- Online Students
- Online Alumni
- Faculty & Staff
- African American/Black
- Asian, Pacific Islander & Desi American
- DACA & Undocumented Students
- First Generation
- Hispanic/Latinx
- Indigenous/Native/First Nations
- International
- Justice Impacted
- Middle Eastern/North African/Arab-American
- Military Members and Veterans
- Neurodivergent
- Students With Disabilities
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Create a Resume / Cover Letter
- Earn Certifications & Badges
- Expand Your Network / Mentor
- Negotiate an Offer
- Prepare for an Interview
- Explore Your Interests / Self Assessment
- Prepare for Graduate School
- Explore Internships
- Search for a Job

Career Readiness Skills

What Is Career Readiness & What Are Career Readiness Skills?
Career readiness is the process of developing the skills and knowledge needed to be successful in the workplace. It’s a framework that helps students and alumni prepare for their careers, and it’s important for both education and employment.
Career readiness skills, often called career readiness competencies , are the skills, experiences, and attributes that prepare you for a successful career. A competency is a skill, task, strength, or personal quality that allows you to do a specific job role well.
The 8 examples of career readiness skills include :
- Career & Self Development
- Communication
- Critical Thinking
- Equity & Inclusion
- Professionalism
Career & Self Development:
- Show an awareness of own strengths and areas for development.
- Identify areas for continual growth while pursuing and applying feedback.
- Develop plans and goals for one’s future career.
- Professionally advocate for oneself and others.
- Display curiosity; seek out opportunities to learn.
- Assume duties or positions that will help one progress professionally.
- Establish, maintain, and/or leverage relationships with people who can help one professionally.
- Seek and embrace development opportunities.
- Voluntarily participate in further education, training, or other events to support one’s career.
Communication:
- Understand the importance of and demonstrate verbal, written, and non-verbal/body language, abilities.
- Employ active listening, persuasion, and influencing skills.
- Communicate in a clear and organized manner so that others can effectively understand.
- Frame communication with respect to diversity of learning styles, varied individual communication abilities, and cultural differences.
- Ask appropriate questions for specific information from supervisors, specialists, and others.
- Promptly inform relevant others when needing guidance with assigned tasks.
Critical Thinking:
- Make decisions and solve problems using sound, inclusive reasoning and judgement.
- Gather and analyze information from a diverse set of sources and individuals to fully understand a problem.
- Proactively anticipate needs and prioritize action steps.
- Accurately summarize and interpret data with an awareness of personal biases that may impact outcomes.
- Effectively communicate actions and rationale, recognizing the diverse perspectives and lived experiences of stakeholders.
- Multi-task well in a fast-paced environment.
Equity & Inclusion:
- Solicit and use feedback from multiple cultural perspectives to make inclusive and equity-minded decisions.
- Actively contribute to inclusive and equitable practices that influence individual and systemic change.
- Advocate for inclusion, equitable practices, justice, and empowerment for historically marginalized communities.
- Seek global cross-cultural interactions and experiences that enhance one’s understanding of people from different demographic groups and that leads to personal growth.
- Keep an open mind to diverse ideas and new ways of thinking.
- Identify resources and eliminate barriers resulting from individual and systemic racism, inequities, and biases.
- Demonstrate flexibility by adapting to diverse environments.
- Address systems of privilege that limit opportunities for members of historically marginalized communities.
Leadership:
- Inspire, persuade, and motivate self and others under a shared vision.
- Seek out and leverage diverse resources and feedback from others to inform direction.
- Use innovative thinking to go beyond traditional methods.
- Serve as a role model to others by approaching tasks with confidence and a positive attitude.
- Motivate and inspire others by encouraging them and by building mutual trust.
- Plan, initiate, manage, complete and evaluate projects.
Professionalism:
- Act equitably with integrity and accountability to self, others, and the organization.
- Maintain a positive personal brand in alignment with organization and personal career values.
- Be present and prepared.
- Demonstrate dependability (e.g., report consistently for work or meetings).
- Prioritize and complete tasks to accomplish organizational goals.
- Consistently meet or exceed goals and expectations.
- Have an attention to detail, resulting in few if any errors in their work.
- Show a high level of dedication toward doing a good job.
- Listen carefully to others, taking time to understand and ask appropriate questions without interrupting.
- Effectively manage conflict, interact with and respect diverse personalities, and meet ambiguity with resilience.
- Be accountable for individual and team responsibilities and deliverables.
- Employ personal strengths, knowledge, and talents to complement those of others.
- Exercise the ability to compromise and be agile.
- Collaborate with others to achieve common goals.
- Build strong, positive working relationships with supervisor and team members/coworkers.
Technology:
- Navigate change and be open to learning new technologies.
- Use technology to improve efficiency and productivity of their work.
- Identify appropriate technology for completing specific tasks.
- Manage technology to integrate information to support relevant, effective, and timely decision-making.
- Quickly adapt to new or unfamiliar technologies.
- Manipulate information, construct ideas, and use technology to achieve strategic goals.
Why Is Career Readiness Important?
These critical skills give students & alumni the edge they need to land jobs. Career readiness education is critical because it prepares students for life after college as they begin their careers, equipping them with the skills necessary to navigate the workforce. Career readiness also helps employers understand your abilities and experience. When employers notice that you’ve prepared to enter the workforce, this may influence their hiring decision.
According to the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Foundation , career readiness skills, or what they refer to as transferable or employability skills, “provide students with a competitive edge during interviews and internships for current and future careers” and “can differentiate a good employee from a great one.”
By understanding career readiness skills and how and when to use them in the job search, students and alumni can better prepare themselves for landing jobs during school or after graduation. SNHU Career Services is here to help you do just that.

Career Videos & Testimonials
Defining the skills citizens will need in the future world of work
We know that digital and AI technologies are transforming the world of work and that today’s workforce will need to learn new skills and learn to continually adapt as new occupations emerge. We also know that the COVID-19 crisis has accelerated this transformation . We are less clear, however, about the specific skills tomorrow’s workers will require.
Research by the McKinsey Global Institute has looked at the kind of jobs that will be lost, as well as those that will be created, as automation, AI, and robotics take hold. And it has inferred the type of high-level skills that will become increasingly important as a result. 1 For more information, see “ Skill shift: Automation and the future of the workforce ,” May 23, 2018. The need for manual and physical skills, as well as basic cognitive ones, will decline, but demand for technological, social and emotional, and higher cognitive skills will grow.
Governments are keen to help their citizens develop in these areas, but it is hard to devise curricula and the best learning strategies without being more precise about the skills needed. It is difficult to teach what is not well defined.
We, therefore, conducted research that we hope will help definitions take shape and could contribute to future-proof citizens’ skills for the world of work. 2 For previous McKinsey work on the role of governments in adapting to the future of work, see Marco Dondi, Solveigh Hieronimus, Julia Klier, Peter Puskas, Dirk Schmautzer, and Jörg Schubert, “ A government blueprint to adapt the ecosystem to the future of work ,” February 7, 2020. The research identified a set of 56 foundational skills that will benefit all citizens and showed that higher proficiency in them is already associated with a higher likelihood of employment, higher incomes, and job satisfaction. 3 The research was conducted in 2019.
Defining foundational skills for citizens
Some work will, of course, be specialized. But in a labor market that is more automated, digital, and dynamic, all citizens will benefit from having a set of foundational skills that help them fulfill the following three criteria, no matter the sector in which they work or their occupation:
- add value beyond what can be done by automated systems and intelligent machines
- operate in a digital environment
- continually adapt to new ways of working and new occupations
We used academic research and McKinsey’s experience in adult training to define what these foundational skills might be (Exhibit 1). We started from four broad skill categories—cognitive, digital, interpersonal, and self-leadership—then identified 13 separate skill groups belonging to those categories. 4 To drive toward a more detailed definition of future skills required, we found it useful to divide the social and emotional category used by the McKinsey Global Institute into two separate ones: interpersonal and self-leadership. Communication and mental flexibility are two skill groups that belong to the cognitive category, for example, while teamwork effectiveness belongs to the interpersonal category.
Looking for still more precision, we identified 56 distinct elements of talent (DELTAs) that fall within these skills groups. We call them DELTAs, rather than skills, because they are a mix of skills and attitudes. “Adaptability” and “coping with uncertainty” are attitudes, for example. 5 A still finer segmentation of each skill group into more DELTAs would be possible. We limited ourselves, however, to DELTAs that require a distinct approach to their development and assessment.
DELTA proficiency and outcomes
From here, we conducted two further pieces of research. First, we sought to gauge the level of proficiency in the 56 DELTAs among today’s workers compared with the level we believe will be required to future-proof citizens’ ability to work. Second, we sought to gauge whether proficiency in these DELTAs was already associated with certain work-related outcomes.
Proficiency
Example: evaluating proficiency levels for deltas.
To assess respondents’ proficiency levels for each DELTA, we gave them three different sentences that described certain behaviors, choices, and preferences in different situations. Respondents were asked to choose the sentence that best described themselves, even though none or more than one might be relevant. Each sentence was associated with a different level of proficiency.
For example, here are the options we provided to gauge efficiency in the “structured problem solving” DELTA (within the critical thinking skill group):
- Option 1: I can solve day-to-day problems easily, but I often need assistance with complex problems
- Option 2: I can break larger problems into parts and find solutions for them
- Option 3: I routinely break complex problems down into parts, identify their causes, and find solutions
To ascertain proficiency levels, we defined a desirable level of proficiency in each of the 56 DELTAs, then devised a psychometric questionnaire to assess respondents’ proficiency against this bar. Eighteen thousand people from 15 countries completed the online questionnaire and were given a score on a scale of 0 to 100 for each DELTA (see the sidebar “Example: Evaluating proficiency levels for DELTAs”).
The results showed respondents’ proficiency was lowest in two skill groups in the digital category—software use and development and understanding digital systems. Proficiency in the skill groups for communication and planning and ways of working—both in the cognitive category—was also lower than average (Exhibit 2).
Overall, survey participants with a university degree had higher average proficiency scores across 56 distinct elements of talent, suggesting that those with higher levels of education are better prepared for changes in the workplace.
We also examined whether proficiency was linked to education. Overall, survey participants with a university degree had higher average DELTA proficiency scores than those without, suggesting—perhaps not surprisingly—that participants with higher levels of education are better prepared for changes in the workplace. However, a higher level of education is not associated with higher proficiency in all DELTAs. The association holds true for many DELTAs in the cognitive and digital categories. But for many within the self-leadership and interpersonal categories, such as “self-confidence,” “coping with uncertainty,” “courage and risk-taking,” “empathy,” “coaching,” and “resolving conflicts,” there is no such association. 6 Predictive models based on three different statistical techniques failed to find a correlation. For some DELTAs, more education was associated with lower proficiency, “humility” being an example.
Exhibit 3 lists the DELTAs where proficiency has the highest and lowest correlation with the level of education. (Some have a negative coefficient.)
We went on to test whether proficiency in the DELTAs was already helping people in the world of work; the results showed that survey respondents with higher DELTA proficiencies were, on average, more likely to be those that were employed, with higher incomes, and higher job satisfaction. Different DELTAs were more strongly associated with these three work-related outcomes, however.
Holding all variables constant—including demographic variables and proficiency in all other elements—we found employment was most strongly associated with proficiency in several DELTAs within the self-leadership category, namely “adaptability,” “coping with uncertainty,” “synthesizing messages,” and “achievement orientation” (Exhibit 4, part 1). 7 These DELTAs were selected based on their individual contribution—holding all other variables constant—to the probability of a survey participant being employed among those whose income was below the median or those with no income. People with income above the median were excluded to avoid skewed results because of their higher proficiency in DELTAs.
High incomes were most strongly associated with proficiency in the four skill groups where overall proficiency levels were lowest among respondents—namely understanding digital systems, software use and development, planning and ways of working, and communication (the first two fall within the digital category and the latter two within the cognitive category). 8 These skill groups show the largest difference in proficiency between survey participants with income below the median income in their country and those in the top quintile.
Digital proficiency seems to be particularly associated with higher incomes: a respondent with higher digital proficiency across all digital DELTAs was 41 percent more likely to earn a top-quintile income than respondents with lower digital proficiency. 9 Our assessment model had three levels of proficiency (3 being the highest level) for each of the 56 DELTAs. Here, respondents with higher digital proficiency are those judged to be at level 3. Those with lower digital proficiency are those at level 2. All else being constant, a respondent at level 3 is 41% more likely to be earning a top-quintile income than a respondent at level 2. The equivalent comparison was 30 percent for cognitive DELTAs, 24 percent for self-leadership DELTAs, and 14 percent for interpersonal DELTAs.
That said, the four DELTAs most strongly associated with high incomes were “work-plan development” and “asking the right questions,” both in the cognitive category; “self-confidence,” a self-leadership DELTA; and “organizational awareness,” an interpersonal DELTA (Exhibit 4, part 2). 10 These DELTAs were selected based on their individual contribution—holding all other variables constant—to the probability of a survey participant being in the top quintile for income.
Job satisfaction is also associated with certain DELTAs, especially those in the self-leadership category. Holding all variables, including income, constant, “self-motivation and wellness,” “coping with uncertainty,” and “self-confidence,” had the highest impact on respondents’ job satisfaction (Exhibit 4, part 3). 11 These DELTAs were selected based on their individual contribution—holding all other variables constant—to the probability of a survey participant being either “fulfilled and satisfied” or “satisfied” with their job, as opposed to “somewhat satisfied” or “dissatisfied.”
Notably, proficiency in two self-leadership DELTAs—“self-confidence” and “coping with uncertainty”—ranked among the top three most predictive DELTAs for two out of the three outcomes (Exhibit 5).
How DELTAs could help shape education and adult training
Our findings help define the particular skills citizens are likely to require in the future world of work and suggest how proficiency in them can influence work-related outcomes, namely employment, income, and job satisfaction. This, in turn, suggests three actions governments may wish to take.
Reform education systems
Our research suggests governments could consider reviewing and updating curricula to focus more strongly on the DELTAs. Given the weak correlation between proficiency in self-leadership and interpersonal DELTAs and higher levels of education, a strong curricula focus on these soft skills may be appropriate.
Governments could also consider leading further research. Many governments and academics have started to define the taxonomies of the skills citizens will require, but few have done so at the level described here. Moreover, few, if any, have undertaken the considerable amount of research required to identify how best to develop and assess such skills. For instance, for each DELTA within the curriculum, research would be required to define progression and proficiency levels achievable at different ages and to design and test developmental strategies and assessment models. The solutions for different DELTAs are likely to differ widely. For example, the solutions to develop and assess “self-awareness and self-management” would differ from those required for “work-plan development or “data analysis.”
In addition, governments could consider setting up institutions for research and innovation in education to fund the research, facilitate researchers’ access to schools to test innovative solutions, and establish which methods work for which DELTAs. They could also make the emerging data and insights available to researchers and educators in the private sector.
Reform adult-training systems
The majority of respondents we surveyed—like the majority of people in society at large—were no longer in national education systems. Raising proficiency in the DELTAs would therefore require continuous adult training. The fact that proficiency in digital DELTAs—shown to improve the chances of achieving higher incomes—was lower among older survey respondents who had left the national educational system illustrates this point.
The curricula of adult-training courses may also have to change. For example, our research has shown that self-leadership DELTAs may be particularly important for employment outcomes, yet these are not commonly covered by adult-training programs. For example, in an online scan of adult-training programs, we found that courses or modules to develop DELTAs within the skill groups of goal achievement or self-awareness and self-management were 20 times less common than those to develop communication DELTAs. That could be an urgent gap to fill to adequately respond to the wave of unemployment caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Specific actions that might encourage relevant adult learning include the following:
- Establish an AI aggregator of training programs to attract adult learners and encourage lifelong learning. AI algorithms could guide users on whether they need to upskill or reskill for a new profession and shortlist relevant training programs. To develop accurate algorithms, governments would need to collect and organize data on market demand for jobs and skills, as well as data on training programs. Programs listed should include those that teach DELTAs correlated to work-related outcomes. Self-leadership DELTAs could be particularly important given their link to employment.
- Introduce a skill-based certification system. Occupation-based qualifications risk becoming outdated rapidly as occupations requiring new skills emerge. Hence, skills-based accreditation may better suit employers’ needs. Providers could develop programs that cover the practical skills and DELTAs required to perform a certain occupation, but add new components or remove old ones as those occupations evolved. Several AI start-ups have developed algorithms capable of identifying and updating the skill sets required for different occupations. Governments could adapt these to enable a dynamic, skill-based certification system.
- Fund schemes that encourage a higher focus on DELTAs. Some governments award lifelong learning grants to their citizens, who can enroll in training programs within a national aggregator. To help equip citizens for the future world of work, governments could funnel funds toward programs that include the DELTAs associated with employment. For example, trainees could be offered spending vouchers for particular programs only, while funding to program providers could be conditional upon employment outcomes or the provision of training modules that include certain DELTAs.
Ensure affordability of lifelong education
Most children around the world have access to primary and secondary schooling, but not all of it is of high quality, and early education for the very young—the best age at which to develop certain mindsets and attitudes—is unaffordable for most people in most countries. In addition, very few countries have worked out a system to provide affordable access to quality adult training.
Hence, just as the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century drove an expansion of access to education, today’s technological revolution should drive further expansion to ensure universal, high-quality, affordable access to education from early childhood to retirement and to ensure that curricula include the DELTAs that will future-proof citizens’ skills in the world of work.
Marco Dondi is a consultant in McKinsey’s Geneva office, Julia Klier is a partner in the Munich office, Frédéric Panier is a partner in the Brussels office, and Jörg Schubert is a senior partner in the Dubai office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The future of work after COVID-19

What’s next for remote work: An analysis of 2,000 tasks, 800 jobs, and nine countries

Grabbing hold of the new future of work
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Can emotional intelligence be improved? A randomized experimental study of a business-oriented EI training program for senior managers
Raquel gilar-corbi, teresa pozo-rico, bárbara sánchez, juan-luís castejón.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
* E-mail: [email protected] (RGC); [email protected] (TPR)
Received 2018 Sep 11; Accepted 2019 Oct 9; Collection date 2019.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Purpose: This article presents the results of a training program in emotional intelligence. Design/methodology/approach: Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves two important competencies: (1) the ability to recognize feelings and emotions in oneself and others, and (2) the ability to use that information to resolve conflicts and problems to improve interactions with others. We provided a 30-hour Training Course on Emotional Intelligence (TCEI) for 54 senior managers of a private company. A pretest-posttest design with a control group was adopted. Findings: EI assessed using mixed and ability-based measures can be improved after training. Originality/value: The study’s results revealed that EI can be improved within business environments. Results and implications of including EI training in professional development plans for private organizations are discussed.
Introduction
This research study focused on EI training in business environments. Accordingly, the aim of the study was to examine the effectiveness of an original EI training program in improving the EI of senior managers. In this article, we delineate the principles and methodology of an EI training program that was conducted to improve the EI of senior managers of a private company The article begins with a brief introduction to the main models of EI that are embedded with the existing scientific literature. This is followed by a description of the EI training program that was conducted in the present study and presentation of results about its effectiveness in improving EI. Finally, the present findings are discussed in relation to the existing empirical literature, and the limitations and conclusions of the present study are articulated.
Defining EI
Various models of emotional intelligence (EI) have been proposed. The existing scientific literature offers three main models of EI: mixed, ability, and trait models. First, mixed models conceptualize EI as a combination of emotional skills and personality dimensions such as assertiveness and optimism [ 1 , 2 ]. Thus, according to the Bar-On model [ 3 ], emotional-social intelligence (ESI) is a multifactorial set of competencies, skills, and facilitators that determine how people express and understand themselves, understand and relate to others, and respond to daily situations The construct of ESI consists of 10 key components (i.e., self-regard, interpersonal relationships, impulse control, problem solving, emotional self-awareness, flexibility, reality-testing, stress tolerance, assertiveness, and empathy) and five facilitators (optimism, self-actualization, happiness, independence, and social responsibility). Emotionally and socially intelligent people accept and understand their emotions; they are also capable of expressing themselves assertively, being empathetic, cooperating with and relating to others in an appropriate manner, managing stressful situations and changes successfully, solving personal and interpersonal problems effectively, and having an optimistic perspective toward life. Second, ability models of EI focus on the processing of information and related abilities [ 3 ]. Accordingly, Mayer and Salovey [ 4 ] have conceptualized EI as a type of social intelligence that entails the ability to manage and understand one’s own and others’ emotions. Indeed, this implies that EI also entails the ability to use emotional information to manage thoughts and actions in an adaptive manner [ 5 ]. Third, the trait EI approach understands EI as emotion-related information [ 6 ]. According to trait models, EI refers to self-perceptions and dispositions that can be incorporated into fundamental taxonomies of personality. Therefore, according to Petrides and Furnham [ 7 ], trait EI is partially determined by several dimensions of personality and can be situated within the lower levels of personality hierarchies. However, it is a distinct construct that can be differentiated from other personality constructs. In addition, the construct of trait EI includes various personality dispositions as well as the self-perceived aspects of social intelligence, personal intelligence, and ability EI. The following facets are subsumed by the construct of trait EI: adaptability, assertiveness, emotion perception (self and others), emotion expression, management (others), and regulation, impulsiveness (low), relationships, self-esteem, self-motivation, social awareness, stress management, trait empathy, happiness, and optimism [ 7 ]. Finally, as Hodzic et al. [ 8 ] have indicated, most existing definitions of EI permit us to draw the conclusion that EI is a measurable individual characteristic that refers to a way of experiencing and processing emotions and emotional information. It is noteworthy that these models are not mutually exclusive [ 7 ].
Effects of EI on different outcomes
EI has been found to be related to workplace performance in highly demanding work environments (see e.g. [ 9 ]). Consequently, companies, entities, and organizations tend to recognize the importance of EI, promote it on a daily basis to facilitate career growth, and recruit those who possess this ability. [ 10 ].
With regard to research that has examined the EI-performance link, Van Rooy and Viswesvaran [ 11 ] conducted a metanalytic study to examine the predictive power of EI in the workplace. They found that approximately 5% of the variance in workplace performance was explained by EI, and this percentage is adequately significant to increase savings and promote improvements within organizations. In addition, the authors concluded that further in-depth investigations are needed to comprehensively understand the construct of EI.
However, the EI-performance link must be interpreted with caution. Specifically, Joseph and Newman [ 12 ] examined emotional competence in the workplace and found that EI predicts performance among those with high emotional labor jobs but not their counterparts with low emotional labor jobs. In addition, they indicated that further research is required to delineate the relationship between EI and actual job performance, gender and race differences in EI, and the utility of different types of EI measures that are based on ability or mixed models in training and selection. Accordingly, Pérez-González and Qualter [ 13 ] have underscored the need for emotional education. Further, Brasseur et al. [ 14 ] found that better job performance is related to EI, especially among those with jobs for which interpersonal contact is very important.
It is noteworthy that EI is positively related to job satisfaction. Accordingly, Chiva and Alegre [ 15 ] found that there was an indirect positive relationship between self-reported EI (i.e., as per mixed models) and job satisfaction. A total of 157 workers from several companies participated in this study. These findings suggest that people with higher levels of EI are more satisfied with their jobs and demonstrate a greater capacity for learning than their counterparts with lower levels of EI.
Similarly, Sener, Demirel, and Sarlak [ 16 ] adopted a mixed model of EI and examine its effect on job satisfaction. They found that individuals with strong emotional and social competencies demonstrated greater self-control. A total of 80 workers participated in this study. They were able to manage and understand their own and others’ emotions in an intelligent and adaptive manner in their personal and professional lives.
In addition, EI (i.e., as per mixed models) predicts job success because it influences one’s ability to deal with environmental demands and pressures [ 17 ]. Therefore, it has been contended that several components of EI (i.e., as per mixed models) contribute to success and productivity in the workplace [ 18 ]; future research studies should extend this line of inquiry. Several studies have shown that people with high levels of ability EI communicate in an interesting and assertive manner, which in turn makes others feel more comfortable in the workplace [ 19 ]. In addition, it has been contended that EI (i.e., as per mixed models) plays a valuable role in group development because effective teamwork occurs when team members possess knowledge about the strengths and weaknesses of others and the ability to use these strengths when necessary [ 15 , 20 ]. It is especially important for senior managers to demonstrate high levels of EI because they play a predominant role in team management, leadership, and organizational development.
Finally, studies that have examined the relationship between EI and wellbeing have found that ability EI is a predictor of professional success, wellbeing, and socially relevant outcomes [ 21 – 23 ]. Extending this line of inquiry, Slaski and Cartwright [ 24 ] investigated the relationship between EI and the quality of working life among middle managers and found that higher levels of EI is related to better performance, health, and wellbeing.
EI and leadership
The actions of organizational leaders play a crucial role in modulating the emotional experiences of employees [ 25 ]. Accordingly, Thiel, Connelly, and Griffith [ 26 ] found that, within the workplace, emotions affect critical cognitive tasks including information processing and decision making. In addition, the authors have contended that leadership plays a key role in helping subordinates manage their emotions. In another study, Batool [ 27 ] found that the EI of leaders have a positive impact on the stress management, motivation, and productivity of employees.
Gardner and Stough [ 28 ] further investigated the relationship between leadership and EI among senior managers and found that leaders’ management of positive and negative emotions had a beneficial impact on motivation, optimism, innovation, and problem resolution in the workplace. Therefore, the EI of directors and managers is expected to be positively correlated with employees’ work motivation and achievement.
Additionally, EI competencies are involved in the following activities: choosing organizational objectives, planning and organizing work activities, maintaining cooperative interpersonal relationships, and receiving the support that is necessary to achieve organizational goals [ 29 ]. In this regard, some authors have provided compelling theoretical arguments in favor of the existence of a relationship between EI and leadership [ 30 – 34 ]. In this way, several researches [ 30 – 34 ] show that EI is a core and key variable positively related to effective and transformational leadership and this is important for positive effects on job performance and attitudes that are desirable in the organization.
Further, people with high levels of EI are more capable of regulating their emotions to reduce work stress [ 35 ]; thus, it is necessary to emphasize the importance of EI in order to meet the workplace challenges of the 21st century.
In conclusion, EI competencies are considered to be key qualities that individuals who occupy management positions must possess [ 36 ]. Further, EI transcends managerial hierarchies when an organization flourishes [ 37 ]. Finally, emotionally intelligent managers tend to create a positive work environment that improves the job satisfaction of employees [ 38 ].
EI trainings
Past studies have shown that training improves the EI of students [ 22 , 39 , 40 – 44 ], employees [ 45 – 47 ], and managers [ 48 – 52 ]. More specifically, within the academic context, Nelis et al. [ 22 ] found that group-based EI training significantly improved emotion identification and management skills. In another study, Nelis et al. [ 39 ] found that EI training significantly improved emotion regulation and comprehension and general emotional skills. It also had a positive impact on psychological wellbeing, subjective perceptions of health, quality of social relations, and employability. Similarly, several studies that have been conducted within the workplace have shown that EI can be improved through training [ 45 – 52 ] and have underscored the key role that it plays in effective performance [ 53 , 54 ].
In addition, two relevant metanalyses [ 8 , 55 ] concluded that there has been an increase in research interest in EI, recognition of its influence on various aspects of people’s lives, and the number of interventions that aim to improve EI. Relatedly, Kotsou et al. [ 55 ] and Hodzic et al. [ 8 ] reviewed the findings of past studies that have examined the effects of EI training to explore whether such training programs do indeed improve EI.
First, Hodzic et al. [ 8 ] concluded that EI training has a moderate effect on EI and that interventions that are based on ability models of EI have the largest effects. In addition, the improvements that had resulted from these interventions were found to have been temporally sustained.
Second, the conclusions of Kotsou et al.’s [ 55 ] systematic review of the literature on the effectiveness of EI training make it evident that more rigorous and controlled studies are needed to permit one to draw concrete conclusions about whether training improves ability EI. Studies that had adopted mixed models of EI tended to more consistently find that training improves EI. Accordingly, the results of Kotsou et al.’s [ 55 ] metanalytic study revealed that EI training enhances teamwork, conflict management, employability, job satisfaction, and work performance.
Finally, it is necessary to identify and address the limitations of past interventions in future studies to improve their quality and effectiveness.
Purpose of the study
In the systematic review conducted by Kotsou et al. [ 55 ] regarding research published on interventions to improve EI in adults, one out of five studies with managers, was performed on a sample of middle managers, without randomization, with an inactive control group, no immediate measures after the training, and only one evaluation was performed six months after the training. In the other four studies collected in Kotsou et al.’s systematic review [ 55 ], only one study utilized a control group (inactive control group), one employed randomizations, and two studies performed follow-up measures six months after the intervention.
The two metanalyses confirmed and identified some problems or gaps we have tried to overcome in the present study. For this reason, in our study, we propose to deepen the assessment of EI training for senior managers, aiming to overcome most of the limitations mentioned in the studies of Kotsou et al. [ 55 ] and Hodzic et al. [ 8 ] by implementing the following: 1) Include a control group (waiting list group); 2) Conduct follow-up measurements (12 months later); 3) Employ an experimental design; 3) Include a workshop approach with group discussions and interactive participation; 4) Identify specific individual differences (i.e., age, gender) that might determine the effects of interventions; and 5) Use self-report and ability measures. For these reasons, two different ways of evaluating EI have been selected in this study to assess the emotional competencies applied within the labor and business world to solve practical problems: the EQ-i questionnaire [ 2 ], based on mixed models to provide a self-perceived index of EI, and the Situational Test of Emotional Management (STEM) and the Situational Test of Emotional Understanding (STEU) [ 56 ] based on the ability model. Thus, including two different EI measure we aim at obtaining a more reliable validation of the intervention used.
Therefore, the objective of our study was to investigate whether EI can be improved among employees who occupy senior management positions in a private company. Thus, the research hypothesis was that participation in the designed program would improve EI among senior managers.
EI training development
The Course on Emotional Intelligence (TCEI) was created to provide senior managers with emotional knowledge and practical emotional skills so that they can apply and transfer their new understanding to teamwork and find solutions to real company problems and challenges. In this way, TCEI prepares workers to use the emotional learning resources appropriate to each work situation. In addition, TCEI combines face-to-face work sessions with a cross-sectional training through an e-learning platform. For more details, see S1 Appendix 1.
According to Mikolajczak [ 57 ], three interrelated levels of emotional intelligence can be differentiated: a) conceptual-declarative emotion knowledge, b) emotion-related abilities, and c) emotion-related dispositions. The TCEI aims at developing emotional skills, which are included on the second level of Mikolajczak’s model. Moreover, the present study uses the mixed model and the ability model measures to assess the level of EI. In using these measures, it is possible to assess the second level of Mikolajczak’s model. Pérez-González and Qualter [ 13 ] also suggest that activities related to ability EI should be included in emotional education programs.
Thus, this EI program was designed to allow senior managers to make use of their understanding and management of emotions as a strategy to assist them in facing the challenges within their work environment and managing their workgroups. Following the recommendation of Pérez-Gonzáles and Qualter, the training intervention methodology is founded in DAPHnE key practices [ 13 ]. It is important to emphasize that this training is grounded in practicality since it works based on the resolution of real cases, utilizing participative teaching-learning techniques and cooperative learning, while promoting the transfer of all aspects of EI and applied to various situations that can occur in the workplace. The e-learning system in the Moodle platform also provides an added value since it allows the creation of an environment providing exposure to professional experiences and continuous training. This type of pedagogical approach based on skills training and mediated through e-learning is a methodology that emerged in the 1990s when business organizations sought to create environments better suited to improving the management of large groups of employees. After its success, it began to be used in other contexts, including higher education and organizational development [ 58 – 60 ].
Finally, in order to justify the chosen training, it is important to note that the following official competencies for senior managers have been designated by the company:
Supervise the staff and guarantee optimum employee performance by fostering a motivational working environment where employees receive the appropriate support and respect and their initiatives are given the consideration they deserve.
Make decisions and promote clear goals, efficient leadership, competitive compensation, and acknowledgment of the employees’ achievements.
Justify their decisions to executives and directors, explaining how they have ensured training by creating opportunities for appropriate professional development for all employees and how they have facilitated conditions for a better balance in achieving the company’s objectives.
In conclusion, considering the above-mentioned professional competencies required, senior managers were selected as participants in this study since they need to possess and apply aspects related to EI in order to accomplish their leadership and staff management responsibilities.
Participants
The company participating in this study was an international company with almost 175 years of history that occupies a select position in a branch of industry in the natural gas value chain, from the source of supply to market, including supply, liquefaction, shipping, regasification, and distribution. The company is present in over 30 countries around the world.
This study was conducted involving a sample of 54 senior managers selected from a company in a European country. The sample was extracted from the entire population of senior managers within this company following a stratified random sampling procedure, taking into account the gender of the population in order to select 50% of each gender.
The mean age of participants was 37.61 years (standard deviation = 8.55) and the percentage of female senior managers was 50%. For evaluation purposes, these employees were randomly divided into two groups: the experimental group ( n = 26; mean age = 35.57 (7.54); 50% women) and the control group ( n = 28; mean age = 39.50 (9.11); 50% women). The control group received EI training after the last data collection.
Initially, a group of senior managers from the company was selected to participate in the study, as they are employees who need a special domain of EI due to the competencies assigned to their professional category. In all cases, informed consent was requested for their participation in the study.
Assignment of participants to each condition, experimental or control, was performed using a random-number program. In addition, to avoid the Hawthorne effect, participants were not told if they were assigned to the experimental or control group; only their consent to participate in research on the development of EI was asked. Participants from the control group completed the same evaluations as the training group but were not exposed to the training.
The scales were administered during the pretest phase (Time 1) on an online platform for the experimental and control groups. On average, approximately 90 minutes were needed to complete the tests.
After the data were collected in the pre-test phase, only the experimental group participated in the TCEI over seven weeks, and they received a diploma.
Later, the scales were administered during the posttest phase (Time 2). Similarly, we collected the same data one year later (Time 3). A lapse of one year was allowed to pass because all training programs carried out in this company are re-evaluated one year later to determine whether improvements in employees’ skills were maintained over time. In fact, this demonstrates a clear commitment to monitoring the results achieved. Other studies have also used reevaluations of their results. For example, according to Nelis et al. [ 22 ] and Nelis et al. [ 39 ], the purpose of their studies was to evaluate whether trait EI could be improved and if these changes remained. To accomplish this, the authors performed three assessments: prior to the intervention, at the end of the intervention, and six months later. Therefore, as recommended by Kirkpatrick [ 61 ], research on the effectiveness of training should also include a long-term assessment of skills transfer.
Finally, is important to remark that all participants were properly informed of the investigation, and their written consent was obtained. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations and the study was approved by University of Alicante Ethics Committee (UA-2015-07-06) and carried out in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
As mentioned before, two different ways of defining and evaluating EI were selected for this study: (1) EQ-i, based on mixed models, and (2) the STEM/STEU questionnaires, based on the ability model of EI.
The Emotional Quotient Inventory [ 2 ]
To measure EI based on the mixed models, the short version of the EQ-i was used, which comprises 51 self-referencing statements and requires subjects to rate the extent to which they agree or disagree with each statement on a five-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree; 5 = strongly agree). An example item is the following; “In handling situations that arise, I try to think of as many approaches as I can.” The EQ-i comprises five factors: Intrapersonal EI and Self-Perception, Interpersonal EI, Adaptability and Decision Making, General Mood and Self-Expression, Stress Management, and a Total EQ-i score, which serves as a global EI measure. The author of this instrument reports a Cronbach’s alpha ranging from .69 to .86 for the 5 subscales [ 2 , 62 ] and the Cronbach’s alpha of the Emotional Quotient Inventory was .80 for the present sample of senior manager.
Situational Test of Emotional Understanding (STEU) and Situational Test of Emotion Management (STEM) [ 63 ]
Two tests were used to measure EI based on the ability model. Emotion understanding was evaluated by the short version of the Situational Test of Emotional Understanding (STEU) [ 63 ]. This test is composed of 25 items that present an emotional situation (decontextualized, workplace-related, or private-life-related). For each item, participants have to choose which emotion will most likely elicit the described situation. Cronbach’s alpha of STEU is .83 [ 63 ] and the Cronbach’s alpha of the Situational Test of Emotional Understanding was .86 for the present sample of senior manager. An example item is the following: “An unwanted situation becomes less likely or stops altogether. The person involved is most likely to feel: (a) regret, (b) hope, (c) joy, (d) sadness, (e) relief” (in this case, the correct answer is “relief”).
On the other hand, emotion management was evaluated by the short version of the Situational Test of Emotion Management (STEM) [ 63 ]. This test is composed of a 20-item situational judgment test (SJT) that uses hypothetical behavioral scenarios followed by a set of possible responses to the situation. Respondents must choose which option they would most likely select in a “real” situation. Cronbach’s alpha of STEM is .68 [ 63 ] and the Cronbach’s alpha of the Situational Test of Emotion Management was .84 for the present sample of senior manager. An example item is the following: “Pete has specific skills that his workmates do not, and he feels that his workload is higher because of it. What action would be the most effective for Pete? (a) Speak to his boss about this; (b) Start looking for a new job; (c) Be very proud of his unique skills; (d) Speak to his workmates about this.”
TCEI content and organization
The program schedule spanned seven weeks with a face-to-face session of 95 minutes each week, which was delivered by one of the researchers specifically trained for this purpose. All the experimental group participants were taught together in these sessions. The content of each session was the following:
1st Session : Introduction. The objectives and methodology of the training were explained to participants.
2nd Session : Intrapersonal EI and self-perception. Trainees learned to identify their own emotions.
3rd Session : Interpersonal EI. Participants learned to identify others’ emotions.
4th Session : Adaptability and decision making. The objective was to improve trainees’ ability to identify and understand the impact that their own feelings can have on thoughts, decisions, behavior, and work performance resulting in better decisions and workplace adaptability.
5th Session : General mood and self-expression. Trainees worked on expressing their emotions and improving their skills to effectively control their mood.
6th Session : Stress management. Participants learned EI skills to manage stress effectively.
7th Session : Emotional understanding and emotion management. Trainees learned skills to effectively manage their emotions as well as skills that influence the moods and emotions of others.
In addition, access to the virtual environment (Moodle platform) was required after each face-to-face session. The time spent in the platform was registered, with a minimum of five hours required per week.
The virtual environment allowed the researcher to review all the content completed in each face-to-face session.
All of the EI abilities included in the virtual part of the training have been previously used in the face-to-face part; thus, virtual training is simply a method used to consolidate EI knowledge. In fact, the virtual environment has the same function as completing a workbook about the information presented during the face-to-face session. However, the added advantage of working in an e-learning environment is that all of the trainers are connected and can share their tasks and progress with others. At times, in addition to reviewing the contents of the previous session, the e-learning environment also introduces some important terms for the next session utilizing the principles of the well-known flipped classroom methodology. In short, the following activities were carried out through the Moodle platform to consolidate the participants’ knowledge:
1st Session: Participants were informed that e-learning would be part of the training in order to consolidate EI knowledge.
2nd Session: Participants explored the skills of Intrapersonal EI and self-perception in the virtual environment through discussion forums.
3rd Session: Participants learned the skills of identifying others’ emotions and utilizing this emotional information for decision-making. This information was summarized in the virtual environment through discussion forums.
4th Session: Participants sharpened their skills of adaptability and decision-making through the production of innovative ideas and the utilization of critical thinking skills in assessing the impact that their own feelings can have on others’ work performance. Trainees learned how to express their own emotions, as well as the skill of effectively controlling their mood, through the resolution of practical cases in the virtual environment; in these cases, innovative ideas and critical thinking skills were required in order to make better decisions during emotionally impactful; situations. In addition, trainees utilized the forum to reflect on why their own emotional regulation is important for ensuring long-term workplace adaptability.
5th Session: Verbal quiz, discussion, and forum contribution. Trainees participated in an online debate about key emotional skills in order to understand how to apply them in a real work environment. In particular, the debate focused on regulating the self-expression skill and equilibrating the general mood when there are difficult situations within the company. In this way, the participants identified the skills required to effectively manage the stress experienced in order to maintain a positive mood A discussion about common stressful situations at work was carried out in the virtual environment, and strategies for regulating the mood during critical work situations were shared.
6th Session: Discussion of ideas related to EI. Trainees participated in an online debate about key emotional skills in order to understand how to apply stress management skills to the real work environment. It was necessary to share previous work experiences where stress was a significant challenge and reevaluate the emotionally intelligent way to deter stress and maintain a balanced senior manager life.
7th Session: Participants concluded the training on target strategies to effectively manage their emotions as well as skills that influence the moods and emotions of others. This session, therefore, was a period for feedback where brief answers to specific doubts were provided. In addition, the outcomes of the training were established by the participants. Finally, senior managers were encouraged to stay connected through the Moodle platform in order to resolve future challenges together using the EI skills learned and internalized during the training period.
Data analysis
An experimental pretest-posttest with a control group design was adopted. Under this design, multivariate variance analysis (MANOVA) and univariate variance analysis (ANOVA) of repeated measures were performed, in which the measures of dependent variables were treated as variables evaluated within the same subjects, and groups operated as variables between subjects. Finally, all statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS statistical software, version 21.0 (IBM, Armonk, USA).
First, sample normality analysis indicated that the population followed a normal distribution. The results of Box’s M test did not show homogeneity in the variance-covariance matrix on the EQ-i Total Scale (M = 59.29; F = 9.26, p ≥ 0.00) or on the STEM/STEU (M = 231.01; F = 36.07, p ≥0.00). However, Hair et al. [ 64 ] have stated that if the control and the experimental groups are of equal size, which was the case in this study, then that factor tends to mitigate the effects of violations of the normality assumption.
Second, to test whether there was any significant difference between the experimental group and control group at the time of pretest, Student’s t -test was performed to determine the differences in means of all the variables measured ( Table 1 ). Table 1 shows that there were no significant differences at the time of pretest. This finding suggests that both groups began in analogous situations.
Table 1. Student’s t-test of differences in means (t1, t2, t3).
Note. t1 = pretest; t2 = posttest; t3 = follow-up.
1 = direct score
Therefore, we came to the conclusion that the two groups of workers could not be distinguished by EI level before the TCEI program. In addition, the mean age of each group was analyzed and no baseline differences were found between the two groups.
To assess the impact of the program on EI, the scores obtained by both groups were compared before its implementation (pretest–Time 1) and shortly after the program was delivered (posttest–Time 2), as well as one year later (follow-up–Time 3). Group membership was the independent factor or variable, and the scores obtained by the subjects regarding EI were the criteria or dependent variables.
Two control variables, gender and age, were included in the analysis because they could affect the results. However, none of these variables showed a statistically significant effect in any of the variables assessed (p≥ .50 in all cases).
Regarding the implementation of the program, Table 2 presents the test results for intra-subject effects, which showed significant Group x Time interaction for all variables except for Adaptability.
Table 2. Summary of intra- and inter-subject univariate ANOVA.
The observed power was highest in the key scales: 1.00 for the STEU/STEM and Total EQ-i. Regarding the subscales, the observed power was also 1.00 for the Intrapersonal, Stress Management, and General Mood subscales; on the other hand, the observed power for the Interpersonal and the Adaptability subscales was .66 and .55, respectively.
Similarly, the effect size (η 2 ), the proportion of total variability attributable to a factor, and the magnitude of the difference between one time and another resulting from the interaction between the time of assessment and implementation of the program, was high for the key scales: ≥.71 for the STEU/STEM, and .82 for the Total EQ-i. With regards to the subscales, the effect size (η 2 ) was the following: .44 for Intrapersonal, .07 for Interpersonal, .32 for Stress Management, .05 for Adaptability, and .26 for General Mood.
To further explain these results, complementary analyses were performed. On the one hand, as shown in Table 1 , we carried out an average comparison between the experimental and control groups at the measurement moments T2 and T3. Results revealed significant differences between the experimental group and the control group regarding all variables and in both moments (T2 and T3), except for the Interpersonal variable, in which the experimental group obtained higher scores in these two moments but without being statistically significant these differences. This could explain the small effect size obtained for this variable.
In addition, the Adaptability variable showed statistically significant differences between the experimental group and the control group at time T2, with the control group scoring higher, while at time T3, the experimental group also obtains higher scores regarding Adaptability; however, this score difference with regards to the control group was not statistically significant. This could explain why the interaction was not significant and the small effect size obtained for this variable.
In order to compare differences between moments T1, T2, and T3, the marginal means were analyzed for both groups (experimental and control) per moment and variable ( Table 3 ).
Table 3. Marginal means comparing t1-t2, t1-t3, and t2-t3.
Note. EG = experimental group; CG = control group; t1 = pretest; t2 = posttest; t3 = follow-up.
In general, in the experimental group, there was a significant improvement between moments T1 and T2 in all variables, except Interpersonal and Adaptability, which did not present changes at any of the three moments (T1, T2, T3). On the other hand, scores remained without significant changes regarding all variables between moments T2 and T3, except in the case of STEU and STEM, in which the scores continued to improve between moments T2 and T3.
In the control group, the results were the same as in the experimental group concerning the Interpersonal and Adaptability variables. However, with regards to other variables, the trend was inverse to the experimental group between moments T1 and T2; in this case, there was a significant decrease in the scores between these two moments in the rest of the variables. Between moments T2 and T3, the scores remained without significant changes in all the variables measured with the EQ-i. In the case of variables measured with the ability test, there was a significant decrease in the STEU scores between moments T2 and T3, whereas the STEM scores remained without significant changes.
Figs 1 – 3 show the scores obtained in the EQ-i total scale and STEM/STEU total scales by both groups at Times 1, 2, and 3. At Times 2 and 3, the experimental group, which had received the EI training, had an increase in its scores, whereas the control group did not present any substantial change in scores.
Fig 1. Total EQi performance of the groups at pre-test (Time 1), post-test (Time 2), and one year after (Time 3).

Fig 3. STEM performance of the groups at pre-test (Time 1), post-test (Time 2), and one year after (Time 3).

Fig 2. STEU performance of the groups at pre-test (Time 1), post-test (Time 2), and one year after (Time 3).

The objective of this study was to examine the effectiveness of an EI training program among the senior managers (N = 54) of a private company. Consistent with Pérez-González and Qualter [ 13 ], Hodznik et al. [ 8 ], and Kotsou et al.’s [ 55 ] recommendations, we aimed to contribute new research findings and extend the existing literature on the effectiveness of EI training in the workplace. The main findings of this study revealed that intrapersonal EI, self-perception, general mood, self-expression, and stress management were maintained after the completion of the training. On the other hand, improvements in emotional understanding and emotion management had strengthened over time. However, the results also revealed that training did not result in similar improvements across all variables. Specifically, training had a nonsignificant impact on interpersonal and adaptability skills.
Theoretical implications of the study
With regard to the theoretical implications of the present findings, the observed effectiveness of the TCEI, which was conducted using an innovative methodology that entailed face-to-face training and a virtual campus support system among senior managers, extends the existing literature on the development of EI training programs.
The training program that was conducted as a part of this study failed to improve two dimensions of EI: interpersonal and adaptability skills. There are two possible explanations for why these variables did not demonstrate improvement. First, high-quality training that addresses all the dimensions of EI is necessary to produce large effects. Therefore, the time and exercises that are devoted to these two dimensions of EI may need to be redefined. Accordingly, the second and fourth sessions of this training (i.e., interpersonal and adaptability skills, respectively) can be enriched by adding new activities and including long-term evaluation of the transfer of skills to real workplace situations in which these abilities are required to resolve challenges. Indeed, allocating more time and exercises to these topics may have offered participants greater experience in practicing these interpersonal and adaptability skills in regular and virtual classroom settings before applying them in the workplace.
On the other hand, changes in these two dimensions of EI may not be detectable immediately after the completion of the training or soon after a year has elapsed. Similarly, the studies that Kotsou et al. reviewed [ 55 ] also indicated that improvements in EI may not be detectable immediately or shortly after the completion of an intervention. Further, the conclusions of this review appear to suggest that shorter training programs do not improve some dimensions of EI. Therefore, a more intensive training and longer time gap between completion of training and assessment (i.e., after more than a year has elapsed) may yield significant results for these two dimensions of EI. Indeed, other studies have used longer time gaps such as more than two years [ 40 ] and yearly evaluations across three years [ 47 ].
In any case, the present findings suggest that the proposed training intervention is effective in improving some dimensions of EI. In particular, senior managers who received EI training demonstrated significant improvements in their ability to perceive, understand, and accept their own and others’ emotions in an effective way, be self-reliant, achieve personal goals, manage stress, have a positive attitude, and control and manage emotions; these findings are consistent with those of past studies that have aimed to improve EI by providing training in workplaces [ 45 – 52 ].
The largest effects emerged for the total scores for EI (as per mixed models; total EQ-i), followed by emotion management (STEM) and understanding (STEU), intrapersonal aspects, stress management, and finally, general mood. Moreover, improvements in emotional understanding and emotion management that had resulted from the training intervention had strengthened over time.
Similarly, several researchers have indicated that EI plays a key role in leadership development and success in the workplace [ 65 , 66 ]. The behaviors of managers shape critical stages of their subordinates’ careers as well as the provision of optimal training and promotion [ 67 , 68 ]. Given the unique significance that EI and optimal leadership bears to this group of professionals, the present study aimed to improve the EI of senior managers.
In sum, the proposed program is a training intervention that can be used to enhance the EI of senior managers because, as the previously articulated extensive literature review has demonstrated, EI plays a key role within work environments. Therefore, the present findings suggest that the TCEI is an effective training program that can improve the ability to identify one’s own and others’ emotions as well as identify and understand the impact of one’s feelings on thoughts, decisions, behaviors, and performance at work.
Practical implications
The present findings serve as empirical evidence of the effectiveness of the training program that was conducted in the present study in improving key dimensions of EI that foster the emotional skills that are both necessary and desirable in the workplace. Accordingly, the present findings have practical implications because they support the future use of the EI training program that was used in the present study. In this regard, the present findings revealed that EI training can promote the emotional development of senior managers.
In addition, the methodology of the training program is noteworthy because it required participants to use communication and work as a group to solve real practical problems that necessitate the application of EI skills in the workplace. Similarly, the use of face-to-face training alongside an e-learning platform helped participants acquire the ability to learn independently as well as synergically (i.e., with other senior managers). This encouraged the group to reflect on their knowledge about EI and apply their EI skills to handle workplace challenges.
It is important to emphasize that there were significant temporal changes in the scores of measures of emotional understanding and emotion management; in other words, the scores continued to improve a year after the completion of training. It is interesting to note that the methodology of the last training session was unique because it involved the creation of a “life and career roadmap” and “commitment to growth and development. We believe that these exercises were responsible for the continued improvement in important EI skills over time that was observed in the present study.
This finding has important practical implications because it underscores the importance of requiring senior managers to indicate their commitment to the transfer of knowledge. Indeed, the roadmap defines the results that are expected to follow the implementation of the learned emotional strategies and verifies the achievement of these results. In addition, all managers signed an online contract to indicate their commitment to remain connected through the virtual campus support system to resolve any conflicts that may arise within the company in an emotionally intelligent manner.
We believe that the method of learning that our intervention entailed is more effective than conventionally used methods. Further, the uniqueness of this method may have contributed to the observed change in scores because it allowed frustrated senior managers to share their unresolved issues. Finally, by practicing emotional understanding and emotional management during the training, the created a plan of action and implemented their solutions using EI strategies.
In addition, we believe that signing the online contract helped them understand their responsibilities and the impact that their emotional understanding and emotion management can have on the organization. The fact that their scores on measures of emotional understanding and emotion management continued to increase over time indicates that the subjects had acquired these skills and that, once they had acquired them, they continued to develop them. Similarly, Kotsou et al. [ 55 ] also found that training resulted in stable improvements in EI. In addition to providing their participants with EI tools and skills as a part of their training, they also motivated them to apply these skills and use these tools in the future.
Taken together, the present findings have promising practical implications. Specifically, the findings suggest that a training methodology that facilitates knowledge transfer (i.e., application of knowledge about EI in the management of workplace challenges) can enhance the following dimensions of EI: emotional understanding, emotion management, self-perception (through training activities that pertain to self-regard, self-actualization, and emotional self-awareness), decision making (through training activities that pertain to problem solving, reality testing, and impulse control), self-expression (through training activities that pertain to emotional expression, assertiveness, and independence), and stress management (through training activities that pertain to flexibility, stress tolerance, and optimism).
Limitations and future studies
The present study has several limitations that require explication. First, we included only age and gender as control variables and omitted other individual differences that could have influenced the results. However, it is important for future researchers to define and examine the role of individual differences in the effects of EI training in greater detail. In addition, in accordance with Kotsou et al. [ 55 ] and Hodzic et al.’s [ 8 ] suggestions, detailed behavioral indicators must be examined because they may play a crucial role in the effectiveness of EI training. Another limitation of the present study is that the intervention program was conducted in only one company. Therefore, future studies must implement this program in different companies and across varied business contexts. The present results make it apparent that further refinements are needed in order to address the aforementioned limitations of this intervention.
Another limitation of the present study is that it did not assess the effect that improvements in EI can have on other variables. Accordingly, recommendations for further research include the determination of whether improvements in EI that result from training lead to improvements in other variables such as job satisfaction and performance and successful leadership, in accordance with the results of other research studies [ 69 – 72 ]. Thus, future research studies must consider these possibilities when they examine whether the TCEI has the potential to produce all the aforementioned outcomes at an organizational level. Furthermore, the intervention can be redesigned in such a manner that it yields specific performance outcomes. Further, longitudinal studies on the effectiveness of EI training must be conducted across several sectors and countries.
Finally, senior managers define and direct the careers of the rest of a company’s personnel; Therefore, future research studies must examine how EI training can be used to promote its previously observed desirable effects such as the demonstration of good leadership behaviors, effective cooperation, and teamwork [ 29 , 31 , 34 – 38 , 69 ]. In fact, this is an interesting line of inquiry for future researchers.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the present findings contribute to the existing knowledge on the development of EI because they indicate that the training program resulted in improvements in many dimensions of the EI of senior managers. More specifically, the longitudinal effects of EI training on senior managers’ emotional skills had maintained over time, whereas the corresponding effects on emotional understanding and emotion management had strengthened at one-year follow up. Finally, the implementation of this intervention in organizational settings can nurture and promote a sense of fulfillment among employees.
Supporting information
Data underlying the findings described.
TCEI planning schedule.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (EDU2015-64562-R)
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This research was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (EDU2015-64562-R) to R.G-C. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
- 1. Goleman D. Emotional intelligence: Why it can matter more than IQ. Learning. 1996; 24(6), 49–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Bar-On R. EQ-i: Bar On emotional quotient inventory: A measure of emotional intelligence: Technical manual. North Tonawanda: Multi-Health System; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Bar-On R. EQ-i: The Bar-On model of emotional-social intelligence (ESI). Psicothema. 2002; 18, 13–25. Available from: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=72709503 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Mayer J. D., Salovey P., and Caruso D. R. Emotional intelligence: Theory, findings, and implications. Psychological Inquiry. 2004; 15, 197–215. [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Mayer J. D., and Salovey P. The intelligence of emotional intelligence. Intelligence. 1993; 17, 433–442. [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Petrides K. V., Pita R., and Kokkinaki F. The location of trait emotional intelligence in personality factor space. British Journal of Psychology. 2007; 98(2), 273–289. 10.1348/000712606X120618 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Petrides K. V., and Furnham A. Trait emotional intelligence: Psychometric investigation with reference to established trait taxonomies. European Journal of Personality, 2001; 15, 425–448. [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Hodzic S., Scharfen J., Ripoll P., Holling H., and Zenasni F. How Efficient Are Emotional Intelligence Trainings: A Meta-Analysis. Emotion Review. 2018; 10(2), 138–148. 10.1177/1754073917708613 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Schutte N. S., Malouff J. M., and Thorsteinsson E. B. Increasing emotional intelligence through training: Current status and future directions. International Journal of Emotional Education. 2013; 5(1), 56. [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Moon T. W., and Hur W. M. Emotional intelligence, emotional exhaustion, and job performance. Social Behavior and Personality. 2011; 39(8), 1087–1096. 10.2224/sbp.2011.39.8.1087 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Van Rooy DL, Viswesvaran C Emotional intelligence: A meta-analytic investigation of predictive validity and nomological net. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2014; 65, 71–95. 10.1016/S0001-8791(03)00076-9 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Joseph DL, Newman DA Emotional intelligence: An integrative meta-analysis and cascading model. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2010; 95, 54–78. 10.1037/a0017286 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Pérez-González JC, and Qualter P Emotional intelligence and emotional education in school years In Dacree Pool L., Qualter P, editors. An Introduction to Emotional Intelligence. Chichester: Wiley; 2018. pp. 81–104. [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Brasseur S, Grégoire J, Bourdu R, Mikolajczak M. The Profile of Emotional Competence (PEC): Development and Validation of a Self-Reported Measure that Fits Dimensions of Emotional Competence Theory. 2013; PLOS ONE, 8 (5) e62635 10.1371/journal.pone.0062635 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Chiva R., and Alegre J. Emotional intelligence and job satisfaction: The role of organizational learning capability. Personnel Review. 2008; 37(5–6), 680–701. 10.1108/00483480810906900 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 16. Sener E., Demirel O., and Sarlak K. The effect of the emotional intelligence on job satisfaction. Connecting Health and Humans. 2009; 146, 710–711. 10.3233/978-1-60750-024-7-710 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. Moreno-Jimenez B., Blanco-Donoso L. M., Aguirre-Camacho A., de Rivas S., and Herrero M. Social skills for the new organizations. Behavioral Psychology-Psicologia Conductual. 2014; 22, 585–602. [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Kinman G., and Grant L. Exploring stress resilience in trainee social workers: The role of emotional and social competencies. British Journal of Social Work. 2011; 41, 261–275. [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Froman L. Positive psychology in the workplace. Journal of Adult Development. 2010; 17, 59–69. [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Humphrey R. H., Pollack J. M., and Hawver T. Leading with emotional labor. Journal of Managerial Psychology. 2008; 23, 151–168. [ Google Scholar ]
- 21. Mayer J. D., Salovey P., and Caruso D. R. Emotional intelligence: New ability or eclectic traits? American Psychologist. 2008; 63, 503–517. 10.1037/0003-066X.63.6.503 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 22. Nelis D., Kotsou I., Quoidbach J., Hansenne M., Weytens F., Dupuis P., et al. Increasing emotional competence improves psychological and physical well-being, social relationships, and employability. Emotion. 2011; 11(2), 354–366. 10.1037/a0021554 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 23. Hur Y., van den Berg P. T., and Wilderom C. P. M. Transformational leadership as a mediator between emotional intelligence and team outcomes. Leadership Quarterly. 2011; 22(4), 591–603. 10.1016/j.leaqua.2011.05.002 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 24. Slaski M., and Cartwright S. Health, performance and emotional intelligence: An exploratory study of retail managers. Stress and Health: Journal of the International Society for the Investigation of Stress. 2002; 18(2), 63–68. [ Google Scholar ]
- 25. Kaplan S., Cortina J., Ruark G., LaPort K., and Nicolaides V. The role of organizational leaders in employee emotion management: A theoretical model. The Leadership Quarterly. 2014; 25(3), 563–580. [ Google Scholar ]
- 26. Thiel C. E., Connelly S., and Griffith J. A. Leadership and emotion management for complex tasks: Different emotions, different strategies. The Leadership Quarterly. 2012; 23(3), 517–533. [ Google Scholar ]
- 27. Batool B. F. Emotional intelligence and effective leadership. Journal of Business Studies Quarterly. 2013; 4(3), 84. [ Google Scholar ]
- 28. Gardner L., and Stough C. Examining the relationship between leadership and emotional intelligence in senior level managers. Leadership and organization development journal. 2002; 23(2), 68–78. [ Google Scholar ]
- 29. Sunindijo R. Y., Hadikusumo B. H. W., and Ogunlana S. Emotional intelligence and leadership styles in construction project management. Journal of Management in Engineering. 2007; 23, 166–170. [ Google Scholar ]
- 30. Cooper R. K. Applying emotional intelligence in the workplace. Training and Development, 51. 1997; 31–42. [ Google Scholar ]
- 31. George J. M. Emotions and Leadership: The Role of Emotional Intelligence. Human Relations. 2000; 53(8), 1027–1055. 10.1177/0018726700538001 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 32. Wong C. S., and Law K. S. The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude: An exploratory study. The leadership quarterly. 2002; 13(3), 243–274. [ Google Scholar ]
- 33. Palmer B., Walls M., Burgess Z., and Stough C. Emotional intelligence and effective leadership. Leadership and Organization Development Journal. 2001; 22(1), 5–10. [ Google Scholar ]
- 34. Yammarino F. J., Spangler W. D., and Bass B. M. Transformational leadership and performance: A longitudinal investigation. The Leadership Quarterly. 1993; 4(1), 81–102. [ Google Scholar ]
- 35. Cha J, Cichy RF, Kim SH. The contribution of emotional intelligence to social skills and stress management skills among automated foodservice industry executives. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality and Tourism. 2008; 8(1),15–31. [ Google Scholar ]
- 36. Dulewicz V, Higgs M. Leadership at the top: The need for emotional intelligence in organizations. The International Journal of Organizational Analysis. 2003;11(3), 193–210. [ Google Scholar ]
- 37. Goleman D, Boyatzis R. McKee. The New Leaders: Transforming the Art of Leadership into the Science of Results. London: Little Brown, 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- 38. Goleman D. and Boyatzis R. Social intelligence and the biology of leadership. Harvard Business Review. 2008; 86, 74–85. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 39. Nelis D., Quoidbach J., Mikolajczak M., and Hansenne M. Increasing emotional intelligence: (How) is it possible? Personality and Individual Differences. 2009; 47(1), 36–41. [ Google Scholar ]
- 40. Boyatzis R. E., and Saatcioglu A. A 20-year view of trying to develop emotional, social and cognitive intelligence competencies in graduate management education. Journal of Management Development. 2008; 27, 92–108. 10.1108/02621710810840785 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 41. Clarke N. Developing emotional intelligence abilities through team-based learning. Human Resource Development Quarterly. 2010; 21(2), 119–138. 10.1002/hrdq.20036 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 42. Dacre Pool L., and Qualter P. Improving emotional intelligence and emotional self-efficacy through a teaching intervention for university students. Learning and Individual Differences. 2012; 22(3), 306–312. 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.01.010 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 43. Gilar-Corbi R., Pozo-Rico T., and Castejon-Costa J. L. Improving emotional intelligence in higher education students: testing program effectiveness in tree countries. Educacion Xx1. 2019; 22(1), 161–187. 10.5944/educXX1.1988044 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 44. Pool L. D., and Qualter P. Improving emotional intelligence and emotional self-efficacy through a teaching intervention for university students. Learning and Individual Differences. 2012; 22(3), 306–312. 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.01.010 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 45. Beigi M., and Shirmohammadi M. Effects of an emotional intelligence training program on service quality of bank branches. Managing Service Quality. 2011; 21(5), 552–567. 10.1108/09604521111159825 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 46. Turner R., and Lloyd-Walker B. (2008). Emotional intelligence (EI) capabilities training: Can it develop EI in project teams? International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 1(4), 512–534. 10.1108/17538370810846450 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 47. Dugan J. W., Weatherly R. A., Girod D. A., Barber C. E., and Tsue T. T. A longitudinal study of emotional intelligence training for otolaryngology residents and faculty. JAMA Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery. 2014; 140(8), 720–726. 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.1169 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 48. Cherniss C., Grimm L. G., and Liautaud J. P. Process-designed training: A new approach for helping leaders develop emotional and social competence. Journal of Management Development. 2010; 29(5), 413–431. 10.1108/02621711011039196 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 49. Clarke N. The impact of a training program designed to target the emotional intelligence abilities of project managers. International Journal of Project Management. 2010; 28(5), 461–468. 10.1016/j.ijpro-man.2009.08.004 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 50. Dulewicz V., and Higgs M. Can emotional intelligence be developed? International Journal of Human Resource Management. 2004: 15, 95–111. 10.1080/0958519032000157366 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 51. Slaski M., and Cartwright S. Emotional intelligence training and its implications for stress, health and performance. Stress and Health. 2003: 19(4), 233–239. 10.1002/smi.979 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 52. Daus C. S., Cage T., Cooper C. L., and Ashkanasy N. M. Learning to face emotional intelligence: Training and workplace applications. Research companion to emotion in organizations. 2008; 245–260. [ Google Scholar ]
- 53. Coté S., and Miners C.T.H. Emotional intelligence, cognitive intelligence, and job performance. Administrative science quarterly. 2006; 51, 1–28. [ Google Scholar ]
- 54. Sy T., Tram S., and O'hara L.A. Relaction of employee and manager emotional intelligence to job satisfaction and performance. Journal of vovational behavior. 2006; 68(3), 461–473. 10.1016/j.jvb.2005.10.003 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 55. Kotsou I., et al. Improving Emotional Intelligence: A Systematic Review of Existing Work and Future Challenges. Emotion Review, 2018, 10.1177/1754073917735902 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 56. MacCann C., and Roberts R. D. New paradigms for assessing emotional intelligence: theory and data. Emotion. 2008; 8(4), 540–551. 10.1037/a0012746 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 57. Mikolajczak M. Moving beyond the ability-trait debate: A three level model of emotional intelligence. E-Journal of Applied Psychology. 2009; 5, 25–32 [ Google Scholar ]
- 58. Halasz G., and Michel A. Key competences in Europe: Interpretation, policy formulation and implementation. European Journal of Education. 2011; 46(3), 289–306. [ Google Scholar ]
- 59. Staudel T. Key competences for apprentices. International Journal of Psychology. 2008; 43(3–4), 336–336. [ Google Scholar ]
- 60. Clarke N. Emotional intelligence and its relationship to transformational leadership and key project manager competences. Project Management Journal. 2010; 41(2), 5–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- 61. Kirkpatrick D. Evaluating training programs: The four levels (2nd ed). San Francisco, CA: Berrett–Koehler Publishers; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- 62. Bar-On R. The Bar-On Emotional Quotient Inventory (EQ-i): rationale, description and summary of psychometric properties In Glenn G, editors. Measuring emotional intelligence: common ground and controversy. Hauppauge, NY: Nova Science Publishers; 2004. pp. 111–142. [ Google Scholar ]
- 63. MacCann C., and Roberts R. D. The brief assessment of emotional intelligence: Short forms of the Situational Test of Emotional Understanding (STEU) and Situational Test of Emotion Management (STEM). Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- 64. Hair J. F., Anderson R. E., Tatham R. L., and Black W. C. Análisis Multivariante, 5ª Ed. Madrid: Prentice Hall Iberia; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- 65. Wolff S. B., Pescosolido A. T., and Druskat V. U. Emotional intelligence as the basis of leadership emergence in self-managing teams. Leadership Quarterly. 2002; 13(5), 505–522. 10.1016/S1048-9843(02)00141-8 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 66. Buono A. F. Primal leadership: Realizing the power of emotional intelligence. Leadership Quarterly. 2003; 14(3), 353–356. 10.1016/S1048-9843(03)0019-5 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 67. Rosete D., and Ciarrochi J. Emotional intelligence and its relationship to workplace performance outcomes of leadership effectiveness. Leadership and Organization Development Journal. 2005; 26(5), 388–399. [ Google Scholar ]
- 68. Goleman D. What makes a leader? Harvard Business Review. 2004; 82(1), 82–94. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 69. Kerr R., Garvin J., Heaton N., and Boyle E. Emotional intelligence and leadership effectiveness. Leadership and Organization Development Journal. 2006; 27(4), 265–279. [ Google Scholar ]
- 70. Carmeli A. The relationship between emotional intelligence and work attitudes, behavior and outcomes: An examination among senior managers. Journal of managerial Psychology. 2003; 18(8), 788–813. [ Google Scholar ]
- 71. Pescosolido A. T. Emergent leaders as managers of group emotion. The Leadership Quarterly, 13(5). 2002; 583–599. [ Google Scholar ]
- 72. Foster C., and Roche F. Integrating trait and ability EI in predicting transformational leadership. Leadership and Organization Development Journal. 2014; 35, 316–334. [ Google Scholar ]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data availability statement.
- View on publisher site
- PDF (733.6 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
The impact of collaborative learning and personality on satisfaction in innovative teaching context.

- 1 Institute of Technology Management, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung City, Taiwan
- 2 Department of Information Management, Tunghai University, Taichung City, Taiwan
Flipped teaching is one of the most popular innovative teaching methods which has attracted a lot of attention and lead to amount of discussion in recent years. Many educators have generally encountered same doubt when implementing flipped education: Is this kind of teaching mode only applicable to students with high learning achievements? In addition, collaborative learning is often applied in flip teaching and it is also an issue worth to explore. In this study, both quantitative and qualitative studies were conducted to examine the potential factors in affecting the learners’ satisfaction in flipped education. The survey results from 171 participants showed that collaborative learning and need for cognition are significant predictors of learning satisfaction. In addition, a deeper look at the collaborative learning process was further examined by conducting deep interview. A total of 12 students from 6 different flipped-teaching courses participated the interview. The findings suggested that arranging some activities to encourage students to know each other before class that helps students find corresponding group and facilitates their expertise for collaborative learning. The mechanism significantly influenced team members’ engagement, discussion atmosphere, and efficiency. In addition, when learning tasks diversity, it will also enhance students’ innovative ability, empathy, and even promote mutual learning.
Introduction
In recent years, flipped teaching has attracted considerable attention and aroused widespread discussion. Since 2011, the search trend of relevant keywords on Google has increased exponentially ( Abeysekera and Dawson, 2015 ). Many studies have compared student performance before and after the implementation of flipped teaching, evidencing that flipped teaching can help improve academic performance ( O'flaherty and Phillips, 2015 ). When the science control system of the Department of Mechanical Engineering of Seattle University implemented flipped teaching, the course divided students into two different groups: the traditional learning method group and the flipped learning method group. Results show that the group receiving flipped teaching generally performed better in tests and examinations and had a higher degree of mastery of design issues ( Mason et al., 2013 ). A course on renal drug therapy conducted flipped teaching to evaluate its impact on students’ professional performance. The results show that compared with the previous year’s performance in a traditional classroom environment, students’ performance in the final exam improved significantly ( Pierce and Fox, 2012 ). Most of the topics discussed in the existing literature mainly focus on the comparison of the effectiveness and acceptance of flipped teaching and traditional teaching among students.
After a systematic review of research related to flipped teaching, O'flaherty and Phillips (2015) pointed out that individual differences can be explored in the future, for example, whether there are specific demographics or personalities that can predict students’ responses to flipped lessons. To explore the individual differences of students under flipped teaching, this study refers to the research of Abeysekera and Dawson (2015) . Although the research on flipped teaching has been conducted in a variety of domains ( Chang and Hwang, 2018 ; Lee and Wallace, 2018 ; Javier et al., 2020 ), this study aimed at examining the potential factors in affecting the learning satisfaction in flipped education by combining both qualitative and quantitative study. Thus, the first objective of this study is to examine the influential factors of learners’ satisfaction from the perspective of personality, self-efficacy, and collaborative learning. Specifically, this study focuses on the impact of students’ personality traits and collaborative learning on learning satisfaction under flipped teaching so as to understand the response of individual differences to flipped teaching. This study uses the cognitive needs theory and learning self-efficacy as the entry point to explore personality traits and provides a reference for educators who plan to practice in flipped teaching in the future.
Further, as most of the flipped teaching courses require students form into groups and collaborative with each other to finish the projects, the second objective of this study is to look deeper into the collaborative learning process for students participating the flipped learning. Thus, deep interviews were conducted to understand the collaborative learning process when the students participated the flipped learning and the findings can provide significant insight for educators who want to teach in a more innovative way and increase students’ engagement in flipped teaching.
Literature Review
Flipped teaching.
The term “flipped teaching” is commonly used to describe a teaching method wherein the completion of homework after class is carried out in the classroom and the classwork is to be completed by the students themselves before class ( Abeysekera and Dawson, 2015 ). The idea of flipped teaching first occurred as an accidental discovery by a high school chemistry teacher in the United States when he wanted to conduct remedial classes for absent students. He bought a set of software and uploaded the classwork teachings on the Internet so that absent students could keep up with their studies. However, in addition to the students who were absent from class, students who had originally attended the class also used the online teaching resources to review the course content and benefited from it. This discovery made Bergmann and Sams rethink the allocation of class time in the teaching process ( Tucker, 2012 ).
Many studies have proven that the flipped teaching method can improve students’ learning motivation. In a statistics course at a university, it is understood through interviews that students are more willing to accept collaborative learning and innovative teaching methods than traditional teaching ( Strayer, 2012 ). After the introduction of flipped teaching in the British chemistry curriculum, students expressed that they preferred this interactive mode, because it gave them more opportunities to develop more advanced learning skills in the classroom than before ( Yeung, 2014 ). It not only improves learning motivation but also stimulates students’ active learning because of the changes in the teaching process. In addition to the teaching content of the course itself, when the course is conducted in the form of group discussions, communication and critical thinking abilities also improve. In a study on the implementation of flipped teaching in nursing courses, students had more opportunities to discuss and solve unfamiliar problems with their peers and teachers in the classroom. Through the redesigned curriculum, students were required to criticize various scenarios, collect information, and provide insights for patients. Such learning activities combine knowledge of patient assessment, critical thinking, and evaluation skills ( Ferreri and O’connor, 2013 ).
The European Higher Education Framework proposes a shift from the previous one-way teaching of courses by teachers to a student-centered learning approach ( Schreurs and Dumbraveanu, 2014 ). Honeycutt and Garrett (2014) refer to the flipped classroom as paying attention to a learner’s learning status through their participation in solving problems, creating, criticizing, and integrating problems with peers and teachers in the classroom. Bergmann and Sams (2012) believe that the core of flipping is to focus on students’ needs, and Bloom Taxonomy provides a framework for judging whether it is flipped teaching: courses centered on past lectures usually focus on the lower level of Bloom Taxonomy, such as the cognition and understanding of basic knowledge. Teachers with flipped teaching will focus more on the high-level learning results of Bloom’s taxonomy in the classroom, such as analysis, judgment, and creation.
Sáiz Manzanares et al. (2017) analyze the effect of blend learning on students’ learning outcomes. The results showed that different learning patterns can predict student learning outcomes. Further, Yin and Yuan (2021) examined the learning performance in a blended learning environment in China and the factors of perceived precision teaching, self-efficacy, learning motivation, and social presence were examined. The results indicated that all the predictors showed significant effect on learning performance, of which self-efficacy is one of the most important factors in predicting learning performance. In addition, Yokoyama and Miwa (2021) examined the effects of self- and peer-assessment on the growth of learning goal orientation. Results from the experiment showed that peer-assessment is effective in enhancing the growth of learning goal orientation.
The above discussion revealed that studies on flipped teaching are varied. However, most of the studies are focusing on language learning. For example, Lee and Wallace (2018) provided empirical evidence about whether flipped learning can promote students’ English learning. Andujar et al. (2020) examine the effect of integrating the flipped teaching and the usage of mobile devices in language learning. Further, Amiryousefi (2019) investigated the effects of flipped learning on EFL (English as a foreign language) learners’ engagement.
This study refers to Abeysekera and Dawson (2015) to explore flipped teaching with the following three characteristics: (1) process-oriented and inquiry-based learning, (2) peer-based team learning, and (3) peer interaction and learning.
Learning Satisfaction
Learning satisfaction has always been a very important research indicator in education-related research. According to a study by Ko and Chung (2014) , there is a significant positive correlation between student learning satisfaction and academic performance. A report on innovative teaching also pointed out that students’ learning satisfaction directly affects their academic performance; thus, it is also one of the main items used to measure or predict learning effectiveness ( Lee, 2011 ).
Chang and Chang (2012) defined learning satisfaction as the degree of happiness that students experience after learning activities. Learning satisfaction exists in the balance between personal expectations and self-realization. When the results of self-realization are equal to or higher than personal expectations, learning satisfaction can be improved; however, when the results of self-realization are not as good as personal expectations, one cannot obtain a sense of achievement in learning ( Martin, 1988 ).
Many factors can affect students’ learning satisfaction. In a study on learning satisfaction among adults receiving computer-related skills teaching, divided learning satisfaction into five items: teacher’s teaching, classroom materials, learning outcomes, interpersonal relationships, and learning environment. In a survey of learning satisfaction among college students, the questionnaire was divided into five items: learning environment, academic performance, administrative services, interpersonal relationships, and attitudes toward teachers and administrators ( Starr, 1971 ). Corts et al. (2000) used five environmental factors to study how student satisfaction was affected. The results of the study show that employability development and curriculum planning have the deepest impact on student satisfaction. Teven and Mccroskey (1997) also prove that teachers’ attention toward students’ learning conditions and their interactions with students contribute to improving students’ learning satisfaction.
Based on the above views of scholars, although the factors affecting learning satisfaction have different research results and opinions because of the research focus of scholars, in fact, the external factors that affect students’ learning satisfaction are mainly constituted by teachers’ teaching methods, arrangement of learning activities, curriculum content planning, classroom teaching materials, learning outcomes, employment skills training, interpersonal interactions with peers and teacher interactions, and other factors.
Learning Self-Efficacy Theory
The self-efficacy theory was first proposed by Bandura in 1977, and Bandura defined it as the degree to which people believe they can accomplish tasks and achieve goals ( Bandura, 2010 ). The influencing factors of self-efficacy mainly come from the following four types: (1) through the successful experience of learning to build a stronger self-efficacy; (2) by seeing people similar to themselves who have worked consistently to achieve success and thus believing that they have similar abilities to be successful; (3) through the verbal encouragement of others, which makes people believe that they have the relevant abilities needed to complete the task, and they are willing to try to improve their self-efficacy; and (4) physiological conditions, negative emotions, and unhealthy physical conditions will lead to low self-efficacy ( Bandura, 2010 ).
Because self-efficacy affects people’s feelings, thinking, and behaviors, it has been widely studied and applied in many fields after it was proposed, which include addiction problems ( Bandura, 1995 ), smoking behavior ( Garcia et al., 1990 ), and athletic performance ( Barling and Abel, 1983 ). In education research, the value of self-efficacy has drawn increasingly more attention ( Pajares, 1997 ). In education, research on self-efficacy focuses on the following three aspects: (1) the relationship between self-efficacy and university majors and career choices ( Lent and Hackett, 1987 ); (2) teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs, teaching practices, and student academic performance ( Ashton and Webb, 1986 ); and (3) the relationship between students’ learning self-efficacy beliefs and academic achievement ( Bartimote-Aufflick et al., 2016 ).
In the research on the relationship between students’ learning self-efficacy and academic performance, students with high learning self-efficacy treat it as a challenge when they encounter difficulties in learning. Such students set challenging goals and continue to work hard. When faced with failure, they attribute the failure to insufficient effort or insufficient knowledge and skills, and they are more willing to keep working hard. On the contrary, students with low self-efficacy choose to escape when faced with difficulties and do not ask for learning goals. They usually give up easily when faced with problems, because they regard insufficient learning self-efficacy as insufficient ability ( Bandura, 2010 ).
According to Bandura’s narrative, it is reasonable to infer that learning self-efficacy has a positive effect on learning effectiveness. In many studies, learning self-efficacy has also been proven to be an important indicator used to predict academic performance ( Elias and Loomis, 2002 ). In addition, because learning outcomes affect learning satisfaction ( Starr, 1971 ), Aitken (1982) also pointed out that grade point average (GPA) has a positive effect on learning satisfaction. After reviewing the literature related to both learning self-efficacy and learning satisfaction, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H1 : Learning self-efficacy will positively influence learning satisfaction.
Need for Cognition
Need for cognition is a personality trait. Cohen et al. (1955) first defined this concept as “a need for individuals to organize their experience meaningfully.” Cacioppo and Petty (1982) modified this viewpoint, thinking that cognitive needs reflect people’s enthusiasm for activities related to cognitive thinking types.
People with low cognitive needs do not like cognitive tasks when dealing with complex problems and tend to rely on others or even expert opinions ( Petty et al., 1981 ). People with high cognitive needs are relatively more willing to devote themselves to thinking tasks or work and are more likely to use systematic thinking to process information. Such people are described as having a high degree of intrinsic motivation, aspiration, and curiosity, so they actively search for information ( Olson et al., 1984 ). As for causes of individual differences in cognitive needs in various social environments, the main reason is intrinsic motivation. This individual difference is stable for a while and not easy to change ( Cacioppo et al., 1996 ).
Most contemporary research involving the cognitive needs theory is based on the discourse of Cacioppo and Petty (1982) . Research involving cognitive needs includes social cognitive psychology, medicine ( Haugtvedt et al., 1992 ), and online consumer behavior ( Lin et al., 2011 ). In the literature related to education, Sadowski and Gülgös (1996) studied how cognitive needs affect academic performance, and the results prove that students with high cognitive needs achieve more academic achievements than those with low cognitive needs, because the former can deal with information more effectively than the latter. Dole and Sinatra (1998) also put forward similar research viewpoints, because students with high cognitive needs also have a higher level of performance in speculation and problem-solving during the learning process; on the contrary, students with lower cognitive needs have a lower level of performance. In a study that discussed the relationship between cognitive needs and the ability to solving complex problems ( Nair and Ramnarayan, 2000 ), it was pointed out that current cognitive needs have a significant positive correlation with solving complex problems, because people with high cognitive needs collect information and make multifaceted decisions about problems; they are more likely to succeed in solving problems.
According to the above discussion about cognitive needs in education literature, we understand that cognitive needs have a significant positive correlation with learning effectiveness. In a study by Elias and Loomis (2002) , the correlation between cognitive needs, learning self-efficacy, and learning effectiveness was verified. It has been proven that cognitive needs and learning self-efficacy are important predictors of GPA ( Strobel et al., 2019 ). Besides, it was also found that the relationship between cognitive needs and GPA was affected by the mediation of learning self-efficacy. Thus, the following hypotheses were proposed:
H2 : Need for cognition will positively influence learning satisfaction.
H3 : Need for cognition will positively influence learning self-efficacy.
Level of Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning is defined as when students achieve a common learning goal, they complete it in a group and are responsible for each other’s learning ( Gokhale, 1995 ). It is worth noting the difference between “cooperative learning” and “collaborative learning.” Cooperative learning refers to a model in which a learning task is divided into subtasks that can be solved independently by partners at the beginning. Collaborative learning is solving a problem together in an asynchronous and interactive way. The difference between the two is that collaborative learning emphasizes the discussion in the process of participating in tasks and believes that cognition must be adjusted through communication between students ( Curtis and Lawson, 2001 ). Verdejo (1996) emphasizes collaborative learning based on dialogue.
Gokhale (1995) pointed out that active exchange of ideas within the group will not only increase students’ interest but also promote critical thinking. Studies have shown that compared to individual learning, collaborative learning provides students the opportunity to discuss and have a higher level of thinking, and information can also be memorized for longer.
According to the observation of Tuckman and Jensen (1977) , it is pointed out that the interpersonal relationship between group members in collaborative learning will generally go through the following four stages: (1) Formation stage: a transitional period when group members are not familiar with each other; (2) Conflict stage: the transition period in the growth of the group, when group members adapt to each other and run-in; (3) Cohesion stage: If the conflict is handled properly, a balance that is acceptable to the members of a group is sought, gradually forming a consensus, and the cohesion of the group will increase day by day; and (4) Execution stage: team members will focus on the completion of the task and the achievement of the goal. Members depend more on each other, and each person’s role positioning will be more productive.
In the collaborative learning environment, regardless of the level of learning achievement, students generally perform better than their peers who study alone ( Aitken, 1982 ), and in the process of collaborative learning, students’ communication with each other is also considered helpful ( Bruffee, 1982 ). According to the current research on collaborative learning, it is clearly pointed out that collaborative learning can improve learning more effectively ( Hertz-Lazarowitz et al., 2013 ) and reinforce students’ satisfaction with the entire learning process ( Bligh, 1998 ; Ocker, 2001 ). Thus, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H4 : Collaborative learning will positively influence learning satisfaction.
Research Method
Research design.
The study applied both quantitative and qualitative research methods to examine the factors in flipped teaching outcome. In the first stage, a survey was conducted and questionnaires were distributed to students who experienced the flipped learning method. The objective of the survey is to examine predicting factors of learning satisfaction. The study uses need for cognition, learning self-efficacy, and collaborative learning as the predictors that affect the satisfaction of flipped teaching. In the second stage, deep interviews were conducted to understand the collaborative learning process as it is one of the most important mechanisms in flipped learning. The objective of the second stage is to explore the learners’ collaborative learning process in terms of team formation, discussion atmosphere, discussion efficiency, decision-making mode, cooperation mode, and cross-domain learning. In the second stage, semi-structured in-depth interviews were conducted. The interview comprises open questions, starting with the interviewee’s personal background, including questions about name, gender, school, department, grade, and major courses, and then cutting into the core questions of the research gradually. The two-staged research design is depicted in Figure 1 .
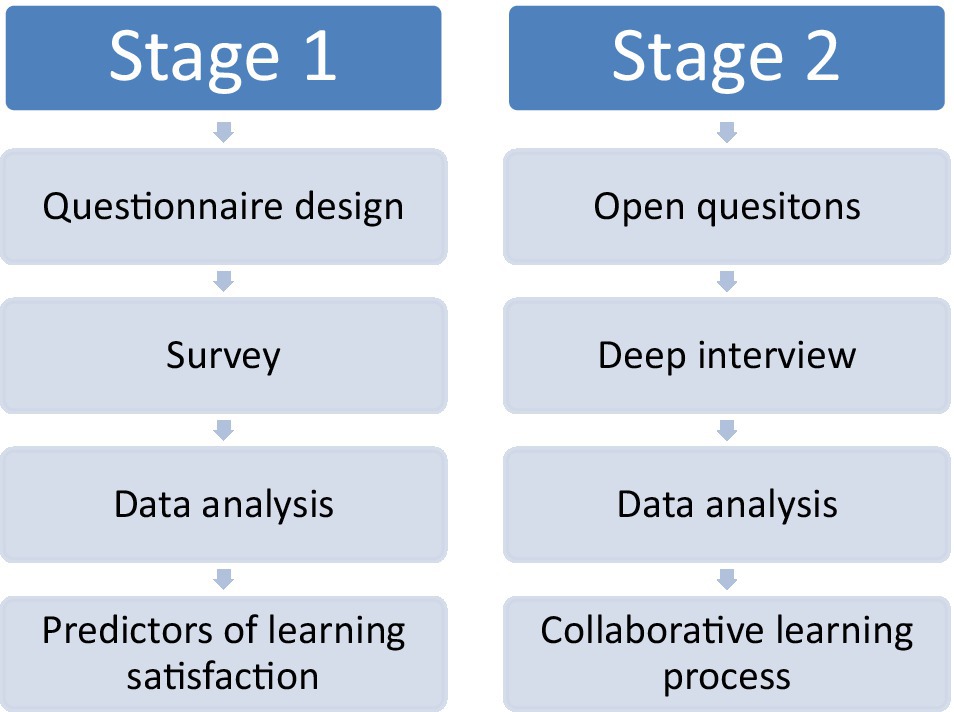
Figure 1 . Two-staged research design.
Data Collection
All the participants in this study (including stage 1 and stage 2) were recruited from six courses which were given as flipped teaching methods. The students were either asked to fill out the questionnaire for qualitative research or invited as an interviewee for qualitative research in this study.
This study refers to the flipped teaching model proposed by Abeysekera and Dawson (2015) . The flipped teaching curriculum must have the following three elements: (1) process-oriented inquiry learning, (2) team-based learning, and (3) peer learning. According to this standard, a total of six courses have been selected as the experimental situation, which was described in Table 1 .

Table 1 . The description of courses selected in the study.
The sample of survey and interview are students from the same pool (the six courses listed in Table 1 ). The objective is to examine the factors of learning satisfaction from qualitative study. At the same time, students from the same courses were invited to participate the interview in order to illustrate in more detail about the collaborative learning process in flipped classroom.
The data in this study were collected in two ways. First, students who take the courses illustrated in Table 1 were invited to fill out the questionnaire at the end of the semester. The questionnaires were distributed under the permission of the instructors, and a total of 171 valid samples were returned.
Second, the participants in qualitative study were invited from the six courses in Table 1 . Student was randomly selected to represent each of the top 25% and bottom 25% of the course scores. A total of 12 students from the six courses participated in this research interview. To protect the privacy of interviewees, the student names on the recording form are presented anonymously.
Research Framework
The research framework of this study is depicted in Figure 2 , in which two independent variables (collaborative learning and need for cognition), one mediator (learning self-efficacy) and one dependent variable (learning satisfaction), were included.
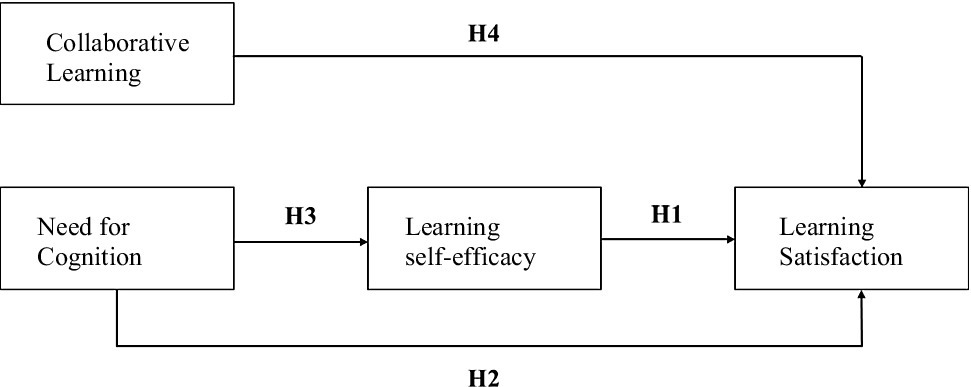
Figure 2 . Research framework.
Research Analysis and Results
Quantitative results.
SMART PLS (partial least square) software was used for data analysis, and structural equation model (SEM) was applied. Structural equation model is composed of two parts: measurement model and structural model. The measurement model is used to observe the relationship between potential variables; structural model is used to measure the relationship between variables and potential variables. This study applied confirmatory factors in the measurement model for theory verification and applied path analysis in the structural model to explore the causal relationship between variables.
Demographics
In terms of the gender distribution of the participants (as shown in Table 2 ), the proportion of males was 43.86% of the total subjects, and the proportion of females was 56.14%. In terms of grade distribution, 28.65% of juniors formed the group with the highest distribution, followed by 27.49% of seniors (and above), 26.90% of the first year of graduate school, 7.01% for both the freshman and sophomores, and lastly, 2.92% for the second year of graduate school (and above); as for the distribution of the colleges, the College of Management had the most students, accounting for 53.80% of the total, followed by 14.04% in the College of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 12.87% in the College of Agricultural and Natural Resources, 9.94% in the College of Liberal Arts, 4.09% in the College of Science, 2.34% in the College of Engineering, 1.75% in the College of Law and Politics, and 1.17% in the College of Life Sciences.
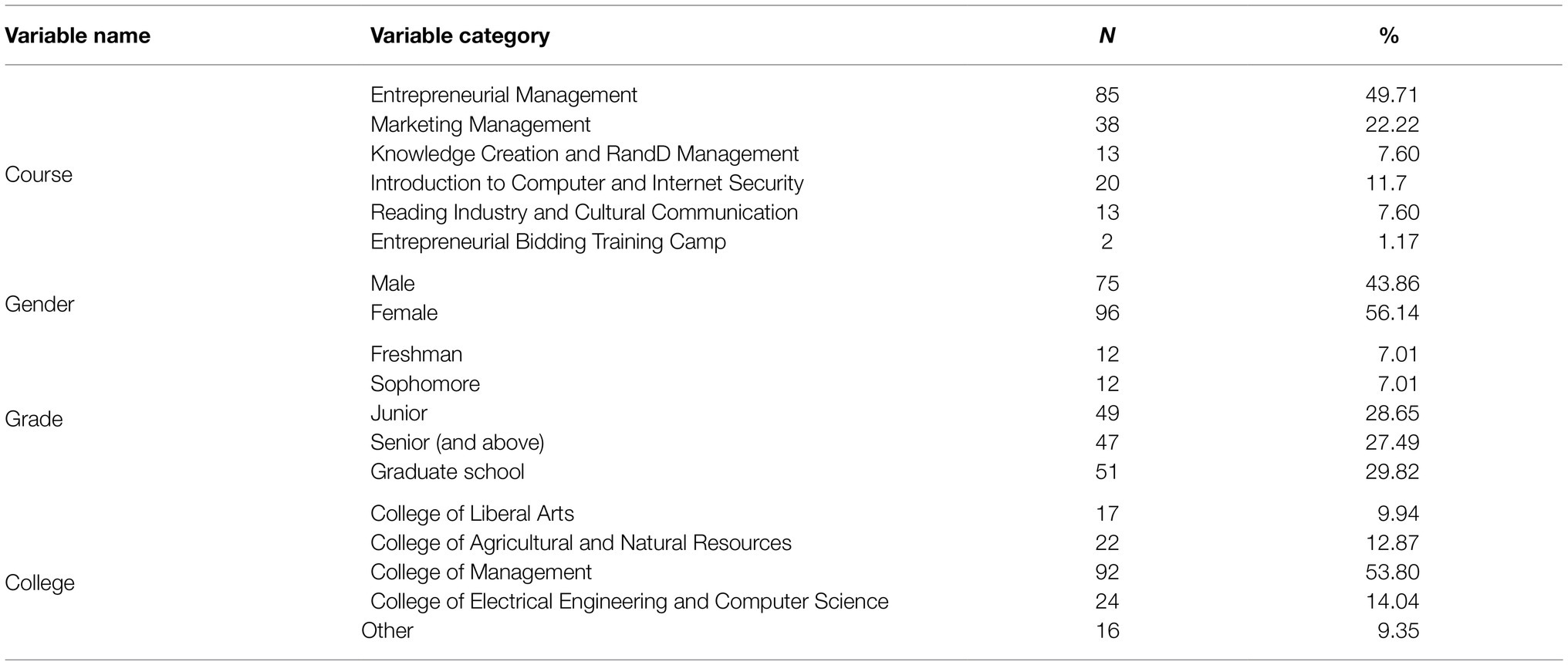
Table 2 . Demographics ( N =171).
Since the students at the College of Management were set as the largest number of participants in this study, the demographic variables were also affected by the composition of the grade and the college of the testing class. First, gender was the most influential part, as most of the students in the College of Management were female, which led to the reason that most of the subjects were female.
In addition, in terms of grades, it is noteworthy that most departments and colleges generally require courses with a higher level of implementation, and they are generally offered in the upper grades of the university department. This also explains why the distribution of the test subjects was mainly junior and senior students and the first grade of graduates.
Reliability and Validity Analysis
Validity refers to the theoretical extent to which the questionnaire can measure. The commonly applied method to test the validity in structural equation model is the confirmatory factor analysis in the measurement model. In the same factor dimension, if the factor load of each topic is larger, it means the degree of convergence is greater. Usually, it must be greater than 0.7, and the average variance extracted (Schreurs and Dumbraveanu) must be greater than 0.5. Based on these data as the test standard, after running the PLS statistical analysis, the items that did not meet the factor load were deleted: The first 18 questions about cognitive needs retained the first 1, 8, 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15 questions; 10 questions about learning self-efficacy were reserved for Questions 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, and 10; for the level of collaborative learning, except for Question 6, the remaining 6 questions were reserved; for learning satisfaction, the questions were reserved except for Question 6. The AVE of the retained items after organizing all the dimensions was greater than 0.5.
Reliability represents the stability of the subject’s answer. The most applied verification method is Cronbach’s alpha. When the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is greater than 0.7, the question items of the scale which the respondents fill in are consistent. The Cronbach’s alpha values of the above items that passed the validity test were all greater than 0.7. The validity and reliability analysis results are summarized in Table 3 .
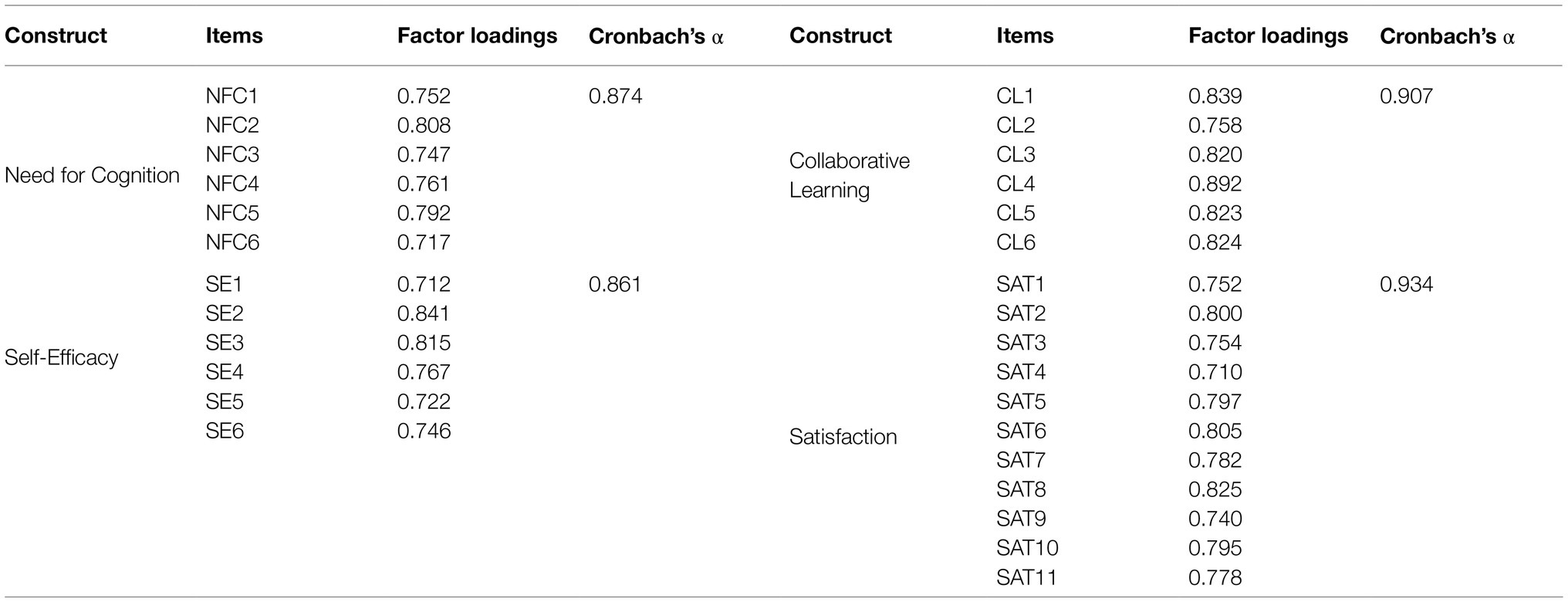
Table 3 . Validity and reliability test results.
Path Analysis
In the structural model, the results were obtained by applying path analysis (as shown in Figure 3 ). In the structural equation model with cognitive needs, learning self-efficacy, and collaborative learning as the independent variables and learning satisfaction as the dependent variable, the adjusted R 2 is 0.594; the model has a certain reference level. In the structural equation model with cognitive needs as the independent variable and learning self-efficacy as the dependent variable, the adjusted R 2 is 0.354, and the explanatory power of the model reached a significant level.
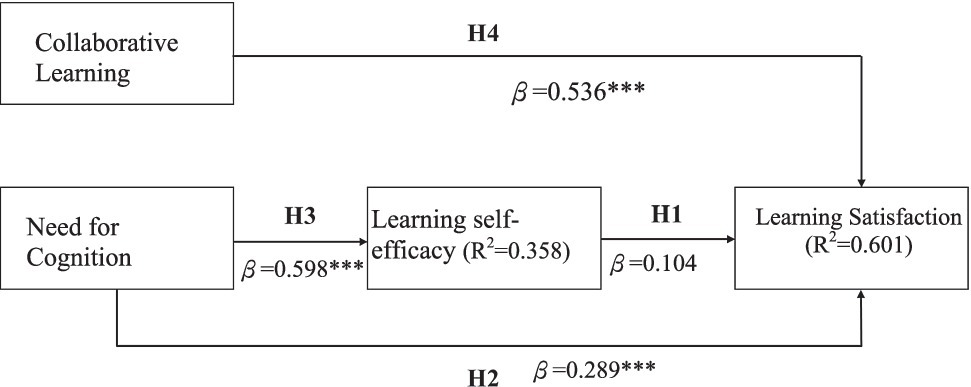
Figure 3 . Path analysis results. *** p <0.05
In addition, the β coefficient of the path of learning self-efficacy to learning satisfaction is 0.104, and the p value is 0.117; the β coefficient of cognitive needs to learning satisfaction is 0.289, and the p value is 0.000; the β value of collaborative learning degree is 0.536, and the p value is 0.000. In addition, the β coefficient of the path of cognitive needs to learning self-efficacy is 0.598, and the p value is 0.000.
Qualitative Research
Design of interview outline.
Due to the finding in the quantitative research results that the level of collaborative learning has a very critical impact on learning satisfaction, more in-depth research will be conducted on collaborative learning after the quantitative research.
Since the interview was conducted in May, there had been a period of time since the end of class last semester. Therefore, in addition to referring to the items in the questionnaire that involve collaborative learning ( Kitchen and Mcdougall, 1999 ; Driver, 2002 ; So and Brush, 2008 ), the questions of the interview outline were also designed to be combined with Tuckman’s five stages of group development ( Tuckman and Jensen, 1977 ), and the questions were presented in a chronological manner to prevent the interviewee’s course experience from being distorted by time factors, as shown in Table 4 .
Table 4 . Interview outline.
Results of the Interview
The interview time ended within 15min on average, and sometimes, the order and direction of questions were adjusted according to the interviewee’s responses. During the interview process, questions outside the interview outline were also asked to get more in-depth details. The interviews were recorded using audio recording. Before recording, relevant explanations on research ethics and privacy were be provided to inquire about the interviewee’s willingness to record.
After the interview, the interview records were sorted into verbatim drafts based on the recording content, and after the interview records were converted into verbatim manuscripts, the words were segmented for each verbatim manuscript. The meaningless auxiliary words were removed, and the units with clear semantic meaning and readability were retained. After that, the meaningful units were coded. There were six codes in total; for example (consult the teaching assistant, or check it online to see if you have found a solution), the code from left to right is the interviewee’s number, interview question number, and verbatim serial number.
Interviewees codes 01 and 02 are for Marketing Management; 03 and 04 for Knowledge Creation and RandD Management; 05 and 06 for Entrepreneurial Management; 07 and 08 for Fundraising Platforms; 09 and 10 for Introduction to Computer and Internet Security; and 11 and 12 for the Reading Industry and Cultural Communication. When the interviewee’s number is an odd number, it means that the respondent was sampled from the high subgroup (top 25%); when a respondent number is an even number, it means that the respondent was sampled from the low subgroup (bottom 25%).
The two codes of the interview questions were based on the interviewee’s response to the question number of the interview at that moment and are noted with 01~07. The two codes at the end of the number are the serial numbers of a single independent verbatim manuscript that were marked as meaningful sentence units.
Finally, after sorting out all the coded sentences in each verbatim manuscript, the study performed thematic classification to obtain the classification result. Six topics about collaborative learning, including team formation, discussion atmosphere, discussion efficiency, decision-making mode, cooperation mode, and cross-domain learning, were obtained. The following section will discuss in detail each topic.
Formation of the Team
When the curriculum design is carried out in a flipped way, if there is not enough planning before the course for students to understand each other’s expertise and motivation to execute the project, the team composition tends to be random and members tend to find people who they already know to work with. This leads to the cohesion of team members to assume certain risks when the team executes the project, which indirectly affects the degree of classroom engagement; for example, “We started with a very fragmented consensus, because we all have different levels of expectations or understanding of this team.”
However, before the course starts officially, it is necessary to arrange some courses that can help students understand each other’s expertise and motivation. This will reduce unnecessary risks and help students find the right group before the course and is a better way to build team consensus when motivation is the same. Especially, when the project of the course involves interdisciplinary learning, it is also beneficial for students to combine their respective expertise for collaborative learning. For example, “there are some occupations in the publishing industry, such as editor-in-chief, editor-in-charge, and editor-in-art. Then, because the teacher has made this part of the assignment, the team members have a clear sense of their responsibilities and position. I think this is very helpful for grouping.”
It is worth noting that the consensus within the team will change with the development of the team, and the team goals may be more focused due to the organizational changes in the team. “After we started to do something, I think things were more on track.” When members were more willing to participate in the learning task of the course, members would also be more likely to focus on the overall goal of the team.
Discussion Atmosphere
The discussion process of collaborative learning may also lead to conflicts, which will affect the degree of engagement of the members. When there is a conflict in the discussion process, the group with a higher willingness to invest tends to face it actively and is more willing to take the initiative to put forward its own opinions and communicate with the members of the group: “We were livelier when we had meetings. We had a lot of trash-talking, so everyone … everyone felt that there is no sense of distance. Thus, we just kept throwing out ideas like this.” The group with a lower level of involvement was more inclined to avoid expressing their true ideas: “The discussions in our group are not particularly enthusiastic. It is more like ‘business is business’, that is, finish what you are responsible for and then hand over the results. Then nobody will raise too many objections; however, I do not think this is a good thing.”
One thing that can be noticed from here is that when team members encounter conflicts during a discussion, that does not deteriorate team relationships. When team members are more willing to communicate, moderate conflicts are often a boost for the team to generate innovative ideas.
Discussion Efficiency
Discussions between groups can be divided into three: (1) online plus in-person discussion, (2) online discussion, and (3) in-person discussion. From the feedback of the interviewees, it can be found that the efficiency of the group that only has online discussions is low. Online discussions often rely on social software, such as Line to communicate in asynchronous text. This mode of discussion may be inefficient because of the time gap in information: “It may be that everyone discusses a question, but the time taken by each person to answer it is different, and sometimes, it could be a long time. That is, the group must wait for everyone to give feedback and may have to wait for a long time.” In addition, this type of discussion often leads to team members only focusing on completing their assigned learning tasks and not communicating ideas.
Compared with the purely online text discussion, the physical discussion can encourage students to exchange more ideas, but there are also problems of inefficiency, and the underlying cause is often too many ideas among members. Opinions cause the discussion topics to lose focus, which is different from online discussions because of delays in the transmission of information; for example, “I think our group is mostly discussing… There are real discussions, where everyone would throw ideas, but we tend to have no conclusion.”
The online plus physical discussion approach has the characteristic of balancing the lack of the above two approaches. Face-to-face discussions ensure that participants exchange ideas, while implementation details can be tracked through an online communication software. It must be noted that compared to the form of pure online communication, this method focuses on communication software to track implementation details, rather than communicating ideas: “You can complete your large framework in the classroom, and the rest are the details. We have created a similar group for the details. If you have a problem or if you have any ideas, you can just type them and drop them in the group first.”
Decision-Making Mode
When team members face making important decisions, they can do so in two ways: (1) by reaching a consensus within the team members or (2) by seeking external resources. Consensus reached by group members can be further divided into two types: group members with clear roles and decentralization. Based on the results of this research interview, the group to which the sampled interviewees belonged generally tended to make important decisions in a decentralized manner. Compared to the group with a clear leader making decisions, it seems impossible to clearly point out the advantages and disadvantages, but from the results of this study, it is found that the decision-making model of group members without clear roles allowed each group member’s opinions to be fully heard and ensured that each member could participate in collaborative learning and jointly take the risk of decision-making; for example, “We will first listen to everyone’s opinions, and then, if there are different opinions, we will, for example, have different people come up with different solutions, after which we will analyse each solution individually and discuss the current situation, see the advantages and disadvantages of each plan, and, finally, see what solution will be most suitable for us.”
When there is no consensus within the group or when team members’ knowledge is not yet sufficient to make decisions, students will seek external resources such as classroom teachers. In the context of flipped teaching, when students’ abilities are not enough to cope with the problem, the teacher’s timely initiative to provide assistance is a link that must be paid attention to in flipped teaching design, which helps students to have a clearer direction when analyzing problems; for example, “When our team members just could not make a decision, we would ask the opinions of others, such as the teaching assistants or teachers, and then reach a unified opinion.”
Cooperation Mode
The results of this part of the text analysis are directly related to the formation of the first part of the team. In the initial stage of team formation, if students fully understand the specific expertise of the project that needs to be implemented in the course tasks, they will look for team members with relevant expertise when forming the team. The division of roles will also be more efficient in collaborative learning; for example, “Those who have a professional background are really good at certain aspects of tasks, that is, when they are good in the field, they will be relatively helpful, and they can do better than someone who spent the same amount of time.”
In contrast, if the division of labor cannot rely on the distribution of expertise among students, it will lead to a decline in efficiency: “Sometimes, I feel the function was allocated a little bit. The function was not evenly distributed, and then it did not show us what the team should be doing clearly.”
Interdisciplinary Learning
We can find from the results of text analysis that when the learning task of collaborative learning needs to be executed across domains, it is helpful to make use of the students’ own expertise, thereby enhancing students’ creativity, empathy, and even promoting mutual learning.
This result is directly related to the cooperation model in point (5). When the project is based on the division of expertise among group members so that the students’ own expertise or professional knowledge can be used, it will help improve the level of collaborative learning: “In fact, he might have learned this expertise in the club or in a school department, but because of this course and that we got together, we all have something to offer to the group. I think this is very important.”
In this learning process, students with different backgrounds of expertise can learn from each other and even improve their ability to innovate: “If we have different backgrounds, we may have different ideas. We may see different levels and different aspects. After discussion or communication, I may be able to understand why the other people would think a certain way, I can understand more things, or why I have never thought about it from his perspective. I need these things instead.”
Of course, in the process of communication, students will also improve their empathy and the ability to step into someone’s shoes, because they see the differences between group members: “If you work with people with varied information backgrounds, the points of concern will be different.”
It is worth noting that the above-mentioned positive responses can be observed regardless of the student’s learning effectiveness.
Research Findings
From the survey-based regression model, it is found that the cognitive needs of students and the degree of collaborative learning are directly related to the learning satisfaction of flipped teaching. This is in line with the focus of this study: Can specific personality traits be used to predict individual differences in students’ responses to flipped teaching? The results of this study prove that students with high cognitive needs have a relatively high degree of investment in the learning context of flipped teaching. The explanation for this phenomenon is the fact that flipped teaching in curriculum design requires students to show higher-order learning skills, such as analysis, judgment, and creativity in Bloom Taxonomy. Cognitive needs are directly related to these abilities. The research results of Nair and Ramnarayan (2000) prove that people with higher cognitive needs are more likely to succeed in solving problems. While Day et al. (2007) explored the association between cognitive needs and learning complex skills, they also confirmed that groups with high cognitive needs are helpful for learning complex skills.
In addition, the peer learning elements that flipped teaching emphasizes ( Abeysekera and Dawson, 2015 ) are described as follows. The level of student engagement in the degree of collaborative learning also has a significant impact on the learning satisfaction of flipped teaching. In the regression model, it can be found that the β value of 0.536 for the level of collaborative learning is much higher than the 0.289 for cognitive needs. A phenomenon can be found here that the key factor affecting students’ investment in flipped teaching is that the needs of groups are greater than those of individuals. In fact, this result is not difficult to understand. When flipped teaching requires a large number of team-based methods, the interaction between the subjects and their peers in the classroom will naturally affect the degree of students’ involvement in the classroom. A study on the impact of teamwork on individual engagement and performance in the workplace environment also puts forward a similar viewpoint ( Stashevsky and Levy, 2014 ), which argued that the quality of teamwork is what affects an individual’s willingness to engage in work.
In the relationship between cognitive needs and learning self-efficacy, the β value is 0.598 and has a significant impact, which proves that students with high cognitive needs will also have a higher level of learning self-efficacy, in other words, higher self-confidence, which is in line with our common sense judgment: When faced with a problem that requires time to think, students who like to think often have more confidence in solving the problem than students who are unwilling to think.
It should be noted that the results obtained in this study are mainly focused on learning satisfaction rather than learning effectiveness; thus, the impact of flipped teaching on learning effectiveness is not included in the discussion.
Thus, the qualitative study based on deep interview is worth to demonstrate the collaborative learning process of students participating the flipped learning. The results showed six important issues in facilitating the collaborative learning: team formation, discussion atmosphere, discussion efficiency, decision-making mode, cooperation mode, and cross-domain learning. (1) Team formation is the first important step of collaborative learning. The ice breaking activities helping students understand each other are an important mechanism before the course formally begin. (2) The building of discussion atmosphere is the second step facilitating collaborative learning, especially when there is a conflict in the discussion process. When team members are more willing to communicate, moderate conflicts are often a boost for the team to generate innovative ideas. (3) The discussion efficiency can be enhanced by using in-person discussion, and online discussion is discouraged for effective group discussion. (4) Team members showed two ways to achieve consensus—centralized and decentralized decision-making mode. (5) As team members have different background, the division of roles will be more efficient in collaborative learning. (6) If the team members corporate with each other by respecting the expertise, the team work efficiency can be improved.
Prior studies on flipped learning mainly focused on language teaching ( Lee and Wallace, 2018 ; Andujar et al., 2020 ). This study is one of the limited studies that addressed the flipped learning in a variety of different courses, covering a wider range of domain and student background. Further, Tomas et al. (2019 ) explore how a flipped classroom supported students’ engagement and learning. The survey results suggested that the mechanism to enhance learning should be designed according to students’ learning needs and their readiness for a flipped learning approach. The results correspond to current study that the collaborative learning, atmosphere, and learners’ personality are important facilitators for learning outcome in flipped classroom.
To summarize, this study examined the predicting factors of learning satisfaction in flipped learning by using questionnaire survey, and the result suggested that collaborative learning if one of the most important predictors of learning outcome. Thus, a follow-up deep interview was further conducted to explore the collaborative learning process in flipped learning and six different important factors in collaborative learning were explored.
Research Contribution
The results of this study prove that the level of collaborative learning is important to the engagement of students in the classroom. When implementing flipped teaching, apart from paying attention to students’ individual differences, it is also necessary to think about how to build a better team learning environment. This provides a direction of thought for educators who want to promote flipped teaching in the future.
In addition, according to the results of interview, when the course is carried out in groups, the teacher can arrange engagement motivation that can promote students’ understanding of each other’s expertise and course tasks. This enables students to find suitable groups before the course to facilitate the subsequent integration of their respective expertise. It also helps students build consensus within the team, and it is easier to build consensus within the team as the course is in progress. It can prevent students who do not know each other at all during the course from forming a group of students who may be inconsistent with their own goals for the course tasks. Besides, when the group members are faced with conflicts of views, if they can maintain good communication, it will help improve the students’ participation in the classroom; on the contrary, in the face of conflict, if there is no timely communication and mutual discussion among team members, the degree of students’ engagement in the classroom will be affected to a certain extent. When the students in the team do not have enough professional knowledge to reach a consensus in the face of conflict decision-making, it is very important to provide appropriate resource assistance in the classroom, such as teachers and teaching assistants. When the group is composed of members with diverse backgrounds, it will help enhance creativity and empathy and also enable students to contribute their knowledge and learn from each other in the process.
Research Limitations and Future Research Directions
The first research limitation of this study is the small sample size caused by inviting only the participants from one of the six courses that meet the criteria of flipped teaching and get the permission of the instructors. Although the sample size is small, both qualitative and quantitative studies were conducted to answer the research questions deeply and broadly. Further, the courses considered in this study are restricted mainly in college of management and thus can limit the domains to be applied based on the current findings. As courses given in different domains (i.e., management, medical, science, and liberal) may have very different characteristics, the flipped teaching methods will also be different. Thus, the future studies can be suggested to include more courses in different domains in order to compare the facilitating factors of flipped learning satisfaction and outcome.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author Contributions
FF-C: study conception and design. P-CS: data collection. P-CS and C-SW: analysis and interpretation of results. FF-C and C-SW: draft manuscript preparation. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan for financially supporting this research under Contract No. MOST-110-2410-H-029-023.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abeysekera, L., and Dawson, P. (2015). Motivation and cognitive load in the flipped classroom: definition, rationale and a call for research. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 34, 1–14. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2014.934336
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Aitken, N. D. (1982). College student performance, satisfaction and retention: specification and estimation of a structural model. J. High. Educ. 53, 32–50. doi: 10.1080/00221546.1982.11780423
Amiryousefi, M. (2019). The incorporation of flipped learning into conventional classes to enhance efl learners’ l2 speaking, l2 listening, and engagement. Innov. Lang. Learn. Teach. 13, 147–161. doi: 10.1080/17501229.2017.1394307
Andujar, A., Salaberri-Ramiro, M. S., and Martínez, M. S. C. (2020). Integrating flipped foreign language learning through mobile devices: technology acceptance and flipped learning experience. Sustainability 12:1110. doi: 10.3390/su12031110
Ashton, P. T., and Webb, R. B. (1986). Making a Difference: Teachers' Sense of Efficacy and Student Achievement. United Kingdom: Longman Publishing Group.
Google Scholar
Bandura, A. (1995). “Exercise of personal and collective efficacy in changing societies,” in Self-efficacy in changing societies. ed. A. Bandura. (Cambridge University Press), 1–45.
Bandura, A. (2010). “Self-efficacy”, The Corsini encyclopedia of psychology : June 1, 2010, 1–3. doi: 10.1002/9780470479216.corpsy0836
Barling, J., and Abel, M. (1983). Self-efficacy beliefs and tennis performance. Cogn. Ther. Res. 7, 265–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01205140
Bartimote-Aufflick, K., Bridgeman, A., Walker, R., Sharma, M., and Smith, L. (2016). The study, evaluation, and improvement of university student self-efficacy. Stud. High. Educ. 41, 1918–1942. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2014.999319
Bergmann, J., and Sams, A. (2012). Flip your Classroom: Reach every Student in every Class every Day. United States: International society for technology in education.
Bligh, D. A. (1998). What's the Use of Lectures? United Kingdom: Intellect books.
Bruffee, K. A. (1982). Liberal education and the social justification of belief. Lib. Educ. 68, 95–114.
Cacioppo, J. T., and Petty, R. E. (1982). The need for cognition. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 42:116. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.42.1.116
Cacioppo, J. T., Petty, R. E., Feinstein, J. A., and Jarvis, W. B. G. (1996). Dispositional differences in cognitive motivation: The life and times of individuals varying in need for cognition. Psychol. Bull. 119:197. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.119.2.197
Chang, I.-Y., and Chang, W.-Y. (2012). The effect of student learning motivation on learning satisfaction. Int. J. Org. Innov. (Online) 4:281
Chang, S.-C., and Hwang, G.-J. (2018). Impacts of an augmented reality-based flipped learning guiding approach on students’ scientific project performance and perceptions. Comp. Edu. 125, 226–239. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2018.06.007
Cohen, A. R., Stotland, E., and Wolfe, D. M. (1955). An experimental investigation of need for cognition. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 51:291. doi: 10.1037/h0042761
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Corts, D. P., Lounsbury, J. W., Saudargas, R. A., and Tatum, H. E. (2000). Assessing undergraduate satisfaction with an academic department: A method and case study. Coll. Stud. J. 34, 399–399.
Curtis, D. D., and Lawson, M. J. (2001). Exploring collaborative online learning. JALN 5, 21–34. doi: 10.24059/olj.v5i1.1885
Day, E. A., Espejo, J., Kowollik, V., Boatman, P. R., and Mcentire, L. E. (2007). Modeling the links between need for cognition and the acquisition of a complex skill. Personal. Individ. Differ. 42, 201–212. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.06.012
Dole, J. A., and Sinatra, G. M. (1998). Reconceptalizing change in the cognitive construction of knowledge. Educ. Psychol. 33, 109–128. doi: 10.1080/00461520.1998.9653294
Driver, M. (2002). Exploring student perceptions of group interaction and class satisfaction in the web-enhanced classroom. Internet High. Educ. 5, 35–45. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7516(01)00076-8
Elias, S. M., and Loomis, R. J. (2002). Utilizing need for cognition and perceived self-efficacy to predict academic performance 1. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 32, 1687–1702. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2002.tb02770.x
Ferreri, S. P., and O’connor, S. K. (2013). Redesign of a large lecture course into a small-group learning course. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 77:13. doi: 10.5688/ajpe77113
Garcia, M. E., Schmitz, J. M., and Doerfler, L. A. (1990). A fine-grained analysis of the role of self-efficacy in self-initiated attempts to quit smoking. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 58:317. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.58.3.317
Gokhale, A. A. (1995). Collaborative learning enhances critical thinking. J. Educ. 7, 22–30. doi: 10.21061/jte.v7i1.a.2
Haugtvedt, C. P., Petty, R. E., and Cacioppo, J. T. (1992). Need for cognition and advertising: understanding the role of personality variables in consumer behavior. J. Consum. Psychol. 1, 239–260. doi: 10.1016/S1057-7408(08)80038-1
Hertz-Lazarowitz, R., Kagan, S., Sharan, S., Slavin, R., and Webb, C. (2013). Learning to Cooperate, Cooperating to Learn. Germany: Springer Science and Business Media.
Honeycutt, B., and Garrett, J. (2014). Expanding the Definition of a Flipped Learning environment. Available at: https://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/blended-flipped-learning/expanding-definition-flipped-learning-environment/ (Accessed May 3, 2021).
Javier, F. J. H. L. F., Belmonte, J. L., Cabrera, A. F., Torres, J. M. T., and Sanchez, S. P. (2020). Academic effects of the use of flipped learning in physical education. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:276. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010276
Kitchen, D., and Mcdougall, D. (1999). Collaborative learning on the internet. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 27, 245–258. doi: 10.2190/5H41-K8VU-NRFJ-PDYK
Ko, W.-H., and Chung, F.-M. (2014). Teaching quality, learning satisfaction, and academic performance among hospitality students in Taiwan. World J. Edu. 4, 11–20. doi: 10.5430/wje.v4n5p11
Lee, Y.-J. (2011). A study on the effect of teaching innovation on learning effectiveness with learning satisfaction as a mediator. World Trans. Eng. Tech. Edu. 9, 92–101.
Lee, G., and Wallace, A. (2018). Flipped learning in the english as a foreign language classroom: outcomes and perceptions. TESOL Q. 52, 62–84. doi: 10.1002/tesq.372
Lent, R. W., and Hackett, G. (1987). Career self-efficacy: empirical status and future directions. J. Vocat. Behav. 30, 347–382. doi: 10.1016/0001-8791(87)90010-8
Lin, C.-L., Lee, S.-H., and Horng, D.-J. (2011). The effects of online reviews on purchasing intention: The moderating role of need for cognition. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 39, 71–81. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2011.39.1.71
Martin, C. L. (1988). Enhancing children's satisfaction and participation using a predictive regression model of bowling performance norms. Phys. Educ. 45:196
Mason, G. S., Shuman, T. R., and Cook, K. E. (2013). Comparing the effectiveness of an inverted classroom to a traditional classroom in an upper-division engineering course. IEEE Trans. Educ. 56, 430–435. doi: 10.1109/TE.2013.2249066
Nair, K. U., and Ramnarayan, S. (2000). Individual differences in need for cognition and complex problem solving. J. Res. Pers. 34, 305–328. doi: 10.1006/jrpe.1999.2274
Ocker, R. J. (2001). Collaborative learning environments: exploring student attitudes and satisfaction in face-to-face and asynchronous computer conferencing settings. J. Interact. Learn. Res. 12, 427–448.
O'flaherty, J., and Phillips, C. (2015). The use of flipped classrooms in higher education: A scoping review. Internet High. Educ. 25, 85–95. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.02.002
Olson, K., Camp, C., and Fuller, D. (1984). Curiosity and need for cognition. Psychol. Rep. 54, 71–74. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1984.54.1.71
Pajares, F. (1997). Current directions in self-efficacy research. Adv. Motiv. Achiev. 10, 1–49.
Petty, R. E., Cacioppo, J. T., and Goldman, R. (1981). Personal involvement as a determinant of argument-based persuasion. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 41:847. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.41.5.847
Pierce, R., and Fox, J. (2012). Vodcasts and active-learning exercises in a “flipped classroom” model of a renal pharmacotherapy module. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 76:196. doi: 10.5688/ajpe7610196
Sadowski, C. J., and Gülgös, S. (1996). Elaborative processing mediates the relationship between need for cognition and academic performance. J. Psychol. 130, 303–307. doi: 10.1080/00223980.1996.9915011
Sáiz Manzanares, M. C., Marticorena Sánchez, R., García Osorio, C. I., and Díez-Pastor, J. F. (2017). How do b-learning and learning patterns influence learning outcomes? Front. Psychol. 8:745. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00745
Schreurs, J., and Dumbraveanu, R. (2014). A shift from teacher centered to learner centered approach. Int. J. Eng. Pedagogy 4, 36–41. doi: 10.3991/ijep.v4i3.3395
So, H.-J., and Brush, T. A. (2008). Student perceptions of collaborative learning, social presence and satisfaction in a blended learning environment: relationships and critical factors. Comp. Edu. 51, 318–336. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2007.05.009
Starr, A. M. (1971). College student satisfaction questionnaire (cssq) manual.
Stashevsky, S., and Levy, S. (2014). “The effects of teamwork quality on team objective and subjective outcomes,” in Values in Shock: The role of contrasting management, economic, and religious paradigms in the workplace. eds. J. F. S. Gomes and J. P. Coelho. Shreveport, LA, USA. 44–51.
Strayer, J. F. (2012). How learning in an inverted classroom influences cooperation, innovation and task orientation. Learn. Environ. Res. 15, 171–193. doi: 10.1007/s10984-012-9108-4
Strobel, A., Behnke, A., Gärtner, A., and Strobel, A. (2019). The interplay of intelligence and need for cognition in predicting school grades: A retrospective study. Personal. Individ. Differ. 144, 147–152. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.02.041
Teven, J. J., and Mccroskey, J. C. (1997). The relationship of perceived teacher caring with student learning and teacher evaluation. Commun. Educ. 46, 1–9. doi: 10.1080/03634529709379069
Tomas, L., Evans, N., Doyle, T., and Skamp, K. (2019). Are first year students ready for a flipped classroom? A case for a flipped learning continuum. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 16:5. doi: 10.1186/s41239-019-0135-4
Tucker, B. (2012). The flipped classroom. Educ. Next 12, 82–83. doi: 10.4236/oalib.1107398
Tuckman, B. W., and Jensen, M. A. C. (1977). Stages of small-group development revisited. Group Org. Studies 2, 419–427. doi: 10.1177/105960117700200404
Verdejo, M. F. (1996). “Interaction and collaboration in distance learning through computer mediated technologies,” in Advanced Educational Technology: Research Issues and Future Potential. ed. T. T. Liao (New York: Springer), 77–88.
Yeung, K. (2014). Making ‘the flip’work: barriers to and implementation strategies for introducing flipped teaching methods into traditional higher education courses. New Direct. Teaching of Phy. Sci. 10, 59–63. doi: 10.29311/ndtps.v0i10.518
Yin, B., and Yuan, C.-H. (2021). Precision teaching and learning performance in a blended learning environment. Front. Psychol. 12:631125. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.631125
Yokoyama, M., and Miwa, K. (2021). A class practice study of intervention effect of interactive assessment on learning goal orientation. Front. Psychol. 12:3473. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.599480
Keywords: flipped education, need for cognition, learning self-efficacy, collaborative learning, learning satisfaction
Citation: Cheng F-F, Wu C-S and Su P-C (2021) The Impact of Collaborative Learning and Personality on Satisfaction in Innovative Teaching Context. Front. Psychol . 12:713497. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.713497
Received: 23 May 2021; Accepted: 23 August 2021; Published: 29 September 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Cheng, Wu and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chin-Shan Wu, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Study Skills
- Critical Thinking
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Top Tips for Study
- Staying Motivated When Studying
- Student Budgeting and Economic Skills
- Getting Organised for Study
- Finding Time to Study
- Sources of Information
- Assessing Internet Information
- Using Apps to Support Study
- What is Theory?
- Styles of Writing
- Effective Reading
- Critical Reading
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Planning an Essay
- How to Write an Essay
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Report
- Academic Referencing
- Assignment Finishing Touches
- Reflecting on Marked Work
- 6 Skills You Learn in School That You Use in Real Life
- Top 10 Tips on How to Study While Working
- Exam Skills
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally, understanding the logical connection between ideas. Critical thinking has been the subject of much debate and thought since the time of early Greek philosophers such as Plato and Socrates and has continued to be a subject of discussion into the modern age, for example the ability to recognise fake news .
Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking.
In essence, critical thinking requires you to use your ability to reason. It is about being an active learner rather than a passive recipient of information.
Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyse and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct.
Someone with critical thinking skills can:
Understand the links between ideas.
Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas.
Recognise, build and appraise arguments.
Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Critical thinking is thinking about things in certain ways so as to arrive at the best possible solution in the circumstances that the thinker is aware of. In more everyday language, it is a way of thinking about whatever is presently occupying your mind so that you come to the best possible conclusion.
Critical Thinking is:
A way of thinking about particular things at a particular time; it is not the accumulation of facts and knowledge or something that you can learn once and then use in that form forever, such as the nine times table you learn and use in school.
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking
The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making.
Specifically we need to be able to:
Think about a topic or issue in an objective and critical way.
Identify the different arguments there are in relation to a particular issue.
Evaluate a point of view to determine how strong or valid it is.
Recognise any weaknesses or negative points that there are in the evidence or argument.
Notice what implications there might be behind a statement or argument.
Provide structured reasoning and support for an argument that we wish to make.
The Critical Thinking Process
You should be aware that none of us think critically all the time.
Sometimes we think in almost any way but critically, for example when our self-control is affected by anger, grief or joy or when we are feeling just plain ‘bloody minded’.
On the other hand, the good news is that, since our critical thinking ability varies according to our current mindset, most of the time we can learn to improve our critical thinking ability by developing certain routine activities and applying them to all problems that present themselves.
Once you understand the theory of critical thinking, improving your critical thinking skills takes persistence and practice.
Try this simple exercise to help you to start thinking critically.
Think of something that someone has recently told you. Then ask yourself the following questions:
Who said it?
Someone you know? Someone in a position of authority or power? Does it matter who told you this?
What did they say?
Did they give facts or opinions? Did they provide all the facts? Did they leave anything out?
Where did they say it?
Was it in public or in private? Did other people have a chance to respond an provide an alternative account?
When did they say it?
Was it before, during or after an important event? Is timing important?
Why did they say it?
Did they explain the reasoning behind their opinion? Were they trying to make someone look good or bad?
How did they say it?
Were they happy or sad, angry or indifferent? Did they write it or say it? Could you understand what was said?
What are you Aiming to Achieve?
One of the most important aspects of critical thinking is to decide what you are aiming to achieve and then make a decision based on a range of possibilities.
Once you have clarified that aim for yourself you should use it as the starting point in all future situations requiring thought and, possibly, further decision making. Where needed, make your workmates, family or those around you aware of your intention to pursue this goal. You must then discipline yourself to keep on track until changing circumstances mean you have to revisit the start of the decision making process.
However, there are things that get in the way of simple decision making. We all carry with us a range of likes and dislikes, learnt behaviours and personal preferences developed throughout our lives; they are the hallmarks of being human. A major contribution to ensuring we think critically is to be aware of these personal characteristics, preferences and biases and make allowance for them when considering possible next steps, whether they are at the pre-action consideration stage or as part of a rethink caused by unexpected or unforeseen impediments to continued progress.
The more clearly we are aware of ourselves, our strengths and weaknesses, the more likely our critical thinking will be productive.
The Benefit of Foresight
Perhaps the most important element of thinking critically is foresight.
Almost all decisions we make and implement don’t prove disastrous if we find reasons to abandon them. However, our decision making will be infinitely better and more likely to lead to success if, when we reach a tentative conclusion, we pause and consider the impact on the people and activities around us.
The elements needing consideration are generally numerous and varied. In many cases, consideration of one element from a different perspective will reveal potential dangers in pursuing our decision.
For instance, moving a business activity to a new location may improve potential output considerably but it may also lead to the loss of skilled workers if the distance moved is too great. Which of these is the more important consideration? Is there some way of lessening the conflict?
These are the sort of problems that may arise from incomplete critical thinking, a demonstration perhaps of the critical importance of good critical thinking.
Further Reading from Skills You Need

The Skills You Need Guide for Students

Develop the skills you need to make the most of your time as a student.
Our eBooks are ideal for students at all stages of education, school, college and university. They are full of easy-to-follow practical information that will help you to learn more effectively and get better grades.
In Summary:
Critical thinking is aimed at achieving the best possible outcomes in any situation. In order to achieve this it must involve gathering and evaluating information from as many different sources possible.
Critical thinking requires a clear, often uncomfortable, assessment of your personal strengths, weaknesses and preferences and their possible impact on decisions you may make.
Critical thinking requires the development and use of foresight as far as this is possible. As Doris Day sang, “the future’s not ours to see”.
Implementing the decisions made arising from critical thinking must take into account an assessment of possible outcomes and ways of avoiding potentially negative outcomes, or at least lessening their impact.
- Critical thinking involves reviewing the results of the application of decisions made and implementing change where possible.
It might be thought that we are overextending our demands on critical thinking in expecting that it can help to construct focused meaning rather than examining the information given and the knowledge we have acquired to see if we can, if necessary, construct a meaning that will be acceptable and useful.
After all, almost no information we have available to us, either externally or internally, carries any guarantee of its life or appropriateness. Neat step-by-step instructions may provide some sort of trellis on which our basic understanding of critical thinking can blossom but it doesn’t and cannot provide any assurance of certainty, utility or longevity.
Continue to: Critical Thinking and Fake News Critical Reading
See also: Analytical Skills Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories Introduction to Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)
Explore the Impact of the Aging Workforce in our latest Skills Trends Report. Learn more

What is workplace skills plan and why is it important?
When Kodak filed for bankruptcy in 2012, it wasn’t just because they failed to adapt to digital photography. It was because they failed to adapt their workforce .
Despite inventing the first digital camera, Kodak couldn’t shift its employees’ skills from film to digital fast enough. The result? A once-dominant company became a cautionary tale.
This story underscores a critical truth for today’s businesses: your workforce’s skills can make or break your company.
And that is where the workplace skills plan comes into play: To help companies have a strategic roadmap for ensuring your workforce can meet tomorrow’s challenges.
In this article, we’ll dive into what workplace skills plans are, why you need one, and how to create an effective plan that keeps your organization ahead of the curve.
Note : Ready to transform into a skills-based organization? Fuel50’s talent marketplace can help you map your skills landscape, develop targeted learning paths, and create a more agile, future-ready workforce. Request a demo today .
What is a workplace skills plan?
A workplace skills plan (WSP) is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s approach to developing and maintaining the skills of its workforce. It serves as a roadmap for identifying, addressing, and closing skills gaps within the company to ensure that employees have the necessary competencies to perform their roles effectively and contribute to the organization’s overall objectives.
At its core, a WSP is a comprehensive analysis of the current skills landscape within an organization, paired with a forward-looking strategy to enhance those skills. It typically covers a specific period, often annually, and is designed to align with the company’s broader business goals and objectives.
The purpose of a WSP is multifaceted. It aims to:
Enhance employee performance and productivity
Improve organizational efficiency and competitiveness
Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations
Support career development and employee retention
Facilitate succession planning within the organization
In certain countries like South Africa, there are even regulations about workplace skills planning. They, for instance, have a Skills Development Act that mandates that organizations with 50 or more employees establish a training committee for effective skills planning. This act emphasizes the importance of broad stakeholder consultation and adequate resources for implementing skills development and training strategies.
Key stakeholders involved in developing and implementing a workplace skill plan typically include:
Human Resources department
Senior management
Department heads or team leaders
Employees at various levels
Training and development specialists
Skills development facilitator (SDF)
External consultants or training providers (when applicable)
The skills development facilitator (SDF) plays a crucial role in managing training needs, compiling the WSP, and ensuring compliance with skills development regulations.
By creating a structured approach to skills development, a workplace skills plan helps organizations stay agile, competitive, and prepared for future challenges in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Workforce skills vs. workplace skills
While often used interchangeably, workforce skills and workplace skills have distinct meanings and implications for organizations.
What’s the difference between workforce skills and workplace skills?
Workforce skills refer to the broad set of competencies that individuals possess or need to succeed in the job market across various industries and roles. These are often transferable skills that remain valuable regardless of the specific workplace or position.
Key characteristics of workforce skills:
- Broadly applicable across industries
- Often transferable between different roles
- Reflect overall employability
- Tend to evolve with broader economic and technological trends
Examples of workforce skills:
Communication
Problem-solving
Adaptability
Digital literacy
Leadership
Critical thinking
Time management
On the other hand, workplace skills are the specific abilities and knowledge required to perform effectively in a particular job role or within a specific organizational context. These skills are often more technical or job-specific in nature.
Key characteristics of workplace skills:
- Specific to a particular job or industry
- Often require specialized training or education
- May be unique to a particular organization or work environment
- Can change rapidly with technological advancements or industry shifts
Examples of workplace skills:
Proficiency in specific software or tools
Knowledge of company-specific processes
Familiarity with industry regulations
Technical skills related to specific machinery or equipment
Understanding of organizational protocols and procedures
Relationship to workplace skills plan:
When developing a workplace skills plan, it’s essential to consider both workforce and workplace skills:
- Workforce skills form the foundation of an employee’s overall capability and adaptability. They should be nurtured to ensure long-term employability and organizational flexibility.
- Workplace skills are crucial for immediate job performance and organizational efficiency. They often form the core of role-specific training and development initiatives.
- A comprehensive workplace skills plan should aim to balance the development of both types of skills, ensuring employees are both proficient in their current roles and prepared for future career growth.
- The plan should account for the evolving nature of both skill sets, particularly as industries undergo digital transformation and other significant changes.
- Assessment of workforce skills can help identify potential for internal mobility and career development, while evaluation of workplace skills can pinpoint immediate training needs.
Why does your organization need a workplace skills plan?
The primary driver behind the need for a workplace skills plan is the ever-widening skills gap. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2020 , a staggering 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025 due to the adoption of new technologies.
This statistic underscores the urgency for organizations to take proactive measures in developing their workforce.
Take AT&T, for example. Recognizing the seismic shifts in the telecommunications industry, the company launched its massive reskilling program, Future Ready, in 2013 . With an investment of $1 billion, AT&T has since retrained more than 100,000 employees.

The results speak volumes: 40% of the company’s technology management jobs were filled by internal candidates, showcasing how a robust skills plan can not only bridge skills gaps but also significantly reduce hiring and onboarding costs.
Skills development interventions play a crucial role in addressing identified skills gaps by providing targeted training and development strategies.
Here are more reasons why your organization needs a workplace skills plan.
Keeping good people around
Let’s imagine you’ve just spent months training a star employee, Sarah, on a new software system. She’s become the go-to person for troubleshooting. Then, out of the blue, she hands in her resignation. Why? “I don’t see a future for myself here,” she says.
This scenario plays out in companies every day. It’s frustrating, costly, and completely avoidable with a solid workplace skills plan.
A skills plan doesn’t just train people for their current job. It maps out potential career paths within the company and provides the training to get there. For Sarah, this might mean seeing a clear path from her current IT support role to a future as a project manager or systems architect.
This approach works. LinkedIn found that 94% of employees would stay longer at a company that invests in their career development. But it’s not just about retention numbers – it’s about building a culture of growth.
Amazon’s “Upskilling 2025” program shows how this can work on a large scale. They’re investing $700 million to retrain 100,000 U.S. employees by 2025. The program isn’t just about teaching new tech skills; it’s designed to show employees a future within the company.
For example, Amazon’s “Machine Learning University” isn’t just for current data scientists. It’s open to any employee with a tech background who wants to move into this high-demand field. A warehouse worker with a knack for coding could see a path to becoming a machine learning specialist without leaving the company.
This approach solves multiple problems at once. Employees like Sarah see a future with the company and stay engaged. Amazon fills critical roles internally, saving on recruitment costs. And the company builds a reputation as a great place to grow, attracting even more talent.
A workplace skills plan turns “dead-end” jobs into launching pads for exciting careers. It transforms the “I don’t see a future here” conversation into “I can’t wait to see where I’ll be in five years.”
Growing future leaders
Now imagine this.
Your company’s star VP of Marketing, John, just announced he’s retiring next year. He’s been with the company for 20 years and knows the ins and outs of your industry like no one else. The board is in a panic. Who could possibly fill his shoes?
This is where a workplace skills plan proves its worth. Instead of scrambling to headhunt an expensive external hire, you could have a pool of internal candidates ready to step up.
A good skills plan doesn’t just focus on immediate needs. It looks ahead, identifying potential leaders and giving them the skills they’ll need years before they take the reins. It’s like planting seeds for trees you’ll need shade from in the future.
For John’s replacement, this might mean identifying promising marketing managers years ago. Your skills plan would have ensured they received training not just in marketing, but in leadership, strategy, and the broader business landscape.
General Electric (GE) has mastered this approach. Their leadership development program is so effective that “GE leadership tree” has become a term in the business world. Other companies often poach GE executives because they know these leaders come with a rich, diverse skill set.
Here’s how GE does it: They rotate promising employees through different roles and departments. A finance whiz might spend time in operations, then marketing, then international assignments. Along the way, they’re given increasing responsibilities and continuous training.
This approach solves multiple challenges:
- It prevents the panic when a key leader leaves.
- It saves millions in executive search and signing bonuses for external hires.
- It boosts morale by showing employees they can rise to the top.
- It ensures new leaders understand the company inside and out.
A workplace skills plan turns leadership development from a reactive scramble into a proactive, ongoing process. It transforms the “Who could replace John?” crisis into a “We have three great candidates ready to step up” opportunity.
Remember, every senior leader in your company will retire someday. A skills plan ensures that day is an orderly transition, not a fire drill.
Boosting productivity and profits
Many companies view training as a necessary expense, but a well-crafted workplace skills plan can actually be a powerful profit driver. Here’s how:
When employees have the right skills, they work smarter, not just harder. They solve problems faster, make fewer mistakes, and come up with innovative ideas. All of this translates directly to the bottom line.
Let’s look at the numbers: A study by the National Center on the Educational Quality of the Workforce found that a 10% increase in workforce education level led to an 8.6% gain in total productivity. That’s a significant return on investment for any training program.
But it’s not just about productivity. Skilled, engaged employees have a direct impact on profitability. Gallup’s research shows that businesses with highly engaged employees are 23% more profitable than those with low engagement.
A workplace skills plan addresses both these factors. It not only upskills employees but also boosts engagement by showing them the company is invested in their growth.
Take Motorola as an example. In the early 1990s, they calculated that every dollar invested in training yielded $30 in productivity gains within three years. This wasn’t just a happy accident. It was the result of a carefully planned and executed skills development strategy.
Here’s what Motorola did right:
- They aligned their training with specific business goals.
- They made learning accessible, offering a mix of classroom and on-the-job training.
- They measured the impact of training on performance metrics.
- They created a culture where continuous learning was expected and rewarded.
The result wasn’t just improved skills, but a workforce that was more adaptable, innovative, and committed to the company’s success.
A workplace skills plan, when done right, isn’t a cost center—it’s a profit generator. It transforms training from a box-ticking exercise into a strategic tool for business growth. In today’s competitive market, can you afford not to have one?
Key components of a workplace skills plan
A workplace skills plan is more than just a document; it’s a living strategy that evolves with your organization. Let’s break down its key components and see how they work together to create a robust framework for employee development and organizational success.
Skills assessment and gap analysis
At the heart of any effective workplace skills plan is a thorough understanding of where your organization stands. This component involves taking stock of your current workforce’s skills and comparing them to what you’ll need in the future.
Imagine you’re running a marketing agency. Your team excels at traditional advertising, but you’ve noticed a shift towards digital marketing among your clients. A skills assessment might reveal that while your team is strong in areas like brand strategy and copywriting, they’re lacking in skills like SEO, social media marketing, and data analytics.
This gap analysis becomes the foundation of your entire plan. It highlights the occupational shortages and skills gaps identified by employers, which are crucial for developing a well-structured Workplace Skills Plan (WSP). The WSP outlines the necessary training programs to bridge these gaps, ensuring that your training efforts are focused and resources are prioritized effectively. Without this step, you’re essentially flying blind, potentially wasting time and money on unnecessary training while critical skill gaps remain unfilled.
Training and development programs
Once you’ve identified your skill gaps, the next step is to create targeted skills development programmes. This isn’t about sending everyone to the same generic workshop. Instead, it’s about crafting tailored learning experiences that address specific needs and align with your organization’s overall development strategy.
Continuing with our marketing agency example, you might set up a series of workshops on digital marketing techniques, bring in experts for hands-on SEO training, or enroll key team members in advanced analytics courses. The key is to align these programs closely with the gaps you’ve identified and the skills your organization needs to thrive. Drafting a Workplace Skills Plan (WSP) can be essential in ensuring that these training initiatives are responsive to skill gaps and contribute to the overall effectiveness of the workplace.
But training isn’t just about formal courses. It could include mentoring programs, job rotations, or project-based learning opportunities. For instance, you might pair your traditional marketers with digital specialists on real client projects, allowing them to learn on the job.
This component is crucial because it’s where the rubber meets the road. It’s how you actually start closing those skill gaps and building the capabilities your organization needs.
Implementation timeline and budget
A plan without a timeline is just a wish list. That’s why a clear implementation schedule is crucial. This component lays out when each training initiative will take place, who will participate, and how long it will take.
In our marketing agency, you might decide to roll out basic digital marketing training to all staff over the first quarter, followed by specialized courses for different teams in the subsequent months. You’d also need to factor in busy periods for your agency when training might need to take a back seat.
A comprehensive training plan, as part of a Workplace Skills Plan (WSP), is essential. This plan identifies occupational shortages, skills gaps, and specifies which training programs and staff will be targeted to address these issues. Alongside the timeline, a realistic budget is essential. Training and development can be expensive, but remember, it’s an investment in your organization’s future. Your budget should cover not just the direct costs of courses or trainers, but also factors like employee time away from billable work.
This component keeps your plan grounded in reality. It ensures you’re not overreaching and that your skills development efforts are sustainable over the long term.
Evaluation and feedback mechanisms
The final key component is a system for measuring the effectiveness of your skills plan. This isn’t just about tallying up how many people attended a training session. It’s about assessing whether the training is actually improving performance and contributing to your organizational goals.
An essential part of this evaluation process is the Annual Training Report (ATR). In conjunction with the Workplace Skills Plan (WSP), the ATR allows organizations to report on their training activities and progress. This reporting is crucial for accountability and improvement in addressing prioritized skills needs.
In our marketing agency, this might involve tracking metrics like the number of digital projects successfully completed, client satisfaction scores, or even the agency’s ability to win pitches for digital marketing work.
But don’t forget the human element. Regular check-ins with employees can provide valuable insights into how they’re applying their new skills and where they might need additional support.
This component closes the loop, feeding back into your skills assessment and helping you refine your plan over time. It ensures your workplace skills plan remains relevant and effective, adapting as your organization’s needs evolve.
By weaving these components together, you create a workplace skills plan that’s more than the sum of its parts. It becomes a dynamic tool for driving your organization forward, ensuring you have the right skills in the right place at the right time.
Note : Ready to transform into a skills-based organization? Fuel50’s talent marketplace can help you map your skills landscape, develop targeted learning paths, and create a more agile, future-ready workforce. Request a demo today .
How to create an effective workplace skills plan
Creating a workplace skills plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all process, but there are key steps that can guide you toward developing a robust and effective strategy. Let’s walk through these steps, understanding their importance and how they contribute to the overall success of your plan.
Align with organizational goals
The first step in creating an effective workplace skills plan is to align it with your organization’s broader goals and strategy. This alignment ensures that your skills development efforts directly contribute to your company’s success.
Start by sitting down with key stakeholders across your organization. If you’re a manufacturing company aiming to adopt more sustainable practices, for instance, your skills plan should reflect this.
You might need to develop expertise in green technologies, sustainable supply chain management, or environmental compliance.
This alignment is crucial because it gives your skills plan purpose and direction. It helps you prioritize which skills to develop and ensures that your training efforts directly support your company’s strategic objectives.
Without this alignment, you risk investing time and resources into developing skills that, while potentially interesting, don’t move your organization forward.
Conduct a comprehensive skills audit
Once you’ve aligned your plan with organizational goals, the next step is to take stock of your current skills landscape. This involves conducting a thorough skills audit across your workforce.
In practice, this might involve a combination of methods. You could use self-assessment surveys where employees rate their proficiency in various skills. You might also incorporate manager evaluations, performance data, and even practical skills tests.
Let’s say you’re a tech company planning to expand into artificial intelligence. Your skills audit might reveal that while you have strong software development skills, you’re lacking in specific AI competencies like machine learning algorithms or neural network design.
This step is vital because it gives you a clear picture of your starting point. It highlights your organization’s strengths and weaknesses, allowing you to identify skill gaps that need to be addressed. Without this baseline, you’d be planning in the dark, potentially missing critical skill shortages or wasting resources on unnecessary training.
Identify future skill needs
With a clear understanding of your current skills, the next step is to look ahead and identify the skills your organization will need in the future. This involves analyzing industry trends, technological developments, and your own strategic plans.
For a financial services company, this might involve recognizing the growing importance of skills in areas like blockchain technology, data privacy, or sustainable finance. You’d need to consider not just the technical skills required but also the soft skills that will be crucial in a rapidly changing industry.
This forward-looking approach is essential because it allows you to be proactive rather than reactive in your skills development. It helps you stay ahead of the curve, preparing your workforce for future challenges and opportunities before they arise.
Without this foresight, you risk falling behind competitors or scrambling to develop critical skills when it’s already too late.
Prioritize skill gaps
Once you’ve identified both your current skills and future needs, the next step is to prioritize which skill gaps to address first. Not all skill gaps are created equal, and you likely won’t have the resources to tackle everything at once.
This prioritization should consider factors like the urgency of the need, the potential impact on your business, and the resources required to develop each skill. In the context of a Workplace Skills Plan (WSP), having your priority skills defined is essential. This reporting is crucial for accessing mandatory grants for skills training, as it highlights how your organization addresses specific skill priorities outlined in your plan. You might use a matrix that plots the importance of each skill against the current skill level in your organization.
For example, if you’re a retail company moving towards an omnichannel strategy, you might prioritize skills in areas like digital marketing, data analytics, and customer experience design over other less critical gaps.
This step is crucial because it helps you focus your efforts and resources where they’ll have the most significant impact. It ensures that your skills plan addresses the most pressing needs first, maximizing its effectiveness and return on investment.
Design targeted learning interventions
With your priorities set, the next step is to design learning interventions that will effectively close your identified skill gaps. This is where skills training comes into play, particularly within the framework of a Workplace Skills Plan (WSP).
Remember, effective learning isn’t one-size-fits-all. For a software development company aiming to upskill in cloud computing, this might involve a combination of online courses, hands-on projects, peer mentoring, and attendance at industry conferences. The key is to match the learning method to the skill being developed and the learners themselves.
This step is crucial because it’s where your plan starts to take tangible form. Well-designed learning interventions ensure that your employees are not just exposed to new information, but actually develop practical, applicable skills. Without careful design, you risk ending up with training that looks good on paper but fails to deliver real-world results.
Develop an implementation plan
With your learning interventions designed, the next step is to create a detailed implementation plan. This should outline who will participate in which training, when it will occur, and how it will be delivered.
For instance, if you’re a healthcare provider implementing a new electronic health record system, your plan might involve a phased approach. You could start with IT staff training, followed by clinician super-users, and then roll out to the broader staff. Your plan should also account for factors like shift schedules and patient care demands.
This step is vital because it transforms your skills plan from a concept into an actionable roadmap. It helps ensure that your training efforts are coordinated, efficient, and minimally disruptive to your regular operations. Without a solid implementation plan, even the best-designed learning interventions can fall flat due to poor execution.
Allocate resources
With your implementation plan in place, you need to ensure you have the resources to make it happen. This involves not just financial budgeting, but also allocating time, personnel, and technological resources.
For example, if you’re a manufacturing company investing in robotics training, you’ll need to budget not just for the training itself, but potentially for equipment, software licenses, and the time employees will spend away from their regular duties. You might also need to bring in external trainers or send key staff to specialized courses.
This step is crucial because it ensures your skills plan is realistic and achievable. Without proper resource allocation, including the effective use of skills development levies, you risk having a great plan on paper that you can’t actually execute, leading to frustration and wasted effort.
Establish monitoring and evaluation mechanisms
The final step in creating your workplace skills plan is to establish how you’ll monitor its progress and evaluate its effectiveness. This involves setting up systems to track participation in training, measure skill development, and assess the impact on job performance and business outcomes.
For a sales organization, this might involve tracking metrics like completion rates for sales training modules, improvements in key sales metrics, and feedback from both sales staff and customers. You might also conduct regular skills assessments to measure progress in closing identified gaps.
This step is essential because it allows you to gauge the success of your plan and make data-driven adjustments as needed. It helps you demonstrate the ROI of your skills development efforts and provides insights for continual improvement. Without robust monitoring and evaluation, you’re essentially flying blind, unable to tell if your skills plan is actually delivering the intended results.
Turn your organization into a skills-based organization by leveraging Fuel50
Fuel50’s comprehensive talent marketplace platform offers several features that significantly support and enhance your transition to a skills-based model.
Here’s how Fuel50 can help you become a skills-based organization:
Create a dynamic skills inventory
Fuel50’s expert-driven skills ontology goes beyond traditional skills tracking methods. It creates a detailed map of skills across your organization, allowing you to identify and categorize skills based on actual capabilities rather than just job titles or roles.

The platform’s expert-powered skills mapping tools enable you to visualize the skills landscape within your organization, helping you spot skill clusters, gaps, and emerging trends. This approach ensures you have a real-time, accurate picture of your organization’s skill base.
By combining skills mapping with career aspirations, Fuel50 helps you create a more nuanced and forward-looking view of your talent pool, essential for a skills-based approach.
Align skills with business objectives
One of the challenges in becoming a skills-based organization is ensuring that your skills inventory aligns with your strategic goals. Effective workplace skills planning is crucial in this context, as it involves addressing skills development and training needs while engaging stakeholders to ensure adequate resources and support for the process. Fuel50 addresses this by providing comprehensive skills gap analysis against your organization’s objectives.

The platform compares the current skills of your workforce against the skills required to meet your business goals, highlighting areas where development or acquisition is needed.
This visibility allows you to create targeted strategies for skill development and acquisition. Instead of generic training programs, you can focus on developing the specific skills that will drive your organization forward.
Foster a culture of continuous skill development
Fuel50’s personalized learning and development recommendations transform skill development from a periodic event to an ongoing process. The platform offers tailored suggestions for courses, resources, and experiences that align with both the employee’s career goals and your organization’s skill needs.

Moreover, the platform’s gig marketplace feature allows employees to take on short-term projects or assignments that develop new skills or apply existing ones in different contexts.
This experiential learning is crucial for developing a versatile, multi-skilled workforce that can adapt to changing business needs. By integrating learning so closely with skills development, Fuel50 helps create a culture where employees are constantly expanding their skill sets.
Enhance retention through skill-based career pathing
A skills-based approach isn’t just about organizational efficiency; it’s about providing clear growth opportunities for employees. Fuel50’s focus on skill-based career pathing plays a crucial role in keeping your employees engaged and committed to your organization.

The platform’s transparency about skill requirements for various roles and development paths gives employees a clear vision of how they can grow within your company based on their skills and interests.
Furthermore, Fuel50’s mentoring features facilitate skill transfer between employees. These relationships not only aid in knowledge sharing but also help employees feel valued and invested in, increasing their likelihood of developing new skills and seeking growth opportunities within your organization.
Provide data-driven insights for strategic workforce planning
Effective skills-based management requires a deep understanding of your current skills landscape and future needs. Fuel50’s analytics capabilities provide valuable insights that can inform your skills strategy.

The platform can help you identify trends in skill development, track the progress of skill acquisition across the organization, and even predict future skill needs based on your organization’s direction and market trends.
These insights allow you to take a more proactive approach to skills management. Instead of simply reacting to skill gaps as they occur, you can strategically develop your skills pipeline to meet future needs across all departments.
This data-driven approach ensures your skills development efforts align closely with your overall business strategy, creating a more resilient and adaptable organization.
What is talent mobility and how to develop an effective strategy?

What is Internal Mobility And Why Do You Need It?

7 Best Talent Marketplace Software for Enterprise Organizations

What is Paycor HCM and Its Alternatives?

What is PeopleSoft HCM and Its Alternatives?

Fuel50 Launches A Bold New Brand — What Does It Mean For Our Customers
Subscribe to get fresh research and insights delivered to your inbox.

- Programs & Services
- Delphi Center
Ideas to Action (i2a)
- What is Critical Thinking?
The ability to think critically calls for a higher-order thinking than simply the ability to recall information.
Definitions of critical thinking, its elements, and its associated activities fill the educational literature of the past forty years. Critical thinking has been described as an ability to question; to acknowledge and test previously held assumptions; to recognize ambiguity; to examine, interpret, evaluate, reason, and reflect; to make informed judgments and decisions; and to clarify, articulate, and justify positions (Hullfish & Smith, 1961; Ennis, 1962; Ruggiero, 1975; Scriven, 1976; Hallet, 1984; Kitchener, 1986; Pascarella & Terenzini, 1991; Mines et al., 1990; Halpern, 1996; Paul & Elder, 2001; Petress, 2004; Holyoak & Morrison, 2005; among others).
After a careful review of the mountainous body of literature defining critical thinking and its elements, UofL has chosen to adopt the language of Michael Scriven and Richard Paul (2003) as a comprehensive, concise operating definition:
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.
Paul and Scriven go on to suggest that critical thinking is based on: "universal intellectual values that transcend subject matter divisions: clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness. It entails the examination of those structures or elements of thought implicit in all reasoning: purpose, problem, or question-at-issue, assumptions, concepts, empirical grounding; reasoning leading to conclusions, implication and consequences, objections from alternative viewpoints, and frame of reference. Critical thinking - in being responsive to variable subject matter, issues, and purposes - is incorporated in a family of interwoven modes of thinking, among them: scientific thinking, mathematical thinking, historical thinking, anthropological thinking, economic thinking, moral thinking, and philosophical thinking."
This conceptualization of critical thinking has been refined and developed further by Richard Paul and Linder Elder into the Paul-Elder framework of critical thinking. Currently, this approach is one of the most widely published and cited frameworks in the critical thinking literature. According to the Paul-Elder framework, critical thinking is the:
- Analysis of thinking by focusing on the parts or structures of thinking ("the Elements of Thought")
- Evaluation of thinking by focusing on the quality ("the Universal Intellectual Standards")
- Improvement of thinking by using what you have learned ("the Intellectual Traits")
Selection of a Critical Thinking Framework
The University of Louisville chose the Paul-Elder model of Critical Thinking as the approach to guide our efforts in developing and enhancing our critical thinking curriculum. The Paul-Elder framework was selected based on criteria adapted from the characteristics of a good model of critical thinking developed at Surry Community College. The Paul-Elder critical thinking framework is comprehensive, uses discipline-neutral terminology, is applicable to all disciplines, defines specific cognitive skills including metacognition, and offers high quality resources.
Why the selection of a single critical thinking framework?
The use of a single critical thinking framework is an important aspect of institution-wide critical thinking initiatives (Paul and Nosich, 1993; Paul, 2004). According to this view, critical thinking instruction should not be relegated to one or two disciplines or departments with discipline specific language and conceptualizations. Rather, critical thinking instruction should be explicitly infused in all courses so that critical thinking skills can be developed and reinforced in student learning across the curriculum. The use of a common approach with a common language allows for a central organizer and for the development of critical thinking skill sets in all courses.
- SACS & QEP
- Planning and Implementation
- Why Focus on Critical Thinking?
- Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
- Culminating Undergraduate Experience
- Community Engagement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is i2a?
Copyright © 2012 - University of Louisville , Delphi Center
- Request Quote
- Research Hub
- Digital Reader

How Interactive Read-Alouds Build Comprehension & Engagement (+ Free Lesson Plan)
Reading books aloud invites students into the world of literature and informational texts and creates a community of active listeners who carefully listen, think, and talk about books. By adding interactive elements to the traditional read-aloud, teachers can deepen students' comprehension, expand their vocabulary, and strengthen critical thinking skills, all while building a love of reading.
Interactive read-alouds provide all students—regardless of their independent reading abilities — the chance to experience high-quality texts and develop essential literacy skills in a supportive and engaging environment. Interactive read-alouds also create opportunities for students to connect with diverse literature, learn how to engage with peers, and practice thinking deeply about the meaning of the text.
What is an interactive read-aloud?
An interactive read-aloud is a teaching strategy where a teacher reads a book aloud to students while actively engaging them in discussion and activities related to the content. The teacher pauses reading at key moments to ask questions, invite predictions, and engage the listeners in discussions.
The goal of interactive read-aloud is to foster the joy of reading while developing students' background knowledge , oral language development, comprehension, and critical thinking skills.
During an interactive read-aloud, the reader typically:
- Models fluent reading: Demonstrates tone, expression, and pacing.
- Bolsters oral language development: Engages students to talk about text and share their thinking in partnerships and with the class.
- Asks open-ended questions: Encourages students to think critically and teaches them to make predictions and inferences about the text.
- Teaches comprehension strategies: Introduces students to a comprehension focus or relates the text back to strategies being taught in the classroom, such as understanding story elements or main idea and details.
- Encourages connections: Helps students relate the story to their own lives, each other, other books, or broader concepts.
- Fosters vocabulary development: Determines the meaning of unfamiliar words and discusses new or unfamiliar concepts in context.
This approach makes the reading experience more engaging by inviting students to be active participants who think deeply about the text and connect it to their own experiences.

5 Benefits of Interactive Read-Alouds
Research supports the effectiveness of interactive read-alouds in promoting literacy development and other educational outcomes. Some key findings from the research include:
1. Deepen Comprehension Skills
Studies show ( Duke et al., 2021 ; Swanson et al., 2011 ) that interactive read-alouds enhance students' comprehension skills. Even the youngest learners benefit from comprehension instruction through read-alouds. By engaging students in discussion and prompting them to think critically about the text, teachers help students better understand and retain information.
2. Vocabulary Growth
Research indicates ( Swanson et al., 2011 ) that interactive read-alouds support vocabulary acquisition and usage. By exposing students to rich and varied language in context, teachers help them learn new words and understand their meanings.
3. Foster Critical Thinking & Engagement
A study by Duke et al. (2021 ) demonstrates that when teachers involve students in predicting, questioning, and discussing the text, students develop higher-order thinking skills and a deeper engagement with reading. Opportunities to discuss and ask questions about the text increases learning and brain development ( Darling-Hammond et al., 2019 ). Additionally, Fisher et al. (2004) found that interactive read-alouds significantly increased student engagement and motivation to read. The social setting of interactive read-alouds helps build engagement and motivation ( Afflerbach, 2022 ).
4. Strengthen Foundational Skills
Interactive read-alouds are effective in developing foundational literacy skills such as phonological awareness, concepts of print, and oral language. Studies, such as Swanson et al. (2011) , have demonstrated that read-alouds contribute to foundational skills that are critical for later reading success.
5. Develop SEL and Growth Mindset
Helping students relate to characters, understand different perspectives, and discuss feelings and experiences can support social and emotional development. For example, a study by Thompson and Melchior (2019) found that interactive read-alouds help students build empathy.
How to Get Started with Interactive Read-Aloud
Select an age-appropriate book or text that features rich language and engaging content and that lends itself to deeper analysis and learning activities. Plan ahead to determine which strategies and comprehension areas to focus on, such as:
- Retelling the story
- Summarizing
- Identifying main ideas
- Analyzing characters
- Making inferences
- Developing vocabulary
- Understanding text structure
Interactive Read-Aloud Sample Lesson Plan

If your schedule allows, consider adding a second day of instruction to review the book and incorporate writing practice.

Engage Readers with Interactive Read-Aloud Kits from Pioneer Valley Books

Interactive Read-Aloud kits from Pioneer Valley Books include curated collections of engaging trade books, each with a corresponding lesson plan to support comprehension instruction in your classroom. Each read-aloud book has been carefully selected to engage young learners.
- Beautifully illustrated books that expand students’ background knowledge and offer exposure to different genres and diverse authors
- An embedded SEL/growth mindset component that guides discussions and encourages reflective thinking
- Lessons that provide engaging opportunities for listening comprehension , oral language development , and writing about texts
These whole-group mini-lessons provide teachers with standards-aligned comprehension strategies to build strong readers who can’t wait to pick up another book!

Improvement of the Process Automation for Students Inscription in Peruvian Education
- Conference paper
- First Online: 23 October 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- Ricardo Arias 11 ,
- Enzo Rojas 11 ,
- Jesus Cabezas 11 &
- Eduardo Garces 11
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems ((LNNS,volume 1118))
Included in the following conference series:
- Computer Science On-line Conference
The enrollment process at the Peruvian schools are manual with large process, it generates significant delays and security problems. This situation affects both parents and administrative and teaching staff, which motivates the need to address and improve this process efficiently. This research project focuses on the automation of this process through the implementation of an efficient School Management System (SMS). Currently, the systematic literature review demonstrates a growing interest in automating enrollment and cyber security in educational settings, highlighting potential benefits and worries in terms of efficiency and user experience. This paper’s objective is to detect the deficiencies present in the current literature and compile recommendations based on the experience of other institutions that have implemented similar automated systems and a proposal to develop a methodology for the evaluation and improvement of the cyber-security and automation in the SMS. The purpose is to establish a solid knowledge that supports decision-making process when planning the implementation of the automation system in the school, with the objective of quantifiable reducing the waiting time in the enrollment process, minimizing errors in data collection, and, increase parental satisfaction with an evaluation of 1654 papers from ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore and Scopus. Therefore, it contributes to improving the efficiency of the enrollment process and optimizing administrative management.
R. Arias—Thanks to Universidad Tecnológica del Perú.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Martínez-Cerdá, J.F., Torrent-Sellens, J., González-González, I.: Socio-technical e-learning innovation and ways of learning in the ICT-space-time continuum to improve the employability skills of adults. Comput. Hum. Behav. 107 , 105753 (2020)
Article Google Scholar
Valtonen, T., et al.: The nature and building blocks of educational technology research. Comput. Hum. Behav. 128 , 107123 (2022)
Longo, A., Zappatore, M., Bochicchio, M.A.: Apollon: towards a citizen science methodology for urban environmental monitoring. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 112 , 899–912 (2020)
Jacqmin, J.: Why are some Massive Open Online Courses more open than others? Technovation 112 , 102395 (2022)
Carlson, S.E., et al.: The design risks framework: understanding metacognition for iteration. Des. Stud. 70 , 100961 (2020)
Bichler, S., et al.: Designing a remote professional development course to support teacher customization in science. Comput. Hum. Behav. 123 , 106814 (2021)
Behutiye, W., et al.: Towards optimal quality requirement documentation in agile software development: a multiple case study. J. Syst. Softw. 183 , 111112 (2022)
Kadenic, M.D., et al.: Investigating the role of product owner in scrum teams: differentiation between organisational and individual impacts and opportunities. J. Syst. Softw. 206 , 111841 (2023)
López, L., et al.: Quality measurement in agile and rapid software development: a systematic mapping. J. Syst. Softw. 186 , 111187 (2022)
Parizi, R., et al.: How has design thinking being used and integrated into software development activities? A systematic mapping. J. Syst. Softw. 187 , 111217 (2022)
Marchezan, L., et al.: Software product line scoping: a systematic literature review. J. Syst. Softw. 186 , 111189 (2022)
Hron, M., Obwegeser, N.: Why and how is Scrum being adapted in practice: a systematic review. J. Syst. Softw. 183 , 111110 (2022)
Kopczyńska, S., et al.: On the benefits and problems related to using definition of done—a survey study. J. Syst. Softw. 193 , 111479 (2022)
Cucolaş, A.A., Russo, D.: The impact of working from home on the success of Scrum projects: a multi-method study. J. Syst. Softw. 197 , 111562 (2023)
Altuwaijri, F.S., Ferrario, M.A.: Factors affecting Agile adoption: an industry research study of the mobile app sector in Saudi Arabia’’. J. Syst. Softw. 190 , 111347 (2022)
Licorish, S.A., et al.: Understanding students’ software development projects: effort, performance, satisfaction, skills and their relation to the adequacy of outcomes developed. J. Syst. Softw. 186 , 111156 (2022)
Dhar, S., Bose, I.: Walking on air or hopping mad? Understanding the impact of emotions, sentiments and reactions on ratings in online customer reviews of mobile apps. Decis. Support Syst. 162 , 113769 (2022)
Yasir, R., Muhammad, S., Mailizar, M., Turki, M., Lal, N., Akhmad, H.: How can we assess the success of information technologies in digital libraries? Empirical evidence from Indonesia. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 3 , 2 (2023)
Google Scholar
Wang, L., et al.: Cognitive process-driven model design: a deep learning recommendation model with textual review and context. Decis. Support Syst. 176 , 114062 (2023)
Anant, J., et al.: Impact of IT governance process capability on business performance: theory and empirical evidence. Decis. Support Syst. 153 , 113668 (2022)
Jatain, D., Singh, V., Dahiya, N.: An exploration of the causal factors making an online course content popular & engaging. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 3 (2), 100194 (2023)
Varsha, D.: How can we manage biases in artificial intelligence systems – a systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 3 (1), 100165 (2023)
Katheriyar, M.M.R., Hadush, A.Z.: Effect of computer inputs, cost of the computer inputs, and users’ competency on the adoption of HRMIS in the Tigray Education sector. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 3 (2), 100189 (2023)
Al-Mamary, Y.: Understanding the use of learning management systems by undergraduate university students using the UTAUT model: credible evidence from Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2 (2), 100092 (2022)
Kumar, R., et al.: A user-priorities-based strategy for three-phase intelligent recommendation and negotiating agents for cloud services. IEEE Access 11 , 26932–26944 (2023)
Goralski, M.A., Tan, T.K.: Artificial intelligence and poverty alleviation: emerging innovations and their implications for management education and sustainable development. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 20 (3), 100662 (2022)
Tseng, T.H., et al.: Developing a value-based online learning model to predict learners’ reactions to internet entrepreneurship education: the moderating role of platform type. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 21 (3), 100867 (2023)
Massyn, L.: Enhancing completion rates of mini-dissertations for a professional master’s degree: an integrated approach. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 16 (1), 114–120 (2018)
Khan, A., Krishnan, S.: Moderating effects of business-systems corruption on corruption in basic national institutions and electronic government maturity: insights from a dynamic panel data analysis. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 59 , 102349 (2021)
Rubens, A., et al.: Self-awareness and leadership: developing an individual strategic professional development plan in an MBA leadership course. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 16 (1), 1–13 (2018)
Getachew, T.: Quantitative skill retention and curriculum integration in a typical business school in the United States – a student perspective. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 16 (2), 292–308 (2018)
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Garber, L.L., et al.: Constituting, testing and validating the gender learner profiles of serious game participants. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 16 (2), 205–223 (2018)
García-Cabrera, A.M., et al.: The relevance of entrepreneurial competences from a faculty and students’ perspective: the role of consensus for the achievement of competences. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 21 (2), 100774 (2023)
McKay, R., et al.: We’re not in Kansas anymore: academic honesty in an international business program. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 17 (1), 1–14 (2019)
Votto, A.M., et al.: Artificial intelligence in tactical human resource management: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 1 (2), 100047 (2021)
Yazdani, M., et al.: Resilient sustainable investment in digital education technology: a stakeholder-centric decision support model under uncertainty. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 188 , 122282 (2023)
Sarker, I., Datta, B.: Re-designing the pension business processes for achieving technology-driven reforms through blockchain adoption: a proposed architecture. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 174 , 121059 (2022)
Zafar, M.W., et al.: ICT and education as determinants of environmental quality: the role of financial development in selected Asian countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 177 , 121547 (2022)
Omar, S.F., et al.: Readiness in using online interactive platforms for remote teaching. Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 24 (2), 1047–1053 (2021)
Mansor, N.A., et al.: Towards electronic learning features in education 4.0 environment: literature study. Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 19 (1), 442–450 (2020)
Moradi, M., Fard, K.R.: An English-language teaching plan for children in the Internet of Things environment. Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 13 (3), 927–932 (2019)
Hieder, I.A., et al.: Utilizing the ATM technology in E-distance learning. Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 20 (2), 1016–1029 (2020)
Velarde, C.L., et al.: Technology in the educational processes of basic education in Peru. Int. J. Eval. Res. Educ. 12 (1), 433–443 (2023)
Herrera Rivera, J.E.: Sistema de recomendación basado en contenido para matrícula de asignaturas electivas en carrera de ingeniería en universidad pública de Arequipa. Latin American and Caribbean Consortium of Engineering Institutions, vol. 7 (2019)
Almonteros, J.R., et al.: Automation of curriculum-based student-subject encoding: a web application. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp. 328–333 (2022)
Carrera-Rivera, A., et al.: How-to conduct a systematic literature review: a quick guide for computer science research. MethodsX 9 , 101895 (2022)
Pati, D., Lorusso, L.N.: How to write a systematic review of the literature. Health Environ. Res. Des. J. 11 (1), 15–30 (2018)
Ahmad, S.F., Alam, M.M., Rahmat, M.K., Mubarik, M.S., Hyder, S.I.: Academic and administrative role of artificial intelligence in education. Sustainability 14 (3), 1101 (2022)
Ruiz, M.F.L., et al.: WISE game: wireless interactive software educational game. Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Science 23 (3), 1357–1365 (2021)
Vieira, E., Gomes, J.: A comparison of Scopus and Web of Science for a typical university. Scientometrics 81 , 587–600 (2009)
Yang, L., et al.: Quality assessment in systematic literature reviews: a software engineering perspective. Inf. Softw. Technol. 130 , 106397 (2021)
Lordan, G., Neumark, D.: People versus machines: the impact of minimum wages on automatable jobs. Labour Econ. 52 , 40–53 (2018)
Admass, W.S., et al.: Cyber security: state of the art, challenges and future directions. Cyber Secur. Appl. 2 , 100031 (2024)
Arias Velásquez, R.M.: Knowledge management methodology to predict student doctoral production. In: Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P. (eds.) CSOC 2023. LNNS, vol. 724, pp. 714–732. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35314-7_60
Chapter Google Scholar
Velásquez, R.M.A., Lara, J.V.M.: Knowledge management in two universities before and during the COVID-19 effect in Peru. Technol. Soc. 64 , 101479 (2021)
Download references
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank to the Universidad Tecnológica del Perú.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Universidad Tecnológica del Perú, Natalio Sanchez Street N° 125, Santa Beatriz, Lima, Peru
Ricardo Arias, Enzo Rojas, Jesus Cabezas & Eduardo Garces
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ricardo Arias .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Applied Informatics, Tomas Bata University in Zlin, Zlin, Czech Republic
Radek Silhavy
Faculty of Applied Informatics, Tomas Bata University in Zlín, Zlin, Czech Republic
Petr Silhavy
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Arias, R., Rojas, E., Cabezas, J., Garces, E. (2024). Improvement of the Process Automation for Students Inscription in Peruvian Education. In: Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P. (eds) Software Engineering Methods Design and Application. CSOC 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 1118. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70285-3_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70285-3_6
Published : 23 October 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-70284-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-70285-3
eBook Packages : Intelligent Technologies and Robotics Intelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Enhance Skills for Vertical-Horizontal Machining
- October 24th, 2024
Understanding Vertical-Horizontal Machining Centers
Vertical-horizontal machining centers are essential in modern manufacturing, offering versatility and precision in metal processing tasks. These machines are categorized based on the orientation of the spindle, which influences their application and efficiency in various industrial processes.
Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs)
Vertical machining centers feature a spindle that is vertically oriented, making them ideal for operations on workpieces that require machining primarily on a single side. The typical setup involves the workpiece being mounted on a fixed or moving table, allowing for operations such as milling, drilling, and tapping. VMCs are particularly suited for industries such as:
- Tool and Die Making : Where precise, single-surface machining is required.
- Electronics : For producing components with intricate top-surface details.
- Automotive : In manufacturing parts like engine blocks and transmission components.
Advantages of VMCs
- Cost-Effectiveness : VMCs generally have lower initial costs and require less floor space, making them a cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized production facilities.
- Flexibility : Capable of handling a wide range of tasks, from simple drilling to complex contouring.
- Ease of Use : The vertical orientation simplifies setup and operation, reducing training requirements for operators.
VMCs may face challenges with chip evacuation, as chips tend to accumulate on the workpiece surface, potentially impacting surface finish and necessitating additional cleaning or processing.
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs)
Horizontal machining centers have a spindle that is horizontally oriented. This configuration is advantageous for multi-sided machining, where the workpiece is mounted on a rotating table. HMCs are particularly beneficial in industries such as:
- Aerospace : For large, complex components that require precision on multiple surfaces.
- Automotive : In the production of parts like engine blocks, where multi-surface machining is crucial.
- Heavy Equipment Manufacturing : For large-scale parts that demand high precision and stability.
Advantages of HMCs
- Efficient Chip Evacuation : Gravity aids in the removal of chips from the workpiece, enhancing surface finish and reducing the need for additional post-processing.
- Stability and Precision : Designed with a rigid box-way structure, providing superior durability and stability essential for maintaining accuracy over long production runs.
- High Productivity : The ability to mount and machine parts simultaneously on different sides of the pallet enhances productivity, making HMCs suitable for high-volume production environments.
For instance, in automotive manufacturing, the efficient chip evacuation of HMCs significantly impacts production efficiency by reducing downtime for cleaning and maintenance.

Selecting the Right Machining Center
Consider the following factors when choosing between a vertical and horizontal machining center:
- Workpiece Complexity and Size : VMCs are better for simpler, single-sided tasks, while HMCs excel in multi-sided, complex machining.
- Precision and Stability Needs : HMCs offer superior stability, making them ideal for high-precision requirements.
- Production Volume : HMCs are suited for high-volume environments due to their productivity advantages.
- Cost and Space Constraints : VMCs are generally more affordable and require less space, beneficial for smaller operations.
Understanding the specific requirements of the manufacturing process and the capabilities of each type of machining center is crucial. Consider how these factors align with your production goals and operational constraints.
Enhancing Capabilities with CNC Technology
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology enhances the capabilities of both VMCs and HMCs by allowing for precise control over machining operations. This technology enables automation, reduces human error, and improves consistency across production runs.
Reader Engagement
Reflect on your specific manufacturing needs. Consider:
- How does the complexity of your parts influence your choice between VMCs and HMCs?
- What role does production volume play in your decision-making process?
- How can CNC technology integrate into your existing operations to enhance efficiency?
By evaluating these questions, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your manufacturing objectives.
Importance of Skill Development for Machining Center Operators
Have you ever wondered how a skilled CNC operator can transform a block of metal into a precision component? Skill development for operators of vertical-horizontal machining centers is crucial in the manufacturing sector, significantly impacting productivity, quality, and safety.
Enhancing Technical Proficiency
Operators of CNC machining centers must possess a comprehensive understanding of machine operation, programming, and maintenance. For example, proficiency in G-code, a language used to control CNC machines, allows operators to create precise machining instructions. Similarly, knowledge of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) programming is essential for automating machine operations, improving efficiency and quality outcomes. Imagine a scenario where an operator optimizes a machining process by adjusting the G-code, resulting in a 15% reduction in production time.
Industry Readiness and Employability
The manufacturing industry demands high precision and efficiency, making skilled CNC operators highly employable. According to industry reports, companies that invest in operator training see up to a 30% increase in productivity. Comprehensive training programs equip operators with the necessary skills to meet these demands, enhancing their job placement prospects across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Employers prioritize hiring operators with robust training backgrounds, ensuring they can handle complex manufacturing tasks and adapt to evolving industry needs.
Problem-Solving and Adaptability
Machining center operators must develop strong problem-solving abilities to address issues that arise during machining processes. This includes material preparation, cutter selection, and troubleshooting unforeseen problems. As technology and machinery evolve, operators must be adaptable, continuously learning new skills to remain relevant and efficient in their roles. The ability to swiftly adapt to new technologies directly links to increased employability and career advancement opportunities.
Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
Proper training in safety protocols is essential. It helps prevent workplace injuries and maintain a secure environment. Operators must understand and adhere to safety labels, operational logs, and records. Once safety is assured, well-trained operators contribute to increased efficiency by minimizing downtime and optimizing production processes through correct machine setup and operation.
Developing Soft Skills for Career Advancement
In addition to technical capabilities, soft skills are crucial for career growth. Key soft skills include:
- Attention to detail
- Communication
- Flexibility
- Time management
These skills enable operators to efficiently solve problems, meet production deadlines, and maintain high-quality standards. By embracing new technologies and automation, operators position themselves at the forefront of the industry, ready to take on more complex and rewarding projects.
Fostering Continuous Learning and Innovation
Ongoing training is vital for operators to master the skills necessary for CNC machining. Continuous learning through training programs and real-world practice allows operators to stay abreast of the latest technologies and software, fostering innovation. This environment encourages operators to experiment with new designs and materials, pushing the boundaries of traditional manufacturing and promoting creative problem-solving.
Key Skills Required for Machining Center Operators
Machining center operators play a crucial role in the manufacturing process, requiring a blend of technical and soft skills to ensure efficient and precise operations. Understanding these key skills is essential for operators to excel in their roles and contribute to the success of production environments.
CNC Programming Proficiency
Proficiency in CNC programming is a fundamental skill for operators. This includes understanding G-code and M-code , which are the languages used to control CNC machines. For example, an operator might use G-code to solve a problem where a machine needs to execute a precise series of movements to produce a complex part. Mastery of these codes enables operators to write, edit, and troubleshoot programs efficiently. Additionally, expertise in CAD/CAM software, such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Mastercam, is vital for creating 3D models and generating toolpaths.
Understanding CNC Machines and Control Systems
Operators encounter a variety of CNC machines, such as lathes, mills, and routers, each with unique control systems. Familiarity with these diverse systems allows operators to navigate control panels, manage axis control, and load and execute programs. For example, they must respond to emergencies by quickly halting operations if a safety issue arises.
Practical and Operational Skills
Hands-on skills are fundamental for machining center operators. These include material preparation, clamping, jig and fixture creation, and cutter selection, all of which require a solid grasp of engineering principles. Operators must be adept in various machining operations, such as milling, drilling, and reaming, and possess the ability to care for machinery and tools, ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
- Machine Setup: Involves preparing the machine for operation by selecting and installing appropriate tools.
- Calibration: Ensures machines are set to produce parts within specified tolerances.
- Troubleshooting: Identifies and resolves issues to prevent downtime and maintain productivity.
Attention to Detail, Inspection Skills, and Problem-Solving
Precision is paramount in machining, necessitating operators to have a keen eye for detail. This involves inspecting parts, measuring tools, and ensuring machines operate according to specifications and quality standards. Familiarity with inspection tools such as dial calipers, micrometers, and height gauges is crucial. In conjunction with these skills, strong problem-solving abilities enable operators to diagnose and address machine issues promptly, fostering innovation and efficiency within production processes.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
Adaptability is crucial as technology and industry practices evolve. Operators must stay informed about new technologies and continuously learn to keep their skills relevant. A commitment to continuous learning involves a proactive approach to acquiring new skills and expertise, enhancing employability and opening up opportunities for career growth.
Safety Awareness
Safety is a top priority in machining environments. Operators should be well-versed in safety protocols and obtain necessary certifications. Technical skills are linked closely to safety, as operators must safely operate complex machinery while adhering to protocols that prevent accidents. Understanding and promoting a culture of safety ensures a secure working environment.
Interpersonal and Mathematical Skills
Operators benefit from possessing strong mathematical skills, particularly in geometric dimensioning and tolerance, which are necessary for interpreting technical drawings and specifications. Additionally, technical writing, comprehension, and critical thinking are valued skills that enhance communication and collaboration within teams.
By mastering these skills, machining center operators can effectively navigate the challenges of modern manufacturing, ensuring efficient, precise, and safe operations that contribute to the overall success and competitiveness of their organizations.
Training Programs for Vertical-Horizontal Machining Centers
Training programs for operators of vertical-horizontal machining centers are essential for ensuring proficiency in machine operation, programming, and maintenance. These programs equip operators with the skills necessary to handle complex machining tasks efficiently and safely. Leading manufacturers and educational institutions offer comprehensive training options tailored to various aspects of machining center operations.
Comprehensive Training Offerings
Okuma america training programs.
Okuma America, in collaboration with Rowan-Cabarrus Community College, offers a variety of training programs:
- Covers controls such as OSP-P300A, OSP-P200A, and P300.
- Example Task: Diagnose and repair electrical faults in a machining center.
- Focuses on maintaining mechanical components of machining centers and lathes.
- Example Task: Perform routine checks and maintenance on spindle systems.
- Includes CNC lathe and machining center operations.
- Example Task: Program a CNC machine to produce a specific component with precise tolerances.
These courses blend theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience, preparing operators for real-world applications.
Mazak Training Programs
Mazak’s National Training Center provides courses tailored to both vertical and horizontal machining centers:
- Mazatrol Smooth G/Smooth X/Smooth Ez Conversational Programming.
- Example Task: Develop a program for a multi-axis milling operation using Mazatrol.
- Focus on preventive maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Example Task: Identify and resolve hydraulic system issues in a machining center.
- Electrical/software PLC troubleshooting and Palletech Smooth PMC scheduling.
- Example Task: Optimize production scheduling using advanced software tools.
Mazak’s programs are designed to build a robust foundation in both basic and advanced machining center operations.
Makino Training Programs
Makino offers a comprehensive suite of training options:
- Focused on vertical and horizontal machining centers.
- Example Task: Set up and operate a horizontal machining center for a large batch production.
- Includes maintenance, programming, and operational strategies.
- Example Task: Develop an efficient workflow to minimize downtime during tool changes.
- A six-week intensive course similar to training provided to Makino Field Service Engineers.
- Example Task: Troubleshoot and repair complex machine malfunctions.
Makino’s approach combines in-depth technical instruction with practical application, fostering a deep understanding of machining processes.
GROB-WERKE Training Programs
GROB-WERKE’s Technical Academy provides targeted training:
- Courses on machine operation, automation, and maintenance specific to GROB systems.
- Example Task: Implement automation solutions to enhance machining efficiency.
- Customizable modules on machining technology and assembly processes.
- Example Task: Assemble and calibrate a new machining center according to specifications.
- Certification upon course completion, validating skills across systems like SIEMENS 840D sl and HEIDENHAIN iTnC530.
GROB-WERKE’s programs emphasize adaptability and expertise in modern machining technologies.
Addressing Programming Challenges
Programming horizontal machining centers involves unique challenges due to rotary devices and multi-surface machining requirements. Key programming strategies include:
- Use a common origin on the workpiece to simplify programming and reduce errors.
- Minimize tool changes and table rotations to maintain an efficient workflow.
Training programs incorporate these strategies, preparing operators to optimize machine performance and productivity.
These training initiatives are vital in developing skilled operators who can confidently manage vertical and horizontal machining centers, contributing to the overall success of manufacturing operations.
Best Practices in Operator Training and Skill Development
Operator training and skill development are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient use of vertical-horizontal machining centers. By implementing best practices, organizations can enhance operator capabilities, leading to improved productivity, quality, and safety in manufacturing processes.
Pre-Training Assessments
Conduct pre-training assessments to evaluate the existing knowledge and skills of operators. This step identifies individual skill gaps and allows for tailored training programs. Categorizing trainees based on experience levels, such as “experienced” or “new operator,” ensures that each participant receives instruction at the appropriate level.
Safety as a Priority
Prioritize safety in operator training. Cover comprehensive safety procedures, including pre-operational checks, proper mounting and dismounting techniques, and emergency procedures. Emphasize the importance of personal protective equipment (PPE) and adherence to safety guidelines to prepare operators for maintaining a secure work environment.
Realistic Simulations
Incorporate realistic simulations to allow operators to practice skills in scenarios they are likely to encounter. For example, simulate navigating a virtual warehouse environment to practice maneuvering around obstacles and handling various loads. This practical approach helps operators apply their training to real-world situations.
Gradual Skill Progression
Follow a gradual skill progression, starting with basic maneuvers and advancing to more complex tasks. This ensures operators build a solid foundation before tackling demanding operations. One-on-one instruction provides personalized feedback, addressing individual learning needs.
Encouraging Questions and Feedback
Create an open environment where operators feel comfortable asking questions and providing feedback. Encourage active participation to foster a supportive learning atmosphere, allowing trainers to address concerns or misconceptions promptly.
Monitoring Progress and Performance
Regularly assess operators’ skills and performance to identify areas needing improvement. Provide constructive feedback to help operators track their development and motivate continuous improvement. Repeat training modules or offer additional practice for operators who require more time to master specific skills.
Team Training Exercises
Incorporate team training exercises to simulate collaborative work environments. These exercises involve coordinating with other operators to safely load, unload, or transfer materials, promoting effective communication and teamwork in maintaining a safe workplace. Integrate these exercises into comprehensive simulation programs for enhanced training coherence.
Advanced Training Technologies
Utilize advanced training technologies for an immersive learning experience. Tools like virtual reality headsets and simulation software allow operators to practice skills in a controlled setting, enhancing learning efficiency, especially in complex and hazardous environments.
Train the Trainer Programs
Implement “train the trainer” programs to equip experienced operators with the skills to train new hires effectively. Focus on key competencies such as instructional delivery, coaching, adaptability, and evaluation. Prepare trainers to communicate instructions clearly and adapt to different learning styles.
Continuous Evaluation and Improvement
Regularly evaluate and improve training programs to ensure ongoing effectiveness. Identify areas for additional training, especially as new technologies and industry changes emerge. Adjust training content to keep pace with these changes, ensuring operators remain well-equipped to meet evolving demands.
Structured Onboarding and Ongoing Skill Development
Integrate a structured learning path into onboarding and ongoing training programs. Ensure operators receive comprehensive instruction from the outset and continue developing their skills throughout their careers. Emphasize both technical and non-technical skills training to ensure operators are well-rounded and capable of performing their roles effectively.
Integrating Technology and Innovation in Training
Integrating technology and innovation into training programs for operators of vertical-horizontal machining centers is transforming skill development in the manufacturing industry. This approach offers enhanced training experiences that meet the modern manufacturing demands. However, it’s important to consider potential challenges, such as implementation costs, ongoing technical support needs, and resistance from less tech-savvy operators.
Real-Time Assessments and Feedback
Digital platforms enable real-time assessments and feedback, crucial for continuous skill development. Trainers can provide immediate feedback on performance, allowing operators to quickly identify and correct mistakes. This accelerates learning and boosts skill proficiency and confidence.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
AI and data analytics enhance training programs by providing insights into operator performance. These technologies help develop targeted training interventions. By analyzing learning patterns and outcomes, organizations can refine training content and strategies. AI can also create dynamic learning paths that evolve as operators progress, ensuring continuous skill development.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Adaptive learning systems and learning management systems (LMS) tailor the training experience to individual operator needs. By analyzing performance data, these systems adjust the complexity and pace of training modules, addressing specific skill gaps and learning preferences. This customization leads to higher engagement and improved retention of knowledge.
Interactive Multimedia Content
Multimedia content, such as videos, tutorials, and interactive simulations, enriches training for machining center operators. These tools allow operators to visualize complex concepts and practice skills in a controlled, risk-free environment. Simulations replicate real-world machining scenarios, enabling operators to hone skills without risking equipment damage.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
VR and AR technologies offer immersive training experiences, beneficial for machining center operators. These technologies create realistic environments where operators can practice complex tasks, such as multi-axis machining or advanced CNC programming, with real-time guidance and feedback. The immersive nature of VR and AR enhances engagement and retention. Studies have shown that VR training can improve retention rates by up to 75% compared to traditional methods.
Gamification and Engaging Training Formats
Incorporating gamification elements boosts motivation and engagement among operators. Features like leaderboards, rewards, and progress tracking incentivize active participation. Engaging formats, including interactive quizzes and scenario-based learning, make learning enjoyable and effective, encouraging continuous skill development.
Continuous Learning and Remote Accessibility
Digital training platforms support continuous learning by providing access to training materials anytime and anywhere. This flexibility accommodates diverse schedules and learning paces. Remote accessibility ensures operators can engage in skill development regardless of location, facilitating ongoing education and upskilling opportunities.
Strategic Alignment and Cultural Integration
Successful technology integration requires alignment with organizational goals and a supportive cultural framework. Training programs should support business objectives, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. Organizations must ensure technological solutions are seamlessly integrated into existing workflows, promoting collaboration and knowledge sharing among operators.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
While integrating technology offers numerous benefits, organizations must consider potential challenges. Implementing advanced technologies can be costly, requiring significant investment in equipment and infrastructure. Ongoing technical support is necessary to maintain and update these systems. Additionally, operators who are less familiar with technology may resist adopting new training methods, necessitating additional support and training to ease the transition.
By addressing these challenges and leveraging technological innovations, organizations can transform their training programs, equipping machining center operators with the skills necessary to excel in a rapidly evolving industry.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Training Programs
Evaluating the effectiveness of training programs for operators of vertical-horizontal machining centers is essential to ensure these initiatives meet organizational goals and provide a return on investment. Effective evaluation identifies areas for improvement, aligns training with business objectives, and supports continuous learning within the organization.
Kirkpatrick’s Four-Level Model
Kirkpatrick’s Four-Level Model is a widely adopted framework for evaluating training effectiveness, encompassing:
- Reaction : This level assesses participants’ immediate responses to the training. Use surveys or questionnaires to gauge satisfaction and engagement. Understanding how participants perceive the training can provide insights into its perceived value and areas for immediate improvement.
- Learning : This level measures the knowledge and skills acquired during training. Conduct pre- and post-training assessments, quizzes, or practical tests to quantify learning outcomes. For example, testing operators’ ability to program a machining center before and after the training can highlight skill improvements.
- Behavior : At this level, observe changes in workplace behavior and performance. Collect supervisor reports, peer feedback, or direct observations to determine if operators apply new skills effectively on the job. A scenario could involve monitoring whether operators reduce setup time on machines after training.
- Results : Evaluate the broader impact of training on organizational goals, such as improved productivity, quality, safety, and customer satisfaction. Use metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to assess tangible benefits. For instance, measure the reduction in machining errors post-training to determine effectiveness.
Additional Evaluation Models
While Kirkpatrick’s model is comprehensive, other approaches can provide further insights:
- Context, Input, Process, Product (CIPP) : This model evaluates the relevance, design, implementation, and outcomes of training programs. It ensures training aligns with organizational needs and achieves intended goals. For example, assess whether the training content is relevant to current technological advancements in machining.
- Balanced Scorecard : Integrates various perspectives—financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth—to assess training effectiveness comprehensively. This approach helps link training outcomes directly to business performance metrics.
Steps in Evaluating Training Effectiveness
- Choose the Appropriate Model : Select a model that aligns with the organization’s objectives and the specific goals of the training program. This ensures a tailored evaluation approach that meets the organization’s unique needs.
- Determine Indicators of Training Effectiveness : Define clear and measurable indicators, such as skill acquisition, performance improvement, and return on investment, to assess the program’s success.
- Data Collection Methods : Use various methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations. This approach ensures comprehensive data collection on training outcomes.
- Data Analysis : Analyze the collected data to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Interpret both quantitative and qualitative data to draw meaningful conclusions about the training program’s effectiveness.
Importance of Measuring Training Effectiveness
- Justifying Investment : Demonstrating the value of training programs helps secure leadership support and ensures continued investment in workforce development.
- Improving Processes : Evaluation identifies areas for enhancement, enabling organizations to refine training content and delivery methods for better alignment with business goals.
- Enhancing Learning Culture : Regular evaluation fosters a culture of continuous improvement and learning, encouraging operators to engage in ongoing skill development and career advancement.
Best Practices for Effective Evaluation
- Act on Findings : Use evaluation results to implement changes and improvements, ensuring training programs remain relevant and effective.
- Continuous Evaluation : Make training evaluation an ongoing process to keep pace with industry changes and evolving organizational needs.
- Tailored Evaluation : Customize evaluation methods to align with the specific objectives and context of the training program, ensuring accurate and meaningful insights.
By employing structured evaluation methods, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of their training programs, ensuring they provide tangible benefits to both operators and the organization as a whole.
Industry Trends and Future Directions in Machining Center Training
The landscape of machining center training is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifts in workforce dynamics. Key trends are shaping the future of training programs for operators of vertical-horizontal machining centers, focusing on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and skill adaptability.
- Increased Automation and Robotics Integration : Automation and robotics are transforming machining operations, streamlining production processes, and reducing reliance on manual labor. This shift requires operators to focus more on programming, monitoring, and maintaining automated systems. For instance, automation in tasks like deburring and finishing optimizes efficiency while minimizing physical strain on operators.
- Addressing Workforce Challenges : The manufacturing sector faces a labor shortage, necessitating innovative approaches to attract and retain skilled workers. Companies invest in training programs to upskill employees and appeal to younger generations like Gen Z, who are more receptive to technology and automation. These programs emphasize the long-term career potential in CNC machining, highlighting roles that are less physically demanding and more technologically advanced.
- Modernization of Roles and Responsibilities : As automation becomes prevalent, there is a growing need for operators skilled in programming, troubleshooting, and quality assurance. Upskilling initiatives prepare workers for higher-value tasks, improving job satisfaction and addressing the labor shortage effectively.
- Emphasis on Specialized Technical Skills : The demand for CNC machine operators with specialized skills is increasing. Training programs develop competencies in reading blueprints, understanding machining techniques, and mastering CNC programming. Collaborations between companies and technical schools help bridge the skills gap, ensuring a steady pipeline of qualified operators.
- Adoption of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning : AI and machine learning are being integrated into CNC machining operations, enhancing shop floor operations through predictive maintenance and quality control. For example, AI can predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. Industries like aerospace and automotive have successfully integrated these technologies to enhance precision and reduce errors.
- Focus on Sustainability and Efficiency : Sustainability and efficiency are central to the future of CNC machining. Innovations such as 5-axis CNC machines and automated deburring tools enhance production time, part quality, and sustainability. These advancements help manufacturers reduce waste and optimize throughput, meeting demands for environmentally responsible production processes. Case studies show that companies adopting these technologies have significantly reduced material waste and energy consumption.
- Global Resourcing and Competitive Dynamics : The CNC machining industry is influenced by global market dynamics, requiring adaptation to changes in supply chains and sourcing strategies. As global markets stabilize, local manufacturers can take on more work, provided they have the right skills and processes. Ensuring competitiveness involves meeting world-class standards and maintaining rigorous quality control.
Future Directions
The future of machining center training will see a continued evolution of CNC machine operator roles, with a greater emphasis on programming, troubleshooting, and quality assurance. As technology advances, operators will need ongoing training to keep pace with innovations. The integration of advanced technologies like AI, ML, and robotics will enhance machine capabilities, improve efficiency, and reduce manual intervention. Manufacturers that adapt to these changes will be better positioned to meet future demands while maintaining a competitive edge. Sustainability and quality will remain focal points, driven by customer expectations for high-mix, low-volume production—a manufacturing approach that emphasizes producing small batches of varied products efficiently. Investing in efficiency-enhancing technologies will be crucial for maintaining a competitive position in the global market.
By addressing these trends and future directions, the machining industry can achieve sustainable growth and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are vertical-horizontal machining centers, and how do they differ.
Vertical-horizontal machining centers are advanced CNC machines used in manufacturing for precise metal processing.
- Example : In the aerospace industry, VMCs are often used for creating complex components like turbine blades due to their ability to handle intricate details.
- Example : In automotive manufacturing, HMCs are preferred for engine block production because they allow for machining on multiple sides without repositioning the workpiece.
Why is skill development crucial for machining center operators?
Skill development enhances productivity, quality, and safety in manufacturing environments.
- Technical Proficiency : Operators must be adept in machine programming and maintenance.
- Problem-Solving : Ability to address machining challenges efficiently.
- Adaptability : Keeping pace with technological advancements is essential for optimizing production processes and minimizing downtime.
What are the essential skills required for operating machining centers?
Operators need a blend of technical and soft skills:
- CNC programming proficiency
- Understanding of CNC machines and control systems
- Machine setup and calibration
- Attention to Detail : Ensures precision and quality.
- Safety Awareness : Prevents workplace injuries.
- Mathematical Skills : Necessary for precise measurements and calculations.
- Communication and Teamwork : Important for effective collaboration in manufacturing environments.
What types of training programs are available for machining center operators?
Training programs offered by manufacturers and educational institutions cover:
- Basic Courses : Focus on machine operation and CNC programming.
- Example : Makino offers hands-on training that combines theoretical knowledge with practical experience to optimize machining efficiency.
How can technology enhance training for machining center operators?
Technology enhances training through:
- Digital Platforms : Enable real-time assessments and feedback.
- AI and Data Analytics : Provide insights into performance and learning patterns.
- Adaptive Learning Systems : Create personalized pathways to address skill gaps.
- Interactive Multimedia : Videos and simulations enrich training experiences.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality : Offer immersive environments for practicing complex tasks.
What are some best practices for effective operator training?
Effective training involves:
- Pre-Training Assessments : Tailor programs to individual needs.
- Safety Focus : Comprehensive coverage of protocols and emergency procedures.
- Realistic Simulations : Help apply training to real-world scenarios.
- Encouraging Feedback : Fosters a supportive learning environment.
- Continuous Evaluation : Ensures training remains relevant and effective.
How can the effectiveness of training programs be evaluated?
Evaluate training effectiveness using frameworks like:
- Kirkpatrick’s Four-Level Model : Assesses reaction, learning, behavior, and results.
- CIPP Model : Evaluates context, input, process, and product.
- Balanced Scorecard : Provides comprehensive insights into training outcomes.
What are the latest industry trends in machining center operator training?
Current trends include:
- Automation and Robotics Integration : Addressing workforce challenges.
- Specialized Technical Skills : Emphasizing the adoption of AI and machine learning.
- Sustainability and Efficiency : Technologies like 5-axis CNC machines optimize production.
- Global Resourcing : Influences training approaches to meet evolving market demands.
Get in touch
Contact details.
- Teaching Methods to Improve Classroom Learning and Student Engagement »
Teaching Methods to Improve Classroom Learning and Student Engagement

According to the Indian Government’s latest Annual UDISE+ Report, there are 26,52,35,830 (over 26 crore) students enrolled in schools across India. India is one of the largest education systems in the world. In the ever-evolving and growing landscape of Indian K-12 education, effective teaching methods and strategies play a pivotal role in shaping the future of millions of students.
With a diverse student population of varying socio-economic backgrounds, there are often disparities in learning outcomes across different states and regions. The need for effective teaching methods is more crucial than ever to bridge these gaps.
With a constant demand for quality education, educators in India face unique challenges that require innovative approaches to teaching. This page will delve into the various teaching methods and strategies employed by educators in India’s K-12 schools. The aim is to provide educators, parents, and policymakers with insights into the strategies that can help improve the overall quality of education in India.
By understanding and implementing effective teaching methods and strategies, we can work towards enhancing the educational experience for students and ensuring that they are better prepared for the challenges of the 21st century.
Quick Links
What are Teaching Methods?
Teaching methods are the different ways teachers guide students in learning new things and building skills. They include a range of techniques and strategies that educators use to help students understand and retain information. Nowadays, many teaching methods focus on being more creative and engaging, aiming to boost students’ success and participation. These modern approaches often highlight the importance of hands-on learning, teamwork, critical thinking, and tailoring instruction to meet individual needs.

2 Main Categories of Teaching Methods
Teaching methods can be divided into two broad categories:
- Teacher-Centred Approach – In this approach, the teacher is the central figure who delivers knowledge to a student. This could be done through traditional instruction-based teaching, assessments , and reviews. Here, the teacher is the active giver, and the student is the receiver of knowledge. Methodologies under this approach include different styles of classroom instruction, practice and tests.
- Student-Centred Approach – Under this approach, the student actively participates in gaining knowledge from the teacher, who acts as a facilitator and guide. This approach’s methods include special projects, group participation, class participation, etc., where teaching and assessment is an ongoing process.
Both approaches consist of methodologies that fall on a high-to-low spectrum of technology. Low-tech methodologies like written assessments, classroom teamwork, hands-on projects, analytical papers, etc., hone a student’s ability to process information and develop individual skills. The use of devices, recorded lectures, and the use of the internet for research, project presentations, etc., on the other hand, are on the high-tech side, allowing for a wider range of knowledge.
Extramarks Smart Class Plus – Experience the Power of High-tech School Solutions to Transform Your Classroom.
Importance of teaching methods.
With shrinking attention spans and high digital exposure, the right teaching methods can help students engage with a topic, understand it and be able to see its usefulness in real life. By choosing appropriate and innovative teaching methods, educators can make the learning experience easy and enjoyable for their students and, at the same time, help them develop useful social skills for life. With teaching strategies more aligned to the required outcome, educators can guide their students in mastering the concept and applying it practically in specific situations. Some of these teaching strategies became extremely useful during the pandemic when educators and students could not rely on direct instruction.
27 Teaching Methods and Strategies
To assist you in selecting the best approach for your students, we’ve compiled a list of 27 modern teaching strategies. Let’s take a closer look at them below:
Teacher-Centred Approaches
1) lecture-based learning.

Lecture-based learning is the conventional method of teaching, where a teacher shares knowledge through material and visual cues on a given topic. A student observes, listens, takes notes and tries to process the information shared. The teacher would assign some part of the lecture to answer questions from students on the topic being taught, thus clarifying any doubts. This is a fairly low-tech approach where concepts can be shared via presentations and visual aids, while students lean on their longer attention spans and note-making skills.
Example of Lecture-Based Learning
In a history class, the teacher might present a lecture on World War II, using slides with maps and important events. Students take notes on important dates and figures, and afterwards, the teacher opens the floor for questions. This allows students to ask about things they didn’t understand, making the lesson clearer.
Impact of Lecture-Based Learning
The impact of lecture-based learning includes:
- Foundation of Knowledge: It gives students a strong base of information on various topics.
- Listening Skills Development: Students improve their ability to listen attentively and follow along.
- Critical Thinking: When students ask questions, they engage in critical thinking and learn to analyse information more deeply.
- Focus on Note-Taking: This method emphasises the importance of good note-taking habits, which can be beneficial for future studies.
2) Direct Instruction

Slightly different from lecture-based learning, under the Direct Instruction approach, a teacher can divide the allotted lecture time into three segments. Sharing knowledge, making the students practice the concept under guidance and independent work with the concept by the students. Again, low on technology, this method has the students work on the concept immediately after understanding, thereby strengthening their fundamental grasp of the topic.
Example of Direct Instruction Teaching Method
In a math class that focuses on fractions, the teacher begins by explaining how to add and subtract them. After the explanation, students practice solving problems with the teacher’s support. Finally, they work independently on similar problems to reinforce their understanding. This clear step-by-step process helps students understand the concepts.
Impact of Direct Instruction
- Better Understanding of Topics: By breaking lessons into clear steps, students can understand and use what they’ve learned more effectively.
- Immediate Practice: Working on problems right after the lesson reinforces their knowledge and builds confidence.
- Supportive Learning Environment: The teacher’s guidance during practice encourages students to ask questions and get help, creating a positive classroom atmosphere.
3) Flipped Classroom

An evolved teaching structure where teachers share pre-recorded lectures, and texts to peruse on a given topic as pre-study material. The students work with it at their own pace. Classroom time is then used to discuss understanding, answer questions and engage in activities on the application of the acquired knowledge. Thus flipping the practice of classwork and homework. This method requires both teachers and students to have access to devices and be comfortable with using digital technology for learning.
Example of Flipped Classroom
In a history class, instead of a traditional lecture, the teacher might assign a video on the Civil War for students to watch at home. In class, students could break into groups to debate the causes and effects of the war, using what they learned from the video. This group activity encourages students to share ideas and perspectives, making the learning experience more interactive.
Impact of the Flipped Classroom Method
- Increased Student Participation: When students come to class prepared, they are more likely to engage in discussions and activities.
- Better Critical Thinking Skills: Class time is dedicated to deeper thinking and problem-solving rather than just listening to lectures.
- Tailored Learning Experiences: Students can take their time with challenging topics, allowing them to learn in a way that suits them best.
Read more on Flipped Classroom here !
4) Kinesthetic Learning

A teaching methodology where the teacher moves around the classroom and has the students engage in activities. Also referred to as hands-on learning, this method utilises drawing, building, acting, role-playing and project work in groups or individually to keep students engaged. Students experience the concepts, their challenges and applicability firsthand.
This method is also a great low-tech method that requires only physical props or materials and no digital or virtual setup. Another advantage of this method is that instead of using technology, students learn the concepts using their physical and mental skills, enjoying a total involvement with the concept being taught.
Example of Kinesthetic Learning
In a science class about simple machines, instead of simply discussing the topic, the teacher sets up stations with different materials like levers, pulleys, and ramps. Students rotate through each station, building their own simple machines. They get to see how each machine works and discuss its advantages and disadvantages. By actively participating, students not only understand the concepts better but also learn to collaborate and think critically about the mechanics behind each machine.
Impact of Kinesthetic Learning
- Increased Engagement: Students are more involved in their learning because they’re actively participating in hands-on activities rather than just listening.
- Deeper Understanding: Through direct experience, students can connect theory with practice, leading to a stronger understanding of concepts.
- Improved Collaboration Skills: Working in groups encourages communication and teamwork, helping students learn from one another.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Students face real challenges during activities, allowing them to think critically and develop solutions.
5) Play-Based Learning

Children can learn through unstructured play, for example, by simply going outside and playing with their friends. By playing with sticks, in sandpits, or with toys, children develop motor skills, social skills, and communication skills. This form of play isn’t just for children, though. As adults, we still learn by playing. For example, we develop strategic thinking skills when we play tactical games like football and teamwork skills when we play team games like basketball.
Example of Play-Based Learning
Imagine a classroom where instead of sitting quietly while the teacher lectures, the students are outside playing a game of tag. In this game, they not only have fun but also learn about concepts like speed, strategy, and cooperation. After the game, the teacher gathers the students to discuss what they learned about movement and teamwork. This interactive experience helps reinforce lessons in a way that sticks with them.
Impact of Play-Based Learning
- More Engagement: Kids are more excited to learn when they can play. This keeps their interest and makes learning enjoyable.
- Improved Social Skills: Through group play, children learn how to interact, share, and resolve conflicts, which are important life skills.
- Better Problem-Solving: Play encourages kids to think creatively and find solutions to challenges, helping them in everyday situations.
- Increased Confidence: When children successfully navigate play activities, they build self-esteem and feel a sense of accomplishment.
6) Norman Webb’s Depth of Knowledge
The depth of knowledge methodology is a four-level strategy to ensure a deeper understanding of the concepts being taught.
- The first level requires students to be able to Recollect and Reproduce the concept being taught. This usually is the basic framework such as a formula.
- The second level requires the Application of the said framework to a given problem or scenario. This requires the students to work through the problem in a step-wise approach and apply the formula at the right stage.
- The third level involves Strategic Thinking on the part of the student where they are given more abstract scenarios to work through than the previous stage. Here, they use an individualised approach to solve the problem and might come up with different ways of solving it.
- The fourth level is that of Extended Critical Thinking . At this stage, the students justify and reason out their approach and why they chose it particularly. They go over their considerations and their subsequent solutions to what are sometimes similar to real-world problems.
Example of Norman Webb’s Depth of Knowledge
In a science class, instead of just listening to a lecture about ecosystems, students might work on a project where they create a model of a local ecosystem. They start by recalling facts about plants and animals (level one). Then, they apply their knowledge by arranging the components of their model correctly (level two). After that, they explore how different factors, like pollution or climate change, affect the ecosystem (level three). Finally, they present their findings and explain why their ecosystem model works the way it does, discussing different viewpoints (level four).
Impact of Depth of Knowledge
Using the Depth of Knowledge framework in teaching leads to several positive outcomes:
- Better Student Engagement : Students are more involved in their learning, as they move beyond simple memorisation to active participation and problem-solving.
- Stronger Critical Thinking Skills : Classroom activities focus on higher-level thinking, encouraging students to analyse and evaluate information.
- Personalised Learning : This approach allows students to learn at their own pace. They can take the time they need to understand complex topics, ensuring no one gets left behind. Learn more on personalised learning .
7) Summative Assessment

These are the standard end-of-unit tests that check the degree to which the students have understood the topics covered and how to apply them. Educators assign grades to students based on their performance through this assessment. Though sometimes stressful for students, these are good markers of a student’s broad understanding of the topics covered in the classroom. This tool can be completely low-tech or be aided by technology, at the discretion of the school and the educator.
Example of Summative Assessments
In a history class, instead of a typical test, students might be asked to create a project that showcases what they’ve learned about a particular historical event. They could work in groups to create a presentation or a timeline, using both visual elements and written summaries. This allows students to express their understanding creatively and collaboratively, rather than just through multiple-choice questions.
Impact of Summative Assessments
- Clear Understanding of Knowledge: These assessments help teachers see what students know and what areas may need more focus.
- Encourages Accountability: Students take responsibility for their learning as they prepare for these assessments, which can motivate them to engage more with the material.
- Guides Future Teaching: The results from these assessments can inform teachers about which topics need to be revisited in future lessons, ensuring that everyone is on the right track.
Read more about Summative Assessments here !
8) Formative Assessment

In ways the opposite of Summative assessment, the formative assessment method works on gauging the student’s grasp on the topic being covered at the end of class and before moving on to the next topic. This helps educators identify any gaps in the lessons and, at the same time, inform them if certain students need more personalised or one-on-one time for a better understanding of the concept. This method is extremely low-tech in the form of class tests or a viva at the end of a lesson.
Example Activity for Formative Assessment
In a math class, the teacher might ask students to solve a problem on the board after teaching a new concept. Instead of just lecturing, the teacher encourages students to work in pairs to discuss their methods and solutions. After a few minutes, they share their answers with the class, allowing the teacher to see who understands the material and who might need more support. This interactive session helps students clarify their thoughts and learn from each other.
Impact of Formative Assessment
The use of formative assessment can lead to several positive outcomes:
- Improved Student Engagement : Students feel more involved in their learning and are encouraged to actively participate in discussions.
- Better Understanding of Concepts : By identifying gaps in knowledge right away, teachers can adjust their lessons to address these issues, ensuring students understand the material before moving forward.
- Targeted Support : Teachers can provide tailored assistance to those who need it, helping each student learn at their own pace.
Read more about Formative Assessment here !
Student-Centred Approaches
9) blended learning.

As the name suggests, this method is the middle ground between traditional lecture-style teaching and the online technology-driven style of studying. This hybrid teaching strategy combines classroom instruction, digital research, use of technology for assessment and project work.
While being physically in a classroom, teaching material can be accessed virtually through smart classroom devices . Teachers use technology to teach or explain concepts and submissions are made through devices.
This method allows for both in-person interaction of the students with their teachers and peers and, at the same time, uses collaborative tech for projects and assessments. The students can further seek individual time with their educators for clarifications or inputs, making this a more Student-centric approach.
Example of Blended Learning
In a history class, instead of just listening to a lecture, students might watch a documentary on a historical event and then discuss it in groups. The teacher can provide guidance and answer questions while students work together to explore the topic further. This method encourages collaboration and allows students to learn from each other while still benefiting from direct interaction with their teacher.
Impact of Blended Learning
- Improved Student Engagement: Students are more involved in their learning because they can connect with both their peers and the material in different ways.
- Boosted Critical Thinking Skills: With a mix of activities, class time can focus on discussions and problem-solving instead of just lectures.
- Customised Learning Experiences: Each student can move at their own pace, giving them the chance to revisit tricky topics whenever they need.
Read more about Blended Learning here !
10) Differentiated Instruction

Initially devised to ensure equal education to children of all backgrounds and learning needs, the differentiated instruction method promotes an inclusive learning environment for all students. Based on the premise that different students learn differently, this strategy utilises several teaching tools such as books, activities, prompts and visual aids to connect with all learners. Assessments are also made through a combination of tools, giving all students of a mixed-ability class a fair opportunity to apply their learnings.
Example of Differentiated Instruction
In a history class, instead of everyone reading the same textbook chapter, the teacher might create different activities. Some students might read a text, while others watch a video or create a timeline of events. They could also work in groups to discuss what they learned and present their findings to the class. This way, students can choose the method that works best for them, making the lesson more relevant and engaging.
Impact of Differentiated Instruction
- Increased Engagement : When students can choose how they learn, they are more likely to be interested and involved in the material.
- Improved Understanding : By using different methods, students have more chances to understand complex concepts in a way that makes sense to them.
- Support for Mixed Abilities : This approach allows teachers to effectively reach students of all skill levels, ensuring that everyone is included in the learning process.
Read more on best practice for differentiated instructions here !
11) Inquiry-based Learning

Largely a student-centric teaching method, Inquiry-based learning requires a student to explore and investigate a topic, seeking answers through multiple sources and active research. The teacher plays the role of a facilitator, guiding the student through the process. An educator’s focus in this method is on the direction of enquiry, resources used, as well as the process followed.
The student, by actively engaging, gets in-depth knowledge on the subject. They enjoy being able to pursue their interest while the educator instils the important skills of critical thinking in the student.
Example of Inquiry-based Learning
For instance, in a history class about ancient civilisations, students could be assigned to research different cultures. Instead of simply listening to a lecture, they might use books, documentaries, and online resources to gather information. They would then present their findings to the class, discussing their insights and answering questions from their peers. This way, students learn not just from their own research but also from the perspectives of others, making the learning experience richer.
Impact of Inquiry-based Learning
- Active Student Participation: Students take charge of their learning, which keeps them engaged and interested in the subject matter.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: As students ask questions and seek answers, they develop their ability to analyse information and draw conclusions.
- Collaborative Learning: Students work together, sharing ideas and learning from one another, which enhances their teamwork skills.
Read more about Inquiry-based learning here !
12) Expeditionary Learning

Literally meaning learning-through-expeditions, this teaching method involves students being able to apply concepts learned in the classroom to practical, real-world scenarios. This could be in the form of field trips, outdoor group activities, nature exploration, or real-life experiments, giving students a holistic experience. Students gain practical experience and, at the same time, the opportunity to work on multifaceted problem solutions. This helps them build collaborative skills, teamwork and key personal attributes for life.
Example of Expeditionary Learning
For instance, in a science class focused on environmental studies, students might take a trip to a local river. While there, they collect water samples to test for pollution levels. They work in groups to analyse the data and discuss the implications of their findings. This hands-on experience not only reinforces what they learned in the classroom but also encourages teamwork and critical thinking as they work through real-world environmental issues.
Impact of Expeditionary Learning
- Greater Student Engagement: Students become more involved in their learning when they see how it connects to the real world. This active participation makes learning more enjoyable.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: By facing real challenges during their expeditions, students enhance their ability to think critically and find solutions to complex issues.
- Strengthened Teamwork Abilities: Working together on projects helps students develop teamwork skills, which are crucial for their future careers and personal lives.
- Deeper Understanding of Concepts: Applying classroom lessons to practical situations helps solidify their understanding, making the learning more meaningful and memorable.
13) Personalised Learning

A fairly new approach, the Personalised Learning Strategy allows students to create their own study plan based on personal interest and familiarity with the concept.
Also known as Competency-based Learning , Students can work at their own pace and finish lessons as per their own competency with the subject. Teachers engage regularly on a one-on-one basis to address doubts and questions, suggesting useful resources, practice tests and giving specific assessments.
This is progress and an interest-based approach. On one hand, it allows students to work beyond their grade and, on the other, it helps students facing difficulty to catch up with their class. Strongly student-centric, this approach is fairly high-tech as it requires students to access extra learning material beyond the classroom.
Example of Personalised Learning
In a math class, instead of following a set curriculum, students might choose to focus on topics they find challenging or exciting, like geometry or algebra. The teacher would provide tailored support, helping them work through problems and guiding them to additional resources. This flexible approach enables students who are struggling to catch up while allowing those who excel to work ahead. It is a student-centred method that often involves using technology to access extra learning materials beyond what is taught in class.
Impact of Personalised Learning
- Increased Engagement : Students are more motivated because they are studying topics that interest them, leading to greater involvement in their learning.
- Greater Understanding : Since students learn at their own pace, they can take the time they need to grasp complex subjects, resulting in deeper knowledge.
- Stronger Relationships : One-on-one interactions with teachers build trust and support, making students feel more comfortable seeking help.
- Better Skills Development : As students work on their own, they develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for their future.
Read more about Personalised Learning here !
14) Game-Based Learning

As the name suggests, this teaching strategy uses games (digital or non-digital) to help students master soft skills and, at the same time, build a better understanding of the concept application. Extremely engaging for students, this method keeps them going with the possibility of winning points or badges, fulfilling quests and using their skills in a gamified environment. Students internalise insights without a lot of effort through the immersive aspect, inherent to games. They also learn to make choices, problem-solve and think independently to navigate various stages of the game.
Example of Game-Based Learning
In a history class, instead of just reading from a textbook, students might play a simulation game where they step into the roles of historical figures. They work in groups to make decisions based on the challenges those figures faced, such as leading a country during a war or managing resources during a crisis. Through this interactive experience, students gain a deeper understanding of historical events and develop teamwork and critical thinking skills.
Impact of Game-Based Learning
- Increased Engagement: Students are more interested in learning because the games are enjoyable and interactive. This keeps them motivated and eager to participate.
- Better Understanding of Concepts: By applying what they’ve learned in a game setting, students can see how different ideas connect, making the learning experience more meaningful.
- Development of Problem-Solving Skills: As students encounter challenges in the game, they practice figuring out solutions, which enhances their ability to think critically and tackle real-life problems.
Read more on Gamification in Education .
15) Group Learning

A teaching strategy that fosters collaboration, Group Learning requires students to work in groups towards a common goal. It teaches them valuable skills such as teamwork, insight sharing, building on ideas, active participation, working towards a common goal and ownership.
Also known as Collaborative Learning, it requires students to research, discuss and divide tasks before collectively arriving at the outcome. The outcome is then shared with the teacher and the rest of the class in the form of a presentation.
This method also teaches students to be open to critique by their peers and answer questions on the process and choices made. The teacher’s role here is that of a guide, supervising the process and providing feedback on the outcome.
Example of Group Learning
In a history class, instead of just listening to a lecture, students might form groups to explore different aspects of a historical event, like the Dandi March. Each group could focus on a specific area, such as key figures, major events, or important laws. They would research their topics, share their findings with one another, and then create a presentation to teach the rest of the class. This collaborative effort not only helps them understand the material better but also allows them to practice presenting and answering questions from their peers.
Impact of Group Learning
- Improved Communication Skills: Working in groups helps students learn to express their ideas clearly and listen to others, which enhances their overall communication abilities.
- Stronger Teamwork Abilities: As students collaborate, they gain experience in working with others, learning how to negotiate roles and responsibilities within the group.
- Deeper Understanding of Content: When students discuss and teach each other, they reinforce their understanding of the material, making it easier to remember and apply.
- Increased Confidence: Presenting their work and receiving feedback boosts students’ confidence in their knowledge and abilities.
Read more about Collaborative Learning here !
16) Role Playing

Slightly different from game-based learning and group learning, this teaching method assigns specific roles to the students as they work together in a structured manner. Role-playing helps students build empathy while developing an understanding of real-life scenarios and situations.
This method ensures active participation from students. By rotating different roles, students can begin to gain deeper insights into the dynamics of teamwork, responsibility and relationships. The teacher does the job of a facilitator in this learning technique, which is also known as Cooperative Learning .
Example of Role Playing
In a social studies class, students might role-play as different community members during a town hall meeting. Some might represent local business owners, while others take on the roles of parents, teachers, or government officials. As they discuss a new school policy, students must listen to each other’s viewpoints and negotiate solutions. This activity allows them to understand various perspectives and practice important communication skills. The teacher guides the discussion, helping students reflect on the importance of collaboration and conflict resolution.
Impact of Role Playing
- Increased Engagement: Students are more involved in the learning process because they actively participate and relate to the scenarios.
- Empathy Development: By stepping into different roles, students learn to appreciate others’ feelings and viewpoints, enhancing their social skills.
- Improved Teamwork Skills: Role-playing teaches students how to work effectively with others, preparing them for future collaborative environments.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Students learn to think critically as they navigate real-world situations and find solutions collectively.
- Practical Application of Knowledge: This method helps students apply what they’ve learned in a hands-on way, making it easier to remember and understand complex topics.
17) Project-Based Learning

Project-based learning can either be a group activity or an individual project. In this method, students apply concepts learned in the classroom to solve a problem or deliver a specific outcome. These projects can be multidisciplinary and might require students to use concepts learned in one subject to deliver a desired outcome in another field.
Being long-term and in-depth in nature, this teaching method helps students hone their soft skills, enhance their critical thinking and practice concept applicability. This is a student-centric approach, with the students playing an active role in choosing, designing and executing the projects.
Example of Project-Based Learning
For instance, in a history class, students might work on a project where they research a historical event. They could create a documentary video that includes interviews, visuals, and narratives. By collaborating, students will learn how to organise their research, share tasks, and present their findings creatively. This not only helps them understand history better but also teaches them skills like communication, organisation, and teamwork.
Impact of Project-Based Learning
- Active Engagement: Students are more involved in their learning, which keeps them interested and motivated.
- Skill Development: They improve their problem-solving and critical thinking skills by facing real challenges.
- Collaboration: Working in groups helps them learn how to communicate effectively and work as a team.
- Application of Knowledge: Students see how what they learn in class can be used in real life, making their education feel more relevant.
Read more about Project-Based learning here !
18) Thinking-Based Learning

This teaching method pushes the students towards ‘Critical and Creative thinking’. Thinking-based learning gets the students to understand the ‘Why’ behind the application of the concepts learned in the classroom. This is a kind of post-analysis style of learning where once the students have applied their learnings to an actual project, they begin to analyse what worked (or didn’t) and why. This helps clarify and strengthen the theoretical knowledge of students in practical scenarios.
Example of Thinking-Based Learning
In a math class, instead of just solving equations, students might be asked to plan a budget for a community event using their math skills. After presenting their plans, they reflect on how their calculations worked out—whether their estimates were accurate or if adjustments were needed. The teacher guides them to think about why certain calculations succeeded and where they may have gone wrong. This encourages them to see math as more than just numbers but as a tool for real-world problem-solving.
Impact of Thinking-Based Learning
- Deeper Understanding of Concepts: Students learn not just the “how” but the “why” behind the lessons, leading to a more thorough understanding of the material.
- Improved Critical and Analytical Skills: Analysing their work helps students think critically about their decisions, allowing them to approach problems from different angles.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: By reflecting on what worked and what didn’t, students become better at finding solutions and improving their methods over time.
- Increased Engagement and Interest: Applying their knowledge to real-life scenarios makes learning more engaging and meaningful, motivating students to dive deeper into the subject matter.
Also read: Problem-Based Learning
19) Discussion-Based Learning

Discussion-based learning can be used in smaller groups or as a directed classroom discussion strategy. The educator picks a concept and plays the role of a moderator, moving the discussion along, finding the gaps and leading students to a broad conclusion.
A key method to build quick information processing, collaboration, building evidence and sharp reasoning skills amongst students. Discussion-based learning also helps students build their listening and communication skills.
Example of Discussion-Based Learning
In a history class, instead of simply listening to a lecture on the causes of World War I, students are asked to participate in a group discussion. The teacher presents key events, and the students debate the impact of each event on the war’s outbreak. Through this discussion, they exchange ideas, challenge each other’s opinions, and support their arguments with facts from their readings. This not only deepens their understanding of the topic but also strengthens their reasoning and communication skills.
Impact of Discussion-Based Learning
- Faster Information Processing: Students learn to quickly analyse and process information during the discussion, sharpening their ability to grasp complex ideas in a short time.
- Better Collaboration: Students work together, sharing different viewpoints and learning to build on each other’s ideas, which helps improve teamwork.
- Stronger Reasoning Skills: By defending their opinions and analysing others’ perspectives, students develop clearer, more logical reasoning abilities.
20) Flexible Seating

Specifically useful teaching strategy for younger kids who are just starting school at the primary level. Young children find it difficult to remain in the structured seating of a formal classroom, making them fidgety and easily attention fatigued.
Moving around and engaging kinaesthetically in the learning process with the option of different seating such as beanbags, floor seating, and different levels of stools and chairs, keeps their attention on the lesson being taught instead of fussing about having to be still in one place.
Example of Flexible Seating
In a reading class, instead of having all the students sit at desks, the teacher might let some students sit on floor mats while others choose beanbags or stools. As the teacher reads a story, the children are allowed to change positions as they listen. After the story, the students gather in small groups around the classroom, discussing the plot or acting out parts of the story in their chosen seating spots. This helps them stay focused and makes the lesson more interactive.
Impact of Flexible Seating
- Increased Focus and Engagement: When students are comfortable and allowed to move around, they tend to pay more attention to the lesson.
- Reduced Restlessness: Flexible seating reduces the need for children to fidget, making the classroom environment calmer.
- Improved Participation: The option to choose where to sit gives students a sense of control, making them more willing to participate in class activities.
- Better Collaboration: Different seating setups encourage group work, helping students communicate and work together more effectively.
21) Active Learning

Active learning is a teaching strategy that puts the student into the driving seat in a classroom lesson. This is a combination technique where initially, an educator outlines and explains the concept and then allows the students to switch roles.
With activities such as peer-to-peer teaching, the muddiest point technique, and reciprocal questioning, the educator lets the students play an active role in clarifying doubts for their peers, explaining the toughest points to each other and playing the role of the teacher by questioning other students to strengthen their understanding of the concept.
Not only can this teaching method be very engaging for the students, but it also helps them break down complex concepts in a way that is easier for them to retain.
Example of Active Learning
In a math class, instead of simply listening to the teacher solve problems, students might work in pairs to teach each other how to solve algebraic equations. They would then explain to the group the steps they took to solve a problem. By discussing what they found challenging and asking questions, they reinforce their learning. The teacher is there to guide and clarify when needed, but the focus is on student collaboration and understanding.
Impact of Active Learning
- Higher Engagement: Students get more involved when they explain ideas themselves rather than just listening.
- Stronger Critical Thinking: It encourages students to think through problems and communicate their understanding, which deepens learning.
- Better Retention: Breaking down complex ideas and discussing them with peers makes it easier for students to remember and apply concepts in the future.
Read more about Active Learning here !
Extramarks Smart Class Plus: Empowers Your Students with Active and Interactive Learning to Aid Deeper Knowledge.
22) peer instruction.

Peer Instruction is a way of learning where students explain what they’ve learned to each other. This helps them understand the material better and see if they really get it.
Example of Peer Instruction
In a math class, instead of just listening to the teacher, students are given a problem to solve on their own. Afterward, they talk with a partner to explain how they solved it. Each student shares their method, and together they figure out which way is correct. The teacher steps in only when needed, letting the students discuss most of it.
Impact of Peer Instruction
- More Engagement : Students get more involved because they actively teach and learn from each other.
- Better Understanding : Explaining things to others helps students understand the material more clearly and see where they might be confused.
- Improved Communication : Talking with peers about their ideas helps students get better at explaining things and understanding different viewpoints.
23) Response to Intervention

A method that promotes a more inclusive classroom environment, this teaching strategy focuses on frequent intervention and learning assessment for students with different learning needs. As a response to the increased intervention, students find it easier to keep up with the rest of the class. Another advantage of this method is that it reduces the stress of assessment on all students due to their informal and frequent nature.
Example of Response to Intervention
In a math class, the teacher may notice that some students are having difficulty understanding fractions. Instead of waiting until the next big test to address the issue, the teacher uses the RTI method by offering short, targeted lessons on fractions during class. These lessons are designed to help struggling students without singling them out. The teacher also provides practice problems and checks in regularly to see how students are progressing. Over time, the students get a better grasp of the material and catch up with the rest of the class.
Impact of Response to Intervention
- Improved Student Performance: Students who receive frequent, targeted help are able to better understand difficult topics and keep up with their classmates.
- Reduced Anxiety Around Assessments: Since assessments are more frequent and informal, students feel less pressure, making it easier for them to perform well.
- Personalised Learning Support: RTI allows teachers to give individualised attention to students based on their specific learning needs, helping them succeed in areas they struggle with.
- Inclusive Classroom Environment: With RTI, all students feel supported, and no one is left behind, fostering a classroom where everyone has an opportunity to learn and grow.
24) Convergent and Divergent Thinking

Two countering methods to enhance problem-solving through critical, strategic and creative thinking amongst students. Convergent thinking uses multiple pieces of information that converge on a single solution, while divergent thinking uses a single prompt to generate multiple solutions to the situations.
The first is a function of sifting through all information to arrive at the most effective solution, while the second is the function of attacking a problem from all angles to find as many solutions as possible. Both have a place in real-life scenarios, preparing students to handle real-world challenges effectively.
Impact of Convergent and Divergent Thinking
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills : Students learn to look at problems from different angles and find effective solutions.
- Increased Creativity : Encouraging students to come up with various ideas helps them feel more confident in sharing their thoughts.
- Better Teamwork : Working together on projects helps students communicate and listen to each other, which improves collaboration.
- Stronger Critical Thinking : Analysing information and deciding on the best solution teaches students how to think critically and make good decisions in real life.
25) Reciprocal Teaching

Different from the reciprocal questioning tool under Active Learning, the Reciprocal Teaching method is a tool to promote reading amongst the students. It asks students to predict, paraphrase and summarise the text they are studying.
Engaging students in activities like predicting the course of a plot breaks a lengthy read into many interesting twists and turns, building creative thinking and imagination amongst students. This strategy can also be applied to subjects like maths where students find it difficult to break down text-based mathematical problems. Paraphrasing the problem in their language gives the students a means to work out the solutions.
Example of Reciprocal Teaching
In a literature class, instead of just reading a chapter from a novel, students could work in groups to predict what might happen next in the story. Each group would take turns sharing their predictions and discussing why they think those events might occur. This active participation encourages them to think deeply about the characters and plot, leading to a richer understanding of the material.
Impact of Reciprocal Teaching
The impact of the reciprocal teaching method includes:
- Improved Comprehension Skills: Students learn to understand and analyse texts as they predict and summarise the material.
- Increased Engagement: By participating in discussions and activities, students become more involved in their learning, making it enjoyable and interactive.
- Development of Critical Thinking: This method encourages students to think critically about what they read, allowing them to make connections and draw conclusions.
- Confidence in Learning: As students paraphrase and discuss texts, they gain confidence in their ability to understand and articulate complex ideas.
26) Interdisciplinary Teaching

This teaching strategy requires students to take learnings from one subject and apply them to another real-world problem, of a different subject. Climate change with geography, mathematics with music, and physics with carpentry are just a few examples of this. The interdisciplinary teaching method helps students widen the scope of the concepts they are learning and how a lot of them can be practically applied to diverse problems thus finding lasting solutions. Tapping into a student’s interest and creativity makes this strategy strongly student-centric.
Example of Interdisciplinary Teaching
In a science class, students could study the importance of ecosystems while also learning about art. They might go on a nature walk to observe different plants and animals, then create a piece of art inspired by what they saw. This project would allow students to express their understanding of ecological concepts through creativity, connecting science and art in a meaningful way.
Impact of Interdisciplinary Teaching
- Broader Understanding of Concepts: Students gain a deeper understanding of subjects as they see how they relate to each other and the real world.
- Increased Engagement: By applying their learning to practical problems, students become more interested and motivated to participate.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Working on interdisciplinary projects fosters collaboration, as students often need to communicate and work together to find solutions.
Also read : Interdisciplinary Approach in Teaching
27) Asynchronous Learning

Simply put these are blocks of curriculum and learning that are stand-alone in an academic year. They are not time-bound or required to be in any sequence of learning.
With the pandemic, the education sector was caught unprepared. To ensure the teaching and curriculum don’t come to a complete stop in the event of a temporary challenge, it is a good practice to have certain stand-alone pieces that can be injected whenever the need arises.
Whether it is something as basic as a student or teacher illness or simply reduced school days because of inclement weather, these projects (such as portfolio work, recorded lessons or online discussion boards) can be assigned to be done at home or at a student’s own pace during an unforeseen break.
Example of Asynchronous Learning
In a math class, instead of following a strict lesson plan, students might work on a project where they design a budget for a fictional event. They would research costs, calculate expenses, and present their budget to the class. This project allows students to apply their math skills in a real-world context and collaborate with classmates to solve problems.
Impact of Asynchronous Learning
- Flexibility in Learning: Students can complete assignments when it suits them, which helps them balance their studies with other commitments.
- Encourages Independence: As students manage their own learning, they develop skills in self-discipline and time management, preparing them for future academic and professional challenges.
- Enhanced Understanding: With the ability to revisit materials as needed, students can deepen their grasp of complex concepts and reinforce their learning at their own pace.
Read more about Asynchronous Learning here !
Benefits of Using Different Teaching Methods
It is easy to be overwhelmed by a large list of new-age teaching methodologies. With large curriculums, it can seem like a lot of extra work. But remember that a lot of these methods are just building on existing strategies that teachers might already be using. Additionally, using appropriate teaching methods might make a teacher more effective and their job a little easier.
Essential Teaching Strategies You Shouldn’t Ignore
- Use Technology : Incorporating technology in the classroom is important. Tools like Extramarks Smart Class+ , which give you access to various interactive education modules and online videos can make lessons more interesting and help students learn in different ways.
- Don’t Just Use Textbooks : While textbooks are helpful, relying only on them can limit how much students learn. Using a mix of materials, like articles, videos, and hands-on projects, can keep students engaged and cater to different learning styles.
- Include Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) : It’s not just about academics. Teaching social skills, like teamwork and empathy, is essential for students’ overall growth and helps them connect better with their peers.
- Avoid Yelling : Yelling can create a negative classroom environment and make students feel scared or anxious. Using calm communication encourages a more positive atmosphere where students feel safe to participate.
- Be Fair to All Students : Every student deserves respect and equal chances to succeed. Treating everyone fairly builds a supportive classroom where students can thrive.
- Move Away from Teacher-centred Learning : Focusing only on lectures can be boring. Encouraging group work, discussions, and student-led activities makes learning more interactive and fun.
- Reconsider Popcorn Reading : Popcorn reading, where students read aloud randomly, can be stressful. Allowing students to read in smaller groups or prepare ahead of time can help build their confidence.
- Don’t Punish the Whole Class : Punishing the entire class for one person’s behaviour can create resentment. It’s better to address issues with individuals to keep a positive environment.
- Skip Pre-Written Notes : Giving students pre-written notes can prevent them from engaging with the material. Encouraging them to take their own notes helps them listen actively and remember better.
Final Words:
Teaching is an age-old profession with an inherent process and deep knowledge garnered through centuries of best practices. However, many new methodologies have evolved with changing times and morphing classrooms. Educators now have many tools to experiment with for better effectiveness in the classroom.
Every teacher wants their lessons to be engaging and students to be able to retain and use the learnings most effectively. Based on the principle that every educator and student is unique, the methods allow educators to pick a combination of different strategies most suitable for a given subject, topic, and classroom demographics.
The key to using these methods effectively is to identify the goal of the lesson, and then pick a couple of methods that work well together. Be sure to discuss the methods with your colleagues and pick the ones that align most with the mission of your institute and your personal style of teaching. Be open and flexible, making this process as much fun for you as it will become for your students.
Last Updated on October 25, 2024

More Recent Blogs

From Classroom Success to Career Growth: Key Strategies...
Teaching, like every other career path, demands continuous growth and advancement. Most teachers are motivated […]

A Guide to Parent-Teacher Communication Strategies for K-12...
As a school leader or teacher in India’s K-12 ecosystem, your role in fostering effective […]

Leveraging Classroom Tests For Effective Teaching And Learning
Classroom tests or topical assessments are a common device used to evaluate students’ understanding of […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Found the blog insightful?
Get such ed tech insights delivered weekly to your inbox, for free. Subscribe to our newsletter.
- Teaching App
- Live Classes
- Learning App
- School Solutions
- STAR Program
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- Solved Board Paper CBSE
- Solved Board Paper ICSE
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- ICSE Class 12
- Sample Paper CBSE
- Exam Weightage CBSE
- CBSE Class 12 Solution
- Terms of Use
Transform Your School With Extramarks

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Career readiness skills, often called career readiness competencies, are the skills, experiences, and attributes that prepare you for a successful career. A competency is a skill, task, strength, or personal quality that allows you to do a specific job role well. The 8 examples of career readiness skills include:
Collaboration and Communication: These skills involve working in concert with others, especially in a diverse team setting. They also include the aptitude for conveying ideas and information effectively verbally and in writing. Cognitive Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: These skills involve evaluating information and
The technique involves the periodic assessment (via surveys) of employee attitudes and feelings. The results are conveyed to organizational stakeholders, who may want to take the organization in a particular direction. Another tool is the team-building technique. Because many if not most tasks within an organization are completed by small ...
Each stage is designed to give you the ability to demonstrate a greater awareness of critical analysis than in the previous stage. Furthermore, the ability to think, read and write critically will help you to solve problems more creatively, which is not only an academic skill, but also one of the top employability skills prized by employers.
For example, here are the options we provided to gauge efficiency in the "structured problem solving" DELTA (within the critical thinking skill group): Option 1: I can solve day-to-day problems easily, but I often need assistance with complex problems ; Option 2: I can break larger problems into parts and find solutions for them
Abstract. Purpose: This article presents the results of a training program in emotional intelligence. Design/methodology/approach: Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves two important competencies: (1) the ability to recognize feelings and emotions in oneself and others, and (2) the ability to use that information to resolve conflicts and problems to improve interactions with others.
Such learning activities combine knowledge of patient assessment, critical thinking, and evaluation skills (Ferreri and O'connor, ... The results showed that different learning patterns can predict student learning outcomes. ... The results of the study show that employability development and curriculum planning have the deepest impact on ...
Arguably, the best quality of data measuring the skills of workers involves the direct assessment of skills. One particular survey that uses this direct method of skill assessment is the PIAAC survey, however, it took seven years (from 2011 to 2018) to conduct the first wave of the survey.
Implementing the decisions made arising from critical thinking must take into account an assessment of possible outcomes and ways of avoiding potentially negative outcomes, or at least lessening their impact. Critical thinking involves reviewing the results of the application of decisions made and implementing change where possible.
This paper explores some of the trends and predictions in the rapidly changing world of work and proposes a re-worked definition of employability (based on Yorke's widely-accepted definition ...
Soft skills create a positive and functional work environment, but aren't enough alone to perform job duties. Hard skills are necessary to achieve the work tasks or goals but don't indicate how you interact with others. Both skill types combined will paint a better picture of your work style. Technical skills
Creative and Critical Thinker received a mean score of 3.95, classified as "High." This indicates that graduates are proficient in applying creative and critical thinking skills. They are capable of analyzing complex problems and developing innovative solutions, which are crucial for adapting to and excelling in dynamic environments.
Skills assessment and gap analysis At the heart of any effective workplace skills plan is a thorough understanding of where your organization stands. This component involves taking stock of your current workforce's skills and comparing them to what you'll need in the future. Imagine you're running a marketing agency.
Rather, critical thinking instruction should be explicitly infused in all courses so that critical thinking skills can be developed and reinforced in student learning across the curriculum. The use of a common approach with a common language allows for a central organizer and for the development of critical thinking skill sets in all courses.
Employability is related to work and the ability to be employed, such as: The ability to gain initial employment; hence the interest in ensuring that 'key competencies', careers advice and an understanding about the world of work are embedded in the education system [1]; The ability to maintain employment and make 'transitions' between jobs and roles within the same organization to meet new ...
Reading books aloud invites students into the world of literature and informational texts and creates a community of active listeners who carefully listen, think, and talk about books. By adding interactive elements to the traditional read-aloud, teachers can deepen students' comprehension, expand their vocabulary, and strengthen critical thinking skills, all while building a love of reading ...
3.9 Evaluation of Database Storage and Management of Records. Figure 9 shows the evaluation of administrative staff in relation to the system, from a technological perspective, adequately storing and managing records within a database. This question seeks to understand administrative staff's satisfaction with the underlying technological ...
A commitment to continuous learning involves a proactive approach to acquiring new skills and expertise, enhancing employability and opening up opportunities for career growth. ... and critical thinking are valued skills that enhance communication and collaboration within teams. By mastering these skills, machining center operators can ...
The third level involves Strategic Thinking on the part of the student where they are given more abstract scenarios to work through than the previous stage. Here, they use an individualised approach to solve the problem and might come up with different ways of solving it. The fourth level is that of Extended Critical Thinking. At this stage ...