- My Account |
- StudentHome |
- TutorHome |
- IntranetHome |
- Contact the OU Contact the OU Contact the OU |
- Accessibility Accessibility

Postgraduate
- International
- News & media
- Business & apprenticeships
- Contact Contact Contact
- A to Z of courses
- Course types
- Masters degrees
- Postgraduate diplomas
- Postgraduate certificates
- Microcredentials
- Postgraduate modules
- Postgraduate distance learning
- Postgraduate qualifications
- Postgraduate entry requirements
- How will I study?
- Tutors and assessment
- Support, networking and community
- Disability support
- Fees and funding
- Postgraduate loan
- Credit or debit card
- Employer sponsorship
- Mixed payments
- Credit transfer
- OU bursaries
- Grant funding
- Study costs funding
- Carers' Bursary
- Care Experienced Bursary
- Disability financial assistance
- STEMM bursary
- Over 60s bursary
- Creative Writing Scholarship
- Hayes Postgraduate Scholarship
- Disabled Veterans' Scholarships
- How to apply
- Research degrees
- Research areas
- Degrees we offer
- Fees and studentships
- Application process
- Being an OU research student
- Student views
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
What is a phd.
A PhD is a Doctorate of Philosophy, a prestigious qualification which is the highest level of degree that a student can achieve, demonstrating talent, academic excellence and a thirst for knowledge. In a modern knowledge-based economy, highly educated and skilled people such as doctoral graduates, are in great demand. They form the most highly educated and skilled group in the UK and internationally. Many will go on to use their skills within academia or in research-intensive occupations in industry. However, there will be others who will draw on their research background and the skills gained through a doctoral degree in a wide variety of other occupations. Examples of the type of employment opportunities taken up by PhD holders can be found at Vitae: researcher careers .
What will I get from a PhD?
You will get a huge sense of personal achievement. Our doctoral training programme will help you develop transferable skills that will be invaluable in your subsequent career. The research techniques and methodologies you master will enable you to make a direct contribution to the advancement of knowledge in your particular subject area.
Successful candidates are awarded the degree of Doctor of Philosophy and are permitted to use the title ‘Dr’.
How does it work?
The maximum registration for a PhD programme is four years with full-time study, or eight years with part-time study.
All PhD students are initially registered for a Master of Philosophy (MPhil), and the PhD registration is confirmed after the successful completion of an upgrade assessment (at the end of year 1 for full-time students and year 2 for part-time study). You will be registered for a PhD when you pass this upgrade. Your academic progress will be monitored throughout your degree studies, via formal progress reports and regular meetings with your supervisors.
You complete a body of primary, novel research and submit a doctoral thesis of up to 100,000 words, which you then defend via an oral examination (the viva) to the satisfaction of the examiners. Your thesis must meet the expectations specified in the Quality Code .
Entry requirements
Entry requirements vary according to the research topic and/or specific studentships. The normal minimum entrance requirement is an upper second class honours degree or masters degree, relevant to the proposed area of study, from a recognised higher education institution in the UK or other recognised degree-awarding body. The comparability of qualifications from outside the UK with The Open University requirements will be determined through reference to UK ENIC .
The research topic pages (within research areas ) give details of specific entry requirements, and provide contact details to discuss your suitability for the PhD.
English language proficiency
To study with us, you will need to have a good command of English. If your first language is not English, you will need to demonstrate your competence in the English Language in all four elements (reading, writing, listening and speaking). The University requires a minimum IELTS score of 6.5 with no less than 6.0 in any of the four categories (or approved equivalent). If you are an overseas student, you must have your level of proficiency certified through a provider approved by UK Visas and Immigration and provide your certificate and grade with your application.
Application closing dates
Entry may be permitted for direct registration with The Open University at the following points of year: October and February. This ensures that students benefit from development and training in peer groups. For further information on how to apply, see our Application process section. Application deadlines may differ between research topics and studentships; full details of topic application period is detailed in the topic page (within research areas ).
PhD student, Hannah Sargeant. Her research is focussed on water production from Moon rocks as part of the ProSPA instrument that will be flown to the Moon in 2025.
My PhD journey so far has been a wonderful learning experience that made me reflect upon my beliefs and stretch my thinking.
The sweetest thing about the PhD is that you’ve worked hard for it. It is an opportunity to make an original contribution to an academic area I have always found fascinating.
Your questions
For advice about applying for a research degree, or sponsoring a research student, email the Graduate School or call +44 (0)1908 653806.
The Open University
- Study with us
- Supported distance learning
- Funding your studies
- International students
- Global reputation
- Apprenticeships
- Develop your workforce
- Contact the OU
Undergraduate
- Arts and Humanities
- Art History
- Business and Management
- Combined Studies
- Computing and IT
- Counselling
- Creative Writing
- Criminology
- Early Years
- Electronic Engineering
- Engineering
- Environment
- Film and Media
- Health and Social Care
- Health and Wellbeing
- Health Sciences
- International Studies
- Mathematics
- Mental Health
- Nursing and Healthcare
- Religious Studies
- Social Sciences
- Social Work
- Software Engineering
- Sport and Fitness
- Postgraduate study
- Masters in Art History (MA)
- Masters in Computing (MSc)
- Masters in Creative Writing (MA)
- Masters degree in Education
- Masters in Engineering (MSc)
- Masters in English Literature (MA)
- Masters in History (MA)
- Master of Laws (LLM)
- Masters in Mathematics (MSc)
- Masters in Psychology (MSc)
- A to Z of Masters degrees
- Accessibility statement
- Conditions of use
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Manage cookie preferences
- Modern slavery act (pdf 149kb)
Follow us on Social media
- Student Policies and Regulations
- Student Charter
- System Status
- Contact the OU Contact the OU
- Modern Slavery Act (pdf 149kb)
© . . .
Imperial College London Imperial College London
Latest news.

Why heart rhythm problems tend to happen early in the morning

Plastic-free vegan leather that dyes itself grown from bacteria

New synthesis platform allows for rapid cancer drug synthesis and testing
- Postgraduate doctoral
- Application process
- Choose a course
Looking for funding?
Use our scholarships search tool to look for available scholarships. Also explore our latest funded PhD vacancies .
A PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) is the most common type of doctoral degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve.
It normally takes between three and four years of full-time work to complete. It is also possible to undertake a PhD part time, over five to six years.
The main activity of a PhD is to carry out an original research project under the direction of one or more supervisors, to be written up as a thesis.
Different routes to achieving a PhD
There are a number of ways to achieving a PhD at Imperial:
- by undertaking a course of study based on your own research proposal
- by joining a research project that comes with funding attached (known as a studentship)
- by combining it with Master's study in an integrated route that typically lasts four years
Pursuing your own research idea
To search for PhD opportunities based on your own research proposal you first need to identify a research group within Imperial whose area of expertise best matches your idea.
Use the links below to search the different PhD opportunities within our academic departments, centres and institutes. This includes information about current studentships and often guidance on finding a supervisor.
Our interdisciplinary approach means our expertise often spans departmental boundaries – and so do our courses – so you may find opportunities in an unexpected area of the university.
Faculty of Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Bioengineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- School of Design Engineering
- Earth Science and Engineering
- Electrical and Electronic Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
Faculty of Medicine
- Department of Brain Sciences
- Department of Immunology and Inflammation
- Department of Infectious Disease
- Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction
- Department of Surgery and Cancer
- National Heart and Lung Institute
- School of Public Health
Faculty of Natural Sciences
- Life Sciences
- Mathematics
- Centre for Environmental Policy
Imperial College Business School
- Doctoral programme
Centre for Languages, Culture and Communication
- PhD in Arabic, German, Italian, Russian and Spanish Studies
- PhD in science communication studies
Global Challenge institutes
We have six Global Challenge institutes, which were created to address some of society's biggest challenges.
If you have an idea for a PhD that falls within the remit of one of our Global Challenge institutes please contact them directly to discuss before making a formal application.
- Data Science Institute
- Grantham Institute – Climate Change and the Environment
- Institute for Molecular Science and Engineering
- Institute for Security Science and Technology
- Institute of Global Health Innovation
Energy Futures Lab does not offer PhD programmes, but does deliver the MSc in Sustainable Energy Futures .
Joint Academy of Doctoral Studies | Imperial College London-Technical University of Munich
We have recently formed a strategic partnership in education, research and innovation with the Technical University of Munich, one of Germany’s most international and entrepreneurial universities, producing highly ranked research, like Imperial, in science, engineering and medicine.
As part of the partnership, Imperial and TUM have launched a 'Joint Academy of Doctoral Studies' with the aim of co-developing cross-disciplinary clusters of PhD students who will have access to world-leading academic supervisors and state-of-the art facilities at both institutions.
The first round of the programme will focus on the theme of 'Artificial Intelligence, Healthcare and Robotics'.
Find out more about the Joint Academy of Doctoral Studies and apply

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Course Directory
- Qualification types
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
Postgraduate Study
- Why Cambridge overview
- Chat with our students
- Cambridge explained overview
- The supervision system
- Student life overview
- In and around Cambridge
- Leisure activities
- Student unions
- Music awards
- Student support overview
- Mental health and wellbeing
- Disabled students
- Accommodation
- Language tuition
- Skills training
- Support for refugees
- Courses overview
- Department directory
- Funded studentships
- Part-time study
- Research degrees
- Visiting students
- Finance overview
- Fees overview
- What is my fee status?
- Part-time fees
- Application fee
- Living costs
- Funding overview
- Funding search
- How to apply for funding
- University funding overview
- Research Councils (UKRI)
- External funding and loans overview
- Funding searches
- External scholarships
- Charities and the voluntary sector
- Funding for disabled students
- Widening participation in funding
- Colleges overview
- What is a College?
- Choosing a College
- Terms of Residence
- Applying overview
- Before you apply
- Entry requirements
- Application deadlines
- How do I apply? overview
- Application fee overview
- Application fee waiver
- Life Science courses
- Terms and conditions
- Continuing students
- Disabled applicants
- Supporting documents overview
- Academic documents
- Finance documents
- Evidence of competence in English
- Terms and Conditions
- Applicant portal and self-service
- After you apply overview
- Confirmation of admission
- Student registry
- Previous criminal convictions
- Deferring an application
- Updating your personal details
- Appeals and Complaints
- Widening participation
- Postgraduate admissions fraud
- International overview
- Immigration overview
- ATAS overview
- Applying for an ATAS certificate
- Current Cambridge students
- International qualifications
- Competence in English overview
- What tests are accepted?
- International events
- International student views overview
- Akhila’s story
- Alex’s story
- Huijie’s story
- Kelsey’s story
- Nilesh’s story
- Get in touch!
- Events overview
- Upcoming events
- Postgraduate Open Days overview
- Discover Cambridge: Master’s and PhD Study webinars
- Virtual tour
- Research Internships
- How we use participant data
- Postgraduate Newsletter
The degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the University's principal research degree for graduate students and is available in all faculties and departments.
A Cambridge PhD is intellectually demanding and you will need to have a high level of attainment and motivation to pursue this programme of advanced study and research.
In most faculties, a candidate is expected to have completed one year of postgraduate study, normally on a research preparation master's course, prior to starting a PhD.
Completion normally requires three or four years of full-time study, or at least five years of part-time study, including a probationary period.
Terms of research are normally consecutive and, for full-time students, require residency in Cambridge. Not all departments offer part-time research degrees.
Various routes to the PhD are possible and, if you are made an offer of admission, it will be made clear whether you are required to study for a master's degree or certificate in the first instance, or will be admitted directly to the probationary year for the PhD. You are registered for the PhD only after a satisfactory progress assessment at the end of the probationary year (five terms for part-time degrees). The assessment is designed also to focus your mind on the stages necessary for the completion of your research within the normal time limit and to address any structural problems that have arisen during the first year. Students must pass the first year assessment in order to continue their PhD study.
During your PhD, your effort will be focused on writing a dissertation. The word count of the dissertation is dependent on the department and the Student Registry or Educational Student Policy will be able to tell you the maximum word limit. This must represent a significant contribution to learning, for example through the discovery of new knowledge, the connection of previously unrelated facts, the development of a new theory, or the revision of older views, and must take account of previously published work on the subject. Some Cambridge dissertations go on to form the basis of significant publications.
Although you will spend long hours working independently, your department and College will both support you throughout your PhD. You are also able to attend regular seminars in your subject area and could be involved in teaching, perhaps giving seminars or supervising, or in the social life of your department and College.
PhD course search
Go to the Course Directory and filter courses using the relevant checkboxes.
Term Information
Explanation of terms, postgraduate admissions office.
- Admissions Statistics
- Start an Application
- Applicant Self-Service
At a glance
- Bringing a family
- Current Postgraduates
- Cambridge Students' Union (SU)
University Policy and Guidelines
Privacy Policy
Information compliance
Equality and Diversity
Terms of Study
About this site
About our website
Privacy policy
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
We value your privacy
We use cookies to allow this site to work for you, improve your user experience, and to serve you advertising tailored to your interests. Let us know if you agree to all cookies. You can manage your preferences at any time
Your Privacy
We use cookies, which are small text files placed on your computer, to allow the site to work for you, improve your user experience, to provide us with information about how our site is used, and to deliver personalised ads which help fund our work and deliver our service to you for free.
The information does not usually directly identify you, but it can give you a more personalised web experience.
You can accept all, or else manage cookies individually. However, blocking some types of cookies may affect your experience of the site and the services we are able to offer.
You can change your cookies preference at any time by visiting our Cookies Notice page. Please remember to clear your browsing data and cookies when you change your cookies preferences. This will remove all cookies previously placed on your browser.
For more detailed information about the cookies we use, or how to clear your browser cookies data see our Cookies Notice
Manage consent preferences
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems.
They are essential for you to browse the website and use its features.
You can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but some parts of the site will not then work. We can’t identify you from these cookies.
These help us personalise our sites for you by remembering your preferences and settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers, whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, then these services may not function properly.
These cookies allow us to count visits and see where our traffic comes from, so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are popular and see how visitors move around the site. The cookies cannot directly identify any individual users.
If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site and will not be able to improve its performance for you.
These cookies may be set through our site by social media services or our advertising partners. Social media cookies enable you to share our content with your friends and networks. They can track your browser across other sites and build up a profile of your interests. If you do not allow these cookies you may not be able to see or use the content sharing tools.
Advertising cookies may be used to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other sites. They do not store directly personal information, but work by uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies, you will still see ads, but they won’t be tailored to your interests.
The shortcut to your shortlist
Make your university search faster and less stressful. Get a personalised shortlist by selecting what matters to you.
- CHOOSE ONE OR MORE
Popular universities
- University of Kent
- University of East Anglia UEA
- University of Chester
- Coventry University
- University of Aberdeen
- University of Portmouth
- Nottingham Trent University
- University of Sunderland
- London Metropolitan University
- London South Bank University
- University of East London
- BROWSE ALL UNIVERSITIES
Course search
Popular undergraduate courses.
- Computer Science
- LLB Bachelor of Laws
- Biomedical Sciences
- Physiotherapy
- Sports Science
Open days search
Upcoming open days.
- BIMM University
- University of Wales Trinity Saint David
- Arts University Bournemouth
- University of Roehampton
Article search
Popular articles.
- What is UCAS Extra?
- Replying to offers
- What's a university open day
- Student finance and funding
- Types of degree in the UK
- BROWSE ALL ARTICLES
Popular topics
- Choosing what to study
- Choosing where to study
- Applying to university
- League tables
- Student life - after you start
What is a PhD?
Are you considering a phd degree we take a look at what a phd is, how long it takes and how you can go about getting one..
What’s a PhD?
What does phd stand for, how long is a phd, how much does a phd cost, how to get a phd, can you do a phd without a master’s, is a phd worth it.
A PhD is the highest postgraduate-level qualification offered by universities in the UK. It’s for those who are looking to build on what they studied during their master’s degree, or for those currently working who wish to research a particular area within their field.
PhDs are research-based degrees. The student comes up with an original research question, often in collaboration with a university professor, and explores that topic in depth. At the end of the degree a final thesis is produced that could range from 40,000 to 120,000 words.
The number of students enrolling in PhD degrees is increasing year-on-year. From 2015/16 to 2019/20 enrolments increased by 2.9%, according to 2019/20 HESA data on student enrolments . This highlights the growing interest in and demand for the postgraduate qualification.
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. You’ll often find this abbreviated to just ‘Doctorate’ as a PhD falls under the umbrella of doctorate degrees.
They vary in length, based on what you decide to research and whether you choose to study part-time or full-time. Full-time PhD students often take three or four years, with part-time students taking up to seven. Some universities even offer deadline extensions of up to four years.
You can expect to pay anywhere from £3,000 to £6,000 per year. This applies to all UK and EU students, with other international students paying more. Most PhD students fund their degree through scholarships, bursaries, and grants. Many UK research organisations also offer studentships through UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) , which can be another form of funding.
- Bursaries and scholarships
- Postgraduate funding
Having a strong interest in a particular subject is the first step to a PhD. You’ll either be applying for an already funded project being offered by a university, or you’ll be pitching your own research proposal. Admissions teams want to see your dedication and enthusiasm, so make sure you’re passionate about the subject first.
Universities tend to list available research projects and who’ll be supervising them on their website. Don’t hesitate to contact any professors you know that are doing research in an area you’re interested in. They may have a PhD position available they haven’t yet advertised.
When applying, you’ll need a:
- Cover letter
- Research proposal (if pitching an original research idea)
- Reference (may be asked to provide three people, who know you in an academic setting or can comment on your research capability)
Use your application as a chance to really convey your passion for the subject. It’s important to expand on your interest, explain why you have that interest and cite examples of you pursuing this interest through past experiences. You’ll be studying for at least three to four years and the admissions teams will want to make sure you’ll be dedicated.
Yes, but this will depend on the course you’re applying for and what previous experience you have. Most PhD degrees will require you to have completed a master’s degree or equivalent, but exceptions can be made if you can demonstrate your capability. Universities want to see that you’re passionate, hard-working, and determined.
This is up to you and your career aspirations. Consider how important it is that you have a doctorate degree and what contribution it’ll make to your future.
Boost your employability
Many choose to do a PhD because it’ll increase their chances of employment. This’ll depend on what you want to study and what industry you want to work in, but doing so could increase your job prospects. Recent data from HESA on graduate activities by level of qualification found that 78.9% of doctorate students were employed upon graduating in the academic years 2017/18 to 2019/20. Only 3.4% were unemployed.
Helps you pursue an academic career
Many students use a PhD as a pathway into academia, progressing into full-time roles at a university or other higher education institution. This could be as a professor, researcher, or other role. PhD students are often employed by the university while they study, helping in lectures, labs, tutorials or as research assistants.
Make a significant contribution to your field
Doctorate degrees offer the opportunity to explore an original research question and advance your knowledge in your chosen field. It's a satisfying position to be in and comes with recognition from your peers. This could also open up a wealth of further research to be explored by either you or your peers.
Develop a range of transferrable skills
Through a doctorate degree you’ll learn a range of invaluable skills, transferrable beyond your studies. These can include:
- Project management
- Time management
- Independence
- Writing and presentation skills
- Communication skills
- Research skills
- Teaching others
Related articles

What if you don’t get an offer from your...
Don't panic. This isn't the end, it's a detour with exciting possibilities. Let's explore...

What are the Whatuni student reviews?
Find out all about Whatuni reviews, what they are, how they are collected and how you can...

What are university rankings?
University rankings, or league tables, rank universities overall and by a number of...
Is this page useful?
Sorry about that..., how can we improve it, thanks for your feedback.

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
career-advice.jobs.ac.uk
What is a PhD and Why Should YOU do one?

In the UK, a PhD stands for ‘Doctor of Philosophy’, sometimes referred to as a ‘doctorate’. It is the highest level of degree that a student can achieve. At some institutions, including Oxford University, a Doctor of Philosophy is known as a DPhil. It is distinct from professional doctorates such as an Engineering Doctorate (EngD).
Entry requirements
An undergraduate degree is a minimum requirement and many will also require a master’s degree (such as an MA, MSc or MRes). Some scholarships will be on a 1+3 basis, which is one year of a master’s plus three years of PhD funding.
How to apply for a PhD
Prospective students are usually expected to submit a research proposal to the department they wish to undertake their study in. Some departments will encourage students to discuss their ideas with an academic working in that field first. The proposal will outline what they intend their research to investigate, how it relates to other research in their field and what methods they intend to use to carry out their research. Some PhD’s however, particularly in the sciences, are advertised as studentships where the research aims are more prescriptive.
How long is the course?
A PhD usually lasts three years (four for a New Route PhD – see below), or rather, any available funding usually lasts for that time. Students may be able to take extra time in order to complete their thesis but this will usually be at their own expense. For part-time, self-funded students, it can take up to seven years.
What’s involved
A PhD usually culminates in a dissertation of around 80,000-100,000 words , based on research carried out over the course of their study. The research must be original and aim to create new knowledge or theories in their specialist area, or build on existing knowledge or theories. Many departments initially accept students on an MPhil basis and then upgrade them to PhD status after the first year or two, subject to satisfactory progress. Students who are not considered to be doing work appropriate for the level can instead submit a shorter thesis and gain an MPhil.
There is little taught element, students are expected to work independently, supported by their department and a supervisor. There may be seminars to attend and/or lab work to complete, depending on the subject. During their study, students will try and get academic papers published and present their work at conferences, which will allow them to get feedback on their ideas for their dissertation.
New Route PhD
Introduced in 2001, the New Route PhD is a four-year programme that combines taught elements, including professional and transferable skills, with the student’s research. There are now hundreds of doctoral students studying a variety of subjects at a consortium of universities across the UK.
Career prospects for PhD Students
PhD graduates who go on to work in academia usually start off by undertaking postdoctoral research and then a fellowship or lectureship. Other career options will depend on what the PhD was in – commercial research is an option for some, and many are able to use their specialist knowledge and research skills in areas of business and finance.
For a real insight into what it’s like to study at PhD level, see our vlog series , where we have invited students at various stages of their PhD and locations to film themselves over a month and share their videos with you.
Why do a PhD?
If you are considering doing one make sure that you do it with a purpose. Do one because you want to and know why you want to do it and have a clear idea of what it could lead to . How is doing a PhD going to help you achieve what you want to in your future?
Reasons to do a PhD.
- It’ll be good for your career. No one expects you to have your whole career plan mapped out when you start a PhD, but having some ideas of where you want to get to can be useful. Be aware though that you may not get the career benefits of a PhD straight away.
- You want to be an expert in a particular area of your subject. If you complete a PhD you will be. No-one, not your supervisor, not your external examiner at the end of your PhD, no-one, will know more about the subject you researched than you do.
- You want to achieve something. You want to work hard and demonstrate a passion for your subject and show how much time and effort you put in and how motivated you are.
- Showing your ability to motivate yourself is one of many skills you’ll be able to demonstrate to employers after doing a PhD, which is handy for entering a competitive job market .
Reasons not to do a PhD.
- Don’t do it just because your degree research project supervisor asked you if you wanted to do one with them. If you wanted to do one and it’s in an area that interests you then great, go for it. If you hadn’t thought about doing one before they asked, and you’re not sure why you want to do one, make sure you work that out before saying yes to them.
- Don’t do it because you don’t know what else to do. Many people do a PhD because they don’t know what else to do and think it will give them time to work that out. Doing a PhD is a huge commitment, at least 3-4 years of your life, and hard work, so before you take one on, make sure you understand why.
- And do it because YOU want to, not because your family, or others expect it of you, or because your family or friends are doing one, or have done one. Make it your decision, not someone else’s.
Why Should YOU Do A PhD?
It is your decision to commit to a significant period of time and work and it needs to be something you approach positively and with enthusiasm but also with realism about the pros and cons of undertaking original research.
Who does a PhD?
The idea of the “perpetual student”, i.e. someone who stays on after an undergraduate and/or masters degree, to do a PhD, is perhaps a traditional view of PhDs. Some of you reading this will fall into the category of those who work through the tiers of higher education in this sequential fashion (it does not necessarily make you a “perpetual student” though!). The PhD population today is very diverse and not made up entirely of 21 to 25-year-olds who have stayed in educational settings for the majority of their lives. Others may be considering a return to education in order to change your career or as part of your professional development within an existing career. Some of you may be considering coming to study in the UK independently or with support from an organisation in your home country. Whatever your situation it is very important that you take time to recognise and understand why you are making this commitment and what it entails.
Let us move to the positives of why YOU should do a Ph.D. Broadly, the positive reasons can be classified into:
You WANT to or You NEED to
Some academic colleagues were asked to give reasons why someone should do a PhD and all came back with statements that had the word “passion” in them. This is having a real passion for your subject and an area of it that you want to investigate further. My colleagues also offered some interesting comments on the reality of making a decision to do a PhD even when you have this passion. Some commented on the need to consider doing the right PhD for you and not just any PhD, and I think it is important that you take this seriously as it can be dangerous to compromise too far and embark on research that you are not interested in just because it will lead to a PhD.
Academic colleagues also wanted you to look ahead and consider where your PhD may take you. Do you want to continue in an academic career or apply for jobs in industry or other organisations where a PhD is a requirement or will help you to work at a different level? Interestingly, research on the career intentions of students, undertaken by Vitae revealed that less than one-third had firm career ideas even in the latter stages of their Ph.D. This statistic is concerning as it may mean that PhD students miss opportunities to add to their range of experience. You don’t need to have an exact career plan in place at the start of your Ph.D., but doing research on where it may take you is valuable. For those already in a career and undertaking a PhD as part of their professional development, or those who are viewing a PhD as part of a career change into academia, they should also look ahead and ensure that plans for the future are realistic and achievable.
A decision to undertake a PhD involves the same steps as any other career decision, you need to find out as much as possible about what a Ph.D. really involves. Alongside considering where your passions lie and where they might lead to, you need to research such things as:
- The working environment and how you will adapt to any differences with your current situation
- Working with a supervisor
- What funding is available and what it covers, i.e. fees only or fees and living costs?
- Most importantly what behaviours, skills and experiences YOU have that will make you a successful and productive researcher
These points and others are covered in more detail in 7 Ph.D Application Tips .
Find your PhD here
For further PhD tips see:
What Can You Do With a PhD?
Share this article
Reader Interactions
You may also like:.
20th August 2020 at 12:31 am
Excellent article. I am know more motivate to get a scholorship for my PHD program. I have to enhance my all effort because it’s not easy to get a fully funded, require more effort and time taken.
10th March 2022 at 9:58 am
Good morning,
Hope are well? I am thinking of gong for PHD. In any UK universities. Hope to hear from you soonest.
10th March 2022 at 1:08 pm
Cool, thanks for your advice. It’s an inspiration to let my “passion” be abroad. Best for you.
9th November 2022 at 8:33 pm
This article is timely and so educative. I’m now better informed on how to make a decision on going for my PhD. Thanks a lot.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: 6 + eleven =
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Log in
- Site search
5 routes to getting a Doctorate
While most of those studying for a PhD take the PhD by thesis pathway, there are five viable routes to achieving a Doctorate degree
PhD by thesis
This is the most common means of getting a Doctorate degree. Over the three or four years of research at university, your PhD supervisor will support you as you aim to produce a thesis based on your research proposal .
A thesis is typically 60,000-90,000 words in length - although this can vary between institutions. For instance, the University of Glasgow's College of Social Sciences expects a thesis to be 70,000-100,000 words including references, bibliography and appendices, while the University of Cambridge has set an upper limit of 80,000 words.
Once completed, you'll need to defend your PhD thesis in front of a panel of examiners during your viva voce .
PhD by publication
This route involves submitting previously published work - such as books, book chapters and journal articles, which together form a coherent body of work and show evidence of an original contribution to a particular field of study.
It's often taken by mid-career academics that haven't had the opportunity to undertake a standard Doctorate degree.
Generally, a minimum of five to eight published pieces are required, but this varies between institutions and depends on their length. The published work will be assessed to the same rigorous standards as a traditional PhD by thesis.
You must also provide a written supporting statement, which can range from 5,000 to 20,000 words, and present your work to an academic committee. A supervisor will assist you with selecting which publications to submit and with the supporting statement.
Some universities accept only their own graduates for a PhD by publication, while others restrict this route to their academic staff. In general, you should have graduated from your first degree at least seven years ago to be eligible.
For example, The University of Manchester has published its own Guidance for the PhD By Published Work , with eligibility only extending to current members of staff.
Professional Doctorate
Geared primarily towards current professionals in vocational sectors such as healthcare , teaching and education , and engineering and manufacturing , this type of Doctorate degree includes a significant taught component and a smaller research project.
Professional Doctorates are often taken on a part-time basis and can last between two and eight years. Like their standard PhD counterparts, they usually begin in October or January.
While you won't typically be looking to get an academic job , your research is expected to contribute to theory as well as professional practice. Projects often revolve around a real-life issue that affects your employer.
Several professional Doctorates, such as the Doctorate in Clinical Psychology (DClinPsy), are accredited by a professional body - for instance, the Health & Care Professions Council (HCPC) and The British Psychological Society (BPS) - and may also lead to a professional qualification .
Common titles for graduates of professional Doctorate degrees include:
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
- Doctor of Education (EdD)
- Doctor of Engineering (EngD)
- Doctor of Medicine (MD).
Unlike many professional Doctorates, the EngD is typically offered as a full-time course and is aimed at young engineering graduates with little or no professional experience.
Explore what's currently available at Find a Professional Doctorate .
Integrated PhD
This four-year qualification, also known as the New Route PhD, involves studying a one-year research Masters degree (MRes) before progressing onto a three-year PhD.
Offered by a select number of universities across the UK, integrated PhDs are supported by the government and the British Council through UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) . Visit Research Council funding for further information on research and funding for different types of PhD.
The integrated PhD involves a combination of taught materials, practical experience and advanced research. This allows you to learn subject-specific methodologies, while building the transferable skills that will enable you to become a leader in your chosen profession.
Institutions can also develop personalised integrated PhD programmes to meet each student's needs. For example, universities may offer you the opportunity to gain a postgraduate certificate (PGCert) in Learning and Teaching in Higher Education - perfect if you're considering a career as a higher education lecturer .
As PhDs are based primarily on independent research rather than time spent in lectures and seminars, distance learning has always been a viable route for many Doctoral students.
PhDs by distance learning offered by course providers such as The Open University are therefore a good option to consider if you've got family or work commitments or are an international student - as this gives you the chance to undertake Doctoral research without having to live close to your chosen institution. It's also a suitable mode of study if your subject requires you to be based in a specific location away from the university.
For the most part, you'll be in touch with your supervisor by phone, email or Skype/Zoom. You'll need to bear in mind that even if you opt for this form of research, you'll generally still need to attend university for one or two weeks of each academic year for meetings and to receive research skills training. Your final examination may be undertaken either face-to-face or virtually.
With online PhDs, you can usually register as a full or part-time student. The level of fees you pay varies between institutions - some charge the same as for a standard PhD while others offer a reduced rate.
Check that any funding you plan to apply for is available to distance learning students, as this isn't always the case.
Search for distance learning PhDs .
Find out more
- Explore what is a PhD?
- Sort out funding for postgraduate study .
- Consider what to do after completing your PhD .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page
Our cookies
We use cookies for three reasons: to give you the best experience on PGS, to make sure the PGS ads you see on other sites are relevant , and to measure website usage. Some of these cookies are necessary to help the site work properly and can’t be switched off. Cookies also support us to provide our services for free, and by click on “Accept” below, you are agreeing to our use of cookies .You can manage your preferences now or at any time.
Privacy overview
We use cookies, which are small text files placed on your computer, to allow the site to work for you, improve your user experience, to provide us with information about how our site is used, and to deliver personalised ads which help fund our work and deliver our service to you for free.
The information does not usually directly identify you, but it can give you a more personalised web experience.
You can accept all, or else manage cookies individually. However, blocking some types of cookies may affect your experience of the site and the services we are able to offer.
You can change your cookies preference at any time by visiting our Cookies Notice page. Please remember to clear your browsing data and cookies when you change your cookies preferences. This will remove all cookies previously placed on your browser.
For more detailed information about the cookies we use, or how to clear your browser cookies data see our Cookies Notice
Manage consent preferences
Strictly necessary cookies
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems.
They are essential for you to browse the website and use its features.
You can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but some parts of the site will not then work. We can’t identify you from these cookies.
Functional cookies
These help us personalise our sites for you by remembering your preferences and settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers, whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, then these services may not function properly.
Performance cookies
These cookies allow us to count visits and see where our traffic comes from, so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are popular and see how visitors move around the site. The cookies cannot directly identify any individual users.
If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site and will not be able to improve its performance for you.
Marketing cookies
These cookies may be set through our site by social media services or our advertising partners. Social media cookies enable you to share our content with your friends and networks. They can track your browser across other sites and build up a profile of your interests. If you do not allow these cookies you may not be able to see or use the content sharing tools.
Advertising cookies may be used to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other sites. They do not store directly personal information, but work by uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies, you will still see ads, but they won’t be tailored to your interests.
What is a PhD?
A PhD is a postgraduate degree. It stands for ‘Doctor of Philosophy’ and is one of the highest academic qualifications you can achieve.
Courses involve both research and academic learning where you take on a significant amount of independent work.
For most PhDs, you’ll research for, write and publish an extensive thesis on a specialist subject area.
How long is a PhD?
PhDs courses usually last between three to four years if you study full-time. Students often extend their thesis deadlines and finish the work in their fourth year. If you study part-time, courses can last six or seven years.
Courses can begin anytime throughout the year, though most studentships (doctorate scholarships) start in September or October.
What qualifications do you need for a PhD?
You usually need a good second-class (2.1) undergraduate honours degree in a relevant subject area, or equivalent. Many courses also ask for a master’s degree.
When applying, you may need to demonstrate an ability to conduct research. This could be by showing your experience of independently working on a research project. You’ll probably also have to submit a research proposal that outlines what you’ll be studying.
How is a PhD taught?
There’s very little teaching involved in a PhD degree. Your course may begin with five or six hours per week of classes where you learn about research methods and techniques. Aside from this, you’re in control of your studies, though you’ll receive some guidance from an academic tutor.
How is a PhD assessed?
PhD students are assessed mainly by a thesis, and a closed oral examination where examiners ask questions about the thesis.
Degrees are usually graded as pass or fail.
What skills do you learn during a PhD?
As well as subject-specific skills, you develop transferable skills such as:
- Organisation
- Research
- Work habits
- Project management
- Critical thinking
- Written communication
- Presentation
How much does a PhD cost?
Fees vary widely between courses and institutions, but are commonly between £3,000 and £6,000 per year for UK students. International students often pay more.
Many degrees are partly or fully funded, and lots of students receive scholarships and bursaries. UK Research Councils provide universities with grants of around £4,000 per year for each funded PhD student.
PhD degree facts
Some new PhDs are more vocational and offer practical experiences as well as research. These are designed for those looking to advance their careers.
When applying for a PhD, you show the university that you’re the right person for an advertised position, or that you’d be suitable to complete your research proposal.
Popular PhD subjects
Archaeology, top rated universities, liverpool john moores university, bangor university, heriot-watt university, more phd advice, a phd in the humanities: why.
Our PhD blogger, David Spittle, is currently studying for a PhD in English Literature (focussing on ...
06 th August 2014
Staying motivated on a phd.
There will be times during your PhD where you feel like you lack motivation. Studying for these degr...
06 th June 2023
Five time management tips for phd students.
Due to the limited contact time you’ll receive during y...
16 th August 2022
5 reasons to study a phd.
A PhD is both financially draining and incredibly challenging. Lasting for 3 – 4 years (depending up...
21 st February 2020
Funding your phd, 5 things to consider when you apply for postgraduate finance.
It’s no secret that studying for a postgraduate course ...
01 st September 2020
Loan options for postgraduate students.
The routes for postgraduate students to get loans for their continuing education have changed quite ...
27 th September 2022
How to fund your postgraduate course.
Knowing if you can fund your studying is a key deciding factor when taking a postgraduate degree, es...
08 th February 2023
How to fund a phd.
Planning on studying for a PhD but wondering how to fund it? If you’ve been researching PhDs, you’ll...
15 th August 2022
Upcoming open days, city, university of london, university of roehampton, manchester metropolitan university.
How to apply for a PhD in the UK
Applying for a phd is not quite as daunting as you might think. a postgraduate student recruitment officer from the university of sussex shares his tips for putting together a phd application.

Ben Osborne
There are many different reasons for wanting to pursue a PhD – to move into an academic role at a university, to continue studying a subject you are passionate about or to further your career.
Whatever your motivation, many students are now choosing to pursue a PhD abroad. This guide will help you understand how to apply for a PhD at a UK university and answer any questions you might have around doing PhDs.
How to apply for a PhD
Application rules and methods vary for each university. The number of courses that you can apply for in a year will vary. For example, at the University of Sussex , you can apply for up to three postgraduate courses per year using the postgraduate application system.
If you are applying for more than one degree, you must submit a research proposal/statement specific to each area of study you apply for.
You can also apply to different universities to improve your chances of being accepted to a PhD course of your choosing.
What qualifications do I need?
Each PhD will have specific entry requirements and you will also need to meet a university’s general entry requirements. This may be an upper second-class undergraduate honours degree (2:1) or an equivalent international qualification. For some PhDs you may need a master’s qualification, and you may be asked to attend an interview.
International students may also be required to prove language proficiency. This will vary across institutions so do check what level universities expect before starting your application.
Applicants should always check the specific entry requirements in a university’s online prospectus before making an application.
When should I start applying?
This will depend on when your term start date is. Most research degrees will start in September but some courses offer additional entry points in January or May.
You can apply all year round for research degrees starting in September, January and May, and the deadlines for applying are usually one month before the course start date for UK applicants, and three months before for international applicants.
If you’re applying for funding from an external organisation you’ll need to be aware that they may have different deadlines for the funding application. So give yourself plenty of time to research your funding options, and ensure you know how long the application process takes.
Many universities offer a number of funded PhD opportunities and PhD scholarships for UK and international students, and it’s always worth investigating funding routes such as research councils and other organisations, both in the UK and overseas.
In some cases, it may be possible to study a PhD by distance which means you’ll be able to learn online and have virtual meetings with your supervisor.
If this is something you would be interested in doing you should check before applying whether your university can accommodate this option.
Nine things to know before doing a PhD Starting a PhD during the pandemic Studying for a part-time PhD: the challenges and the benefits Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student?
How should I look for a supervisor?
Usually if you are applying for a funded project, or to a research centre or group, you will normally be asked to provide a statement explaining your suitability for working in that area, and if successful you will be allocated a supervisor.
If you wish to propose your own area of research, you need to decide on a research topic, and you will be expected to write a research proposal. In some cases you may only be required to provide a summary of academic interests and this can be used to match you to a researcher that suits you.
If you are proposing your own research topic, there may be a research database at your university that you can search, or your university will match you with a supervisor during the assessment of your application. It may be possible to request supervision by a particular member of faculty – this will be considered but not all requests can be accommodated.
If you do find a potential supervisor who matches your research area, check their online profile for indications of their doctoral supervision capacity. If they are open to doctoral applications, you can contact them directly to check their availability for supervising you.
It is a good idea to draw up a shortlist of two to three potential supervisors, and take an in-depth look into their research history. You can also find out more about your potential supervisors by looking in the reference sections of academic textbooks and searching for articles in research databases and academic blogs.
When you contact your potential supervisor, it is important to tell them something interesting about yourself, and explain your research interests and how you feel your research proposal matches their expertise.
How do I write a research proposal?
If you are proposing your own research you will need to write a strong proposal that formulates a precise, interesting research question, and establishes the relevance and value of the proposed research question in the context of current academic thinking.
You’ll need to make sure your proposal describes the data or source material your research requires, and outlines a clear and practical methodology that enables you to answer the research question and that states clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research, and what new areas it might open up.
The precise content and structure of your research proposal will depend on your subject area, and the University of Sussex has some helpful resources on our website to guide you through the process.
How long does the application process take?
Completing an application and writing a research proposal may take some time and should not be left until just before the application deadline.
It’s not easy to give a definite idea of how long it takes to hear if your application has been successful, as it will depend on when the application is made and the nature of the specific PhD, and you would need to meet any conditions contained within the offer before you can start the PhD.
What are the associated costs?
There won’t typically be an application fee for PhDs but there are tuition fees. If a university does charge application fees they will usually be between £50-£100.
The tuition fees for students studying in the UK are set by UK Research and Innovation . Fees for international students are £18,975 for non-lab-based subjects, and £22,975 for lab-based subjects per year.
You’ll also need to factor in living costs, but there are a number of funding routes you can apply for to help with this. As well as PhD scholarships and funded research projects there are research council awards, PhD loans for those eligible, and various organisations to which international students can apply for funding, such as The Gen Foundation and Open Society Foundations.
It’s important to be aware of the costs involved, but it’s also worth remembering that the educational, career and personal benefits of PhD study can be worth it.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} How to apply for a PhD in the US
Giulia Evolvi

Women in STEM: undertaking PhD research in cancer
Grace McGregor

PhD diary: Where do I begin?
Charlie Pullen
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer
- Accessibility options

- Business and employers
- Alumni and supporters
- For students

- Postgraduate research degrees
- Our postgraduate research disciplines
- Apply for a PhD
- Funding and studentships
- International
- Support and training
- Research Masters
- Postgraduate info session
International students: PhD/doctoral study in the UK at the University of Brighton
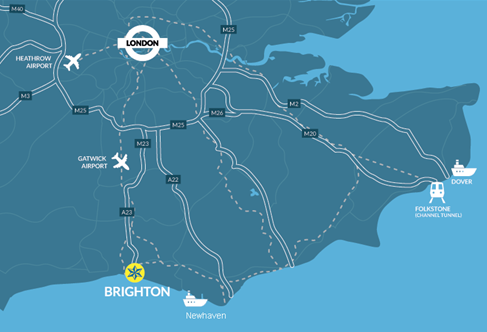
Brighton is a vibrant and creative seaside city on the South-East coast of the United Kingdom. By train it is 60 minutes south from London and only 30 minutes from London's major international Gatwick airport.
The University of Brighton is a contemporary, forward-thinking university with world-leading and internationally excellent research recognised in the latest national research assessment (REF2021) . Most importantly, we put our students at the heart of everything we do.
Find out more about your opportunities to join the University of Brighton as an international research student.
Our Frequently Asked Questions from International applicants (FAQs) below will give you a sense of:
- Brighton as a city and the University of Brighton as a place to study
- Entry requirements
- Visas / CAS / ATAS
- Working during and after study
- Costs and funding
- How to apply
- Support when coming to the UK
There are further, general PhD applicant FAQs to explore, as well as our International pages on the university website , and you can contact our Doctoral College if you have further questions.
Find your PhD discipline area using key terms or browse through our lists .
Application to the University of Brighton should generally be made after a preliminary approach to a chosen lead supervisor.
When you are ready, apply through our application portal.
FAQs: Brighton as a city and the University of Brighton as a place to study

Where is Brighton located in the UK?
Brighton is a vibrant and creative seaside city on the South-East coast of the United Kingdom.
By train, Brighton is only one hour away from London, 30 minutes away from London's Gatwick Airport and 90 minutes away from London's Heathrow Airport.
Being close to London and within easy reach of international transport, Brighton attracts visitors and students to a growing international population. The city is famously accepting of new people and different ways of living. Its progressive attitudes mean it has led the way in arts, creative technology, modern notions of sexuality and gender, as well as environmental and sustainable education and policy.
There are opportunities to build on your studies by getting involved in city as well as university life. We have campuses in the heart of Brighton, close to the seafront and on the outskirts near the South Downs National Park, all in a city that is in the top 10 most visited towns in the UK by overseas visitors.
Is Brighton a diverse place to study?
Please enable targeting cookies in order to view this video content on our website, or you can watch the video on YouTube .
Brighton is one of the liveliest and most diverse places in the UK to live and study.
According to Brighton and Hove Council,16 per cent of our population is born outside the UK. With a mix of cultures, nationalities and religions, you’ll soon feel at home here no matter what country or background you’re from.
It is an authentic student city, too. Around 500 PhD students study at the University of Brighton and a quarter are international students. The diversity of students has always been evident at the Summer Graduation Ceremonies with 83 countries recently represented among our 3,000 graduates from all levels.
Inclusivity is one of our four core values at the University alongside sustainability, creativity, and partnership.
The University of Brighton is committed to providing a fair environment that embodies and promotes equality of opportunity. We value the different contributions and experiences of all who make up our community, promoting mutual respect and understanding as well as freedom of thought and expression.
For more information visit our university page on Equality, diversity and inclusion .
What type of university is the University of Brighton?
The University of Brighton is a modern, forward-thinking university.
Our identity hinges on our belief in developing knowledge and sharing it in places where it can make a difference to other people’s lives.
Our oldest departments trace their history over 160 years, while we embrace the modern and progressive values of a contemporary and rapidly changing world.
We foster world-leading research across traditional and more recently-established disciplines that include: health and medicine, computer science, engineering, geography and environmental studies, business and management studies, social studies, education, sport and exercise sciences, art, design and architecture, cultural and media studies.
Ninety-eight per cent of our research was rated as world-leading, internationally excellent or internationally recognised in the most recent national research assessment (Research Excellence Framework, REF2021).
The university's campuses are all convenient for the city. Outside of your studies, Brighton offers festivals, galleries, museums, street art, nightlife, sports facilities, and a huge range of independent shops, cafés and entertainment venues.
Is PhD in UK better than US?

Research in any English language environment gives you an opportunity for maximum outreach and impact from your work.
There are some differences between the PhD offers from the different English-language-speaking countries. Each of them do however provide support for students’ research towards new knowledge and the production and defence of a thesis detailing the research.
Some special features of a doctorate in the UK:
- There are very few, if any, taught course elements in most UK PhD degrees
- Typically, the doctorate in the UK can be completed in three years as a full-time student
- In the UK, the student is a researcher right from the start and dedicates most of their time to their own research work and written thesis.
In the UK, doctoral students are usually supported by two or three expert supervisors from the start of their programme. Wider support is developed through PhD discussion groups and research communities.
Whichever option you choose, research in an English language environment will give you the fluent writing and spoken English skills that will take you a long way in your research career.
How will I learn at doctorate level? What teaching, supervision and academic support will I get?
All our postgraduate research students are part of a dynamic, enthusiastic, and creative research community. From research plan to viva, our workshops and specialist staff guide doctoral students through the major milestones of their PhD.
You will have the support of two or three supervisors at the University of Brighton, who will help you to pursue your research passion. Our doctoral training programme and vibrant research environment will nurture and liberate your talent.
If you need support with your academic English language , we offer developmental courses and one-to-one tutorials specifically for students at doctoral level.
The teaching, learning environment and educational outcomes we provide for our students consistently exceed rigorous national requirements for all UK higher education providers.
To meet fellow students and the wider PhD community there are plenty of events organised by the university, the Doctoral College, your school and the research centres you belong to.
For further information on supervision and support, see our general FAQ page .
How will I build a relationship with my supervisor? This film was made by the University of Brighton for UKRI and features University of Brighton students and academics as well as those from other partner universities.
FAQs: PhD entry, funding, visas and language requirements

What are the entry requirements for a PhD in the UK?
The application process requires documentation that demonstrates the suitability of you and your topic of study for a timely completion of the PhD programme.
These will include references and a research proposal as well as evidence of eligibility to study in the form of language level and relevant visa.
Find out more on our application pages
Is it possible to do a PhD after bachelor's degree in the UK?
The University of Brighton will consider applications from those without masters degrees but would normally expect an undergraduate degree with evidence of suitably high performance. A master's degree is considered stronger evidence that you are able to study at higher levels and that you have a strong theoretical background in your subject.
What are the English language requirements to study for a doctorate in the UK?
For subjects in medicine and laboratory sciences, including engineering, requirements are usually an IELTS score 6.5 overall, no component below 6.0.
For subjects with an extensive text-based research and writing element, a 7.0 overall, 7.0 for writing, with no component below 6.5 is required.
These are the overall requirements at the University of Brighton. Where there are any differences, the requirements for your area of research will be found on the relevant PhD Programme Page .

Will I need a visa to study for PhD in the UK?

How do I apply for a Confirmation of Acceptance for Studies (CAS) number?
Once you have been made an unconditional offer, you will be able to complete a visa questionnaire. Our visa compliance team will review your eligibility and issue a CAS number, as appropriate. More information is available on the university's general international pages .
Will I need to pay a deposit to progress with visa application?
If you are self-funded, we cannot issue you with a CAS until you have paid your tuition fee deposit. We would advise that you pay this as soon as possible so that you are able to make your visa application in plenty of time. More information about the tuition fee deposit and how to pay the deposit is available on our confirmation of acceptance for studies page .
If you are a funded student, you will need to provide proof of your sponsorship before the tuition fee deposit can be waived.
See more information on visa applications

Will I need an Academic Technology Approval Scheme (ATAS) number for PhD study?
Depending on which country you are from, you may need to obtain an ATAS certificate every time you make a Student Visa application, if you are studying or going to study one of the following research degree programmes:
Pharmacy; Biomedical Sciences; Healthcare Professions; Physiotherapy; Occupational Therapy; Engineering; Environment; Civil Engineering: Built Environment; Computing; Mathematical and Information Sciences; or Information Technology.
PhD students should apply through the student route, not the researcher route.
Where an ATAS statement is required, the process of how to apply for this will be provided in your offer letter, so do read your offer letter carefully.
For details about the scheme and how to apply for your ATAS certificate, visit the Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) information about ATAS.
Can I work in the UK during and after my PhD?
There are opportunities to undertake work in the UK while studying.
However, the full-time course and the nature of PhD study does not easily allow for work hours and this should not be seen as a means to fund your studies.
Teaching at the university, while possible, is not guaranteed and opportunities to teach would have to be discussed with your supervisor and relevant school leaders while undertaking the course.
Working in the UK on a Student Visa as a PhD research student
It is likely that you will be able to work in the UK based on your Student Visa, although some types of employment are prohibited.
Where you are on a Student Visa, your eligibility to work will be outlined on your visa vignette or BRP card, and in your visa decision letter.
During your full-time PhD programme at the University of Brighton, you can work up to 20 hours per week in paid employment.
Working in the UK after graduation with a PhD research degree
- You can work unlimited hours once you have submitted your final thesis after corrections, but not in a permanent role.
- You are likely to be eligible for a Graduate Visa on completion of your studies and can work for a further three years.

How much does a doctorate cost in the UK for international students?
Tuition fees and other costs..
The tuition fees for each discipline are located on our Programme pages .
It is important to recognise possible costs beyond the tuition fees. Research can involve costs for, for example, travel to conference venues, archives or libraries; copyrighted imagery payments and so on. Fees are also likely to incur a small inflation rise each year of a research programme.
You will also need to fund normal living costs in the UK during your studies.
Is there funding for PhD in the UK?
There are many opportunities for partial and complete funding of PhD studies in the UK, with funders offering stipends for living costs as well as tuition fees. There are also opportunities for ongoing funds to help aspects of a project such as travel for conference or library access.
Find out more advice on funding as well as our latest offers from the University of Brighton.
How do I apply for a PhD in the UK?
To apply for a PhD, you will need to provide a research proposal along with academic references and documentation to show that you are eligible for study in the UK.
We recommend you do this with the assistance and cooperation of a possible supervisor. When ready, your documents must be submitted through the application portal available from our Programme pages .
For full information on the application process, see our Apply for your PhD page .
Who can be my PhD referees?
You will need to ask two people to provide references for you. They should be able to detail your fitness for academic study and research. At least one of your referees should be from your most recent period of study.
You can provide your referees’ contact details as part of the application process and we will contact them on your behalf. Alternatively, you can approach your referees directly to provide a reference. All references should have been written within the last 12 months and need to be signed, dated and stamped with the organisation's stamp.
Can I study part time for PhD in the UK?
Can you study for a phd part-time as an international student.
The University of Brighton does not normally consider visa sponsorship for international students to undertake study wholly on a part-time basis.
However, where there are significant personal or other extenuating circumstances, visa sponsorship of postgraduate students wholly on a part-time basis will be considered on a case-by-case basis.
Please contact the Doctoral College for further information.
Can you do a PhD by distance learning UK?
We do not offer enrolment specifically as a distance learning student and, usually, international students are expected to live within a commutable distance from the university. This brings a fuller experience with better chances of success.
However , if you’re a promising PhD candidate with home commitments and employment and would struggle to attend university full time in the UK for the whole period of study, we may be able to register you for a PhD and agree a mode of attendance.
If you would like more information on studying for a PhD without fully relocating to the UK, please contact the Doctoral College for further guidance before applying.
I speak English / have studied in the UK: Do I still need to provide IELTS for PhD?
If you are from the UK, have studied in the UK within the last three years, or are from one of the countries approved by the UK Visa and Immigration Authority (UKVI), you may not need to provide results of a Secure English Language Test (SELT).
If your UK study was more than three years ago, or you are not from one of the UKVI listed countries, you will be required to provide further evidence of your English Language in the form of one of the accepted English tests for research study .
If you already have a SELT certificate, like IELTS for UKVI, please note that this is valid for two years from the test date. The results must be valid on your course start date.

What support do you offer students who are moving to the UK?

We know that moving to a new country can be daunting. That's why we offer our international students lots of support and advice, to help you settle in, gain new academic skills and get the most out of your time here.
Detailed help and guidance is available on our preparing for university page for students at all levels.
Accommodation for PhD students
The university has an accommodation service who can help you find somewhere to live. Once you have accepted your offer with us, we advise you to contact the accommodation service who will be happy to help you. You can contact them via [email protected]
More information about living in Brighton and the surrounding areas can be found on the university's general accommodation and location pages
Registering with a doctor
We recommend that you register with a university doctor or local doctor as soon as possible when you arrive at university.
If you are not registered with a local doctor, you will have difficulty getting an appointment, and crucial time could be wasted in an emergency.
For more information, visit our register with a doctor page
Can my family move to the UK with me as a PhD student?
Yes, they can. For those studying for a PhD or other doctorate (RQF level 8) or a research-based higher degree, you are entitled to bring dependents with you to the UK.
Further information can be found on relevant government websites for student visas pertaining to families and children .

Find your PhD research discipline and apply
Find your disciplinary home through our search or A–Z listings. Our disciplinary programme areas will help you find a supervisor and focus your application.

PhD funding opportunities and studentships
Find out more about the funding available for postgraduate research/PhD doctoral study at the University of Brighton.

How to apply for your PhD
Details of our application process and frequently asked questions (FAQs) on the PhD journey.

Alternatively, use our A–Z index
Attend an open day
Discover more about this subject area
PhD Education / Entry requirements
Year of entry: 2024
- View full page
Academic entry qualification overview
- Bachelor's (Honours) degree at 2:1 or above (or overseas equivalent); and
- Master's degree in a relevant subject - with an overall average of 60% or above, a minimum mark of 60% in your dissertation (or overseas equivalent)
English language
- IELTS test minimum score - 7.0 overall, 7.0 in writing, 6.0 in other sections.
- TOEFL (internet based) test minimum score - 100 overall, 25 in all sections.
- Pearson Test of English (PTE) UKVI/SELT or PTE Academic minimum score - 76 overall, 76 in writing, 70 in other sections.
- To demonstrate that you have taken an undergraduate or postgraduate degree in a majority English speaking nation within the last 5 years.
- Other tests may be considered.
English language test validity
Some English Language test results are only valid for two years. Your English Language test report must be valid on the start date of the programme.
Other international entry requirements
We accept a range of qualifications from different countries. For these and general requirements including English language see entry requirements from your country.
The University requires you to reside within a commutable distance from Manchester during your time as a registered student, unless you are on approved fieldwork/a formal placement or are on a period of Submission pending. This is to ensure that you are able to meet attendance expectations and participate in wider research activities within your discipline area and/or School.
Recommended pages
- Undergraduate open days
- Postgraduate open days
- Accommodation
- Information for teachers
- Maps and directions
- Sport and fitness
PhD Public Administration and Policy
For 2024-2025 UK Full time: £4,778* Part time: £2,389 International students Full time: £21,360 More Fees and funding details.
- Visit an Open Day
- Request a prospectus
- Course details
- Entry Requirements
- Teaching and assessment
- Employability
This advanced degree is not just an academic pursuit; it's a transformative journey that equips you with the knowledge, skills, and influence to shape the future of governance and public affairs.
The Department of Public Administration and Policy has a vibrant and close-knit international research community of early-career and established researchers. Our engaged scholarship is theoretically-driven, and demonstrates a commitment to methodological pluralism, with particular strengths in qualitative, collaborative and participative approaches.
Undertaking a PhD in Public Administration and Policy, you will have the opportunity to conduct original research under the guidance of academic supervisors within an active research environment, leading to an 80,000 word thesis. You will take a number of research training modules in your first year and may attend further courses offered by the Department or the University that enhance your personal discipline-specific and transferable skills.
The Department of Public Administration and Policy is in the School of Government, one of the leading UK and international centres for governance, politics, international development, and public management. As one of the largest Schools of Government, in the United Kingdom, it is home to more than 80 full-time academic staff, more than 1,200 undergraduate and taught postgraduate students, and more than 70 doctoral researchers.
The School of Government offers much more than a degree. As a doctoral student here, you have the opportunity to take part in a wide range of research events with staff and other doctoral students, including a PGR Colloquium and departmental speaker series. In addition, an individual training plan is drawn up to meet the needs of each student, covering coursework and skills development. As such, completing this research degree will cultivate specialist knowledge in your field and professional skills for a range of career settings.
We are particularly interested in receiving applications on the following themes:
- Governance, institutional design and leadership
- Co-production, democratic and social innovation, and inclusion
- Policy-making, implementation and service delivery
- Smart, sustainable and creative approaches to policy challenges
Applications to study for a research degree on either a full- or part-time basis are welcomed.
Further information
- Guidance on preparing a research proposal
- Doctoral Research Scholarships and funding
Doctoral Research Student Administration Tel: +44 (0)121 414 3497, Email: [email protected]
Research degree fees 2024 - 2025
- Full time £4,778 (UK)
- Full time £21,360 (International students Band D)
- Part time £2,389 (UK)
*Research fees also apply to combined research and taught programmes unless otherwise indicated.
Learn more about fees
Scholarships and studentships
The Department of Public Administration and Policy occasional offers teaching assistantships for those enrolled on a full-time research degree. These provide bursaries to cover living costs, payment of the fee and the opportunity to gain additional income through a limited amount of tutorial work.
International students can often gain funding through overseas research scholarships, Commonwealth scholarships or their home government.
Explore our Postgraduate scholarship and funding database
How To Apply
- How to apply
To apply for a postgraduate research programme, you will need to submit your application and supporting documents online. We have put together some helpful information on the research programme application process and supporting documents on our how to apply page . Please read this information carefully before completing your application.
Our Standard Requirements
Applicants for degrees by research should have at least a good Honours degree or equivalent academic qualification. Our normal policy is to register PhD applicants for an MPhil, and transfer them to PhD if their work is of an acceptable standard. If you have registered for the MSc you may, after nine months full-time (18 months part-time), apply to transfer to an MPhil or PhD.
You will need to show evidence of satisfactory progress with your thesis, and have provided an acceptable programme of further research. MPhil students may apply to transfer to a PhD by meeting similar conditions.
Learn more about entry requirements and see our Guidance for applying for a PhD .
International Requirements
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and a Masters degree, with a GPA of 14/20 from a recognised institution to be considered. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of the Licenciado or an equivalent professional title from a recognised Argentinian university, with a promedio of at least 7.5, may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. Applicants for PhD degrees will normally have a Maestria or equivalent
Applicants who hold a Masters degree will be considered for admission to PhD study.
Holders of a good four-year Diplomstudium/Magister or a Masters degree from a recognised university with a minimum overall grade of 2.5 will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students with a good 5-year Specialist Diploma or 4-year Bachelor degree from a recognised higher education institution in Azerbaijan, with a minimum GPA of 4/5 or 80% will be considered for entry to postgraduate taught programmes at the University of Birmingham.
For postgraduate research programmes applicants should have a good 5-year Specialist Diploma (completed after 1991), with a minimum grade point average of 4/5 or 80%, from a recognised higher education institution or a Masters or “Magistr Diplomu” or “Kandidat Nauk” from a recognised higher education institution in Azerbaijan.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and a Masters degree, with a GPA of 3.0/4.0 or 75% from a recognised institution to be considered. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree, with a CGPA of 3.0-3.3/4.0 or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Students who hold a Masters degree from the University of Botswana with a minimum GPA of 3.0/4.0 or 3.5/5.0 (70%/B/'very good') will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Please note 4-year bachelor degrees from the University of Botswana are considered equivalent to a Diploma of Higher Education. 5-year bachelor degrees from the University of Botswana are considered equivalent to a British Bachelor (Ordinary) degree.
Students who have completed a Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study.
A Licenciatura or Bacharelado degree from a recognised Brazilian university:
- A grade of 7.5/10 for entry to programmes with a 2:1 requirement
- A grade of 6.5/10for entry to programmes with a 2:2 requirement
Holders of a good Bachelors degree with honours (4 to 6 years) from a recognised university with a upper second class grade or higher will be considered for entry to taught postgraduate programmes. Holders of a good Masters degree from a recognised university will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a good post-2001 Masters degree from a recognised university will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students with a minimum average of 14 out of 20 (or 70%) on a 4-year Licence, Bachelor degree or Diplôme d'Etudes Superieures de Commerce (DESC) or Diplôme d'Ingénieur or a Maîtrise will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Holders of a bachelor degree with honours from a recognised Canadian university may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. A GPA of 3.0/4, 7.0/9 or 75% is usually equivalent to a UK 2.1.
Holders of the Licenciado or equivalent Professional Title from a recognised Chilean university will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Applicants for PhD study will preferably hold a Magister degree or equivalent.
Students with a bachelor’s degree (4 years minimum) may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. However please note that we will only consider students who meet the entry guidance below. Please note: for the subject areas below we use the Shanghai Ranking 2022 (full table) , Shanghai Ranking 2023 (full table) , and Shanghai Ranking of Chinese Art Universities 2023 .
需要具备学士学位(4年制)的申请人可申请研究生课程。请根据所申请的课程查看相应的入学要求。 请注意,中国院校名单参考 软科中国大学排名2022(总榜) , 软科中国大学排名2023(总榜) ,以及 软科中国艺术类高校名单2023 。
Business School - MSc programmes (excluding MBA)
商学院硕士课程(MBA除外)入学要求
School of Computer Science – all MSc programmes 计算机学院硕士课程入学要求
College of Social Sciences – courses listed below 社会科学 学院部分硕士课程入学要求 MA Education (including all pathways) MSc TESOL Education MSc Public Management MA Global Public Policy MA Social Policy MA Sociology Department of Political Science and International Studies 全部硕士课程 International Development Department 全部硕士课程
All other programmes (including MBA) 所有其他 硕士课程(包括 MBA)入学要求
Please note:
- Borderline cases: We may consider students with lower average score (within 5%) on a case-by-case basis if you have a relevant degree and very excellent grades in relevant subjects and/or relevant work experience. 如申请人均分低于相应录取要求(5%以内),但具有出色学术背景,优异的专业成绩,以及(或)相关的工作经验,部分课程将有可能单独酌情考虑。
- Please contact the China Recruitment Team for any questions on the above entry requirements. 如果您对录取要求有疑问,请联系伯明翰大学中国办公室 [email protected]
Holders of the Licenciado/Professional Title from a recognised Colombian university will be considered for our Postgraduate Diploma and Masters degrees. Applicants for PhD degrees will normally have a Maestria or equivalent.
Holders of a good bachelor degree with honours (4 to 6 years) from a recognised university with a upper second class grade or higher will be considered for entry to taught postgraduate programmes. Holders of a good Masters degree from a recognised university will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a good Bacclaureus (Bachelors) from a recognised Croatian Higher Education institution with a minimum overall grade of 4.0 out of 5.0, vrlo dobar ‘very good’, or a Masters degree, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a Bachelors degree(from the University of the West Indies or the University of Technology) may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. A Class II Upper Division degree is usually equivalent to a UK 2.1. For further details on particular institutions please refer to the list below. Applicants for PhD level study will preferably hold a Masters degree or Mphil from the University of the West Indies.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a good Bachelors degree from a recognised institution with a minimum overall grade of 6.5 out of 10, or a GPA of 3 out of 4, and will usually be required to have completed a good Masters degree to be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a good Bakalár from a recognised Czech Higher Education institution with a minimum overall grade of 1.5, B, velmi dobre ‘very good’ (post-2004) or 2, velmi dobre ‘good’ (pre-2004), or a good post-2002 Magistr (Masters), will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a good Bachelors degree from a recognised institution with a minimum overall grade of 7-10 out of 12 (or 8 out of 13) or higher for 2:1 equivalence and will usually be required to have completed a good Masters/ Magisterkonfereus/Magister Artium degree to be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of the Licenciado or an equivalent professional title from a recognised Ecuadorian university may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. Grades of 70% or higher can be considered as UK 2.1 equivalent. Applicants for PhD level study will preferably hold a Magister/Masterado or equivalent qualification, but holders of the Licenciado with excellent grades can be considered.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and a Masters degree, with a GPA of 3.0/4.0 or 75% from a recognised institution. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a good Bakalaurusekraad from a recognised university with a minimum overall grade of 4/5 or B, or a good one- or two-year Magistrikraad from a recognised university, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students who hold a Masters degree with very good grades (grade B, 3.5/4 GPA or 85%) will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Holders of a good Kandidaatti / Kandidat (old system), a professional title such as Ekonomi, Diplomi-insinööri, Arkkitehti, Lisensiaatti (in Medicine, Dentistry and Vetinary Medicine), or a Maisteri / Magister (new system), Lisensiaatti / Licenciat, Oikeustieteen Kandidaatti / Juris Kandidat (new system) or Proviisori / Provisor from a recognised Finnish Higher Education institution, with a minimum overall grade of 2/3 or 4/5, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters/Maîtrise with a minimum overall grade of 13 out of 20, or a Magistère / Diplôme d'Etudes Approfondies / Diplôme d'Etudes Supérieures Specialisées / Mastère Specialis, from a recognised French university or Grande École to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a Magister Artium, a Diplom or an Erstes Staatsexamen from a recognised university with a minimum overall grade of 2.5, or a good two-year Lizentiat / Aufbaustudium / Zweites Staatsexamen or a Masters degree from a recognised university, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students who hold a Bachelor degree from a recognised institution will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most taught Masters programmes require a minimum of an upper second class degree (2.1) with a minimum GPA of at least 3.0/4.0 or 3.5/5.0 Students who have completed a Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a good four-year Ptychio (Bachelor degree) with a minimum overall grade of 6.5 out of 10, from a recognised Greek university (AEI), and will usually be required to have completed a good Metaptychiako Diploma Eidikefsis (Masters degree) from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
4-year Licenciado is deemed equivalent to a UK bachelors degree. A score of 75 or higher from Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala (USAC) can be considered comparable to a UK 2.1, 60 is comparable to a UK 2.2. Private universities have a higher pass mark, so 80 or higher should be considered comparable to a UK 2.1, 70 is comparable to a UK 2.2
The Hong Kong Bachelor degree is considered comparable to British Bachelor degree standard. Students with bachelor degrees awarded by universities in Hong Kong may be considered for entry to one of our postgraduate degree programmes.
Students with Masters degrees may be considered for PhD study.
Holders of a good Alapfokozat / Alapképzés or Egyetemi Oklevel from a recognised university with a minimum overall grade of 3.5, or a good Mesterfokozat (Masters degree) or Egyetemi Doktor (university doctorate), will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree, with a 60% or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of the 4 year Sarjana (S1) from a recognised Indonesian institution will be considered for postgraduate study. Entry requirements vary with a minimum requirement of a GPA of 2.8.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and a Masters degree, with a score of 14/20 or 70% from a recognised institution to be considered. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree from a recognised institution, with 100 out of 110 or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Students who hold the Maitrise, Diplome d'Etude Approfondies, Diplome d'Etude Superieures or Diplome d'Etude Superieures Specialisees will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees (14-15/20 or Bien from a well ranked institution is considered comparable to a UK 2.1, while a score of 12-13/20 or Assez Bien is considered comparable to a UK 2.2).
Students with a Bachelor degree from a recognised university in Japan will be considered for entry to a postgraduate Masters degree provided they achieve a sufficiently high overall score in their first (Bachelor) degree. A GPA of 3.0/4.0 or a B average from a good Japanese university is usually considered equivalent to a UK 2:1.
Students with a Masters degree from a recognised university in Japan will be considered for PhD study. A high overall grade will be necessary to be considered.
Students who have completed their Specialist Diploma Мамаң дипломы/Диплом специалиста) or "Magistr" (Магистр дипломы/Диплом магистра) degree (completed after 1991) from a recognised higher education institution, with a minimum GPA of 2.67/4.00 for courses requiring a UK lower second and 3.00/4.00 for courses requiring a UK upper second class degree, will be considered for entry to postgraduate Masters degrees and, occasionally, directly for PhD degrees. Holders of a Bachelor "Bakalavr" degree (Бакалавр дипломы/Диплом бакалавра) from a recognised higher education institution, with a minimum GPA of 2.67/4.00 for courses requiring a UK lower second and 3.00/4.00 for courses requiring a UK upper second class degree, may also be considered for entry to taught postgraduate programmes.
Students who hold a Bachelor degree from a recognised institution will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most taught Masters programmes require a minimum of an upper second class degree (2.1) with a minimum GPA of at least 3.0/4.0 or 3.5/50
Holders of a good Postgraduate Diploma (professional programme) from a recognised university or institution of Higher Education, with a minimum overall grade of 7.5 out of 10, or a post-2000 Magistrs, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and a Masters degree, with a score of 16/20 or 80% from a recognised institution to be considered. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a Bachelors degree from a recognised university in Libya will be considered for postgraduate study. Holders of a Bachelors degree will normally be expected to have achieved score of 70% for 2:1 equivalency or 65% for 2:2 equivalency. Alternatively students will require a minimum of 3.0/4.0 or BB to be considered.
Holders of a good pre-2001 Magistras from a recognised university with a minimum overall grade of 8 out of 10, or a good post-2001 Magistras, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes
Holders of a good Bachelors degree from a recognised Luxembourgish Higher Education institution with a minimum overall grade of 16 out of 20, or a Diplôme d'Études Supérieures Spécialisées (comparable to a UK PGDip) or Masters degree from a recognised Luxembourgish Higher Education institution will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students who hold a Masters degree will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees (70-74% or A or Marginal Distinction from a well ranked institution is considered comparable to a UK 2.1, while a score of 60-69% or B or Bare Distinction/Credit is considered comparable to a UK 2.2).
Holders of a Bachelors degree from a recognised Malaysian institution (usually achieved with the equivalent of a second class upper or a grade point average minimum of 3.0) will be considered for postgraduate study at Diploma or Masters level.
Holders of a good Bachelors degree from the University of Malta with a minimum grade of 2:1 (Hons), and/or a Masters degree, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students who hold a Bachelor degree (Honours) from a recognised institution (including the University of Mauritius) will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most taught Masters programmes require a minimum of an upper second class degree (2:1).
Students who hold the Licenciado/Professional Titulo from a recognised Mexican university with a promedio of at least 8 will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Students who have completed a Maestria from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree, licence or Maîtrise and a Masters degree, with a score of 14/20 or 70% from a recognised institution to be considered. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Students with a good four year honours degree from a recognised university will be considered for postgraduate study at the University of Birmingham. PhD applications will be considered on an individual basis.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree, with 60-74% or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a good Doctoraal from a recognised Dutch university with a minimum overall grade of 7 out of 10, and/or a good Masters degree, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students who hold a Bachelor degree (minimum 4 years and/or level 400) from a recognised institution will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most taught Masters programmes require a minimum of an upper second class degree (2.1) with a minimum GPA of at least 3.0/4.0 or 3.5/5.0
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a good Bachelors degree from a recognised institution with a minimum GPA of B/Very Good or 1.6-2.5 for a 2.1 equivalency, and will usually be required to have completed a good Masters, Mastergrad, Magister. Artium, Sivilingeniør, Candidatus realium or Candidatus philologiae degree to be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree, with a CGPA of 3.0/4 or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a Bachelors degree from a recognised university in the Palestinian Territories will be considered for postgraduate study. Holders of Bachelors degree will normally be expected to have achieved a GPA of 3/4 or 80% for 2:1 equivalency or a GPA of 2.5/4 or 70% for 2:2 equivalency.
Holders of the Título de Licenciado /Título de (4-6 years) or an equivalent professional title from a recognised Paraguayan university may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. Grades of 4/5 or higher can be considered as UK 2.1 equivalent. The Título Intermedio is a 2-3 year degree and is equivalent to a HNC, it is not suitable for postgraduate entry but holders of this award could be considered for second year undergraduate entry or pre-Masters. Applicants for PhD level study will preferably hold a Título de Maestría / Magister or equivalent qualification, but holders of the Título/Grado de Licenciado/a with excellent grades can be considered.
Holders of the Licenciado, with at least 13/20 may be considered as UK 2.1 equivalent. The Grado de Bachiller is equivalent to an ordinary degree, so grades of 15+/20 are required. Applicants for PhD level study will preferably hold a Título de Maestría or equivalent qualification.
Holders of a good pre-2001 Magister from a recognised Polish university with a minimum overall grade of 4 out of 5, dobry ‘good’, and/or a good Swiadectwo Ukonczenia Studiów Podyplomowych (Certificate of Postgraduate Study) or post-2001 Magister from a recognised Polish university with a minimum overall grade of 4.5/4+ out of 5, dobry plus 'better than good', will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a good Licenciado from a recognised university, or a Diploma de Estudos Superiores Especializados (DESE) from a recognised Polytechnic Institution, with a minimum overall grade of 16 out of 20, and/or a good Mestrado / Mestre (Masters) from a recognised university, will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a good Bachelors degree from a recognised Romanian Higher Education institution with a minimum overall grade of 8 out of 10, and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree/Diploma de Master/Diploma de Studii Academice Postuniversitare (Postgraduate Diploma - Academic Studies) or Diploma de Studii Postuniversitare de Specializare (Postgraduate Diploma - Specialised Studies) to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a good Диплом Специалиста (Specialist Diploma) or Диплом Магистра (Magistr) degree from recognised universities in Russia (minimum GPA of 4.0) will be considered for entry to taught postgraduate programmes/PhD study.
Students who hold a 4-year Bachelor degree with at least 16/20 or 70% will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Students who hold a Maitrise, Diplome d'Etude Approfondies,Diplome d'Etude Superieures or Diplome d'Etude Superieures Specialisees will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. A score of 14-15/20 or Bien from a well ranked institution is considered comparable to a UK 2.1, while a score of 12-13/20 or Assez Bien is considered comparable to a UK 2.2
Students who hold a Bachelor (Honours) degree from a recognised institution with a minimum GPA of 3.0/4.0 or 3.5/5.0 (or a score of 60-69% or B+) from a well ranked institution will be considered for most our Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees with a 2:1 requirement.
Students holding a good Bachelors Honours degree will be considered for postgraduate study at Diploma or Masters level.
Holders of a good three-year Bakalár or pre-2002 Magister from a recognised Slovakian Higher Education institution with a minimum overall grade of 1.5, B, Vel’mi dobrý ‘very good’, and/or a good Inžinier or a post-2002 Magister from a recognised Slovakian Higher Education institution will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a good Diploma o pridobljeni univerzitetni izobrazbi (Bachelors degree), Diplomant (Professionally oriented first degree), Univerzitetni diplomant (Academically oriented first degree) or Visoko Obrazovanja (until 1999) from a recognised Slovenian Higher Education institution with a minimum overall grade of 8.0 out of 10, and/or a good Diploma specializacija (Postgraduate Diploma) or Magister (Masters) will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students who hold a Bachelor Honours degree (also known as Baccalaureus Honores / Baccalaureus Cum Honoribus) from a recognised institution will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most Masters programmes will require a second class upper (70%) or a distinction (75%).
Holders of a Masters degree will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a Bachelor degree from a recognised South Korean institution (usually with the equivalent of a second class upper or a grade point average 3.0/4.0 or 3.2/4.5) will be considered for Masters programmes.
Holders of a good Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study on an individual basis.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree, with 7 out of 10 or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and will usually be required to have completed a Masters degree, with 60-74% or a CGPA 3.30/4.0 or higher for 2:1 equivalency from a recognised institution to be considered for entry. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a good Kandidatexamen (Bachelors degree) or Yrkesexamen (Professional Bachelors degree) from a recognised Swedish Higher Education institution with the majority of subjects with a grade of VG (Val godkänd), and/or a good Magisterexamen (Masters degree), International Masters degree or Licentiatexamen (comparable to a UK Mphil), will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a good "PostGraduate Certificate" or "PostGraduate Diploma" or a Masters degree from a recognised Swiss higher education institution (with a minimum GPA of 5/6 or 8/10 or 2/5 (gut-bien-bene/good) for a 2.1 equivalence) may be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a Bachelors degree and a Masters degree, with a GPA of 3.0/4.0, 3.5/5 or 75% from a recognised institution to be considered. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
Holders of a good Bachelor degree (from 75% to 85% depending upon the university in Taiwan) from a recognised institution will be considered for postgraduate Masters study. Holders of a good Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study.
Students who hold a Bachelor degree from a recognised institution will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most taught Masters programmes require a minimum of an upper second class degree (2.1) Students who have completed a Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study.
Holders of a good Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for entry to our postgraduate research programmes.
Holders of a good Masters degree or Mphil from a recognised university will be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes.
Students with a Bachelors degree from the following universities may be considered for entry to postgraduate programmes:
- Ateneo de Manila University - Quezon City
- De La Salle University - Manila
- University of Santo Tomas
- University of the Philippines - Diliman
Students from all other institutions with a Bachelors and a Masters degree or relevant work experience may be considered for postgraduate programmes.
Grading Schemes
1-5 where 1 is the highest 2.1 = 1.75 2.2 = 2.25
Out of 4.0 where 4 is the highest 2.1 = 3.0 2.2 = 2.5
Letter grades and percentages 2.1 = B / 3.00 / 83% 2.2 = C+ / 2.5 / 77%
Holders of a postdoctoral qualification from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study. Students may be considered for PhD study if they have a Masters from one of the above listed universities.
Holders of a Lisans Diplomasi with a minimum grade point average (GPA) of 3.0/4.0 from a recognised university will be considered for postgraduate study at Diploma or Masters level.
Holders of a Yuksek Diplomasi from a recognised university will be considered for PhD study.
Students who hold a Bachelor degree from a recognised institution will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees. Most Masters programmes will require a second class upper (2.1) or GPA of 3.5/5.0
Applicants for postgraduate research programmes should hold a good Bachelors degree / Диплом бакалавра (Dyplom Bakalavra), Диплом спеціаліста (Specialist Diploma) or a Dyplom Magistra from a recognised Ukrainian higher education institution with a minimum GPA of 4.0/5.0, 3.5/4, 8/12 or 80% or higher for 2:1 equivalence and will usually be required to have completed a good Masters degree to be considered for entry to postgraduate research programmes. Applicants with lower grades than this may be considered on an individual basis.
The University will consider students who hold an Honours degree from a recognised institution in the USA with a GPA of:
- 2.8 GPA (on a 4.0 scale) for entry to programmes with a 2:2 requirement
- 3.2 GPA (on a 4.0 scale) for entry to programmes with a 2:1 requirement
Please note that some subjects which are studied at postgraduate level in the USA, eg. Medicine and Law, are traditionally studied at undergraduate level in the UK.
Holders of the Magistr Diplomi (Master's degree) or Diplomi (Specialist Diploma), awarded by prestigious universities, who have attained high grades in their studies will be considered for postgraduate study. Holders of the Fanlari Nomzodi (Candidate of Science), where appropriate, will be considered for PhD study.
Holders of the Licenciatura/Título or an equivalent professional title from a recognised Venezuelan university may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. Scales of 1-5, 1-10 and 1-20 are used, an overall score of 70% or equivalent can be considered equivalent to a UK 2.1. Applicants for PhD level study will preferably hold a Maestria or equivalent qualification
Holders of a Bachelors degree from a recognised Vietnamese institution (usually achieved with the equivalent of a second class upper or a grade point average minimum GPA of 7.0 and above) will be considered for postgraduate study at Diploma or Masters level. Holders of a Masters degree (thac si) will be considered for entry to PhD programmes.
Students who hold a Masters degree with a minimum GPA of 3.5/5.0 or a mark of 2.0/2.5 (A) will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Students who hold a good Bachelor Honours degree will be considered for Postgraduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
International Students
You can satisfy our English language requirements in two ways:
- by holding an English language qualification to the right level - IELTS 6.5 with no less than 6.0 in any band
- by taking and successfully completing one of our English courses for international students
Research within the School of Government is aligned to one of three departments and Institutes:
The Department of Political Science and International Studies (POLSIS)
Dr Columba Achilleos-Sarll Feminist and post/decolonial theory; the Women, Peace and Security agenda; civil society and advocacy; visual global politics.
Dr David Bailey Protest, critical political economy and contemporary capitalism
Dr Stephen Bates British politics; Parliamentary Studies (in comparative perspective or focused on the UK Parliament).
Dr Tendayi Bloom Noncitizenship; Statelessness; Migration governance.
Dr Verena K. Brändle Digital democracy; social media and politics; European politics; border and migration studies; political communication
Dr Sarah Bufkin Racism and racialization; Black Atlantic political thought; Critical Theory; Cultural Studies.
Professor Peter Burnham Restructuring of the state in the global political economy; State theory and radical theories of IPE; Marx and contemporary Marxism; Economic policy and capitalist crisis.
Dr Mwita Chacha Regional integration; International cooperation; Politics of coups d’état; Public opinion.
Dr Licia Cianetti Democracy and institutional change; democratic regression; inclusion and exclusion from policymaking processes; cities and local democracy.
Dr Laurence Cooley Politics of deeply divided societies (especially Northern Ireland and Bosnia and Herzegovina); post-conflict power-sharing; politics of the census and identity categorisation.
Professor David Cutts Political and electoral behaviour; Party campaigning turnout; Civic engagement; Populist parties; Social media and politics.
Dr May Darwich International Relations Theory and the Middle East; Foreign policies of Middle Eastern states; Identity politics in the Middle East; Security policies in the Middle East.
Professor David Dunn US foreign and security policy; Strategic and security studies, and diplomacy and statecraft.
Dr Rita Floyd Ethics of emergency politics, theories of security (especially securitization theory), the English school and environmental security.
Dr Guiditta Fontana Peace processes and war-to-peace transitions. The design of peace accords, Powersharing and Reform of cultural and educational institutions in conflict-affected societies. Multi-method research designs. Politics of Lebanon, Northern Ireland, North Macedonia.
Dr Emma Foster Environmental politics; gender/sexuality and international relations; gender/sexuality and international relations.
Dr Charlotte Galpin European and national identities; European public sphere and media; Euroscepticism, EU citizenship and social movements; The role of Germany or Britain in Europe; Brexit; Gender and feminist approaches to these topics.
Dr Julie Gilson Japanese foreign policy; East Asian regionalism and institutions; Asia-Europe and Japan-Europe relations; Civil society in Asia; Climate change and environmentalism in Asia.
Dr Ruben Gonzalez-Vicente South-South relations; Global China; the political economy of development, especially in Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean; critical political economy; political geography.
Dr Tim Haughton Contemporary politics of Central and Eastern Europe; Political campaigning; Party politics; Electoral politics.
Dr Laura Jenkins Feminist political theory; Contemporary political theory and British politics.
Dr Deema Kaneff Resources and Social Change; Postsocialist transformations and global capitalism; Property relations; Markets and moralities; Transnational migration, Social exclusion and inequalities. (Europe, Eastern Europe, Bulgaria and Ukraine)
Dr Peter Kerr British politics; State theory and theories of social and political change; UK party politics and party modernisation; Political leadership and governing strategies in the UK; Citizenship and political participation and political sociology.
Dr George Kyris International conflict, conflict management and resolution; International organisations, especially the European Union; State recognition; Statehood and sovereignty; Secession; unrecognised/ de facto states.
Professor René Lindstädt American Politics; Political Institutions; Accountability; Representation; Legislative politics and institutions; Elections; Political methodology
Dr Huw Macartney International or Comparative Political Economy; Banking and financial market governance; Globalisation, and historical materialism.
Dr Cerwyn Moore Political violence; international relations theory; Post-Soviet and post-communist security; Interpretive approaches to global politics and Chechnya.
Dr Richard North Any area of contemporary political philosophy, but particularly on justice and liberal and democratic political philosophy.
Dr Julian Panke European Union Politics; European Neighbourhood Policy; German foreign policy and Eastern European foreign policies (Poland, Slovakia).
Professor Patrick Porter The interaction of power and ideas in the making of foreign and defence policy in the U.S. and U.K, and in shaping their conflicts, classical realism, strategic thought and great power diplomacy.
Dr Adam Quinn US ‘grand strategy’; American national identity; American foreign and security policy; Ideological contest in American politics (contemporary and historical).
Dr Robert Ralston International Security; Civil-Military Relations; Grand Strategy.
Dr Richard Shorten Political theory, ideology, and rhetoric; fascism, Marxism and totalitarianism; reactionaries and conservatives; the political thought of Hannah Arendt, Albert Camus and George Orwell; intellectual politics of the Cold War.
Dr Asaf Siniver International mediation and conflict resolution; The politics, diplomacy and history of the Arab-Israeli conflict; The Israeli-Palestinian peace process; Contemporary US foreign policy and Foreign Policy Analysis.
Dr Nicola Smith Gender and sexuality; Feminist political economy; Queer theory; Biopolitics; Body politics; Sex Work; Obesity; Austerity.
Dr Graham Timmins Areas related to the external relations and foreign policy role of the European Union with specific reference to EU-Russia and German-Russian relations.
Dr Tsering Topgyal Chinese foreign and security policy; Tibet and China’s Nationality Policy; Asia-Pacific security and politics; US-China relations; Sino-Indian relations and Security studies.
Dr Sevasti-Eleni Vezirgiannidou International Environmental Politics; Climate change politics; Environment and trade negotiations; Environmental Regime effectiveness and compliance and The trade-environment debate.
Dr Marco Vieira Rising powers and global order; South-South political cooperation/identity/institutions, South American/Latin American politics; Brazilian foreign policy and International relations theory.
Dr Yi Wang Memory politics; Nationalism and national identity; Contemporary China; International relations of East Asia; Political communication
Dr Robert Watt Military History, power and networks, Small Wars/Insurgencies; Native American History & Politics.
Professor Mark Webber NATO; transatlantic relations; European security; American, Russian and British foreign policy; Theories and practices of security
Dr Mark Wenman Continental philosophy; Contemporary political theory; The philosophy of the social sciences; The history of political thought.
Professor Nicholas Wheeler Trust-building between adversaries, especially nuclear armed states; Nuclear weapons and proliferation.
Professor Kataryna Wolczuk Politics of Russia and post-Soviet countries; EU’s Eastern policy, Russia’s policy towards the post-Soviet states; Regional integration in the post-Soviet space; Nationalism and national identities (across Europe and Eurasia).
Professor Stefan Wolff - Ethnic conflict, civil war, post-conflict state-building; Geopolitics and great-power rivalry; Central Asia, South Caucasus, Eastern Europe, Western Balkans, Middle East & North Africa.
Dr Christalla Yakinthou Conflict transformation, particularly post-settlement; Transitional justice both in theory and practice, and transitions in the MENA region; The relationship between constitutional design and transitional justice; Power sharing, Cypriot, Lebanese, and Tunisian politics and conflicts and the right to truth in international law and practice, and issues around enforced disappearance and missing people during conflict.
Dr Sotirios Zartaloudis European Union politics and policies; Migration in Europe; European politics; Discourse
The International Development Department (IDD)
Dr Sameen A. Mohsin Ali Bureaucratic politics; politics of development, donor engagement, and public sector reform; public health, especially with regard to vaccination; politics of South Asia (especially Pakistan)
Dr Philip Amis Urbanisation; Urban policy; Poverty and housing.
Not currently accepting new PhD supervision applications
Dr Danielle Beswick UK development policy, including parliamentary scrutiny and public engagement in this; UK Africa relations; The UK Conservative Party and development; Politics, identity and security in Sub-Saharan Africa, particularly Rwanda; Knowledge exchange between universities and legislatures.
Dr Brock Bersaglio The political ecology of biodiversity conservation, wild meat (including food sovereignty), and zoonotic disease in eastern/southern Africa; anti-, post- and settler colonial development studies
Dr Adrian Campbell Public and local government reform, especially in transitional states.
Professor Nic Cheeseman Elections and democratization; The formation of a social contract in new democracies; Power-sharing and the politics of inclusion; Populism and strategies of political mobilization; African political thought.
Dr David Cobley Disability-inclusive approaches to development, especially in the areas of poverty reduction, livelihood development, inclusive education and disaster risk reduction.
Dr Niheer Dasandi Politics of international development and foreign aid; development and human rights; politics of climate change and health; foreign policy and development
Dr Jonathan Fisher Authoritarianism and authoritarian rule; (in)security and conflict; international politics of aid and peacekeeping; particular interest in sub-Saharan Africa.
Professor David Hudson Politics of leadership and coalitions; public opinion, survey analysis, and experiments; migration decision making; network analysis.
Professor Paul Jackson Conflict and post-conflict reconstruction; security sector reform and international intervention; combatants, politics and social reintegration; peacebuilding; economic development.
Dr Chris Lyon Politics of development; political theory; democracy, participation, decentralisation; social justice; development ethics
Professor Heather Marquette The politics of development and foreign policy; Corruption, kleptocracy and organised crime; Anti-corruption/counter-organised crime strategies and interventions
Dr Claire McLoughlin State legitimacy; The politics of public service delivery; The role of ideas in development.
Dr Emeka Njoku Critical security studies; Terrorism and counter-terrorism; Nonprofit organisations; conflict-related gender/sexual violence; State-civil society relations; peacebuilding.
Professor Fiona Nunan Renewable natural resource governance, management and livelihoods in low- and middle-income countries, especially fisheries and coastal ecosystems and community-based or collaborative governance.
Dr Martin Ottmann Political economy of civil war and development, including peace processes and negotiated settlements; Power-sharing, resource redistribution, elections, and political trust after war. PhD applications relying on advanced statistical research methods, mixed-methods designs, and modern methods of causal inference are particularly welcome.
Dr Emily Scott Humanitarianism, health, and migration; international organisation (IOs) and international non-governmental organisations (INGOs); state-society relations, particularly in the Middle East; conflict and security; localization and the international politics of aid.
Dr Merisa Thompson Feminist political economy; food and agrarian studies; the politics of gender and development; histories of colonialism, particularly the Caribbean.
Dr Kailing Xie Contemporary Chinese society, Gender and reproductive politics, the politics of nation-building; Civil Society; governance beyond the state; collective memory and emotions; Chinese diaspora;feminist epistemologies and methodologies.
Department of Public Administration and Policy (DPAP)
Dr Koen Bartels Social innovation; Democratic innovation; Public encounters; Urban governance; Action research; Interpretive policy analysis; Communication; Practice theory; Relational public policy and administration.
Dr Karin Bottom The role of small parties; Comparative politics; Policy analysis; Elections and quantitative methodologies.
Dr May Chu Risk regulation; Collaborative governance; Food safety and sustainability
Dr Abena Dadze-Arthur Transfer and brokering of knowledge across cultural and institutional boundaries. Decolonizing, transforming, and indigenising approaches to public management and governance. The scientific study of subjectivity (Q Methodology)
Dr Stephen Jeffares Projects that draw on social media data to understand change or controversies in public policy.
Dr Timea Nochta Networks in governance and policy; Complexity; Smart cities, digitalisation and e-government; Climate change and net zero; Network analysis; Mixed methods
Dr Louise Reardon Multi-level governance; Policy networks; Agenda setting; Policy change; Policy implementation; Transport policy; Wellbeing and quality of life; Smart cities.
Dr Philip Whiteman Policy implementation studies; Central and local government relations; Regulation of local government; Local authority corporate management scrutiny; Public sector performance, procurement and efficiency; Public consultation and participation; Organisation dynamics.
You will meet your supervisor approximately fortnightly (monthly for part-time students) over the course of your study. Supervisors are experienced in managing the research process and are chosen to complement your area of interest. You will discuss your research with a panel every six months (part-time: every 12 months). The panel is chaired by an experienced researcher from the department, and includes your supervisor and another member of staff. It provides an important opportunity to present progress on your research and to have a wider discussion about your work.
Your supervisor will read and comment on drafts of your thesis before it is finally submitted. An external and an internal examiner (who will not be your supervisor) will then examine it, and will normally meet with you for a viva. They will judge whether your thesis demonstrates:
- Knowledge of the relevant academic literature
- Skill in use of research methods
- Independent investigation
- Clear presentation of information
- Arguments presented in a coherent and appropriate form
MPhil students must show original work of merit that is worthy of publication. The requirement for PhDs is that the work is an original contribution to knowledge that is worthy of publication.
Departments from across the School of Government are all based within the Muirhead Tower on the University of Birmingham campus. Muirhead Tower offers state-of-the-art teaching and research study facilities including free wifi throughout the building and dedicated study areas for postgraduate research students.
The space has been designed to create modern, attractive spaces for teaching and research accommodating 150 academic offices, 230 "hubs" for post graduate research students, teaching rooms for up to 100 people and a 200 seat lecture theatre.
If I gain a postgraduate research degree in Local Government Studies, what are my career prospects?
In addition to the academic knowledge gained through their course, postgraduates from the Department of Public Administration and Policy develop transferable skills that are useful in many occupations. These include familiarity with research methods; the ability to manage large and diverse quantities of information; the ability to organise information in a logical and coherent manner; judging and evaluating complex information; and making reasoned arguments, both orally and in written work.
Graduates are attracted to careers in both public and private sectors. These include local government, policing, health services, transport, legal services, prison services and housing. Some of these careers require further professional training, and/or building a portfolio of relevant work experience. Many PhD graduates also successfully gain academic research and teaching posts.
What type of career assistance is available to doctoral researchers in this department?
The College of Social Sciences, to which the Department of Public Administration and Policy belongs, has specially designated careers advisors and careers consultants who can provide guidance for doctoral researchers on career paths, CVs, training opportunities, application and interviews. The University’s central Careers’ Service also runs workshops and offers personally tailored advice and guidance including 1-1 careers advice, 1-1 CV advice. The Career’s Service also runs CV writing workshops especially for postgraduates in the College of Social Sciences, giving advice on how to compile CVs for both employment and for academic roles.
The University also has dedicated careers advisors for International students who run workshops and networking opportunities with potential employers. These are especially popular with International postgraduate researchers.
- Online chat events
View the latest institution tables
View the latest country/territory tables
8 big differences between the US and UK PhD experience
And one important similarity.
Helen Robertson

Credit: Malte Mueller/Getty
And one important similarity.
11 March 2020

Malte Mueller/Getty
In 2019, I took a risk by moving halfway around the world as a postdoctoral researcher in molecular evolution.
Since then, I’ve been struck by how different the grad school experience is here at the University of Chicago in the US, compared with my time at the University College London in the UK, where I completed my PhD in 2017.
Here’s what I’ve noticed:
1. UK grad school interviews are shorter and more lab-specific
In the UK, you’re likely to apply directly to a lab for an advertised project or one that you develop with your supervisor.
In the US, the application process is more centralized. You usually apply to a school instead of a lab. Some programs even require you to take a standardized Graduate Entry Program test, though this seems to be on the decline .
Grad school interviews in the US tend to be longer. They can involve a series of interviews, tours, and faculty events over a number of days.
2. In the US, a work-life balance is harder to achieve
I’ve been surprised by how all-encompassing a US doctorate can be. Even after the first year of teaching, the number of seminars, journal clubs, and university-related activities make the US PhD experience very grad school-centric.
I was fortunate during my UK-based PhD to approach it more like a full-time job than a continuation of my masters year. There were intense periods that required late nights in the lab, but I had time to pursue other interests , which provided some balance and made me more productive at work.
Of course, it’s difficult to generalize about working patterns. Demanding schedules are not wholly dictated by the country you’re studying in. A recent study found that 76% of surveyed grad students spent more than 41 hours a week on their project.
3. It takes longer to complete a PhD in the US
Probably the best-known difference is the time it takes to complete a PhD.
UK PhD programs tend towards three years in length, although it’s increasingly getting closer to four years – a trend that might soon be reflected in funding arrangements .
It’s a different story in the US, where, according to the Survey of Earned Doctorates , students take an average of 5.7 years to graduate.
4. UK PhD fees tend to be lower
Fees err on the more expensive side in the US, as they do for undergraduate degrees – although this isn’t always true for international students.
US PhD fees, coupled with the longer study time, means that the costs associated with grad school are generally higher than in the UK, even before living costs are considered.
If you have a funding body attached to your project, it will likely pay your tuition fees as part of its finance package. But this flags a major difference between the two countries: funding and scholarships.
5. Many US students need to apply for their own funding
From my understanding, most advertised science-based PhD projects in the UK are attached to funding, which covers tuition fees, bench costs, and living expenses. The tax-free PhD stipend set by all UK Research Councils is £15,285 (approximately US$20,000), although other funding bodies pay more.
In the US, there is no national funding level – your level of financial support will be dictated by your school or lab. This means there is generally much more encouragement for US PhD students to apply for their own funding than there is in the UK.
This is good experience for a future scientific career, but if you have to work additional hours to supplement scholarships, you’ll ultimately end up with less time for your project.
6. US PhD programs are more structured
This is particularly true in the first year for US PhDs, which includes lectures, exams, and lab rotations. Only at the end of the first year, after passing your qualifying exam, do you have the opportunity to pick the lab you’re going to pursue your PhD research in.
In the UK, I started in the lab that I spent the duration of my studies in. This meant no structured classes or rotations in my first year, and I began my own research right away.
PhDs that are run through a Doctoral Training Centre (DTC) – centres that manage the Research Council-funded PhD degrees – are increasingly popular in the UK, and include classes and rotations during the first year, but often without the frequent exams and coursework that characterize grad school in the US.
7. There is more focus on defending your thesis in the UK
Writing my thesis was the final hurdle of my UK PhD experience. It gave me the opportunity to document my ideas, successes (and failures), and the context of my project. I defended my thesis in a closed session with two examiners: one internal to my institution, and one external.
From what I’ve seen, finishing a doctorate in the US is less focused on a thesis. Instead, your committee determines that you have completed sufficient work and skill attainment to warrant your defense. Only then can you write your thesis, and defend it in a public session.
In the UK, it’s unlikely you’ll know your examiners well, but a US PhD defense is assessed by the same thesis committee that have known you for the duration of your studies.
8. Teaching is an added bonus in the UK
My UK PhD funding set no teaching requirements: instead, I was free to teach labs and mark coursework at the discretion of my supervisor. And I was paid for any teaching hours I did.
Teaching requirements in the US vary from school to school. For some students, working as a teaching assistant is necessary to pay fees and living expenses – particularly if you don’t have comprehensive funding.
There might also be minimum teaching requirements for the duration of your PhD in the US. In this respect, the time commitment and financial compensation of teaching is very institution-specific.
One important similarity: The lab you join will determine your experience
Despite the differences in structure and requirements between UK and US PhDs, one thing that is common to them all is that, ultimately, your PhD is going to be shaped by the lab you decide to join.
If have a positive working environment and appropriate guidance and support from your supervisor, and you’re interested in and motivated by your thesis topic, then your grad school experience will likely be rewarding.
And that’s true regardless of the country you’re studying in.
- Enquire Now
- SI-UK Hong Kong
- SI-UK London
- All Global Offices
- Find Your UK University Course
- Free Service
- Premium Service
- Oxbridge Service
- Medicine Service
- View all Services
- UCAS and Applying
- UK University Rankings
- University Subject Guide
- Scholarships and Funding
- All UK Study Information
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- All Study Options
- UK University Profiles
- UK University Blog
- Study IELTS
- IELTS About
- University News
- Open Days and Events
Updates for International Students UK universities are offering international students financial support worth up to £1,750 to help them cover hotel quarantine costs, meaning no further charges will be incurred when travelling to study in the UK this Autumn. Stay up to date with the latest Studying in the UK and Coronavirus (COVID-19) information.
Connect with one of our team who can help with your September 2021 application and answer any questions you may have about quarantine and finance options. Enquire Now Close
Connect with one of our team who can help with your September 2021 application and answer any questions you may have about quarantine and finance options.
Enquire Now Close

- Study Options in the UK
- PhD and Research Degrees
PhD Study in the UK
What is a phd.
A PhD is a research degree and is the highest award available at universities in the UK. Study is based around a substantial research project on an area of academic interest, typically up to 100,000 words in length, written as a thesis which then must be defended in an oral examination in front of a panel of experts. Students are assigned a supervisor and the duration of a PhD is typically three years full-time and six years part-time.
Very few research degrees feature taught modules, and as such a student is expected to take more responsibility for their work and schedule.
PhD Entry Requirements
UK universities are free to admit anyone to a PhD programme, with admission generally conditional on the prospective student having successfully completed an undergraduate degree with at least upper second-class honours, as well as a masters degree . English language ability will need to be proved and a minimum IELTS score of 7.0 is generally required.
PhD Research Proposal
A research proposal ( example ) is required by all students when applying to study a PhD. The proposal should clearly address the research you wish to undertake, how you will do it, and why it is important. The proposal must be accepted by a panel of experts before your programme can begin.
Other types of Research Degree
- mphil (master of philosophy).
If you wish to study a PhD, you may first need to begin an MPhil and then transfer to a PhD programme after 12-18 months. An MPhil is also a qualification in its own right and is generally thesis-only, lasting one year full-time and two years part-time. The thesis must present the results of a study and research and be a maximum of 60,000 words.
Students choose to study an MPhil if the proposed research has insufficient scope for a full PhD.
- MRes (Master of Research)
An MRes is an advanced postgraduate research degree within the areas of art, humanities and social sciences. Some PhDs require an MRes qualification before beginning a PhD proper, and the student is required to complete a 40,000 word dissertation.
An MRes is a good test to see if you enjoy conducting your research without fully committing to and funding a full PhD.
- Professional Doctorate
Professional doctorates are similar to a PhD, but are intended to advance professional practice, rather than improve academic ability. Common professional doctorates include law, education, business, engineering and medicine.
How much does a PhD cost?
Funding and researching a PhD can be expensive, with EU students paying up to £6,000 per year, and international students more.
It is rare for a PhD student to not be supported by some form of bursary, grant or scholarship though, and many universities and research councils provide monetary support for part or all of a PhD programme.
How do I apply for a PhD?
Once you have decided on an area of research and have looked into how you will fund your study, there are a number of documents required when submitting your application. They can include:
- Academic transcripts
- Academic references
- Personal statement
- Research proposal ( example )
Students will also need to identify a supervisor who will oversee their PhD.
Study a PhD in the UK
If you are interested in studying a research degree in the UK, arrange a free consultation in Hong Kong today. The PhD Service can also help you apply with expert application advice, interview practice and research proposal editing.
Your Bookmarks
View all Bookmarks
Cẩm nang du học
20 july 2023, 5 june 2023, 7 june 2022, 1 june 2022, 26 may 2022, 18 may 2022, 11 may 2022, 28 april 2022, 21 april 2022, 13 april 2022, 5 april 2022, 12 march 2022, 29 november 2021, 4 november 2021, 18 october 2021, 6 october 2021, studying in the uk, study at ucl, five reasons to study at ucl.
- UCL Graduate Programme Guide for Hong Kong Students
Business and Management
Top five universities in the uk to study business.
- Five Reasons to Study an MBA in the UK
UK University Courses
Study engineering in the uk.
- Physiotherapy vs Occupational Therapy
- Ten Reasons to Study in the UK
- Top 10 Most Popular UK Degrees for International Students
SI-UK's service is fast, reliable and efficient - their consultants are specialists, working closely with all UK universities; through my consultants' advice, and application assistance I was able to get offers from top ranked universities. Carla Termini King's College London, Accounting and Finance
Leading Universities and SI-UK Partners

- © 2024 SI-UK
- All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy

Please select a country
The americas.
- United States
- United Kingdom
Middle East and Central Asia
- Saudi Arabia
Asia Pacific
- Philippines
92 Global offices in 40 countries
Book your free consultation.
We will be in touch within 24 hours to arrange your initial consultation at your nearest SI-UK office. If you are unable to visit us in person, consultations can also be arranged over Skype.
Scholarships and funding
Would you like to turn your dream of studying in the uk into a reality.
Deciding to study in the UK is an investment in your future. A prestigious degree from the UK is a valuable and transformative experience and will take your education - and your employability - to the next level.
There are many funding options available for international students who want to study in the UK. They range from part-funding, for example paying part of your fees, to full-funding which covers programme fees, living expenses, and return flights to the UK.
You can search for the right scholarship for you on the course and scholarships finder below.
Postgraduate funding
The UK government runs a variety of scholarship programmes to financially support international students who are looking for help funding their studies in the UK.
The three main UK government scholarships on offer are:
GREAT Scholarships
GREAT Scholarships are scholarships to UK universities across a variety of subjects, for students from 15 countries. Applications for 2024-25 are open.
Chevening Scholarships
Chevening Scholarships offers fully funded master's degrees in the UK. Learn more about one of the UK's most prestigious scholarships.
Commonwealth Scholarships
Commonwealth Scholarships are UK university scholarships given to talented individuals with the potential to make a positive impact on the global stage.
Wider UK government funding
The UK government offers hundreds of scholarships, bursaries and additional financial support to students from a large number of countries.
You can visit the UK Council for International Student Affairs (UKCISA) website to find out more about the funding available if you are studying in the UK as a postgraduate student, including whether or not you are eligible to apply for a scholarship. Just scroll down to the relevant section of the webpage.
UKCISA is the UK’s national advisory body serving the interests of international students and those who work with them.
Hear from international scholars What's involved in receiving a UK scholarship?
Tips for choosing a scholarship, international scholars in the uk.
Thinking of applying for a scholarship? Here are some top tips from international students who have received a scholarship to study in the UK.
GREAT scholarships
Nadine, university of kent.
What are GREAT scholarships and who is eligible? Watch as Nadine, a GREAT scholar, and Maria from the University of Kent explain everything you need to know.
Commonwealth scholarships
Commonwealth scholars.
Are you a high-achieving student living in the Commonwealth? Watch as scholars Suahib and Hamna explain all you need to know about Commonwealth scholarships.
Chevening scholarships
Chevening scholars.
If you have a vision to make the world a better place, the Chevening scholarships might be for you. Watch to learn more about the programme.
Being a GREAT scholar
Ismet, university of essex.
Ismet tells us about receiving his GREAT Scholarship for Sustainable Futures, and why he chose the University of Essex.
Being a Commonwealth scholar
Olaoluwa, nigeria.
Olaoluwa has received a Commonwealth shared scholarship. See her impressions on studying in the UK and receiving this life-changing scholarship.
Postgraduate studentships
Many universities offer fully-funded postgraduate studentships for PhD programmes. Find out more .
Institution-specific scholarships
Many UK higher-education institutions offer their own scholarship programmes.
These are offered based on a number of factors, which can be broadly split out into the following categories:
- Academic, merit and excellence scholarships - These are usually awarded to students with a strong academic background, including achieving strong grades in their school exams.
- Performance-based scholarships - These are usually awarded to those who have exceptional ability in an extracurricular activity such as sports, music or performing arts like drama or dance.
- Subject-specific scholarships - These are often offered by individual departments for students studying a particular course or subject.
- Equal access or sanctuary scholarships - These scholarships can take the form of a tuition fee reduction or waiver or maintenance award and are offered to refugees and asylum seekers who have fled persecution from their home countries.
- Disability scholarships - These scholarships support international students with a disability, long-term mental health condition, learning difficulty or other special needs.
Always check out different institutions’ websites to discover what is available, and take a look at specialist websites like Postgraduate Studentships and Prospects for curated information that covers different institutions.
Application advice Six top tips on applying for a scholarship
Read our essential advice on how to apply for a scholarship, from eligibility criteria to tailoring your application.
Global scholarships
A.S. Hornby Trust Scholarship
Scholarships for English language teachers to develop their English language skills
Selected countries - see website >
Commonwealth Scholarship and Fellowship Plan
Master's and doctoral courses (for study in the UK and distance learning), plus academic, professional and medical fellowships
Commonwealth countries >
Scholarships for one-year master's courses across a range of subjects at a variety of UK universities.
British Council scholarships for women in STEM
Scholarships for women undertaking master's degrees in a science, technology, engineering or mathematics course at one of 19 UK universities.
Americas, South Asia and South East Asia >
Global Wales Scholarships for International Students
Global Wales offers a variety of scholarship opportunities for international students.
USA; India; Vietnam and EU countries >
Country-specific scholarships
Young Cell Scheme
Postgraduate master's studies in the EU
Kosovo - see website >
Charles Wallace Pakistan Trust Scholarships
Doctoral studies, research, visiting fellows and Scottish summer school
Pakistan - see website >
Marshall Scholarship
Master's and doctoral courses at any university in the UK
USA - see website >
Science and research funding
Marshall Sherfield Fellowships
Post-doctoral research in science and engineering at any university in the UK
Euraxess UK
Research placements in the UK
Global - see website >
Royal Society grants
Postdoctoral science research
Undergraduate funding
While undergraduate scholarships and bursaries for EU and international students studying in the UK are less common than they are for postgraduate studies, they do exist. You just need to know where to look for them.
Funding for EU and international undergraduate students in the UK can generally be split into two categories: those offered by UK universities themselves and those offered by third parties - usually governments or organisations in your home country.
You can visit the UK Council for International Student Affairs (UKCISA) website to find out more about the funding available if you are studying in the UK as an undergraduate student, including whether or not you are eligible to apply for a scholarship. Just scroll down to the relevant section of the webpage.
You can also visit the Universities and Colleges Admissions Service in the UK (UCAS)’s page about scholarships, grants, and bursaries: EU and international students for more detailed information on what to look out for and where.
Cost of studying in the UK
Studying in the UK is good value for money. Find out how much you can expect to pay to study and live in the UK, and how to make the most of your budget.
Sign up to our newsletter
Get the latest updates and advice on applications, scholarships, visas and events.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Inflation in UK shops drops to lowest level in two years
Retailers cut the price of Easter treats, clothing and electrical items as consumer spending slowed
Inflation in shop prices in the UK has eased to the lowest level for more than two years after retailers cut prices on Easter treats, clothing and electrical goods amid a slowdown in spending by consumers in the cost of living crisis.
Industry figures show prices rose at an annual rate of 1.3% in March, down from a rate of 2.5% in February – the slowest pace since December 2021, according to the latest monitor from the British Retail Consortium (BRC) trade body and the market research firm NielsenIQ.
Non-food inflation dived to just 0.2% from 1.3% in the previous month, while food inflation fell to 3.7% from 5%.
The figures come amid growing hopes that the worst of the toughest increase in inflation for 40 years has passed, with anticipation that the Bank of England could begin cutting interest rates within months to ease pressure on households.
Helen Dickinson, the chief executive of the BRC, said inflation had fallen back amid fierce competition between retailers to entice consumer spending, as hard-pressed households cut back to make ends meet.
“While Easter treats were more expensive than in previous years due to high global cocoa and sugar prices, retailers provided cracking deals on popular chocolates, which led to price falls compared to the previous month,” she said.
“Dairy prices also fell on the month as farm gate prices eased, and retailers worked hard to lower prices for many essentials. In non-food, prices of electricals, clothing and footwear fell as retailers increased promotions to entice consumer spending.”
Competition has stepped up as households continue to rein in spending on non-essentials amid high energy bills and food costs as well as increases in mortgages and rents as a result of higher interest rates.
The advisory firm BDO’s regular survey of mid-sized retailers, many of which are fashion chains, found shoppers spent about 2% less in equivalent stores in the week to 24 March compared with the same week a year before, with homewares and fashion hit particularly hard. In-store sales were poor despite more people visiting shopping destinations, where footfall was up by about 2%.
Mike Watkins, the head of retailer insight at NielsenIQ, said that a key driver of easing inflation was weaker growth in food prices : “A year ago, food inflation was 15% so this was to be expected. But it is also helped by intense competition among the supermarkets as they look to drive footfall, with focused price cuts and promotional offers earlier in the month for Mother’s Day and now again in the weeks leading up to Easter.”
The fall in shop prices will increase hopes that overall inflation is dropping closer to the Bank of England target of 2%. The Bank is forecasting that headline inflation as measured by the consumer prices index will fall below that level in April.
However, a drop in the rate of inflation does not mean the overall cost of living will fall – prices will continue to rise but at a slower pace than over the past year.
Financial markets expect Threadneedle Street to begin cutting rates from the current level of 5.25% from as early as May or June. Such a development would be seized on by Rishi Sunak, the prime minister, as evidence of progress in the economy as the Conservatives battle to overturn a commanding Labour lead in opinion polls.
However, Dickinson warned that increases in the legal minimum wage and business rates for many firms, combined with additional Brexit-related border checks and new recycling plans “could put progress on bringing down inflation at risk”.
These costs include a 6.7% business rates rise, recycling proposals and new border checks. The national living wage also increased from Monday from £10.42 an hour to £11.44 an hour , the largest funding increase for more than a decade.
“The industry needs pro-growth government policy that supports investment and helps keep down prices for households up and down the country,” she said.
- UK cost of living crisis
- Shops and shopping

UK food price inflation slows to 4.5% but many shoppers still struggling

UK inflation: which goods and services have changed most in price?

The fight against UK inflation is being won – but when will interest rates be cut?

UK inflation falls to 3.4% in February as food price rises slow

Bank of England governor dampens hopes of interest rate cut

UK households face battle to regain former living standards even if inflation eases

Central banks must beat inflation before cutting interest rates, says OECD

Paying more for less: Which? lays bare size of ‘shrinkflation’ and ‘skimpflation’

UK inflation unexpectedly rises as cost of tobacco and alcohol increases
Most viewed.
Helldivers 2 level cap explained and all titles
In Helldivers 2, you can unlock new titles to show off your rank as you work towards the level cap
The Helldivers 2 level cap has been increased substantially, letting you up your level with XP and unlock new titles to show off your rank. From a lowly Cadet, you can work your way up the Helldivers 2 ranks to Death Captain, and Skull Admiral, but now you can go beyond to Admirable Admiral and 10-star General before capping out at the illustrious… Super Private. Demoting yourself to one of the lowest ranks after reaching General to keep fighting? Now that's a fine Super Earth soldier. Here are all the details on the Helldivers 2 level cap and all the titles you can get as you level up.
New Helldivers 2 level cap

After an update on April 2, the new Helldivers 2 level cap is 150 , tripling the previous cap of 50. Unfortunately, an increase to the level cap is actually quite meaningless as all Stratagems – the only things locked behind level requirements – are unlocked by level 25, with Helldivers 2 Mechs being the final one to get (for now). However, Arrowhead has added 10 new and ridiculous titles for the extra 100 levels.
All Helldivers 2 titles

Helldivers 2 beginner's guide Helldivers 2 tips Helldivers 2 Gunships Helldivers 2 Shriekers Helldivers 2 Major Orders
There are 21 titles for you to unlock in Helldivers 2 by earning XP to increase your level. All of them are unlocked automatically as soon as you reach the required level. You can choose a title to display on your player card by visiting your Destroyer's Armory, navigating to the 'Character' tab, then selecting 'Title', presenting a list of all the ones you have unlocked. If you want to know what title is up next for you, or what the new Helldivers 2 titles are, here's a quick list of them all, along with the level you unlock them at:
- Cadet – 1
- Space Cadet – 5
- Sergeant – 10
- Master Sergeant – 15
- Chief – 20
- Space Chief Prime – 25
- Death Captain – 30
- Marshall – 35
- Star Marshall – 40
- Admiral – 45
- Skull Admiral – 50
- Fleet Admiral – 60
- Admirable Admiral – 70
- Commander – 80
- Galactic Commander – 90
- Hell Commander – 100
- General – 110
- 5-Star General – 120
- 10-Star General – 130
- Private – 140
- Super Private – 150
Of course, there's also the Super Citizen title, but the only way you can get this is if you buy the Super Citizen edition of Helldivers 2 or the Super Citizen upgrade pack if you already own the game.
© GamesRadar+. Not to be reproduced without permission.
Sign up to the GamesRadar+ Newsletter
Weekly digests, tales from the communities you love, and more

Will Sawyer is a guides writer at GamesRadar+ who works with the rest of the guides team to give readers great information and advice on the best items, how to complete a particular challenge, or where to go in some of the biggest video games. Will joined the GameRadar+ team in August 2021 and has written about service titles, including Fortnite, Destiny 2, and Warzone, as well as some of the biggest releases like Halo Infinite, Elden Ring, and God of War Ragnarok.
New space RPG from Mass Effect veteran takes a hard sci-fi approach to FTL travel, and that means there's nothing that can save you from the ravages of time
The Suicide Squad battle pass can be smashed through in just 17 hours - as long as you skip all the missions and murder hordes of giant red spiders
Rediscovering the 25-year-old console JRPG whose jaw-dropping CGI cutscenes I once considered the indisputable pinnacle of video game graphics
Most Popular
By Joel Franey 2 April 2024
By Ben Wilson 29 March 2024
By Will Sawyer 28 March 2024
By Iain Wilson 28 March 2024
By Grace Dean 28 March 2024
By Joel Franey 28 March 2024
By Will Sawyer 27 March 2024
Watch CBS News
Many allergy sufferers rely on pollen counts to avoid the worst, but science may offer a better solution
By Ian Lee , Tina Kraus
Updated on: April 3, 2024 / 9:55 AM EDT / CBS News
London — Spring is in the air, and so is misery for millions of seasonal allergy sufferers . Stopping to smell the flowers can lead to sneezing, watery eyes or worse for Londoner Alex Hill.
"It's like stuffy nose, sinus headaches, like nosebleeds," he told CBS News as he walked his dog Roxie through a park in the British capital.
But scientists in the U.K. say they've found a better way to measure exactly what makes people like Hill miserable, and they're hoping it can lead to more useful advice than the currently available pollen counts.
Researchers at King's College London and Imperial College London believe measuring and reporting the levels of airborne grass allergens, instead of the pollen particles that carry the tiny offenders, could be more beneficial for hay fever sufferers.
For years, hay fever sufferers have monitored peak pollen count times in a bid to help manage their symptoms. But authors of the study, published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, say measuring allergen levels gives a more accurate picture of the stuff that actually makes people's eyes water and noses drip.
About one in four U.S. adults suffers from hay fever, and the researchers say grass pollen is the most common hay fever trigger. They measured the levels of grass allergen (Phl p 5) over a period of time and found spikes were more consistently associated with allergic respiratory symptoms than grass pollen counts. They hope their findings will lead to policy changes that can help people better prepare to tackle this tough time of year.
"The pollen counts, they're good, and they can be associated with health outcomes, but once you account for the allergen levels, it's clear from the study that we did that it's the allergen levels that count," Dr. Elaine Fuertes of Imperial College London, who helped write the report, told CBS News.
Pollen carries the allergens that cause hay fever symptoms, and it can be released at different times and in different amounts.
"Knowing when the allergen levels themselves are going to be high can help people stay indoors when they need to, maybe take showers when they get home to rinse off some of the allergen they might have been exposed to," said Fuertes.
In a lab at Imperial College London, Dr. Jennifer Canizales showed CBS News how researchers have been monitoring allergen levels on a small scale using special filters placed inside air samplers.
No country in the world currently tracks allergen levels, as it's expensive and time consuming, but Fuertes said the researchers believe "that if you could incorporate regular monitoring of allergen levels, the forecasting would get better."
She hopes their research will encourage governments and organizations around the world to start monitoring and reporting allergen levels — especially as scientists have predicted that as the Earth's climate continues warming, the annual plight of allergy sufferers is likely to get worse.
- United Kingdom

Ian Lee is a CBS News correspondent based in London, where he reports for CBS News, CBS Newspath and CBS News Streaming Network. Lee, who joined CBS News in March 2019, is a multi-award-winning journalist, whose work covering major international stories has earned him some of journalism's top honors, including an Emmy, Peabody and the Investigative Reporters and Editors' Tom Renner award.
More from CBS News

British Museum faces probe over handling of sacred artifacts

Suspects fled U.K. hours after stabbing of Iranian journalist in London

JetBlue brings dynamic pricing to checking bags. Here's what to know.

Arizona organizers say abortion ballot measure qualifies to be on ballot
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Environment
Low Level Waste Repository Limited (NPS/WR/039935): application made to abstract water
The Environment Agency has received an application from Low Level Waste Repository Limited for a licence to abstract (take) water.
Applies to England
Low level waste repository limited: application made to abstract water.
The Environment Agency consult the public on certain applications for the abstraction and impoundment of water.
These notices explain:
what the application is about
which Environment Agency offices you can visit to see the application documents on the public register
when you need to comment by
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
What is a PhD? A PhD is a Doctorate of Philosophy, a prestigious qualification which is the highest level of degree that a student can achieve, demonstrating talent, academic excellence and a thirst for knowledge. In a modern knowledge-based economy, highly educated and skilled people such as doctoral graduates, are in great demand.
Level 7 qualifications are: integrated master's degree, for example master of engineering ( MEng) level 7 award. level 7 certificate. level 7 diploma. level 7 NVQ. master's degree, for example ...
A PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) is the most common type of doctoral degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve. It normally takes between three and four years of full-time work to complete. It is also possible to undertake a PhD part time, over five to six years. The main activity of a PhD is to carry out an original ...
The term PhD or Doctorate of Philosophy is an abbreviation of the Latin phrase 'philosophiae doctor'. A PhD degree typically involves students independently conducting original and significant research in a specific field or subject, before producing a publication-worthy thesis. While some Doctorates include taught components, PhD students are ...
You may be able to get a PhD loan of up to £27,892 for a UK doctorate. Our guide explains eligibility, applications and repayments. Our guide explains the best ways to fund international PhD study in the UK, with information on all the main scholarships available to you.
A Cambridge PhD is intellectually demanding and you will need to have a high level of attainment and motivation to pursue this programme of advanced study and research. In most faculties, a candidate is expected to have completed one year of postgraduate study, normally on a research preparation master's course, prior to starting a PhD.
A PhD is the highest postgraduate-level qualification offered by universities in the UK. It's for those who are looking to build on what they studied during their master's degree, or for those currently working who wish to research a particular area within their field. PhDs are research-based degrees. The student comes up with an original ...
In the UK, a PhD stands for 'Doctor of Philosophy', sometimes referred to as a 'doctorate'. It is the highest level of degree that a student can achieve. At some institutions, including Oxford University, a Doctor of Philosophy is known as a DPhil. It is distinct from professional doctorates such as an Engineering Doctorate (EngD).
This is the most common means of getting a Doctorate degree. Over the three or four years of research at university, your PhD supervisor will support you as you aim to produce a thesis based on your research proposal. A thesis is typically 60,000-90,000 words in length - although this can vary between institutions.
PhD tuition fees for international students in the UK depend on factors such as the university, field of study, and location. On average, fees range from £15,000 to £35,000 per year. However, it's important to note that actual fees can vary significantly. Register for Free Consultation.
Presentation. How much does a PhD cost? Fees vary widely between courses and institutions, but are commonly between £3,000 and £6,000 per year for UK students. International students often pay more. Many degrees are partly or fully funded, and lots of students receive scholarships and bursaries.
There won't typically be an application fee for PhDs but there are tuition fees. If a university does charge application fees they will usually be between £50-£100. The tuition fees for students studying in the UK are set by UK Research and Innovation. Fees for international students are £18,975 for non-lab-based subjects, and £22,975 for ...
Standard PhD requirements in the UK are a Bachelors degree with at least an upper second class honours degree (2.1). You may also need a Masters degree with a Merit or Distinction grade. All your previous qualifications must be in a field of study relevant to the PhD you are applying for. Typically, Arts and Humanities PhDs are more likely to ...
The length of a UK PhD thesis varies by subject. Dissertations in the Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences tend to be between 60,000 and 100,000 words. Dissertations in STEM subjects are shorter, as much of the information is conveyed through graphs and data tables.
Around 500 PhD students study at the University of Brighton and a quarter are international students. The diversity of students has always been evident at the Summer Graduation Ceremonies with 83 countries recently represented among our 3,000 graduates from all levels.
English language. International applicants must provide one of the following: IELTS test minimum score - 7.0 overall, 7.0 in writing, 6.0 in other sections. TOEFL (internet based) test minimum score - 100 overall, 25 in all sections. Pearson Test of English (PTE) UKVI/SELT or PTE Academic minimum score - 76 overall, 76 in writing, 70 in other ...
Level 6 qualifications are at a level equivalent to bachelor's degrees with honours, graduate certificates and graduate diplomas. Level 5 ... Honours-level courses are coded H and non-honours bachelor's-level courses I (across the whole of the UK, not just Scotland, thus splitting level 6 on the England, Wales and Northern Ireland framework). ...
After receiving the QS Academic Scholarship (worth US$10,000) in 2012, Indian student Rajesh Kumar headed to the UK's University of Glasgow to complete an MRes in Biomedical Science. Having thoroughly enjoyed both the course and the wider research environment offered by the UK, he was keen to stay on and find a PhD program.. He's spent the past six months immersed in researching PhD ...
Students who have completed a Masters degree from a recognised institution will be considered for PhD study. Holders of a bachelor degree with honours from a recognised Canadian university may be considered for entry to a postgraduate degree programme. A GPA of 3.0/4, 7.0/9 or 75% is usually equivalent to a UK 2.1.
It's a different story in the US, where, according to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, students take an average of 5.7 years to graduate. 4. UK PhD fees tend to be lower. Fees err on the more ...
A PhD is a research degree and is the highest award available at universities in the UK. Study is based around a substantial research project on an area of academic interest, typically up to 100,000 words in length, written as a thesis which then must be defended in an oral examination in front of a panel of experts.
There are many funding options available for international students who want to study in the UK. They range from part-funding, for example paying part of your fees, to full-funding which covers programme fees, living expenses, and return flights to the UK. You can search for the right scholarship for you on the course and scholarships finder below.
There are over 150 universities in the UK. The vast majority are public universities, meaning that they receive funding (including budgets for PhD studentships) from the UK Government.All British universities are free to pursue their own research objectives, but the amount of funding each institution receives is partly based on regular assessments of its performance as part of the Research ...
Inflation in shop prices in the UK has eased to the lowest level for more than two years after retailers cut prices on Easter treats, clothing and electrical goods amid a slowdown in spending by ...
Amazon spends $2.75 billion on AI startup Anthropic in its largest venture investment yet. Amazon is spending billions more to back an artificial intelligence startup as it looks for an edge in ...
If you want to know what title is up next for you, or what the new Helldivers 2 titles are, here's a quick list of them all, along with the level you unlock them at: Cadet - 1. Space Cadet - 5 ...
Oakland Athletics. Martín Gallegos covers the A's for MLB.com. The A's saw a bevy of their top prospects graduate to the Major League level last season, and several more could be joining them in 2024. Jacob Wilson headlines the promising wave of young talent, ranked as Oakland's No. 1 prospect and the No. 64 prospect in baseball by MLB.
About one in four U.S. adults suffers from hay fever, and the researchers say grass pollen is the most common hay fever trigger. They measured the levels of grass allergen (Phl p 5) over a period ...
The Environment Agency consult the public on certain applications for the abstraction and impoundment of water. These notices explain: what the application is about. which Environment Agency ...