Eat App for
How it works.


How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan in 2024 (Step by Step Guide with Templates)

A comprehensive restaurant business plan is a framework that guides you to plan and forecast every element of restaurant management and operations.
This includes anything from your restaurant's menu design, location, financials, employee training, and a lot more.
Crafting a solid business plan is important, as it helps:
- Transform your restaurant ideas into reality.
- Boosts entrepreneurial success by 16% (Harvard Business Study) .
- Equips you to navigate challenges before they arise.
- Attracts potential investors.
“You have to show any potential investor that you have an actual plan, you know what you’re talking about, it looks professional, and you’re not just screwing around.” - Charles Bililies, owner of Souvla
Planning is key to restaurant success. Without a plan, you're more likely to join the 26% of restaurants that fail within a year.
Create a business plan to set yourself up for success.
Here's how to get started.

A step-by-step guide to writing a restaurant business plan
Embarking on a restaurant venture is an exciting prospect filled with endless possibilities.
However, the key to transforming your culinary dreams into reality lies in the foundation of a well-crafted restaurant business plan.
This guide will walk you through creating a winning restaurant business plan , from defining your niche to seeking expert advice.
So, are you ready to cook up some success? Let's get started.
Essential components of a restaurant business plan
A well-structured restaurant business plan typically consists of the following key components:
- Executive Summary
Company Description
- Market Analysis
- Restaurant Design
- Market Overview
- External help
- Financial Analysis
Delving into each section
Now, let's take a closer look at each section of your restaurant business plan and explore the key elements to consider:
1. Executive summary
A restaurant business plan should always begin with an executive summary. Why?
- 80% of venture capitalists say they read the executive summary first.
- 62% of investors say they would not continue reading a business plan if the executive summary did not capture their interest.
- A strong executive summary can increase the likelihood of securing funding by up to 40%.
An executive summary not only acts as the introduction to your restaurant business plan samples but also as a summary of the entire idea.
The main aim of an executive summary is to draw the reader (oftentimes an investor) into the rest of your business plan.
The executive summary also helps you envision the identity of your restaurant which essentially shapes the customer experience and sets you apart from competitors.
To establish a distinct identity, you need to focus on c ommon elements of an executive summary, including:
- A mission statement
- Proposed concept development
- Cuisine selection
- The overall execution
- The potential costs
- Expected return on investments (ROI)
Let's take a more in-depth look at the concept development, cuisine selection, and mission statement.
Further reading
- How to write a restaurant executive summary
Concept Development
Selecting the type of restaurant, service style, and atmosphere is the first step towards creating a unique dining experience. Whether you envision a sample menu for a:
- cozy, intimate bistro
- bustling quick-service deli
- fast-casual restaurant
- fine dining establishment
Your concept should reflect your passion and expertise in the industry.
With a broad range of options, it’s critical to scrutinize your target market and pinpoint the most suitable choice considering their preferences and your capabilities.
When planning your restaurant design, keep in mind that it should effectively complement your chosen theme and cuisine.
Additionally, consider the potential for patio seating and the involvement of your management team in making these critical decisions.
A well-thought-out concept will not only set the stage for an unforgettable dining experience but also pique the interest of potential investors.
Cuisine Selection
The cuisine you select for your restaurant can significantly influence its success.
Choosing the appropriate cuisine is vital for distinguishing your establishment from competitors and attracting your target market.
To make an informed decision, consider factors such as:
- Market demand
- Expertise and passion
- Ingredient availability
- Competition
- Profitability
- Cultural fit
- Seasonality
Dietary restrictions and trends
In the highly competitive restaurant industry, keeping track of current and emerging cuisine trends can be a significant advantage.
From regional delicacies to innovative fusion dishes, understanding what’s popular and in demand can help you tailor your offerings to the desires of your target audience.
By thoroughly analyzing the market and adapting to evolving tastes, your restaurant can remain relevant and successful in the long run.
Crafting a mission statement
A well-constructed mission statement communicates the purpose, values, and goals of your restaurant to potential investors and customers alike.
A mission statement serves as a guiding light for decision-makers and employees, fueling their efforts to achieve your restaurant’s objectives.
To create an impactful mission statement, consider the following steps:
- Identify the purpose of the restaurant.
- Contemplate the brand’s image.
- Account for the target audience.
- Incorporate company values.
- Ensure brevity and comprehensiveness.
Related content: How to Write a Restaurant Mission Statement
Remember, your mission statement should not only differentiate your restaurant from competitors but also resonate with your target market.
By articulating your restaurant’s unique values and vision, you’ll create a strong foundation upon which to build a thriving and successful business.
2. Company description
This is the part of the restaurant business plan where you fully introduce the company.
Start this section with the name of the restaurant you are opening along with the location, contacts, and other relevant information.
Also, include the owner’s details and a brief overview or description of their experience.
The second part of the company description should highlight the legal standing of the restaurant and outline the restaurant’s short and long-term goals.
Provide a brief market study showing that you understand the trends in the regional food industry and why the most independent restaurant investors will succeed in this market.
Here's an example of the page layout:
Restaurant Name: [Restaurant Name]
Location: [Restaurant Address]
Contact: [Restaurant Phone Number] | [Restaurant Email Address]
Owner: [Owner Name]
Experience: [Owner Name] has over [Number] years of experience in the restaurant industry. They have worked in various roles, including [List of Roles]. They are passionate about food and creating a memorable dining experience for their guests.
Legal Standing: [Restaurant Name] is a [Type of Legal Entity] registered in [State/Province].
Short-term Goals:
- Generate [Amount] in revenue within the first year of operation.
- Achieve a [Percentage] customer satisfaction rating within the first six months of operation.
Long-term Goals:
- Expand to a second location within five years.
- Become a recognized leader in the regional food industry.
Market Study:
The regional food industry is experiencing a number of trends, including:
- An increasing demand for fresh, local ingredients.
- A growing interest in ethnic cuisine.
- A preference for casual dining experiences.
3. Market analysis
The market analysis portion of the restaurant business plan is typically divided into three parts.
3.1 Industry analysis
What is your target market? What demographics will your restaurant cater to?
This section aims to explain your target market to investors and why you believe guests will choose your restaurant over others.
Comprehending your target market is key to customizing your restaurant offerings to their preferences and needs.
By diving into demographics, preferences, dining habits, and trends, you can fine-tune your concept and marketing strategy to reach and appeal to your target audience effectively.
An example of analyzing your target market
Comprehending your target market is key to customizing your restaurant offerings to their preferences and needs.
Demographics and preferences
Identifying your primary target market involves considering factors such as:
For example, a neighborhood with a high concentration of families might prefer a family-friendly restaurant with a diverse menu catering to various age groups and dietary preferences.
Conversely, a trendy urban area with a predominantly young and affluent population may gravitate towards upscale dining experiences and innovative cuisine.
Cultural and ethnic backgrounds also have a significant impact on restaurant preferences, with people from different backgrounds having distinctive tastes and customs that influence their dining choices.
By thoroughly understanding the demographics and preferences of your target market, you’ll be better equipped to create a restaurant concept that resonates with them and ultimately drives success.
Dining habits and trends
As the restaurant industry continues to evolve, staying informed about dining habits and trends is crucial for adapting your offerings and attracting customers.
For example, the rise of online ordering and delivery services has significantly influenced dining habits, with many consumers seeking the convenience of having their meals delivered to their doorstep.
Health trends have also had an impact on dining habits, with an increasing number of individuals seeking healthier options when dining out.
By staying abreast of current habits and trends, you can anticipate the needs and desires of your target market and tailor your restaurant’s offerings accordingly.
This forward-thinking approach will not only help you stay competitive but also foster long-term success in the ever-changing restaurant landscape.
- How to find your restaurant's target market
3.2 Competition analysis
It's easy to assume that everyone will visit your new restaurant first, so it is important to research your competition to make this a reality.
What restaurants have already established a customer base in the area?
Take note of everything from their prices, hours, and service style to menu design to the restaurant interior.
Then explain to your investors how your restaurant will be different.
3.3 Marketing analysis
Your investors are going to want to know how you plan to market your restaurant. How will your marketing campaigns differ from what is already being done by others in the restaurant industry?
How do you plan on securing your target market? What kind of offers will you provide your guests? Make sure to list everything.
The most important element to launching a successful restaurant is the menu . Without it, your restaurant has nothing to serve.
At this point, you probably don’t have a final version, but for a restaurant business plan, you should at least try to have a mock-up.
Add your logo to the mock-up and choose a design that you can see yourself actually using. If you are having trouble coming up with a menu design or don’t want to pay a designer, there are plenty of resources online to help.
The key element of your sample menu though should be pricing. Your prices should reflect the cost analysis you’ve done for investors. This will give them a better understanding of your restaurant’s target price point. You'll quickly see how important menu engineering can be, even early on.
5. Employees
The company description section of the restaurant business plan briefly introduces the owners of the restaurant with some information about each. This section should fully flesh out the restaurant's business plan and management team.
The investors don’t expect you to have your entire team selected at this point, but you should at least have a couple of people on board. Use the talent you have chosen thus far to highlight the combined work experience everyone is bringing to the table.
6. Restaurant design
The design portion of your restaurant business plan is where you can really show off your thoughts and ideas to the investors. If you don’t have professional mock-ups of your restaurant rendered, that’s fine.
Instead, put together a mood board to get your vision across. Find pictures of a similar aesthetic to what you are looking for in your restaurant.
The restaurant design extends beyond aesthetics alone and should include everything from restaurant software to kitchen equipment.
7. Location
The location you settle on for your restaurant should be well aligned with your target market (making it easier to cater to your ideal customer) and with your business plans.
At this stage in the process, its not uncommon to not have a specific location in mind - but you should at the very least have a few options to narrow down.
Tip: When you approach your investors about potential locations, make sure to include as much information as possible about each venue and why it would be ideal for your brand. Go into as much detail as possible - including everything from square footage to the demographics of the area.
Example for choosing an ideal location
Choosing the ideal location for your restaurant is a pivotal decision that can greatly influence your success.
To make the best choice, consider factors such as foot traffic, accessibility, and neighborhood demographics.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you’ll be better equipped to maximize visibility and attract your target market.
Foot traffic and accessibility
Foot traffic and accessibility are essential factors in selecting a location that will attract customers and ensure convenience.
A high-traffic area with ample parking and public transportation options can greatly increase the likelihood of drawing in potential customers.
Additionally, making your restaurant accessible to individuals with disabilities can further broaden your customer base and promote inclusivity.
It’s also important to consider the competition in the area and assess whether your restaurant can stand out among existing establishments.
By choosing a location with strong foot traffic and accessibility, you’ll be well on your way to creating a thriving restaurant that appeals to your target market.
Neighborhood demographics
Analyzing neighborhood demographics can help you determine if your restaurant’s concept and cuisine will appeal to the local population.
Factors such as income levels, family structures, and cultural diversity can all influence dining preferences and habits.
By understanding the unique characteristics of the neighborhood, you can tailor your offerings and marketing efforts to resonate with the local community.
Conducting a market analysis can be a valuable step in this process.
To gather demographic data for a particular neighborhood, you can utilize resources such as the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey and reference maps.
Armed with this information, you can make informed decisions about your restaurant’s concept, menu, and pricing, ensuring that your establishment is well-positioned for success within the community.
Conducting market research will further strengthen your understanding of the local demographic.
8. Market overview
The market overview section is heavily related to the market research and analysis portion of the restaurant business plan. In this section, go into detail about both the micro and macro conditions in the area you want to set up your restaurant.
Discuss the current economic conditions that could make opening a restaurant difficult, and how you aim to counteract that. Mention all the other restaurants that could prove to be competition and what your strategy is to set yourself apart.
9. Marketing
With restaurants opening left and ride nowadays, investors are going to want to know how you will get word of your restaurant to the world.
The next marketing strategy and publicity section should go into detail on how you plan to market your restaurant before and after opening. As well as any plans you may have to bring a PR company on board to help spread the word.
Read more: How to write a restaurant marketing plan from scratch
10. External help
To make your restaurant a reality, you are going to need a lot of help. List any external companies or software you plan on hiring to get your restaurant up and running.
This includes everything from accountants and designers to suppliers that help your restaurant perform better, like POS systems and restaurant reservation systems .
Explain to your other potential investors about the importance of each and what they will be doing for your restaurant.
11. Financial analysis
The most important part of your restaurant business plan is the financial section . We would recommend hiring professional help for this given its importance.
Hiring a trained accountant will not only help you get your own financial projections and estimates in order but also give you a realistic insight into owning a restaurant.
You should have some information prepared to make this step easier for the accountant.
He/she will want to know how many seats your restaurant has, what the check average per table will be, and how many guests you plan on seating per day.
In addition to this, doing rough food cost calculations for various menu items can help estimate your profit margin per dish. This can be achieved easily with a free food cost calculator.
- Important restaurant metrics to track
A well-crafted restaurant business plan serves as a roadmap to success, guiding every aspect of the venture from menu design to employee training.
By carefully considering each component of the plan, aspiring restaurateurs can increase their chances of securing funding, attracting customers, and achieving their long-term goals.
Remember, a restaurant business plan is not just a document to satisfy investors; it is a living tool that should be revisited and updated regularly as the business grows and evolves.
By staying committed to the plan and adapting it as needed, restaurateurs can ensure that their culinary dreams have a solid foundation for success.
Share this article!
Saif Alnasur used to work in his family restaurant, but now he is a food influencer and writes about the restaurant industry for Eat App.
How to Calculate Food Cost in:...
Whether you're putting together a menu for your...

The A to Z Guide to:...
86 that dish? Camper? Kill it? In the weeds?

OpenTable vs. Resy::...
When it comes to choosing an online restaurant...
Join restaurants in 70+ countries using Eat App

Empowering restaurants, one table at a time Discover seamless dining with Eat App
- Reservation system
- Table management
- CRM and guest profiles
- Reports & trends
- Integrations
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
- The 16 Best Reservation Systems
- Guide to Restaurant Marketing
- Guide to Customer Service
- Guide to Making a Restaurant Website
- All articles
"> "> Compare us
- Seven Rooms
- Compare All
© Eat App. All rights reserved.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
When starting a business—no matter what type of business that may be—a business plan is essential to map out your intentions and direction. That’s the same for a restaurant business plan, which will help you figure out where you fit in the landscape, how you’re going to differ from other establishments around you, how you’ll market your business, and even what you’re going to serve. A business plan for your restaurant can also help you later if you choose to apply for a business loan .
While opening a restaurant isn’t as risky as you’ve likely heard, you still want to ensure that you’re putting thought and research into your business venture to set it up for success. And that’s where a restaurant business plan comes in.
We’ll go through how to create a business plan for a restaurant and a few reasons why it’s so important. After you review the categories and the restaurant business plan examples, you can use the categories to make a restaurant business plan template and start your journey.

Why you shouldn’t skip a restaurant business plan
First-time restaurateurs and industry veterans alike all need to create a business plan when opening a new restaurant . That’s because, even if you deeply understand your business and its nuances (say, seasonal menu planning or how to order correct quantities), a restaurant is more than its operations. There’s marketing, financing, the competitive landscape, and more—and each of these things is unique to each door you open.
That’s why it’s so crucial to understand how to create a business plan for a restaurant. All of these things and more will be addressed in the document—which should run about 20 or 30 pages—so you’ll not only have a go-to-market strategy, but you’ll also likely figure out some things about your business that you haven’t even thought of yet.
Additionally, if you’re planning to apply for business funding down the line, some loans—including the highly desirable SBA loan —actually require you to submit your business plan to gain approval. In other words: Don’t skip this step!
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
How to write a restaurant business plan: Step by step
There’s no absolute format for a restaurant business plan that you can’t stray from—some of these sections might be more important than others, for example, or you might find that there’s a logical order that makes more sense than the one in the restaurant business plan example below. However, this business plan outline will serve as a good foundation, and you can use it as a restaurant business plan template for when you write your own.
Executive summary
Your executive summary is one to two pages that kick off your business plan and explain your vision. Even though this might seem like an introduction that no one will read, that isn’t the case. In fact, some investors only ask for the executive summary. So, you’ll want to spend a lot of time perfecting it.
Your restaurant business plan executive summary should include information on:
Mission statement: Your goals and objectives
General company information: Include your founding date, team roles (i.e. executive chef, sous chefs, sommeliers), and locations
Category and offerings: What category your restaurant fits into, what you’re planning to serve (i.e. farm-to-table or Korean), and why
Context for success: Any past success you’ve had, or any current financial data that’ll support that you are on the path to success
Financial requests: If you’re searching for investment or financing, include your plans and goals here and any financing you’ve raised or borrowed thus far
Future plans: Your vision for where you’re going in the next year, three years, and five years
When you’re done with your executive summary, you should feel like you’ve provided a bird’s eye view of your entire business plan. In fact, even though this section is first, you will likely write it last so you can take the highlights from each of the subsequent sections.
And once you’re done, read it on its own: Does it give a comprehensive, high-level overview of your restaurant, its current state, and your vision for the future? Remember, this may be the only part of your business plan potential investors or partners will read, so it should be able to stand on its own and be interesting enough to make them want to read the rest of your plan.
Company overview
This is where you’ll dive into the specifics of your company, detailing the kind of restaurant you’re looking to create, who’s helping you do it, and how you’re prepared to accomplish it.
Your restaurant business plan company overview should include:
Purpose: The type of restaurant you’re opening (fine dining, fast-casual, pop-up, etc.), type of food you’re serving, goals you have, and the niche you hope to fill in the market
Area: Information on the area in which you’re opening
Customers: Whom you’re hoping to target, their demographic information
Legal structure: Your business entity (i.e. LLC, LLP, etc.) and how many owners you have
Similar to your executive summary, you won’t be going into major detail here as the sections below will get into the nitty-gritty. You’ll want to look at this as an extended tear sheet that gives someone a good grip on your restaurant or concept, where it fits into the market, and why you’re starting it.
Team and management
Barely anything is as important for a restaurant as the team that runs it. You’ll want to create a section dedicated to the members of your staff—even the ones that aren’t yet hired. This will provide a sense of who is taking care of what, and how you need to structure and build out the team to get your restaurant operating at full steam.
Your restaurant business plan team and management section should have:
Management overview: Who is running the restaurant, what their experience and qualifications are, and what duties they’ll be responsible for
Staff: Other employees you’ve brought on and their bios, as well as other spots you anticipate needing to hire for
Ownership percentage: Which individuals own what percentage of the restaurant, or if you are an employee-owned establishment
Be sure to update this section with more information as your business changes and you continue to share this business plan—especially because who is on your team will change both your business and the way people look at it.
Sample menu
You’ll also want to include a sample menu in your restaurant business plan so readers have a sense of what they can expect from your operations, as well as what your diners can expect from you when they sit down. This will also force you to consider exactly what you want to serve your diners and how your menu will stand out from similar restaurants in the area. Although a sample menu is in some ways self-explanatory, consider the following:
Service : If your brunch is as important as your dinner, provide both menus; you also might want to consider including both a-la-carte and prix fixe menus if you plan to offer them.
Beverage/wine service: If you’ll have an emphasis on specialty beverages or wine, a separate drinks list could be important.
Seasonality: If you’re a highly seasonal restaurant, you might want to consider providing menus for multiple seasons to demonstrate how your dishes (and subsequent purchasing) will change.
Market analysis
This is where you’ll begin to dive deeper. Although you’ve likely mentioned your market and the whitespace you hope to address, the market analysis section will enable you to prove your hypotheses.
Your restaurant business plan market analysis should include:
Industry information: Include a description of the restaurant industry, its size, growth trends, and other trends regarding things such as tastes, trends, demographics, structures, etc.
Target market: Zoom in on the area and neighborhood in which you’re opening your restaurant as well as the type of cuisine you’re serving.
Target market characteristics: Describe your customers and their needs, how/if their needs are currently being served, other important pieces about your specific location and customers.
Target market size and growth: Include a data-driven section on the size of your market, trends in its growth, how your target market fits into the industry as a whole, projected growth of your market, etc.
Market share potential: Share how much potential there is in the market, how much your presence will change the market, and how much your specific restaurant or restaurant locations can own of the open market; also touch on any barriers to growth or entry you might see.
Market pricing: Explain how you’ll be pricing your menu and where you’ll fall relative to your competitors or other restaurants in the market.
Competitive research: Include research on your closest competitors, how they are both succeeding and failing, how customers view them, etc.
If this section seems like it might be long, it should—it’s going to outline one of the most important parts of your strategy, and should feel comprehensive. Lack of demand is the number one reason why new businesses fail, so the goal of this section should be to prove that there is demand for your restaurant and show how you’ll capitalize on it.
Additionally, if market research isn’t your forte, don’t be shy to reach out to market research experts to help you compile the data, or at least read deeply on how to conduct effective research.
Marketing and sales
Your marketing and sales section should feel like a logical extension of your market analysis section, since all of the decisions you’ll make in this section should follow the data of the prior section.
The marketing and sales sections of your restaurant business plan should include:
Positioning: How you’ll describe your restaurant to potential customers, the brand identity and visuals you’ll use to do it, and how you’ll stand out in the market based on the brand you’re building
Promotion: The tools, tactics, and platforms you’ll use to market your business
Sales: How you’ll convert on certain items, and who/how you will facilitate any additional revenue streams (i.e. catering)
It’s likely that you’ll only have concepts for some of these elements, especially if you’re not yet open. Still, get to paper all of the ideas you have, and you can (and should) always update them later as your restaurant business becomes more fully formed.
Business operations
The business operations section should get to the heart of how you plan to run your business. It will highlight both internal factors as well as external forces that will dictate how you run the ship.
The business operations section should include:
Management team: Your management structure and hierarchy, and who is responsible for what
Hours: Your hours and days of operation
Location: What’s special about your location that will get people through the door
Relationships: Any advantageous relationships you have with fellow restaurateurs, places for sourcing and buying, business organizations, or consultants on your team
Add here anything you think could be helpful for illustrating how you’re going to do business and what will affect it.
Here, you’ll detail the current state of your business finances and project where you hope to be in a year, three years, and five years. You’ll want to detail what you’ve spent, what you will spend, where you’ll get the money, costs you might incur, and returns you’ll hope to see—including when you can expect to break even and turn a profit.
Financial statements: If you’ve been in business for any amount of time, include existing financial statements (i.e. profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow, etc.)
Budget: Your current budget or a general startup budget
Projections: Include revenue, cash flow, projected profit and loss, and other costs
Debt: Include liabilities if the business has any outstanding debt or loans
Funding request: If you’re requesting a loan or an investment, lay out how much capital you’re looking for, your company’s valuation (if applicable), and the purpose of the funding
Above all, as you’re putting your financials together, be realistic—even conservative. You want to give any potential investors a realistic picture of your business.
Feel like there are other important components but they don't quite fit in any of the other categories (or make them run too long)? That’s what the restaurant business plan appendix section is for. And although in, say, a book, an appendix can feel like an afterthought, don’t ignore it—this is another opportunity for you to include crucial information that can give anyone reading your plan some context. You may include additional data, graphs, marketing collateral (like logo mockups), and more.

Start Your Dream Business
The bottom line
Whether you’re writing a restaurant business plan for investors, lenders, or simply for yourself and your team, the most important thing to do is make sure your document is comprehensive. A good business plan for a restaurant will take time—and maybe a little sweat—to complete fully and correctly.
One other crucial thing to remember: a business plan is not a document set in stone. You should often look to it to make sure you’re keeping your vision and mission on track, but you should also feel prepared to update its components as you learn more about your business and individual restaurant.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...
Goals & Objectives of Opening a Restaurant
- Small Business
- Types of Businesses to Start
- Opening a Restaurant
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Sample of a SWOT Analysis for a Restaurant
What are some qualities or characteristics that make a good restaurant, objectives of a buffet restaurant.
- How to Start a Buffet Restaurant
- How to Own & Manage a Fast Food Restaurant
If you’re planning to open a new restaurant, your business plan must include specific goals and objectives. This doesn’t just mean detailing the ambiance and look of your restaurant or the type of food you intend to serve, it also means setting goals centered on customer service, sales and staffing. Whether you operate a franchise or you are opening an independent restaurant, there are several major goals and objectives you should establish to achieve the success you desire.
Provide an Outstanding Patron Experience
In the restaurant business, you aren’t just serving food. You are selling a dining experience. So one of your major goals should be to provide a customer experience that encourages repeat business. From the moment a patron enters your restaurant until that patron leaves, that person should feel as if they are valued. But you can’t achieve this goal without having a way to measure the type of experience you are offering.
Set measurable customer experience goals such as greeting patrons as soon as they enter, serving meals within 20 minutes and having each server communicate the specials to every diner.
Establish Customer Loyalty
Another major objective of a restaurant is to create a sense of loyalty in their patrons to make them regular customers. Your restaurant won’t survive if you can’t convert first-time visitors into repeat customers. One of the best ways to create loyalty is by offering some type of reward program.
One example is a reward program that allows patrons to build up points with regular visits and use those points for free meals and drinks. Another idea is to offer gift cards to your regular customers, which can help attract new patrons.
Offer a Diverse Menu
Even if your restaurant specializes in one type of food, you can still make it an objective to offer a diverse menu that will attract patrons. As you plan the menu for your restaurant, consider the fact that potential diners may have a varied palate. For example, if you specialize in Asian fusion, make it a key objective to keep a few simple options on the menu.
This caters to those customers who might enjoy your delicious food but aren’t necessarily adventurous when it comes to food. Plan a menu that gives several key options and a few more basic recipes, as well as a number of sides to draw different types of foodies to your eatery.
The National Restaurant Association has identified some popular trends that can help your menu planning. This includes more international cuisine, vegetable-inspired dishes, locally-sourced food, new cuts of meat that vary from the standard and zero-waste cooking. This refers to a cooking style in which no ingredients are thrown away or wasted, which helps the environment and also reduces your cost-per-menu-item.
Creating a Brand
Branding isn’t just for big names such as Apple and Zappos, it has also become one of the main goals of small businesses, including restaurants. Fortunately, the evolution of social media has leveled the playing field, allowing smaller companies to communicate their brand without needing a huge budget. You can brand your restaurant in several ways, including:
- Choosing a catchy name
- Designing a distinct logo
- Creating a theme or concept
- Identifying the experience (fun, high-end, casual)
- Developing a distinct look and ambiance
Branding is all about selling the “why” of your restaurant rather than the “what,” because patrons already know you offer food. The key is to identify what makes your place unique and worth a visit. Then you must find ways to grab your audience’s attention. One means of doing that is to hold an event in which you invite the public to come and sample different items on your menu and offer giveaways.
- Toast: How To Set Short and Long Term Goals For Your Restaurant
- National Restaurant Association
Sampson Quain is an experienced content writer with a wide range of expertise in small business, digital marketing, SEO marketing, SEM marketing, and social media outreach. He has written primarily for the EHow brand of Demand Studios as well as business strategy sites such as Digital Authority.
Related Articles
How to build a bistro bar, swot analysis for burgers, how to open a french restaurant, how to make a promotion plan for a restaurant, the importance of a restaurant's name & their specialty to the success of the business, how to open a spaghetti restaurant, how to develop a marketing strategy for a restaurant, how to create a marketing plan for a restaurant, restaurant customer expectations survey questions, most popular.
- 1 How to Build a Bistro Bar
- 2 SWOT Analysis for Burgers
- 3 How to Open a French Restaurant
- 4 How to Make a Promotion Plan for a Restaurant
Sling is now Sling by Toast! Learn more
More Features

- Restaurants
- Get Started

Restaurant Business Plan: What To Include, Plus 8 Examples
- Business Growth & Management , Templates & Guides
Do you want to ensure the success of your new foodservice endeavor? Write a restaurant business plan.
In this article, the experts at Sling tell you why a business plan is vital for both new and existing businesses and give you tips on what to include.
Table Of Contents
What Is A Restaurant Business Plan?
Why is a restaurant business plan important, questions to ask first, what to include in an effective restaurant business plan, how to format a restaurant business plan, efficient workforce management is essential for success.

At its most basic, a restaurant business plan is a written document that describes your restaurant’s goals and the steps you will take to make those goals a reality.
This business plan also describes the nature of the business itself, financial projections, background information, and organizational strategies that govern the day-to-day activity of your restaurant.

A restaurant business plan is vital for the success of your endeavor because, without one, it is very difficult — sometimes even impossible — to obtain funding from an investor or a bank.
Without that all-important starting or operational capital, you may not be able to keep your doors open for long, if at all.
Even if funding isn’t a primary concern, a business plan provides you — the business owner or manager — with clear direction on how to translate general strategies into actionable plans for reaching your goals.
The plan can help solidify everything from the boots-on-the-ground functional strategy to the mid-level business strategy all the way up to the driving-force corporate strategy .
Think of this plan as a roadmap that guides your way when things are going smoothly and, more importantly, when they aren’t.
If you want to give your restaurant the best chance for success, start by writing a business plan.

Sitting down to write a restaurant business plan can be a daunting task.
As you’ll see in the What To Include In An Effective Restaurant Business Plan section below, you’ll need a lot of information and detail to ensure that the final document is both complete and effective.
Instead of starting with word one, it is hugely beneficial to answer a number of general questions first.
These questions will help you narrow down the information to include in your plan so the composition process feels less difficult.
The questions are:
- What problem does the business’s product or service solve?
- What niche will the business fill?
- What is the business’s solution to the problem?
- Who are the business’s customers?
- How will the business market and sell its products to them?
- What is the size of the market for this solution?
- What is the business model for the business?
- How will the business make money?
- Who are the competitors?
- How will the business maintain a competitive advantage?
- How does the business plan to manage growth?
- Who will run the business?
- What makes those individuals qualified to do so?
- What are the risks and threats confronting the business?
- What can you do to mitigate those risks and threats?
- What are the business’s capital and resource requirements?
- What are the business’s historical and projected financial statements?
Depending on your business, some of these questions may not apply or you may not have applicable answers.
Nevertheless, it helps to think about, and try to provide details for, the whole list so your finished restaurant business plan is as complete as possible.
Once you’ve answered the questions for your business, you can transfer a large portion of that information to the business plan itself.
We’ll discuss exactly what to include in the next section.
In this section, we’ll show you what to include in an effective restaurant business plan and provide a brief example of each component.
1) Executive Summary
You should always start any business plan with an executive summary. This gives the reader a brief introduction into common elements, such as:
- Mission statement
- Overhead costs
- Labor costs
- Return on investment (ROI)
This portion of your plan should pique the reader’s interest and make them want to read more.
Fanty & Mingo’s is a 50-seat fine-dining restaurant that will focus on Sweruvian (Swedish/Peruvian) fusion fare.
We will keep overhead and labor costs low thanks to simple but elegant decor , highly skilled food-prep staff, and well-trained servers.
Because of the location and surrounding booming economy, we estimate ROI at 20 percent per annum.
2) Mission Statement
A mission statement is a short description of what your business does for its customers, employees, and owners.
This is in contrast to your business’s vision statement which is a declaration of objectives that guide internal decision-making.
While the two are closely related and can be hard to distinguish, it often helps to think in terms of who, what, why, and where.
The vision statement is the where of your business — where you want your business to be and where you want your customers and community to be as a result.
The mission statement is the who , what , and why of your business — it’s an action plan that makes the vision statement a reality
Here’s an example of a mission statement for our fictional company:
Fanty and Mingo’s takes pride in making the best Sweruvian food, providing fast, friendly, and accurate service. It is our goal to be the employer of choice and offer team members opportunities for growth, advancement, and a rewarding career in a fun and safe working environment.
3) Company Description

In this section of your restaurant business plan, you fully introduce your company to the reader. Every business’s company description will be different and include its own pertinent information.
Useful details to include are:
- Owner’s details
- Brief description of their experience
- Legal standing
- Short-term goals
- Long-term goals
- Brief market study
- An understanding of the trends in your niche
- Why your business will succeed in these market conditions
Again, you don’t have to include all of this information in your company description. Choose the ones that are most relevant to your business and make the most sense to communicate to your readers.
Fanty & Mingo’s will start out as an LLC, owned and operated by founders Malcolm Reynolds and Zoe Washburne. Mr. Reynolds will serve as managing partner and Ms. Washburne as general manager.
We will combine atmosphere, friendly and knowledgeable staff, and menu variety to create a unique experience for our diners and to reach our goal of high value in the fusion food niche.
Our gross margin is higher than industry average, but we plan to spend more on payroll to attract the best team.
We estimate moderate growth for the first two years while word-of-mouth about our restaurant spreads through the area.
4) Market Analysis
A market analysis is a combination of three different views of the niche you want to enter:
- The industry as a whole
- The competition your restaurant will face
- The marketing you’ll execute to bring in customers
This section should be a brief introduction to these concepts. You can expand on them in other sections of your restaurant business plan.
The restaurant industry in our chosen location is wide open thanks in large part to the revitalization of the city’s center.
A few restaurants have already staked their claim there, but most are bars and non-family-friendly offerings.
Fanty & Mingo’s will focus on both tourist and local restaurant clientele. We want to bring in people that have a desire for delicious food and an exotic atmosphere.
We break down our market into five distinct categories:
- High-end singles
- Businessmen and businesswomen
We will target those markets to grow our restaurant by up to 17 percent per year.

Every restaurant needs a good menu, and this is the section within your restaurant business plan that you describe the food you’ll serve in as much detail as possible.
You may not have your menu design complete, but you’ll likely have at least a handful of dishes that serve as the foundation of your offerings.
It’s also essential to discuss pricing and how it reflects your overall goals and operating model. This will give potential investors and partners a better understanding of your business’s target price point and profit strategy.
We don’t have room to describe a sample menu in this article, but for more information on menu engineering, menu pricing, and even a menu template, check out these helpful articles from the Sling blog:
- Menu Engineering: What It Is And How It Can Increase Profits
- Restaurant Menu Pricing: 7 Tips To Maximize Profitability
- How To Design Your Menu | Free Restaurant Menu Template
6) Location
In this section, describe your potential location (or locations) so that you and your investors have a clear image of what the restaurant will look like.
Include plenty of information about the location — square footage, floor plan , design , demographics of the area, parking, etc. — to make it feel as real as possible.
We will locate Fanty & Mingo’s in the booming and rapidly expanding downtown sector of Fort Wayne, Indiana.
Ideally, we will secure at least 2,000 square feet of space with a large, open-plan dining room and rich color scheme near the newly built baseball stadium to capitalize on the pre- and post-game traffic and to appeal to the young urban professionals that live in the area.
Parking will be available along side streets and in the 1,000-vehicle parking garage two blocks away.
7) Marketing

The marketing section of your restaurant business plan is where you should elaborate on the information you introduced in the Market Analysis section.
Go into detail about the plans you have to introduce your restaurant to the public and keep it at the top of their mind.
Fanty & Mingo’s will employ three distinct marketing tactics to increase and maintain customer awareness:
- Word-of-mouth/in-restaurant marketing
- Partnering with other local businesses
- Media exposure
We will direct each tactic at a different segment of our potential clientele in order to maximize coverage.
In the process of marketing to our target audience, we will endeavor to harness the reach of direct mail and broadcast media, the exclusivity of the VIP party, and the elegance of a highly trained sommelier and wait staff.
8) Financials
Even though the Financials section is further down in your restaurant business plan, it is one of the most important components for securing investors and bank funding.
We recommend hiring a trained accountant to help you prepare this section so that it will be as accurate and informative as possible.
Fanty & Mingo’s needs $250,000 of capital investment over the next year and a half for the following:
- Renovations to leased space
- Dining room furniture
- Kitchen and food-prep equipment
- Liquor license
Projected profit and loss won’t jump drastically in the first year, but, over time, Fanty & Mingo’s will develop its reputation and client base. This will lead to more rapid growth toward the third and fourth years of business.

Most entrepreneurs starting a new business find it valuable to have multiple formats of their business plan.
The information, data, and details remain the same, but the length and how you present them will change to fit a specific set of circumstances.
Below we discuss the four most common business plan formats to cover a multitude of potential situations.
Elevator Pitch
An elevator pitch is a short summary of your restaurant business plan’s executive summary.
Rather than being packed full of details, the elevator pitch is a quick teaser of sorts that you use on a short elevator ride (hence the name) to stimulate interest in potential customers, partners, and investors
As such, an effective elevator pitch is between 30 and 60 seconds and hits the high points of your restaurant business plan.
A pitch deck is a slide show and oral presentation that is designed to stimulate discussion and motivate interested parties to investigate deeper into your stakeholder plan (more on that below).
Most pitch decks are designed to cover the executive summary and include key graphs that illustrate market trends and benchmarks you used (and will use) to make decisions about your business.
Some entrepreneurs even include time and space in their pitch deck to demonstrate new products coming down the pipeline.
This won’t necessarily apply to a restaurant business plan, but, if logistics permit, you could distribute small samples of your current fare or tasting portions of new dishes you’re developing.
Stakeholder Plan (External)
A stakeholder plan is the standard written presentation that business owners use to describe the details of their business model to customers, partners, and potential investors.
The stakeholder plan can be as long as is necessary to communicate the current and future state of your business, but it must be well-written, well-formatted, and targeted at those looking at your business from the outside in.
Think of your stakeholder plan as a tool to convince others that they should get involved in making your business a reality. Write it in such a way that readers will want to partner with you to help your business grow.
Management Plan (Internal)
A management plan is a form of your restaurant business plan that describes the details that the owners and managers need to make the business run smoothly.
While the stakeholder plan is an external document, the management plan is an internal document.
Most of the details in the management plan will be of little or no interest to external stakeholders so you can write it with a higher degree of candor and informality.
After you’ve created your restaurant business plan, it’s time to take steps to make it a reality.
One of the biggest challenges in ensuring that your business runs smoothly and successfully is managing and optimizing your team. The Sling app can help.
Sling not only includes powerful and intuitive artificial-intelligence-based scheduling tools but also many other features to help make your workforce management more efficient, including:
- Time and attendance tracking
- Built-in time clock
- Labor cost optimization
- Data analysis and reporting
- Messaging and communication
- And much more…
With Sling, you can schedule faster, communicate better, and organize and manage your work from a single, integrated platform. And when you use Sling for all of your scheduling needs, you’ll have more time to focus on bringing your restaurant business plan to life.
For more free resources to help you manage your business better, organize and schedule your team, and track and calculate labor costs, visit GetSling.com today.
See Here For Last Updated Dates: Link
This content is for informational purposes and is not intended as legal, tax, HR, or any other professional advice. Please contact an attorney or other professional for specific advice.
Find the article useful? Share with others:
Related articles

How To Write Your Ideal Restaurant Mission Statement + 15 Inspiring Examples
Whether you run a one-person food cart, a small eatery with fewer than five empl...

12 Examples of Small Business Goals, Plus How to Achieve Your Own
Want to improve the way your business operates? Learn some of the more common bu...

55 Restaurant Marketing Tips To Win Your Market
Discover the best restaurant marketing tips and learn how you can harness onlin...
Get started today
Schedule faster, communicate better, get things done.

Sample Restaurant Business Plans For a New Business Owner

Writing a business plan is an essential part of starting a restaurant. Not only does it provide a roadmap for the future but it also helps to create funding opportunities and attract potential investors. For new business owners, having access to sample restaurant business plans can be especially helpful in providing direction and insights into how to write a restaurant business plan on their own.
Download our Ultimate Restaurant Business Plan Template
Having a comprehensive business plan in place is vital for any successful restaurant venture. It will serve as the foundation for your operations, setting out the goals and objectives that will help guide your decisions and actions. A well-written business plan will help you understand your restaurant’s startup costs and can also give you clarity on realistic financial projections and help you secure financing from investors and/or get a loan to start a restaurant. Examples of restaurant business plans are great resources to draw upon when creating your own plan to ensure that all the key elements are included in your document.
Below is an example restaurant business plan to help you see what one should look like. It is not however nearly as comprehensive and successful in raising capital for your restaurant as Growthink’s Ultimate Restaurant Business Plan Template , but it can help you write a business plan for your restaurant.
Restaurant Business Plan Example #1 – Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant
Table of contents.
Executive Summary
Company Overview
Industry analysis, customer analysis, competitive analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team, financial plan.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant is a high-end seafood restaurant located in the heart of the historic district in New Orleans, LA. The restaurant will serve fresh seafood dishes with a modern twist and provide an unforgettable culinary experience for its guests.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant is seeking to raise $200,000 in startup capital from a group of private investors. The funds will be used to cover the costs of building out the restaurant’s specific location, purchasing equipment and supplies, and hiring staff.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant has a projected annual revenue of $1,200,000 and is expected to be profitable within its first year of operation. The restaurant’s target market is affluent diners who are looking for an exquisite seafood dining experience.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant offers a unique and innovative menu that features fresh seafood dishes with a modern twist. The restaurant’s menu includes items such as:
- Blackened salmon with shrimp and grits
- Fried catfish po’ boy with remoulade sauce
- Grilled Louisiana shrimp skewers
- Crawfish etouffee
- Shrimp gumbo
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant also offers a wide selection of wine and beer to complement its menu.
Company Description
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant is owned and operated by John Doe. Mr. Doe has over 10 years of experience in the food and beverage industry. He has worked as a chef at several renowned restaurants in New Orleans and has also owned and operated his own catering business.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will be located at 123 Main Street in New Orleans, LA. The restaurant will occupy a 3,000-square-foot space that was formerly occupied by a pizzeria. The location is in close proximity to several hotels and tourist attractions, which will generate significant foot traffic for the business. It is also located within walking distance of the Central Business District attracting local office workers and residents.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will have a seating capacity of 60 guests. The restaurant will also have a full-service bar that will serve beer, wine, and cocktails.
The seafood restaurant industry is one of the fastest-growing segments of the food service industry. Over the past five years, the industry has experienced strong growth due to an increase in the popularity of seafood as a healthy dietary choice.
The seafood restaurant industry is expected to continue to grow over the next five years as consumers’ preference for healthy and delicious food continues to rise. In addition, the industry will benefit from an increase in per capita disposable income, which will allow consumers to spend more on dining out.
Other Industry Analysis Points
- The seafood restaurant industry is regulated by the FDA
- Changes in government policies could impact the industry
- The seafood restaurant industry is sensitive to changes in the economy
- An economic downturn could lead to a decline in revenue and profit margins
- The seafood restaurant industry is influenced by consumer trends and preferences
- Health-conscious consumers are increasingly seeking out seafood as a healthy dietary choice
Technological:
- The seafood restaurant industry is impacted by advances in food technology
- New cooking techniques and equipment can help to improve the quality of dishes served
- The seafood restaurant industry is subject to food safety and sanitation regulations
- Changes in the law could impact the way that restaurants operate
Environmental:
- The seafood restaurant industry is impacted by changes in the environment
- The quality of seafood dishes can be impacted by pollution and other environmental factors
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will target two primary customer market segments: tourists and local residents.
The tourist market segment consists of individuals who are visiting New Orleans for leisure or business purposes. This market segment is significant for the business as it represents a large portion of the city’s population. New Orleans is a major tourist destination, with over 16 million visitors per year.
The local resident market segment consists of individuals who live and work in New Orleans. This market segment is significant for the business as it represents a stable source of income. Local residents are more likely to visit the restaurant on a regular basis and recommend it to friends and family.
Competitor Analysis
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will compete in the seafood restaurant industry. Through our competitive research, the restaurant’s closest direct competitors will be Red Fish Grill, Bourbon House, and GW Fins.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will compete in the seafood restaurant industry. The restaurant’s closest competitors will be Red Fish Grill, Bourbon House, and GW Fins.
Red Fish Grill is a seafood restaurant located in the French Quarter of New Orleans. The restaurant offers a casual dining experience with a menu that features fresh seafood dishes.
Bourbon House is a seafood restaurant located in the French Quarter of New Orleans. The restaurant offers a more upscale dining experience with a menu that features fresh seafood and steak dishes.
GW Fins is a seafood restaurant located in the Warehouse District of New Orleans. The restaurant offers an upscale dining experience with a menu that features fresh seafood dishes.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will differentiate itself from its competitors by offering a more innovative and modern menu with fresh seafood dishes that are prepared using unique cooking techniques. In addition, the restaurant will provide a superior level of customer service and create an unforgettable dining experience for its guests.
Our competitive advantages include:
- Unique menu with fresh seafood dishes that are prepared using unique cooking techniques
- Superior level of customer service
Products : The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will serve a variety of fresh seafood dishes that are prepared using unique cooking techniques.
Price : The price of menu items will be competitive with other seafood restaurants in the area.
Promotion : The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will use a combination of marketing strategies to promote the business and attract customers.
- Develop a website and create social media accounts to reach a wider audience
- Develop a promotional video to generate interest in the restaurant
- Participate in local food festivals and events to generate awareness
- Launch a targeted advertising campaign in local publications and on radio and television
- Develop relationships with local tour operators to promote the restaurant to visitors
- Offer discounts and special promotions to generate repeat business
Place : The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will be located in the French Quarter of New Orleans.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will be open for lunch and dinner seven days a week. The restaurant will be closed on Thanksgiving and Christmas Day.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will source seafood from local suppliers and growers to ensure the freshest ingredients are used in dishes.
The restaurant will use a point-of-sale system to manage inventory and track sales.
The restaurant will seat up to 100 guests at a time. Reservations will be accepted for parties of eight or more. Walk-in guests will be accommodated on a first-come, first-served basis.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will have a staff of 20 employees, including a head chef, sous chefs, kitchen staff, servers, and hostesses.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will be owned and operated by John and Jane Doe.
John Doe has over 10 years of experience in the restaurant industry. He has worked as a chef, manager, and consultant for a variety of restaurants.
Jane Doe has over 20 years of experience in the hospitality industry. She has worked as a hotel manager, event planner, and marketing consultant.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will have start-up costs of $500,000. The majority of the start-up costs will be for leasing and outfitting the restaurant space. Other start-up costs include purchasing kitchen equipment, hiring staff, and marketing the business.
The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant is projected to generate $1.5 million in sales in the first year of operation. The restaurant is expected to have net profits of $250,000 in the first year.
Sample Menu
Appetizers:
- Jumbo shrimp cocktail
- Oysters Rockefeller
Soups and salads:
- Seafood bisque
- Caesar salad with grilled shrimp
- House salad with tuna steak
- Spinach salad with scallops
- Shrimp scampi
- Surf and turf (filet mignon and lobster tail)
- Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables
- Blackened redfish
- Bread pudding with rum sauce
- Bananas Foster
- Cheesecake with berry sauce
- Key lime pie
- Soda, coffee, tea, milk
- Beer, wine, cocktails
Financial Projections
Balance sheet.
[insert financial statement]
Income Statement
Cash flow statement, restaurant business plan example #2 – la cocina de el paso: home of authentic mexican cuisine.
La Cocina de El Paso is a restaurant that specializes in serving authentic Mexican cuisine. The owners, John and Jane Doe, have over 30 years of combined experience in the hospitality and restaurant industry. This wealth of experience will ensure the success and longevity of the business.
Located in the heart of El Paso, La Cocina de El Paso will offer a relaxed and welcoming atmosphere. Guests can expect to be served freshly made dishes, prepared with only the freshest ingredients. The restaurant will also serve a selection of beer, wine, and cocktails.
La Cocina de El Paso will cater to both locals and tourists alike. To promote the business, the owners plan to launch an aggressive marketing campaign that will include print ads, radio spots, and social media. In addition, the restaurant will partner with local businesses to offer discounts and promotional offers.
The owners have estimated start-up costs of $500,000. The majority of this amount will be used to lease and outfit the restaurant space. Income is projected to reach $1.75 million within the first year of operations, with net profits of $350,000.
La Cocina de El Paso is an upcoming restaurant that will offer authentic Mexican cuisine. The restaurant will be located in downtown El Paso, Texas, and will feature a relaxed atmosphere with seating for up to 150 guests.
The restaurant will utilize only the freshest ingredients in its dishes and offer a selection of beer, wine, and cocktails. The menu will feature appetizers, soups and salads, entrees, desserts, and drinks.
The restaurant industry is highly competitive. In particular, Mexican cuisine has gained popularity in recent years. To succeed, La Cocina de El Paso must differentiate itself from other restaurants in the area.
The restaurant will focus on offering fresh and authentic Mexican cuisine with a welcoming atmosphere. The owners plan to partner with local businesses and offer discounts and promotional offers. In addition, the owners plan to launch an aggressive marketing campaign that will include print ads, radio spots, and social media.
The target market for La Cocina de El Paso will be both locals and tourists. The restaurant is located in a tourist area and is close to several attractions. As such, it will be well-positioned to attract customers from out of town as well as local residents.
The restaurant will serve a variety of customers, including young adults and families. To appeal to this demographic, the restaurant will offer an inviting atmosphere with comfortable seating and a selection of entertainment options. Additionally, the menu will feature authentic Mexican dishes that are sure to please all tastes.
Ideal Customer Demographics:
- Young adults: ages 18-34
- Local residents
Psychographics:
- Adventurous eaters
- Value conscious
- Seeking authentic experiences
There are several other restaurants in El Paso that specialize in Mexican cuisine. Main competitors include El Paso’s Best, El Taco Loco, and Casa Azul.
El Paso’s Best is the area’s premier Mexican restaurant. The food is of high quality and the atmosphere is casual yet upscale. Prices are slightly higher than La Cocina de El Paso, but the quality of the food makes it worth the price.
El Taco Loco is a fast-food Mexican restaurant. The food is inexpensive, but the quality is not as high as La Cocina de El Paso.
Casa Azul is a family-style Mexican restaurant with more of a casual atmosphere. Prices are slightly lower than La Cocina de El Paso and the menu features traditional Mexican dishes.
To differentiate itself, La Cocina de El Paso will focus on fresh ingredients and authentic Mexican dishes. The restaurant will also offer a selection of beer, wine, and cocktails, as well as discounts and promotional offers. Finally, the owners plan to launch an aggressive marketing campaign that will help spread the word about La Cocina de El Paso.
To attract customers, La Cocina de El Paso will focus on marketing its fresh and authentic Mexican cuisine.
Below is a sample menu for La Cocina de El Paso, featuring traditional Mexican dishes and a selection of beer, wine, and cocktails.
- Quesadillas
- Guacamole and Chips
- Stuffed Jalapenos
- Queso fundido, taquitos
Soups & Salads:
- Chicken Tortilla Soup
- Caldo de Res (Beef Soup)
- Taco Salad with Ground Beef or Grilled Chicken
- Ensalada de la Casa (House Salad)
- Ensalada Fresca (Fresh Salad)
- Tacos al Carbon (Grilled Steak Tacos)
- Fajitas (Steak, Chicken, or Vegetarian)
- Chiles Rellenos (Stuffed Peppers)
- Carne Asada con Papas
- Camarones a la Diabla
- Enchiladas Verdes
- Churros con Chocolate
- Tres Leches Cake
- Flan Napolitano
- Beer & Wine
Promotions:
The restaurant will offer promotional discounts and specials. For example, customers who purchase two entrees may receive a complimentary appetizer or dessert. The owners plan to partner with local businesses to offer additional discounts and promotional offers.
La Cocina de El Paso will offer competitive pricing. Prices will be slightly lower than El Paso’s Best, but higher than El Taco Loco and Casa Azul.
The restaurant will be located in downtown El Paso, close to several attractions and tourist sites. The owners hope that the convenient location will help bring in both tourists and local residents.
Marketing Mix
To reach its target customers, La Cocina de El Paso will use a combination of traditional marketing strategies such as print ads, radio spots, and TV commercials, as well as digital marketing tactics such as content marketing, social media campaigns, email newsletters, and online advertising.
- Print Advertising : The owners plan to run print ads in local newspapers and magazines that target young adults and families.
- Radio & TV Spots : The restaurant will also air radio spots and TV commercials that feature its menu items and promotional offers.
- Content Marketing : La Cocina de El Paso will create content that highlights the freshness of its ingredients and the authenticity of its Mexican dishes. The content will be shared on social media, in email newsletters, and on the restaurant’s website.
- Social Media Campaigns : The restaurant will run campaigns on Facebook and Instagram that feature customer reviews, contests, and giveaways.
- Online Advertising : The owners plan to use Google Ads and other online platforms to reach potential customers.
The owners of La Cocina de El Paso are confident that their marketing strategy will help the restaurant stand out from its competitors and attract customers. With its fresh and authentic Mexican cuisine, competitive prices, convenient location, and aggressive marketing campaigns, La Cocina de El Paso is sure to be a success.
Collaborative Promotion: The owners of La Cocina de El Paso plan to partner with local businesses in order to create mutually beneficial promotional offers. For example, the restaurant may offer discounts to customers who use services from one of its partners. The owners believe that this type of collaborative promotion will help draw in more customers and generate additional revenue for the business.
Events: La Cocina de El Paso plans to host events such as cooking classes and live music performances in order to build relationships with customers and increase brand awareness. The restaurant will also use these events to showcase the freshness of its ingredients, its Mexican cuisine, and the quality of its drinks (margaritas, beer & wine, cocktails).
These strategies are designed to help La Cocina de El Paso build a strong customer base and become a popular destination in downtown El Paso. The owners are confident that these tactics will help the restaurant stand out and create a positive impact on the local community.
La Cocina de El Paso will have a skilled team of servers, cooks, and bartenders who are knowledgeable about the restaurant’s Mexican cuisine. The owners plan to focus on delivering high-quality customer service in order to ensure customers have a great experience. The owners also plan to invest in modern kitchen equipment that can help streamline the cooking process.
The restaurant will be open from 11 am to 10 pm on weekdays and from 11 am to 11 pm on weekends. The owners plan to hire additional staff during peak hours in order to handle the influx of customers. The owners also plan to use advanced reservation systems and delivery services to accommodate customers who would prefer not to wait in line.
The owners of La Cocina de El Paso have extensive experience in the restaurant industry. They plan to hire a team of experienced managers who can handle day-to-day operations and ensure that the restaurant runs smoothly. The management team will also be responsible for developing marketing strategies, overseeing staff training programs, and creating promotional offers.
The job description for the management team includes:
- Overseeing day-to-day operations
- Developing marketing strategies and managing promotional campaigns
- Creating training programs for staff members
- Handling customer inquiries and complaints
- Ensuring that food safety standards are met
- Analyzing data to identify areas for improvement.
The total start-up cost of La Cocina de El Paso is estimated at $500,000.
This includes:
- $100,000 for lease deposits and renovations costs;
- $200,000 for furniture and fixtures;
- $50,000 for marketing and advertising;
- $50,000 for kitchen equipment;
- $100,000 for the salary of the management team.
The owners plan to finance the start-up costs through a combination of their personal savings and bank loans. They also plan to generate additional revenue by offering catering services and hosting special events at the restaurant.
The financial forecast for La Cocina de El Paso is optimistic. The owners expect to break even in the first year of operations and reach profitability within five years.
Free Restaurant Business Plan Example PDF
Download our restaurant business plan pdf here. This is a free restaurant business plan example to help you get started on your own restaurant plan.
How to Finish Your Restaurant Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your restaurant business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!

- QR Code Menu
Table of Contents
The restaurant industry is as dynamic as it is diverse, with various types of restaurants catering to different culinary preferences. For those aspiring to open a new restaurant, understanding this vast landscape is crucial. One of the pivotal steps before diving into this venture is to create a business plan. It not only defines the unique essence of your eatery but also lays out a roadmap for its successful operation. Familiarizing oneself with the different types of restaurants is essential to pinpoint your niche and stand out in a bustling market.
What is A Restaurant Business Plan?
When you’re planning to open a restaurant, a comprehensive restaurant business plan is your blueprint to success. It serves as a strategic guide, outlining your restaurant’s vision, objectives, and operational procedures. But beyond its functional use for the business owner, a well-crafted plan becomes a tool to attract potential investors.
Writing a business plan requires detailing every aspect of your restaurant dream, from the concept and target demographic to the financial projections and marketing strategies. For restaurant owners, this document encapsulates the essence of their establishment, ensuring they remain on the right track. Moreover, presenting this plan to potential investors offers a clear, organized view of your vision, increasing their confidence in the venture.
Ff you want to get your restaurant off the ground and appeal to both patrons and investors, a restaurant business plan is not just a recommendation—it’s a necessity.
Why A Business Plan Is Important For A Successful Restaurant Business?
Making a restaurant a reality isn’t just about great food or an attractive interior; it’s about laying the groundwork for success with a good business plan. A well-crafted restaurant business plan comes with a slew of benefits, not least of which are:
Clear Vision and Objectives: One of the foremost reasons to plan for your restaurant is to articulate a clear vision and set definitive objectives. This process helps you refine your restaurant ideas, making them more viable in the real world. With a concrete vision, you can maintain a consistent direction and avoid being swayed by fleeting trends that don’t align with your brand.
Financial Planning: Money is the lifeline of any venture. A restaurant business plan provides a detailed financial blueprint, determining startup costs, projecting revenues, and outlining budgetary constraints. It anticipates potential financial hurdles, allowing restaurant owners to make informed decisions. By meticulously charting out every financial detail, restaurant owners can ensure they have the necessary funds to sustain the business, even during lean periods.
Operational Efficiency: Operational hiccups can turn even the most promising restaurant ideas into failures. With a comprehensive business plan, you can optimize staffing, inventory management, customer service, and daily operations. A good plan streamlines the restaurant’s workflow, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
In a world teeming with culinary ventures, a business plan is essential to stand out. It gives clarity to your vision, ensures sound financial footing, and optimizes operations, paving the way for the restaurant needs to thrive.
Step-by-step Guide To Write A Restaurant Business Plan
Starting a restaurant is a dream for many, but to make that restaurant dream into a reality, one needs a structured approach. A winning restaurant business plan provides a comprehensive roadmap to bring your vision to life. Here’s how to craft that perfect plan:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a snapshot of your entire restaurant business plan. Typically, it should be concise, about one to two pages long, capturing the essence of what your restaurant is about and what it aims to achieve.
What should you cover in an Executive Summary?
- Introduce your bakery business : Begin by describing the kind of restaurant you’re opening.
- State your mission and vision : Your mission statement reflects your restaurant’s core purpose, while the vision paints a picture of its future.
- Outline your objective : Define the goals for your new business.
- Provide a financial overview : Offer a brief insight into the financial state of your business.
2. Restaurant Business Description
This section provides an in-depth look into what your restaurant is and what it aims to offer to the diner.
What should you cover in the restaurant description section?
- Talk about your bakery concept : Describe your restaurant, its theme, and its unique approach to serving patrons.
- Explain your unique selling proposition (USP) : What sets your restaurant apart?
- Operational model : Explain how you’ll operate your restaurant before and after opening.
3. Market Analysis
Market analysis provides data-driven insights derived from thorough market research. It helps restaurant owners understand their audience and the market landscape.
- Target market : Delve into the demographics of your potential clientele.
- Location : Describe where your restaurant fits geographically and why it’s an ideal spot.
- Competition : Analyze other restaurants in the area and their offerings.
4. Organization and Management
This section presents the business structure and the key players driving your restaurant’s operations.
What should you cover in the organization and management plan?
- Restaurant ownership information : Detail the type of business entity (e.g., LLC, Partnership) and ownership distribution.
- Profiles of your Restaurant management team : Introduce your core team members, their roles, and their experience in the restaurant industry.
5. Sample Menu
This section is a sneak peek into what diners can expect when they visit.
What should you consider when creating a sample menu?
- Menu items : List down dishes and beverages you’ll offer.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP) : What makes your menu stand out?
- Menu Pricing : Provide a range or specific prices for your offerings.
6. Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy outlines how you plan to market your restaurant and drive sales.
What should you cover in the marketing strategy for your restaurant business?
- Define your brand : Discuss the brand identity – from logo to restaurant design.
- Plan how you’ll attract diners, from online promotions to loyalty programs, SEO for website, and partnerships with local local businesses
- Considering using an online food ordering system in your food truck
- Create a digital menu with QR code to make your menu easy for your customers to access online
7. Business Operations
This section delves into the day-to-day operations of running your restaurant.
What operational issues should you address in your business plan?
- Supply chain : Detail how you’ll procure ingredients and manage inventory.
- Operating hours : What days and hours will you operate? Consider peak meal times and special events.
- Staffing : Discuss hiring, training, and staff management plans.
- Equipment : List the equipment needed to run the restaurant.
8. Financial and Loans
How Much Does It Cost to Start a Restaurant?
Depending on the type of restaurant you’re opening, costs can vary significantly. Starting a bar business, for instance, can range anywhere from $95,000 to over $2 million. Several factors can influence these numbers. The size of the restaurant, its location, and the culinary offerings play crucial roles in the total investment. Want to delve deeper into the specifics? This comprehensive guide on how much it costs to open a small restaurant breaks down the various expenses you can expect.
How Many Ways to Fund Your Restaurant?
For every restaurant dream, funding is a pivotal aspect. From traditional bank loans to seeking angel investors or crowd-funding, there’s a multitude of avenues available for those considering opening a restaurant.
Important Questions to Consider When You Create Your Funding Request
Beyond just how much you plan to spend, you’ll want to include details on projected ROI, repayment strategies, and how the funds will directly help grow your business. Remember, lenders and investors are most interested in understanding how their contributions will help the restaurant flourish and ensure a return on their investment.
9. Financial Projections
Financial projections are a crucial aspect of the business plan, providing a roadmap for operating the restaurant and giving potential investors a clear picture of your business strategy.
Break-even analysis
This analysis tells you when your restaurant may start to turn a profit, balancing out initial investments and operational costs. It’s essential to understand this when you plan to gain traction and open the restaurant.
To calculate the break-even point, use this formula: Fixed Costs / (Price – Variable Costs) = Break Even Point
Projected profit and loss statement
This section should include estimations of your future revenues, costs, and profits over a specific period, helping you and investors visualize the financial health of your restaurant.
Cash flow analysis
A comprehensive cash flow analysis is part of your business plan, showing the movement of cash in and out of your business. This plan can help identify periods of potential cash shortages and allow for strategic preparations.
Restaurant Business Plan Template
As you embark on the journey to make your restaurant dream come true, using a free template for guidance can be invaluable. This example provides a glimpse into what a business plan can look like. However, always remember to choose your restaurant’s features that align with your vision and market demand. For more insights, consider consulting various restaurant business plan examples and business plan samples to get a holistic view.
Mission : “To provide an unforgettable dining experience by blending authentic flavors with a modern twist.”
Vision : “To be the leading global chain offering our signature fusion cuisine.”
Restaurant Description : “DineFusion, an innovative blend of Italian and Japanese cuisines, located at the heart of downtown.”
Costs : Initial investment of $150,000.
Profits : Expected yearly net profit of $75,000 after operating costs.
2. Description of the Restaurant
Restaurant Concept : A fusion of Italian and Japanese cuisines, bringing together the best of both worlds.
Restaurant Name : “DineFusion”
Restaurant Type : Casual dining
Restaurant Location : 123 Downtown Street, Metropolis
Order Fulfillment : Dine-in, takeaway, and online delivery through partnering platforms.
Working Hours : 10 AM – 10 PM daily.
Type of Cuisine : Italian-Japanese Fusion
Offer : From sushi rolls with a twist of Italian herbs to pizzas topped with sashimi. Include a sample menu for a detailed look.
Unique Selling Point : “Where East meets West on a Plate!”
4. Market and Competition Analysis
Market Analysis :
Target Customer : Young professionals aged 25-40 and tourists.
Size of the Target Customer : Approximately 150,000 individuals fit our target profile in Metropolis.
Competition Analysis :
Size of the Competition : Collectively serve an estimated 500 customers daily.
Competitors’ Offer : Traditional fusion dishes without the unique Italian-Japanese blend.
Competitors’ Prices : Average meal price is $25.
5. Investment Plan (Detailed Cost Analysis)
Investment Cost :
- Renovation: $50,000
- Kitchen Equipment: $40,000
- Initial Inventory: $10,000
- Licenses and Permits: $5,000
- Marketing and Promotion: $20,000
- Miscellaneous: $25,000
Operating Costs (Monthly) :
- Rent: $5,000
- Salaries: $15,000
- Utilities: $1,000
- Inventory Replenishment: $4,000
- Marketing: $2,000
- Miscellaneous: $3,000
Total Cost : Estimated monthly operating cost of $30,000.
6. Financial Forecast
Based on the expected customer footfall and average ticket size, we anticipate monthly revenues of $60,000, with a profit of $30,000 before taxes.
Owner/Manager : Jane Smith, with 10 years of experience in the restaurant industry.
Chef : Marco Tanaka, a specialist in both Italian and Japanese cuisines.
Supporting Staff : 10 members, including servers, cleaners, and kitchen assistants.
8. Marketing Plan
Our marketing strategy involves an initial launch on social media platforms, collaborations with influencers, and partnerships with delivery platforms. Periodic offers, loyalty programs, and events like “fusion food fests” will help in consistent customer engagement.
Tips For Creating A Successful Restaurant Business Plan
Opening your restaurant is exhilarating, but to transform your culinary dreams into business a reality, a well-crafted business plan is paramount. Here are some tips to ensure success:
Thorough Research : Before you put pen to paper, conduct in-depth research. Understand your target market, competition, and potential challenges. This will not only guide the rest of your plan but also demonstrate your commitment and seriousness to potential restaurant investors.
Use a Template : If you’re unsure where to begin, use a business plan template to get started. It will offer structure and ensure you cover essential sections of your business plan.
Clarity is Key : Your business plan should be concise yet comprehensive. Avoid jargon. Remember, you may be presenting this to individuals who might not be familiar with restaurant terminologies.
Be Realistic with Projections : Overestimating your future success can be as detrimental as underselling it. Ensure your financial forecasts are realistic and achievable.
Highlight What Sets You Apart : Whether it’s a unique theme, a special dish, or an innovative service model, pinpoint what makes your restaurant stand out.
Seek Feedback : Before finalizing, seek feedback. Whether from industry peers, potential restaurant investors, or mentors, a fresh set of eyes can offer invaluable insights.
Remember, to make a restaurant business plan truly effective, it should be a living document, revised and updated as you gather more information, make decisions, and choose your restaurant’s path forward. Keep refining and adjusting to ensure the best path to make the business a thriving success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what should be included in a restaurant plan, 2. what is a strategy plan of a restaurant, 3. how do i write a business proposal for a food business, 4. how do you write a marketing plan for a restaurant.
A marketing plan for a restaurant should start with an understanding of your target customers. Identify where they spend their time online and offline and strategize accordingly. Outline your brand voice and how you’ll communicate your unique selling proposition. Factor in promotions, advertising campaigns, and loyalty programs. Also, consider modern restaurant technology tools that can aid in marketing, such as CRM systems or social media analytics tools. Ensure that each marketing initiative has clear objectives, a set budget, and methods to track effectiveness.
Opening a restaurant is a thrilling yet intricate endeavor. Every section of the restaurant business plan serves as a roadmap, guiding entrepreneurs towards realizing their culinary dreams. As you choose your restaurant’s concept, location, and design, always revert to your business plan to ensure alignment with your vision. In essence, a meticulously crafted plan not only provides clarity and direction but also instills confidence in potential stakeholders. Remember, success in the restaurant industry goes beyond delectable dishes; it lies in foresight, strategy, and relentless execution.
Related articles

QR Code on Table Tents for Restaurants and Bars

How much does it cost to open a small restaurant

How much does it cost to open a bakery

Menubly LLC 8 The Green Suite R, Dover, Delaware 19901
Privacy Policy
Terms of service
Cookie Policy
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
- Food, Beverage & Restaurant
How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan + Free Template

2. Company Overview
Company overview is a part where you fully introduce your restaurant business including legal business structure, location, and your restaurant’s proposed concept.
Here you have the liberty to be a little more creative in describing your restaurant in the whole business plan.
Here are some points to incorporate in the company overview:
- Detailed vision and mission statement
- Type of restaurant (fine dining, small restaurant, bistro, cafe, etc.)
- Legal business structure
- Service style
- History and background of the restaurant (if existing)
- Owners’ names and qualifications
- Cusinies & menu highlights
- Restaurant size and seating capacity
- Operating hours & meal plans
- Related service availability (delivery, catering, etc)
Mainly emphasize the chosen location because easily accessible locations with high foot traffic will attract more walk-in customers. And if you haven’t decided on a specific location yet, then mention the type of place you are looking for to give an idea about it to your readers.
Besides, mention the short-term and long-term goals of your restaurant business in the later part of the company description. Along with that mention regional industry trends and your USPs.

Need Assistance Writing a Restaurant Business Plan?
Get Upmetrics’ business plan template, import data directly into the editor, and start editing using Upmetrics AI Assistant.
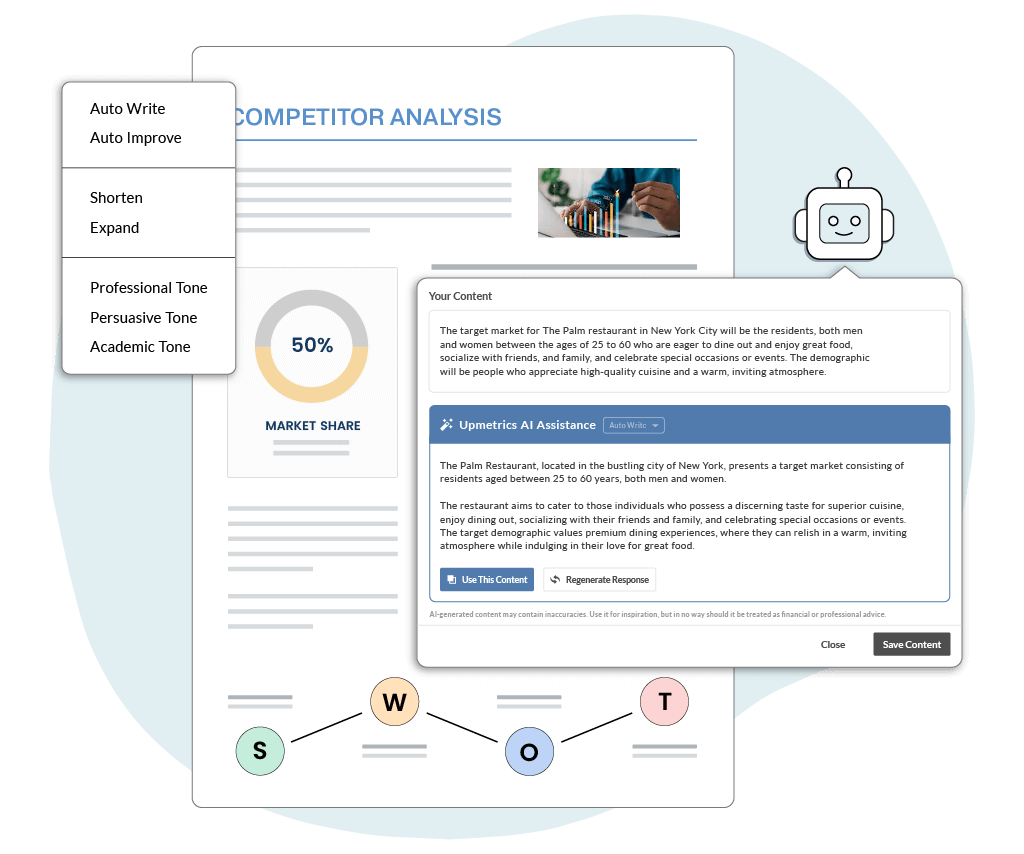
Start Planning Now
3. Market analysis
The market analysis section provides you with a clearer picture of your target market, competitors, and industry trends.
Based on the above details, one can make informed decisions while creating strategies. Therefore, make this section precise and concise to understand.
Here are some steps to follow to write an engaging market analysis section of the restaurant business plan:
- Define your customer base: Identify and describe whom you are going to serve. Make a consumer base after considering the demographics, location, and concept of your restaurant.
- Competitive analysis: List out the names of other restaurants in your location and do the SWOT analysis. You can get the competitive advantage of your restaurant this way.
- Market trends: Discuss any shift in consumer behavior like healthy choices, an increase in vegan food consumption, or technological breakthroughs that might affect your restaurant.
Consider conducting market research, TAM-SAM-SOM analysis , and SWOT analysis to get insights for this section.
Remember, this section helps your readers and potential investors understand your target market, restaurant market overview, market size, and growth potential, so make sure you play your cards right.

4. Sample Menu
The most vital step in launching your restaurant business is the menu. A well-curated menu design will sell itself for your restaurant. Even if you are a new restaurant, then present the sample menu with the name and logo of your restaurant on it.
The menu will showcase all the unique offerings your direct competitors might not provide. Not just the list of cuisines but the pricing is also crucial. This way potential investors and readers can understand your restaurant’s target price point.
Plus your menu should be in sync with target customers; for example, a restaurant near the university should contain more beverages and delicious food options for brunch as students prefer those things more.
Consider your menu as a part of branding, choose the same theme for the menu as for the restaurant.
5. Restaurant Design
Restaurant design is the part where you can show your restaurant concept to potential investors and readers practically. Moreover, create a mood board to explain things smoothly.
Utilize this section to show the uniqueness of your restaurant, and how it is different from competitors.
Explain how your design represents your restaurant’s branding and visual identity. Furthermore, mention how your target market will enjoy and appreciate the ambiance you plan to provide.
Note that restaurant design is one of the key elements to running a successful restaurant, so match the theme and cuisines accordingly.
In this section, you also have to provide a detailed description of how many seats are going to be there along with the floor plan of your restaurant.
6. Management Team
As the name suggests, the management team section of your restaurant’s business plan introduces restaurant owners, key executives, and the management team. It also incorporates the experience, qualification, and restaurant industry knowledge of every individual who is on the team.
A strong management team section can be essential to weigh authority and help potential investors be confident about your restaurant’s idea and vision.
You might consider including the following information in the management team section:
- Business owner or founder’s information
- Executive chef and culinary team
- Front-of-house manager
- Operations and back-of-house team
- Advisors/consultants
- The organizational structure of the team
Showcase how each member fits and what roles & responsibilities they will play. You should include a resume-styled summary for each person in the restaurant’s management section.
7. Operations Plan
The operations plan section outlines the daily business processes and activities centered on achieving the restaurant dream and objectives described in the rest of the plan.
A detailed operations plan helps you and your team define your responsibilities, daily tasks, and short-term goals you need to achieve, keeping track of your long-term objective.
Here are a few key elements to include in your operations plan section:
- Staffing and training
- Operating hours
- Operational process
- Tools and equipment
- Inventory control
- Technology and software
- Quality control measures
- Customer service policies
Remember it should incorporate all important daily tasks. Also, an operations plan is a living document, you can change it often according to the change in the dynamics of the work.
Read More: The Ultimate Guide to Restaurant Operations Planning
8. Marketing Plan
Even with great food, prices, and ambiance, you won’t attract enough diners without marketing.
Thus, a well-crafted restaurant marketing plan is necessary to spread awareness and build a strong brand presence.
The marketing plan can help you streamline your marketing efforts and create impactful and effective marketing campaigns while keeping track of the projected budget and maximizing return on investment.
Hence, this is the section in which you give an idea to your potential investors about how you will acquire new customers and retain existing ones. This section should include:
- Target market and their dining habits
- Branding and positioning
- Marketing strategies (website, social media accounts, etc.)
- Marketing Calendar
- USPs of your restaurant (unique ambiance, amiable staff, new cuisines in the local area)
- Your marketing goals
- Customer retention strategies (loyalty program, giving coupons or discounts on bulk orders or events)
Even if you are going to hire a PR agency for marketing, then mention it and the reason why you chose them.
After taking care of marketing, let us move further to finances.
Read More: Step-by-Step Guide to Restaurant Marketing Plan
9. Financial Plan
The financial plan is the most crucial and demanding section of any business plan. It is one of the deciding factors for potential investors, banks, or any financial institute to invest in your restaurant business.
This section of your plan details your restaurant’s financial information and how it will reach its financial goals or how much revenue potential it has.
Here are key components and statements that you should include in your financial plan section:
- Pro forma profit and loss statement
- Break-even analysis
- Balance sheet
- Sales forecast
- Detailed cost analysis
- Cash flow projections
- Business ratios
- Funding request
- Tax considerations
- Exit strategy
Before you create financial projections, know how many seats the restaurant will have and what services you plan to provide. This will help you in making realistic financial projections if you are going to start a new business.
Also, if you are asking for funding, then mention where you will utilize your funds.
We hope that this sample restaurant business plan will provide you with an idea for writing a successful plan.
Restaurant Industry Highlights 2024
- Growth forecast : National Restaurant Association predicted US restaurant sales to reach $898 billion in 2022 which would further grow by 4% yearly to reach $1.2 trillion by 2030.
- Technology is everywhere : Automation is helping staff maximize their efficiency by handling orders, deliveries, and communication effectively.
- Sustainability & ethical sourcing : Eco-friendly practices such as minimizing food waste, avoiding single-use plastics, and ethical plus local sourcing are encouraged by customers.
- Delivery is the new deal : People prefer deliveries over dining out as they are time-saving. So, there is an incline in the number of delivery apps and delivery services providing restaurants.
- Kiosks are the preference : The number of people who prefer ordering and paying through kiosks is increasing due to the convenience.
How to Refine & Present a Restaurant Business Plan
Once you have written your entire business plan, it is time to read and re-read it and make it error-free. You have to be confident about every aspect of the plan before you present it in front of your audience.
Moreover, alter your plan to suit different audiences to enhance your communication. For instance, keep your plan professional and include all the growth potential, profitability, and ROI data when you present your restaurant business plan for seeking funding.
Also, when you present your restaurant business plan to potential partners or vendors, emphasize collaboration benefits and how it can help in their individual growth.
Apart from the above points, make sure your plan has various engaging visuals, interactive elements, and enhanced storytelling to present all the data interestingly. Thus, make a digital presentation of your plan to incorporate all the above things clutter-free.
Once you are confident, it is time to email your plan to the people already on your mind. And give a pat to yourself for finally taking that step.
Download a sample business plan for a restaurant
Ready to kick-start your business plan writing process? And not sure where to start? Here you go, download our free restaurant business plan pdf , and start writing.
This intuitive, modern, and investment-ready template is designed specifically for restaurants. It includes step-by-step instructions & examples to help in creating your own restaurant business plan.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.

Related Restaurant Resources
- Restaurant Marketing Plan
- Restaurant Financial Plan
- Restaurant Operations Plan
- Restaurant Industry Trends
Discover how Upmetrics can help you write a business plan
With Upmetrics, you will receive step-by-step guidance, customizable templates, 400+ sample business plans , and AI assistance to streamline your business planning process.
In fact, if you are not adept with finances, the financial forecasting tool Upmetrics provides will help you create realistic financial forecasts for 3 or more years.
Whether you’re starting a new venture or looking to grow one, Upmetrics offers the resources and insights you need to develop a successful & professional business plan that aligns with your goals.
Related Posts
Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan
Seafood Restaurant Business Plan
Tips for Business Plan Cover Pages
AI Tools for Writing Business Plan
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a restaurant business plan.
A solid business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful restaurant business. It helps to get clarity in your business, raise money, and identify potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
How to get funding for your restaurant business?
There are several ways to get funding for your restaurant business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
What is the easiest way to write your restaurant business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of restaurant business plan samples and edit it as per your needs. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
Can a good restaurant business plan help me secure funding?
Indeed. A well-crafted restaurant business plan will help your investors better understand your business domain, market trends, strategies, business financials, and growth potential—helping them make better financial decisions.
What's the importance of a marketing strategy in a restaurant business plan?
Marketing strategy is a key component of your restaurant business plan. Whether it is about achieving goals or helping your investors understand the return on investment—an impactful marketing strategy is the way to do it!
Here are a few pointers to help you understand the importance of having a marketing strategy:
- It provides your business an edge over your competitors.
- It helps investors better understand your business and growth potential.
- It helps you develop products with the best profit potential.
- It helps you set accurate pricing for your products or services.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Opportunity
Integrations
Request a Demo
Revolution Demo Request
Restaurant Business Plan | 12 Key Components to Include
Restaurant business plans are a critical tool for success in the restaurant industry . If you’re thinking of opening a restaurant , opening a coffee shop , or even opening a bakery , a business plan is a must.
But what goes into a restaurant business plan? And more importantly, how to write a business plan ?
In this blog post, we’ll discuss what a restaurant business plan is and what are the key components in writing one. Keep reading.

What Is a Restaurant Business Plan?
A restaurant business plan is a detailed document outlining the various aspects of starting and running a restaurant business . It includes information on the restaurant ’s concept, menu, marketing, and financial strategy. The business plan also serves as a tool for securing financing from investors or lenders.
You should create a restaurant business plan before starting a new restaurant business. It will help the business owner validate their idea, determine the venture’s feasibility, and develop a roadmap for success.
How to Start a Restaurant Business Plan
Creating a restaurant business plan can be a daunting task, but it is essential to the restaurant success . A well-thought-out business plan will help you to make informed decisions about your restaurant, attract investors, and ultimately grow your business. Here are some tips to get you started on creating your restaurant business plan:
- Define your concept : What kind of restaurant do you want to open? What is your target niche market ? What is your unique selling proposition (USP)?
- Do your research : Understand the industry, the competition, and the target market. This will help you to determine your USP and how to position your restaurant in the market.
- Create a financial plan : Project your revenue, restaurant expenses , and asset requirements. This will help you to understand your start-up costs and how much capital you will need to raise.
- Write your business plan : Once you have all the information, you can start writing your business plan. Include an executive summary, company overview, market analysis, financial plan, and details about your team and operations.
Now that we know how to start a restaurant business plan let’s write one. This section will provide an overview of the components you should include in your plan. Keep reading!
How to Write a Business Plan for a Restaurant
As you write your restaurant business plan, there are a few key components you will want to include. These components will help you paint a clear picture of your restaurant concept, the market opportunity, and your plans for making your restaurant a success.
There are 12 key components of a restaurant business plan.
- Executive Summary
The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire business plan. It should highlight the most important aspects of your plan, including your restaurant concept, target market, value proposition for restaurant brands, marketing, and advertising strategy, and financial projections.
This section should be no more than two pages in length and should include the following information:
- The name, location, and opening date of your restaurant
- A brief description of your restaurant concept and business model
- Your target market and marketing strategy
- An overview of your competition and competitive advantage
- Your financial projections for the next three to five years
- Company Description
The company description section of your business plan should provide an overview of your company’s structure, ownership, and management team. You’ll need to give an overview of your company, including your mission statement, values, and goals.
This section should include information on the following:
- Your restaurant’s concept and restaurant menus
- Your choice of location and facility type
- Your business model (e.g., full-service, fast casual, etc.)
- Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should provide an overview of the restaurant industry and the specific market opportunity you are targeting. This section should include industry trends, demographic data, and economic indicators.
- The size and growth of the restaurant industry
- The types of restaurants that are popular with consumers
- The trends that are affecting the restaurant industry
%2520(1).png)
- Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis section of your business plan should provide an overview of the competition in your market. This section should include information on the number of restaurants in your market, their average sales volume, their marketing and advertising strategies, and their pricing structures.
This should include information on the following:
- The type of competition you face (e.g., direct, indirect, etc.)
- The number of competitors in your market
- The competitive landscape (e.g., who is the market leader, niche players, etc.)
The menu section of your business plan should provide an overview of the dishes that you will be offering at your restaurant. It should include information on your recipes, ingredient sourcing, and pricing.
In this section, you will provide a sample of your restaurant menu. This should include information on the following:
- Your choice of cuisine (e.g., American, Italian, Chinese, etc.)
- Your pricing strategy
- Your portion sizes, servings per dish, and plate presentation
The employees’ section of your business plan should provide an overview of the team you will assemble to help you operate your restaurant. This section should include your staffing needs, job descriptions, and compensation structures.
In this section, you will describe your employee requirements. This should include information on the following:
- The types of employees you will need to fill (e.g., chefs, dishwashers, wait staff , servers , bartenders, etc.)
- The number of employees you will need to hire
- The qualifications and experience you require of employees
- Restaurant Design
The restaurant design section of your business plan should provide an overview of the physical space you will be leasing or purchasing for your restaurant. This section should include information on the layout of your dining room, kitchen, and restrooms.
In this section, you will describe your restaurant’s overall design and concept. This should include information on the following:
- The style of your restaurant (e.g., casual dining , fine dining, family style dining , etc.)
- The theme or decor of your restaurant
- The layout and design of your restaurant
- Your choice of furnishings and fixtures
- Branding elements

The location section of your business plan should provide an overview of the geographic market that you will be targeting with your restaurant. This section should include information on the demographics of your target market, the competition in your market, and the visibility of your restaurant location.
In this section, you will describe your restaurant’s location. This should include information on the following:
- The location you are looking for (e.g., downtown, suburban, strip mall, etc.)
- The size of the area you are looking for (e.g., 2,000 square feet, 3,000 square feet, etc.)
- The features of the location you are looking for (e.g., parking, visibility, etc.)
- The traffic patterns near your restaurant
- Market Overview
The market overview section of your business plan should provide an overview of the restaurant industry. It includes information on industry trends, demographic data, and economic indicators.
In this section, you will provide an overview of the restaurant market. This should include information on the following:
- The trends that are affecting the restaurant industry such as supply chain management trends , food trends , beverage trends , and restaurant tech trends .
- Marketing and Advertising
The marketing and advertising section of your business plan should provide an overview of how you will promote your restaurant. This section should include your marketing budget, promotional strategies, and media mix.
In this section, you will describe your marketing strategy. This should include information on the following:
- Your target market and target customer profile
- Your marketing mix (e.g., product, price, place, promotion)
- Your direct to consumer advertising and promotion strategy (e.g., print, online, social media, etc.)
- Your direct marketing efforts (e.g., coupon, loyalty program , etc.)
- SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis for restaurant is a tool you can use to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your restaurant business. This section should include your restaurant’s unique selling proposition, key marketing initiatives, and competitive advantage.
In this section, you will conduct a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis of your business. This should include information on the following:
- Your restaurant’s strengths and weaknesses
- The opportunities and threats posed by your competition
- Your restaurant’s strengths and weaknesses (internal factors)
- The opportunities and threats facing your restaurant business (external factors)
- Financial Analysis
The financial analysis section of your business plan should provide an overview of your restaurant’s financial projections. It includes your start-up costs, operating expenses, and revenue streams.
This section will provide a detailed financial projection for your restaurant business. This should include information on the following:
- Your start-up costs and funding sources
- Capital requirements
- Your projected income and expenses
- Your expected return on investment (ROI)
- Your sales, revenue, and profitability projections for the next three to five years
- Your exit strategy (e.g., IPO, sale, etc.)
When writing your business plan, be sure to include all the important sections listed above. These will give you the best chance for success when starting a new restaurant.

Frequently Asked Questions About Restaurant Business Plan
In light of what you’ve learned about restaurant business plans and their components, let’s explore some questions you may have about them.
What Is a Perfect Business Plan?
There are a few key things that make a business plan perfect.
- First, it should be clear and concise. It should lay out your goals and objectives for the business in a way that is easy to understand.
- Second, it should be realistic. It should consider your resources and limitations and craft an achievable plan.
- Finally, it should be adaptable. Your business plan should change with it as it grows and changes.
How Long Should a Business Plan Be?
There’s no rule of thumb for how long a business plan should be, but 15-20 pages is a good starting point. The length of your business plan will depend on the scope and complexity of your business, as well as your goals and objectives.
What are the Four Types of Business Plan?
The four types of business plans are:
- Short plans , or miniplans, are concise versions of a full business plan.
- Presentation plans , or decks, are visual representations of your business plan.
- Working plans are more detailed and comprehensive versions of your business plan.
- What-if plans are contingency plans that outline how you would respond to various risks and challenges that could impact your business.
A Roadmap to Success
A well-executed restaurant business plan is the key to a successful restaurant. By creating a plan that outlines your business goals, strategies, and financials, you can ensure that your restaurant will be on track for success.
While no plan is ever foolproof, following a sound plan gives you the best chance for success. If you are looking to start or expand your restaurant business, be sure to create a comprehensive business plan that will help you achieve your goals.
.png)
- Value of Culinary Education
- Financing Your Education
- Austin Student Life
- Boulder Student Life
- Culinary & Pastry Careers
- Hospitality Careers
- Health & Wellness Careers
- Food Entrepreneurship
- Success Stories
- World of Food & Drink
- Recipes & Techniques
- Culinary Arts
- Baking & Pastry Arts
- Blog Search
- Campuses & Online
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Career Services
- Culinary Arts Programs
- Baking & Pastry Programs
- Food Entrepreneurship Programs
- Plant-Based Programs
- Holistic Nutrition & Wellness Programs
- Hospitality & Restaurant Operations Management
- Online Programs
- Austin Campus
- Boulder Campus
- Tuition & Fees
- Financial Aid Process
- Scholarships & Grants
- Application Process
- Military & Veterans
- High School Students
- International Students
- Student Stories
- Open Houses & Events
- Our Chef Instructors
- Farm to Table ® Experience
- Accreditations
- Vision, Mission & Core Values
- Alumni Profiles
- History & Timeline
- Enthusiast Cooking Classes (not related to degree or diploma programs)
- Student Login
- (855) 955-7555
- Search for:
- Request Information
How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan
An overview of how to write a restaurant business plan for foodservice entrepreneurs, from concept and menu planning to kitchen design and marketing.

Get the Essential Guide to Starting a Restaurant
Download our guide to explore budget-friendly restaurant startup concepts, necessary licenses and permits, business planning tips, and more!
Clicking the "Get the Survey Now" button constitutes your express request, and your express written consent, to be contacted by and to receive automated or pre-recorded call, texts, messages and/or emails from via phone, text, and/or emails by Auguste Escoffier School of Culinary Arts at the number(s)/email you provided, regarding furthering your education and enrolling. You understand that these calls , texts, messages and/or emails may be generated using an automated or pre-recorded technology. You are not required to agree to receive automated or pre-recorded calls, texts, messages or emails as a condition of enrolling at Escoffier. You can unsubscribe at any time or request removal of street address, phone number, email address via Escoffier website .
Here’s the truth about starting a restaurant. According to a study by Cornell University , over 26% of independent restaurants don’t survive their first year and nearly 60% fail by their third year. That’s why creating a solid restaurant business plan is so important. It may give you an opportunity to put concrete structure around your thinking and assess your ideas from a higher viewpoint, before spending a single dollar.
Although there are no guarantees in life (and especially in business) with a little preparation, education, and mentorship, you can avoid many of the pitfalls that upend others. In this article, you’ll discover how to begin writing a restaurant business plan—and how you can get an education that may help you start your own foodservice business .
Define Your Business Concept
A business plan should start with a basic conceptual overview. Where did the idea for your restaurant or food business come from? And how is your idea unique compared to what else is currently in the market? Who is your target market, and what (in general) will you be serving them?
Think of the concept as the bird’s eye view of your business.
You may also wish to include a mission statement in this section. This will be a short sentence or two that outlines the value the business provides to customers and employees, and may set an inspirational objective. A good example is The Kitchen American Bistro in Boulder, Colorado, which has the following mission:
“We believe in the power of good food and good drink to connect people as family, friends and a community. The Kitchen remains committed to our mission of creating community through food.”*
Verbalizing the bigger picture as a stated mission gives your business depth beyond just making money. When you use it as a guiding principle, it will be reflected in your marketing, operations, and the attitudes of those who join your team.
Do a Market Analysis
Where will your proposed restaurant fit into the overall foodservice market? Is there a niche in your area that’s not being served? Or will you be competing with established businesses? And if so, how will your concept stand out?
Everything from local factors like lack of competition to nationwide factors like a booming economy can contribute to your restaurant’s success or failure. A market analysis can help you to assess both the challenges and opportunities that you’ll face when you open your doors.
Food Entrepreneurship at Escoffier
Dive into greater detail on many of the topics covered in this article in Escoffier’s Food Entrepreneurship programs . The Culinary Entrepreneurship course specifically explores topics like business planning and begin writing a business plan.
Describe Your Service Style
Will your restaurant be fine dining? Counter service? An all-day café with servers? A buffet? A beer garden?
Make sure it’s clearly defined. If your service style is simple, you may include this in your concept section. But if it’s more complex, it may warrant its own section in your business plan. For example, perhaps you plan to offer elevated table service with a number of thoughtful touchpoints. You’ll want to be very clear about what that will look like.
Your service style will directly impact your staffing levels, which will affect your labor costs. That’s why it’s vital to include this information and the associated cost estimates in your business plan.

A full-service waitstaff like this will be more costly than a lean counter-service staff.
Build Your Sample Menu
A great restaurant menu is specifically designed to appeal to your target market, while staying true to your concept. Even if you’re not 100% sure what your final restaurant menu will include, create a sample version for your business plan.
The menu is your product, and it will impact everything about your restaurant from food costs (typically between 25% and 35% of the menu price) to the number of cooks you’ll need to the layout of your kitchen.
You should also calculate pricing for this menu to verify if it can be served at a price point that fits with your target demographic. A family-friendly spot with $20 burgers, for example, is creating a disconnect between its target market and its menu price.
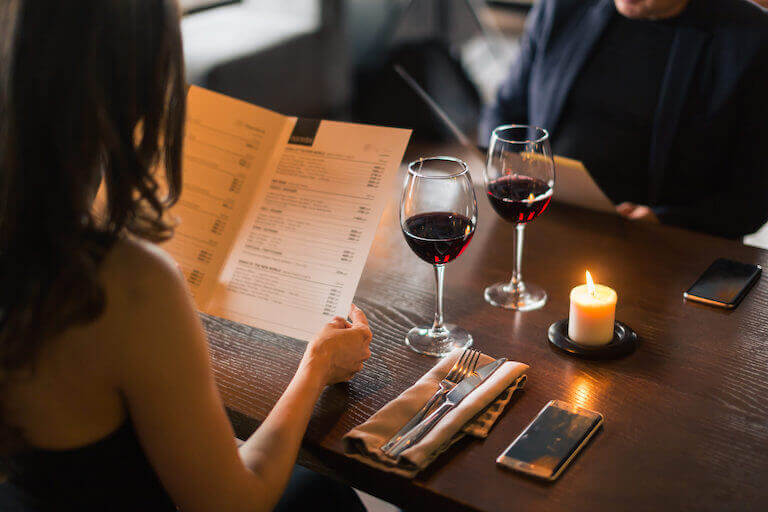

The Science Behind Menu Design
Creating and designing a menu can be complex. You have to balance the art of making great food with the practicalities of food and labor costs. In Escoffier’s Food Entrepreneurship programs, students may explore topics like visual design and price analysis.
Determine Your Facility Design and Location
Once you have a sense of your concept and menu, you can begin to plan what your restaurant should look like and where it will be.
The kitchen is the most expensive part of a restaurant’s total cost. And every square foot taken up by cooking space is a square foot that can’t hold customers. Industry wisdom states that a kitchen should be between 25% and 30% of the total restaurant space—including storage. So you have to plan your kitchen as efficiently as possible.
In the dining room, you’ll need tables and chairs, possibly a host stand, and maybe a bar. You may have plans for art and custom light fixtures, or a high-end tap system for draft beer. Renderings from your architect and/or interior designer can help to show what you’re envisioning.
Include all of the equipment, furnishings , and supplies that you plan to purchase for both the back of house and front of house, so you can estimate the cost of building out your restaurant.
You will also need to decide where your restaurant will be. This will impact rent, guest parking, foot traffic, and even your operating hours. If you’re in a business district, for example, you may choose to only be open for lunch.

Choose Your Management Team and Determine Staff Needs
A great plan without a great team is likely to fail. An important part of your business plan is determining the various roles and responsibilities for your managers and employees.
Depending on the size of your business, your plan may include an organizational chart that explains which position is reporting to whom, how many people you will be hiring, the main skill sets of the management team, and the unique things that each employee brings to the table.
You can also call out any special achievements or accolades for the managers you plan to bring on board, like a general manager with a great deal of experience or a chef with impressive certifications .
If you attend culinary school or enroll in a food entrepreneurship program, some of those team members could even be former classmates. Business is ultimately about the relationships between people, and culinary school is a ripe environment to build those critical connections that may serve you down the road.
Forecast Your Costs, Revenue, and Potential Profit
Anyone looking to launch a foodservice business probably wonders how much the whole endeavor is going to cost, and what the return on investment might be. If you’ve gone through all of these steps, you’ll be well on your way to better awareness of the fundamental costs of business and what you can do to help guide it toward being a profitable venture.
Your business plan should detail the financing that will be required to get your business up and running, the associated costs of marketing and staff, and variable costs such as ingredients. Your business plan should be sufficiently detailed to estimate the profits and expenses for the first few years of your business, in order to help ensure that your plan is economically feasible.

Keeping An Eye On Restaurant Profits
Restaurant profit margins are relatively low compared to other businesses. A key course in Escoffier’s curriculum for the Food Entrepreneurship Associate Degree explores managerial accounting concepts, culinary math, and an overview of basic business accounting transactions such as how to read financial statements. It may explain the practical application of these concepts to the hospitality industry and how to manage costs for long-term profitability.
Create a Marketing Plan
The first step in restaurant or food truck marketing is to identify who your ideal customer will be. Are they looking for date spots, family-friendly restaurants, or group dining? What do they like to eat? What are their wants and needs? Will you be targeting specific dietary profiles, like vegan , paleo, or gluten-free?
Once you know who your customers are, how will you reach them? You will probably need to start a website, including your location, hours, and menu. You may also choose to promote your restaurant on social media , sharing photos and videos on platforms like Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook. You can also work with local food influencers , leveraging their larger platforms to spread the word about your new restaurant.

Share photos taken by your customers to connect with your audience.
While your marketing plan is sure to change and evolve over time, it’s wise to have a general strategy in place before you open your doors so you can have a successful grand opening.
Marketing 101
Escoffier’s Food Entrepreneurship programs include coursework in food styling and photography , social media, and hospitality marketing. Graduates could be prepared to identify their ideal customers and reach them for better visibility and higher sales.
An Entrepreneurial Education Can Mean Being Prepared
While it is obvious that you need a passion for the world of food and drink before launching a food service business, starting any venture is difficult without mentorship from professionals who have real-world experience.
In Escoffier’s Food Entrepreneurship programs , students can work with skilled experts from the culinary world who may help them avoid the pitfalls common to new business owners. A blend of culinary theory and practical, hands-on business operations experience can prepare students for the intricacies of foodservice, with a steady eye on profitability.
To learn more about what students can expect in our Food Entrepreneurship programs, get in touch with our Admissions Department . They can answer your questions and help you develop a plan to get closer to your dreams of business ownership.
Enjoyed this article? Here are a few more you may like.
- How to Start a Restaurant with Little to No Money
- Ghost Kitchens & Ghost Restaurants: What Are They and How Do You Start One ?
- The Complete Guide to Starting a Home-Based Catering Business
*Information may not reflect every student’s experience. Results and outcomes may be based on several factors, such as geographical region or previous experience.
This article was originally published on June 29, 2020, and has since been updated.
Latest Articles
How restaurants can get involved in their community.
Restaurants are often vital parts of their communities. Explore some strategies restaurants can use to give back to the communities that support them.
Kitchen Slang: A Guide to Jargon Used in Professional Kitchens
Professional kitchens use a wild amount of unique language. Here’s a guide to some of the most common kitchen jargon you’ll hear from chefs.
Which Chefs Have Earned the Most Michelin Stars?
For many chefs, a Michelin Star represents the peak of culinary achievement. Here are the ten chefs with the most Michelin Stars of all-time.
Subscribe to the King of Chefs Blog
Get the King of Chefs email newsletter delivered to your inbox weekly. You'll get everything you need to know about culinary & pastry careers, food entrepreneurship, financing your culinary education, and more.
The Essential Culinary School Planner & Checklist

We’ve compiled a checklist of all of the essential questions into one handy workbook: Career options, academic plans, financing your education, and more.
Clicking the "Get the Workbook Now" button constitutes your express request, and your express written consent, to be contacted by and to receive automated or pre-recorded call, texts, messages and/or emails from via phone, text, and/or emails by Auguste Escoffier School of Culinary Arts at the number(s)/email you provided, regarding furthering your education and enrolling. You understand that these calls , texts, messages and/or emails may be generated using an automated or pre-recorded technology. You are not required to agree to receive automated or pre-recorded calls, texts, messages or emails as a condition of enrolling at Escoffier. You can unsubscribe at any time or request removal of street address, phone number, email address via Escoffier website .

12 Examples of SMART Goals for Restaurants
Running a successful restaurant requires more than just quality food and excellent customer service. Establishing SMART goals can ensure that your restaurant successfully meets its objectives.
The SMART framework is an effective tool when strategizing for restaurant success. This post will cover examples of SMART goals that can be applied in a restaurant setting, giving owners insight into creating a solid foundation for their business.
Table of Contents
What is a SMART Goal?
The SMART ( Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-based ) framework will allow you to develop practical goals for your restaurant business.
Do you still want more clarity? Here is a deeper dive into each component:
You need to ask yourself what success means for your restaurant. By brainstorming and creating specific goals for each area of your business, you’ll have a better chance of meeting or even exceeding them.
In an ever-changing restaurant industry, businesses must stay ahead of the curve. Establishing measurable goals is vital to achieving success.
It helps owners and managers realize their vision and encourages them to focus on long-term objectives. Understanding these goals from the outset allows restaurants to track progress and adjust as needed.
The adage “shoot for the stars and you’ll reach the moon” doesn’t always apply when setting goals. It would be best to develop realistic goals, as reaching sky-high expectations can be mentally and emotionally draining.
For example, suppose your goal is to start a new business . You’d want to chunk it down into smaller steps, such as researching ideas, writing a business plan, and securing funding.
Having personal values keeps you grounded and reminds you of your purpose. That’s why aligning your goals with your values is so important—it gives you something tangible to strive towards, allowing you to laser-focus on the bigger picture during tough times.
A successful timeline contains all the critical steps of the goal-setting process, from planning and scheduling different tasks to regularly checking progress.
It’s like having a map to reach success—you know where to go and how long it will take you. You will guarantee you’re taking steady strides toward attaining your desired outcome.
Let’s take a look at 12 SMART goals examples for your restaurant business:
1. Increase Revenue
“I want to increase our restaurant’s revenue by 5% within the next 6 months by implementing creative promotions and marketing campaigns. I’ll focus on leveraging our social media channels, creating stronger relationships with current customers, and developing new partnerships.”
Specific: The SMART goal is explicit because it details how to increase revenue within a set period.
Measurable: The person could check the restaurant’s revenues every month.
Attainable: Increasing revenue by 5% within the 6 months is doable.
Relevant: The goal is relevant to boosting restaurant revenue.
Time-based: You will ideally meet success after 6 whole months.
2. Boost Customer Satisfaction
“I want to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty by improving the speed of our service. To do so, I will implement a new ordering system and train staff to use it. The aim is to have the system running in the following three months.”
Specific: The statement is well-defined, stating precisely the objective and how to achieve it.
Measurable: By monitoring the speed of service, it will be possible to determine whether customer satisfaction has improved.
Attainable: It is achievable to implement a new system and train staff.
Relevant: This is pertinent to customer satisfaction because it will ensure that patrons are served quickly and efficiently.
Time-based: There is a three-month timeline for reaching this particular goal.
3. Invest in Employee Wellness
“I’m committed to helping my employees stay physically and mentally healthy. I will provide free access to resources such as gym memberships, counseling services, and healthy meal options by the end of 8 months.”
Specific: The goal outlines what you intend to do (provide resources) and when it should be done (within 8 months).
Measurable: You could track the progress of providing access to resources.
Attainable: Identifying and setting up these resources can be done within 8 months.
Relevant: Investing in employee wellness is essential for a business and can lead to longer-term benefits such as increased employee engagement and loyalty.
Time-based: The goal must be completed within 8 months.
4. Optimize Menu Selection
“By the end of four months, I aim to optimize the restaurant’s menu selection, minimizing waste and enabling customers to find something they love while keeping the food cost low.”
Specific: This is explicit because the individual wants to optimize their restaurant’s menu selection.
Measurable: The goal should be measurable if you track the number of customer orders and waste levels.
Attainable: This SMART statement is feasible if the person takes the time to assess the menu and adjust it accordingly.
Relevant: Optimizing a restaurant’s menu selection is vital for customer experience and financial sustainability.
Time-based: Goal attainment is expected after four months.
5. Improve Cost Efficiency
“In order to improve our bottom line, I will increase cost efficiency within the restaurant by 8% over the 7 months ahead. This could include reducing waste, looking for more affordable suppliers, and finding ways to streamline processes.”
Specific: The goal is clear. The restaurant aims to improve its bottom line by increasing cost efficiency.
Measurable: You can evaluate the change in cost efficiency every month.
Attainable: This is definitely possible if given the necessary time and resources.
Relevant: The goal is appropriate for the restaurant’s desire to increase its cost efficiency.
Time-based: You have a 7-month window to achieve success.
6. Upgrade Technology Infrastructure
“I’ll upgrade my restaurant’s technology infrastructure to increase efficiency and customer experience for 6 months. I want to install new computers, tablets, and software to streamline operations and provide customers with an enhanced dining experience.”

Specific: You have precise tasks available, such as installing new computers and tablets.
Measurable: You could count the number of upgrades completed each month.
Attainable: This is achievable in 6 months if you have the right resources and personnel to help with the upgrades.
Relevant: The statement is directly related to your restaurant’s objectives of improving efficiency and customer experience.
Time-based: Six months is required to accomplish this certain goal.
7. Expand Brand Awareness
“We need to be connected and consistent with how we communicate our brand messages. I plan to increase our brand visibility outside the local market by launching new campaigns and advertising on social media channels in 5 months.”
Specific: The goal is clear and concise: increase the visibility of our brand outside the local market.
Measurable: You will measure success based on the number of campaigns and messages launched on social media channels.
Attainable: The 5-month timeline gives you enough time to conduct market research, design campaigns, and launch advertising on social media.
Relevant: This is relevant and valuable because it helps build the brand’s presence in other markets.
Time-based: There is a 5-month end date for effective brand awareness.
8. Promote Sustainable Practices
“I aim to reduce our restaurant’s carbon footprint by 10% next year. To accomplish this, I will introduce initiatives that promote sustainable practices such as using reusable utensils, composting food scraps, and reducing water usage.”
Specific: The individual will reduce their restaurant’s carbon footprint by 10%.
Measurable: Make sure you actively introduce initiatives to promote sustainable practices.
Attainable: This is a reachable goal because it’s possible to implement more sustainable practices in the restaurant.
Relevant: This statement is appropriate because it addresses a critical environmental issue.
Time-based: The SMART goal is time-bound by the end of next year.
9. Develop Loyalty Program
“My goal is to develop and launch a loyalty program for our customers after 6 months. I will encourage customer retention and help our business grow by rewarding returning customers for their loyalty.”
Specific: The goal states the objective , what will be done to achieve it, and the deadline.
Measurable: You could track the number of customers who sign up for the loyalty program.
Attainable: This is possible because it is realistic to develop and launch a loyalty program in 6 months.
Relevant: Encouraging customer loyalty and retention is important for growing the business.
Time-based: There is a 6-month time frame for goal completion.
10. Reduce Food Waste
“I will reduce food waste in my restaurant by 10% within 7 months by instituting a system of regular checks and monitoring inventories more closely. This will be more cost-effective and show my commitment to going green.”
Specific: The goal is to reduce food waste and institute a system of checks and monitoring inventories.
Measurable: You could measure the reduction of food waste in percentage.
Attainable: Minimizing food waste is a realistic goal that you can accomplish.
Relevant: This is relevant to your restaurant’s environmental commitment.
Time-based: You have 7 months to reduce food waste by 10%.
11. Create Unique Experiences
“I want to create memorable dining experiences by implementing a monthly special menu that reflects our local culture. I’ll work with creative chefs to create interesting dishes using local ingredients and provide the best service.”
Specific: This is specific because the goal outlines an actionable plan to create unique experiences.
Measurable: You could count how many customers consistently order the monthly special.
Attainable: Creating a special menu and working with creative chefs are realistic activities that can be done regularly.
Relevant: Promoting unique experiences for diners allows restaurants to stand out from the competition and retain customers.
Time-based: It is implied that the goal is ongoing, so you must pursue it regularly.
12. Add Delivery Services
“I want to expand our services and give customers the convenience of delivery. I will research and create a plan to add delivery services to our restaurant within 6 months.”
Specific: This goal focuses on adding delivery services to the restaurant.
Measurable: Ensure the successful addition of delivery services within the given time frame.
Attainable: With research and a plan, adding delivery services is undoubtedly feasible.
Relevant: Customers appreciate the convenience of delivery services, so this goal is relevant to restaurant success.
Time-based: You have 6 months to add delivery services for your business.
Final Thoughts
The SMART goal-setting method is critical to restaurant success. With well-defined and measurable goals, businesses can monitor progress and make necessary changes to stay competitive in their industry.
Restaurants that establish SMART goals can experience positive growth and long-term sustainability. It’s a worthwhile investment of time and energy that will pay off in the end. So take the plunge and devise your own SMART goals today—you won’t regret it.
This post may feature products and services that we think you’ll find useful. Please read our disclosure for more information.
- View all solutions
- Restaurant reservation software
- Restaurant marketing solutions
- Restaurant table management
- Experiences
- Reputation and reviews
- Relationship management
- OpenTable integrations
- For Restaurants
- For Restaurant groups
- For Bars & wineries
- For Hotels & casinos
- The best customer service
- Robust reporting and insights
- The largest diner network
- View all industry insights
- Hospitality
- Industry Expertise
- Get started
How to write a comprehensive restaurant business plan

fanWhen opening a new restaurant, having a solid restaurant business plan is key for the success of a a business. The best ones identify, describe and analyse business opportunities while setting a blueprint. Here, we’ve put together a guide for how to write a restaurant business plan so life at your spot starts off on the right foot.
What your restaurant business plan should cover
The strongest restaurant business plans always include all or most of the components described below. Charles Bililies , founder and CEO of Souvla , advises that first-time restaurateurs read plenty of different business plans for other restaurants, technology and retail companies to get a better sense of layout options, writing styles and clarity of concept. Put the sections that you feel would be most compelling to someone who’s never met you first: the “Management Team” section if you’re coming from high-profile establishments, for example. The goal is for the reader to keep turning the page.
Quick links Branded cover Concept Sample menu Service Management team Design Target market Location Market overview Marketing and publicity Specialists and consultants Business structure Financials
1. Branded cover
Include your logo (even if it’s not finalised), the date, and your name.
Describe your restaurant concept and get the reader excited about your idea. Go into detail about the food you’ll be serving, inspiration behind your concept and an overview of service style. Define clearly what will be unique about your restaurant.
3. Sample menu
The menu is the most important touchpoint of any restaurant’s brand, so this should be more than just a simple list of items. Incorporate your logo and mock up a formatted menu design (tap a designer for help if needed).
Your sample menu should also include prices based on a detailed cost analysis. This will give investors a clear understanding of your targeted price point, provide the first building block to figuring out average bill estimations needed to create financial projections and show investors that you’ve done the homework needed to be confident that you’ll be able to sell these items at these prices and operate within your budget.
This section is most relevant for fine-dining concepts, concepts that have a unique service style or if you have particularly strong feelings about what role service will play in your restaurant. It can be a powerful way of conveying your approach to hospitality to investors by explaining the details of the guest’s service experience.
Will your restaurant have counter service designed to get guests on their way as quickly as possible, or will it look more like theatre, with captains putting plates in front of guests simultaneously? If an extensive wine program is an integral part of what you’re doing, will you have a sommelier? If you don’t feel that service is a noteworthy component of your operation, address it briefly in the concept section.
5. Management team
Write a brief overview of yourself and the team you have established so far. You want to demonstrate that the work experience you’ve acquired over the course of your career has provided you with the necessary skills to run a successful restaurant. Ideally, once you have described the strong suit of every member of your team, you’ll be presenting a full deck. Most independent restaurant investors are in this for more than just money, so giving some indication of what you value and who you are outside of work may also be helpful.
6. Menu Design
Incorporate some visuals. Create a mood board that shows images related to the design and feeling of your restaurant. Planning on cooking in a wood-burning oven? Include that. Photos of materials and snippets of other restaurants that you love that are similar to the brand you’re building are also helpful.
7. Restaurant target market
Who is going to eat at your restaurant? What do they do for a living, how old are they, and what’s their average income? Once you’ve described them in detail, reiterate why your specific concept will be appealing to them.
8. Location
There should be a natural and very clear connection between the information you present in the ‘Target Market’ section and this one. You probably won’t have a specific site identified at this point in the process, but you should talk about viable neighbourhoods. Don’t assume that potential investors will be familiar with the areas you’re discussing and who works or lives there — make the connections clear. You want readers to be confident that your restaurant’s ‘ideal’ diner intersects with the neighbourhood(s) you’re proposing as often as possible.
If you don’t have a site, this is a good place to discuss what you’re looking for in terms of square footage, foot traffic, parking, road accessibility and other important details.
9. Market overview
Address the micro and macro market conditions in your area. At a macro level, what are the local and regional economic conditions? If restaurants are doing poorly, explain why yours won’t; if restaurants are doing well, explain how you’ll be able to compete in an already booming restaurant climate. At a micro level, discuss your direct competitors. Talk about what restaurants share your target market and how you’ll differentiate yourself.
10. Marketing and publicity
The restaurant landscape is only getting more competitive. Talk about your pre- and post-opening marketing plan to show investors how you will gain traction leading up to opening day, as well as how you’ll keep the momentum going. If you’re going to retain a PR/marketing company, introduce them and explain why you’ve chosen them over other companies (including some of their best-known clients helps). If not, convey that you have a solid plan in place to generate attention on your own through social media , your website , and media connections. To help you get started be sure to check out our zero budget marketing checklist .
11. Specialists and consultants
List any outside contractors you plan to retain, such as:
- Main Contractor
- PR & Marketing
Briefly explain the services they’ll be providing for you and why you chose them, along with any notable accomplishments.
12. Business structure
This section should be short and sweet. What type of business structure have you set up and why did you make that specific decision? You will need to work with a lawyer to help you determine what business structure is best for you.
“ Step one : write a restaurant business plan. Step two : hire a good lawyer. In addition to helping me build a smart, sustainable business structure, my lawyer was also a great resource for reviewing my business plan because she’s read thousands of them. She was a very helpful, experienced outside perspective for more than just legal matters”, Charles Bililies explains.
13. Restaurant financials and funding
Let your accountant guide you through this portion of your business plan. It is crucial that whoever you retain to help you with your finances has a wealth of restaurant experience (not just one or two places), as they should be familiar with the specifics of restaurant finances and know what questions to ask you.
Before creating realistic financial projections, your accountant will want to know approximately how many seats you’re planning on having, what your average bill will be, and how many covers you expect per day. Being conservative in these estimations is key as these three data points will be used as the basis for figuring out whether your concept is financially feasible.
Lou Guerrero, Principal at Kross, Baumgarten, Kniss & Guerrero, emphasises that, “You’ll get a lot of accountants that tell you that they’ve done a couple of restaurants, but you have to choose someone that has a deep expertise in what you’re doing. There’s nothing to gain from going with someone that doesn’t have a very restaurant-centric practice.”
A well-vetted accountant with restaurant experience will know exactly what you’ll need to have prepared to show investors. The key projections you can expect to work on are:
- Pro forma profit and loss statement for the first three to five years of operation
- Break even analysis
- Capital requirements budget
Free tools to build a restaurant business plan in Australia:
If design is not your forte, consider using a free online template. There are plenty of templates available on the web that can aid in this process. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or need help getting started, there are some great options
- Canva : Bring your descriptions and its templates will help you do the rest. Canva hosts a library of thousands of free menu templates to choose from.
- Australian Government: a collection of free tools and templates to help you build your first business plan
- VistaCreate: The plug-and-play menu templates are easy to use, and the platform has the option for print and delivery.
Get the tools, resources and fresh ideas for running a successful restaurant
Let’s Go
Explore more articles

Find your table for any occasion
- Reservations
- Relationships
- Integrations
- Restaurants
- Restaurant groups
- Bars & wineries
- Hotels & casinos
- Private dining
- POS Integrations
- Data & security
- Online waitlist
- Table categories
- Direct messaging
- About OpenTable
- New on OpenTable
Need help deciding which option is best for you? Give us a call at
+61 (03) 4240 3297
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cookies and Interest-Based Ads
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Goals and Objectives for Business Plan with Examples
NOV.05, 2023

Every business needs a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and how it plans to get there. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and actions to achieve them. A well-written business plan from business plan specialists can help a business attract investors, secure funding, and guide its growth.
Understanding Business Objectives
Business objectives are S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound (SMART) statements that describe what a business wants to accomplish in a given period. They are derived from the overall vision and mission of the business, and they support its strategic direction.
Business plan objectives can be categorized into different types, depending on their purpose and scope. Some common types of business objectives are:
- Financial objectives
- Operational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Social objectives
For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be:
- To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year.
- To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months.
- To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
- To improve its customer satisfaction rating by 15% in the next month.
The Significance of Business Objectives
Business objectives are important for several reasons. They help to:
- Clarify and direct the company and stakeholders
- Align the company’s efforts and resources to a common goal
- Motivate and inspire employees to perform better
- Measure and evaluate the company’s progress and performance
- Communicate the company’s value and advantage to customers and the market
For example, by setting a revenue objective, a bakery can focus on increasing its sales and marketing efforts, monitor its sales data and customer feedback, motivate its staff to deliver quality products and service, communicate its unique selling points and benefits to its customers, and adjust its pricing and product mix according to market demand.
Advantages of Outlining Business Objectives
Outlining business objectives is a crucial step in creating a business plan. It serves as a roadmap for the company’s growth and development. Outlining business objectives has several advantages, such as:
- Clarifies the company’s vision, direction, scope, and boundaries
- Break down the company’s goals into smaller tasks and milestones
- Assigns roles and responsibilities and delegates tasks
- Establishes standards and criteria for success and performance
- Anticipates risks and challenges and devises contingency plans
For example, by outlining its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer in its business plan, a bakery can:
- Attract investors with its viable business plan for investors
- Secure funding from banks or others with its realistic financial plan
- Partner with businesses or organizations that complement or enhance its products or services
- Choose the best marketing, pricing, product, staff, location, etc. for its target market and customers
Setting Goals and Objectives for a Business Plan
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan is not a one-time task. It requires careful planning, research, analysis, and evaluation. To set effective goals and objectives for a business plan, one should follow some best practices, such as:
OPTION 1: Use the SMART framework. A SMART goal or objective is clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with the company’s mission and vision, and has a deadline. SMART stands for:
- Specific – The goal or objective should be clear, concise, and well-defined.
- Measurable – The goal or objective should be quantifiable or verifiable.
- Achievable – The goal or objective should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant – The goal or objective should be aligned with the company’s vision, mission, and values.
- Time-bound – The goal or objective should have a deadline or timeframe.
For example, using the SMART criteria, a bakery can refine its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer as follows:
- Specific – Increase revenue with new products and services from $5 to $5.50.
- Measurable – Track customer revenue monthly with sales reports.
- Achievable – Research the market, develop new products and services, and train staff to upsell and cross-sell.
- Relevant – Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, profitability and cash flow, and market competitiveness.
- Time-bound – Achieve this objective in six months, from January 1st to June 30th.
OPTION 2: Use the OKR framework. OKR stands for O bjectives and K ey R esults. An OKR is a goal-setting technique that links the company’s objectives with measurable outcomes. An objective is a qualitative statement of what the company wants to achieve. A key result is a quantitative metric that shows how the objective will be achieved.
OPTION 3: Use the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats. A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps the company assess the internal and external factors that affect its goals and objectives.
- Strengths – Internal factors that give the company an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses – Internal factors that limit the company’s performance or growth.
- Opportunities – External factors that allow the company to improve or expand.
- Threats – External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the company.
For example, using these frameworks, a bakery might set the following goals and objectives for its SBA business plan :
Objective – To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Key Results:
- Research gluten-free cake market demand and preferences by month-end.
- Create and test 10 gluten-free cake recipes by next month-end.
- Make and sell 100 gluten-free cakes weekly online or in-store by quarter-end.
SWOT Analysis:
- Expertise and experience in baking and cake decorating.
- Loyal and satisfied customer base.
- Strong online presence and reputation.
Weaknesses:
- Limited production capacity and equipment.
- High production costs and low-profit margins.
- Lack of knowledge and skills in gluten-free baking.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand and awareness for gluten-free products.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
- Potential partnerships and collaborations with health-conscious customers and organizations.
- Increasing competition from other bakeries and gluten-free brands.
- Changing customer tastes and preferences.
- Regulatory and legal issues related to gluten-free labeling and certification.
Examples of Business Goals and Objectives
To illustrate how to write business goals and objectives for a business plan, let’s use a hypothetical example of a bakery business called Sweet Treats. Sweet Treats is a small bakery specializing in custom-made cakes, cupcakes, cookies, and other baked goods for various occasions.
Here are some examples of possible startup business goals and objectives for Sweet Treats:
Earning and Preserving Profitability
Profitability is the ability of a company to generate more revenue than expenses. It indicates the financial health and performance of the company. Profitability is essential for a business to sustain its operations, grow its market share, and reward its stakeholders.
Some possible objectives for earning and preserving profitability for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase the gross profit margin by 5% in the next quarter by reducing the cost of goods sold
- To achieve a net income of $100,000 in the current fiscal year by increasing sales and reducing overhead costs
Ensuring Consistent Cash Flow
Cash flow is the amount of money that flows in and out of a company. A company needs to have enough cash to cover its operating expenses, pay its debts, invest in its growth, and reward its shareholders.
Some possible objectives for ensuring consistent cash flow for Sweet Treats are:
- Increase monthly operating cash inflow by 15% by the end of the year by improving the efficiency and productivity of the business processes
- Increase the cash flow from investing activities by selling or disposing of non-performing or obsolete assets
Creating and Maintaining Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of output to input. It measures how well a company uses its resources to produce its products or services. Efficiency can help a business improve its quality, productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Some possible objectives for creating and maintaining efficiency for Sweet Treats are:
- To reduce the production time by 10% in the next month by implementing lean manufacturing techniques
- To increase the customer service response rate by 20% in the next week by using chatbots or automated systems
Winning and Keeping Clients
Clients are the people or organizations that buy or use the products or services of a company. They are the source of revenue and growth for a company. Therefore, winning and keeping clients is vital to generating steady revenue, increasing customer loyalty, and enhancing word-of-mouth marketing.
Some possible objectives for winning and keeping clients for Sweet Treats are:
- To acquire 100 new clients in the next quarter by launching a referral program or a promotional campaign
- To retain 90% of existing clients in the current year by offering loyalty rewards or satisfaction guarantees
Building a Recognizable Brand
A brand is the name, logo, design, or other features distinguishing a company from its competitors. It represents the identity, reputation, and value proposition of a company. Building a recognizable brand is crucial for attracting and retaining clients and creating a loyal fan base.
Some possible objectives for building a recognizable brand for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase brand awareness by 50% in the next six months by creating and distributing engaging content on social media platforms
- To improve brand image by 30% in the next year by participating in social causes or sponsoring events that align with the company’s values
Expanding and Nurturing an Audience with Marketing
An audience is a group of people interested in or following a company’s products or services. They can be potential or existing clients, fans, influencers, or partners. Expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing is essential for increasing a company’s visibility, reach, and engagement.
Some possible objectives for expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing for Sweet Treats are:
- To grow the email list by 1,000 subscribers in the next month by offering a free ebook or a webinar
- To nurture leads by sending them relevant and valuable information through email newsletters or blog posts
Strategizing for Expansion
Expansion is the process of increasing a company’s size, scope, or scale. It can involve entering new markets, launching new products or services, opening new locations, or forming new alliances. Strategizing for expansion is important for diversifying revenue streams, reaching new audiences, and gaining competitive advantages.
Some possible objectives for strategizing for expansion for Sweet Treats are:
- To launch a new product or service line by developing and testing prototypes
- To open a new branch or franchise by securing funding and hiring staff
Template for Business Objectives
A template for writing business objectives is a format or structure that can be used as a guide or reference for creating your objectives. A template for writing business objectives can help you to ensure that your objectives are SMART, clear, concise, and consistent.
To use this template, fill in the blanks with your information. Here is an example of how you can use this template:
Example of Business Objectives
Our business is a _____________ (type of business) that provides _____________ (products or services) to _____________ (target market). Our vision is to _____________ (vision statement) and our mission is to _____________ (mission statement).
Our long-term business goals and objectives for the next _____________ (time period) are:
S pecific: We want to _____________ (specific goal) by _____________ (specific action).
M easurable: We will measure our progress by _____________ (quantifiable indicator).
A chievable: We have _____________ (resources, capabilities, constraints) that will enable us to achieve this goal.
R elevant: This goal supports our vision and mission by _____________ (benefit or impact).
T ime-bound: We will complete this goal by _____________ (deadline).
Repeat this process for each goal and objective for your business plan.
How to Monitor Your Business Objectives?
After setting goals and objectives for your business plan, you should check them regularly to see if you are achieving them. Monitoring your business objectives can help you to:
- Track your progress and performance
- Identify and overcome any challenges
- Adjust your actions and strategies as needed
Some of the tools and methods that you can use to monitor your business objectives are:
- Dashboards – Show key data and metrics for your objectives with tools like Google Data Studio, Databox, or DashThis.
- Reports – Get detailed information and analysis for your objectives with tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or SEMrush.
- Feedback – Learn from your customers and their needs and expectations with tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Google Forms.
Strategies for Realizing Business Objectives
To achieve your business objectives, you need more than setting and monitoring them. You need strategies and actions that support them. Strategies are the general methods to reach your objectives. Actions are the specific steps to implement your strategies.
Different objectives require different strategies and actions. Some common types are:
- Marketing strategies
- Operational strategies
- Financial strategies
- Human resource strategies
- Growth strategies
To implement effective strategies and actions, consider these factors:
- Alignment – They should match your vision, mission, values, goals, and objectives
- Feasibility – They should be possible with your capabilities, resources, and constraints
- Suitability – They should fit the context and needs of your business
How OGSCapital Can Help You Achieve Your Business Objectives?
We at OGSCapital can help you with your business plan and related documents. We have over 15 years of experience writing high-quality business plans for various industries and regions. We have a team of business plan experts who can assist you with market research, financial analysis, strategy formulation, and presentation design. We can customize your business plan to suit your needs and objectives, whether you need funding, launching, expanding, or entering a new market. We can also help you with pitch decks, executive summaries, feasibility studies, and grant proposals. Contact us today for a free quote and start working on your business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the goals and objectives in business.
Goals and objectives in a business plan are the desired outcomes that a company works toward. To describe company goals and objectives for a business plan, start with your mission statement and then identify your strategic and operational objectives. To write company objectives, you must brainstorm, organize, prioritize, assign, track, and review them using the SMART framework and KPIs.
What are the examples of goals and objectives in a business plan?
Examples of goals and objectives in a business plan are: Goal: To increase revenue by 10% each year for the next five years. Objective: To launch a new product line and create a marketing campaign to reach new customers.
What are the 4 main objectives of a business?
The 4 main objectives of a business are economic, social, human, and organic. Economic objectives deal with financial performance, social objectives deal with social responsibility, human objectives deal with employee welfare, and organic objectives deal with business growth and development.
What are goals and objectives examples?
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan describes what a business or a team wants to achieve and how they will do it. For example: Goal: To provide excellent customer service. Objective: To increase customer satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the quarter.
At OGSCapital, our business planning services offer expert guidance and support to create a realistic and actionable plan that aligns with your vision and mission. Get in touch to discuss further!
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

How to Set, Track, and Achieve Business Objectives with 60 Examples
By Kate Eby | April 10, 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Businesses that set objectives make better decisions. Business objectives allow companies to focus their efforts, track progress, and visualize future success. We’ve worked with experts to create the most comprehensive guide to business objectives.
Included in this article, you’ll find the differences between business objectives and business goals , the four main business objectives , and the benefits of setting business objectives . Plus, find 60 examples of business objectives , which you can download in Microsoft Word.
What Is a Business Objective?
A business objective is a specific, measurable outcome that a company works to achieve. Company leaders set business objectives that help the organization meet its long-term goals. Business objectives should be recorded so that teams can easily access them.
Business objectives cover many different factors of a company’s success, such as financial health, operations, productivity, and growth.
One easy way to make sure that you are setting the right business objectives is to follow the SMART goal framework . SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
To learn about setting project objectives using the SMART framework, see this comprehensive guide to writing SMART project objectives .
Business Objectives vs. Business Goal
A business goal is a broad, long-term outcome that a company works toward. Goals usually inform which strategies that department leaders will implement. A business objective , however, is a specific, short-term outcome or action that helps the company achieve long-term goals.
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, goals and objectives are not the same . In general, goals are broad in scope and describe an outcome, while objectives are narrow in scope and describe a specific action or step.
While these differences are important to understand, many of the common frameworks for successful goal-setting — such as SMART, objectives and key results ( OKRs ), and management by objectives (MBO) — can be useful when writing business objectives.
When deciding on objectives for a team or department, keep in mind the overarching goals of a business. Each objective should move the company closer to its long-term goals.
Project Goals and Objectives Template
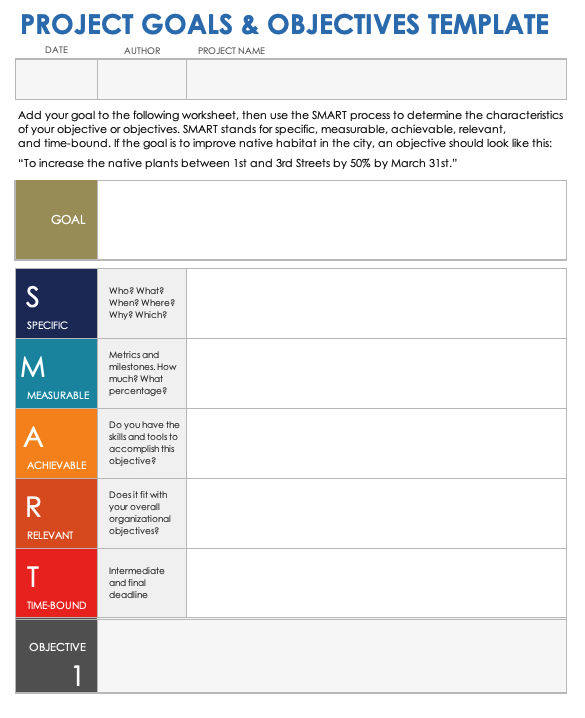
Download the Project Goals and Objectives Template for Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Use this free, printable template to learn how to break down project goals into individual objectives using the SMART framework. Write the primary goal at the top of the worksheet, then follow the SMART process to create one or more specific objectives that will help you achieve that goal.
For resources to help with setting and tracking goals at your company, see this all-inclusive list of goal tracking and setting templates .
What Are the Four Main Business Objectives?
The four main business objectives are economic, social, human, and organic. Each can help a business ensure their prolonged health and growth. For example, human objectives refer to employees’ well-being, while economic objectives refer to the company’s financial health.
These are the four main business objectives:
- Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
- Example: Reduce average customer wait times from eight minutes to four minutes.
- Example: Hire two new chemical engineers by the end of Q2.
- Example: Improve the efficiency of a specific software product by 15 percent.
Types of Business Objectives
There are many types of business objectives beyond the main four. These range from regulation objectives to environmental objectives to municipal objectives. For example, a global objective might be to distribute a product to a new country.
In addition to economic, social, human, and organic objectives, here are some other types of business objectives companies might set:
- Regulatory: These objectives relate to compliance requirements, such as meeting quality standards or conducting internal audits.
- National: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and how they contribute to the country they operate in, such as promoting social justice causes and creating employment opportunities.
- Global: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and its contribution to many countries, such as improving living standards and responding to global demands for products and services.
- Environmental: These objectives relate to a company’s environmental impact, such as reducing chemical waste or making eco-friendly investments.
- Healthcare: These objectives relate to the health and well-being of a population, whether within or outside an organization. These objectives might be improving healthcare benefit options for employees or refining a drug so that it has fewer side effects.
The Importance of Having Business Objectives
Teams need business objectives to stay focused on the company’s long-term goals. Business objectives help individual employees understand how their roles contribute to the larger mission of the organization. Setting business objectives facilitates effective planning.
Here are some benefits to setting business objectives:

- Develops Leadership: Company leaders are more effective when they have a clear vision and can delegate tasks to make it a reality. Setting objectives is a great way to improve one’s leadership skills.
- Increases Motivation: People tend to be more invested in work when they have clear, attainable objectives to achieve. Plus, each completed objective provides a morale boost to keep teams happy and productive.
- Encourages Innovation and Productivity: With increased motivation and workplace satisfaction come more innovations. Set attainable but challenging objectives, and watch teams come up with creative solutions to get things done.
- Improves Strategy: Setting objectives that align with overarching company goals means that everyone across the company can stay aligned on strategic implementation.
- Enhances Customer Satisfaction: Overall customer satisfaction is more likely to increase over time when measurable quality improvements are in place.
- Improves Prioritization: When they are being able to see all of the current objectives, team members can more easily prioritize their work, which in turn makes their workloads feel more manageable.
- Improves Financial Health: Setting economic objectives in particular can help companies stay on top of their financial goals.
60 Examples of Business Objectives
Company leaders can use business objectives to improve every facet of an organization, from customer satisfaction to market share to employee well-being. Here are 60 examples of business objectives that can help a company achieve its goals.
Economic Business Objectives
- Increase profit margins by 5 percent by the end of the Q4.
- Recover 50 percent of total outstanding debts from each quarter the following quarter for the next year.
- “Increase revenue by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer three new holiday sales events in the coming year.
- Move 30 percent of surplus stock by the end of Q2.
- “Reduce costs by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Reduce monthly interest payments by 1.5 percent by consolidating debt.
- Introduce a new credit payment option to expand the potential customer base.
- Apply for six government grants by the end of the year.
- Hire an accountant to track expenses and file the company’s taxes.
- Secure a $100,000 loan to start a business.
- Pitch your business ideas to a venture capital firm.
- Improve your business credit score from 75 to 85 in two years.
- Invest in solar panels for your company headquarters to reduce building energy costs by 75 percent.
- Establish a monthly practice to analyze your cash flow statement.
Social Business Objectives
- Decrease customer average customer wait times by 20 percent in two months.
- Improve the average customer service satisfaction rating from 3.2/5 to 3.8/5 in six months through targeting trainings.
- Hire a contract UX designer to redesign the company website interface in four months.
- Decrease customer churn by 15 percent in one year.
- “Triple the customer base within two years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer 20 percent more customer discounts and specials over the course of two years.
- Increase market share by 5 percent in three years.
- Increase monthly sales quotas for sales associates by 10 percent.
- Develop a sales incentive program to reward top-performing sales associates with vacations, bonuses, and other prizes.
- Donate $10,000 to local causes, such as public school funds or local charities.
- Partner with a charitable organization to host a company-wide 5K.
- Increase your marketing budget by 15 percent.
- Hire a new marketing director by the end of Q3.
- Donate 40 percent of surplus stock to a relevant charity.
- Increase engagement across all social media platforms by 10 percent with a multiplatform ad campaign.
Human Business Objectives
- Hire three new employees by the end of Q1.
- Hire a contractor to train your IT team on new software.
- Rewrite and distribute your company values statement.
- Conduct a quarterly, company-wide productivity training over the next two years.
- Establish a diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) committee.
- Design and implement a mentorship program for diverse employees.
- Create an incentive program that grants additional vacation days for all employees when company-wide productivity goals are met.
- Offer a free monthly happy hour to improve the employee experience.
- Select change leaders across multiple teams to provide support for a corporate reorg.
- Start three employee resource groups (ERGs) within the next six months.
- Diversify websites and career fairs where the hiring team recruits applicants to encourage a more diverse pool of candidates for new jobs.
- Invest in an office redesign that improves the office atmosphere and provides more in-office resources, such as free coffee and snacks, to on-site employees.
- Upgrade employee laptops to improve productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Conduct a yearly, comprehensive employee experience survey to identify areas of improvement.
- Throw office parties to celebrate change milestones.
Organic Business Objectives
- Increase the top line by 15 percent every year for the next five years.
- Achieve 20 percent net profit from 10 product enhancements in the next two years.
- Decrease raw materials costs by 10 percent by the end of the year.
- Reduce downtime by 25 percent by the end of the year.
- Within two years, attain a rate of 25 percent new revenue from products released within the last year.
- Improve customer acquisition ration by 10 percent every quarter for the next two years.
- Reduce total inventory levels by 20 percent over four months.
- Interact with at least 20 Instagram users every month for one year.
- Have a new product launch covered by at least three reputable industry publications within two months of the launch date.
- Grow both the top line and the bottom line by 60 percent every year for three years.
- Reduce product defects by 15 percent every year for four years.
- Increase on-time delivery dates for top customers by 25 percent over the span of three quarters.
- Conduct yearly workplace safety reviews.
- Decrease average customer wait times for responses to social media queries from 45 minutes to 15 minutes by the end of Q4.
- Improve your company website to be on the first page of search results within six months.
Download 60 Example Business Objectives for
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Track the Progress of Business Objectives with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Stary Oskol, Belgorod Oblast /
Best in the city This award is based on the analysis of multiple factors, including reviews, ratings, and user engagement trends on Restaurant Guru.
Frequently mentioned in reviews, ratings of garazh, visitors' opinions on garazh.
Similar restaurants nearby
Tasty dishes in stary oskol.

Restaurant features in Stary Oskol

Plan Your Trip to Stary Oskol: Best of Stary Oskol Tourism
Essential stary oskol.

Stary Oskol Is Great For
Art & history.

Eat & drink

- Iceberg Premium Hotel
- Party Bar Aisberg
- Restaurant Triumf
- Starooskolsky Zoo
- Temple of St. Sergius of Radonezh
- Stary Oskol Art Museum
- Monument to the Founders of Stary Oskol

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make sure to list everything. 4. Menu. The most important element to launching a successful restaurant is the menu. Without it, your restaurant has nothing to serve. At this point, you probably don't have a final version, but for a restaurant business plan, you should at least try to have a mock-up.
Your restaurant business plan company overview should include: Purpose: The type of restaurant you're opening (fine dining, fast-casual, pop-up, etc.), type of food you're serving, goals you ...
The short-term goals and objectives of a restaurant typically focus on making the business run better or generating a quick injection of cash into your bank account. Here are a few examples of short-term restaurant goals, along with several restaurant objectives to support each of these goals. 1. Increase Daily Net Restaurant Sales.
As you plan the menu for your restaurant, consider the fact that potential diners may have a varied palate. For example, if you specialize in Asian fusion, make it a key objective to keep a few ...
5) Menu. Every restaurant needs a good menu, and this is the section within your restaurant business plan that you describe the food you'll serve in as much detail as possible. You may not have your menu design complete, but you'll likely have at least a handful of dishes that serve as the foundation of your offerings.
6. Management team. Write a brief overview of yourself and the team you have established so far. You want to show that your experience has provided you with the necessary skills to run a successful restaurant and act as a restaurant business owner.
Financial Plan. The Black Pearl Seafood Restaurant will have start-up costs of $500,000. The majority of the start-up costs will be for leasing and outfitting the restaurant space. Other start-up costs include purchasing kitchen equipment, hiring staff, and marketing the business.
The objectives of a restaurant should ideally extend beyond merely serving food. As a restaurant owner, you need a long-term vision that focuses on business aspects like: ... SMART goals are a great tool for creating or re-designing your restaurant business plan. The acronym 'SMART' stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and ...
State your mission and vision: Your mission statement reflects your restaurant's core purpose, while the vision paints a picture of its future. Outline your objective: Define the goals for your new business. Provide a financial overview: Offer a brief insight into the financial state of your business. 2.
The operations plan section outlines the daily business processes and activities centered on achieving the restaurant dream and objectives described in the rest of the plan. A detailed operations plan helps you and your team define your responsibilities, daily tasks, and short-term goals you need to achieve, keeping track of your long-term ...
Revolution Ordering. December 7, 2022. Alipio Umiten IV. Restaurant Business Plan | 12 Key Components to Include. Restaurant business plans are a critical tool for success in the restaurant industry. If you're thinking of opening a restaurant, opening a coffee shop, or even opening a bakery, a business plan is a must.
5. How to Help Your Restaurant Staff Set Personal Goals. Goals for restaurant managers. Restaurant kitchen goals and objectives. Restaurant server goals. 6. Conclusion. Organizing your restaurant based on a clear set of goals will help you boost sales and become more successful quicker. Learning to set restaurant goals is a must-have for ...
And every square foot taken up by cooking space is a square foot that can't hold customers. Industry wisdom states that a kitchen should be between 25% and 30% of the total restaurant space—including storage. So you have to plan your kitchen as efficiently as possible. In the dining room, you'll need tables and chairs, possibly a host ...
Attainable: This is a reachable goal because it's possible to implement more sustainable practices in the restaurant. Relevant: This statement is appropriate because it addresses a critical environmental issue. Time-based: The SMART goal is time-bound by the end of next year. 9. Develop Loyalty Program.
Go into detail about the food you'll be serving, inspiration behind your concept and an overview of service style. Define clearly what will be unique about your restaurant. 3. Sample menu. The menu is the most important touchpoint of any restaurant's brand, so this should be more than just a simple list of items.
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Economic Business Objective: Also called financial objectives, economic objectives relate to the financial health and growth of the company. These objectives can involve profits, revenue, costs, cash flow, sustainable growth, debt management, and investments. Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
6 examples of short-term and long-term restaurant goals. 1. Increase monthly net restaurant sales. Net restaurant sales might be the most important metric for your business. It's the foundation for all of your restaurant analytics. In fact, your restaurant's success — and your investors' success, if applicable — is wholly dependent on ...
A restaurant business plan template is a written document that describes in detail how your restaurant defines its objectives and how it'll go about achieving its goals. It can serve as a blueprint that outlines your entire vision, and it explains in detail how your business will take shape and operate.
Garazh #15 among Stary Oskol restaurants: 356 reviews by visitors and 43 detailed photos. This place provides food for RUB 1,500. Find on the map and call to book a table.
Very good. 3 reviews. #1 of 3 lodges in Stary Oskol. Location. 3.0. Service. 3.0. The hotel can accommodate up to 100 people and offer rooms in different price categories and the placement. A hotel room is a comfortable apartment consisting of separate rooms (one to four) with kitchenette, private bathroom fully equipped with appliances.
4.7. Service. 4.0. Value. 4.3. Welcome to Grand Hotel, your Stary Oskol "home away from home.". Grand Hotel aims to make your visit as relaxing and enjoyable as possible, which is why so many guests continue to come back year after year. For those interested in checking out popular landmarks while visiting Stary Oskol, Grand Hotel is ...
Stary Oskol Hostels Stary Oskol Business Hotels Stary Oskol Family Hotels. By Hotel Class. 4-Star Hotels in Stary Oskol. ... Plan Your Trip to Stary Oskol: Best of Stary Oskol Tourism. Essential Stary Oskol. Do. ... Restaurant Triumf. 30 $$ - $$$ • Russian, Eastern European. Abazhur. 35