
- Introduction: Role of Purchasing Function
Table of Contents
The purchasing function within an organization is a linchpin of its operations, impacting its ability to procure materials, products, and services efficiently and cost-effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore the pivotal role of the purchasing function, its significance, and how it contributes to the overall success of an organization.

Unpacking the Purchasing Function
Purchasing , also referred to as procurement, is the process of acquiring goods, materials, services, or assets from external suppliers. The purchasing function is the dedicated department or team responsible for managing and executing these procurement activities on behalf of an organization.
The Multifaceted Role of the Purchasing Function
The purchasing function plays a multifaceted role within an organization, encompassing several critical aspects:
1. Strategic Sourcing:
- Purchasing professionals identify and select suppliers strategically to ensure a consistent supply of high-quality materials or services at competitive prices.
2. Cost Management:
- Managing costs is a core function of purchasing. This involves negotiating prices, terms, and contracts to maximize cost-efficiency.
3. Supplier Relationships:
- Building and maintaining positive relationships with suppliers are crucial for securing reliable sources, favorable terms, and value-added services.
4. Risk Management:
- The purchasing function assesses and mitigates risks related to supply chain disruptions, quality issues, or unforeseen market changes.
5. Quality Assurance:
- Purchasing ensures that materials and products meet quality standards, aligning with the organization’s quality goals.
6. Efficiency and Timeliness:
- Efficiency in procurement processes and timely delivery of materials are vital to prevent disruptions in production or service delivery.
7. Compliance:
- Purchasing professionals ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and organizational policies, minimizing legal and financial risks.
The Significance of the Purchasing Function
The purchasing function holds immense significance for an organization:
– Cost Control:
- Effective purchasing directly impacts the organization’s bottom line by managing costs and optimizing resource allocation.
– Quality Assurance:
- It ensures that materials and products meet or exceed quality standards, safeguarding the organization’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
– Supply Chain Resilience:
- The purchasing function helps organizations build resilient supply chains, reducing vulnerability to disruptions.
– Competitive Advantage:
- Strategic sourcing can provide a competitive edge by securing access to unique resources or enabling cost leadership.
– Innovation:
- Collaborative supplier relationships can drive innovation and product development.
The purchasing function is a linchpin of an organization’s success, influencing cost management, quality assurance, supply chain resilience, and competitiveness. By strategically managing procurement, organizations can build strong foundations for sustainable growth and excellence.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Management of Machines and Materials
1 Operations Management-An Overview
- Systems Concepts in Operations Management
- Objectives in Operations Management
- Operations Management Decisions
- Types of Production Systems
- Management of Materials in Production Systems
- Concepts in System Life-cycle
- Role of Scientific Method in Operations Management
- Historical Development of Operations Management
2 Product Selection and Process Selection
- Introduction to Product Selection
- The Product Selection Process
- Selection of the Products
- Product Development
- Product Design
- Introduction to Process Selection
- Forms of Transformation Processes
- The Project Form
- Intermittent Flow Processes
- Continuous Flow Processes
- Processing Industries
- Selection of the Process
3 Facilities Location
- When does a Location Decision Arise?
- Steps In the Facility Location Study
- Subjective, Qualitative and Semi-Quantitative
- Techniques Locational Break-Even Analysis
- Some Quantitative Models for Facility Location
- Some Case Examples
4 Facilities Layout and Material Handling
- Basic Types of Plant Layouts
- Plant Layout Factors
- Layout Design Procedure
- Flow and Activity Analysis
- Space Determination and Area Allocation
- Computerised Layout Planning
- Evaluation, Specification, Presentation and Implementation
- Materials Handling Systems
- Materials Handling Equipment
5 Planning and Control for Mass Production
- When to Go For Mass Production
- Features of a Mass Production System
- Notion of Assembly Lines and Fabrication Lines
- Design of an Assembly Line
- Line Balancing Methods
- Problems and Prospects of Mass Production Modular
- Production and Group Technology
- Automation and Robotics
6 Planning and Control for Batch Production
- Features of Batch Production
- How to Determine the Optimum Batch Size
- Aggregate Production Planning
- Material Requirements Planning
- The Line of Balance (LOB)’ for Production Control and Monitoring
- Problems and Prospects of Batch Production
7 Planning and Control for Job Shop Production
- Variety of Problems in Job Production
- n Jobs One Machine Case
- n Jobs Two Machines Case
- Two Jobs m Machines Case
- Scheduling Rules for Job Shops (Job Shop Scheduling)
- Problems and Prospects of Job Production
8 Planning and Control of Projects
- Defining Projects
- Network Representation of Projects
- Time Management of the Project
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Programme Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Time Cost Relationship and Project Crashing
- Resource Allocation
- Project Updating and Monitoring
9 Capacity Planning
- Meaning, Definition and Measure Of Capacity
- Process for Capacity Planning
- Predicting Future Capacity Requirements
- Generation of Capacity Plans
- Evaluation of Alternate CapacityPlans
10 Work and Job Design
- Introduction to Work Design
- The Work Study Approach
- Method Study
- Work Measurement
- Work Study Application
- Introduction to Job Design
- Design Factors
- Environmental Factors
- Organisational Factors
- Behaviour Dimensions of Job Design
- Socio-Technical Approach to Job Design
11 Value Engineering and Quality Assurance
- Basic Concepts in Value Engineering
- Historical Perspectives
- Functions and Value
- Value Engineering Job Plan
- Fast Diagram as Value Engineering Tool
- Some Case Studies in Value Engineering
- Behavioural and Organisational aspects of Value Engineering
- Benefits of Value Engineering and concluding Remarks
- Introduction of Quality Assurance
- Concept of Quality
- Cost of Quality
- Quality Management
- Quality Organisation
- Acceptance Sampling
- Process Control
- Use of Computers in Quality Control
12 Purchase System and Procedure and Inventory Management
- Preparation of Inputs
- Restraints and Factors
- Purchasing Decisions
- Purchasing Organisation
- Procedures, Forms, Records and Reports
- Evaluation of Departmental Procedures
- Vendor Evaluation and Rating
- Computerized Purchasing Systems
- Purchasing in Government Organisations
- Introduction to Inventory Systems
- Functions of Inventory
- Classification of Inventory Systems
- Selective Inventory Management
- Exchange Curve and Aggregate Inventory Planning
- Deterministic inventory Models
- Probabilistic inventory Models
- Inventory Control of Slow Moving items
- Recent Developments in Inventory Management
13 Standardization, Codification and Variety Reduction
- Classification of Materials
- Codification
- Standardisation and Variety Reduction
14 Waste Management
- Complementarity of Waste Management and Resource Management
- Taxonomy of Wastes
- Definition of Wastivity: Gross and Net Wastivity
- The Functional Classification of Waste Management
- Outline of I-O-W (Input Output Waste) Model
- Treatment of Wastage in Cost Accounts
How do you assess your purchasing function?

The objective of every company, whatever its size and organisation, is to generate profits and run a profitable business . Calculating the profitability of a company and its departments is often determined by a management controller, who monitors budgets and, above all, performance indicators (operating costs, purchasing families, overall expenditure). It is therefore important to evaluate the purchasing function in order to determine the company’s efficiency. How do you know if your purchasing organisation is performing well? Find out in this article how to evaluate it effectively.
- 1.1 Purchasing performance
- 1.2 Supplier performance
- 2 When is a company classified as efficient?
- 3.1 Carry out a stakeholder approach
- 3.2 Carry out benchmarks
- 3.3 Evaluating customer satisfaction
The importance of evaluating performance
Purchasing management is an important step in a company’s development . It provides the opportunity to make the right strategic decisions , with the aim of establishing the right purchase price and determining the quality of the products and services on offer. It is therefore necessary to measure performance.
Purchasing performance
Evaluating this performance is essential to finding out whether all the purchasing function’s processes are effective or need to be improved . Measuring purchasing performance is also a means of defining the priorities of each department and determining the necessary and appropriate budget for each of the company’s purchasing categories. In short, purchasing performance measurement is an indispensable method for making the best decisions for the company (guaranteeing its success). To facilitate its evaluation, it is important to pay particular attention to quality, price and lead time.
Supplier performance
In order to properly assess the company’s performance, the purchasing department must also determine the objectives of the purchasing function in line with the company’s challenges. The purchasing policy enables suppliers to know the goals to be achieved , and plays a direct part in improving their services . By defining the company’s needs and deliverables in advance, the right procurement strategies can be put in place . The purchasing team is required to draw up a performance plan for suppliers, such as an SLA or Service Level Agreement. This programme must include the cost of goods, delivery times, the contracts binding the parties involved, the procedure for resolving any difficulties and all the information necessary for a good relationship between the two parties.
Measuring the performance of all the company’s processes depends essentially on a number of indicators , such as:
- The cost of purchasing and expenditure ,
- Levels of social responsibility requirements for responsible purchasing,
- Supplier evaluation ,
- Risk mapping .
If your partners do not meet these requirements, communicating areas for improvement is part of good practice and ensures effective and responsible supplier relations.

When is a company classified as efficient?
A company is said to be efficient when it is capable of generating profits and managing its activities profitably . It should be noted that profitability or return is the ratio between the revenues received by the company and the costs associated with the expenditure required to generate these revenues. If your company manages to generate more income than it spends , then it can be said that your business is efficient and profitable . On the other hand, if your business is generating lower revenues than expenses, your company is not profitable, so you will need to review your business strategy and manage your invoices . Sales are a good indicator, but you need to look at the total costs that went into making them (human resources, operating costs, acquisition costs, etc.)
Measuring company objectives
There are several parameters to take into account when assessing whether a company has achieved its objectives . It is important to be familiar with the systems and methods used to determine the company’s efficiency in order to ensure that it complies with the defined strategy. To do this, it is important to:
Carry out a stakeholder approach
There are a number of factors involved in determining your company’s performance and evaluating your purchasing function. In fact, analysing purchasing performance requires statistics from the company’s various departments. It is therefore important to extract the right information from this data. To avoid getting lost in the analysis of this data, it is essential to find and adopt a tool that can bring together and classify all this information in a single place. You can therefore opt for a single data platform or for purchasing management software.
Carry out benchmarks
Benchmarking is a method of comparing a company’s performance with that of its competitors . It essentially depends on a number of parameters. Accessing this information can be difficult, but not impossible. Today there are solutions dedicated to collecting this data . However, make sure you have reliable information to avoid a distorted analysis. This practice provides an opportunity to compare your company’s strengths and weaknesses , and to identify good and bad operations.
Evaluating customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is important, if not essential. Evaluating this parameter also helps to determine your company’s performance and efficiency . It is the responsibility of the purchasing function to ensure that this objective is achieved. It is important to ensure that orders are processed quickly, that products and services are of a high quality, that people are willing to listen, that disputes are resolved and that the company is professional ..
For better purchasing management, you need to be able to carry out a proper assessment of your purchasing organisation . This will ensure that your company is as efficient as possible , making it easier to achieve your objectives, such as implementing a sustainable and responsible purchasing policy . Weproc gives you the opportunity to gather the data you need to evaluate your purchasing function and your company’s overall performance. This management software is an effective and indispensable tool for situating the strategies adopted in your company and determining its effectiveness.
Want to learn more about our procurement management software Weproc? Contact us or request your free 15-minutes demo below!

Weproc is a SaaS software specialized in digitizing the procurement process of companies. From purchase requests to supplier invoicing, through the validation process, Weproc is designed to simplify the purchase management of SMEs and mid-sized companies by centralizing all purchase-related activities.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You may also like
Top 5 invoicing software to manage your invoices.
Invoicing is an essential part of commercial management, ensuring the smooth running of a business. In recent years, the digital transformation of […]
Purchasing function: how the process works
Before buying, a purchasing organisation first goes through a succession of operational tasks. Each phase must be implemented rigorously and methodologically. The […]
5 tips to simplify your purchasing function
Long seen as a simple administrative task, the purchasing function was relegated to a secondary role within companies. However, it has been […]
Recevez chaque mois nos meilleurs articles ! En bonus, nous vous mettons à disposition nos nouveaux modèles de documents en avant première.
Alors, pas mal non ?
- SaaS Solution Weproc
- Free Ressources
- Discover our tool
Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies Essay
Introduction, the role of finance function (q1), quality management (q2), supplier development (q3), risks associated with contracts (q4), avoidance of litigation and purchasing performance (q5), forecasting sales (q6), case of ben gibson (q7), calculation of economic order quantity (q8).
This report covers different aspects of procurement by companies. It focuses on the role of the finance function, quality management, supplier development and its challenges, risks associated with different types of contracts, avoidance of litigation, purchasing performance, and acceptance of a discounted price. Furthermore, this report includes calculations of ordering costs and forecasting methods.
The purchase function and finance function work together to furnish purchase orders and fulfill the requirements of the business. The finance department determines the available sources of funds and informs the purchasing department about the possibility of completing their purchases. The purchasing department is related to the operations of a business, which regularly monitors the requirements of the production process to ensure that it does not halt at any time due to the shortage of supplies. It is not concerned with the availability of finance; instead, it is responsible for the continuation of the production process.
Therefore, it places purchase orders to suppliers or sends them to the finance department for approval. This department decides to assess whether the purchase order can be completed or not. The cost of maintaining a certain level of inventory and reordering of supplies also need to be monitored and decided by the finance function. The finance management draws limits to the purchasing that the company can make. It knows the level of funds available and plays a leading role in negotiating the terms of payment with the seller. It is in a better position to negotiate a price discount or a more extended payment period, for example, if the company has cash shortage, then the finance management can negotiate credit terms with suppliers and make payments when the firm’s cash position improves.
In the same way, the finance department is responsible for large accounts receivable and related losses (Lasher, 2017). Therefore, it can be stated that the finance department plays a crucial role in sustaining the financial viability of the business. The purchasing and sale departments cannot operate efficiently without effective management of the finance function.
It is crucial for manufacturing companies to ensure that they have an uninterrupted supply of materials for production. It is argued that quality is an important factor throughout the firm’s supply chain. Moreover, it is essential for the purchasing department to make sure that the desired level of quality is maintained throughout the production cycle, starting from the acquisition of supplies to the development of the final product. The purchasing department works with suppliers so that they comply with its quality requirements. This has a direct impact on the production process and the costs associated with it. If the quality of supplies is unsatisfactory, then the company will incur high costs due to production losses. It implies that the purchasing department needs to perform quality checks at all stages of the supply chain (Musau, 2015). It performs inspections during the manufacturing process and receives quality reports from the production function.
The production department provides its requirements for supplies to the purchasing department, which then works with suppliers to fulfill its requirements, including physical description, dimensional requirements, chemical composition, industry standards, and performance specifications. It ensures that the production process continues without problems and the final product to be delivered to customers meets their demands or specifications. If the process is examined backward, then it could be stated that the purchasing department is responsible for attaining the desired level of quality that the company wants to offer to its customers. It is the responsibility of the purchasing department to find suitable suppliers who can meet the increasing demand for production and, at the same time, do not compromise the quality of supplies (Monczka, Handfield, & Giunipero, 2016).
Supplier development refers to the process through which companies establish and maintain close working relationships with certain suppliers to achieve a high-level of organizational efficiency. In this arrangement, firms work with specific suppliers on a one-to-one basis to assist them and improve their capabilities, performance, and quality that would ensure timely delivery of products and services. Therefore, it is essential for companies to create a network of suppliers who can confirm that their products will meet business requirements (Monczka et al., 2016). Moreover, it helps in lowering the cost of inputs by effectively managing relationships with suppliers. However, it is argued that this is not an easy task, and the outcomes of the firm-supplier relationship are not always fruitful. It often leads to a significant loss to both entities in terms of time and higher costs.
I agree with the statement of Chrysler’s executive as it is not possible to maintain 100% successful relationships between companies and suppliers. It also means that companies must develop relationships with multiple suppliers to avoid any disruption. There are various reasons for the failure of supplier development efforts. The primary reason is the differences in the organizational framework, approach, culture, values, and financial objectives between firms and suppliers. The problems between firms and suppliers intensify in the absence of effective leadership or ownership as most of the vendors are reluctant to commit their resources to innovation or improvement. Although such relationships initiate with common goals, they become difficult to manage as the deal or project expands in scope, and the lack of trust between entities worsens (Genovese, Koh, Kumar, & Tripathi, 2014).
Moreover, expectations on both sides may change, and supplier relationship managers need to address them beyond contractual terms. It is also common that companies and suppliers operate in different markets, which makes it challenging to monitor suppliers’ activities. Furthermore, interventions by the government or regulatory bodies can make it challenging to continue a business arrangement, for example, a Chinese firm is recently banned in the US, which is likely to affect the telecom industry that depends on its products and services. Thus, it could be stated that many uncontrollable factors affect supplier development.
Various risks associated with the three types of contracts, including fixed-price, incentive, and cost-based contracts are discussed in the following.
Fixed-price Contracts
These contracts have a fixed-price term, which means that the price of goods or services cannot be altered based on the contractors’ cost experience. Buyers face the risk of incurring a high cost of procurement (Eckerd & Girth, 2017). It means that the buyer has to pay a higher price despite a reduction in the cost of goods or services. However, fixed-price contracts have the least risk for the buyer. In this case, the Sharpe ratio is 0/100, which implies that the entire burden is on the contractor to make sure that goods or services are rendered within the set time at a price decided in the contract (Nyambuu & Tapiero, 2018).
Incentive Contracts
These contracts combine fixed price and incentive terms, which implies that the buyer pays additional compensation to the contractor if it fulfills all requirements of the contract. In this case, there is a higher risk to buyers in the case of inappropriate incentive measures for assessing the performance of the contractor (Eckerd & Girth, 2017).
Cost-based Contracts
There are three variations of cost-based contracts, namely Cost-Plus-Fee (CPF), Cost-Plus-Fixed-FEE (CPFF), and Cost-Plus-Incentive (CPIF). In all of these contracts, the buyer bears a high risk of paying the cost plus additional compensation (Eckerd & Girth, 2017). If the contractor overruns the procurement cost, the buyer is still responsible for paying this amount.
Litigation is one of the seven different methods of dispute resolution in which the case is submitted to the court and facts are presented to the independent jury that decides the dispute which has to be accepted by all involved parties. However, this method is avoided by many firms in settling contractual disputes due to the high cost of litigation. Moreover, companies prefer alternative methods of resolution that are less time intensive and helpful to avoid a procedure from which it may be difficult for them to recover. It is also noted that there are emotional effects of litigation on the management and employees of companies, which distracts them from their responsibilities. Litigation can also affect the firm’s relationships with other businesses, investors, employees, and customers as the negative outcome of the case can adversely affect its reputation and standing (Malm, Adhikari, Krolikowski, & Sah, 2017).
Effectiveness measures refer to the course of action that the management could follow to achieve the corporate objectives. When assessing purchasing effectiveness, the price paid for supplies is not an appropriate measure. For this purpose, inventory turnover, which determines that the number of times that the company converts its inventory into sales is a more useful measure. The company should focus on purchasing effectiveness measure when there is greater stability in the market or fluctuations in economic conditions are as expected. On the other hand, efficiency measures refer to the difference between planned and actual sacrifices that the management has to make to achieve the corporate objectives. Purchasing efficiency measure is not related to the number of units procured. It relates to the performance of the department responsible for this process. If the department manages its purchases within the budget, then it is considered efficient. The company should focus on purchasing efficiency measure when assessing the internal performance of the firm. Measuring purchasing performance is crucial as it is a crucial part of the firm’s supply chain. In this regard, effectiveness and efficiency measures are useful as they both assist in determining the overall purchasing performance.
The three-month moving average and exponential smoothing forecast are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Forecasting.
MAD and MSE are calculated for each forecast in Table 2.
Table 2. MAD and MSE.
Exponential Smoothing:
Based on the results given in Table 2, it is noted that 3-month moving average provides a better forecast as its MAD and MSE is lower. Moreover, error (%) of this method is lower than the exponential forecasting method.
It could be argued that Ben Gibson legally acted as he has the right to seek new suppliers of corrugated boxes, who can sell them at a lower price. The company has the legal right to rebid the corrugated contract and find latest offers. However, it can be stated that Gibson did not act ethically. His decision to initiate the bidding process to put pressure on the present supplier to lower its price of corrugated boxes can be regarded as sharp practices. Such practices fall short of actual fraud as Gibson was involved in misrepresentation of the issue faced by his company. It can be stated that he was willfully creating a competition between suppliers to take advantage of the situation by deceiving its current vendor.
My decision as the marketing manager for Southeastern Corrugated would be not to submit a bid by lowering the price of corrugated boxes. It may be possible to discuss the situation with Coastal Products and negotiate an acceptable price of corrugated boxes. However, if the discussion is unsuccessful, then it is logical for Coastal Products to seek a new supplier.
The assumptions of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) are given below:
- There is a uniform demand rate throughout the period.
- There is a fixed item cost.
- The ordering and holding cost does not change over the period.
The economic order quantity is calculated in the following.
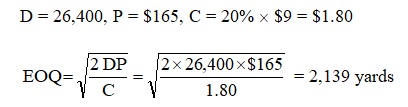
The number of orders per year is calculated as follows.
26,400 / 2,139 = 12 orders
The order level is determined by determining demand for denim cloth per working day and per week is calculated as follows.
26,400 / 250 = 105.6 yards per day
105.6 x 5 = 528 yards per week
Purchasing lead time = 2 weeks
Order level = 1,056 yards.
The total annual cost for the item is calculated as follows.
Total cost per yard ($9 + $1.80) = $10.80
Total annual cost = $10.80 x 26,400 = $285,120
Acceptance of Discounted Price (Q9)
Vendors often offer a price discount to encourage buyers to buy large quantities. However, the decision to avail this offer depends on the assessment of the business requirements by the purchasing manager. There are various factors which can affect the choice to buy a large quantity of a product at a discounted price. First, the purchasing manager needs to estimate production requirements. Since the company uses this product regularly, it may be feasible for the company to buy it and store it for the full year’s production. However, the storage life of the product and the company’s warehousing capacity should also be evaluated to make sure that it does not incur an inventory loss (Li, 2014). Second, the purchasing manager must consult with the finance department and determine if the benefit of a low price exceeds inventory management and reordering costs to be incurred by the company.
In case if the financial benefit of buying a large quantity of the product is greater than its related costs and expenses, then the purchasing manager should go ahead with it. Third, the finance department will assist by determining the availability of finance as the decision to purchase a large quantity of the product will incur a significant expenditure. Therefore, the purchasing manager should seek approval from the finance department, which will evaluate the use of funds between different alternate investments that the company may be considering. If there are no issues of liquidity, then it will be an appropriate decision to buy the product. Fourth, the purchasing manager should ensure that there are no quality issues with the product. In some cases, vendors try to get rid of their huge stocks by offering a large-quantity discount. Therefore, the manager must conduct an in-depth evaluation of the available product’s quality before accepting this offer.
Calculation of Relevant Cost (Q10)
The calculation of the relevant cost is given in Table 3.
Table 3. Relevant Cost.
Table 3 shows that the total annual relevant cost when choosing Sontek is $183,380, and that of Denton is $185,254. John should buy from Sontek as there is an annual difference in favor of this supplier.
Calculation of Safety Stock (Q11)
The calculation of the safety stock is given in Table 4.
The most likely demand is 600 units for two weeks as it has the highest probability, as shown in Table 4. Since the carrying cost is not identified, it is assumed to be $5. Stockouts can occur if demand is 700 and 800. If the demand is less than 600, there will be no stockout costs, but it will have carrying costs.
Eckerd, A., & Girth, A. M. (2017). Designing the buyer–supplier contract for risk management: Assessing complexity and mission criticality. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 53 (3), 60-75.
Genovese, A., Koh, S. L., Kumar, N., & Tripathi, P. K. (2014). Exploring the challenges in implementing supplier environmental performance measurement models: A case study. Journal Production Planning & Control – The Management of Operations, 25 (13-14), 1198-1211.
Lasher, W. R. (2017). Practical financial management. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
Li, X. (2014). Operations management of logistics and supply chain: Issues and directions. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2014 , Web.
Malm, J., Adhikari, H. P., Krolikowski, M., & Sah, N. (2017). Litigation risk and investment policy. Journal of Economics and Finance, 41 (4), 829–840.
Monczka, R. M., Handfield, R. B., & Giunipero, L. C. (2016). Purchasing and supply chain management (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
Musau, E. G. (2015). Determinants of procurement function and its role in organizational effectiveness. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 17 (2), 12-25.
Nyambuu, U., & Tapiero, C. S. (2018). Globalization, gating, and risk finance. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 23). Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies. https://ivypanda.com/essays/purchasing-and-sourcing-strategy-in-companies/
"Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies." IvyPanda , 23 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/purchasing-and-sourcing-strategy-in-companies/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies'. 23 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies." February 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/purchasing-and-sourcing-strategy-in-companies/.
1. IvyPanda . "Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies." February 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/purchasing-and-sourcing-strategy-in-companies/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Purchasing and Sourcing Strategy in Companies." February 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/purchasing-and-sourcing-strategy-in-companies/.
- Stock-Outs and Their Impact on the Company’s Progress
- Inventory Management
- Procter & Gamble's Enterprise System Management
- Operations Management: Inventory Control
- The Shryne Supply Chain Manager Interview
- Procurement of Goods: Decision Support System Development
- Simulation Reflective Report: Inventory Basics Strategy Discussion
- A Proper Pattern of Supply Chain Management
- Consolidated Electric Company's Inventory Control System
- Gabler Trucking, Inc.: Inventory Management Systems
- Agile Supply Chain in the Fashion Industry
- Zara, H&M, United Colors of Benetton: Supplying Fast Fashion
- Walmart China's Transportation and Warehousing
- Outsourcing the Cleaning Services of Abu Dhabi National Oil Company
- Apple Incorporation: Supply Chain Management

The Role of The Purchasing and Supply Functions
Cite this chapter.

829 Accesses
- Supply Chain
- Supply Function
- Supply Management
- Purchasing Manager
- Purchasing Department
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers
About this chapter
(2004). The Role of The Purchasing and Supply Functions. In: Global Purchasing and Supply Management. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-7817-X_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-7817-X_1
Publisher Name : Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN : 978-1-4020-7816-3
Online ISBN : 978-1-4020-7817-0
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Contract Management
Supplier Management
Savings Management
- Data & Security
FAQ’s
oboloo FAQ's
What is the procurement function and why is it important.
Are you familiar with the procurement function in your company? Have you ever wondered why it’s crucial for businesses to have effective procurement strategies? In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment , efficient procurement practices are more important than ever. Procurement is not just about buying goods and services; it involves a strategic approach that ensures cost-effectiveness, timely delivery, quality control, risk management , and supplier relationship management. So let’s delve deeper into what the procurement function entails and why it plays such a pivotal role in organizational success.
What is the procurement function?
The procurement function is one of the most important functions in any organization, as it is responsible for ensuring that the necessary goods and services are available to meet the needs of the company. It also plays a crucial role in ensuring that the company is able to get the best possible deals on these goods and services, thus saving money.
The procurement function can be broken down into three main areas: purchasing, sourcing , and contracting. Purchasing is responsible for acquiring the necessary goods and services on behalf of the company . Sourcing is responsible for finding the best possible suppliers for these goods and services, while contracting deals with these suppliers to provide them with products and services. Together, these areas ensure that the company has everything it needs to meet its goals, no matter what they may be.
The procurement function is an essential part of every organization , as it ensures that all of the necessary goods and services are available to meet company needs. This saves money in the long run, as better deals can be struck on products and services than would be possible otherwise. Together, purchasing, sourcing, and contracting make up the procurement function – ensuring that everything needed by the company is available when needed.
The procurement function and its importance
The procurement function is responsible for acquiring goods and services that are needed by an organization . The procurement function can be broken down into three main areas: planning, acquiring, and managing. Planning is the process of deciding what needs to be purchased and how much of each item will be necessary. Acquiring is the process of finding a supplier that can provide the desired product or service at a price that is acceptable to the organization. Managing is the process of monitoring and controlling the acquisition process to ensure that the desired product or service is delivered on time, within budget, and meets the organization’s specifications.
The procurement function is important because it ensures that the organization has the necessary items to carry out its missions. In addition, good procurement practices help avoid waste and fraud, which can cost organizations money in terms of lost profits and damaged relationships with suppliers . Good procurement practices also help ensure that products are high quality and meet the needs of customers. Finally, good procurement practices help organizations save money by purchasing items in bulk when possible.
There are a number of things organizations can do to improve their procurement processes . First, they should develop a clear understanding of what they need and want in order to purchase products or services. Next, they should identify potential suppliers based on price, quality, delivery time, and other factors. Finally, they should conduct rigorous reviews of potential suppliers to make sure that they meet all requirements for purchase
The different types of procurement
Procurement is the process of identifying, acquiring and awarding a good or service to meet the needs of an organization. There are three main types of procurement: buying, contracting and leasing.
Buying is when an organization purchases goods and services from suppliers. Contracting is when an organization hires a third party to provide goods or services on its behalf. Leasing is when an organization leases goods or services from a supplier or third party .
Buying is the most common form of procurement because it’s cheaper than hiring someone else. Organizations can buy goods and services online , in stores or through catalogs. Buying can be done through private companies , government agencies or nonprofit organizations.
Contracting is the second most common form of procurement because it allows organizations to get quality goods and services without having to pay upfront. Contractors offer competitive bids and usually have experience with the type of service being provided. Contracting can be done through private companies , government agencies or nonprofit organizations.
Leasing is the least common form of procurement because it requires less time commitment than buying or contracting. Leasing allows organizations to use resources for a set period of time without having to purchase them outright. Leases can be short-term (up to six months) or long-term (up to five years).
How the procurement function helps businesses run more effectively
The procurement function helps businesses run more effectively by providing a system for acquiring the right goods and services at the right price. This system can help businesses save money, time, and energy by making sure they get what they need when they need it.
The procurement function can help businesses save money by improving efficiency. For example, if a business needs 10 widgets but only has enough money to buy 8 widgets, the procurement function can help find a supplier who will sell the remaining 2 widgets at a lower cost than if the business bought them directly.
The procurement function can also help businesses save time by speeding up the process of finding the right supplier. For example, if a business needs 100 widget parts but only has 20 widget parts in stock, the procurement function can help find a supplier who will make all 100 widget parts in a shorter amount of time than if the business had to search for and buy each part individually.
The procurement function can also help businesses save energy by reducing waste . For example, if a business is manufacturing 100 widget parts but only needs 90 widget parts to complete its order, the procurement function can negotiate with suppliers to get them to sell extra widgets so that the business won’t have to waste any energy manufacturing unnecessary parts.
Procurement is one of the most important functions in any business . It’s responsible for ensuring that the company gets the resources it needs to do its job, no matter how big or small those resources may be. It can also play a role in safeguarding the company’s reputation and preventing costly mistakes. In a nutshell, procurement is essential for running any business successfully. Thanks for reading!
Want to find out more about procurement?
Access more blogs, articles and FAQ's relating to procurement
The smarter way to have full visibility & control of your suppliers
Contract Management
Partnerships
Charities/Non-Profits
Service Status
Release Notes
Feel free to contact us here. Our support team will get back to you as soon as possible
Sustainability
Essay on Purchasing: Top 8 Essays | Phases | Materials Management
Here is an essay on the ‘Purchasing of Materials’ for class 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on the ‘Purchasing of Materials’ especially written for school and management students.
Essay on Purchasing
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Evaluation of Purchasing Performance
Essay # 1. Meaning of Purchasing:
Purchasing is the first phase of Materials Management. Purchasing means procurement of goods and service from some external agencies.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The object of purchase department is to arrange the supply of materials, spare parts and services or semi-finished goods, required by the organisation to produce the desired product, from some agency or source outside the organisation.
The purchased items should be of specified quality in desired quantity available at the prescribed time at a competitive price. In the words of Alford and Beatty, “ Purchasing is the procuring of materials, supplies, machines, tools and services required for equipment, maintenance, and operation of a manufacturing plant “.
According to Walters, purchasing function means “the procurement by purchase of the proper materials, machinery, equipment and supplies for stores used in the manufacture of a product adopted to marketing in the proper quality and quantity at the proper – time and at the lowest price, consistent with quality desired.”
Thus purchasing is an operation of market exploration to procure goods and services of desired quality, quantity at lowest price and at the desired time. Suppliers who can provide standard items at the competitive price are selected.
Purchasing in an enterprise has now become a specialised function. It was experienced that by giving the purchase responsibility to a specialist, the firm can obtain greater economies in purchasing. Moreover purchasing involves more than 50% of capital expenditure budgeted by the firm.
According to Westing, Fine and Zenz “ Purchasing is a managerial activity that goes beyond the simple act of buying. It includes research and development for the proper selection of materials and sources, follow up to ensure timely delivery; inspection to ensure both quantity and quality; to control traffic, receiving, storekeeping and accounting operations related to purchases . ”
The modern thinking is that Purchasing is a strategic managerial function and any negligence will ultimately result into decrease in profits.
Essay # 2. Objectives of Purchasing:
The objectives of Purchasing should conform with the overall objectives of the organisation. It is one activity where reasonable economies can be accomplished.
The following are the main objectives of purchasing:
(i) Purchase of Satisfactory Material:
To procure materials, which are most appropriate to the product and are supplied in right quantity and quality at right time and right price.
(ii) To Control the Quantity of Material:
Purchase of material needs investment. Buying too much or too little quantity may not be in economic interest of the organisation i.e. too much quantity may unnecessary block the capital whereas too little purchase order may affect the regular supply of production. By analysing the requirements of different items and regulating the appropriate ordering policy the purchasing department ensures economic capital investment and regular flow of production:
(iii) Proper Negotiations with Suppliers:
Search for potential suppliers is an important activity of purchasing. This ensures timely supply of materials in the most economic manner. Wrong selection of supplier may be harmful to the enterprise both in terms of price and delivery time. Purchasing department through its dealing with suppliers creates goodwill and enhances the reputation of the enterprise.
(iv) Controls Proper use of Materials:
By analysing the requirements of various departments of the organisation, the purchase department avoids duplication, waste and obsolescence of materials and equipment’s.
(v) Co-Ordination with other Departments:
The purchase department should develop full co-ordination and maintain close relationship between various departments of the organisation.
(vi) Maintenance of Company’s Goodwill:
By maintaining the quality standards of the material the purchasing activity is instrumental in generating the confidence of consumer in the product of the company.
(vii) Other objectives can be:
(a) Exploration to locate new suppliers.
(b) Information about new materials and processes, which can reduce the cost of production and improve the performance of the product.
(c) To achieve economy and efficiency in the activities of the purchase department by analysing.
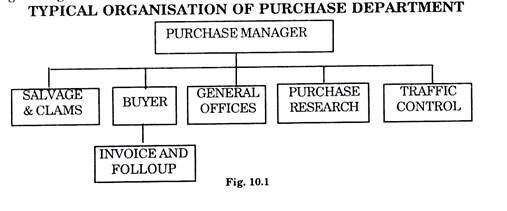
Essay # 3. Organisation of Purchase Department :
The composition purchase department varies according to the size of the enterprise its comparative significance towards procurement and the capability of the purchase personnel.
In organisations engaged in procurement of smaller range of items but from limited number of suppliers the purchase officer is attached to controller of accounts. In organisations with job or batch system of production, purchasing becomes a complicated exercise and needs regular thorough co-ordination with production department. In such cases purchase manager is directly attached to production manager.
The size of the purchasing departments depends on the nature of products manufactured by the organisation, sizes of the production runs type of the manufacturing system.
In general, the purchasing department can have the composition given fig. 10.1.
Typical Organisation of Purchase Department :
The purchase requisition is prepared in duplicate and the original copy is sent to the purchase department. The purchase department processes and scrutinizes the requisition and then proceeds to other operations for making purchases.
2. Location and Choice of Suppliers:
The potential vendors are contacted through authorised representatives; their catalogues and sample of the items are inspected and examined either at the purchaser’s place or at the vendor’s place. On the basis of findings from inspection, examination of samples and analysis of the quoted prices, suppliers are approved for placing the orders.
The criterion for the ultimate choice of a vendor is based on following aspects:
(i) Reliability of Supply:
Past performance specially in the time of crisis as well as sound financial position of a supplier classifies him to be reliable.
(ii) Assurance of Timely Delivery:
The punctuality pattern in observing the delivery schedule provided by the purchaser during past deals ensures the prompt supply by the vendor.
(iii) Other Considerations:
After sales service, technical assistance, attitude with regard to the goods rejected by the purchaser and co-operation in disposal of waste are some important guiding factors for the choice suppliers.
Purchasing agents continually scan the market place in search of potential new suppliers. Continued monitoring and evaluation of the supplier performance is necessary and should be based upon actual results.
3. Placing of Orders:
The purchase department tries to purchase the materials with desired quality and quantity at the most advantageous terms. All purchases should be made through a purchase order in a specified form and duly signed by some authorised person. The purchase order must contain the details about the supplier, description of the items required, corresponding prices and amount required.
The format of standard purchase order can be:

(ii) Purchasing department consolidates the requirements from various departments to know the total requirement for each item.
(iii) Market exploration is made to locate the goods and services of desired quality and quantity at the reasonable price.
(iv) Potential suppliers are identified from catalogues, quotations and past records.
(v) Purchase order in specified form (see fig.10.3) is prepared and sent to the approved suppliers. Purchase order is the commitment of the buyer to the supplier establishing a contractual relationship between buyer and seller.

(vi) After some time of placing the order, follow-up process starts to get quick delivery of the items. The follow-up procedure implies acceptance of the order and promise to supply the items on desired date.
(vii) The items are received by the purchasing department at the time of delivery and the items received are compared with purchase order. The checking of the delivered goods is done with regard to (i) Prices charged and quoted (ii) approval of the invoice (iii) to ascertain the quality and quantity of the items.
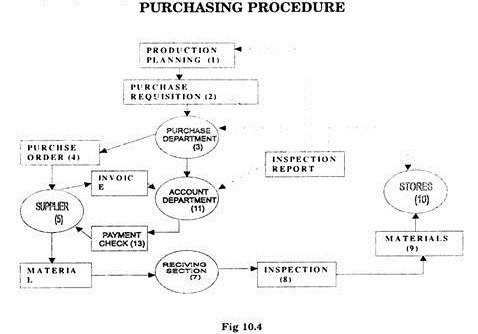
The receiving report can be given on a specified form given below:

(viii) Defective items i.e. items which are not in accordance with the -specifications laid down in the purchase order are returned to the supplier on credit note for exchange.
The received consignment is then delivered to the stores department or the department which requisitioned the material.
Essay # 8. Evaluation of Purchasing Performance:
Purchasing performance in most areas is quite difficult to be expressed in quantitative terms. The intangible nature of primary purchasing responsibilities prohibits the direct measurement of purchasing accomplishments.
Most of the organisations follow fairly broad approach on the lines described below:
(i) Evaluation of Purchasing Managerial Personnel:
The experience, qualifications and knowledge of purchasing managers in relation to the materials purchased, suppliers and markets etc. are analysed.
(ii) Analysis of the procedures adopted for purchasing.
(iii) Buying Proficiency:
This is measured by:
(a) Checking the actual price paid with target price
(b) Savings resulted from negotiations
(c) Percentage of overdue orders
(d) Percentage of stock outs caused by late deliveries
(e) Gains and losses from forward buying activities
(f) Number of orders issued/period.
(iv) Purchasing Efficiency:
It involves evaluation of workloads, personnel utilisation, operating costs and processing times as related to specific volumes of purchasing operations. Some organisations continually audit a small random sample of completed orders to determine.
Correct method of purchase, consolidation of orders requirements advantageously, selection of suitable vendor. Such audit frequently detects newly developing problems more quickly. Moreover the psychological effect of the audit generally stimulates to more consistent levels of performance.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Store-Keeping: Top 6 Essays | Phases | Materials Management
- Essay on Materials Management: Top 7 Essays | Branches | Management
- Essay on Materials Management: Top 6 Essays | Production
- Essay on Purchasing | Materials Management
We use cookies
Privacy overview.

- Order Now
The importance of the purchasing function
Published Date: 23 Mar 2015
Disclaimer: This essay has been written and submitted by students and is not an example of our work. Please click this link to view samples of our professional work witten by our professional essay writers . Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of EssayCompany.
In the hospitality industry, purchasing may be defined as " a function concerned with the search, selection, purchase, receipt, storage, and final use of a commodity in accordance with the catering policy of the establishment". (Davis and Kotas, 1986:47)
Davis and Kotas (1986) suggest that purchasing is a fundamental function in the beverage control cycle. If this function is managed efficiently, then any hotel can attain quality beverage products at the minimum cost possible according to the company's financial objectives.
The objective of beverage purchasing is to procure the best quality of items, at the lowest price for a specific purpose. It is a must to give considerable attention to the beverage cost control since beverages will normally throw in more profits than food. Fewer staff is required to process beverage into a finished item for consumption by the customers compares to food. (Davis et al, 2008)
3.2 The Purchasing Personnel
Staff members that are responsible for the beverage purchases vary depending on the type and size of the establishment. (Davis and Kotas, 1986)
The purchasing manager is responsible for the beverage purchasing function in Hotels One and Two. In Hotel-Three the purchasing manager and the food and beverage manager are responsible for the beverage purchasing function whereas in Hotel-Four the purchasing manager and the cost controller are accountable for this function. In Hotel-Two when there is a special theme night, the food and beverage manager will join the purchasing manager for such occasions.
The purchasing function is centralised as hotel purchasing for Hotels One and Four. On the other hand the purchasing function is centralised as a group purchasing for Hotels Two and Three. It was agreed by all the interviewed personnel that the purchasing personnel have to be experienced and knowledgeable about the products that they have to order. In fact the purchasing manager in Hotel-Three has over thirty years of experience in this function. In the case of Hotel-Two it was mentioned that although experience and knowledge are vital for the purchasing function, most items in Malta are standard. Additionally it was also pointed out that the purchasing function depends on the demand of other departments. There have to be cross functional teams (that is team effort) and strong communication among all the hotel departments.
Standards for beverage purchasing are developed for all the four hotels interviewed. Quality is given primary priority in all the hotels interviewed apart from for Hotel-Two where the first preference is on the price. In the case of Hotel-One, the products have to satisfy the bar manager and afterwards the purchasing personnel will deal for the best price for the pre-established quality. They will try to obtain the best price at the best quality. In Hotel-Three the purchasing personnel will try to attain a balance between price and quality however 'Quality is on top of the agenda.' It is essential to consider the purchase of some of beverage items of each outlet separately. For example the wines offered at the pool bar will be at a lower quality and at a lower price when compared to the main bar. Each product can have a good quality, very good quality or best quality. The purchasing personnel have to choose the quality that is adequate for the specific outlet. In Hotel-Four both quality and price are given right of way however quality will always win. In Hotel-Two price is given precedence in the sense that, when choosing between two products with similar quality but different prices, the purchasing personnel will go for the cheaper product.
The quantities of beverages to be ordered are determined by the storekeeper with the skilled assistance of the purchasing manager using a par stock level. When required in Hotel-One the cost controller will help out to determine the quantities to be ordered. In Hotel-Three the food and beverage manager will assist when needed to determine such quantities.
3.3 The Selection of Suppliers
The suppliers selected can be either existing suppliers or potential suppliers. The advantage of the existing suppliers is that the quality of the goods received, the price and the service offered would all be already known. According to Dopsen, Hayes and Miller (2007) when dealing with new suppliers it is vital to exercise prudence and to get the subsequent information as a minimum:
Full details of the firm and the range of items it is selling;
Copies of recent price lists;
Details of trading terms;
Details of other customers they deal with;
Samples of products.
Ideally there should be a visit to any potential supplier to enhance knowledge about the size of the company; the range of the products; the size of processing and storage facilities and to meet members of the management team. All these factors facilitate a sustainable long-term business relationship. (Dopsen, Hayes and Miller, 2007)
Suppliers can be chosen on the basis of their reputation in the market, upon an investigation of a supplier and on the basis of their performance. "The best supplier is the one who provides the firm with the most efficient service with regard to quantity, quality, price and delivery performance''. (Davis and Kotas, 1986:53)
In all the hotels except for Hotel-Four there is a list of agreed suppliers from whom products are bought. Hotel-One has a list of preferred suppliers from whom the purchasing personnel will buy continually. It is a preferred suppliers' list rather than an approved suppliers' list. The advantage of having a preferred rather than an approved list is that if any particular supplier will give you a hard time (not reliable towards the hotel), then this supplier can be immediately replaced. Hotel-Two has an approved supplier when it comes to soft drinks and beers. When it comes to spirits, the suppliers are preferred rather than approved.
Hotel-Three has contracts with the suppliers containing pre-agreed prices and pre-agreed quality of the listed products, however if something will not vary for example the quality will deteriorate, the purchasing personnel will alter the supplier if the problems will not be tackled. Although there is a contract, it is not a fixed contact that is the hotel personnel are not obliged to buy the beverage products from the specific supplier. Hotel-Four does not have any suppliers' list. In this hotel the suppliers are chosen according to the quality of the products, the type of brands required and the services that the supplier will offer to the hotel.
When selecting the suppliers, the criteria evaluated by Hotel-One are credit term, quality and prices. The credit term period is given top priority. According to Hotel-One it is useless to go for the best quality and the best price if the credit terms period is short. In Hotel-Two price is given top priority when selecting suppliers while quality and lead time are also analysed to make the right decision. In the other two hotels quality is the most influential factor used to determine the suppliers to be chosen for the beverage products.
Dopsen, Hayes and Miller (2007) explained that the supplier performance can be evaluated using the rating system which usually includes: price, quality and delivery performance. Potential suppliers' performance is only evaluated by Hotel-Three. Every now and then the purchasing manager will pick some items and verify if there is a better product in the market than the one that the hotel is currently using. The purchasing manager without involving employees in operation will pick up different products and will make a blind presentation and tasting of the product. The purchasing department will decant the product that will be identifiable (delete the tag and the supplier' name) and the food and beverage manager will rate the product using a rating sheet including quality, yields among other factors. The person rating the product will not know who the supplier is.
Although the decision taken will not be based on price, the food and beverage personnel will know the price to be able to match the product being tasted with its price accordingly. There have to be a balance between quality and price. It can be that the product quality is superior compared to the hotel standard thus the product will not be affordable. Then the rating sheet is filled out.
Hotel-One pointed out that the suppliers' evaluation and performance is not prepared because this does not add any value on the hotel sales.
The cheapest item is not automatically the best to buy since low-cost products can lead to low quality. Normally the responsible persons go for the supplier on the basis of the quality required and then negotiate the best price for it. There is always a trade-off between quality and price.
3.4 The Purchasing Procedure
According to Dopsen, Hayes and Miller (2007) the various steps in the purchasing procedure are:
The initiation of a request to purchase beverages by an authorised employee such as the head of department or restaurant manager;
The selection of the source of supply from which the goods are to be purchased, and the price to be paid;
Entering into a contract with the supplier by telephone, electronically or in writing;
Obtaining a satisfactory delivery performance from the supplier with regard to time, date and place of delivery;
The acceptance of goods ordered and the transfer to the ordering department or to the stores.
"Purchasing is not a separate activity. What, how and when you buy must always reflect the overall goals of your establishment. Trends change - so must you, the purchaser." (Brown, 2005:396)
Dopsen, Hayes and Miller (2007) recommend that the procedure should reflect the type of the establishment and the market where it operates. Those responsible should consider: the location of the establishment in relation to its suppliers; the size of the storage facilities of the hotel; the shelf life of the beverage product; and the company's purchasing power. Whatever the establishment is, it is crucial to have a sound purchasing policy so that satisfactory standards will be achieved.
3.5 Purchasing Orders
In every hotel it is vital to have purchasing policies and procedures which are planned to allow business transactions to take place smoothly between supplier and receiver. Documentary evidence should confirm that the procedures are actually being followed.
In Hotel-One purchase orders are authorised by the purchasing officer and the financial controller while in Hotel-Two these are authorised by the group purchasing manager. In Hotel-Three the purchase orders are authorised by the cost controller or the general manager while in Hotel-Four these are authorised by the head of department and the latter will also communicate with the financial controller and the general manager, if deemed necessary. In all the hotels those authorising purchase orders are independent from those responsible for issuing requisitions. This prevents certain abuses that can be carried out when the same person will be responsible for both authorising purchase orders and for issuing requisitions.
In Hotel-Two the persons issuing requisitions are the head of departments or the supervisors. Then the storekeeper will deliver the items that were previously ordered and the cost controller will verify that every order is in its perspective. In Hotel-Four the purchase orders are prepared by the head of departments while for the other three hotels, the purchase orders are prepared by the purchasing manager.
Every hotel has a system of par stock level. In Hotel-One the cost controller will work to create a par stock level which will depend on the period of the year, the type of functions that the hotel has, and the type of clients that the hotel has. The aim of these par stock levels is to have some items of every stock with a limited quantity since excessive stock means cash put down the drain. Additionally useless stock will lead to negative cash flows.
In Hotel-Two it was remarked that the par stock level used is an informal one that will be adapted according to the company needs. A point to note is that in Malta, hoteliers work a lot on a last minute purchases. This can be used since distances are short and so if there is a stock item missing, you can phone the supplier and the latter will bring the item in a few hours. In Hotel-Three the cost controller is responsible to ensure that stocks in the stores are kept lowest as possible as these will represent idle money.
The information contained in the purchase orders of each hotel is nearly identical to each other. Hotels One and Three does not have the terms of payments listed in the purchase orders. The purchase order of Hotel-Three contained a disclaimer that declares that if the supplier (who will receive the purchase order) will not agree with the purchase order in terms of quantity or price or he does not have the pre-agreed brand, the supplier shall inform the purchasing manager before the delivery. In Hotel-Four the type of brand is not listed in the purchase orders.
All the hotels have sequentially pre-numbered purchase orders. Normally a copy of the purchase order is being received by the supplier. The goods received clerk/storekeeper will also receive the purchase order and the same copy will go to the cost controller who will attach it with the invoice and passes it through his system and then the cost controller will give the purchase order to the accounts clerk who will pass it through the accounting system.
On receipt of an authorised requisition form, it is vital to check the economic quantity to be purchased by checking the existing stocks and the sales volume forecast. After establishing the purchase requirements, a formal written purchase order is prepared. This serves as the basis for ordering. Written records lessen misunderstandings so it is better to maintain some written record of purchases, preferably on a purchase order, to verify the accuracy of deliveries received. (Dopsen, Hayes and Miller, 2007)
3.6 Concluding Remark
"Think of purchasing as a cycle, not a one-time activity. Purchasing is not just a matter of phoning or emailing another order. You don't want to run out, nor do you want to overstock.'' (Brown, 2005:395)

Our Service Portfolio
- Essay Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Assignment Writing Service
- Coursework Writting Service
- Article Writting Service

Want To Place An Order Quickly?
Then shoot us a message on Whatsapp, WeChat or Gmail. We are available 24/7 to assist you.

Do not panic, you are at the right place

Visit Our essay writting help page to get all the details and guidence on availing our assiatance service.
Get 20% Discount, Now £19 £14 / Per Page 14 days delivery time
Our writting assistance service is undoubtedly one of the most affordable writting assistance services and we have highly qualified professionls to help you with your work. So what are you waiting for, click below to order now.
Get An Instant Quote

I DON'T WANT DISCOUNT
Our experts are ready to assist you, call us to get a free quote or order now to get succeed in your academics writing.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
There’s No Such Thing as an American Bible

By Esau McCaulley
Contributing Opinion Writer
The presumptive Republican nominee for president of the United States, who weeks ago started selling shoes , is now peddling Bibles. During Holy Week.
What’s special about this Bible? So many things. For example, according to a promotional website, it’s the only Bible endorsed by Donald Trump. It’s also the only one endorsed by the country singer Lee Greenwood. Admittedly, the translation isn’t distinctive — it’s your standard King James Version — but the features are unique. This Bible includes the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, the Declaration of Independence, the Pledge of Allegiance and part of the lyrics of Mr. Greenwood’s song “God Bless the USA.” Perhaps most striking, the cover of the Bible does not include a cross or any symbol of the Christian tradition; instead, it is emblazoned with the American flag.
While part of me wants to laugh at the absurdity of it — and marvel at the sheer audacity — I find the messaging unsettling and deeply wrong. This God Bless the USA Bible, as it’s officially named, focuses on God’s blessing of one particular people. That is both its danger and, no doubt for some, its appeal.
Whether this Bible is an example of Christian nationalism I will leave to others. It is at least an example of Christian syncretism, a linking of certain myths about American exceptionalism and the Christian faith. This is the American church’s consistent folly: thinking that we are the protagonists in a story that began long before us and whose main character is in fact the Almighty.
Holy Week is the most sacred portion of the Christian calendar, a time when the church recounts the central events of our faith’s narrative, climaxing in the death and resurrection of Jesus. That story, unlike the parochial God Bless the USA Bible, does not belong to any culture.
Holy Week is celebrated on every continent and in too many languages to number. Some of the immigrants Mr. Trump declared were “ poisoning the blood” of America will probably shout “Christ is risen!” this Easter. Many of them come from the largely Christian regions of Latin America and the Caribbean. They may have entered the country with Bibles in their native tongues nestled securely among their other belongings.
One of the beauties of the Christian faith is that it leaps over the lines dividing countries, leading the faithful to call fellow believers from very different cultures brothers and sisters. Most of the members of this international community consist of the poor living in Africa, Asia and Latin America. There are more Spanish-speaking Christians than English- speaking ones .
If there are central messages that emerge from the variety of services that take place during Holy Week, for many Christians they are the setting aside of power to serve, the supremacy of love, the offer of divine forgiveness and the vulnerability of a crucified God.
This is not the stuff of moneymaking schemes or American presidential campaigns.
It was Pontius Pilate , standing in as the representative of the Roman Empire, who sentenced Jesus to death. The Easter story reminds believers that empires are more than willing to sacrifice the innocent if it allows rulers to stay in power. The church sees Christ’s resurrection as liberating the believer from the power of sin. The story challenges imperial modes of thinking, supplanting the endless pursuit of power with the primacy of love and service.
Easter, using the language of St. Augustine, represents the victory of the City of God over the City of Man. It declares the limits of the moral reasoning of nation-states and has fortified Christians who’ve resisted evil regimes such as fascists in South America, Nazis in Germany, apartheid in South Africa and segregation in the United States.
For any politician to suppose that a nation’s founding documents and a country music song can stand side by side with biblical texts fails at a theological and a moral level. I can’t imagine people in other countries going for anything like it. It is hard to picture a modern “God Bless England” Bible with elements of British common law appended to Christianity’s most sacred texts.
I am glad for the freedoms that we share as Americans. But the idea of a Bible explicitly made for one nation displays a misunderstanding of the story the Bible attempts to tell. The Christian narrative culminates in the creation of the Kingdom (and family) of God, a transnational community united by faith and mutual love.
Roman Catholics , Anglicans and Orthodox Christians, who together claim around 1.5 billion members, describe the Bible as a final authority in matters of faith. Evangelicals, who have overwhelmingly supported Mr. Trump over the course of three election cycles, are known for their focus on Scripture, too. None of these traditions cite or refer to any American political documents in their doctrinal statements — and for good reason.
This Bible may be unique in its form, but the agenda it pursues has recurred throughout history. Christianity is often either co-opted or suppressed; it is rarely given the space to be itself. African American Christians have long struggled to disentangle biblical texts from their misuse in the United States. There is a reason that the abolitionist Frederick Douglass said that between the Christianity of this land (America) and the Christianity of Christ, he recognized the “widest possible difference.”
And while Christianity was used to give theological cover to North American race-based chattel slavery, it was violently attacked in places like El Salvador and Uganda, when leaders including the archbishops Oscar Romero and Janani Luwum spoke out against political corruption.
The work of the church is to remain constantly vigilant to maintain its independence and the credibility of its witness. In the case of this particular Bible, discerning what is happening is not difficult. Christians are being played. Rather than being an appropriate time to debut a patriotic Bible, Easter season is an opportune moment for the church to recover the testimony of the supremacy of the cross over any flag, especially one on the cover of a Bible.
Esau McCaulley ( @esaumccaulley ) is a contributing Opinion writer, the author of “ How Far to the Promised Land: One Black Family’s Story of Hope and Survival in the American South ” and an associate professor of New Testament at Wheaton College.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

COMMENTS
The purchasing function is described by Lysons and Gillingham (2003) as a function with resource to procure supplies. It is usually argued that the purchasing function is not strategically important to enable organisations to gain competitive advantage. Carr and Pearson (2002) described nonstrategic purchasing as a function that is clerical in ...
The purchasing function in a business organization is a critical component of the overall supply chain and procurement process. It involves acquiring goods and services from external suppliers to ...
FUNCTIONS Purchasing is indeed an unusual and multifaceted job. It operates at the vital intersection between buyer and seller, where supply and demand forces meet. As such, its scope is broad, encompassing both internal and external elements of supply interaction. Purchasing is an exciting and challenging profession that is evolving rapidly.
The Multifaceted Role of the Purchasing Function. The purchasing function plays a multifaceted role within an organization, encompassing several critical aspects: 1. Strategic Sourcing: Purchasing professionals identify and select suppliers strategically to ensure a consistent supply of high-quality materials or services at competitive prices. 2.
The importance of the purchasing function. In the hospitality industry, purchasing may be defined as " a function concerned with the search, selection, purchase, receipt, storage, and final use of a commodity in accordance with the catering policy of the establishment". (Davis and Kotas, 1986:47)
The purchasing function minimizes delivery pressures and stock-outs in the supplier-company relationship. With a working methodology well in place, the purchasing department is constantly informed of any problems relating to stock management. Suppliers inform them of any price increases or stock-outs, and a good policy ensures that suppliers ...
The corporate purchasing function is an emerging concept no more than thirty years old. This means that academic knowledge is still relatively young compared to other internal departments. For a long time, and still today, it has not been given the importance it deserves. However, the context is increasingly reversing, and purchasing is rising to its rightful status as a strategic function.
Evaluating this parameter also helps to determine your company's performance and efficiency. It is the responsibility of the purchasing function to ensure that this objective is achieved. It is important to ensure that orders are processed quickly, that products and services are of a high quality, that people are willing to listen, that ...
Purchasing is indeed an unusual and multifaceted job. It operates at the vital intersection between buyer and seller, where supply and demand forces meet. As such, its scope is broad, encompassing both internal and external elements of supply interaction. Keywords. Supply Function; Supply Management; Purchasing Manager; Demand Force; Sales Dollar
The supply management concept is a formal organizational concept that is involved with the flow of materials through a manufacturing firm. The functional areas af-fected include (1) purchasing, (2) inventory control, (3) traffic, (4) production control, 18 Part One. Introduction to Purchasing and Supply Chain Management.
1612 Words 7 Pages. Purchasing function is an organizational function, which involves the buying of raw materials and/ or services from an external supplier. According to Steele & Court (1996), purchasing is defined as "the process by which organizations contract with third parties to obtain the goods and services required to fulfill its ...
The purpose of this paper is to identify the major changes that have taken place in the role of the purchasing function in organizations over the last two decades. These are as follows: The purchasing function is taking on a more strategic role in many organizations. An emerging view is that the purchasing function should be on an equal level ...
3 June 2022. Business Functions. Chapter 7: The Purchasing Function. INTRODUCTION Objectives of Purchasing Function. To buy material of the Right Quality, from the Right Source, delivered to the Right Place, at the Right Time and at the Right Price.
Research on organizing the purchasing function has seen the rise and fall of different topics, for example the buying centre. And although the increasingly strategic role of purchasing still possesses practical challenges to its effective organizational setup, one has to question whether, after 50 years, there really is a need for more research in this specific domain.
Introduction. This report covers different aspects of procurement by companies. It focuses on the role of the finance function, quality management, supplier development and its challenges, risks associated with different types of contracts, avoidance of litigation, purchasing performance, and acceptance of a discounted price.
Supply Function; Supply Management; Purchasing Manager; Purchasing Department; These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
The procurement function is important because it ensures that the organization has the necessary items to carry out its missions. In addition, good procurement practices help avoid waste and fraud, which can cost organizations money in terms of lost profits and damaged relationships with suppliers. Good procurement practices also help ensure ...
Figure 6: Mind map of lesson 6, The purchasing function. 73 BSM1602/ 6 THE IMPORTANCE OF THE PURCHASING FUNCTION. As you can see, the purchasing function plays a very important role in an enterprise. It. determines whether enterprises can achieve their strategic goals and objectives. Without. stock, the enterprise cannot manufacture or sell ...
Here is an essay on the 'Purchasing of Materials' for class 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on the 'Purchasing of Materials' especially written for school and management students. Essay on Purchasing Essay Contents: Essay on the Meaning of Purchasing Essay on the Objectives of Purchasing Essay on the Organisation of Purchase Department Essay on the Centralised or ...
The purchasing function is centralised as hotel purchasing for Hotels One and Four. On the other hand the purchasing function is centralised as a group purchasing for Hotels Two and Three. It was agreed by all the interviewed personnel that the purchasing personnel have to be experienced and knowledgeable about the products that they have to order.
Housing experts say the $418 million settlement will effectively demolish the current real estate business model, in which home sellers pay both their agent and their buyers' agent, which ...
The Christian narrative culminates in the creation of the Kingdom (and family) of God, a transnational community united by faith and mutual love. Roman Catholics, Anglicans and Orthodox Christians ...