- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to make a business plan
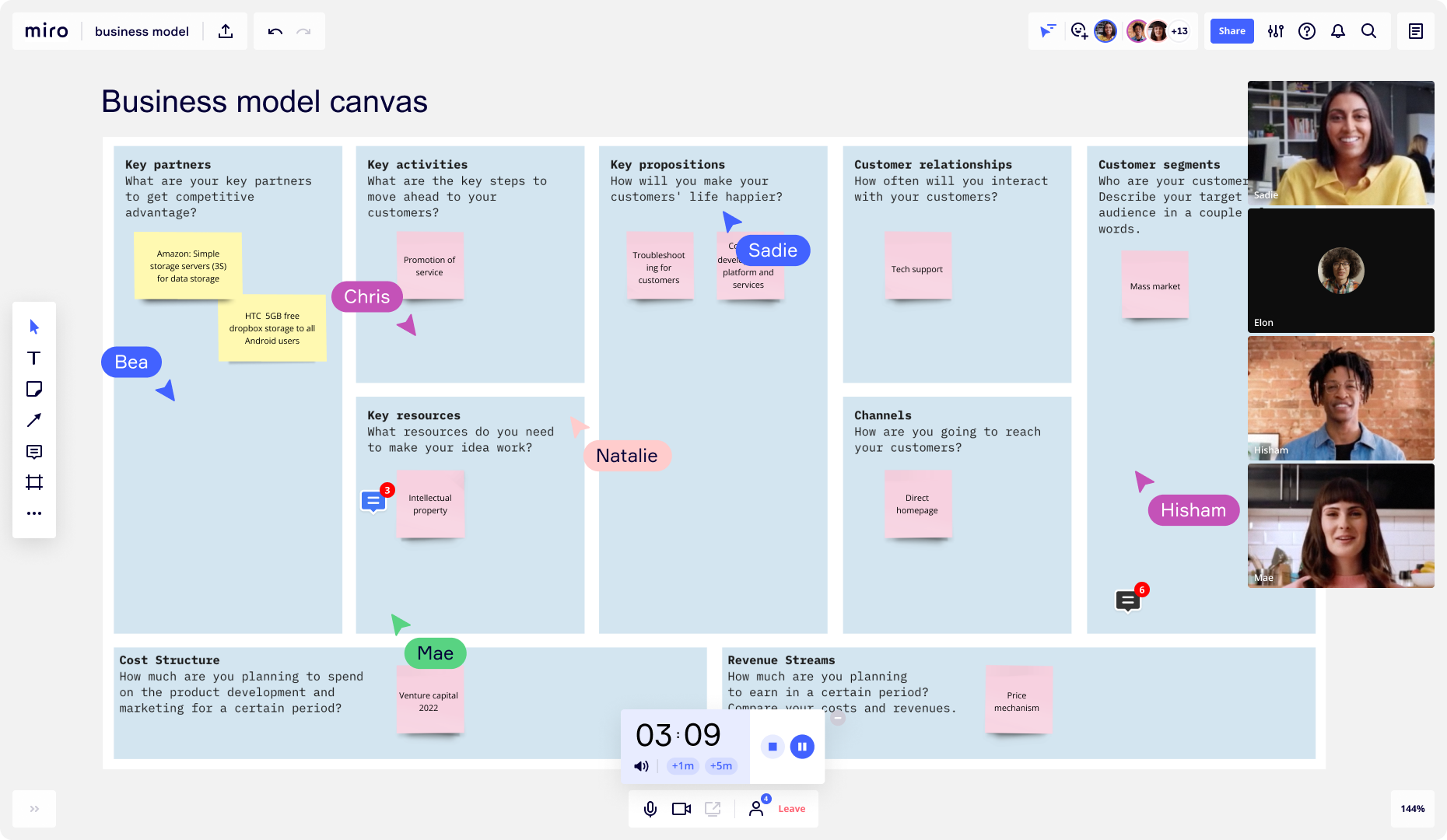
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » business ideas, the definitive guide to writing a startup business plan.
Our guide covers all the components of your startup business plan and explains why startups have unique business plan needs.

To understand what should be included in a business plan, you have to understand who the plan is for and what stage of your business you’re in. If you’ll be taking a business plan to a financial institution as part of a loan application, you’re going to want a more traditional plan. These tend to be on the longer side and should be as detailed as possible, without getting too technical.
If you’re in the early planning stages of your business or just want something to show to a few angel investors, you might consider a startup business plan format, which will be more of a summary of key points. That might only be one page long but should still hit on all the major highlights and goals of the business.
According to the Small Business Administration, the length of your business plan should be long enough to accomplish three goals: (1) excite the financing source, (2) prove that you truly understand the market, and (3) fully detail the execution strategy.
Regardless of length, your business plan must get across why you are passionate about your company and why you think it will succeed. You should have a command of your market, your subject area and be authoritative. You should include market data and financial projections, but not come across overly dry. You want the readers of your business proposal—even bank loan officers—to see your commitment to your goals and the emotional connection you have formed to your business idea. At the same time, you want your plan to appear factual and professional.
Startup business plan requirements
If you’re writing a business plan for a bank or lending institution, consider including the following major components in your plan. Keep your plan in a binder with numbered pages and provide a table of contents to make it easy to follow.
Executive summary. This is a brief (1-2 page) explanation of what your company is, what it does and why it will be successful. Although this summary will come first in the plan, you should write it last so that you have all the information to draw from. Not succinctly summarizing your business idea is one of the biggest mistakes that can be made in a business plan. If you don’t hook your reader with your executive summary, that person is not going to want to keep reading. Here are some of the pieces to include:
- The mission statement — a short statement summing up your business and explaining your product or services
- A brief overview of the structure of your company and the leadership team
- Some basic financial information, such as banking relationships and any investors
- A summary of your company growth and any financial highlights
- Company facts like number of employees, date founded and location
Mission statement. Although this is a part of the executive summary section, the mission statement deserves a separate callout because you’ll need to carefully craft your message. The statement needs to pack a punch, but remain a tight and coherent thought. Mission statements should be written in the present tense, and answer questions like who your customers are, what values are important to your business and what marker you’ll use to decide if your company is successful.
Market analysis. In your company description you started to explain why your company is a good idea. Your market analysis is where you’ll back up those statements with an authoritative understanding of your industry and target market. Address why your competitors are successful and prove that you know why what they’re doing is working. You also need to establish why your idea is better or will be more successful. The market analysis section should be between 9 and 22 pages long. In this section, include information like:
- Trends and themes in your industry
- A description and size of your target market
- Your pricing and gross margin targets
- Industry risks
- Key personnel
- Five-year projected revenues
If you need help with market research there are several free tools available. The U.S. Census is obviously data rich and can help you answer questions about the size of specific industries and businesses and which products in your industry are growing. The U.S. Census also offers Economic Indicator data that can help you digest what’s going on in different industrial sectors.
The SBA offers a tool called Sizeup that helps you process data points to get details on your competition, figure out where your competitors are located and where there might be gaps in the market. It’s important to remember that having a similar business plan as a competitor doesn’t necessarily mean you won’t be successful. It’s possible that two similar businesses can thrive, but you should be able to explain why the market you are entering is conducive to that.
Your business plan must get across why you are passionate about your company and why you think it will succeed.
You should also be able to prove that you know the customers to whom your business caters and be able define and research their habits. Know when they buy, how often they buy or how often they will need your service.
Company description. A good way to describe your company is by answering this question: What problem does your company solve? That can help determine who your customers are and what advantages your company has over your competitors. The question will also lead you to explain and highlight the expertise of your team and the benefits of your physical location. A company description is an easy place to show your commitment and passion for the company as well as boast your company's strengths.
Organization and management. Here’s another place to show your team’s competence and explain the passion behind your business. This is where you’ll outline who is running your company, how it’s structured and what you all bring to the table. The main components to include are:
- An organizational chart
- The name of all owners and percentages they own
- Resumes of some of your key staff/leaders
- The legal structure of your business (i.e., an LLC, a partnership, etc.)
Marketing and sales. It’s not enough to simply say you have a great product. In a traditional business plan, you have to explain how you intend to get this great product or service to the right customers. You should convey how your strategy is going to evolve once you have more (or any) customer data. Still, you should lay out a roadmap for how to start and potential opportunities to attract and retain customers. Consider including the following:
- An explanation of your business model and how your product leads to revenue
- How and when you will introduce new products or services
- Potential new territories for your company to enter
- The plan to boost sales on a particular product
- Potential long-term relationships with other companies or clients
- The possibility of price increases
- Improvements to your product or your processes for manufacturing or delivery
- Ideas for advertising and social media strategy
Service or product line. In this section you will need to again answer what your company does and what you’re selling. You can go into more detail about what sets your product and company apart from your competitors, as well as how you target customer benefits. Some items to include are:
- The life cycle of your product
- Information on any copyrights, patents and any other ways you protect your intellectual property
- Any non-disclosure or non-compete agreements
- Any research and development you’ve done
Funding request. If the goal of your business plan is to secure an investment or a loan, then this is where you’ll explain how much funding you need and why. In addition, you want to explain how you will pay off your debt. Also include any information that would majorly impact your future financial situation, like plans to take the company public or sell the company.
Financial information. It might seem obvious, but in your financial projections you want to show that your business is strong. If you have an established business, this is where you’ll include cash flow statements, income statements and balance sheets as well as collateral that you could put up against a loan. You should also discuss how the business is being funded and your current costs. Also, make sure that the projections clearly match up to your funding requests, avoiding overreaching. This section of your business plan should also have some heft, possibly as long as 12 to 25 pages.
Some of the documents you should provide include:
- Current financial data of all owners
- Financial data from the past three years, such as balance sheets and profit and loss statements
- A list of all your debt, including what you owe and to whom
- A five-year forecast of income and expenses
- A certification or review letter from a financial advisor saying that your information meets generally accepted accounting principles
Appendix. This section is for any supporting documents that can be used to support your plan statements. Consider including credit histories, the resumes of your staff or key leaders, product pictures, permits, patents or other relevant contracts.
Startup business plan template
For a startup business, it might be worthwhile to look at a less involved version of a traditional business plan. A popular one is the Business Model Canvas developed by Alex Osterwalder. The idea of the canvas is to explain your business model in a simple way to relevant parties, such as partners and potential investors.
Here are the main components of the Canvas model:
Key partnerships. Discuss the other businesses or services required to run your new business. This can include suppliers, contractors, manufacturers or other partners that are necessary for your company to operate.
Key activities. Format a list of how your business will gain an advantage in your industry through your chosen business model. You should highlight what makes your company more effective at reaching your target customer than your competitors.
Key resources. List your important business assets which may include staff, capital or intellectual property. These are the things that will make your chosen business model successful and help you deliver to your customer.
Value proposition. This is a good place to showcase your passion as well as your understanding of your market. You should make a compelling case for why a customer would choose you over the competition.
Customer relationships. Describe a customer’s experience working and interacting with your business. Address both customer acquisition and customer retention.
Customer segments. Explain who your customers are. You’ll want to give a clear sense of your target market and who is being served by your business. Be specific.
Channels. Describe how you will communicate with your customers and why those methods are effective. Most businesses use a mix of channels and optimize them over time.
Cost structure. Address how your company will reduce cost, maximize value and make money on your product or service. Be honest about the most significant costs that you anticipate facing.
Revenue streams. List all the revenue opportunities in your plan, including the product or service you're selling, advertising space for sale and membership fees.
See Also: Business Plan Mistakes to Avoid
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
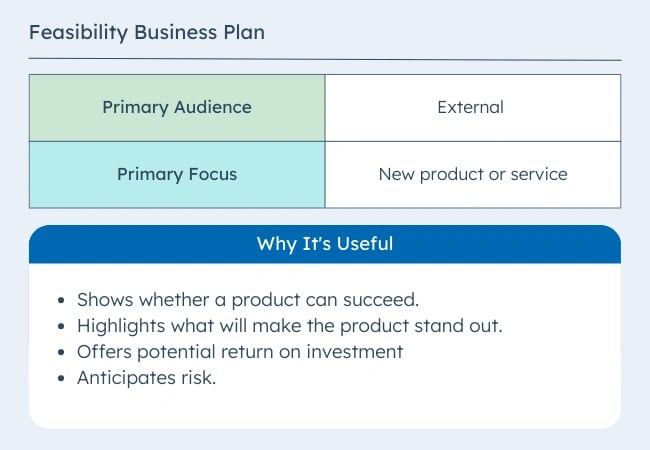
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![what should be on a business plan How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

19 Best Sample Business Plans & Examples to Help You Write Your Own

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![what should be on a business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![what should be on a business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
What Should a Business Plan Include?
A business plan serves as a roadmap to successfully launch a business. It helps you overcome the challenges you might experience in your industry. Learn how to create and use a business plan for your startup.
One of the most fatal mistakes that aspiring entrepreneurs make in launching a startup is forgetting a business plan . You wouldn’t launch a ship at sea without establishing its routes and the direction you’ll steer it to. Without proper planning, your ship will end up adrift or worst, dramatically sink when the tides hit. And in a volatile commercial industry, the tides are constantly changing.
Avoid common startup mistakes by creating a business plan. A business plan not only strengthens your foundation but also helps you navigate the ever-changing field of business. Chances are your customers’ preferences will change over time and you have to keep up with them. Hence, a business plan also changes accordingly.
But how exactly do you create a business plan ? Is there a template to follow? Should you enlist the help of other experts to write it? Today, we’ll look into what should be included in your business plan and how it should be written. The first step is by understanding what it is and what it is for.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is an official company document that breaks down all the goals of a business and how to achieve them. It basically lays out the groundwork for your idea to come alive. It’s often referred to as the “blueprint of the business”, summarizing your goals.
Although there are many ways to write it, its key point usually discusses the financial, marketing, and operational strategies of the business.
What is it for?
A business plan serves as a guide for a growing company. It’s a consistent reference for business owners and stakeholders to base critical decisions on. It’s especially useful for early-stage startups to attract investors. When a company doesn’t have a proven track record, it can lay out its full potential instead.
Not only is the business plan useful for the initial launching of a business, but it also helps with pivotal changes. Since the market is perpetually changing, it’s crucial that your plan also evolves with it. Hence, the goals and methods of achieving will be updated. In some cases, a whole new plan is created if the company wants to drastically move in a new direction.
What’s included in a Business Plan
Although there’s no fixed formula for writing a business plan, there are some identifiable key points. These are generally the items factored in its creation:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary outlines the whole plan. You start with a clear introduction of who you are, what you sell, and what your ambitions are as a business. This section includes your mission statement, product description, and the basic overview of your company’s structure. It should also include your financial plans.
2. Business Description
The business description provides detailed information about your industry. It must describe its current outlook as well as its profit potential. You will go into detail about your target market and other organizations or businesses you cater to. Also, this section briefly discusses what problem the business is trying to solve.
3. Market Analysis
A business must have a firm understanding of its target market and should be able to prove its sustainability. The market analysis provides trends and studies about the target consumers—their size, demographics, buying power, and frequent activities. This section also touches briefly on the competitors.
4. Product Development
Investors need a clear idea of how you would create and maintain your product. The development plan section contains the details of the product’s design; its production methods, lifecycle, marketing, and development budget. This includes the overall strategy of how it will be sold in the market.
5. Marketing Strategies
The product is only as good as how much it will sell. Therefore, this section describes how you will present your products and services to the market. This will discuss your marketing campaigns, distribution channels, and types of media you’ll tap into. You will summarize how you intend to reach your customers and pitch your products to them.
6. Operations and Management
Your investors need an overview of how the business functions. The operations plan highlights the logistics of the company such as team responsibilities, division tasks, and operational expenses. This helps track down who is responsible for certain areas of the business.
7. Financial Plans
Money mobilizes the idea. Hence, it’s important to keep an accurate record of where it’s going. This section shows the company’s monetary plans and its future projections. This includes financial statements, balance sheets, and third-party business transactions. For startups, it will mostly contain the target profit and estimates of expenses.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
Now that we have an idea of the business plan template , it’s time to learn how to write it effectively.
Here are some things to keep in mind when you’re writing one for your business.
- Keep it concise. It serve as a guide for the company and the investors. It needs to be easy to understand and direct to the point. You can’t afford to waste a reader’s time by creating a 100-page business plan. Instead, aim for a summarized version of your plan, only highlighting the important points and outlining the rest.
- Avoid jargon. Ensure that everyone, especially investors, can understand your business plan. Do not include complex jargon in your content. Save the technicalities for the experts and simplify the terms in explaining your ideas.
- Keep it up-to-date. As previously mentioned, business plans are not static. Over time, a lot of things in the industry will change and might make your original plans obsolete. Frequently update your business plan according to what’s new in the field and with new methods you’re employing. Remember, a business plan is only useful if it’s still relevant.
Build your Business
Business plans are important when you’re starting your business from scratch. However, the success of your business still heavily relies on their execution. A lot of startups fail because they can’t push through with what was proposed in the business plans.
More than just articulating your ideas, you need to do a lot more to make them come to life. For one, you’ll need the capital to kick things off and make everything operational. Second, you’ll need to hire the best people to run your operations. Lastly, you have to find investors to sustain your business.
One way to ensure that your business plan is properly executed is by enlisting the help of business experts. Full Scale is an offshore software development company that specializes in helping startups.
We can provide the talent and resources needed to begin your operations. Whether you need project managers, marketing specialists, or technical experts; we’ve got them all. We’ll take care of all the processes of recruitment and management so you can focus on your core competencies.
Ready to begin your entrepreneurial journey? Get your FREE consultation today!
Learn More about Offshore Development
Copyright 2024 © Full Scale
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
- 3 years ago

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!

What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”
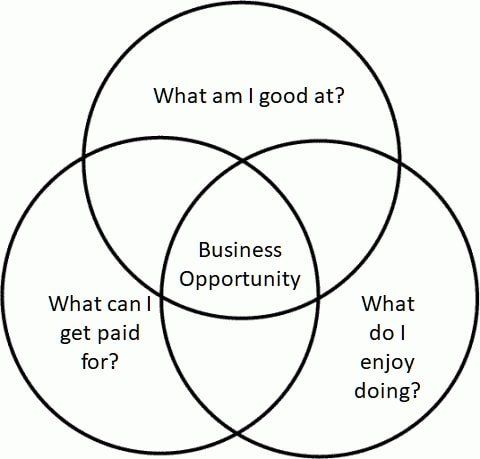
If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand
A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:

When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples
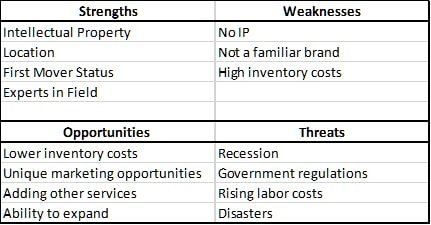
Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.

Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:
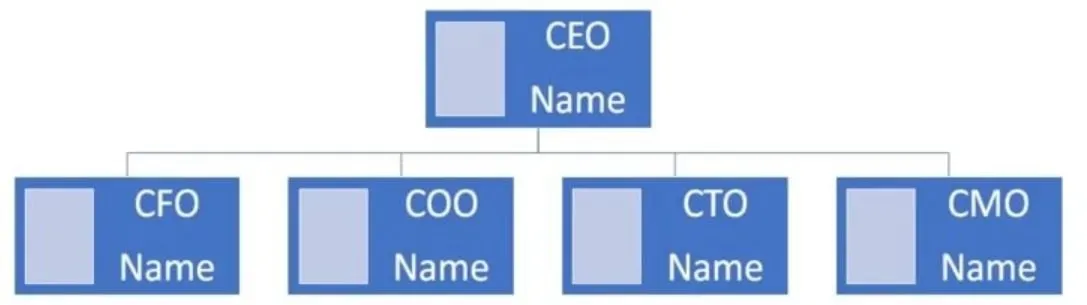
Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.
The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?

Brandon Boushy
Brandon Boushy lives to improve people’s lives by helping them become successful entrepreneurs. His journey started nearly 30 years ago. He consistently excelled at everything he did, but preferred to make the rules rather than follow him. His exploration of self and knowledge has helped him to get an engineering degree, MBA, and countless certifications. When freelancing and rideshare came onto the scene, he recognized the opportunity to play by his own rules. Since 2017, he has helped businesses across all industries achieve more with his research, writing, and marketing strategies. Since 2021, he has been the Lead Writer for UpFlip where he has published over 170 articles on small business success.
Related posts

- September 27, 2023
How to Start a Business: The Ultimate Guide (2024)

- August 3, 2022
Free Business Plan Template (With Examples)

- May 3, 2022
How to Get a Business License (In 3 Steps)
Join the discussion cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
2 thoughts on “How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)”
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
Compare listings
Reset Password
Please enter your username or email address. You will receive a link to create a new password via email.

How to Write a Professional Business Plan in 10 Easy Steps
Home » Blog » How to Write a Business Plan in 10 Easy Steps
During financial uncertainty, many of us press pause on our entrepreneurial aspirations.
Wondering if now’s the right time to start our business . Doubting our ideas and worrying about the what-ifs and maybes!
A business plan removes the uncertainty and what-ifs from the equation. It validates our business ideas, confirms our marketing strategies, and identifies potential problems before they arise.
Replacing our doubts with positivity, ensuring we see the complete picture, and increasing our chances of success.
Because you could be starting and running your own business . But you’ll only know for sure it’s the right move for you when you write your business plan.
Here’s everything you need to know to create the perfect business plan.
What is a business plan?
A well-written business plan contains the recipe for your new business’s growth and development.
It’s your compass.
It describes your goals and how you’ll achieve them by infusing the ingredients you need to turn your dream into a reality.
- Your business description- Tells readers about your idea, why it'll succeed, and how you'll make it happen.
- A market analysis- That backs up your company description.
- Your management and organization plan- Includes employees or contractors because even a one-person show may need a team's help on a contract basis, like bookkeeping services, graphic design, research, and if your business grows, with time, also full-time employees.
- Your products or services descriptions- Explaining how they work, where you'll get them, and how much they`ll cost.
- A target audience analysis- So, you know exactly who you`re selling to and what makes them buy what you`re offering.
- Your marketing and sales plan- Proving your chosen niche is profitable and how you'll reach your customers.
- A financial funding request/projections - What you need and how you'll get it.
Your business plan is like a GPS, guiding your business to its destination for the next 3 to 5 years.
Why is a business plan important?
Here’s the short answer.
A business plan enables you to convey your vision to those who can help you make it a reality.
It does it in 2 ways:
- It empowers you to evaluate your goals and confirm their viability before entering a marketplace.
- And equips you with the information, using a proven outline, that convinces others to help you achieve them.
A business plan does it by explaining who you are, what you are going to do, and how you’ll do it. It clarifies your strategies, identifies future roadblocks, and determines your immediate and future financial and resource needs.
Let’s look at what that means and why each part is important.
A business plan helps you evaluate your ideas
Do you have over one business idea or a range of products or services you believe you could bring to a single marketplace?
If so, a business plan helps determine which is worth focusing on and where to apply your energy and resources by evaluating your idea’s possible market share and profitability before investing.
Clarifies your costs
Your chosen market determines your initial investment and future revenue. And it would be best if you knew those before you invest a dollar in your business idea.
With your chosen idea, your business plan can help you understand your set-up and running costs, the resources you’ll need, and the time it’ll take to get started.
It’s also where you’ll calculate your future sales and revenue goals to ensure they fit your budget and required breakeven point.
And those are essential because every business needs a consistent cash flow to stay afloat!
Steers your business in the right direction
Your business plan guides you through every stage of starting and running your business .
It acts as your GPS, giving you a course to steer. Ensuring your business stays on track, helping you achieve your goals every step of the way.
Acts as your financial guide
As your new business grows, you might need to expand.
But with expansion come big spending decisions, such as purchasing expensive equipment, leasing a new location, or hiring your first employees.
Your business plan’s financial forecast gives you a solid foundation to build on by clarifying when you’re ready to make those investments, ensuring you don’t overreach.
And when you are ready to employ staff, it helps you with that too!
Helps recruit the people you need
Your business is often only as good as its employees. A business plan helps you communicate your vision and pitch your dream to the best candidates. Building their confidence in your venture and encouraging them to join you.
It's essential if seeking a loan or investment
Do you need a loan from a bank or a venture capitalist/angel investor?
If so, you’ll need a business plan that shows your past and future financial trajectory so potential investors can evaluate your business’ feasibility to determine whether you’re worth the risk.
It's an asset if you want to sell your business
Owners of legal entities, such as LLCs, can sell all or part of their business to raise funds for other business ventures or expand their existing ones.
A solid business plan with proven financial recordings and realistic forecasts based on current performance can make your business more attractive to potential investors.
And it makes sense because when buyers understand your business model and its potential growth, they’ll see the value in it for them.
All great reasons to write a business plan, don`t you agree?
Okay, here’s how you do it:
The steps for creating a business plan
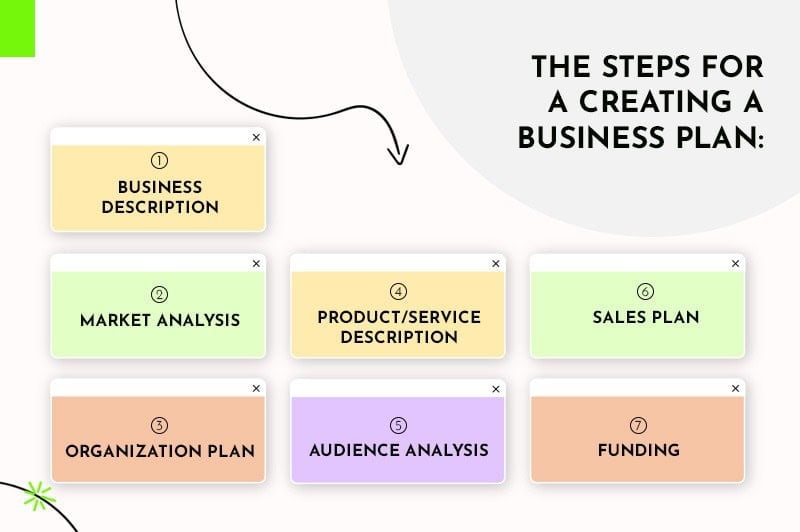
Most business plan templates are similar, containing several steps for writing a conclusive plan. If you’re interested in a very short plan, we prepared a lean (one-page) version, including a template .
The perfect business plan isn’t one or the other; it’s the plan that meets your business needs.
That said, every business plan should contain crucial elements and essential details . And a rhythm to your outline that encourages action, growth, and investors to read it from start to finish. Our step-by-step guide, along with our template, will help you achieve both.
But first, you must choose the style that works for you:
Pick a business plan format that works for you
You can tackle creating a business plan in different ways; one could be a long-form, more traditional approach or a one-page business plan that acts as a summarized road map.
Traditional business plans use a standard, industry-expected structure, with each section written in great detail. They require a lot of research because businesses often use them to gain investment, and they can be anywhere from 10 to 50 pages long.
A one-page business plan uses a similar structure but summarizes each step by highlighting the key points.
You can write a one-page plan in an hour and use it as a personal blueprint for running your business or as a guide to writing a future traditional plan.
Here are the core component that create a great business plan:
1. An executive summary
2. Your company’s description
3. Market analysis
4. management and organization outline, 5. products and service description, 6. target audience analysis, 7. marketing and sales plan.
8. Financial funding request
9. Financial projections
10. an appendix, 1. an executive summary.
The first section of your business plan’s an executive summary that tells anyone reading in simple terms what your business is and why you believe it’ll be successful.
It’s the most crucial part of your plan because anyone reviewing it often decides whether to continue reading based on what’s in your executive summary.
Your executive should contain your mission statement (why you’re starting your business). A product/service description. Your leadership team and financial information.
Even though the first thing people read is your executive summary, it’s the last section you write.
The next step is about you:
2. Your company's description
Here you sell yourself and your business by telling readers why you’re starting your business and know it’ll succeed.
You must be realistic, business-like, and detailed.
Begin by explaining who you are, what you plan on doing, and how you’ll do it. Describe your future market, your target audience, and why they need your product/service.
Elaborate on your unique selling point (USP) and how your competitive advantage will ensure your success.
Describe your team, highlight their skills and technical expertise, and if you`re a brick-and-mortar business, discuss your location and why it’s right for your target audience or logistics.
Now your market:
A great business idea is only as good as its future marketplace. Enter a declining market with an insufficient or uninterested audience, and you’ll be toast.
Choose one on an upward trajectory with people you understand and need your product, and you’ll be in business.
That makes your market analysis a crucial step in your business plan outline. Here’s where you identify your target audience, competitors’ performance, strengths and weaknesses, and whether the market can sustain your business needs.
Your market analysis should include the following:
- Your market description and outlook- Provide a detailed outline defining your market, including its size, trends, growth rate, and outlook.
- Target Market- Describe your ideal customers, including their demographics such as age, gender, employment status, income level, and lifestyle preferences. Also, include your market size, what motivates your ideal clients, and how you'll reach them.
- Competitive Analysis- Identify your main competitors and list their strengths and weaknesses. Also, highlight any potential roadblocks that might prevent you from entering your chosen marketplace.
Step 4 is where you tell readers how you’ll construct your business and who’ll run it.
Describe your business’s legal structure, whether you’re a sole proprietor intending to form an LLC or a limited/general partnership with dreams of incorporating an S or C corps.
Include your registered business name and any DBA brand name you have. And any member’s percentage ownership and managerial duties per your operating agreement.
And consider using a chart to show who runs what section of the business. Explain how each employee, manager, or owner’s experience and expertise will contribute to your venture’s success. And if you have them, include your team’s resumes and CVs.
Now you must get technical about what you plan to offer.
List your products or services and explain how they work. If in the development stage, describe the process and when you’ll be market ready.
Include the following product/service information:
- Describe how your product/service will benefit your target audience.
- Provide a breakdown of costs per unit made/sold, life cycle, and expected profit margins.
- Explain your supply chain, order fulfillment, and sales strategy.
- Include your plans for intellectual property, like trademarks and patents.
Your product and service description brings you to those who matter most. Your target audience:
The target audience section of your business plan is the most important one to get right. After all, your customers are your business. And the better you know them, the easier it’ll be to sell to them.
To gain a clear picture of your ideal clients, learn about their demographics and create a client persona.
Those include:
- Their location
- Education level
- Employment status
- Where they work
- How much they earn
- How they communicate
- Preferred social media platforms
- Common behavior patterns
- Free time interests
- And what their values and beliefs are
You need your target audience’s demographics to create a branding style that resonates with them. To build marketing strategies that engage their interest. And to identify where to spend your advertising dollars.
Target market’s persona in place, your next step is to describe how you’ll reach and sell to them:
Your marketing plan outlines your strategies to connect with and convert your ideal clients.
Here’s where you explain how you’ll reach your audience, describe your sales funnel, and develop customer loyalty to keep customers.
Your business plan doesn’t require your complete marketing/sales plan but should answer basic questions like:
- Who's your target market?
- Which channels will you use to reach them? (Social media, email, website, traditional marketing, etc.)
- What sales strategies will you use?
- Which resources do you need to implement those strategies?
- Do you have the resources, and if not, where will you get them?
- What are the potential marketing obstacles, and how you'll overcome them?
- What's your initial marketing campaign timeline and budget?
- What your success metrics are, and how you'll measure them?
8. Financial funding request
This step applies if you require funding to start or grow your business.
Similar to the marketing plan step, including your entire financial plan is unnecessary. However, you’ll need to answer specific questions to explain how much investment you require and how you’ll use it.
The following financial funding outline will suffice:
- Your current capital balance and how much future capital you'll need.
- Specify whether you want equity or debt.
- The terms and conditions you need and the duration of any loan repayments.
- Provide a detailed description of why you need investment, IE., to pay salaries, buy equipment or stock, and what percentage will go where.
Start-ups that need investment must rely on something other than past sales and balance sheets. Here, you’ll need to use financial projections to persuade lenders you’ll generate enough profit to repay their loans. And that investors will get a worthwhile return.
Your goal is to convince potential lenders or investors that your business will make enough profit to repay any loans or fulfill your equity promises.
Depending on your loan requirements and market, these projections can vary from 3 to 5 years.
Financial projections aren’t an exact science; you’re forecasting the future! However, accuracy is essential (meaning your projected numbers must add up correctly). And while your goals should be positive, they must also be realistic.
What to include in your financial forecast:
- Forecasted income statements.
- Capital expenditures, fixed and variable.
- Quarterly and annual balance sheets.
- Projected cash flow statements.
Be specific with your projections and ensure they match your funding requests. And if you have collateral to put against a loan, include it at the end of your financial projections to improve your chances of approval.
Also, consider using charts and graphs to tell your financial story, as visuals are great for conveying your message.
Use your appendix to list and provide supporting information, documents, or additional materials you couldn’t fit in elsewhere.
If the appendix is lengthy, start it with a table of contents.
What to include:
- Key employee resumes.
- Letters of reference.
- Licenses and permits.
- Intellectual property - patents or trademarks.
- Legal documents.
- Any current contracts.
- Product pictures and information.
- Bank statements/credit history.

Financial uncertainty shouldn`t stop you from following your dreams. In fact, recessions are often the best time to start a business .
And your business plan is one of the main things that can help you make your dream of owning a business a reality.
Take it one step at a time, do your research, and use your business plan to remove the uncertainty of the unknown.
Because then you’ll know if the time is right to start your business.
This portion of our website is for informational purposes only. Tailor Brands is not a law firm, and none of the information on this website constitutes or is intended to convey legal advice. All statements, opinions, recommendations, and conclusions are solely the expression of the author and provided on an as-is basis. Accordingly, Tailor Brands is not responsible for the information and/or its accuracy or completeness.
- Form an LLC
- Licenses & permits
- Sales tax permit
- Business insurance
- Business banking
- Business email
- Taxes & accounting
- Invoices & bookkeeping
- Legal documents
- Business cards
- Digital business card
- Graphic design
- Print store
- Help center
- LLC by state
- Affiliate program
- Partner with us
- Brand guidelines
@2024 Copyright Tailor Brands
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Do not sell my personal information
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

Use This Business Plan Format to Expertly Write Your Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

In this guide, you’ll learn how to format your business plan professionally. Business plan structure and format helps readers look beyond distracting style to the real meat of your idea.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
How to Format Your Business Plan: The Cover Sheet
Every business plan should begin with a simple business plan cover page including the business name, your name and contact information. An easy to read table of contents should follow.
Example Business Plan Table of Contents
I: Executive Summary a. Business Overview b. Success Factors c. Financial Highlights
II: Company Overview a. Who is [Company Name]? b. [Company Name]’s History c. [Company Name]’s Products & Services
III: Industry Analysis a. Industry Trends
IV: Customer Analysis a. Customer Segmentation
V: Competitive Analysis a. Direct & Indirect Competitors b. Competitive Advantage
VI: Marketing Plan a. The [Company Name] Brand b. Promotions Strategy c. Pricing Strategy
VII: Operations Plan a. Functional Roles b. Goals and Milestones
VIII: Management Team a. Management Team Members b. Hiring Plan
IX: Financial Plan a. Revenue Model b. Revenue and Cost Drivers c. Key Assumptions & Forecasts
X: Appendix
The cover sheet should leave no question for readers to be able to identify the business plan when it is in a stack with dozens of others on their desk. The table of contents allows them to easily refer to sections within the plan. For example, after reading the executive summary, some investors with an eye for numbers may turn directly to the financial plan and statements. Proper business plan format allows readers to quickly get the information they want.
Example Business Plan Format
There are 10 business plan components or sections that every entrepreneur and business owner must include in their plan. These include:
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Industry analysis
- Customer analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Marketing plan
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Financial plan
You should recognize these if you’ve ever worked with a business plan template .
Formatting your business plan with charts and graphs is welcomed to break up long blocks of text. However, charts and graphs shouldn’t be used for their own sake. They must make the information easier to pass on than text would.
The business plan format that investors and lenders expect includes the following 10 sections. You can download our business plan format pdf here, to help you get started. We’ve included important notes in each section specific to business plan formatting to help you as you write your plan.
1. Start with Your Executive Summary
An executive summary gives readers a crisp overview of your business at the start of your plan. This section should not be more than two pages long and should include the following:
- What is the business about?
- Where and why did the idea of the business originate?
- Who are the owners?
- Which industry is it operating in?
- What is its core function?
- Where is it located?
- How is it going to make money?
- How much money (if any) is it already making?
- What are its financial projections?
The best format for your executive summary is paragraphs. Utilizing bullets and headings is also useful formatting within an executive summary, as it aids the reader in scanning the content on the page.
2. Company Overview Section
The company overview is the perfect place to highlight the strengths of your business. This section gives the reader additional information about your products and/or services and describes your company’s past accomplishments.
Including the below in this section will provide further clarity about your business:
- What type of business you are (e.g., C-Corporation, sole proprietor)
- When your business started
- Business’ accomplishments to date
The best formatting to use in this section is paragraphs to describe your company’s strengths and products/services. You should also include a chart that outlines your company’s achievements to date.
3. Industry or Market Analysis
The industry or market analysis gives the reader a clear understanding of your industry and the audience it serves. It includes a detailed explanation of your market size and trends.
Typically, the format of this section should be paragraphs. Feel free to include charts and graphs to best convey the information to the reader.
4. The Customer Analysis States Who Your Customers Are and What They Need
In this section of your plan, explain who your target customers are and identify their specific needs. Doing this will help you better target and attract customers.
5. Competitive Analysis
The Competitive Analysis section identifies your direct and indirect competitors. It discusses who they are and their strengths and weaknesses. It then details your areas of competitive advantages.
Whether your competitors are small or large businesses, describe them. Telling investors there are no competitors (big or small) often gives the impression that a market does not exist for your company.
With regards to formatting, use paragraphs to describe each competitor. As appropriate, adding a competitor matrix to show similarities and differences between your company and the competition can be very powerful.
6. Your Marketing Plan is a Key Section
The marketing & sales section of your business plan should outline how you plan to attract new customers and retain old ones. This section should outline the ways customers can be introduced to and engage with your offerings and describe how you will convert these prospects into paying customers.
Set marketing objectives that include the following (if applicable):
- Introducing new products
- Extending the market reach
- Exploring new markets
- Boosting sales
- Cross-selling
- Creating a long-term partnership with clients
- Increasing prices without affecting sales
- Creating a content marketing strategy
Organize your Marketing Plan into the 4 P’s – Price, Product, Promotions and Place. If you have multiple products or services, include a menu with each key item and its price.
7. The Operations Plan Format
Your Operations Plan identifies your key operational processes and milestones you expect to accomplish. Using a Gantt chart is a great way to show your expected future milestones. You can also format this section with tables that document the dates of future milestones.
8. You Need to Prove Your Management Team Can Execute
“A company is only as good as the people it keeps.” – Mary Kay Ash, American Entrepreneur and Businesswoman
The Management Team section of your business plan focuses on the people who run the business.
Who are the decision-makers, who is the product expert, who is the operations head, and who is running the entire show? A glimpse into the expertise and capabilities of your team members and how their experiences will help grow your business will boost stakeholder confidence.
To improve the formatting and best convey your management team to readers, consider adding an organizational chart that shows your team members and reporting structure.
9. Format Your Financial Plan
The goal of this section is to convince the reader that your business is stable and will be financially successful. Arm this section with past and/or forecasted cash flow statements, balance sheets, profit & loss statements, expense budgeting and sales forecasts.
If you run an operational business, include 3 years of historical data to help investors gain an understanding of how feasible your funding request is and if your business is capable of generating good returns.
Also include your funding request, if applicable, in this section. You should mention how much investment is required to take your business to the next significant milestone and how the money will be spent. You should also define if you are seeking debt or equity funding. If you are seeking debt financing like an SBA loan, ensure your financial projections include the debt and show steady repayments of both the principal and return under reasonable loan terms.
If you are seeking equity financing, you don’t need to include your valuation expectations in the business plan, but you should be aligned within your ownership team on the amount of equity you are willing to exchange before you pitch investors.
Example Financial Plan
Projected sales, gross profit & net income.
5 Year Annual Income Statement
5 year annual balance sheet, 5 year annual cash flow statement, 10. appendix.
This section includes supporting documentation of your business case. This could include renderings of a planned store location, market research reports referenced in the plan, key supplier or buyer contracts that substantiate your financial projections or historical marketing and sales data.
Formatting Your Business Plan
Overall, business plans should use simple and standard formatting. Twelve point font size in a standard font like Arial or Times New Roman is best, as well as the standard margin size of one inch on each side. Pages should be numbered, and the name of the company should appear on each page in the header or footer.
Use charts whenever possible as it makes it much easier for readers to consume the information in your plan.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
How to write a business plan in seven simple steps
When written effectively, a business plan can help raise capital, inform decisions, and draw new talent.

Companies of all sizes have one thing in common: They all began as small businesses. Starting small is the corner for those just getting off the ground. Learn about how to make that first hire, deal with all things administrative, and set yourself up for success.
Writing a business plan is often the first step in transforming your business from an idea into something tangible . As you write, your thoughts begin to solidify into strategy, and a path forward starts to emerge. But a business plan is not only the realm of startups; established companies can also benefit from revisiting and rewriting theirs. In any case, the formal documentation can provide the clarity needed to motivate staff , woo investors, or inform future decisions.
No matter your industry or the size of your team, the task of writing a business plan—a document filled with so much detail and documentation—can feel daunting. Don’t let that stop you, however; there are easy steps to getting started.
What is a business plan and why does it matter?
A business plan is a formal document outlining the goals, direction, finances, team, and future planning of your business. It can be geared toward investors, in a bid to raise capital, or used as an internal document to align teams and provide direction. It typically includes extensive market research, competitor analysis, financial documentation, and an overview of your business and marketing strategy. When written effectively, a business plan can help prescribe action and keep business owners on track to meeting business goals.
Who needs a business plan?
A business plan can be particularly helpful during a company’s initial growth and serve as a guiding force amid the uncertainty, distractions, and at-times rapid developments involved in starting a business . For enterprise companies, a business plan should be a living, breathing document that guides decision-making and facilitates intentional growth.
“You should have a game plan for every major commitment you’ll have, from early-stage founder agreements to onboarding legal professionals,” says Colin Keogh, CEO of the Rapid Foundation—a company that brings technology and training to communities in need—and a WeWork Labs mentor in the UK . “You can’t go out on funding rounds or take part in accelerators without any planning.”
How to make a business plan and seven components every plan needs
While there is no set format for writing a business plan, there are several elements that are typically included. Here’s what’s important to consider when writing your business plan.
1. Executive summary
No longer than half a page, the executive summary should briefly introduce your business and describe the purpose of the business plan. Are you writing the plan to attract capital? If so, specify how much money you hope to raise, and how you’re going to repay the loan. If you’re writing the plan to align your team and provide direction, explain at a high level what you hope to achieve with this alignment, as well as the size and state of your existing team.
The executive summary should explain what your business does, and provide an introductory overview of your financial health and major achievements to date.
2. Company description
To properly introduce your company, it’s important to also describe the wider industry. What is the financial worth of your market? Are there market trends that will affect the success of your company? What is the state of the industry and its future potential? Use data to support your claims and be sure to include the full gamut of information—both positive and negative—to provide investors and your employees a complete and accurate portrayal of your company’s milieu.
Go on to describe your company and what it provides your customers. Are you a sole proprietor , LLC, partnership, or corporation? Are you an established company or a budding startup? What does your leadership team look like and how many employees do you have? This section should provide both historical and future context around your business, including its founding story, mission statement , and vision for the future.
It’s essential to showcase your point of difference in your company description, as well as any advantages you may have in terms of expert talent or leading technology. This is typically one of the first pieces of the plan to be written.
3. Market analysis and opportunity
Research is key in completing a business plan and, ideally, more time should be spent on research and analysis than writing the plan itself. Understanding the size, growth, history, future potential, and current risks inherent to the wider market is essential for the success of your business, and these considerations should be described here.
In addition to this, it’s important to include research into the target demographic of your product or service. This might be in the form of fictional customer personas, or a broader overview of the income, location, age, gender, and buying habits of your existing and potential customers.
Though the research should be objective, the analysis in this section is a good place to reiterate your point of difference and the ways you plan to capture the market and surpass your competition.
4. Competitive analysis
Beyond explaining the elements that differentiate you from your competition, it’s important to provide an in-depth analysis of your competitors themselves.
This research should delve into the operations, financials, history, leadership, and distribution channels of your direct and indirect competitors. It should explore the value propositions of these competitors, and explain the ways you can compete with, or exploit, their strengths and weaknesses.
5. Execution plan: operations, development, management
This segment provides details around how you’re going to do the work necessary to fulfill this plan. It should include information about your organizational structure and the everyday operations of your team, contractors, and physical and digital assets.
Consider including your company’s organizational chart, as well as more in-depth information on the leadership team: Who are they? What are their backgrounds? What do they bring to the table? Potentially include the résumés of key people on your team.
For startups, your execution plan should include how long it will take to begin operations, and then how much longer to reach profitability. For established companies, it’s a good idea to outline how long it will take to execute your plan, and the ways in which you will change existing operations.
If applicable, it’s also beneficial to include your strategy for hiring new team members and scaling into different markets.
6. Marketing plan
It’s essential to have a comprehensive marketing plan in place as you scale operations or kick off a new strategy—and this should be shared with your stakeholders and employees. This segment of your business plan should show how you’re going to promote your business, attract customers, and retain existing clients.
Include brand messaging, marketing assets, and the timeline and budget for engaging consumers across different channels. Potentially include a marketing SWOT analysis into your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Evaluate the way your competitors market themselves, and how your target audience responds—or doesn’t respond—to these messages.

7. Financial history and projections
It’s essential to disclose all finances involved in running your company within your business plan. This is so your shareholders properly understand how you’re projected to perform going forward, and the progress you’ve made so far.
You should include your income statement, which outlines annual net profits or losses; a cash flow statement, which shows how much money you need to launch or scale operations; and a balance sheet that shows financial liabilities and assets.
“An income statement is the measure of your financial results for a certain period and the most accurate report of business activities during that time, [whereas a balance sheet] presents your assets, liabilities, and equity,” Amit Perry, a corporate finance expert, explained at a WeWork Labs educational session in Israel.
It’s crucial to understand the terms correctly so you know how to present your finances when you’re speaking to investors. Amit Perry, CEO and founder of Perryllion Ltd.
In addition, if you’re asking for funding, you will need to outline exactly how much money you need as well as where this money will go and how you plan to pay it back.
12 quick tips for writing a business plan
Now that you know what components are traditionally included in a business plan, it’s time to consider how you’ll actually construct the document.
Here are 12 key factors to keep in mind when writing a business plan. These overarching principles will help you write a business plan that serves its purpose (whatever that may be) and becomes an easy reference in the years ahead.
1. Don’t be long-winded
Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon. When business plans are too long-winded, they’re less likely to be used as intended and more likely to be forgotten or glazed over by stakeholders.
2. Show why you care
Let your passion for your business shine through; show employees and investors why you care (and why they should too).
3. Provide supporting documents
Don’t be afraid to have an extensive list of appendices, including the CVs of team members, built-out customer personas, product demonstrations, and examples of internal or external messaging.
4. Reference data
All information regarding the market, your competitors, and your customers should reference authoritative and relevant data points.
5. Research, research, research
The research that goes into your business plan should take you longer than the writing itself. Consider tracking your research as supporting documentation.
6. Clearly demonstrate your points of difference
At every opportunity, it’s important to drive home the way your product or service differentiates you from your competition and helps solve a problem for your target audience. Don’t shy away from reiterating these differentiating factors throughout the plan.
7. Be objective in your research
As important as it is to showcase your company and the benefits you provide your customers, it’s also important to be objective in the data and research you reference. Showcase the good and the bad when it comes to market research and your financials; you want your shareholders to know you’ve thought through every possible contingency.
8. Know the purpose of your plan
It’s important you understand the purpose of your plan before you begin researching and writing. Be clear about whether you’re writing this plan to attract investment, align teams, or provide direction.
9. Identify your audience
The same way your business plan must have a clearly defined purpose, you must have a clearly defined audience. To whom are you writing? New investors? Current employees? Potential collaborators? Existing shareholders?
Related articles
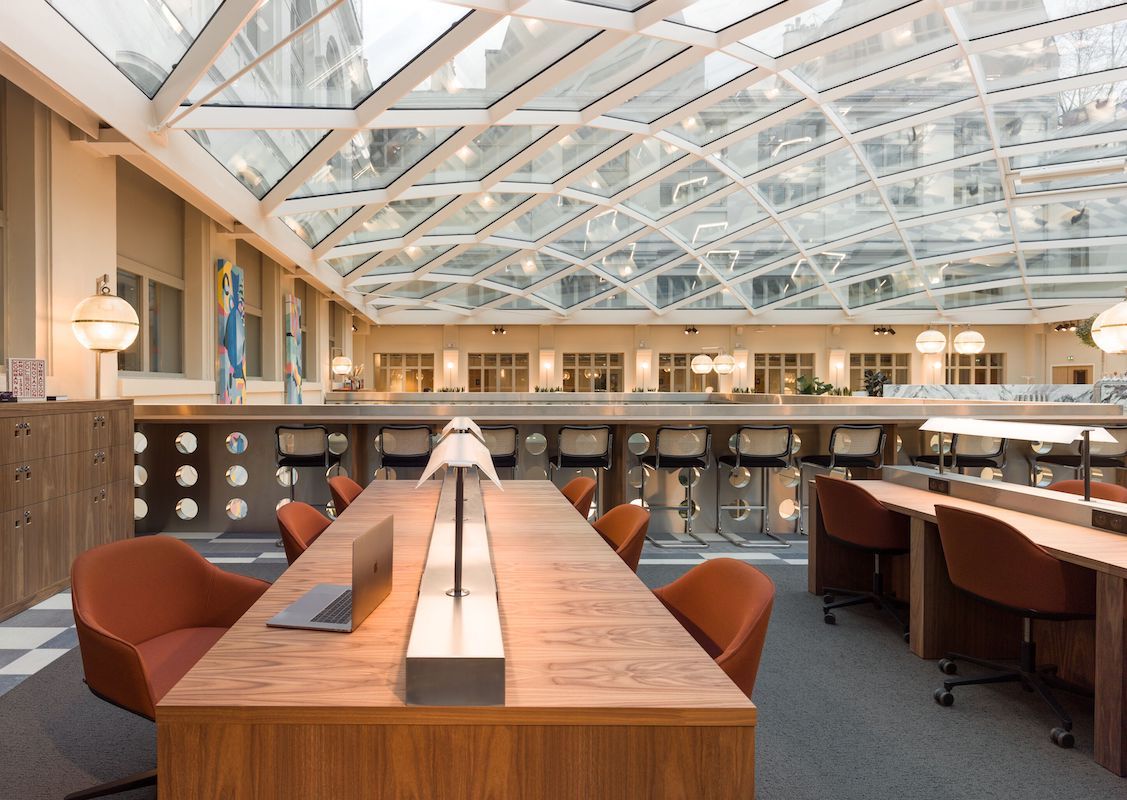

10. Avoid jargon
Avoid using industry-specific jargon, unless completely unavoidable, and try making your business plan as easy to understand as possible—for all potential stakeholders.
11. Don’t be afraid to change it
Your business plan should evolve with your company’s growth, which means your business plan document should evolve as well. Revisit and rework your business plan as needed, and remember the most important factor: having a plan in place, even if it changes.
A business plan shouldn’t just be a line on your to-do list; it should be referenced and used as intended going forward. Keep your business plan close, and use it to inform decisions and guide your team in the years ahead.
Creating a business plan is an important step in growing your company
Whether you’re just starting out or running an existing operation, writing an effective business plan can be a key predictor of future success. It can be a foundational document from which you grow and thrive . It can serve as a constant reminder to employees and clients about what you stand for, and the direction in which you’re moving. Or, it can prove to investors that your business, team, and vision are worth their investment.
No matter the size or stage of your business, WeWork can help you fulfill the objectives outlined in your business plan—and WeWork’s coworking spaces can be a hotbed for finding talent and investors, too. The benefits of coworking spaces include intentionally designed lounges, conference rooms, and private offices that foster connection and bolster creativity, while a global network of professionals allows you to expand your reach and meet new collaborators.
Using these steps to write a business plan will put you in good stead to not only create a document that fulfills a purpose but one that also helps to more clearly understand your market, competition, point of difference, and plan for the future.
For more tips on growing teams and building a business, check out all our articles on Ideas by WeWork.
Caitlin Bishop is a writer for WeWork’s Ideas by WeWork , based in New York City. Previously, she was a journalist and editor at Mamamia in Sydney, Australia, and a contributing reporter at Gotham Gazette .

Learn the differences between Class A, Class B, and Class C buildings based on their visual appeal, location, and amenities to see which of them best suits your business.

Short-term leases can offer startups and established companies some much-needed flexibility

From federal taxes to 401(k)s, figuring out payroll deductions can be a headache. Here’s how to get started
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Business and self-employed
- Business finance and support
Write a business plan
Download free business plan templates and find help and advice on how to write your business plan.
Business plan templates
Download a free business plan template on The Prince’s Trust website.
You can also download a free cash flow forecast template or a business plan template on the Start Up Loans website to help you manage your finances.
Business plan examples
Read example business plans on the Bplans website.
How to write a business plan
Get detailed information about how to write a business plan on the Start Up Donut website.
Why you need a business plan
A business plan is a written document that describes your business. It covers objectives, strategies, sales, marketing and financial forecasts.
A business plan helps you to:
- clarify your business idea
- spot potential problems
- set out your goals
- measure your progress
You’ll need a business plan if you want to secure investment or a loan from a bank. Read about the finance options available for businesses on the Business Finance Guide website.
It can also help to convince customers, suppliers and potential employees to support you.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Should You Stick to the Business Plan or Change It?
5 min. read
Updated April 9, 2024
Is it time for plan B?
The best and most useful kind of business planning is not just a use-once business plan, but rather a continuous process.
The first business plan is just the first step. For the rest of your business’s life, you review the plan once a month. Compare actual results to what you had planned, determine what steps to take to optimize, and revise the plan.
You’ll find that continuous business planning helps in many ways:
- It helps maintain focus
- You’ll be able to align the team with priorities
- You can address changes in the marketplace as they happen
- It helps you tune strategy and tactics to what’s working and what’s not working
- It starts with knowing what happened
Review means comparing what actually happened to what you expected. Business plans are always wrong, so there will always be a difference between the plan and the actual results.
For the actual business numbers, such as sales, expenses, and such, accountants call the difference between the estimates in the plan and the actual results variance. Variance analysis looks at these differences to determine where the numbers are different, and in what direction.
What’s important here is not the accounting or the calculations, but rather the resulting management. You look for indications of problems or unexpected positives, so you can react.
In the illustration above, revenue is lower than planned and expenses are higher. Operating income is less than planned. Cash and cash flow are improving, which is good news. However, that may be because this company is stretching out its payments, averaging about six months, which is seven times more than in their plan. So accounts payable is 25 percent higher than planned. That’s good because it’s helping with financing and keeping money in the bank, but may also be bad because it could be spoiling reputation and relations with vendors.
The point is the management, not the hard numbers. What should be done, given these results, to make the company better?
- The monthly review meeting
The monthly review meeting is absolutely essential to real business planning— Lean Planning . The real value of business planning is the decisions it causes, and the management that results; and for that, you need not just a plan but a regular monthly review to track results and revise as necessary.
And the toughest part of the review meeting is this crucial question: Do we stick to the plan, or do we change it?
That comes up often because in the real world things never go exactly as planned. Business plans are supposed to set goals, tracking, milestones, and expectations.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
The review meeting is when you ask:
- What happened? What went right and what went wrong?
- If I change the plan, then is my plan (forecast) versus actual result valid?
- Doesn’t it take consistent execution to make strategy work?
You won’t find some set of best practices to make this easy. You’ll end up deciding on a case-by-case basis.
- The arguments for staying the course with your plan
I consider this an awkward, difficult fact about business strategy:
It’s better to have a mediocre strategy consistently applied over three or more years, than a series of brilliant strategies, each applied for six months or so.
Too often, management teams get bored with strategy before it’s had a chance to be effective. I was consulting with Apple Computers during the 1980s when the Macintosh platform became the foundation for what we now call “desktop publishing.” We take it for granted today, but back in 1985 when the first laser printers came out, it was like magic. Suddenly, a single person in a home office could produce documents that looked professional.
What I saw in Apple at that time was smart young managers getting bored with desktop publishing long before the market even understood what it was. They started looking at multimedia instead. They were attracted to new technologies and innovation. As a result, they lost the concentration on desktop publishing and lost a lot of market potential as Windows vendors moved in with competitive products.
That argues for staying the course. Strategy takes time.
- The arguments for revising the plan
On the other hand, this is also true:
There is no virtue in sticking to the plan for its own stake. Nobody wants the futility of trying to implement a flawed plan.
Generally accepted best practices have changed over the three decades I’ve been focusing on business planning.
Back in the 80s, business timeframes stretched longer and many business leaders recommended sticking to the plan. But times have changed. You’ve probably dealt with the problem of people doing something “because that’s the plan” when in fact it just isn’t working. I certainly have. That kind of thinking is one reason why some web companies survived the first dotcom boom and others didn’t. It also explains why some business experts question the value of the business plan.
This is sloppy thinking, in my opinion—confusing the value of the planning with the mistake of implementing a plan without change or review, just because it’s the plan.
- How to decide: Stay the course, or revise the plan?
This consistency versus revision dilemma is one of the best and most obvious reasons for having people—owners and managers—run the business planning, rather than algorithms or artificial intelligence. It takes people to deal with this critical judgment.
One good way to deal with it is by focusing on the assumptions. Identify the key assumptions and whether or not they’ve changed. When assumptions have changed, there is no virtue whatsoever in sticking to the plan you built on top of them.
Use your common sense . Were you wrong about the whole thing, or just about timing? Has something else happened, like market problems, disruptive technology, or new competition, that has changed your basic assumptions?
Do not revise your plan glibly . Remember that some of the best strategies take longer to implement. Remember also that you’re living with it every day; it is naturally going to seem old and boring to you long before the target audience gets it. But do revise your plan if it is out of date, inaccurate, or based on false assumptions.
That’s why you have the plan in the first place: to manage your business better.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- You’ll find that continuous business planning helps in many ways:
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Real Estate Business Plan + Example Templates
8 Min. Read
How to Write a Home Health Care Business Plan

How to Create A Digital Marketing Plan and Strategy

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Tax changes small business owners should be aware of as the tax deadline looms
FILE - A cash register is seen on the front counter at the Alpha Shoe Repair Corp., Feb. 3, 2023, in New York. As Tax Day, April 15, approaches, there are plenty of things small business owners should keep in mind when filing taxes this year. (AP Photo/Mary Altaffer, File)

- Copy Link copied
As Tax Day approaches, there are plenty of things small business owners should keep in mind when filing taxes this year.
April 15 is still the annual tax deadline for many small businesses although, unlike individuals, small businesses can have varying deadlines depending on the type of company, the state the taxes are filed in, and other factors. Quarterly estimated tax payments are generally required throughout the year. And certain types of small businesses had to file by March 15.
Since business tax filing is complex, most experts recommend small business owners work with a professional tax adviser rather than trying to file on their own or even with tax-filing software.
“Taxes should not be scary, especially when you have a certified tax professional or someone who is your trusted adviser,” said Amber Kellogg, vice president of affiliate origination and management at business consultancy Occams Advisory. “I always say you don’t go to the dentist to get your oil changed, and you certainly shouldn’t do (taxes) yourself unless you’re an expert.”
But even if small business owners aren’t filing taxes themselves, it’s still important to stay informed about any tax changes during the year. Here are things small business owners should consider as the April 15 deadline looms.
Consider an extension
Because of some pending tax legislation in Congress this year, Mitch Gerstein, senior tax adviser at accounting firm Isdaner & Co., said it might be a good idea to file for an extension. When you file an extension you still pay estimated taxes, but final paperwork isn’t due until September.
This gives your tax provider adequate time to file a return. And it’s cheaper to file an extension than an amended return, which costs more in administrative fees.
One reason Gerstein recommends an extension this year: a bonus depreciation write-off used by many small businesses is set to decrease for 2023. The bonus depreciation allowance was designed to spur capital purchases and it let businesses write off 100% of certain new and used assets in 2022. But beginning in 2023, that will decrease to 80% for used assets, dropping another 20% each year thereafter. However, a tax bill pending in Congress could restore the write-off to 100%. It’s rare that there is such a significant tax bill pending in Congress when taxes are due, Gerstein said.
Optimize your retirement plan
The Secure Act 2.0 passed by Congress in late 2022 gives small businesses some tax advantages if they offer a retirement plan. There’s a tax credit for small businesses starting new employee plans. The credit is up to 100% of the startup costs for adopting and maintaining a new 401(k) plan, capped at $5,000. There’s also a tax credit based on employer contribution, up to $1,000 annually per employee, over the plan’s first five years.
Changes in research and development write-offs
Scott Orn, chief operating officer of Kruze Consulting, works with startups backed by venture capital. Orn said the number one concern his clients are calling about is “Section 174,” a part of the tax code that involves writing off research and development costs.
In the past, companies were able to deduct 100% of research and development expenses from their taxable income. That was helpful because often that deduction meant the company was operating at a loss and wouldn’t have to pay taxes.
But starting in 2022 due to new legislation, companies have had to “capitalize” the expense – or spread it out over several years. That means they must now write off the expenses over five years for U.S.-based R&D, or 15 years for foreign R&D expenses.
Large and small companies alike are affected by the change, but small businesses are hurt the most, Orn said.
“(Small businesses) are the ones who are swinging into profit where they thought they were like safely losing money and not ever going to pay taxes for a while,” Orn said. “And that’s why it’s such a big surprise for them. It’s hurting people, it’s like it’s a lot of money these companies don’t have.”
Avoid underpayment penalties
Yet another reason for small business owners to use a tax professional is the fact that underpaying will cost more this year. In the past, underpayment penalties hovered at around 3%, but this year they’re more than double at 8% . That’s because the penalties are based on the federal short term interest rate plus three points, said Danny Castro, Florida Market Tax Leader at BDO USA, part of BDO Global, a global accounting network.
“The cost of underpayment is as high as it’s been in a long time,” he said.
One credit to skip: the ERC
At one time, the pandemic-era Employee Retention Credit seemed like a boon for small businesses. Designed to help small businesses keep employees during pandemic-era shutdowns, the generous credit let businesses file amended tax returns to claim the credit.
But that led to a cottage industry of scammers trying to entice small businesses to help them file for the credit – for a fee – even if they didn’t qualify. The IRS has launched several initiatives to claw back some money improperly given to businesses. To date, the IRS said 500 taxpayers have given back $225 million via a voluntary disclosure program, which ended on March 22, that let small businesses who thought they received the credit in error give back the money and keep 20%. And 1,800 businesses have withdrawn unprocessed claims totaling $251 million.
Get organized, stay organized
The best thing small businesses can do to help their tax advisers file their taxes is stay organized. A shoe box full of receipts isn’t helpful when trying to file timely taxes. Owners should log receipts in an orderly database they can turn over to their adviser. And stay on top of quarterly estimated payments.
“(Small business owners) need to be able to keep accurate records throughout the year and not have to go back in April and go, gosh, what what was this receipt for,” said Occams Advisory’s Amber Kellogg, “Keeping those, accurate records is very, very important.”
This story has been corrected to show that BDO USA is part of BDO Global, not BBO Global.

I'm a manager who has put several people on performance improvement plans. Here's why you should see it as a positive opportunity.
- A PIP outlines an employee's deficiencies and provides a roadmap for improvement.
- Managers may use a PIP to help an employee improve or to manage them out of a role.
- A PIP can be an opportunity to elevate your skills or assess your commitment to the job and company.

A performance improvement plan — or a PIP — typically details an employee's deficiencies, failures to meet job goals, or issues with behavior. It should also provide a road map and timeline for rectifying these failures.
The plan typically outlines skill gaps and lack of goal achievement, including steps to improve performance and meet expectations. A PIP is not delivered for a one-time issue but for habitual failure to perform job tasks.
As a manager of global credit and collection teams for over two decades, I've issued several PIPs and learned how to navigate the process properly.
Here's what managers really want you to know and how you should reframe the process.
What does a PIP actually mean?
If you receive a PIP, study the document and allow time to process your emotions . It's easy to feel like you're being threatened or like you are a failure at your job. But you can't let your thoughts and feelings get the best of you. You need to start acting proactively — and quickly.
First, you need to assess what the company really means in giving you a PIP. You can do this by simply analyzing how your manager presents the PIP and if they offer assistance in completing the plan.
In many cases, the company might just be trying to manage you out of the role — for a variety of reasons. But in other situations, you may simply not be performing up to par, and they want to ensure you get the necessary skills to succeed.
Do you still want the job?
If you believe the company actually wants to see you succeed and help you, then you should ask yourself a series of questions. First, it's crucial to consider your own goals.
Ask yourself: How strong is my commitment to this job and the company? Is this my dream job ? Is there a possibility of advancement? How much have I invested in this company? Do I like and respect management and the company's mission statement, commitment to diversity, and corporate social responsibility?
Related stories
Think of this as a chance to really analyze your feelings about your job and career.
Once you answer these questions, you can move forward.
I once presented a PIP to one of my employees. They were keen to improve their skills and were committed to the company. Together, we made an attainable plan.
In another case, the employee was simply in the wrong role and was more suited to another job function. They felt more suited to customer service instead of collections, so in lieu of the PIP, they transferred to another department.
Once you understand what you want from the company, you can move forward.
How do you succeed and keep your job?
If you are committed to the role and the company and want to survive the PIP , you should first study the timeline for improvement goals to ensure they are attainable.
Next, you should objectively evaluate your skills and performance gaps. Once you understand the skills you need to succeed, create a plan for yourself on how to obtain those skills. For example, get advice from other team members with those skills and ask them how they do it. Ask if there are any resources or support at the company that will teach you the skills you are missing.
In each meeting with your manager , highlight your progress and show them what you are learning. Don't forget to document all meetings and conversations regarding your progress.
Lastly, don't be afraid to ask for an adjustment of the timeline or the goals — as long as you are showing progress.
A PIP can be seen as a positive opportunity
A PIP can become an opportunity to learn or even elevate your skills. It can lead to success. It is also a check-in on your commitment to the job and the company.
You should either believe you can survive the PIP and thrive in your current position or choose to work elsewhere.
If you think it's time to quit, o rganize your résumé and references and start job hunting. If you want to stay in your position, get ready to work hard.
- Main content
FinCEN’s Anti-Money Laundering Plan Should Put Advisers on Alert

The Treasury Department may finally see success in its third attempt to extend anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism, or AML/CFT, requirements under the Bank Secrecy Act to investment advisers.
The protectionist political climate, coupled with the Treasury’s additional efforts in publishing the risk assessment, suggest persistence may pay off this time.
While some advisers already implement many AML/CFT requirements, either voluntarily or due to affiliations with banks and broker-dealers, all SEC-registered investment advisers and exempt reporting advisers may want to start evaluating risks and identifying steps to compliance.
They can start this process by reviewing extensive guidance already available to other entities already subject to AML/CFT. One such resource, an AML tool for broker-dealers, available on the SEC’s website , is full of practical lists, examples, FAQs, and other resources for compliance.
The Treasury had proposed a rule in February requiring registered investment and exempt reporting advisers to implement an AML/CFT program, including written policies, procedures, and internal controls reasonably designed to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit financing activities.
These intentionally include advisers to private funds, such as hedge funds, venture capital funds, and private equity funds. Investment advisers registered at the state level—generally meaning advisers with less than $100 million of assets under management—would be excluded.
In the notice, the Treasury reported that investment advisers are a major vulnerability in defenses against financial crimes, money laundering, and terrorism finance in its 2024 investment adviser risk assessment , asserting that lack of uniform applicability and compliance across the industry creates opportunities for illicit activity.
It cites examples such as Russian oligarchs obscuring wealth derived from corruption or other illicit activity, as well as governments, such as China, investing in venture capital funds as a back door to steal critical and emerging US technology.
Any AML/CFT program would have to be approved by the adviser’s board of directors or equivalent. A specific person would be designated as responsible for implementation. Affected advisers would be expected to tailor such programs to identify and mitigate specific risks for their unique business, clients, geographies, and strategies.
For now, the proposal doesn’t extend the Bank Secrecy Act’s customer identification program, nor related beneficial ownership information requirements, to registered investment and exempt reporting advisers—although the Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network has indicated it may do so in the future.
FinCEN is accepting comments on the proposal through April 15 and has requested comments in areas that may change before finalization, such as whether other exclusions are warranted in lower risk areas. The compliance date would be 12 months after the effective date of any final rule, and enforcement would be largely delegated to the SEC.
AML/CFT rules already apply to other financial institutions, such as banks and broker-dealers. Attempts to expand the definition in 2003 and 2015 were withdrawn following stiff industry opposition.
As with any new, major proposed federal regulation, court challenges are possible. The presidential election in November also could impact implementing the proposed rule.
Despite this uncertainty, a prudent investment adviser will begin the internal review and preparation process to be ready for timely compliance. Keeping abreast of comments and any court challenges while the rule is pending may provide advance insight as to whether, and if so in what form, the rule will eventually be implemented.
This article does not necessarily reflect the opinion of Bloomberg Industry Group, Inc., the publisher of Bloomberg Law and Bloomberg Tax, or its owners.
Author Information
Eric Mikkelson is partner at Stinson, where he co-chairs its investment management practice group.
Write for Us: Author Guidelines
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Rebecca Baker at [email protected] ; Daniel Xu at [email protected]
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Get Student Loan Forgiveness in 2024

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Student loan forgiveness has a mixed track record. Last summer, the Supreme Court struck down a broad plan that would’ve erased up to $20,000 per borrower. Still, student loan forgiveness is more accessible now than ever before. A handful of existing federal student loan forgiveness programs have erased $143.6 billion in student debt for 3.96 million borrowers as of March 21, according to the Education Department, with more to come this year.
The White House is currently trying to push through a narrower forgiveness ‘Plan B’ version of its failed broad forgiveness plan. The proven paths to forgiveness, however, include programs that range from income-driven repayment (IDR) plans — which cap monthly bills at a percentage of your income and forgive your remaining balance after 10 to 25 years — to niche programs for borrowers with certain loan types, jobs or school circumstances.
Here’s how to get student loan forgiveness in 2024 — and what you need to know before pursuing this path.
Check your eligibility
You must have federal student loans to qualify for a forgiveness program. Private student loans aren’t eligible.
To verify you have federal loans, go to StudentAid.gov , and try to log in or recover your account.
Next, check which types of federal student loans you have. If you have certain types of loans, like commercially held FFELP or Perkins loans, you may have to consolidate them before going after forgiveness .
Income-driven repayment
The newest IDR plan — Saving on a Valuable Education, or SAVE — is the most accessible path to forgiveness. All borrowers with federal direct loans are eligible to enroll.
The SAVE plan forgives remaining student debt in as little as 10 years if you have an original balance of $12,000 or less, and in up to 20 or 25 years for other borrowers. While working toward forgiveness, your monthly bills could be $0 per month if you earn less than $32,800 as an individual or $67,500 as a family of four; otherwise, they’ll be capped at 5%-10% of your income.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness
If you work for a qualifying government or nonprofit employer, you could be eligible for Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) . This program erases your remaining balance after a decade of repayment.
“Generally, the PSLF program is the best one if you have access to it,” says Scott Stark, a financial coach and certified financial planner at Financial Finesse, a workplace financial wellness company.
Other forgiveness programs
Outside of IDR and PSLF, your student loan forgiveness options may include:
Teacher Loan Forgiveness , if you work in a qualifying low-income school.
Borrower defense to repayment , if you think your school defrauded you.
Closed school discharge , if your school closed during or shortly after your time there.
Perkins loan cancellation , if you have Perkins loans and work in public service.
State-based student loan payment assistance , if you work in health care or are willing to relocate to a new area.
Do the math
Use the Education Department’s loan simulator to see how much debt you could get erased under various forgiveness programs and repayment plans, how much your monthly payments could be and how long you’ll be in repayment.
If an IDR plan will result in you paying more interest for a longer period or paying off your debt before getting forgiveness, then it may not be a good choice for you. (Public Service Loan Forgiveness also requires enrollment in an IDR plan.)
“It really is a case-by-case kind of thing, but generally speaking, for people whose income is relatively high compared to their student debt loads, the income-driven repayment plans can be pretty unattractive,” says Tisa Silver Canady, founder of the Maryland Center for Collegiate Financial Wellness. “It might behoove them to just stay on a balance-driven plan and pay extra when they feel it makes sense.” Making extra payments toward the principal while on a balance-driven plan — like the standard 10-year plan , which splits your loan into 120 payments — allows you to shrink your debt faster and reduce total interest costs.
On the other hand, if the math for IDR works out such that borrowers can have smaller payments and keep more of their money to reach other financial goals, pursuing forgiveness is a good option, Stark says.
Prepare for a future tax bomb
IDR student loan forgiveness is exempt from federal taxes through 2025. After that, any amount forgiven could result in a student loan tax bomb . A small number of states tax IDR forgiveness, too.
It’s important to plan for a tax bomb if your forgiveness timeline will extend past 2025. Put a small amount of money aside each month to cover your future tax bill, Stark says.
Use the loan simulator to determine how much forgiveness you could ultimately receive: Your taxable income will increase by that amount in the year you get forgiveness. In some cases, the forgiveness could push you into a higher tax bracket, which could further increase your tax burden. If the amount you have to set aside each month to cover the tax bill is larger than the amount you’d save on the IDR plan, it might not be worth it.
Loan balances forgiven through PSLF, Teacher Loan Forgiveness, borrower defense to repayment, closed school discharge and Perkins loan cancellation are exempt from federal taxation.
Change your repayment plan
If you decide IDR forgiveness is the right choice, you must switch to an IDR plan like SAVE.
To sign up for an IDR plan, submit an online application at StudentAid.gov/IDR or call your student loan servicer.
You must also sign up for an IDR plan if you’re striving for PSLF. Choose the plan that gives you the smallest monthly bill to maximize the amount you could get forgiven after 10 years. It’s a good idea to submit your PSLF employer verification form each year to stay on track for forgiveness, Canady says. You can do this through the Education Department’s online PSLF Help Tool .
On a similar note...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Sell your business and explain why it matters. Additionally, supplement your sell with a high level summary of your plan and operating model. However, don't go over one or two pages. Feel free to include the following as well: Business Name. Key Employees. Address.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
To understand what should be included in a business plan, you have to understand who the plan is for and what stage of your business you're in. If you'll be taking a business plan to a financial institution as part of a loan application, you're going to want a more traditional plan. These tend to be on the longer side and should be as ...
Determine how you can best reach potential customers. Evaluate your competition. Your marketing plan must set you apart from your competition, and you can't stand out unless you know your ...
Business Plan Template [Download Now]Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template.Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
1. Executive Summary. The executive summary outlines the whole plan. You start with a clear introduction of who you are, what you sell, and what your ambitions are as a business. This section includes your mission statement, product description, and the basic overview of your company's structure. It should also include your financial plans.
The one-page business plan is essentially an executive summary — in other words, the TL;DR version of your business plan where you distill down each of the core sections of your business plan to a paragraph or two, giving investors an at-at-glance look at the key takeaways.
A business plan is a formal document (about 15-25 pages in length) that precisely defines a company's objectives in fine detail. It also describes how the company plans to achieve its goals. All companies — including startups and established institutions — create and use business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Provide a breakdown of costs per unit made/sold, life cycle, and expected profit margins. Explain your supply chain, order fulfillment, and sales strategy. Include your plans for intellectual property, like trademarks and patents. Your product and service description brings you to those who matter most.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Organize your Marketing Plan into the 4 P's - Price, Product, Promotions and Place. If you have multiple products or services, include a menu with each key item and its price. 7. The Operations Plan Format. Your Operations Plan identifies your key operational processes and milestones you expect to accomplish.
This is typically one of the first pieces of the plan to be written. 3. Market analysis and opportunity. Research is key in completing a business plan and, ideally, more time should be spent on research and analysis than writing the plan itself. Understanding the size, growth, history, future potential, and current risks inherent to the wider ...
A business plan is a written document that describes your business. It covers objectives, strategies, sales, marketing and financial forecasts. A business plan helps you to: You'll need a ...
The first business plan is just the first step. For the rest of your business's life, you review the plan once a month. Compare actual results to what you had planned, determine what steps to take to optimize, and revise the plan. You'll find that continuous business planning helps in many ways: It helps maintain focus
Optimize your retirement plan. The Secure Act 2.0 passed by Congress in late 2022 gives small businesses some tax advantages if they offer a retirement plan. There's a tax credit for small businesses starting new employee plans. The credit is up to 100% of the startup costs for adopting and maintaining a new 401(k) plan, capped at $5,000.
A performance improvement plan — or a PIP — typically details an employee's deficiencies, failures to meet job goals, or issues with behavior. It should also provide a road map and timeline ...
People traveling to see the eclipse should plan accordingly, including downloading maps and directions beforehand to have with them offline, in case of poor connection.
Any AML/CFT program would have to be approved by the adviser's board of directors or equivalent. A specific person would be designated as responsible for implementation. Affected advisers would be expected to tailor such programs to identify and mitigate specific risks for their unique business, clients, geographies, and strategies.
Making extra payments toward the principal while on a balance-driven plan — like the standard 10-year plan, which splits your loan into 120 payments — allows you to shrink your debt faster and ...