
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


5.15: Area of Parallelograms- Squares, Rectangles and Trapezoids
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4999
Find the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids.
Find the Dimensions and Area of Quadrilaterals
Montgomery Middle School is going to host a school wide Olympics for the first time. The initial preparations have already started and a fantastic two day Olympic event will take place in six weeks. Mrs. Meery’s class will be building the platform for the award’s ceremony. The platform is in the shape of a trapezoid with bases 35 feet and 41 feet and a height of 7.5 feet. If one bucket of cement covers 25 square feet, how many buckets will the students need to build the platform?
In this concept, you will learn to find the dimensions and areas of different quadrilaterals.
Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are four-sided polygons. They are classified by the characteristics of their sides and angles. Rectangles, squares, parallelograms, rhombi, and trapezoids are all quadrilaterals. The images below show some of the quadrilaterals and their characteristics.
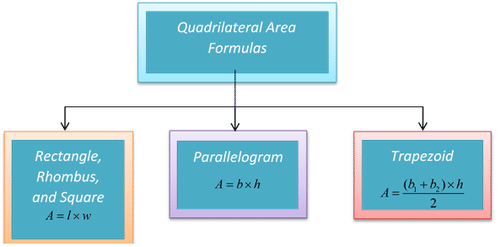
Each of these quadrilaterals has its own area formula.
Let’s look at an example.
What is the area of a rectangle with a length of 6 inches and a width of 4 inches?
First, fill in what you know into the formula for the area of a rectangle.
\(\begin{aligned} A&=l\times w \\ A&=6\times 4 \end{aligned}\)
Next, solve for \(A\).
\(\begin{aligned}A&=6\times 4 \\ A&=24\end{aligned}\)
The answer is 24.
The area of the rectangle is \(24\text{ in }^2\), or 24 square inches.
Let’s look at another example.
What is the area of the parallelogram below?
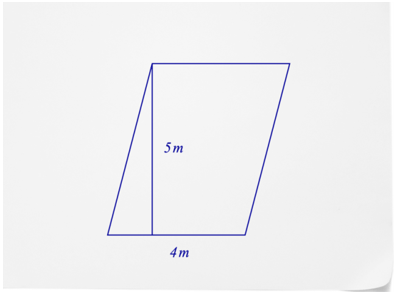
First, substitute what you know into the formula for the area of a parallelogram.
\(\begin{aligned} A&=b\times h \\ A&=4\times 5\end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned}A&=4\times 5 \\ A&=20\end{aligned}\)
The answer is 20.
The area of the parallelogram is \(20\text{ m}^2\), or 20 square meters.
Let’s look at one more example.
Find the area of the trapezoid below.
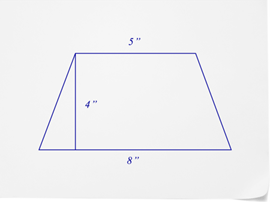
First, substitute what you know into the formula for the area of a trapezoid.
\(\begin{aligned} A&=\dfrac{(b_1+b_2)\times h}{2} \\ A&=\dfrac{(5+8)\times 4}{2} \end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned} A&=\dfrac{(5+8)\times 4}{2} \\ A&=26 \end{aligned}\)
The answer is 26.
The area of the trapezoid is \(26\text{ in }^2\), or 26 square inches.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Earlier, you were given a problem about the school’s podium.
The podium is in the shape of a trapezoid that has base measures of 35 feet and 41 feet and a height of 7.5 feet. The podium is being made of cement where one bucket of cement covers 25 square feet. You need to find the area of the podium and then the number of buckets of cement to make it.
\(\begin{aligned} A&=\dfrac{(b_1+b_2)\times h}{2} \\ A&=\dfrac{(35+41)\times 7.5}{2} \end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned}A&=\dfrac{(35+41)\times 7.5}{2} \\ A&=285 \end{aligned}\)
Then, divide the area by 25 in order to determine the number of buckets of cement to use.
\(\text{ # of buckets}=\dfrac{285}{25}\)
\(\text{ # of buckets}=11.4\)
The answer is 11.4.
The students will have to buy 12 buckets of cement for their project.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
A parallelogram has an area of \(105\: m^2\). The height of the parallelogram is 7 m. What is its base?
\(\begin{aligned} A&=b\times h \\ 105&=b\times 7\end{aligned}\)
Next, divide both sides by 7 to solve for \(b\).
\(\begin{aligned} 105&=b\times 7 \\ \dfrac{105}{7}&=\dfrac{7b}{7} \\ b&=15\end{aligned}\)
The answer is 15.
The base of the parallelogram has a length of 15 m.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
What is the area of a square with a side length of 4.5 inches?
First, substitute what you know into the formula for the area of a square.
\(\begin{aligned} A&=l\times w \\ A&=4.5\times 4.5\end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned} A&=4.5\times 4.5 \\ A&=20.25 \end{aligned}\)
The answer is 20.25. Therefore the area of the square is \(20.25 \text{ in}^2\), or 20.25 square inches.
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
What is the area of a rectangle with a length of 8 feet and a width of 6.25 feet?
First, substitute what you know into the formula for the area of a rectangle.
\(\begin{aligned} A&=l\times w \\ A&=8\times 6.25 \end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned} A&=8\times 6.25 \\ A&=50 \end{aligned} \)
The answer is 50.
The area of the rectangle is 50 ft^2\), or 50 square feet.
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
What is the area of a parallelogram with a base of 10 meters and a height of 7.5 meters?
\(\begin{aligned} A&=b\times h \\ A&=10\times 7.5 \end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned} A&=10\times 7.5 \\ A&=75 \end{aligned}\)
The answer is 75.
The area of the parallelogram is 75 m2, or 75 square meters.
1. \(l=10\text{ in },\: w=7.5\text{ in }\)
2. \(l=12\text{ ft },\: w=9\text{ ft }\)
3. \(l=14\text{ ft },\: w=11\text{ ft }\)
4. \(l=21\text{ ft },\: w=19\text{ ft }\)
Find the area of each parallelogram.
5. \(b=11\text{ ft },\: h=9\text{ ft }\)
6. \(b=13\text{ in },\: h=11\text{ in }\)
7. \(b=22\text{ ft },\: h=19\text{ ft }\)
8. \(b=31\text{ meters },\: h=27\text{ meters }\)
Find the area of each trapezoid.
9. \(Bases=5\text{ in } \:and \:8 in,\: height=4 \text{ inches }\)
10. \(Bases=6 \:in \:and \:8\text{ in },\: height=5 \text{ inches }\)
11. \(Bases=10\text{ feet }\: and\: 12\text{ feet },\: height=9\text{ feet }\)
Find the area of each square.
12. side length of 8 inches
13. side length of 15 feet
14. side length of 22.5 mm
15. side length of 18.25 cm
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 8.2.
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Determine the Area of a Rectangle Involving Whole Numbers
Practice: Area of Parallelograms: Squares, Rectangles and Trapezoids

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

13.4.5: Use Properties of Rectangles, Triangles, and Trapezoids (Part 2)
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 46187

Use the Properties of Triangles
We now know how to find the area of a rectangle. We can use this fact to help us visualize the formula for the area of a triangle. In the rectangle in Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\), we’ve labeled the length b and the width h, so it’s area is bh.

Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) - The area of a rectangle is the base, b, times the height, h.
We can divide this rectangle into two congruent triangles (Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)). Triangles that are congruent have identical side lengths and angles, and so their areas are equal. The area of each triangle is one-half the area of the rectangle, or \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)bh. This example helps us see why the formula for the area of a triangle is A = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)bh.

Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) - A rectangle can be divided into two triangles of equal area. The area of each triangle is one-half the area of the rectangle.
The formula for the area of a triangle is A = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)bh, where b is the base and h is the height. To find the area of the triangle, you need to know its base and height. The base is the length of one side of the triangle, usually the side at the bottom. The height is the length of the line that connects the base to the opposite vertex, and makes a 90° angle with the base. Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) shows three triangles with the base and height of each marked.

Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) - The height h of a triangle is the length of a line segment that connects the the base to the opposite vertex and makes a 90° angle with the base.
Definition: Triangle Properties
For any triangle ΔABC, the sum of the measures of the angles is 180°.\[m \angle A + m \angle B + m \angle C = 180°$$The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of the sides.$$P = a + b + c$$The area of a triangle is one-half the base, b, times the height, h.$$A = \dfrac{1}{2} bh\]

Example \(\PageIndex{9}\):
Find the area of a triangle whose base is 11 inches and whose height is 8 inches.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{17}\):
Find the area of a triangle with base 13 inches and height 2 inches.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{18}\):
Find the area of a triangle with base 14 inches and height 7 inches.
Example \(\PageIndex{10}\):
The perimeter of a triangular garden is 24 feet. The lengths of two sides are 4 feet and 9 feet. How long is the third side?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{19}\):
The perimeter of a triangular garden is 48 feet. The lengths of two sides are 18 feet and 22 feet. How long is the third side?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{20}\):
The lengths of two sides of a triangular window are 7 feet and 5 feet. The perimeter is 18 feet. How long is the third side?
Example \(\PageIndex{11}\):
The area of a triangular church window is 90 square meters. The base of the window is 15 meters. What is the window’s height?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{21}\):
The area of a triangular painting is 126 square inches. The base is 18 inches. What is the height?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{22}\):
A triangular tent door has an area of 15 square feet. The height is 5 feet. What is the base?
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
Besides the right triangle, some other triangles have special names. A triangle with two sides of equal length is called an isosceles triangle . A triangle that has three sides of equal length is called an equilateral triangle . Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) shows both types of triangles.

Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) - In an isosceles triangle, two sides have the same length, and the third side is the base. In an equilateral triangle, all three sides have the same length.
Definition: Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
An isosceles triangle has two sides the same length.
An equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length.
Example \(\PageIndex{12}\):
The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 93 inches. Find the length of each side.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{23}\):
Find the length of each side of an equilateral triangle with perimeter 39 inches.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{24}\):
Find the length of each side of an equilateral triangle with perimeter 51 centimeters.
Example \(\PageIndex{13}\):
Arianna has 156 inches of beading to use as trim around a scarf. The scarf will be an isosceles triangle with a base of 60 inches. How long can she make the two equal sides?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{25}\):
A backyard deck is in the shape of an isosceles triangle with a base of 20 feet. The perimeter of the deck is 48 feet. How long is each of the equal sides of the deck?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{26}\):
A boat’s sail is an isosceles triangle with base of 8 meters. The perimeter is 22 meters. How long is each of the equal sides of the sail?
Use the Properties of Trapezoids
A trapezoid is four-sided figure, a quadrilateral , with two sides that are parallel and two sides that are not. The parallel sides are called the bases. We call the length of the smaller base b, and the length of the bigger base B. The height, h, of a trapezoid is the distance between the two bases as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\).

Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\) - A trapezoid has a larger base, B, and a smaller base, b. The height h is the distance between the bases.
The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
\[Area_{trapezoid} = \dfrac{1}{2} h(b + B)\]
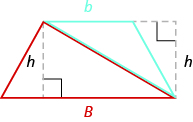
Splitting the trapezoid into two triangles may help us understand the formula. The area of the trapezoid is the sum of the areas of the two triangles. See Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\).

Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\) - Splitting a trapezoid into two triangles may help you understand the formula for its area.
The height of the trapezoid is also the height of each of the two triangles. See Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\).

Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)
The formula for the area of a trapezoid is
\[Area_{trapezoid} = \dfrac{1}{2} h (\textcolor{blue}{b} + \textcolor{red}{B})\]
If we distribute, we get,

Definition: Properties of Trapezoids
- A trapezoid has four sides. See Figure 9.25.
- Two of its sides are parallel and two sides are not.
- The area, A, of a trapezoid is A = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)h(b + B).

Example \(\PageIndex{14}\):
Find the area of a trapezoid whose height is 6 inches and whose bases are 14 and 11 inches.
If we draw a rectangle around the trapezoid that has the same big base B and a height h, its area should be greater than that of the trapezoid.
If we draw a rectangle inside the trapezoid that has the same little base b and a height h, its area should be smaller than that of the trapezoid.

The area of the larger rectangle is 84 square inches and the area of the smaller rectangle is 66 square inches. So it makes sense that the area of the trapezoid is between 84 and 66 square inches
Exercise \(\PageIndex{27}\):
The height of a trapezoid is 14 yards and the bases are 7 and 16 yards. What is the area?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{28}\):
The height of a trapezoid is 18 centimeters and the bases are 17 and 8 centimeters. What is the area?
Example \(\PageIndex{15}\):
Find the area of a trapezoid whose height is 5 feet and whose bases are 10.3 and 13.7 feet.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{29}\):
The height of a trapezoid is 7 centimeters and the bases are 4.6 and 7.4 centimeters. What is the area?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{30}\):
The height of a trapezoid is 9 meters and the bases are 6.2 and 7.8 meters. What is the area?
Example \(\PageIndex{16}\):
Vinny has a garden that is shaped like a trapezoid. The trapezoid has a height of 3.4 yards and the bases are 8.2 and 5.6 yards. How many square yards will be available to plant?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{31}\):
Lin wants to sod his lawn, which is shaped like a trapezoid. The bases are 10.8 yards and 6.7 yards, and the height is 4.6 yards. How many square yards of sod does he need?
40.25 sq. yd
Exercise \(\PageIndex{32}\):
Kira wants cover his patio with concrete pavers. If the patio is shaped like a trapezoid whose bases are 18 feet and 14 feet and whose height is 15 feet, how many square feet of pavers will he need?
ACCESS ADDITIONAL ONLINE RESOURCES
Perimeter of a Rectangle
Area of a Rectangle
Perimeter and Area Formulas
Area of a Triangle
Area of a Triangle with Fractions
Area of a Trapezoid
Practice Makes Perfect
Understand linear, square, and cubic measure.
In the following exercises, determine whether you would measure each item using linear, square, or cubic units.
- amount of water in a fish tank
- length of dental floss
- living area of an apartment
- floor space of a bathroom tile
- height of a doorway
- capacity of a truck trailer
In the following exercises, find the (a) perimeter and (b) area of each figure. Assume each side of the square is 1 cm.

Use the Properties of Rectangles
In the following exercises, find the (a) perimeter and (b) area of each rectangle.
- The length of a rectangle is 85 feet and the width is 45 feet.
- The length of a rectangle is 26 inches and the width is 58 inches.
- A rectangular room is 15 feet wide by 14 feet long.
- A driveway is in the shape of a rectangle 20 feet wide by 35 feet long.
In the following exercises, solve.
- Find the length of a rectangle with perimeter 124 inches and width 38 inches.
- Find the length of a rectangle with perimeter 20.2 yards and width of 7.8 yards.
- Find the width of a rectangle with perimeter 92 meters and length 19 meters.
- Find the width of a rectangle with perimeter 16.2 meters and length 3.2 meters.
- The area of a rectangle is 414 square meters. The length is 18 meters. What is the width?
- The area of a rectangle is 782 square centimeters. The width is 17 centimeters. What is the length?
- The length of a rectangle is 9 inches more than the width. The perimeter is 46 inches. Find the length and the width.
- The width of a rectangle is 8 inches more than the length. The perimeter is 52 inches. Find the length and the width.
- The perimeter of a rectangle is 58 meters. The width of the rectangle is 5 meters less than the length. Find the length and the width of the rectangle.
- The perimeter of a rectangle is 62 feet. The width is 7 feet less than the length. Find the length and the width.
- The width of the rectangle is 0.7 meters less than the length. The perimeter of a rectangle is 52.6 meters. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
- The length of the rectangle is 1.1 meters less than the width. The perimeter of a rectangle is 49.4 meters. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
- The perimeter of a rectangle of 150 feet. The length of the rectangle is twice the width. Find the length and width of the rectangle.
- The length of a rectangle is three times the width. The perimeter is 72 feet. Find the length and width of the rectangle.
- The length of a rectangle is 3 meters less than twice the width. The perimeter is 36 meters. Find the length and width.
- The length of a rectangle is 5 inches more than twice the width. The perimeter is 34 inches. Find the length and width.
- The width of a rectangular window is 24 inches. The area is 624 square inches. What is the length?
- The length of a rectangular poster is 28 inches. The area is 1316 square inches. What is the width?
- The area of a rectangular roof is 2310 square meters. The length is 42 meters. What is the width?
- The area of a rectangular tarp is 132 square feet. The width is 12 feet. What is the length?
- The perimeter of a rectangular courtyard is 160 feet. The length is 10 feet more than the width. Find the length and the width.
- The perimeter of a rectangular painting is 306 centimeters. The length is 17 centimeters more than the width. Find the length and the width.
- The width of a rectangular window is 40 inches less than the height. The perimeter of the doorway is 224 inches. Find the length and the width.
- The width of a rectangular playground is 7 meters less than the length. The perimeter of the playground is 46 meters. Find the length and the width.
In the following exercises, solve using the properties of triangles.
- Find the area of a triangle with base 12 inches and height 5 inches.
- Find the area of a triangle with base 45 centimeters and height 30 centimeters.
- Find the area of a triangle with base 8.3 meters and height 6.1 meters.
- Find the area of a triangle with base 24.2 feet and height 20.5 feet.
- A triangular flag has base of 1 foot and height of 1.5 feet. What is its area?
- A triangular window has base of 8 feet and height of 6 feet. What is its area?
- If a triangle has sides of 6 feet and 9 feet and the perimeter is 23 feet, how long is the third side?
- If a triangle has sides of 14 centimeters and 18 centimeters and the perimeter is 49 centimeters, how long is the third side?
- What is the base of a triangle with an area of 207 square inches and height of 18 inches?
- What is the height of a triangle with an area of 893 square inches and base of 38 inches?
- The perimeter of a triangular reflecting pool is 36 yards. The lengths of two sides are 10 yards and 15 yards. How long is the third side?
- A triangular courtyard has perimeter of 120 meters. The lengths of two sides are 30 meters and 50 meters. How long is the third side?
- An isosceles triangle has a base of 20 centimeters. If the perimeter is 76 centimeters, find the length of each of the other sides.
- An isosceles triangle has a base of 25 inches. If the perimeter is 95 inches, find the length of each of the other sides.
- Find the length of each side of an equilateral triangle with a perimeter of 51 yards.
- Find the length of each side of an equilateral triangle with a perimeter of 54 meters.
- The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 18 meters. Find the length of each side.
- The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 42 miles. Find the length of each side.
- The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 42 feet. The length of the shortest side is 12 feet. Find the length of the other two sides.
- The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 83 inches. The length of the shortest side is 24 inches. Find the length of the other two sides.
- A dish is in the shape of an equilateral triangle. Each side is 8 inches long. Find the perimeter.
- A floor tile is in the shape of an equilateral triangle. Each side is 1.5 feet long. Find the perimeter.
- A road sign in the shape of an isosceles triangle has a base of 36 inches. If the perimeter is 91 inches, find the length of each of the other sides.
- A scarf in the shape of an isosceles triangle has a base of 0.75 meters. If the perimeter is 2 meters, find the length of each of the other sides.
- The perimeter of a triangle is 39 feet. One side of the triangle is 1 foot longer than the second side. The third side is 2 feet longer than the second side. Find the length of each side.
- The perimeter of a triangle is 35 feet. One side of the triangle is 5 feet longer than the second side. The third side is 3 feet longer than the second side. Find the length of each side.
- One side of a triangle is twice the smallest side. The third side is 5 feet more than the shortest side. The perimeter is 17 feet. Find the lengths of all three sides.
- One side of a triangle is three times the smallest side. The third side is 3 feet more than the shortest side. The perimeter is 13 feet. Find the lengths of all three sides.
In the following exercises, solve using the properties of trapezoids.
- The height of a trapezoid is 12 feet and the bases are 9 and 15 feet. What is the area?
- The height of a trapezoid is 24 yards and the bases are 18 and 30 yards. What is the area?
- Find the area of a trapezoid with a height of 51 meters and bases of 43 and 67 meters.
- Find the area of a trapezoid with a height of 62 inches and bases of 58 and 75 inches.
- The height of a trapezoid is 15 centimeters and the bases are 12.5 and 18.3 centimeters. What is the area?
- The height of a trapezoid is 48 feet and the bases are 38.6 and 60.2 feet. What is the area?
- Find the area of a trapezoid with a height of 4.2 meters and bases of 8.1 and 5.5 meters.
- Find the area of a trapezoid with a height of 32.5 centimeters and bases of 54.6 and 41.4 centimeters.
- Laurel is making a banner shaped like a trapezoid. The height of the banner is 3 feet and the bases are 4 and 5 feet. What is the area of the banner?
- Niko wants to tile the floor of his bathroom. The floor is shaped like a trapezoid with width 5 feet and lengths 5 feet and 8 feet. What is the area of the floor?
- Theresa needs a new top for her kitchen counter. The counter is shaped like a trapezoid with width 18.5 inches and lengths 62 and 50 inches. What is the area of the counter?
- Elena is knitting a scarf. The scarf will be shaped like a trapezoid with width 8 inches and lengths 48.2 inches and 56.2 inches. What is the area of the scarf?
Everyday Math
- Fence Jose just removed the children’s playset from his back yard to make room for a rectangular garden. He wants to put a fence around the garden to keep out the dog. He has a 50 foot roll of fence in his garage that he plans to use. To fit in the backyard, the width of the garden must be 10 feet. How long can he make the other side if he wants to use the entire roll of fence?
- Gardening Lupita wants to fence in her tomato garden. The garden is rectangular and the length is twice the width. It will take 48 feet of fencing to enclose the garden. Find the length and width of her garden.
- Fence Christa wants to put a fence around her triangular flowerbed. The sides of the flowerbed are 6 feet, 8 feet, and 10 feet. The fence costs $10 per foot. How much will it cost for Christa to fence in her flowerbed?
- Painting Caleb wants to paint one wall of his attic. The wall is shaped like a trapezoid with height 8 feet and bases 20 feet and 12 feet. The cost of the painting one square foot of wall is about $0.05. About how much will it cost for Caleb to paint the attic wall?

Writing Exercises
- If you need to put tile on your kitchen floor, do you need to know the perimeter or the area of the kitchen? Explain your reasoning.
- If you need to put a fence around your backyard, do you need to know the perimeter or the area of the backyard? Explain your reasoning.
- Look at the two figures. (a) Which figure looks like it has the larger area? Which looks like it has the larger perimeter? (b) Now calculate the area and perimeter of each figure. Which has the larger area? Which has the larger perimeter?

- The length of a rectangle is 5 feet more than the width. The area is 50 square feet. Find the length and the width. (a) Write the equation you would use to solve the problem. (b) Why can’t you solve this equation with the methods you learned in the previous chapter?
(a) After completing the exercises, use this checklist to evaluate your mastery of the objectives of this section.

(b) On a scale of 1–10, how would you rate your mastery of this section in light of your responses on the checklist? How can you improve this?
Contributors and Attributions
Lynn Marecek (Santa Ana College) and MaryAnne Anthony-Smith (Formerly of Santa Ana College). This content is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License v4.0 "Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] ."

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
CHAPTER 3 Measurement, Perimeter, Area, and Volume
3.2 Use Properties of Rectangles, Triangles, and Trapezoids
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Understand linear, square, and cubic measure
- Use properties of rectangles
- Use properties of triangles
- Use properties of trapezoids
Understand Linear, Square, and Cubic Measure
When you measure your height or the length of a garden hose, you use a ruler or tape measure (Figure.1) . A tape measure might remind you of a line—you use it for linear measure, which measures length. Inch, foot, yard, mile, centimetre and metre are units of linear measure.
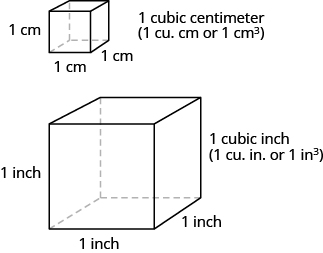
When you want to know how much tile is needed to cover a floor, or the size of a wall to be painted, you need to know the area, a measure of the region needed to cover a surface. Area is measured is square units. We often use square inches, square feet, square centimetres, or square miles to measure area. A square centimetre is a square that is one centimetre (cm) on each side. A square inch is a square that is one inch on each side (Figure.2) .
When you measure how much it takes to fill a container, such as the amount of gasoline that can fit in a tank, or the amount of medicine in a syringe, you are measuring volume. Volume is measured in cubic units such as cubic inches or cubic centimetres. When measuring the volume of a rectangular solid, you measure how many cubes fill the container. We often use cubic centimetres, cubic inches, and cubic feet. A cubic centimetre is a cube that measures one centimetre on each side, while a cubic inch is a cube that measures one inch on each side (Figure.4) .
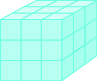
A cube that measures 3 inches on each side is made up of 27 one-inch cubes, or 27 cubic inches.
For each item, state whether you would use linear, square, or cubic measure:
a) amount of carpeting needed in a room
b) extension cord length
c) amount of sand in a sandbox
d) length of a curtain rod
e) amount of flour in a canister
f) size of the roof of a doghouse.
Determine whether you would use linear, square, or cubic measure for each item.
a) amount of paint in a can b) height of a tree c) floor of your bedroom d) diametre of bike wheel e) size of a piece of sod f) amount of water in a swimming pool
a) volume of a packing box b) size of patio c) amount of medicine in a syringe d) length of a piece of yarn e) size of housing lot f) height of a flagpole
Many geometry applications will involve finding the perimeter or the area of a figure. There are also many applications of perimeter and area in everyday life, so it is important to make sure you understand what they each mean.
Picture a room that needs new floor tiles. The tiles come in squares that are a foot on each side—one square foot. How many of those squares are needed to cover the floor? This is the area of the floor.
Next, think about putting new baseboard around the room, once the tiles have been laid. To figure out how many strips are needed, you must know the distance around the room. You would use a tape measure to measure the number of feet around the room. This distance is the perimeter.
Perimeter and Area
The perimeter is a measure of the distance around a figure.
The area is a measure of the surface covered by a figure.
a) What is the perimeter of the figure?
b) What is the area?
Find the a) perimeter and b) area of the figure:

- 3 sq. inches
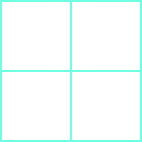
- 8 centimetres
- 4 sq. centimetres
Use the Properties of Rectangles
A rectangle has four sides, and four right angles. The sides are labeled L for length and W for width.
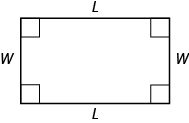
Properties of Rectangles
- The lengths of opposite sides are equal.
For easy reference as we work the examples in this section, we will state the Problem Solving Strategy for Geometry Applications here.
HOW TO: Use a Problem Solving Strategy for Geometry Applications
- Read the problem and make sure you understand all the words and ideas. Draw the figure and label it with the given information.
- Identify what you are looking for.
- Name what you are looking for. Choose a variable to represent that quantity.
- Translate into an equation by writing the appropriate formula or model for the situation. Substitute in the given information.
- Solve the equation using good algebra techniques.
- Check the answer in the problem and make sure it makes sense.
- Answer the question with a complete sentence.
- 6000 sq. yd
- 2976 sq. ft
In the next example, the width is defined in terms of the length. We’ll wait to draw the figure until we write an expression for the width so that we can label one side with that expression.
11 ft , 19 ft
8 ft, 24 ft
30 ft, 70 ft
60 yd, 90 yd
Use the Properties of Triangles
A rectangle can be divided into two triangles of equal area. The area of each triangle is one-half the area of the rectangle.
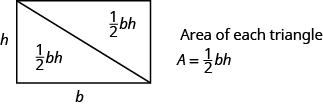
Triangle Properties
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of the sides.
TRY IT 10.1
TRY IT 10.2
TRY IT 11.1
TRY IT 11.2
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
Besides the right triangle, some other triangles have special names. A triangle with two sides of equal length is called an isosceles triangle. A triangle that has three sides of equal length is called an equilateral triangle. (Figure.12) shows both types of triangles.
In an isosceles triangle, two sides have the same length, and the third side is the base. In an equilateral triangle, all three sides have the same length.
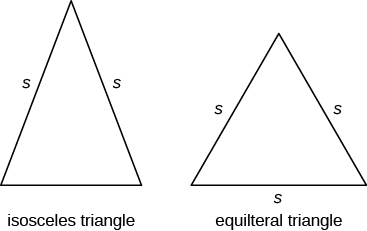
An isosceles triangle has two sides the same length.
An equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length.
TRY IT 12.1
TRY IT 12.2
TRY IT 13.1
TRY IT 13.2
Use the Properties of Trapezoids
Formula for the A rea of a Trapezoid
Splitting the trapezoid into two triangles may help us understand the formula. The area of the trapezoid is the sum of the areas of the two triangles. See (Figure.14) .
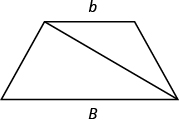
The height of the trapezoid is also the height of each of the two triangles. See (Figure.15) .
The formula for the area of a trapezoid is
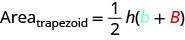
If we distribute, we get,
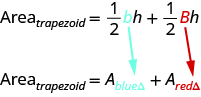
Properties of Trapezoids
- A trapezoid has four sides. See (Figure.13) .
- Two of its sides are parallel and two sides are not.
TRY IT 14.1
TRY IT 14.2
TRY IT 15.1
TRY IT 15.2
TRY IT 16.1
40.25 sq. yd
TRY IT 16.2
240 sq. ft.
Access Additional Online Resources
- Perimeter of a Rectangle
- Area of a Rectangle
- Perimeter and Area Formulas
- Area of a Triangle
- Area of a Triangle with Fractions
- Area of a Trapezoid
Key Concepts
- Rectangles have four sides and four right (90°) angles.
Practice Makes Perfect
In the following exercises, determine whether you would measure each item using linear, square, or cubic units.
In the following exercises, find the a) perimeter and b) area of each rectangle.
In the following exercises, solve.
In the following exercises, solve using the properties of triangles.
In the following exercises, solve using the properties of trapezoids.
Everyday Math
Writing exercises, attributions.
This chapter has been adapted from “Use Properties of Rectangles, Triangles, and Trapezoids” in Prealgebra (OpenStax) by Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith, and Andrea Honeycutt Mathis, which is under a CC BY 4.0 Licence . Adapted by Izabela Mazur. See the Copyright page for more information.
Introductory Algebra Copyright © 2021 by Izabela Mazur is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 11: Geometry
Summary: using properties of rectangles, triangles, and trapezoids, key concepts.
- Rectangles have four sides and four right ([latex]90^\circ[/latex]) angles.
- The lengths of opposite sides are equal.
- [latex]P=2L+2W[/latex]
- [latex]A=L\cdot W[/latex]
- [latex]m\angle A+m\angle B+m\angle C=180^\circ [/latex]
- [latex]P=a+b+c[/latex]
- [latex]A=\Large\frac{1}{2}\normalsize bh[/latex]
- Prealgebra. Provided by : OpenStax. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]


Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Area of triangles, parallelograms & trapezoids

Download & Print Only $7.90
Area of triangles, trapezoids & parallelograms
Area worksheets: triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids.
Below are our grade 5 geometry worksheets on finding the area of triangles, parallelograms and trapezoids . The height of each shape is shown. These worksheets are printable pdf files.

These worksheets are available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
More geometry worksheets
Browse all of our geometry worksheets , from the basic shapes through areas and perimeters, angles, grids and 3D shapes.
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.
Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
- Forgot Password?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
h = √3. An isosceles trapezoid has base angles equal to 45 and bases of lengths 6 and 12. Find the area of the trapezoid. 27 sq. units. Find the area of a trapezoid if the altitude is 6 inches and the median is 8 inches. (Hint: Recall that the median of a trapezoid is equal to half the sum of the bases.) 48 sq. units.
Figure 5.15.8 5.15. 8. First, substitute what you know into the formula for the area of a parallelogram. A A = b × h = 4 × 5 A = b × h A = 4 × 5. Next, solve for A A. A A = 4 × 5 = 20 A = 4 × 5 A = 20. The answer is 20. The area of the parallelogram is 20 m2 20 m 2, or 20 square meters. Let's look at one more example.
The diagonal of a parallelogram creates alternate interior angles. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral. A quadrilateral is always a parallelogram. If a diagonal is drawn in a parallelogram, then two congruent triangles are formed. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like parallelogram, Select all that apply.
Figure 9.22 A rectangle can be divided into two triangles of equal area. The area of each triangle is one-half the area of the rectangle. The formula for the area of a triangle is A = 1 2bh, where b is the base and h is the height. To find the area of the triangle, you need to know its base and height.
Question 21. HL. Question 22. SAS. Question 23. CPCTE. Question 24. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 9, 50, 10 and more.
Definition: Properties of Rectangles. Rectangles have four sides and four right (90°) angles. The lengths of opposite sides are equal. The perimeter, P, of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width. See Figure 9.19.
Essential Skills. Name the properties of each type of quadrilateral. Determine if a quadrilateral with certain properties is a parallelogram or not. Identify the type of parallelogram based on given properties. Find the lengths of sides and measures of angles of each type of quadrilateral. Solve algebraic equations using properties of ...
The height of a trapezoid is 48 feet and the bases are 38.6 and 60.2 feet. What is the area? Find the area of a trapezoid with a height of 4.2 meters and bases of 8.1 and 5.5 meters. Find the area of a trapezoid with a height of 32.5 centimeters and bases of 54.6 and 41.4 centimeters. Laurel is making a banner shaped like a trapezoid.
Close this tab and proceed to the assignment Key Concepts. Properties of Rectangles. Rectangles have four sides and four right ([latex]90^\circ[/latex]) angles. The lengths of opposite sides are equal. The perimeter, [latex]P[/latex] , of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width. [latex]P=2L+2W[/latex]
The area of the trapezoid is less than the area of a rectangle with a base of 8.2 yd and height 3.4 yd, but more than the area of a rectangle with base 5.6 yd and height 3.4 yd. Step 7. Answer the question.
Section 5.2 Parallelogram Properties. G.3.2: Describe, classify, and explain relationships among the quadrilaterals square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, and kite; G.3.4: Determine the sum of both the interior and exterior angle measures of a polygon.
8.4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles and Squares 8.5 Trapezoids Practice Problems Classify the parallelogram. Explain your reasoning. 1.) 2.) 3.)
a. A trapezoid can have four equal sides. b. A trapezoid can have three right angles. c. The base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent. d. The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid bisect each other. 10. The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are represented by 4x - 47 and 2x + 31. What is the value of x? a. 37 c. 107 b. 39 d. 109 11.
Below are six versions of our grade 6 math worksheet on area of triangles, parallelograms & trapezoids. The height of shapes is shown where required so that areas can be calculated without the use of trigonometry. These worksheets are pdf files. Worksheet #1 Worksheet #2 Worksheet #3 Worksheet #4 Worksheet #5 Worksheet #6.
Section 7.5 Properties of Trapezoids and Kites 401 7.5 Properties of Trapezoids and Kites EEssential Questionssential Question What are some properties of trapezoids and kites? Recall the types of quadrilaterals shown below. Trapezoid Isosceles Trapezoid Kite Making a Conjecture about Trapezoids Work with a partner. Use dynamic geometry ...
Section 5.6 Kites and Trapezoids. G.3.2: Describe, classify, and explain relationships among the quadrilaterals square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, and kite; G.3.4: Determine the sum of both the interior and exterior angle measures of a polygon.
So, the long diagonal is equal to 8 ÷ 2, or 4 inches. Step 3 Find the area of one rhombus. From Postulate 11.1, the area of each rhombus is the same. So, the area of each rhombus is 48 ÷ 12 or 4 square inches. Each rhombus in the pattern has an area of 4 square inches and diagonals. 3 inches and 2 inches long. 5A.
Key Concepts. Properties of Rectangles. Rectangles have four sides and four right ( 90∘ 90 ∘) angles. The lengths of opposite sides are equal. The perimeter, P P , of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width. P = 2L+2W P = 2 L + 2 W. The area, A A , of a rectangle is the length times the width. A= L⋅W A = L ⋅ W.
Area worksheets: triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids. Below are our grade 5 geometry worksheets on finding the area of triangles, parallelograms and trapezoids. The height of each shape is shown. These worksheets are printable pdf files. Worksheet #1 Worksheet #2 Worksheet #3 Worksheet #4 Worksheet #5 Worksheet #6. 5 More.
Section 5.4. Properties of Rectangles, Rhombuses and Squares. G.3.2: Describe, classify, and explain relationships among the quadrilaterals square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, and kite; G.3.4: Determine the sum of both the interior and exterior angle measures of a polygon.
Section 9.2: Area of Trapezoids, Kites, and Rhombi. G.5.1 Determine the perimeter, circumference, and area of common geometric figures such as parallelograms, trapezoids, circles, and triangles; Geometry- Area of Trapezoids, Kites and Rhombus. Watch on. Need a tutor?
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like How can you decompose the composite figure to determine its area?, The area of one of the small right triangles outlined in blue is A cm2, while the area of the square outlined in red is B cm2. Which expressions show the area of the shaded region in terms of A and B? Check all that apply., For a class project, a teacher cuts out ...
Section 5.5 Conditions for Rectangles, Rhombuses and Squares. G.3.2: Describe, classify, and explain relationships among the quadrilaterals square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, and kite; G.3.4: Determine the sum of both the interior and exterior angle measures of a polygon.