
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Dissertations and research projects
- Book a session
- Planning your research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
Introductions
Literature review, methodology, conclusions, working with your supervisor.
- e-learning and books
- SkillsCheck This link opens in a new window
- ⬅ Back to Skills Centre This link opens in a new window
- Review this resource
What is an abstract?
The abstract is a brief summary of your dissertation to help a new reader understand the purpose and content of the document, in much the same way as you would read the abstract of a journal article to help decide whether it was relevant to your work. The function of the abstract is to describe and summarise the contents of the dissertation, rather than making critical or evaluative statements about the project.
When should I write the abstract?
The abstract should be the last section you write before submitting your final dissertation or extended project report, as the content will only be decided once the main document is complete.
What should I include?
One of the best ways to find the right ‘voice’ for the abstract is to look at other examples, either from dissertations in your field or study, or from journal articles. Look out for examples that you feel communicate complex ideas in a simple and accessible way. Your abstract should be clear and understandable to a non-specialist, so avoid specialist vocabulary as far as possible, and use simple sentence structures over longer more complex constructions. You can find a list of phrases for abstract writing here .
Most abstracts are written in the present tense, but this may differ in some disciplines, so find examples to inform your decision on how to write. Avoid the future tense - ‘this dissertation will consider’ - as the research has already been completed by the time someone is reading the abstract! You can explore some key phrases to use in abstract writing here.
Examples of dissertation abstracts Dissertation abstracts, University of Leeds Overview of what to include in your abstract, University of Wisconsin - Madison Abstract structures from different disciplines, The Writing Center For examples from Sheffield Hallam University, use the 'Advanced Search' function in Library Search to access ‘Dissertations/Theses’.
What should the introduction include?
Your introduction should cover the following points:.
- Provide context and set the scene for your research project using literature where necessary.
- Explain the rationale and value of the project.
- Provide definitions and address general limitations in the literature that have influenced the topic or scope of your project.
- Present your research aims and objectives, which may also be phrased as the research ‘problem’ or questions.
Although it is important to draft your research aims and objectives early in the research process, the introduction will be one of the last sections you write. When deciding on how much context and which definitions to include in this section, remember to look back at your literature review to avoid any repetition. It may be that you can repurpose some of the early paragraphs in the literature review for the introduction.
What is the ‘research aim’?
The research aim is a mission statement, that states the main ambition of your project. in other words, what does your research project hope to achieve you may also express this as the ‘big questions’ that drives your project, or as the research problem that your dissertation will aim to address or solve..
You only need one research aim, and this is likely to change as your dissertation develops through the literature review. Keep returning to your research aim and your aspirations for the project regularly to help shape this statement.
What are the research objectives? How are they different from research questions?
Research objectives and questions are the same thing – the only difference is how they are written! The objectives are the specific tasks that you will need to complete – the stepping stones – that will enable you to achieve your overall research aim.
You will usually have 3-5 research objectives, and their order will hep the reader to understand how you will progress through your research project from start to finish. If you can achieve each objective, or answer each research question, you should meet your research aim! It is therefore important to be specific in your choice of language: verbs, such as ‘to investigate’, ‘to explore’, ‘to assess’ etc. will help your research appear “do-able” (Farrell, 2011).
Here’s an example of three research objectives, also phrased as research questions (this depends entirely on your preference):
For more ideas on how to write research objectives, take at look at this list of common academic verbs for creating specific, achievable research tasks and questions.
We have an online study guide dedicated to planning and structuring your literature review.
What is the purpose of the methodology section?
The methodology outlines the procedure and process of your data collection. You should therefore provide enough detail so that a reader could replicate or adapt your methodology in their own research.
While the literature review focuses on the views and arguments of other authors, the methodology puts the spotlight on your project. Two of the key questions you should aim to answer in this section are:
- Why did you select the methods you used?
- How do these methods answer your research question(s)?
The methodology chapter should also justify and explain your choice of methodology and methods. At every point where you faced a decision, ask: Why did choose this approach? Why not something else? Why was this theory/method/tool the most relevant or suitable for my project? How did this decision contribute to answering my research questions?
Although most students write their methodology before carrying out their data collection, the methodology section should be written in the past tense, as if the research has already been completed.
What is the difference between my methodology and my methods?
There are three key aspects of any methodology section that you should aim to address:.
- Methodology: Your choice of methodology will be grounded in a discipline-specific theory about how research should proceed, such as quantitative or qualitative. This overarching decision will help to provide rationale for the specific methods you go on to use.
- Research Design: An explanation of the approach that you have chosen, and the type of data you will collect. For example, case study or action research? Will the data you collect be quantitative, qualitative or a mix of both?
- Methods: The concrete research tools used to collect and analyse data: questionnaires, in-person surveys, observations etc.
You may also need to include information on epistemology and your philosophical approach to research. You can find more information on this in our research planning guide.
What should I include in the methodology section?
Research paradigm: What is the underpinning philosophy of your research? How does this align with your research aim and objectives?
Methodology : Qualitative or quantitative? Mixed? What are the advantages of your chosen methodology, and why were the other options discounted?
- Research design : Show how your research design is influenced by other studies in your field and justify your choice of approach.
- Methods : What methods did you use? Why? Do these naturally fit together or do you need to justify why you have used different methods in combination?
- Participants/Data Sources: What were your sources/who were your participants? Which sampling approach did you use and why? How were they identified as a suitable group to research, and how were they recruited?
- Procedure : What did you do to collect your data? Remember, a reader should be able to replicate or adapt your methodology in their own research from the information you provide here.
- Limitations : What are the general limitations of your chosen method(s)? Don’t be specific here about your project (ie. what you could have done differently), but instead focus on what the literature outlines as the disadvantages of your methods.
Should I reflect on my position as a researcher?
If you feel your position as a researcher has influenced your choice of methods or procedure in any way, the methodology is a good place to reflect on this. Positionality acknowledges that no researcher is entirely objective: we are all, to some extent, influenced by prior learning, experiences, knowledge, and personal biases. This is particularly true in qualitative research or practice-based research, where the student is acting as a researcher in their own workplace, where they are otherwise considered a practitioner/professional.
The following questions can help you to reflect on your positionality and gauge whether this is an important section to include in your dissertation (for some people, this section isn’t necessary or relevant):
- How might my personal history influence how I approach the topic?
- How am I positioned in relation to this knowledge? Am I being influenced by prior learning or knowledge from outside of this course?
- How does my gender/social class/ ethnicity/ culture influence my positioning in relation to this topic?
- Do I share any attributes with my participants? Are we part of a s hared community? How might this have influenced our relationship and my role in interviews/observations?
- Am I invested in the outcomes on a personal level? Who is this research for and who will feel the benefits?
Visit our detailed guides on qualitative and quantitative research for more information.
- Quantitative projects
- Qualitative projects
T he purpose of this section is to report the findings of your study. In quantitative research, the results section usually functions as a statement of your findings without discussion.
Results sections generally begin with descriptive statistics before moving on to further tests such as multiple linear regression, or inferential statistical tests such as ANOVA, and any associated Post-Hoc testing.
Here are some top tips for planning/writing your results section:
- Explain any treatments you have applied to your data.
- Present your findings in a logical order.
- Describe trends in the data/anomalous findings but don’t start to interpret them. Save that for your discussion section.
- Figures and tables are usually the clearest way to present information. It is important to remember to title and label any titles/diagrams to communicate their meaning to the reader and so that you can refer to them again later in the report (e.g. Table 1).
- Remember to be consistent with the rounding of figures. If you start by rounding to 2 decimal places, ensure that you do this for all data you report.
- Avoid repeating any information - if something appears in a table it does not need to appear again in the main body of the text.
Presenting qualitative data
In qualitative studies, your results are often presented alongside the discussion, as it is difficult to include this data in a meaningful way without explanation and interpretation. In the dsicussion section, aim to structure your work thematically, moving through the key concepts or ideas that have emerged from your qualitative data. Use extracts from your data collection - interviews, focus groups, observations - to illustrate where these themes are most prominent, and refer back to the sources from your literature review to help draw conclusions.
Here's an example of how your data could be presented in paragraph format in this section:
Example from 'Reporting and discussing your findings ', Monash University .
What should I include in the discussion section?
The purpose of the discussion section is to interpret your findings and discuss these against the context of the wider literature. This section should also highlight how your research has contributed to the understanding of a phenomenon or problem: this can be achieved by responding to your research questions.
Though the structure of discussion sections can vary, a relatively common structure is offered below:
- State your major findings – this can be a brief opening paragraph that restates the research problem, the methods you used to attempt to address this, and the major findings of your research.
- Address your research questions - detail your findings in relation to each of your research questions to help demonstrate how you have attempted to address the research problem. Answer each research question in turn by interpreting the relevant results: this may involve highlighting patterns, relationships or statistically significant differences depending on the design of your research and how you analysed your data.
- Discuss your findings against the wider literature - this will involve comparing and contrasting your findings against those of others and using key literature to support the interpretation of your results; often, this will involve revisiting key studies from your literature review and discussing where your findings fit in the pre-existing literature. This process can help to highlight the importance of your research through demonstrating what is novel about your findings and how this contributes to the wider understanding of your research area.
- Address any unexpected findings in your study - begin with by stating the unexpected finding and then offer your interpretation as to why this might have occurred. You may relate unexpected findings to other research literature and you should also consider how any unexpected findings relate to your overall study – especially if you think this is significant in terms of what your findings contribute to the understanding of your research problem!
- Discuss alternative interpretations - it’s important to remember that in research we find evidence to support ideas, theories and understanding; nothing is ever proven. Consequently, you should discuss possible alternative interpretations of your data – not just those that neatly answer your research questions and confirm your hypotheses.
- Limitations/weaknesses of your research – acknowledge any factors that might have affected your findings and discuss how this relates to your interpretation of the data. This might include detailing problems with your data collection method, or unanticipated factors that you had not accounted for in your original research plan. Likewise, detail any questions that your findings could not answer and explain why this was the case.
- Future directions (this part of your discussion could also be included in your conclusion) – this section should address what questions remain unanswered about your research problem. For example, it may be that your findings have answered some questions but raised new ones; this can often occur as a result of unanticipated findings. Likewise, some of the limitations of your research may necessitate further work to address a methodological confound or weakness in a tool of measurement. Whatever these future directions are, remember you’re not writing a proposal for this further research; a brief suggestion of what the research should do and how this would address one of the new problems/limitations you have identified is enough.
Here are some final top tips for writing your discussion section:
- Don’t rewrite your results section – remember your goal is to interpret and explain how your findings address the research problem.
- Be clear about what you have found, how this has addressed a gap in the literature and how it changes our understanding of your research problem.
- Structure your discussion in a logical way that highlights your most important/interesting findings first.
- Be careful about how you interpret your data: be wary over-interpreting to confirm a hypothesis. Remember, we can still learn from non-significant research findings.
- Avoid being apologetic or too critical when discussing the limitations of your research. Be concise and analytical.
How do I avoid repetition in the conclusion?
The conclusion is your opportunity to synthesise everything you have done/written as part of your research, in order to demonstrate your understanding.
A well-structured conclusion is likely to include the following:
- State your conclusions – in clear language, state the conclusions from your research. Crucially, this not just restating your results/findings: instead, this is a synthesis of the research problem, your research questions, your findings (and interpretation), and the relevant research literature. From your conclusions, it should be clear to your reader how our understanding of the research topic has changed.
- Discuss wider significance – this is your opportunity to highlight (potential) wider implications of your conclusions. Depending on your discipline, this might include recommendations for policy, professional practice or a tentative speculation about how an academic theory might change given your findings. It is important not to over-generalise here; remember the limitations of your theoretical and methodological choices and what these mean for the applicability of your findings/conclusions. If your discipline encourages reflection, this can be a suitable place to include your thoughts about the research process, the choices you made and how your findings/conclusions might influence your professional outlook/practice going forwards.
- Take home message – this should be a strong and clear final statement that draws the reader’s focus to the primary message of your study. Whilst it’s important to avoid being overly grandiose, this is your closing argument, and you should remind the reader of what your research has achieved.
Ultimately, your conclusion is your final word about the research problem you have investigated; don’t be afraid of emphasising your contribution to the understanding of that problem. Your conclusion should be clear, succinct and provide a summary of everything that has been learned as a result of your research project.
What supervisors expect from their dissertation students:
- to determine the focus and direction of the dissertation, particularly in terms of identifying a topic of interest and research question.
- to work independently to explore literature and research in the chosen topic area.
- to be proactive in arranging supervision meetings, email draft work before meetings for feedback and prepare specific questions and issues to discuss in supervision time.
- to be honest and open about any challenges or difficulties that arise during the research or writing process.
- to bring a problem-solving approach to the dissertation (you are not expected to know all the answers but should show initiative in exploring possible solutions to any problems that might arise).
What you can expect from your supervisor:
- to offer guidance on the best way to structure and carry out a successful research project in the timescale for your dissertation, and to help you to set achievable and appropriate research objectives.
- to act as an expert in your discipline and sounding board for your ideas, and to advise you on the literature search and theoretical background for your project.
- to serve as a 'lifeline' and point of support when the dissertation feels challenging.
- to read your drafts and give feedback in supervision meetings.
- to offer practical advice and strategies for managing your time, securing ethics approval, collecting data and common pitfalls to avoid during the research process.
Making the most of your supervision meetings
Meeting your supervisor can feel daunting at first but your supervision meetings offer a great opportunity to discuss your research ideas and get feedback on the direction of your project. Here are our top tips to getting the most out of time with your supervisor:
- Y ou are in charge of the agenda. If you arrange a meeting with your supervisor, you call the shots! Here are a few tips on how to get the most out of the time with your supervisor.
- Send an email in advance of the meeting , with an overview of the key ideas you want to talk about. This can save time in the meeting and helps to give you some structure to follow. If this isn't possible, run through these points quickly when you first sit down as you introduce the meeting - "I wanted to focus on the literature review today, as I'm having some trouble deciding on the order my key themes and points should be introduced in."
- What do you want to get out of the meeting? Note down any questions you would like the answers to or identify what it is you will need from the meeting in order to make progress on the next stage of your dissertation. Supervision meetings offer the change to talk about your ideas for the project, but they can also be an opportunity to find out practical details and troubleshoot. Don't leave the meeting until you have addressed these and got answers/advice in each key area.
- Trust your supervisor. Your supervisor may not be an expert in your chosen subject, but they will have experience of writing up research projects and coaching other dissertation students. You are responsible for reading up on your subject and exploring the literature - your supervisor can't tell you what to read, but they can give you advice on how to read your sources and integrate them into your argument and writing.
- Choose a short section to discuss in the meeting for feedback - for example, if you're not sure on structure, pick a page or two that demonstrate this, or if you want advice on being critical, find an example from a previous essay where you think you did this well and ask your supervisor how to translate this into dissertation writing.
- Agree an action plan . Work with your supervisor to set a goal for your next meeting, or an objective that you will meet in the week following your supervision. Feeling accountable to someone can be a great motivator and also helps you to recognise where you are starting to fall behind the targets that you've set for yourself.
- Be open and honest . It can feel daunting meeting your supervisor, but supervision meetings aren't an interview where you have to prove everything is going well. Ask for help and advice where you need it, and be honest if you're finding things difficult. A supervisor is there to support you and help you to develop the skills and knowledge you need along the journey to submitting your dissertation.
- << Previous: Quantitative research
- Next: e-learning and books >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.shu.ac.uk/researchprojects

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
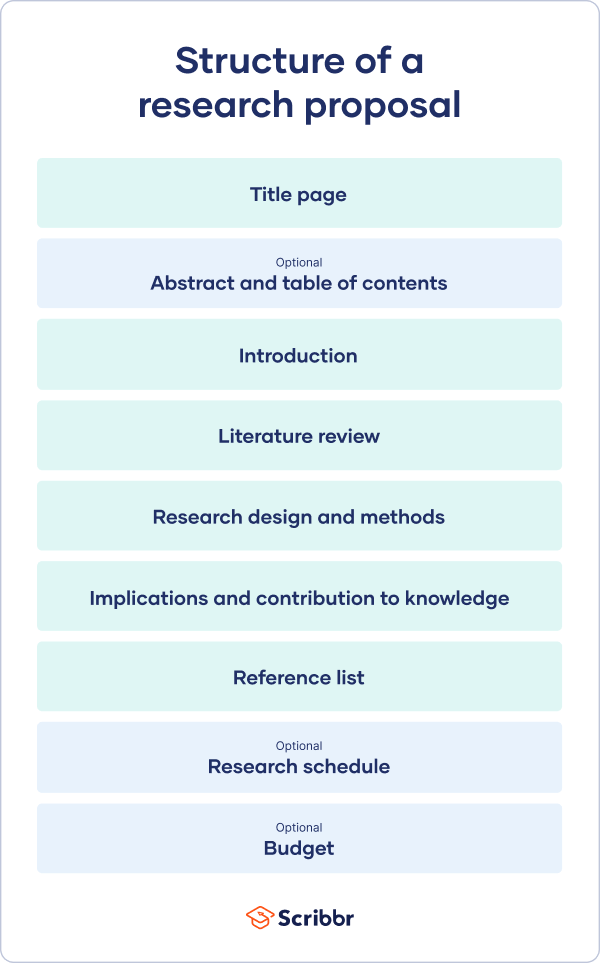
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Get Started With a Research Project
Last Updated: October 3, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Chris Hadley, PhD . Chris Hadley, PhD is part of the wikiHow team and works on content strategy and data and analytics. Chris Hadley earned his PhD in Cognitive Psychology from UCLA in 2006. Chris' academic research has been published in numerous scientific journals. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 311,963 times.
You'll be required to undertake and complete research projects throughout your academic career and even, in many cases, as a member of the workforce. Don't worry if you feel stuck or intimidated by the idea of a research project, with care and dedication, you can get the project done well before the deadline!
Development and Foundation

- Don't hesitate while writing down ideas. You'll end up with some mental noise on the paper – silly or nonsensical phrases that your brain just pushes out. That's fine. Think of it as sweeping the cobwebs out of your attic. After a minute or two, better ideas will begin to form (and you might have a nice little laugh at your own expense in the meantime).

- Some instructors will even provide samples of previously successful topics if you ask for them. Just be careful that you don't end up stuck with an idea you want to do, but are afraid to do because you know someone else did it before.

- For example, if your research topic is “urban poverty,” you could look at that topic across ethnic or sexual lines, but you could also look into corporate wages, minimum wage laws, the cost of medical benefits, the loss of unskilled jobs in the urban core, and on and on. You could also try comparing and contrasting urban poverty with suburban or rural poverty, and examine things that might be different about both areas, such as diet and exercise levels, or air pollution.

- Think in terms of questions you want answered. A good research project should collect information for the purpose of answering (or at least attempting to answer) a question. As you review and interconnect topics, you'll think of questions that don't seem to have clear answers yet. These questions are your research topics.

- Don't limit yourself to libraries and online databases. Think in terms of outside resources as well: primary sources, government agencies, even educational TV programs. If you want to know about differences in animal population between public land and an Indian reservation, call the reservation and see if you can speak to their department of fish and wildlife.
- If you're planning to go ahead with original research, that's great – but those techniques aren't covered in this article. Instead, speak with qualified advisors and work with them to set up a thorough, controlled, repeatable process for gathering information.

- If your plan comes down to “researching the topic,” and there aren't any more specific things you can say about it, write down the types of sources you plan to use instead: books (library or private?), magazines (which ones?), interviews, and so on. Your preliminary research should have given you a solid idea of where to begin.
Expanding Your Idea with Research

- It's generally considered more convincing to source one item from three different authors who all agree on it than it is to rely too heavily on one book. Go for quantity at least as much as quality. Be sure to check citations, endnotes, and bibliographies to get more potential sources (and see whether or not all your authors are just quoting the same, older author).
- Writing down your sources and any other relevant details (such as context) around your pieces of information right now will save you lots of trouble in the future.

- Use many different queries to get the database results you want. If one phrasing or a particular set of words doesn't yield useful results, try rephrasing it or using synonymous terms. Online academic databases tend to be dumber than the sum of their parts, so you'll have to use tangentially related terms and inventive language to get all the results you want.

- If it's sensible, consider heading out into the field and speaking to ordinary people for their opinions. This isn't always appropriate (or welcomed) in a research project, but in some cases, it can provide you with some excellent perspective for your research.
- Review cultural artifacts as well. In many areas of study, there's useful information on attitudes, hopes, and/or concerns of people in a particular time and place contained within the art, music, and writing they produced. One has only to look at the woodblock prints of the later German Expressionists, for example, to understand that they lived in a world they felt was often dark, grotesque, and hopeless. Song lyrics and poetry can likewise express strong popular attitudes.

Expert Q&A

- Start early. The foundation of a great research project is the research, which takes time and patience to gather even if you aren't performing any original research of your own. Set aside time for it whenever you can, at least until your initial gathering phase is complete. Past that point, the project should practically come together on its own. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- When in doubt, write more, rather than less. It's easier to pare down and reorganize an overabundance of information than it is to puff up a flimsy core of facts and anecdotes. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

- Respect the wishes of others. Unless you're a research journalist, it's vital that you yield to the wishes and requests of others before engaging in original research, even if it's technically ethical. Many older American Indians, for instance, harbor a great deal of cultural resentment towards social scientists who visit reservations for research, even those invited by tribal governments for important reasons such as language revitalization. Always tread softly whenever you're out of your element, and only work with those who want to work with you. Thanks Helpful 8 Not Helpful 2
- Be mindful of ethical concerns. Especially if you plan to use original research, there are very stringent ethical guidelines that must be followed for any credible academic body to accept it. Speak to an advisor (such as a professor) about what you plan to do and what steps you should take to verify that it will be ethical. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/research/research_paper.html
- ↑ https://www.nhcc.edu/academics/library/doing-library-research/basic-steps-research-process
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185905
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/using-an-interview-in-a-research-paper
- ↑ https://www.science.org/content/article/how-review-paper
About This Article

The easiest way to get started with a research project is to use your notes and other materials to come up with topics that interest you. Research your favorite topic to see if it can be developed, and then refine it into a research question. Begin thoroughly researching, and collect notes and sources. To learn more about finding reliable and helpful sources while you're researching, continue reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jun 30, 2016
Did this article help you?
Maooz Asghar
Aug 14, 2016
Jun 27, 2016
Calvin Kiyondi
Apr 24, 2017
Nov 2, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
There’s general research planning; then there’s an official, well-executed research plan. Whatever data-driven research project you’re gearing up for, the research plan will be your framework for execution. The plan should also be detailed and thorough, with a diligent set of criteria to formulate your research efforts. Not including these key elements in your plan can be just as harmful as having no plan at all.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project.
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement, devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes, demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:
Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews: this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies: this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting: participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups: use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies: ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys: get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing: tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing: ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project. Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty. But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform

Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Popular searches
- How to Get Participants For Your Study
- How to Do Segmentation?
- Conjoint Preference Share Simulator
- MaxDiff Analysis
- Likert Scales
- Reliability & Validity
Request consultation
Do you need support in running a pricing or product study? We can help you with agile consumer research and conjoint analysis.
Looking for an online survey platform?
Conjointly offers a great survey tool with multiple question types, randomisation blocks, and multilingual support. The Basic tier is always free.
Research Methods Knowledge Base
- Navigating the Knowledge Base
- Foundations
- Measurement
- Research Design
- Key Elements
- Sample Paper
- Table of Contents
Fully-functional online survey tool with various question types, logic, randomisation, and reporting for unlimited number of surveys.
Completely free for academics and students .
So now that you’ve completed the research project, what do you do? I know you won’t want to hear this, but your work is still far from done. In fact, this final stage – writing up your research – may be one of the most difficult. Developing a good, effective and concise report is an art form in itself. And, in many research projects you will need to write multiple reports that present the results at different levels of detail for different audiences.
There are several general considerations to keep in mind when generating a report:
Formatting Considerations
Are you writing a research report that you will submit for publication in a journal? If so, you should be aware that every journal requires articles that you follow specific formatting guidelines. Thinking of writing a book. Again, every publisher will require specific formatting. Writing a term paper? Most faculty will require that you follow specific guidelines. Doing your thesis or dissertation? Every university I know of has very strict policies about formatting and style. There are legendary stories that circulate among graduate students about the dissertation that was rejected because the page margins were a quarter inch off or the figures weren’t labeled correctly.
To illustrate what a set of research report specifications might include, I present in this section general guidelines for the formatting of a research write-up for a class term paper. These guidelines are very similar to the types of specifications you might be required to follow for a journal article. However, you need to check the specific formatting guidelines for the report you are writing – the ones presented here are likely to differ in some ways from any other guidelines that may be required in other contexts.
I’ve also included a sample research paper write-up that illustrates these guidelines. This sample paper is for a “make-believe” research project. But it illustrates how a final research report might look using the guidelines given here.
Cookie Consent
Conjointly uses essential cookies to make our site work. We also use additional cookies in order to understand the usage of the site, gather audience analytics, and for remarketing purposes.
For more information on Conjointly's use of cookies, please read our Cookie Policy .
Which one are you?
I am new to conjointly, i am already using conjointly.
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide [With Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write A Proposal
Writing a Proposal involves several key steps to effectively communicate your ideas and intentions to a target audience. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step:
Identify the Purpose and Audience
- Clearly define the purpose of your proposal: What problem are you addressing, what solution are you proposing, or what goal are you aiming to achieve?
- Identify your target audience: Who will be reading your proposal? Consider their background, interests, and any specific requirements they may have.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant information: Conduct thorough research to support your proposal. This may involve studying existing literature, analyzing data, or conducting surveys/interviews to gather necessary facts and evidence.
- Understand the context: Familiarize yourself with the current situation or problem you’re addressing. Identify any relevant trends, challenges, or opportunities that may impact your proposal.
Develop an Outline
- Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content.
- Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution.
- Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers understand the situation.
- Objectives/Goals: Clearly state the objectives or goals of your proposal.
- Methodology/Approach: Describe the approach or methodology you will use to address the problem.
- Timeline/Schedule: Present a detailed timeline or schedule outlining the key milestones or activities.
- Budget/Resources: Specify the financial and other resources required to implement your proposal.
- Evaluation/Success Metrics: Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points and restate the benefits of your proposal.
Write the Proposal
- Grab attention: Start with a compelling opening statement or a brief story that hooks the reader.
- Clearly state the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you are addressing and explain its significance.
- Present your proposal: Introduce your proposed solution, project, or idea and explain why it is the best approach.
- State the objectives/goals: Clearly articulate the specific objectives or goals your proposal aims to achieve.
- Provide supporting information: Present evidence, data, or examples to support your claims and justify your proposal.
- Explain the methodology: Describe in detail the approach, methods, or strategies you will use to implement your proposal.
- Address potential concerns: Anticipate and address any potential objections or challenges the readers may have and provide counterarguments or mitigation strategies.
- Recap the main points: Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the proposal.
- Reinforce the benefits: Emphasize the positive outcomes, benefits, or impact your proposal will have.
- Call to action: Clearly state what action you want the readers to take, such as approving the proposal, providing funding, or collaborating with you.
Review and Revise
- Proofread for clarity and coherence: Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure a logical flow: Read through your proposal to ensure the ideas are presented in a logical order and are easy to follow.
- Revise and refine: Fine-tune your proposal to make it concise, persuasive, and compelling.
Add Supplementary Materials
- Attach relevant documents: Include any supporting materials that strengthen your proposal, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Appendices: Add any additional information that might be useful but not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Formatting and Presentation
- Follow the guidelines: Adhere to any specific formatting guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
- Use a professional tone and language: Ensure that your proposal is written in a clear, concise, and professional manner.
- Use headings and subheadings: Organize your proposal with clear headings and subheadings to improve readability.
- Pay attention to design: Use appropriate fonts, font sizes, and formatting styles to make your proposal visually appealing.
- Include a cover page: Create a cover page that includes the title of your proposal, your name or organization, the date, and any other required information.
Seek Feedback
- Share your proposal with trusted colleagues or mentors and ask for their feedback. Consider their suggestions for improvement and incorporate them into your proposal if necessary.
Finalize and Submit
- Make any final revisions based on the feedback received.
- Ensure that all required sections, attachments, and documentation are included.
- Double-check for any formatting, grammar, or spelling errors.
- Submit your proposal within the designated deadline and according to the submission guidelines provided.
Proposal Format
The format of a proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements of the organization or institution you are submitting it to. However, here is a general proposal format that you can follow:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization’s name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines.
2. Executive Summary:
- Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
- Summarize the problem, proposed solution, and anticipated benefits.
- Keep it brief and engaging, as this section is often read first and should capture the reader’s attention.
3. Introduction:
- State the problem or issue you are addressing and its significance.
- Provide background information to help the reader understand the context and importance of the problem.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of your proposal.
4. Problem Statement:
- Describe the problem in detail, highlighting its impact and consequences.
- Use data, statistics, or examples to support your claims and demonstrate the need for a solution.
5. Proposed Solution or Project Description:
- Explain your proposed solution or project in a clear and detailed manner.
- Describe how your solution addresses the problem and why it is the most effective approach.
- Include information on the methods, strategies, or activities you will undertake to implement your solution.
- Highlight any unique features, innovations, or advantages of your proposal.
6. Methodology:
- Provide a step-by-step explanation of the methodology or approach you will use to implement your proposal.
- Include a timeline or schedule that outlines the key milestones, tasks, and deliverables.
- Clearly describe the resources, personnel, or expertise required for each phase of the project.
7. Evaluation and Success Metrics:
- Explain how you will measure the success or effectiveness of your proposal.
- Identify specific metrics, indicators, or evaluation methods that will be used.
- Describe how you will track progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed.
- Present a detailed budget that outlines the financial resources required for your proposal.
- Include all relevant costs, such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other expenses.
- Provide a justification for each item in the budget.
9. Conclusion:
- Summarize the main points of your proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and positive outcomes of implementing your proposal.
- Emphasize the value and impact it will have on the organization or community.
10. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as research findings, charts, graphs, or testimonials.
- Attach any relevant documents that provide further information but are not essential to the main body of the proposal.
Proposal Template
Here’s a basic proposal template that you can use as a starting point for creating your own proposal:
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to submit a proposal for [briefly state the purpose of the proposal and its significance]. This proposal outlines a comprehensive solution to address [describe the problem or issue] and presents an actionable plan to achieve the desired objectives.
Thank you for considering this proposal. I believe that implementing this solution will significantly contribute to [organization’s or community’s goals]. I am available to discuss the proposal in more detail at your convenience. Please feel free to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
Yours sincerely,
Note: This template is a starting point and should be customized to meet the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the organization or institution to which you are submitting the proposal.
Proposal Sample
Here’s a sample proposal to give you an idea of how it could be structured and written:
Subject : Proposal for Implementation of Environmental Education Program
I am pleased to submit this proposal for your consideration, outlining a comprehensive plan for the implementation of an Environmental Education Program. This program aims to address the critical need for environmental awareness and education among the community, with the objective of fostering a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Executive Summary: Our proposed Environmental Education Program is designed to provide engaging and interactive educational opportunities for individuals of all ages. By combining classroom learning, hands-on activities, and community engagement, we aim to create a long-lasting impact on environmental conservation practices and attitudes.
Introduction: The state of our environment is facing significant challenges, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. It is essential to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to understand these issues and take action. This proposal seeks to bridge the gap in environmental education and inspire a sense of environmental stewardship among the community.
Problem Statement: The lack of environmental education programs has resulted in limited awareness and understanding of environmental issues. As a result, individuals are less likely to adopt sustainable practices or actively contribute to conservation efforts. Our program aims to address this gap and empower individuals to become environmentally conscious and responsible citizens.
Proposed Solution or Project Description: Our Environmental Education Program will comprise a range of activities, including workshops, field trips, and community initiatives. We will collaborate with local schools, community centers, and environmental organizations to ensure broad participation and maximum impact. By incorporating interactive learning experiences, such as nature walks, recycling drives, and eco-craft sessions, we aim to make environmental education engaging and enjoyable.
Methodology: Our program will be structured into modules that cover key environmental themes, such as biodiversity, climate change, waste management, and sustainable living. Each module will include a mix of classroom sessions, hands-on activities, and practical field experiences. We will also leverage technology, such as educational apps and online resources, to enhance learning outcomes.
Evaluation and Success Metrics: We will employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures to evaluate the effectiveness of the program. Pre- and post-assessments will gauge knowledge gain, while surveys and feedback forms will assess participant satisfaction and behavior change. We will also track the number of community engagement activities and the adoption of sustainable practices as indicators of success.
Budget: Please find attached a detailed budget breakdown for the implementation of the Environmental Education Program. The budget covers personnel costs, materials and supplies, transportation, and outreach expenses. We have ensured cost-effectiveness while maintaining the quality and impact of the program.
Conclusion: By implementing this Environmental Education Program, we have the opportunity to make a significant difference in our community’s environmental consciousness and practices. We are confident that this program will foster a generation of individuals who are passionate about protecting our environment and taking sustainable actions. We look forward to discussing the proposal further and working together to make a positive impact.
Thank you for your time and consideration. Should you have any questions or require additional information, please do not hesitate to contact me at [your email address or phone number].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Writing the Introduction/Background of a Research Article
Writing the introduction and background of a research article can be daunting. Where do you start? What information should you include?
A great place to start is creating an argument structure for why your research topic is relevant and important. This structure should clearly walk the reader through current, relevant literature and lead them to the gap in the literature that your topic fills. To do this I use the following 4-step argument creation structure.
- Create argument funnel questions/statements
- Harvest article quotes that explain/backup each of the argument funnel questions/statements
- Organize article quotes to best support each section of the argument funnel
- Write prose that utilizes the article quotes to progress your argument from most well known to your specific topic
1. Argument Funnel Creation
Create an argument funnel with statements that take the reader form the most well known and widely accepted knowledge connected to my topic down to your specific research topic.
Completed Argument Funnel Example
When creating your funnel statements think about what research exists related to your topic. Where are the gaps in the existing literature? How do you know those are the gaps? If you get stuck, think about the 50,000 ft view of your topic and how you would explain the necessity of your research to people not in your field.
2. Harvesting Article Quotes
Find research articles that pertain to each of your funnel statements to back them up with evidence. As you find the articles put them into a citation manager (e.g., Zotero) now to save yourself time later. While reading the articles, pull (copy and paste) article quotes/excerpts that MAY be relevant. Pull more than you think you need, especially duplicates of the same idea by different authors to strengthen your argument. Store your quotes/excerpts in a document organized by your funnel statements with in-text citations with the page number you pulled it from. The National Academy of Engineering reports can be valuable top of funnel resources.
3. Organizing Article Quotes
Once you have harvested many article quotes for each of your funnel statements, organized them in an order that walks your reader through the literature landscape in a logical way. As you do this assume the reader doesn’t know anything about your topic so start at the beginning. Chronological order is a good place to start but may not always fit your argument. Think about your quotes/excerpts as puzzle pieces, where do they logically fit together?
4. Writing Prose
Now that your article quotes are organized, summarize the quotes in your own voice with appropriate citations. This is the time to begin including transition/connecting words and phrases between summarized quotes to bring your reader through your argument. Don’t forget to include “so what?” sentences and phrases after summarized quotes. In other words don’t only report what other authors said or found, tell the reader why that is important to your argument.
ENGL 2A: Critical Thinking & Writing (Krane)
- Welcome & Hello
- Find Articles
- Extra: Find eBooks
- Extra: Find Newspapers
- Library Workshop Day: 04/30
The Trust Project
https://thetrustproject.org/
Group Activity Part 2
Trust Indicator Worksheet - Complete one worksheet for the group
Warm up Activity (5 min)
Group Activity Part 1
- << Previous: Extra: Find Newspapers
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 1:39 PM
- URL: https://libguides.scu.edu/engl2a_krane
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Hypothesis? Types and Examples

All research studies involve the use of the scientific method, which is a mathematical and experimental technique used to conduct experiments by developing and testing a hypothesis or a prediction about an outcome. Simply put, a hypothesis is a suggested solution to a problem. It includes elements that are expressed in terms of relationships with each other to explain a condition or an assumption that hasn’t been verified using facts. 1 The typical steps in a scientific method include developing such a hypothesis, testing it through various methods, and then modifying it based on the outcomes of the experiments.
A research hypothesis can be defined as a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study. 2 Hypotheses help guide the research process and supplement the aim of the study. After several rounds of testing, hypotheses can help develop scientific theories. 3 Hypotheses are often written as if-then statements.
Here are two hypothesis examples:
Dandelions growing in nitrogen-rich soils for two weeks develop larger leaves than those in nitrogen-poor soils because nitrogen stimulates vegetative growth. 4
If a company offers flexible work hours, then their employees will be happier at work. 5
Table of Contents
- What is a hypothesis?
- Types of hypotheses
- Characteristics of a hypothesis
- Functions of a hypothesis
- How to write a hypothesis
- Hypothesis examples
- Frequently asked questions
What is a hypothesis?

A hypothesis expresses an expected relationship between variables in a study and is developed before conducting any research. Hypotheses are not opinions but rather are expected relationships based on facts and observations. They help support scientific research and expand existing knowledge. An incorrectly formulated hypothesis can affect the entire experiment leading to errors in the results so it’s important to know how to formulate a hypothesis and develop it carefully.
A few sources of a hypothesis include observations from prior studies, current research and experiences, competitors, scientific theories, and general conditions that can influence people. Figure 1 depicts the different steps in a research design and shows where exactly in the process a hypothesis is developed. 4
There are seven different types of hypotheses—simple, complex, directional, nondirectional, associative and causal, null, and alternative.
Types of hypotheses
The seven types of hypotheses are listed below: 5 , 6,7
- Simple : Predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
Example: Exercising in the morning every day will increase your productivity.
- Complex : Predicts the relationship between two or more variables.
Example: Spending three hours or more on social media daily will negatively affect children’s mental health and productivity, more than that of adults.
- Directional : Specifies the expected direction to be followed and uses terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment.
- Non-directional : Does not predict the exact direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship between two variables but rather states the existence of a relationship. This hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or if findings contradict prior research.
Example: Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express.
- Associative and causal : An associative hypothesis suggests an interdependency between variables, that is, how a change in one variable changes the other.
Example: There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health.
A causal hypothesis, on the other hand, expresses a cause-and-effect association between variables.
Example: Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage.
- Null : Claims that the original hypothesis is false by showing that there is no relationship between the variables.
Example: Sleep duration does not have any effect on productivity.
- Alternative : States the opposite of the null hypothesis, that is, a relationship exists between two variables.
Example: Sleep duration affects productivity.

Characteristics of a hypothesis
So, what makes a good hypothesis? Here are some important characteristics of a hypothesis. 8,9
- Testable : You must be able to test the hypothesis using scientific methods to either accept or reject the prediction.
- Falsifiable : It should be possible to collect data that reject rather than support the hypothesis.
- Logical : Hypotheses shouldn’t be a random guess but rather should be based on previous theories, observations, prior research, and logical reasoning.
- Positive : The hypothesis statement about the existence of an association should be positive, that is, it should not suggest that an association does not exist. Therefore, the language used and knowing how to phrase a hypothesis is very important.
- Clear and accurate : The language used should be easily comprehensible and use correct terminology.
- Relevant : The hypothesis should be relevant and specific to the research question.
- Structure : Should include all the elements that make a good hypothesis: variables, relationship, and outcome.
Functions of a hypothesis
The following list mentions some important functions of a hypothesis: 1
- Maintains the direction and progress of the research.
- Expresses the important assumptions underlying the proposition in a single statement.
- Establishes a suitable context for researchers to begin their investigation and for readers who are referring to the final report.
- Provides an explanation for the occurrence of a specific phenomenon.
- Ensures selection of appropriate and accurate facts necessary and relevant to the research subject.
To summarize, a hypothesis provides the conceptual elements that complete the known data, conceptual relationships that systematize unordered elements, and conceptual meanings and interpretations that explain the unknown phenomena. 1

How to write a hypothesis
Listed below are the main steps explaining how to write a hypothesis. 2,4,5
- Make an observation and identify variables : Observe the subject in question and try to recognize a pattern or a relationship between the variables involved. This step provides essential background information to begin your research.
For example, if you notice that an office’s vending machine frequently runs out of a specific snack, you may predict that more people in the office choose that snack over another.
- Identify the main research question : After identifying a subject and recognizing a pattern, the next step is to ask a question that your hypothesis will answer.
For example, after observing employees’ break times at work, you could ask “why do more employees take breaks in the morning rather than in the afternoon?”
- Conduct some preliminary research to ensure originality and novelty : Your initial answer, which is your hypothesis, to the question is based on some pre-existing information about the subject. However, to ensure that your hypothesis has not been asked before or that it has been asked but rejected by other researchers you would need to gather additional information.
For example, based on your observations you might state a hypothesis that employees work more efficiently when the air conditioning in the office is set at a lower temperature. However, during your preliminary research you find that this hypothesis was proven incorrect by a prior study.
- Develop a general statement : After your preliminary research has confirmed the originality of your proposed answer, draft a general statement that includes all variables, subjects, and predicted outcome. The statement could be if/then or declarative.
- Finalize the hypothesis statement : Use the PICOT model, which clarifies how to word a hypothesis effectively, when finalizing the statement. This model lists the important components required to write a hypothesis.
P opulation: The specific group or individual who is the main subject of the research
I nterest: The main concern of the study/research question
C omparison: The main alternative group
O utcome: The expected results
T ime: Duration of the experiment
Once you’ve finalized your hypothesis statement you would need to conduct experiments to test whether the hypothesis is true or false.
Hypothesis examples
The following table provides examples of different types of hypotheses. 10 ,11

Key takeaways
Here’s a summary of all the key points discussed in this article about how to write a hypothesis.
- A hypothesis is an assumption about an association between variables made based on limited evidence, which should be tested.
- A hypothesis has four parts—the research question, independent variable, dependent variable, and the proposed relationship between the variables.
- The statement should be clear, concise, testable, logical, and falsifiable.
- There are seven types of hypotheses—simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative and causal, null, and alternative.
- A hypothesis provides a focus and direction for the research to progress.
- A hypothesis plays an important role in the scientific method by helping to create an appropriate experimental design.
Frequently asked questions
Hypotheses and research questions have different objectives and structure. The following table lists some major differences between the two. 9
Here are a few examples to differentiate between a research question and hypothesis.
Yes, here’s a simple checklist to help you gauge the effectiveness of your hypothesis. 9 1. When writing a hypothesis statement, check if it: 2. Predicts the relationship between the stated variables and the expected outcome. 3. Uses simple and concise language and is not wordy. 4. Does not assume readers’ knowledge about the subject. 5. Has observable, falsifiable, and testable results.
As mentioned earlier in this article, a hypothesis is an assumption or prediction about an association between variables based on observations and simple evidence. These statements are usually generic. Research objectives, on the other hand, are more specific and dictated by hypotheses. The same hypothesis can be tested using different methods and the research objectives could be different in each case. For example, Louis Pasteur observed that food lasts longer at higher altitudes, reasoned that it could be because the air at higher altitudes is cleaner (with fewer or no germs), and tested the hypothesis by exposing food to air cleaned in the laboratory. 12 Thus, a hypothesis is predictive—if the reasoning is correct, X will lead to Y—and research objectives are developed to test these predictions.
Null hypothesis testing is a method to decide between two assumptions or predictions between variables (null and alternative hypotheses) in a statistical relationship in a sample. The null hypothesis, denoted as H 0 , claims that no relationship exists between variables in a population and any relationship in the sample reflects a sampling error or occurrence by chance. The alternative hypothesis, denoted as H 1 , claims that there is a relationship in the population. In every study, researchers need to decide whether the relationship in a sample occurred by chance or reflects a relationship in the population. This is done by hypothesis testing using the following steps: 13 1. Assume that the null hypothesis is true. 2. Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. 3. If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. If the relationship would not be unlikely, accept the null hypothesis.

To summarize, researchers should know how to write a good hypothesis to ensure that their research progresses in the required direction. A hypothesis is a testable prediction about any behavior or relationship between variables, usually based on facts and observation, and states an expected outcome.
We hope this article has provided you with essential insight into the different types of hypotheses and their functions so that you can use them appropriately in your next research project.
References
- Dalen, DVV. The function of hypotheses in research. Proquest website. Accessed April 8, 2024. https://www.proquest.com/docview/1437933010?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals&imgSeq=1
- McLeod S. Research hypothesis in psychology: Types & examples. SimplyPsychology website. Updated December 13, 2023. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.simplypsychology.org/what-is-a-hypotheses.html
- Scientific method. Britannica website. Updated March 14, 2024. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-method
- The hypothesis in science writing. Accessed April 10, 2024. https://berks.psu.edu/sites/berks/files/campus/HypothesisHandout_Final.pdf
- How to develop a hypothesis (with elements, types, and examples). Indeed.com website. Updated February 3, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-hypothesis
- Types of research hypotheses. Excelsior online writing lab. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/research-hypotheses/types-of-research-hypotheses/
- What is a research hypothesis: how to write it, types, and examples. Researcher.life website. Published February 8, 2023. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://researcher.life/blog/article/how-to-write-a-research-hypothesis-definition-types-examples/
- Developing a hypothesis. Pressbooks website. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://opentext.wsu.edu/carriecuttler/chapter/developing-a-hypothesis/
- What is and how to write a good hypothesis in research. Elsevier author services website. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/manuscript-preparation/what-how-write-good-hypothesis-research/
- How to write a great hypothesis. Verywellmind website. Updated March 12, 2023. Accessed April 13, 2024. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-a-hypothesis-2795239
- 15 Hypothesis examples. Helpfulprofessor.com Published September 8, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://helpfulprofessor.com/hypothesis-examples/
- Editage insights. What is the interconnectivity between research objectives and hypothesis? Published February 24, 2021. Accessed April 13, 2024. https://www.editage.com/insights/what-is-the-interconnectivity-between-research-objectives-and-hypothesis
- Understanding null hypothesis testing. BCCampus open publishing. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://opentextbc.ca/researchmethods/chapter/understanding-null-hypothesis-testing/#:~:text=In%20null%20hypothesis%20testing%2C%20this,said%20to%20be%20statistically%20significant
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
Measuring Academic Success: Definition & Strategies for Excellence
What are scholarly sources and where can you find them , you may also like, 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade, paperpal’s new ai research finder empowers authors to..., what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &....

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Develop a structure and outline. With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it's time to move on to planning your actual research paper. It might sound obvious, but it's really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
This describes who the problem affects, why research is needed, and how your research project will contribute to solving it. >>Read more about defining a research problem. Step 3: Formulate research questions. Next, based on the problem statement, you need to write one or more research questions. These target exactly what you want to find out.
Online study guides for every stage of your research project, from planning to writing up. Also includes advice on writing a remote dissertation while social distancing measures are in place.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Briefly put, these are the things you should have on your checklist: 1) Have an idea, 2) turn that idea into a question, and anticipate new questions, 3) identify resources, 4) establish what has already been done (literature review), 5) brainstorm around focused topic, 6) organise ideas, 7) write outline, 8) start filling in the.
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic. To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you ...
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data. You might have to write up a research design as a standalone assignment, or it might be part of a larger research proposal or other project. In either case, you should carefully consider which methods ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Methodology - the methods you will use for your primary research. Findings and results - presenting the data from your primary research. Discussion - summarising and analysing your research and what you have found out. Conclusion - how the project went (successes and failures), areas for future study.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Just be careful that you don't end up stuck with an idea you want to do, but are afraid to do because you know someone else did it before. 4. Think from all angles. If you have at least a little direction based on the project guidelines, take that basic direction and start turning it over and over in your mind.
Start by defining your project's purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language. Thinking about the project's purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section: ... and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental ...
Open in a separate window. First section: Description of the core center, contacts of the investigator/s, quantification of the involved centers. A research protocol must start from the definition of the coordinator of the whole study: all the details of the main investigator must be reported in the first paragraph.
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or 'blueprint' for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project ...
To illustrate what a set of research report specifications might include, I present in this section general guidelines for the formatting of a research write-up for a class term paper. These guidelines are very similar to the types of specifications you might be required to follow for a journal article. However, you need to check the specific ...
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
1. Title Page: Include the title of your proposal, your name or organization's name, the date, and any other relevant information specified by the guidelines. 2. Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of your proposal, highlighting the key points and objectives.
2. Harvesting Article Quotes. Find research articles that pertain to each of your funnel statements to back them up with evidence. As you find the articles put them into a citation manager (e.g., Zotero) now to save yourself time later. While reading the articles, pull (copy and paste) article quotes/excerpts that MAY be relevant.
Step 1: Explain your methodological approach. Step 2: Describe your data collection methods. Step 3: Describe your analysis method. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Tips for writing a strong methodology chapter. Other interesting articles.
Offices and Services at Santa Clara University Campus Safety; Enrollment Services; Campus Ministry; Diversity and Inclusion; Technology at SCU; Recreation
Here are two hypothesis examples: Dandelions growing in nitrogen-rich soils for two weeks develop larger leaves than those in nitrogen-poor soils because nitrogen stimulates vegetative growth.4. If a company offers flexible work hours, then their employees will be happier at work.5.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Step 6: Tie it all together. End your proposal with a conclusion that briefly summarizes the problem, solution, and benefits. Emphasize the significant parts, and make your proposal stand out by ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.