Doctorate in Psychology (Ph.D. and Psy.D.) – everything you need to know in 2024
What’s in this guide, ph.d. or psy.d., why do a doctorate in psychology, entry requirements, phd in psychology jobs, how long does it take to study, is a doctorate program all theory/studying, career path, earning potential , find psychology doctorate degree programs.

By PsychologyJobs.com Staff Writer
A doctorate in psychology is the highest level of graduate degree in the field. As a result, there are lots of career options to choose from, including research roles, and clinical roles.
There are many reasons you may want to pursue a doctorate degree in Psychology, the following guide will provide everything you need to know; from the options, costs, timeframes, career advantages and more.

First up, what are the two types of doctorate degree you can get and what are the differences?
The two doctorate degrees you can get in psychology are Ph.D. and Psy.D.
In simple terms, a Ph.D. in psychology is more research-focused, while a Psy.D. emphasizes clinical practice. The best choice between the two depends on your career goals and whether you prefer research and academia or direct clinical work.
- Doctorate-level psychologists typically have higher earning potential compared to those with a master’s degree or bachelor’s degree in the field.
- Gain in-depth knowledge and expertise in your chosen area of specialization within psychology.
- Potentially make significant contributions to the field.
- Advanced career opportunities in various settings, such as academia, research institutions, government agencies, hospitals, and private practice.
- Connect with other professionals, researchers, and academics in the field of psychology, expanding your professional network
The minimum requirements to study a doctorate degree in psychology will vary from institution to institution. However, there are several common requirements:
- Bachelor’s degree: all programs require applicants to have completed a bachelor’s degree , in psychology or a related field. Some programs may accept candidates with a degree in another discipline if they have completed prerequisite coursework in psychology.
- Master’s degree : Some doctoral programs require applicants to have a master’s degree in psychology or a related field. Others may admit students directly from their bachelor’s degree and incorporate a master’s degree into the doctorate program.
- GPA : Many programs have a minimum GPA requirement, usually 3.0 or higher. Some competitive programs require a higher GPA.
- Letters of recommendation : Applicants typically need to submit letters of recommendation from professors or professionals who can speak to their academic and research abilities.
- Research experience : Prior research experience is often valued by doctoral programs in psychology. This may include experience working on research projects, completing a thesis, or participating in research internships or assistantships.
- Personal statement: Applicants usually need to submit a personal statement or statement of purpose that outlines their academic and research interests, career goals, and why they are interested in the specific doctoral program.
- Addiction Counselor
- ABA Therapist
- Mental Health Therapist
- Licensed Mental Health Conselor
- Licensed Professional Counselor
- Licensed Clinical Social Worker
- Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist
- School Psychologist
- Organizational Psychologist
- Forensic Psychologist
- Sports Psychologist
- Clinical Psychologist
- Counseling Psychologist
- Research Psychologist
- Professor of Psychology
- Child Psychologist
*Outside of the licensed psychologist jobs listed above many of the above roles do not require a PhD but it is important to note that employers for these roles are increasingly favoring candidates with a PhD.
For the majority of students, a doctorate in Psychology may take anywhere from 4-7 years to finish, which will include a research dissertation and most likely residency or an internship in clinical or medical environments.

No. Psy.D. and Ph.D. programs in clinical or counseling psychology usually require students to complete a pre-doctoral internship as part of their training.
This internship typically lasts one year and involves supervised clinical practice in various settings, such as hospitals, mental health clinics, or community agencies.
The internship experience is intended to provide students with practical, hands-on training in their chosen area of specialization and help them develop the skills necessary for independent practice.
For Ph.D. programs in other areas of psychology, such as experimental, social, or developmental psychology , internships or practicum experiences may be less common or not required. Instead, these programs may emphasize research experience and skills development.
With a PHD in psychology, you have a whole host of options when it comes to your career. With this kind of degree, you can work in specialty areas of psychology, depending on your studies and particular interests, or you can work as a researcher, an educational consultant, a forensic psychologist, political strategist, staff psychologist, private psychologist, professor of psychology, psychiatrist, or a clinical psychologist.
The earning potential for psychologists with doctoral degrees or PHDs can vary greatly depending on the specific specialty of psychology in which they work. General psychologists may earn around $90,000 a year, with the average salary around $84,000 per year.
On the other hand, clinical, counseling and school psychologists with PHDs tend to earn around $81,000 per year. The highest paying psychology careers can average up to $167,000, so studying a PHD in psychology will be worth it in the long run when it comes to career prospects.
- PhD in Organizational Psychology
- PhD in Educational Psychology
- PhD in Forensic Psychology
- PhD in Counseling Psychology
- PhD in Behavioral Psychology
- PhD in Child Psychology
- PhD in Clinical Psychology
- PhD in Neuropsychology
- PhD in Sports Psychology

What is a PhD in Psychology?
Created by careersinpsychology
Sponsored School(s)

When surveying the options available in PhD programs, an important distinction to make is whether you want to work in a psychology-related field such as counseling, social work, therapy or education; or if you are striving to get a diploma conferring a "Doctorate of Psychology." Novices quite frequently confuse the academic Discipline of Psychology with alternative disciplines which are psychology-related and in the mental health field.
The "Doctorate of Psychology"
If you want to earn a doctorate in the discipline of psychology, you will be presented with 2 options from which to choose within the field: you will be able to enroll in either a doctoral program which grants a Ph.D. or one that will culminate in the awarding of the Psy.D. Scholars who are focused on research, data collection and processing, academics, professorship and authorship are best suited for the Ph.D. in Psychology. Individuals who are interested in research but are more people and practice-driven as well as; desirous of being on the front lines working with patients, interested in methodologies and enjoy making educational theory a reality are well served by enrolling in a Psy.D. program.
Dr. Emma Mansour is a licensed psychologist and founder of "Life Matters Counseling and Psychological Services, LLC., with locations in Salt Lake City and Farmington, Utah. Dr. Mansour is a graduate of the Counseling Psychology Program at the University of Utah, as well as a former instructor. She has taught classes in Developmental Psychology, Group Counseling, Personality Psychology and Counseling Skills. In her capacity as educator, Dr. Mansour has come in contact and consulted with many students facing these exact questions. Regarding the choice between the Ph.D. and the Psy.D. her advice is straightforward;
"My advice would depend on the student's ultimate career goal. If the goal is to become a professor and engage in teaching and research as a career, there is really no option but to get a PhD. If the student is not interested in teaching or research and just wanted to be a private practicing psychologist, I would advise that they consider a PsyD program."
Learn more about a psychology doctoral degree .
Do I need a PhD to Achieve My Goals?
One of the pressing questions doctoral candidates face is whether or not they are primarily only interested in a career as a practicing counselor, therapist or educator. If this happens to be the case, technically speaking they do not need to go beyond the Master's Degree in Counseling, Therapy, Social Work, etc., to reach their goals. In other words, various careers are accessible with a master's degree and do not require a PhD. On the other hand, some careers are only available if you have a PhD. This is the point at which clarification of your career objectives becomes imperative. Getting a PhD is an arduous process and if you are unsure of your ultimate goals, it is advised you thoroughly research all of your options. Experts agree: it pays to do your "homework" before you enroll in a doctoral program.

"Becoming a psychologist, versus a counselor or therapist, is certainly a longer process but it affords you many more possibilities and will ultimately open many more doors for you as a professional, both from the status of the degree to the possibility of branching out into many other areas. It is important to bear in mind that a students' current interests will likely change over the course of their career so the broader degree allows for ongoing growth and opportunity."
How Long Will it Take to Get a PhD in Psychology?
Universities are highly unique in their approaches to their doctoral programs. For example, UCLA's program is 6 years. In describing their program they write, "The Ph.D. program is a six year, full-time only program." In other words, students do not have the option of attending part-time. Many PhD programs can be completed within 5 years; most of them typically require the equivalent of 72 semester units. The design of the program can greatly influence the length of time it takes to earn the PhD; even for doctorates earned at the same institution. For example, NYU has 2 Psychology PhD programs: the PhD in Cognition and Perception and the PhD in Social Psychology. Although each doctorate requires 72 semester units, students who are "Teaching or Research Assistants" in the Cognition and Perception program usually take 3 courses per semester; the remaining student schedules are more flexible. Thus someone taking 2 courses a semester will graduate later than those taking 3 classes a semester. Most programs also have a maximum time limit to complete the PhD; at NYU if the matriculant has not finished their requirements after 7 years, their enrollment in the program is likely to be terminated.
Some of the questions you'll want to research with regards to the amount of time you will be in school are:
- Is the college on a semester or quarter system and how many units are required to complete the PhD in Psychology?
- Does the program have a minimum number of units to complete each quarter or semester?
- Is the program strictly full-time or is there a part-time option?
- Is there a time maximum within which the program must be completed?
- Is there a time limit condition on program grants, awards or special financing?
What Types of Classes Will I Take in a PhD Program?
PhD programs in the field of psychology consist of some or all of the following categories of study:
- Core Content Classes and Advanced Elective Courses
- Oral Examinations
- Presentation of Papers
- Practicum & Teaching
- Internships
- Special Event, Conference or Convention Attendance
- Doctoral Dissertation Proposal, Submission and Defense
Elements of the PhD in Psychology
- Core Content Classes and Advanced Elective Courses: The length and depth of core classes depend heavily on the nature of the PhD program and the university. Each college program varies on how many units are required, the title of the courses and how much emphasis is put on the ratio of research/clinical. Below is a very generalized sampling of what to expect.
Core classes prepare the student for the in-depth research they will embark upon as they advance in their prospective careers. Statistical proficiency is an important aspect of every program; examples of courses include:
- Mathematical Tools for Cognitive Science and Neuroscience (NYU)
- Statistics courses (UCLA)
- Developmental Psychology (Stanford)
- Foundations of Cognition (Stanford)
- Exploratory-Graphical Data Analysis (Vanderbilt)
- Multivariate Analysis (Vanderbilt)
- Psychological and Educational Measurement (Vanderbilt)
Advanced Electives: Some examples of Advanced Elective courses from NYU are:
- Principles of Neuroimaging
- Research in Social Psychology
- Cognitive Development
- Psycholinguistics
- Cellular, Molecular & Developmental Neuroscience
- Language Acquisition
- Biobehavioral Mechanisms of Stress and Disease
- Research: Every university expects the student to constantly be involved with research throughout their years of training. Throughout the process of research, students are supervised by at least one member of the faculty in some form of an advisory role. However, differences in a university's research emphasis, timing, manner of execution and application of research requirements is one of the factors you will confront when choosing a PhD program. For example, research dominates the 8 UCLA program specialties from which to choose. They write:
"Students are admitted by one of the department's eight areas: Behavioral Neuroscience, Clinical, Cognitive, Developmental Psychology, Health Psychology, Learning and Behavior, Quantitative and Social. With rare exception, this area affiliation is retained throughout a student's stay in the program. Much of the program is administered by the areas." Also- " All areas are research-oriented. This applies to the Clinical area as well: although this area offers excellent clinical training, the emphasis lies in research, not in training private practitioners."
At UCLA research is included in the core curriculum and has a designated time sequence:
"The core program has three parts: a two-quarter statistics series, four courses selected from among special offerings in each of the seven areas, and a two or three quarter research sequence. In the latter sequence the student designs, conducts, and writes up a research project under the direction of two faculty members. Core-program work is completed by the end of the second year."
In slight contrast, while the program at Vanderbilt also emphasizes research- "We expect students to be continually involved in research throughout their tenure in our program;" their description of the first 2 years is quite different:
"The faculty attempt always to tailor graduate training to meet the needs and the interests of each individual student" and "The curriculum is designed to: (a) familiarize students with the major areas of psychology; (b) provide specialized training in at least one of the five specific areas of psychology emphasized in the program; and (c) provide students sufficient flexibility to enroll in classes consistent with their interests and long-term developmental trajectory. During the first two years, students take several core courses in quantitative methods and in substantive areas. Beyond this, the program consists of seminars, further research participation, and other inquiries expressly designed to fulfill career objectives."
- Oral Examinations: As a PhD candidate you will need to be prepared to undertake oral examinations as part of the qualifying and requirements processes. Oral examinations can take place at both the MA/MS level as well as the PhD level. This method of examination may prove helpful in preparing for a license; according to the American Psychological Association (APA) 21 states require an oral examination to qualify for licensure.
- Presentation of Papers : Some universities may require the submission of yearly papers and encourage students to present these papers at conventions or other academic events. For example, one of the research requirements at NYU is a first, second and third year paper (the third year paper may or may not be the dissertation proposal, depending on the program). While students are not required to present papers, under a bold heading in the PhD Cognition and Perception program requirements it reads:
Highly Recommended
" Presentation of Research Papers at Professional Meetings The Program strongly encourages its students to present papers (or posters) on their research at relevant professional meetings around the country as a "real life" part of their education in becoming professional scientists and educators and to aid them in forming contacts for possible jobs and postdocs after the Ph.D."
- Practica: If you have tried to understand what a practicum is and have failed, do not dismay. Even the experts in the field admit that it means different things in different places. In the report, "Report on Practicum Competencies" by The Association of Directors of Psychology Training Clinics (ADPTC) Practicum Competencies Workgroup: Robert L. Hatcher, Ph.D. & Kim Dudley Lassiter, Ph.D. answer the question in the following way:
What is a Practicum?
Psychology programs vary considerably in their definition of practicum. Some consider the experience at their department’s in-house clinic to be the practicum, and may call subsequent pre-internship training in other settings “traineeships.” Others classify all pre-internship clinical experience as practica; others limit this definition to supervised experience only. This document is based on the definition that practicum experience includes all supervised pre-internship clinical training."
One of the strong suggestions made by the APA is that your practicum time is a phase of preparation for your internship. In the APA published cover article, "Steps to the Match: Laying the groundwork to land an internship starts on day one of your program" by Christopher Munsey, the author offers an informative, easy-to-read and must-read regarding practica for every psychology PhD candidate. The author outlines the best possible uses of time during "all supervised pre-internship clinical training." Munsey advises that during your practicum you:
- Establish a positive connection with all practicum supervisors
- Acknowledge areas in which you excel and be sure to become and remain teachable in areas in which you perform poorly
- Work with all types of people; diversity in experience is a plus
- Develop superior communication skills
- Identify target internships
- Progress check to ensure your experiences are in alignment with your internship goals
- Accumulate lots of hours and keep immaculate records
- Network with psychologists
- Rehearse interviewing
- Give presentations
Teaching Requirements
Doctoral programs can include teaching experience as a requirement for successful completion of the degree. Each university has unique mandates about the nature of the teaching experience and when it occurs.
- Pre-Doctoral Internships: Currently (2016) the topic of the psychology internship is of serious concern. CareersInPsychology.org explains in detail the current dilemma which the APA is addressing in the article, " Internships in Counseling: Shedding Light on the Explosive 'Match .'"
To summarize, doctoral students are paired with internships which have earned APA approval. This process is called the "Match." The crisis stems from a profound lack of APA approved internships. While the APA is making strides in bridging the gap, the problem remains substantial. The progress made since 2012 is hopeful: in 2012 there were 1,041 students who could not progress in their doctoral studies because there were not enough matches. By 2015 the APA had reduced the number to 689 students. ( The APA Report can be accessed by following this link . ) For some students, waiting the year(s) to be matched was not an option. Some did non-approved internships, which had lifelong consequences.
A doctorate which includes a non-approved internship means that even when the PhD is granted, the graduated can never work for the Veterans Administration (one of, if not the largest employer of psychologists in the nation) or any military/government organizations. Secondly, many states will not grant a license to practice without an APA approved internship. The Association of State and Provincial Psychology Boards (ASPPB) has a database within which the Handbook of Licensing and Certification Requirements can be accessed. Before reviewing the handbook, however, you will have to provide the ASPPB with basic information about yourself. (The link provided for the Handbook will take you immediately to the questionnaire.) In retrospect, it becomes clear why the APA advises you to begin to work on getting your internship as soon as you begin your doctoral program; if you do not, you might not finish the program.
- Special Event, Conference or Convention Attendance: While not every university requires you to attend events, some have a form of scholastically-based group which is a graduation requirement. The PhD degree requirements at NYU have two examples:
"Brown Bag Seminar: All members of the program are expected to participate in the weekly Brown Bag seminar. The seminar meets informally, over lunch, and is a forum for presenting current and planned research. Each student is required to present on his or her research once a year. The seminar is a key component of student training over the five years of doctoral study.
Mini-Convention: The Mini-Convention is a day-long, convention-type meeting currently held on the Friday a week-and-a-half after Labor Day in September. Faculty and students of the Program attend this meeting which provides a training experience in convention-style oral presentation. All first- and second-year students are required to present talks based on their research projects. Upper-year students with well-worked-out, interesting findings to report are encouraged to present talks, as well as those who have not presented at a Brown Bag for the past academic year."
- Doctoral Dissertation Proposal, Submission and Defense: The dissertation is required by all PhD students. This voluminous composition includes and represents the entirety of the candidate's body of work, research and study focus. It presents an original thesis which the student is prepared to propose, submit and defend.
Proposal: Preparation for the dissertation-the proposal, begins and varies according to each university program. Examples of requirements from the colleges utilized thus far are:
NYU: " Dissertation Proposal . In the third year, it is expected that each student will have sufficiently clarified his or her interests to be able to formally propose a dissertation project." Note: NYU offers 2 choices regarding the dissertation. The student can present the Traditional Thesis or choose a " Publication Route ."
UCLA: " By the fourth year a student should have enough experience and knowledge of current research issues to begin formulating a dissertation proposal."
HARVARD: " The Dissertation Prospectus: By the end of the spring semester of their penultimate year, students must complete a dissertation prospectus for an original project that is meant to culminate in the dissertation."
Basic Elements of a Proposal: The following is a general list of what is contained in the proposal.
- Importance of the topic: The proposal should provide intellectual rationale for why the thesis is critical to the field of study
- A review of the literature currently in existence on the topic
- An explanation of the theoretical basis of the proposed thesis
- Detailed description of the research methods to be used
- Comprehensive discussion of proposed analyses
- Projected implications of the topic for the field
Proposal Resources: There are numerous proposal support avenues, the most obvious being the APA website. A valuable listing of their publications specifically dealing with the dissertation from start to finish can be found in their Education section under " Dissertations and Research " (link provided).
Submitting: The proposal is typically submitted to the student's advisor(s); following their approval it is submitted to department/governing committee for approval. The final "paper(s)" or dissertation is also submitted for final acceptance.
Defense: Dissertations are defended by the PhD candidate in a formal setting. Scholars in the field test the ability of the student to orally explain and defend their research findings. There are usually university-specific "norms" regarding the event and knowing what they are should be of utmost importance.
Funding : The time and research materials for the dissertation can run into the thousands of dollars. There are many ways to receive financial assistance; the APA is a good place to start. Their " Student Funding " page is helpful for finding grants, scholarships and the like. (link provided) They also have many advisory articles which offer real life examples of how others have managed the costs involved.
- What is a Master's Degree in Psychology?
- What is a BA in Psychology?
Related Psychology Education Guides
- Online Psychology Degrees
- Psychology Schools
Related Articles
- The Need for Self-Care
- Experts Discuss Their Inspirations & Experiences on the Way to Getting a Degree in Psychology
- 15 Psychology Apps You Should Be Using
- The Practice of Psychology: Art or Science?
- The Emergence of Fashion Psychology
- How Psychologist's Stimulate The Economy
- Choosing a Doctorate Program in Psychology
- What is a Master’s Degree in Psychology?
- Experts Reveal the Keys to Successful Study Habits
- How to Survive Introduction to Psychology Without Hating It
- Never Fear: Your Past is Helpful for a Career in Psychology
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Cultural Psychologists
- Understanding Attachment Styles and How They Affect Your Relationships
- I Majored in Psychology - Now What?
- Choosing a Master's Degree Program in Psychology
- Can a Psychology License Make Me Rich?
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Consumer Psychologists
- 3 Ways Technology Has Affected the Field of Psychology
- A Master’s Degree in Psychology: It’s Your Time to Shine
- Important Reasons for Getting Involved with Psychology Associations
- 2 Ways to Choose a Specialty in Your Psychology Career
- Guide to Kickstarting Your Career in Psychology
- Expert Advice: Cures for the College Blues
- How Fortune 500 Companies Use Psychology to Increase Success
- Essential Tools to Help Prepare for Your Psychology Education
- How We Picked The Top Undergraduate Programs in Sports Psychology
- A Guide to Understanding the Full Ramifications of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Positive Psychologists
- The Impact Of Media – Good, Bad Or Somewhere In Between
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Transpersonal Psychologists
- Fixed Mindset vs Growth Mindset: Your Success Hinges On It
- Psychology or Social Work: Which Graduate Program is Right for You?
- Overcoming Educational Challenges on the Way to a Career in Psychology
- What is a BA in Psychology?
- How to Get Better Grades in Your Psychology Degree Program
- How to Set Professional Boundaries as a Psychologist
- 50 BEST JOBS WITH A PSYCHOLOGY DEGREE
- What Is Depression And How Can We Help?
- Overcoming Challenges on the Way to a Degree in Psychology
- What Is PTSD and What Can We Do About It?
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Political Psychologists
- How Your Reputation Impacts Your Career in Psychology
- 10 Things to Know Before Becoming a Psychologist
- Rehabilitation Psychologists Maximize Outcomes for Individuals with Cognitive and Physical Disabilities
- 10 Must Take Psychology Professors in Washington, D.C.
- The Mind-Boosting Effects of Exercise: How 30 Minutes Can Improve Your Mental Health
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Military Psychologists
- The Psychology of Media Censorship
- The Opportunities Available with Each Level of Psychology
- Why Political Psychology is Increasing in Popularity in 2016
- Experts Offer Encouragement to Students & the “Almost Licensed”
- 100 Psychology Twitter Accounts to Follow
- Everything You Need To Know About Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Community Psychologists
- Following in the Footsteps of the Psychology Experts
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Gerontologists
- A Career in Psychology is More Than Just a Job
- How to Help Your Patients Cope During the Pandemic
- Should I Major in Psychology or Counseling?
- Psychology Careers That Don't Require a License
- A Bachelor’s Degree in Psychology: Begin Your Career Before You Graduate
- Financial Aid and Finance Management for Psychology Programs
- An Unforgettable Memory: How Your Memory Works and Ways You Can Make It Work Better
- Looking For Advice? Psychology Professors Give Key Tips to Students
- Employment Outlook & Career Guidance for Media Psychologists
- Choosing a Psychology Specialty
Research Psychology Programs
- Master's Programs
- Doctoral Programs
- Psychology Degree Path
Licensing & Certification Information
- Psychologist Licensing by State
- Counselor Licensing by State
- Social Worker Licensing by State
- Therapist Licensing by State

PhD Admission FAQ

General Information
When is the application due and how do i apply .
NOW CLOSED- The application is due on November 30, 2023 at 11:59 PM Pacific Time.
Apply using the application portal .
How long does it take to get a PhD in Psychology at Stanford?
The PhD program is designed to be completed in five years of full-time study. Actual time will depend on students' prior background, progress, and research requirements. The minimum residency requirement for the PhD degree is 135 units of completed coursework and research units.
What are the requirements for the PhD degree in Psychology?
Please consult the PhD Requirements page .
What are the different subfields within the graduate program in Psychology?
- Affective Science
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Neuroscience
- Social Psychology
What is the Department's teaching requirement?
PhD students must complete at least five quarters of teaching assistantship (TA) under the supervision of a faculty member. Students are required to attend a TA training workshop in their second year. In addition, students are encouraged to take advantage of department and university teacher training programs. Students for whom English is a second language are expected to acquire sufficient fluency in English. All international students must be approved by Stanford’s EFS department .
How many students apply to the Stanford Psychology PhD? How many are admitted? What are the demographics?
Stanford provides public reports with summary data about graduate programs and graduate admissions. Please consult the public dashboards published by Stanford's office of Institutional Research & Decision Support on doctoral admissions , doctoral enrollment and demographics , and doctoral completion and time-to-degree .
Is there a standalone Master of Arts program in Psychology?
The Department of Psychology does not offer a terminal Master’s degree program. Current doctoral students within the Department or in another Stanford graduate program may apply to be awarded a Master of Arts in Psychology during the course of their PhD program.
Does your department have a program in Clinical Psychology? Are you accredited by the APA?
No. Our department does not have a program in Clinical Psychology. As such, we are not accredited by the APA.
Do you have any advice about getting into grad school?
The Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences offers an online resource for prospective graduate school applicants: Guide on Getting Into Grad School . We encourage applicants to take advantage of this resource.
Financial Support
What is the annual cost of attending your program.
All students admitted to the Psychology PhD program receive five years of 12-month funding. Financial support is provided through a combination of fellowship stipend and salary, and assistantship salary and tuition allowance. Information about the cost of attendance and funding options are available from the Financial Aid Office .
What type of financial support do you offer?
All students admitted to the Psychology PhD program receive five years of 12-month funding. Financial support is provided through a combination of fellowship stipend and salary, and assistantship salary and tuition allowance. Funding is contingent upon satisfactory academic progress. Students are encouraged to pursue fellowships offered by the University and by national organizations, such as the National Science Foundation.
Stanford University also offers the Knight-Hennessy Scholars program, designed to build a multidisciplinary community of Stanford graduate students dedicated to finding creative solutions to the world's greatest challenges. The program awards up to 100 high-achieving students every year with full funding to pursue graduate education at Stanford, including the PhD in Psychology. To be considered, you must apply to Knight-Hennessy Scholars and separately apply to the Psychology Department. Note that the Knight-Hennessy Scholars program application deadline is in the spring before the autumn application cycle.
Do you offer support for the summer months?
Yes, funding is offered for 12 months a year for 5 full years, including 5 summers.
Preparing for Admission
Am i eligible to apply if my undergraduate major is not in psychology.
An undergraduate major in Psychology is not required; applicants from other backgrounds can apply and be admitted. All applicants should have sufficient foundational knowledge and research experience prior to the program to allow them to go straight into graduate-level coursework and conduct research.
My undergraduate degree was completed outside the United States. Is my degree eligible?
Please refer to the Stanford Graduate Admission Office's table of minimum level requirements for international academic credentials . These credential requirements are set by the University and nonnegotiable.
If I have prior graduate work, can it be transferred to the PhD program?
No, the Department of Psychology does not allow the transfer of unit credits from your previous program.
How competitive is admission to the PhD program?
Admission to our program is highly competitive. About 10-15 admits enter the program each year and are chosen from a pool of over 600 applicants. These students are selected on the basis of a strong academic background as demonstrated by previous coursework, research experience, and letters of recommendation. Please be assured that the Department reviews each application very carefully and makes decisions on an individual basis.
The Application Process
How do i apply.
Please visit the PhD Admissions page for instructions on how to apply to the Psychology PhD Program, graduate application requirements, and the link to the online application.
Is there an application fee? If so, can I apply for a fee waiver?
The fee to apply for graduate study at Stanford is $125, see Application Fee . Fee waivers are available for some applicants. Please visit Graduate Admissions for information on applying for an Application Fee Waiver .
Can I submit another application to a different department within the University?
You may only apply to one degree program per academic year. However, you may apply concurrently to one departmental program and to a professional school program (law, medicine, or business).
I'm interested in the joint JD/PhD in Law and Psychology - how does it work?
Students interested in the JD/Ph.D. joint degree must apply and gain entrance separately to the School of Law and the Psychology Ph.D. program. Additionally, students must secure permission from each degree program to pursue the joint degree. Interest in both degrees should be noted on the student’s admissions applications and may be considered by the admissions committee of each program. Alternatively, an enrolled student in either the Law School or the Psychology department may apply to add the other degree and undertake the joint degree program, preferably during their first year of study. Students participating in the JD/Ph.D. joint degree program are not eligible to transfer and receive credit for a masters, or other degree, towards the Psychology Ph.D.
Students interested in the MPP/Ph.D. joint degree must apply and gain entrance to the Public Policy program’s MPP degree and the Psychology Ph.D. program. Students should note their interest in both degrees on their graduate admissions applications. Additionally, students must secure permission from each degree program to pursue the joint degree
Which faculty are accepting new students this year?
All active faculty are potentially accepting new students each year. In your application, we ask you to list the top 3 faculty you are most interested in working with. Multiple readers will review your application in full regardless of who you list.
My institution does not report GPAs on a 4.0 grading scale. How should I report my GPA on the application?
Please do not convert your GPA to a 4.0 grading scale. You should enter “0.00” for the GPA and use the “Unconverted GPA” and “Unconverted GPA System” fields instead. A link to detailed instructions for reporting GPA is located near these fields on the application.
I attended multiple undergraduate institutions. In what order should I list them on the application?
The institution where you earned or expect to earn your Bachelor's degree should be listed as "Post-Secondary Institution 1." The remaining institutions don’t have to follow a particular order. List all institutions that were attended for at least one full academic year. Please note that you must submit a transcript for all courses taken towards your undergraduate degree, including those from your nonprimary institutions.
When should I submit my transcripts if my degree will still be in progress at the time of the application deadline?
The most current version of your unofficial transcript must be submitted as part of your electronic application, even if the grades from your fall term are not available. The absence of these grades will have no impact on the review of your application. If you are admitted and enrolled, we will ask you to submit your final transcript showing all grades and proof of degree conferral.
Should I submit official transcripts?
At the time of your initial application, please only submit your unofficial transcripts. Submit the unofficial transcripts as part of your electronic application, per the instructions in the application portal. A short list of applicants who move forward to the next stage of the review process will be contacted with instructions for submitting official transcripts at a later stage.
It may be helpful to understand the difference. Unofficial transcripts are transcripts issued by your college or university directly to you, the student, which you then submit to Stanford for review. Official transcripts are transcripts issued by your college or university directly to Stanford University, usually by secure electronic transfer and sometimes in hard copy in signed and sealed envelopes. The key difference is that an official transcript has never been directly handled by the applicant.
Do you have a minimum GPA score?
We do not require applicants to have a minimum GPA for consideration, and we do not release information about the average GPAs of accepted students. As a guideline, successful applicants typically earn undergraduate cumulative GPAs among the top of their class. However, please keep in mind that admission to our graduate program depends on a combination of factors, and all areas of a student’s application are weighed similarly when applications are reviewed. If our research areas meet your educational goals, we encourage you to submit an application.
May I contact the faculty directly during the application process?
Applicants are not prohibited from reaching out to faculty directly during the application cycle. However, please understand that our faculty are extremely busy, and it is quite possible that you will receive either a very short response or no response at all. This does not mean the faculty are not interested in your application. All applications will be read and reviewed in full during the formal review process. Note that per Department policy, all faculty are potentially accepting graduate students in any given cycle, so you do not need to contact faculty in advance to see if that specific mentor is accepting students for the coming year.
Can I meet with Department staff either by phone or email before I apply to discuss my application materials or ask general questions about the program?
No, the Department staff do not have meetings with or provide individualized advising for prospective applicants. Please understand that this is a matter of bandwidth and equity. We do not have the ability to offer personalized service to all interested applicants, so we do not offer them at all. By Department policy, our staff do not provide any evaluative feedback on prospective applicants' materials, so please do not contact us with CVs, academic histories, etc to request feedback or ask about odds for acceptance. For support in crafting your application, we recommend that you turn to your existing network of mentors (e.g., your letter writers) and/or the resources offered by your current or prior academic institution(s).
TOEFL and GRE
Is the general gre required is the subject gre required.
No, the Stanford Psychology PhD program does not require the general GRE or the subject GRE. We will not be collecting any information related to GRE exam scores on the application. Please do not submit GRE scores to Stanford for our program.
What is the TOEFL exam, and am I required to take it?
The TOEFL is a standardized test of English language proficiency. Per University policy, the TOEFL exam is required for international, non-native English speakers who apply to any Stanford graduate program.
The TOEFL score requirements are waived for international non-native English speakers who have received a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree from an institution in the United States or another English-speaking country. Therefore, applicants with these degrees from the U.S., Australia, Canada (except Quebec), New Zealand, Singapore, Ireland, and the United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, Wales) are exempt from taking the TOEFL and do not need to submit the TOEFL waiver request form.
When should I take the TOEFL?
The TOEFL must be taken by the published application deadline.
What is the minimum TOEFL score required for admission?
Please visit the website of Stanford's Office of Graduate Admissions for more information on the University’s minimum requirements.
If my TOEFL score falls below the University’s minimum, am I still eligible to apply?
Yes, you may still apply. If your TOEFL scores fall below the University's minimum requirements and you are admitted, Stanford may require you to take an English placement exam and/or English classes.
May I submit the IELTS instead of the TOEFL to demonstrate English proficiency?
The IELTS is not accepted at Stanford University; only the TOEFL is accepted to provide proof of proficiency in English.
How do I request a TOEFL exemption or waiver?
For all questions related to TOEFL exemptions or waivers please refer to the website of Stanford’s Office of Graduate Admissions . Please note that the central office makes all final decisions regarding TOEFL waivers; the Department of Psychology is not involved in the approval of TOEFL waivers.
How do I check the status of my TOEFL scores?
Log in to your application account. It may take up to two weeks after submitting your application or sending the scores (whichever occurs later) for your official scores to show as received. Processing may be delayed or halted if the name or birthdate on the score report does not exactly match the information on your application.
Why does my TOEFL status show as “Not Applicable” even though I submitted a TOEFL score?
This may be because you listed English as your first language in the application. Please note that “first language” refers to your native language.
Is there a department code for ETS to use in order to send in my scores?
No, there are no individual department code. Use the Stanford University score recipient code 4704 to send your TOEFL scores.
Statements of Purpose
How long should my statement of purpose be.
We strongly recommend that your statement of purpose be around two pages in length.
What should I include in my statement of purpose?
Please consult the Stanford Graduate Admissions FAQ page for more information on the Statement of Purpose.
Letters of Recommendation
When are the letters of recommendation due.
The letters of recommendation have the same deadline as the rest of the application. This year, the deadline is November 30, 2023.
How many recommendations do I need, and who should I ask to be my recommenders?
Applicants need three recommendations from faculty or others qualified to evaluate your potential for graduate study. At least one evaluation and letter should be from a faculty member at the last school you attended as a full-time student (unless you have been out of school for more than five years). Substitutions for faculty recommendations may include work associates or others who can comment on your academic potential for graduate work.
My recommender will not be able to submit his/her letter by the application deadline. Will my application still be considered?
Letters of recommendation must be submitted by the application deadline. As such, we strongly encourage you to contact your recommenders directly to remind them of our deadline. If your recommender misses the deadline, please contact psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Depending on the circumstances, Department staff may collect the letter via email and forward it to the faculty to add to your file. That said, the program expects applicants to do everything possible to ensure that letters are submitted on time via the secure online system.
Can my recommenders submit their letters via email, fax, or postal service?
No. Recommenders must submit their letters via Stanford’s online recommender system.
My recommenders are having technical difficulties with the online letters of recommendation process. Who should they contact?
Should any of your recommenders experience technical difficulties with the online letters of recommendation process, please refer them to our application database provider's letters of recommendation help page or have them submit a Help Request Form directly to our application database provider.

Additional Materials and Updates
I realized i made a mistake on my application and/or uploaded the wrong version of my documents. what do i do.
Depending on the timing and the nature of the error, our staff may be able to correct your application. Please send an email to psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Include your full name, a complete description of the error, and attach the correct version of the file (if applicable). The Department reserves the right to decline to update your application after the deadline has passed. Requests will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis.
If you need to change your recommenders, please use the Activity Status Page. Note: The order of recommenders cannot be changed.
May I submit a resume/CV, list of publications, etc. as part of my application?
Applicants are permitted to upload one additional document to the online application, under the “Document Uploads” section.
Is there an interview process?
Yes, our faculty interview prospective students before making final admission decisions.
When are the interviews?
The interviews for the current admissions cycle are likely to be in February 2021. We anticipate that all interviews will take place virtually.
When can I expect to find out the decision on my application?
The Department of Psychology aims to issue all offers of admission to PhD degree applicants by the end of March.
I applied in a prior cycle and was not admitted. Can I apply again?
Applicants who applied in prior cycles and were previously not admitted are welcome to reapply if they can demonstrate significant progress made since they last applied. We encourage you to use your Statement of Purpose to explain this progress.
All documents must be resubmitted with a new application. We do not keep records from past applications.
I still have questions!
If you have questions that are not answered on this page or the Stanford Graduate Admissions FAQ page , please email psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . If your questions are already covered on this page, your email may not receive a response.
Note that our Department staff are experts on the logistics and administration of the application, but do not answer questions related to research topics or faculty fit. Per Department policy, Department staff will not offer any evaluative feedback on application materials or applicants' academic background. Unfortunately, due to the extremely high volume of inquiries, we cannot provide individual status updates for applicants at any point in the process.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD in Psychology?
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Ariel Skelley/Getty Images
- How Long Will It Take?
Before You Earn PhD in Psychology
Which type of degree should you get, can you finish your degree early.
Just how long does it take to get a PhD in psychology? The answer can vary depending on your program, educational background, and academic schedule. In general, most PhD psychology programs take anywhere from five to seven years to complete.
Learning more about what it takes to get a doctorate in psychology can help you better plan your educational and career journey.
At a Glance
Getting a PhD in psychology can take several years of graduate study. If you are thinking about becoming a psychologist, research your degree options to figure out what type of degree you need and how long it will take to enter your chosen profession. No matter what you decide, plan to spend anywhere from three to seven years in graduate school to earn a doctorate.
How Long Will It Take to Get a Doctorate Degree?
How long it takes to get a doctorate in psychology depends on various factors, including the type of degree you have selected, your educational background, and the individual doctorate program in which you have enrolled.
Most doctorate programs in psychology take between four to seven years to complete.
PhD in Psychology
Most PhD programs require at least five to seven years to complete. These programs often follow a scientist-practitioner model that trains professionals both in research and clinical practice.
In addition to regular coursework, you may also be expected to complete an internship or supervised residency. The program usually culminates in completing an original research project or dissertation.
PsyD Degree
Most PsyD programs require between four to six years to complete. A PsyD is a degree designed to train professionals to apply psychological knowledge to treating and helping people in real-world settings.
According to the American Psychological Association, PsyD programs focus more on applying psychological science, usually in the form of service.
Most EdD programs require between three to five years to complete. EdD programs are often focused on psychology, counseling, or counselor education. They explore topics that involve both education and psychology.
It is important to note that many applicants to EdD programs already hold a master's degree in a related field. This differs from applicants to PhD and PsyD programs, who often begin their program of study with a bachelor's degree.
Before you begin your academic journey, it is a good idea to look at just how long it will take you to complete your degree. The amount of time it will take can depend upon various factors, including:
- Your chosen specialty area
- The program you select
- The course load you can take each semester
A doctorate-level degree in psychology is required to work in many job areas, including as a licensed clinical psychologist or counseling psychologist. According to the American Psychological Association, a doctorate degree is also often required in fields such as school psychology or health psychology .
So how long does it take to get a PhD in Psychology ? First, it is essential to realize that the degree requirements can vary depending on the field that you decide to pursue. A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy degree is not necessarily your only option. In some cases, you might want also to consider the PsyD (Doctor of Psychology) or the EdD (Doctor of Education) degree options.
The PhD, PsyD, and EdD are all great options, but don't let how long it takes to complete be the primary deciding factor. Before you decide to get a doctorate degree, start by deciding which type of degree is most suited to your professional goals.
If you want to conduct research:
A PhD in Psychology tends to focus on a research-based model of education. People with a PhD in Psychology are qualified for a wide range of teaching, research, and clinical positions in colleges, universities, hospitals, government offices, and private mental health practices.
If you want to treat mental health issues:
The PsyD degree option generally focuses on a practitioner-based model of education. Individuals with a PsyD degree can also teach or conduct psychology research, but they frequently work in applied settings to provide direct mental health services.
If you want to apply psychology to help students:
Finally, there is also a third doctorate option that you might also want to consider depending on your career goals. If you are interested in working as a school psychologist or in a related educational field, the EdD, or Doctor of Education, is a possible option.
Despite the years of work, earning your PhD, PsyD, or EdD can be well worth the effort. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics suggests that workers with a doctoral or education specialist degree in clinical, counseling, and school psychology will find the strongest job opportunities.
Generally, if you have a strong background in psychology and have completed all of the necessary prerequisites, you can finish your doctorate sooner than students who have not taken the prerequisite courses.
Carefully planning your degree can also help ensure you complete the program requirements quickly.
Be sure you have a clear idea of what you want to do with your psychology degree once you've completed it. Do you want to teach, or is research more appealing to you? Are you interested in seeing clients, or are you planning to combine your training in psychology with another field, such as law or medicine?
If you need help deciding, make an important with an academic advisor at your school. They can help you explore your options and answer any questions you may have.
What This Means For You
No matter the degree you decide to pursue, earning a doctorate in psychology requires a significant investment of time, money, and effort. Because of this, it is essential to carefully consider your goals before deciding on a graduate program. You should also think about whether you need a doctorate or if a master's might be more appropriate.
Gee DG, DeYoung KA, McLaughlin KA, et al. Training the next generation of clinical psychological scientists: A data-driven call to action . Annu Rev Clin Psychol . 2022;18:43-70. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-081219-092500
Loyola University. Can I get my Psy.D. without a Master's in Psychology?
American Psychological Association. Doctoral degrees in psychology: How are they different, or not so different ?
Franklin University. Is getting a Doctorate in Education worth it?
American Psychological Association. Frequently asked questions about graduate school .
Bureau of Labor Statistics. Psychologists . Occupational Outlook Handbook .
Carr, A. Clinical Psychology: An Introduction . London: Routledge; 2012.
Kuther, TL. The Psychology Major's Handbook . Boston, MA: Cengage Learning; 2016.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- Psychology Programs

What Can I Do With a PhD in Psychology? – PhD in Psychology Career Options
Professionals who earn their Ph.D. in psychology have many more career options available to them than Masters level and Bachelors prepared individuals.
Not only are incomes generally higher with a Ph.D. but jobs are more plentiful and varied after the completion of doctoral level training. Also, in order to actually be considered a psychologist, a doctoral degree in psychology is generally mandatory .
Doctoral prepared professionals generally choose between applied psychology careers and research oriented careers . Applied psychology careers consist of the professional delivering psychological services directly to clients.
Psychologists deals with the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of mental health disorders. They also frequently provide preventative services for various entities. Some psychologists also apply psychological theories to help businesses overcome challenges and improve workplace productivity.
Other doctoral level professionals choose to dedicate their careers to conducting research. In many universities, doctoral level faculty only spend a small amount of time teaching classes as they spend the majority of their time engaged in research. They often manage laboratories, recruit research trainees, and publish their findings in academic journals.
Research psychologists also spend a lot of time giving talks about their research findings, attending conferences, and more experienced professionals are sometimes called upon to give peer reviews for well-respected academic and professional journals.
Additionally, many research psychologists also find themselves writing grant applications to get funding for their research projects.
What are the Career Options With a PhD in Psychology?
Listed below are some of the popular career options that you can pursue with a PhD in psychology:
Clinical Psychologist
Industrial organizational psychologist, forensic psychologist, rehabilitation psychologist, experimental psychologist, school psychologist.
- Sports Psychologist
- Educational Psychologist
- Social Psychologist
- Child Psychologist
- Mental Health Psychologist
Clinical psychologists often work in private practice providing evaluations and treatment for individuals who are experiencing mental health issues. However, you will also find a significant amount of these professionals working in hospitals, clinics, residential facilities, and other institutions that provide mental health services. A clinical psychologist in these settings might be a practitioner or an administrator.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, clinical psychologists earn an average mean wage of $102,740 annually, as of May 2023.
Companies hire industrial-organizationalpPsychologists to develop strategies to increase productivity and improve employee retention rates. These professionals focus on organizational structure, employee recruitment and selection, job satisfaction, and the development of better machines and systems for employee comfort. Industrial-organizational psychologists identify methods that work best in the workplace and make recommendations for improvement.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, industrial-organizational psychologists earn an average mean wage of $144,610 annually, as of May 2023.
Forensic psychologists take psychological insights and apply that to legal matters. This specialized area of psychology focuses on criminal and civil matters to include law enforcement, jury selection, probation and parole, victim advocacy, family law, mental status competency, risk assessments, civil commitments, juvenile delinquency, insurance claims, and many other areas of the justice system.
Careers for forensic psychologists are diverse and can include functioning as a court consultant, providing mental health services in correctional facilities, working with law enforcement, or providing victim advocacy.
Although a specific wage for a forensic psychologist was not noted, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Forensic Science Technicians who also serve as Expert Witnesses, earn an average mean wage of $147,585 annually, as of January 2024.
Rehabilitation psychologists work with people who have suffered a significant loss or are struggling with adjusting to life with a disability. These professionals focus on the psychological aspects of loss, disability, and rehabilitation.
Typical clients could include someone who has recently become a paraplegic, is dealing with cancer, or is experiencing a chronic medical condition. Practitioners give their clients the support that they need as they adjust to their new life with the condition.
Researchers in the field of rehabilitation psychology explore how various factors, including biological, social, and environmental issues, affect people with disabilities and other chronic illnesses.
According to ZipRecruiter, the related field of rehabilitation counselor earns an average mean wage of $95,854 annually, as of January 2024.
Experimental psychologists are professionals who specialize in the study of human behavior and cognition. Their research generally explores thinking, learning, attention, motivation, and other cognitive functions. Although they do work with humans, they also study animals such as rats, monkeys, and pigeons.
Experimental psychologists can work in research settings, as consultants for businesses, and are even called upon to develop strategies to help lessen the psychological impact of high intensity training on military personnel.
School psychologists are employed by public school districts, private schools, and learning centers to help students overcome challenges related to disabilities, emotional issues, social adjustment, or other behavioral problems that impede learning. They evaluate the effectiveness of the educational process for students and use available resources as well new strategies to help students improve performance.
School psychologists also help students indirectly by working with teachers, parents, and school administrators to create individualized educational programs for students who are struggling to learn.
In many school districts, they also help administrators with the development of programs for Gifted learners. The goal of school psychologists in this role is to support teachers and parents in implementing individualized instructional strategies for students.
Some professionals specialize in working with specific groups of students such as children with Learning Disabilities, Gifted learners, or Adult learners.
According to ZipRecruiter, school psychologists earn an average mean wage of $92,813 annually, as of January 2024.
Sports psychologists are qualified professionals who help athletes to overcome problems, improve performance and achieve their goals. They draw their knowledge from many fields such as physiology, biomechanics, psychology, and kinesiology.
Sports psychologists explore the link between the psychological and physical factors that affect performance and try to establish what issues are preventing athletes from performing at full potential.
Their role may also involve acting as a consultant, a trainer or a therapist. Therapy may be needed for issues such as career transitions, eating disorders or off-field problems that effect on-field performance.
Working as a trainer may include assistance with rehabilitation after an injury. Athletic teams often consult with sports psychologists or employ one to help with various issues such as group dynamics and leadership issues.
Some sports psychologists become researchers who explore issues such as factors that lead to success, the effects of athletic participation on individuals or the psychological effects of a physical injury.
According to the American Psychological Association’s (APA), sports psychologists can expect to earn between $60,000 and $180,000 a year, with some annual salaries reaching $100,000.
What is the Job Outlook for Psychology Careers?
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) indicates that although the employment growth of psychologists is expected to grow by 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, career prospects are far better for those who have a doctoral degree in psychology.
Related Reading
- How to Prepare for a Career in Psychology
- Top Psychology PhD Programs That Don’t Require GRE
- What is the Difference Between a Master’s and a PhD in Psychology
- Associate Degrees
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- PhD Programs
- Addiction Counselor
- Criminal Psychologist
- Family Therapist
- General Psychologist
- Health Psychologist
- Industrial-Organizational
- See More Careers
- Applied Psychology
- Business Psychology
- Child Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Industrial Psychology
- Sports Psychology
- See More Programs
- Clinical Psychology Degree
- Cognitive Psychology Degree
- Forensic Psychology Degree
- Health Psychology Degree
- Mental Counseling Degree
- Social Psychology Degree
- School Counseling Degree
- Behavioral Psychologist Career
- Clinical Psychologist Career
- Cognitive Psychologist Career
- Counseling Psychologist Career
- Forensic Psychologist Career
- School Psychologist Career
- Social Psychologist Career


- Select spacebar or enter to search Florida Tech website Search

Clinical Psychology
- College of Psychology and Liberal Arts
- Areas of Study
- Undergraduate Programs
- Centers & Programs
- Student Senate
- Psy.D. Student Handbooks
- Advanced Emphasis Coursework
- Employment Opportunities
- Behavioral Health Grant
- I/O Psychology
- Online Learning
- Faculty and Research
- Students and Alumni
- Connect with Us
Psy.D. In Clinical Psychology
Welcome to the Clinical Psychology Psy.D. Program at Florida Institute of Technology. The program at Florida Tech that leads to a Psy.D. in clinical psychology is accredited by the American Psychological Association* and offers students training based on a practitioner-scholar model that prepares students for entry-level positions as clinical psychologists. To achieve that goal, we are committed to training students with strong and continually developing clinical competencies, whose clinical work is informed by the scientific and theoretical knowledge base of the discipline of psychology, and whose graduates respect and value cultural and individual difference, and who maintain the highest professional principles and standards.
What Makes Florida Tech's Psy.D. in Clinical Psychology Stand Out?
- Accredited by the American Psychological Association* since 1983
- Opportunities for advanced coursework and practica in emphasis areas: Neuropsychology, Child/Family, Integrated Behavioral Health, and Forensic.
- In-depth training in psychological assessment and integrated psychodiagnostics
- Curriculum that addresses current trends in psychology including Integrated Behavioral Health Care, Clinical Neuropsychology, Assessment, Trauma and Child Psychology
- On-site practicum training facility
- A large network of community-based practicum sites offering many different training opportunities
- Good student-to-faculty ratio, with annual cohorts of approximately 20
- Colleague-in-training atmosphere
- Excellent internship match rate
- Flat-rate tuition program
- Warm climate, great location, close to beaches
- Relatively low cost of living, ample and reasonably priced housing available off campus
Our program leading to a Psy.D in Clinical Psychology trains students to become practicing clinical psychologists with core competencies in relational/clinical skills, comprehensive psychological assessment, clinical treatment interventions, research and evaluation skills, consultation and education, management and supervision, and diversity issues.
We have several opportunities for advanced course work. These areas are:
- Family/Child Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Integrated Behavioral Healthcare/Health Psychology
Admission Requirements
An applicant must possess a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution of higher learning. Although it is not necessary for the major area to have been psychology, it is required that those entering without a previous degree in psychology will have completed at least 18 credit hours of psychology coursework at the time of application. These courses must have been taken in a department of psychology, and should include statistics, personality theory, abnormal psychology, learning, physiological psychology and social psychology.
All application materials must be received by December 1 of each year.
Visit the graduate admissions information page for all the information you need to apply to the program. Admissions applications must include transcripts, GRE general test scores, a personal statement, two letters of recommendation, and a resume or CV.
Students we will consider for admission will receive an invitation approximately two weeks prior to our Interview Day, typically held in February. Attendance at Interview Day is VERY strongly recommended.
*Questions related to the program's accredited status should be directed to the Commission on Accreditation:
Office of Program Consultation and Accreditation American Psychological Association 750 1st Street, NE Washington, DC 20002
Phone: (202) 336-5979 Email: [email protected] Web: www.apa.org/ed/accreditation
Clinical Program
Clinical Psychology, Psy.D
APA Student Data
Student Admissions, Outcomes, and Other Data
Clinical Psychology Information
Info Session: Funding a Clinical Doctoral Degree
2023-2024 PsyD Program Addendum
2023-2024 SOP Grad Handbook

Dr. Caitlin Wolford Clevenger
Psychologist , phd (she, her).

My Practice at a Glance
3840 Ridgeway Drive
Homewood, AL 35209
Psychotherapy Services of Alabama
Trussville, AL 35173

- Individual Sessions $200
- Couple Sessions $250
- Pay by ACH Bank transfer, American Express, Cash, Discover, Health Savings Account, Mastercard, Visa
- BlueCross and BlueShield
- Out of Network
Qualifications
- Verified by Psychology Today Licensed by State of Alabama / 2186 Dr. Caitlin Wolford Clevenger
- In Practice for 10 Years
- Degree/Diploma from University of Tennessee-Knoxville MA / 2015
- Degree/Diploma from University of South Alabama MS / 2013
- Attended University of Tennessee-Knoxville , PhD, Clinical Psychology , Graduated 2019
Specialties and Expertise
Top specialties.
- Women's Issues
- Trauma and PTSD
- Pregnancy, Prenatal, Postpartum
- Alcohol Use
- Life Transitions
- Marital and Premarital
- Relationship Issues
- Self Esteem
- Sex Therapy
- Sexual Abuse
- Substance Use
- Testing and Evaluation
2 Endorsements

Client Focus
Participants, communities, treatment approach, types of therapy.
- Acceptance and Commitment (ACT)
- Cognitive Behavioral (CBT)
- Interpersonal
- Psychodynamic
- Transdiagnostic Treatments
Primary Location
Additional location, nearby areas.
- Gardendale, AL
- Homewood, AL
- Trussville, AL
What If We’re Telling the Wrong Story about Climate Change?

Chika Okafor’s research merges economics with educational psychology to understand how the methods we use to communicate about important issues influence public action.
In recent years, the news has been filled with a seemingly endless stream of articles about the negative effects of climate change: extreme temperatures, flooding, increasingly destructive hurricanes and earthquakes, lost crops, and much more. Engaging with this influx of negative material can be intimidating and demoralizing. It can even lead to the impression that the climate crisis is just too big of a problem to solve and that, therefore, it’s not worth trying.
Repeated exposure to disaster coverage may also lead to “ crisis fatigue ,” a burnout response to prolonged stress resulting from difficult situations. This phenomenon has been well-documented with respect to the COVID-19 pandemic , and researchers have also linked it to climate change. Over time, those experiencing crisis fatigue can develop psychological trauma . So what can we do differently?
According to Chika Okafor, the 2023–2024 Edna Newman Shapiro, Class of 1936, and Robert Newman Shapiro, Class of 1972, Graduate Student Fellow at Harvard Radcliffe Institute, climate disaster stories employ what’s called a “deficit-based approach” to communication, which might be problematic when it comes to mobilizing support to fight climate change.
Educational psychology, a field of study that is often drawn on in the context of teaching students who come from challenging backgrounds, defines two different approaches to instruction: the deficit-based approach and the asset-based approach. In basic terms, the deficit-based approach emphasizes the problems that students are facing, while the asset-based approach focuses on students’ strengths and the opportunities available to them. Imagine your teacher says to you, “If you fail this exam, you won’t be able to get into college.” How does that make you feel? Now imagine she says, instead, “If you pass this exam, you’ll have a better chance of getting into your dream school.”
The problem with the deficit-based approach, says Okafor—who is also the inaugural fellow in law and political economy at Harvard Law School and a PhD candidate in Harvard’s Department of Economics—is it can create a “self-fulfilling prophecy, where students may not elevate beyond the lowered expectations of their instructors.” In contrast, educational psychology researchers have shown that an asset-based approach can be used to enable students to overcome the barriers they face.
Okafor was born and raised in Chicago, the son of two Nigerian immigrants and the youngest of four children. Growing up, Okafor’s father instilled in him the idea that “education is arming yourself to the teeth.” Education allowed his father to escape extreme poverty in southeastern Nigeria, immigrate to the United States, and raise his family there.
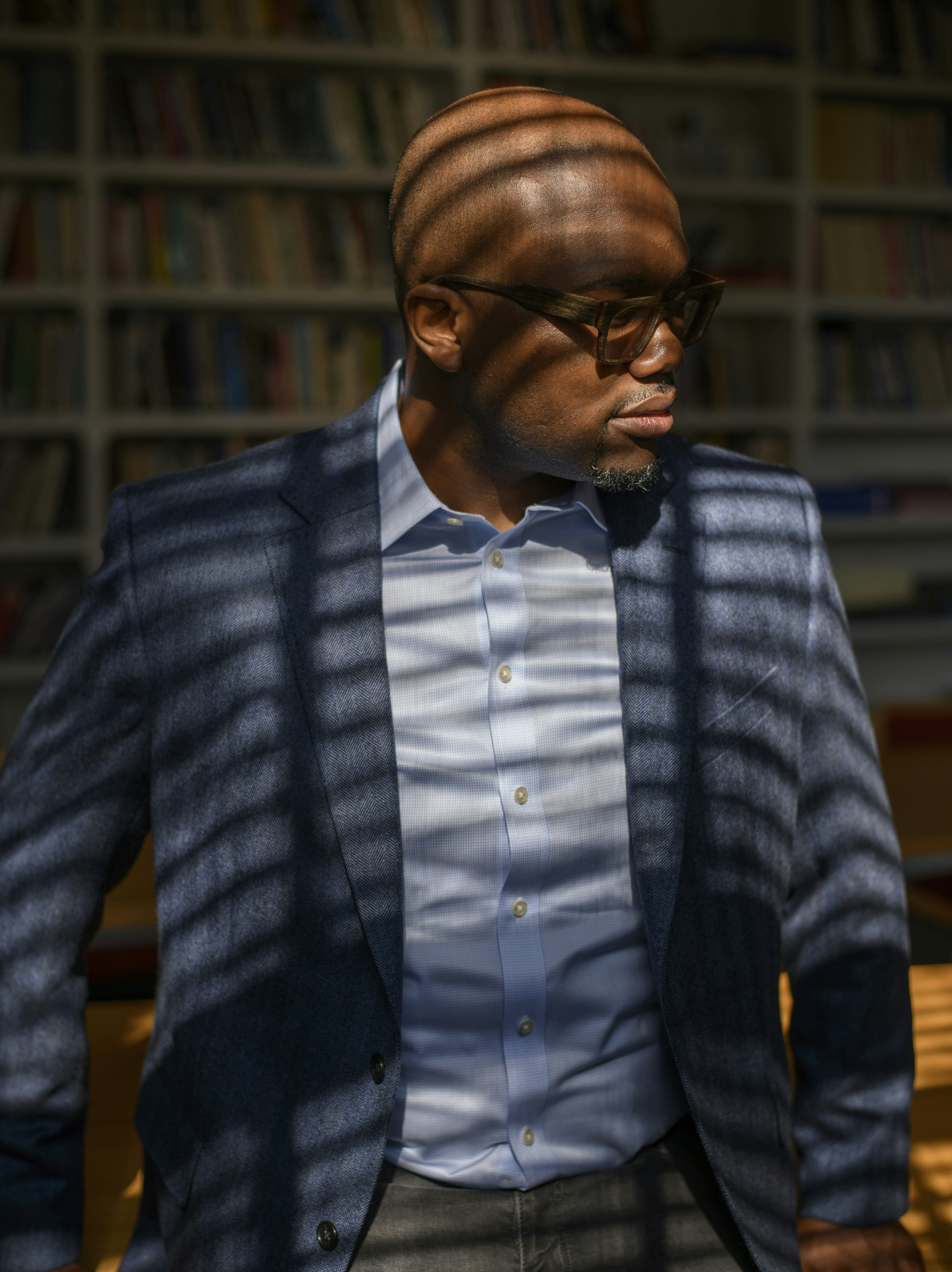

Photo by Tony Rinaldo
After college (and a brief stint in consulting), Okafor returned to Chicago to work in the public school system. He recalls roaming the halls of Paul Robeson High School, in the South Side of Chicago, and thinking that, in some ways, the school resembled a prison—police cars remained permanently parked outside, metal grates were used to control the flow of adolescents, and a police chopper hovered overhead while students were released at the end of the school day.
For Okafor, the experience was so impactful that he decided to continue arming himself, first by enrolling at Yale Law School and then in Harvard’s economics PhD program. He saw law and economics as two powerful means to make progress on some of the complex social and economic issues he had witnessed play out at Robeson and elsewhere.
Okafor’s doctoral project is expansive and ambitious, addressing several major social and economic problems, including economic inequality, rising incarceration rates, and, of course, climate change. What unites these disparate chapters is the application of economic theory and experimental methods, along with econometric techniques, to better understand important issues.
Okafor chose climate change for the third and final chapter, and the focus of his time at Radcliffe, because it’s “the 800-pound gorilla in the room that will make just about every index of inequality wider and significantly impact the people who are already most vulnerable in our society.”
One of the challenges of addressing climate change, Okafor notes, is its complexity. Video produced by Alan C. Grazioso/Harvard Radcliffe Institute
Drawing on lessons learned from working in education, and inspired by the New York Times interactive children’s guide “ Bad Future, Better Future ,” Okafor designed an experiment to test the public’s response to deficit-based and asset-based approaches to instructional materials.
First, he worked with a multimedia design team to develop two versions of an educational video on climate change: one that relies on a deficit-based approach and one that relies on an asset-based approach. Next, Okafor devised a survey to record respondents’ reactions upon exposure to either the deficit-based video, the asset-based video, or both, and he administered it to 2,500 participants across the United States.
Okafor is currently in the process of collecting and analyzing the survey results, which he will use to assess the videos’ impact on climate change beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Through the surveys, he also collected data on demographic characteristics such as race, gender, and income—data which he hopes will shed light on the extent to which these characteristics might influence ideas and behaviors regarding climate change.
“What I’m trying to see in my research is if there is a different way of talking about climate change that could have a much greater impact on generating the amount of public support that is required to mitigate the worst effects,” says Okafor.
Following his line of reasoning, we must question our approaches to talking and writing about climate change if we want to maximize the impact of our words. What if we were to shift the focus of our climate-related reporting toward a more solution-oriented perspective? What implications would this shift in communication strategy have as far as motivating public action?
Importantly, deploying an asset-based approach does not necessitate minimizing hardship. The point is not to gloss over or obscure challenges but, rather, to acknowledge them and figure out how to address them.
In the context of news reporting, this might look like increasing the number of stories about how to reduce environmental degradation, cut greenhouse gas emissions, and mitigate the consequences of climate change, without reducing the level of coverage on climate disasters. Disaster stories are important insofar as they elicit an emotional response and underscore the importance of taking action. But they don’t tell us how to act, which can lead to a sense of helplessness.
We might also add sections with possible solutions to stories about climate-related issues. There are many approaches, but the key is to emphasize opportunities for progress, to avoid painting a picture of such doom that our audience simply gives up and tunes out.
That education is a powerful tool may be a truism, but Okafor’s story bears it out. “When I was growing up, I thought that arming yourself to the teeth meant doing so for yourself, to escape or stave off poverty or unequal opportunities, or to shore up financial security” he reflects. “But through this journey toward a PhD, I more deeply understand the extent to which education can be arming yourself in service of others, particularly those who are most vulnerable.”
Sam Zuniga-Levy is a writer at Harvard Radcliffe Institute .
News & Ideas

Episode 208: Kindness—It’s Good for You!

Episode 207: Let’s Talk about Climate Resilience

Episode 206: Tackling Environmental Inequality across Academic Disciplines

Student Spotlight: Chassidy Winestock PhD ’24
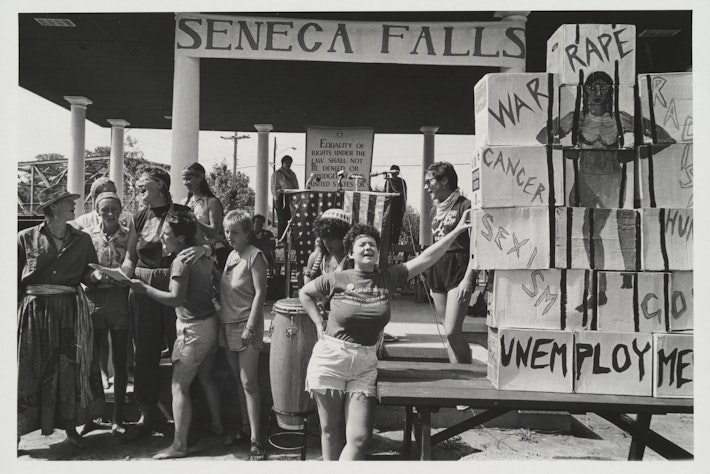
The Sounds of Change

Episode 205: A Conversation with Ruth J. Simmons
Episode 204: Math—It’s Not Just Numbers

by Heather Riske | Apr 25, 2024

Monica Treviño, a PhD clinical psychology student, has been strengthening her linguistic and clinical skills to better serve the Latinx community. (Photo by Derik Holtmann)
Monica Treviño was born in Mexico and grew up speaking Spanish conversationally with her family in Texas, but she wasn’t quite as comfortable providing mental health services in the language. Hoping to strengthen her linguistic and clinical skills to better serve the Latinx community – which has grown by more than 40% in St. Louis over the past decade – she spent six weeks last summer in Huanchaco, Peru, completing PASEO’s immersion and practicum experience . In October, she attended the National Latinx Psychological Association conference. Now, she’s using what she learned from both experiences to help make the services at UMSL’s Community Psychological Service culturally and linguistically accessible to Spanish speakers.
1. How do conversational and clinical Spanish differ?
It’s a very different type of Spanish. There’s so much niche terminology that we don’t even realize that we’re learning. I’ve been studying psychology for 10 years now. That’s a decade of pretty specialized language in English that I had limited exposure to in Spanish. Prior to this program, I would have struggled to speak about fairly basic therapeutic assessment concepts with a client.
2. What are you taking away from these experiences?
My clinical vocabulary in Spanish has grown tremendously and I’ve gained the confidence I needed to actually do this type of clinical work effectively. It’s one thing to have the knowledge, but it’s easy to feel imposter syndrome when you haven’t had any opportunities to use it and prove to yourself that you can do it well. I also have a better understanding of how I can hopefully supervise bilingual trainees effectively some day in the near future.
3. What have you been able to implement so far?
To start, we wanted to at least have some translated psychoeducational materials that we could share with families as they’re waiting for their next treatment touchpoint. We’re getting all of the paperwork, resource packets and referrals ready, making sure that all of our consent forms and HIPAA forms are translated and implementing more standard tools for measuring competency in this area for any future bilingual trainees.
4. Why is it so important to measure competency?
In the field of psychology, there are core competencies for specialized areas of training. We don’t have the same for bilingual psychologists. Having standard competencies and measurement tools is important because it allows us to create effective training programs, empowers people who are able to provide the services and ensures that clients are receiving high-quality care.
5. How would you like to see these services continue to grow?
Being able to have that infrastructure where we already have everything translated and ready to go will make it easier for us to start providing services in Spanish. I am hopeful that we will continue to have new cohorts coming into the program with interest and experience in providing services in Spanish, and it can just keep growing from there.
This story was originally published in the spring 2024 issue of UMSL Magazine . If you have a story idea for UMSL Magazine, email [email protected] .

LATEST NEWS

Heather Riske
You might also like.

Natissia Small helping prepare girls for future success as CEO of Girl Scouts of Eastern Missouri
Small stepped into the role of CEO in April 2023 after nearly 28 years working at UMSL, most recently as vice provost for access, academic support and workforce integration.
Apr 25, 2024

Accomplished student-athletes lead UMSL Athletics to new heights
The past two years have witnessed a string of successes for UMSL Athletics led by student-athletes who shine in the classroom as well as in the arena.
Biology Professor Michi Tobler uncovers lessons from fish living in extreme environments
Tobler, the E. Desmond Lee Endowed Professor in Zoological Studies, has developed a particular focus on studying livebearer fish that have adapted to live in the presence of hydrogen sulfide.

UMSL alum Laura Burkemper helps others build their brands and scale their businesses
She also recently co-authored a book, “Empathy and Understanding in Business,” with expert negotiator Chris Voss.
People think 'old age' starts later than it used to, study finds
Increases in life expectancy, later retirement could explain shift in public perception of when old age begins.
Middle-aged and older adults believe that old age begins later in life than their peers did decades ago, according to a study published by the American Psychological Association.
"Life expectancy has increased, which might contribute to a later perceived onset of old age. Also, some aspects of health have improved over time, so that people of a certain age who were regarded as old in the past may no longer be considered old nowadays," said study author Markus Wettstein, PhD, of Humboldt University in Berlin, Germany.
However, the study, which was published in the journal Psychology and Aging , also found evidence that the trend of later perceived old age has slowed in the past two decades.
Wettstein, along with colleagues at Stanford University, the University of Luxembourg and the University of Greifswald, Germany, examined data from 14,056 participants in the German Ageing Survey, a longitudinal study that includes people living in Germany born between 1911 and 1974. Participants responded to survey questions up to eight times over 25 years (1996-2021), when they were between 40 and 100 years old. Additional participants (40 to 85 years old) were recruited throughout the study period as later generations entered midlife and old age. Among the many questions survey participants answered was, "At what age would you describe someone as old?"
The researchers found that compared with the earliest-born participants, later-born participants reported a later perceived onset of old age. For example, when participants born in 1911 were 65 years old, they set the beginning of old age at age 71. In contrast, participants born in 1956 said old age begins at age 74, on average, when they were 65.
However, the researchers also found that the trend toward a later perceived onset of old age has slowed in recent years.
"The trend toward postponing old age is not linear and might not necessarily continue in the future," Wettstein said.
The researchers also looked at how individual participants' perceptions of old age changed as they got older. They found that as individuals aged, their perception of the onset of old age was pushed further out. At age 64, the average participant said old age started at 74.7. At age 74, they said old age started at 76.8. On average, the perceived onset of old age increased by about one year for every four to five years of actual aging.
Finally, the researchers examined how individual characteristics such as gender and health status contributed to differences in perceived onset of old age. They found that women, on average, said that old age started two years later than men -- and that the difference between men and women had increased over time. They also found that people who reported being more lonely, in worse health, and feeling older said old age began earlier, on average, than those who were less lonely, in better health, and felt younger.
The results may have implications for when and how people prepare for their own aging, as well as how people think about older adults in general, Wettstein said.
"It is unclear to what extent the trend towards postponing old age reflects a trend towards more positive views on older people and aging, or rather the opposite -- perhaps the onset of old age is postponed because people consider being old to be an undesirable state," Wettstein said.
Future research should examine whether the trend toward a "postponement" of old age continues and investigate more diverse populations in other countries, including non-Western countries, to understand how perceptions of aging vary by country and culture, according to the researchers.
- Healthy Aging
- Teen Health
- Children's Health
- K-12 Education
- Racial Issues
- Eustachian tube
- Child prodigy
- Developmental psychology
- Adult attention-deficit disorder
- Biological tissue
Story Source:
Materials provided by American Psychological Association . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Markus Wettstein, Rinseo Park, Anna E. Kornadt, Susanne Wurm, Nilam Ram, Denis Gerstorf. Postponing old age: Evidence for historical change toward a later perceived onset of old age. . Psychology and Aging , 2024; DOI: 10.1037/pag0000812
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Advance in Heart Regenerative Therapy
- Bioluminescence in Animals 540 Million Years Ago
- Profound Link Between Diet and Brain Health
- Loneliness Runs Deep Among Parents
- Food in Sight? The Liver Is Ready!
- Acid Reflux Drugs and Risk of Migraine
- Do Cells Have a Hidden Communication System?
- Mice Given Mouse-Rat Brains Can Smell Again
- How Do Birds Flock? New Aerodynamics
- Cancer: Epigenetic Origin Without DNA Mutation
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
September Payscale data for 2023 reports the average salary for graduates with a Psy.D. as $92,000. This is considerably higher than the 2023 national median salary of $48,060, and for many psychologists, the financial and emotional rewards justify the cost and time spent in a doctorate of psychology program.
The two doctorate degrees you can get in psychology are Ph.D. and Psy.D. In simple terms, a Ph.D. in psychology is more research-focused, while a Psy.D. emphasizes clinical practice. The best choice between the two depends on your career goals and whether you prefer research and academia or direct clinical work.
In order to earn a Ph.D. in psychology, you need to first begin by earning your bachelor's degree. While earning your undergraduate degree in psychology can be helpful, students with bachelor's degrees in other subjects can also apply their knowledge to psychology Ph.D. programs. Some students in doctorate programs may have a master's degree in ...
Preparing and applying for graduate school in psychology. This series of 12 videos takes prospective graduate students step-by-step through the preparation, application, interview, and admission processes. The presenters combine decades of advising experience and research findings with evidence-based and anxiety-reducing strategies for ...
The PhD in Psychology is the highest level graduate degree in the field to which a student can aspire. The PhD and PsyD prepare the bearer for a variety of career options representing a wide range of research and practice areas; each of which is unique in its educational scope and training. Although the entrance requirements differ according to ...
Students in our PhD program conduct in-depth research in at least one of five areas of study: Affective, Cognitive, Developmental, Neuroscience, or Social Psychology. All students are expected to spend at least half of their time engaged in research. Each quarter, students should register for 8 - 10 research units (PSYCH207: Graduate Research ...
The PhD program in Psychology trains students for careers in research and teaching. In addition to a wide range of courses, the PhD program is characterized by close collaboration between students and their faculty advisors. ... The Department of Psychology welcomes graduate applications from individuals with a broad range of life experiences ...
The Department of Psychology offers a PhD program in four areas: Clinical Science, Social, Developmental, and Cognition, Brain, and Behavior (CBB). Admissions information, program requirements, funding and financial aid details, and other resources for the graduate program are detailed on the Psychology Graduate Program website and on the Harvard Griffin GSAS website.
Welcome to the Psychology PhD program at Harvard University! Our work is united in the focus on the science of mental life, yet highly interdisciplinary. The Psychology Department is organized into four research areas: Clinical Science/ Experimental Psychopathology. Developmental Psychology. Social Psychology. Cognition, Brain, and Behavior (CBB)
Graduate Study in Psychology allows you to search and compare admissions information for masters and doctoral programs at schools and departments of psychology in the United States and Canada.
These degrees cover the basics of psychology and allow you to take elective classes to learn about special topics. In a bachelor's degree, you are also expected to take a wide range of courses in different subjects. Median annual salary for social and community service managers: $74,240.
The program awards up to 100 high-achieving students every year with full funding to pursue graduate education at Stanford, including the PhD in Psychology. To be considered, you must apply to Knight-Hennessy Scholars and separately apply to the Psychology Department. Note that the Knight-Hennessy Scholars program application deadline is in the ...
By Daniel S. Michalski, PhD, and Garth Fowler, PhD. Doctoral degrees in psychology offer individuals preparation to conduct scientific research, professional practice or both. Most individuals receive either the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) or the Doctor of Psychology (PsyD) degree. Although each of these degrees is designed to engage students in ...
The answer can vary depending on your program, educational background, and academic schedule. In general, most PhD psychology programs take anywhere from five to seven years to complete. Learning more about what it takes to get a doctorate in psychology can help you better plan your educational and career journey.
What is a Clinical Psychology PhD? A few (brief) notes about Clinical Psychology PhD programs: Clinical psych are best for people who want to focus on research and clinical work; though skills can be applied to a range of fields (e.g, public health, policy, etc). If you are interested in only clinical work, PhDs may not be the best fit!
The PhD in Psychology Curriculum. The PhD in general psychology curriculum emphasizes research, teaching, and leadership in the field. The coursework is intended to provide students with the unique perspective of a scientist-practitioner. Most PhD in psychology programs require a dissertation, which count toward a set number of credits.
A PsyD program focuses on clinical training, while a PhD in psychology is more oriented towards scientific research. It is essential to evaluate your goals for obtaining a graduate degree and choose the program that best aligns with those goals. Although many PsyD-holders work in research or teaching roles, and many non-clinical PhD-holders ...
Psychology PhD programs are rigorous, requiring a great commitment of time and effort. With the ability to learn at your own pace and on your own timeline, many seeking a doctorate in psychology find that online PhD in Psychology programs suit their busy schedules. Walden University's PhD in Psychology is also offered in a popular Fast-Track ...
Listed below are some of the popular career options that you can pursue with a PhD in psychology: Clinical Psychologist. Industrial Organizational Psychologist. Forensic Psychologist. Rehabilitation Psychologist. Experimental Psychologist. School Psychologist. Sports Psychologist. Educational Psychologist.
Earning a doctor of philosophy (Ph.D.) in psychology provides you with extensive knowledge about human behavior and thought processes. You can apply your Ph.D. in psychology to clinical environments, research positions, academic roles and corporate development projects. If you have a Ph.D. in psychology or want to explore potential career paths ...
PhDs advance knowledge, whereas MDs merely apply existing knowledge. If you ask someone in the psychology world how people with PhDs (Doctor of Philosophy) differ from those with MD (Doctor of ...
Psy.D. In Clinical Psychology. Welcome to the Clinical Psychology Psy.D. Program at Florida Institute of Technology. The program at Florida Tech that leads to a Psy.D. in clinical psychology is accredited by the American Psychological Association* and offers students training based on a practitioner-scholar model that prepares students for entry-level positions as clinical psychologists.
Located in Nashua, New Hampshire, Rivier University offers a hybrid Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.) with a limited number of online classes. The American Psychology Association-accredited program ...
Dr. Caitlin Clevenger, PhD, Psychologist, Homewood, AL, 35209, (205) 827-5190, Are you successful in your career but still unhappy? ... Verified by Psychology Today Licensed by State of Alabama ...
After college (and a brief stint in consulting), Okafor returned to Chicago to work in the public school system. He recalls roaming the halls of Paul Robeson High School, in the South Side of Chicago, and thinking that, in some ways, the school resembled a prison—police cars remained permanently parked outside, metal grates were used to control the flow of adolescents, and a police chopper ...
Discover the multifaceted world of clinical psychology through the insights of volunteer Michael Meinzer, PhD, as he shares his experiences and upcoming initiatives, including the inaugural Society for Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology conference, and his passion for exploration, both in his field and beyond.
Monica Treviño, a PhD clinical psychology student, has been strengthening her linguistic and clinical skills to better serve the Latinx community. (Photo by Derik Holtmann) Monica Treviño was born in Mexico and grew up speaking Spanish conversationally with her family in Texas, but she wasn't quite as comfortable providing mental health ...
However, the study, which was published in the journal Psychology and Aging, also found evidence that the trend of later perceived old age has slowed in the past two decades.