Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 11 March 2021

Addressing the digital skills gap for future education
- Joshua A. Jackman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1800-8102 1 , 2 ,
- Douglas A. Gentile ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5934-2860 1 , 3 ,
- Nam-Joon Cho ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8692-8955 4 &
- Yuhyun Park ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8991-755X 1
Nature Human Behaviour volume 5 , pages 542–545 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
21k Accesses
26 Citations
96 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused rushed digitalization of primary and secondary (K12) student education, and cyber-risks such as bullying, technology addiction, and misinformation must be addressed. There is an urgent need to coordinate global efforts for digital skills education and training, which can help students succeed in the digital age while curbing risks and inequality.
The digital world is an indelible part of modern life. For many people, it is the world where we communicate, learn, shop, and entertain ourselves. The digital world has transformative power to connect people across the world.
Nonetheless, the digital world has many challenges. It is associated with a wide range of cyber-threats such as hacking, bullying, identity theft, human trafficking, technology addiction, and privacy invasion, while gaming disorder has been recognized as a medical condition by the World Health Organization (WHO).
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the widespread digitalization of numerous sectors that were unprepared. One of the most affected groups has been K12 students, many of whom have been forced to switch to online schooling. The rapid transition has been challenging and compounded by issues such as limited digital skills, technology access, inequality, and systemic racism.
We urgently need a globally coordinated response to help students acquire digital skills, which are needed to keep pace with this fast-changing landscape. It is especially important to cultivate digital citizenship along with a broader set of digital skills that can facilitate participation and support students in maximizing opportunities and minimizing risks in the digital world.
Cyber-risk impacts
The impact of the digital world on students began long before the COVID-19 pandemic. The digital world has brought tremendous benefits, but the rate of digital technology advances is far greater than the speed at which we have adapted in terms of education, policies, and culture.
This mismatch has allowed cyber-risks to proliferate among children who are left exposed without adequate preparation or safeguards. To understand the prevalence of cyber-risks worldwide, our team conducted a survey of over 145,000 children and adolescents across 30 countries 1 . The participants were asked questions about their personal experiences with different types of cyber-risks and evaluation metrics were developed based on the frequency of exposure.
Among the survey results, it was found that 60% of 8- to 12-year-old children were exposed to cyber-risks such as cyberbullying, gaming disorder, sexual grooming, and violence (Fig. 1a ). Notably, 45% of children online were affected by cyberbullying, 39% experienced reputational risks, 29% were exposed to violent and sexual content, 28% experienced cyber threats, 17% had risky contacts such as an offline meeting with strangers or sexual contact, 13% were at risk of a gaming disorder, and 7% were at risk of a social media disorder.
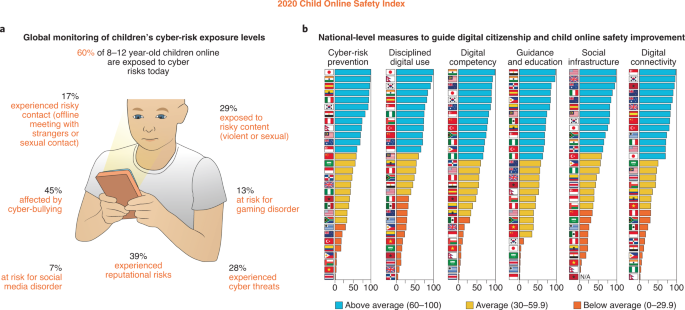
a , Percentages of 8- to 12-year-old children in the survey who reported encountering different types of cyber-risks. b , National comparisons in six different assessment categories: cyber-risk prevention, disciplined digital use, digital citizenship, guidance and education, social infrastructure, and digital connectivity. The scores were standardized across the 30 countries included in the Child Online Safety Index, with higher scores indicating better performance. Adapted with permission from ref. 1 , DQ Institute.
The results also showed that countries varied greatly in critical aspects of digital safety and infrastructure (Fig. 1b ). East Asian and Western countries tended to rank higher for child online safety. East Asian countries also tended to score high on cyber-risk prevention, disciplined digital use, digital citizenship, and digital connectivity. On the other hand, Western countries tended to have strong social infrastructure, guidance, and education. These data highlight that nations in all regions of the world have room for improvement and could learn from each other’s best practices—an issue which has gained heightened attention due to COVID-19.
An educational crisis
Over the past year, the global K12 education system has largely moved online, which has influenced student learning performance and wellbeing. Indeed, school closures caused by COVID-19 are estimated to have affected up to over 84% of the world’s student population and continue in many locations worldwide 2 .
As a stopgap measure, many schools started using digital education tools to offer online teaching while students stay at home. These efforts have helped students and teachers interact in a physically safe manner and also spurred renewed interest in educational technology innovation. However, there have been concerns about introducing new forms of digital education so abruptly, especially in terms of learning effectiveness and cybersecurity 3 . Such challenges will likely be addressed over time as school systems, teachers, and students become more familiar with the digital learning environment and online teaching approaches are refined.
Of more immediate concern, the switch to online learning has also deepened the exposure of students to cyber-risks and affected socialization 4 . Online classes are leading students to grow accustomed to spending more time online, blurring the distinction between physical and digital spaces. For example, it has been estimated that children are spending around twice as much time on social media sites and video-sharing platforms as compared to the previous year, and increased screen time is associated with technology addiction and mental health effects 5 , 6 , 7 . In addition to technology addiction, there has also been a rise in cyberbullying that coincides with school closures and the switch to online learning 8 , 9 .
It is imperative to address these growing cyber-risk issues. Even before COVID-19, most students were already suffering from inadequate online safety support and were unprepared to study primarily in the digital world. COVID-19 is a trigger to enact change and help students acquire critically needed digital skills.
Digital skills education
To date, there have been extensive efforts to create digital skills education programs. The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Learning Framework 2030 cites digital literacy as a core fundamental competency for future education 10 . However, until recently, there was weak coordination between programs and no globally accepted meaning of concepts such as digital literacy. Hence, the impact of digital skills education programs was limited even while the digitalization of K12 student education accelerates.
To address this issue, the Coalition for Digital Intelligence—comprising the OECD, IEEE Standards Association, and DQ Institute, in association with the World Economic Forum—spearheaded development of the recently approved IEEE Standard for Digital Intelligence (DQ) Framework for Digital Literacy, Skills, and Readiness ( 3527.1-2020 ). This set of internationally accepted standards establishes a common framework to coordinate digital-competency-building efforts worldwide.
These global standards build on the emerging concept of the DQ framework, which describes the collective set of technical, cognitive, meta-cognitive, and socio-emotional competencies that can help individuals thrive in the digital world 1 . While digital intelligence has been previously discussed in terms of human interactions with digital technology 11 and incorporating digital technology into business strategies 12 , the DQ framework focuses on digital skills education across eight competencies, including identity, use, safety, security, emotional intelligence, literacy, communication, and rights, and across three levels of citizenship, creativity, and competitiveness 13 . It was first described in a World Economic Forum article 14 followed by a DQ Institute white paper in 2017 (ref. 15 ).
The DQ framework has been used within the #DQEveryChild digital citizenship educational program to strengthen fundamental digital skills (the first level of the DQ framework) in over 1 million children in more than 80 countries 1 (Fig. 2 ). The program was centred on the DQ World online learning platform, and evaluation of student learning outcomes demonstrated that the competencies are learnable using this program. Numerous government agencies, non-profit organizations, and schools have begun adopting the DQ framework, as demonstrated by successful case study examples in various countries such as Mexico, Turkey, and Thailand.
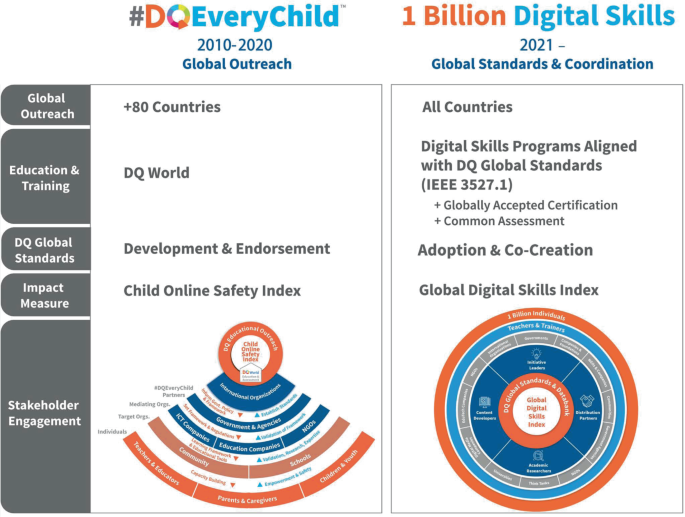
Over the past decade, the #DQEveryChild educational outreach program was implemented to empower K12 students with digital skills based on the DQ framework. The 1 Billion Digital Skills project is a new call to action for stakeholders to adopt DQ global standards and to co-create a wide range of digital skills education and training programs that address societal needs.
The #DQEveryChild program set an important precedent for enhancing digital skills among students, and we believe that the greatest potential of the DQ framework lies in fostering an innovation ecosystem in which different stakeholders can work together to build and deploy a wide range of digital skills education and training programs that are tailored to specific needs and learning objectives. The newly launched 1 Billion Digital Skills Project, led by the Coalition for Digital Intelligence, embodies this vision and is a call to action for committed stakeholders to work together to empower 1 billion people, especially K12 students, teachers, and parents, with digital skills within 10 years. The project is built on the belief that digital intelligence is a universal human right and can enable the sustainable development of nations with more inclusive growth, wellbeing, and prosperity. To achieve this goal, the project seeks to bring together various stakeholders such as content developers, initiative leaders, academic researchers, and educators to achieve the following objectives:
Build a global network of partners that are committed to developing and implementing digital skills education and training programs based on the DQ global standards and to inspiring cooperation. A recent example is the new partnership between the DQ Institute, Alannah & Madeline Foundation, and Accenture to enable 11- to 14-year-old children in Australia and New Zealand to earn an eSmart Digital Licence that is based on Accenture’s Skills to Succeed and incorporates the eight competencies of the DQ framework.
Develop a program certification system to evaluate digital skills programs and drive alignment with DQ global standards. This system will provide information about what types of competencies are taught in different programs to guide curriculum planning.
Develop microbadge credits that students can earn when they complete learning objectives within certified digital skills programs. The credits can incentivize learning and provide evidence of learning accomplishments, and such approaches can also be extended to teacher training and parent awareness.
Create an online assessment platform where individuals and organizations can measure digital skill levels across competencies based on microbadge credits. The results can provide guidance for developing globally accepted performance standards to evaluate digital skills education and training outcomes as well as to measure the impact of specific initiatives.
Support ongoing improvement of the DQ global standards based on performance outcomes, student and teacher feedback, stakeholder input, and academic research. Further conceptual development of the DQ framework and quotient will strengthen the pedagogy of digital skills education and training programs. There is also a need to develop rigorous methods for evaluating the educational efficacy of different programs to achieve specific learning objectives. Such feedback can also be used to improve programs and to identify best practices within the DQ framework.
Conclusions and outlook
The widespread digitalization of the educational sector is happening now, and we must ensure that this transformation occurs inclusively while stemming the tide of rising inequality. Such outcomes would go a long way towards ensuring sustainable development of the digital economy and its potential to transform the lives of countless individuals through digital skills education. We believe that online learning will play an increasingly important role in the K12 education system. We must do more to support student success in the digital world, and these efforts should focus on empowering students with a core set of digital skills. The digitalization of the education sector is the latest example of broader trends in the global economy as a whole and the efforts we describe here can also be applied to teacher training as well as to workforce training in general. Online and offline options are no longer dichotomies; the digital world is becoming increasingly fused into our daily lives and we must make a concerted effort to ensure that all individuals are supported with digital skills education and training to thrive in this digital age.
Child Online Safety Index. A Findings and Methodology Report. https://www.dqinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/2020-COSI-Findings-and-Methodology-Report.pdf (DQ Institute, 2020).
Education: From Disruption to Recovery. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse (UNESCO, 2020).
Reimers, F.M. & Schleicher, A. Schooling Disrupted, Schooling Rethought: How the COVID-19 Pandemic Is Changing Education (OECD, 2020).
Colao, A. et al. Lancet Public Health 5 , e370 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Dong, H., Yang, F., Lu, X. & Hao, W. Front. Psychiatry 11 , 00751 (2020).
Gupta, S. & Jawanda, M. K. Acta Paediatr. 109 , 2181–2183 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Gentile, D. A. et al. Pediatrics 140 , S81–S85 (2017). Suppl 2.
Karmakar, S. & Sanchari, D. Proc. Eur. Interdiscip. Cybersecur. Conf ., https://doi.org/10.1145/3424954.3424960 (2020).
Jain, O., Gupta, M., Satam, S. & Panda, S. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbr.2020.100029 (2020).
The Future of Education and Skills. Education 2030. https://www.oecd.org/education/2030/E2030%20Position%20Paper%20(05.04.2018).pdf (OECD, 2020).
Adams, N. B. J. Technol. Stud. 30 , 93–97 (2004).
Mithas, S. & McFarlan, F. W. IT Prof. 19 , 3–6 (2017).
Singh Chawla, D. Nature 562 , S15–S16 (2018).
Park, Y. 8 Digital Skills We Must Teach Our Children. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/06/8-digital-skills-we-must-teach-our-children/ (World Economic Forum, 2016).
Digital Intelligence (DQ). A Conceptual Framework & Methodology for Teaching and Measuring Digital Citizenship. https://www.dqinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/DQ-Framework-White-Paper-Ver1-31Aug17.pdf (DQ Institute, 2017).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
DQ Institute, Singapore, Singapore
Joshua A. Jackman, Douglas A. Gentile & Yuhyun Park
School of Chemical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Republic of Korea
Joshua A. Jackman
Department of Psychology, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA
Douglas A. Gentile
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
Nam-Joon Cho
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yuhyun Park .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Y.P. is the founder and an employee of the DQ Institute, an international think-tank dedicated to setting global standards for digital intelligence education, outreach, and policies. J.A.J., D.A.G., and N.-J.C. are advisors to the DQ Institute.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Human Behaviour thanks Judy Robertson and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jackman, J.A., Gentile, D.A., Cho, NJ. et al. Addressing the digital skills gap for future education. Nat Hum Behav 5 , 542–545 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01074-z
Download citation
Published : 11 March 2021
Issue Date : May 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01074-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Updating digital citizenship education for a postdigital society.
- Jack Webster
New Zealand Journal of Educational Studies (2023)
Digitalisation in Italy: Evidence from a New Regional Index
- Andrea Benecchi
- Carlo Bottoni
- Elisa Scarinzi
Social Indicators Research (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Digitalization in Education: Developing Tools for Effective Learning and Personalisation of Education
Original Research 07 September 2023 Fostering future music teachers' professional skills: developing a signature pedagogy using e-learning Svetlana Karkina , 4 more and Mandeep Bhullar 1,436 views 0 citations
Original Research 08 August 2023 Impact of an inquiry-oriented proposal for promoting technology-enhanced learning in a post-pandemic context José-María Campillo-Ferrer and Pedro Miralles-Martínez 874 views 0 citations
Original Research 27 July 2023 Students’ acceptance on computer-adaptive testing for achievement assessment in Japanese elementary and secondary school Takayuki Goto , 1 more and Takayuki Shiose 1,744 views 1 citations
Original Research 29 June 2023 Digitalization as a way to promote the holistic approach to faculty development: a developmental evaluation Roberta Silva 1,409 views 0 citations
Original Research 15 May 2023 Evaluating gifted students’ perceptions of the characteristics of their effective teachers Yusra Zaki Aboud 2,739 views 0 citations
Loading... Perspective 24 April 2023 The necessary, albeit belated, transition to computerized cognitive assessment David Asensio and Jon Andoni Duñabeitia 1,422 views 3 citations
Loading... Original Research 31 March 2023 Factors influencing teachers’ satisfaction and performance with online teaching in universities during the COVID-19 Wenbin Du , 2 more and Lei Wang 4,252 views 4 citations
Brief Research Report 22 March 2023 Factors affecting Malaysian ESL teachers' behavioral intentions for technology use in the post-COVID-19 era Teo Woon Chun and Melor Md Yunus 2,457 views 1 citations
Loading... Original Research 30 January 2023 How does online social interaction promote students’ continuous learning intentions? Shunan Zhang , 2 more and Jang Hyun Kim 3,946 views 5 citations
Loading... Original Research 15 December 2022 Mobile-learning adoption in teacher education amidst COVID-19: Identifying two critical stages by exploring teachers’ emotions Yulia Muchnik-Rozanov , 1 more and Orit Avidov-Ungar 970 views 5 citations
Original Research 30 November 2022 “The whole is greater than the sum of its parts” – Exploring teachers’ technology readiness profiles and its relation to their emotional state during COVID-19 emergency remote teaching Marcela Pozas , 1 more and Christoph Schneider 2,052 views 1 citations

Related Expertise: Education , K–12 Education
Closing the Digital Divide in US Education—for Good
June 03, 2021 By Sumit Chandra , Hannah Hill , Tejus Kothari , Lane McBride , and Nithya Vaduganathan
When American K-12 public schools in all 50 states closed their doors in March 2020, the inequities and scale of the digital divide were abruptly unmasked. According to BCG research in 2020, coauthored with Common Sense, roughly 30% of children in grades K-12 (15 million to 16 million students) did not have adequate internet service or e-learning devices to effectively continue their schooling from home. While this is a challenge in every state, the digital divide most acutely affects students from rural and Southern communities. It also disproportionately affects Black, Latinx, and Native American students and those from lower-income households.
When the pandemic struck, many states and districts swiftly mobilized to address the needs of their digitally underserved students, often making use of the emergency funding authorized in March by the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act. They purchased devices, hot spots, and other resources and partnered with providers to offer sponsored service at no cost to eligible households, among other initiatives. Yet BCG research showed that while these measures were significant, up to 12 million K-12 students nationwide remained inadequately connected at the start of 2021 and more than 75% of these efforts will expire in the next one to three years. Progress in serving these students was hampered by poor broadband mapping data, limitations of infrastructure and supply chains , insufficient marketing and adoption support, and inadequate funding.
Digital Access, Educational Inclusion, and Economic Opportunity
Even as students return to school in person, eliminating the digital divide for good is essential. Lack of access away from the school building contributes to significant curtailment of students’ learning, which translates to income losses that can last throughout their lives. Our research estimates that even when students are learning in the classroom, the lower lifetime income of the cohort of K-12 students caught in the digital divide will result in a $22 billion to $33 billion annual GDP loss. This number is likely to grow as learning at all levels continues to shift to digital platforms and jobs increasingly rely on digital skills.
- K–12 Education
- How COVID-19 Advanced Digital Learning for Lower-Income Populations
- Closing the K–12 Digital Divide in the Age of Distance Learning
- The Economic Case for Bringing Broadband to the Rural US
The lower lifetime income of the current cohort of students caught in the digital divide will result in a $22 billion to $33 billion annual GDP loss.
Closing the digital divide and investing in innovative delivery that leverages digital connectivity is about stimulating step changes in pedagogy—unlocking new ways of learning and teaching students the skills essential to their future, next-generation jobs, and economic growth. With fully connected students and interactive technology tools and data, teachers can hone new models for teaching and learning; for instance, by unlocking more personalized learning pathways for students and analyzing data on learning progressions to tailor practices and enhance curricula.
To close the digital divide for good, we must address the three major barriers to access: affordability, availability, and adoption. Our research found that up to 60% of students without digital access (9 million), especially disconnected Black and urban students, are unable to afford it. Up to 25% (4 million) lack access to readily available and reliable broadband service, a barrier that disproportionately affects rural and Native American students. Finally, up to 40% (6 million) face adoption challenges such as digital literacy and language barriers. Many students face more than one barrier to adoption.
The Long Game for States and Districts
Since the adoption of the CARES Act, Congress has passed two other economic recovery bills: the Coronavirus Response and Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2021 in December 2020 and the American Rescue Plan Act (ARP) in March 2021. This legislation includes additional funding for K-12 education that can be applied to a range of pandemic-related expenses, including distance learning, broadband-specific data collection, infrastructure deployment, service cost support, and other digital inclusion initiatives with a special focus on vulnerable communities. Notably, the ARP budgets more than $7 billion to expand the federal E-Rate connectivity program for schools and libraries to include delivering affordable connectivity directly into students’ homes.
These funds offer a unique opportunity for states and districts to lay the foundation for permanently eliminating the digital divide. Many are already doing so. More than 40 states now have offices dedicated to expanding broadband availability, affordability, and adoption—double the number of just a year ago.
To drive universal access, our analysis of strategies across the US highlights promising practices to replicate going forward.
Repeatable collection of data, with input from internet service providers, will help identify which providers could best service specific households.
- Create replicable data collection processes for needs assessments. Plan for repeatable collection of both student-level needs data through student information systems (SIS) and household-level coverage data, with input from internet service providers, to help inform and target solutions. Wisconsin’s Department of Public Instruction partnered with two education nonprofits and local providers to launch a data governance strategy in less than a month. They rolled out a survey using three SIS vendors serving 98% of schools in the state, and then securely overlaid data from broadband coverage maps to identify which providers could best service specific households.
- Reduce the cost of universal infrastructure deployment . Maximize use of available funds at the federal, state, and local levels for state projects. Decrease upfront investment costs, including lowering middle mile costs (the cost of connecting local internet service networks to the broader internet backbone). Coordinate broadband delivery through relevant frameworks, including “dig-once,” (a policy to reduce the number and scale of excavations for infrastructure), capacity leasing, and municipal network regulations. Consider a portfolio of strategies and technologies, such as satellites and mesh networks, especially in rural areas where fiber deployment may not be financially feasible. In the 1990s, North Dakota used federal funds to aggregate rural carriers into one statewide network. Their effort made rural broadband expansion in remote communities more financially attractive.
- Support affordable solutions with aggregated procurement. Create state- and district-level discounted or no-cost sponsored-service offerings to maximize volume discounts and minimize risk and churn for internet service providers (ISPs). Consider bundling broadband and device access for students. Alabama’s state-led voucher program covered the cost of installation, equipment, and service for up to 450,000 low-income students. The program focused on addressing upfront affordability challenges so that households were best positioned to take over ongoing service fees when the program ended. In addition, awareness and adoption campaigns promoting financial assistance programs—such as Lifeline, the recently launched Emergency Broadband Benefit, and rental assistance programs where broadband is an allowed expenditure—can help expand affordable access for students and the community at large.
- Engage stakeholders to support hard-to-reach families and address nonfinancial adoption barriers . Develop strategies to address barriers such as low digital and technical literacy . Trusted school districts and educators can play a focal role in the community, offering technical support and digital skills training for students, parents, and other residents. Chicago Connected, a multistakeholder partnership with schools and 35 community-based organizations, offers one-on-one assistance to families, including digital literacy training and internet adoption support. The program ensured that the voices of parents and community advocates were integral to the design and implementation process. The program continues to evolve; for example, a project-wide working group was set up to identify the digital literacy resources needed by applicants and participants.
Cross-Sector Stakeholder Strategies
Closing the divide requires strong policy direction and funding from federal, state, and local entities, as well as engagement and ongoing investment from stakeholders across the private and social sectors. The federal government, ISPs, school districts, education nonprofits, and philanthropies all have critical roles to play—individually and collectively.
Closing the divide requires strong policy direction and funding from government entities, as well as engagement and ongoing investment from stakeholders across the private and social sectors.
- Federal, state, and local policies can collectively unlock sustainable funding. This will ensure that there is transparent, affordable pricing for low-income families and support for broader digital inclusion and skill-building programs. These programs should incentivize tech-agnostic investment to establish broadband access where none exists and to expand connectivity where speeds are inadequate for remote learning or cost is a challenge.
- Broadband providers and device manufacturers can establish cost-effective offerings and invest in infrastructure to expand access and improve the quality of connections and devices. They must work jointly with local stakeholders to encourage adoption and support families and students.
- Philanthropies, EdTech companies, and education industry associations are critical catalysts of change and continuous improvement—for example, conducting ongoing research on family and learning needs and amplifying messages for specific groups or unifying them for all groups. The support and advocacy of these education sector players are crucial to inform policy and to stimulate ongoing investment in digitally enabled learning.
The Bigger Picture of the Digital Divide
While our three research reports on the digital divide in the US have focused mainly on K-12 students, it exists at all educational levels, affecting 3 million to 4 million US postsecondary students or about 15% of all students attending four-year private and public colleges and two-year community colleges. In addition, 20 million to 30 million US households that do not have children enrolled in primary or secondary schools cannot afford high-speed internet, do not have access to it in their communities, or have experienced other adoption barriers.
The same technical and economic challenges we found in the US are amplified many times over in countries with the largest populations living in extreme poverty. In India, more than 60% of the country’s 250 million pre-K-12 students do not have access to optimal educational technology in school or at home. During the early days of the pandemic, BCG worked with the National Institution for Transforming India and three state governments to expand connectivity and develop educational content across smartphones, television, and radio.
Although the global pandemic has been extremely disruptive for learning, it has greatly heightened awareness of the longer-term consequences of the digital divide throughout the world and stimulated both governments and the private sector to act. In the US, economic recovery funds, state- and district-level initiatives, and digital access commitments from ISPs have put society on the cusp of what could be a generational milestone—when all students and households have the technology and support they need to succeed. Federal momentum is growing to provide additional funding and support to ensure that this happens. President Biden’s proposed infrastructure plans include billions of dollars to fund initiatives that address racial and social inequities and deliver broadband access to every American.
As leaders in every country anticipate a post-COVID future, this is a unique moment to make transformative investments in K-12 education and beyond. Actions taken today to eliminate systemic inequities and to strengthen the connection between a solid formative education and economic opportunity can advance human well-being for years to come.

Managing Director & Senior Partner
Washington, DC

Managing Director & Partner

ABOUT BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP
Boston Consulting Group partners with leaders in business and society to tackle their most important challenges and capture their greatest opportunities. BCG was the pioneer in business strategy when it was founded in 1963. Today, we work closely with clients to embrace a transformational approach aimed at benefiting all stakeholders—empowering organizations to grow, build sustainable competitive advantage, and drive positive societal impact.
Our diverse, global teams bring deep industry and functional expertise and a range of perspectives that question the status quo and spark change. BCG delivers solutions through leading-edge management consulting, technology and design, and corporate and digital ventures. We work in a uniquely collaborative model across the firm and throughout all levels of the client organization, fueled by the goal of helping our clients thrive and enabling them to make the world a better place.
© Boston Consulting Group 2024. All rights reserved.
For information or permission to reprint, please contact BCG at [email protected] . To find the latest BCG content and register to receive e-alerts on this topic or others, please visit bcg.com . Follow Boston Consulting Group on Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) .
How Big is Digital Education in the United States? An End of Year Review
Subscribe to the center for technology innovation newsletter, joshua bleiberg and joshua bleiberg assistant professor - university of pittsburgh @joshbleiberg darrell m. west darrell m. west senior fellow - center for technology innovation , douglas dillon chair in governmental studies.
December 15, 2014
Buzz about the potential of digital learning abounds. Despite the excitement, relatively little is known about how many students are actually taking advantage of digital learning opportunities. This is partly due to online learning tools having numerous forms , rendering them difficult to track. In addition, policies also vary greatly across states. A new report, Keeping Pace with K-12 Digital Learning , helps to shed light on the state of online learning in the United States.
Digital Schools are Growing
Thirty states offer fully online schools that grant degrees. There are approximately 315,000 students enrolled in this type of digital school. This represents about half of one percent of the overall primary and secondary school population. But, the number of students enrolled in online schools is growing rapidly. This past school year enrollment increased by 6.2 percent. In addition, virtual schools, which provide supplementary course offerings, have about 740,000 course enrollments in the 2013-2014 school year.
State Virtual School: Course Enrollment
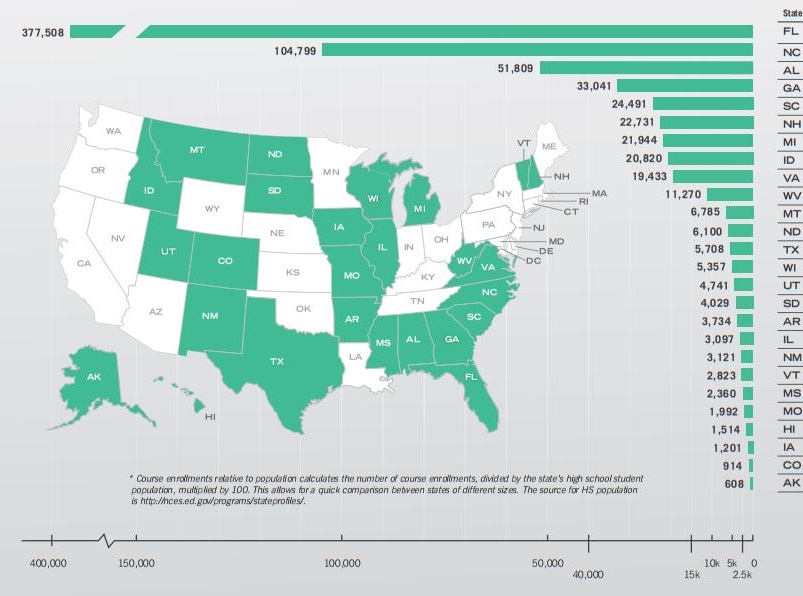
Click to enlarge. Source: Evergreen Education Group
Few Major Policy Changes in 2014
Although digital schools have many more students and course enrollments, states did not make many major policy changes to promote continued growth. According to the report, “few states passed laws that signal a significant change in direction and will have a substantial impact on digital learning.” There were some unheralded policy changes that could potentially strengthen digital learning. Ohio and California created a dedicated funding stream for digital learning. North Carolina created the position of “chief academic and digital learning officer” to administer the state’s online learning programs.
Policy Remains a Major Constraint on Digital Education
Many states maintain policies that inhibit the growth of digital learning. Currently, twenty states have laws banning the enrollment of students in digital schools. If these laws remain unchanged, the growth of online learning will be severely limited. Seat-time requirements are also a major barrier. These laws mandate that students must spend a certain number of hours in a brick-and-mortar school to graduate regardless of their grades or performance on exams.
Digital learning has two chief benefits. First, virtual schools are typically less costly to implement on a per-pupil basis. Second, digital schools also expand the number of course choices for students. Some states have used virtual schools to make Advanced Placement classes available to highly motivated students who could otherwise not enroll in those classes. There is also new evidence from an evaluation of the Florida Virtual School that digital courses are not inherently worse than traditional schools. Given this promising new research and the economic benefits outlined, all states should seek to make it easier for students to enroll in advanced courses online.
Education Technology
Governance Studies
Center for Technology Innovation
Online only
9:00 am - 10:00 am EDT
Kelli Bird, Ben Castleman
April 23, 2024
Ariell Bertrand, Melissa Arnold Lyon, Rebecca Jacobsen
April 18, 2024
- Digitalisation of Education

The introduction of technology into education has never – alone – solved the problems that education faces. Yet processes of digitalisation have transformed education – and will continue to do so – in ways that are evolving, complex, and often seem to outstrip our ability to analyse them.

COVID-19 brought about catastrophic disruptions and new formations in teaching and learning under circumstances of global emergency, which accelerated the pace of this change. The pandemic also accelerated multiple “digital divides”. Despite resurgent interest in technology in education policy, planning and practice, as well as in research, many areas that are critical to understanding the digitalisation of education remain under-studied, and the evidence that does exist remains under-shared.
Our publication Policy Insights: The Digitalisation of Education is available. The multi-disciplinary collection presents profound but digestible insights gained from a year of expert consultations, focused on what education policy and practice can learn from cutting-edge research and evidence.
Policy Dialogues on the digitalisation of education
Our partnership with the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the Right to Education , Dr Koumbou Boly Barry, informed her 2022 report to the Human Rights Council: The impact of the digitalisation of education on the right to education .
In a series of Policy Dialogues , NORRAG convened experts from diverse disciplines to engage with the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the Right to Education to explore the challenges and opportunities that digitalisation poses for children and young people, nations and communities, and education systems. The series of expert consultations aimed to explore fresh perspectives and surface under-represented expertise, particularly from the Global South, to expand understandings of the issues at stake and, vitally, possible solutions and pathways for change.
Key themes:
- The role of technology in education
- Data, datafication and surveillance
- Privatisation and the digitalisation of education
- Diversity, digital divides and digital education
- Digital citizens or consumers?
- The health impacts of the digitalisation
News and events

EdTech from the Perspective of Edtech Firms and Investors

Sneak Preview: A Blueprint For An AI Bill of Rights For Education

Metrics and International Education Policy

Education, technology and private sector actors: towards a research agenda

Contemporary Digital Literacy: Open Education as a Digital Right

EdTech’s precarious futures: are there material limits to data-driven higher education?

An intersectional approach to digital education: facilitating empowerment and justice

Post-EdTech Futures
- Artificial Intelligence and Education
- Top Stories
- Stock Market
- BUYING RATES
- FOREIGN INTEREST RATES
- Philippine Mutual Funds
- Leaders and Laggards
- Stock Quotes
- Stock Markets Summary
- Non-BSP Convertible Currencies
- BSP Convertible Currencies
- US Commodity futures
- Infographics
- B-Side Podcasts
- Agribusiness
- Arts & Leisure
- Special Features
- Special Reports
- BW Launchpad

- Editors' Picks
PHL digitalization efforts aim to address health, education gaps

THE GOVERNMENT is looking to adopt artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technologies to advance digitalization in key areas like healthcare and education, the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) told the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP).
“We will harness the power of data analytics to inform evidence-based policy making and drive greater efficiency and effectiveness in government services,” DICT Secretary Ivan John E. Uy said during the ESCAP’s 80th ses-sion in Bangkok, Thailand on Monday.
The Philippines is working to keep up with global digitalization efforts to boost healthcare access and address climate-related risks and an ongoing learning crisis.
“We will leverage emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain… to address some of the most pressing challenges, from healthcare, education, to climate change and disaster resilience,” Mr. Uy said.
He said the Philippines is also looking to invest in digital skills development to upskill Filipino workers in the digital economy, a sector that is projected to reach up to $150 billion in gross merchandise value by 2030.
The value of digital transactions in the Asia-Pacific region are expected to reach $6.7 trillion by 2026, according to ESCAP.
“We will foster an environment that encourages innovation and entrepreneurship, providing support and resources to startups and small businesses as they harness the power of technology to drive economic growth and create jobs,” Mr. Uy said.
Oleg Shamanov, deputy permanent representative of the Russian Federation to ESCAP, said countries must also consider the risks associated with AI tools.
“AI can be useful, but why don’t we raise the issue of the risks that come with its utilization in an irresponsible fashion?,” he said.
“In the digital era, using new tools, platforms, methods for lifelong and continuous learning has got much more important,” Davood Manzoor, vice-president and the head of Planning and Budget Organization in Iran, told the forum.
Digital innovations should also be in line with countries’ commitment to reduce global emissions to net zero by 2050 under the Paris Agreement, said George Lam, chairman of the ESCAP Sustainable Business Network.
“We urge governments to create clear and predictable policy frameworks that foster and accelerate green innovation and transformation to a net zero carbon emission,” he said. — B.M.D. Cruz
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Budget deficit narrows in March
Philippines’ main grids placed under red, yellow alerts
Philippines lags Southeast Asian neighbors in smart tourism index

Debates on economic ‘Cha-cha’ begin
Bill seeks waiver of fees for small transactions in electronic wallets, philippines urged to fast-track grave threat case vs duterte.
- Download event
- Add to google
- Add to Outlook
- Add to Office365
Digitalization of Education
- First Online: 16 June 2022
Cite this chapter

- Đorđe Nadrljanski 7 ,
- Mila Nadrljanski 7 &
- Mira Pavlinović 8
Part of the book series: Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems ((LAIS,volume 29))
489 Accesses
2 Citations
This paper discusses features and diversity of concepts and initiatives for digitalization in education. It also briefly discusses the advantages and challenges related to development of digitalized environments in education, as well as greater need for professional development of people working in digitalization. In addition, they encourage and promote innovation in many different spheres of life. The innovative capacity of technology is highly conditioned by the levels of digital skills of the population. It is not surprising that there is a very strong link between education and skills needed to utilize digital technologies in different spheres of life. An efficient, diverse, and strong higher education sector and research system will help the higher education sector to achieve this goal in the best possible way. Universities and faculties manage a significant portion of community resources and must use those resources effectively and for the benefit of society. Institutions will develop their positions according to their strengths and individuality and will contribute to higher quality and to other sectors of society. Furthermore, they will meet the needs of society in various fields and help each country to internationally affirm itself as an outstanding knowledge society. Digitalization is a tool for making fundamental changes in the processes, content, and various forms of work, which can put the education sector in a better position to achieve the goals of education and research, to increase quality and relevance in the approach to education for all. The time when experts talked about education technology in terms of audio, visual and experiential technology has passed. They also talked about hardware technology, software technology and a system based on technology. These are expressions from the past, as the old concepts in the field of educational technology or EdTech have been outdated during the last decade.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Many mistakenly confuse digital transformation with other applications of information technology in work and personal life.
Ibidem op. citatum.
The research was conducted by the authors in the area of Split, the Republic of Croatia.
The study was carried out by the authors on a sample of primary school pupils in Split, the Republic of Croatia.
The Department of Educational Programs and Institutional Effectiveness (EPIE) provides leadership and coordination of education and service initiatives across the United States, course and program approval, accreditation, strategic planning, class attendance, and institutional research.
Students and teachers at eligible institutions can apply for Office 365 Education free of charge, including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and now Microsoft Teams, plus additional tools in the classroom. Also cloud services to create a modern classroom. Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology company based in Redmond. The company's core business includes the development, production, licensing, support, and sale of computer software.
The Education Capital Planning Division in Alberta is responsible for developing and implementing policies, plans and strategies to support infrastructure and capital planning and investment in the education system.
Simply explained, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services — including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence — over the Internet (the “cloud”) to deliver faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Usually, only the cloud services used are paid for, which helps reducing operating costs, run infrastructure more efficiently, and adapt to education needs.
A.W.T. Bates, Upravljanje tehnološkim promjenama: strategije za vođe fakulteta i sveučilišta. Jossey-Bassova serija visokog obrazovanja i obrazovanja odraslih; Publishers Jossey-Bass, 350 Sansome St., San Francisco, CA 94104 (2014)
Google Scholar
T. de Lange, Tehnologija i pedagogija: Analiza digitalnih praksi u medijskom obrazovanju (AIT Oslo AS, Oslo, 2010)
D.M. Griffioen, U. de Jong, Implementing research in professional higher education: factors that influence lecturers’ perceptions. Educ. Manage. Administr. Lead. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1741143214523008
Article Google Scholar
M. Håkansson-Lindqvist, F. Pettersson, Digitalizacija i školsko vodstvo: o složenosti vođenja digitalizacije u školi. Međunarodni časopis za informacijske i obrazovne tehnologije 36 (3), 218–230 (2019)
C. Marcelo-García, C. Yot-Domínguez, C. Mayor Ruiz, University teaching with digital technologies. Comunicar 23 (45), 117–124 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3916/C45-2015-12
D. Nadrljanski, Digitalni mediji – obrazovni softver, Pedagoški fakultet Sombor (2006)
O.I. Popova, Transformation of higher education in the conditions of the digital economy. Manage. Issues 5 (35), 158–160 (2018)
A. Scholkmann, “What I learn is what I like.” How do students in ICT-supported problem-based learning rate the quality of the learning experience, and how does it relate to the acquisition of competences? Educ. Inf. Technol. 22 (6), 2857–2870 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-017-9629-7
A. Scholkmann, E. Lauridsen Lolle, K. Otrel-CassTobias, A. Tretow-Fish, Building a partnership for thinking through technology-facilitated iterative processes: an approach to iterative practice (IPA) in higher education; ECER 2019 session provided by 22. Res. Higher Educ. (2019)
R.M. Tamim, R.M. Bernard, E. Borokhovski, P.C. Abrami, R.F. Schmid, What forty years of research says about the impact of technology on learning: A second-order meta-analysis and validation study. Rev. Educ. Res. 81 (1), 4–28 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654310393361
G.L. Tulchinsky, Digital transformation of education: challenges to higher school. Philos. Sci. 6 , 121–136 (2017)
E. Zhadko, O. Popova, N. Gagarina, University brand management in the conditions of education digitalization, in 16 th International Conference Efficiency and Responsibility in Education (2019), pp.1737–1746
https://www.wiscogroup.com/types-of-educational-software-and-other-classroom-aids/. https://techlancings.com/educational-software-types-and-advantages/
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Inspection and Personnel Management of Maritime Studies, 209 Zrinsko Frankopanska, 21000, Split, Croatia
Đorđe Nadrljanski & Mila Nadrljanski
Faculty of Maritime Studies, University of Split, 37 Ruđera Boškovića, 21000, Split, Croatia
Mira Pavlinović
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Đorđe Nadrljanski .

Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Sciences, Department of Mathematics and Informatics, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Serbia
Mirjana Ivanović
Aleksandra Klašnja-Milićević
KES International, Selby, UK
Lakhmi C. Jain
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Nadrljanski, Đ., Nadrljanski, M., Pavlinović, M. (2022). Digitalization of Education. In: Ivanović, M., Klašnja-Milićević, A., Jain, L.C. (eds) Handbook on Intelligent Techniques in the Educational Process. Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems, vol 29. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04662-9_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04662-9_2
Published : 16 June 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-04661-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-04662-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
RuSat — Digital Decisions (RDD)
Cooperation agreement with mda.
On October 18, 2023, representatives of Rosatom State Corporation announced that, represented by RuSat - Digital Solutions (RCR LLC) and the country office in Belarus (RuSat Bel LLC), the company had entered into an agreement with one of the oldest Belarusian IT companies - International Business Alliance CJSC (MDA CJSC) on the implementation of joint digitalization projects based on digital products and Rosatom solutions. Read more here .
Start of distribution network
Rosatom Rusatom - Digital Solutions (RCR) has begun building a distribution network to present its digital products on the market. The work starts with ensuring the availability to consumers of the State Corporation's flagship software - the Logos engineering analysis and mathematical modeling system . RCR has concluded a number of framework agreements with partners and is starting to actively promote this software product in the Russian and foreign markets.
RCR forms a distribution network for the sale of licenses . In addition, technical support will be organized for users of the Logos system by specialists from the developer company.
As part of ensuring digital technological independence, Logos is actively used not only in the nuclear power , but also at more than a hundred enterprises in high-tech sectors of the Russian economy . At the same time, the plans for accelerated economic growth require the construction of a more efficient and convenient system of interaction between industrial consumers and manufacturers of a digital product.
{{quote "As of July 2023, a number of Russian industrial and scientific organizations use various Logos modules, but we need to reduce the path that this product goes from developer to enterprise, simplify it, make it as flexible and transparent as possible - convenient for manufacturers. This is the only way to count on the acceleration of import substitution of CAE-class software in various industries - concluded Alexander Vibe . }}
The created distribution network will allow, first of all, to optimize marketing - logistic activities aimed at promoting Logos to the markets - both domestic and foreign: the time for passing the software implementation procedure, user training, and technical support will be significantly simplified and reduced.
The RCR focuses on expertise and a clear understanding of work in various industrial segments. The "single window" principle provides industrial customers with well-functioning interaction processes, including operational communication with developers - in the end, individual features of implementation and further development of the digital product for the specifics of the consumer are taken into account.
The development of Rosatom's digital products is carried out within the framework of ensuring the digital technological sovereignty of Russian industry. The Logos CAE system is a competitive offer for foreign consumers.
Rosatom bought 50% of the company "Security Code"
On December 27, 2022, it was announced the sale of 50% of the Security Code company to Rosatom State Corporation. Its participants did not disclose the financial side of the transaction. Read more here .
Rosatom acquired control at AT Consulting
Rosatom represented by RuSat - Digital Solutions LLC acquired a controlling stake in the AT Consulting group of companies. TAdviser was told about this in AT Consulting, which is now part of Rosatom, in early April. The state corporation received control in the group through JSC "ATI Group" - the holding company AT Consulting. Read more here .
2021: Participation in the creation of the CAD/CAE Consortium
On July 6, 2021, it became known about the signing of the Agreement on the Creation of consortium the Russian CAD System Developers/CAE, whose activities will be aimed at ensuring the technological independence industrial of enterprises and research organizations RUSSIAN FEDERATION in the field of systems ( supercomputer mathematical) modeling and engineering analysis. More. here
2019: Decision to form a company
In January 2019, the Board of Directors of Atomenergoprom (part of Rosatom State Corporation ) decided to create a new company - Rusatom-Digital Solutions. It will be 100% owned by Atomenergoprom, and the authorized capital of Rusatom-Digital Solutions will amount to 80 million rubles . Atomenergoprom announced this on the website of the corporate information disclosure center.
Atomenergoprom consolidates the civil assets of the Russian nuclear industry. The company provides a full cycle of production in the field of nuclear power : from uranium mining to the construction of nuclear power plants and electricity generation.
At the time of publication, Rosatom could not explain to TAdviser what the main areas of activity of Rusatom-Digital Solutions will be and how they will relate to digital projects of other divisions of the state corporation.

Prerequisites for creating a company related to digital solutions could be considered Rosatom's participation in the Digital Economy national project, digital transformation in Atomenergoprom itself, the beginning of which the company announced in its annual report for 2017, as well as Atomenergoprom's interest in diversifying its business. The latter is also mentioned in the annual report.
In the annual report of Atomenergoprom there is a mention of the company's digital projects. It says, for example, that in addition to the digital transformation program, "promising projects related to supercomputers, additive technologies, and life cycle management of complex engineering objects" were launched.
As part of business diversification, Atomenergoprom in 2017 signed a contract with the Ministry of Education and Science to create a digital production of precision products for medicine based on additive technologies (endoprostheses, implants and augments).
In the mining division belonging to Atomenergoprom, in particular, Khiagda (part of Atomredmetzolot , where Atomenergoproekt is a co-founder) developed intelligent methods for modeling underground leaching processes - the Smart Mine project. We are talking about an IT system based on a 3D model of the ore field. The system will be able to simulate and track production processes in real time using video surveillance and intelligent sensors.
Prior to the decision to create Rusatom-Digital Solutions, Atomenergoprom established another company related to IT - Berkut Monitoring Systems (Rusatom Monitoring Systems brand). It was created in 2016 and operates within the framework of the Digital Economy project.
Areas of activity of the Berkut Monitoring System: geoinformation systems (GIS), diagnostic services for roads and road infrastructure, comprehensive monitoring of protected facilities, the introduction of the Safe City agro-industrial complex.
Ekaterina Solntsevov , director of digitalization at Rosatom, told TAdviser that in 2018 the state corporation began to develop a full-fledged business out of sales of digital products and services to external customers. This includes digital technologies supplied jointly with nuclear power plants, software solutions for mathematical modeling of physical processes and to support the construction of complex engineering objects, supercomputers . In addition, in January 2019, Rosatom began providing cloud services based on its own mega-data center .
Within the framework of certain projects, Rosatom previously participated in the development of digital products, including those aimed at external customers. For example, in a project to create a domestic product lifecycle management system () PLM with. Rostec
" Greenatom "
Rosenergoatom

- Solutions for industry
- Manufacturing and logistics
- Public sector
- Transportation
- Patent licensing
- Technology licensing
- SEP licensing principles
- Standardization
- Go to market
- Virtual events
- Video series
- Sustainability
- Security and privacy
Choose your language
- English (International)
- Chinese, Simplified
- Core networks
- Data center
- Fixed networks
- Internet of Things
- IP networks
- Mobile networks
- Optical networks
- Private networks
- Fixed networks services
- Services for mobile networks
- Cable operators
- Neutral hosts
- Rural broadband
- Subsea terrestrial networks
- Webscale network providers
- Training and certifications
- Financial services
- Manufacturing
- Research and education
- Stadiums, arenas and entertainment venues
- Transportation and logistics
- Services for industry
- Solutions for industry and the public sector
- Go to market partners
- Nokia Bell Labs
- We are Nokia
Nokia expands segment solutions to include digital transformation of manufacturing and logistics
Press Release Nokia expands segment solutions to include digital transformation of manufacturing and logistics
- Latest Nokia segment solutions guide manufacturing and logistics companies on the implementation of Industry 4.0 use cases to achieve strategic goals and realize ROI.
- Segment solutions leverage industry best practices, industrial OEM equipment and Nokia’s extensive expertise in delivering critical networks and digitalization solutions for enterprise digital transformation across industries.
- Based on Nokia one platform for industrial digitalization comprising 4.9G/LTE and 5G private wireless connectivity, industrial edge processing, ruggedized devices and ecosystem neutral applications.
22 April 2024 Espoo, Finland – Nokia today announced new pre-tested and pre-integrated segment solutions to guide manufacturing and logistics companies on how to approach their digital transformation to achieve strategic goals, use case needs and return of investment (ROI). Nokia’s industrial segment solutions help customers select the most suitable network design based on their specific use case and performance requirements.
Findings from the Industry 4.0 maturity index for industrial campuses showed that there are many barriers to industry digital transformation, including lack of alignment between IT and OT teams, lack of technology expertise and concerns about data. Use cases include implementation of automated guided vehicles (AGVs), process automation, predictive maintenance, digitalizing pencil and paper operations, and situational awareness, as well as critical communications to improve hazard detection, lower risk and create overall safer working conditions.
As part of their digital transformation, manufacturing and logistics companies will need to understand how to connect legacy assets to cut through data silos, how to use operational data to inform processes and optimize assets and how to manage their transformation while maintaining critical operations.
Nokia’s already available segment solutions include digitalization of ports, open pit and underground mining, utilities, and airports. These segment solutions leverage industry best practices and are backed by Nokia one platform for industrial digitalization, which is comprised of Nokia Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) and Nokia Modular Private Wireless (MPW) 4.9G/LTE and 5G private wireless connectivity solutions, ruggedized Industrial devices, MX Industrial Edge (MXIE) computing, an array of ecosystem neutral industrial applications, and systems integration services.
The segment solution concept leverages Nokia’s extensive expertise developed through more than 30 years of delivering critical communications solutions and systems integration for enterprise digital transformations. Nokia has deployed private wireless to more than 730 customers while collaborating with a portfolio of industrial OEM ecosystem partners and application providers.
Matt Hoover, Global Product Manager, Wireless and IIoT at Rockwell, said: “Embarking on the digitalization journey can be a daunting prospect. You need to understand your wireless application requirements and get started with initial projects so you can quantify the benefits. Gaining management approval is the next step and working with a proven vendor like Nokia is critical. Creating a roadmap that clearly shows how vital operations are maintained during the transformation, as well as how to achieve benefit or ROI is key. Using a pre-tested and pre-integrated solution from Nokia can reduce the risk of implementation and guide companies every step of the way.”
Ryan Martin, Senior Research Director at ABI Research, said: “Pre-tested and pre-integrated solutions like those of Nokia remove implementation risks and accelerate time-to-value. They provide a route map that shows clearly how vital operations are maintained during the transformation, as well as how to achieve a positive ROI, which drives alignment and allows companies to efficiently scale.”
Stephan Litjens, Vice President of Enterprise Solutions at Nokia, said: “With these new segment solutions we answer the difficult questions for manufacturing and logistics companies, ensuring they ‘keep the lights on’ as they manage their transformation. We have already demonstrated how quickly customers can reap the benefits from Industry 4.0 use cases using our pre-tested Nokia one platform for industry digitalization and we want to use these segment solutions to help more companies achieve their goals.”
Resources and additional information Webpage: I ndustrial Partners | Nokia Webpage: Application catalog | Nokia DAC
About Nokia At Nokia, we create technology that helps the world act together.
As a B2B technology innovation leader, we are pioneering networks that sense, think and act by leveraging our work across mobile, fixed and cloud networks. In addition, we create value with intellectual property and long-term research, led by the award-winning Nokia Bell Labs.
Service providers, enterprises and partners worldwide trust Nokia to deliver secure, reliable and sustainable networks today – and work with us to create the digital services and applications of the future.
Media inquiries Nokia Communications, Corporate Email: [email protected]
Follow us on social media LinkedIn X Instagram Facebook YouTube

- Agri-Commodities
- Asean Economic Community
- Banking & Finance
- Business Sense
- Entrepreneur
- Executive Views
- Export Unlimited
- Harvard Management Update
- Monday Morning
- Mutual Funds
- Stock Market Outlook
- The Integrity Initiative
- Editorial cartoon
- Design&Space
- Digital Life
- 360° Review
- Biodiversity
- Environment
- Envoys & Expats
- Health & Fitness
- Mission: PHL
- Perspective
- Today in History
- Tony&Nick
- When I Was 25
- Wine & Dine
- Live & In Quarantine
- Bulletin Board
- Public Service
- The Broader Look
Today’s front page, Thursday, April 25, 2024

BCCP: Digitalization to boost PHL’s ease of doing business
- April 25, 2024
- 2 minute read
THE British Chamber of Commerce in the Philippines (BCCP) believes digitalization will greatly help facilitate the ease of doing business (EODB) in the country.
That is why it is working closely with the Philippine government to ensure the quick passage of important legislative measures, with focus on cybersecurity.
“We’re working closely with the government, and we’d like to see priority measures or pieces of legislation—particularly in the areas of cybersecurity; so, we’d like the ‘Cybersecurity Act’ passed as a priority measure,” stated BCCP executive director and trustee Chris Nelson. “We see that cybersecurity is critically important. It’s an issue not only in the Philippines and the United Kingdom, so it’s important [for us that the national] government is taking serious action on cybersecurity that reinforces overseas investors, and it helps them to come in and know that they will be safe.”
Actions such as the passage of the “Cybersecurity Act,” he said, is important.
He made the remarks during the “Securing the Digital Frontier: Breaking Through Digital Boundaries” event that was organized in partnership with BCCP members CyberQ Group and Colliers.
Aside from that, Nelson shared that one of the advocacies of the chamber is to ensure increased investments from UK-based companies, as well as local trade and investments. He emphasized the need for a breakdown or further removal of economic barriers, particularly those stated in the Philippine Constitution that bars investments from foreign companies or ownership.
He added that the BCCP is also meeting with the Anti-Red Tape Authority (ARTA) as part of the chamber’s commitment to championing regulatory reform and enhancing economic competitiveness: “We’re close to supporting them in their aims such as those [regarding EODB], which is…very critical in getting those businesses moving forward.”
Nelson reiterated that the chamber continues to maintain its leadership in making more people aware of the business opportunities in the Philippines, trying to drive investment and trade, and getting key legislation passed as soon as possible.

PHL, Thailand eye ‘two-countries, one destination’ tie-up in June
- Joyce Ann L. Rocamora | PNA
- April 18, 2024
US provides P4 million to further protect Filipino women, children
- BusinessMirror

Paris 2024: French Embassy leads relay, sets photo exhibit of Olympic, Paralympic athletes

Malaysia celebrates ‘Eid’ through cultural culinary fusion with DoT

Norway, Palawan bolster efforts in environmental, social governance
- Izza Reynoso | PNA

UNDP prods private sector for more local investments thru new SDG Investor Map

New Japanese ambassador: Amity with PHL built upon ‘mutual trust’

PHL, Germany stage second Joint Economic Commission in Manila

1st MECO Fil-Tai invitational tees off Wednesday
- April 14, 2024

Czech minister forges local agricultural ties
- April 11, 2024

PHL-India Cooperation
- Ben Briones | PNA
PHL, Malaysia to elevate agriculture industries
- Roderick Abad

DFA launches e-Apostille service; 1st in Asean

EU launches DRRM program with PHL to enhance LGUs’ readiness capacities

PHL, Australia usher new era in their Strategic Partnership
- HK Yu, PSM | Australian Ambassador to the Philippines
- April 4, 2024

Senate president leads bilateral meets in Geneva with Thai, Vietnamese reps
- Kary Villaflor, Senate Social Media Unit | OIRP

Malaysia’s mid-tier firms to set local market footprints

Italy brings opera to Tondo; envoy cites value of cultural diplomacy

Malaysian Embassy engages in ‘food diplomacy’ with PHL
- March 28, 2024
UNCTAD to start 60th year with ‘Global Leaders Forum’
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
Tax pros: Register now for the 2024 IRS Nationwide Tax Forum
More in news.
- Topics in the News
- News Releases for Frequently Asked Questions
- Multimedia Center
- Tax Relief in Disaster Situations
- Inflation Reduction Act
- Taxpayer First Act
- Tax Scams/Consumer Alerts
- The Tax Gap
- Fact Sheets
- IRS Tax Tips
- e-News Subscriptions
- IRS Guidance
- Media Contacts
- IRS Statements and Announcements
Attendees get up to 19 continuing education credits, networking opportunities, case resolution, advice on practice management and more
IR-2024-117, April 22, 2024
WASHINGTON — The IRS encourages tax professionals to register now for the 2024 IRS Nationwide Tax Forum , coming this summer to Chicago, Orlando, Baltimore, Dallas and San Diego.
The Nationwide Tax Forum is the IRS’s largest annual outreach event designed and produced for the tax professional community. This year’s agenda will feature more than 40 sessions on tax law and ethics as well as hot topics like beneficial ownership information, cybersecurity, tax scams and schemes, digital assets and clean energy credits.
Enrolled agents, certified public accountants, Annual Filing Season Program (AFSP) participants and other tax professionals can earn up to 19 continuing education (CE) credits. A complete listing of seminar courses will be available in May.
IRS transformation: A historic time
Attendees at the forums will also learn how the IRS is evolving to meet their needs and those of their clients. The IRS is continuing to make changes across the agency as part of its transformation work under the Strategic Operating Plan , which is made possible with funding from the Inflation Reduction Act.
“This is a historic time at the IRS, with change taking place across the agency with our ongoing transformation work,” said IRS Commissioner Danny Werfel. “This summer you’ll have a chance to learn more about these changes. We encourage you to register soon. Some of these locations will fill up quickly.”
See Werfel’s YouTube video inviting tax professionals to the 2024 forums.
Locations and registration details
The following is the 2024 Nationwide Tax Forum lineup:
Attendees who act by the June 17 early bird deadline can take advantage of the lowest registration rate of $255 per person. Standard pricing of $309 begins on June 17 and ends two weeks before the start of each forum. Onsite registration is also available at a cost of $390.
Please note, members of the following associations can save $10 on their registration:
- American Bar Association (ABA)
- American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA)
- National Association of Enrolled Agents (NAEA)
- National Association of Tax Professionals (NATP)
- National Society of Accountants (NSA)
- National Society of Tax Professionals (NSTP)
Members should contact their association directly for a tax forum discount code.
Forum highlights
Attendees get more than continuing education when they attend the IRS Nationwide Tax Forum. Here are some additional benefits for attendees:
Exhibit hall – In addition to the seminars, the forums also feature a two-day expo with representatives from tax, financial and business communities offering their products, services and expertise designed with the tax professional in mind. Inside the exhibit hall, attendees can visit the IRS Zone to share their perspectives with IRS representatives and to learn more about the IRS’s vision for transformation and digitalization.
Case Resolution Program – Tax professionals can once again bring their toughest unresolved IRS case to the Case Resolution Program room. IRS representatives with specialized expertise will be available to meet one-on-one with tax professionals (by appointment only). A new addition to the 2024 IRS Tax Forum will be the ability to book an appointment with TAS case resolution in advance. Because of the popularity of the program, tax professionals can bring only one client case per meeting with IRS representatives in the Case Resolution Program. For complete details including what tax professionals need to bring to the appointment, visit the case resolution information page.
En español – This year the IRS is increasing the number of Spanish-language seminar courses available to attendees. Details will be provided next month in the seminar course list. Also, see the Spanish practice management offering below.
Hiring – Curious about career paths at the IRS? IRS hiring staff will be on hand to talk with attendees about jobs currently open in examination and other areas across the agency.
Monday pre-forum activities – Attendees arriving early can maximize their time at the Tax Forum by participating in additional events. On Monday, IRS partner associations NATP and NSTP will offer an optional annual filing season refresher course for participants in the IRS Annual Filing Season Program.
Following that, at 5 p.m., IRS partners will present a 90-minute panel discussion on practice management . Experts from the NAEA, NATP, NSA, NSTP and Padgett Business Services will present ideas on how new, as well as established tax professionals can attract and manage customers, increase productivity and have a more satisfying work-life balance. A Spanish-language version of the panel will be presented at 7 p.m.
National Taxpayer Advocate town hall – Meet National Taxpayer Advocate Erin Collins on Wednesday during the forum networking reception to discuss issues facing taxpayers and tax practitioners. The Taxpayer Advocate wants to hear from tax pros and learn about issues facing taxpayers and practitioners. Includes Q&A.
Registration information
For more information, and to register online, visit www.irstaxforum.com .
ZEISS and Argolight announce partnership to enhance microscopy imaging quality control
Today, ZEISS and Argolight announced their strategic partnership. The collaboration aims to seamlessly integrate cutting-edge quality control solutions of the French company into the extensive line of ZEISS microscopes. This will enable users to accurately measure and assess the performance of their microscopy systems.
An indispensable solution for comprehensive quality control
With a shared commitment to empowering customers and advancing scientific research, this partnership brings together the expertise of ZEISS and the innovative technology developed by Argolight. By utilizing Argolight's quality control solution with ZEISS microscopes, users will gain a powerful tool to document and verify the performance of their systems, subsequently ensuring the quality of their acquired images.
ZEISS recognizes the critical importance of precise and consistent imaging results in scientific research and manufacturing processes. Through this collaboration, the company aims to further support researchers, scientists, and professionals in numerous industries in achieving superior imaging outcomes by enabling them to assess and enhance the quality of their microscopy systems.
"We are excited to partner with Argolight to advance the field of microscopy," said Michael Albiez, Head of ZEISS Research Microscopy Solutions. "By integrating Argolight's quality control solution for use with our microscopes, we enable our customers to document the reliability and reproducibility of their imaging, ultimately driving scientific progress and discovery."
"We are delighted to join forces with ZEISS, a true pioneer in the field," said Arnaud Royon, CEO at Argolight. "Our shared vision of improving the reliability and reproducibility of microscopy imaging will undoubtedly bring immense benefits to users worldwide. This partnership signifies a significant step forward in setting new standards for automated quality control in microscopy."
The partnership between ZEISS and Argolight marks a significant milestone in the quest for more precise and reliable microscopy imaging. By integrating Argolight's microscope quality control solution into ZEISS microscopes, customers can expect enhanced confidence in their results and an improved understanding of the performance of their imaging systems.
- +49 (0)3641 64-3949
- Download vCard
- +33 (0)564 310 850
About ZEISS
ZEISS is an internationally leading technology enterprise operating in the fields of optics and optoelectronics. In the previous fiscal year, the ZEISS Group generated annual revenue totaling 10 billion euros in its four segments Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology, Industrial Quality & Research, Medical Technology and Consumer Markets (status: 30 September 2023).
For its customers, ZEISS develops, produces and distributes highly innovative solutions for industrial metrology and quality assurance, microscopy solutions for the life sciences and materials research, and medical technology solutions for diagnostics and treatment in ophthalmology and microsurgery. The name ZEISS is also synonymous with the world's leading lithography optics, which are used by the chip industry to manufacture semiconductor components. There is global demand for trendsetting ZEISS brand products such as eyeglass lenses, camera lenses and binoculars.
With a portfolio aligned with future growth areas like digitalization, healthcare and Smart Production and a strong brand, ZEISS is shaping the future of technology and constantly advancing the world of optics and related fields with its solutions. The company's significant, sustainable investments in research and development lay the foundation for the success and continued expansion of ZEISS' technology and market leadership. ZEISS invests 15 percent of its revenue in research and development – this high level of expenditure has a long tradition at ZEISS and is also an investment in the future.
With around 43,000 employees, ZEISS is active globally in almost 50 countries with around 30 production sites, 60 sales and service companies and 27 research and development facilities (status: 30 September 2023). Founded in 1846 in Jena, the company is headquartered in Oberkochen, Germany. The Carl Zeiss Foundation, one of the largest foundations in Germany committed to the promotion of science, is the sole owner of the holding company, Carl Zeiss AG.
Further information at www.zeiss.com
ZEISS Research Microscopy Solutions
ZEISS Research Microscopy Solutions is the leading provider of light, electron, X-ray microscope systems, correlative microscopy and software solutions leveraging AI technologies. The portfolio comprises of products and services for life sciences, materials and industrial research, as well as education and clinical routine applications. The unit is headquartered in Jena. Additional production and development sites are located in Germany, UK, USA and China. ZEISS Research Microscopy Solutions is part of the Industrial Quality & Research segment.
Further information at www.zeiss.com/microscopy
Argolight Argolight is a French company specializing in quality control solutions for microscopy. By developing advanced calibration and quality control tools, Argolight empowers users to assess and enhance the performance of their imaging systems, leading to improved reliability and reproducibility in scientific research, industrial processes, and medical diagnostics.
Further information at www.argolight.com
Further press releases

Oxford-ZEISS Centre of Excellence officially opened

Super-resolution microscopy across all scales and applications

“Introduction of a new fuel is an option to improve technical and economic performance of a nuclear power plant without substantial investment. We are actively engaged in development of new models and modifications of VVER-440 fuel for power plants in Europe. The projects of the new fuels for Loviisa NPP in Finland, Dukovany NPP in the Czech Republic, Mochovce and Bohunice NPPs in Slovakia, are currently at various stages of implementation. Despite the same reactor model, these projects are quite different technically and conceptually, since we take into account the individual needs and requirements of our customers,” commented Natalia Nikipelova, President of TVEL JSC.
For reference:
The project of development and validation of the new fuel has been accomplished with participation of a number of Russian nuclear industry enterprises, such as OKB Gidropress (a part of Rosatom machine-building division Atomenergomash), Bochvar Institute (material science research facility of TVEL Fuel Company), Elemash Machine-building plant and Kurchatov Institute national research center. At the site of OKB Gidropress research and experiment facility, the new fuel passed a range of hydraulic, longevity and vibration tests.
Paks NPP is the only functioning nuclear power plant in Hungary with total installed capacity 2000 MWe. It operates four similar units powered by VVER-440 reactors and commissioned one by one in 1982-1987. Currently, Paks NPP is the only VVER-440 plant in the world operating in extended 15-monthes fuel cycle. The power plant produces about 15 bln kWh annually, about a half of electric power generation in Hungary. In 2018, the project of increasing the duration of Paks NPP fuel cycle won the European competition Quality Innovation Award in the nomination “Innovations of large enterprises”. Russian engineers from TVEL JSC, Kurchatov Institute, OKB Gidropress, Bochvar Institute and Elemash Machine-building plant provided assistance to the Hungarian colleagues in accomplishment of the project.
TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom incorporates enterprises for the fabrication of nuclear fuel, conversion and enrichment of uranium, production of gas centrifuges, as well as research and design organizations. It is the only supplier of nuclear fuel for Russian nuclear power plants. TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom provides nuclear fuel for 73 power reactors in 13 countries worldwide, research reactors in eight countries, as well as transport reactors of the Russian nuclear fleet. Every sixth power reactor in the world operates on fuel manufactured by TVEL. www.tvel.ru

COMMENTS
Digital learning and transformation of education. Open digital learning opportunities for all. Digital technologies have evolved from stand-alone projects to networks of tools and programmes that connect people and things across the world, and help address personal and global challenges. Digital innovation has demonstrated powers to complement ...
Digitalization of education and the ensuing digital transformation of education include challenges occurring simultaneously on many levels in education, as described above. Yet the advancement of digital technology forces another fundamental challenge which affects the entire framework. Use and fluency of digital technologies is an inherent ...
The education system is changing with the development of technology. ... Xiao (2019) investigates how the importance of digitalization is framed in the strategic growth plans of 75 of China's best institutions. The sustainable management of digital transformation in higher education is presented by Abad-Segura et al. (2020).
A variety of stakeholders must be mutually committed to creating digitally competent schools (Pettersson, 2018; Sailer et al., 2021), and teachers are seen as crucial to this process of digitalization (Bridwell-Mitchell, 2015; Lockton & Fargason, 2019).Moreover, the role of teachers in digitalizing education must be recognized as a complex, holistic phenomenon (Ertmer & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, 2010).
2.3. Digital education strategies and strategies on digital innovation Digital education has become an important strategic topic in virtually all OECD countries. Half of them have published a digital education strategy. In Australia, Belgium and Canada, state governments have taken responsibility for the digital education strategy, sometimes
The COVID-19 education disruption clearly revealed the urgent need to ally technologies and human resources to transform schooling models and to build inclusive, open and resilient learning systems. UNESCO supports the use of digital innovation in expanding access to educational opportunities and advancing inclusion, enhancing the relevance and ...
Education has become much more accessible, with a wide choice of learning techniques and degree options available. Teachers should think about why students want to use technology in the classroom rather than need it. It will surely assist educators in tracking student progress and developing innovative lesson strategies. Students who learn ...
The digitalization of the education sector is the latest example of broader trends in the global economy as a whole and the efforts we describe here can also be applied to teacher training as well ...
According to Vial, structural changes in four areas are critical for Dx: organizational structure, organizational culture, leadership, employee roles, and skills. 3 Our Dx framework for digital learning in higher education discusses seven aspects within each of those four areas: digital learning technologies, instructional modality, personnel ...
Abstract. The overwhelming importance of the digitalization of international education stems from the migration of student activities from the physical to the digital campus, which has been taking place over the past three decades. Many new and exciting learning opportunities have become possible for staff and students in higher education ...
As shown in research and practice digitalization processes are many times limited to implementation of digital technologies without pedagogical and organizational change. In this study it is argued for a broader perspective on the concept of digitalization, viewing it as a process involving change and transformation in different stages and several organizational levels. Based on cultural ...
Such transformations create a need for Institutions to prioritize identification of perspective models of digitalization in education (Salmon, 2013). Teachers, teacher educators and policymakers need to collaborate for co-constructing the technology-assisted classroom that will gradually evolve from teaching supplements to pivotal support for ...
Closing the Digital Divide in US Education—for Good. When American K-12 public schools in all 50 states closed their doors in March 2020, the inequities and scale of the digital divide were abruptly unmasked. According to BCG research in 2020, coauthored with Common Sense, roughly 30% of children in grades K-12 (15 million to 16 million ...
Digital Schools are Growing. Thirty states offer fully online schools that grant degrees. There are approximately 315,000 students enrolled in this type of digital school. This represents about ...
The best part about the digitization of education in the 21st century is that it is combined with the aspects of both; classroom learning and online learning methods. Walking hand in hand both act as a support system to each other, which gives a stronghold to our modern students. Digitization in education has also proved to be the right method ...
Today, during the National Digital Equity Summit hosted by the U.S. Department of Education, the Office of Educational Technology (OET) launched Advancing Digital Equity for All: Community-based Recommendations for Developing Effective Digital Equity Plans to Close the Digital Divide and Enable Technology-Empowered Learning.This resource provides recommendations for equitable broadband ...
Digitalization in education can be defined as using digital technolo gy to teach students. Digitalization is considered to be an indispensable concept to pr epare for the future following ...
Wide-ranging and digestible insights on the digitalisation of education, highlighting - from the cutting-edge of research - what we can learn for better and more equitable education and technology policy and practice. NORRAG is commissioning a blog series on the digitalisation of education, sharing perspectives from our work, as well as ...
THE GOVERNMENT is looking to adopt artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technologies to advance digitalization in key areas like healthcare and education, the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) told the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP). "We will harness the power of data analytics to inform evidence-based policy […]
Global Education Monitoring Report (GEM Report) Established in 2002, the GEM Report is an editorially independent report, hosted and published by UNESCO. ... Seminar on Digitalization of Education and Language for SIDS. 22 April 2024 - 2:00 pm - 23 April 2024 - 1:00 pm. Location. UNESCO Headquarters, Paris, France. Rooms : Room IV. Room II ...
Digitalization in education is a great opportunity, but also a challenge in terms of proper use, which implies critical thinking, and by no means superficiality and mere consumerism. The paper also deals with pedagogical possibilities and effects of education in the electronic environment. A variety of applications is found in digital media in ...
A special event that focused on AI technology and digitalization from a women's point of view took place in China on March 8, International Women's Day. This online event, held in partnership with the local Power Platform community and Microsoft Reactor, attracted more than 2,000 attendees.. Christina Liang, a Microsoft Community Program Manager, was instrumental in organizing the event from ...
Round table 2021. "Electrostal" Metallurgical plant" JSC has a number of remarkable time-tested traditions. One of them is holding an annual meeting with customers and partners in an extеnded format in order to build development pathways together, resolve pressing tasks and better understand each other. Although the digital age ...
2019: Decision to form a company. In January 2019, the Board of Directors of Atomenergoprom (part of Rosatom State Corporation) decided to create a new company - Rusatom-Digital Solutions. It will be 100% owned by Atomenergoprom, and the authorized capital of Rusatom-Digital Solutions will amount to 80 million rubles.
In 1938, it was granted town status. [citation needed]Administrative and municipal status. Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction is incorporated as Elektrostal Urban Okrug.
These segment solutions leverage industry best practices and are backed by Nokia one platform for industrial digitalization, which is comprised of Nokia Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) and Nokia Modular Private Wireless (MPW) 4.9G/LTE and 5G private wireless connectivity solutions, ruggedized Industrial devices, MX Industrial Edge (MXIE ...
THE British Chamber of Commerce in the Philippines (BCCP) believes digitalization will greatly help facilitate the ease of doing business (EODB) in the country. That is why it is working closely ...
Attendees get up to 19 continuing education credits, networking opportunities, case resolution, advice on practice management and more. IR-2024-117, April 22, 2024. WASHINGTON — The IRS encourages tax professionals to register now for the 2024 IRS Nationwide Tax Forum, coming this summer to Chicago, Orlando, Baltimore, Dallas and San Diego.
ZEISS Research Microscopy Solutions is the leading provider of light, electron, X-ray microscope systems, correlative microscopy and software solutions leveraging AI technologies. The portfolio comprises of products and services for life sciences, materials and industrial research, as well as education and clinical routine applications.
Access education focused on new and emerging trends like decarbonization, distributed energy resources, and the hydrogen economy, as well as traditional electric… Oct 9 — Oct 11, 2024 Orlando ...