
- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class

Capstone Project: Definition, Types, Structure, and Examples
by Antony W
January 2, 2024
If you're reading this, chances are that you're in your final year of school and the words "capstone project" have come up somewhere in your first or second semester.
You're probably looking for a quick score on the topic - what it's about, a project template, or even a sample. If so, you're in the right place.
Before we get into it, you' need to know that you're in the hands of consummate capstone project experts.
Help for Assessment is composed of scholars at all levels of academic achievement including Masters and Ph.D., all inspired and motivated to help students like you achieve their academic goals. The expertise and experience we have spans years. Even better, this combined academic expertise is placed at your disposal. If your capstone research project is already giving you goosebumps, we will do it for you from scratch including the project proposal, research, write up, and final review before submission.
Remember, you can trust Help for Assessment to complete your capstone project successfully and earn you top grades. All you have to do is order the service here on our service page.
In the meantime, let us explore the definition of the capstone project, types of projects for students, and a sample capstone project.
What Is a Capstone Project?
A capstone project in college is a final independent project undertaken in a program of study designed to assess the skills, knowledge, and expertise acquired by the student.
As the name suggests, it is the capstone or crowning achievement of academic life and the last class taken before graduation. It gives you the final credits required to pass the course, which is why every student must take the project.
Since it is designed to assess knowledge and skills gained in a particular discipline, capstone projects vary from school to school and discipline to discipline.
Such a project might involve something as simple as research on a topic, an evaluation of a new technique or method, development of a health program, research into a historical figure or event, or even composing a skit or theatre presentation.
No matter what kind of project you choose to undertake, the result is the same. You get to showcase your understanding of the coursework material learned and display your readiness to enter the professional world to start your career. It is a rewarding experience if done right, but can mess up your final year and possibly your graduation if you manage to mess it up.
Do you know that a successful capstone project also helps to land you lucrative jobs? That’s right, capstone projects are one of the ways potential employers find out just how learned, resourceful, and talented you are. Think of it as a kind of thesis.
Capstone projects are also called culminating projects, experience, senior exhibition, or other similar names. The project is usually self-directed, and most students find it a challenge to even come up with the right capstone project topic.
Capstone Project Vs. Thesis

A capstone project and a thesis are both very similar in that they represent a final effort from the student just before graduation.
They are done in partial fulfillment of the requirements of the course being undertaken. The comprehensive approach and assessment involved are very similar, and sometimes the structure and methodology might overlap.
Both also have to be reviewed and approved by the institution and will remain in the public domain after publishing.
However, there are some important differences.
- A thesis is purely academic while a capstone project focuses more on the practical preparation of the student for the real world/job market.
- A thesis is guided by a research question resulting in the addition of new knowledge to the field, while a capstone project is guided by the practical importance of the project to the field.
- A thesis involves academic research and analysis, while a capstone project can be anything including a dance or film.
- A thesis is expected to be original and authentic, while a capstone project will have more loose requirements. You can borrow another person’s capstone project ideas , so long as you demonstrate your own advancement in the field.
- A capstone project will usually only have a brief write-up or report, while a thesis generates a detailed, extensive writeup.
- The final presentation of a thesis, called a defense, is meant to prove and show that you have mastered the subject. You are supposed to be a mini-expert in the field. A capstone project presentation comes off as a kind of exhibition where you showcase your project without having to defend it.
Types of Capstone Projects

Capstone projects vary not just in the type of project, also in the level at which they are done.
There are projects for juniors and seniors in college as well as for postgraduate students.
Here are some examples of the forms of projects depending on the academic level.
- In-depth research projects.
- Developing the concept of a product, tool, or service.
- Expositions.
- Experiments.
Capstone projects can be conducted either individually or in a group.
However, the key thing is to make sure that the project proposal has been reviewed and approved by the instructor/panel/institution in charge before proceeding.
Senior Capstone Project
Senior projects are so called because they are done by high school students in their senior year.
Just like other projects, they represent a culmination of the coursework with an interdisciplinary application of knowledge and skills gained so far.
The project usually takes the better part of the final academic year and will have different parts to it, depending on the type of project chosen.
It will also require a presentation where the student(s) explain and describe the project to an audience, including their classmates.
Sample Capstone Project Outline
The write up for a project consists of several parts. However, even before starting the write-up, you need to do a few things:
- Come up with an idea for your project. What will be your subject matter, topic, or premise?
- Find sources for the project and review them beforehand to ensure that they will be of help to you.
- Come up with a step-by-step methodology for your project.
Using this information, you will then write a capstone project proposal for your project. It informs your instructor or review panel exactly what you intend to present so that they can approve or reject it.
Once approved, you can go on to the next stage. The final write-up has the following parts.
- A title page.
- Project outline.
- A description/abstract.
- Introduction
- Rationale/relevance/reason for doing the project.
- Objectives of the project.
- Procedures/methodology.
- Research and analysis.
- Evaluation of results and findings.
- Conclusion and future work/suggestions.
- Bibliography/works cited/reference list.
Note that the project is carried out in stages. Once approved, you will need to be submitting weekly or monthly status reports to your supervisor. After the project report is submitted, you will also have to make a presentation about the whole project.
This brief outline is only meant to be a rough guide. We have a much more detailed article detailing how you can do your capstone project, including a project template.
Capstone Project Examples
Help for Assessment has extensive experience when it comes to capstone projects of all kinds.
Whether it’s a high school project, a college capstone, or a senior capstone project, you can trust us to carry it out successfully for you.
You can check out various project samples here .
Get Help With Your Capstone Project
Capstone projects in every level of school are a make or break it deal. Given that they complete the graduation credits required, it makes sense to leave this important part of your coursework to experts.
We are proud to offer you a guide on how to write a capstone project here . If you need help, you can take advantage of our capstone project writing service at affordable, student-friendly rates with amazing discounts.
Check it out here and make your order to experience excellence, peace of mind, and success thanks to our stellar services.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

AP Capstone Project: APA Format & Paper Organization
- APA Format & Paper Organization
- Quantitative Research
- How to Avoid Scientific Misconduct
Your Capstone Paper
Your capstone paper will fall into one of the following categories:
L iterature review : A literature review is a critical summary of what the scientific literature says about your specific topic or question. This kind of paper demonstrates your familiarity with work in the field. If you chose to research a certain topic or concept in depth, you will most likely write a literature review.
Experimental Report: If you conducted original research for your capstone or collected data based on observations , your paper will be an experimental report. You will still need to include a summary of the past and current research about your topic, but unlike a literature review, you will also include some analysis as well as your own data gathered from an experiment or observations.
Everyone's capstone paper should contain the following elements: a title page, abstract, introduction, body, conclusion, and reference list. Click on the link below to open and make a copy of the capstone paper template. If you have any questions, please come see Ms. Forfa (earlier is always better!)
Capstone Paper Editable Template
Other Helpful Resources:
- Help with In-Text Citations in APA Format
- APA Sample Paper This is useful, especially if you need help formatting your reference list!
- Citing & Referencing in APA Format
- << Previous: Welcome
- Next: Quantitative Research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2018 12:03 PM
- URL: https://shhs-southhadleyschools.libguides.com/apcapstone
How to Write a Capstone Project like an Expert
This guide describes all the steps needed to create a capstone project, including choosing a topic, structuring the paper, and writing in a scholarly manner.
A capstone project is a research assignment that many students must complete as part of their undergraduate or master’s degree. It differs from other types of final papers such as a thesis or dissertation because it has a practical nature. Capstone projects call for a student to review a certain problem, often specific to the writer’s interests or experience, and conduct research to evaluate or resolve the detected issues. The goal of such assignments is to involve students in their future professional sphere (Weaver 2). Moreover, capstone projects assess how students use critical thinking skills and the knowledge they have acquired during a course.
Choosing a Topic
It is clear that your selection must be connected to your sphere of education. For example, if you are a medical student, your capstone project will likely be focused on health-care interventions. For future biologists and chemists, chosen topics will reflect their field of expertise. Nevertheless, these assignments can be made more personal as follows:
- Search for a topic that interests you. Selecting a theme that does not spark your interest can negatively affect your attention and the quality of your writing. You may neither be able to concentrate on your paper nor conduct in-depth research. Think about your experience, both educational and professional. Has there been a problem or issue that you noticed and wanted to solve? This capstone project may be your chance to do that.
- Consider the format of the assignment. What does your instructor ask you to include in the project? Anticipate the composition of the future paper and the various components it should contain. Do you have to conduct research, and do the results have to be measurable? Adjust your topic to reflect the instructions. Since in most cases students have to confirm the topic with their advisors before writing, you will be able to get some help if you are struggling to find suitable subject matter.
- Take into account the project’s length. Depending on the number of requested pages, you may need to broaden or narrow your topic. Try to estimate how much space each part of the project will take up, and choose a research area that has enough information.
- Research existing literature on the topic. If your topic is too narrow or too recent, you may not find enough academic literature to support your research. In contrast, if the topic is too broad, you may be overwhelmed by the amount of available information.
Capstone projects usually follow a specific structure:
- Abstract. Although it is located at the beginning of the written project, the abstract should be written last. It is a summary of the entire study; you can approach it as soon as you are sure that every other part is complete. Do not confuse the abstract with the introduction of the paper—abstracts contain enough information to interest the reader in the entire project. Thus, they must capture the essence and relay main concepts, hypotheses, research methods, and findings.
- Introduction. In this section, you will acquaint your readers with the topic you have selected. Sometimes, an introduction is split into multiple smaller categories such as “Purpose of the Paper” or “Research Questions,” but they can be located in this part since they present the topic. Here, you should introduce the issue and connect it to your sphere of academic knowledge or course. In addition, you may discuss why this research problem is significant. Next, list the formulated research questions or hypotheses that will guide the investigation. State the objectives that you wish to achieve with the help of this project. Finally, if it is required, include a thesis that succinctly describes the aims and beliefs of the capstone project.
- Literature Review. A review of the existing literature is a vital component of any research endeavor. Here, you will search for academic and other reliable sources that are connected to your topic. These articles, books, trials, and studies will be used as a foundation for the research. Sources can contain pertinent findings, discuss well-examined methodologies, present new ideas, and confirm or refute earlier findings. Document the results of your search and analyze them; look for gaps in knowledge. What themes are not explored well or missing altogether? What should or can be researched in more detail? You can attempt to fill in these gaps with your findings.
- Methodology. In this section of the project, you will talk about how your research is to be conducted.
- First, describe your research design; it can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed (a combination of the two). Each type also has many subcategories. Choose one, and explain why it works the best for your topic.
- Next, state your independent and dependent variables if needed for your selected design. Independent variables are what you choose to investigate (for example, different training programs for employees). Dependent variables are affected by independent ones (for example, employee performance after training).
- Describe the sample for your project. Who are the participants, and how many of them are involved? What are the inclusion and exclusion criteria for research?
- List the materials and tools you used in conducting research. Here, you can introduce questionnaires, online tests, and other media created for this project.
- Write about the process of conducting research, discussing all the major elements of the procedure. What were the participants asked to perform? How were the results collected?
- Discuss how you analyzed the results, listing measurements, tests, and calculations. Explain why you chose each method, and support your selections with previous research.
- Results. This is a significant part of the project, where you show the results of the conducted research. Refrain from making any assumptions or conclusions here—state the results without interpretation. You can use graphs, tables, and images to illustrate findings. Remember to present data that will answer all the research questions and hypotheses you introduced earlier. Check the findings’ validity and significance if required by the chosen research style.
- Discussion. Here, you should analyze the revealed results—be critical and attentive. Try to find patterns or show correlations in the findings. Talk about the context. What does previous academic literature tell you about this study? Does it contradict or align with your findings? Think about the importance and implications of your results. Does this study add something new to the sphere of knowledge? Do not forget to consider the limitations of your project—what could make the research more reliable? Finally, introduce some questions for future research and encourage additional investigation.
- Conclusion. Some papers include a conclusion in addition to the discussion. Restate all major information from the study here, presenting it concisely. Do not propose any new ideas or data in this part. The function of a conclusion is to wrap up the project and talk about all important judgments.
Writing Process
In addition to adhering to the structure described above, you should also remember to pay attention to your writing process. Do not be afraid of making drafts before writing the final version; they will help you structure your arguments and findings. After completing the paper, be sure to proofread it as mistakes and inconsistencies can make the written project difficult to read, confusing, or even incorrect. If you think you need someone else’s opinion, ask for it—turn to your instructor, writing center, or other knowledgeable persons that will help you revise the text if necessary. Check all tables and graphs, and make sure that a reader can understand them as well as you do.
Capstone projects give students an opportunity to apply their knowledge in practice. They are designed around a narrow topic that investigates a real problem, using a specific structure that is followed in the majority of cases: an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and discussion are essential elements of every capstone project. These assignments use a scholarly voice and require in-depth knowledge of previous scholarly literature. Like all academic papers, they need to be substantiated with evidence and be clear and unbiased. Lastly, proofreading is an important part of scholarly writing as well. This paper shows the writer’s level of preparedness after completing a course. Follow the provided guidelines and remember to be attentive—these rules should help you complete a high-quality capstone project.
Weaver, K. F., et al. “The Benefits of Peer Review and a Multisemester Capstone Writing Series on Inquiry and Analysis Skills in an Undergraduate Thesis.” CBE—Life Sciences Education, vol. 15, no. ar51, 2016, 1-9.
Unfortunately, your browser is too old to work on this site.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.

CAPSTONE PROJECT: Parts of a Capstone Project
- Parts of a Capstone Project
- Voice in the Capstone Project
- Analysis of Qualitative Data
What a Table of Contents Could Contain
I Introduction A Statement Of Problem/Opportunity (Research Question) B Background, Context, And Significance Of Study C Project Researcher Identification II Literature Review A Subheadings (Themes Discovered In Review) B Notice Of Gaps In Knowledge III Methods A Subjects/Participants B Data Collection Approaches/Strategies 1 Advantage Of Strategy 2 Limitation Of Strategy 3 Potential Risk 4 Ethical Issues About Collection Upon The Subjects/Participants C Data Analysis Approaches And/Or Software (NOT The Results Themselves, Just How You Are Going To Analyze The Data – Coding Method, Analysis Of Interviews/Recordings, Mathematics And Stats Analysis) IV Results, Findings, Interpretation, And Discussion V Recommendations, Application, And Conclusion VI Reference Pages
What Goes Into Each Section
- Next: Voice in the Capstone Project >>
- Last Updated: Jun 27, 2019 9:31 AM
- URL: https://lifepacific.libguides.com/capstone
Life Pacific University Alumni Library | 1100 W. Covina Blvd | San Dimas, CA 91773 | Ph: (909) 706-3009 | Email: [email protected]
- Other Guides
- What Is a Capstone Project & How to Write It: Definition, Outline, Steps
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
What Is a Capstone Project & How to Write It: Definition, Outline, Steps

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A capstone project is a culminating academic project. It typically requires students to apply the skills they have gained during the course to a real-world problem. Capstone projects are common in undergraduate and graduate programs across a range of disciplines, including business, engineering, healthcare, and education.
Interesting fact, the first documented capstone project was completed in 1937 by Edgar F. Batten, who proposed to build an airport. It was considered a novel idea at that time, but it led to the development of Cleveland Municipal Airport. Today, they have come a long way, allowing students to showcase their creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. In this guide, we will define a capstone project and state its purpose in academics. We will also delve into its significance and provide an outline of how to do a capstone project. So, get ready for an exciting journey to become a capstone pro! Remember that you can always buy a capstone project from our academic gurus if you strive for maximum output.
What Is a Capstone Project: Definition
Capstone projects are vital in every school. Then, what is a capstone project ? Generally, it is research designed to showcase students’ knowledge, skills, and abilities in specific fields of study. This task is challenging and time-consuming, but once completed, it is rewarding. Capstone project is interdisciplinary in nature and can be completed in various formats, such as a written report, research paper , term paper , or presentation. It often involves independent research and analysis by an individual college or university student or group. For example, you could be asked to explore one topic or social problem that interests you, do extensive research about it, assess findings, and propose a solution. Based on the definition of capstone project, it is a culminating academic experience that typically takes place at the end of students' college education. Other basics include:
- Use of academic knowledge Students apply knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout their academic program to their papers.
- Collaboration with faculty members or industry professionals Students may work with faculty members or industry professionals to gain additional insight and guidance on their capstones.
- Presentation or defense Students may also be required to defend their capstone project in front of a panel of experts or live audience.
- Evaluation by committee A committee evaluates the student's paper to determine if they have met all academic requirements and project standards.
What Is the Capstone Project Purpose?
The main purpose of a capstone project is to assess your ability to integrate and apply knowledge acquired throughout your academic program. It gives you a chance to demonstrate mastery of a particular field of study, showcasing critical thinking, research, and communication skills. Capstone project serves several key goals:
- Demonstrate student’s learning abilities As an educational strategy, capstone project can be used to show if the learner has acquired knowledge gained over the entire course.
- Improve students’ self-perception and confidence Typically, capstone projects allow students to take on new responsibilities and show commitment all through. Completing them boosts their self-esteem, self-awareness, as well as confidence.
- Boost career aspirations Since capstone projects involve working on real-world problems, students gain practical experience and prepare them for their future careers.
- Foster motivation and engagement Creativity involved in senior capstone projects, especially since students select them based on their personal interests, can motivate them to learn, engaging others in that process.
Importance of Capstone Projects
The importance of capstone projects cannot be overstated. They supplement your academic journey, providing opportunities for you to demonstrate mastery of skills and knowledge, build real-world experience, and showcase your abilities to potential employers. Writing capstone paper can serve several important reasons, including:
- Preparing for future careers By working on real-world issues and engaging in independent capstone research project, you develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and presentation skills that are essential for successful careers.
- Encouraging innovation By providing you with an opportunity to tackle complex problems and come up with innovative solutions, capstone projects encourage creativity.
- Demonstrating mastery of a particular field By successfully completing a capstone project, you demonstrate mastery of a particular field, setting yourself apart from others in the academic program as well as enhancing your marketability in the job market.
- Building your CV Prospective employers want to know more than just your academic performance. What is the capstone project you undertook in school? Adding them to your CV will inform them of your additional skills you possess.
- Building a sense of accomplishment Completing capstone essays can be a significant accomplishment, giving you pride and satisfaction for your hard work.
Senior Capstone Project Structure
A capstone project structure plays a crucial role in helping you write a successful paper. It provides a clear, organized framework for the capstone project, helping you ensure that you include all necessary parts. It will also guide you in the right direction, helping you find the best approach to complete your paper. Before you begin writing a capstone project paper, it is important to carefully review all guidelines provided by your academic program to ensure that it meets all requirements and is structured clearly and effectively. Here is a general structure of senior capstone project:
- Abstract Brief summary of the capstone project, typically around 250-300 words. It provides a concise overview of background information, objectives, methodology, results, and conclusion. It is often the first section that readers view to better understand your study's purpose and findings.
- Introduction This section provides an overview of the paper and sets context for your study. It includes a background on the topic, a clear problem statement or issue being addressed, research questions, and objectives. It should also highlight how your paper will be structured.
- Literature Review It provides a comprehensive overview of relevant research on the topic, including an analysis of previous studies, gaps in literature, and theoretical framework that will guide your study. It is important to provide thorough and well-structured literature review to support your research questions.
- Methodology In this section, you outline research design types, data collection and analysis methods, and sampling procedures that will be used to address your research questions. It should also give detailed description of the research process, including rationale for methods chosen and procedures followed to ensure validity and reliability of data collected.
- Results Here you present your study findings, including statistical analyses, tables, graphs, and figures that illustrate the results. They should be presented in a well-organized manner, focusing on answering your research questions.
- Discussion This section provides an interpretation of results, connecting findings to literature and research questions, further discussing their implications. The discussion should give critical evaluation of results, considering the limitations for future research.
- Conclusion It summarizes the main study findings, providing recommendations for future research. This section should be a clear and concise summary of results, tying the findings to research questions and objectives.
- References This section provides a comprehensive list of all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to appropriate citation style (APA, MLA, etc.).
- Appendices If necessary, this section includes additional materials that support the main study findings, such as survey instruments, raw data, or transcripts of interviews.
Capstone Project Outline
A sample capstone project outline is a visual representation of the paper structure and organization. It acts as a roadmap for writing, helping ensure that the project stays on track. The purpose of the capstone project outline is to provide an overview of all main elements and order in which they will be presented. Here is a template example of an outline for a capstone project:
- Background of the topic
- Purpose of study
- Research questions
- Overview of paper structure
- Overview of relevant research
- Analysis of previous studies
- Gaps in literature
- Theoretical framework
- Research design
- Data collection and analysis methods
- Sampling procedures
- Rationale for methods chosen
- Procedures to ensure validity and reliability of data
- Presentation of study findings
- Statistical analyses
- Tables, graphs, and figures
- Focus on answering research questions
- Interpretation of results
- Connection of findings to literature and research questions
- Implications of findings
- Critical evaluation of results
- Study limitations
- Implications for future research
- Summary of main findings and conclusions
- Recommendations for future research
- Comprehensive list of all sources cited in paper
- Additional materials that support main study findings
How to Write a Capstone Project Paper?
A capstone project requires careful planning to show that you have a grasp of a particular discipline or subject. As such, it is important to understand the steps involved in the process and have a well-defined plan in place. The following subsections will guide you in writing a capstone project paper, from start to finish, giving you the roadmap to ensure a successful outcome. Each part is carefully detailed to help you understand what’s expected of you. Follow these steps to learn how to write a capstone paper:
1. Choose a Topic
Choosing a topic is an important step in writing a capstone project. It sets the foundation for your paper, determining how successful the final product will be. Always go for capstone project ideas that have not been extensively researched, allowing you to add new insights. Here are some steps to follow when choosing research topics :
- Identify area of interest Think about your interests, passions, and academic strengths. This will help you choose a topic that you are genuinely interested in or are well-suited to research.
- Consider the project scope Make sure the topic is manageable within a specified timeframe and resources available to you. In particular, it should be narrow enough to allow you to focus, but broad enough to provide enough material for a comprehensive analysis.
- Review the coursework Take a look at all courses you have taken so far and consider how they relate to your chosen topic. Remember the paper should be built on knowledge you have acquired throughout your academic journey.
- Consult your supervisor A capstone project advisor can provide valuable guidance and feedback on the topic. They can help you refine it, ensuring that it is relevant to the field of study.
- Research your topic Once you have a few potential topics, research each one to determine their feasibility, availability of resources, as well as scope of literature.
- Make a decision After you have conducted your research, choose one topic that you are most interested in and that you believe will be the most rewarding.
Choosing a topic that is relevant, manageable, and of personal interest to you will help you stay motivated throughout your capstone writing process.
2. Research Existing Literature
Conducting a thorough literature review is crucial in helping you understand the current state of knowledge on the topic, identifying gaps your capstone senior project can fill. Here's how to go about it:
- Start by brainstorming keywords or phrases related to the topic, using them to search databases, such as Google Scholar , JSTOR , and other relevant academic sources.
- Pay attention to relevant theories and studies as you research. This will help you get a sense of what has already been done, what questions remain unanswered, and what you can contribute to the field.
- Keep track of all sources, taking notes as you read. Organize them into categories, like creating an annotated bibliography that you can refer to later.
- Evaluate the quality of sources you found. Check if they are peer-reviewed or have been published in reputable academic journals.
- Synthesize the information you have gathered to identify themes or patterns. This will help you see the bigger picture and understand the research context.
- Use the synthesized information to refine the research question and hypothesis. Make sure that your research is original and adds to the existing body of knowledge.
By conducting a thorough literature review, you will write a capstone paper that is well-informed, grounded in latest research, and makes a meaningful contribution.
3. Define a Problem
Based on research, define the problem statement you aim to address in your capstone research paper. It should be well-defined and specific. The problem statement should be clear, concise, and align with the research question. It should also be justified, explaining why the problem is important, including how it relates to current literature. Here are some steps to follow when defining a problem for a capstone project:
- Review existing literature Conduct a thorough review of existing literature in your area of interest. This will help you identify any gaps in knowledge or areas that need further research.
- Identify the problem Based on literature review, identify a specific problem or issue that you would like to address. It should be relevant and of interest to you.
- Refine the problem Make it more specific and focused. Consider the project scope, available resources, and own abilities.
- Formulate a research question Based on the problem you have defined, formulate a research question that will guide your paper. It should be clear, concise, and answerable through research.
- Develop a hypothesis Develop a hypothesis that you will test through research. It should provide a potential answer to the research question.
Defining a problem is important because it provides focus and direction for research. A well-defined problem will ensure that your capstone project writing is of high quality.
4. Introduce Your Research Methods
This section should describe methods you will use to collect and analyze data, as well as the rationale behind your choice. They should be appropriate, accurate, and reliable for the capstone project. You should also explain any final capstone project limitations, including how you plan to address them. Here are some steps to follow when introducing graduate capstone research methods:
- Choose research methods that are appropriate for the research question and hypothesis. Consider the strengths and weaknesses of different methods, and select the ones that are most suitable.
- Provide a clear explanation of why you chose the methods you did. Explain how they will help you answer the research question and test your hypothesis.
- Give a detailed description of research methods, including how you will collect data and analyze it. Be specific about what steps you will take, tools you will use, and data you will collect.
- Consider any ethical issues that may arise from using those research methods. Explain how you will ensure that research is conducted in a responsible manner.
- Review previous research that has used similar methods, considering any lessons learned from that. Explain how you will apply these lessons to your own research.
Introducing research methods is important because it sets a foundation for your research. It will provide readers with a clear understanding of your methods, including rationale behind them.
5. Discuss Your Key Findings
This step involves presenting findings of the study and analyzing all data. When writing a capstone paper, provide a clear presentation of the results in addition to how they relate to the problem they aim to address. They should be presented in a logical, organized manner, and supported by evidence. In your capstone work, discuss their implications, including how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge. Here are some steps to follow when discussing key findings:
- Present results in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and charts to help illustrate your findings.
- Interpret results based on your research question and hypothesis. Explain what the findings mean and why they are significant.
- Compare your results to those of previous research in similar fields. Explain how the results you got are similar or different from previous findings.
- Discuss research limitations and the strengths of methods used. Explain how they may impact the results.
- Discuss implications of the findings for your field of study or society as a whole. Explain how that research contributes to a broader understanding of the topic.
- Conclude your discussion of key findings by summarizing results and their significance. Highlight key takeaways while explaining why they are important.
6. Present a Capstone Project
In this final step, you should present your capstone project in a clear, organized manner, highlighting key findings and significance of research conducted. This should be a well-structured, well-written paper or oral presentation that showcases your knowledge of how to do a capstone project on a specific subject. Capstone in college or university should be written in an academic style, following the guidelines set by the institution. The paper should also include an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results section, discussion, and conclusion. For oral presentation, you may also be required to answer questions from the audience. So, it is important to be well-prepared and familiar with the paper content. It should effectively communicate your research findings to them. To make a successful presentation, here are a few suggestions:
- Plan your presentation carefully.
- Use visual aids, such as slides, charts, graphs, and images, to help you effectively communicate ideas or findings to the audience.
- Rehearse the presentation several times until you are confident and comfortable with its content and flow.
- Present only the most important information to avoid going into too much detail.
- Interact with the audience by asking questions or allowing for discussion.
- Be ready to answer questions from the audience, discussing your work in great detail.
Capstone Paper Format
A capstone project format can vary depending on the discipline or requirements set forth by your instructor or program. Most times, you may encounter the following common formats used in most capstone papers.
- APA paper format Mostly used in social sciences, education, and psychology. It contains a cover page, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, references, and appendices.
- MLA paper format Commonly used in humanities, such as literature and language. You must include in-text citations and the Works Cited page.
- Chicago format Often used in history, business, and other disciplines. It involves using either footnotes or in-text citations and a bibliography page.
Regardless of the chosen format, ensure that your capstone paper is well-organized, has proper grammar, and is easy to read.
Capstone Project Writing Tips
To ensure success in writing your capstone project, it is important to keep in mind some key practices. In this section, we will introduce you to common tips that can help you effectively plan, research, and write the paper. From choosing a suitable topic to proofreading the final draft, these tips on how to write a good capstone project will help you produce a successful paper that meets academic standards:
- Start early Give yourself enough time to research, write, and revise. Starting early will also give you enough time to address any obstacles that may arise when writing.
- Choose a suitable topic Pick a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study.
- Research thoroughly Gather as much information as possible from reliable sources. Conduct a comprehensive literature review to gain a deep understanding.
- Outline your ideas Organize ideas to create an outline for the capstone project. This will help you stay focused, ensuring the paper has a clear structure.
- Write clearly and concisely Use clear, concise language to communicate ideas. Avoid using technical jargon unless it is absolutely necessary.
- Cite your sources Properly cite all sources you use in the capstone project to avoid plagiarism. Follow the required citation style specified.
- Revise Take time to proofread the work. Check for grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors. Also, ensure that ideas are presented well.
- Seek feedback Ask a friend, mentor, or academic advisor to review your capstone assignment and provide feedback. This will help you identify any mistakes.
Bottom Line on Capstone Project
In this guide, you have learned what’s a capstone project definition, its benefits in education, purpose, and structure. Before you embark on writing your paper, make sure you fully understand the meaning of a capstone project paper and what it entails. This means taking the time to carefully research a topic, identify a clear problem to address, and develop a research plan that will help you find answers. Remember that the final product should be well-written, well-organized, and effectively communicate your key research findings. Once you begin to write your capstone, keep in mind the following tips:
- Strictly follow the instructor’s guidelines.
- Only pick reliable sources for your capstone paper.
- Pay attention to the layout, format, and structure.
- Plan your time for completing the project wisely.
- Always seek feedback to ensure you are going the right way.
Feel free to check out our capstone project writing services and see how else we can assist you with this program! Our writers can always get you well-written texts before the deadline!
FAQ About Capstone Projects
1. what is a capstone project in college.
A capstone project in college is the final piece of stone needed to complete a degree program. It often involves significant research proposal, presentation, or practical application of skills and knowledge acquired during their program. By definition, it is a requirement for graduation and may be evaluated for grades or other forms of academic recognition.
2. What is capstone project significance?
Capstone projects are significant because:
- They provide an opportunity for students to demonstrate their mastery of a particular subject area.
- They allow students to apply knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout their college degree in a real-world setting.
- They provide students with a sense of completion and achievement, helping them demonstrate the value of their college performance to potential employers or other stakeholders.
3. How long should a capstone paper be?
The length of a capstone project paper varies depending on set guidelines by the academic institution or instructor. On average, they can be between 20-25 pages long, sometimes 35, including any supporting materials, such as appendices or references. However, check specific requirements from your institution as they can cap the number of pages.
4. What is the difference between a capstone project and a thesis?
A capstone project and thesis are both academic works, but they carry significant differences between them. A thesis is typically longer, and more in-depth than a capstone project. It is often required for graduate students and is based on original research. Its focus is narrower and more specialized. A capstone project is often required for undergraduate students, mostly based on research or practical application. It is more interdisciplinary in nature, involving solving world problems.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

A Comprehensive Guide on High School Senior Capstone Projects (With Examples)

Reviewed by:
Former Admissions Committee Member, Columbia University
Reviewed: 4/26/24
As you near the end of your high school journey, it's time to explore the world of senior capstone projects.
If you're a high school student, especially in your senior year, you're likely gearing up for the culmination of your academic journey: the senior capstone project.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about capstone projects, complete with examples to spark your inspiration and help you succeed. Whether you're just starting to explore project ideas or fine-tuning your plans, you've come to the right place!
What Is a Capstone Project?
A capstone project is like the grand finale of your academic or personal journey. It's a focused effort that you tackle within a set timeframe, bringing together everything you've learned or accomplished. Unlike a passion project , which you can work on whenever you feel like it, a capstone project has a clear deadline.
For instance, let’s say you're a culinary arts student nearing graduation. Your passion lies in sustainable cooking practices, and for your capstone project, you decide to create a cookbook featuring locally sourced, eco-friendly recipes.
Your cookbook project demands months of research, recipe development, testing, and layout design. It's a big commitment that demonstrates your expertise in culinary arts and your dedication to sustainable food practices.
Similarly, in school, a capstone project could take various forms, such as conducting research on a scientific topic, developing a business plan, or creating a multimedia presentation. These projects all reflect your broader interests and passions, demonstrating your skills and knowledge in a specific area.
Overall, your capstone project in high school is a major milestone, allowing you to demonstrate your expertise, creativity, and dedication. It's a chance to bring everything you've learned together and show what you're capable of achieving.
Different Between Capstone and Passion Project
Capstone projects are typically a mandatory part of a school or college program. They're serious business involving thorough research, problem-solving, and often collaboration with teachers or experts. The goal is to demonstrate your mastery of the subject matter and readiness to tackle real-world challenges.
On the other hand, passion projects are all about following your interests and doing something you love. You could focus on writing a novel, starting a community project, or diving into a hobby—passion projects are driven by personal motivation rather than academic requirements. They're more flexible and allow you to explore your passions on your own terms.
So, while both capstone and passion projects are valuable ways to dive deep into a topic you're passionate about, capstone projects are more structured and tied to academic goals, while passion projects offer more freedom and personal expression.
How to Find Ideas for Capstone Project
Looking for capstone project ideas? Let's take a look at some effective strategies to spark inspiration and find the perfect project for you.
Follow Your Interests
Think about what excites you the most. Do you love helping the environment or dreaming up better ways to teach? Pick a topic that really speaks to you. When you're passionate about what you're working on, you'll stay motivated and focused from start to finish.
Use What You've Learned
Consider the subjects you've learned in school. Think about how you can use that knowledge to solve real-life issues. For example, if you've studied marketing, you could create a marketing plan for a nearby business. Or, if you're good at finance, you could analyze a company's finances and propose ways to make them better.
Don't hesitate to reach out to your professors, advisors, or mentors for guidance. They've been through similar experiences and can offer valuable insights and suggestions. They might even be able to connect you with industry contacts or organizations that could provide support or resources for your project. Their feedback can help you refine your ideas and ensure you're on the right track.
Check Feasibility
As you narrow down your options, it's crucial to assess the feasibility of each potential project idea. Consider factors such as the availability of resources, the complexity of the task, and your own time constraints.
While you want to choose a project that's challenging and meaningful, it's also essential to be realistic about what you can accomplish within the given timeframe. Setting achievable goals will increase your chances of success and prevent unnecessary stress along the way.
Identify Current Issues
Keep up to date with the latest news and trends in your field of study or topics that interest you. Identify important issues or new challenges that you could focus on for your capstone project. By addressing relevant and current topics, you can actively contribute to important discussions and possibly have a bigger impact with your project.
Consider Community Needs
Consider the issues that matter most to your local community or a specific group of people. Is there a problem or something missing that you could help with through your project? By talking to people in your community through volunteer work or doing surveys, you can find project ideas that match real needs and make a positive impact.
Broaden Your Horizons
Think outside the box! Don't stick to just one subject for your capstone project. Instead, think about how you can mix ideas from different areas. By combining different perspectives, you can come up with creative and innovative solutions that you might not have thought of otherwise. This can make your project stand out and bring new insights to your work.
Look for Inspiration from Previous Projects
When searching for ideas for your capstone project, take a look at projects completed by students who came before you. Looking at successful past projects can give you helpful ideas about topics, methods, and how big your project should be.
Remember, it's important not to copy someone else's work exactly, but you can use it to inspire your own unique ideas and ways of doing things.
Think About Long-Term Goals
Think about how your capstone project can help you achieve your long-term goals, both in school and beyond. Are there particular skills you want to improve or experiences you want to have during the project? By making sure your project connects to your bigger plans, you can make it even more meaningful and helpful for your future journey.
Stay Flexible and Open-Minded
Stay open to exploring new directions and adjusting your project as you learn and receive feedback. Sometimes, the best projects come from unexpected changes or improvements along the way. Stay flexible and welcome the chance to learn and develop throughout your capstone project.
By blending your interests, what you've learned in school, and advice from mentors, you can create a capstone project that shows off your abilities and makes a difference in your field or community.
Tips on How to Execute Capstone Project
Ready to tackle your capstone project head-on? Here are some practical tips to guide you through the execution process smoothly.
Junior Fall
Brainstorm Ideas : This is your chance to explore a wide range of topics and ideas that pique your interest. Consider what issues or subjects you're passionate about, what challenges you want to address, or what questions you want to explore further. Keep an open mind and jot down any potential project ideas that come to mind, even if they seem unconventional at first.
Set Goals : Once you've generated some project ideas, it's time to clarify your objectives. Think about what you want to accomplish with your capstone project and break it down into smaller, actionable goals. Consider both short-term goals, such as completing research or gathering resources, and long-term goals, such as presenting your findings or implementing a solution.
Junior Spring
Recruit and Fundraise : Depending on the scope of your project, you may need additional support from teammates or financial resources. Reach out to classmates, friends, or faculty members who share your interests and might be interested in collaborating on the project. Additionally, explore fundraising opportunities to secure funding for project-related expenses, such as materials, equipment, or travel.
Hit Milestones : As you begin working on your project, set specific milestones to track your progress and stay on schedule. These milestones could include completing research, conducting experiments or surveys, drafting project proposals or reports, or presenting preliminary findings to peers or advisors. Regularly assess your progress and adjust your approach as needed to ensure you're meeting your goals.
Rising Senior Summer
Stay Busy : Although summer break is a time for relaxation, don't let your momentum wane. Dedicate consistent time each week to work on your capstone project, whether it's conducting research, analyzing data, drafting project documents, or refining your presentation skills. Establish a schedule and stick to it to maintain progress and prevent last-minute rushes.
Stay Connected : While you may be physically distanced from campus during the summer months, stay connected with your advisors, mentors, or project collaborators through email, phone calls, or virtual meetings. Keep them updated on your progress, seek their input or feedback when needed, and leverage their expertise to overcome any challenges you encounter.
Senior Fall
Keep Pushing : As the new school year begins, ramp up your efforts and focus on achieving your project goals. Set new objectives for the upcoming semester and prioritize tasks that will bring you closer to project completion. If your project involves organizing events, conducting experiments, or presenting findings, plan and execute these activities with diligence and attention to detail.
Senior Spring
Plan Ahead : As you approach the final months of your capstone project, take time to reflect on your accomplishments and consider the next steps. Evaluate the impact of your project, gather feedback from stakeholders or participants, and identify any areas for improvement or follow-up activities. Prepare for project completion by documenting your findings, finalizing project deliverables, and communicating your results to relevant audiences.
By following these guidelines and staying committed to your goals, you'll be well-equipped to execute your capstone project successfully and make meaningful contributions to your field of study or community.
Common Mistakes
Let's take a look at nine common mistakes students make in their capstone projects, along with tips on how to sidestep them.
Choosing a Topic That’s Too Broad
Your topic should be relevant to your field of study, but many students make the mistake of selecting broad topics that lack focus. To avoid this, consult with professors or career advisors to narrow down your focus and ensure your topic is both relevant and manageable.
Choosing a Topic You Don’t Really Care About
Passion is key to success. If you're not genuinely interested in your topic, your motivation and enthusiasm will dwindle over time. Select a topic that excites you and aligns with your interests to stay engaged throughout the project.
Not Doing Your Research Properly
Research is the backbone of your project. Skipping this step or relying on inaccurate information can derail your project. Take the time to conduct thorough research, cite credible sources, and ensure the accuracy of your findings.
Not Writing Your Paper in the Correct Format
A well-structured paper is essential for clarity and coherence. Follow a standard format, including sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, and conclusion, to ensure your paper is organized and easy to follow.
Not Taking Advantage of All the Resources Available
Don't overlook the resources at your disposal, whether it's the library, the internet, peers, professors , or academic advisors. Utilize these resources for research, guidance, feedback, and support throughout your project.
Not Proofreading Thoroughly Enough
Typos, grammatical errors, and formatting inconsistencies can undermine the credibility of your project. Take the time to proofread your work multiple times, or enlist the help of a peer or professional proofreader to ensure your paper is error-free.
Forgetting to Reference Your Sources
Proper citation is essential to avoid plagiarism and give credit to the original sources of information. Ensure you cite all sources accurately and consistently throughout your paper, following the required citation style guidelines.
Poor Presentation
Your presentation is the final show of your hard work. Neglecting to prepare adequately or rushing through your presentation can detract from the quality of your project. Practice your presentation, create engaging visuals, and rehearse your delivery to captivate your audience.
Waiting Until the Last Minute to Start Writing Your Paper
Procrastination is a common pitfall that can lead to rushed and subpar work. Start early, create a timeline, and break down your project into manageable tasks to avoid last-minute stress and ensure a polished final product.
By steering clear of these common mistakes and approaching your capstone project with diligence and dedication, you'll set yourself up for success and leave a lasting impression with your academic masterpiece.
Ideas and Examples of Capstone Projects
Need some capstone project ideas for high school? Let’s take a look at some high school capstone project examples.
- Study green marketing strategies that promote sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Engineering
- Develop a system to detect red traffic lights using image processing for safer roads.
- Create a solar panel system with adjustable angles to maximize energy capture.
- Analyze how social media can be used to effectively engage and retain customers through content marketing strategies.
- Design educational programs for nurses on asthma care and point-of-care testing protocols for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Computer Science
- Develop a smartphone interface for managing medical records to improve accessibility and patient engagement.
- Design a web-based survey system for collecting feedback and analysis in academic or business settings.
- Evaluate the impact of project management practices on the success of political campaigns.
- Assess how technology influences accounting practices and the effectiveness of accounting software in improving financial reporting.
- Explore the benefits of virtual classrooms and digital engagement strategies for remote learning.
Information Technology
- Investigate cybersecurity issues and propose solutions to protect against threats like intrusion and data breaches.
- Create object recognition systems using machine learning for security surveillance and image analysis.
Looking to gain clarity on your senior capstone project? Here are some frequently asked questions to guide you through the process.
1. How Does a Capstone Project Differ from Other High School Projects?
A high school capstone project typically involves more in-depth research and interdisciplinary exploration compared to other projects.
2. How Do I Choose a Topic for My High School Capstone Project?
To choose a topic for your high school capstone project, consider your interests, skills, and academic goals, and seek advice from teachers or mentors.
3. Are High School Capstone Projects Required for Graduation?
High school capstone projects are not always required for graduation and can vary depending on the school or program.
4. Can High School Capstone Projects Be Related to Extracurricular Activities?
Yes, high school capstone projects can be related to extracurricular activities and allow students to integrate their interests and experiences into their academic projects.
Final Thoughts
In short, high school senior capstone projects are your chance to shine. By picking the right topic, steering clear of common pitfalls, and tapping into available resources, you can leave a lasting mark. Whether it's in marketing, engineering, education, or any other field, capstone projects let you show off your skills and get ready for what's next.
Get A Free Consultation
You may also like.

How to Show Leadership Experience When Applying to College + Examples

Harvard vs. Yale: Which Is Better?


- Broken Arrow
- Graduate College

Gather Here. Go Far
NSU is where success begins. Here professors know their subjects and how to get you ready for a career after you graduate. We empower individuals to become socially responsible global citizens by creating and sustaining a culture of learning and discovery.
Thesis and Capstone Formatting Guidelines
The paper for the two official copies of the manuscript is 8 x 11, at least 20% cotton content. Text should only be printed on one side.
The margins for the text, including page numbers, must be 1 inch at the top, bottom, and right side of the page, and 1 inches on the left side to allow for binding. Page numbers should be included within these margins.
The body of the document must be double-spaced. Tables may be single-spaced. Consult the style manual of your discipline for spacing after title, headings, quotations, references, etc.
The typeface for the text must be 12-point, serif typeface, e.g., Courier, Times Roman. Black ink should be used unless color is approved by the thesis/capstone director.
Page Numbering
Number all preliminary pages with lower case Roman numerals. Place numbers one inch from bottom of page, three spaces to the right of center. Count but do not number the title page. Number the thesis main body with Arabic numbers in the upper right-hand corner of the page one inch from the top with a double space before the first line of text, and 1 inch from the right-hand side of paper edge. Count but do not number the first page of the main body of the text. Also, do not place a running head on this first page.
Preliminary Pages
Title Page. On the title page, the following information is vertically and horizontally centered: the title of the master's thesis; the full name of the author (this must be the name of the student record); "A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of (Master of Arts, Master of Business Administration, Master of Science, etc.)"; "Northeastern State University"; and the month and year in which the degree sought is to be awarded (contact the Graduate College for the correct month and year). There should be an equal number of spaces between title/author text and the degree text and the date.
Signature/Approval Page
The signature/approval page begins with the thesis title keyed two inches down from top of page. Use inverted pyramid for longer titles and center within margins. Double-space typed lines. Include signature lines for all of your committee members and the Graduate College Dean. Instructions on inserting signatures in the final document are available on the web or see your adviser for assistance.
The abstract is a one-paragraph, double-spaced, self-contained summary of the most important elements of the paper. The abstract begins on a new page.
Acknowledgments (departmental designation)
The format of the acknowledgments page is determined by the discipline style manual. An acknowledgments page is included immediately before the table of contents. Acknowledgments should be made of any grants that supported the research. The thesis/capstone advisor, readers and any others who contributed significantly to the project is typically also noted here.
Table of Contents (departmental designation)
The format of the table of contents is determined by the discipline style manual. The table of contents will list the page numbers of the chapters and specific pages that follow. Double space each entry, beginning with the list of tables, if applicable, chapters of the main body, references, and appendices.
List of Tables and Figures (if applicable)
The format of the list of tables and figures is determined by the discipline style manual. Tables are data presented in tabular form (rows and columns) and should not include any artwork or graphics. Tables should be formatted with clear labels for the rows and columns. Figures are any illustrations that are not in table format. Both tables and figures should be designed to communicate information quickly and clearly. Refer to the style manual for your discipline for documenting tables and figures.
Body of Thesis/Capstone
The format of the body of the thesis is determined by the discipline style manual. The text is to be double spaced with paragraph indentions. Margins are one-inch at top, bottom and right. A one and one-half inch margin on left side of the paper will allow for binding. All main body pages are to be numbered consecutively with Arabic numerals in the upper right-hand corner of each page (except for the first page which is counted but not numbered), one inch from the top and one inch from the right-hand edge of the paper. Double-space between the page number and the top line of text. Do not use the abbreviation p. or any other mark before the page number.
The number of chapters, chapter titles, headings, and subheadings within chapters should be chosen to present the material in a logical and comprehensible manner and formatted according to the discipline style manual. Thesis/capstone content and form should be discussed with your thesis/capstone committee or thesis/capstone advisor/first reader before you complete the thesis/capstone. Formatting will be according to the style manual used by the discipline.
Bibliography/References/Works Cited
The thesis/capstone must contain documentation for all sources cited in the text. This documentation takes the form of the Bibliography, References, or Works Cited page(s), depending on the style manual used in your discipline. Each source that is mentioned in the text of the thesis/capstone must be documented. Formatting will be according to the style manual used by the discipline.
One or more appendix may be included for material which would detract from the flow of the manuscript, but which is relevant to the thesis/capstone. Examples include large data sets, computer programs, and stimulus materials. Formatting will be according to the style manual used by the discipline.
Order of Pages
The following indicates the correct order of pages. Some pages are required for all theses while other pages are optional and should be included as needed.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Capstone Components
12 Research Design
The story continues….
“So, how do we go about answering our research questions?” asked Harry.
Physicus explained that they will have to analyze their questions to see what types of answers are required. Knowing this will guide their decisions about how to design the needs assessment to answer their questions.
“There are two basic types of answers to research questions, quantitative and qualitative. The types of answers the questions require tell us what type of research design we need,” said Physicus.
“I guess if I ask how we decide which type of research design we should choose, you will say, ‘It depends?'” uttered Harry.
Physicus’ face brightened as he blurted out, “Absolutely not! Negative!” Physicus continued, “If the research questions are stated well, there will only be two ways in which they can be answered. The research questions are king; they make all the decisions.”
“How come?” Harry appeared confused.
“Well, let us see. Think about our first question. How many mice will Pickles attack at one time? What type of answer does this question require? It requires a numeric answer, correct?” Physicus asked.
“Yes, that is correct,” Harry said.
Physicus continued, “Good. So, does our second question also require a numeric answer?”
“The second question is also answered with a number,” replied Harry
Physicus blurted, “Correct! This means we need to use a quantitative research design!”
Physicus continued, “Now if we had research questions that could not be answered with numbers, we would need to use a qualitative research design to answer our questions with words or phrases instead.”
Harry now appeared relieved, “I get it. So in designing a research project, we simply look for a way to answer the research questions. That’s easy!”
“Well, it depends,” answered Physicus smiling.
Interpreting the Story
There are qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods, and applied research designs. Based on the research questions, the research design will be obvious. Physicus led Harry in determining their investigation would need a quantitative design, because they only needed numerical data to answer their research questions. If Harry’s questions could only be answered with words or phrases, then a qualitative design would be needed. If the friends had questions needing to be answered with numbers and phrases, then either a mixed methods or an applied research design would have been the choice.
Research Design
The Research Design explains what type of research is being conducted in the needs assessment. The writing in this heading also explains why this type of research is needed to obtain the answers to the research or guiding questions for the project. The design provides a blueprint for the methodology. Articulating the nature of the research design is critical for explaining the Methodology (see the next chapter).
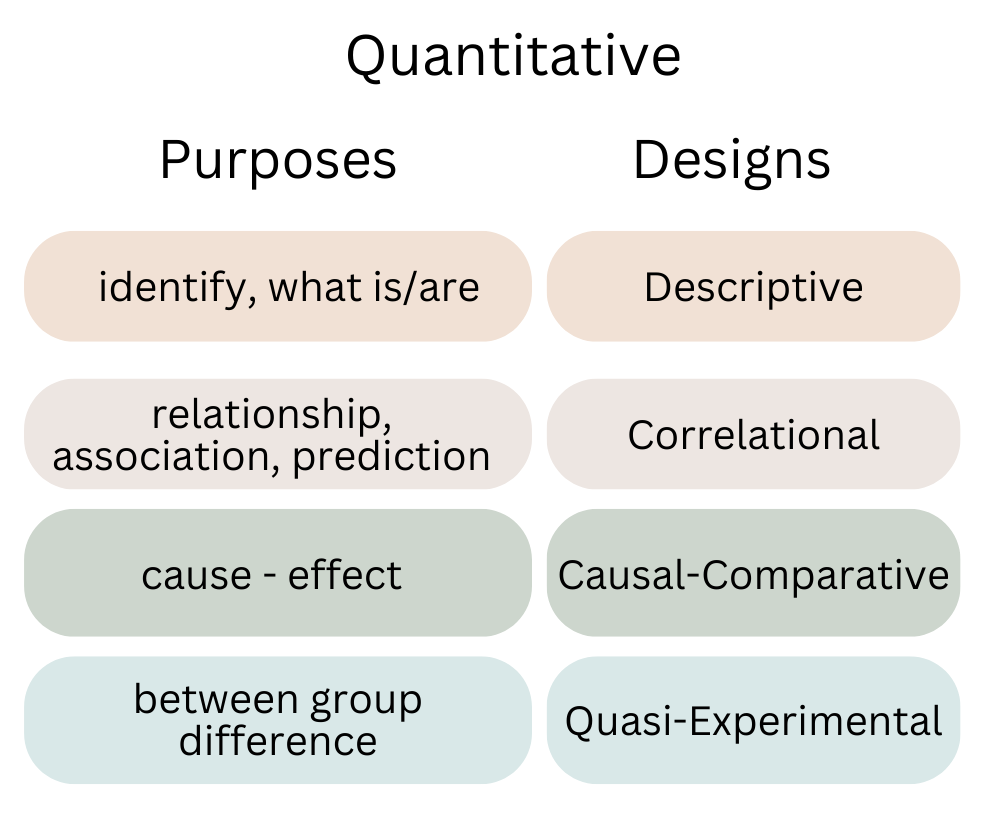
There are four categories of research designs used in educational research and a variety of specific research designs in each category. The first step in determining which category to use is to identify what type of data will answer the research questions. As in our story, Harry and Physicus had research questions that required quantitative answers, so the category of their research design is quantitative.
The next step in finding the specific research design is to consider the purpose (goal) of the research project. The research design must support the purpose. In our story, Harry and Physicus need a quantitative research design that supports their goal of determining the effect of the number of mice Pickles encounters at one time on his behavior. A causal-comparative or quasi-experimental research design is the best choice for the friends because these are specific quantitative designs used to find a cause-and-effect relationship.
Quantitative Research Designs
Quantitative research designs seek results based on statistical analyses of the collected numerical data. The primary quantitative designs used in educational research include descriptive, correlational, causal-comparative, and quasi-experimental designs. Numerical data are collected and analyzed using statistical calculations appropriate for the design. For example, analyses like mean, median, mode, range, etc. are used to describe or explain a phenomenon observed in a descriptive research design. A correlational research design uses statistics, such as correlation coefficient or regression analyses to explain how two phenomena are related. Causal-comparative and quasi-experimental designs use analyses needed to establish causal relationships, such as pre-post testing, or behavior change (like in our story).
The use of numerical data guides both the methodology and the analysis protocols. The design also guides and limits how the results are interpreted. Examples of quantitative data found in educational research include test scores, grade point averages, and dropout rates.
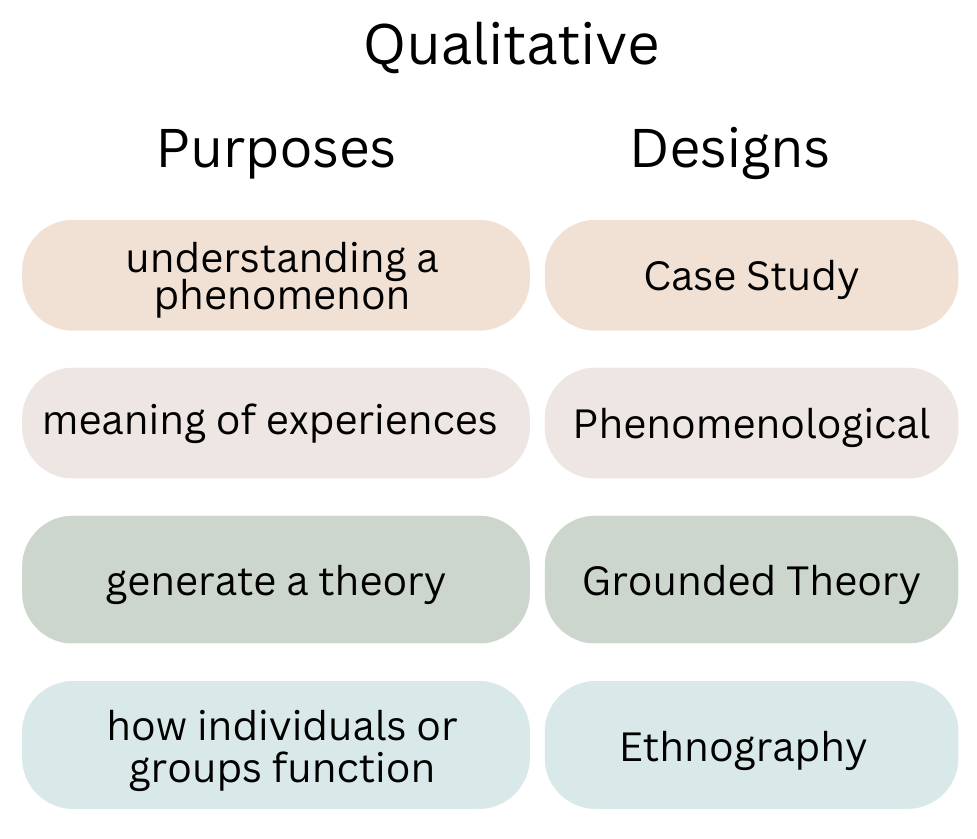
Qualitative Research Designs
Qualitative research designs involve obtaining verbal, perspective, and/or visual results using code-based analyses of collected data. Typical qualitative designs used in educational research include the case study, phenomenological, grounded theory, and ethnography. These designs involve exploring behaviors, perceptions/feelings, and social/cultural phenomena found in educational settings.
Qualitative designs result in a written description of the findings. Data collection strategies include observations, interviews, focus groups, surveys, and documentation reviews. The data are recorded as words, phrases, sentences, and paragraphs. Data are then grouped together to form themes. The process of grouping data to form themes is called coding. The labeled themes become the “code” used to interpret the data. The coding can be determined ahead of time before data are collected, or the coding emerges from the collected data. Data collection strategies often include media such as video and audio recordings. These recordings are transcribed into words to allow for the coding analysis.
The use of qualitative data guides both the methodology and the analysis protocols. The “squishy” nature of qualitative data (words vs. numbers) and the data coding analysis limits the interpretation and conclusions made from the results. It is important to explain the coding analysis used to provide clear reasoning for the themes and how these relate to the research questions.
Mixed Method Designs
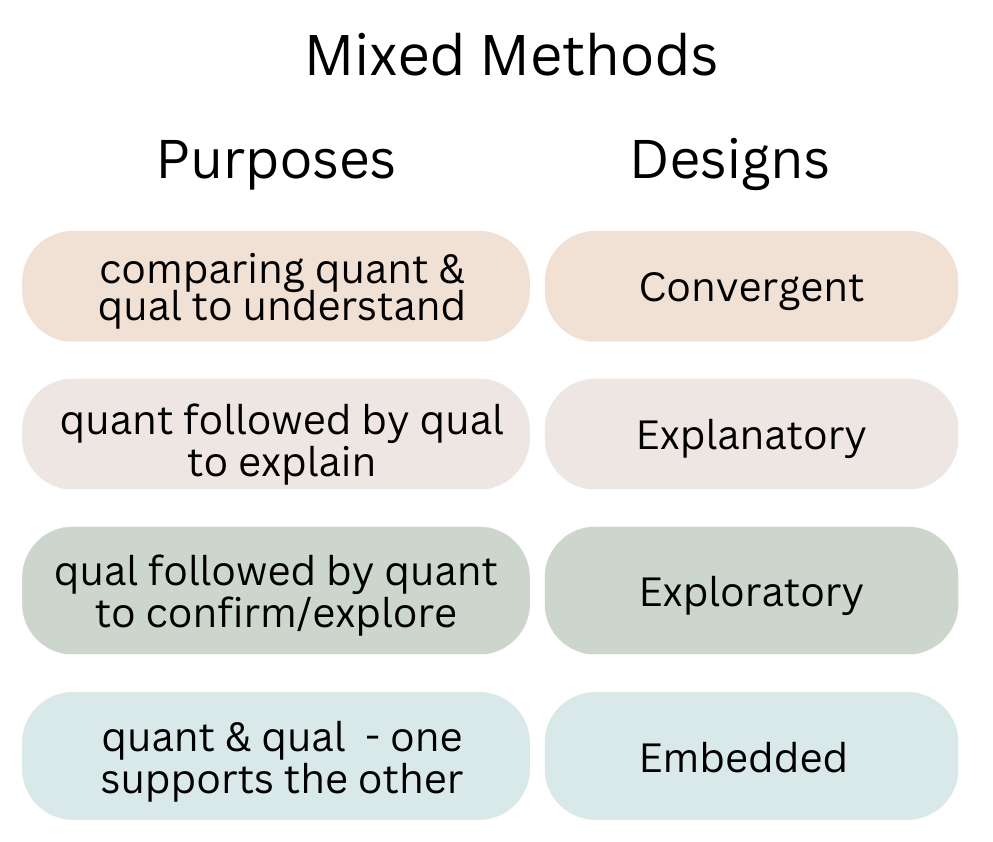
Mixed Methods research designs are used when the research questions must be answered with results that are both quantitative and qualitative. These designs integrate the data results to arrive at conclusions. A mixed method design is used when there are greater benefits to using multiple data types, sources, and analyses. Examples of typical mixed methods design approaches in education include convergent, explanatory, exploratory, and embedded designs. Using mixed methods approaches in educational research allows the researcher to triangulate, complement, or expand understanding using multiple types of data.
The use of mixed methods data guides the methodology, analysis, and interpretation of the results. Using both qualitative (quant) and quantitative (qual) data analyses provides a clearer or more balanced picture of the results. Data are analyzed sequentially or concurrently depending on the design. While the quantitative and qualitative data are analyzed independently, the results are interpreted integratively. The findings are a synthesis of the quantitative and qualitative analyses.
Applied Research Designs
Applied research designs seek both quantitative and qualitative results to address issues of educational practice. Applied research designs include evaluation, design and development, and action research. The purposes of applied research are to identify best practices, to innovate or improve current practices or policies, to test pedagogy, and to evaluate effectiveness. The results of applied research designs provide practical solutions to problems in educational practice.
Applied designs use both theoretical and empirical data. Theoretical data are collected from published theories or other research. Empirical data are obtained by conducting a needs assessment or other data collection methods. Data analyses include both quantitative and qualitative procedures. The findings are interpreted integratively as in mixed methods approaches, and then “applied” to the problem to form a solution.
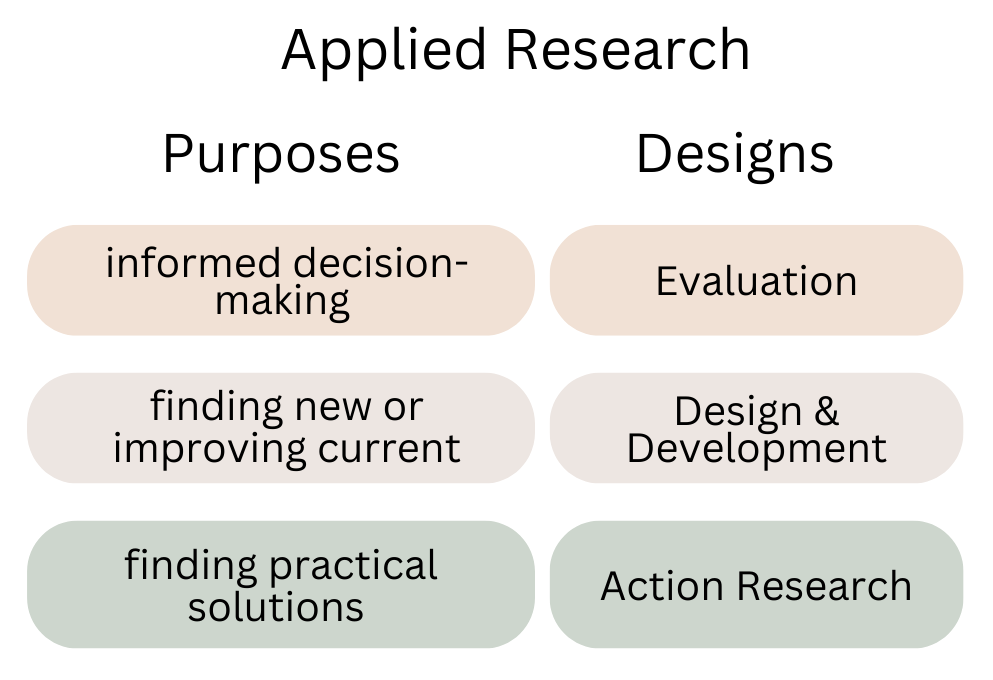
Telling the research story
The Research Design in a research project tells the story of what direction the plot of the story will take. The writing in this heading sets the stage for the rising action of the plot in the research story. The Research Design describes the journey that is about to take place. It functions to guide the reader in understanding the type of path the story will follow. The Research Design is the overall direction of the research story and is determined before deciding on the specific steps to take in obtaining and analyzing the data.
The Research Design heading appears in Chapter 2 of a capstone project. In the capstone project, the Research Design explains the type of design used for conducting the needs assessment.
Capstone Projects in Education: Learning the Research Story Copyright © 2023 by Kimberly Chappell and Greg I. Voykhansky is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
2022 Capstone Design Projects
Biomedical engineering, chemical engineering, civil, environmental & geological engineering, electrical & computer engineering, interdisciplinary engineering , management engineering, mechanical engineering, mechatronics engineering, nanotechnology engineering, software engineering, systems design engineering.
Department of Engineering
- Toggle Navigation
Capstone Design Projects

Real Solutions for the Real World
Grounded in a culture and curriculum that values the liberal arts and positive societal change, Wake Engineering students are uniquely prepared to tackle the real-world, multi-disciplinary engineering problems presented in their Capstone Design Projects.
Project teams of 3-5 seniors design, build, and test innovative solutions that meet real-world client, user, and stakeholder needs, with a focus on how their work positively impacts the human experience in the spirit of Wake Forest’s motto, Pro Humanitate. Yearlong Capstone Design Projects require students to work under the guidance of engineering faculty advisors and industry mentors – to think entrepreneurially, creatively, critically and ethically to develop functional prototypes not yet imagined. In their iterative quest to fill an unmet societal need, students dedicate more than 1,600 person-hours to each project, gaining invaluable technical engineering experience in team-based designing, project management, leadership development and professional communication.
The Design Process
At WFU Engineering, we implement an iterative 4-stage process that guides the student teams through a thorough and systematic undertaking. Throughout this process, we hope to demonstrate to students how they can apply the breadth of knowledge they learned throughout their curriculum to the real-world problems they are facing in capstone. A summary of the process is provided below:
- Discovery Design – background information, project scoping, solution benchmarking, generating design requirements
- Conceptual Design – generating and selecting viable concepts to solve the problem
- Embodiment Design – translating rough concepts into preliminary prototypes and models
- Detailed Design – testing, refinement, and improvement of prototypes
In between each of these stages, we students participate in technical design reviews where they interact with subject area experts who can provide critical input on their progress and plans.
Project Proposals
Wake Engineering students understand that tackling real-world problems requires diverse perspectives, including their own. Our Capstone Design Projects embrace this mindset by soliciting project ideas from many sources. Industry, government and non-profit sponsors may submit projects to meet identified needs, while students, faculty and staff may propose their own entrepreneurial ideas.
If you are interested in proposing a project or getting involved with the capstone experience, please visit the following webpages:
Proposing a Project
Ways to get involved
- myPNW Login
- Brightspace Login
- PNW Calendar
- Scholarships
- Tuition and Fees
Senior Design Students Present Capstone Projects
As a new semester starts, we want to quickly revisit the Fall and acknowledge our excellent 2022 Senior Design Presentations.
Presentations, alongside a written report, are the final milestones of a Senior Design/Capstone Project during the semester that requires students to develop innovative problem solutions while implementing computer graphics usage. They are supervised and mentored by faculty members who help explore research interests and create strong project proposals.
As projects evolve from conception to realistic design, students must demonstrate professional attitudes and attributes while providing enough context that a person outside of their discipline could understand key details in non-technical language.
Students presented the following projects in conjunction with CIVS faculty:
Numerical Simulation of wall shear stress and mixing in steel refining Ladle Furnace
Saleh Alshammari (ME), Ghazi Saad G Alharbi (ME) Advisors: Chenn Zhou, Tyamo Okosun
This project research and work cover the three-dimensional Computational Fluid Dynamics simulations performed on a Gas-stirred ladle used for refining and mixing of steel. The purpose of this project is to do research and explore the parameters which impact the life of these ladles and the phenomenon of refractory lining erosion and shear in the ladle wall which leads to its degradation. A real-life scale model experiment is to be performed for the validation of CFD results. Ansys applications were used to develop and run the simulation. Ansys workbench for development and Fluent for running the case.
Design of a Proof of Concept Software for Virtual Solar Farm Safety Training
David Gill (ECE), Cinthia Tafolla (ECE)
Advisors: chenn zhou, kyle toth.
Technicians working with high-power electricity face many possible dangers while working with their equipment. Prevention and mitigation are easier than treatment and effectively training employees in electrical safety is a large part of that, helping prevent more deaths and pose fewer risks to the workplace regarding safety. The main focus of our project was to complete a proof of concept for a virtual solar farm safety trainer to educate trainees in a simulated virtual environment to prevent risk to the trainee, equipment, and easier accessibility to complete training. Additionally, a simulated environment has allowed us to perform different safety scenarios and present hazards to test the trainee’s knowledge, how to overcome these hazards in the workplace, and safety practices to follow to maintain safety while working on a solar farm.
To achieve this, the programs Unity, Blender, and GIMP were utilized to create a virtual environment using 3D technology to simulate different scenarios. The virtual simulator features three different modules designed to train in using the proper personal protective equipment depending on the task, properly performing lock-out tag out, and situational hazards. Utilizing this simulated training and even improving on it in the future may help further safety practices, the importance of utilizing these safety practices anytime they’re applicable, and preventing any electrical-related workplace injuries.
Feasibility Study and Simulation of adding Hydrogen Fuel to a Combined Cycle Natural Gas Combustion Turbine at an Electric Generation Plant
Jon Heins (ME) Advisors: Chenn Zhou, Tyamo Okosun, Mike Melvin
In the electric power industry, organizations are investigating transitioning combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) power plants from natural gas to hydrogen combustion to decrease dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, hydrogen can serve as a complement to natural gas and syngas as an additional fuel source to protect organizations from price volatility. This design project reviews current work in the transition of CCGT engines to hydrogen fuel and develops a parametric combustion computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study of methane blended with hydrogen gas. The CFD study uses a generic can-combustor design and calculations were performed to determine the amount of blended fuel required to produce an equitable amount of thermal energy to the baseline (100% methane) case. From the parametric study, the impact hydrogen has on the performance, materials, and flue gas composition of the combined cycle gas turbine engine combustor was determined.

- MusiCentral
- Scheduler X
- Silhou Sports
- Steel Exile
- Turf Connect
- turn-based-rpg
- USC Faculty Dashboard
- Welcome Together
- WorkplaceWise
Layout Generator ¶
Website Repository
Description ¶
Our client, Advanced Smart Systems and Evaluation Technologies (ASSET), is a startup based in Columbia, South Carolina. Founded by a team of researchers, ASSET focuses on automatically detecting falls in senior citizen communities. They utilize a variety of sensors to monitor activity in and around client facilities. To optimize sensor coverage for each room, the research team develops specific room layouts. However, due to the unique architectural designs of each facility, the team is required to create new layouts for every new client building. Currently, the process of building these room layouts takes an average of one month from start to finish, which includes collecting measurements and finalizing the layout in PDF format. The overarching goal of the project is to significantly reduce the time it takes for the research team to develop these room layouts by constructing a software solution for layout generation.
Tech: A webapp using django, lualatex, railway.
Authors ¶
Tyler Beetle, Jordan Fowler, Anna Michelitch, Joseph Missan, James Ward.
Screenshots ¶

Admissions Visit Opportunities
Capstone design expo 2023, a note from professor ismail orabi, capstone design project coordinator.
The Capstone Design Expo is an opportunity for our students to showcase the results from their capstone design course. Student teams work to create a specific design solution for a "customer’s" real and unique need. Design and design education are, by their nature, experiential and collaborative, and our design team sponsors are our key collaborators. As a result of this collaboration, students bring energy and new ideas to meet the design need.
The design projects enable our students to put into practice what they have learned to prepare them for the workforce.
Acknowledgments
The Capstone Design Expo is the culmination of the hard work of the capstone design students. We thank them for their hard work and perseverance and wish them success in their new engineering careers. We also acknowledge the faculty members who served as mentors for our students. We wish to acknowledge Dean Harichandran of the Tagliatela College of Engineering for his inspiration and commitment to the Design Expo.

Ismail Orabi, Ph.D. Professor of Mechanical Engineering
Have A Question?
For additional information or future participation, please contact:

Self-Production of Raw Materials for Flame Retardant Unit

Upgrade of Laboratory Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor

Carbon Capture and Utilization to Produce Valuable Products

Deadman Anchor System Replacement

Dewatering System Design of Lake Whitney Dam

Design of a New Wheel Truing Facility for the New Haven Railyard

Ella T. Grasso Blvd: Traffic Calming with Intersection and Traffic Light Design
A Novel Smart Electronic Liaison to Support International Students

Virtual Reality Situational Awareness Training for First Responders Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles

Sentiment Analysis of Social Media (SASM)

StellariumVR

PXE Server on a Campus Enterprise Network

Enterprise Network Topology for Bradley International Airport

Digital NoteKeeper: Secure Audio & Cloud Recording

Network Security Developments in Working from Home

Embedded Systems in an Enterprise Network

Quick Disconnect Redesign for Space Applications

Actuator Redesign of a Laparoscopic Surgical Stapler

Experimental Rotor Test Rig

Singulation of Razor Handles through a Tumbler Feeder

SMART Bearings – Load Sensing CAM Follower

Plunger Head Leakage Tester

Falls Village Power Station Bearing Cooler Redesign

Modernized Notification Appliance Certification Testing Device

Automated Western Blot Process System

Ozone Measurement in Stratosphere During Solar Eclipse

Transceiver for Use on Submarine
We thank our industry sponsors who served as customers for our students as well as supporting their prototyping expenses. As customers, they gave valuable time and insights that uniquely benefited our students with an experiential design education in a real-world setting, which greatly complements the team mentoring by our faculty colleagues. Their generous commitment to our students brought their design education to life.

- MBA/MPA Program - University of New Haven
- Arts & Sciences: Art & Design | University of...
- Make Your Gift
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
College of engineering, mobility innovation shines as ece interdisciplinary teams take top prizes at spring capstone design expo.
Navigating a bustling airport can be a daunting challenge for visually impaired individuals, but Seekr , an interdisciplinary team of students , including three computer engineering majors , believes it has created a viable solution to the challenge.
Attendees at the Spring 2024 Senior Capstone Expo agreed, voting Seekr to a tie for Best Overall Project during the event, which took place on April 23 at McCamish Pavillion
The project aims to restore independence to blind and visually impaired airline passengers . Team members discovered that travelers with limited vision frequently rely on video calls with friends or family for assistance, while others depend on airport staff to push them to their gates in wheelchairs.
Seekr offers independence with a crossbody bag that provides guided voice directions and beeps to help travelers make their way through the terminal. Users would borrow the bag from the airport and turn in as they board their flight.

Team Seekr pictured Aislinn Abbot- ME ,Alaz Cig-ME, Andrew Gunawan - CmpE, Hanrui Wang -CS, Jackie Chen – CmpE, James Mead – ME , Rithvi Ravichandran - CmpE, and their advisor David Anderson.

Team Seekr created a wearable device to help visually impaired travelers walk through airports.

ECE winning team Electric Pump for Rocket Propellants designed an electric pump which can be used to deliver liquid propellants into a rocket engine.
Another mobility project, Team EMG, comprised of six electrical and one mechanical engineering students, won for Best Interdisciplinary Team. They developed a cost-effective, electromyography (EMG)-controlled locomotion system for tetraplegics that allows users to control an electrified wheelchair through detectable arm movements, enhancing their independence with technology that can be adapted to any manual wheelchair.
Electric Pump for Rocket Propellants won Best School of Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) Project chosen from 20 ECE teams represented at the Expo. The team designed an electric pump that can be used to deliver liquid propellants into a rocket engine.
This semester’s Senior Design Expo showcased 204 team projects from 12 schools and three different Georgia Tech colleges. Students across disciplines collaborated to innovate, underscoring the importance of bringing diverse minds together, paving the way for innovative solutions that hold promise for shaping a better future.

Team Zoomee seeks to provide an affordable and easy-to-use alternative to the currently available bicycle electrification packages.

Team Roller Coaster Tycoon built a real-world roller coaster simulator control system.

Team Vitamin ECE created an automated produce peeler that uses computer vision to peel fruit.

Team Analog Vector-Matrix Multiplier in FPAA implemented a neural network classifier using analog circuit components.

Team FaceID Door Unlock created a hands-free door unlocking system that uses facial recognition to automatically lock or unlock the door based on the user's identity.

Team BeatBox developed an interactive multi-sensory musical experience in a phone booth-like enclosure.
ECE teams developed transformative solutions that look to revolutionize how humans interact with the world around them from improving urban mobility with AI-enabled traffic monitoring systems to pioneering low-power neural networks.
The Expo judges were industry professionals, as well as faculty and staff from across campus. This year’s Expo also welcomed more than 200 high school students as part of an outreach initiative where they explored science, technology, engineering, and math while serving as reviewers. The high schoolers picked two projects for special honorable mentions including one ECE team, AIRplanes, that is working to develop an autonomous drone design that can follow the terrain and fly low to the ground.
See all the winners from Capstone Expo and visit expo.gatech.edu for more projects.
ECE CAPSTONE DESIGN TEAMS
Smart traffic data collection.
Smart Traffic Data Collection through a AI-enabled traffic camera system.
VIEW PROJECT
Neural Network Classifier Implementation in Field-Programmable Analog Array (FPAA)
A neural network classifier using analog circuit components that reduces the strain on the hardware and the supporting power grids.
Not So Cleanroom
This project is focused on giving those inexperienced with semiconductor fabrication an opportunity to bridge the gap between theoretical and practical knowledge by building a simple solar cell.
A drone that can safely fly low to the ground by following the contours of the terrain unlocks many new autonomous flight possibilities.
The Landmine Detector, code-named Project MIDAS, is an avant-garde approach designed to revolutionize the daunting challenge of landmine detection.
A standard method to label passives using a minimal invasive process where an automatic process can be used to identify components on a board with prior knowledge; a process to remove components from a moderate complexity board and then sort those components by value.
The NESO (Nano Environmental Swimming Oceanographer) project is a pioneering initiative aimed at developing a state-of-the-art autonomous robotic vehicle, specifically designed for in-depth marine research.
Electric Pump for Rocket Propellants
We are designing a 3-kW inverter to drive an electric pump which can be used to deliver liquid propellants into a rocket engine.
FaceID Door Unlock
The project is a consumer-oriented door unlocking mechanism which is designed to be hands-free by the use of an embedded system using a facial identification algorithm to determine if a door should be locked or unlocked based on the identity of the user trying to enter.
Smart Countertop
The Smart Countertop is a countertop that uses inductive power transfer to wirelessly power small kitchen appliances.
Roller Coaster Tycoon
A control system compatible with the CoasterDynamix system capable of simulating a real-world roller coaster’s control system.
The purpose of this project is to transform a standard fan into an intelligent and automated appliance that enhances user comfort and energy efficiency by monitoring and regulating room conditions.
Vitamin ECE
Automated Produce Peeler: peel fruits using computer vision.
Treble Makers
A guitar pedal that uses digital signal processing to alter the sound of an electric guitar with multiple audio effects.
BeatBox is an interactive multi-sensory musical experience in a phone booth-like enclosure.
Zoomee seeks to provide an affordable and easy-to-use alternative to the currently available bicycle electrification packages.
Botany Bros
The Plant Health Tracker is a device that monitors a plant’s humidity, soil moisture, temperature, and ambient light.
VIEW PROJECTS
BreathBand is a wearable device that monitors the depth and rhythm of a user’s breathing cycle for athletic performance.
Sand Filtering Robot
SandE is a robot that can autonomously clean beaches by picking up and storing trash while filtering out sand.
FPGA Hardware Accelerator
Implementation of the LZW Compression Algorithm in SystemVerilog for Hardware implementation on an FPGA to demonstrate performance and efficiency gains over software
Related Content

From Smart Farming to Delivery Drones, Fall Capstone Design Expo Highlights Student Innovation
Electrical and computer engineering students addressed real world problems with their novel project designs during this semester’s Fall Capstone Design Expo. “Big Hero 6” team tied for Best Overall Project and “FRMBX” won Best ECE Team.

Surgical Tool, Airport Navigation Aid Top Spring 2024 Capstone Expo
Projects that could help doctors save lives and restore independence for visually impaired travelers impress judges at semester-ending showcase.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 7: Go over your paper one more time. Review and make necessary revisions to your paper. Check for clarity, completeness, and coherence. Ensure that your outline reflects the scope and depth of your project. 💡 Extra tip: Seek feedback from your capstone project supervisor, peers, or mentors.
A capstone project in college is a final independent project undertaken in a program of study designed to assess the skills, knowledge, and expertise acquired by the student. As the name suggests, it is the capstone or crowning achievement of academic life and the last class taken before graduation. It gives you the final credits required to ...
The thesis or capstone project title should be informative and concise, no more than 175 characters including spaces, using uppercase and lowercase letters, centered between the left and right margins, formatted in an inverted pyramid. g. The last sentence of the abstract must start with the word "Keywords:" followed
A 20-minute presentation might ideally have between 15-20 slides. Don't have too much text on slides. Keep slides to a minimum of five or six lines of text on them. Stick to one font size for bullet text. Don't resize text to fit it on one slide: insert a new slide!
Everyone's capstone paper should contain the following elements: a title page, abstract, introduction, body, conclusion, and reference list. Click on the link below to open and make a copy of the capstone paper template. If you have any questions, please come see Ms. Forfa (earlier is always better!) Capstone Paper Editable Template.
1. Introduction: What is a Capstone Project? The Capstone Project is an academic study that offers an opportunity to explore a particular issue in much greater depth than is feasible in a class paper, and to argue your own perspective on that issue. LIS 4901 Capstone (4 credit hours) is an alternative to the Practicum. Either the Capstone OR the
The capstone project is a unique opportunity to carry out independent group research in order to devise an innovative solution for a real-world problem. While a project of this scope and scale can be challenging, it can also be very rewarding. The capstone project is usually the final assignment and plays a vital role in preparing students for ...
3. Write a clear problem statement. Write a concise description of the problem that needs to be solved. Explain the background of the problem, whom it affects, and how it impacts the organization. Include the 4Ws using the information you gathered in the 'Empathize' phase (the first phase of the design thinking process).
an inter-professional team to design and implement a practical improvement project for your organization. You will also share what you have learned with your peers through a 'teach-back' presentation at the final CHC Leadership Institute session. 2. oWhat Is the Value of the Capstone Project? The Capstone Project allows you to strengthen your
It is a comprehensive and interdisciplinary project that often requires students to apply the knowledge and skills acquired throughout their academic careers to solve real-world problems or issues. Capstone projects come in all shapes and sizes, including research papers, case studies, creative works, internships, and field placement projects.
This chapter focuses on visual mapping tools that can help you plan and implement your capstone project. The purpose of Logic Models and Concept Mapping in relation to capstone projects are explained. Problem Tree and Root Cause analyses are described in the context of identifying and planning for capstone project development.
Moreover, capstone projects assess how students use critical thinking skills and the knowledge they have acquired during a course. Choosing a Topic. It is clear that your selection must be connected to your sphere of education. For example, if you are a medical student, your capstone project will likely be focused on health-care interventions.
A capstone project is a major, culminating project for a student in higher education. Generally, it is the final step of a college degree program, such as a Bachelor's or Master's degree.
What a Table of Contents Could Contain. I Introduction. A Statement Of Problem/Opportunity (Research Question) B Background, Context, And Significance Of Study. C Project Researcher Identification. II Literature Review. A Subheadings (Themes Discovered In Review) B Notice Of Gaps In Knowledge. III Methods.
2. Capstone project timeline and guidelines FALL 2020. The Introduction to capstone course 14:33:449 in the fall of 2020 will include two tracks: Track 1: Teaming up, choosing a project, and getting an adviser. Track 2: Information sessions, including faculty panels, industry panels, alumni panels, and various workshop.
A capstone project is a culminating academic project. It typically requires students to apply the skills they have gained during the course to a real-world problem. Capstone projects are common in undergraduate and graduate programs across a range of disciplines, including business, engineering, healthcare, and education.
We discuss how to find ideas for your senior capstone project, tips on executing the project, common mistakes, and examples! Get in touch: +1-800-991-0126. Get in touch: +1-800-991-0126. Programs. ... Design educational programs for nurses on asthma care and point-of-care testing protocols for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The capstone design project is an opportunity for you and your teammates to solve a practical engineering design problem using the engineering skills and knowledge that you have developed over the past three years.
Body of Thesis/Capstone. The format of the body of the thesis is determined by the discipline style manual. The text is to be double spaced with paragraph indentions. Margins are one-inch at top, bottom and right. A one and one-half inch margin on left side of the paper will allow for binding.
It functions to guide the reader in understanding the type of path the story will follow. The Research Design is the overall direction of the research story and is determined before deciding on the specific steps to take in obtaining and analyzing the data. The Research Design heading appears in Chapter 2 of a capstone project.
Systems Design Engineering. Contact Waterloo Engineering. Waterloo Engineering Home. Support Waterloo Engineering. Work for Waterloo Engineering. Provide Website Feedback. 2022 Capstone Design Projects.
Capstone design projects are complex by their very nature. Open-ended design problems have many plausible solutions and there are an infinite number of ways that a project could produce a successful design. Developing a framework for the design process is a critical part of running successful capstone design courses.
Yearlong Capstone Design Projects require students to work under the guidance of engineering faculty advisors and industry mentors - to think entrepreneurially, creatively, critically and ethically to develop functional prototypes not yet imagined. In their iterative quest to fill an unmet societal need, students dedicate more than 1,600 ...
As a new semester starts, we want to quickly revisit the Fall and acknowledge our excellent 2022 Senior Design Presentations. Presentations, alongside a written report, are the final milestones of a Senior Design/Capstone Project during the semester that requires students to develop innovative problem solutions while implementing computer graphics usage.
The overarching goal of the project is to significantly reduce the time it takes for the research team to develop these room layouts by constructing a software solution for layout generation. Tech: A webapp using django, lualatex, railway. Authors¶ Tyler Beetle, Jordan Fowler, Anna Michelitch, Joseph Missan, James Ward. Screenshots¶
A Note from Professor Ismail Orabi, Capstone Design Project Coordinator. The Capstone Design Expo is an opportunity for our students to showcase the results from their capstone design course. Student teams work to create a specific design solution for a "customer's" real and unique need. Design and design education are, by their nature ...
Navigating a bustling airport can be a daunting challenge for visually impaired individuals, but Seekr, an interdisciplinary team of students, including three computer engineering majors, believes it has created a viable solution to the challenge.. Attendees at the Spring 2024 Senior Capstone Expo agreed, voting Seekr to a tie for Best Overall Project during the event, which took place on ...