

Sample Exam Questions
Sample certification exam questions.
The following samples are available to demonstrate exam question format only.
Anatomic Pathology Exam
Directions: All ABPath exam questions are multiple choice, single best answer. Choose the single best answer.
Question 1.
A pathologist was asked to assess the margins on a 3 x 1.5-cm skin specimen removed for suspected basal cell carcinoma. Separate frozen sections were performed on each of the four margins. What is the CPT coding for this intraoperative consultation?
A) 88305 x 4 B) 88331 x 4 C) 88331 x 1 and 88332 x 3 D) 88332 x 4
Question 2.
What is the major morphologic manifestation of chronic rejection of a lung allograft?
A) bronchiolitis obliterans B) interstitial fibrosis C) nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis D) perivascular mononuclear infiltrates
Question 3.
What is the most frequent cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
A) chronic renal disease B) malabsorption syndrome C) parathyroid adenoma D) parathyroid carcinoma E) primary parathyroid hyperplasia
Question 4.
A melanoma is most likely to arise in which type of nevus?
A) blue nevus B) compound nevus in a fair-skinned, blue-eyed redhead C) giant congenital nevus D) pigmented spindle cell nevus E) Spitz nevus
Directions: Choose the single best answer.
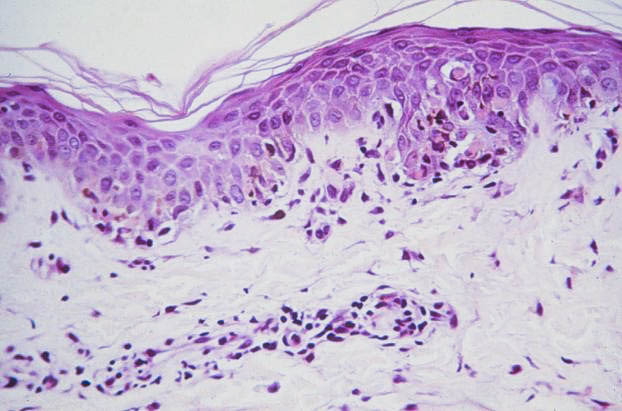
This biopsy specimen is from an 18-year-old male who underwent bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A) graft-versus-host disease B) junctional nevus C) leukemic infiltration D) lymphoma cutis E) mycosis fungoides
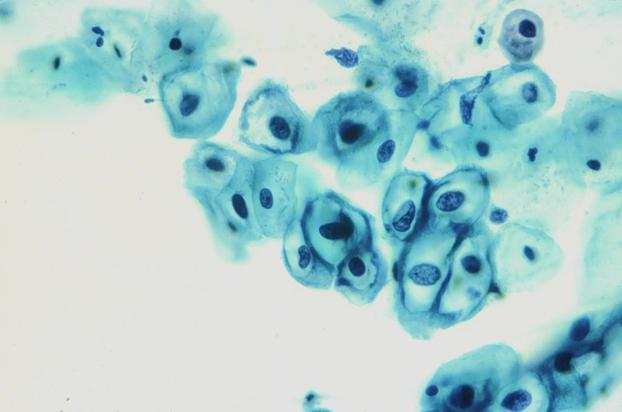
What is the best interpretation for this cervicovaginal cytology specimen from a 32-year-old patient?
A) negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy B) reactive cellular changes associated with inflammation C) atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance D) low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion E) high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
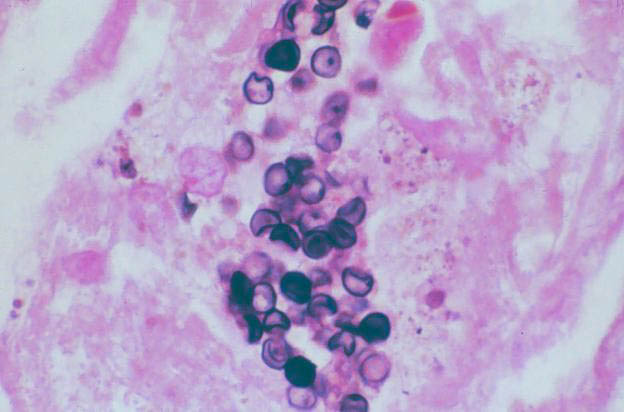
What are these GMS-stained organisms?
A) Blastomyces dermatitidis B) Cryptococcus neoformans C) Pneumocystis jiroveci D) trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica E) yeasts of Candida species
What is the most likely diagnosis for this 4-cm tumor from the neck of a 51-year-old male?
A) carotid body tumor B) granular cell tumor C) malignant melanoma D) metastatic renal carcinoma E) mucoepidermoid carcinoma
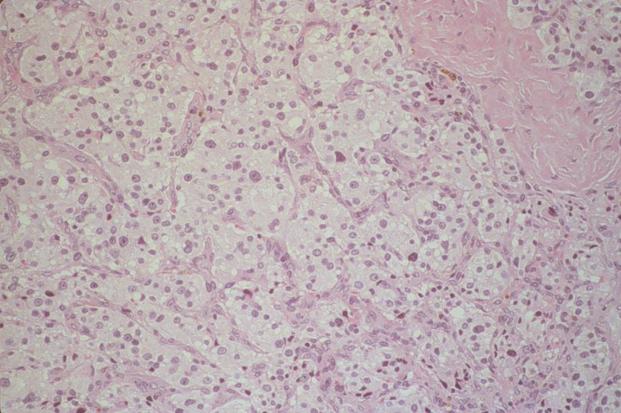
Question 5.
What is the most likely diagnosis for this section of patient kidney biopsy stained with anti-IgG?
A) acute post streptococcal glomerulonephritis B) Goodpasture syndrome C) minimal-change disease D) systemic lupus erythematosus E) granulomatosis with polyangiitis
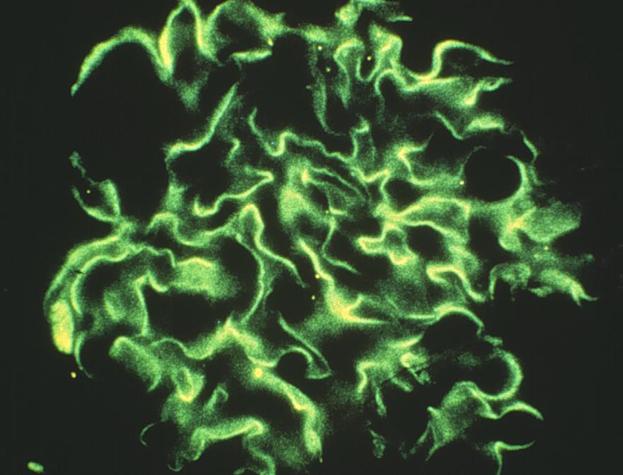
Question 6.
What is the most likely diagnosis for this brain lesion?
A) arteriovenous malformation B) glioblastoma multiforme C) infarction D) pilocytic astrocytoma E) radiation necrosis
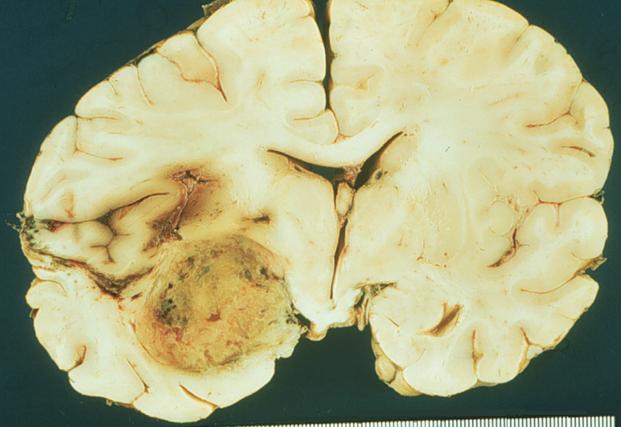
Question 7.
This PAS-stained section of a 3-cm nodule is from the parotid gland of a 45-year-old female. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A) acinic cell carcinoma B) adenoid cystic carcinoma C) normal parotid tissue D) pleomorphic adenoma E) Warthin tumor
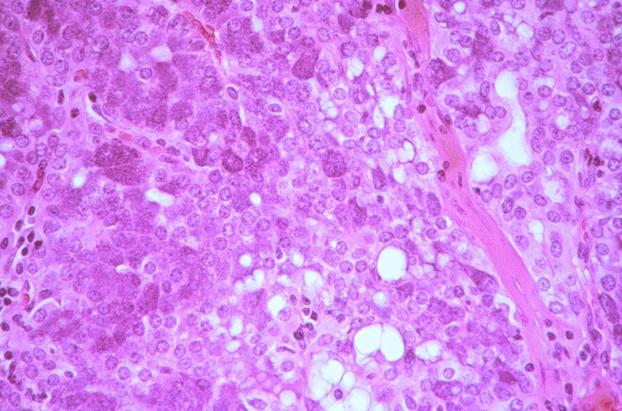
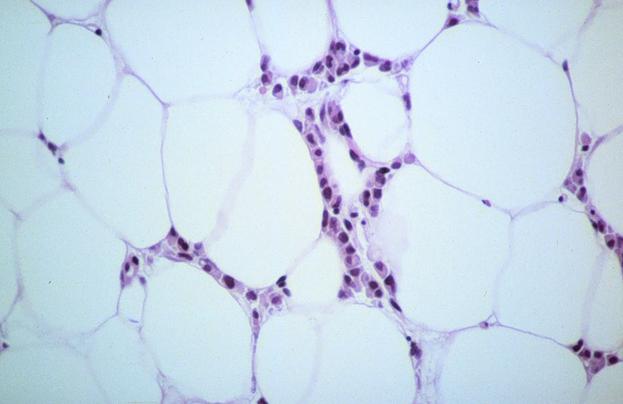
Question 8.
What is the most likely diagnosis for this needle core biopsy from the breast of a 52-year-old female?
A) chronic mastitis B) fat necrosis C) invasive lobular carcinoma D) metastatic small cell carcinoma E) myeloma
Question 9.
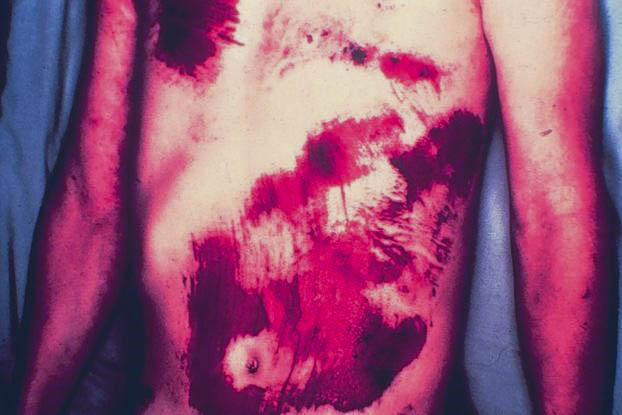
This photograph is of the driver of a car that overturned and caught fire after a head-on collision. What is the most likely cause of these injuries?
A) falling on gravel B) postmortem burns caused by gasoline C) second-degree burns caused by heat D) steering-wheel impact E) the body’s dragging on the ground
Clinical Pathology Exam
Directions: Choose the one answer that is best in each case.
A 77-year-old male with severe peripheral vascular disease presented with severe abdominal pain of several hours’ duration. There was no history of trauma or chest pain. Laboratory studies included the following:
| Test (units) | Patient Result | Reference Range |
| Total creatine kinase (CK) (IU/L) | 275 | 21-232 |
| CK-MB (ng/mL) | 3 | 0-5 |
What is the most likely source of the elevated CK activity?
A) hepatic congestion B) infarcted bowel C) myocardial infarction D) renal infarction E) rhabdomyolysis
Which myelodysplastic syndrome is most likely to transform to acute leukemia?
A) chronic myelomonocytic leukemia B) refractory anemia C) refractory anemia with excess blasts D) refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts E) refractory thrombocytopenia
A patient with recurrent episodes of venous and arterial thrombosis received therapeutic doses of heparin, but the heparin failed to exert an anticoagulant effect. The patient most likely has a deficiency of which of the following?
A) antithrombin B) factor VIII C) plasminogen D) platelets E) protein C
What is the most common type of allogeneic transfusion reaction from packed red blood cells?
A) acute hemolytic B) allergic C) delayed hemolytic D) febrile, nonhemolytic E) transfusion-related acute lung injury
What is the most common cause of fatal hemolytic transfusion reactions?
A) clerical errors related to misidentification of patients B) emergency transfusion of uncrossmatched blood C) excessively rapid transfusion of red blood cells D) failure to premedicate patients with acetaminophen E) laboratory technical or testing mistakes
A 55-year-old female presented with pulmonary necrotizing granulomatous inflammation, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, and necrotizing crescentic glomerulonephritis. She would most likely test positive for which of the following?
A) anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies B) anti-nuclear antibodies C) anti-phospholipid antibodies D) hepatitis C virus antibodies E) IgA fibronectin aggregates
Which oncogene becomes activated in the t(14;18) that is often associated with follicular lymphoma?
A) Bcl-2 B) Bcr/abl C) Ets-1 D) Myc E) Mos
A blood agar plate had small, nonhemolytic colonies isolated from an intra-abdominal abscess. The isolate was catalase negative, bile esculin positive, and pyrrolidonyl arylamidase (PYR) positive, and grew in 6.5% sodium chloride. What is the most likely identification?
A) Enterococcus species B) group B Streptococcus C) Pneumococcus D) Staphylococcus species
The acquired B phenomenon is associated with antigens from which organism?
A) Candida albicans B) Escherichia coli O86 C) Legionella pneumophila D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae E) Treponema pallidum
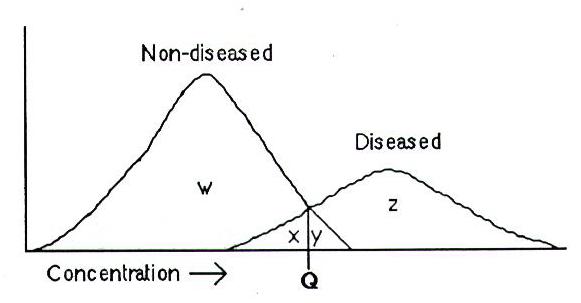
The concentration of an analyte was measured in nondiseased and diseased populations, and cutoff point Q was chosen. The number of false-positive results is represented by which area?
A) W B) X C) Y D) Z
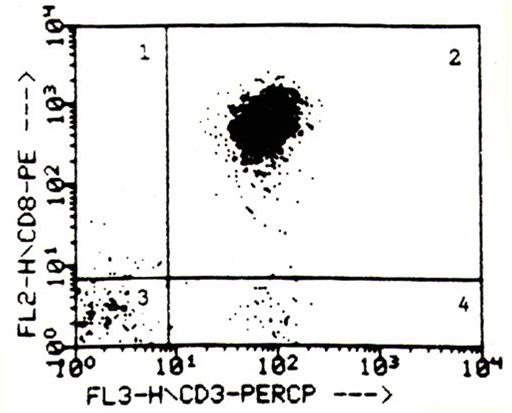
This flow cytometric dot plot of peripheral blood lymphocytes stained for CD3 and CD8 is from a patient with a decreased absolute number of lymphocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A) AIDS B) cytomegalovirus infection C) infectious mononucleosis D) no pathologic change E) T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
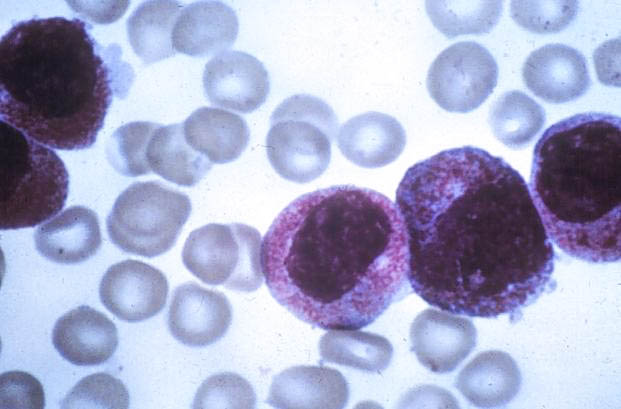
What is the most likely diagnosis for this blood film from a 38-year-old female?
A) acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13q22) B) acute myeloid leukemia with maturation C) acute myelomonocytic leukemia D) acute promyelocytic leukemia E) mast cell leukemia
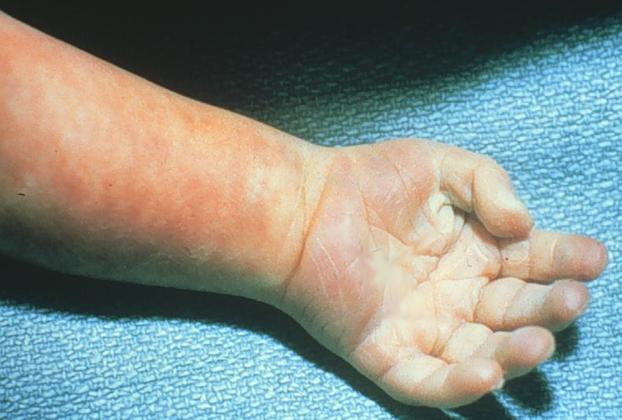
The appearance of the hand suggests that this infant has which of these disorders?
A) a chromosomal abnormality B) a cleft lip and palate C) a short fourth metacarpal D) holoprosencephaly E) rocker-bottom feet
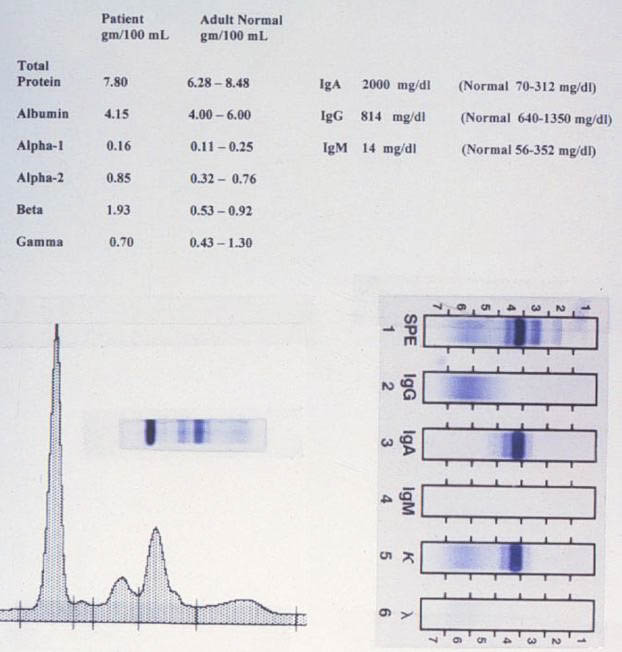
These data are serum electrophoresis and immunofixation from an 85-year-old female. What is the best interpretation?
A) acute-phase reactant pattern B) IgA monoclonal gammopathy C) normal study D) Waldenström macroglobulinemia
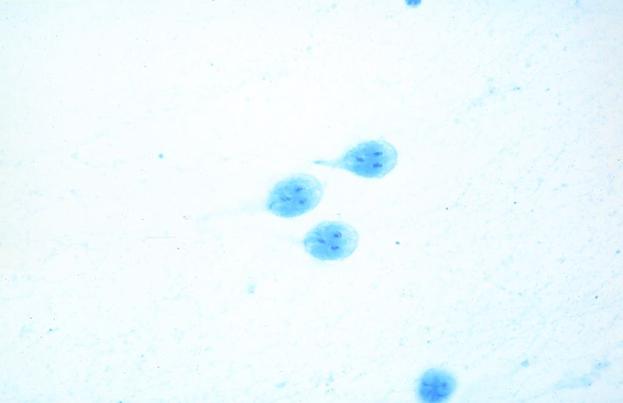
What is the most likely diagnosis for this bile duct brush cytology from a 45-year-old female?
A) amoebae B) Cryptosporidium C) degenerated epithelial cells D) Giardia E) normal epithelial cells
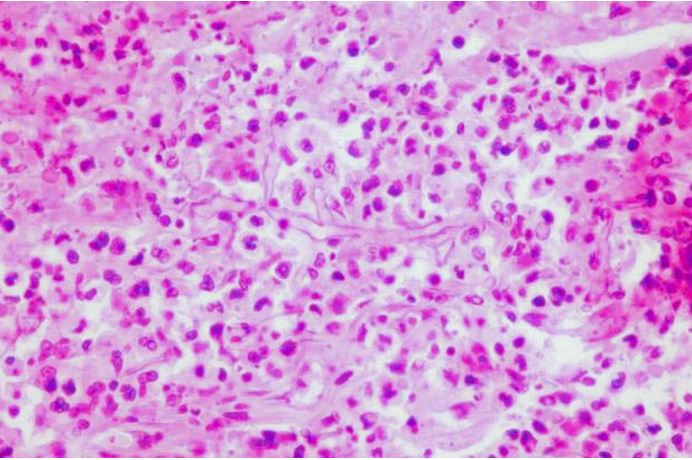
This subcutaneous tissue biopsy is from a patient who sustained a firecracker injury. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A) aspergillosis B) botryomycosis C) phaeohyphomycosis D) sporotrichosis E) zygomycosis
- Cancer / Oncology
- Exam stuffs
- Health tips
- NURSES Stuffs
- Procedure Video
- PGI Questions
- Surgery Steps
General Pathology Revision questions for Exam 1
General pathology revision questions for exam part 1 ..

These exam points are useful for for the NMCLE, USMLE, FCPS, and many other medical exam
Answer or Keys are at the end for General Pathology Revision questions for Exam one .
1. Leading cause of death due to poisoning? 2. CO poisoning inhibit which enzyme? 3. Name mitochondrial toxins ? 4. Most susceptible to hypoxia in nephron? 5. Irreversible damage to neuron occurs after —– minutes of global hypoxia? 6. Most destructive free radicals? 7. Which vitamin is the best neutralizer of free radical? 8. Marker of intermediate filament degradation? 9. Mallory bodies are present in ? 10. Acetaminophen free radicals are formed in? 11. Wear and tear pigment? 12. Hemosedrin laden macrophages present in left sides heart failure are called? 13. What is called green bile ? 14. Disordered cell growth is calle ? 15. Examples of permanent cells? 16. Most common cause of caseous necrosis? 17. Programmed cell death is called? 18. Guardian of genome is? 19. Which is specific for pancreatitis? 20. Heterophagy is seen in which cell organelle? 21. Cerebral infarct is example of? 22. What is called red bile? 23. Extrinsic pathway in apoptosis require? 24. In lead poisoning lead deposits in? 25. Only endogenous pigment? 26. Which metaplasia occurs in brain? 27. Most susceptible zone in hypoxia of hepatocyte ? 28. Oxidase reaction produce which radicals? 29. Primary lysosomes are derived from ? 30. Lewy body seen in ? 31. Most common cause of tissues hypoxia? 32. Most common site for metastatic calcification? Kidney 33. Vitamin as an antioxidant? 34. Central organ in apoptosis? 35. Caspases are involved in which phenomenon? 36. Female had silicon breast implant which was then removed , wich cells would be numerous ? 37. Omental necrosis is of which type? 38. Superimposed infection on necrosis is called ? 39. Metaplasia of surface epithelium most commonly causes by? 40. In our country the most common cause of cell injury is ? 41. Immediate affect after injury to a vessel is ? 41. Major circulating phagocyte? 42. Most important chemical mediator of inflammation? 43. Clearance of neutrophils in acute inflammation is by? 44. Neutrophil leucocytosis is caused by? 45. The hallmark of acute inflammation is increased ? 46. Acute phase reactants mostly synthesized in? 47. Most common cause of skin abscess? 48. Hall mark of chronic inflammation? 49. Kininogen converts into bradykinin due to? 50. Prostaglandin that helps in protection of gastrointestinal mucosa is?? 51. Prostacyclin is produced by? 52. Fever in inflammation is caused by ? 53. ICAM and VCAM are responsible for ? 54. Most common cause of increases permeability? 55. Chemotaxis is a feature of ? 56. Most common cause of hyperkalemia? 57. Virchows triad? 58. Pulmonary thromboembolism originate from? 59. Best indicator of tissues hypoxia? 60. Most common cause of respiratory acidosis ? 61. Cushing triad? 62.most common manifestation of septic patient is ? 63. Most important distinguishing feature if hypo volumic and septic shock is ? 64. Last mediator of endo toxic shock ? 65. Death due to embolism after accident ? 66. Severe generalized Edema is called ? 67. Which vitamin involved in synthesis of collagen? 68. Keyloid is excess of which type of collagen? 69. Corticosteroid inc which wbc? 70. The hallmark of healing? 71. The element act as cofactor in collagen synthesis is? 72. Polyclonal gammopathy is sign of ? 73. The liver contain stem cells in? 74. Most important cells for wound contraction is? 75. Resistance to tension in main function of which collagen? 76. Liver regenerates in how many days? 77. Most common cause of impaired wound healing? 78. Cells increasing in number Is called? 79. Grading of tumor is done by? 80. Sarcoma involves which origin? 81. Down syndrome is associated with which malignancy? 82. Most common metastatic cancer to bone? 83. Barrets esophagous associated with ? 84. Bcl-2 gene associated with which tumor ? 85. Ret gene associated with which tumor? 86. Li fraumani syndrome associated with which gene? 87. Colorectal carcinoma associated with which gene? 88. TRAP is tumor marker of? 89. S-100 tumor marker of? 90. Calcitonin tumor marker of? 91. Disease associated with asbestosis? 92. Vinyl chloride associated with which disease ? 93. ACTH like peptide are secreted by which tumor? 94. Name disease associated with Psamomma bodies? 95. Most common site of metastasis ? 96. Most common cancer related death? 97. Alkylating agents associated with which malignancy? 98. Polycythemia is associated with which carcinoma? 99. CA-125 tumor marker of ? 100. HTLV-1 virus associated cancer is?
General Pathology Revision questions for Exam Part 2
KEYS 1. CO poisoning 2. Cytochrome oxidase. 3. Alcohol and salicylate 4. Proximal tubule 5. 5 min 6. Hydroxyl free radicals 7. Vit C 8. Ubiquitine 9. Alcoholic liver disease 10. Liver 11. Lipofuschin 12. Heart failure cells 13. Biliverdin 14. Dysplasia 15. Neurons, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells 16. TB 17. Apoptosis 18. P53 19. Lipase 20. Lysosomes 21. Liquifactve infarct 22. Bilirubin 23. TNF 24. Proximal renal tubule 25. Melanin 26. No metaplasia occurs in brain 27. Zone 3 28. Superoxide free radicals 29. Golgi apparatus 30. Idiopathic parkinson disease 31. Ischemia 32. Kidney 33. Vit E 34. Mitochondria 35. Apoptosis 36. Plasma cells 37. Fat necrosis 38. Wet gangrene 39. Chronic irritation. 40. Ischemia 41. Vasoconstriction 41. Neutrophil 42. Histamine 43. Apoptosis 44. Catecholamines , corticosteroids and lithium 45. Vascular permeability. 46. Liver 47. Staph aureus 48. Tissue destruction 49. Hageman factor 50. PGE2 51. Endothelial cells 52. IL1 and TNF-a 53. Leukocyte adhesion 54. Inflammation 55. Acute inflammation 56. Renal failure 57. Endothelial injury, abnormal blood flow and hypercoagubility 58. Femoral vein 59. Mixed venous O2 60. Anxiety 61. Inc bp, HTN, bradycardia 62. Hypotension 63. Temperature 64. IL6 65. Fat embolism 66. Anasarca 67. Vit c 68. Type 3 69. Neutrophils 70. Granulation tissue 71. Zinc 72. Chronic inflammation 73. Canal of hering 74. Myocibroblasts 75. Type 1 collagen 76. 10-14 days 77. Infections 78. Hyperplasia 79. Degree of cellular differentiation on histological appearance 80. Mesenchymal 81. ALL 82. Breast 83. Esophageal adenocarcinoma 84. Follicular lymphoma 85. MEN IIA and IIB 86. P53 87. APC 88. Hairy cell leukemia 89. Melanoma, astrocytoma 90. Thyroid medullary carcinoma 91. Mesothelioma and Bronchogenic carcinoma 92. Angiosarcoma 93. Small cell lung carcinoma 94. Papillary ca of thorid, serous papillary cystadebocarcinoma of ovary, meningioma, malignant mesothelioma 95. Lymph nodes 96. Lung carcinoma 97. Leukemia 98. RCC 99. Ovarian carcinoma 100.Adult T cell leukemia/ lymphoma
- fcps question
- General Pathology Revision questios
- nmcle notes
- nmcle questions
- usmle notes
- usmle questions
High Yields in Orthopedics |medical study notes
Medical education common medical entrance exam pg (mecee-pg) programs in nepal, 115 medical one-liners revision notes for usmle and medical exams, leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment
Most Popular
Medicospace: visual decision-support for doctor-patient consultations using medical concept spaces from ehrs, postpartum psychosis, her2-positive breast cancer treatment, gall stone disease – cholelithiasis, recent comments.


Test: General Pathology - Exam 1 - Review Questions
58 multiple choice questions.
Term describes how disease develops and outlines steps of development (ie cell & molecular changes) p1 Choose matching definition etiology pathogenesis necrosis hemosiderin Don't know? 1 of 58
Definition pathology Choose matching term study of maps study of hiking trails study of disease or suffering study of roadways Don't know? 2 of 58
Term origin of disease, "why" Choose matching definition etiology finding pathogenesis pathology Don't know? 3 of 58
Definition adapt (hypertrophy, hyperplasia, atrophy, metaplasia) OR injury (irreversible or reversible aka death ) Choose matching term cell responses to stress which pattern of tissue necrosis involves histologic examination p9 tuberculosis often leads to chronic ischemia or hypoxic injury leads to Don't know? 4 of 58
Definition morphologic changes that occur during states of disease Choose matching term cells that have been irreversibly injured will p2 cardiac myoctyes undergo ___ to compensate for chronic hypertension p2 pathological hypercalcemia causing deposition of calcium into normal tissues is termed ___ p26 pathology is concerned with p1 Don't know? 5 of 58
Term cells that have been irreversibly injured will p2 Choose matching definition become stronger and more resilient always die as a result of this type of injury adapt to the injury without any consequences recover fully and function normally Don't know? 6 of 58
Term increased size of cells, incapable of replication Choose matching definition hypertrophy hyperplasia hypercalcemia steatosis Don't know? 7 of 58
Term T/F cells that undergo atrophy are dead Choose matching definition yes saltatory conduction. true! false! Don't know? 8 of 58
Term GERD gastric reflux causes esophagus to have increased risk for cancer because esophageal cells turn into "stomach cells" via what adaptation? Choose matching definition metaplasia atrophy necrosis hyperplasia Don't know? 9 of 58
Term causes of hypertrophy Choose matching definition always die as a result of this type of injury overloading curls for the girls increased growth factors GFs adapt (hypertrophy, hyperplasia, atrophy, metaplasia) OR injury (irreversible or reversible aka death ) caseous necrosis & granuloma (walled off collection of macrophages) Don't know? 10 of 58
Term rhinophyma (enlarged nose) is an example of Choose matching definition hyperplasia of sebaceous glands hypertrophy timing of injury liquefactive necrosis Don't know? 11 of 58
Term myocardium subjected to persistent increased load, as with progressive hypertension, will adapt via p2 Choose matching definition necrosis hyperplasia hypertrophy steatosis Don't know? 12 of 58
Term increase in number of cells Choose matching definition metaplasia atrophy hyperplasia necrotic Don't know? 13 of 58
Term one type of mature cells turn into a different type of mature cells Choose matching definition necrotic metaplasia hyperplasia atrophy Don't know? 14 of 58
Term cardiac myoctyes undergo ___ to compensate for chronic hypertension p2 Choose matching definition necrosis hyperplasia hypertrophy metaplasia Don't know? 15 of 58
Term viral infection resulting in wart formation is an example of pathological ___ p4 Choose matching definition dysplasia hyperplasia fibrosis apoptosis Don't know? 16 of 58
Term diminished blood supply or loss of innervation to a cell are likely to produce p5 Choose matching definition hyperplasia necrosis atrophy metaplasia Don't know? 17 of 58
Term decreased cellular protein synthesis with increased protein degradation is hallmark feature of p5 Choose matching definition metaplasia fibrinoid necrosis often associated with autoimmune reactions (immune complexes + fibrin) common with lupus atrophy hyperplasia Don't know? 18 of 58
Term one adult cell type replaced with another adult cell type p5 Choose matching definition necrosis atrophy hyperplasia metaplasia Don't know? 19 of 58
Term which adaptation to stress increases risk of developing cancer p5 Choose matching definition metaplasia apoptosis hyperplasia atrophy Don't know? 20 of 58
Term what type of cell death involves a loss of membrane integrity p6&9 Choose matching definition necrosis apoptosis atrophy steatosis Don't know? 21 of 58
Term if a cell has been injured, cellular ___ occurs before cellular ___ p8 Choose matching definition repair deterioration dysfunction death growth division activation deactivation Don't know? 22 of 58
Term what type of cell death is inflammation assoc w p9 Choose matching definition steatosis atrophy necrosis apoptosis Don't know? 23 of 58
Term which pattern of tissue necrosis involves histologic examination p9 Choose matching definition fibrinoid necrosis often associated with autoimmune reactions (immune complexes + fibrin) common with Lupus replicative senescence lipofuscin adapt (hypertrophy, hyperplasia, atrophy, metaplasia) OR injury (irreversible or reversible aka death ) Don't know? 24 of 58
Term fat destruction and saponification with lipase enzyme (acute pancreatitis, pancreatic trauma, or trauma to breast) Choose matching definition atrophy coagulative necrosis caseous necrosis fat necrosis Don't know? 25 of 58
Term severe ischemia, death of a solid organ tissue (kidney, heart) denatures enzymes Choose matching definition fat necrosis coagulative necrosis apoptosis caseous necrosis Don't know? 26 of 58
Term coagulative necrosis in an extremity Choose matching definition fibrinoid necrosis often associated with autoimmune reactions (immune complexes + fibrin) common with Lupus gangrene due to peripheral vascular disease (diabetes, atherosclerosis) or frost bite can be dry, wet ("dry" gets infected), or gas autophagy lysosomal digestion of cell's components survival during nutrient deprivation rids misfolded proteins adapt (hypertrophy, hyperplasia, atrophy, metaplasia) OR injury (irreversible or reversible aka death ) Don't know? 27 of 58
Term dead cells are completely digested by WBCs often causes cavitation common in CNS or due to infections Choose matching definition liquefactive necrosis caseous necrosis apoptosis fat necrosis Don't know? 28 of 58
Term tuberculosis often leads to Choose matching definition caseous necrosis & granuloma (walled off collection of macrophages) chronic inflammation & fluid accumulation in lungs excessive bleeding & tissue death (necrosis) increased bone density & joint stiffness Don't know? 29 of 58
Term gas gangrene can be caused by Choose matching definition clostridium botulinum clostridium perfringens mucous membrane staphylococcus aureus Don't know? 30 of 58
Term what pathology is most likely to cause gangrene in the US? why? Choose matching definition lipofuscin always die as a result of this type of injury diabetes bc limited blood supply damages blood vessels morphologic changes that occur during states of disease Don't know? 31 of 58
Term destructive fragmentation of nucleus within a dying cell p9 Choose matching definition pyknosis karyorrhexis karyolysis karyokinesis Don't know? 32 of 58
Term apoptosis mitochondrial (intrinsic) pathway Choose matching definition binds with surface molecules aka death receptors activates caspase-8 gangrene due to peripheral vascular disease (diabetes, atherosclerosis) or frost bite can be dry, wet ("dry" gets infected), or gas depletion of ATP mitochondrial damage influx of calcium (activates caspases --> apoptosis) oxidative stress (accumulation of ROS) defects in memb permeability (--> necrosis) DNA & protein damage (--> apoptosis) reduced Growth Factors, DNA damage, misfolded proteins increased mitochondrial membrane permeability activates caspase-9 Don't know? 33 of 58
Term apoptosis death receptor (extrinsic) pathway Choose matching definition overloading curls for the girls increased growth factors GFs diabetes bc limited blood supply damages blood vessels binds with surface molecules aka death receptors activates caspase-8 reduced Growth Factors, DNA damage, misfolded proteins increased mitochondrial membrane permeability activates caspase-9 Don't know? 34 of 58
Term cell is alive but starving Choose matching definition adapt (hypertrophy, hyperplasia, atrophy, metaplasia) OR injury (irreversible or reversible aka death ) autophagy lysosomal digestion of cell's components survival during nutrient deprivation rids misfolded proteins gangrene due to peripheral vascular disease (diabetes, atherosclerosis) or frost bite can be dry, wet ("dry" gets infected), or gas overloading curls for the girls increased growth factors GFs Don't know? 35 of 58
Term chronic ischemia or hypoxic injury leads to Choose matching definition atrophy necrosis steatosis apoptosis Don't know? 36 of 58
Definition karyolysis Choose matching term describes how disease develops and outlines steps of development (ie cell & molecular changes) p1 low ATP and high ROS production leads to what cell death p9 prolonged ischemia that produces irreversible cell death will stimulate ___ p17 Don't know? 37 of 58
Term low ATP and high ROS production leads to what cell death Choose matching definition atrophy necrosis apoptosis autophagy Don't know? 38 of 58
Definition depletion of ATP mitochondrial damage influx of calcium (activates caspases --> apoptosis) oxidative stress (accumulation of ROS) defects in memb permeability (--> necrosis) DNA & protein damage (--> apoptosis) Choose matching term types of cellular injury mechanisms of cellular injury irreversible cell injury complications of metabolic acidosis Don't know? 39 of 58
Definition pyknosis Choose matching term accumulation of triglycerides within hepatic parenchyma is termed ___ p23 what type of cell death is inflammation assoc w p9 low ATP and high ROS production leads to what cell death p9 Don't know? 40 of 58
Definition nucleoside Choose matching term dystrophic calcification involves deposisting calcium into ___ tissues p25 accumulation of triglycerides within hepatic parenchyma is termed ___ p23 what type of cell death is inflammation assoc w p9 p9 Don't know? 41 of 58
Term hypoxia to neurons in CNS produces ___ necrosis p10 Choose matching definition caseous necrosis fibrinoid necrosis liquefactive necrosis fat necrosis Don't know? 42 of 58
Term which of the following has the least impact on cellular resp to injurious stimuli p12 duration of injury timing of injury type of injury severity of injury Choose matching definition apoptosis lipofuscin timing of injury mitochondrial pathway Don't know? 43 of 58
Term are mitochondria resistant to deleterious effects of hypoxia? p13 Choose matching definition Yes Well... NO! Who, Me? Don't know? 44 of 58
Term influx of intracellular calcium will stimulate ____ by activating caspases p13 Choose matching definition autophagy necrosis apoptosis cellular senescence Don't know? 45 of 58
Term are reactive oxygen species produced in all cells during normal aerobic respiration? p14 Choose matching definition necrosis hepatocytes yes NO! Don't know? 46 of 58
Term which site of membrane damage is least likely to produce cellular death? p16 mitochondrial memb plasma memb mucous memb lysosomal memb Choose matching definition metaplasia mitochondrial pathway fat necrosis mucous membrane Don't know? 47 of 58
Term ischemia to a tissue will inhibit ___ & ____ p17 Choose matching definition fatty acid oxidation ketogenesis protein synthesis cell division dna replication rna transcription oxidative phosphorylation glycolysis Don't know? 48 of 58
Term prolonged ischemia that produces irreversible cell death will stimulate ___ p17 Choose matching definition necrosis regeneration metaplasia apoptosis Don't know? 49 of 58
Term restoration of blood flow to ischemic tissue is most likely to cause damage to which tissue type? p17 skeletal muscle cells nephrons myocardium hepatocytes Choose matching definition karyorrhexis hepatocytes hypertrophy necrosis Don't know? 50 of 58
Term which apoptosis pathway involves activating caspase-9? p19 Choose matching definition basement membrane pathway hepatocytes mitochondrial membrane mitochondrial pathway Don't know? 51 of 58
Term accumulation of triglycerides within hepatic parenchyma is termed ___ p23 Choose matching definition hepatitis cirrhosis steatosis fibrosis Don't know? 52 of 58
Term what is the "wear and tear" pigment commonly found in older cells? p24 Choose matching definition lipofuscin hemosiderin melanin steatosis Don't know? 53 of 58
Term dystrophic calcification involves deposisting calcium into ___ tissues p25 Choose matching definition fibrotic inflammatory healthy necrotic Don't know? 54 of 58
Term pathological hypercalcemia causing deposition of calcium into normal tissues is termed ___ p26 Choose matching definition pathological ossification physiological calcification metastatic calcification apoptosis Don't know? 55 of 58
Definition hypercalcemia Choose matching term viral infection resulting in wart formation is an example of pathological ___ p4 increased size of cells, incapable of replication metastatic calcification occurs in presence of p26 mechanisms of cellular injury Don't know? 56 of 58
Term which of the following involves telomere shortening and limitation of the capacity for a cell to replicate p26&28 Choose matching definition atrophy autophagy replicative senescence apoptosis Don't know? 57 of 58
Definition improves DNA repair inhibits aging Choose matching term cells that have been irreversibly injured will p2 rhinophyma (enlarged nose) is an example of calorie restriction has what effect on DNA & aging p27 ischemia to a tissue will inhibit ___ & ____ p17 Don't know? 58 of 58

Pathology Important Questions For MBBS 2nd Year [Question Bank]
Here is a list of important Pathology questions for second-year MBBS students. Students can make use of this question bank for the preparation of the subject. For your convenience, the questions have been arranged in a chapter-wise format.
As you complete each chapter in Pathology, refer to the following list of important questions. You can bookmark this page for a quicker revisit .
There are dozens of Pathology Textbooks out there, making it difficult for medical students to decide which ones to purchase. To make it easier for you, I’ve handpicked BEST and MOST RECOMMENDED textbooks:
Also, check out my complete list of NMC recommended books for MBBS 2nd year.
Best Books for MBBS Second Year [NMC Recommended List]
The questions have been arranged according to the following chapters :
Cell Injury and Adaptation
Inflammation and healing, infections and infestations, hemodynamic disorders, thromboembolism and shock, immunopathology, aids and amyloidosis, genetic and pediatric diseases, environmental and nutritional diseases, basic diagnostic cytology, introduction to hematology and disorders of red blood cell, disorders of white blood cells, lymph node and spleen, disorders of hemostasis, clinical pathology, blood banking and transfusion, cardiovascular disorders, respiratory system, disorders of oral cavities and gastrointestinal tract, hepatobiliary and pancreatic disorders, kidney and urinary tract disorders, male genital tract disorders, female gential tract disorders, breast disorders, endocrine disorders, bones, joints and soft tissue tumours, skin disorders, disorders of central nervous system and eye.
A star ★ indicates that the question is extremely important, so these should be the first ones to concentrate on.
Pathology Important Questions
Long Questions
- Define necrosis. Mention the types, and explain the causes and pathology of each type of necrosis.
Short Questions
- Steatosis (fatty change).
- Fatty liver.
- Exogenous and endogenous pigments.
- Necrosis – definition, types with examples. ★
- Apoptosis – definition and mechanism. ★
- Difference between necrosis and apoptosis.
- Gangrene and its types. ★
- Difference between dry and wet gangrene.
- Pathological calcification. ★
- Dystrophic calcification.
- Metastatic calcification.
- Metaplasia with examples. ★
- Hyaline change.
- Psamoma bodies.
- Hyperplasia.
- Inflammation – definition and types. Describe the causes and vascular and cellular events in acute inflammation. ★
- Compare with the help of suitable diagrams wound healing by primary and secondary intention. Discuss the factors promoting and delaying the process.
Short Questions
- Vascular changes in acute inflammation.
- Difference between transudate and exudate.
- Chemotaxis. ★
- Phagocytosis. ★
- Chemical mediators of inflammation. ★
- Role of arachidonic acid metabolites in acute inflammation.
- Role of complements in inflammation.
- Granulomatous lymphadenitis.
- Angiogenesis (neovascularization) in repair.
- Factors influencing wound healing. ★
- Complications of wound healing. ★
- Granulation tissue.
- Define and classify leprosy. Describe the pathogenesis and pathology.
- Morphology of tuberculoid leprosy.
- Morphology of lepromatous leprosy. ★
- Difference between tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy.
- Granuloma.
- Congenital syphilis.
- Etiopathogenesis of endotoxic (septic) shock. ★
- Define and describe the pathogenesis of thrombus. Add a note on fate of the thrombus. ★
- Discuss the causes and pathogenesis of generalized edema.
- What is embolism? Mention different types of embolism with examples. ★
- Chronic venous congestion of the lung.
- Chronic venous congestion of the liver.
- Air embolism.
- Define infarction. What are the different types of infarcts with common sites of occurrence? ★
- Opportunistic infections in AIDS. ★
- Type I hypersensitivity reaction. ★
- Type II hypersensitivity reaction.
- Type III hypersensitivity reaction. ★
- Type IV hypersensitivity (delayed type of hypersensitivity).
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Lupus erythematosus (LE) cell and its associated conditions.
- Graft versus host disease (GVHD).
- Staining characteristics of amyloid and its appearances.
- Special stains to confirm amyloid. ★
- Define metastasis and describe its mechanism. ★
- Differences between benign and malignant neoplasms. ★
- Routes of the spread of malignant tumours with examples. ★
- Role of tumour suppressor genes in oncogenesis.
- TP53 gene. ★
- Chemical carcinogenesis. ★
- Chemical carcinogens.
- Paraneoplastic syndrome.
- Tumour markers. ★
- Oncogenic viruses.
- Barr body (sex chromatin).
- Down syndrome. ★
- Klinefelter’s syndrome. ★
- Turner’s syndrome. ★
- Laboratory diagnosis of genetic diseases.
- Gaucher disease.
- Enumerate the cancers associated with chronic smoking. ★
- Enumerate the cancers associated with chronic alcoholism. ★
- Vitamin A deficiency. ★
- Osteomalacia.
- Exfoliative cytology. ★
- Papanicolaou (Pap) smear – indications and importance.
- Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC).
- Describe the etiology, clinical features and laboratory diagnosis of Iron deficiency anaemia. ★
- Hemolytic anaemia. ★
- RBC indices.
- Define and classify anaemia.
- Microcytic hypochromic anaemia.
- Megaloblastic anaemia. ★
- Aplastic anaemia.
- Diagnosis of sickle cell anaemia. ★
- Sickling test.
- Pernicious anaemia.
- Pancytopenia
- Significance of reticulocytosis.
- Coomb’s test.
- Define and classify leukaemias. Discuss peripheral blood smear findings and bone marrow findings associated with acute myeloid leukaemia. ★
- Define and classify leukaemias. Discuss peripheral blood smear findings and bone marrow findings associated with chronic myeloid leukaemia. ★
- Tabulate the differences between myeloblast and lymphoblast.
- Leukemoid reaction. ★
- Agranulocytosis. ★
- Difference between leukaemia and leukemoid reaction.
- Causes of eosinophilia. ★
- Causes of monocytosis. ★
- Philadelphia chromosome.
- Blood picture in chronic myeloid leukaemia.
- Blood picture in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
- Laboratory findings in multiple myeloma. ★
- Bence Jones proteins and their demonstration.
- Lymphadenopathy.
- Lymphadenitis.
- Burkitt’s lymphoma. ★
- Classification of Hodgkin’s disease (Hodgkin’s lymphoma). ★
- Causes of splenomegaly.
- Types of Reed-Sternberg cells.
- Leukocytosis.
- Functional defect in neutrophils.
- List the causes of thrombocytopenia. Discuss idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. ★
- Hemophilia A. ★
- Von Willebrand’s disease – clinical feature and laboratory diagnosis. ★
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (aetiology and pathogenesis).
- Types of anticoagulants used in hematology.
- Indications and contraindications of bone marrow aspiration. ★
- Microscopic examination of urine.
- CSF findings in various types of meningitis.
- What are Romanowsky stains? Give examples.
- Packed cell volume (hematocrit) – define and its significance.
- What is buffy coat? Mention its importance.
- Wintrobe’s tube and its function.
- Osmotic fragility test.
- Proteinuria.
- Glucosuria.
- Benedict’s test.
- Causes of dry tap of dry tip in bone marrow aspiration.
- Urine examination – sample collection and preservatives.
- Sulfosalicylic acid test.
- Hay’s sulfur test.
- Indications of lumbar puncture.
- Methods of blood grouping.
- Bombay blood group.
- Blood donor selection criteria. ★
- Name the available blood components.
- Infections transmitted by blood transfusion. ★
- Blood transfusion reactions. ★
- Define atherosclerosis. Discuss the risk factors, etiopathogenesis and pathology of atherosclerosis. Also briefly write about the sites and clinical significance of atherosclerosis. Describe the morphology (along with a neat and labelled diagram) of an atherosclerotic plaque. Mention the complications of atherosclerosis. ★
- Classify myocardial infarction. Describe the etiopathogenesis, morphology/sequential changes seen over time. Add a note on laboratory diagnosis. ★
- Causes, types and complications of aneurysms.
- Laboratory diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
- Describe various types of cardiac vegetations in endocarditis.
- Infective endocarditis.
- Rheumatic heart disease. ★
- Libman Sacks endocarditis.
- Patent ductus arteriosus.
- Fallot’s tetralogy – components and complications.
- Coarctation of the aorta.
- What is emphysema? Write the types of emphysema. Describe the pathogenesis of emphysema. ★
- Types of emphysema. ★
- Bronchial asthma.
- Bronchiectasis. ★
- Lobar pneumonia.
- Lung abscess.
- Primary tuberculosis.
- Ghon lesion. ★
- Asbestosis. ★
- Classify lung tumours. Discuss the pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features including paraneoplastic syndromes of squamous cell carcinoma lung.
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung.
- Leukoplakia – definition and morphology. ★
- Pleomorphic adenoma.
- Warthin’s tumour – microscopy. ★
- Barrett’s esophagus. ★
- Etiopathogenesis of peptic ulcer. ★
- Role of Helicobacter pylori in gastric ulcer. ★
- Gastric carcinoma. ★
- Carcinoid tumour.
- Carcinoid syndrome.
- Tabulate the differences between Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. ★
- Hirschsprung disease.
- Etiopathogenesis of colonic carcinoma.
- Meckel’s diverticulum.
- Hyperbilirubinemia.
- Laboratory investigations in jaundice. ★
- Squeal of hepatitis B infection.
- Alcoholic liver disease – etiopathogenesis and pathology. ★
- Cirrhosis. ★
- Portal hypertension.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Amebic liver abscess – morphology. ★
- Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Gallstones (cholelithiasis) – etiopathogenesis and complications. ★
- Acute pancreatitis – etiopathogenesis, morphology and complications. ★
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Describe the etiopathogenesis of acute diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis or post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
- Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Minimal lesion glomerulonephritis/or minimal change disease.
- Difference between nephrotic syndrome and nephritic syndrome. ★
- Renal changes in diabetes mellitus (diabetic nephropathy). ★
- Chronic pyelonephritis.
- Kidney changes in malignant hypertension.
- Horseshoe kidney.
- Cystic disease of the kidney.
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Hydronephrosis. ★
- Enumerate types of renal stones. ★
- Morphology of renal cell carcinoma. ★
- Flea-bitten kidney.
- Microalbuminuria.
- Morphology of Wilm’s tumour.
- Premalignant lesions of the penis.
- Benign hyperplasia of the prostate. ★
- Cryptochidism.
- Classify testicular tumours. Describe the etiology and morphology of seminoma. ★
- Classify ovarian tumours. Describe the morphological features of serous tumours of ovary. ★
- Classify ovarian tumours. Describe the morphological features of mucinous tumours of ovary.
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). ★
- Endometriosis.
- Leiomyoma – sites and morphology. ★
- Brenner tumour of ovary.
- Ovarian germ cell tumours.
- Teratoma of ovary. ★
- Dermoid cyst.
- Dysgerminoma.
- Granulosa cell tumour of ovary.
- Kruckenberg’s tumour – morphology. ★
- Trophoblastic tumours.
- Hydatidiform mole. ★
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Fibrocystic disease of breast or fibrocystic change.
- Classification of breast carcinoma.
- Medullary carcinoma of breast.
- Prognostic and predictive factors of carcinoma of the breast. ★
- Fibroadenoma of the breast. ★
- Phyllodes tumour – morphology. ★
- Gynecomastia.
- Discuss the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mention its major long-term complications. ★
- Hashimato’s thyroiditis – etiopathogenesis and morphology. ★
- Grave’s disease – etiopathogenesis and morphology. ★
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Iodine deficiency goitre.
- Multinodular goitre. ★
- Thyroid adenoma.
- Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. ★
- Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. ★
- Pheochromocytoma. ★
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia.
- List the complications of diabetes mellitus. ★
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Renal glycosuria.
- HbA1C (glycosylated hemoglobin).
- Classify tumours of the bone. Describe the etiopathogenesis and morphology of osteogenic sarcoma/osteosarcoma. ★
- Complications of osteomyelitis.
- Tuberculous osteomyelitis.
- Paget’s disease of bone. ★
- Classify tumours of the bone. Describe the morphology of osteoclastoma (giant cell tumour of bone). ★
- Ewing’s tumour/Ewing sarcoma.★
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Sequestrum.
- Renal osteodystrophy.
- Pott’s spine.
- Morphology of chondrosarcoma.
- Gouty tophi.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma.
- Basal cell carcinoma of the skin (rodent ulcer) – etiopathogenesis and morphology. ★
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin – etiopathogenesis and morphology. ★
- Malignant melanoma – etiopathogenesis and morphology. ★
- Pilomatrixoma.
- Molluscum contagiosum.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Pyogenic meningitis. ★
- Astrocytoma.
- Medulloblastoma.
- Meningioma. ★
- Schwannoma.
- TB meningitis.
- Brain abscess.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Comprehensive Multiple-Choice Questions in Pathology
A Study Guide
- © 2022
- Vinay Kumar Kohli 0 ,
- Chitra Kohli 1 ,
- Akanksha Singh 2
MCI Diagnostic Center, LLC, Dallas, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Dallas, USA
Department of pathology, king george’s medical university, lucknow, india.
- An intuitive and systematic approach reinforces the fundamental concepts
- Provides a very concise, to-the-point and up-to-date text
- Written by experts in the field
13k Accesses
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
About this book
Similar content being viewed by others.

Developing Multiple-Choice Questions for Anatomy Examinations

Knowledge, Training, and Experience
Blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, neoplastic disorders, head and neck, table of contents (23 chapters), front matter, cellular pathology, inflammation, and repair.
- Vinay Kumar Kohli, Chitra Kohli, Akanksha Singh
Genetic Disorders
Immune system disorders, infectious diseases, hematopathology of red blood cells and white blood cells, liver and biliary tract, male genital tract, female genital tract, endocrine system, skin disorders, authors and affiliations.
Vinay Kumar Kohli
Chitra Kohli
Akanksha Singh
About the authors
Vinay Kumar Kohli M.D, MBA is the Chief Medical Officer, Senior Pathologist and Vice-Chancellor at MCI Diagnostic Center, Dallas, Texas, USA. He is an accomplished physician, professor, healthcare executive with more than 25 years of leadership experience in Pathology. He holds a MBA with a concentration in Healthcare management from Drexel University LeBow College of Business, Philadelphia, USA. He also received his Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) as well as his Medical Doctor (MD) degrees inPathology & Bacteriology at King George Medical University where he stayed on for more than two decades as Professor in the Department of Pathology. He has worked at leading national and international medical institutions and has published in leading scientific journals.
Chitra Kohli M.D, is Medical Director and Attending Pathologist at MCI Diagnostic Center, Dallas, Texas, USA. She completed her Anatomical Pathology/Clinical Pathology (AP/CP) residency from Pennsylvania Hospital, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, USA. After completing 4 years of Anatomical and Clinical Pathology Residency, she did a fellowship in Surgical Pathology also from the same institution. She has served as Medical Director and Consultant Surgical Pathologist at Coffeyville Regional Medical Center, Coffeyville, Kansas, USA for eight years. She also completed Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) and Medical Doctor (MD) in Pathology degrees from King George's Medical University, India. She has been a successful Pathologist for the last 31 years. She has been honored with multiple awards and published in leading scientific journals. She has been nominated as a Top Pathologist representing Richardson,Texas USA.
Akanksha Singh MD is currently pursuing her PhD within the Department of Pathology, King George’s Medical University, Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow, India. She completed her Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) from MLN Medical College, Allahabad and Doctor of Medicine (MD) Pathology from King George’s Medical University, Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow, India. She has been actively involved in teaching and training medical, undergraduate and postgraduate students of Pathology for the past 5 years.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Comprehensive Multiple-Choice Questions in Pathology
Book Subtitle : A Study Guide
Authors : Vinay Kumar Kohli, Chitra Kohli, Akanksha Singh
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08767-7
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Medicine , Medicine (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2022
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-031-08766-0 Published: 23 August 2022
eBook ISBN : 978-3-031-08767-7 Published: 22 August 2022
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XI, 205
Number of Illustrations : 11 b/w illustrations, 270 illustrations in colour
Topics : Pathology
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Pathology Exam Questions and Answers Past Exam Essay Questions and Answers: Describe five different types of immunoglobulins. Explain the role of each type and how they provide an integrated defence against invading pathogens.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Short notes on metaplasia, Short notes on tumour metastases, Dysplasia short notes and more.
General knowledge pathology practice examinations of 30 questions each incorporate different question types from different subject areas. They are in multiple choice format and time just like a real exam.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In the remodeling phase what type of collagen is replaced?, Which phase of wound healing is associated with the intermolecular cross-linking of collagen?, Vascular maturation is associated with? and more.
Clinical Pathology Written Sample Questions. Directions: Choose the one answer that is best in each case. A 77-year-old male with severe peripheral vascular disease presented with severe abdominal pain of several hours’ duration. There was no history of trauma or chest pain.
General Pathology Revision questions for Exam part 1 . These exam points are useful for for the NMCLE, USMLE, FCPS, and many other medical exam. Answer or Keys are at the end for General Pathology Revision questions for Exam one . 1. Leading cause of death due to poisoning? 2. CO poisoning inhibit which enzyme? 3. Name mitochondrial toxins ? 4.
Quiz yourself with questions and answers for General Pathology - Exam 1 - Review Questions, so you can be ready for test day. Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students or create one from your course material.
Here is a list of important Pathology questions for second-year MBBS students. Students can make use of this question bank for the preparation of the subject. For your convenience, the questions have been arranged in a chapter-wise format.
The multiple choice questions in the General Pathology, Organ System Pathology, Clinical Pathology, and Extended Matching banks have three formats. For single answer questions, click on the checkbox next to the letter for the answer.
Through dedicated questions and answers over 23 chapters covering every major organ system, the book will develop skills needed to deal with different aspects of pathology in a systematic yet summarized manner. The book helps solve problems faced by trainees by providing the highest yield content.