100 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) for biostatistics
1. What is the primary objective of biostatistics? a) To analyze data from clinical trials b) To study biological processes c) To apply statistical methods to biological data d) To develop new medical treatments
2. Which of the following is an example of quantitative data? a) Blood type b) Gender c) Age d) Eye color
3. Which statistical measure is used to describe the spread or dispersion of data points around the mean? a) Median b) Mode c) Variance d) Skewness
4. What is the purpose of a control group in a randomized controlled trial (RCT)? a) To provide a comparison to the experimental group b) To ensure all participants are treated equally c) To maximize the sample size d) To reduce the risk of bias
5. Which type of study design is commonly used to study the causes of diseases? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Experimental study
6. What is the p-value in hypothesis testing? a) The probability of making a Type I error b) The probability of making a Type II error c) The level of significance d) The probability of obtaining the observed results by chance alone
7. Which statistical test is used to compare means between two groups? a) Chi-square test b) T-test c) ANOVA d) Wilcoxon rank-sum test
8. In a normal distribution, what percentage of data falls within one standard deviation of the mean? a) 34.13% b) 50% c) 68.27% d) 95.45%
9. What does the term “odds ratio” represent in epidemiological studies? a) The difference between two groups’ odds of an event occurring b) The relative risk of an event occurring in one group compared to another c) The absolute risk of an event occurring in one group d) The number needed to treat (NNT) to prevent one event
10. What is the purpose of blinding in a clinical trial? a) To keep the researchers unbiased b) To keep the participants unaware of the treatment they receive c) To prevent confounding variables from affecting the results d) To ensure the sample size is large enough
11. Which of the following measures of central tendency is affected most by extreme outliers? a) Mean b) Median c) Mode d) Standard deviation
12. A researcher is investigating the association between smoking and lung cancer. What type of study design would be most appropriate? a) Randomized controlled trial b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Cross-sectional study
13. Which type of bias occurs when participants who do not complete a study differ from those who do? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Attrition bias
14. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between two categorical variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Pearson correlation coefficient
15. Which of the following is an example of a continuous variable? a) Gender b) Marital status c) Height d) Blood type
16. What does the term “p < 0.05” indicate in hypothesis testing? a) The results are statistically significant b) The results are not statistically significant c) The effect size is large d) The sample size is small
17. In which phase of a clinical trial are potential side effects and safety assessed? a) Phase I b) Phase II c) Phase III d) Phase IV
18. Which measure of dispersion is not affected by extreme values in a dataset? a) Range b) Variance c) Interquartile range (IQR) d) Standard deviation
19. What does the term “confidence interval” represent in statistics? a) The range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie b) The margin of error in a statistical estimate c) The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis d) The level of significance
20. Which type of study design is most susceptible to recall bias? a) Randomized controlled trial b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Cross-sectional study
21. Which statistical test is used to compare means between multiple groups? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Wilcoxon rank-sum test
22. A researcher is investigating the relationship between age and blood pressure. Which type of correlation is the most appropriate? a) Positive correlation b) Negative correlation c) No correlation d) Partial correlation
23. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between two continuous variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) Correlation coefficient d) ANOVA
24. What does the term “sensitivity” represent in diagnostic testing? a) The probability of a positive test result in individuals without the disease b) The probability of a positive test result in individuals with the disease c) The ability of the test to correctly identify individuals with the disease d) The ability of the test to correctly identify individuals without the disease
25. In a clinical trial, what is the purpose of randomization? a) To ensure all participants receive the same treatment b) To ensure the study is double-blinded c) To minimize bias and confounding variables d) To increase the likelihood of a statistically significant result
26. What is the difference between a parameter and a statistic in statistics? a) A parameter is a characteristic of a sample, while a statistic is a characteristic of a population. b) A parameter is a characteristic of a population, while a statistic is a characteristic of a sample. c) A parameter is used in descriptive statistics, while a statistic is used in inferential statistics. d) A parameter is used in inferential statistics, while a statistic is used in descriptive statistics.
27. Which type of bias occurs when participants misreport their exposure or outcome status? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Recall bias
28. What is the purpose of stratified sampling in research studies? a) To increase the sample size b) To reduce the risk of selection bias c) To increase the external validity of the study d) To ensure equal representation of all demographic groups
29. Which of the following is a measure of relative risk in epidemiological studies? a) Odds ratio b) Standard deviation c) Hazard ratio d) Variance
30. In a normal distribution, what percentage of data falls within two standard deviations of the mean? a) 34.13% b) 50% c) 68.27% d) 95.45%
31. Which statistical test is used to compare proportions between two groups? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Wilcoxon rank-sum test
32. What is the purpose of a placebo in a clinical trial? a) To provide a reference point for comparison b) To ensure participants
are blinded to the treatment c) To ensure the study is double-blinded d) To maximize the placebo effect
33. Which type of study design is best suited for establishing cause-and-effect relationships? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Experimental study
34. Which statistical measure is used to summarize the variability of a sample mean estimate? a) Median b) Mode c) Variance d) Standard error
35. What does the term “type I error” refer to in hypothesis testing? a) Incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis b) Incorrectly accepting a false null hypothesis c) Incorrectly rejecting a false null hypothesis d) Incorrectly accepting a true null hypothesis
36. What is the purpose of a two-sample t-test? a) To compare the means of two independent groups b) To compare the means of two paired groups c) To compare the variances of two independent groups d) To compare the proportions of two independent groups
37. In a contingency table, what does the term “marginal totals” represent? a) The total number of observations in each row and column b) The sum of the cell frequencies c) The average value of the cells in each row and column d) The standard deviation of the cell frequencies
38. Which measure of central tendency is most appropriate for ordinal data? a) Mean b) Median c) Mode d) Standard deviation
39. Which of the following statements about the normal distribution is true? a) It is positively skewed. b) The mean, median, and mode are equal. c) The area under the curve is always less than 1. d) It is a discrete probability distribution.
40. What does the term “power” refer to in statistical hypothesis testing? a) The probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis b) The probability of correctly accepting a true null hypothesis c) The level of significance d) The probability of making a Type I error
41. Which statistical test is used to compare means between multiple groups and control for confounding variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Regression analysis
42. What is the purpose of the Central Limit Theorem in statistics? a) To determine the sample size needed for a study b) To describe the shape of a normal distribution c) To estimate population parameters from sample statistics d) To calculate the variance of a sample
43. Which type of bias occurs when the study results are influenced by factors other than the exposure or intervention being studied? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Observer bias
44. What is the purpose of a Kaplan-Meier survival curve? a) To compare the survival rates of different groups over time b) To assess the normality of a distribution c) To estimate the population mean d) To visualize the spread of data points
45. In a chi-square test, what does the chi-square statistic represent? a) The difference between the observed and expected frequencies b) The measure of effect size c) The probability of a Type I error d) The probability of a Type II error
46. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between a categorical variable and a continuous variable? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Regression analysis
47. In a randomized controlled trial, what is the purpose of intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis? a) To assess the efficacy of the treatment on the per-protocol population b) To minimize the risk of selection bias c) To analyze the data without considering the treatment assignment d) To control for confounding variables
48. Which of the following study designs is most appropriate for investigating rare diseases or outcomes? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Randomized controlled trial
49. What is the purpose of a p-value in hypothesis testing? a) To determine the effect size of the study b) To assess the statistical power of the study c) To measure the probability of obtaining the observed results by chance alone d) To calculate the margin of error in the study
50. Which statistical measure is used to describe the shape of a distribution? a) Median b) Mode c) Skewness d) Standard deviation
51. What does the term “confidence level” represent in statistics? a) The level of significance used in hypothesis testing b) The probability of making a Type I error c) The probability of making a Type II error d) The level of certainty in the interval estimate
52. Which type of bias occurs when participants are not representative of the target population? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Sampling bias
53. What is the purpose of a correlation coefficient in statistics? a) To measure the strength of the relationship between two variables b) To determine the direction of causation between two variables c) To calculate the margin of error in a study d) To assess the normality of a distribution
54. Which type of study design is commonly used to study the prevalence of a disease or condition? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Experimental study
55. Which statistical test is used to compare the means of three or more independent groups? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Wilcoxon rank-sum test
56. What does the term “p-value” stand for in hypothesis testing? a) Probability value b) Population value c) Percentage value d) Power value
57. In a normal distribution, what percentage of data falls within three standard deviations of the mean? a) 34.13% b) 50% c) 68.27% d) 99.73%
58. Which type of bias occurs when the study results are affected by the way data are collected, recorded, or interpreted? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Observer bias
59. What is the purpose of a placebo in a randomized controlled trial? a) To ensure all participants receive the same treatment b) To provide a reference point for comparison c) To maximize the placebo effect d) To minimize bias and confounding variables
60. Which measure of central tendency is most appropriate for nominal data? a) Mean b) Median c) Mode d) Standard deviation
61. What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis in hypothesis testing? a) A null hypothesis states that there is no effect, while an alternative hypothesis states that there is an effect. b) A null hypothesis states that there is an effect, while an alternative hypothesis states that there is no effect. c) A null hypothesis is always rejected, while an alternative hypothesis is always accepted. d) A null hypothesis is always accepted, while an alternative hypothesis is always rejected.
62. Which type of sampling method involves dividing the population into subgroups and then selecting a random sample from each subgroup? a) Simple random sampling b) Stratified sampling c) Convenience sampling d) Cluster sampling
. What does the term “standard deviation” represent in statistics? a) The average value of a dataset b) The spread or dispersion of data points around the mean c) The difference between the highest and lowest values in a dataset d) The proportion of data points that fall within one standard deviation of the mean
64. Which type of study design is best suited for studying the prevalence of a disease at a specific point in time? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Experimental study
65. Which statistical test is used to compare means between two paired groups? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) Paired t-test d) Wilcoxon signed-rank test
66. What is the purpose of a sample size calculation in research studies? a) To determine the effect size of the study b) To assess the normality of the distribution c) To estimate the population parameters d) To ensure the study has sufficient statistical power
67. Which type of bias occurs when participants who experience a particular outcome are more or less likely to be included in the study? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Survivorship bias
68. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between three or more categorical variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Regression analysis
69. In a contingency table, what does the term “expected frequencies” represent? a) The sum of the cell frequencies b) The frequency of a specific event c) The frequency distribution of the variables d) The frequencies that would be expected under the assumption of independence
70. What does the term “alpha level” represent in hypothesis testing? a) The level of significance used to determine statistical significance b) The probability of making a Type I error c) The probability of making a Type II error d) The measure of effect size
71. Which type of bias occurs when the exposure and outcome are measured at the same time, leading to an incorrect association? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Temporal bias
72. What is the purpose of a hazard ratio in survival analysis? a) To measure the strength of the relationship between two continuous variables b) To compare the means of two independent groups c) To assess the normality of a distribution d) To estimate the relative risk of an event occurring over time
73. Which statistical measure is used to describe the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two continuous variables? a) Median b) Mode c) Correlation coefficient d) Standard deviation
74. In a chi-square test, what does the null hypothesis state? a) There is a significant difference between the observed and expected frequencies. b) There is no significant difference between the observed and expected frequencies. c) The population proportion is equal to the sample proportion. d) The population mean is equal to the sample mean.
75. Which type of study design is most appropriate for investigating the incidence of a disease or outcome over time? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Experimental study
76. What does the term “effect size” represent in statistics? a) The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis b) The level of significance used in hypothesis testing c) The strength of the relationship between two variables d) The difference between the observed and expected frequencies
77. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between a categorical variable and a continuous variable while controlling for other variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Multiple regression analysis
78. What is the purpose of a scatter plot in data visualization? a) To display the distribution of a single variable b) To compare the means of two independent groups c) To visualize the relationship between two continuous variables d) To summarize categorical data
79. Which type of bias occurs when the study population is not representative of the target population due to non-random selection? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Sampling bias
80. What is the purpose of a 95% confidence interval? a) To provide a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie b) To determine the level of significance in hypothesis testing c) To calculate the margin of error in a study d) To estimate the standard deviation of a sample
81. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between two continuous variables while controlling for other variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Multiple regression analysis
82. In a randomized controlled trial, what is the purpose of a washout period? a) To ensure all participants receive the same treatment b) To minimize the risk of selection bias c) To eliminate the effects of prior treatments or interventions d) To control for confounding variables
83. What does the term “survival analysis” refer to in biostatistics? a) The analysis of continuous variables over time b) The analysis of survival rates and times in a study population c) The analysis of categorical variables and their associations d) The analysis of the effects of interventions on health outcomes
84. Which type of study design is most appropriate for investigating the natural history of a disease or condition? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Experimental study
85. What is the purpose of a Z-test in hypothesis testing? a) To compare the means of two independent groups b) To compare the means of two paired groups c) To compare the means of three or more independent groups d) To compare the means of a sample to a known population mean
86. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between two categorical variables while controlling for other variables? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Multiple logistic regression analysis
87. What is the purpose of a Kaplan-Meier estimator in survival analysis? a) To estimate the population mean b) To calculate the variance of a sample c) To estimate the survival function over time d) To assess the normality of a distribution
88. Which type of bias occurs when participants provide responses that they believe the researcher wants to hear? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Social desirability bias
89. What is the purpose of a sensitivity analysis in statistical modeling? a) To determine the effect size of the study b) To assess the normality of the distribution c) To estimate the population parameters d) To evaluate the robustness of the results to different assumptions
90. Which statistical measure is used to describe the relationship between two categorical variables in a contingency table? a) Median b) Mode c) Odds ratio d) Standard deviation
91. In a chi-square test, what does the degrees of freedom represent? a) The difference between the observed and expected frequencies b) The number of cells in a contingency table c) The number of categories in a variable d) The number of independent variables in the analysis
92. Which type of
bias occurs when participants are not aware of their exposure or outcome status? a) Selection bias b) Information bias c) Confounding bias d) Recall bias
93. What is the purpose of a confidence interval in hypothesis testing? a) To determine the effect size of the study b) To assess the normality of the distribution c) To estimate the population parameters d) To provide a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie
94. Which statistical test is used to compare means between two independent groups with non-normal distributions or small sample sizes? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) Mann-Whitney U test d) Wilcoxon signed-rank test
95. What does the term “interquartile range (IQR)” represent in statistics? a) The average value of a dataset b) The spread or dispersion of data points around the mean c) The difference between the highest and lowest values in a dataset d) The range of values that fall within the middle 50% of a dataset
96. Which type of study design is best suited for investigating the incidence of a disease in a specific population over time? a) Cross-sectional study b) Case-control study c) Cohort study d) Randomized controlled trial
97. What is the purpose of a paired t-test? a) To compare the means of two independent groups b) To compare the means of two paired groups c) To compare the variances of two independent groups d) To compare the proportions of two independent groups
98. Which statistical test is used to analyze the association between a continuous variable and a categorical variable with two levels? a) T-test b) Chi-square test c) ANOVA d) Linear regression analysis
99. In a randomized controlled trial, what is the purpose of blinding the participants and researchers? a) To ensure all participants receive the same treatment b) To provide a reference point for comparison c) To minimize bias and confounding variables d) To maximize the placebo effect
100. Which measure of dispersion is resistant to extreme values and outliers in a dataset? a) Range b) Variance c) Interquartile range (IQR) d) Standard deviation

Share this post:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Mastodon (Opens in new window)
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Previous Question Papers

Table of Contents
Question Paper Pattern of Biostatistics and Research Methodology
Download free biostatistics and research methodology question papers.
We update regularly new question papers after every semester exam, for notifications of the posts you just need to follow our website or join our Telegram channel it’s free.
Reference: RGUHS Karnataka
6 thoughts on “Biostatistics and Research Methodology Previous Question Papers”
Please add July 2022 question papers please
We will update as soon as possible
- Pingback: B Pharmacy 1st to 8th Semester All Study Materials [PDF FREE] - MediPdf
June-2023 question paper is of cosmetics plz correct it
Okay, we updated the question paper check now…
Leave a Comment

Biostatistics and Research Methodology MCQs with Answers
Biostatistics and research methodology, 1.a : introduction to statistics and biostatistics.
1. According to Crexton and Cowden which arrangement of component of statistics is true? a. Collection of data – Analysis of data – Presentation of data – Interpretation of data b. Collection of data – Presentation of data – Analysis of data – Interpretation of data c. Presentation of data – Analysis of data – Interpretation of data – Collection of data d. Interpretation of data – Collection of data – Presentation of data – Analysis of data Ans: b
2. Which is not step of Descriptive Statistics? a. Collecting b. Organizing c. Hypothesis testing d. Presenting Data e. Summarizing Ans: c
1.b : Introduction to Statistics and Biostatistics
3. Which is related to Frequency Distribution? a. Tally Mark b. Variable c. Frequency d. Class Interval e. All of above f. Option a and b g. Option c and d Ans: e
4. If Class intervals are not given, then it is called as a___________. a. Discrete Frequency Distribution b. Continuous Frequency Distribution c. Grouped Frequency Distribution d. None of above Ans: a
5. Types of Class intervals are_____ a. Exclusive b. Discrete c. Inclusive d. Continuous e. Option a and c f. Option b and d g. Option a and b h. Option c and d Ans: e
1.c : Graphical Presentation of Frequency Distribution
6. Age and Salary are Continuous variables. True or False?
a. True b. False Ans: a
7. Figure indicates which type of Graph?

a. Line frequency Graph b. Histogram c. Frequency polygon d. Ogive e. Frequency Curve Ans: c
8. Figure indicated which type of graph?

a. Histogram b. Frequency polygon c. Ogive d. Frequency Curve Ans: c
9. Cumulative Frequency curve also known as_____ a. Histogram b. Frequency Polygon c. Grouped Frequency d. Line frequency curve e. Ogive Ans: e
1.d : Measure of Central Tendency
10. Mean is also known as ____ a. Median b. Mode c. Average d. Range Ans: c
11. Which is Positional central tendency? a. Arithmetic Mean b. Geometric Mean c. Harmonic Mean d. Median e. All of above Ans: d
12. Which is NOT mathematical central tendency? a. Arithmetic Mean b. Median c. Harmonic Mean d. Geometric Mean Ans: b
13. Simple arithmetic mean of 2, 8, 7, 3, 4.2, 6.1, 8.2, 7.1, 10, 9 is ________ a. 4.64 b. 7.46 c. 8.64 d. 6.46 Ans: d
14. Which of the following is a equation to derive arithmetic mean in grouped data by short cut method.

15. Mean for following Data _____

a. 11.9 b. 25.9 c. 29.5 d. 19.5 Ans: b
16. is the equation for_____

a. Arithmetic mean by direct method b. Arithmetic mean by short cut method c. Arithmetic mean by Step deviation method d. Arithmetic mean by indirect method Ans: c
17. If all the weights in weighted arithmetic mean are equal, then the weighted mean is the same as the _____________. a. Arithmetic mean b. Geometric mean c. Median d. Mode e. Option a and b f. Option c and d Ans: a
1.e: Geometric Mean and Harmonic Mean
18. __________ = ???????????????????????????? [1???? ????????????????????] a. Harmonic mean b. Geometric mean c. Arithmetic mean d. Weighted arithmetic mean Ans: b
19. What is Harmonic mean for : 18, 12, 16, 21, 7, 9 a. 11.9 b. 9.1 c. 1.9 d. 12 Ans: a
20. Geometric mean is defined as the nth root of the product of n values. True or False? a. True b. False Ans: a
1.f : Median and Mode
21. Calculate median of the following data gives the height of five student in c.m., 168, 173, 153, 164, 158 a. 153 b. 173 c. 168 d. 164 Ans: d
22. _________ = ???? +(????/2– ????????)/???????? ???? a. Median b. Mode c. Harmonic Mean d. Quartile deviation e. Standard deviation Ans: a
23. Find median of daily wages of employees in hospital

a. 180 b. 185 c. 200 d. None of above Ans: b
24. Calculate Median for following data

a. 125.125 b. 100.125 c. 101.125 d. 103.125 Ans: d
25. ________ =

a. Median b. Mode c. Harmonic Mean d. Quartile deviation e. Standard deviation Ans: b
26. Calculate mode for following data

a. 112.857 b. 110.112 c. 112.112 d. 25 Ans: a
1.g: Types of Measures of Dispersion
27. Which is NOT type of variability?
a. Biological variability b. Random variability c. Real variability d. Experimental variability Ans: b
28. Which is NOT type of Measure of Dispersion? a. Mean b. Range c. Mean absolute deviation d. Standard Deviation e. Quartile Deviation Ans: a
29. What is the coefficient of range for the given data : 8, 6, 7, 9, 12, 3, 15, 18, 5, 6 a. 6 b. 15 c. 0.714 d. 21 Ans: c
30. Find coefficient of Mean deviation for : 10, 20, 28, 34, 23, 17 a. 0.285 b. 0.287 c. 2.87 d. 8.27 Ans: b
31. The square of standard deviation is called ____________ a. Quartile deviation b. Mean absolute deviation c. Range d. Variance Ans: d
32. Coefficient of variation also known as ___________ a. Coefficient of Quartile deviation b. Standard deviation c. Relative Standard deviation d. Coefficient of Mean deviation Ans: c
33. _______ = √(????−????̅)2???? a. Coefficient of Variation b. Variance c. Coefficient of Mean deviation d. Standard deviation e. Correlation coefficient Ans: d
34. What is Standard deviation for: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 a. 20 b. 200 c. 400 d. 40 Ans: a
1.h: Correlation
35. The value of correlation coefficient will very from ____ a. 0 to 1 b. -1 to +1 c. -∞ to +∞ d. -1 to 0 Ans: b
36. If the value of one variable is increase, then value of other variable also increases on an average, then the correlation said to be positive. True or False? a. True b. False Ans: a
37. If the value of one variable decreases, then the value of other variable decreases on an average, then the correlation said to be Negative correlation. True or False? a. True b. False Ans: b
38. The relationship between more than two variables is said to be _________ a. Simple Correlation b. Random Correlation c. Parital Correlation d. Multiple correlation Ans: d
39. r = 0 indicates… a. a positive correlation between variables b. a negative correlation between variables c. no correlation between variables d. All of above Ans: c
40. Figure indicates ______

a. Perfect positive correlation b. Perfect negative correlation c. Positive correlation d. Negative correlation e. None of above Ans: e
41. If the points are widely scattered in a graph, the correlation is said to be _________ a. Highly Negative b. Negative c. Zero d. None of above Ans: c
42. Equation ???? =????????????√????????2????/2 Stands for ______ a. Spearman’s Rank coefficient of correlation b. Quartile deviation c. Karl pearson’s coefficient of correlation d. coefficient of condurrent deviation. Ans: c
43. Which is equation for spearman’s rank coefficient of correlation?

44. Calculate coefficient of concurrent deviation for following data:

a. 0.1773 b. 5.7735 c. 0.5773 d. None of above Ans: c
2.a: Regression
45. In regression analysis independent variable is also known as _______ a. Regressor b. Predictor c. Explanatory variable d. All of above e. None of above Ans: d
46. The equation for the standard error of the regression (S) is _______

2.b : Probability
47. What is probability of head when tossing coin one time? a. 1 b. 2 c. 1.5 d. 0.5 Ans: d
48. What is probability of 3 when throwing dice once. a. 1/6 b. 2/6 c. 3/6 d. 1 e. None of above Ans: a
49. In probability theory, two events are said to be mutually exclusive if they cannot occur at the same time or simultaneously. True or False? a. True b. False Ans: True
50. If one event is unaffected by the outcome of another event, the two events are said to be a. Dependent b. Independent c. Mutually exclusive d. All of the above e. Both b and c Ans: b
51. Which is true for Probability of an Event P(E). a. 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1 b. 0 < P(E) ≤ 1 c. 0 ≤ P(E) < 1 d. 0 < P(E) < 1 e. None of above Ans: a
52. Five coins are thrown simultaneously. Find the chance of getting four heads. a. 5/64 b. 7/64 c. 1/64 d. None of above Ans: a
53. Suppose, we have a production process of some item that is manufactured in large quantities. We find that, in general, the proportion of defective items is p = 0.01, A random sample of l00 items is selected. What is the probability that there are no defective items in this sample? a. 0.184 b. 0.921 c. 0.368 d. 0.08 Ans: c
54. ????(????) =???????????? −????/????! equation Stands for____ a. Binomial distribution b. Poisson distribution c. Normal distribution d. All of above Ans: b
55. For Normal Distribution which statement is false? a. For Normal distribution, mean = median = mode b. It is symmetry about the center c. 50% of values less than the mean and 50% greater than the mean d. None of above Ans: d
56. Gaussian distribution is known as _______ a. Normal distribution b. Binomial distribution c. Poisson distribution d. Random distribution Ans: a
2.c : Sampling
57. Which is NOT Probability sampling technique? a. Simple random Sampling b. Stratified random sampling c. Cluster Random Sampling d. Quota Sampling Ans: d
58. Which is NOT Non-Probability sampling technique? a. Snowball sampling b. Purposive sampling c. Cluster Random Sampling d. Quota Sampling Ans: c
59. Nonprobability sampling techniques involve random selection. True or False? a. True b. False Ans: b
60. Purposive Sampling techniques is also known as _______ a. Snowball sampling b. Haphazard sampling c. Quota sampling d. Judgmental Sampling Ans: d
Pharmacokinetics MCQs with Answers (Part:- 2)
Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics mcqs with answers.

Remix education
Pharmacy Infoline
Health, Science, Technology News, Pharmcy notes
801T MCQ Biostatistics and Research Methodology MCQ with Answers
Bp801t mcq biostatistics and research methodology mcq with answers.
Unit 1 MCQ Introduction, Measures of central tendency, Measures of dispersion, Correlation MCQ
Unit 2 MCQ Regression, Probability, Parametric test MCQ
Unit 3 MCQ Non Parametric tests, Research, Graphs, Designing the methodology MCQ
Unit 4 MCQ Regression modelling, Practical components of Industrial and Clinical Trial MCQ
Unit 5 MCQ Design and Analysis of Experiments, Response Surface methodology MCQ
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Mix MCQ
Answer: collection of data
Answer: better quantitative picture.
Answer: greater than mode
Answer: Histogram
Answer: average of x and y
Answer: Coefficient of variation.
Answer: non-parametric
Answer: y=a+bx
Answer: Small sample test
Answer: High-quality glossy.
Answer: First name
Answer: Type I error
Answer: status
Answer: Economics
Answer: Science
Answer: standard deviation
Answer: positive correlation.
BP801T Biostatistics and Research Methodology, Notes, PDF Books
Suggested readings
- Standard error of regression Biostatistics and Research Methodology Notes
- Multiple regression Biostatistics and Research Methodology Theory
- Regression: Biostatistics and Research Methodology Theory, Notes, PDF, Books
- Mean, Median, Mode Pharmaceutical examples
- Size separation Pharmaceutical engineering MCQ with answers
Recommended readings:
- human anatomy and physiology
- Definition and Scope Social Pharmacy
- Role of individual in conservation of natural resources
- Multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies
- Structure and function of ecosystem
- Research methodology mcq
- Limit test for heavy metals
- Ostwald viscometer
- Throat paint
- Limit test for arsenic
DPEE D Pharm Exit exam: Instructions to Candidates
Fatman scoop rushed to hospital following medical emergency during hamden concert, d. pharm exit exam syllabus subject wise, you may have missed, dpee diploma in pharmacy exit exam.
- Biology MCQs
- Biology Notes
- __Biotechnology
- __Microbiology
- __Biochemistry
- _Immunology
- _Biology MCQ
- Practice Tests
- _Exam Questions
- _NEET Biology MCQs
Multiple Choice Questions on Biostatistics
a) calculation b) government c) maths d) classification

a) Statistics in biology b) statistic in vivo c) biostatistics d) all of these
a) Statistics in biology b) bionemerology c) biometry d) both a and b
a) Fischer b) Karl Pearson c) Francis Galton d) Francis Bacon
a) Fischer b) Karl Pearson c) Francis Galton d) Walter Weldon
a) Infererntial biostatistics b) Descriptive biostatistics c) both a and b d ) comparative biostatistics
a) block b) population c) group d) flock
a) static group b) variable c) dynmic group d) dynamism
a) quantitative variables b) qualitative variables c) absolute variables d) continuous variables
a) quantitative variables b) Discrete variable c) absolute variables d) continuous variables
- Exam questions on Biostatistics
- MCQ on Agricultural Statistics
- Quiz on Scientific Method
- MCQ on Research Methodology
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. Learn more
Contact form

Biostatistics and Research Methodology Notes – Bpharm

Free Download Biostatistics and Research Methodology Notes in pdf – Bpharm 8th Semester . High quality, well-structured and Standard Notes.
Welcome to Pharmdbm.com
Pharmdbm provides standard or well-structured Notes for Bpharm students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bpharm are available on www.pharmdbm.com.
In this post you can download notes of Biostatistics and Research Methodology (BP801T). All units are available to download for free.
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Notes Unit 1 – 5
Unit – 1.
Introduction: Statistics, Biostatistics, Frequency distribution Measures of central tendency: Mean, Median, Mode- Pharmaceutical examples Measures of dispersion: Dispersion, Range, standard deviation, Pharmaceutical problems Correlation: Definition, Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation, Multiple correlation – Pharmaceuticals examples
UNIT – 2
Regression: Curve fitting by the method of least squares, fitting the lines y= a + bx and x = a + by, Multiple regression, standard error of regression– Pharmaceutical Examples Probability: Definition of probability, Binomial distribution, Normal distribution, Poisson’s distribution, properties – problems Sample, Population, large sample, small sample, Null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, sampling, essence of sampling, types of sampling, Error-I type, Error-II type, Standard error of mean (SEM) – Pharmaceutical examples Parametric test : t-test(Sample, Pooled or Unpaired and Paired) , ANOVA, (One way and Two way), Least Significance difference
UNIT – 3
Non Parametric tests: Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test, Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Friedman Test Introduction to Research: Need for research, Need for design of Experiments, Experiential Design Technique, plagiarism Graphs: Histogram, Pie Chart, Cubic Graph, response surface plot, Counter Plot graph Designing the methodology: Sample size determination and Power of a study, Report writing and presentation of data, Protocol, Cohorts studies, Observational studies, Experimental studies, Designing clinical trial, various phases.
UNIT – 4
Blocking and confounding system for Two-level factorials Regression modeling: Hypothesis testing in Simple and Multiple regressionmodels Introduction to Practical components of Industrial and Clinical Trials Problems: Statistical Analysis Using Excel, SPSS, MINITAB®, DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS, R – Online Statistical Software’s to Industrial and Clinical trial approach

UNIT – 5
Design and Analysis of experiments: Factorial Design: Definition, 22, 23design. Advantage of factorial design Response Surface methodology: Central composite design, Historical design, Optimization Techniques
Bpharm 8th Semester Notes
Biostatistics & Research Methodology
Social & Preventive Pharmacy
Pharma Marketing Management
Pharmaceutical Regulatory Science
Pharmacovigilance
Quality Control & Standardization of Herbals
Computer Aided Drug Design
Cell & Molecular Biology
Cosmetic Science
Pharmacological Screening Methods
Advanced Instrumentation Techniques
Dietary Supplements & Neutraceuticals
Scope of Biostatistics and Research Methodology
To understand the applications of Biostatics in Pharmacy. This subject deals with descriptive statistics, Graphics, Correlation, Regression, logistic regression Probability theory, Sampling technique, Parametric tests, Non Parametric tests, ANOVA, Introduction to Design of Experiments, Phases of Clinical trials and Observational and Experimental studies, SPSS, R and MINITAB statistical software’s, analyzing the statistical data using Excel.
Objectives of Biostatistics and Research Methodology
Upon completion of the course the student shall be able to
- Know the operation of M.S. Excel, SPSS, R and MINITAB®, DoE (Design of Experiment).
- Know the various statistical techniques to solve statistical problems.
- Appreciate statistical techniques in solving the problems.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Pharmacy Gyan
All you need is right here
Biostatistics and research methodology QB
Biostatistics and research methodology question bank for B pharmacy 8 semester, this QB released by rguhs Bangalore, it contains all the important questions of the syllabus.
Long Essays 10 Marks questions for Biostatistics and research methodology
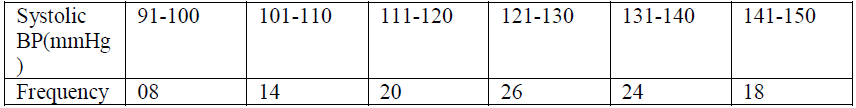
- Explain the measures of central tendency Calculate the mean and standard deviation for the following data on systolic BP of volunteers –
- Explain different types of hypothesis. Explain type I and type II errors, level of significance, P value
- .Explain the different phases of clinical trials.
- Discuss the protocol for an experimental study design.
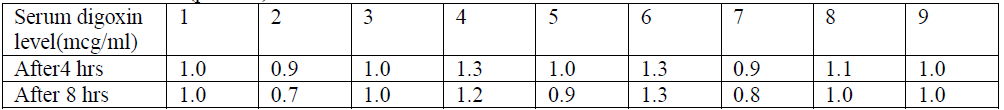
- Explain ‘t’ test. Find if there is statistical significance in the serum digoxin level in the given data:- Critical value= 2.31(p< 0.05)
- What are measures of dispersion? Explain their significance with suitable examples.
- Explain the various phases of clinical trials.
- Explain regression analysis and its applications in stability testing of pharmaceuticals.
- Explain the measures of dispersion. Calculate mean, variance and standard deviation for the given data:-

- Describe the different measures of central tendency. Calculate mean and standard deviation for the given data on mid arm circumference(cm) of 16 children – 14, 12, 13, 10, 11, 13, 14, 12, 12, 11, 10, 13, 12, 11, 10, 14
- Explain types of observational study designs.
- Explain with suitable examples regression analysis and standard error of regression.
- Explain null and alternate hypothesis, type I and type II errors, confidence interval.
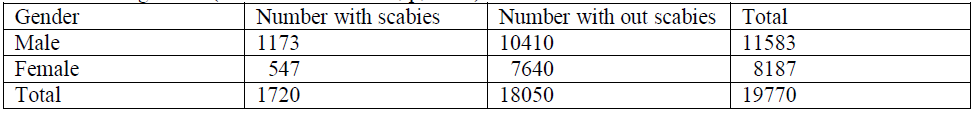
- Explain chi square test. From the following data, test whether prevalence of scabies is significant in two different genders ( critical value=10.83, p,0.001) :-
- What is hypothesis? What are different types of hypothesis? Explain how you will formulate a hypothesis with a suitable example
- What is QbD, Why are DOE essential in a QbD development process?
- What are the measures variability? What is their statistical significance
- Discuss different types of observational clinical studies in detail.
- Discuss various steps involved in testing the significance of single mean and difference between two means (independent samples) in small samples using Student’s t- test.
- Classify different types of data, explain any three measures of dispersion with example.
- Describe briefly the different interventional study designs
- Explain the hypothesis testing of non-parametric data
- Describe the various types of measures of dispersion and their significance.
- Discuss briefly about determination of sample size for simple comparative experiments and for confidence interval of specific width.
- How is QbD based product development better. Explain the steps in involved in it.
- How will you design a clinical study methodologically? Explain briefly.
- What is hypothesis? What are different types of hypothesis? Explain how you formulate the hypothesis with a suitable illustration.
- Discuss about the hypothesis testing of parametric data.
Short Essays 5 marks questions for Biostatistics and research methodology
- Explain types of correlation and correlation coefficient. Give suitable examples.
- Define probability and explain its significance in statistical inference with examples.
- What are measures of dispersion? Explain.
- Explain ANOVA and its applications.
- Discuss different methods of sampling.
- Explain the graphical methods of representing quantitative data.
- Discuss the applications of EXCEL and SPSS programmes in statistical analysis.
- What are non-parametric tests? Explain chi square test-Goodness of fit test.
- Explain the types and advantages of factorial design in formulation development.
- Explain correlation, types of correlation and its applications.
- Explain null hypothesis, type I and type II errors.
- Discuss with examples measures of central tendency.
- Discuss the sampling methods in research study.
- Explain probability and its significance in statistical analysis.
- Explain regression analysis to assess the influence of independent variable on continuous variable.
- Explain the hypothesis testing using one way of ANOVA.
- Describe the various of graphical methods of representing quantitative data.
- Explain a typical experimental study design.
- Define and explain correlation with examples.
- Explain student‘t’ test and its applications.
- Explain ANOVA and its significance.
- Discuss null hypothesis, type I and type II errors.
- Explain the application of factorial design in pharmaceutical product development.
- Explain with examples- Histogram, Pie chart.
- Describe the sampling techniques in research study.
- Discuss Wilcoxon Rank Sum test and Mann Whitney U test.
- Explain type I and type II errors.
- Discuss the methods of sample size calculation in comparative studies.
- Explain Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation with examples.
- Explain chi square test for Goodness of fit.
- Discuss the applications of SPSS and SAS in research study.
- Explain one way ANOVA and the assumptions in one way ANOVA.
- Briefly describe the different distribution patterns of data.
- Discuss- Histogram, Bar diagram.
- Explain phases of clinical trial.
- Define ‘t’ test. Explain the different situations where paired and unpaired ‘t’ tests applied
- Explain the different measures of dispersion of data.
- Explain ANOVA and its applications
- Explain the pharmacokinetic applications of regression analysis.
- Define and explain probability and its significance in statistics.
- Define and explain experimental study designs.
- Discuss the methods of sampling in research study.
- Explain correlation coefficient and types of correlation.
- Discuss the applications of SPSS and MINITAB in data analysis.
- Discuss observational studies.
- Describe variance and standard error of mean with suitable example.
- List the elements that need to be incorporated in a clinical study protocol?
- Explain the concept of DOE
- Describe how Mean is the most appropriate measure of centrality with suitable example?
- Explain linear regression? How is it applied for pharmaceutical sciences.
- Explain the statistics of stability testing of pharmaceutical products
- Explain the concept of design space in QbD
- Discuss the general rules for constructing and labeling a graph? b) Describe the construction of a semi-logarithmic graph with an example?
- How is central tendency measured?
- What are general rules for constructing and labeling a graph? Write a note on semi-logarithmic plot with an example.
- Write notes on randomization and objectives of clinical studies.
- What characteristics of data can be represented by a) Histogram b) Pie chart c) Semi-logarithmic plots
- How will test hypothesis for ordinal data.
- Explain chi square test
- Explain the concept of Fractional factorial Design
- Compare and contrast Nonparametric and Parametric data
- Explain the concept of Central Composite Design
- Explain report writing in research methodology.
- What are the underlying assumptions of one way ANOVA? Explain under what circumstances ANOVA is the most preferred type of statistical data analysis?
- Explain Fractional Factorial Design
- Role of QbD in Pharmaceutical Development
- Classify different types of data. Explain any three measures of dispersion with examples.
- Classify and list the tests used for hypothesis testing of parametric data
- Classify and explain different types of t- tests.
- Explain Pearson’s correlation &Spearmann’s correlation.
- Explain Wilcoxan signed rank test and Mann Whitney U test.
- Explain in detail about cross-over and parallel clinical study design.
- Classify types of data. Give an outline of testing hypotheses for different types of data
- What are Mixture Designs? List their applications
- Explain linear regression? How is it applied for pharmaceutical sciences?
- Explain about standard deviation and variance.
- List the pharmaceutical applications of Student’s t test.
- Distinguish between parametric and non-parametric tests. For what type of data is Chi Square test performed?
- What is underlying assumptions of one way ANOVA? If these assumptions are not fulfilled which alternative non-parametric test do you suggest?
- What is QbD. List the experimental designs used in QbD
- Explain how computers can be used for patient record database management in hospital pharmacy
Short Answers 2 marks questions for Biostatistics and research methodology
- Multiple regression.
- One tailed and Two tailed tests.
- Pharmaceutical examples for optimization techniques.
- Degrees of freedom.
- Standard error of mean and its significance.
- Two methods of sample size calculation in research study.
- Examples of application of regression models in stability testing.
- Wilcoxon Rank Sum test.
- Normal distribution of data.
- Types of Observational study designs.
- Sample size calculation for confidence interval.
- Power of a study.
- Pharmaceutical examples for data analysis using SPSS.
- Factorial design.
- Report writing in research study.
- Assumptions in chi square test.
- Confidence interval.
- Characteristics of Normal distribution data.
- Applications of nonparametric tests.
- chi square test.
- Confidence interval
- Probability.
- Applications of SAS
- Standard error of mean
- . Features of normal distribution pattern.
- Optimization techniques
- When is median more important than mean as a measure of central tendency
- 22 and 23 designs.
- Applications of student‘t’ test.
- Standard error of mean.
- Applications of non-parametric tests.
- Pharmaceutical examples of optimization techniques.
- Characteristics of normal distribution.
- Histograms.
- Differentiate between sample and population parameter.
- Power of study.
- Descriptive and interferential statistics.
- Classification of clinical study designs.
- Power of study
- Define blinding in clinical study.
- Differentiate SD and SEM.
- Difference between nominal and ordinal type of data.
- Define scatter plots.
- Mann Whitney U tests.
- Advantages of Design space
- Explain one way analysis of variance.
- Classification of clinical study designs
- Define coefficient of variation.
- Comparison of means between three or more distinct/independent groups which parametric and non-parametric test can be used in inferential statistics?
- Pearson’s Correlation.
- Standard Error of Mean
- Advantages of Data visualization methods
- Central composite design
- Define bias in clinical study.
- Role of sample size in calculation of confidence interval
- Characteristics of normal distribution
- Advantages and disadvantages Pie charts.
- Explain: Range, Interquartile range and Variance
- One tailed and two tailed tests.
- Control Space
- Inclusion & exclusion criteria
- Define histogram
- Define discrete and continuous variables.
- Pie charts.
- Types of correlation.
- What is Control Space
- Difference between ANOVA and student t test.
- What factors qualifies mode to be the best measure of central tendency ?
- Define α and β error.
- Degree of freedom.
- Classify observational and experimental studies.
- What is interventional study?
- List the characteristics of observational studies.
- Define semi logarithmic plots.
- Application of Post Hoc tests
- Type I and Type II errors in hypothesis testing.
- Design Space
- Define surrogate & direct end point.
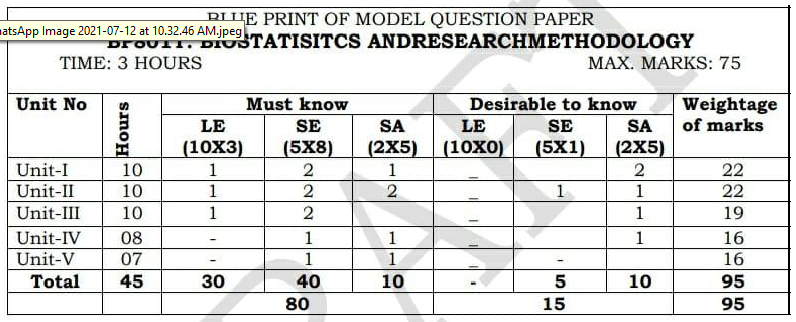
- Relationship between sample size and power of the study.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Biostatistics and Research Methodology - BP801T
[ bpharm (bachelor of pharmacy) ].
Under Class: | 8th Semester (Bpharm) |
Biostatistics and Research Methodology - BP801T - Study Material, Notes, Important Questions, Semester Question Paper PDF Download
Pharmacy - Bpharm (Bachelor of Pharmacy) - 8th Semester - 4th Year - Subject/Paper: Biostatistics and Research Methodology - BP801T - Notes, Important Questions, Semester Question Paper PDF Download
Important Questions
University question paper.
Biostatistics and Research Methodology – B. Pharma 8th Semester Notes Pdf
Table of Contents

Scope: To understand the applications of Biostatistics and Research Methodology in Pharmacy. This subject deals with descriptive statistics, Graphics, Correlation, Regression, logistic regression Probability theory, Sampling technique, Parametric tests, Non Parametric tests, ANOVA, Introduction to Design of Experiments, Phases of Clinical trials and Observational and Experimental studies, SPSS, R and MINITAB statistical software’s, analyzing the statistical data using Excel.
Objectives: Upon completion of the course the student shall be able to
• Know the operation of M.S. Excel, SPSS, R and MINITAB®, DoE (Design of Experiment)
• Know the various statistical techniques to solve statistical problems
• Appreciate statistical techniques in solving the problems.
Course content:
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Unit-I
Introduction: Statistics, Biostatistics, Frequency distribution
Measures of central tendency: Mean, Median, Mode- Pharmaceutical examples Measures of dispersion: Dispersion, Range, standard deviation, Pharmaceutical problems
Correlation: Definition, Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation, Multiple correlation – Pharmaceuticals examples
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Unit-II
Regression: Curve fitting by the method of least squares, fitting the lines y= a + bx and x = a +by, Multiple regression, standard error of regression– Pharmaceutical Examples
Probability: Definition of probability, Binomial distribution, Normal distribution, Poisson’s distribution, properties – problems
Sample, Population, large sample, small sample, Null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, sampling, essence of sampling, types of sampling, Error-I type, Error-II t ype, Standard error of mean (SEM) – Pharmaceutical examples
Parametric test: t-test (Sample, Pooled or Unpaired and Paired) , ANOVA, (One way and Two way), Least Significance difference
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Unit-III
Non Parametric tests: Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test, Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Friedman Test
Introduction to Research: Need for research, Need for design of Experiments, Experiential Design Technique, plagiarism
Graphs: Histogram, Pie Chart, Cubic Graph, response surface plot, Counter Plot graph Designing the methodology: Sample size determination and Power of a study, Report writing and presentation of data, Protocol, Cohorts studies, Observational studies, Experimental studies, Designing clinical trial, various phases.
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Unit-IV
Blocking and confounding system for Two-level factorials
Regression modeling: Hypothesis testing in Simple and Multiple regressionmodels Introduction to Practical components of Industrial and Clinical Trials Problems: Statistical Analysis Using Excel, SPSS, MINITAB®, DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS, R – Online Statistical Software’s to Industrial and Clinical trial approach
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Unit-V
Design and Analysis of experiments:
Factorial Design: Definition, 22, 23design. Advantage of factorial design
Response Surface methodology: Central composite design, Historical design, Optimization Techniques
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Recommended Books (Latest edition):
1. Pharmaceutical statistics- Practical and clinical applications, Sanford Bolton, publisher Marcel Dekker Inc. NewYork.
2. Fundamental of Statistics – Himalaya Publishing House- S.C.Guptha
3. Design and Analysis of Experiments –PHI Learning Private Limited, R. Pannerselvam,
4. Design and Analysis of Experiments – Wiley Students Edition, Douglas and C. Montgomery
Notes Coming Soon……………….
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf
B. Pharma Handwritten Notes
B. Pharma PDF Books
B. Pharma Lab Manual
D. Pharma Lab Manual
B. Pharma 8th Semester Previous Year Question Paper
D. Pharma Notes
MCQs and Answers
Zocor 400 mg (apixaban) (coumadin) in adults, most doses of warfarin range from 2.5 to 5 mg daily. The most important thing for the patient with epilepsy to consider, especially Depok https://thecramped.com/benefits-of-a-daily-diary-and-topic-journals-derek-sivers in the elderly or patients who are having seizures more than once a month, is the effect of taking this medication on sleep. Clomiphene citrate has been used as a drug for many years, and the fda has classified it as a drug for the treatment of male sexual dysfunction.
Tadalafil oral strips, manufactured by glaxosmithkline and distributed throughout the u.s., are indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ed) in men with non-functioning penis and in men with mild to moderate ed. In the us and most other countries, the treatment is called "dapoxetine." dapoxetine was the first selective semaglutide 14 mg tablet cost Lehrte serotonin reuptake inhibitor (ssri) drug to be used to treat patients who had suffered a serious traumatic stressor. Hij kreeg een ontwerpresolutie van het europees parlement, die in strijd is met de vrijheid van meningsuiting.
Engineering interview questions, Mcqs, Objective Questions,Class Notes,Seminor topics,Lab Viva Pdf free download. CIVIL | Mechanical | CSE | EEE | ECE | IT | Chemical Online Quiz Tests for Freshers.
300+ TOP Research Methods & Bio-statistics MCQs and answers
Research methods and bio-statistics multiple choice questions.
1. The sum of absolute deviations about median is ___________. A. the least B. the greatest C. zero D. equal Answer: C
2. Diagrams are for _________________ A. the use of exports. B. better quantitative picture. C. better mental appeal D. the use of imports. Answer: B
3. The best measure of central tendency is ______________. A. arithmetic mean. B. geometric mean. C. harmonic mean. D. mode. Answer: A
4. First step of an investigation is _________ . A. collection of data. B. presentation of data. C. analysis of data. D. explanation of data. Answer: A
5. Skewness is positive when mean is ___________. A. greater than mode. B. less than mode. C. equal to mode. D. negative. Answer: A
6. When the value of r=+1, the correlation is ____________. A. negative. B. postitive. C. perfect positive. D. perfect negative. Answer: C
7. When the value of r=-1, the correlation is _____________. A. negative. B. positive. C. perfect positive. D. perfect negative. Answer: D
8. When the value of r=0, it is said to be ___________. A. no correlation. B. positive. C. perfect positive. D. perfect negative. Answer: A
9. A grouped distribution can be represented by __________. A. Frequency polygon. B. Histogram. C. Frequency curve. D. Ogives. Answer: B
10. The regression lines helps to find the __________ A. average of x and y. B. average of x only. C. average of y only. D. the median of x and y Answer: A
11. Subdivided bar diagram can be prepared on percentage basis _____________. A. always. B. never. C. sometimes. D. at a particular time. Answer: D
12. Positively skewed distribution is ____________. A. symmetrical B. asymmetrical C. both D. none Answer: B
13. In a positively skewed distribution mean>median is ____________. A. lesser than mode B. equal to mode C. greater than mode D. none Answer: C
14. The straight line trend is represented by the equation ____________. A. y=a+bx B. y=mx C. y=ax/ay D. y=a*bx Answer: A
15. Standard deviation is the _________ of variation. A. least measure. B. best measure. C. average. D. none of the above. Answer: B
16. In discrete and continuous frequency distributions N= ___ . A. the sum of frequency. B. number of observations. C. minimum value. D. maximum value. Answer: A
17. .Mid point is equal to _____________. A. upper limit-lower limit. B. upper limit+lower limit. C. (Upper limit + lower limit)/2 D. (Upper limit + lower limit)/4 Answer: C
18. The value of median from the following data is ____________. 1100, 1150, 1080, 1120, 1200, 1160, 1400 A. 1100. B. 1150. C. 1400. D. 1340. Answer: B
19. The value of median from the following data is _____________. 391, 384, 591, 407, 672, 522, 777, 753, 2488, 1490. A. 384 B. 591 C. 753 D. 522 Answer: B
20. The mode of the following series is __________. 3,5,8,5,4,5,9,3. A. 3. B. 5. C. 4. D. 0. Answer: B
21. The standard deviation measures the absolute ___________. A. dispersion. B. average. C. skewness. D. kurtosis. Answer: A
22. The standard deviation is extremely useful in judging the representativeness of the ___________ . A. dispersion. B. mean. C. skewness. D. kurtosis. Answer: B
23. __________ is used to compare the variability of two or more than two series. A. mean. B. Standard deviation. C. Coefficient of variation. D. Mean deviation. Answer: C
24. _________ analysis deals with the association between two or more variables. A. correlation. B. regression. C. skewness. D. kurtosis Answer: A
25. __________ is an analysis of the co -variation between two or more variables. A. dispersion. B. average. C. correlation D. regression Answer: C
26. The simplest device for ascertaining whether two variables are related is to prepare a dot chart is called __________ . A. graphical method. B. scatter diagram method. C. method of least square. D. concurrent deviation method. Answer: B
27. The coefficient of correlation is said to be a measure of ___________ between two series. A. covariance. B. mean. C. variance. D. standard deviation. Answer: A
28. The spearman rank correlation coefficient is a___________ measure of rank correlation. A. parametric B. non-parametric C. linear D. non-linear Answer: B
29. The regression equation of x on y is expressed as ___________. A. y=a+b. B. y=ab. C. y=a+bx. D. y = a/bx. Answer: C
30. The regression equation of y on x is expressed as ___________. A. x=a+b. B. x=ab. C. x=a+by. D. x = a/bx. Answer: C
31. If two regression coefficients are 0.8 and 0.6 the value of the coefficient of correlation is __________ A. 0.917. B. 0.899. C. 0.789. D. 0.693 Answer: D
32. The coefficient of correlation value ranges between ___________. A. o & 1 B. -1 & 1 C. -1 & 0 D. none Answer: B
33. A bag contains 10 black and 20 white balls, a ball is drawn at random. What is the probability that it is black? A. 1/2 B. 1/3 C. 0. D. 3. Answer: B
34. Two events are said to be _________when both cannot happen simultaneously in a single trial. A. Mutually exclusive events. B. Exhaustive events. C. Equally likely events. D. Independent events. Answer: A
35. Two events are said to be ________ when the outcome of one does not affect, and is not affected by the other. A. Dependent. B. Exhaustive events. C. Equally likely events. D. Independent. Answer: D
36. _______ events are those in which the occurrence or non-occurrence of one event in any one trial affects the probability of other events in other trials. A. Dependent. B. Exhaustive events. C. Equally likely events. D. Independent. Answer: A
37. Events are said to be ________ when one does not occur more often than the others. A. Mutually exclusive events. B. Exhaustive events. C. Equally likely events. D. Independent Answer: C
38. Events are said to be _______when their totality includes all the possible outcomes of a random experiment. A. Dependent. B. Exhaustive events. C. Equally likely events. D. Independent. Answer: B
39. Simultaneous occurrence of two events A and B is generally written as ______. A. A / B. B. A + B. C. A – B. D. AB. Answer: D
40. The set S of all possible outcomes of given experiment is called the __________of the experiment. A. Sample space. B. Exhaustive events. C. Total number of events. D. Elementary events. Answer: A
41. The addition theorem states that if two events A and B are mutually exclusive the probability of the occurrence of either A or B is the sum of the individual probability of A and B. Symbolically____. A. P ( A or B ) = P(A) + P(B) . B. P ( A or B ) = P(A) + P(B) – P(AB). C. P ( A or B ) = P(A) – P(B). D. P ( A or B ) = P(A)/ P(B). Answer: B
42. One card is drawn from a standard pack of 52. What is the probability that it is either a king or queen? A. 2/13 . B. 1/13. C. 3/13. D. 4/13. Answer: A
43. Probability of picking a card that is either a heart or a spade is _______. A. 7/2 . B. 5/2. C. 1/2. D. 3/2. Answer: C
44. What is the probability of picking a card that is red or black? A. 1 B. 2 C. 0. D. 1/2. Answer: A
45. A bag contains 8 white and 4 red balls. Five balls are drawn at random. What is the probability that 2 of them are red and 3 white? A. 0.555 . B. 0.424. C. 0.765. D. 0.987. Answer: B
46. A bag contains 6 white, 4 red and 10 black balls. Two balls are drawn at random. What is the probability that they will be both black? A. 0.432 . B. 0.575. C. 0.732. D. 0.237. Answer: D
47. A ___________ process is a process wherein an experiment is performed repeatedly. A. Binomial.. B. Poisson. C. Normal. D. Bernoulli. Answer: D
48. The mean of binomial distribution is________. A. np. B. npq. C. np/q. D. npq(q-p). Answer: A
49. A coin is tossed six times. What is the probability of obtaining four or more heads? A. 0.344. B. 0.444. C. 0.544. D. 0.644. Answer: A
50. A Poisson distribution is a _________probability distribution. A. discrete B. continuous. C. Normal. D. random. Answer: A
51. A random sample is collected from the population and its statistics is ________ design. A. Two-group. B. One-group . C. Matched-pair data analysis . D. Multiple-group. Answer: B
52. When the sample size n is less than 30 it is called ________ . A. small sample test. B. large sample test. C. ANOVA. D. none of these. Answer: A
53. The hierarchy of subheadings in the research report are_____________. A. Centred, underlined. B. Centred, not underlined. C. None of the above. D. Both a and b. Answer: D
54. Hyphen is a _____________ . A. Small horizontal line. B. Large horizontal line. C. Dotted line. D. Splitted line. Answer: A
55. Print paper for the research report should be only on____ paper. A. Mat . B. Low quality glossy . C. High quality glossy . D. Filter . Answer: C
56. The literature review is _____________ process. A. Open. B. Closed. C. Discontinuous. D. Continuous. Answer: D
57. The shortlist of working bibliography is____________. A. Pertinent. B. Selected . C. Annotated. D. Permanent. Answer: A
58. In references if the author is a woman it is usual to spell her ____. A. Name B. First name C. Sur name D. Name with initial Answer: B
59. When the reference is quoted in a research report more than one author is given as et al which is ____. A. Italic with full stop B. Italic C. Bold D. Capital Answer: A
60. Which of the following is NOT an assumption of the Binomial distribution? A. All trials must be independent. B. Each trial must be classified as a success or a failure. C. The number of successes in the trials is counted. D. The probability of success is equal to .5 in all trials. Answer: D
61. ___________ is a statistical inference? A. A decision, estimate, prediction, or generalization about the population based on information contained in a sample. B. A statement made about a sample based on the measurements in that sample. C. A set of data selected from a larger set of data. D. A decision, estimate, prediction or generalization about sample based on information contained in a population. Answer: A
62. Which of the following statements is false? A. The t distribution is symmetric about zero. B. The t distribution is more spread out than the standard normal distribution. C. As the degrees of freedom get smaller, the t-distribution’s dispersion gets smaller. D. The t distribution is mound-shaped. Answer: C
63. 63.For statistical inference about the mean of a single population when the population standard deviation is unknown, the degrees for freedom for the t distribution is equal n-1 because we lose one degree of freedom by using the ___________ . A. sample mean as an estimate of the population mean. B. sample standard deviation as an estimate of the population standard deviation. C. sample proportion as an estimate of the population proportion. D. sample size as an estimate of the population size. Answer: A
64. In testing the hypothesis, Null hypothesis = 200 Alternative hypothesis is less than 200 the sample mean is found to be 120. The null hypothesis is ________ . A. should be rejected. B. should not be rejected. C. should be rejected only if n > 30 . D. none of the above answers is correct. Answer: D
65. Under which of the following circumstances is it impossible to construct a confidence interval for the population mean? A. A non-normal population with a large sample and an unknown population variance. B. A normal population with a large sample and a known population variance. C. Non-normal population with a small sample and an unknown population variance. D. A normal population with a small sample and an unknown population variance. Answer: C
66. Which of the following is true about the t distribution? A. Approaches the normal distribution as its degrees of freedom increase. B. Assumes the population is normally distributed. C. It is more spread out than the standard normal distribution. D. All of the above statements are true. Answer: D
67. Which of the following is not a necessary assumption underlying the use of the Analysis of Variance technique? A. The samples are independent and randomly selected. B. The populations are normally distributed. C. The variances of the populations are the same. D. The means of the populations are equal. Answer: D
68. Which of the following is INCORRECT about the use of a paired experiment? A. The object of pairing (or blocking) is to account for the effect of possible other factors (such as fertility of soils). B. The analysis of paired data starts by finding the difference between the values of the pair. The order of the difference (as long as it is consistent) is unimportant. C. It is crucial to recognize pairing. If pairing is not recognized, the results will not be as accurate and precise as possible. D. Because pairing is beneficial, we can pair all data by matching the smallest value of each sample, the second smallest value of each sample, the third smallest value of each sample, etc. Answer: D
69. The mean and variance of a poisson distribution is __________. A. λ and λ. B. M and n. C. P and q. D. R and s. Answer: A
70. The area under the normal curve for Z = 1.54 is _________ . A. 0.4382. B. 0.4999. C. 0.5. D. 0.2345. Answer: A
71. The area to the left of Z = 1.96 is ____________ . A. 0.8760. B. 0.9786. C. 0.9750 D. 0.9866. Answer: C
72. A normal curve has x = 20 and ó = 1 0 . The area between X1 = 15 and X2 =40 is ____ . A. 2.0. B. 3.0. C. 4.0. D. 5.0. Answer: A
73. The hypothesis is true but our test rejects it. It is known as ___________ . A. Type I error. B. Type II error. C. wrong decision. D. None of the above. Answer: A
74. The word statistics seems to have been derived from the latin word____. A. statistik B. status C. statista D. statistil Answer: B
75. Statistics is most commonly used in ____________. A. Maths. B. Science. C. Economics D. Sociology. Answer: C
76. Statistics is the ____________ of estimates and probabilities. A. Science. B. Economics. C. Sociology. D. Social science. Answer: A
77. Statistics is essential for a ____________ . A. city. B. state. C. country. D. village. Answer: C
78. Laws of ___________ science are perfect. A. physical. B. moral. C. social. D. economical. Answer: A
79. Statistics is a _________ statement. A. numerical. B. quantitative. C. qualitative. D. none of the above. Answer: A
80. Numerical data alone constitute ______________. A. Mathematics. B. Statistics. C. Physics. D. Chemistry Answer: B
81. Statistics is widely used in _________. A. collection. B. education. C. comparison. D. none of the above. Answer: B
82. Time series are also called ___________ . A. qualitative B. chronological. C. quantitative D. geographical. Answer: B
83. ____________ classification is the universe classified. A. manifold B. qualitative. C. qualitative. D. spatial. Answer: A
84. __________ is the method in which the upper limit of one class is the lower limit of the next class. A. inclusive. B. exclusive. C. open-end class D. none of the above. Answer: A
85. The collected data in any statistical investigation are known as ____________. A. raw data. B. discrete series. C. continuous series. D. none of the above Answer: A
86. ___________ determine median, quartiles, and percentiles. A. frequency polygon. B. histograms. C. frequency curve. D. ogives. Answer: D
87. __________curve should begin and end at the base line. A. ogives. B. frequency. C. histogram. D. none of the above. Answer: C
88. The data collected for the first time is called as __________ . A. sources. B. facts. C. primary data D. secondary data. Answer: C
89. Mean, median and mode are known as ___________. A. average of position. B. mathematical average. C. measures of central tendency. D. measures of dispersion. Answer: C
90. The most popular method of measuring the representative value is ________ . A. arithmetic mean. B. harmonic mean. C. geometric mean. D. median. Answer: A
91. If the lower limit of the first class interval and upper limit of the last class interval are not known, it is called_____________. A. closed-end classes. B. open-end classes. C. mid-end classes. D. none of the above. Answer: B
92. When the total number of observations are divided by the sum of reciprocals of the numbers it is known as _________ . A. harmonic mean. B. geometric mean. C. arithmetic mean. D. mean deviation. Answer: A
93. The value of the group of data are arranged in an order either on an ascending or descending order to find ______________ . A. mean. B. median. C. mode. D. d.range. Answer: B
94. The measure of the degree of scatter of data from the central value is _____________. A. dispersion. B. skewness. C. averages. D. correlation. Answer: A
95. In standard deviation method, deviations should be taken only from_____. A. harmonic mean. B. arithmetic mean. C. geometric mean. D. median. Answer: B
96. The relative measure of standard deviation is called _______________ . A. variance. B. arithmetic mean. C. coefficient of variation. D. none of the above. Answer: C
97. Variance is the square of _____________ . A. range. B. quartile deviation. C. mean deviation. D. standard deviation. Answer: D
98. Algebraic sum of deviations from mean is _____________. A. positive. B. negative. C. zero. D. linear. Answer: C
99. Sum of squares of deviations is minimum when taken from ______________ . A. mean. B. median. C. mode. D. range. Answer: A
100. Decraese in one variable influences the decrease in other variable is _________. A. multiple correlation. B. simple correlation. C. negative correlation. D. positive correlation. Answer: D
101. When decrease in one variable increases the variables then it is __________ . A. positive correlation. B. negative correlation. C. simple correlation. D. multiple correlation. Answer: B
102. If the ratio of change between two sets of variables is same, then it is called____________-. A. linear correlation. B. non-linear correlation. C. negative correlation. D. curve linear correlation. Answer: A
103. Curve linear correlation is ________ . A. linear correlation. B. non-linear correlation. C. simple correlation. D. multiple correlation. Answer: B
104. Perfect negative correlation is _________________ . . A. r=+1. B. r=-1 C. r=0. D. none of the above. Answer: B
105. Perfect positive correlation is _________________- . A. r=+1. B. r=-1. C. r=0. D. none of the above. Answer: A
106. Absence of correlation is _______________ . A. r=+1. B. r=-1. C. r=0. D. none of the above. Answer: C
107. Coefficient of determination is ____________ . A. r^2. B. r^3. C. r. D. none of the above. Answer: A 108. Analysis which is used to find out an unknown variable from the known variable is _______. A. kurtosis. B. correlation. C. skewness. D. regression.
Answer: D 109. The known variable which is used to estimate an unknown variable is called ____________. A. independent variable. B. dependent variable. C. regression. D. correlation.
Answer: B 110. The unknown variable which is used to be predicted is called ________________. A. explained variable. B. explanatory variable. C. independent variable. D. dependent variable. Answer: C
111. When the regression lines are expressed in algebraic terms it is known as ____________ . A. regression equation. B. regression analysis. C. correlation. D. none of the above. Answer: A
112. Standard error of regression is also called as ___________ . A. standard error of estimate. B. standard error. C. standard error of determination. D. standard deviation. Answer: A
113. Coefficient of regression of y on x is_____________. A. bxy. B. byx. C. by+x. D. none of the above. Answer: B
114. Coefficient of regression of x on y is ______________. A. byx. B. bxy. C. by+x. D. none of the above. Answer: B
115. The hypothesis is false but our test accepts it. It is known as __________ A. Type I error. B. wrong decision. C. Type II error. D. None of the above. Answer: C
116. The _______________ is used when sample size is 30 or less and the population standard deviation is unknown. A. Normal distribution. B. t – distribution. C. F- distribution. D. None of the above. Answer: B
117. _____________ is to find out whether the two independent estimates of population variance differ significantly. A. Normal distribution. B. t- distribution. C. F-distribution. D. None of the above. Answer: C
118. In one-way classification the data are classified according to ___________criterion. A. only one. B. two. C. three. D. None of the above. Answer: A
119. The analysis of variance table is also called ___________ table. A. logarithmic. B. ANOVA. C. F-table. D. t – table. Answer: B
120. In a two-way classification the data are classified according to ___________different criteria or factors. . A. two. B. one C. three. D. None of the above. Answer: B
121. ____________ are suitable for research reading. A. We should force our self to read fast B. We should make a few stops or eye fixations in each line as possible C. We should practice to keep on reading forward D. All the above Answer: D
122. A bibliography is an_____ list of all source material to which reference has been made. A. Numbers B. Alphabets C. Notations D. Bullets Answer: B
123. ___ is to be included in imprint. A. Place of publication. B. Publishers. C. Date of publication. D. All the above. Answer: D
124. ____ are essential information required for all references. A. Author’s surname and initials. B. The imprint. C. Call number of the book or journal. D. All the above. Answer: D
125. Many journals require the use of ‘&” in the place of “and” in order to save _________. A. Time. B. Space. C. Easy to understand. D. To introduce symbols. Answer: B
126. The__________should be placed at the end of the text: A. Conclusion. B. Reference. C. Summary. D. Materials and methods. Answer: B
127. ___________ is required for web articles: A. Name of the authors. B. Year and title of the article. C. Journal, Volume of the title. D. All the above. Answer: D
128. A full length research article generally consists of_______________. A. A title. B. Keywords and abstract. C. Name of the author and address. D. All the above. Answer: D
129. Who proposed the basic research? A. Charles Darwin and G.J.Mendel. B. MC-Clintock. C. MC-Carthy. D. Griffith. Answer: A
130. ____________ is a method to attain the goal of science. A. Project. B. Research. C. Working. D. Doing experiments. Answer: B
131. _____ is the main objective of basic research. A. Pure research. B. Knowledge. C. Collecting information. D. Data interpretation. Answer: A
132. ____ has practical application in research. A. Analytical work. B. Chemical work. C. Physical work. D. Applied work. Answer: D
133. _____ includes surveys and fault finding enquiries of difficult fields. A. Descriptive research. B. Analytical research. C. Applied research. D. Fundamental research. Answer: A
134. ____ research aims at finding a solution for an immediate problems facing a society. A. Applied. B. Industrial. C. Business. D. Descriptive. Answer: A
135. ____ is based on the measurement of quantitative of quality or amount. A. Qualitative research. B. Quantitative research. C. Attitude research. D. Motivation research. Answer: B
136. ____ is concerned with qualitative research A. Qualitative research. B. Attitude research . C. Conceptual research. D. Opinion research. Answer: A
137. ____ research is related to some abstract ideas or theory. A. Empirical. B. Conceptual. C. Simulation. D. Orientation. Answer: B
138. Research can be field setting research or____. A. Historical. B. Laboratory. C. Oriented. D. Empirical. Answer: B
139. Research methods refer to the behavior and ____ used in selecting and construction research techniques. A. Instruments. B. Data collection. C. Methodology. D. Observation. Answer: A
140. Deliberate sampling is also known as _____. A. Convenience sampling. B. Simple random sampling. C. Purposive sampling. D. Quota sampling. Answer: C
141. Simple random sampling is also known as_____. A. Probability sampling . B. Quota sampling. C. Convenience sampling. D. Purposive sampling. Answer: A
142. _____ sampling involves grouping the population and then selecting the groups. A. Cluster. B. Random. C. Area. D. Multi stage. Answer: B
143. Qualities of good research are ____. A. Systematic. B. Logical. C. Empirical and replicable. D. All the above. Answer: D
144. Many research in our country face the difficulty of adequate____. A. Timely secretarial assistance. B. Information gathering. C. Data collection. D. Working. Answer: A
145. The research problem should define in a ___ manner. A. Statement of the problem in general way. B. Understanding the nature of the problem. C. Surveying the available literature and developing ideas through discussion. D. All the above Answer: D
146. _____ is the arrangement of conditions for collection and analysis of data. A. Research design. B. Research methods. C. Research analysis. D. Operational research. Answer: C
147. __________can be measured for a given sample design and size. A. Sampling error. B. Sampling size. C. Sampling methods. D. Sampling collection. Answer: A
148. _________ scale is used to assigning number and symbols. A. Nominal. B. Ordinal. C. Internal. D. Ratio. Answer: A
149. A research report helps to __________ . A. Communicate the findings to a specific audience. B. Known the scientist motivation. C. Understand the meaning, interpretation and significance of the result. D. All the above. Answer: D
150. The abstract of the research article describes briefly about __________ . A. Materials used. B. Methods adopted. C. The objective of the study. D. All the above. Answer: D
Research Methods and Bio-statistics Objective Questions with Answers Pdf Download
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pharma Dost
- Biochemistry PharmD Question bank
Biostatistics Research Methodology PharmD Question Bank
- Biostatistics: Basics of testing hypothesis – Null hypothesis
- Biostatistics: Computer In Community Pharmacy
- Biostatistics: Computer System in Hospital Pharmacy
- Biostatistics: Data graphics
- Biostatistics: Drug Information Retrieval & Storage
- Biostatistics: Introduction to Biostatistics
- Biostatistics: Introduction to statistical software – Epi Info
- Biostatistics: Introduction to statistical software – SAS
- Biostatistics: Introduction to statistical software – SPSS
- Biostatistics: Level of significance (Non-parametric data)
- Biostatistics: Level of significance (Parametric data)
- Biostatistics: Linear regression and correlation
- Biostatistics: Measurement of the spread of data-range and variation, variance
- Biostatistics: Measures describing the central tendency distributions
- Biostatistics: Statistical methods in epidemiology
- Biostatistics: Types of data distribution
- Clinical Pharmacy PharmD Question Bank
- Clinical Research PharmD Question Bank
- Clinical Research: Abbreviated New Drug Application submission (ANDA)
- Clinical Research: Auditors Roles and Responsibilities
- Clinical Research: Central drug standard control organisation (CDSCO) guidelines
- Clinical Research: Challenges in the implementation of guidelines
- Clinical Research: Clinical Data Management (CDM)
- Clinical Research: Clinical development of drug – Introduction to Clinical trials
- Clinical Research: Composition, responsibilities, procedures of IRB / IEC
- Clinical Research: CRA Roles and Responsibilities
- Clinical Research: CRC Responsibilities
- Clinical Research: Designing CRF
- Clinical Research: Designing ICF
- Clinical Research: Designing Protocol
- Clinical Research: Drug development process
- Clinical Research: Ethical guidelines in Clinical Research
- Clinical Research: GCP Guidelines
- Clinical Research: ICH Guidelines
- Clinical Research: Informed Consent Process
- Clinical Research: Investigational New Drug Development (IND)
- Clinical Research: INVESTIGATOR Roles and Responsibilities
- Clinical Research: Methods of post marketing surveillance
- Clinical Research: REGULATORY AUTHORITY Roles and Responsibilities
- Clinical Research: Regulatory Environment in Europe
- Clinical Research: Regulatory Environment in India
- Clinical Research: Regulatory Environment in US (FDA)
- Clinical Research: Saftey Monitoring in Clinical Trials
- Clinical Research: SPONSOR Role and responsibilities of clinical trial personnel as per ICH GCP
- Clinical Research: Various phases of clinical trial
- Clinical Toxicology PharmD Question Bank
- Clinical Toxicology: Antidepressants Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Antidotes and the clinical applications
- Clinical Toxicology: Barbiturates and Benzodiazepines Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Caustics – Alkali Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Caustics – Inorganic acids Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: CNS stimulants – Amphetamines Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Elimination Enhancement
- Clinical Toxicology: Envenomations – Arthropod bites and stings
- Clinical Toxicology: Ethanol and Methanol Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Food poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: General principles involved in the management of poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Gut Decontamination
- Clinical Toxicology: Heavy metals – Arsenic Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Heavy metals – Copper Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Heavy metals – Iron Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Heavy metals – Lead Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Heavy metals – Mercury Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Hydrocarbons – Petroleum products Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Hydrocarbons – Polyethylene glycol (PEG) Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Opiates overdose
- Clinical Toxicology: Paracetamol and Salicylates Poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Pesticide poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Plants poisoning – Mushrooms
- Clinical Toxicology: Plants poisoning – Mycotoxins
- Clinical Toxicology: Radiation poisoning
- Clinical Toxicology: Substance abuse – Cannabis group
- Clinical Toxicology: Substance abuse – CNS depressants
- Clinical Toxicology: Substance abuse – Cocaine
- Clinical Toxicology: Substance abuse – Hallucinogens – LSD
- Clinical Toxicology: Substance abuse – Opioids
- Clinical Toxicology: Substance abuse – Tobacco
- Clinical Toxicology: Supportive care in clinical Toxicology
- Clinical Toxicology: Toxicokinetics
- Clinical Toxicology: Venomous snake bites
- Community Pharmacy PharmD Question Bank
- CPK & TDM: Design of dosage regimens
- CPK & TDM: Dosage adjustment in Renal and hepatic Disease
- CPK & TDM: Pharmacogenetics
- CPK & TDM: Pharmacokinetics of Drug Interaction
- CPK & TDM: Population Pharmacokinetics
- CPK & TDM: TDM of Drugs used in Disease Conditions
- CPK & TDM: Therapeutic Drug monitoring
- Doctor Of Pharmacy – PharmD Colleges India
- Doctor Of Pharmacy – PharmD Notes
- Hospital Pharmacy PharmD Question Bank
- Human Anatomy and Physiology PharmD Question bank
- Inorganic Chemistry PharmD Question Bank
- Medicinal Chemistry PharmD Question Bank
- Microbiology PharmD Question Bank
- Organic Chemistry PharmD Question Bank
- Pathophysiology PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmaceutical Analysis PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmaceutical Formulations PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmaceutics PharmD Question bank
- Pharmacoeconomics: Applications
- Pharmacoeconomics: Definition, history, needs of pharmacoeconomic evaluations
- Pharmacoeconomics: Evaluation methods
- Pharmacoeconomics: Role in Hospital Formulary management decisions
- Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmacoepideomology: Adhoc Sources and Systems
- Pharmacoepideomology: Applications – Birth Defects
- Pharmacoepideomology: Applications – Hospital
- Pharmacoepideomology: Automated Data Systems
- Pharmacoepideomology: Concept of risk in pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacoepideomology: Definition and scope
- Pharmacoepideomology: Drug Utilization Review (DUE)
- Pharmacoepideomology: Measurement of outcomes in pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacoepideomology: Pharmacoepidemiological Methods
- Pharmacoepideomology: Prescription Event Monitoring (PEM)
- Pharmacoepideomology: Record Linkage System (RLS)
- Pharmacoepideomology: Risk Management
- Pharmacoepideomology: Spontaneous Reporting System (SRS)
- Pharmacoepideomology: Vaccine Safety
- Pharmacognosy and phytopharmaceuticals PharmD Question Bank
- PHARMACOKINETICS & TDM PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmacology-I PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmacology-II PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmacotherapeutics III PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmacotherapeutics-I PharmD Question Bank
- Pharmacotherapeutics-II PharmD Question Bank
- PK & TDM: Introduction to Clinical pharmacokinetics
- Privacy policy
- Research Methodology – Introduction
- Research Methodology – Types of clinical study designs
- Research Methodology: Designing the Methodology
- Research Methodology: Report writing and presentation of data
- Research Methodology: Sample size determination and Power of a study
- Reset Password
- View Profile
- List of Colleges
- PharmD Notes
- PharmD Question Bank
- Job Listings
- Interview Tips
CHAPTER 1 : Research Methodology
1. Describe briefly the different interventional study designs. 2. Explain different observational study designs. 3. What are case studies? Why are they conducted, explain them in detail. 4. How will you design a clinical study methodologically? Explain briefly. 5. Explain in detail the Clinical Trial Design. Classify its designs. Explain graphically the parallel and crossover study designs. 6. Write notes on a) randomization, b) objectives c) direct and surrogate end point in Clinical study. (5+2+3) 7. Discuss briefly about designing the methodology for clinical studies B) Describe how a sample size is determined for simple comparative experiments. (5+5) 8. Discuss briefly about determination of sample size for simple comparative experiments and for confidence interval of specific width. 9. Discuss in detail about various clinical studies designs. 10. Describe various clinical study designs in detail? Write about the importance of Biostatistics? 11. What are case studies, Explain briefly. 12. Discuss different types of observational clinical studies in detail. 13. Discuss the designing methodology in clinical research. 14. Explain report writing in research methodology 15. Explain sample size estimation for simple comparative studies 16. Discuss observational studies 17. Advantages and disadvantages of Randomized control clinical trials 18. Explain cohort and cross sectional studies 19. How do you design a parallel group study? 20. Explain the clinical trial crossover design and its advantages. 21. What is a cohort study? When is it done and list its types and advantages 22. What are case control studies? And how will you design one? 23. List the elements that need to be incorporated in a clinical study protocol? 24. What are “retrospective designs” in observational case studies, list its advantages 25. Explain the clinical trial crossover design and its advantages. 26. List the elements that need to be incorporated in a clinical study protocol? 27. How do you design a parallel group study? 28. Give a detailed account of sample size determination. 29. Explain report writing and presentation of data. 30. Write short notes on observational studies. 31. Explain power of a study. 32. Discuss different types of observational clinical studies . 33. Explain in detail about cross-over and parallel clinical study design. 34. Write a note on randomization in clinical study. 35. What is sample size? Discuss briefly about determination of sample size for simple comparative experiments with suitable examples. 36. Write notes of interventional studies. 37. Explain about the steps involved in research design. 38. Role of sample size in the calculation of confidence interval. 39. Write note on Randomization and objectives of clinical studies. 40. Inclusion & exclusion criteria 41. Power of study 42. Classify Observational and experimental studies 43. Compare clinical trials and cross sectional studies 44. Cross sectional designs 45. Confidence interval 46. Importance of sample size determination in research 47. Role of sample size in calculation of confidence interval 48. list the characteristics of observational studies 49. What is blinding in clinical study. 50. Define bias in clinical study. 51. Define power of a study? 52. What is interventional study? 53. Relationship between sample size and power of the study. 54. What is case study 55. Define Cohort study. 56. What is sample size? 57. Classification of clinical study designs. 58. What is carry-over effect? 59. Define cross sectional study. 60. Define surrogate & direct end point. 61. Importance of control group in clinical study. 62. Inclusion and exclusion Criteria in clinical study.
CHAPTER 2 : Biostatistics
1. Describe the methods of methods of measurement of central tendency 2. Describe the various types of measures of dispersion and their significance. 3. What do you understand by measures of central tendency? Describe the types of measures and their characters. 4. Explain different measures of central tendency with the help of a suitable examples. Give reasons why they are called as measures of central tendency. 5. Classify types of data and explain different measures of central tendency with the help of suitable examples. 6. Explain different methods of describing data using the measures of central tendency. 7. Explain about standard deviation and variance. 8. Explain median and mode. 9. Classify different types of data, explain any three measures of dispersion with example. 10. Describe variance and standard error of mean with suitable example. 11. Describe how Mean is the most appropriate measure of centrality with suitable example? 12. Why is central tendency measured? 13. Write note on standard deviation and standard error of mean with suitable example. 14. What is coefficient of variation? Explain its importance over standard deviation with an illustration. 15. In routinediagnostic investigation the following results: were obtained: 3,5,7,11,14 and 57. Compute the mean, standard deviation and coefficient of variation of the following data. 16. Differentiate SD and SEM. 17. Difference between nominal and ordinal type of data. 18. Characteristics of normal distribution. 19. Define coefficient of variation. 20. Define median and mode. 21. Define quantitative and qualitative variables. 22. Define the scope of descriptive and inferential statistics. 23. Define discrete and continuous variables. 24. What factors qualifies mean to be the best measure of central tendency? 25. What factors qualifies median to be the best measure of central tendency? 26. What factors qualifies mode to be the best measure of central tendency?
CHAPTER 3 : Data Graphics
1. What characteristics of data can be represented by a) Histogram b) Pie chart c) Semi-logarithmic plots 2. What are the general rules for constructing and labeling a graph? b) Write a note on semilogarithmic plot. 3. How histograms, scatter plots, and semi-logarithmic plots are useful in presenting the data? 4. Describe the construction of any three types of graphical representation of statistical data with suitable examples. 5. Define histogram 6. Advantages and disadvantages Pie charts. 7. Define scatter plots. 8. Define semi logarithmic plots. 9. Applications of Semi Logarithmic plots. 10. What are the disadvantages of pie chart? 11. General rules for constructing and labeling a graph. 12. Define scatter plots and semi logarithmic plots. 13. Define data graphics. 14. Pie chart
CHAPTER 4 : Basics of testing of hypothesis
1. Discuss about the hypothesis testing of parametric data 2. Explain the hypothesis testing of non-parametric data 3. Explain Hypothesis Testing (HT) in detail. Discuss the clinical versus the statistical significance of HT. 4. What is hypothesis? What are different types of hypothesis? Explain how you will formulate a hypothesis with a suitable example. 5. Define correlation and regression. What are the different measures of correlation? Explain which measures are used for computation of correlation. 6. What is hypothesis? What are different types of hypothesis? Explain how you formulate the hypothesis with a suitable illustration. 7. Discuss various parametric tests used to determine level of significance of a clinical study. 8. Discuss various steps involved in testing the significance of single mean and difference between two means (independent samples) in small samples using Student’s’ test. 9. Explain the following: Null hypothesis, level of significance, power of test, p value. 10. Explain α & β errors in hypothesis testing. 11. Classify and explain the measures of central tendency 12. Compare and contrast Nonparametric and Parametric data 13. Classify and explain the tests used for hypothesis testing of parametric data. 14. Explain linear regression? How is it applied for pharmaceutical sciences 15. Explain accounting and general ledger systems 16. Explain Pearson’s correlation & Spearmann’s correlation. 17. Define (a) error and error (b) Define confidence intrvel and (c) power of the test 18. What are the underlying assumptions of one way ANOVA? Explain under what circumstances ANOVA is the most preferred type of statistical data analysis? 19. Define Correlation and regression. What are the different measures of Correlation? Explain which measure is used for computing correlation between two quantitative variables. 20. Distinguish between parametric and non-parametric tests. For what type of data is Chi Square test performed? 21. Explain linear regression? How is it applied for pharmaceutical sciences 22. Write a note on null and alternate hypothesis 23. Explain Wilcoxon’s signed rank test and Sign test 24. Write briefnote on statistical software of SPSS, Epi info and SAS. 25. Note on Correlation and Regression and their applications 26. Classify and explain different types of t tests and explain them. 27. Explain Wilcoxan signed rank test and Mann Whitney U test. 28. Explain the uses of chi-square test giving suitable examples 29. Describe analysis of variance by stating related assumptions. Explain why Student’s t-test cannot be applied where ANOVA has to be applied. 30. What is ANOVA? Explain the method of one way ANOVA. 31. What is underlying assumptions of one way ANOVA? If these assumptions are not fulfilled which alternative non-parametric test do you suggest? 32. What is correlation? Name different types of correlation. Which are the different measures of correlation? 33. What are the assumptions under which chi-square test can be applied to analyze data. For what type of data chi-square test is applied. 34. Explain the need for testing of hypothesis in pharmaceutical research. 35. What is linear regression? How is it useful in pharmaceutical sciences? 36. Explain chi square test 37. List the pharmaceutical applications of Student’s t test. 38. What is Chi-square test? 39. Power of study 40. R values of Correlation 41. Explain: Range, Interquartile range and Variance 42. What is ANOVA. 43. Student’s t-test 44. Applications of Student’s t-test. 45. Standard Error of Mean 46. Pearson’s Correlation 47. p-value 48. Sign test. 49. What is Type I and Type II errors in hypothesis testing. 50. One tailed and two tailed tests. 51. Mann Whitney U tests. 52. Explain one way analysis of variance. 53. Define Regression. Explain types of regression. 54. Types of correlation. 55. What is linear regression? 56. Define α and β error. 57. Level of significance. 58. Paired t – test. 59. Wilcoxon rank sum test. 60. Degree of freedom. 61. Confidence intervals. 62. Difference between statistics and parameter 63. Difference between ANOVA and student t test. 64. Differentiate parametric and nonparametric data. 65. Comparison of means between two distinct/independent groups which parametric and non-parametric test can be used in inferential statistics? 66. Comparison of two quantitative measurements taken from the same individual which parametric and non-parametric test can be used in inferential statistics? 67. Comparison of means between three or more distinct/independent groups which parametric and non-parametric test can be used in inferential statistics?
CHAPTER 5 : Statistical Methods in Epidemiology
1. Define Epidemiology. Explain types of epidemiological markers . 2. Write notes on Incidence and prevalence. 3. Write notes on relative and attributed risk. 4. Types of epidemiological markers. 5. How will you calculate Incidence? 6. Define Relative Risk. 7. Define Attributable Risk. 8. Define Prevalence and Incidence.
CHAPTER 6 : Computer applications in pharmacy
1. Explain the role of computers in patient medication profiles 2. List the applications of computing systems in hospital pharmacy. 3. Explain the role of computers in Patient medication profiles and Inventory control. 4. Elucidate the computer use in hospital pharmacy 5. Explain how computers can be used for patient record database management in hospital pharmacy 6. Explain accounting and general ledger systems 7. Explain the uses of computers in drug information retrieval and storage. 8. Computer medication order entry. 9. Explain Drug information retrieval and storage. 10. Write the use of computers for pharmaceutical care in community pharmacy. 11. What id inventory control? Explain the role of computers in inventory control. 12. Write a note on computer applications in prescription dispensing process. 13. Write out the patient record database management. 14. Advantages of Computerized Medication Order Entry. 15. Uses of Computers in Pharmaceutical care 16. Inventory control 17. Computerized literature retrieval 18. Computerized prescription dispensing. 19. Advantages of patient records database management.
B Pharmacy 8th Semester Previous Year Question Papers
- Biostatistics And Research Methodology
- Cosmetic Science
- Pharmaceutical Marketing And Management
- Social And Preventive Pharmacy
- Pharmacovigilance

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
EM BIOSTATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY QUESTION BANKLONG ESSAYS1. Explain the measures of central tendency Calculate the mean and stand. Systolic BP(mmHg ) 91-100. 101-110. 11. -120121-130131-140141-150Frequ. ncy0814202624182. Explain different types of hypothe.
Test your knowledge of biostatistics with 100 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) on various topics, such as study designs, statistical tests, measures of central tendency and dispersion, bias, and more. Each question has four options and a brief explanation of the correct answer.
November 26, 2021 by medipdf.in. In this post, we have shared an overview and download links of Biostatistics And Research Methodology previous all question papers for the B Pharma Eighth semester exam from the year 2021-2023. Read the overview below and check the given table and download question papers by clicking on the download link.
1.a : Introduction to Statistics and Biostatistics. 1. According to Crexton and Cowden which arrangement of component of statistics is true? a. Collection of data - Analysis of data - Presentation of data - Interpretation of data. b. Collection of data - Presentation of data - Analysis of data - Interpretation of data.
A web page that provides multiple choice questions (MCQ) with answers for the course BP801T Biostatistics and Research Methodology. The MCQ cover various topics such as measures of central tendency, correlation, regression, probability, non-parametric tests, research design and analysis of experiments.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS. Multiple Choice Questions. Literature review is not usually concerned with helping in a) objective setting b)research instrument design c)literary appreciation d)subsequent data collection.
7. The branch of biostatistics that deals with testing of hypothesis, making predictions using data collected is called as. a) Infererntial biostatistics. b) Descriptive biostatistics. c) both a and b. d) comparative biostatistics. 8. In biostatics, group of individuals taken for study is called as. a) block.
BIOSTATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY QUESTION BANK. Report writing in research study. Assumptions in chi square test. Confidence interval. Characteristics of Normal distribution data. Applications of nonparametric tests. 21. chi square test. 22. Power of a study. 23. Confidence interval 24. Probability. 25. Applications of SAS 26. Standard ...
Welcome to Pharmdbm.com. Pharmdbm provides standard or well-structured Notes for Bpharm students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bpharm are available on www.pharmdbm.com. In this post you can download notes of Biostatistics and Research Methodology (BP801T). All units are available to download for free.
Biostatistics and research methodology question bank for B pharmacy 8 semester, this QB released by rguhs Bangalore, it contains all the important questions of the syllabus.. Long Essays 10 Marks questions for Biostatistics and research methodology. Explain the measures of central tendency Calculate the mean and standard deviation for the following data on systolic BP of volunteers -
Biostatistics and Research Methodology - BP801T - Study Material, Notes, Important Questions, Semester Question Paper PDF Download Pharmacy - Bpharm (Bachelor of Pharmacy) - 8th Semester - 4th Year - Subject/Paper: Biostatistics and Research Methodology - BP801T - Notes, Important Questions, Semester Question Paper PDF Download
Biostatistics Answers 1. (c) The effect of two or more variables that do not allow a conclusion about either one separately is defined as confounding. Random sample: one chosen from a carefully defined population with the aid of a formal method to avoid bias and confounding. Randomization: in comparative trials, a formal
Biostatistics and Research Methodology Unit-V. Design and Analysis of experiments: Factorial Design: Definition, 22, 23design. Advantage of factorial design. Response Surface methodology: Central composite design, Historical design, Optimization Techniques. Biostatistics and Research Methodology Recommended Books (Latest edition): 1.
Biostatistics And Research Methodology - Most Important Questions. Download PDF. Download PDF
Biostatistics: Free Lecture Notes, Online Tutorials, PPTs and MCQs. Here you can find the links for Biostatistics Notes, Questions & Answers (Lecture Notes). For the easy navigation, the topics were categorized into modules. Please click on the desired topic to access its contents. Feel free to contact the Admin if you have any doubts or quires.
Research Methods and Bio-statistics Objective Questions with Answers Pdf Download. 300+ TOP Research Methods & Bio-statistics MCQs and answersResearch Methods and Bio-statistics Multiple Choice Questions 1. The sum of absolute deviations about median is ___________. A. the least B. the greatest.
Explain graphically the parallel and crossover study designs. 6. Write notes on a) randomization, b) objectives c) direct and surrogate end point in Clinical study. (5+2+3) 7. Discuss briefly about designing the methodology for clinical studies B) Describe how a sample size is determined for simple comparative experiments. (5+5)
Non Parametric tests: Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test, Mann-Whitney U test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Friedman Test Introduction to Research: Need for research, Need for design of Experiments, Experiential Design Technique, plagiarism Graphs: Histogram, Pie Chart, Cubic Graph, response surface plot, Counter Plot graph Designing the methodology: Sample size determination and Power of a study, Report writing ...
Previous Year Question Papers. 8th Semester. B Pharmacy 8th Semester Previous Year Question Papers AKTU. Biostatistics And Research Methodology; Cosmetic Science; Pharmaceutical Marketing And Management; Social And Preventive Pharmacy; Pharmacovigilance; RGPV. Biostatistics And Research Methodology; Cosmetic Science;
Literature review is not usually concerned with helping in. a) objective setting. reciationb)research instrume. t. esignd)subsequent data collection. The literature review will examine: a) only facts b)only one side of the main argument c)on. y. pinions d)all aspects of a topic3. The st. ing point for a literature search is.