
What is the history of corporate governance and how has it changed?

The history of corporate governance is long, rich and packed with twists and turns. It’s a topic that touches on managerial accountability, board structure and shareholder rights — including both periods of shareholder passivity and shareholder power. Governance began with the rise of corporations, dating back to the East India Company, the Hudson’s Bay Company, the Levant Company and other major chartered companies during the 16th and 17th centuries.
While the concept of corporate governance has existed for centuries, the name didn’t come into vogue until the 1970s. The United States was the only country using the term at the time. The balance of power and decision-making between board directors, executives and shareholders has been evolving for centuries. The issue has been a hot topic among academic experts, regulators, executives, and investors, making corporate governance history critical to understanding why corporate governance is so important .
This article will highlight key milestones in the history of corporate governance, including:
- A complete corporate governance timeline
- The growing emphasis on corporate governance
- The impact of economic activity on corporate governance history
- How technology has influenced modern governance
- Trends that point to the future of corporate governance
Corporate governance history at a glance
The history of corporate governance dates back to World War II when robust economic growth put massive power in the hands of corporate managers. Review a timeline of critical events before diving into each corporate governance evolution in-depth.
World War II - 1980s: Corporate growth emphasizes developing corporate governance
Post-world war ii.
After World War II, the United States experienced strong economic growth, which strongly impacted the history of corporate governance. Corporations were thriving and proliferating. Managers primarily called the shots and expected board directors and shareholders to follow. In most cases, they did. This was an interesting dichotomy since managers highly influenced the selection of board directors. Unless it came to matters of dividends and stock prices, investors tended to steer clear of governance matters.
In the 1970s, corporate governance history began to change as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) brought the issue of corporate governance to the forefront when they brought a stance on official corporate governance reforms. In 1976, the term corporate governance first appeared in the Federal Register, the official journal of the federal government.In the 1960s, the Penn Central Railway diversified by starting pipelines, hotels, industrial parks and commercial real estate. Penn Central filed for bankruptcy in 1970, and the public scrutinized the board. In 1974, the SEC brought proceedings against three outside directors for misrepresenting the company’s financial condition and a wide range of misconduct by Penn Central executives.Around the same time, the SEC caught on to widespread payments by corporations to foreign officials over falsifying corporate records. Corporations formed audit committees and appointed more outside directors during this era. In 1976, the SEC prompted the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) to require each listed corporation to have an audit committee composed of all independent board directors, and they complied. Advocates pushed to get governance right by requiring audit committees, nomination committees, compensation committees and only one managerial appointee.
The 1980s: A corporate governance reform counter-reaction
The 1980s ended the 1970s movement for corporate governance reform due to a political shift to the right and a more conservative Congress. This era brought much opposition to deregulation, another significant change in the history of corporate governance. Lawmakers advanced The Protection of Shareholders’ Rights Act of 1980 , but it stalled in Congress.Debates on corporate governance focused on a new project called the Principles of Corporate Governance by the American Law Institute (ALI) in 1981. The NYSE had previously supported this project but changed their stance after they reviewed the first draft. The Business Roundtable also opposed ALI’s attempts at reform. Advocates for corporations felt they were strong enough to oppose regulatory reform outright without the restrictive ALI-led reforms.
Businesses had concerns about some of the issues in Tentative Draft No. 1 of the Principles of Corporative Governance. The draft recommended that boards appoint mostly independent directors and establish audit and nominating committees. Corporate advocates were concerned that if companies implemented these measures, it would increase liability risks for board directors .Law and economic scholars also heavily criticized the initial ALI proposals. They expressed concerns that the proposals didn’t account for the pressures of the market forces and didn’t consider empirical evidence. In addition, they didn’t believe that fomenting litigation would serve a purpose in advancing effective corporate governance .In the end, the final version of ALI’s Principles of Corporate Governance was so watered down that it had little impact on the history of corporate governance by the time it was approved and published in 1994. Scholars maintained that market mechanisms would keep managers and shareholders aligned.
The ‘Deal Decade’ leads to shareholder activism
The 1980s was also referred to as the ‘Deal Decade.’ Institutional shareholders grabbed more shares, which gave them more control. They stopped selling out when times got tough. Executives went on the defensive and struck deals to prevent hostile takeovers.State legislators countered takeovers with anti-takeover statutes at the state level. That, combined with an increased debt market and an economic downturn, discouraged merger activity. The Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) was formed to help with voting rights. Shareholders fought with legal defenses, but judges often favored corporate decisions when outside directors supported board decisions. Investors started to advocate for more independent directors and to base executive pay on performance rather than corporate size.
2008: Financial crisis changes corporate governance history
By 2007, banks had been taking excessive risks, and there was growing concern about a possible collapse of the world financial system. Governments sought to prevent fallout by offering massive bailouts and other financial measures.
The collapse of the Lehman Brothers Bank developed into a major international banking crisis, which became the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression in the 1930s. Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Act in 2010 to promote economic stability in the United States, a significant milestone in corporate governance history.
2010s: Corporate governance surges as risks are on the rise
The fallout from the financial crisis placed a heavier focus on best practices for corporate governance principles throughout the 2010s. Boards of directors felt more pressure than ever before to implement good governance practices like transparency and accountability. Strong governance principles encouraged corporations to have a majority of independent directors and well-composed, diverse boards. Advancements in technology improved efficiency in governance and created new risks as well. Data breaches were a new and genuine concern for corporations. The first targets were banks and financial institutions. As these institutions have bolstered the security measures in their governance framework , hackers have turned their efforts to smaller corporations within various industries, including governments.
2020s: Global economic uncertainty rattles stakeholders — and the board room
Uncertainty has so far characterized the 2020s, a decade that will surely go down in the history of corporate governance. Kicked off by the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent breakdown of the supply chain, 2020 pushed many Americans to question the purpose of corporations. Global geopolitics like the war in Ukraine and the Israel-Palestine conflict have only further galvanized consumers to press corporations to make a stand.
Many corporations increasingly turned to a stakeholder model of corporate governance , which equally weighs and prioritizes the interests of all people affected by corporate activity — investors, employees, and the communities in which they operate. Consumers’ focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) partly drove that shift, but so did regulations like the SEC’s new Climate Disclosure Rules, which up the ante on accountability .
The 2023 adoption of the universal proxy rules also gave shareholders a new voice in the boardroom. That rule put shareholders’ director nominations on the same proxy card as the corporations’ nominations, affirming shareholders’ power to influence decision-making.
2024: The history of corporate governance in the making
In 2024, boards of corporations and organizations of all sizes are finding that the best way for them to protect themselves, their shareholders and their stakeholders is to use technology to their advantage by taking a centralized approach to governance that helps boards put their best foot forward. However, the history of corporate governance continues to be rewritten. How we define corporate governance will continue to evolve in the coming years. See our list of top corporate governance trends for 2024 and beyond to master the current governance landscape and the changes that may be on the horizon.
Solutions Solutions
- Board Management
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Audit Management
- Market Intelligence
Resources Resources
- Research & Reports
Company Company
Your data matters.

Corporate Governance in America: A Brief History
Entrepreneurial, managerial, and fiduciary capitalism.
In the first part of the twentieth century, large U.S. corporations were controlled by a small number of wealthy entrepreneurs—Morgan, Rockefeller, Carnegie, Ford, and DuPont, to name a few. These “captains of industry” not only owned the majority of the stock in companies, such as Standard Oil and U.S. Steel, but they also exercised their rights to run these companies.
By the 1930s, however, the ownership of U.S. corporations had become much more widespread. Capitalism in the United States had made a transition from entrepreneurial capitalism , the model in which ownership and control had been synonymous, to managerial capitalism , a model in which ownership and control were effectively separated—that is, in which effective control of the corporation was no longer exercised by the legal owners of equity (the shareholders) but by hired, professional managers.
With the rise of institutional investing in the 1970s, primarily through private and public pension funds, the responsibility of ownership became once again concentrated in the hands of a relatively small number of institutional investors who act as fiduciaries on behalf of individuals. This large-scale institutionalization of equity brought further changes to the corporate governance landscape. Because of their size, institutional investors effectively own a major fraction of many large companies. And because this can restrict their liquidity, the de facto may have to rely on active monitoring (usually by other, smaller activist investors) than trading. This model of corporate governance, in which monitoring has become as or more important than trading, is sometimes referred to as fiduciary capitalism . [1]
The 1980s: Takeovers and Restructuring
As the ownership of American companies changed, so did the board-management relationship. For the greater part of the 20th century, when managerial capitalism prevailed, executives had a relatively free rein in interpreting their responsibilities toward the various corporate stakeholders and, as long as the corporation made money and its operations were conducted within the confines of the law, they enjoyed great autonomy. Boards of directors, mostly selected and controlled by management, intervened only infrequently, if at all. Indeed, for the first half of the last century, corporate executives of many publicly held companies managed with little or no outside control.
Example 2.9 – Modern Takeovers
In a recent takeover case, Walt Disney Co. announced it would take over 21st Century Fox at the price of $71.3 billion. The deal unites both companies Marvel franchises and adds Fox’s Deadpool to Disney’s Star Wars in addition to Fox television, FX Networks, and National Geographic. The now smaller Fox Corp. will operate as a stand alone company and retain ownership of a broadcast network and its affiliates as well as Fox News, Fox Business, and Fox Sports. Disney hopes to position itself against increasing competition from Netflix, Amazon, and possibly Apple. Unfortunately, as Disney consolidates its properties thousands of people are likely to lose their jobs.
Source: NPR.org, Disney Officially Owns 21st Century Fox , Zeqing Liu, 2019Sp
In the 1970s and 1980s, however, serious problems began to surface, such as exorbitant executive payouts, disappointing corporate earnings, and ill-considered acquisitions that amounted to little more than empire building, and depressed shareholder value. Led by a small number of wealthy, activist shareholders seeking to take advantage of the opportunity to capture underutilized assets, takeovers surged in popularity. Terms, such as leveraged buyout, dawn raids, poison pills, and junk bonds, became household words, and individual corporate raiders, including Carl Icahn, Irwin Jacobs, and T. Boone Pickens, became well known. The resulting takeover boom exposed underperforming companies and demonstrated the power of unlocking shareholder value.
Of lasting importance from this era was the emergence of institutional investors who knew the value of ownership rights, had fiduciary responsibilities to use them, and were big enough to make a difference. [2] And with the implicit assent of institutional investors, boards substantially increased the use of stock option plans that allowed managers to share in the value created by restructuring their own companies. Shareholder value, therefore, became an ally rather than a threat. [3]
The Meltdown of 2001
The year 2001 will be remembered as the year of corporate scandals. The most dramatic of these occurred in the United States—in companies such as Enron, WorldCom, Tyco, and others—but Europe also had its share, with debacles at France’s Vivendi, the Netherlands’ Ahold, Italy’s Parmalat, and ABB, a Swiss-Swedish multinational company. Even before these events fully unfolded, a rising number of complaints about executive pay, concerns about the displacement of private-sector jobs to other countries through offshoring, and issues of corporate social responsibility had begun to fuel emotional and political reactions to corporate news in the United States and abroad.
Most of these scandals involved deliberately inflating financial results, either by overstating revenues or understating costs, or diverting company funds to the private pockets of managers. Two of the most prominent examples of fraudulent “earnings management” include Enron’s creation of off–balance sheet partnerships to hide the company’s deteriorating financial position and to enrich Enron executives and WorldCom’s intentional misclassification of as much as $11 billion in expenses as capital investments—perhaps the largest accounting fraud in history.
The Enron scandal came to symbolize the excesses of corporations during the long economic boom of the 1990s. [4] Hailed by Fortune magazine as “America’s Most Innovative Company” for six straight years from 1996 to 2001, Enron became one of the largest bankruptcies in U.S. history. Its collapse in December 2001 followed the disclosure that it had reported false profits, using accounting methods that failed to follow generally accepted procedures. Both internal and external controls failed to detect the financial losses disguised as profits for a number of years. At first, Enron’s senior executives, whose activities brought the company to the brink of ruin, escaped with millions of dollars as they retired or sold their company stock before its price plummeted. Enron employees were not so lucky. Many lost their jobs and a hefty portion of retirement savings invested in Enron stock. Because the company was able to hide its losses for nearly five years, the Enron scandal shook the confidence of investors in American governance around the world.
Outside agencies, such as accounting firms, credit rating businesses, and stock market analysts had failed to warn the public about Enron’s business losses until they were obvious to all. Internal controls had not functioned, either. And Enron’s board of directors, especially its audit committee, apparently did not understand the full extent of the financial activities undertaken by the firm and, consequently, had failed in providing adequate oversight. Some experts believed that the federal government also bore some responsibility. Politicians in both the legislative and executive branches received millions of dollars in campaign donations from Enron during the period when the federal government decided to deregulate the energy industry, removing virtually all government controls. Deregulation was the critical act that made Enron’s rise as a $100 billion company possible.
In June 2002, shortly after the Enron debacle, WorldCom admitted that it had falsely reported $3.85 billion in expenses over 5 quarterly periods to make the company appear profitable when it had actually lost $1.2 billion during that period. [5] Experts said it was one of the biggest accounting frauds ever. In its aftermath, the company was forced to lay off about 17,000 workers, more than 20% of its workforce. Its stock price plummeted from a high of $64.50 in 1999 to 9 cents in late July 2002 when it filed for bankruptcy protection. In March 2004, in a formal filing with the SEC, the company detailed the full extent of its fraudulent accounting. The new statement showed the actual fraud amounted to $11 billion and was accomplished mainly by artificially reducing expenses to make earnings appear larger. After restructuring its debt and meeting other requirements imposed by a federal court, the company emerged from bankruptcy protection in April 2004 and formally changed its name to MCI Inc.
Even as it emerged from bankruptcy, industry observers anticipated that MCI would need to merge with another telecommunications firm to compete against larger companies that offered a broader range of telecommunications services. The merger materialized less than a year later, in February 2005, when Verizon Communications Inc. announced its acquisition of MCI for about $6.7 billion in cash, stocks, and dividend payments. MCI ceased to exist as an independent company under the terms of the merger, which was completed in 2006.
As Edwards (2003) notes, these scandals raised fundamental questions about the motivations and incentives of executives and about the effectiveness of existing corporate governance practices, not just in the United States, but globally. What motivated executives to engage in fraud and earnings mismanagement? Why did boards either condone or fail to recognize and stop managerial misconduct and allow managers to deceive shareholders and investors? Why did external gatekeepers, for example, auditors, credit rating agencies, and securities analysts, fail to uncover the financial fraud and earnings manipulation, and alert investors to potential discrepancies and problems? Why were shareholders themselves not more vigilant in protecting their interests, especially large institutional investors? What does this say about the motivations and incentives of money managers? [6]
Because of the significance of these questions and their influence on the welfare of the U.S. economy, the government, regulatory authorities, stock exchanges, investors, ordinary citizens, and the press all started to scrutinize the behavior of corporate boards much more carefully than they had before. The result was a wave of structural and procedural reforms aimed at making boards more responsive, more proactive, and more accountable, and at restoring public confidence in our business institutions. The major stock exchanges adopted new standards to strengthen corporate governance requirements for listed companies; then Congress passed the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, which imposes significant new disclosure and corporate governance requirements for public companies, and also provides for substantially increased liability under the federal securities laws for public companies and their executives and directors; and the SEC adopted a number of significant reforms.
The Financial Crisis of 2008
Just as investor confidence had (somewhat) been restored and the avalanche of regulatory reform that followed the 2001 meltdown digested, a new, even more damaging crisis, global in scale and scope, emerged. While it has not (yet) been labeled as a “corporate governance” crisis, the “financial crisis of 2008” once again raises important questions about the efficacy of our economic and financial systems, board oversight, and executive behavior.
Specifically, as the economic news worsened—rising inflation and unemployment, falling house prices, record bank losses, a ballooning federal deficit culminating in a $10 trillion national debt, millions of Americans losing their homes, a growing number of failures of banks and other financial institutions—CEOs, investors, and creditors are walking away with billions of dollars, while American taxpayers are being asked to pick up the tab (Freddie Mac’s chairman earned $14.5 million in 2007; Fannie Mae’s CEO earned $14.2 million that same year). Ordinary citizens who had seen the value of their 401K investment plans shrink by 40% or more.
Example 2.10 – Financial Regulation
Since 2002, companies in the United States have had to comply with the Sarbanes Oxley Act which requires that executives personally certify their company’s accounts. If the executive misrepresents something they are subject to criminal penalties. External auditors — companies other than ones that maintain record of accounts — must certify the validity of the books.
Source: The Balance, Do Regulations Keep Your Money Safer? , 2019Wi
Certainly, the 2008 crisis was complicated and even ten years later, answers remain evasive. Many believe bankers, central banks, and regulators did indeed mishandle the crisis by failing to foresee the coming disaster and for failing to impose checks and balances on financial institutions. Following the repeal of Glass-Steagall (a rule that separated commercial and investment banking) in 1999, banks needed to find ever more risky vehicles for growth. Many gave risky mortgage loans to people who could not afford them. The central bank ignored warnings signs as the emerging disaster was building up. Regulators were understaffed and overwhelmed to the point where they could not read what was available to them.
While the causes of the crisis will be debated for some time—Did we rely too much on free markets or not enough? Did special interests shape public policy? Did greed rule once again? Where were the boards of Bear Stearns, Lehman Brothers, and AIG? Were regulators asleep at the wheel? Incompetent? One thing is for sure, another wave of regulatory reform—this time possibly global in reach—is around the corner. And once again we will be asking those familiar questions: What will be the impact on investor confidence? On corporate behavior? On boards of directors? On society?
- This section is based on the essay by Hawley and Williams (2001). ↵
- Romano (1994). ↵
- Holmstrom and Kaplan (2003). ↵
- Lindstrom (2008). ↵
- “MCI, Inc.,” Microsoft® Encarta® Online Encyclopedia (2008). ↵
- Edwards (2003). ↵
Strategic Management Copyright © 2020 by John Morris is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 22 January 2019
A literature review of the history and evolution of corporate social responsibility
- Mauricio Andrés Latapí Agudelo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7157-4015 1 ,
- Lára Jóhannsdóttir 1 &
- Brynhildur Davídsdóttir 1
International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility volume 4 , Article number: 1 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
415k Accesses
309 Citations
70 Altmetric
Metrics details
There is a long and varied history associated with the evolution of the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). However, a historical review is missing in the academic literature that portrays the evolution of the academic understanding of the concept alongside with the public and international events that influenced the social expectations with regards to corporate behavior. The aim of this paper is to provide a distinctive historical perspective on the evolution of CSR as a conceptual paradigm by reviewing the most relevant factors that have shaped its understanding and definition, such as academic contributions, international policies and significant social and political events. To do so, the method used is a comprehensive literature review that explores the most relevant academic contributions and public events that have influenced the evolutionary process of CSR and how they have done so. The findings show that the understanding of corporate responsibility has evolved from being limited to the generation of profit to include a broader set of responsibilities to the latest belief that the main responsibility of companies should be the generation of shared value. The findings also indicate that as social expectations of corporate behavior changed, so did the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility. The findings suggest that CSR continues to be relevant within the academic literature and can be expected to remain part of the business vocabulary at least in the short term and as a result, the authors present a plausible future for CSR that takes into consideration its historical evolution. Finally, this paper gives way for future academic research to explore how CSR can help address the latest social expectations of generating shared value as a main business objective, which in turn may have practical implications if CSR is implemented with this in mind.
Introduction
The current belief that corporations have a responsibility towards society is not new. In fact, it is possible to trace the business’ concern for society several centuries back (Carroll 2008 ). However, it was not until the 1930’s and 40’s when the role of executives and the social performance of corporations begun appearing in the literature (Carroll 1999 ) and authors begun discussing what were the specific social responsibilities of companies. In the following decades, the social expectations towards corporate behavior changed and so did the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). The aim of this article is to find out which have been the main factors and/or events that have influenced the evolutionary process of CSR and how they have shaped the understanding of the concept. This will allow to recognize CSR as a concept that reflects the social expectations of each decade and be able to explore if it will remain relevant in the near future.
This review focuses on the most relevant academic publications and historical events that have influenced the evolution of CSR as a conceptual paradigm. The review begins with the historical roots of social responsibility and then explores the early stages of the formal and academic writing about the social responsibilities of corporations and goes through its evolution to the latest understanding of CSR. Considering that the history of CSR is long and vast, it is necessary to point out that this article focuses on publications that have provided an original perspective and understanding to the concept of CSR along with the most significant papers with regards to the evolution of the social expectations of corporate behavior (see Appendix for additional recommended readings). Along with these papers, the review takes into consideration articles that have been cited the most and can be considered as significant contributors to the evolution of the concept as well as publications that provide new definitions and frameworks. It is relevant to point out that this paper will focus on the development of CSR as a definitional construct and will not explore in detail alternative concepts that emerged in the late twentieth century.
This article reviews the key historical events that played a role in the evolution of CSR. In particular, the paper focuses on events that influenced to a certain extent corporations to assume broader social responsibilities Accordingly, this article focuses on the relevant inputs to the definitional construct of the concept, most of which are of Anglo-American character, but it also considers that the growing attention on CSR has been influenced by specific calls for better business practices, such as the European CSR Strategy. As such, this paper does not portray the entire literature on the subject but highlights the key factors that shaped the evolution of CSR. Accordingly, the authors provide a summary of the evolution of the concept through a chronological timeline that allows the reader to follow the history of CSR by pointing out the most relevant academic contributions as well as the most significant events that played a role in shaping it as a conceptual paradigm.
The main contribution of this paper is a structured historical review that is accompanied with a chronological timeline of the evolution of CSR. Accordingly, the article contributes to the literature by exploring how the societal expectations of corporate behavior of each period have influenced the understanding and definitional construct of CSR. Furthermore, this article contributes to the literature on CSR by providing an innovative review of the evolution of the concept that contextualizes its development with a connection to the wider changes happening in each period. This paper also contributes to the current understanding of CSR by including a review of the development of CSR in the early twenty-first century, a period that has not been reviewed as much as earlier periods of the development of the concept.
Research method
The formal publications and literature on CSR begun as early as the 1930’s and continues to be relevant among academic journals, business magazines, books, and reports from international bodies as well as from non-governmental organizations and associations. This means that the literature on the subject is broad and a specific method is needed to achieve a comprehensive review. Given these aspects, the research was carried out following a systematic literature review (SLR) as understood by Okoli and Schabram ( 2010 ) who built on from Fink’s ( 2005 ) definition of a research literature review to define it as a systematic, explicit, comprehensive and reproducible method. The motivation for following a SLR is because it is commonly used to summarize the existing literature and identify gaps, to describe the available body of knowledge to guide professional practice, to identify effective research and development methods, to identify experts within a given field and to identify unpublished sources of information (Fink 2005 ; Okoli and Schabram 2010 ).
The extensive nature of the CSR literature required to limit the scope of the research to thematic areas directly related to the evolution and history of the concept and also limited to publications of academic or institutional character considering that they have already undergone a rigorous peer review that indicates a suitable quality for this SLR. The initial search was conducted for published journal articles using the search words “corporate social responsibility”, “history of CSR” and “evolution of CSR” on the online databases of Science Direct, ProQuest and Web of Science along with the search engine of Google Scholar. The searches were made within the search windows of the website of each database in the titles, abstracts and body of the articles and the results were provided in order of relevance. The first selection was limited to the titles of the publications and was followed by a review of the keywords and abstracts of the preferred articles. To determine the suitability of some of the articles it was necessary to review their introduction and scope. The next step in the selection of articles was focused on their quality and relevance which was determined by reviewing the level of impact factor of the journal of publication as well as the amount of citations the article has had, looking specifically for a high impact factor for each individual paper. Each article was then reviewed to determine its relevance for the research. Some articles pointed to additional references outside the initial search scope which were then searched online for their review. This included business magazines, books, and reports from international bodies and non-governmental organizations and associations. These references were reviewed and selected according to their pertinence and contribution for this paper. Following this systematic strategy allowed to review published journal articles with high impact factors along with publications of relevance mentioned by the authors of such articles. Some publications with regards to CSR had to be excluded from this review because they did not contribute directly to the evolution of the concept but we believe they are of interest in the CSR literature and thus they are listed in Appendix . Finally, the paper is structured in a way that each section corresponds to a particular period making it easier to follow the evolutionary process of CSR.
Historical roots of social responsibility
For Chaffee ( 2017 ), the origins of the social component in corporate behavior can be traced back to the ancient Roman Laws and can be seen in entities such as asylums, homes for the poor and old, hospitals and orphanages. This notion of corporations as social enterprises was carried on with the English Law during the Middle Ages in academic, municipal and religious institutions. Later, it expanded into the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries with the influence of the English Crown, which saw corporations as an instrument for social development (Chaffee 2017 ). In the following centuries, with the expansion of the English Empire and the conquering of new lands, the English Crown exported its corporate law to its American colonies where corporations played a social function to a certain extent Footnote 1 (Chaffee 2017 ).
During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the Christian religious philosophy and approach to the abiding social context were seen as a response to the moral failure of society, which was visible in terms of poverty of the overall population in the English Empire and some parts of Europe (Harrison 1966 ). This religious approach gave way to social reforms and to the Victorian philanthropy which perceived a series of social problems revolving around poverty and ignorance as well as child and female labor (Carroll 2008 ; Harrison 1966 ). The religious roots of the Victorian social conscience gave Victorian Philanthropists a high level of idealism and humanism, and by the late 1800’s, the philanthropic efforts focused on the working class and the creation of welfare schemes with examples that could be seen in practice both in Europe as in the United States of America (USA) (Carroll 2008 ; Harrison 1966 ). A clear case was the creation of the Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA), a movement that begun in London in 1844 with the objective of applying Christian values to the business activities of the time, a notion that quickly spread to the USA (see: Heald 1970 ).
During the late 1800’s and early 1900’s, the creation of welfare schemes took a paternalistic approach aimed at protecting and retaining employees and some companies even looked into improving their quality of life (Carroll 2008 ; Heald 1970 ). For Heald ( 1970 ), there were clear examples that reflected the social sensitivity of businessmen, such as the case of Macy’s in the USA, which in 1875 contributed funds to an orphan asylum and by 1887 labeled their charity donations as Miscellaneous Expenses within their accounting books, and the case of Pullman Palace Car Company which created a model industrial community in 1893 with the aim of improving the quality of life of its employees.
Also during this period, there was a growing level of urbanization and industrialization marked by large-scale production. This brought new concerns to the labor market such as: new challenges for farmers and smalls corporations to keep up with the new interdependent economy, the creation of unions of workers looking for better working conditions, and a middle class worried for the loss of religious and family values in the new industrial society (Heald 1970 ). As a response to these new challenges, and with the aim of finding harmony between the industry and the working force, some business leaders created organizations for the promotion of values and improvement of the working conditions. Such was the case of the Civic Federation of Chicago, an organization created to promote better working conditions and where religious values merged with economic objectives with a sense of civic pride (Heald 1970 ).
By the 1920’s and early 1930’s, business managers begun assuming the responsibility of balancing the maximization of profits with creating and maintaining an equilibrium with the demands of their clients, their labor force, and the community (Carroll 2008 ). This led to managers being viewed as trustees for the different set of external relations with the company, which in turn translated into social and economic responsibilities being adopted by corporations (Carroll 2008 ; Heald 1970 ). Later, with the growth of business during World War II and the 1940’s, companies begun to be seen as institutions with social responsibilities and a broader discussion of such responsibilities began taking place (Heald 1970 ). Some early examples of the debate of the social responsibilities of corporations can be found in The Functions of the Executive by Barnard ( 1938 ) and the Social Control of Business by Clark ( 1939 ).
1950’s and 1960’s: the early days of the modern era of social responsibility
It was not until the early 1950’s that the notion of specifically defining what those responsibilities were was first addressed in the literature and can be understood as the beginning of the modern definitional construct of Corporate Social Responsibility. In fact, it was during the 1950’s and 1960’s that the academic research and theoretical focus of CSR concentrated on the social level of analysis (Lee 2008 ) providing it with practical implications.
The period after World War II and the 1950’s can be considered as a time of adaptation and changing attitudes towards the discussion of corporate social responsibility, but also a time where there were few corporate actions going beyond philanthropic activities (Carroll 2008 ). Perhaps the most notable example of the changing attitude towards corporate behavior came from Bowen ( 1953 ), who believed that the large corporations of the time concentrated great power and that their actions had a tangible impact on society, and as such, there was a need for changing their decision making to include considerations of their impact.
As a result of his belief, Bowen ( 1953 ) set forth the idea of defining a specific set of principles for corporations to fulfill their social responsibilities. For him, the businessman ’s Footnote 2 decisions and actions affect their stakeholders, employees, and customers having a direct impact on the quality of life of society as a whole (Bowen 1953 ). With this in mind, Bowen defined the social responsibilities of business executives as “the obligations of businessmen to pursue those policies, to make those decisions, or to follow those lines of action which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of our society” (Bowen 1953 , p. 6). As Carroll ( 2008 ) explains, it seems that Bowen ( 1953 ) was ahead of his time for his new approach to management which aimed at improving the business response to its social impact and by his contributions to the definition of corporate social responsibility. Furthermore, the relevance of Bowen’s approach relies on the fact that this was the first academic work focused specifically on the doctrine of social responsibility, making Bowen the “Father of Corporate Social Responsibility” (Carroll 1999 ).
After Bowen, other authors were concerned with corporate behavior and its response to the social context of the time. For example, in the book Corporation Giving in a Free Society published in 1956, Eells ( 1956 ) argued that the large corporations of the time were not living up to their responsibility in a time of generalized inflation. In a similar way, with the book A moral philosophy for management published in 1959, Selekman ( 1959 ) explored the evolution of the moral responsibility of corporations as a response to the labor expectations of the time.
These early explorations of CSR as a definitional construct, along with the social context of the time, gave way to a growing interest of scholars to define what CSR was and what it meant (Carroll 2008 ). Naturally, it is understandable that the interest in CSR during 1960’s was influenced by growing awareness in society and social movements of the time. However, it is necessary to point out that the effect of this growing interest was perhaps more visible in the USA, which is why some examples of the following sections might seem to center on this particular country.
Some of society’s main concerns during this period revolved around rapid population growth, pollution, and resource depletion (Du Pisani 2006 ) and were accompanied with social movements with respect to the environment and human and labor rights (Carroll 1999 ). At the same time, books such as The Silent Spring by Carson ( 1962 ) and The Population Bomb by Ehrlich ( 1968 ) begun raising questions with regards to the limits of economic growth and the impact that society and corporations were having on the environment.
During the 1960’s there was also a new social context marked by a growing protest culture that revolved mainly around civil rights and anti-war protests. In the case of the USA, the protests transformed from being student-led sit-ins, walk-outs and rallies, to more radical political activism which, in most cases, saw business corporations as an integral part of the “establishment” they wanted to change (Waterhouse 2017 ). These protests put pressure on companies that, in the protestors’ view, represented the “establishment” (i.e. banks and financial institutions as well large scale corporations) but had a strong focus on those with direct links to war. An example is the case of the Dow Chemical Company which produced napalm used in the Vietnam War and as a result faced constant protests and accusations (Waterhouse 2017 ).
Accordingly, during the 1960’s scholars approached CSR as a response to the problems and desires of the new modern society. A notable example of this period was Keith Davis ( 1960 ), who explained that the important social, economic and political changes taking place represented a pressure for businessmen to re-examine their role in society and their social responsibility. Davis ( 1960 ) argued that businessmen have a relevant obligation towards society in terms of economic and human values, and asserted that, to a certain extent, social responsibility could be linked to economic returns for the firm (Carroll 1999 ; Davis 1960 ). The significance of Davis’ ideas is that he indicated that the “social responsibilities of businessmen need to be commensurate with their social power” (p. 71) and that the avoidance of such would lead to a decrease of the firm’s social power (Davis 1960 ).
Other influential contributors of the time were Frederick ( 1960 ), McGuire ( 1963 ) and Walton ( 1967 ). Frederick ( 1960 ) saw the first half of the twentieth century as an intellectual and institutional transformation that changed the economic and social thinking and brought with it an increased economic power to large scale corporations. To balance the growing power of businessmen, Frederick ( 1960 ) proposed a new theory of business responsibility based on five requirements: 1) to have a criteria of value (in this case for economic production and distribution), 2) to be based on the latest concepts of management and administration, 3) to acknowledge the historical and cultural traditions behind the current social context, 4) to recognize that the behavior of an individual businessmen is a function of its role within society and its social context, and, 5) to recognize that responsible business behavior does not happen automatically but on the contrary, it is the result of deliberate and conscious efforts; then McGuire ( 1963 ), who reviewed the development of business institutions and observed changes in the scale and type of corporations, changes in public policies, and regulatory controls for businesses as well as changes in the social and economic conditions of the time. As a response to these changes, McGuire ( 1963 ) argued that the firm’s responsibility goes beyond its legal and economic obligations, and that corporations should take an interest in politics, the social welfare of the community, and the education and happiness of its employees; and Walton ( 1967 ), who explored the ideological changes taking place during the 1950’s and 60’s which were reflected in public policies, some of which saw corporations as potential contributors to the improvement of the social and economic conditions of the time (see: Walton 1967 ; Walton 1982 ). Accordingly, he provided a definition of social responsibility with which he acknowledged the relevance of the relationship between corporations and society.
It is relevant to point out that even when some scholars begun applying a wider scope to the social responsibilities of corporations, there were others who were skeptical of the notion of CSR. Notably, Milton Friedman, a renowned economist and later a Nobel laurate in economics (1976), gave in 1962 a particular perspective of the role of corporations in a free capitalist system in which firms should limit to the pursuit of economic benefits (see: Friedman 1962 ). Friedman would further explore this notion in the article The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase its Profits published in (Friedman 1970 ) in which he sees CSR activities as an inappropriate use of company’s resources that would result in the unjustifiable spending of money for the general social interest.
Even when the social context of the 1960’s was, to some extent, reflected in the academic approach to CSR, its practical implementation remained mostly with a philanthropic character (Carroll 2008 ). Nonetheless, by the end of the decade the overall social context was reflected in the form of a strong pressure on corporations to behave according to the social expectations of the time, most of which were vividly expressed in protests and environmental and antiwar campaigns (Waterhouse 2017 ).
The 1970’s: CSR and management
The antiwar sentiment, the overall social context, and a growing sense of awareness in society during the late 1960’s translated into a low level of confidence in business to fulfill the needs and wants of the public (Waterhouse 2017 ). In fact, the low level of confidence in the business sector reached a significant point when in 1969 a major oil spill in the coast of Santa Barbara, California led to massive protests across the USA and eventually resulted in the creation of the first Earth Day celebrated in 1970. During the first Earth Day, 20 million people across the USA joined protests to demand a clean and sustainable environment and to fight against pollution, which was caused mainly by corporations (e.g. oil spills, toxic dumps, polluting factories and power plants) (Earth Day 2018 ). The first Earth Day influenced the political agenda of the USA in such a significant manner that it played a role in pushing forward the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) by the end of 1970 (Earth Day 2018 ) and translated into a new regulatory framework that would later influence corporate behavior and create additional responsibilities for corporations.
It is equally important to mention that in the year 1970 there was a recession in the USA that was marked by a high inflation and very low growth followed by a long energy crisis (Waterhouse 2017 ). As a response to this context, and as a result of the social movements of the 1960’s and early 1970’s, the federal government of the USA made significant advances with regards to social and environmental regulations. The most notable examples were the creation of the EPA, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), all of which addressed and formalized to some extent, the responsibilities of businesses with regards to the social concerns of the time (Carroll 2015 ).
Similarly, two relevant contributions from the early 1970’s that responded to the social expectations of the time came from the Committee for Economic Development (CED) of the USA, first with the publication of A New Rationale for Corporate Social Policy which explored to what extent it is justified for corporations to get involved in social problems (Baumol 1970 ) and then with the publication of the Social Responsibilities of Business Corporations which explored the new expectations that society begun placing on the business sector (Committee for Economic Development 1971 ). These publications are of relevance because they advanced the public debate around CSR by acknowledging that “business functions by public consent, and its basic purpose is to serve constructively the needs of society – to the satisfaction of society” (Committee for Economic Development 1971 , p. 11).
As Carroll ( 1999 ) and Lee ( 2008 ) point out, these publications reflect a new rationale with regards to the roles and responsibilities of corporations. Furthermore, the Committee for Economic Development ( 1971 ) acknowledged that the social contract between business and society was evolving in substantial and important ways and specifically noted that: “Business is being asked to assume broader responsibilities to society than ever before and to serve a wider range of human values. Business enterprises, in effect, are being asked to contribute more to the quality of American life than just supplying quantities of goods and services. Inasmuch as business exists to serve society, its future will depend on the quality of management’s response to the changing expectations of the public” (Committee for Economic Development 1971 , p. 16).
The Club of Rome, formed in 1968 by a group of researchers that included scientists, economists and business leaders from 25 different countries, published in 1972 the report The Limits to Growth (World Watch Institute n.d. ), a study led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) which questioned the viability of continued growth and its ecological footprint (The Club of Rome 2018 ). The report became of relevance for the international community because it brought the attention towards the impact of population growth, resource depletion and pollution, and pointed out the need of responsible business practices and new regulatory frameworks.
The 1970’s saw the creation of some of today’s most renowned companies with respect to social responsibility. Such is the case of the Body Shop, which was created in 1976 in the United Kingdom and Ben & Jerry’s founded in 1978 in the USA. Whether as a response to the new social expectations, a new regulatory framework, or due to a first-mover strategy, these are two notable examples of companies that begun formalizing and integrating policies that addressed the social and public issues of the time, and as a result the 1970’s entered into what Carroll ( 2015 , p. 88) called an era of “managing corporate social responsibility”. This meant that the term Corporate Social Responsibility became increasingly popular which resulted in its use under many different contexts and to such an extent that its meaning became unclear, and as a consequence it meant something different for everybody (Sethi 1975 ; Votaw 1973 ).
For instance, for Preston and Post ( 1975 ), corporations have a public responsibility that is limited by clear boundaries, meaning that anything outside is not an obligation for the firm and explained that going beyond those limits offers no clear direction for achieving the company’s main goals and can translate into an inefficient re-orientation of activities. In fact, Preston and Post stated that companies are not responsible for improving social conditions or addressing social problems and argued that a firm’s responsibility extends only to the direct consequences of their decisions and activities in which they engage (Preston and Post 1975 ). A different perception came from Sethi ( 1975 ), for whom social responsibility entails that corporate behavior should be coherent with the social norms, values and expectations, and as a result it should be prescriptive.
The unrestricted use of the term Corporate Social Responsibility during the 1970’s created an uncertainty with regards to its definition. This lasted until 1979, when Carroll proposed what is arguably the first unified definition of Corporate Social Responsibility stating that: “The social responsibility of business encompasses the economic, legal, ethical, and discretionary expectations that society has of organizations at a given point in time” (Carroll 1979 , p. 500). Even when Carroll’s ( 1979 ) approach to social responsibility corresponded to the discussion on corporate behavior of the time, and was mainly driven by the social movements of the 1960’s and the new legislations in the USA, its relevance relies on the fact that his definition builds on from the work of other scholars (including the CED) to provide a clear and concise conceptualization that could be applicable under any context, which was not the case of previous definitions of CSR (see previous definitions from: Davis 1973 ; Frederick 1960 ; M. Friedman 1962 ; McGuire 1963 ; Walton 1967 ). Another relevant contribution of Carroll’s understanding of CSR is that it does not see the economic and social objectives as incompatible trade-offs but rather as an integral part of the business framework of total social responsibility (Lee 2008 ).
During the 1970’s, the understanding of CSR was influenced by social movements and new legislations. This was reflected in the academic publications which provided companies with an approach that looked into how to comply with the new responsibilities that have been given to them by the new legislations that now covered environmental aspects as well as product safety, and labor rights (Carroll 2008 ). This gave way to the 1980’s where the discussion revolved on the ways for implementing CSR.
The 1980’s: the operationalization of CSR
During the 1970’s, there were a growing number of legislations that attended the social concerns of the time and gave a broader set of responsibilities to corporations. By contrast, during the 1980’s the Reagan and Thatcher administrations brought a new line of thought into politics with a strong focus on reducing the pressure on corporations and aiming to reduce the high levels of inflation that the USA and the United Kingdom (UK) were facing (see: Feldstein 2013 ; Wankel 2008 ). For Reagan and Thatcher, the growth and strength of the economies of their countries depended on their ability to maintain a free market environment with as little as possible state intervention (Pillay 2015 ). To do so, Reagan’s main economic goals focused on reducing the regulations on the private sector complemented with tax reductions (Feldstein 2013 ).
With governments reducing their role in regulating corporate behavior, managers were faced with a need to answer to different interest groups that still expected corporations to fulfill the social expectations of the time. Notably, the reduced regulatory framework led scholars to look into business ethics and the operationalization of CSR as a response to groups such as shareholders, employees and consumers, and the term stakeholder became common (Carroll 2008 ; Wankel 2008 ). However, scholars also begun looking into alternative or complementary concepts to CSR, some of which include corporate social performance, corporate social responsiveness, and stakeholder theory and management (Carroll 2008 ). For the purpose of this paper we will continue to focus our attention on the development of CSR as a definitional construct.
In 1980, Thomas M. Jones ( 1980 ) was arguably the first author to consider CSR as a decision making process that influence corporate behavior. Jones’ ( 1980 ) contribution gave way to a new area of debate around CSR which focused more on its operationalization than on the concept itself. This translated into the creation of new frameworks, models, and methods aimed at evaluating CSR from an operational perspective. Some notable examples of the 1980’s came from Tuzzolino and Armandi ( 1981 ), who presented a need-hierarchy framework through which the company’s socially responsible performance can be assessed based on five criteria (profitability, organizational safety, affiliation and industry context, market position and competitiveness, and self-actualization); Strand ( 1983 ), who proposed a systems model to represent the link between an organization and its social responsibility, responsiveness and responses and who identified internal and external effects of company’s behavior; Cochran and Wood ( 1984 ), who used the combined Moskowitz list Footnote 3 , a reputation index, to explore the relation between CSR and financial performance; and Wartick and Cochran ( 1985 ) who reorganized Carroll’s understanding of CSR (1979) into a framework of principles, processes, and social policies.
Perhaps the best way to understand the operationalization approach to CSR during the 1980’s is by keeping in mind that during this time there were new societal concerns. Notably, these concerns can be observed in a series of events that reflected the approach of the international community towards sustainable development and to a certain extent, to corporate behavior. The most relevant include: the creation of the European Commission’s Environment Directorate-General (1981), the establishment of the World Commission on Environment and Development chaired by the Norwegian Prime Minister Gro Harlem Brundtland (1983), the Chernobyl nuclear disaster (1986), the publication of the report Our Common Future presented by the Brundtland Commission which provided a definition of sustainable development (1987), the United Nations (UN) adoption of the Montreal Protocol (1987), and the creation of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (1988).
Even when these events did not relate directly to CSR, and hence did not influence directly the evolution of the concept, they reflected a growing sense of awareness of the international community with regards to environmental protection and sustainable development, and indirectly to corporate behavior. In fact, for Carroll ( 2008 ), the most relevant societal concerns and expectations of corporate behavior during the 1980’s revolved around “environmental pollution, employment discrimination, consumer abuses, employee health and safety, quality of work life, deterioration of urban life, and questionable/abusiveness practices of multinational corporations” (p. 36). As Carroll ( 2008 ) explained, this context gave way for scholars to begin looking into alternative themes, and during the 1980’s the concepts of business ethics and stakeholder management became part of the business vocabulary being part of a wider discussion around the corporate behavior of the time.
The 1990’s: globalization and CSR
During the 1990’s, significant international events influenced the international perspective towards social responsibility and the approach to sustainable development. The most relevant include: the creation of the European Environment Agency (1990), the UN summit on the Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro which led to the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development, the adoption of Agenda 21 and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) (1992), and the adoption of the Kyoto Protocol (1997). The creation of these international bodies and the adoption of international agreements represented international efforts for setting higher standards with regards to climate-related issues and, indirectly to corporate behavior (see: Union of Concerned Scientists 2017 ).
The 1990’s were no exception to the growing interest in CSR, and in fact, it was during this decade that the concept gained international appeal, perhaps as the result of the international approach to sustainable development of the time in combination to the globalization process taking place. As Carroll ( 2015 ) explained, during the 1990’s the globalization process increased the operations of multinational corporations which now faced diverse business environments abroad, some of them with weak regulatory frameworks. For these global corporations it meant new opportunities that came along with a rising global competition for new markets, an increased reputational risk due to a growth in global visibility, and conflicting pressures, demands, and expectations from the home and the host countries (Carroll 2015 ).
Many multinational corporations understood that being socially responsible had the potential to be a safe pathway to balance the challenges and opportunities of the globalization process they were experiencing and as a result, the institutionalization of CSR became stronger (Carroll 2015 ). The most notable example of the institutionalization of CSR was the foundation in 1992 of the association Business for Social Responsibility (BSR) which initially included 51 companies with the vision of a becoming a “force for positive social change - a force that would preserve and restore natural resources, ensure human dignity and fairness, and operate transparently” (Business for Social Responsibility 2018 , para. 2).
The European Commission (EC) also played a relevant role in encouraging the implementation of CSR and begun promoting it as early as 1995 when 20 business leaders adopted the European Business Declaration against Social Exclusion in response to the EC’s call to combat social exclusion and unemployment (CSR Europe n.d. ). This resulted 1 year later, in the launch of the European Business Network for Social Cohesion (later renamed CSR Europe) which gathered business leaders with the aim of enhancing CSR within their organizations (CSR Europe n.d. ).
Even when the institutionalization of CSR grew stronger in the 1990’s, the concept itself didn’t evolve as much (Carroll 1999 ). Nevertheless, there are three contributions to CSR that are relevant to point out: Donna J. Wood ( 1991 ), driven by what she saw as a need for a systematical integration of conceptual aspects into a unified theory, built on the models of Carroll ( 1979 ) and Wartick and Cochran ( 1985 ) to create a model of Corporate Social Performance (CSP). Wood ( 1991 ) defined three dimensions of CSP: first, the principles of Corporate Social Responsibility, which include legitimacy (institutional level), public responsibility (organizational level), and managerial discretion (individual level). Second, she defined the processes of corporate social responsiveness as environmental assessment, stakeholder management, and issues management. Third, she specified the outcomes of corporate behavior as social impacts, social programs, and social policies. As a result, Wood’s model (1991) was broader and more comprehensive than the ones presented earlier by Carroll ( 1979 ) and Wartick and Cochran ( 1985 ), and its relevance relies on its contextualization of aspects of CSR within the business-social interaction by emphasizing explicitly the outcomes and performance of firms (Carroll 1999 ).
Also in 1991, Carroll ( 1991 ) presented the “Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility” with the aim of providing a useful approach to CSR for the executives that needed to balance their commitments to the shareholders with their obligations to a wider set of stakeholders which originated from the new governmental bodies and regulations of the USA, mainly from the establishment of the EPA, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) (Carroll 1991 ). With the Pyramid of CSR, Carroll ( 1991 ) represented what he defined as the four main responsibilities of any company: 1) the economic responsibilities which are the foundation for the other levels of the pyramid; 2) the legal responsibilities of the firm; 3) the ethical responsibilities that shape the company’s behavior beyond the law-abiding duties, and; 4) the philanthropic responsibilities of the corporation with regards to its contribution to improve the quality of life of society. Besides the graphical representation of CSR in terms of responsibilities , Carroll ( 1991 ) asserted that a firm should be a good corporate citizen , a concept that he would develop further at the end of the 1990’s (see: Carroll 1998 ).
The third notable contribution of the 1990’s to the concept came from Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ), who aimed to find evidence to link CSR to a positive financial performance of the firm, and by doing so they were arguably the first to evaluate the benefits of the strategic implementation of CSR. For them, CSR can be used with a strategic approach with the aim of supporting the core business activities and as a result improve the company’s effectiveness in achieving its main objectives (Burke and Logsdon 1996 ).
Moreover, Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ) identified five dimensions of strategic CSR which, for them, are essential for achieving the business objectives as well as for value creation:1) centrality, which represents how close or fit is CSR to the company’s mission and objectives; 2) specificity, which represents the ability to gain specific benefits for the firm; 3) proactivity, in terms of being able to create policies in anticipation of social trends; 4) voluntarism, explained as the discretionary decision making process that is not influenced by external compliance requirements, and; 5) visibility, which refers to the relevance of the observable and recognizable CSR for internal and external stakeholders (Burke and Logsdon 1996 ). Furthermore, Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ) argued that the implementation of strategic CSR through these five dimensions would translate into strategic outcome in the form of value creation that can be identifiable and measurable, but limited to economic benefits for the firm.
Another key contribution to the debate around corporate behavior came from the concept of “The Triple Bottom Line”, first conceived by Elkington in 1994 as a sustainability framework that balances the company’s social, environmental and economic impact. Later, Elkington ( 1998 ) explained that the way to achieve an outstanding triple bottom line performance (social, environmental, and economic) is through effective and long-term partnerships between the private and public sectors, and also among stakeholders. The triple bottom line concept became popular in the late 1990’s as a practical approach to sustainability and it has remained relevant in the CSR discussion because it indicates that corporations need to have socially and environmental responsible behavior that can be positively balanced with its economic goals. Footnote 4
As mentioned before, the globalization process of the 1990’s increased the global reach of multinational corporations and capitalism expanded rapidly, which meant that corporations began having concerns with regards to competitiveness, reputation, global visibility and an expanded network of stakeholders (Carroll 2015 ). This gave way to alternative subjects such as stakeholder theory (see: Donaldson and Preston 1995 ; Freeman 1994 ), corporate social performance (see: Swanson 1995 ), and corporate citizenship (see: Carroll 1998 ). The introduction of new themes, even when almost all of them were consistent with, and built on the existing CSR definitions and understanding (Carroll 1999 ), created an uncertainty with regards to the definition of CSR to the extent that the concept ended up having “unclear boundaries and debatable legitimacy” (Lantos 2001 , p. 1). This meant that by the end of the 1990’s there was a lack of a globally accepted definition of CSR (Lantos 2001 ), which was accompanied by a social and institutional impetus for making companies become good corporate citizens (see: Carroll 1998 ).
2000’s: recognition and implementation of CSR
The decade of the 2000’s is divided in two sections due to the amount of relevant events around CSR. The first section is focused on the recognition and expansion of CSR and its implementation, while the second section is focused on the strategic approach to CSR provided by the academic publications of the time.
The debate around CSR has been brought forward several times by public figures. Footnote 5 Such was the case of President Reagan who, with the aim of stimulating the economy and generating economic growth in the 1980’s, called upon the private sector for more responsible business practices and emphasized that corporations should take a leading role in social responsibility (Carroll 2015 ). During the 1990’s, it was President Clinton who brought the attention towards the notion of corporate citizenship and social responsibility with the creation of the Ron Brown Corporate Citizenship Award for companies that were good corporate citizens (Carroll 1998 ).
However, it was not until 1999 that CSR gained global attention with the landmark speech of then Secretary General of the United Nations, Kofi Annan, who at the World Economic Forum said: “I propose that you, the business leaders gathered in Davos, and we, the United Nations, initiate a global compact of shared values and principles, which will give a human face to the global market” (United Nations Global Compact n.d. , para. 5). As a result, the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) was launched on July 2000 gathering 44 global companies, 6 business associations, and 2 labor and 12 civil society organizations (United Nations Global Compact n.d. ). Notably, the idea behind the creation of the UNGC was to create an instrument that would fill the gaps in governance of the time in terms of human rights and social and environmental issues and to insert universal values into the markets (United Nations Global Compact n.d. ).
Perhaps the most notable achievement of the UNGC was the definition of ten principles that guide the corporate behavior of its members, who are expected to incorporate them into their strategies, policies and procedures with the aim of creating a corporate culture of integrity with long term aims (United Nations Global Compact n.d. ). Even when the UNGC was never directly linked to CSR, it can be understood that the ten principles, with their focus on human rights, labor, environment, and anti-corruption, brought the global attention towards social responsibility.
It was also in the year 2000 when the United Nations adopted the Millennium Declaration with its eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and set the international agenda for the following 15 years. Even when the MDGs and the debate around them was not directly linked to CSR, the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) pointed it out as a framework for the UN – private sector cooperation with the aim of achieving its goals (Murata n.d. ) and as a result the global recognition of the concept became stronger.
The promotion of CSR as a distinct European strategy begun 1 year after the adoption of the MDGs and the creation of the UNGC, when the EC presented a Green Paper called Promoting a European framework for Corporate Social Responsibility (2001) which derived from the new social expectations and concerns of the time, including the growing concern about the environmental impact of economic activities (Commission of the European Communities 2001 ). Notably, the Green Paper presented a European approach to CSR that aimed to reflect and be integrated in the broader context of international initiatives such as the UNGC (Commission of the European Communities 2001 ). This was the first step towards the European Strategy on CSR adopted in 2002 and since then, the EC has led a series of campaigns for promoting the European approach to CSR which derives from the understanding that CSR is: “the responsibility of enterprises for their impacts on society and outlines what an enterprise should do to meet that responsibility” (European Commission 2011 , para. 2).
Between 2001 and 2004 the EC held a series of conferences for discussing CSR (“What is CSR” in Brussels, “Why CSR” in Helsinki, and “How to promote and implement CSR” in Venice) which resulted in its adoption as a strategic element for the Plan of the General Direction of Business of the European Commission (Eberhard-Harribey 2006 ). Accordingly, in 2005 the EC launched the “European Roadmap for Businesses – Towards a Competitive and Sustainable Enterprise” that outlined the European objectives with regards to CSR for the following years (CSR Europe n.d. ). In practical terms, these events translated into a unified vision and understanding of CSR that would be promoted around European businesses.
In 2011, the EC published the renewed European Union (EU) strategy for CSR for the years 2011–2014 followed by a public consultation in 2014 with regards to its achievements, shortcomings, and future challenges. The 2014 consultation showed that 83% of the respondents believed that the EC should continue engaging in CSR policy and 80% thought that CSR played an important role for the sustainability of the EU economy (European Commission 2014a ). In 2015, the EC held a multi-stakeholder forum on CSR which concluded that the Commission should continue to play an important role in the promotion of CSR and help embed social responsibility into company’s strategies (European Commission 2015 ).
In 2015, CSR Europe launched the Enterprise 2020 Manifesto which aimed to set the direction of businesses in Europe and play a leading role in developing an inclusive sustainable economy (CSR Europe 2016 ) and can be understood as a response to the EU Strategy on CSR as well as to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. The Manifesto is perhaps the most relevant contribution from CSR Europe in the second half of the 2010’s mainly because it has a strategic approach that aims to ensure value creation for its stakeholders through the 10,000 companies reached through its network (CSR Europe 2016 ). The Manifesto focuses on the generation of value on five key areas: 1) societal impact through the promotion of responsible and sustainable business practices; 2) membership engagement and satisfaction which is meant to guarantee the continuity in the work of CSR Europe to achieve its mission and societal impact; 3) financial stability; 4) employee engagement focused on the investment of individual development as well as organizational capacity, and; 5) environmental impact assessment to determine areas of improvement (CSR Europe 2016 ).
The global recognition of CSR has also been influenced by international certifications designed to address social responsibility. Such is the case of the ISO 26000 which history can be traced to 2002 when the Committee on Consumer Policy of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) proposed the creation of CSR guidelines to complement the quality and environmental management standards (ISO 9001 and ISO 14001) (ISO n.d.-a ). A working group led by Brazil and Sweden collaborated with stakeholders and National Standards Bodies for a period of 5 years (2005–2010) and came up with the approved ISO 26000 – Social Responsibility in September 2010 (ISO n.d.-a ).
The development of the ISO 26000 is of relevance for the CSR movement not only because it serves as a guideline for the way in which businesses can operate in a socially responsible way, but more so because it was developed by 450 experts of 99 countries and 40 international organizations and so far it has been adopted by more than 80 countries as a guideline for national standards (ISO n.d.-b , n.d.-c ).
2000’s: strategic approach to CSR
Beyond the institutional and public influence in the implementation of CSR, the 2000’s saw relevant contributions to the concept through the academic literature. In the early years of the twenty-first century, Craig Smith ( 2001 ) explained that corporate policies had changed as a response to public interest and as a result this often had a positive social impact. This meant that the scope of social responsibility (from a business perspective) was now inclusive to a broader set of stakeholders and a new definition was set forward: “Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to the obligations of the firm to its stakeholders – people affected by corporate policies and practices. These obligations go beyond legal requirements and the firm’s duties to its shareholders. Fulfillment of these obligations is intended to minimize any harm and maximize the long-run beneficial impact of the firm on society” (Smith 2001 , p. 142).
Smith’s definition of CSR (2001) gave hints of the need of making CSR part of a company’s strategic perspective in order to be able to fulfill its long term obligations towards society. This was reaffirmed by Lantos ( 2001 ) that same year, who pointed out that during the twenty-first century society would demand corporations to make social issues part of their strategies (see also: Carroll 1998 ).
In fact, Lantos ( 2001 ) built on from Smith’s definition of CSR and included strategic considerations to his own understanding of the concept concluding that: “CSR entails the obligation stemming from the implicit ‘social contract’ between business and society for firms to be responsive to society’s long-run needs and wants, optimizing the positive effects and minimizing the negative effects of its actions on society” (Lantos 2001 , p. 9). Accordingly, Lantos ( 2001 ) explained that CSR can become strategic when it is part of the company’s management plans for generating profits, which means that the company would take part in activities that can be understood as socially responsible only if they result in financial returns for the firm and not necessarily fulfilling a holistic approach such as the triple bottom line.
The way Lantos ( 2001 ) explained the boundaries of CSR was arguably the first time the term strategic was inherently linked to CSR. Since then, the literature on CSR begun including strategic traits to the concept and some academics (see: Husted and Allen 2007 ; Porter and Kramer 2006 ; Werther and Chandler 2005 ) begun using the term Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility (SCSR). During the early 2000’s, Freeman ( 2001 ) and A. L. Friedman and Miles ( 2002 ) provided a new perspective to stakeholder theory which reinforced the belief that corporations should be managed in the benefit of a broader set of stakeholders. Freeman ( 2001 ) argued that corporations have a responsibility towards suppliers, consumers, employees, stockholders and the local community and as a result should be managed accordingly while A. L. Friedman and Miles ( 2002 ) defined that the relation between corporations and their stakeholders is dynamic and has different levels of influence on the firm. With this new perspective, Freeman ( 2001 ) and A. L. Friedman and Miles ( 2002 ) contributed to the CSR evolution by reinforcing the belief that corporations are responsible to a broader set of stakeholder than before.
Marrewijk ( 2003 ) presented an overview of the concepts of CSR and Corporate Sustainability in which he recognized this novel perspective towards CSR. Marrewijk ( 2003 ) explained this new societal approach to CSR as a strategic response to the new corporate challenges which, as he explained, are an outcome of the evolution of the roles and responsibilities of each sector of society [emphasis added]. For Marrewijk ( 2003 ), firms respond to their challenges by adopting different levels of integration of CSR into a company’s structure, a topic that is still discussed in the literature.
Accordingly, Marrewijk ( 2003 ) gave five interpretations to his concept of Corporate Sustainability, which he recognized as the contemporary understanding of CSR. These interpretations can be understood as the level of integration of CSR into the company’s policies and structure. The holistic interpretation provided by Marrewijk ( 2003 ) is perhaps the most relevant for the purpose of this paper because it represents the full integration of CSR motivated by the search for sustainability in the understanding that companies have a new role within society and consequently have to make strategic decisions to adapt to its social context.
The strategic response that companies make to their evolving social context was further explored by Werther and Chandler ( 2005 ) who, with their first work published together, focused on the implementation of strategic CSR as part of brand management in order to achieve and maintain legitimacy in a context of globalized brands. The relevance of their work relies on the emphasis placed on the shift of social responsibility by transforming “CSR from being a minimal commitment … to becoming a strategic necessity” (Werther and Chandler 2005 , p. 319).
Furthermore, Werther and Chandler ( 2005 ) claimed that an effective integration of SCSR must come from a “genuine commitment to change and self-analysis” (p. 322) and must be done with a top-down approach throughout the company’s operations for it to translate into a sustainable competitive advantage. Even when their approach to SCSR focused mainly on the competitiveness and legitimacy of companies, their main contribution comes from explicitly claiming CSR as a strategic necessity and thus making it indispensable for any corporation.
One year afterwards, Porter and Kramer ( 2006 ) built on the notion that companies can achieve a competitive advantage through SCSR and explained that corporations can address their competitive context through a strategic approach that results in the creation of shared value in terms of benefits for society while improving the firm’s competitiveness. For Porter and Kramer ( 2006 ), a company should first look inside out to map the social impact of its value chain and identify the positive and negative effect of its activities on society and then focus on the ones with the greatest strategic value. Then, the firm should look outside in to understand the influence of their social context on their productivity and on the execution of its business strategy (Porter and Kramer 2006 ). This way, corporations would be able to understand its interrelationship with their social environment and be able to adapt its business strategies (Porter and Kramer 2006 ).
The work of Porter and Kramer ( 2006 ) provided a new understanding of SCSR as a way to maximize the interdependence between business and society through a holistic approach to the company’s operations and offered an explanation of the advantages of using SCSR as a holistic business framework instead of a limited goal-oriented perspective. In fact, Porter and Kramer ( 2006 ) argued that if CSR is used without a holistic approach and only focused on certain objectives (e.g. CSR used as a tool for achieving the social license to operate, or for achieving and maintaining a reputational status, or for addressing stakeholder satisfaction) it limits the company’s potential to create social benefits while supporting their business goals.
The notion of creating value through SCSR was reinforced by Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) who performed a survey of Spain’s largest firms by number of employees with the aim of finding out the main strategic dimensions that companies consider essential for generating value through SCSR. To do so, Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) built on four of the five dimensions of strategic CSR established by Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ) to then provide their own definition of SCSR as the company’s ability to: “1) provide a coherent focus to a portfolio of firm resources and assets (centrality); 2) anticipate competitors in acquiring strategic factors (proactivity); 3) build reputation advantage through customer knowledge of firm behavior (visibility); 4) ensure that the added value created goes to the firm (appropriability)” (Husted and Allen 2007 , p. 596). It is important to highlight that Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) left out the concept of voluntarism proposed by Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ) from their definition of strategic CSR but pointed out its relevance as a key dimension in CSR for the creation of value.
Based on the five dimensions of CSR established by Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ), Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) surveyed 110 top managers of Spain’s largest companies and found out that visibility, appropriability, and voluntarism were considered the main strategic dimensions of CSR that can be linked to the creation of value (even when voluntarism is not part of their definition of SCSR). Their findings show that visibility, in terms of the presence of CSR on the media as well as a positive image of the company, can be linked to the creation of value through increased customer loyalty and the attraction of new customers, as well as developing new areas of opportunity for products and markets (Husted and Allen 2007 ). With regards to appropriability, the way in which the company manages to retain the value created, Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) pointed out that the surveyed companies designed their CSR policies with the aim of creating value, but such value seems to be limited to the economic benefits of the companies themselves and not necessarily for all their stakeholders. Finally, Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) acknowledged voluntarism, the strategic management of socially-oriented policies going beyond legal requirements, as a key aspect for the creation of value. Nevertheless, their findings show that the surveyed firms were not implementing CSR policies beyond the legal requirements which might be the consequence of the intangibility and immeasurability of such activities (Husted and Allen 2007 ).
Furthermore, the most relevant contributions provided by Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) to the concept of SCSR are twofold: first, SCSR generates new areas of opportunity through the constant drive for creating value, which in turns results in innovation. Second, implementing SCSR with the aim of creating value is inevitably linked to social demands. However, Husted and Allen ( 2007 ) pointed out that the surveyed companies looked into the generation of value with a perspective limited the economic benefits of the corporations themselves and not necessarily for all their stakeholders which raises the question if those companies were in fact implementing CSR with a holistic approach.
The belief of achieving competitive advantage and creating value through SCSR was further developed by Heslin and Ochoa ( 2008 ) who claimed that even when SCSR practices are most effective when they are tailor made, they still follow common principles. To prove their hypothesis, Heslin and Ochoa ( 2008 ) analyzed 21 exemplary CSR practices and observed that seven common principles guide the strategic CSR approach of the selected companies: cultivate the needed talent, develop new markets, protect labor welfare, reduce the environmental footprint, profit from by-products, involve customers, and green the supply chain.
The relevance of the principles proposed by Heslin and Ochoa ( 2008 ) comes from the belief that companies can improve their business opportunities while they provide benefits to the social context in which they operate. For instance, to cultivate the needed talent is explained as the need of companies to foster and retain qualified and skilled employees which result in better and more stable career opportunities (Heslin and Ochoa 2008 ). Likewise, the strategic relevance of the protection of labor welfare relies not only on the prevention of child labor but on the creation of innovative solutions for the company-specific social context Footnote 6 (Heslin and Ochoa 2008 ).
The exemplary SCSR practices presented by Heslin and Ochoa ( 2008 ) provide an insight of the potential benefits of SCSR for creating shared value, for the companies themselves, their stakeholders, and the social context in which the firms operate. Based on the work of Heslin and Ochoa ( 2008 ), it would seem that at least for some of the globally renowned companies, the belief of generating shared value became a driver for integrating global and complex issues into the company’s SCSR policies. Then, by the end of the 2000’s SCSR was understood as having the potential for generating shared value and for addressing social concerns.
2010’s: CSR and the creation of shared value
The concept of creating shared value was further developed by Porter and Kramer ( 2011 ) who explained it as a necessary step in the evolution of business and defined it as: “policies and operating practices that enhance the competitiveness of a company while simultaneously advancing the economic and social conditions in the communities in which it operates. Shared value creation focuses on identifying and expanding the connections between societal and economic progress” (Porter and Kramer 2011 , p. 2).
For Porter and Kramer ( 2011 ), the need for Creating Shared Value (CSV) is in part the result of the conventional narrow-viewed business strategies which usually don’t take into account the broad factors that influence their long term success. Notably, Porter and Kramer ( 2011 ) place CSR into this category seeing it as an outdated and limited concept that has emerged as a way for improving company’s reputation, and as a consequence, they claim that CSV should replace CSR.
Perhaps Porter and Kramer’s ( 2011 ) most relevant contribution comes from the claim that “the purpose of the corporation must be redefined as creating shared value” (p. 2) and by pointing out that the first step to do so is the identification of the societal needs as well as the benefits or harms that the business embodies through its products. Accordingly, Porter and Kramer ( 2011 ) established three ways for creating shared value: by reconceiving products and markets, by redefining productivity in the value chain, and by creating supportive industry clusters where the company operates.
Even when Porter and Kramer ( 2011 ) did not contribute directly to the concept of CSR, they called for a change in the business strategies which, in their opinion, should now focus on generating shared valued as a main objective. This perspective of the creation of shared value is evident on what Leila Trapp ( 2012 ) called the third generation of CSR, which she explained as the moment in which corporations reflect their concerns about social and global issues on their activities, even when some of those concerns might not be directly linked to their core business. Even when this might seem similar to the philanthropic responsibilities of companies, defined as the fourth level of the Pyramid of CSR proposed by Carroll ( 1991 ), it is in fact rooted on a different understanding of the roles of corporations within their social context.
For Carroll ( 1991 ), companies which engage on activities to improve the social context in which they operate are doing so with a philanthropic perspective that is discretionary and voluntary, and as a result, this perspective is less relevant than the other three categories proposed in the Pyramid of CSR. In contrast, Trapp ( 2012 ) built on the historical understanding of CSR proposed by Marrewijk ( 2003 ) to explain what she called the third generation of CSR as an outcome of the evolution of the roles and responsibilities of each sector of society in which the private, public and social sectors have become increasingly interdependent. Then, the third generation of CSR proposed by Trapp ( 2012 ) can be understood as the result of corporations acknowledging and assuming their new roles and responsibilities towards society.
Trapp ( 2012 ) exemplified the third generation of CSR through a case study of Vattenfall, the Swedish state-owned energy company that in 2008 launched a CSR-backed stakeholder engagement campaign focused on climate change mitigation. The case study showed that even when Vattenfall’s campaign addressed clear social and global issues (climate change), it still reflected typical business objectives (in this case creating an interest in the company’s environmental effort and creating a brand image linked to the fight to climate change that would be a first-mover competitive advantage) (Trapp 2012 ). With this, Trapp ( 2012 ) contributed to the concept of CSR by exemplifying the new roles and responsibilities that corporations are willing to take in order to generate shared value.
In the third edition of Chandler and Werther’s book Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility (2013), the authors acknowledged the relevance of creating shared value, a constant in the previous editions, and highlighted its significance by modifying the subtitle of the book from Stakeholders in a Global Environment to the new version Stakeholders, Globalization, and Sustainable Value Creation . In fact, in the third edition of the book Chandler and Werther ( 2013 ) claim that SCSR has the potential for generating sustainable value and that the first step to do so is by identifying the social problems for which the company can create a market-based solution in an efficient and socially responsible way.
Later, in the fourth and most recent edition of the book, Chandler ( 2016 ) reflects on the evolution of CSR and its growing acceptance as central to the company’s strategic decision making as well as to their day-to-day operations. What is evident from this edition, is that Chandler ( 2016 ) understands the generation of sustainable value as one of the main objectives of SCSR. In fact, the subtitle of the fourth edition, Sustainable Value Creation , summarizes Chandler’s ( 2016 ) new perspective on SCSR in which “value creation cannot be avoided…[instead] it must be embraced” (p. xxvii). A key aspect to point out is that Chandler ( 2016 ) builds from the work of Porter and Kramer ( 2006 ) to conclude that “the firm creates the most value when it focuses on what it does best, which is defined by its core operations” (p. 250).
A key contribution from Chandler and Werther ( 2013 ) is their definition of SCSR which is the result of their exploration of CSR and their pragmatic approach to its effective implementation. Chandler and Werther ( 2013 ) defined SCSR as: “The incorporation of a holistic CSR perspective within a firm’s strategic planning and core operations so that the firm is managed in the interests of a broad set of stakeholders to achieve maximum economic and social value over the medium to long term.” (p. 65). In the fourth edition of the book, Chandler ( 2016 ) presents a slightly modified definition which reflects his new perspective on the generation of value: “The incorporation of a holistic CSR perspective within a firm’s strategic planning and core operations so that the firm is managed in the interests of a broad set of stakeholders to optimize value [emphasis added] over the medium to long term” (Chandler 2016 , p. 248).
Perhaps Chandler and Werther’s (2006; 2010; 2013) most valuable contribution comes from their particular perspective on the implementation of Strategic CSR, which in the fourth edition of the book written by Chandler ( 2016 ) builds from the previous publications to encompass five major components instead of the four proposed in previous editions: first, the complete incorporation of the CSR perspective into the company’s strategic planning process and their corporate culture; second, the understanding that all the company’s actions are directly related to the core operations; third, the belief that companies seek to understand and be responsive to their stakeholders’ needs, which means that the incorporation of a stakeholder perspective is a strategic necessity; fourth, the company passes from a short term perspective to a mid and long term planning and management process of the firm’s resources which is inclusive of its key stakeholders, and; fifth (the new component), firms aim to optimize the value created (Chandler 2016 ; Chandler and Werther 2013 ).
The new component of SCSR, the optimization of value , reinforces Chandler’s ( 2016 ) updated perspective in which the maximization of profit, or tradeoffs, is no longer an acceptable objective. Instead, companies should aim at optimizing value over the long term by focusing on their areas of expertise and by doing so there would be a reorientation of efforts towards the creation of shared value instead of profit maximization (Chandler 2016 ). To do so, an essential aspect of SCSR is the integration of the five components into a corporate framework that sets the parameters for the decision making process as well as their integration into the corporate culture with clear guiding values (Chandler 2016 ). This reflects Chandler’s ( 2016 ) belief that SCSR should be part of the day-to-day operations in order for it to be successful, a notion constantly highlighted by him through his articles and books. Then, the explicit call for the full immersion of SCSR into a company’s corporate culture, decision making process, and day-to-day operations is yet another relevant contribution from Chandler and Werther’s work (Chandler 2016 ; Chandler and Werther 2013 ).
In 2015, Carroll resumed his work on CSR with an overview of the evolution of the concept which complemented his literature review of 1999 and of 2010 (see: Carroll 1999 ; Carroll and Shabana 2010 ), but this time he looked at the competing and complementary concepts that have become part of the modern business vocabulary. Carroll ( 2015 ) reviewed the concepts of stakeholder engagement and management, business ethics, corporate citizenship, corporate sustainability, and the creation of shared value and concluded that all of them are interrelated and overlapping. Notably, Carroll ( 2015 ) pointed out that all of these concepts have been incorporated into CSR which is the reason why he defines it as the benchmark and central piece of the socially responsible business movement (see: Chandler and Werther 2013 ; Heslin and Ochoa 2008 ; Trapp 2012 ).
The year 2015 can be considered as the most relevant in the decade because the 15 years to follow after it will be marked by the Paris Agreement, the launch of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, and the adoption of seventeen Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) which represent a “shared vision of humanity and a social contract between the world’s leaders and the people” (Ban 2015 , para. 1). Even when the SDGs do not represent any commitments for the private sector, the countries that adopt them will have to create specific policies and regulations that will translate into pressure for firms to implement new business practices or to improve their current ones. This is particularly relevant considering that the SDGs cover a wide range of areas, from climate change to the eradication poverty and hunger, as well as the fostering of innovation and sustainable consumption. Beyond that, the SDGs are interconnected, which means that addressing one particular goal can involve tackling issues of another one (UNDP 2018 ).
Considering that the SDGs do not represent any commitments for the private sector, it is relevant to mention that the EU law, through the Directive 2014/95/EU, requires large companies of public interest (listed companies, banks, insurance companies, and other companies designated by national authorities as public-interest entities) to disclose non-financial and diversity information beginning on their 2018 reports and onwards (European Commission 2014b ; n.d. ). The Directive is of interest to this paper because it derives from the European Parlamient’s acknowledgement of the vital role of the divulgation of non-financial information within the EC’s promotion of CSR and as a result can be expected to have an impact on the expansion of CSR reporting within the EU as well as with the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI).
This context presents an opportunity for CSR and SCSR to continue growing in terms of conceptualization and implementation, mainly because businesses can adopt it as a strategic framework with the objective of creating shared value (see: Chandler 2016 ). The expansion is particularly notable within the academic literature where it is possible to see that since 2010 the number of academic publications around CSR has increased considerably (see Table 1 ). As can be seen in Table 1 , in the case of Science Direct, the publications more than doubled from 1097 in the year 2010 to 2845 in 2017 (2.59 times) while in Web of Science they almost quadrupled passing from 479 to 1816 in the same years (3.79 times). In the case of ProQuest the publications increased considerably from 2010 to 2016 passing from 5715 to 8188, but decreased to 5670 in 2017. It is also important to notice that the years 2015 and 2016 had the highest amount of publications around CSR this far. It is also relevant to observe that the number of publications declined after 2015 for Science Direct and after 2016 for Proquest, while for Web of Science the amount kept growing.
The increase in the number of publications is not necessarily linked to the launch of the SDGs, but it shows that the concept has remained relevant after the year 2015, when the Paris Agreement called for a change from business as usual to new business frameworks. A key point to mention is that looking into the newest academic publications available since 2015 it is possible to see that most of these revolve around the implementation of CSR and its impact on specific areas of performance in some way related to the SDGs but do not necessarily contribute to the definitional construct or the evolution of the concept (for example see: Benites-Lazaro and Mello-Théry 2017 ; Chuang and Huang 2016 ; Kao et al. 2018 ).
The aim of this paper is to provide a distinctive historical perspective on the evolution of CSR as a conceptual paradigm through a literature review of the academic contributions to the concept as well as the most relevant factors that have shaped its understanding and definition. As the review shows, the development of the modern understanding of CSR as a definitional construct is long and varied and can be traced as far back to the 1930’s when the debate around the social responsibilities of the private sector begun. However, it was in the 1950’s when Bowen ( 1953 ) defined what those responsibilities were by explaining that the social responsibility of business executives was to make decisions according to the values of society and provided what was perhaps the first academic definition of CSR. During the 1960’s, the academic literature brought forward a new understanding of the concept in which it acknowledged the relevance of the relationship between corporations and society (see: Davis 1960 ; Frederick 1960 ; Walton 1967 ), yet, this perspective remained limited to concerns of employee satisfaction, management and the social welfare of the community and focused mainly on the generation of economic profit.
The 1970’s were influenced by the social momentum of the time in which there was a growing sense of awareness with regards to the environment and human and labor rights which led to higher social expectations of corporate behavior. As a result, a new rationale was brought forward by the Committee for Economic Development ( 1971 ) of the USA based on the premise that the social contract between business and society was evolving and that the private sector was expected to assume broader social responsibilities than before. As a consequence, CSR became increasingly popular during the 1970’s but remained discretionary and with a limited focus on aspects such as waste management, pollution and human and labor rights. Its growing popularity led to the unrestricted use of the term CSR under different contexts and by the end of the decade the concept became unclear and meant something different for everyone.
Perhaps the first unified definition of CSR was presented in 1979 by Carroll ( 1979 ), who placed specific responsibilities and expectations (economic, legal, ethical and discretionary) upon corporations and who understood the economic and social objectives of firms as an integral part of a business framework and not as incompatible aspects. This gave way to the debate around the operationalization of CSR during the 1980’s and into the early 1990’s which brought forward a new understanding of the concept as a decision making process (see: Jones 1980 ) and was accompanied by the proposal of models and frameworks for its implementation (see: Cochran and Wood 1984 ; Strand 1983 ; Tuzzolino and Armandi 1981 ). In 1991, Carroll ( 1991 ) presented the “Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility” to represent what he defined as the four main responsibilities of any company and explicitly placing specific responsibilities on corporations. It was also during this period when the adoption of international agreements on sustainable development reflected, to a certain extent, a growing a sense of awareness with respect to the impact of corporate behavior (e.g. the creation of the World Commission on Environment and Development in 1983, the UN adoption of the Montreal Protocol in 1987, the creation of the IPCC in 1988, the creation of the European Environmental Agency in 1990 and the UN summit on the Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro which translated into the adoption of the Agenda 21 and the UNFCCC in 1992). This represented a change in the understanding of CSR and as a result, international organizations and companies alike saw CSR as a way to balance the challenges and opportunities of the time and its institutionalization begun spreading globally.
In 1996, Burke and Logsdon ( 1996 ) argued that the strategic use of CSR can result in identifiable and measurable value creation in the form of economic benefits for the firm and presented an innovative perspective that gave way to the debate around the strategic implementation of CSR during the late 1990’s. It was also during this period that alternative subjects gained attention such as stakeholder theory, corporate social performance and corporate citizenship, and even when they were consistent with the prevailing CSR understanding, their use created an uncertainty with regards to the definition of CSR and by the end of the decade the concept lacked a globally accepted definition and unclear boundaries (as explained by Lantos 2001 ).
In the year 2000, the adoption of the MDGs and the creation of the UNGC gave a new dimension to the understanding of social responsibility in which broader responsibilities were placed on corporations, mainly in terms of human and labor rights, environment, anti-corruption and sustainable development. As a result, international institutions, such as the EC, saw in CSR a pathway for addressing the new corporate challenges, which translated into a wider recognition of the concept during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
The definitions of CSR of the 2000’s reflected the belief that corporations had a new role in society in which they need to be responsive to social expectations and should be motivated by the search for sustainability, which meant they would have to make strategic decisions to do so (see: Husted and Allen 2007 ; Porter and Kramer 2006 ; Werther and Chandler 2005 ). This opened the discussion around the benefits of strategic CSR and by the early 2010’s it was believed that companies can generate shared value while improving the firm’s competitiveness through a holistic implementation of SCSR.
In the decade of the 2010’s, the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals adopted in 2015, reflected a new social contract in which corporations are expected to play a relevant role in the global efforts to achieve the SDGs. Since then, the literature around CSR has focused on its implementation and its impact on specific areas of performance which can be linked to a certain extent to the SDGs while the understanding of CSR has remained centered on its potential to generate shared value.
At this point in the paper, it is relevant to visualize the most significant academic contributions to the evolution of Corporate Social Responsibility as a conceptual paradigm. To do so, Fig. 1 provides a chronological timeline that highlights the publications that have played a relevant role in modifying the understanding and definition of CSR. It is important to notice that the figures are based on this literature review and do not attempt to represent all the contributions to the evolution of the academic understanding of CSR but only to provide a visual synthesis.
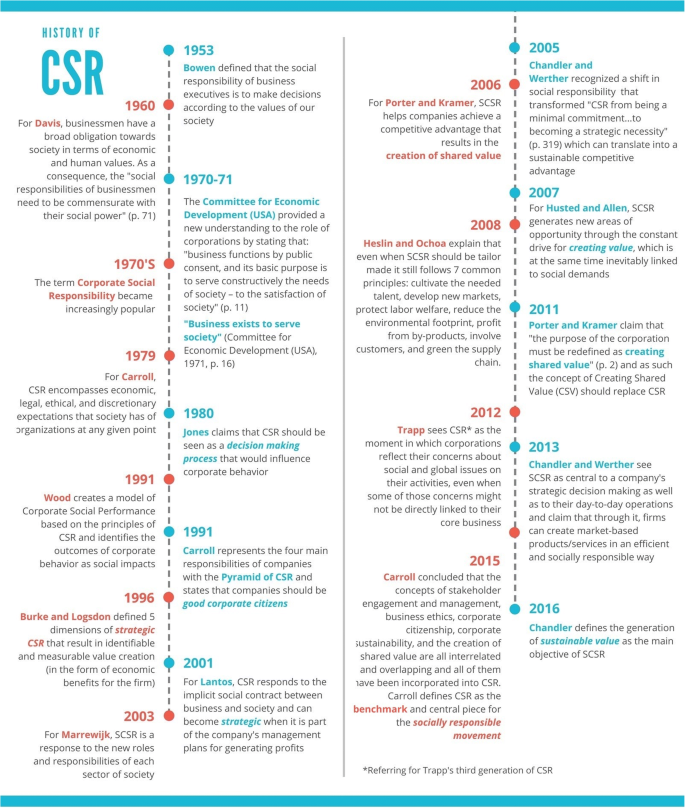
Evolution of the academic understanding of CSR. Source: Developed by the authors as a synthesis of the academic literature
As can be seen in Fig. 1 , the social responsibilities placed upon corporations have evolved from being merely acknowledged in the early publications to being explicitly defined. Perhaps more relevant is the fact that the discussion around what those responsibilities are still continues to this day. Another key aspect that can be visualized with Fig. 1 is that the understanding of CSR evolved from being a personal decision of businessmen in the 1950’s to be understood as decision making process in the 1980’s and to be perceived as a strategic necessity by the early 2000’s. Notably, the purpose of existence of corporations has also evolved from being limited to the generation of economic profits in the 1950’s and 60’s to the belief that business exists to serve society as pointed out in the 1970’s and to the belief in the 2010’s that the purpose of corporations should be to generate shared value.
With Figs. 2 and 3 it is possible to visualize the evolution of CSR from a holistic perspective. The relevance of these figures comes from placing the events that played a significant role in shaping the understanding of CSR within the evolutionary process of the concept, some of them linked to the sustainable development agenda. This graphic synthesis of the evolutionary process of CSR is helpful for observing that the CSR understanding has been influenced by academic publications, governmental decisions (such as the creation of legislations and entities), social movements, public figures, and international movements. More so, from this graphic representation it is possible to observe that the understanding of social responsibility is dynamic and responds to social expectations of corporate behavior.

Visual history of CSR (Part 1 of 2). Source: Developed by the authors based on this literature review. Note: the size of the circles is a subjective representation of the level of influence each aspect had on the evolution of CSR. Hence, a bigger circle represents a higher level of influence
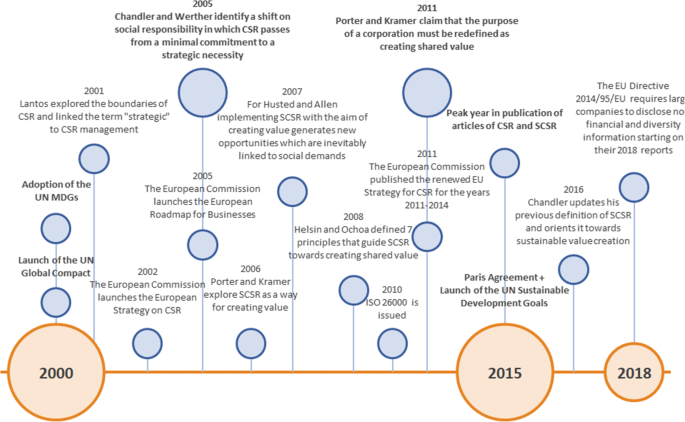
Visual history of CSR (Part 2 of 2). Source: Developed by the authors based on this literature review. Note: the size of the circles is a subjective representation of the level of influence each aspect had on the evolution of CSR. Hence, a bigger circle represents a higher level of influence
The aim of this paper was to provide a distinctive historical perspective on the evolution of CSR which was fulfilled through an exhaustive literature review that shows that the definition and concept of Corporate Social Responsibility has evolved from being limited to the generation of profits to the belief that companies should focus on generating shared value. From the review, it would seem that the evolution of the concept can be linked not only to academic contributions, but also to society’s expectations of corporate behavior. Even when this is not entirely evident across the history of the concept, there are specific cases in which the understanding of CSR clearly reflects the social expectations of the time. A notable example is the publication of A New Rationale for Corporate Social Policy and the Social Responsibilities of Business Corporations by the Committee for Economic Development ( 1971 ) of the USA which were followed by the creation of governmental institutions as a clear response to the social momentum and social demands of corporate behavior of the time. Since then, the definitions and understanding of CSR evolved for the most part in a pragmatic way according to social expectations. For example, during the 1990’s society placed broader responsibilities upon corporations when the international community adopted international agreements with regards to sustainable development and as a response, the debate around CSR centered on its strategic implementation to address the social concerns of the time but still with a limited focus on the economic benefits of the firm. In a similar way, during the early 2000’s the debate around SCSR reflected the new roles and responsibilities placed on corporations by the international community which called on the private sector to play a role in addressing the MDGs and by 2006 it was believed that SCSR could help companies achieve a competitive advantage through the creation of shared value. This belief, of creating shared value through SCSR, is perhaps the most relevant example of how the understanding of CSR reflects the social expectations of the time. The way in which Porter and Kramer ( 2011 ) proposed the creation of shared value to become the main purpose of corporations seems to be fitting to the social expectations of corporate behavior of the 2010’s as well as by those set later by the SDGs adopted in 2015.
From this review it is possible to see ties between some of the events of the sustainable development agenda and the evolution of CSR. These ties are not evident along all the history of CSR, but can be clearly seen in two specific and relevant cases, both of them cases in which events influenced the understanding and evolution of CSR: 1) In the early 1970’s the federal government of the USA established the EPA, the CPSC, the EEOC and the OSHA through which it addressed and formalized to some extent, the social and environmental responsibilities of businesses in response to the social concerns of the time. Years later, Carroll ( 1991 ) presented the Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility with the objective of providing business executives a pragmatic approach to their new obligations to a wider set of stakeholders, obligations that originated from the creation of the EPA, CPSC, EEOC and OSHA. It is then evident that one of the most significant contributions to the literature, Carroll’s Pyramid of CSR, was a direct response to the creation of governmental bodies and regulations, which responded to the social expectations of the time. 2) The promotion of CSR as a specific European strategy begun with the publishing in 2001 of the Green Paper called Promoting a European framework for Corporate Social Responsibility which intended to reflect the broader context of international initiatives, particularly in line with the UNGC. Then, it is clear that the UNGC had a direct influence on the Green Paper which later became the basis for the European Strategy on CSR adopted in 2002 which in turn played a role in shaping the perception and implementation of CSR in Europe. Perhaps these two examples are isolated cases in which specific international events had a direct influence on the understanding and implementation of CSR, but they show that the evolution of CSR can be influenced by international events and not only by academic contributions.
Conclusions
The theoretical contributions of this paper to the literature on CSR begin by providing a distinct historical review of the evolution of the academic understanding of the concept along with the public and international events that played a role in shaping social expectations with regards to corporate behavior. A key contribution comes from the chronological timeline established through the paper with which it is possible to observe the way the concept evolved, an aspect that can be clearly visualized through the figures presented by the authors. As a literature review, the paper is limited to the academic publications that refer directly to CSR as well as to information regarding those events that have influenced to some extents the social expectations of corporate behavior. The findings show that there is a link between social expectations of corporate behavior and the way in which CSR is understood and implemented and opens room for future research. From this review it is possible to see that the literature on CSR seems to be lacking specific research with regards to how to address the core business activities through CSR and seems to point out a reason why CSR can be implemented only partially and even may raise questions about its potential benefits. Beyond that, this paper has practical contributions that can be used as the basis for exploring how CSR can address the latest social expectations of generating shared value as a main business objective, which can translate into practical implications if CSR is implemented with the objective of creating shared value, a topic that only few authors have discussed.
Future of CSR
The amount of recent publications revolving around CSR is vast and it seems that the probable future scenario for CSR presented by Archie B. Carroll in 2015 still prevails. In this scenario Carroll ( 2015 ) foresees an increase in: stakeholder engagement, prevalence and power of ethically sensitive consumers, the level of sophistication of non-governmental organizations (NGOs), employees as a CSR driving-force, along with increased CSR activity up, down, and across the global supply chain. With regards to the concept itself, Carroll ( 2015 ) expects CSR to continue its transactional path but to have a limited transformational evolution. While this scenario seems plausible and highly probable, perhaps it would be necessary to add to it that even when CSR is still relevant and its implementation keeps expanding, at least in the literature, there are competing frameworks and new concepts that might slow the global expansion and implementation of CSR and even shift the public interest towards new areas. Some of these concepts are Corporate Sustainability, Corporate Social Performance, Creation of Shared Value, Corporate Citizenship, Environmental Corporate Social Responsibility, Environmental Social and Governance Criteria, among others. However, it is relevant to highlight Archie B. Carroll’s ( 2015 ) work on the competing and complementary frameworks of CSR in which he concluded that all of them are interrelated and overlapping and pointed out that all of these concepts have already been incorporated into CSR, which is an aspect that is sometimes overlooked. Only time will tell if the institutionalization of CSR continues to expand or if the interest shifts towards other concepts.
The future of CSR will also have to take into consideration the latest technological advances and their role as part of new business frameworks and strategies. The adoption and adaptation to new digitalization processes and tools, as well as the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence into the business environment are relevant challenges not only for the CSR debate, but for corporations in general. In this sense, business frameworks will have to adapt and evolve in order to embrace the latest tools, but they will need to do so through an overarching and holistic framework that is based on the principles of social responsibility in a way that it combines the notions of sustainability, the generation of shared value, and the belief that companies can redefine their purpose to do what is best for the world .
Chaffee ( 2017 ) goes into detail to explain the evolution of corporations under the English Crown and also their evolution in the USA where they became subject of legislatures after the Revolutionary War but still kept relatively social functions.
During the 1940’s, 50’s and 60’s, business executives and corporate managers were commonly referred to as businessmen (see Carroll 1999 ) .
The Moskowitz list is a reputation index developed during the early 1970’s by Milton Moskowitz to rate the social performance of a number of firms.
As 2018 marks 25 years since the creation of the Triple Bottom Line, Elkington ( 2018 ) reviewed the concept in the Harvard Business Review in June 2018 and concluded that there is a need for a new radical approach to sustainability that can tackle the challenges of pace and scale needed. In the same article, Elkington ( 2018 ) points out to the B Corporations (commonly known as B Corps) as an example of firms that now approach business with a dedication to do what is “best for the world” (Elkington 2018 , para. 15).
The debate around the participation of corporations in global governance has brought forward the term Corporate Political Responsibility . For example, Tempels et al. ( 2017 ), build on from the concept of corporate citizenship to argue that corporations and governments share the responsibility to tackle societal problems. Furthermore, they see corporations as responsible for helping or pushing governments to fulfill its responsibilities towards society. Another perspective comes from Djelic and Etchanchu ( 2017 ), who contextualized the political role of CSR by exploring different historical periods to conclude that corporations have played relevant social and political roles. With their historical contextualization, they argue that there is no clear separation between the responsibilities of business and state, and as a result, they consider Friedman’s ( 1962 ) approach to the CSR to be a limited a perspective that “is far from describing a natural state of things” (Djelic and Etchanchu 2017 , p. 658)
To exemplify the principle of protection of labor welfare, Heslin and Ochoa ( 2008 ) briefly present the case of Levi Strauss which was faced with the legal and social challenges of employing children under the age of 15 in Bangladesh. A solution based merely on compliance and simplicity would have been to fire all those children, but as a result of analyzing the social context, Levi Strauss observed that these children were in most cases the only way of income for their families and hence the company decided to send them to school while still paying them their regular wages and providing them with a job after completing their education (Heslin and Ochoa, 2008 ).
Abbreviations
Business for Social Responsibility
Committee for Economic Development (USA)
Consumer Product Safety Commission (USA)
Corporate Social Responsibility
Creating shared value
European Commission
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (USA)
Environmental Protection Agency (USA)
European Union
Global Reporting Initiative
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
International Organization for Standardization
Millennium Development Goals
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (USA)
Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility
Sustainable Development Goals
United Kingdom
United Nations
United Nations Development Programme
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
United Nations Global Compact
United States of America
Young Men’s Christian Association
Aguinis, H., & Glavas, A. (2012). What we know and don’t know about corporate social responsibility: a review and research agenda. Journal of Management, 38 (4), 932–968.
Article Google Scholar
Avram, E., & Avasilcai, S. (2014). Business performance measurement in relation to corporate social responsibility: a conceptual model development. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 109 , 1142–1146.
Ban, K.-M. (2015). Launch of new sustainable development agenda to guide development actions for the next 15 years. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/?page=view&nr=1021&type=230&menu=2059 . Accessed 16 Apr 2018.
Google Scholar
Barnard, C. I. (1938). The functions of the executive . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Baumol, W. J. (1970). A new rationale for corporate social policy . USA: Heath Lexington Books.
Benites-Lazaro, L. L., & Mello-Théry, N. A. (2017). CSR as a legitimatizing tool in carbon market: Evidence from Latin America’s clean development mechanism. Journal of Cleaner Production, 149 , 218–226.
Bowen, H. R. (1953). Social responsibilities of the businessman . University of Iowa Press.
Burke, L., & Logsdon, J. M. (1996). How corporate social responsibility pays off. Long Range Planning, 29 (4), 495–502.
Business for Social Responsibility. (2018). Our Story. https://www.bsr.org/en/about/story . Accessed 2 Mar 2018.
Carroll, A. B. (1979). A three-dimensional conceptual model of corporate performance. Academy of management review, 4 (4), 497–505.
Carroll, A. B. (1991). The pyramid of corporate social responsibility: Toward the moral management of organizational stakeholders. Business Horizons, 34 (4), 39–48.
Carroll, A. B. (1998). The fousr faces of corporate citizenship. Business and Society Review, 100 (1), 1–7.
Carroll, A. B. (1999). Corporate social responsibility. Business & Society, 38 (3), 268–295.
Carroll, A. B. (2008). A history of corporate social responsibility: concepts and practices. In A. M. Andrew Crane, D. Matten, J. Moon, & D. Siegel (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of corporate social responsibility (pp. 19–46). New York: Oxford University Press.
Carroll, A. B. (2015). Corporate social responsibility: The centerpiece of competing and complementary frameworks. Organizational Dynamics, 44 (2), 87–96.
Carroll, A. B., & Shabana, K. M. (2010). The business case for corporate social responsibility: a review of concepts, research and practice. International Journal of Management Reviews, 12 (1), 85–105.
Carson, R. (1962). Silent spring . Boston, Cambridge: Houghton Mifflin, Riverside Press.
Chaffee, E. C. (2017). The origins of corporate social responsibility. University of Cincinnati Law Review, 85 , 347–373.
Chandler, D. (2016). Strategic corporate social responsibility: sustainable value creation . United States of America: SAGE Publications.
Chandler, D., & Werther, W. B. (2013). Strategic corporate social responsibility: stakeholders, globalization, and sustainable value creation (3rd ed.). United States of America: SAGE Publications.
Chuang, S.-P., & Huang, S.-J. (2016). The effect of environmental corporate social responsibility on environmental performance and business competitiveness: the mediation of green information technology capital. Journal of Business Ethics , Springer, 150 (4), 991–1009.
Clark, J. M. (1939). Social control of business (2nd ed.). United States of America: Augustus M Kelley Pubs.
Cochran, P. L., & Wood, R. A. (1984). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance. The Academy of Management Journal, 27 (1), 42–56.
Commission of the European Communities. (2001). Green paper: promoting a European framework for corporate social responsibility (COM(2001) 366 final) . Brussels: E. Commission.
Committee for Economic Development. (1971). Social responsibilities of business corporations . USA: Committee for Economic Development.
Crane, A. (2008). The Oxford handbook of corporate social responsibility . Oxford: OUP.
CSR Europe. (2016). CSR Europe report 2016 .
CSR Europe. (n.d.). CSR Europe - 20 years of business-policy interaction driving the CSR movement. https://www.csreurope.org/history . Accessed 19 Mar 2018.
Dahlsrud, A. (2008). How corporate social responsibility is defined: An analysis of 37 definitions. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 15 (1), 1–13.
Davis, K. (1960). Can business afford to ignore social responsibilities? California Management Review, 2 (3), 70–76.
Davis, K. (1973). The case for and against business assumption of social responsibilities. Academy of Management Journal, 16 (2), 312–322.
Djelic, M.-L., & Etchanchu, H. (2017). Contextualizing corporate political responsibilities: neoliberal CSR in historical perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 142 (4), 641–661.
Donaldson, T., & Preston, L. E. (1995). The stakeholder theory of the corporation: concepts, evidence, and implications. The Academy of Management Review, 20 (1), 65–91.
Du Pisani, J. A. (2006). Sustainable development – historical roots of the concept. Environmental Sciences, 3 (2), 83–96.
Earth Day. (2018). The history of earth day. https://www.earthday.org/about/the-history-of-earth-day/ . Accessed 25 May 2018.
Eberhard-Harribey, L. (2006). Corporate social responsibility as a new paradigm in the European policy: how CSR comes to legitimate the European regulation process. Corporate Governance: The international journal of business in society, 6 (4), 358–368.
Eells, R. S. F. (1956). Corporation giving in a free society . New York: Harper.
Ehrlich, P. R. (1968). The population bomb . New York: Ballantine Books.
Elkington, J. (1998). Partnerships from cannibals with forks: The triple bottom line of 21st-century business. Environmental Quality Management, 8 (1), 37–51.
Elkington, J. (2018). 25 years ago I coined the phrase “triple bottom line.” Here’s why it’s time to rethink it. Harvard Business Review.
European Commission. (2011). Corporate social responsibility: a new definition, a new agenda for action. (MEMO/11/732, MEMO/11/734 and MEMO/11/735) . European Commission Retrieved from http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_MEMO-11-730_en.htm .
European Commission. (2014a). The corporate social responsibility strategy of the European commission: results of the public consultation . Brussels: E. Commission.
European Commission. (2014b). Directive 2014/95/EU of the European parliament and of the council. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32014L0095 . Accessed 20 June 2018.
European Commission. (2015). EU multi stakeholder forum on corporate social responsibility (Ares(2015)580495) . Brussels: E. Commission.
European Commission. (n.d.). Non-financial reporting. https://ec.europa.eu/info/business-economy-euro/company-reporting-and-auditing/company-reporting/non-financial-reporting_en . Accessed 20 June 2018.
Feldstein, M. (2013). The Reagan-Thatcher revolution. https://www.dw.com/en/the-reagan-thatcher-revolution/a-16732731 . Accessed 9 Nov 2018.
Fink, A. (2005). Conducting research literature reviews: from the internet to paper . United States of America: SAGE Publications.
Frederick, W. C. (1960). The growing concern over business responsibility. California Management Review, 2 (4), 54–61.
Freeman, R. E. (1994). The politics of stakeholder theory: Some future directions. Business ethics quarterly , 4 (4), 409–421.
Freeman, R. E. (2001). A stakeholder theory of the modern corporation. Perspectives in Business Ethics Sie, 3 , 144.
Friedman, A. L., & Miles, S. (2002). Developing stakeholder theory. Journal of management studies, 39 (1), 1–21.
Friedman, M. (1962). Capitalism and freedom . United States of America: University of Chicago Press.
Friedman, M. (1970). The social responsibility of business is to increase its profits . The New York Times Magazine.
Harrison, B. (1966). Philanthropy and the Victorians. Victorian Studies, 9 (4), 353–374.
Heald, M. (1970). The social responsibilities of business: company and community 1900–1960 . United States of America: Pr. of Case Western Reserve Univ.
Heslin, P. A., & Ochoa, J. D. (2008). Understanding and developing strategic corporate social responsibility. Organizational Dynamics, 37 (2), 125–144.
Husted, B. W., & Allen, D. B. (2007). Strategic corporate social responsibility and value creation among large firms: Lessons from the Spanish experience. Long Range Planning, 40 (6), 594–610.
ISO. (n.d.-a). History of ISO 26000. http://iso26000.info/history/ . Accessed 17 May 2018.
ISO. (n.d.-b). ISO 26000 - social responsibility. https://www.iso.org/iso-26000-social-responsibility.html . Accessed 17 May 2018.
ISO. (n.d.-c). ISO 26000 guidance on social responsibility. http://iso26000.info /. Accessed 17 May 2018.
Jamali, D., & Carroll, A. B. (2017). Capturing advances in CSR: Developed versus developing country perspectives. Business Ethics A European Review, 26 , 321–325.
Jones, T. M. (1980). Corporate social responsibility revisited, redefined. California Management Review, 22 (3), 59–67.
Kao, E. H., Yeh, C.-C., Wang, L.-H., & Fung, H.-G. (2018). The relationship between CSR and performance: Evidence in China. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal.
Lantos, G. P. (2001). The boundaries of strategic corporate social responsibility. Journal of Consumer Marketing , 18 (7), 595–632.
Latapí, M. A. (2017). Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility in the Container Shipping Industry: A Case Study of the Triple E as part of Maersk's Sustainability Strategy . Unpublished Master Thesis Faculty of Business Administration. University of Iceland. Reykjavik, Iceland.
Lee, M.-D. P. (2008). A review of the theories of corporate social responsibility: Its evolutionary path and the road ahead. International Journal of Management Reviews, 10 (1), 53–73.
Mahoney, J. T., & Godfrey, P. (2014). The Functions of the Executive at 75: An Invitation to Reconsider a Timeless Classic http://business.illinois.edu/working_papers/papers/14-0100.pdf Accessed 21 Apr 2018.
Marrewijk, M. (2003). Concepts and Definitions of CSR and Corporate Sustainability: Between Agency and Communion (Vol. 44).
McGuire, J. W. (1963). Business and society . New York: McGraw-hill.
McWilliams, A., & Siegel, D. (2001). Corporate social responsibility: A theory of the firm perspective. The Academy of Management Review, 26 (1), 117–127.
Murata, S. i. (n.d.). Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTJAPANINJAPANESE/Resources/515610-1138006557271/Mr.Murata-English.pdf . Accessed 29 May 2018.
Okoli, C., & Schabram, K. (2010). A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research .
Book Google Scholar
Pillay, R. (2015). The changing nature of corporate social responsibility: CSR and development – the case of Mauritius . New York: Taylor & Francis.
Porter, M. E., & Kramer, M. R. (2006). Strategy & Society. Harvard Business Review, December, 1–16 .
Porter, M. E., & Kramer, M. R. (2011). Creating shared value. Harvard Business Review (January-February).
Preston, L. E., & Post, J. E. (1975). In S. U. Press (Ed.), Private management and public policy: the principle of public responsibility . United States of America: Pearson Education Inc..
Selekman, B. M. (1959). A moral philosophy for management . United States of America: McGraw-Hill.
Sethi, S. P. (1975). Dimensions of corporate social performance: An analytical framework. California Management Review, 17 (3), 58–64.
Smith, N. C. (2001). Changes in corporate practices in response to public interest advocacy and actions. In P. N. B. a. G. T. Gundlach (Ed.), Handbook of Marketing and Society . Thousand Oaks.
Strand, R. (1983). A systems paradigm of organizational adaptations to the social environment. Academy of management review, 8 (1), 90–96.
Swanson, D. L. (1995). Addressing a theoretical problem by reorienting the corporate social performance model. The Academy of Management Review, 20 (1), 43–64.
Tempels, T., Blok, V., & Verweij, M. (2017). Understanding political responsibility in corporate citizenship: Towards a shared responsibility for the common good. Journal of Global Ethics, 13 (1), 90–108.
The Club of Rome. (2018). History. https://www.clubofrome.org/about-us/history/ . Accessed 28 May 2018.
Trapp, N. L. (2012). Corporation as climate ambassador: Transcending business sector boundaries in a Swedish CSR campaign. Public Relations Review, 38 (3), 458–465.
Tuzzolino, F., & Armandi, B. R. (1981). A need-hierarchy framework for assessing corporate social responsibility. The Academy of Management Review, 6 (1), 21–28.
UNDP. (2018). What are the Sustainable Development Goals? http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sustainable-development-goals.html . Accessed 18 Apr 2018.
Union of Concerned Scientists. (2017). The IPCC: who are they and why do their climate reports matter? https://ucsusa.org/global-warming/science-and-impacts/science/ipcc-backgrounder.html #. Accessed 25 June 2018.
United Nations Global Compact. (n.d.). UN History - A giant opens up. http://globalcompact15.org/report/part-i/un-history-a-giant-opens-up . Accessed 28 May 2018.
Votaw, D. (1973). Genius becomes rare: a comment on the doctrine of social responsibility Pt. II. California Management Review, 15 (3), 5–19.
Walton, C. C. (1967). Corporate social responsibilities . United States of America: Wadsworth Publishing Company.
Walton, C. C. (1982). Corporate social responsibility: The debate revisited. Journal of Economics and Business, 34 (2), 173–187.
Wankel, C. (2008). 21st century management: a reference handbook . United States of America: SAGE Publications.
Wartick, S. L., & Cochran, P. L. (1985). The evolution of the corporate social performance model. Academy of Management Review, 10 (4), 758–769.
Waterhouse, B. C. (2017). The personal, the political and the profitable: Business and protest culture, 1960s-1980s. Financial History, Spring, 2017 , 14–17.
Werther, W. B., & Chandler, D. (2005). Strategic corporate social responsibility as global brand insurance. Business Horizons, 48 (4), 317–324.
Wood, D. J. (1991). Corporate social performance revisited. The Academy of Management Review, 16 (4), 691–718.
World Watch Institute. (n.d.). Environmental Milestones. http://www.worldwatch.org/brain/features/timeline/timeline.htm. Accessed 28 May 2018.
Download references
Acknowledgements
First, we want to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions which were fundamental for the final version of this article. We also want to thank the editors for their assistance throughout the review process.
We are grateful and acknowledge that this research was made possible by the support of the Mexican National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT for its abbreviation in Spanish) which granted a 36 month scholarship to ML to conduct his PhD at the University of Iceland.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of Table 1 is available from the three online data bases consulted (Science Direct, ProQuest and Web of Science) according to the considerations mentioned for the creation of the table. The rest of the data generated or analyzed during this study is included in this published article.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland
Mauricio Andrés Latapí Agudelo, Lára Jóhannsdóttir & Brynhildur Davídsdóttir
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
This paper is derived from ML’s work towards a PhD in Environment and Natural Resources at the University of Iceland. As such, ML performed a literature review of the history and evolution of CSR. Dr. LJ being the main advisor for ML’s PhD and Dr. BD being the secondary advisor, contributed by guiding the direction of the article through comments, suggestions, information and literature and by contributing in the drafting and revising the work to achieve the academic quality required for a PhD at the University of Iceland. Dr. LJ has provided the overall review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mauricio Andrés Latapí Agudelo .
Ethics declarations
Authors’ information.
ML is a PhD student in the Environment and Natural Resources graduate program at the University of Iceland. His current research focuses on the impact of SCSR on the energy sector, in particular on the energy efficiency and environmental performance of energy companies.
Dr. LJ is a professor at the Faculty of Business Administration at the University of Iceland. LJ has published in the areas of CSR, sustainable business models and environmental sustainability. Among her activities, LJ is a Fulbright Arctic Initiative Scholar.
Dr. BD is a professor of Environment and Natural Resources in the Faculties of Life and Environmental Sciences and Economics at the University of Iceland. BD has published in areas of sustainable energy, sustainable development and ecological economics. Among her occupations, BD is the book review editor for the journal Ecological Economics, Director of the University of Iceland Arctic Initiative and sits on the boards of several foundations, institutes and private companies.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended readings
After having done an exhaustive literature review on CSR and its evolution it has been a challenge to select which contributions should be left out of this paper. With this in mind, we would like to bring the attention of the reader towards the following publications: The Functions of the Executive by Barnard ( 1938 ) along with The Functions of the Executive at 75: An Invitation to Reconsider a Timeless Classic by Mahoney and Godfrey ( 2014 ); the Social Control of Business by Clark ( 1939 ); the Social responsibilities of business corporations published by the Committee for Economic Development ( 1971 ); the Green Paper: Promoting a European framework for Corporate Social Responsibility published by the Commission of the European Communities ( 2001 ) which was the first step towards the European Strategy for CSR; Corporate Social Responsibility: A Theory of the Firm Perspective by McWilliams and Siegel ( 2001 ); the search for a definition of CSR by Dahlsrud ( 2008 ) with How corporate social responsibility is defined: an analysis of 37 definitions ; then The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility by Crane ( 2008 ) which provides a summary of CSR history and points out relevant contributions to the concept; the literature review and analysis of the institutional, organizational, and individual levels of CSR provided by Aguinis and Glavas ( 2012 ) with What We Know and Don’t Know About Corporate Social Responsibility: A Review and Research Agenda ; the case study of reporting initiatives from a CSR perspective presented by Avram and Avasilcai ( 2014 ) through their Business Performance Measurement in Relation to Corporate Social Responsibility: A conceptual Model Development ; the internal and external drivers behind SCSR rationale for the maritime transportation sector presented by Latapí ( 2017 ) in his unpublished master thesis; and, Capturing advances in CSR: Developed versus developing country perspectives by Jamali and Carroll ( 2017 ).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Latapí Agudelo, M.A., Jóhannsdóttir, L. & Davídsdóttir, B. A literature review of the history and evolution of corporate social responsibility. Int J Corporate Soc Responsibility 4 , 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40991-018-0039-y
Download citation
Received : 07 September 2018
Accepted : 18 December 2018
Published : 22 January 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40991-018-0039-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Corporate social responsibility
- CSR evolution
- CSR history
- Sustainable development
- Generation of shared value
- Social responsibility
- Corporate behavior

- Home
Welcome to the Yale Law School Legal Scholarship Repository. This repository provides open, global access to the scholarship of Yale Law School faculty and jornals, as well as a selection of unique collections.
Communities in Yale Law School Open Scholarship Repository
Select a community to browse its collections.
Recently Added

Fostering the Intellectual Virtue of Civility in Online Contexts

In the American Tempest: Democracy, Conspiracy, and Machine

The Case for Designing Tech for Social Cohesion: The Limits of Content Moderation and Tech Regulation

Parents in Fact

Local Legislatures and Delegation
Export search results.
The export option will allow you to export the current search results of the entered query to a file. Different formats are available for download. To export the items, click on the button corresponding with the preferred download format.
By default, clicking on the export buttons will result in a download of the allowed maximum amount of items.
To select a subset of the search results, click "Selective Export" button and make a selection of the items you want to export. The amount of items that can be exported at once is similarly restricted as the full export.
After making a selection, click one of the export format buttons. The amount of items that will be exported is indicated in the bubble next to export format.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous
- Next chapter >
I The Genesis of Corporate Governance
- Published: October 2002
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter examines the development of corporate governance over time and seeks to understand why it has become such a matter of debate today. It first looks briefly at the manner in which it has developed, concentrating on the changing balance of power between the main players on the corporate stage, shareholders, boards of directors, and managers. It then discusses the reasons for its recent and rapid emergence as a major and international issue.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:

Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics Research Paper
The roles and services offered by accountants have changed overtime. In the 15 th century, accounting involved bookkeeping only. With emergence of industrial revolution in the 19 th century, accountants’ financial responsibilities have increased with time. To date, roles of an accountant require vital skills and experience to establish and maintain accurate business records.
In the 21 st century, accountants and financial managers will have a role in designing and controlling financial systems. They will need to come up with restricted internal financial control systems. This is because the accounting records of organisations are expected to increase the level of secrecy required. This is as a result of introducing new unique products in the world market. With introduction of these new products, the role of accountants will be to identify areas to be strengthened to make the systems more effective (ACCA, 2009).
With the rapid increase in international businesses, countries and organisations need to develop customized tax systems to suit their business. It is the role of accountants and financial managers to ensure that their organisations are tax compliant.
Expansion of business from national to global level may create loopholes for fraud stars to engage in corrupt activities. Accountants will have a role in ensuring that corporate governance system is working. This will minimize professional fraud in the organisations.
The increase in technology in global business will increase accountants’ responsibilities and duties in the new business environment. Accountants need to be conversant of various e-Business opportunities. Accountants have a responsibility in developing new strategies which will ensure that e-Business is carried out in the most profitable way possible (Hicks, 2004).
Future accounting will require financial managers to offer varying and unique services based on the nature of business. They will offer financial consultation on matters affecting the business. They will give solutions and technical advice to the organizations’ management. Future global business will involve multiple and varying transactions, hence, the need for the consultation services.
Bookkeeping and other services related to the accounting records will be offered by accountants and other financial managers. New financial systems must be implemented diligently to ensure optimum workability. Accountants will offer implementation services of the designed financial systems. Emerging business opportunities result in a competition among companies and employees. To ensure business flourish, employees should be motivated. Appraisal services will be offered by financial managers and accounting firms to ensure that deserving companies or individuals are rewarded.
Current and new businesses face varying risks. These risks may be caused by natural disasters or human error. Actuarial services to ascertain the level and possible cost of the risks will be offered by accountants and financial managers. To ensure that funds in business organisations are used as planned, internal audit will be an important service from accountants (ACCA, 2009).
Accounting financial systems will change with time. This is because of advancement in technology and emergence of new business dimensions. With various business organizations expanding to international levels, changes to disclosures will be witnessed. This will be reflected in financial statements and financial plan characteristics like minimum funding requirements. Management of e-Business income will change as per the level of technology and customer base.
Some aspects of accounting including bookkeeping and appraisal will not change. This is because the concepts are the same. Mode of presentation may change but the aim and the procedure will remain the same.
Financial statements will not change. Auditing will remain the same even when there is a change in business.
ACCA, (2009). Accountancy: The future outlook of Accounting. Web.
Hicks, J. (2004). E-commerce and Its Impact on the Accounting Profession. UNC Greensboro Journal of Student Research in Accounting, 1 , 1-16.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, April 27). The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-history-of-corporate-governance-and-ethics/
"The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics." IvyPanda , 27 Apr. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/the-history-of-corporate-governance-and-ethics/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics'. 27 April.
IvyPanda . 2022. "The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics." April 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-history-of-corporate-governance-and-ethics/.
1. IvyPanda . "The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics." April 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-history-of-corporate-governance-and-ethics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics." April 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-history-of-corporate-governance-and-ethics/.
- Accounting: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Method
- Avenue Park Accountants Marketing Plan
- Sustainability Reporting: Cost and Benefits
- BMW and Cadillac Corporation Financial Accounting Standards
- E-business Programs Implementation
- WorldCom: How Corporations Misuse Data to Make Gains
- Earnings Management and Earnings Quality
- Internet and E-Business
- Preparing an Adjusted Trial Balance
- E-Business Security Concerns
- Business Ethics: A United Arab Emirates’ Perspective
- BP Corporation’s Oil Disaster and Its Reputation
- The Hippocratic Oath of the Manager as a Business Concept: Analysis
- Ethical Implications of Takeovers: A Financial Manager’s Story
- Noting the Error in Projections: Scott Bestor's Ethical Dilemma

Evolution of Corporate Governance in the UK
Evolution of corporate governance standards in the united kingdom.
As the timeline below demonstrates, a number of advances in Corporate Governance thinking and new requirements have arisen through the work and recommendations of Commissions that were set up in the wake of accounting and other scandals that led to high profile corporate collapses that resulted in significant financial losses for investors.
Why is the evolution of UK’s standards relevant beyond UK ?
The evolution of Corporate Governance standards in the United Kingdom is significant in that many countries follow the UK’s example of voluntary adherence to Codes of Corporate Governance which are periodically reviewed and updated in light of experience, rather than seeking to uphold standards via prescriptive legislation and regulation. Moreover, in recent years increasing numbers of US listed companies have began to follow the UK’s practice of splitting the roles of Chairman and CEO to two different individuals, rather than combining these in the hands of one all powerful individual. In addition, where most Codes of Corporate Governance focus on listed companies, the UK’s Institute of Directors has become globally influential with their Guidance on Corporate Governance for unlisted companies. Hence, the evolution of UK’s standards is quite informative not only for the UK itself but also for other jurisdictions.
Timeline of events and reports influencing UK standards on Corporate Governance
1990-1991 bank of credit and commerce international (“bcci”) controversy and collapse.
In 1990, PWC audit of Bank of Credit and Commerce International (“BCCI”) unearths major unaccountable loss and questionable lending practices. Bank eventually collapses in 1991
1990 – Polly Peck plc Serious Fraud Office investigations and collapse
During 1990, accounting investigators at Polly Peck plc, a FTSE 100, find that material amounts of capital had been transferred outside the company at the behest of the Chairman and CEO. He then defies the Board’s request to bring the capital back. Trading in the company’s shares get suspended after a Serious Fraud Office raid of the headquarters of the company and the company goes into voluntary administration in October 1990 after a creditor’s ex parte application to the High Court for provisional liquidation is successful.
1991 The Financial Reporting Council (“FRC”) appoints the Cadbury Commission
In the wake of the BCCI and Polly Peck collapses and the perceived link of the collapses with accounting irregularities and corporate governance failure, the UK’s Financial Reporting Council, the regulator of the accounting profession, appointed a Commission headed by Sir Adrian Cadbury to look into and make recommendations on Corporate Governance Arrangements for listed companies
1992 Maxwell Group collapse
The collapse of the Maxwell Group in 1992 confirms the need for stricter and more prescriptive governance arrangements.
December 1992 – Cadbury Commission publishes the Cadbury Report
Cadbury Commission publishes the Cadbury Report aimed at raising standards in corporate governance with key recommendations being
- separating the roles of CEO and chairman of the Board of Directors
- having a minimum of three non-executive directors on the board
- having a Board Audit Committee of non-executive directors with direct access to the external auditors and the internal audit function without screening by executive management
Importantly, a key and defining recommendation from Cadbury was to leave the adoption and implementation of the Commission’s Cadbury’s to the companies themselves on a voluntary basis. This reflected Cadbury’s view that the onus should be on shareholders to exert appropriate pressure for improvements in corporate governance rather than relying on prescriptive regulation and legislation.
You can download a copy of the Cadbury Report here .
1995 – Greenbury Report released
In January 1995 the Confederation of British Industry (CBI) established the Study Group on Directors’ Remuneration under the chairmanship of Sir Richard Greenbury with a remit to identify good practice in determining directors’ remuneration and to prepare a code of practice for UK PLCs. The study group published its report, the “Greenbury Report” in July 1995 and its main recommendations included
- having a Board Remuneration Committee of non-executive directors deal with setting remuneration
- full disclosure on remuneration including reporting annually to shareholders on remuneration matters
You can download a copy of the Greenbury Report here .
1995-1998 Review of Cadbury by Hampel Committee – Hampel Report
In November 1995, the Financial Reporting Council, established a Committee on Corporate Governance, headed by Ronnie Hampel, (Hampel Committee) to review the Cadbury Committee’s recommendations on corporate governance. The Hampel Committee released a preliminary report in August 1997, followed by a final report in January 1998. Hampel found that there was no need for a revolution in the UK Corporate Governance system. The report aimed to combine, harmonise and clarify the Cadbury and Greenbury recommendations.
On the question of in whose interests companies should be run, the Hampel Committee recognized the single overriding objective shared by all listed companies, whatever their size or type of business, is the preservation and the greatest practical enhancement over time of their shareholders’ investment.
The Hampel Report relied more on broad principles and a “common sense” approach which is necessary to apply to different situations.
You can download a copy of the Hampel Report here .
1999 Turnbull Report for listed companies
In September 1999, a committee chaired by Nigel Turnbull, of the Rank Group plc was published by the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales for companies listed on the London Stock Exchange. The report informed directors of their obligations under the Combined Code with regard to keeping good “internal controls” in their companies or having good audits and checks to ensure the quality of financial reporting and catch any fraud before it becomes a problem.
You can download a copy of the Turnbull Report here .
Revised guidance was issued in 2005. The report was superseded by a further FRC guidance issued in September 2014.
You can download a copy of the revised Turnbull Report of 2005 here and a copy of the FRC Guidance of 2014 here .
2003 Higgs Review of the role and effectiveness of non-executive director by Derek Higgs
In January 2003, a committee chaired by Derek Higgs published its report on the corporate governance commissioned by the UK government. It reviewed the role and effectiveness of non-executive directors and of the Board audit committee, aiming at improving and strengthening the existing Combined Code of Corporate Governance. The review was carried out after a number of scandals in the US, involving Enron, WorldCom and Tyco, had resulted in the Sarbanes-Oxley act as the US opted for legislation.
Higgs strongly backed the existing UK non-prescriptive approach to corporate governance “comply or explain”. At the same time, he advocated more provisions with more stringent criteria for the board composition and evaluation of independent directors and to reduce some of the discretion that the Combined Code allowed. Key Higgs recommendations included :
- at least half of a board (excluding the Chair) to be comprised of non-executive directors
- Non-executives should meet at least once a year on their own to discuss company performance
- A Senior Independent Director (“SID”) be nominated and made available for shareholders to express any concerns to
- The potential non-executive directors should satisfy themselves that they posses the knowledge, skills and time to carry out their duties with due diligence.
The recommendation for a Senior Independent Director (“SID”) was met with some scepticism by some board chairmen as they felt it might undermine their own role. Gradually the concept has been become more mainstream and influential as more boards have introduced a SID.
A copy of the Higgs review can be downloaded here .
2009 Walker Review of Corporate Governance in UK Bank and other financial industry entities (“Walker Report”)
Following the financial crisis of 2008, David Walker undertook a review commissioned by the UK Government to examine examine board practices at UK banks, and later extended to other financial institutions. The necessity for a review was driven at least in part by a perceived imbalance between perceived imbalance between shareholders’ limited liability for institutional debts and the effectively unlimited liability of the taxpayer when obliged to bail them out. ‘Serious deficiencies in prudential oversight’ were noted, along with ‘major governance failures within banks’, but still promotion of best practice rather than formal regulation was identified as the best means to ensure ownership of good corporate governance
The review’s key findings and recommendations included :
- that the prevailing unitary board structure and FRC Combined Code remain ‘fit for purpose’;
- that deficiencies in board practice are predominantly of behavior rather than organization, and that a process of challenging the executive team needs to be embedded, hence a responsibility laid at the door of non-executive directors;
- that greater dedicated non-executive directorial focus on risk management is required, supported by a dedicated Chief Risk Officer;
- that active engagement remains a responsibility of shareholders and, in the case of mutual funds, a commitment to a Stewardship Code; and
- substantial enhancement is necessary of board level oversight of remuneration of all senior employees (not just board level), to be more closely aligned with medium and long-term risk and performance.
A copy of the Walker Report can be downloaded here .
2010 UK Institute of Directors Guidance on Corporate Governance for unlisted companies
As the commissions and their reports on corporate governance had focused primarily on the needs of listed companies, in 2010, the UK Institute of Directors published a guide on Corporate Governance for unlisted companies, thus addressing the needs of such companies. This was considered a major step forward in helping unlisted companies address the issues involved in designing an appropriate corporate governance framework. The guidance sets out practical and pragmatic principles of good governance and makes clear that the manner in which they are to be applied will depend on the circumstances of each company and the judgement of individual boards.
You can download a copy of the IoD Guidance on Corporate Governance for unlisted companies here .
The CLS Blue Sky Blog
Columbia Law School's Blog on Corporations and the Capital Markets
What history tells us about the value of bankruptcy directors.

The proliferation of bankruptcy directors represents a controversial shift in the corporate governance landscape. Independent directors appointed when a company experiences financial distress (known colloquially as “bankruptcy directors”) bring restructuring expertise and experience to a high-stakes situation. Their appointment also insulates conflicted transactions and claims from the elevated scrutiny of derivative standing and entire fairness. What would otherwise be negotiations between insiders on both sides (the board of directors, who are appointed by equity, and equity holders) is transformed into an unconflicted negotiation when the bankruptcy directors are delegated authority by the board of directors. As a result, the bankruptcy court evaluates the bankruptcy directors’ decisions using the deferential business justification standard, and approval is usually perfunctory.
Critics, however, have questioned bankruptcy directors’ independence and cleansing effect. Are bankruptcy directors really independent when their role includes negotiating with or investigating the same parties who appoint them? Should their decisions be given deference when their appointments are associated with lower recoveries for creditors?
In a recent article, I apply historical and practical lessons to explain why bankruptcy courts should apply the entire fairness standard to evaluate whether bankruptcy directors have cleansing effect. The article’s main contribution is to examine the debate over bankruptcy directors through the lens of bankruptcy law’s historic struggles with conflicted corporate governance, informed by two recent cases that emphasize the need for a formal practice and show how my proposal could be applied. This article’s framework for analyzing bankruptcy directors is rooted in the fact that while bankruptcy directors are new, the policy stakes here are not. By tracing the history of case control and the treatment of conflicted transactions, the lessons gleaned from past practice can be applied within the current statutory framework while accounting for the impact of contemporary capital structures.
A bankruptcy case’s trajectory is commonly a function of who controls the case. When the statutory framework is flexible, like the current Bankruptcy Code, market capacities and capital structures can empower parties. Reflecting the prowess of private-equity sponsors and the ubiquitousness of financial distress at their portfolio companies, sponsors often compete with lenders for primacy.
Case control manifests in the treatment of conflicted transactions. The appointment of bankruptcy directors at the behest of powerful insiders like private equity sponsors is simply the most recent example. The appointments of independent co-receivers during the equity receivership era of the early 20th century present a compelling parallel. The corresponding reforms of the Chandler Act, namely the mandatory appointment of independent trustees, went too far. Cases languished because creditors were impotent and trustees lacked industry experience. Reorganizations were rare and creditor recoveries were scant. Reflecting these lessons, the Bankruptcy Code gives creditors more options in the face of conflicted transactions. They can request a disinterested fiduciary (an examiner or trustee) or rely upon common law protections provided by the entire fairness doctrine and derivative standing. Creditors have resoundingly chosen the latter options; examiner and trustee appointments remain rare.
The numerous proposals for evaluating bankruptcy directors’ cleansing effect highlight their salience. None of these suggestions, however, reflect the arc of bankruptcy case control, the development of safeguards covering conflicted corporate governance in bankruptcy, and the realities of bankruptcy case administration.
Professors Ellias, Kamar, and Kastiel propose that the creditors who will be affected by the bankruptcy directors’ decisions vote on whether the bankruptcy directors will have a cleansing effect. Although they appropriately prioritize creditors’ interests, their solution would be hard to put into effect. The identity of the affected creditors can be uncertain because the proposed voting occurs early in the case , when valuation is a moving target and the universe of claims is indefinite. An electoral process, including accompanying education of creditors, would add further complexity to the often-chaotic opening month of the bankruptcy case.
Senator Warren and her legislative co-sponsors would empower unsecured creditor committees as the sole party with standing to prosecute conflicted claims. One drawback of her proposal is that it ignores the debtor’s capital structure. It is the fulcrum creditors (the lowest priority creditors who will receive a distribution) whose recoveries are altered by conflicted transactions. Although unsecured creditors were once the default fulcrum security, blanket liens are now commonplace, and often secured creditors are the fulcrum security holders. Yet, Warren’s proposal would eliminate the bankruptcy judge’s oversight role in granting derivative standing, where she can consider whose money is at issue and, correspondingly, who should have standing to pursue claims. Why should the unsecured creditors committee automatically enjoy power in excess of what they have traditionally possessed, when the committee’s constituents are often out of the money?
Ellis and Yeh suggest more liberal appointment of chapter 11 trustees and examiners and note the possibility of the bankruptcy judge selecting the bankruptcy directors. Creditors have generally shunned court-appointed fiduciaries. Stakeholders naturally prefer to control the litigation of conflicted claims and transactions. Their views should be respected; it is their money that is on the line.
Others, including former-Judge Jones, recommend greater disclosure requirements, including identification of bankruptcy directors’ connections with insiders who engineer their appointments. Disclosure is certainly important, but making it the sole focus does not reflect the empirical findings that bankruptcy director appointments are correlated with lower creditor recoveries. The risks are real and a higher burden for granting them cleansing authority is appropriate.
Indeed, that is what my proposal does by requiring the debtor to satisfy the entire fairness standard to treat bankruptcy directors as independent actors. The proposal gives effect to the fair process and fair selection required by entire fairness through (i) a standardized protocol for the disclosure of connections between bankruptcy directors and the insiders who appoint them and (ii) a heightened burden for approval reflecting the structural bias endemic to bankruptcy directors’ relationship with the insiders. All interested parties could object or support the debtor’s motion, and the bankruptcy judge can consider whose distributions are most at risk and give those parties’ views greater weight. Reflecting the lessons from the past while acknowledging the reality of current bankruptcy practice, the proposal is flexible, workable, and creditor-focused.
This post comes to us from Professor Robert W. Miller at the University of South Dakota’s Knudson School of Law. It is based on his recent article, “Everyone is Talking About Bankruptcy Directors,” available here .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

Corporate Governance Charter
Facts for prelims (ffp).
Context: Recently, CII (Confederation of Indian Industry) introduced a corporate governance charter tailored for startups, featuring a self-evaluative scorecard to assess governance progress.
What is Corporate Governance?
It comprises dynamic principles and measures guiding an organization’s growth . It emphasizes values like transparency, fairness, and accountability. The charter release responds to the erosion of shareholders’ value in Indian startups, prompted by governance failures in notable firms like BharatPe and GoMechanic .
Key Highlights of the Charter:
- Objective : The charter acts as a self-governing code for startups under the Companies Act, 2013.
- Benefits : It aids startups in enhancing value, stability, growth, resilience, competitiveness, and long-term success.
- Guidelines : Tailored for different startup stages: Inception, Progression, Growth, and Going Public, offering clear role definitions.
- Online Scorecard : Enables startups to assess their governance status and track improvements over time.
Definition of Startups:
The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) is a non-governmental trade association and advocacy group based in New Delhi, India, established in 1895. It collaborates with business, political, academic, and societal leaders to influence global, regional, and industry agendas. CII operates on a membership basis and has been designated as the B20 India Secretariat by the Indian government for leading the B20 India process during India’s G20 Presidency in 2023.

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology
- Student Opportunities
About Hoover
Located on the campus of Stanford University and in Washington, DC, the Hoover Institution is the nation’s preeminent research center dedicated to generating policy ideas that promote economic prosperity, national security, and democratic governance.
- The Hoover Story
- Hoover Timeline & History
- Mission Statement
- Vision of the Institution Today
- Key Focus Areas
- About our Fellows
- Research Programs
- Annual Reports
- Hoover in DC
- Fellowship Opportunities
- Visit Hoover
- David and Joan Traitel Building & Rental Information
- Newsletter Subscriptions
- Connect With Us
Hoover scholars form the Institution’s core and create breakthrough ideas aligned with our mission and ideals. What sets Hoover apart from all other policy organizations is its status as a center of scholarly excellence, its locus as a forum of scholarly discussion of public policy, and its ability to bring the conclusions of this scholarship to a public audience.
- Scott Atlas
- Thomas Sargent
- Stephen Kotkin
- Michael McConnell
- Morris P. Fiorina
- John F. Cogan
- China's Global Sharp Power Project
- Economic Policy Group
- History Working Group
- Hoover Education Success Initiative
- National Security Task Force
- National Security, Technology & Law Working Group
- Middle East and the Islamic World Working Group
- Military History/Contemporary Conflict Working Group
- Renewing Indigenous Economies Project
- State & Local Governance
- Strengthening US-India Relations
- Technology, Economics, and Governance Working Group
- Taiwan in the Indo-Pacific Region
Books by Hoover Fellows

Economics Working Papers

Hoover Education Success Initiative | The Papers

- Hoover Fellows Program
- National Fellows Program
- Student Fellowship Program
- Veteran Fellowship Program
- Congressional Fellowship Program
- Media Fellowship Program
- Silas Palmer Fellowship
- Economic Fellowship Program
Throughout our over one-hundred-year history, our work has directly led to policies that have produced greater freedom, democracy, and opportunity in the United States and the world.
- Determining America’s Role in the World
- Answering Challenges to Advanced Economies
- Empowering State and Local Governance
- Revitalizing History
- Confronting and Competing with China
- Revitalizing American Institutions
- Reforming K-12 Education
- Understanding Public Opinion
- Understanding the Effects of Technology on Economics and Governance
- Energy & Environment
- Health Care
- Immigration
- International Affairs
- Key Countries / Regions
- Law & Policy
- Politics & Public Opinion
- Science & Technology
- Security & Defense
- State & Local
- Books by Fellows
- Published Works by Fellows
- Working Papers
- Congressional Testimony
- Hoover Press
- PERIODICALS
- The Caravan
- China's Global Sharp Power
- Economic Policy
- History Lab
- Hoover Education
- Global Policy & Strategy
- National Security, Technology & Law
- Middle East and the Islamic World
- Military History & Contemporary Conflict
- Renewing Indigenous Economies
- State and Local Governance
- Technology, Economics, and Governance
Hoover scholars offer analysis of current policy challenges and provide solutions on how America can advance freedom, peace, and prosperity.
- China Global Sharp Power Weekly Alert
- Email newsletters
- Hoover Daily Report
- Subscription to Email Alerts
- Periodicals
- California on Your Mind
- Defining Ideas
- Hoover Digest
- Video Series
- Uncommon Knowledge
- Battlegrounds
- GoodFellows
- Hoover Events
- Capital Conversations
- Hoover Book Club
- AUDIO PODCASTS
- Matters of Policy & Politics
- Economics, Applied
- Free Speech Unmuted
- Secrets of Statecraft
- Pacific Century
- Libertarian
- Library & Archives
Support Hoover
Learn more about joining the community of supporters and scholars working together to advance Hoover’s mission and values.
What is MyHoover?
MyHoover delivers a personalized experience at Hoover.org . In a few easy steps, create an account and receive the most recent analysis from Hoover fellows tailored to your specific policy interests.
Watch this video for an overview of MyHoover.
Log In to MyHoover
Forgot Password
Don't have an account? Sign up
Have questions? Contact us
- Support the Mission of the Hoover Institution
- Subscribe to the Hoover Daily Report
- Follow Hoover on Social Media
Make a Gift
Your gift helps advance ideas that promote a free society.
- About Hoover Institution
- Meet Our Fellows
- Focus Areas
- Research Teams
- Library & Archives
Library & archives
Events, news & press.

2024 Institutional Investor Survey Finds Governance Issues And Climate Concerns Sway Decision Makers
A significant majority of large investors polled in a new survey say they consider environmental, social, and governance (ESG) concerns when determining which firms to invest in, but basic governance factors far outweigh environmental and social concerns in their calculus.

This is according to the 2024 Institutional Investor Survey on Sustainability, published through a partnership of the Hoover Institution Working Group on Corporate Governance , Stanford’s Arthur and Toni Rembe Rock Center for Corporate Governance , and the Stanford Graduate School of Business . The survey was also conducted in collaboration with the MSCI Sustainability Institute .
In fall 2023, the report’s authors polled decision makers within forty-seven investment institutions based primarily in North America and Europe and a handful located in Asia.
They found governance concerns largely supplant social factors or environmental considerations for institutional investors, with 68 percent of those surveyed saying governance was the main consideration, while 23 percent said environmental factors were key. Only 2 percent cited social factors, such as data security, diversity of leadership, and supply-chain labor practices.
When a firm’s environmental stance is considered, it’s largely to do with climate change and emissions performance rather than other measures such as overall pollution output or sustainable sourcing of input materials.
“While ESG integration has become mainstream, governance reigns supreme,” coauthor Amit Seru , Hoover senior fellow and Steven and Roberta Denning Professor of Finance at the Stanford Graduate School of Business, wrote in the report. “Institutional investors rank governance factors as more important to an investment decision than environmental and social factors. At the same time, climate considerations have come to the forefront, with the largest investors believing overwhelmingly that climate change will impact their portfolios in the coming years.”
Added David Larcker , Hoover distinguished visiting fellow and James Irvin Miller Professor of Accounting, Emeritus, at the Stanford Graduate School of Business, one of the three coauthors of the report, “Corporate governance is table stakes: All companies are expected to have it. Governance has been a topic of investment focus for a very long time and, while critically important, investors see governance quality as already embedded in asset prices.”
“By contrast, despite believing in the impact of climate on portfolios, investors see climate risks as yet to be fully priced,” Larcker continued. “Social factors appear to be largely unimportant for driving investment decisions.”
On climate, 93 percent of investment leaders surveyed said “climate issues are most likely to affect the performance of investments over the next two to five years,” when compared to other staples of ESG such as governance or other environmental concerns.
Within the scope of governance, respondents said bread-and-butter concerns such as the structure of a firm’s board, the diversity of its board members, and the quality of its financial reporting were the most important factors they considered when deciding where to invest.
There were also significant differences in what investment decision makers were looking for dependent on which side of the Atlantic Ocean they were located.
While only 26 percent of North American investor respondents say they are explicitly bound under an investment mandate that compels them to consider ESG criteria, more than 70 percent of European respondents say they are bound by one.
Also, European respondents more heavily scrutinized the impact of climate change on a potential investment and the prospective firm’s data security and privacy policies than did their North American counterparts.
Along with Seru and Larcker, the report was written by Brian Tayan of the Corporate Governance Research Initiative at the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
Read the Report
You May Also Like

Hoover And The Cyber Policy Center Gather European Union Diplomats To Discuss Tech Policy At Stanford

The Hoover Institution Quarterly Briefing on Education – April 2024

The Hoover Institution on Confronting and Competing with China – April 2024

The Hoover Institution Briefing on Revitalizing American Institutions – April 2024

The Hoover Institution Briefing On National Security – April 2024

Hoover Briefing On Answering Challenges To Advanced Economies – February 2024

Join the Hoover Institution’s community of supporters in ideas advancing freedom.
Essay: Where Global Governance Went Wrong—and How to Fix It
Create an FP account to save articles to read later and in the FP mobile app.
ALREADY AN FP SUBSCRIBER? LOGIN

- World Brief
- Editors’ Picks
- Africa Brief
- China Brief
- Latin America Brief
- South Asia Brief
- Situation Report
- Flash Points
- War in Ukraine
- Israel and Hamas
- U.S.-China competition
- Biden's foreign policy
- Trade and economics
- Artificial intelligence
- Asia & the Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
Inside China’s New Diplomatic Push
Fareed zakaria on an age of revolutions, ones and tooze, foreign policy live.

Spring 2024 Issue
Print Archive
FP Analytics
- In-depth Special Reports
- Issue Briefs
- Power Maps and Interactive Microsites
- FP Simulations & PeaceGames
- Graphics Database
From Resistance to Resilience
The atlantic & pacific forum, redefining multilateralism, principles of humanity under pressure, fp global health forum 2024.
By submitting your email, you agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use and to receive email correspondence from us. You may opt out at any time.
Your guide to the most important world stories of the day
Essential analysis of the stories shaping geopolitics on the continent
The latest news, analysis, and data from the country each week
Weekly update on what’s driving U.S. national security policy
Evening roundup with our editors’ favorite stories of the day
One-stop digest of politics, economics, and culture
Weekly update on developments in India and its neighbors
A curated selection of our very best long reads
Where Global Governance Went Wrong—and How to Fix It
International agreements have not balanced our freedoms in the way that they should..
Global governance, never really settled, has recently been having an especially hard time. Everyone believes in a rules-based system, but everyone wants to make the rules and dislikes it when the rules work against them, saying that they infringe on their sovereignty and their freedom. There are deep asymmetries, with the powerful countries not only making the rules but also breaking them almost at will, which raises the question: Do we even have a rules-based system, or is it just a facade? Of course, in such circumstances, those who break the rules say they only do so because others are, too.
The current moment is a good illustration. It is the product of longstanding beliefs and power relations. Under this system, industrial subsidies were a no-no, forbidden (so it was thought) not just by World Trade Organization rules, but also by the dictates of what was considered sound economics. “Sound economics” was that set of doctrines known as neoliberal economics, which promised growth and prosperity through, mostly, supposedly freeing the economy by allowing so-called free enterprise to flourish. The “liberal” in neoliberalism stood for freedom and “neo” for new, suggesting that it was a different and updated version of 19 th -century liberalism.
This essay is adapted from the book T he Road to Freedom: Economics and the Good Society by Joseph E. Stiglitz, W.W. Norton, 384 pp., $29.99, April 2024
In fact, it was neither really new nor really liberating. True, it gave firms more rights to pollute, but in doing so, it took away the freedom to breathe clean air—or in the case of those with asthma, sometimes even the most fundamental of all freedoms, the freedom to live.
“Freedom” meant freedom for the monopolists to exploit consumers, for the monopsonists (the large number of firms that have market power over labor) to exploit workers, and freedom for the banks to exploit all of us—engineering the most massive financial crisis in history, which required taxpayers to fork out trillions of dollars in bailouts, often hidden, to ensure that the so-called free enterprise system could survive.
The promise that this liberalization would lead to faster growth from which all would benefit never materialized. Under these doctrines that have prevailed for more than four decades, growth has actually slowed in most advanced countries. For instance, real growth in GDP per capita (average percent increase per annum) according to data compiled by the St. Louis Fed, was 2.5% from 1960 to 1990, but slowed to 1.5% from 1990 to 2018. Instead of trickle-down economics, where everyone would benefit, we had trickle-up economics, where the top 1 percent and especially the top 0.1 percent, got a larger and larger slice of the pie.
These are illustrations of British political theorist Isaiah Berlin’s dictum that “total liberty for wolves is death to the lambs”; or, as I have sometimes put it less gracefully, freedom for some has meant the unfreedom of others—their loss of freedom.
Just as individuals rightly cherish their freedom, countries do, too, often under the name “sovereignty.” But while these words are easily uttered, there is too little thought about their deeper meanings. Economics has weighed into the debate about what freedom and sovereignty mean, with John Stuart Mill’s contribution in the 19th century ( On Liberty ), and Milton Friedman’s and Friedrich Hayek’s works in the mid-20th ( Capitalism and Freedom and The Road to Serfdom ).
But contrary to what Hayek and Friedman asserted, free and unfettered markets do not lead to efficiency and the well-being of society; that should be obvious to anyone looking around. Just think of the inequality crisis, the climate crisis, the opioid crisis, the childhood diabetes crisis, or the 2008 financial crisis. These are crises created by the market, exacerbated by the market, and/or crises which the market hasn’t been able to deal with adequately.
Economic theorists (including me) have shown that whenever there is imperfect information or imperfect markets (that is to say, always), there is a presumption that markets are not efficient. Even a very little bit of imperfection can have big effects.
The problem is that much of the global economic architecture designed over recent decades has been based on neoliberalism—the kinds of ideas that Hayek and Friedman put forward. The system of rules that evolved from there must be fundamentally rethought.
U.S. President Donald Trump arrives at the G-20 economic summit in Hamburg, Germany, on July 8, 2017. Sean Gallup/Getty Images
From an economist’s perspective, freedom is the “freedom to do,” meaning the size of the opportunity set of what a person can do, or the range of the choices that are available.
Someone on the verge of starvation has no real freedom—she does what she must to survive. A rich person obviously has more freedom to choose. “Freedom to do” is also constrained when an individual is harmed. Obviously, if an individual is killed by a gunman or a virus, or even hospitalized by COVID-19, he has lost freedom in a meaningful sense, and we then have a dramatic illustration of Berlin’s dictum: Freedom for some—the freedom to carry guns, or to not be masked, or to be unvaccinated—may entail a large loss of freedom for others.
The same principle applies to the international arena. The rules-based trade system consists of a set of rules intended to expand the freedoms of all in a meaningful way by imposing constraints. The idea that constraints can be freeing, while seemingly self-contradictory, is obvious: Stoplights force us to take turns going through intersections, but without this seeming constraint, there would be gridlock and no one would be able to move.
All contracts are agreements about constraints—with one party agreeing to do or not do something in return for another person making other promises—with the belief that in doing so, all parties will be better off. Of course, if one party cheats and doesn’t deliver on its promise, then that party gains at the expense of others. And there is always the temptation to do so, which is why we require governments to enforce contracts, so that promises mean something. No government could enforce all contracts, and the so-called free market would crash if all participants were grifters.
But while there are similarities between discussions of freedom at the individual level and the country level, there are also a couple of big differences. Most importantly, there is no global government to ensure that the powerful countries obey an agreement, as we are seeing today in the case of U.S. industrial subsidies. The World Trade Organization (WTO) generally forbids such subsidies and especially disapproves of some of the provisions—such as requiring domestic manufacturing (“Made in America”)—in legislation passed recently by the U.S. Congress, including the CHIPS and Science Act .
Big Tech Is Trying to Prevent Debate About Its Social Harms
The industry’s “digital trade” strategy seeks to preemptively constrain governments.
The Global Credibility Gap
No one power or group can uphold the international order anymore—and that means much more geopolitical uncertainty ahead.
Moreover, within democratic countries, the role of power in the making and enforcement of the rules is often obscure; we know that inequalities in wealth and income get translated into inequalities in political power, which determines who gets to design the rules and how they are enforced. An imbalance of power means that the powerful within a country determine the rules in ways that benefit them, often at the expense of the weak.
Still, the democratic context means that every once in a while, power is checked—as it was when the antitrust laws were passed in the United States in the latter part of the 19th century, or the Wagner Act was passed during the New Deal of the 1930s, giving workers more power.
In an international setting, power is even more concentrated, and democratic forces are even weaker. What has happened in the past few years illustrates this. The United States was at the center in constructing the rules-based system, in both designing the rules and how they were to be enforced, including dispute resolutions through the WTO’s Appellate Body. But when the rules—such as those concerning industrial subsidies—were inconvenient, it decided to ignore them, knowing that there was little, if anything, that any country could or would do about it. So much for the rules-based system.
And the United States’ confidence that nothing could or would be done was reinforced by the fact that it had effectively defenestrated the Appellate Body, because that Body had made decisions it didn’t like, and the U.S. thought that the Body was guilty of overreaching, going beyond what it was entitled to do. But rather than going back to the WTO and clarifying what the Body’s role should be, the U.S. simply hamstrung any adjudication within the WTO. The situation would be like suspending the U.S. Supreme Court while figuring out how to bring the justices back to a reasonable theory of jurisprudence.
This imbalance of power has played out repeatedly in recent years. When developed countries attempted to implement industrial policies—even mild policies, such as Brazil’s effort to provide capital to aerospace corporation Embraer at reasonable interest rates through that country’s development bank (as opposed to the outlandishly high rates then prevailing in its financial markets)—they were attacked . When Indonesia tried to ensure that more of the added value associated with its rich nickel deposits remained in Indonesia, it was attacked .
People line up to receive the Sinopharm COVID-19 vaccination at a local hospital in in Harare, Zimbabwe, on March 29, 2021. Tafadzwa Ufumeli/Getty Images
Even worse, when more than 100 countries proposed a waiver of intellectual property related to COVID-19—in the spirit of the compulsory licenses already seemingly part of the WTO framework, but given the urgency of the moment, a less bureaucratic process was of the essence—they were denied. The result: vaccine apartheid , where the advanced countries had all the vaccines they wanted, and the developing countries had almost zero access. This almost surely resulted in thousands of unnecessary deaths and tens of thousands of unnecessary hospitalizations in the poorer countries.
These are obviously no small matters in the well-being of citizens around the world, especially not for developing countries and emerging markets. Nor are they small matters in geoeconomics and geopolitics. The neoliberal rules forbidding subsidies effectively meant that developing countries couldn’t catch up to the advanced countries; the rules condemned them to being commodity producers, reserving the higher value-added production for the advanced countries.
This tariff structure has been rightly criticized as a crucial tool in the preservation of colonial trade patterns—aided and abetted by other unfair aspects of the trade regime, such as escalating tariffs. As economist Ha-Joon Chang has put it , the advanced countries “kicked away the ladder” from which they themselves had used.
It should be clear, too, that there are geopolitical consequences in refusing to play by the rules. The United States and the advanced countries are losing support for some of the most important issues requiring global cooperation, including climate change , global health, and the support needed to resolve the conflict in Ukraine as well as Washington’s apparent battle for democracy and hegemony with China.
The global south may yet steer the ship of international rules back on course. When the United States was the hegemon, it could do as it wanted, but its influence is now being challenged. China has provided more infrastructure than the United States has; early on in the pandemic, both China and Russia seemed more generous in providing vaccines.
Washington told the developing countries to open their doors to its multinationals, but when those countries asked that the rich corporations pay the taxes they owed, the United States was not supportive—reforms under an Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development initiative called BEPS (Base Erosion and Profit Shifting) generated sparse revenues for the poorer countries, and in return, the developing countries were asked to forego digital taxation. When, accordingly, the African Union asked for a change in venue of the discussions of global tax reform to the United Nations, the United States not only opposed it , but also tried to strong-arm others to do so. Last November, the United States lost the vote overwhelmingly at the U.N.
So whither goes global governance? In the absence of rules, the law of the jungle prevails. While the United States might win that fight, it would simultaneously lose the cooperation it needs so badly in a host of arenas. Overall, it would lose.
It is in the interests of the United States to abandon the corporate-driven rules-based system and work instead to create a set of at least basic rules that would reflect common interests. For instance, instead of the comprehensive so-called free trade agreements, such as the Trans-Pacific Partnership , that were really managed trade agreements (and managed specifically in the interests of Big Pharma and some of the big polluters), the United States should have narrow agreements—say, a green agreement to share knowledge and technology, promote sustainable forests, and work together to save the planet.
We need agreements that do more to constrain the large countries—whose actions can hurt the global economy—and do less to constrain the small, whose actions have little global consequences.
For instance, we need rules that would constrain the European Union and the United States from using monetary policy in ways that benefit their economies at the expense of others, as the United States has repeatedly done. Today, even the United States recognizes that investment agreements (such as NAFTA’s infamous Chapter 11 ) that allow corporations to sue states actually exert constraints on sovereignty without commensurate benefits. A key difference between NAFTA and the trade agreement that succeeded it is the effective dropping of Chapter 11. But the United States should go further, strengthening the ability of any government party to an agreement to sue corporations when terms of the agreement have been violated.
To win the hearts and minds in the new cold war brewing between the United States and China, the United States needs to do more. Washington needs to use the money it has to provide assistance to the poor, and the power that it possesses to construct rules that are fair. Nowhere is that more evident than in response to the debt crisis that the United States faces today and the recent pandemic, another of which the world will almost surely face in the future.
An aerial view shows open graves, left, near recent burials at a cemetery in São Paulo, Brazil, on May 22, 2021, during a surge of deaths from the COVID-19 pandemic. Mario Tama/Getty Images
With most sovereign debt contracts written in the United States, Washington has the power to change the legal framework governing these contracts in ways that make the resolution of crises—where countries can’t pay back what they owe—faster and better. This approach would address the “too little, too late” problem by which one crisis is followed by another, which has plagued the world for so long. With more creditors entering the field, debt resolution is becoming ever more difficult. There are important proposals currently before the New York legislature (where most of the money is raised), but support from the Biden administration would be enormously helpful.
The world has just gone through a terrible pandemic, and the recognition that there will be another has spurred work on a proposed pandemic preparedness treaty. Unfortunately, under the influence of Big Pharma, there are no provisions in the treaty for the kind of intellectual property waiver that the world so badly needs, let alone the technology transfer that would allow the production of all the products—protective gear, vaccines, and therapeutics—necessary to fight the next disease that strikes.
The freedom to live is the most important freedom that we have. Our global agreements have not balanced our freedoms in the way they should. Better global agreements can benefit all countries, though not necessarily all people within them: Such agreements would constrain the power of the exploiters to exploit the rest of us, thereby making a dent on their bottom line, but they would benefit society more generally.
Striving to create global agreements that are fair and generous to the poor would, I believe, be in the United States’ self-interest—in its “enlightened” self-interest, taking into account the new geoeconomics and geopolitics. It was never in the United States’ self-interest to pursue a corporatist global agenda, even when it was the hegemon. But it is especially not so today.
Books are independently selected by FP editors. FP earns an affiliate commission on anything purchased through links to Amazon.com on this page.
Joseph E. Stiglitz is a Nobel laureate in economics and a professor at Columbia University. Twitter: @JosephEStiglitz
Join the Conversation
Commenting on this and other recent articles is just one benefit of a Foreign Policy subscription.
Already a subscriber? Log In .
Subscribe Subscribe
View Comments
Join the conversation on this and other recent Foreign Policy articles when you subscribe now.
Not your account? Log out
Please follow our comment guidelines , stay on topic, and be civil, courteous, and respectful of others’ beliefs.
Change your username:
I agree to abide by FP’s comment guidelines . (Required)
Confirm your username to get started.
The default username below has been generated using the first name and last initial on your FP subscriber account. Usernames may be updated at any time and must not contain inappropriate or offensive language.
More from Foreign Policy
The iran-israel war is just getting started.
As long as the two countries remain engaged in conflict, they will trade blows—no matter what their allies counsel.
New Zealand Becomes the Latest Country to Pivot to the U.S.
Beijing’s bullying tactics have pushed Wellington into Washington’s welcoming arms.
A Tale of Two Megalopolises
What new cities in Saudi Arabia and Egypt tell us about their autocrats.
The Strategic Unseriousness of Olaf Scholz
His latest trip confirms that Germany’s China policy is made in corporate boardrooms.
How to Stave Off a Famine in Gaza
How kyiv plans to use american aid, nobody is competing with the u.s. to begin with, iraqi kurdistan’s ethnic minorities are under attack, xi believes china can win a scientific revolution, congress gives the arsenal of democracy a boost, u.k. detains asylum-seekers for deportation to rwanda, iran makes a play in south asia.
Sign up for World Brief
FP’s flagship evening newsletter guiding you through the most important world stories of the day, written by Alexandra Sharp . Delivered weekdays.

Voters in this 'boomerang' county say they're nostalgic for the Trump economy

EASTON, Pa. — Luis Escarraman says he is nostalgic for the Trump economy. The 41-year-old Republican owns his own truck and hauls freight from New Jersey to California. Maintenance, parts, diesel fuel — it has all become so pricey, he said.
"I can do my living, but compared to what I used to have, I need to work extra to get what I used to have before," Escarraman said.
He is not alone. Poll after poll show voters trust the presumptive Republican 2024 nominee more on the economy than the incumbent, President Biden. It's an important factor as voters look ahead to Election Day in November — but it's far from the only one.
Escarraman said he is weighing a variety of factors in whom he supports politically. Right now, he is concerned about the increase in migration and the money the U.S. government is spending on conflicts overseas, as well as the high cost of living.
But he also remembers that life under former President Donald Trump was at times alarming. "I know it was a lot of fights in the country," he said. "It was kind of like a civil war, but financially, it was better."
Inflation was a top issue in this "boomerang" county back in 2021
Heading into the 2024 election, inflation is one of Biden's biggest and most persistent political challenges.
In the summer of 2021, when the cost of living began ticking up, NPR traveled to Northampton County, Pa., to hear how voters were feeling about the president and his economic agenda ahead of what was expected to be a bruising 2022 midterm election cycle.
Northampton is one of only 25 "boomerang" counties in the U.S., meaning people there voted for Barack Obama in 2008 and 2012, then opted for Trump in 2016 and then most recently in 2020 chose Joe Biden.
It's the type of county that Republicans hope to win back to give Trump a shot at picking up the key swing state of Pennsylvania in November.
Back in 2021, voters in this county and across the nation were concerned about prices for gas, groceries, rent and insurance. But even though the economy dominated the headlines, Democrats did a lot better than expected in midterm races in 2022, including in Northampton County, where Rep. Susan Wild, D-Pa., held her seat.
The high cost of living remains a big concern to voters
Outside grocery stores and polling sites last week in Northampton County, hardly anyone NPR spoke with during more than a dozen interviews felt upbeat about the economy, regardless of their politics.
"When Trump was in office, it was sad, but my 401(k) was just going up and up and up. I mean, it was wonderful to watch it," said Ruthann Arris, 69, a Democrat who is retired.
In Trump's first three years in office, the S&P 500 index rose 46%. Comparatively, during Biden's first three years in office, the S&P 500 index rose 26%.
Like a lot of voters, Arris doesn't mention 2020, Trump's last year in office, when the COVID-19 pandemic brought the economy to a near standstill.
She's frustrated with what she's currently seeing in the grocery store: high prices and smaller packages for the same products she has always bought.
But she said she still intends to vote for Biden this November. "I think he comes across as much better than the alternative," she said. "You have a more stable USA. And it's not worth the short-term gain of a 401(k) going up."
Voters are looking at other issues, too, as they weigh decisions
Polling shows many voters are like Arris: worried about the economy, but looking at other issues as they make their decisions.
A survey from NBC News in April found that voters said inflation was the No. 1 concern facing the country, and they gave Trump a double-digit advantage on the issue. But when it came to identifying an issue that is "so important that you would vote for or against a candidate solely on that basis," voters pointed to democracy, abortion or immigration/border security, depending on their politics.
And that is akin to what NPR found in Northampton County: Many people were frustrated with inflation and the high cost of housing in a region that has seen an influx of transplants from the New York City metro area, but they also pointed to other priorities this election cycle.
"People want to complain about the economy and everything like that," said Greg Poff, 49, a Republican who said he is concerned about border security. "If you can control the flow of people into the country and get the people that aren't supposed to be here out, everything else will fall like dominoes."
Biden's campaign is trying to point to economic successes
Biden has made the economy a central part of his message on the campaign trail, pointing to the strong jobs market and the growth in the infrastructure and semiconductor sectors thanks to legislation he has signed.
He also spends a lot of time talking about his efforts to curb housing and prescription drug costs and eliminate junk fees.
One challenge is that many people are still using pre-pandemic prices as their benchmark, so any other economic message the president is trying to send isn't breaking through.
"I think it's hard because people don't like things to cost more than they did before. And until that adjusts for everyone in their minds, it's going to be hard to convince people perhaps otherwise," said Julie Smith, an economist at Lafayette College in Northampton County.
Copyright 2024 NPR


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4 min read. The history of corporate governance is long, rich and packed with twists and turns. It's a topic that touches on managerial accountability, board structure and shareholder rights — including both periods of shareholder passivity and shareholder power. Governance began with the rise of corporations, dating back to the East India ...
A History of Corporate Governance Around the World (Morck, 2005) illustrates the point. Despite being 687 pages in length, the volume only deals with 11 countries and only addresses one corporate governance issue in detail, this being share ownership patterns. This chapter, rather than surveying the history of corporate governance in a general
The Global History of Corporate Governance: An Introduction. This paper presents a synopsis of recent NBER studies of the history of corporate governance in Canada, China, France, Germany, Japan, India, Italy, the Netherlands, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Together, the studies underscore the importance of path dependence ...
In this essay, we highlight key changes in the corporate governance context over the past two decades and provide scholars a roadmap for future research. The newly transformed shareholder landscape and the shift toward a stakeholder perspective from shareholder primacy present unique contexts for scholars to capture today's dynamic aspects of ...
Abstract. This chapter explores the history of corporate governance and includes an historical perspective on corporate governance. It starts with the emergence of corporate governance during the 1970s in the United States, and then continues to study the developments that occurred sometime during the mid-1970s and the end of the 1990s.
This paper presents a synopsis of recent NBER studies of the history of corporate governance in. Canada, China, France, Germany, Japan, India, Italy, the Netherlands, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Together, the studies underscore the importance of path dependence, often as.
This chapter introduces corporate governance, which has received growing attention and interest over the years. It first looks at the history of corporate governance and the evolution of certain codes and other regulation forms. It then studies the mechanisms and processes of corporate governance, before taking a look at the various life-cycle ...
The Global History of Corporate Governance An Introduction Randall K. Morck and Lloyd Steier 1 To Whom Dare We Entrust Corporate Governance? Capitalism at the beginning of the twenty-first century is a variegated collection of economic systems. In America, capitalism is a system where a huge number of independent corporations compete with each ...
Abstract. "Corporate governance" first came into vogue in the 1970s in the United States. Within 25 years corporate governance had become the subject of debate worldwide by academics, regulators, executives and investors. This paper traces developments occurring between the mid-1970s and the end of the 1990s, by which point "corporate ...
Abstract. This essay provides the introduction to The History of Modern U.S. Corporate Governance, a sourcebook published by Edward Elgar. The essay begins by describing the scope of the sourcebook, indicating that the focus is on developments occurring from the mid-to-late 1970s, when the term corporate governance first came into vogue, onwards.
Corporate Governance. GARY HERRIGEL. This special issue showcases a new wave of historical research. corporate governance. The new wave is reacting to the exhaustion of the intellectual agenda of the initial scholarship devoted to question of the emergence and variable development of corporate. governance systems in different national economies.
What is the history of corporate governance and why does governance matter? In this guide we examine how it developed in various countries.
Entrepreneurial, Managerial, and Fiduciary Capitalism. In the first part of the twentieth century, large U.S. corporations were controlled by a small number of wealthy entrepreneurs—Morgan, Rockefeller, Carnegie, Ford, and DuPont, to name a few. These "captains of industry" not only owned the majority of the stock in companies, such as ...
Abstract. Corporate governance is not an overnight phenomena. It has been existing from a long time. It is only that the beginning of 21st century when colossal enterprises started to fall ...
There is a long and varied history associated with the evolution of the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). However, a historical review is missing in the academic literature that portrays the evolution of the academic understanding of the concept alongside with the public and international events that influenced the social expectations with regards to corporate behavior. The aim ...
ESSAY The End of History for Corporate Law HENRY HANSMANN* AND REINIER KRAAKMAN** INTRODUCTION Much recent scholarship has emphasized institutional differences in corporate governance, capital markets, and law among European, American, and Japanese companies.' Despite very real differences in the corporate systems, the deeper
This chapter examines the development of corporate governance over time and seeks to understand why it has become such a matter of debate today. It first looks briefly at the manner in which it has developed, concentrating on the changing balance of power between the main players on the corporate stage, shareholders, boards of directors, and ...
This dissertation is a collection of three essays that investigate the role and importance of corporate governance in public and private firms. Chapter 1, investigates the role of governance characteristics in determining the probability of a firm undergoing a going private transaction. Firms with greater board control are
Corporate Governance Essay INTRODUCTION Definition Corporate governance is a mechanism to control and monitor corporate behaviour. It comprises of the system of rules, practices and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. Corporate governance essentially involves balancing the interests of a company's many stakeholders.
Corporate governance is a set of policies and rules used to direct and control a company's operations. It is essential for managing a firm and balancing the interests of the stakeholders, shareholders, executive directors, suppliers, and customers. Accountability, transparency, fairness, and responsibility form the corporate governance framework.
The History of Corporate Governance and Ethics Research Paper. The roles and services offered by accountants have changed overtime. In the 15 th century, accounting involved bookkeeping only. With emergence of industrial revolution in the 19 th century, accountants' financial responsibilities have increased with time.
Last, corporate governance practices boost market confidence and ensure effective allocation of capital in the market (Greenspan, 2002). From the forgoing discussions, the realization of the importance of good corporate governance practices is largely dependent on a number of internal factors. As a way of achieving this, a number of principles ...
In November 1995, the Financial Reporting Council, established a Committee on Corporate Governance, headed by Ronnie Hampel, (Hampel Committee) to review the Cadbury Committee's recommendations on corporate governance. The Hampel Committee released a preliminary report in August 1997, followed by a final report in January 1998.
What History Tells Us About the Value of Bankruptcy Directors. The proliferation of bankruptcy directors represents a controversial shift in the corporate governance landscape. Independent directors appointed when a company experiences financial distress (known colloquially as "bankruptcy directors") bring restructuring expertise and ...
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: ET Context: Recently, CII (Confederation of Indian Industry) introduced a corporate governance charter tailored for startups, featuring a self-evaluative scorecard to assess governance progress. What is Corporate Governance? It comprises dynamic principles and measures guiding an organization's growth.It emphasizes values like transparency, fairness, and ...
Governance has been a topic of investment focus for a very long time and, while critically important, investors see governance quality as already embedded in asset prices." "By contrast, despite believing in the impact of climate on portfolios, investors see climate risks as yet to be fully priced," Larcker continued.
The Corporate Governance Charter also prescribes guidelines appropriate for startups based on the specific stages of their life cycle. "This charter is designed for entities incorporated under the ...
International agreements have not balanced our freedoms in the way that they should. April 28, 2024, 6:00 AM. By Joseph E. Stiglitz, a Nobel laureate in economics and a professor at Columbia ...
EASTON, Pa. — Luis Escarraman says he is nostalgic for the Trump economy. The 41-year-old Republican owns his own truck and hauls freight from New Jersey to California. Maintenance, parts, diesel fuel — it has all become so pricey, he said. "I can do my living, but compared to what I used to ...