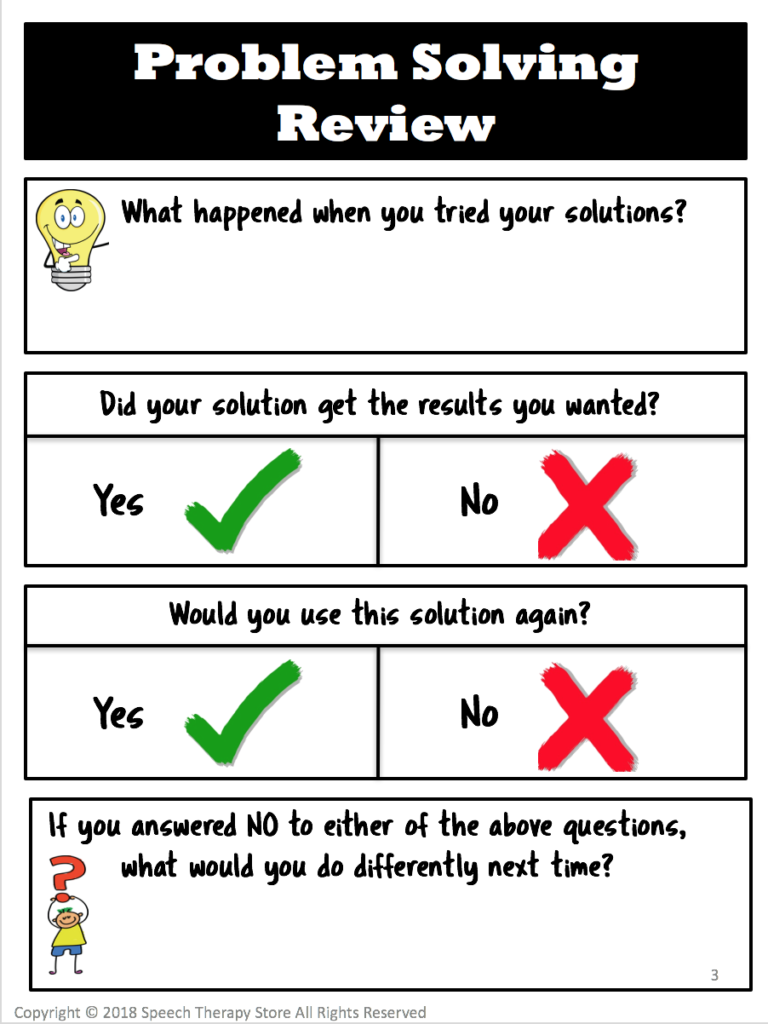
71+ Social Problem Scenarios + 6 Blank Scenarios
Use the 71 social problem-solving scenarios to have your students get great experience practicing how to solve a social problem.
Also, included are 6 blank scenarios. Then laminate them so you can use them over and over again. Therefore, create social problems that the student experiences and needs help solving.
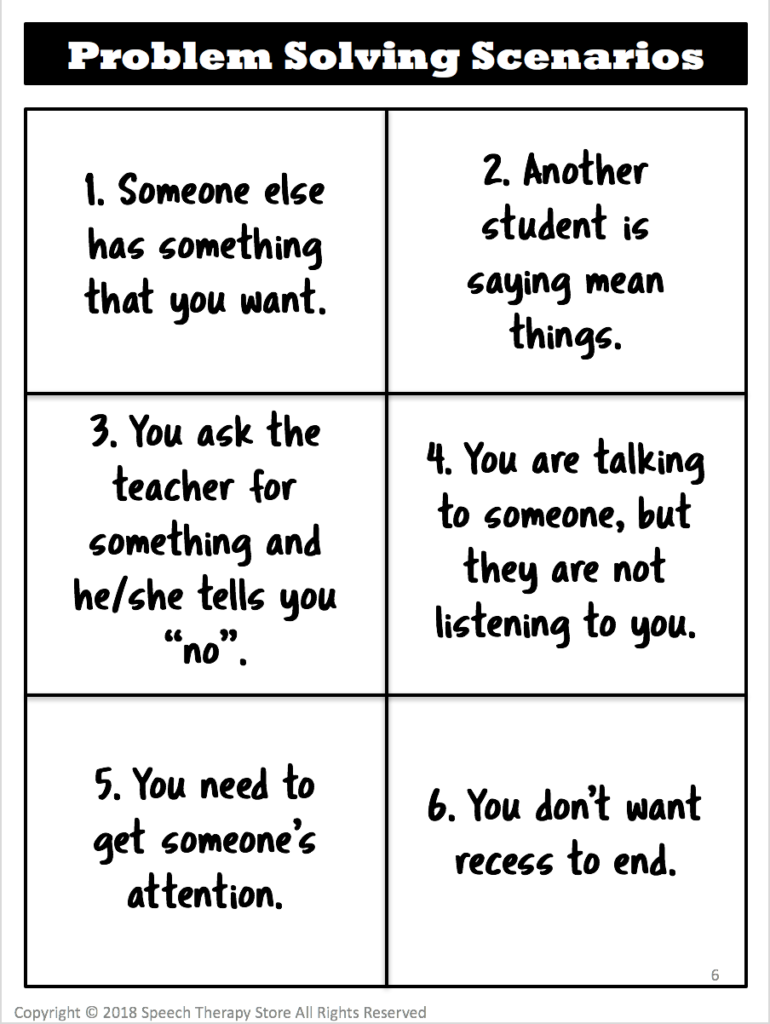
Wordless Video teaching Problem Solving
Watch this super cute wordless animation with your students and have them discuss the problem they see and how to best solve the problem.
Use this as a fun practice example to get your students started towards learning how to problem-solve.
Demonstrate Through Modeling
Model and discuss empathy.
First and foremost, children need to understand how another person might be feeling in a given situation in order to become a good social problem solver. The student needs to learn how to “stand in someone else’s shoes” for a little bit.
One way you can work on this skill is during the reading time you can focus on how a particular character in the story might be feeling.
Ask questions, such as:
- “How do they feel right now?”
- “How would you feel in that same situation?”
- “Why do you think they feel that way?”
Model Problem-Solving Skills as the Teacher
When you are faced with a problem you can solve the problem by thinking aloud for the students to hear how you solve a problem.
You can state the problem, then come up with possible solutions, then identify the possible consequences to each solution, then pick and explain why a solution is the best option.
For example, you could say, “I was hoping to take the class outside for a stress walk around the track before the reading test, but the problem is that it is raining outside. I could still take you outside, but then you will get wet, or we could walk the halls, but then we’d have to be really quiet because there are other classes learning, or we could just skip the walk and take the reading test, but then you might not do as well on the test. I think based on all of those solutions the best solution will be to walk the hallway, but you guys will have to promise to be quiet so that we don’t disrupt other classes.
Modeling the problem-solving process can be very helpful for the students to watch, observe, and later implement themselves.
Teach Communication
Have students communicate how they are feeling.
Teaching your students to share their emotions in a respectful way can improve their ability to problem-solve.
Have students use an “I” sentence frame, such as, “I feel _____ (insert feeling word) when _____ (identify what made you feel that way).”
For example, “I felt sad when Jackson broke my favorite pencil” or “I was mad when I wasn’t picked to be first in line.”
This way students can communicate how they are feeling using honest and open communication. Teaching students to appropriately communicate their emotions can help solve some social problems from the beginning.
Encourage Independency
Encourage your student to problem solve.
If your student is struggling to problem solve independently encourage them to do so using open-ended questions.
- “How could you fix this problem?”
- “What would be a fair solution?”
- “What would happen if you used that solution?”
Let the Student try to Problem Solve Independently
Give your students the space to try and solve their own problems using the guided strategies. Try not to come running to their rescue for every little problem.
Some problems are small and a great opportunity for the student to learn and practice. If an adult does all of the problem solving for a student then what are they really learning?
Give your students the time and space they need to practice solving small problems on their own. Of course, if it is a bigger or more serious problem then have an adult help guide the problem-solving process.
Tell an Adult
Remind your students that there are still some problems that are too big for them to solve on their own and that it is okay to get help from an adult to solve big problems.
For example, if the student doesn’t feel safe, someone is being hurt physically or emotionally, or if they tried to solve a problem independently but it didn’t work and they need help. Let them know that it’s okay to tell an adult.
Teach How to Disagree and How to Make Up
Discuss how to disagree respectfully.
Remind your student that they won’t always agree with their teacher, friends, classmate, or parents and that’s okay. Even the people we like might have different opinions, interests, and likes than we do.
However, even if we disagree with someone we should still treat them with respect. Treating someone with respect means to not call them names, ignore them, yell or hit them. It means that you do try to create solutions that both parties can agree with and to apologize when we hurt others’ feelings.
Role-Play How to Make Up
Practice in everyday life how to make up after a social problem .
Students are really having to stretch their brains today. It's @NSPCC #NumberDay and @problemsolveit are challenging Y9 and 10 to solve the escape room boxes. It's not as easy as it looks! The promise of a few sweet treats for the winners seems to be helping though! pic.twitter.com/AxRRJnJIv2 — CongletonHS (@CongletonHS) February 2, 2018
Be sure to get your free social problem solver today below! I hope you and your students love this freebie.
Have your students use task card scenarios to help them identify how they and others might feel in different social scenarios. Be sure to discuss the problem, identify possible solutions, identify the consequences of those possible solutions, and then based on those consequences pick the best solution.
Make social problem-solving a game by telling the students that they are social detectives and that it is their job to use what they know about social rules to help them identify the possible and best solutions.
Start practicing today with 71+ free social problem social task cards! Do your students need more practice?
Be sure to check out my other freebie for 31 wordless animated videos to teach problem-solving and so much more.
Make Problem Solving Easier with this Freebie!
Download yours today to get started.
Get More Problem Solving Time Saving Materials
Next, be sure to check out the following time-saving materials to continue to teach your students how to solve their social problems in addition to this freebie.
Weekly Social Pragmatics Homework

- Weekly problem-solving. Send home a weekly homework page that includes a problem-solving scenario plus an idiom and a conversational practice scenario.
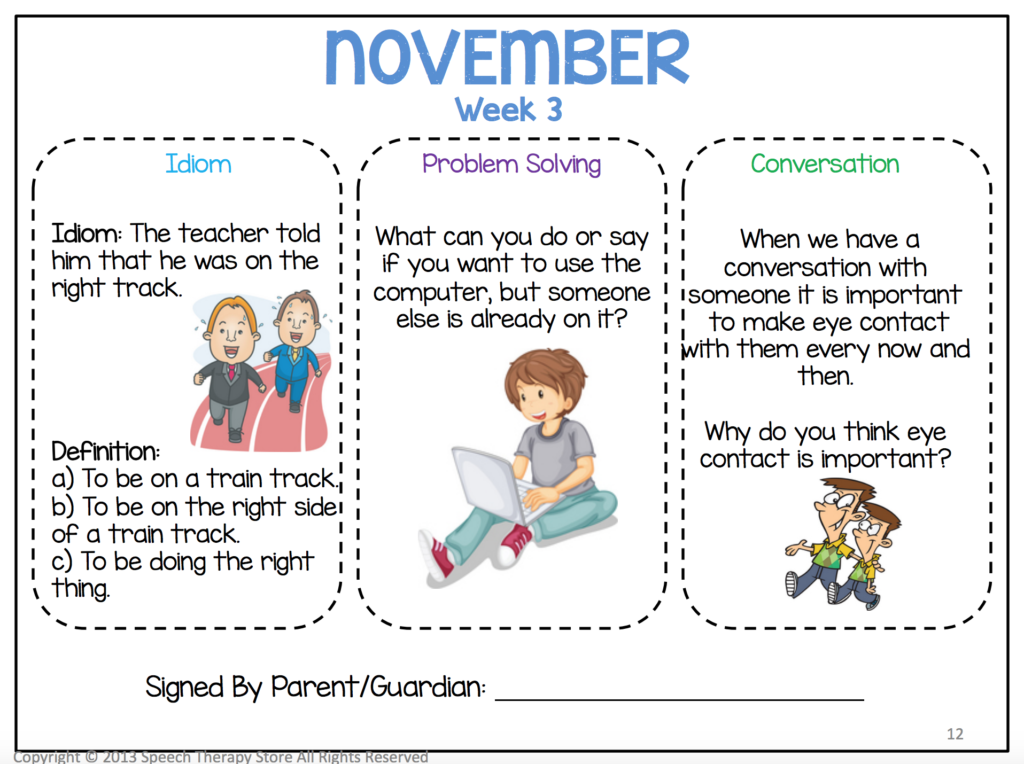
Restorative Justice Problem Solving Flip Book

- Restorative justice graphic visual. Use this graphic visual to help your student restore a social relationship after a social problem.

Self-Advocating Role-Play Scenarios

- Self-advocating in high school. Teach your high schoolers the process to self-advocate for what they need.

5th-12th Grade Life Skills Problem Solving

- Life skills problem-solving. In addition, this life skills differentiated bundle includes a problem-solving lesson plan.
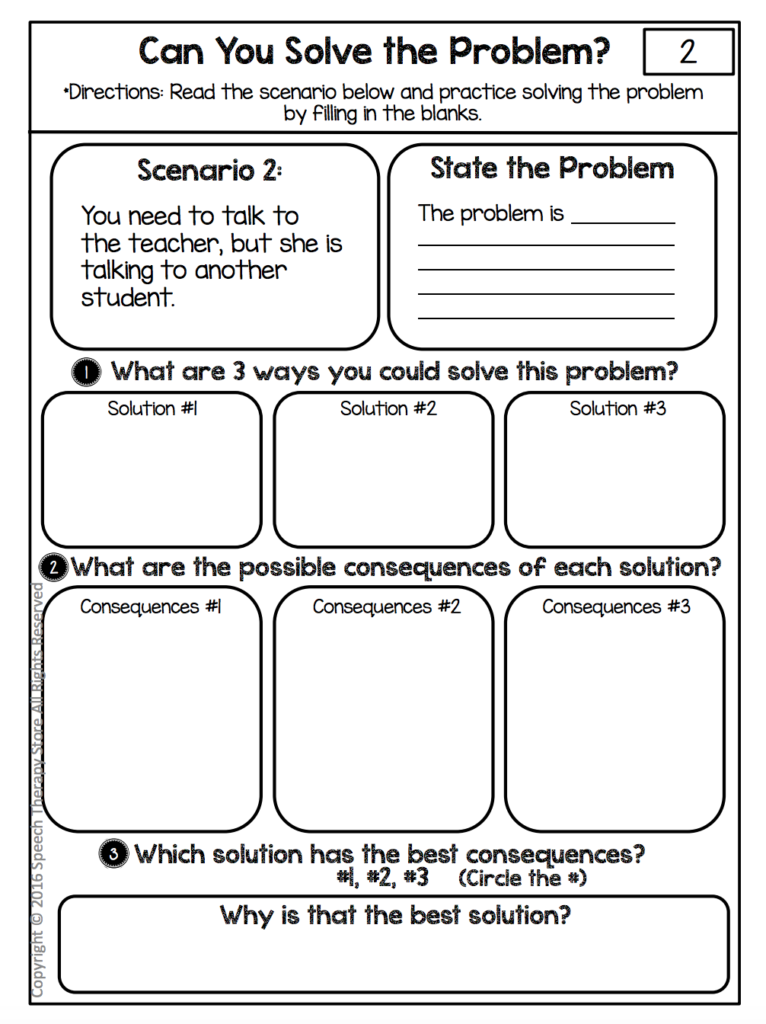
I recommend you read Problem Solving Wheel: Help Kids Solve Their Own Problems , 61+ Free Fillable SLP Planner Pages 2020-2021 , 430+ Free Multisyllabic Words List Activity Bundle , or 432+ Free IEP Goal Bank to Save You Time posts because they include freebies as well and who doesn’t want more freebies!
Got questions? Leave a comment. Let’s chat!
Monday 30th of January 2023
Hello! I have entered my name and email twice (yesterday & today) to receive to 71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Senarios, but I have not received anything yet. Not even an email back to mine in order to subcribe. Thanks for your help! Tracy
Melissa Berg
Tuesday 31st of January 2023
Hi Tracy, Thanks so much for reaching out! Sorry about that. We went ahead and sent you an email with the PDF attached. Wishing you all my best, Melissa
Problem Solving Skills
Tuesday 30th of August 2022
I truly love your site. Excellent colors, theme and writing. Thanks for sharing.
Laura Ricca
Monday 11th of April 2022
Tuesday 12th of April 2022
Hi Laura, I'm glad you found this resource helpful. Melissa
Modified Mental Health and Suicide Prevention - Speech Therapy Store
Monday 11th of May 2020
[…] 71+ FREE SOCIAL PROBLEM-SOLVING SCENARIOS […]
Problem Solving Wheel: Help Kids Solve Their Own Problems - Speech Therapy Store
Monday 4th of May 2020
[…] 71+ Free Social Problem Solving Task Cards Scenarios […]

10 Helpful Worksheet Ideas for Primary School Math Lessons
M athematics is a fundamental subject that shapes the way children think and analyze the world. At the primary school level, laying a strong foundation is crucial. While hands-on activities, digital tools, and interactive discussions play significant roles in learning, worksheets remain an essential tool for reinforcing concepts, practicing skills, and assessing understanding. Here’s a look at some helpful worksheets for primary school math lessons.
Comparison Chart Worksheets
Comparison charts provide a visual means for primary school students to grasp relationships between numbers or concepts. They are easy to make at www.storyboardthat.com/create/comparison-chart-template , and here is how they can be used:
- Quantity Comparison: Charts might display two sets, like apples vs. bananas, prompting students to determine which set is larger.
- Attribute Comparison: These compare attributes, such as different shapes detailing their number of sides and characteristics.
- Number Line Comparisons: These help students understand number magnitude by placing numbers on a line to visualize their relative sizes.
- Venn Diagrams: Introduced in later primary grades, these diagrams help students compare and contrast two sets of items or concepts.
- Weather Charts: By comparing weather on different days, students can learn about temperature fluctuations and patterns.
Number Recognition and Counting Worksheets
For young learners, recognizing numbers and counting is the first step into the world of mathematics. Worksheets can offer:
- Number Tracing: Allows students to familiarize themselves with how each number is formed.
- Count and Circle: Images are presented, and students have to count and circle the correct number.
- Missing Numbers: Sequences with missing numbers that students must fill in to practice counting forward and backward.
Basic Arithmetic Worksheets
Once students are familiar with numbers, they can start simple arithmetic.
- Addition and Subtraction within 10 or 20: Using visual aids like number lines, counters, or pictures can be beneficial.
- Word Problems: Simple real-life scenarios can help students relate math to their daily lives.
- Skip Counting: Worksheets focused on counting by 2s, 5s, or 10s.
Geometry and Shape Worksheets
Geometry offers a wonderful opportunity to relate math to the tangible world.
- Shape Identification: Recognizing and naming basic shapes such as squares, circles, triangles, etc.
- Comparing Shapes: Worksheets that help students identify differences and similarities between shapes.
- Pattern Recognition: Repeating shapes in patterns and asking students to determine the next shape in the sequence.
Measurement Worksheets
Measurement is another area where real-life application and math converge.
- Length and Height: Comparing two or more objects and determining which is longer or shorter.
- Weight: Lighter vs. heavier worksheets using balancing scales as visuals.
- Time: Reading clocks, days of the week, and understanding the calendar.
Data Handling Worksheets
Even at a primary level, students can start to understand basic data representation.
- Tally Marks: Using tally marks to represent data and counting them.
- Simple Bar Graphs: Interpreting and drawing bar graphs based on given data.
- Pictographs: Using pictures to represent data, which can be both fun and informative.
Place Value Worksheets
Understanding the value of each digit in a number is fundamental in primary math.
- Identifying Place Values: Recognizing units, tens, hundreds, etc., in a given number.
- Expanding Numbers: Breaking down numbers into their place value components, such as understanding 243 as 200 + 40 + 3.
- Comparing Numbers: Using greater than, less than, or equal to symbols to compare two numbers based on their place values.
Fraction Worksheets
Simple fraction concepts can be introduced at the primary level.
- Identifying Fractions: Recognizing half, quarter, third, etc., of shapes or sets.
- Comparing Fractions: Using visual aids like pie charts or shaded drawings to compare fractions.
- Simple Fraction Addition: Adding fractions with the same denominator using visual aids.
Money and Real-Life Application Worksheets
Understanding money is both practical and a great way to apply arithmetic.
- Identifying Coins and Notes: Recognizing different denominations.
- Simple Transactions: Calculating change, adding up costs, or determining if there’s enough money to buy certain items.
- Word Problems with Money: Real-life scenarios involving buying, selling, and saving.
Logic and Problem-Solving Worksheets
Even young students can hone their problem-solving skills with appropriate challenges.
- Sequences and Patterns: Predicting the next item in a sequence or recognizing a pattern.
- Logical Reasoning: Simple puzzles or riddles that require students to think critically.
- Story Problems: Reading a short story and solving a math-related problem based on the context.
Worksheets allow students to practice at their own pace, offer teachers a tool for assessment, and provide parents with a glimpse into their child’s learning progression. While digital tools and interactive activities are gaining prominence in education, the significance of worksheets remains undiminished. They are versatile and accessible and, when designed creatively, can make math engaging and fun for young learners.
The post 10 Helpful Worksheet Ideas for Primary School Math Lessons appeared first on Mom and More .
![Mathematics is a fundamental subject that shapes the way children think and analyze the world. At the primary school level, laying a strong foundation is crucial. While hands-on activities, digital tools, and interactive discussions play significant roles in learning, worksheets remain an essential tool for reinforcing concepts, practicing skills, and assessing understanding. Here’s a look […] Mathematics is a fundamental subject that shapes the way children think and analyze the world. At the primary school level, laying a strong foundation is crucial. While hands-on activities, digital tools, and interactive discussions play significant roles in learning, worksheets remain an essential tool for reinforcing concepts, practicing skills, and assessing understanding. Here’s a look […]](https://img-s-msn-com.akamaized.net/tenant/amp/entityid/AA1l9GSr.img?w=768&h=1152&m=6)

(Mobile) Join Mailing List
Dialectical behavior therapy skills training for emotional problem solving for adolescents.

Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Training for Emotional Problem Solving for Adolescents (DBT STEPS-A) is an adaptation of DBT® designed for adolescents in middle and high school. DBT STEPS-A aims to help adolescents “build a life worth living” by developing skills such as emotion management, relationship building, and decision-making to help them navigate challenging situations and stressors that can arise during adolescence. DBT STEPS-A’s approach is grounded in the idea that two seemingly opposing facts can both be true, most notably that the curriculum’s goals include both acceptance and change. DBT STEPS-A instructors strive to help adolescents both accept themselves and make changes in their behavior.
DBT STEPS-A can be delivered school-wide as a general education intervention with just classroom-based group skills training, or in a tiered approach with additional components for adolescents who need more support. The tiered approach can be applied in schools that use a response to intervention model where adolescents are designated into three academic support tiers: (1) general education, (2) needing additional academic or social emotional support, or (3) receiving intensive support through the special education system. All three tiers receive the classroom-based group skills training. Adolescents in Tier 2 and Tier 3 also receive individual coaching focused on practicing the skills learned in group skills training. Adolescents in Tier 3 participate in multi-family group skills training sessions with their parents, and their instructors participate in consultation team meetings where they discuss any implementation challenges and receive support designed to improve their capacity to deliver the curriculum.
During the group skills training, instructors guide adolescents in identifying target behaviors to increase or decrease (e.g., increasing studying and going to school and decreasing substance use). Instructors also teach behavioral skills to groups of adolescents over four modules: (1) mindfulness, (2) distress tolerance, (3) emotion regulation, and (4) interpersonal effectiveness. The mindfulness and distress tolerance modules focus on building acceptance-oriented skills while the emotion regulation and interpersonal effectiveness modules focus on building change-oriented skills. In the mindfulness module, instructors emphasize accepting current circumstances and being present. In the distress tolerance module, instructors instruct adolescents on how to accept and tolerate painful situations without engaging in harmful behaviors. In the emotion regulation module, instructors strive to help participants become less susceptible to painful emotions. Finally, in the interpersonal effectiveness module, instructors teach adolescents to ask for what they want, to say no when necessary, and to maintain respectful relationships with themselves and others.
DBT STEPS-A does not currently meet criteria to receive a rating because no studies of the program achieved a rating of moderate or high on design and execution.
Date Research Evidence Last Reviewed: May 2024
The following sources informed the program or service description, target population, and program or service delivery and implementation information: the program or service manual, and the program or service developer’s website.
This information does not necessarily represent the views of the program or service developers. For more information on how this program or service was reviewed, visit the Review Process page or download the Handbook .
Target Population
DBT STEPS-A is designed for adolescents ages 12–19 in middle and high school. DBT STEPS-A is designed to be delivered school-wide to adolescents in general education settings. In schools with a response to intervention model, instructors can deliver DBT STEPS-A with additional components for students in the special education system or who need more support.
Program or Service Delivery and Implementation
Instructors typically deliver DBT STEPS-A to groups of adolescents over 30 sessions. Sessions can be delivered weekly or over 20–40 weeks depending on the school schedule. Instructors start with an orientation session followed by a session introducing the concept of dialectics. Next, instructors provide three sessions on mindfulness followed by 5-7 sessions on each of the other three skills modules. Instructors also provide an additional two sessions of mindfulness between each module.
When implemented as a school-wide intervention or for adolescents receiving Tier 1 support, instructors typically deliver the classroom-based skills training in 50-minute sessions. Instructors generally deliver the four skills modules once per week over two semesters or twice per week over one semester.
For teens receiving Tier 2 and Tier 3 support, instructors deliver DBT STEPS-A skills training in a smaller classroom setting to groups of 10–15 students. Instructors may complete two cycles of the four skills modules, or split each session over two class periods, to give adolescents more opportunities to learn and practice the skills in each module.
For teens receiving Tier 2 and Tier 3 support, instructors provide individual coaching as needed to adolescents. For adolescents receiving Tier 3 support, instructors typically offer additional monitoring and mentoring for 15–45 minutes weekly. Finally, instructors can offer evening multi-family group skills training sessions once or twice a month for adolescents in Tier 3 and their parents.
Schools may have multiple instructors delivering DBT STEPS-A to adolescents receiving Tier 3 support. In this case, instructor consultation teams meet weekly for 45–90 minutes throughout the program period.
Location/Delivery Setting
Recommended locations/delivery settings.
Instructors deliver DBT STEPS-A in school settings. DBT STEPS-A can be delivered as a standalone mandatory course, as part of an existing course, such as a health course, or as an elective course.
Education, Certifications and Training
Instructors are typically general education teachers or school personnel, such as health teachers, school counselors, school psychologists, or social workers. Instructors delivering DBT STEPS-A to adolescents receiving Tier 2 and Tier 3 support should have adolescent mental health expertise.
DBT STEPS-A training is recommended for instructors. The three-day DBT STEPS-A training provides a comprehensive overview of DBT STEPS-A sessions, describes implementation strategies, identifies potential challenges and solutions for delivering the curriculum and supporting students, and provides instructors with opportunities to practice delivering the curriculum with other training participants.
Program or Service Documentation
Book/manual/available documentation used for review.
Mazza, J. J., Dexter-Mazza, E. T., Miller, A. L., Rathus, J. H., & Murphy, H. E. (2016). DBT skills in schools: Skills Training for Emotional Problem Solving for Adolescents (DBT STEPS-A). Guilford Press.
Available languages
The DBT STEPS-A manual is available in English.
Other supporting materials
Overview of DBT STEPS-A
DBT STEPS-A Training Information
For More Information
Website: https://www.dbtinschools.com/
Email: [email protected]
Note: The details on Dosage; Location; Education, Certifications, and Training; Other Supporting Materials; and For More Information sections above are provided to website users for informational purposes only. This information is not exhaustive and may be subject to change.
Extent of Evidence
Studies reviewed, studies rated low.
Flynn, D., Joyce, M., Weihrauch, M., & Corcoran, P. (2018). Innovations in Practice: Dialectical Behaviour Therapy — Skills training for emotional problem solving for adolescents (DBT STEPS-A): Evaluation of a pilot implementation in Irish post‐primary schools. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 23(4), 376-380. https://doi.org/10.1111/camh.12284
Martinez, R. R., Jr., Marraccini, M., Knotek, S. E., Neshkes, R. A., & Vanderburg, J. (2021). Effects of Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Skills Training for Emotional Problem Solving for Adolescents (DBT STEPS-A) program of rural ninth-grade students. School Mental Health, 14, 165-178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-021-09463-5
- Recommend a Program or Service
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Programs and Services Reviewed
- Programs and Services Planned for Review
- Programs and Services Recommended for Review
- Review Process Overview
- Identify Programs and Services
- Select and Prioritize Programs and Services
- Literature Search
- Study Eligibility Screening and Prioritization
- Evidence Review
- Program and Service Ratings
- Handbook of Standards and Procedures 1.0
- All Clearinghouse Resources
- Related Resources
- Our Equity Action Plan
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Vulnerability Disclosure Policy
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » Lesson Plans » Conversation Skills Game for Middle School

Conversation Skills Game for Middle School
In the dynamic world of middle school education, developing strong communication skills is crucial. These skills are not only fundamental for academic success but also for personal growth and social interactions. Middle school speech-language pathologists (SLPs) are constantly on the lookout for innovative tools that can motivate and engage students in meaningful ways. One such tool is “Operation Pizza,” a conversation skills game for middle school students. This interactive game integrates the excitement of racing against the clock and working together to deliver pizzas with the practical application of conversation skills. This blog explores how “Operation Pizza” can be a game-changer in speech-language therapy sessions.
The Importance of Conversation Skills in Middle School
Conversation skills are more than just the ability to speak to others; they involve listening, interpreting social cues, responding appropriately, and understanding the nuances of verbal and non-verbal communication. For middle schoolers, who are navigating a complex social landscape, these skills are vital. They help students build relationships, resolve conflicts, and express themselves clearly. SLPs play a critical role in teaching these skills, especially to students who struggle with communication challenges.
Introducing a Conversation Skills Game for Middle School
“Operation Pizza” is a highly engaging conversation skills game where students work in teams to “create” and “deliver” pizzas. The game is designed to simulate a fast-paced pizza shop environment where each team member must communicate effectively to complete their orders on time. This setting provides a fun and relatable context for students to practice and hone their communication skills.

Educational Benefits of Operation Pizza
Promotes teamwork and social interaction.
By working in a team, students learn the importance of cooperation and verbal exchange. They gain experience in managing interpersonal dynamics in a supportive, structured environment.
Develops Problem-Solving Skills
The game’s fast-paced nature forces students to think on their feet and solve problems quickly, all while communicating their thoughts and actions to their teammates.
Builds Confidence
As students engage in repeated gameplay, they become more comfortable with speaking up and sharing their ideas. This confidence can translate into improved participation in class discussions and other social settings.

Unlock ALL of our Social Communication activities by signing up for your free trial today – no credit card required!
Access the full social communication curriculum here.
Instant access to thousands of no-prep social skills activities, over 1000+ video lessons, and engaging games designed to enhance learning and development.
Operation Pizza is more than just a game; it’s a powerful tool for middle school speech-language pathologists seeking to enrich their students’ communication abilities. Through the engaging context of making and delivering pizzas, students practice crucial conversation skills that are essential for their academic and social success. By incorporating this game into your speech therapy toolkit, you can provide a fun and effective way for students to learn, grow, and express themselves more confidently.
Sample Video
Students learn best from watching real students their own age model skills. Try out this sample video lesson. We offer our entire Social-Emotional Learning platform free for 14 days here !
Related Blog Posts:
Lesson Plan: Starting a Conversation
3 Activities for Teaching Basic Conversation Skills
Free High School Basic Conversation Skills Material
Looking for Free Social Skills Samples? Click here!

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Bring problem-solving to life in your middle school classroom with these 20 activities. 1. Feelings Expression Scenarios ... Engage problem-solving skills within context while reinforcing math, research, geography, and communication skills, too! Students can plan a road trip from start to finish in small groups. As an added bonus, you can let ...
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
Related Skills. Problem-solving is closely connected to several other essential social-emotional learning skills, including: Empathy: Understanding the feelings and perspectives of others can help students develop more effective solutions to interpersonal problems. Communication: Clear and respectful communication is crucial for presenting and ...
In this lesson, students will: Apply critical thinking, problem solving, and decision-making skills to online gameplay and writing tasks. Analyze situations from multiple perspectives and viewpoints. Distinguish between facts, opinions, and solutions. Demonstrate 21st Century skills such as global awareness, information literacy, communication ...
Sudoku: Introduce sudoku puzzles as a fun and challenging math-based activity. 4. Chess Club: Encourage students to participate in chess clubs or tournaments to practice strategic thinking. 5. Escape Rooms: Plan an age-appropriate escape room activity to develop teamwork and problem-solving skills among the students. 6.
Critical thinking is the process of using higher-order thinking skills in which students observe, conceptualize, apply, evaluate, and synthesize information that they learn in order to solve problems and make decisions effectively. Critical thinking is crucial for middle school students to be equipped to respond to academic, social, and emotional challenges successfully. As an educator, …
Critical thinking is vital for middle school students, as it helps them develop problem-solving skills, make informed decisions, and understand different perspectives. Integrating critical thinking activities into classroom learning experiences can greatly enhance students' cognitive abilities. The following are 20 engaging critical thinking ...
3. 4. 5. TED-Ed lessons on the subject Problem Solving. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. Discover hundreds of animated lessons, create customized lessons, and share your big ideas.
Introduction. Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) is a crucial aspect of education that helps students develop essential life skills, such as problem-solving, empathy, and effective communication. In this blog post, we introduce an engaging activity called "Solve It," designed to help middle school students improve their problem-solving abilities.
Start by teaching students the basic process of problem-solving, or developing a solution to an identified problem. Step 1: Understand the Problem The first step is for students to understand the ...
Problem-solving can be defined as the process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving a problem or challenge. It involves critical thinking, creativity, and decision-making. Developing problem-solving skills in middle school students has numerous benefits. It enhances their ability to think critically, make informed decisions, and adapt to new ...
Teaching kids proper problem solving skills helps boost their self-esteem and self-confidence, helps them become more independent, and has a positive impact on their mental health. ... If you're looking for problem solving activities for kids in middle school or high school, this is a great one to consider - just be careful to review the ...
2. Problem-solving as a group. Have your students create and decorate a medium-sized box with a slot in the top. Label the box "The Problem-Solving Box.". Invite students to anonymously write down and submit any problem or issue they might be having at school or at home, ones that they can't seem to figure out on their own.
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: Student Strategies. These are strategies your students can use during independent work time to become creative problem solvers. 1. Go Step-By-Step Through The Problem-Solving Sequence. Post problem-solving anchor charts and references on your classroom wall or pin them to your Google Classroom - anything to make ...
This process is a fun and in-depth way to practice problem solving skills with students! 5. Power of Perseverance in Middle School. I purposely saved this one for last because, without this skill or trait, it will be tricky for your middle schoolers to do the previous four. Problem solving is hard.
The impact of problem-solving instruction on middle school students' physical science learning: Interplays of knowledge, reasoning, and problem solving. EJMSTE . 2018;14(3):731-743. Vlachou A, Stavroussi P. Promoting social inclusion: A structured intervention for enhancing interpersonal problem‐solving skills in children with mild ...
Problem-solving skills are crucial for middle school students as they face a variety of academic, social, and emotional challenges. By equipping them with effective problem-solving strategies, we can help them develop critical thinking and decision-making skills that will benefit them throughout their lives.
Without further ado, let's take a look at the best problem solving activities for middle school. Share Tweet Email. Page 1 of 11. Next >> Related Insider Monkey Articles.
Problem-solving is one of the most important twenty-first-century skills and should be acquired at an early age. Since programming is a kind of problem-solving process, it may be seen in the context of problem-solving skills development. Hence, this study aims to identify the effectiveness of one of the most popular programming tools "Scratch" on middle school students' problem-solving ...
Problem solving refers to a process. Problem solving covers a process from the individual encountering the problem to solving the problem (Eskin, 2014). Kim, Kim, and Lee (2017) found in their study of 405 middle school students that problem-focused coping ability had a significant impact on the relationship between
71+ Social Problem Scenarios + 6 Blank Scenarios. Use the 71 social problem-solving scenarios to have your students get great experience practicing how to solve a social problem. Also, included are 6 blank scenarios. Then laminate them so you can use them over and over again. Therefore, create social problems that the student experiences and ...
Developing social problem-solving skills in middle school has numerous benefits for students. These skills enhance their ability to communicate effectively, manage conflicts, and make responsible decisions. Additionally, social problem-solving skills promote empathy, self-awareness, and collaboration, which are essential for building positive ...
Logic and Problem-Solving Worksheets Even young students can hone their problem-solving skills with appropriate challenges. Sequences and Patterns: Predicting the next item in a sequence or ...
Developing effective IEP goals for problem-solving skills is crucial in helping middle school students succeed in special education. By applying these goals and strategies, educators can foster independence, confidence, and growth in their students. We invite you to explore more resources at Everyday Speech Sample Materials and engage in the ...
Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Training for Emotional Problem Solving for Adolescents (DBT STEPS-A) is an adaptation of DBT® designed for adolescents in middle and high school. ... (DBT STEPS-A) is an adaptation of DBT® designed for adolescents in middle and high school. DBT STEPS-A aims to help adolescents "build a life worth living ...
The Importance of Conversation Skills in Middle School. Conversation skills are more than just the ability to speak to others; they involve listening, interpreting social cues, responding appropriately, and understanding the nuances of verbal and non-verbal communication. ... Develops Problem-Solving Skills. The game's fast-paced nature ...