
- April 24, 2024 | Quantum Computing Meets Genomics: The Dawn of Hyper-Fast DNA Analysis
- April 24, 2024 | Scientists Turn to Venus in the Search for Alien Life
- April 24, 2024 | NASA Astronauts Enter Quarantine As Boeing Starliner Test Flight Approaches
- April 23, 2024 | Peeking Inside Protons: Supercomputers Reveal Quark Secrets
- April 23, 2024 | A Cheaper and More Sustainable Lithium Battery: How LiDFOB Could Change Everything

Beyond Blood Sugar Control: New Target for Curing Diabetes Unveiled
By Helmholtz Munich March 22, 2024
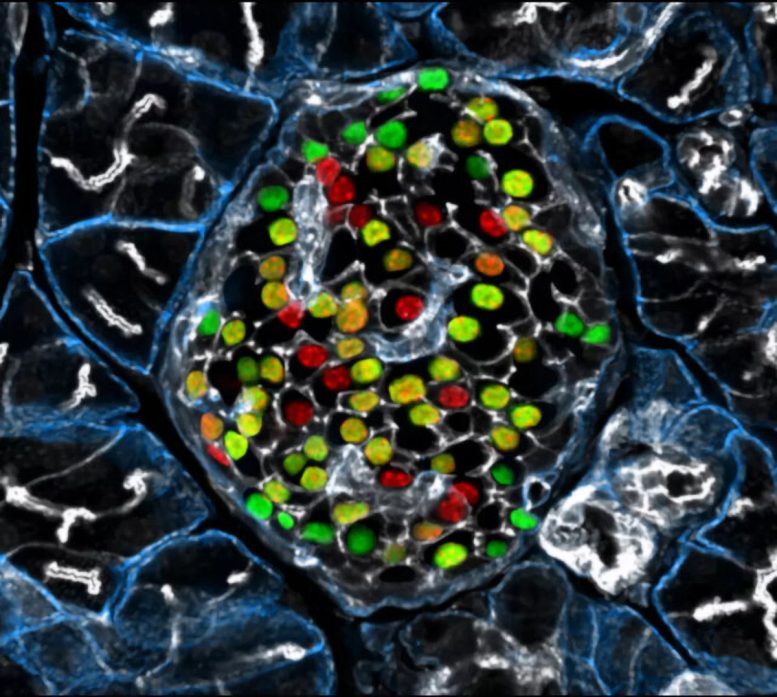
Targeting the inceptor receptor could lead to breakthrough treatments for diabetes by protecting beta cells and improving blood sugar control, with German research institutions leading this promising discovery. Insulin-producing beta cells in the islet of Langerhans. Credit: Helmholtz Munich | Erik Bader
Research focusing on the insulin -inhibitory receptor, known as inceptor, has revealed promising paths for protecting beta cells, providing optimism for therapy that directly addresses diabetes. A groundbreaking study involving mice with obesity caused by diet shows that eliminating inceptor improves glucose management. This finding encourages further investigation into inceptor as a potential therapeutic target for treating type 2 diabetes.
These findings, led by Helmholtz Munich in collaboration with the German Center for Diabetes Research, the Technical University of Munich, and the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, drive advancements in diabetes research.
Targeting Inceptor to Combat Insulin Resistance in Beta Cells
Insulin resistance, often linked to abdominal obesity, presents a significant healthcare dilemma in our era. More importantly, the insulin resistance of beta cells contributes to their dysfunction and the transition from obesity to overt type 2 diabetes. Currently, all pharmacotherapies, including insulin supplementation, focus on managing high blood sugar levels rather than addressing the underlying cause of diabetes: beta cell failure or loss. Therefore, research into beta cell protection and regeneration is crucial and holds promising prospects for addressing the root cause of diabetes, offering potential avenues for causal treatment.
With the recent discovery of inceptor, the research group of beta cell expert Prof. Heiko Lickert has uncovered an interesting molecular target. Upregulated in diabetes, the insulin-inhibitory receptor inceptor may contribute to insulin resistance by acting as a negative regulator of this signaling pathway. Conversely, inhibiting the function of the inceptor could enhance insulin signaling – which in turn is required for overall beta cell function, survival, and compensation upon stress.
In collaboration with Prof. Timo Müller, an expert in molecular pharmacology in obesity and diabetes, the researchers explored the effects of inceptor knock-out in diet-induced obese mice. Their study aimed to determine whether inhibiting inceptor function could also enhance glucose tolerance in diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance, both critical pre-clinical stages in the progression toward diabetes. The results were now published in Nature Metabolism .
Removing Inceptor Improves Blood Sugar Levels in Obese Mice
The researchers delved into the effects of removing inceptor from all body cells in diet-induced obese mice. Interestingly, they found that mice lacking inceptor exhibited improved glucose regulation without experiencing weight loss, which was linked to increased insulin secretion in response to glucose. Next, they investigated the distribution of inceptor in the central nervous system and discovered its widespread presence in neurons. Deleting inceptor from neuronal cells also improved glucose regulation in obese mice. Ultimately, the researchers selectively removed the inceptor from the mice’s beta cells, resulting in enhanced glucose control and a slight increase in beta cell mass.
Research for Inceptor-Blocking Drugs
“Our findings support the idea that enhancing insulin sensitivity through targeting inceptor shows promise as a pharmacological intervention, especially concerning the health and function of beta cells,” says Timo Müller. Unlike intensive early-onset insulin treatments, utilizing inceptor to enhance beta cell function offers promise in alleviating the detrimental effects on blood sugar and metabolism induced by diet-induced obesity. This approach avoids the associated risks of hypoglycemia-associated unawareness and unwanted weight gain typically observed with intensive insulin therapy.
“Since inceptor is expressed on the surface of pancreatic beta cells, it becomes an accessible drug target. Currently, our laboratory is actively researching the potential of several inceptor-blocking drug classes to enhance beta cell health in pre-diabetic and diabetic mice. Looking forward, inceptor emerges as a novel and intriguing molecular target for enhancing beta cell health, not only in prediabetic obese individuals but also in patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes,” explains Heiko Lickert.
Reference: “Global, neuronal or β cell-specific deletion of inceptor improves glucose homeostasis in male mice with diet-induced obesity” by Gerald Grandl, Gustav Collden, Jin Feng, Sreya Bhattacharya, Felix Klingelhuber, Leopold Schomann, Sara Bilekova, Ansarullah, Weiwei Xu, Fataneh Fathi Far, Monica Tost, Tim Gruber, Aimée Bastidas-Ponce, Qian Zhang, Aaron Novikoff, Arkadiusz Liskiewicz, Daniela Liskiewicz, Cristina Garcia-Caceres, Annette Feuchtinger, Matthias H. Tschöp, Natalie Krahmer, Heiko Lickert and Timo D. Müller, 28 February 2024, Nature Metabolism . DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-00991-3
More on SciTechDaily

Quantum Breakthrough Reveals Superconductor’s Hidden Nature
Novel Molecules Discovered to Combat Asthma and COVID-Related Lung Diseases
Orbital Engineering, Yale Engineers Change Electron Trajectories

Finding and Erasing Quantum Computing Errors in Real-Time

“Glow-in-the-Dark” Proteins: The Future of Viral Disease Detection?
A black hole – a million times as bright as our sun – offers potential clue to reionization of universe.

Risk Factors for Falls in Older Americans Identified – A Growing Public Health Concern

Common Fireworks Emit Toxic Metals Into the Air – Damage Human Cells and Animal Lungs
1 comment on "beyond blood sugar control: new target for curing diabetes unveiled".
Interesting study and hopefully another tool which will apply to diabetic patients.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Email address is optional. If provided, your email will not be published or shared.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Cornell Chronicle
- Architecture & Design
- Arts & Humanities
- Business, Economics & Entrepreneurship
- Computing & Information Sciences
- Energy, Environment & Sustainability
- Food & Agriculture
- Global Reach
- Health, Nutrition & Medicine
- Law, Government & Public Policy
- Life Sciences & Veterinary Medicine
- Physical Sciences & Engineering
- Social & Behavioral Sciences
- Coronavirus
- News & Events
- Public Engagement
- New York City
- Photos of the Week
- Big Red Sports
- Freedom of Expression
- Student Life
- University Statements
- Around Cornell
- All Stories
- In the News
- Expert Quotes
- Cornellians
Large-scale study reveals new genetic details of diabetes
By wynne parry weill cornell medicine.
In experiments of unprecedented scale, investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and the National Institutes of Health have revealed new aspects of the complex genetics behind Type 2 diabetes. Through these discoveries, and by providing a template for future studies, this research furthers efforts to better understand and ultimately treat this common metabolic disease.
Previous studies have generally examined the influence of individual genes. In research described Oct. 18 in Cell Metabolism, senior co-author Shuibing Chen , the Kilts Family Professor of Surgery at Weill Cornell Medicine, working alongside senior co-author Dr. Francis Collins , a senior investigator at the Center for Precision Health Research within the National Human Genome Research Institute of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, took a more comprehensive approach. Together, they looked at the contribution of 20 genes in a single effort.
“It’s very difficult to believe all these diabetes-related genes act independently of each other,” Chen said. By using a combination of technologies, the team examined the effects of shutting each down. By comparing the consequences for cell behavior and genetics, she said, “we found some common themes.”
As with other types of diabetes, Type 2 diabetes occurs when sugar levels in the blood are too high. In Type 2 diabetes, this happens in part because specialized cells in the pancreas, known as β-cells, don’t produce enough insulin, a hormone that tells cells to take sugar out of the blood for use as an energy source. Over time, high levels of blood sugar damage tissues and cause other problems, such as heart and kidney disease. According to the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 9% of adults in the United States have been diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
Both genetic and environmental factors, such as obesity and chronic stress, can increase risk for it. Yet evaluating the role of the genetic contributors alone is a massive project. So far, researchers have identified more than 290 locations within the genome where changes to DNA can raise the likelihood of developing the disease. Some of these locations fall within known genes, but most are found in regions that regulate the expression of nearby genes.
For the new research, the team focused on 20 genes clearly identified as contributors. They began their investigation by using the gene editing system CRISPR-Cas9 to shut down these genes, one at a time, within 20 sets of identical stem cells.
These stem cells had the potential to generate any kind of mature cell, but the researchers coaxed them into becoming insulin-producing β-cells. They then examined the effects of losing each gene on five traits related to insulin production and the health of β-cells. They also documented the accompanying changes in gene expression and the accessibility of DNA for expression.
To make sense of the massive amount of data they collected, the team developed their own computational models to analyze it, leading to several discoveries: By comparing the effects of all 20 mutations on β-cells, they identified four additional genes, each representing a newly discovered pathway that contributes to insulin production. They also found that, of the original 20 genes, only one, called HNF4A, contributed to all five traits, apparently by acting as a master controller that regulates the activity of other genes. In one specific example, they explained how a small variation, located in a space between genes, contributes to the risk of diabetes by interfering with HNF4A’s ability to regulate nearby genes.
Ultimately, this study and others like it hold the promise of benefiting patients, Collins said. “We need to understand all the genetic and environmental factors involved so we can do a better job of preventing diabetes, and to develop new ideas about how to effectively treat it.”
Collins and Chen note that their approach may have relevance beyond diabetes, to other common diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Crohn’s disease, that involve many genetic factors.
The work reported in this newsroom story was supported in part by the United States’ National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the American Diabetes Association.
Many Weill Cornell Medicine physicians and scientists maintain relationships and collaborate with external organizations to foster scientific innovation and provide expert guidance. The institution makes these disclosures public to ensure transparency. For this information, see the profile for Shuibing Chen .
Wynne Parry is a freelance writer for Weill Cornell Medicine.
Media Contact
Krystle lopez.
Get Cornell news delivered right to your inbox.
You might also like

Gallery Heading
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
Apologies; the page you are requesting is currently unavailable. The request resembles an abusive automated request. If you believe this an error, please contact us and we will assist in resolving the issue.
Thank you for visiting!
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Diabetes articles from across Nature Portfolio
Diabetes describes a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood sugar levels. Diabetes can be caused by the pancreas not producing insulin (type 1 diabetes) or by insulin resistance (cells do not respond to insulin; type 2 diabetes).
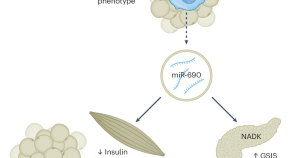
Macrophage vesicles in antidiabetic drug action
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are potent insulin-sensitizing drugs, but their use is accompanied by adverse side-effects. Rohm et al. now report that TZD-stimulated macrophages release miR-690-containing vesicles that improve insulin sensitization and bypass unwanted side-effects.
- Rinke Stienstra
- Eric Kalkhoven
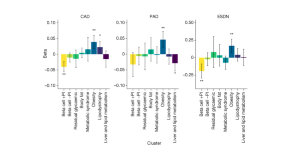
Genetic risk variants lead to type 2 diabetes development through different pathways
The largest genome-wide association study for type 2 diabetes so far, which included several ancestry groups, led to the identification of eight clusters of genetic risk variants. The clusters capture different biological pathways that contribute to the disease, and some clusters are associated with vascular complications.
Related Subjects
- Diabetes complications
- Diabetes insipidus
- Gestational diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
Latest Research and Reviews
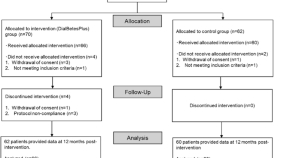
Effectiveness of DialBetesPlus, a self-management support system for diabetic kidney disease: Randomized controlled trial
- Mitsuhiko Nara
- Kazuhiko Ohe
Applications of SGLT2 inhibitors beyond glycaemic control
Here, the authors discuss the beneficial effects of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for a range of clinical outcomes beyond glucose lowering, including kidney and cardiovascular protection. They also discuss the need for implementation and adherence initiatives to help translate the benefits of these agents into real-world clinical outcomes.
- Daniel V. O’Hara
- Carolyn S. P. Lam
- Meg J. Jardine
Novel PLGA-encapsulated-nanopiperine promotes synergistic interaction of p53/PARP-1/Hsp90 axis to combat ALX-induced-hyperglycemia
- Rishita Dey
- Sudatta Dey
- Asmita Samadder
Butyrate and iso-butyrate: a new perspective on nutrition prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus
- Weiling Han
- Guanghui Li
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide improves oocyte maturation of mice with type 1 diabetes
- Fucheng Guo
- Xiaoling Zhang
Folic acid supplementation on inflammation and homocysteine in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Kabelo Mokgalaboni
- Given. R. Mashaba
- Sogolo. L. Lebelo
News and Comment
Repurposing a diabetes drug to treat Parkinson’s disease
In a multicenter clinical trial, patients with early-stage Parkinson’s disease treated with lixisenatide, a drug currently used for the treatment of diabetes, showed improvement in their motor scores compared with those on placebo.
- Sonia Muliyil
A novel system for non-invasive measurement of blood levels of glucose
- Olivia Tysoe
Diabetes drug slows development of Parkinson’s disease
The drug, which is in the same family as blockbuster weight-loss drugs such as Wegovy, slowed development of symptoms by a small but statistically significant amount.
Metformin acts through appetite-suppressing metabolite: Lac-Phe
- Shimona Starling
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
These New Developments Could Make Living With Type 2 Diabetes More Manageable
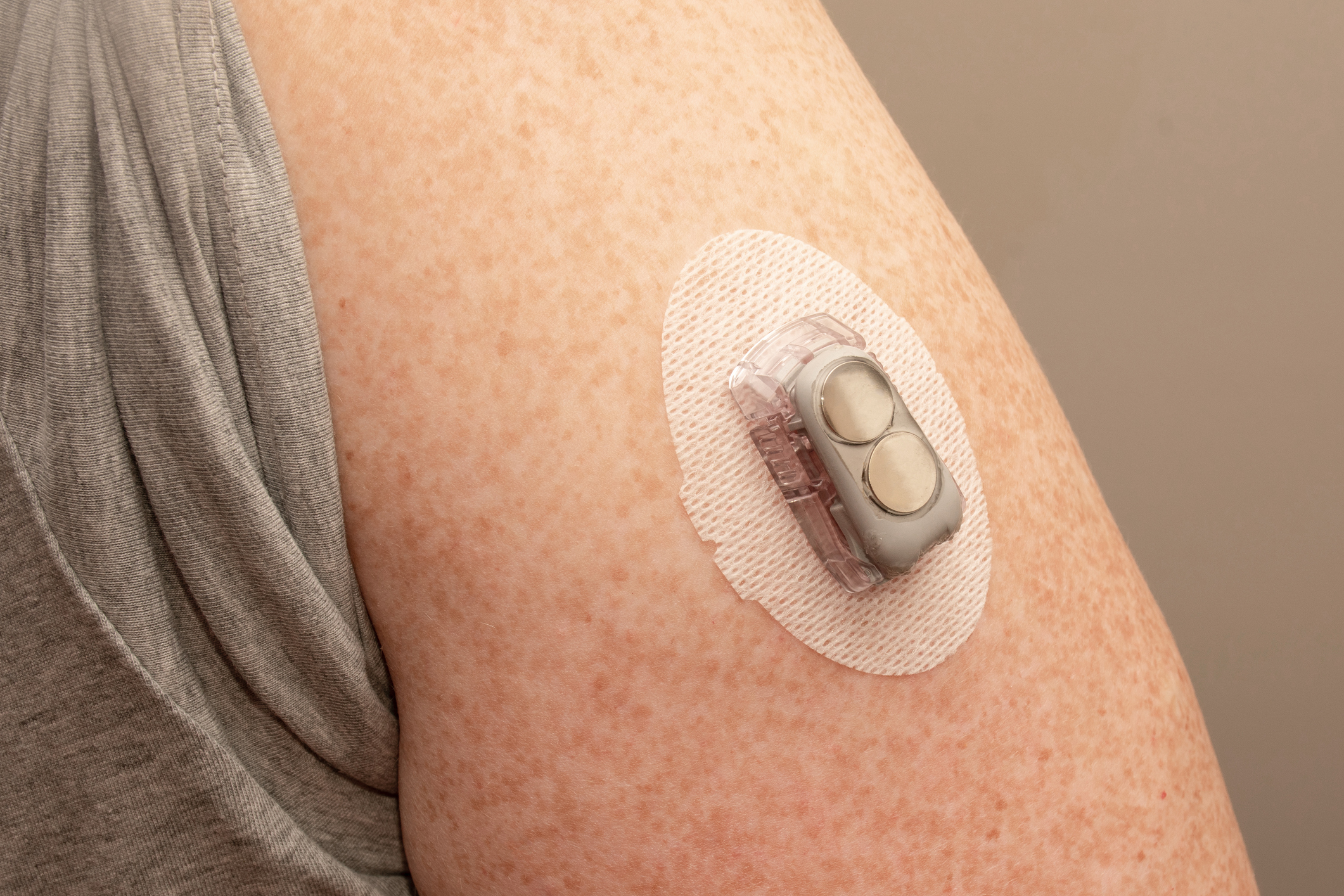
E xperts often talk about the “burden” of a disease or illness. The word acts as a tidy container for all the unpleasantness people with that condition may experience—from their symptoms, to the cost of their care, to the restrictions imposed on their lifestyle, to the health complications that may arise. For people with Type 2 diabetes , this burden can be high.
Routine management of Type 2 diabetes often involves major changes to one’s diet and physical activity . And for many, especially those taking insulin to manage their blood sugar, the disease can necessitate daily blood-glucose monitoring, a process that entails pricking a finger to draw blood and then dabbing that blood onto a glucose monitor’s test strip. Doing this several times a week—month after month—can present overlapping challenges. According to a 2013 survey in the journal Diabetes Spectrum, people find finger-prick glucose monitoring to be painful, and the results can be confusing or unhelpful.
“Patients don’t want to prick their fingers, and they come in all the time and say, ‘I’m tired of this,’” says Dr. Francisco Pasquel, a diabetes specialist and associate professor of medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta.
But relief is on the way. Continuous glucose monitors, or CGMs, are small devices-—often about the size of a quarter-—that use a small under-the-skin needle to continuously monitor blood-glucose levels. This information can be transmitted—in some cases wirelessly and automatically—to a smartphone app or other device. “You can look at glucose levels for a single point in time, but you can also look at trends in values over time,” says Dr. Roy Beck, medical director of the nonprofit Jaeb Center for Health Research in Tampa. Beck’s work has found that continuous glucose monitoring may provide a number of benefits for people with Type 2 diabetes.
These monitors are just one of several new advancements in Type 2 diabetes care and management. From connected technologies to new drug treatments, medical science is making steady and sometimes life-changing progress in the treatment of this condition. Here, experts describe some of the latest and greatest developments.
Continuous glucose monitors
People with Type 1 diabetes typically have to check their blood-sugar levels on a daily basis, or even multiple times each day. Because testing is such a big part of managing that disease, the research on continuous glucose monitors started with these patients. That work has shown that CGMs provide multiple benefits, including reduced hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) levels, which is an important measure of healthy blood glucose. Continuous glucose monitors are now being studied in people with Type 2 diabetes, and research points to multiple benefits.
For a study published in 2021 in the Journal of the American Medical Association, Beck and his colleagues compared continuous glucose monitoring to standard finger-prick tests among people with Type 2 diabetes who were using insulin. They found that continuous monitoring was associated with a significantly greater drop in HbA1c. They also found that continuous monitoring helped people avoid risky and severe drops in blood sugar (a.k.a. hypoglycemia). “It’s pretty clear that there’s a benefit for people with Type 2 diabetes who are using insulin,” he says.
More than 90% of people with diabetes have Type 2 diabetes, and Beck says that roughly 30% of these people are using insulin. In other words, there are many people with Type 2 diabetes who stand to benefit from continuous glucose monitoring. However, use of these monitors is still mostly confined to people with Type 1 diabetes. “Use is slowly increasing in Type 2 patients, but I think it’s still too low considering this is a non-pharmacological approach”—something many people prefer because it avoids the side effects of medications—“that can help people,” he says.
Even for people with Type 2 diabetes who are not taking insulin, Beck says that continuous glucose monitoring could be helpful. “There’s a need for more studies to prove it, but it makes sense that it would likely have benefits,” he says. For example, monitoring blood sugar in real time could help people make diet or lifestyle changes that reduce their risks for long-term health complications. “Normally, blood glucose following a meal shouldn’t go above 140 [mg/dL],” he says. But based on factors like diet, meal timing, and exercise habits, someone with Type 2 diabetes may experience post-meal blood-sugar spikes that surpass 200 or even 300 mg/dL. These spikes could cause few symptoms or short-term consequences, Beck says, but over time they can contribute to the development of common diabetes-related complications such as kidney failure, heart disease, or diabetic retinopathy (an eye condition that can cause blurry vision or blindness). “The first time people use these continuous monitors, it can be a real eye-opener,” he adds. “I think they could be most helpful for self-management, and Type 2 diabetes is a disease where self-management through diet and exercise can make a huge difference.”
Other experts second this. “Patients using these devices can receive a graph of their glucose values over time, which helps them understand the effects of nutrition on glucose control, or how they could modify their exercise to make improvements,” says Dr. Ilias Spanakis, an associate professor of medicine in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and nutrition at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
For patients who are reliant on insulin to manage their blood glucose, combining continuous glucose monitors with insulin pumps—devices that automatically inject insulin as needed—could also lead to major improvements. “Smart algorithms that connect the two can automatically adjust glucose based on glucose values,” Spanakis says. This is already possible, and it’s likely to become much more commonplace, he adds.
For many people with diabetes, continuous glucose monitoring could provide a safer and simpler path forward.
Read More: The Link Between Type 2 Diabetes and Psychiatric Disorders
Bariatric surgery for Type 2 diabetes
Historically, bariatric (weight-loss) surgery has been used primarily to help people manage severe obesity, which the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines as a BMI of 40 or higher. Many people who are severely obese also have diabetes, and research has found that these surgical procedures can help reduce the burden of Type 2 diabetes or even send it into remission.
A 2018 study from researchers at the University of Oklahoma found that Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, a common bariatric procedure, vastly outperformed typical medical management techniques—such as diet changes, doctor’s visits, and prescription drugs—among people with Type 2 diabetes. Surgery led to diabetes remission in roughly 28% of patients, compared with a remission rate of just 4% among the non-surgery group, according to the study results. More research has found that bariatric surgery may effectively send Type 2 diabetes into remission.
“Surgery does not just lead to weight loss, but also to an improvement in glycemic control, which happens even before the weight loss occurs,” says Emory’s Pasquel, who has published work on the benefits of bariatric surgery for people with Type 2 diabetes. Exactly how the surgery does this isn’t well understood, he says. However, bariatric surgery affects appetite, food intake, caloric absorption, and multiple neuroendocrine pathways—all of which could contribute to its beneficial actions for people with Type 2 diabetes.
In the future, Pasquel says these procedures are likely to become more commonplace even for people with Type 2 diabetes who are not severely obese.
More from TIME
New pharmaceutical drugs.
There are a lot of different diabetes drugs on the market, each with its own risks and benefits. But experts say two types are emerging as potential “game changers” when it comes to Type 2 diabetes treatment.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a hormone released in the gut during digestion—one that plays a role in blood-sugar homeostasis. A class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists can interact with GLP-1 receptors in ways that lower appetite, slow digestion, and provide other benefits for people with Type 2 diabetes. These GLP-1 drugs aren’t new. But Pasquel says the latest versions are different in that they work on two different receptors, not one. “Recent evidence shows that activating both receptors has a remarkable impact on weight loss and glycemic control,” he says. Especially for people with Type 2 diabetes who are at high risk for heart or arterial disease, he says that these new drugs seem to be a big upgrade over previous medications.
A second category of drug has also emerged as a standout in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Known as sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, these drugs help the kidneys remove sugar from a person’s blood. Not only does this improve blood-sugar control in people with Type 2 diabetes, but it also helps protect them from heart failure and kidney disease—two common and serious complications. Pasquel says these drugs are so effective that they’re now being used in people with heart failure or kidney disease who do not have Type 2 diabetes.
Read More: The Truth About Fasting and Type 2 Diabetes
Emerging ways to think about weight loss
Experts have long understood that weight loss can help people reduce their Type 2 diabetes symptoms and risks . This recognition has led to research on a number of weight-loss diets . More research is needed, but some of the latest studies suggest that fasting plans—in particular, intermittent fasting—may be particularly beneficial for people with Type 2 diabetes.
Intermittent fasting involves cutting out calorie-containing foods and drinks for an extended period of time—anywhere from 12 hours to two days depending on the approach a person chooses. A 2019 research review in the journal Nutrients found that intermittent fasting promotes weight loss, increases insulin sensitivity, and reduces insulin levels in the blood. All of this is helpful for people with Type 2 diabetes. “Essentially, fasting is doing what we prescribe diabetes medications to do, which is to improve insulin sensitivity,” says Benjamin Horne, director of cardiovascular and genetic epidemiology at Intermountain Healthcare in Utah.
It’s not yet clear which form of intermittent fasting is best. But Horne says that time-restricted eating—a type of fasting that involves squeezing all the day’s calories into single six- or eight-hour feeding windows—is leading the pack, largely because patients are able to stick with it.
There are more new advancements in Type 2 diabetes care. The interventions described here—from continuous glucose monitors to novel drugs—are some of the most promising, but they have company. It’s safe to say that, looking ahead, more people with Type 2 diabetes will be able to effectively manage or mitigate their symptoms.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Coco Gauff Is Playing for Herself Now
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
Type 2 Diabetes Research At-a-Glance
The ADA is committed to continuing progress in the fight against type 2 diabetes by funding research, including support for potential new treatments, a better understating of genetic factors, addressing disparities, and more. For specific examples of projects currently funded by the ADA, see below.
Greg J. Morton, PhD
University of Washington
Project: Neurocircuits regulating glucose homeostasis
“The health consequences of diabetes can be devastating, and new treatments and therapies are needed. My research career has focused on understanding how blood sugar levels are regulated and what contributes to the development of diabetes. This research will provide insights into the role of the brain in the control of blood sugar levels and has potential to facilitate the development of novel approaches to diabetes treatment.”
The problem: Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is among the most pressing and costly medical challenges confronting modern society. Even with currently available therapies, the control and management of blood sugar levels remains a challenge in T2D patients and can thereby increase the risk of diabetes-related complications. Continued progress with newer, better therapies is needed to help people with T2D.
The project: Humans have special cells, called brown fat cells, which generate heat to maintain optimal body temperature. Dr. Morton has found that these cells use large amounts of glucose to drive this heat production, thus serving as a potential way to lower blood sugar, a key goal for any diabetes treatment. Dr. Morton is working to understand what role the brain plays in turning these brown fat cells on and off.
The potential outcome: This work has the potential to fundamentally advance our understanding of how the brain regulates blood sugar levels and to identify novel targets for the treatment of T2D.
Tracey Lynn McLaughlin, MD
Stanford University
Project: Role of altered nutrient transit and incretin hormones in glucose lowering after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery
“This award is very important to me personally not only because the enteroinsular axis (gut-insulin-glucose metabolism) is a new kid on the block that requires rigorous physiologic studies in humans to better understand how it contributes to glucose metabolism, but also because the subjects who develop severe hypoglycemia after gastric bypass are largely ignored in society and there is no treatment for this devastating and very dangerous condition.”
The problem: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery is the single-most effective treatment for type 2 diabetes, with persistent remission in 85% of cases. However, the underlying ways by which the surgery improves glucose control is not yet understood, limiting the ability to potentially mimic the surgery in a non-invasive way. Furthermore, a minority of RYGB patients develop severe, disabling, and life-threatening low-blood sugar, for which there is no current treatment.
The project: Utilizing a unique and rigorous human experimental model, the proposed research will attempt to gain a better understanding on how RYGB surgery improves glucose control. Dr. McLaughlin will also test a hypothesis which she believes could play an important role in the persistent low-blood sugar that is observed in some patients post-surgery.
The potential outcome: This research has the potential to identify novel molecules that could represent targets for new antidiabetic therapies. It is also an important step to identifying people at risk for low-blood sugar following RYGB and to develop postsurgical treatment strategies.
Rebekah J. Walker, PhD
Medical College of Wisconsin
Project: Lowering the impact of food insecurity in African Americans with type 2 diabetes
“I became interested in diabetes research during my doctoral training, and since that time have become passionate about addressing social determinants of health and health disparities, specifically in individuals with diabetes. Living in one of the most racially segregated cities in the nation, the burden to address the needs of individuals at particularly high risk of poor outcomes has become important to me both personally and professionally.”
The problem: Food insecurity is defined as the inability to or limitation in accessing nutritionally adequate food and may be one way to address increased diabetes risk in high-risk populations. Food insecure individuals with diabetes have worse diabetes outcomes and have more difficulty following a healthy diet compared to those who are not food insecure.
The project: Dr. Walker’s study will gather information to improve and then will test an intervention to improve blood sugar control, dietary intake, self-care management, and quality of life in food insecure African Americans with diabetes. The intervention will include weekly culturally appropriate food boxes mailed to the participants and telephone-delivered diabetes education and skills training. It will be one of the first studies focused on the unique needs of food insecure African American populations with diabetes using culturally tailored strategies.
The potential outcome: This study has the potential to guide and improve policies impacting low-income minorities with diabetes. In addition, Dr. Walker’s study will help determine if food supplementation is important in improving diabetes outcomes beyond diabetes education alone.
Donate Today and Change Lives!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Clinical Research on Type 2 Diabetes: A Promising and Multifaceted Landscape
Type 2 diabetes constitutes an imposing epidemiological, economic, and scientific global challenge. The chronic complications of type 2 diabetes are a major cause of mortality and disability worldwide [ 1 , 2 ]. Clinical research is the main way to gain knowledge about long-term diabetic complications and reduce the burden of diabetes. This allows for designing effective programs for screening and follow-up and fine-targeted therapeutic interventions. However, new research methodologies are needed to obtain more accurate and useful insights into the biological and clinical processes involved in diabetic complication development.
During the last few years, new approaches for clinical research have incorporated digital tools to analyze the complex physiopathological background of type 2 diabetes. In this Special Issue, entitled “ Clinical Research on Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications ” and published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine ( https://www.mdpi.com/journal/jcm/special_issues/Type_2_Diabetes_Complications ), some valuable digital methodologies were used in different studies focusing on the type 2 diabetes syndrome. Novel machine learning techniques for predicting long-term complications are one of these approaches, as the studies of Huang, Rashid, and Shin et al. depict [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. The data presented by these authors suggest that machine learning may be more accurate in predicting diabetic microvascular complications than traditional methods. Additionally, digital tools such as artificial intelligence and machine learning can be implemented through an automated and rapid process.
Among the frequent causes of frustration for people with diabetes and the health care providers involved in their management is the delayed detection of diabetic complications. The outlook of clinical research appears promising in the near future owing to the development and implementation of advanced methods for the detection of early alterations in the micro- and macrovascular complications associated with diabetes. Two papers in this Special Issue cover the use of specific biomarkers tracing the progress of diabetic cardiovascular complications [ 6 , 7 ]. In another contribution, Lee et al. revisit the long-term glycemic variability and its relationship with end-stage kidney disease [ 8 ].
Besides the genetic approach, the application of digital techniques, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, and novel biomarkers could be crucial for individualized type 2 diabetes management, which is the backbone of precision medicine.
Two review papers address the complications that are non-traditionally linked to type 2 diabetes, although currently under exhaustive research: bone health and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ 9 , 10 ]. The multifaceted nature of type 2 diabetes is clearly visualized owing to the holistic angle used by these approaches.
The efficacy and safety of new type 2 diabetes pharmacological treatment are covered by three original papers [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. The Yu-Chuan Kang et al. study includes a large population sample and an extended follow-up to evaluate the association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and diabetic retinopathy [ 13 ]. This could be the first signal for a new safety risk of a pharmacological class of drugs used by millions worldwide.
The COVID-19 pandemic was first reported in China in December 2019 and continues to be a devastating condition for global health and economy. The COVID-19 disease has immediate implications for common chronic metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes. Both direct infection and the associated distress due to preventive measures in the general population have worsened the control of type 2 diabetes. Some factors indicate that COVID-19 or other coronavirus-caused diseases can be seasonal or persistent in the future. Type 2 diabetes has a strong negative effect on the prognosis of patients with COVID-19. Three papers in this Special Issue review the implications of this disease in relation to diabetes [ 14 , 15 , 16 ].
Finally, the aim of researchers in this field should be to make all these remarkable advances accessible to those populations experiencing more difficulties due to sociodemographic factors such as cultural deprivation, sex discrimination, or limited income [ 17 , 18 , 19 ].
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the continuous editorial assistance of Nicole Quinn, Always English S.L.
Funding Statement
This research received no external funding.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing were equally done by F.G.-P. and C.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
April 22, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
New findings on pancreatic anatomy may affect diabetes research and treatment
by Claes Björnberg, Umea University
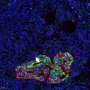
Researchers at Umeå University have succeeded in imaging an entire human organ, a pancreas, in microscopic resolution. By staining different cell-types with antibodies and then using optical 3D imaging techniques to study the entire organ, their data provides a partially new picture of the pancreas.
The results may be of great importance for diabetes research , especially when developing various new forms of treatment. The study is published in Nature Communications .
The pancreas is a key organ for the development of diabetes, a disease that today affects over half a billion people. It contains millions of small cell clusters, the so-called islets of Langerhans, which function to regulate blood sugar levels in the body.
The islets chiefly contain beta- and alpha-cells that produce the hormones insulin and glucagon, respectively. Insulin is secreted into the bloodstream and acts much like a key to unlock the body's cells so that they can take up sugar (glucose) after a meal, the main form of energy used by the body. Glucagon in turn releases glucose stores when we need a supply of energy. These two cell-types also communicate directly with each other to optimize the correct glucose level in the body.
"Both insulin and glucagon cells were discovered over a hundred years ago, and it has long been believed that the islets should contain both cell types to form a fully functioning unit," says Ulf Ahlgren, professor at the Department of Medical and Translational Biology.
Since the islets of Langerhans make up only a small percentage of the pancreas, even though they occur in such large numbers, they have historically been very difficult to study directly within the pancreas. In most cases, researchers have had to study tissue sections that only provide a 2D image of a very small part of the organ. Now, Umeå researchers have used optical 3D techniques in which different cell-types can be marked with fluorescently colored antibodies.
Entire organ at microscopic resolution
"By dividing the entire organ into smaller parts, we enable the antibodies to get where they need to go. Since we know where each piece comes from, we can then, after scanning the different parts individually, 'reassemble' the entire pancreas again using computer software. This allows us to perform a plethora of calculations and study which cell-types are present, as well as where they are located in 3D space, as we know the 3D coordinates, their volume, shape and other parameters for each and every stained object in the entire organ," says Ahlgren.
In addition to new data on how insulin-producing cells are distributed in the pancreas, the researchers now show that glucagon-producing cells are not present in as many as 50% of the islets of Langerhans that do contain insulin cells. This is contrary to what was previously thought, where islets were believed to contain both insulin- and glucagon-expressing cell-types with the same islet.
"This was a surprise to us, and I believe that these results may be of great importance for diabetes research. First, it shows that the islets have a much more uneven composition, or cellularity, than previously thought. This could mean that islets of different composition might be specifically specialized to respond to different signals and/or operate in different metabolic environments. Of course, we really want to find this out," says Ahlgren.
"Second, a great deal of research in the diabetes field is carried out on isolated islets of Langerhans from deceased donors. Since we also show that this uneven composition is largely linked to islet size, it means that results from such experiments may not fully reflect how the islets are structured and function in the living pancreas. This could potentially be important for everything from islet transplants in type 1 diabetes to studies trying to produce islets of Langerhans from stem cells."
Basis for future studies
The research team will now continue to work to see if their methods can be used to determine whether other cell types in the pancreas also contribute to the formation of the islets in a way that has not previously been known. In addition, they will study whether it looks similar in mouse models, which could affect the use of mice for preclinical diabetes research.
"The methods and data we are now publishing will be able to form an important basis for future studies of human material in order to better understand what happens in the pancreas in the development of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but also for diseases such as pancreatic cancer," says Ahlgren.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Research shows 'profound' link between dietary choices and brain health
3 hours ago

Component of keto diet plus immunotherapy may reduce prostate cancer
7 hours ago

Study finds big jump in addiction treatment at community health clinics

Positive childhood experiences can boost mental health and reduce depression and anxiety in teens

Gene linked to epilepsy and autism decoded in new study
Apr 26, 2024


Blood test finds knee osteoarthritis up to eight years before it appears on X-rays

Researchers find pregnancy cytokine levels impact fetal brain development and offspring behavior

Study finds biomarkers for psychiatric symptoms in patients with rare genetic condition 22q

Clinical trial evaluates azithromycin for preventing chronic lung disease in premature babies

Scientists report that new gene therapy slows down amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease progression
Related stories.
Pancreas cells in people who have died show significant signs of stress
Apr 2, 2024
Loss of cells in pancreas in the elderly may cause age-related diabetes
Jan 15, 2024
New DNA methylation-based method for precise assessment of pancreas cell composition
Feb 6, 2024
Understanding the differences between healthy and type 2 diabetes-affected pancreatic islets
Nov 28, 2022
Beta cells under fire
Jun 7, 2017

New method enables 3D microscopy of human organs
Sep 13, 2021
Recommended for you
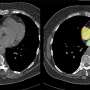
Artificial intelligence can evaluate cardiovascular risk during CT scan
Apr 24, 2024

Researchers map the spatio-temporal human brain dynamics of a visual image being recognized

Genetics predict type 2 diabetes risk and disparities in childhood cancer survivors

The consumption of certain food additive emulsifiers could be associated with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes
Apr 23, 2024

Advancing high-resolution ultrasound imaging with deep learning
Apr 22, 2024
Siblings with unique genetic mutation help scientists progress drug search for type 1 diabetes
Apr 18, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

How old is too old to run?

America’s graying. We need to change the way we think about age.

Can we talk?
“When my son was diagnosed [with Type 1], I knew nothing about diabetes. I changed my research focus, thinking, as any parent would, ‘What am I going to do about this?’” says Douglas Melton.
Kris Snibbe/Harvard Staff Photographer
Breakthrough within reach for diabetes scientist and patients nearest to his heart
Harvard Correspondent
100 years after discovery of insulin, replacement therapy represents ‘a new kind of medicine,’ says Stem Cell Institute co-director Douglas Melton, whose children inspired his research
When Vertex Pharmaceuticals announced last month that its investigational stem-cell-derived replacement therapy was, in conjunction with immunosuppressive therapy, helping the first patient in a Phase 1/2 clinical trial robustly reproduce his or her own fully differentiated pancreatic islet cells, the cells that produce insulin, the news was hailed as a potential breakthrough for the treatment of Type 1 diabetes. For Harvard Stem Cell Institute Co-Director and Xander University Professor Douglas Melton, whose lab pioneered the science behind the therapy, the trial marked the most recent turning point in a decades-long effort to understand and treat the disease. In a conversation with the Gazette, Melton discussed the science behind the advance, the challenges ahead, and the personal side of his research. The interview was edited for clarity and length.
Douglas Melton
GAZETTE: What is the significance of the Vertex trial?
MELTON: The first major change in the treatment of Type 1 diabetes was probably the discovery of insulin in 1920. Now it’s 100 years later and if this works, it’s going to change the medical treatment for people with diabetes. Instead of injecting insulin, patients will get cells that will be their own insulin factories. It’s a new kind of medicine.
GAZETTE: Would you walk us through the approach?
MELTON: Nearly two decades ago we had the idea that we could use embryonic stem cells to make functional pancreatic islets for diabetics. When we first started, we had to try to figure out how the islets in a person’s pancreas replenished. Blood, for example, is replenished routinely by a blood stem cell. So, if you go give blood at a blood drive, your body makes more blood. But we showed in mice that that is not true for the pancreatic islets. Once they’re removed or killed, the adult body has no capacity to make new ones.
So the first important “a-ha” moment was to demonstrate that there was no capacity in an adult to make new islets. That moved us to another source of new material: stem cells. The next important thing, after we overcame the political issues surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells, was to ask: Can we direct the differentiation of stem cells and make them become beta cells? That problem took much longer than I expected — I told my wife it would take five years, but it took closer to 15. The project benefited enormously from undergraduates, graduate students, and postdocs. None of them were here for 15 years of course, but they all worked on different steps.
GAZETTE: What role did the Harvard Stem Cell Institute play?
MELTON: This work absolutely could not have been done using conventional support from the National Institutes of Health. First of all, NIH grants came with severe restrictions and secondly, a long-term project like this doesn’t easily map to the initial grant support they give for a one- to three-year project. I am forever grateful and feel fortunate to have been at a private institution where philanthropy, through the HSCI, wasn’t just helpful, it made all the difference.
I am exceptionally grateful as well to former Harvard President Larry Summers and Steve Hyman, director of the Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research at the Broad Institute, who supported the creation of the HSCI, which was formed specifically with the idea to explore the potential of pluripotency stem cells for discovering questions about how development works, how cells are made in our body, and hopefully for finding new treatments or cures for disease. This may be one of the first examples where it’s come to fruition. At the time, the use of embryonic stem cells was quite controversial, and Steve and Larry said that this was precisely the kind of science they wanted to support.
GAZETTE: You were fundamental in starting the Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology. Can you tell us about that?
MELTON: David Scadden and I helped start the department, which lives in two Schools: Harvard Medical School and the Faculty of Arts and Science. This speaks to the unusual formation and intention of the department. I’ve talked a lot about diabetes and islets, but think about all the other tissues and diseases that people suffer from. There are faculty and students in the department working on the heart, nerves, muscle, brain, and other tissues — on all aspects of how the development of a cell and a tissue affects who we are and the course of disease. The department is an exciting one because it’s exploring experimental questions such as: How do you regenerate a limb? The department was founded with the idea that not only should you ask and answer questions about nature, but that one can do so with the intention that the results lead to new treatments for disease. It is a kind of applied biology department.
GAZETTE: This pancreatic islet work was patented by Harvard and then licensed to your biotech company, Semma, which was acquired by Vertex. Can you explain how this reflects your personal connection to the research?
MELTON: Semma is named for my two children, Sam and Emma. Both are now adults, and both have Type 1 diabetes. My son was 6 months old when he was diagnosed. And that’s when I changed my research plan. And my daughter, who’s four years older than my son, became diabetic about 10 years later, when she was 14.
When my son was diagnosed, I knew nothing about diabetes and had been working on how frogs develop. I changed my research focus, thinking, as any parent would, “What am I going to do about this?” Again, I come back to the flexibility of Harvard. Nobody said, “Why are you changing your research plan?”
GAZETTE: What’s next?
MELTON: The stem-cell-derived replacement therapy cells that have been put into this first patient were provided with a class of drugs called immunosuppressants, which depress the patient’s immune system. They have to do this because these cells were not taken from that patient, and so they are not recognized as “self.” Without immunosuppressants, they would be rejected. We want to find a way to make cells by genetic engineering that are not recognized as foreign.
I think this is a solvable problem. Why? When a woman has a baby, that baby has two sets of genes. It has genes from the egg, from the mother, which would be recognized as “self,” but it also has genes from the father, which would be “non-self.” Why does the mother’s body not reject the fetus? If we can figure that out, it will help inform our thinking about what genes to change in our stem cell-derived islets so that they could go into any person. This would be relevant not just to diabetes, but to any cells you wanted to transplant for liver or even heart transplants. It could mean no longer having to worry about immunosuppression.
Share this article
You might like.
No such thing, specialist says — but when your body is trying to tell you something, listen

Experts say instead of disability, focus needs to shift to ability, health, with greater participation, economically and socially

Study finds that conversation – even online – could be an effective strategy to help prevent cognitive decline and dementia
When math is the dream
Dora Woodruff was drawn to beauty of numbers as child. Next up: Ph.D. at MIT.
Seem like Lyme disease risk is getting worse? It is.
The risk of Lyme disease has increased due to climate change and warmer temperature. A rheumatologist offers advice on how to best avoid ticks while going outdoors.
So what exactly makes Taylor Swift so great?
Experts weigh in on pop superstar's cultural and financial impact as her tours and albums continue to break records.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
How to Thrive as You Age
A cheap drug may slow down aging. a study will determine if it works.

Allison Aubrey

A drug taken by millions of people to control diabetes may do more than lower blood sugar.
Research suggests metformin has anti-inflammatory effects that could help protect against common age-related diseases including heart disease, cancer, and cognitive decline.
Scientists who study the biology of aging have designed a clinical study, known as The TAME Trial, to test whether metformin can help prevent these diseases and promote a longer healthspan in healthy, older adults.
Michael Cantor, an attorney, and his wife Shari Cantor , the mayor of West Hartford, Connecticut both take metformin. "I tell all my friends about it," Michael Cantor says. "We all want to live a little longer, high-quality life if we can," he says.
Michael Cantor started on metformin about a decade ago when his weight and blood sugar were creeping up. Shari Cantor began taking metformin during the pandemic after she read that it may help protect against serious infections.

Shari and Michael Cantor both take metformin. They are both in their mid-60s and say they feel healthy and full of energy. Theresa Oberst/Michael Cantor hide caption
Shari and Michael Cantor both take metformin. They are both in their mid-60s and say they feel healthy and full of energy.
The Cantors are in their mid-60s and both say they feel healthy and have lots of energy. Both noticed improvements in their digestive systems – feeling more "regular" after they started on the drug,
Metformin costs less than a dollar a day, and depending on insurance, many people pay no out-of-pocket costs for the drug.
"I don't know if metformin increases lifespan in people, but the evidence that exists suggests that it very well might," says Steven Austad , a senior scientific advisor at the American Federation for Aging Research who studies the biology of aging.
An old drug with surprising benefits
Metformin was first used to treat diabetes in the 1950s in France. The drug is a derivative of guanidine , a compound found in Goat's Rue, an herbal medicine long used in Europe.
The FDA approved metformin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the U.S. in the 1990s. Since then, researchers have documented several surprises, including a reduced risk of cancer. "That was a bit of a shock," Austad says. A meta-analysis that included data from dozens of studies, found people who took metformin had a lower risk of several types of cancers , including gastrointestinal, urologic and blood cancers.
Austad also points to a British study that found a lower risk of dementia and mild cognitive decline among people with type 2 diabetes taking metformin. In addition, there's research pointing to improved cardiovascular outcomes in people who take metformin including a reduced risk of cardiovascular death .
As promising as this sounds, Austad says most of the evidence is observational, pointing only to an association between metformin and the reduced risk. The evidence stops short of proving cause and effect. Also, it's unknown if the benefits documented in people with diabetes will also reduce the risk of age-related diseases in healthy, older adults.
"That's what we need to figure out," says Steve Kritchevsky , a professor of gerontology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, who is a lead investigator for the Tame Trial.
The goal is to better understand the mechanisms and pathways by which metformin works in the body. For instance, researchers are looking at how the drug may help improve energy in the cells by stimulating autophagy, which is the process of clearing out or recycling damaged bits inside cells.

Shots - Health News
Scientists can tell how fast you're aging. now, the trick is to slow it down.

You can order a test to find out your biological age. Is it worth it?
Researchers also want to know more about how metformin can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which may slow biological aging.
"When there's an excess of oxidative stress, it will damage the cell. And that accumulation of damage is essentially what aging is," Kritchevsky explains.
When the forces that are damaging cells are running faster than the forces that are repairing or replacing cells, that's aging, Kritchevsky says. And it's possible that drugs like metformin could slow this process down.
By targeting the biology of aging, the hope is to prevent or delay multiple diseases, says Dr. Nir Barzilai of Albert Einstein College of Medicine, who leads the effort to get the trial started.
The ultimate in preventative medicine
Back in 2015, Austad and a bunch of aging researchers began pushing for a clinical trial.
"A bunch of us went to the FDA to ask them to approve a trial for metformin,' Austad recalls, and the agency was receptive. "If you could help prevent multiple problems at the same time, like we think metformin may do, then that's almost the ultimate in preventative medicine," Austad says.
The aim is to enroll 3,000 people between the ages of 65 and 79 for a six-year trial. But Dr. Barzilai says it's been slow going to get it funded. "The main obstacle with funding this study is that metformin is a generic drug, so no pharmaceutical company is standing to make money," he says.
Barzilai has turned to philanthropists and foundations, and has some pledges. The National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, set aside about $5 million for the research, but that's not enough to pay for the study which is estimated to cost between $45 and $70 million.
The frustration over the lack of funding is that if the trial points to protective effects, millions of people could benefit. "It's something that everybody will be able to afford," Barzilai says.
Currently the FDA doesn't recognize aging as a disease to treat, but the researchers hope this would usher in a paradigm shift — from treating each age-related medical condition separately, to treating these conditions together, by targeting aging itself.
For now, metformin is only approved to treat type 2 diabetes in the U.S., but doctors can prescribe it off-label for conditions other than its approved use .
Michael and Shari Cantor's doctors were comfortable prescribing it to them, given the drug's long history of safety and the possible benefits in delaying age-related disease.
"I walk a lot, I hike, and at 65 I have a lot of energy," Michael Cantor says. I feel like the metformin helps," he says. He and Shari say they have not experienced any negative side effects.
Research shows a small percentage of people who take metformin experience GI distress that makes the drug intolerable. And, some people develop a b12 vitamin deficiency. One study found people over the age of 65 who take metformin may have a harder time building new muscle.

Millions of women are 'under-muscled.' These foods help build strength
"There's some evidence that people who exercise who are on metformin have less gain in muscle mass, says Dr. Eric Verdin , President of the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. That could be a concern for people who are under-muscled .
But Verdin says it may be possible to repurpose metformin in other ways "There are a number of companies that are exploring metformin in combination with other drugs," he says. He points to research underway to combine metformin with a drug called galantamine for the treatment of sarcopenia , which is the medical term for age-related muscle loss. Sarcopenia affects millions of older people, especially women .
The science of testing drugs to target aging is rapidly advancing, and metformin isn't the only medicine that may treat the underlying biology.
"Nobody thinks this is the be all and end all of drugs that target aging," Austad says. He says data from the clinical trial could stimulate investment by the big pharmaceutical companies in this area. "They may come up with much better drugs," he says.
Michael Cantor knows there's no guarantee with metformin. "Maybe it doesn't do what we think it does in terms of longevity, but it's certainly not going to do me any harm," he says.
Cantor's father had his first heart attack at 51. He says he wants to do all he can to prevent disease and live a healthy life, and he thinks Metformin is one tool that may help.
For now, Dr. Barzilai says the metformin clinical trial can get underway when the money comes in.

7 habits to live a healthier life, inspired by the world's longest-lived communities
This story was edited by Jane Greenhalgh
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Nih research matters.
November 7, 2023
Intermittent fasting for weight loss in people with type 2 diabetes
At a glance.
- People with obesity and type 2 diabetes lost more weight using daily periods of fasting than by trying to restrict calories over a six-month period.
- Blood sugar levels lowered in people in both groups, and no serious side effects were observed.

Around 1 in 10 Americans live with type 2 diabetes, a disease in which levels of blood glucose, or blood sugar, are too high. Diabetes can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, nerve damage, and eye problems.
Excess weight is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes, and weight loss is often recommended for those with excess weight and type 2 diabetes. Calorie restriction—reducing overall calorie intake—is a mainstay of most weight loss programs. But such regimens are very difficult to stick with over the long term.
Time-restricted eating, also called intermittent fasting, has emerged as an alternative weight loss paradigm. In this approach, the time of day during which food can be eaten is restricted, but the amount or types of food are not. Small studies have suggested that intermittent fasting is safe and promotes weight loss in people with type 2 diabetes. But these studies only tracked participants for a short period of time. They also didn’t compare the approach with traditional calorie restriction.
In a new clinical trial, an NIH-funded research team led by Dr. Krista Varady from the University of Illinois Chicago compared fasting and calorie restriction for weight loss and blood-sugar reduction. They recruited 75 people with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Of these, 70 were either Hispanic or non-Hispanic Black—two groups in the U.S. with an especially high prevalence of diabetes. The participants were randomly assigned to one of three diet groups for six months.
The fasting group could eat anything they wanted, but only between the hours of noon and 8 pm. The second group worked with a dietitian to reduce their calories by 25% of the amount needed to maintain their weight. A control group did not change their diet at all. All groups received education on healthy food choices and monitored their blood glucose closely during the study. The results were published on October 27, 2023, in JAMA Network Open .
After six months, participants in the fasting group lost an average of 3.6% percent of their body weight compared to those in the control group. In comparison, people in the calorie-restriction group did not lose a significant amount of weight compared to the control group.
Both groups had similarly healthy decreases in their average blood glucose levels. Both also had reductions in waist circumference. No serious side effects, including time outside of a safe blood glucose range, were seen in either treatment group. People in the fasting group reported that their diet was easier to adhere to than calorie restriction.
“Our study shows that time-restricted eating might be an effective alternative to traditional dieting for people who can’t do the traditional diet or are burned out on it,” Varady says. “For many people trying to lose weight, counting time is easier than counting calories.”
Some medications used to treat type 2 diabetes need adjustment for time-restricted eating. Therefore, people considering intermittent fasting should speak with a doctor before changing their eating pattern.
—by Sharon Reynolds
Related Links
- Research in Context: Obesity and Metabolic Health
- Calorie Restriction and Human Muscle Function
- Popular Diabetes Drugs Compared in Large Trial
- Diabetes Control Worsened Over the Past Decade
- Fasting Increases Health and Lifespan in Male Mice
- Factors Contributing to Higher Incidence of Diabetes for Black Americans
- Diabetes Increasing in Youths
- Benefits of Moderate Weight Loss in People with Obesity
- To Fast or Not to Fast: Does When You Eat Matter?
- Managing Diabetes: New Technologies Can Make It Easier
- Type 2 Diabetes
References: Effect of Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Pavlou V, Cienfuegos S, Lin S, Ezpeleta M, Ready K, Corapi S, Wu J, Lopez J, Gabel K, Tussing-Humphreys L, Oddo VM, Alexandria SJ, Sanchez J, Unterman T, Chow LS, Vidmar AP, Varady KA . JAMA Netw Open . 2023 Oct 2;6(10):e2339337. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.39337. PMID: 37889487.
Funding: NIH’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK); University of Illinois.
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
Research Gaps Around Type 1 Diabetes
A large body of research on Type 2 diabetes has helped to develop guidance, informing how patients are diagnosed, treated, and manage their lifestyle. In contrast, Type 1 diabetes, often mistakenly associated only with childhood, has received less attention.
In this Q&A, adapted from the April 17 episode of Public Health On Call , Stephanie Desmon speaks to Johns Hopkins epidemiologists Elizabeth Selvin , PhD '04, MPH, and Michael Fang , PhD, professor and assistant professor, respectively, in the Department of Epidemiology, about recent findings that challenge common beliefs about type 1 diabetes. Their conversation touches on the misconception that it’s solely a childhood condition, the rise of adult-onset cases linked to obesity, and the necessity for tailored approaches to diagnosis and care. They also discuss insulin prices and why further research is needed on medications like Ozempic in treating Type 1 diabetes.
I want to hear about some of your research that challenges what we have long understood about Type 1 diabetes, which is no longer called childhood diabetes.
MF: Type 1 diabetes was called juvenile diabetes for the longest time, and it was thought to be a disease that had a childhood onset. When diabetes occurred in adulthood it would be type 2 diabetes. But it turns out that approximately half of the cases of Type 1 diabetes may occur during adulthood right past the age of 20 or past the age of 30.
The limitations of these initial studies are that they've been in small clinics or one health system. So, it's unclear whether it's just that particular clinic or whether it applies to the general population more broadly.
We were fortunate because the CDC has collected new data that explores Type 1 diabetes in the U.S. Some of the questions they included in their national data were, “Do you have diabetes? If you do, do you have Type 1 or Type 2? And, at what age were you diagnosed?”
With these pieces of information, we were able to characterize how the age of diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes differs in the entire U.S. population.
Are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes different diseases?
ES: They are very different diseases and have a very different burden. My whole career I have been a Type 2 diabetes epidemiologist, and I’ve been very excited to expand work with Type 1 diabetes.
There are about 1.5 million adults with Type 1 diabetes in the U.S., compared to 21 million adults with Type 2 diabetes. In terms of the total cases of diabetes, only 5 to 10 percent have Type 1 diabetes. Even in our largest epidemiologic cohorts, only a small percentage of people have Type 1 diabetes. So, we just don't have the same national data, the same epidemiologic evidence for Type 1 diabetes that we have for Type 2. The focus of our research has been trying to understand and characterize the general epidemiology and the population burden of Type 1 diabetes.
What is it about Type 1 that makes it so hard to diagnose?
MF: The presentation of symptoms varies by age of diagnosis. When it occurs in children, it tends to have a very acute presentation and the diagnosis is easier to make. When it happens in adulthood, the symptoms are often milder and it’s often misconstrued as Type 2 diabetes.
Some studies have suggested that when Type 1 diabetes occurs in adulthood, about 40% of those cases are misdiagnosed initially as Type 2 cases. Understanding how often people get diagnosed later in life is important to correctly diagnose and treat patients.
Can you talk about the different treatments?
MF: Patients with Type 1 diabetes are going to require insulin. Type 2 diabetes patients can require insulin, but that often occurs later in the disease, as oral medications become less and less effective.
ES: Because of the epidemic of overweight and obese in the general population, we’re seeing a lot of people with Type 1 diabetes who are overweight and have obesity. This can contribute to issues around misdiagnosis because people with Type 1 diabetes will have signs and will present similarly to Type 2 diabetes. They'll have insulin resistance potentially as a result of weight gain metabolic syndrome. Some people call it double diabetes—I don't like that term—but it’s this idea that if you have Type 1 diabetes, you can also have characteristics of Type 2 diabetes as well.
I understand that Type 1 used to be considered a thin person's disease, but that’s not the case anymore. MF: In a separate paper, we also explored the issue of overweight and obesity in persons with Type 1 diabetes. We found that approximately 62% of adults with Type 1 diabetes were either overweight or obese, which is comparable to the general U.S. population.
But an important disclaimer is that weight management in this population [with Type 1 diabetes] is very different. They can't just decide to go on a diet, start jogging, or engage in rigorous exercise. It can be a very, very dangerous thing to do.
Everybody's talking about Ozempic and Mounjaro—the GLP-1 drugs—for diabetes or people who are overweight to lose weight and to solve their diabetes. Where does that fit in with this population?
ES: These medications are used to treat Type 2 diabetes in the setting of obesity. Ozempic and Mounjaro are incretin hormones. They mediate satiation, reduce appetite, slow gastric emptying, and lower energy intake. They're really powerful drugs that may be helpful in Type 1 diabetes, but they're not approved for the management of obesity and Type 1 diabetes. At the moment, there aren't data to help guide their use in people with Type 1 diabetes, but I suspect they're going to be increasingly used in people with Type 1 diabetes.
MF: The other piece of managing weight—and it's thought to be foundational for Type 1 or Type 2—is dieting and exercising. However, there isn’t good guidance on how to do this in persons with Type 1 diabetes, whereas there are large and rigorous trials in Type 2 patients. We’re really just starting to figure out how to safely and effectively manage weight with lifestyle changes for Type 1 diabetics, and I think that's an important area of research that should continue moving forward.
ES: Weight management in Type 1 diabetes is complicated by insulin use and the risk of hypoglycemia, or your glucose going too low, which can be an acute complication of exercise. In people with Type 2 diabetes, we have a strong evidence base for what works. We know modest weight loss can help prevent the progression and development of Type 2 diabetes, as well as weight gain. In Type 1, we just don't have that evidence base.
Is there a concern about misdiagnosis and mistreatment? Is it possible to think a patient has Type 2 but they actually have Type 1?
MF: I think so. Insulin is the overriding concern. In the obesity paper, we looked at the percentage of people who said their doctors recommended engaging in more exercise and dieting. We found that people with Type 1 diabetes were less likely to receive the same guidance from their doctor. I think providers may be hesitant to say, “Look, just go engage in an active lifestyle.”
This is why it's important to have those studies and have that guidance so that patients and providers can be comfortable in improving lifestyle management.
Where is this research going next?
ES: What's clear from these studies is that the burden of overweight and obesity is substantial in people with Type 1 diabetes and it's not adequately managed. Going forward, I think we're going to need clinical trials, clear clinical guidelines, and patient education that addresses how best to tackle obesity in the setting of Type 1 diabetes.
It must be confusing for people with Type 1 diabetes who are hearing about people losing all this weight on these drugs, but they go to their doctor who says, “Yeah, but that's not for you.”
ES: I hope it's being handled more sensitively. These drugs are being used by all sorts of people for whom they are not indicated, and I'm sure that people with Type 1 diabetes are accessing these drugs. I think the question is, are there real safety issues? We need thoughtful discussion about this and some real evidence to make sure that we're doing more good than harm.
MF: Dr. Selvin’s group has published a paper, estimating that about 15% of people with Type 1 diabetes are on a GLP-1. But we don't have great data on what potentially can happen to individuals.
The other big part of diabetes that we hear a lot about is insulin and its price. Can you talk about your research on this topic?
MF: There was a survey that asked, “Has there been a point during the year when you were not using insulin because you couldn’t afford it?” About 20% of adults under the age of 65 said that at some point during the year, they couldn't afford their insulin and that they did engage in what sometimes is called “cost-saving rationing” [of insulin].
Medicare is now covering cheaper insulin for those over 65, but there are a lot of people for whom affordability is an issue. Can you talk more about that?
MF: The fight is not over. Just because there are national and state policies, and now manufacturers have been implementing price caps, doesn't necessarily mean that the people who need insulin the most are now able to afford it.
A recent study in the Annals of Internal Medicine looked at states that adopted or implemented out-of-pocket cost caps for insulin versus those that didn't and how that affected insulin use over time. They found that people were paying less for insulin, but the use of insulin didn't change over time. The $35 cap is an improvement, but we need to do more.
ES: There are still a lot of formulations of insulin that are very expensive. $35 a month is not cheap for someone who is on insulin for the rest of their lives.
- Overweight and Obesity in People With Type 1 Diabetes Nearly Same as General Population
- The Impacts of COVID-19 on Diabetes and Insulin
- Why Eli Lilly’s Insulin Price Cap Announcement Matters
Related Content

To Protect Human Health, We Must Protect the Earth’s Health

A South African Soup Kitchen Is Bringing Relief to Caregivers

New Grant Enables Johns Hopkins Researchers to Implement Community Health Worker-Led Health Interventions for Noncommunicable Diseases in Nepal

The Omnipresence of PFAS—and What We Can Do About Them

Summer Institute in Data to Policy
Genetics predict type 2 diabetes risk and disparities in childhood cancer survivors
Survivors of childhood cancer are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease, for which a risk factor is their greater prevalence of type 2 diabetes, with a disproportionate impact on those of non-European heritage. St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have identified four previously unknown genetic variants associated with diabetes risk in all survivors. Published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology , their work also found an association between a previously reported genetic risk score for type 2 diabetes developed in the general population with diabetes risk in survivors. The findings also provide novel insights into differences in risk between individuals of varying ancestries.
The work relied on the St. Jude Lifetime cohort study (St. Jude LIFE), a long-term follow-up study for individuals treated for cancer as children. This cohort enabled the researchers to identify the four previously unknown genetic variants. Those variants were more frequent in people of African descent than those of European ancestry. They also determined that compared to a polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes derived in the general population of European ancestry, polygenic risk scores generated from diverse ancestry datasets were more informative in assessing diabetes risk in survivors of both European and African ancestries. All genetic risks appeared magnified by childhood exposure to alkylating agents, a common class of chemotherapeutics.
"We found DNA variants in survivors that increase the risk of type 2 diabetes," said co-senior and corresponding author Yadav Sapkota, PhD, St. Jude Department of Epidemiology and Cancer Control. "Among survivors exposed to alkylating agents, these variants are conferring differential risk based on the ancestry, which may partially explain some of the disparity in type 2 diabetes burden in survivors."
Childhood cancer survivors are at a three times increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes than their siblings. However, non-Hispanic Black survivors experience three times more risk than non-Hispanic white survivors. To understand those differences, the researchers performed whole genome sequencing on the patients from the St. Jude LIFE cohort involved in this study, comparing the DNA of survivors that had type 2 diabetes to those that did not, divided by ancestry. Through this work, the team created a rich and rare trove of combined clinical and genetic data.
Ancestry affects type 2 diabetes risk in childhood cancer survivors
"The genetic risk disproportionately affected survivors of African or African American ancestry previously treated with alkylating agents," Sapkota said. "The same variant is implicated in both European and African-ancestry groups, but the amount of risk conferred by carrying the variant differs."
To address that disparity in greater detail, the scientists compared previously reported polygenic risk scores for diabetes in the general population. Earlier research used many genetic variants, considered as a group, to assess disease risk. However, these risk scores were traditionally derived from those of European descent. The researchers compared three risk scores, a traditional score based only on those of European descent and two others developed by including people of different ancestries. The more inclusive scores both performed better in survivors of both European and African ancestries.
"The two risk scores derived from multiple ancestries were strongly associated with type 2 diabetes risk in survivors of diverse ancestries compared to the score developed in European-only ancestry," Sapkota said.
Genetics amplify diabetes risk from alkylating agents in survivors
The research also suggested that another contributor to increased type 2 diabetes risk is exposure to alkylating agents, a class of chemotherapy commonly used in childhood cancer treatments.
"We saw very consistently, in three out of our four identified variants, and all of our polygenic risk scores, a significant increase in diabetes risk when survivors were exposed to alkylating agents during their initial treatment," Sapkota said. "So genetic factors in the presence of alkylating agents can significantly enhance type 2 diabetes risk."
The alkylating agent effect also had a greater impact on those of African ancestry. While the reasons for these differences in risk remain unclear, the study is a step in the right direction toward addressing them.
"We hope this information will help reduce disparities in the type 2 diabetes burden," Sapkota said. "Now we know how to identify childhood cancer survivors most at risk of type 2 diabetes so we can provide more personalized opportunities for interventions and prevent cardiovascular complications down the road."
Authors and funding
The study's first author is Cindy Im, University of Minnesota. The study's other co-senior author is Carmen Wilson, St. Jude. The study's other authors are Eric Chow, Fred Hutchinson Research Center; Sogol Mostoufi-Moab, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia; Tianzhong Yang, University of Minnesota; Melissa Richard, M. Monica Gramatges and Philip Lupo, Baylor College of Medicine; Noha Sharafeldin and Smita Bhatia, University of Alabama at Birmingham; Achal Neupane, Jessica Baedke, Brian Lenny, Angela Delaney, Stephanie Dixon, Gregory Armstrong, Melissa Hudson, Kirsten Ness, Leslie Robison and Yutaka Yasui, all of St. Jude.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (R21 CA261833, R01 CA261898, R01 CA216354, U01 CA195547, U24 CA55727, CA21765), Children's Cancer Research Fund and University of Minnesota Foundation Pediatric Scholar Award and ALSAC, the fundraising and awareness organization of St. Jude.
- Breast Cancer
- Personalized Medicine
- Colon Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Wounds and Healing
- Diabetes mellitus type 1
- Diabetes mellitus type 2
- Diabetic diet
- Personalized medicine
- Hyperglycemia
Story Source:
Materials provided by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Cindy Im, Achal Neupane, Jessica L. Baedke, Brian Lenny, Angela Delaney, Stephanie B. Dixon, Eric J. Chow, Sogol Mostoufi-Moab, Tianzhong Yang, Melissa A. Richard, M. Monica Gramatges, Philip J. Lupo, Noha Sharafeldin, Smita Bhatia, Gregory T. Armstrong, Melissa M. Hudson, Kirsten K. Ness, Leslie L. Robison, Yutaka Yasui, Carmen L. Wilson, Yadav Sapkota. Trans-Ancestral Genetic Risk Factors for Treatment-Related Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Survivors of Childhood Cancer . Journal of Clinical Oncology , 2024; DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02281
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- New Circuit Boards Can Be Repeatedly Recycled
- Collisions of Neutron Stars and Black Holes
- Advance in Heart Regenerative Therapy
- Bioluminescence in Animals 540 Million Years Ago
- Profound Link Between Diet and Brain Health
- Loneliness Runs Deep Among Parents
- Food in Sight? The Liver Is Ready!
- Acid Reflux Drugs and Risk of Migraine
- Do Cells Have a Hidden Communication System?
- Mice Given Mouse-Rat Brains Can Smell Again
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The new research, published in the journal Nature Communications, offers a potential strategy for developing new therapies that could restore dysfunctional pancreatic beta-cells or, perhaps, even prevent Type 2 diabetes from developing. The new study shows that the beta-cells of Type 2 diabetes patients are deficient in a cell trafficking ...
New cause of diabetes discovered, offering potential target for new classes of drugs to treat the disease. ScienceDaily . Retrieved April 26, 2024 from www.sciencedaily.com / releases / 2023 / 12 ...
This finding encourages further investigation into inceptor as a potential therapeutic target for treating type 2 diabetes. These findings, led by Helmholtz Munich in collaboration with the German Center for Diabetes Research, the Technical University of Munich, and the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, drive advancements in diabetes research.
June 24, 2021 — Across the world, type 2 diabetes is on the rise. A research group has discovered a new gene that may hold the key to preventing and treating lifestyle related diseases such as ...
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, the most frequent subtype of diabetes, is a disease characterized by high levels of blood glucose (hyperglycaemia). It arises from a resistance to and relative deficiency ...
Amelioration of Both Central and Peripheral Neuropathy in Mouse Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes by the Neurogenic Molecule NSI-189. Diabetes, 68(11), 2143-2154. Read more. ADA-funded researcher studying link between ageing and type 2 diabetes. One of the most important risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes is age.
Large-scale study reveals new genetic details of diabetes. In experiments of unprecedented scale, investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and the National Institutes of Health have revealed new aspects of the complex genetics behind Type 2 diabetes. Through these discoveries, and by providing a template for future studies, this research ...
Methods. In this trial involving participants with type 2 diabetes of less than 10 years' duration who were receiving metformin and had glycated hemoglobin levels of 6.8 to 8.5%, we compared the ...
More than 7,000 clinical trials are currently ongoing involving new drugs for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). ... Dallas Diabetes Research Center at Medical City, Dallas, TX, USA. Julio Rosenstock.
For Immediate Release: May 13, 2022. Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Mounjaro (tirzepatide) injection to improve blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes, as an ...
The largest genome-wide association study for type 2 diabetes so far, which included several ancestry groups, led to the identification of eight clusters of genetic risk variants.
In a potential game changer for patients with type 2 diabetes, a team of researchers at the Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism Institute (DOMI) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has identified a therapeutic target for the preservation and regeneration of beta cells (β cells)—cells in the pancreas that produce and distribute insulin.
I. Introduction. Diabetes mellitus, a metabolic disease defined by elevated fasting blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin production, has reached epidemic proportions worldwide (World Health Organization, 2020).Type 1 and type 2 diabetes (T1D and T2D, respectively) make up the majority of diabetes cases with T1D characterized by autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing ...
Surgery led to diabetes remission in roughly 28% of patients, compared with a remission rate of just 4% among the non-surgery group, according to the study results. More research has found that ...
A new study found that tiny biodegradable particles improved insulin sensitivity in the liver cells of humans and in diabetic mice, which could offer a promising new treatment for type 2 diabetes.
The ADA is committed to continuing progress in the fight against type 2 diabetes by funding research, including support for potential new treatments, a better understating of genetic factors, addressing disparities, and more. For specific examples of projects currently funded by the ADA, see below. Greg J. Morton, PhD.
The study recently published in Nature is the largest genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes to date, and it included genomic data from 2,535,601 individuals, of whom 428,452 had type 2 ...
The chronic complications of type 2 diabetes are a major cause of mortality and disability worldwide [ 1, 2 ]. Clinical research is the main way to gain knowledge about long-term diabetic complications and reduce the burden of diabetes. This allows for designing effective programs for screening and follow-up and fine-targeted therapeutic ...
Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90% of all diabetes cases, with social risk factors such as high BMI, poor diet, environmental hazards, and low physical activity contributing to the burden.
Insulin-inhibitory receptor research offers hope for type 2 diabetes therapy. by Verena Schulz, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres. Central inceptor immunoreactivity is restricted to ...
Genetics predict type 2 diabetes risk and disparities in childhood cancer survivors Apr 24, 2024 The consumption of certain food additive emulsifiers could be associated with the risk of ...
Both are now adults, and both have Type 1 diabetes. My son was 6 months old when he was diagnosed. And that's when I changed my research plan. And my daughter, who's four years older than my son, became diabetic about 10 years later, when she was 14. When my son was diagnosed, I knew nothing about diabetes and had been working on how frogs ...
Type 2 diabetes affects more than 38.4 million Americans, with an estimated 1.4 million new cases diagnosed every year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Andrew Stewart, MD, director, Mount Sinai Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism Institute, New York. Type 2 diabetes is one of the world's greatest health problems. It affects about 400 million ...
The FDA approved metformin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the U.S. in the 1990s. Since then, researchers have documented several surprises, including a reduced risk of cancer. "That was a ...
People with obesity and type 2 diabetes lost more weight using daily periods of fasting than by trying to restrict calories over a six-month period. ... In a new clinical trial, an NIH-funded research team led by Dr. Krista Varady from the University of Illinois Chicago compared fasting and calorie restriction for weight loss and blood-sugar ...
Physical activity in nature helps prevent several diseases, including depression and type 2 diabetes. ScienceDaily . Retrieved April 27, 2024 from www.sciencedaily.com / releases / 2024 / 04 ...
Study findings. Data from 104,139 individuals, 79.2% female, were obtained between 2009 and 2023. The average age of the study participants was 42.7 years during baseline data collection.
Recent research has highlighted disparities in research between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, with Type 1 long—and mistakenly—associated only with childhood onset. ... New Grant Enables Johns Hopkins Researchers to Implement Community Health Worker-Led Health Interventions for Noncommunicable Diseases in Nepal. April 04, 2024.
The research also suggested that another contributor to increased type 2 diabetes risk is exposure to alkylating agents, a class of chemotherapy commonly used in childhood cancer treatments.