- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Design
Definition:
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study. Research design is important because it guides the entire research process and ensures that the study is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner.
Types of Research Design
Types of Research Design are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
This type of research design is used to describe a phenomenon or situation. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations. The aim of descriptive research is to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a particular group, event, or situation. It can be useful in identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. This type of research design involves collecting data from participants and analyzing the relationship between the variables using statistical methods. The aim of correlational research is to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable. The aim of experimental research is to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. This type of research design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to conduct a true experiment.
Case Study Research Design
Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The aim of case study research is to provide an in-depth understanding of a particular case or situation.
Longitudinal Research Design
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
Structure of Research Design
The format of a research design typically includes the following sections:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem, the research questions, and the importance of the study. It also includes a brief literature review that summarizes previous research on the topic and identifies gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: This section identifies the specific research questions or hypotheses that the study will address. These questions should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Research Methods : This section describes the methods that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes details about the study design, the sampling strategy, the data collection instruments, and the data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This section describes how the data will be collected, including the sample size, data collection procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: This section describes how the data will be analyzed, including the statistical techniques that will be used to test the research questions or hypotheses.
- Results : This section presents the findings of the study, including descriptive statistics and statistical tests.
- Discussion and Conclusion : This section summarizes the key findings of the study, interprets the results, and discusses the implications of the findings. It also includes recommendations for future research.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research design.
Example of Research Design
An Example of Research Design could be:
Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school students?
Research design:
- Research approach : The research approach will be quantitative as it involves collecting numerical data to test the hypothesis.
- Research design : The research design will be a quasi-experimental design, with a pretest-posttest control group design.
- Sample : The sample will be 200 high school students from two schools, with 100 students in the experimental group and 100 students in the control group.
- Data collection : The data will be collected through surveys administered to the students at the beginning and end of the academic year. The surveys will include questions about their social media usage and academic performance.
- Data analysis : The data collected will be analyzed using statistical software. The mean scores of the experimental and control groups will be compared to determine whether there is a significant difference in academic performance between the two groups.
- Limitations : The limitations of the study will be acknowledged, including the fact that social media usage can vary greatly among individuals, and the study only focuses on two schools, which may not be representative of the entire population.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations will be taken into account, such as obtaining informed consent from the participants and ensuring their anonymity and confidentiality.
How to Write Research Design
Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a research question or hypothesis. Here are some steps to help you write a research design:
- Define the research question or hypothesis : Before beginning your research design, you should clearly define your research question or hypothesis. This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods.
- Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
- Develop a sampling plan : If your research involves collecting data from a sample, you will need to develop a sampling plan. This should outline how you will select participants and how many participants you will include.
- Define variables: Clearly define the variables you will be measuring or manipulating in your study. This will help ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Choose data collection methods : Decide on the data collection methods you will use to gather information. This may include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data sources.
- Create a data analysis plan: Develop a plan for analyzing your data, including the statistical or qualitative techniques you will use.
- Consider ethical concerns : Finally, be sure to consider any ethical concerns related to your research, such as participant confidentiality or potential harm.
When to Write Research Design
Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Ideally, the research design should be developed as early as possible in the research process, before any data is collected. This allows the researcher to carefully consider the research question, identify the most appropriate research methodology, and plan the data collection and analysis procedures in advance. By doing so, the research can be conducted in a more efficient and effective manner, and the results are more likely to be valid and reliable.
Purpose of Research Design
The purpose of research design is to plan and structure a research study in a way that enables the researcher to achieve the desired research goals with accuracy, validity, and reliability. Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis.
Some of the key purposes of research design include:
- Providing a clear and concise plan of action for the research study.
- Ensuring that the research is conducted ethically and with rigor.
- Maximizing the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
- Minimizing the possibility of errors, biases, or confounding variables.
- Ensuring that the research is feasible, practical, and cost-effective.
- Determining the appropriate research methodology to answer the research question(s).
- Identifying the sample size, sampling method, and data collection techniques.
- Determining the data analysis method and statistical tests to be used.
- Facilitating the replication of the study by other researchers.
- Enhancing the validity and generalizability of the research findings.
Applications of Research Design
There are numerous applications of research design in various fields, some of which are:
- Social sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, research design is used to investigate human behavior and social phenomena. Researchers use various research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and correlational designs, to study different aspects of social behavior.
- Education : Research design is essential in the field of education to investigate the effectiveness of different teaching methods and learning strategies. Researchers use various designs such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and case study designs to understand how students learn and how to improve teaching practices.
- Health sciences : In the health sciences, research design is used to investigate the causes, prevention, and treatment of diseases. Researchers use various designs, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to study different aspects of health and healthcare.
- Business : Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey research, experimental research, and case studies, to study different aspects of the business world.
- Engineering : In the field of engineering, research design is used to investigate the development and implementation of new technologies. Researchers use various designs, such as experimental research and case studies, to study the effectiveness of new technologies and to identify areas for improvement.
Advantages of Research Design
Here are some advantages of research design:
- Systematic and organized approach : A well-designed research plan ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner, which makes it easier to manage and analyze the data.
- Clear objectives: The research design helps to clarify the objectives of the study, which makes it easier to identify the variables that need to be measured, and the methods that need to be used to collect and analyze data.
- Minimizes bias: A well-designed research plan minimizes the chances of bias, by ensuring that the data is collected and analyzed objectively, and that the results are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or preferences.
- Efficient use of resources: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the resources (time, money, and personnel) are used efficiently and effectively, by focusing on the most important variables and methods.
- Replicability: A well-designed research plan makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study, which enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings.
- Validity: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings are valid, by ensuring that the methods used to collect and analyze data are appropriate for the research question.
- Generalizability : A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or situations, which increases the external validity of the study.
Research Design Vs Research Methodology
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 20 March 2023.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall aims and approach
- The type of research design you’ll use
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, frequently asked questions.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities – start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships, while descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends, and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analysing the data.
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region, or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalise your results to the population as a whole.
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study, your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalise to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question.
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviours, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews.
Observation methods
Observations allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviours, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected – for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are reliable and valid.
Operationalisation
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalisation means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in – for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced , while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method, you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample – by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method, it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method, how will you avoid bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organising and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymise and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well organised will save time when it comes to analysing them. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings.
On their own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyse the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarise your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarise your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
There are many other ways of analysing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, March 20). Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
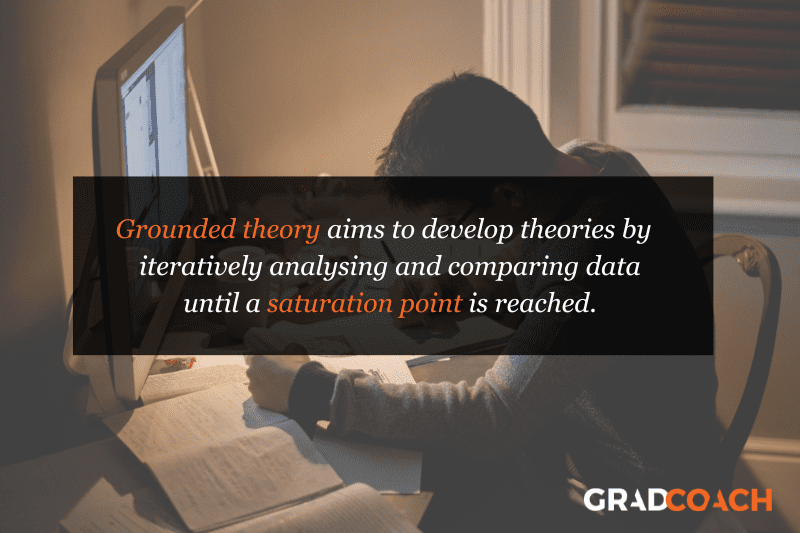
Grounded Theory Research Design
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.
Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
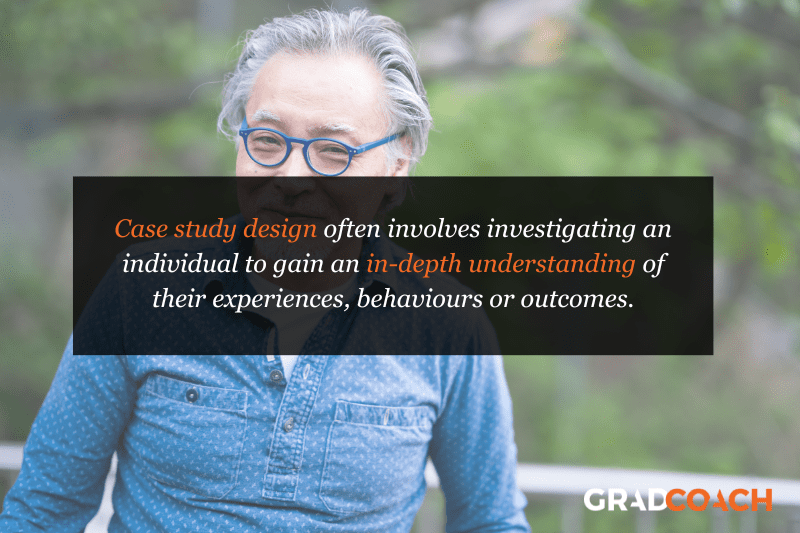
Case Study Design
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

10 Comments
Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
how can I put this blog as my reference(APA style) in bibliography part?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Research Design & Method
Research Methods Guide: Research Design & Method
- Introduction
- Survey Research
- Interview Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Research Design & Method
Research Methods (sociology-focused)
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods (intro)
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods (advanced)

FAQ: Research Design & Method
What is the difference between Research Design and Research Method?
Research design is a plan to answer your research question. A research method is a strategy used to implement that plan. Research design and methods are different but closely related, because good research design ensures that the data you obtain will help you answer your research question more effectively.
Which research method should I choose ?
It depends on your research goal. It depends on what subjects (and who) you want to study. Let's say you are interested in studying what makes people happy, or why some students are more conscious about recycling on campus. To answer these questions, you need to make a decision about how to collect your data. Most frequently used methods include:
- Observation / Participant Observation
- Focus Groups
- Experiments
- Secondary Data Analysis / Archival Study
- Mixed Methods (combination of some of the above)
One particular method could be better suited to your research goal than others, because the data you collect from different methods will be different in quality and quantity. For instance, surveys are usually designed to produce relatively short answers, rather than the extensive responses expected in qualitative interviews.
What other factors should I consider when choosing one method over another?
Time for data collection and analysis is something you want to consider. An observation or interview method, so-called qualitative approach, helps you collect richer information, but it takes time. Using a survey helps you collect more data quickly, yet it may lack details. So, you will need to consider the time you have for research and the balance between strengths and weaknesses associated with each method (e.g., qualitative vs. quantitative).
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Survey Research >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Types of Research Designs
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Introduction
Before beginning your paper, you need to decide how you plan to design the study .
The research design refers to the overall strategy and analytical approach that you have chosen in order to integrate, in a coherent and logical way, the different components of the study, thus ensuring that the research problem will be thoroughly investigated. It constitutes the blueprint for the collection, measurement, and interpretation of information and data. Note that the research problem determines the type of design you choose, not the other way around!
De Vaus, D. A. Research Design in Social Research . London: SAGE, 2001; Trochim, William M.K. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
General Structure and Writing Style
The function of a research design is to ensure that the evidence obtained enables you to effectively address the research problem logically and as unambiguously as possible . In social sciences research, obtaining information relevant to the research problem generally entails specifying the type of evidence needed to test the underlying assumptions of a theory, to evaluate a program, or to accurately describe and assess meaning related to an observable phenomenon.
With this in mind, a common mistake made by researchers is that they begin their investigations before they have thought critically about what information is required to address the research problem. Without attending to these design issues beforehand, the overall research problem will not be adequately addressed and any conclusions drawn will run the risk of being weak and unconvincing. As a consequence, the overall validity of the study will be undermined.
The length and complexity of describing the research design in your paper can vary considerably, but any well-developed description will achieve the following :
- Identify the research problem clearly and justify its selection, particularly in relation to any valid alternative designs that could have been used,
- Review and synthesize previously published literature associated with the research problem,
- Clearly and explicitly specify hypotheses [i.e., research questions] central to the problem,
- Effectively describe the information and/or data which will be necessary for an adequate testing of the hypotheses and explain how such information and/or data will be obtained, and
- Describe the methods of analysis to be applied to the data in determining whether or not the hypotheses are true or false.
The research design is usually incorporated into the introduction of your paper . You can obtain an overall sense of what to do by reviewing studies that have utilized the same research design [e.g., using a case study approach]. This can help you develop an outline to follow for your own paper.
NOTE : Use the SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases and the SAGE Research Methods Videos databases to search for scholarly resources on how to apply specific research designs and methods . The Research Methods Online database contains links to more than 175,000 pages of SAGE publisher's book, journal, and reference content on quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research methodologies. Also included is a collection of case studies of social research projects that can be used to help you better understand abstract or complex methodological concepts. The Research Methods Videos database contains hours of tutorials, interviews, video case studies, and mini-documentaries covering the entire research process.
Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2018; De Vaus, D. A. Research Design in Social Research . London: SAGE, 2001; Gorard, Stephen. Research Design: Creating Robust Approaches for the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Leedy, Paul D. and Jeanne Ellis Ormrod. Practical Research: Planning and Design . Tenth edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2013; Vogt, W. Paul, Dianna C. Gardner, and Lynne M. Haeffele. When to Use What Research Design . New York: Guilford, 2012.
Action Research Design
Definition and Purpose
The essentials of action research design follow a characteristic cycle whereby initially an exploratory stance is adopted, where an understanding of a problem is developed and plans are made for some form of interventionary strategy. Then the intervention is carried out [the "action" in action research] during which time, pertinent observations are collected in various forms. The new interventional strategies are carried out, and this cyclic process repeats, continuing until a sufficient understanding of [or a valid implementation solution for] the problem is achieved. The protocol is iterative or cyclical in nature and is intended to foster deeper understanding of a given situation, starting with conceptualizing and particularizing the problem and moving through several interventions and evaluations.
What do these studies tell you ?
- This is a collaborative and adaptive research design that lends itself to use in work or community situations.
- Design focuses on pragmatic and solution-driven research outcomes rather than testing theories.
- When practitioners use action research, it has the potential to increase the amount they learn consciously from their experience; the action research cycle can be regarded as a learning cycle.
- Action research studies often have direct and obvious relevance to improving practice and advocating for change.
- There are no hidden controls or preemption of direction by the researcher.
What these studies don't tell you ?
- It is harder to do than conducting conventional research because the researcher takes on responsibilities of advocating for change as well as for researching the topic.
- Action research is much harder to write up because it is less likely that you can use a standard format to report your findings effectively [i.e., data is often in the form of stories or observation].
- Personal over-involvement of the researcher may bias research results.
- The cyclic nature of action research to achieve its twin outcomes of action [e.g. change] and research [e.g. understanding] is time-consuming and complex to conduct.
- Advocating for change usually requires buy-in from study participants.
Coghlan, David and Mary Brydon-Miller. The Sage Encyclopedia of Action Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2014; Efron, Sara Efrat and Ruth Ravid. Action Research in Education: A Practical Guide . New York: Guilford, 2013; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 18, Action Research. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007; Gorard, Stephen. Research Design: Creating Robust Approaches for the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Kemmis, Stephen and Robin McTaggart. “Participatory Action Research.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. 2nd ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2000), pp. 567-605; McNiff, Jean. Writing and Doing Action Research . London: Sage, 2014; Reason, Peter and Hilary Bradbury. Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2001.
Case Study Design
A case study is an in-depth study of a particular research problem rather than a sweeping statistical survey or comprehensive comparative inquiry. It is often used to narrow down a very broad field of research into one or a few easily researchable examples. The case study research design is also useful for testing whether a specific theory and model actually applies to phenomena in the real world. It is a useful design when not much is known about an issue or phenomenon.
- Approach excels at bringing us to an understanding of a complex issue through detailed contextual analysis of a limited number of events or conditions and their relationships.
- A researcher using a case study design can apply a variety of methodologies and rely on a variety of sources to investigate a research problem.
- Design can extend experience or add strength to what is already known through previous research.
- Social scientists, in particular, make wide use of this research design to examine contemporary real-life situations and provide the basis for the application of concepts and theories and the extension of methodologies.
- The design can provide detailed descriptions of specific and rare cases.
- A single or small number of cases offers little basis for establishing reliability or to generalize the findings to a wider population of people, places, or things.
- Intense exposure to the study of a case may bias a researcher's interpretation of the findings.
- Design does not facilitate assessment of cause and effect relationships.
- Vital information may be missing, making the case hard to interpret.
- The case may not be representative or typical of the larger problem being investigated.
- If the criteria for selecting a case is because it represents a very unusual or unique phenomenon or problem for study, then your interpretation of the findings can only apply to that particular case.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 4, Flexible Methods: Case Study Design. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Greenhalgh, Trisha, editor. Case Study Evaluation: Past, Present and Future Challenges . Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing, 2015; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Stake, Robert E. The Art of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 1995; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Theory . Applied Social Research Methods Series, no. 5. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2003.
Causal Design
Causality studies may be thought of as understanding a phenomenon in terms of conditional statements in the form, “If X, then Y.” This type of research is used to measure what impact a specific change will have on existing norms and assumptions. Most social scientists seek causal explanations that reflect tests of hypotheses. Causal effect (nomothetic perspective) occurs when variation in one phenomenon, an independent variable, leads to or results, on average, in variation in another phenomenon, the dependent variable.
Conditions necessary for determining causality:
- Empirical association -- a valid conclusion is based on finding an association between the independent variable and the dependent variable.
- Appropriate time order -- to conclude that causation was involved, one must see that cases were exposed to variation in the independent variable before variation in the dependent variable.
- Nonspuriousness -- a relationship between two variables that is not due to variation in a third variable.
- Causality research designs assist researchers in understanding why the world works the way it does through the process of proving a causal link between variables and by the process of eliminating other possibilities.
- Replication is possible.
- There is greater confidence the study has internal validity due to the systematic subject selection and equity of groups being compared.
- Not all relationships are causal! The possibility always exists that, by sheer coincidence, two unrelated events appear to be related [e.g., Punxatawney Phil could accurately predict the duration of Winter for five consecutive years but, the fact remains, he's just a big, furry rodent].
- Conclusions about causal relationships are difficult to determine due to a variety of extraneous and confounding variables that exist in a social environment. This means causality can only be inferred, never proven.
- If two variables are correlated, the cause must come before the effect. However, even though two variables might be causally related, it can sometimes be difficult to determine which variable comes first and, therefore, to establish which variable is the actual cause and which is the actual effect.
Beach, Derek and Rasmus Brun Pedersen. Causal Case Study Methods: Foundations and Guidelines for Comparing, Matching, and Tracing . Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2016; Bachman, Ronet. The Practice of Research in Criminology and Criminal Justice . Chapter 5, Causation and Research Designs. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge Press, 2007; Brewer, Ernest W. and Jennifer Kubn. “Causal-Comparative Design.” In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 125-132; Causal Research Design: Experimentation. Anonymous SlideShare Presentation; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 11, Nonexperimental Research: Correlational Designs. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007; Trochim, William M.K. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Cohort Design
Often used in the medical sciences, but also found in the applied social sciences, a cohort study generally refers to a study conducted over a period of time involving members of a population which the subject or representative member comes from, and who are united by some commonality or similarity. Using a quantitative framework, a cohort study makes note of statistical occurrence within a specialized subgroup, united by same or similar characteristics that are relevant to the research problem being investigated, rather than studying statistical occurrence within the general population. Using a qualitative framework, cohort studies generally gather data using methods of observation. Cohorts can be either "open" or "closed."
- Open Cohort Studies [dynamic populations, such as the population of Los Angeles] involve a population that is defined just by the state of being a part of the study in question (and being monitored for the outcome). Date of entry and exit from the study is individually defined, therefore, the size of the study population is not constant. In open cohort studies, researchers can only calculate rate based data, such as, incidence rates and variants thereof.
- Closed Cohort Studies [static populations, such as patients entered into a clinical trial] involve participants who enter into the study at one defining point in time and where it is presumed that no new participants can enter the cohort. Given this, the number of study participants remains constant (or can only decrease).
- The use of cohorts is often mandatory because a randomized control study may be unethical. For example, you cannot deliberately expose people to asbestos, you can only study its effects on those who have already been exposed. Research that measures risk factors often relies upon cohort designs.
- Because cohort studies measure potential causes before the outcome has occurred, they can demonstrate that these “causes” preceded the outcome, thereby avoiding the debate as to which is the cause and which is the effect.
- Cohort analysis is highly flexible and can provide insight into effects over time and related to a variety of different types of changes [e.g., social, cultural, political, economic, etc.].
- Either original data or secondary data can be used in this design.
- In cases where a comparative analysis of two cohorts is made [e.g., studying the effects of one group exposed to asbestos and one that has not], a researcher cannot control for all other factors that might differ between the two groups. These factors are known as confounding variables.
- Cohort studies can end up taking a long time to complete if the researcher must wait for the conditions of interest to develop within the group. This also increases the chance that key variables change during the course of the study, potentially impacting the validity of the findings.
- Due to the lack of randominization in the cohort design, its external validity is lower than that of study designs where the researcher randomly assigns participants.
Healy P, Devane D. “Methodological Considerations in Cohort Study Designs.” Nurse Researcher 18 (2011): 32-36; Glenn, Norval D, editor. Cohort Analysis . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Levin, Kate Ann. Study Design IV: Cohort Studies. Evidence-Based Dentistry 7 (2003): 51–52; Payne, Geoff. “Cohort Study.” In The SAGE Dictionary of Social Research Methods . Victor Jupp, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), pp. 31-33; Study Design 101. Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library. George Washington University, November 2011; Cohort Study. Wikipedia.
Cross-Sectional Design
Cross-sectional research designs have three distinctive features: no time dimension; a reliance on existing differences rather than change following intervention; and, groups are selected based on existing differences rather than random allocation. The cross-sectional design can only measure differences between or from among a variety of people, subjects, or phenomena rather than a process of change. As such, researchers using this design can only employ a relatively passive approach to making causal inferences based on findings.
- Cross-sectional studies provide a clear 'snapshot' of the outcome and the characteristics associated with it, at a specific point in time.
- Unlike an experimental design, where there is an active intervention by the researcher to produce and measure change or to create differences, cross-sectional designs focus on studying and drawing inferences from existing differences between people, subjects, or phenomena.
- Entails collecting data at and concerning one point in time. While longitudinal studies involve taking multiple measures over an extended period of time, cross-sectional research is focused on finding relationships between variables at one moment in time.
- Groups identified for study are purposely selected based upon existing differences in the sample rather than seeking random sampling.
- Cross-section studies are capable of using data from a large number of subjects and, unlike observational studies, is not geographically bound.
- Can estimate prevalence of an outcome of interest because the sample is usually taken from the whole population.
- Because cross-sectional designs generally use survey techniques to gather data, they are relatively inexpensive and take up little time to conduct.
- Finding people, subjects, or phenomena to study that are very similar except in one specific variable can be difficult.
- Results are static and time bound and, therefore, give no indication of a sequence of events or reveal historical or temporal contexts.
- Studies cannot be utilized to establish cause and effect relationships.
- This design only provides a snapshot of analysis so there is always the possibility that a study could have differing results if another time-frame had been chosen.
- There is no follow up to the findings.
Bethlehem, Jelke. "7: Cross-sectional Research." In Research Methodology in the Social, Behavioural and Life Sciences . Herman J Adèr and Gideon J Mellenbergh, editors. (London, England: Sage, 1999), pp. 110-43; Bourque, Linda B. “Cross-Sectional Design.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods . Michael S. Lewis-Beck, Alan Bryman, and Tim Futing Liao. (Thousand Oaks, CA: 2004), pp. 230-231; Hall, John. “Cross-Sectional Survey Design.” In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods . Paul J. Lavrakas, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 173-174; Helen Barratt, Maria Kirwan. Cross-Sectional Studies: Design Application, Strengths and Weaknesses of Cross-Sectional Studies. Healthknowledge, 2009. Cross-Sectional Study. Wikipedia.
Descriptive Design
Descriptive research designs help provide answers to the questions of who, what, when, where, and how associated with a particular research problem; a descriptive study cannot conclusively ascertain answers to why. Descriptive research is used to obtain information concerning the current status of the phenomena and to describe "what exists" with respect to variables or conditions in a situation.
- The subject is being observed in a completely natural and unchanged natural environment. True experiments, whilst giving analyzable data, often adversely influence the normal behavior of the subject [a.k.a., the Heisenberg effect whereby measurements of certain systems cannot be made without affecting the systems].
- Descriptive research is often used as a pre-cursor to more quantitative research designs with the general overview giving some valuable pointers as to what variables are worth testing quantitatively.
- If the limitations are understood, they can be a useful tool in developing a more focused study.
- Descriptive studies can yield rich data that lead to important recommendations in practice.
- Appoach collects a large amount of data for detailed analysis.
- The results from a descriptive research cannot be used to discover a definitive answer or to disprove a hypothesis.
- Because descriptive designs often utilize observational methods [as opposed to quantitative methods], the results cannot be replicated.
- The descriptive function of research is heavily dependent on instrumentation for measurement and observation.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 5, Flexible Methods: Descriptive Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Given, Lisa M. "Descriptive Research." In Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics . Neil J. Salkind and Kristin Rasmussen, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2007), pp. 251-254; McNabb, Connie. Descriptive Research Methodologies. Powerpoint Presentation; Shuttleworth, Martyn. Descriptive Research Design, September 26, 2008; Erickson, G. Scott. "Descriptive Research Design." In New Methods of Market Research and Analysis . (Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2017), pp. 51-77; Sahin, Sagufta, and Jayanta Mete. "A Brief Study on Descriptive Research: Its Nature and Application in Social Science." International Journal of Research and Analysis in Humanities 1 (2021): 11; K. Swatzell and P. Jennings. “Descriptive Research: The Nuts and Bolts.” Journal of the American Academy of Physician Assistants 20 (2007), pp. 55-56; Kane, E. Doing Your Own Research: Basic Descriptive Research in the Social Sciences and Humanities . London: Marion Boyars, 1985.
Experimental Design
A blueprint of the procedure that enables the researcher to maintain control over all factors that may affect the result of an experiment. In doing this, the researcher attempts to determine or predict what may occur. Experimental research is often used where there is time priority in a causal relationship (cause precedes effect), there is consistency in a causal relationship (a cause will always lead to the same effect), and the magnitude of the correlation is great. The classic experimental design specifies an experimental group and a control group. The independent variable is administered to the experimental group and not to the control group, and both groups are measured on the same dependent variable. Subsequent experimental designs have used more groups and more measurements over longer periods. True experiments must have control, randomization, and manipulation.
- Experimental research allows the researcher to control the situation. In so doing, it allows researchers to answer the question, “What causes something to occur?”
- Permits the researcher to identify cause and effect relationships between variables and to distinguish placebo effects from treatment effects.
- Experimental research designs support the ability to limit alternative explanations and to infer direct causal relationships in the study.
- Approach provides the highest level of evidence for single studies.
- The design is artificial, and results may not generalize well to the real world.
- The artificial settings of experiments may alter the behaviors or responses of participants.
- Experimental designs can be costly if special equipment or facilities are needed.
- Some research problems cannot be studied using an experiment because of ethical or technical reasons.
- Difficult to apply ethnographic and other qualitative methods to experimentally designed studies.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 7, Flexible Methods: Experimental Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Chapter 2: Research Design, Experimental Designs. School of Psychology, University of New England, 2000; Chow, Siu L. "Experimental Design." In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 448-453; "Experimental Design." In Social Research Methods . Nicholas Walliman, editor. (London, England: Sage, 2006), pp, 101-110; Experimental Research. Research Methods by Dummies. Department of Psychology. California State University, Fresno, 2006; Kirk, Roger E. Experimental Design: Procedures for the Behavioral Sciences . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Trochim, William M.K. Experimental Design. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Rasool, Shafqat. Experimental Research. Slideshare presentation.
Exploratory Design
An exploratory design is conducted about a research problem when there are few or no earlier studies to refer to or rely upon to predict an outcome . The focus is on gaining insights and familiarity for later investigation or undertaken when research problems are in a preliminary stage of investigation. Exploratory designs are often used to establish an understanding of how best to proceed in studying an issue or what methodology would effectively apply to gathering information about the issue.
The goals of exploratory research are intended to produce the following possible insights:
- Familiarity with basic details, settings, and concerns.
- Well grounded picture of the situation being developed.
- Generation of new ideas and assumptions.
- Development of tentative theories or hypotheses.
- Determination about whether a study is feasible in the future.
- Issues get refined for more systematic investigation and formulation of new research questions.
- Direction for future research and techniques get developed.
- Design is a useful approach for gaining background information on a particular topic.
- Exploratory research is flexible and can address research questions of all types (what, why, how).
- Provides an opportunity to define new terms and clarify existing concepts.
- Exploratory research is often used to generate formal hypotheses and develop more precise research problems.
- In the policy arena or applied to practice, exploratory studies help establish research priorities and where resources should be allocated.
- Exploratory research generally utilizes small sample sizes and, thus, findings are typically not generalizable to the population at large.
- The exploratory nature of the research inhibits an ability to make definitive conclusions about the findings. They provide insight but not definitive conclusions.
- The research process underpinning exploratory studies is flexible but often unstructured, leading to only tentative results that have limited value to decision-makers.
- Design lacks rigorous standards applied to methods of data gathering and analysis because one of the areas for exploration could be to determine what method or methodologies could best fit the research problem.
Cuthill, Michael. “Exploratory Research: Citizen Participation, Local Government, and Sustainable Development in Australia.” Sustainable Development 10 (2002): 79-89; Streb, Christoph K. "Exploratory Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Albert J. Mills, Gabrielle Durepos and Eiden Wiebe, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 372-374; Taylor, P. J., G. Catalano, and D.R.F. Walker. “Exploratory Analysis of the World City Network.” Urban Studies 39 (December 2002): 2377-2394; Exploratory Research. Wikipedia.
Field Research Design
Sometimes referred to as ethnography or participant observation, designs around field research encompass a variety of interpretative procedures [e.g., observation and interviews] rooted in qualitative approaches to studying people individually or in groups while inhabiting their natural environment as opposed to using survey instruments or other forms of impersonal methods of data gathering. Information acquired from observational research takes the form of “ field notes ” that involves documenting what the researcher actually sees and hears while in the field. Findings do not consist of conclusive statements derived from numbers and statistics because field research involves analysis of words and observations of behavior. Conclusions, therefore, are developed from an interpretation of findings that reveal overriding themes, concepts, and ideas. More information can be found HERE .
- Field research is often necessary to fill gaps in understanding the research problem applied to local conditions or to specific groups of people that cannot be ascertained from existing data.
- The research helps contextualize already known information about a research problem, thereby facilitating ways to assess the origins, scope, and scale of a problem and to gage the causes, consequences, and means to resolve an issue based on deliberate interaction with people in their natural inhabited spaces.
- Enables the researcher to corroborate or confirm data by gathering additional information that supports or refutes findings reported in prior studies of the topic.
- Because the researcher in embedded in the field, they are better able to make observations or ask questions that reflect the specific cultural context of the setting being investigated.
- Observing the local reality offers the opportunity to gain new perspectives or obtain unique data that challenges existing theoretical propositions or long-standing assumptions found in the literature.
What these studies don't tell you
- A field research study requires extensive time and resources to carry out the multiple steps involved with preparing for the gathering of information, including for example, examining background information about the study site, obtaining permission to access the study site, and building trust and rapport with subjects.
- Requires a commitment to staying engaged in the field to ensure that you can adequately document events and behaviors as they unfold.
- The unpredictable nature of fieldwork means that researchers can never fully control the process of data gathering. They must maintain a flexible approach to studying the setting because events and circumstances can change quickly or unexpectedly.
- Findings can be difficult to interpret and verify without access to documents and other source materials that help to enhance the credibility of information obtained from the field [i.e., the act of triangulating the data].
- Linking the research problem to the selection of study participants inhabiting their natural environment is critical. However, this specificity limits the ability to generalize findings to different situations or in other contexts or to infer courses of action applied to other settings or groups of people.
- The reporting of findings must take into account how the researcher themselves may have inadvertently affected respondents and their behaviors.
Historical Design
The purpose of a historical research design is to collect, verify, and synthesize evidence from the past to establish facts that defend or refute a hypothesis. It uses secondary sources and a variety of primary documentary evidence, such as, diaries, official records, reports, archives, and non-textual information [maps, pictures, audio and visual recordings]. The limitation is that the sources must be both authentic and valid.
- The historical research design is unobtrusive; the act of research does not affect the results of the study.
- The historical approach is well suited for trend analysis.
- Historical records can add important contextual background required to more fully understand and interpret a research problem.
- There is often no possibility of researcher-subject interaction that could affect the findings.
- Historical sources can be used over and over to study different research problems or to replicate a previous study.
- The ability to fulfill the aims of your research are directly related to the amount and quality of documentation available to understand the research problem.
- Since historical research relies on data from the past, there is no way to manipulate it to control for contemporary contexts.
- Interpreting historical sources can be very time consuming.
- The sources of historical materials must be archived consistently to ensure access. This may especially challenging for digital or online-only sources.
- Original authors bring their own perspectives and biases to the interpretation of past events and these biases are more difficult to ascertain in historical resources.
- Due to the lack of control over external variables, historical research is very weak with regard to the demands of internal validity.
- It is rare that the entirety of historical documentation needed to fully address a research problem is available for interpretation, therefore, gaps need to be acknowledged.
Howell, Martha C. and Walter Prevenier. From Reliable Sources: An Introduction to Historical Methods . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2001; Lundy, Karen Saucier. "Historical Research." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods . Lisa M. Given, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 396-400; Marius, Richard. and Melvin E. Page. A Short Guide to Writing about History . 9th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2015; Savitt, Ronald. “Historical Research in Marketing.” Journal of Marketing 44 (Autumn, 1980): 52-58; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 16, Historical Research. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007.
Longitudinal Design
A longitudinal study follows the same sample over time and makes repeated observations. For example, with longitudinal surveys, the same group of people is interviewed at regular intervals, enabling researchers to track changes over time and to relate them to variables that might explain why the changes occur. Longitudinal research designs describe patterns of change and help establish the direction and magnitude of causal relationships. Measurements are taken on each variable over two or more distinct time periods. This allows the researcher to measure change in variables over time. It is a type of observational study sometimes referred to as a panel study.
- Longitudinal data facilitate the analysis of the duration of a particular phenomenon.
- Enables survey researchers to get close to the kinds of causal explanations usually attainable only with experiments.
- The design permits the measurement of differences or change in a variable from one period to another [i.e., the description of patterns of change over time].
- Longitudinal studies facilitate the prediction of future outcomes based upon earlier factors.
- The data collection method may change over time.
- Maintaining the integrity of the original sample can be difficult over an extended period of time.
- It can be difficult to show more than one variable at a time.
- This design often needs qualitative research data to explain fluctuations in the results.
- A longitudinal research design assumes present trends will continue unchanged.
- It can take a long period of time to gather results.
- There is a need to have a large sample size and accurate sampling to reach representativness.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 6, Flexible Methods: Relational and Longitudinal Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Forgues, Bernard, and Isabelle Vandangeon-Derumez. "Longitudinal Analyses." In Doing Management Research . Raymond-Alain Thiétart and Samantha Wauchope, editors. (London, England: Sage, 2001), pp. 332-351; Kalaian, Sema A. and Rafa M. Kasim. "Longitudinal Studies." In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods . Paul J. Lavrakas, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 440-441; Menard, Scott, editor. Longitudinal Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002; Ployhart, Robert E. and Robert J. Vandenberg. "Longitudinal Research: The Theory, Design, and Analysis of Change.” Journal of Management 36 (January 2010): 94-120; Longitudinal Study. Wikipedia.
Meta-Analysis Design
Meta-analysis is an analytical methodology designed to systematically evaluate and summarize the results from a number of individual studies, thereby, increasing the overall sample size and the ability of the researcher to study effects of interest. The purpose is to not simply summarize existing knowledge, but to develop a new understanding of a research problem using synoptic reasoning. The main objectives of meta-analysis include analyzing differences in the results among studies and increasing the precision by which effects are estimated. A well-designed meta-analysis depends upon strict adherence to the criteria used for selecting studies and the availability of information in each study to properly analyze their findings. Lack of information can severely limit the type of analyzes and conclusions that can be reached. In addition, the more dissimilarity there is in the results among individual studies [heterogeneity], the more difficult it is to justify interpretations that govern a valid synopsis of results. A meta-analysis needs to fulfill the following requirements to ensure the validity of your findings:
- Clearly defined description of objectives, including precise definitions of the variables and outcomes that are being evaluated;
- A well-reasoned and well-documented justification for identification and selection of the studies;
- Assessment and explicit acknowledgment of any researcher bias in the identification and selection of those studies;
- Description and evaluation of the degree of heterogeneity among the sample size of studies reviewed; and,
- Justification of the techniques used to evaluate the studies.
- Can be an effective strategy for determining gaps in the literature.
- Provides a means of reviewing research published about a particular topic over an extended period of time and from a variety of sources.
- Is useful in clarifying what policy or programmatic actions can be justified on the basis of analyzing research results from multiple studies.
- Provides a method for overcoming small sample sizes in individual studies that previously may have had little relationship to each other.
- Can be used to generate new hypotheses or highlight research problems for future studies.
- Small violations in defining the criteria used for content analysis can lead to difficult to interpret and/or meaningless findings.
- A large sample size can yield reliable, but not necessarily valid, results.
- A lack of uniformity regarding, for example, the type of literature reviewed, how methods are applied, and how findings are measured within the sample of studies you are analyzing, can make the process of synthesis difficult to perform.
- Depending on the sample size, the process of reviewing and synthesizing multiple studies can be very time consuming.
Beck, Lewis W. "The Synoptic Method." The Journal of Philosophy 36 (1939): 337-345; Cooper, Harris, Larry V. Hedges, and Jeffrey C. Valentine, eds. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis . 2nd edition. New York: Russell Sage Foundation, 2009; Guzzo, Richard A., Susan E. Jackson and Raymond A. Katzell. “Meta-Analysis Analysis.” In Research in Organizational Behavior , Volume 9. (Greenwich, CT: JAI Press, 1987), pp 407-442; Lipsey, Mark W. and David B. Wilson. Practical Meta-Analysis . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2001; Study Design 101. Meta-Analysis. The Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library, George Washington University; Timulak, Ladislav. “Qualitative Meta-Analysis.” In The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis . Uwe Flick, editor. (Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2013), pp. 481-495; Walker, Esteban, Adrian V. Hernandez, and Micheal W. Kattan. "Meta-Analysis: It's Strengths and Limitations." Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 75 (June 2008): 431-439.
Mixed-Method Design
- Narrative and non-textual information can add meaning to numeric data, while numeric data can add precision to narrative and non-textual information.
- Can utilize existing data while at the same time generating and testing a grounded theory approach to describe and explain the phenomenon under study.
- A broader, more complex research problem can be investigated because the researcher is not constrained by using only one method.
- The strengths of one method can be used to overcome the inherent weaknesses of another method.
- Can provide stronger, more robust evidence to support a conclusion or set of recommendations.
- May generate new knowledge new insights or uncover hidden insights, patterns, or relationships that a single methodological approach might not reveal.
- Produces more complete knowledge and understanding of the research problem that can be used to increase the generalizability of findings applied to theory or practice.
- A researcher must be proficient in understanding how to apply multiple methods to investigating a research problem as well as be proficient in optimizing how to design a study that coherently melds them together.
- Can increase the likelihood of conflicting results or ambiguous findings that inhibit drawing a valid conclusion or setting forth a recommended course of action [e.g., sample interview responses do not support existing statistical data].
- Because the research design can be very complex, reporting the findings requires a well-organized narrative, clear writing style, and precise word choice.
- Design invites collaboration among experts. However, merging different investigative approaches and writing styles requires more attention to the overall research process than studies conducted using only one methodological paradigm.
- Concurrent merging of quantitative and qualitative research requires greater attention to having adequate sample sizes, using comparable samples, and applying a consistent unit of analysis. For sequential designs where one phase of qualitative research builds on the quantitative phase or vice versa, decisions about what results from the first phase to use in the next phase, the choice of samples and estimating reasonable sample sizes for both phases, and the interpretation of results from both phases can be difficult.
- Due to multiple forms of data being collected and analyzed, this design requires extensive time and resources to carry out the multiple steps involved in data gathering and interpretation.
Burch, Patricia and Carolyn J. Heinrich. Mixed Methods for Policy Research and Program Evaluation . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2016; Creswell, John w. et al. Best Practices for Mixed Methods Research in the Health Sciences . Bethesda, MD: Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research, National Institutes of Health, 2010Creswell, John W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014; Domínguez, Silvia, editor. Mixed Methods Social Networks Research . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2014; Hesse-Biber, Sharlene Nagy. Mixed Methods Research: Merging Theory with Practice . New York: Guilford Press, 2010; Niglas, Katrin. “How the Novice Researcher Can Make Sense of Mixed Methods Designs.” International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches 3 (2009): 34-46; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Nancy L. Leech. “Linking Research Questions to Mixed Methods Data Analysis Procedures.” The Qualitative Report 11 (September 2006): 474-498; Tashakorri, Abbas and John W. Creswell. “The New Era of Mixed Methods.” Journal of Mixed Methods Research 1 (January 2007): 3-7; Zhanga, Wanqing. “Mixed Methods Application in Health Intervention Research: A Multiple Case Study.” International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches 8 (2014): 24-35 .
Observational Design
This type of research design draws a conclusion by comparing subjects against a control group, in cases where the researcher has no control over the experiment. There are two general types of observational designs. In direct observations, people know that you are watching them. Unobtrusive measures involve any method for studying behavior where individuals do not know they are being observed. An observational study allows a useful insight into a phenomenon and avoids the ethical and practical difficulties of setting up a large and cumbersome research project.
- Observational studies are usually flexible and do not necessarily need to be structured around a hypothesis about what you expect to observe [data is emergent rather than pre-existing].
- The researcher is able to collect in-depth information about a particular behavior.
- Can reveal interrelationships among multifaceted dimensions of group interactions.
- You can generalize your results to real life situations.
- Observational research is useful for discovering what variables may be important before applying other methods like experiments.
- Observation research designs account for the complexity of group behaviors.
- Reliability of data is low because seeing behaviors occur over and over again may be a time consuming task and are difficult to replicate.
- In observational research, findings may only reflect a unique sample population and, thus, cannot be generalized to other groups.
- There can be problems with bias as the researcher may only "see what they want to see."
- There is no possibility to determine "cause and effect" relationships since nothing is manipulated.
- Sources or subjects may not all be equally credible.
- Any group that is knowingly studied is altered to some degree by the presence of the researcher, therefore, potentially skewing any data collected.
Atkinson, Paul and Martyn Hammersley. “Ethnography and Participant Observation.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 248-261; Observational Research. Research Methods by Dummies. Department of Psychology. California State University, Fresno, 2006; Patton Michael Quinn. Qualitiative Research and Evaluation Methods . Chapter 6, Fieldwork Strategies and Observational Methods. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002; Payne, Geoff and Judy Payne. "Observation." In Key Concepts in Social Research . The SAGE Key Concepts series. (London, England: Sage, 2004), pp. 158-162; Rosenbaum, Paul R. Design of Observational Studies . New York: Springer, 2010;Williams, J. Patrick. "Nonparticipant Observation." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods . Lisa M. Given, editor.(Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 562-563.
Philosophical Design
Understood more as an broad approach to examining a research problem than a methodological design, philosophical analysis and argumentation is intended to challenge deeply embedded, often intractable, assumptions underpinning an area of study. This approach uses the tools of argumentation derived from philosophical traditions, concepts, models, and theories to critically explore and challenge, for example, the relevance of logic and evidence in academic debates, to analyze arguments about fundamental issues, or to discuss the root of existing discourse about a research problem. These overarching tools of analysis can be framed in three ways:
- Ontology -- the study that describes the nature of reality; for example, what is real and what is not, what is fundamental and what is derivative?
- Epistemology -- the study that explores the nature of knowledge; for example, by what means does knowledge and understanding depend upon and how can we be certain of what we know?
- Axiology -- the study of values; for example, what values does an individual or group hold and why? How are values related to interest, desire, will, experience, and means-to-end? And, what is the difference between a matter of fact and a matter of value?
- Can provide a basis for applying ethical decision-making to practice.
- Functions as a means of gaining greater self-understanding and self-knowledge about the purposes of research.
- Brings clarity to general guiding practices and principles of an individual or group.
- Philosophy informs methodology.
- Refine concepts and theories that are invoked in relatively unreflective modes of thought and discourse.
- Beyond methodology, philosophy also informs critical thinking about epistemology and the structure of reality (metaphysics).
- Offers clarity and definition to the practical and theoretical uses of terms, concepts, and ideas.
- Limited application to specific research problems [answering the "So What?" question in social science research].
- Analysis can be abstract, argumentative, and limited in its practical application to real-life issues.
- While a philosophical analysis may render problematic that which was once simple or taken-for-granted, the writing can be dense and subject to unnecessary jargon, overstatement, and/or excessive quotation and documentation.
- There are limitations in the use of metaphor as a vehicle of philosophical analysis.
- There can be analytical difficulties in moving from philosophy to advocacy and between abstract thought and application to the phenomenal world.
Burton, Dawn. "Part I, Philosophy of the Social Sciences." In Research Training for Social Scientists . (London, England: Sage, 2000), pp. 1-5; Chapter 4, Research Methodology and Design. Unisa Institutional Repository (UnisaIR), University of South Africa; Jarvie, Ian C., and Jesús Zamora-Bonilla, editors. The SAGE Handbook of the Philosophy of Social Sciences . London: Sage, 2011; Labaree, Robert V. and Ross Scimeca. “The Philosophical Problem of Truth in Librarianship.” The Library Quarterly 78 (January 2008): 43-70; Maykut, Pamela S. Beginning Qualitative Research: A Philosophic and Practical Guide . Washington, DC: Falmer Press, 1994; McLaughlin, Hugh. "The Philosophy of Social Research." In Understanding Social Work Research . 2nd edition. (London: SAGE Publications Ltd., 2012), pp. 24-47; Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy . Metaphysics Research Lab, CSLI, Stanford University, 2013.
Sequential Design
- The researcher has a limitless option when it comes to sample size and the sampling schedule.
- Due to the repetitive nature of this research design, minor changes and adjustments can be done during the initial parts of the study to correct and hone the research method.
- This is a useful design for exploratory studies.
- There is very little effort on the part of the researcher when performing this technique. It is generally not expensive, time consuming, or workforce intensive.
- Because the study is conducted serially, the results of one sample are known before the next sample is taken and analyzed. This provides opportunities for continuous improvement of sampling and methods of analysis.
- The sampling method is not representative of the entire population. The only possibility of approaching representativeness is when the researcher chooses to use a very large sample size significant enough to represent a significant portion of the entire population. In this case, moving on to study a second or more specific sample can be difficult.
- The design cannot be used to create conclusions and interpretations that pertain to an entire population because the sampling technique is not randomized. Generalizability from findings is, therefore, limited.
- Difficult to account for and interpret variation from one sample to another over time, particularly when using qualitative methods of data collection.
Betensky, Rebecca. Harvard University, Course Lecture Note slides; Bovaird, James A. and Kevin A. Kupzyk. "Sequential Design." In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 1347-1352; Cresswell, John W. Et al. “Advanced Mixed-Methods Research Designs.” In Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social and Behavioral Research . Abbas Tashakkori and Charles Teddle, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2003), pp. 209-240; Henry, Gary T. "Sequential Sampling." In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods . Michael S. Lewis-Beck, Alan Bryman and Tim Futing Liao, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2004), pp. 1027-1028; Nataliya V. Ivankova. “Using Mixed-Methods Sequential Explanatory Design: From Theory to Practice.” Field Methods 18 (February 2006): 3-20; Bovaird, James A. and Kevin A. Kupzyk. “Sequential Design.” In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010; Sequential Analysis. Wikipedia.
Systematic Review
- A systematic review synthesizes the findings of multiple studies related to each other by incorporating strategies of analysis and interpretation intended to reduce biases and random errors.
- The application of critical exploration, evaluation, and synthesis methods separates insignificant, unsound, or redundant research from the most salient and relevant studies worthy of reflection.
- They can be use to identify, justify, and refine hypotheses, recognize and avoid hidden problems in prior studies, and explain data inconsistencies and conflicts in data.
- Systematic reviews can be used to help policy makers formulate evidence-based guidelines and regulations.
- The use of strict, explicit, and pre-determined methods of synthesis, when applied appropriately, provide reliable estimates about the effects of interventions, evaluations, and effects related to the overarching research problem investigated by each study under review.
- Systematic reviews illuminate where knowledge or thorough understanding of a research problem is lacking and, therefore, can then be used to guide future research.
- The accepted inclusion of unpublished studies [i.e., grey literature] ensures the broadest possible way to analyze and interpret research on a topic.
- Results of the synthesis can be generalized and the findings extrapolated into the general population with more validity than most other types of studies .
- Systematic reviews do not create new knowledge per se; they are a method for synthesizing existing studies about a research problem in order to gain new insights and determine gaps in the literature.
- The way researchers have carried out their investigations [e.g., the period of time covered, number of participants, sources of data analyzed, etc.] can make it difficult to effectively synthesize studies.
- The inclusion of unpublished studies can introduce bias into the review because they may not have undergone a rigorous peer-review process prior to publication. Examples may include conference presentations or proceedings, publications from government agencies, white papers, working papers, and internal documents from organizations, and doctoral dissertations and Master's theses.
Denyer, David and David Tranfield. "Producing a Systematic Review." In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods . David A. Buchanan and Alan Bryman, editors. ( Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2009), pp. 671-689; Foster, Margaret J. and Sarah T. Jewell, editors. Assembling the Pieces of a Systematic Review: A Guide for Librarians . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017; Gough, David, Sandy Oliver, James Thomas, editors. Introduction to Systematic Reviews . 2nd edition. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2017; Gopalakrishnan, S. and P. Ganeshkumar. “Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis: Understanding the Best Evidence in Primary Healthcare.” Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care 2 (2013): 9-14; Gough, David, James Thomas, and Sandy Oliver. "Clarifying Differences between Review Designs and Methods." Systematic Reviews 1 (2012): 1-9; Khan, Khalid S., Regina Kunz, Jos Kleijnen, and Gerd Antes. “Five Steps to Conducting a Systematic Review.” Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 96 (2003): 118-121; Mulrow, C. D. “Systematic Reviews: Rationale for Systematic Reviews.” BMJ 309:597 (September 1994); O'Dwyer, Linda C., and Q. Eileen Wafford. "Addressing Challenges with Systematic Review Teams through Effective Communication: A Case Report." Journal of the Medical Library Association 109 (October 2021): 643-647; Okoli, Chitu, and Kira Schabram. "A Guide to Conducting a Systematic Literature Review of Information Systems Research." Sprouts: Working Papers on Information Systems 10 (2010); Siddaway, Andy P., Alex M. Wood, and Larry V. Hedges. "How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-analyses, and Meta-syntheses." Annual Review of Psychology 70 (2019): 747-770; Torgerson, Carole J. “Publication Bias: The Achilles’ Heel of Systematic Reviews?” British Journal of Educational Studies 54 (March 2006): 89-102; Torgerson, Carole. Systematic Reviews . New York: Continuum, 2003.
- << Previous: Purpose of Guide
- Next: Design Flaws to Avoid >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5 Research design
Research design is a comprehensive plan for data collection in an empirical research project. It is a ‘blueprint’ for empirical research aimed at answering specific research questions or testing specific hypotheses, and must specify at least three processes: the data collection process, the instrument development process, and the sampling process. The instrument development and sampling processes are described in the next two chapters, and the data collection process—which is often loosely called ‘research design’—is introduced in this chapter and is described in further detail in Chapters 9–12.
Broadly speaking, data collection methods can be grouped into two categories: positivist and interpretive. Positivist methods , such as laboratory experiments and survey research, are aimed at theory (or hypotheses) testing, while interpretive methods, such as action research and ethnography, are aimed at theory building. Positivist methods employ a deductive approach to research, starting with a theory and testing theoretical postulates using empirical data. In contrast, interpretive methods employ an inductive approach that starts with data and tries to derive a theory about the phenomenon of interest from the observed data. Often times, these methods are incorrectly equated with quantitative and qualitative research. Quantitative and qualitative methods refers to the type of data being collected—quantitative data involve numeric scores, metrics, and so on, while qualitative data includes interviews, observations, and so forth—and analysed (i.e., using quantitative techniques such as regression or qualitative techniques such as coding). Positivist research uses predominantly quantitative data, but can also use qualitative data. Interpretive research relies heavily on qualitative data, but can sometimes benefit from including quantitative data as well. Sometimes, joint use of qualitative and quantitative data may help generate unique insight into a complex social phenomenon that is not available from either type of data alone, and hence, mixed-mode designs that combine qualitative and quantitative data are often highly desirable.
Key attributes of a research design
The quality of research designs can be defined in terms of four key design attributes: internal validity, external validity, construct validity, and statistical conclusion validity.
Internal validity , also called causality, examines whether the observed change in a dependent variable is indeed caused by a corresponding change in a hypothesised independent variable, and not by variables extraneous to the research context. Causality requires three conditions: covariation of cause and effect (i.e., if cause happens, then effect also happens; if cause does not happen, effect does not happen), temporal precedence (cause must precede effect in time), and spurious correlation, or there is no plausible alternative explanation for the change. Certain research designs, such as laboratory experiments, are strong in internal validity by virtue of their ability to manipulate the independent variable (cause) via a treatment and observe the effect (dependent variable) of that treatment after a certain point in time, while controlling for the effects of extraneous variables. Other designs, such as field surveys, are poor in internal validity because of their inability to manipulate the independent variable (cause), and because cause and effect are measured at the same point in time which defeats temporal precedence making it equally likely that the expected effect might have influenced the expected cause rather than the reverse. Although higher in internal validity compared to other methods, laboratory experiments are by no means immune to threats of internal validity, and are susceptible to history, testing, instrumentation, regression, and other threats that are discussed later in the chapter on experimental designs. Nonetheless, different research designs vary considerably in their respective level of internal validity.
External validity or generalisability refers to whether the observed associations can be generalised from the sample to the population (population validity), or to other people, organisations, contexts, or time (ecological validity). For instance, can results drawn from a sample of financial firms in the United States be generalised to the population of financial firms (population validity) or to other firms within the United States (ecological validity)? Survey research, where data is sourced from a wide variety of individuals, firms, or other units of analysis, tends to have broader generalisability than laboratory experiments where treatments and extraneous variables are more controlled. The variation in internal and external validity for a wide range of research designs is shown in Figure 5.1.
Some researchers claim that there is a trade-off between internal and external validity—higher external validity can come only at the cost of internal validity and vice versa. But this is not always the case. Research designs such as field experiments, longitudinal field surveys, and multiple case studies have higher degrees of both internal and external validities. Personally, I prefer research designs that have reasonable degrees of both internal and external validities, i.e., those that fall within the cone of validity shown in Figure 5.1. But this should not suggest that designs outside this cone are any less useful or valuable. Researchers’ choice of designs are ultimately a matter of their personal preference and competence, and the level of internal and external validity they desire.
Construct validity examines how well a given measurement scale is measuring the theoretical construct that it is expected to measure. Many constructs used in social science research such as empathy, resistance to change, and organisational learning are difficult to define, much less measure. For instance, construct validity must ensure that a measure of empathy is indeed measuring empathy and not compassion, which may be difficult since these constructs are somewhat similar in meaning. Construct validity is assessed in positivist research based on correlational or factor analysis of pilot test data, as described in the next chapter.
Statistical conclusion validity examines the extent to which conclusions derived using a statistical procedure are valid. For example, it examines whether the right statistical method was used for hypotheses testing, whether the variables used meet the assumptions of that statistical test (such as sample size or distributional requirements), and so forth. Because interpretive research designs do not employ statistical tests, statistical conclusion validity is not applicable for such analysis. The different kinds of validity and where they exist at the theoretical/empirical levels are illustrated in Figure 5.2.
Improving internal and external validity
The best research designs are those that can ensure high levels of internal and external validity. Such designs would guard against spurious correlations, inspire greater faith in the hypotheses testing, and ensure that the results drawn from a small sample are generalisable to the population at large. Controls are required to ensure internal validity (causality) of research designs, and can be accomplished in five ways: manipulation, elimination, inclusion, and statistical control, and randomisation.
In manipulation , the researcher manipulates the independent variables in one or more levels (called ‘treatments’), and compares the effects of the treatments against a control group where subjects do not receive the treatment. Treatments may include a new drug or different dosage of drug (for treating a medical condition), a teaching style (for students), and so forth. This type of control is achieved in experimental or quasi-experimental designs, but not in non-experimental designs such as surveys. Note that if subjects cannot distinguish adequately between different levels of treatment manipulations, their responses across treatments may not be different, and manipulation would fail.
The elimination technique relies on eliminating extraneous variables by holding them constant across treatments, such as by restricting the study to a single gender or a single socioeconomic status. In the inclusion technique, the role of extraneous variables is considered by including them in the research design and separately estimating their effects on the dependent variable, such as via factorial designs where one factor is gender (male versus female). Such technique allows for greater generalisability, but also requires substantially larger samples. In statistical control , extraneous variables are measured and used as covariates during the statistical testing process.
Finally, the randomisation technique is aimed at cancelling out the effects of extraneous variables through a process of random sampling, if it can be assured that these effects are of a random (non-systematic) nature. Two types of randomisation are: random selection , where a sample is selected randomly from a population, and random assignment , where subjects selected in a non-random manner are randomly assigned to treatment groups.
Randomisation also ensures external validity, allowing inferences drawn from the sample to be generalised to the population from which the sample is drawn. Note that random assignment is mandatory when random selection is not possible because of resource or access constraints. However, generalisability across populations is harder to ascertain since populations may differ on multiple dimensions and you can only control for a few of those dimensions.
Popular research designs
As noted earlier, research designs can be classified into two categories—positivist and interpretive—depending on the goal of the research. Positivist designs are meant for theory testing, while interpretive designs are meant for theory building. Positivist designs seek generalised patterns based on an objective view of reality, while interpretive designs seek subjective interpretations of social phenomena from the perspectives of the subjects involved. Some popular examples of positivist designs include laboratory experiments, field experiments, field surveys, secondary data analysis, and case research, while examples of interpretive designs include case research, phenomenology, and ethnography. Note that case research can be used for theory building or theory testing, though not at the same time. Not all techniques are suited for all kinds of scientific research. Some techniques such as focus groups are best suited for exploratory research, others such as ethnography are best for descriptive research, and still others such as laboratory experiments are ideal for explanatory research. Following are brief descriptions of some of these designs. Additional details are provided in Chapters 9–12.
Experimental studies are those that are intended to test cause-effect relationships (hypotheses) in a tightly controlled setting by separating the cause from the effect in time, administering the cause to one group of subjects (the ‘treatment group’) but not to another group (‘control group’), and observing how the mean effects vary between subjects in these two groups. For instance, if we design a laboratory experiment to test the efficacy of a new drug in treating a certain ailment, we can get a random sample of people afflicted with that ailment, randomly assign them to one of two groups (treatment and control groups), administer the drug to subjects in the treatment group, but only give a placebo (e.g., a sugar pill with no medicinal value) to subjects in the control group. More complex designs may include multiple treatment groups, such as low versus high dosage of the drug or combining drug administration with dietary interventions. In a true experimental design , subjects must be randomly assigned to each group. If random assignment is not followed, then the design becomes quasi-experimental . Experiments can be conducted in an artificial or laboratory setting such as at a university (laboratory experiments) or in field settings such as in an organisation where the phenomenon of interest is actually occurring (field experiments). Laboratory experiments allow the researcher to isolate the variables of interest and control for extraneous variables, which may not be possible in field experiments. Hence, inferences drawn from laboratory experiments tend to be stronger in internal validity, but those from field experiments tend to be stronger in external validity. Experimental data is analysed using quantitative statistical techniques. The primary strength of the experimental design is its strong internal validity due to its ability to isolate, control, and intensively examine a small number of variables, while its primary weakness is limited external generalisability since real life is often more complex (i.e., involving more extraneous variables) than contrived lab settings. Furthermore, if the research does not identify ex ante relevant extraneous variables and control for such variables, such lack of controls may hurt internal validity and may lead to spurious correlations.
Field surveys are non-experimental designs that do not control for or manipulate independent variables or treatments, but measure these variables and test their effects using statistical methods. Field surveys capture snapshots of practices, beliefs, or situations from a random sample of subjects in field settings through a survey questionnaire or less frequently, through a structured interview. In cross-sectional field surveys , independent and dependent variables are measured at the same point in time (e.g., using a single questionnaire), while in longitudinal field surveys , dependent variables are measured at a later point in time than the independent variables. The strengths of field surveys are their external validity (since data is collected in field settings), their ability to capture and control for a large number of variables, and their ability to study a problem from multiple perspectives or using multiple theories. However, because of their non-temporal nature, internal validity (cause-effect relationships) are difficult to infer, and surveys may be subject to respondent biases (e.g., subjects may provide a ‘socially desirable’ response rather than their true response) which further hurts internal validity.
Secondary data analysis is an analysis of data that has previously been collected and tabulated by other sources. Such data may include data from government agencies such as employment statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Services or development statistics by countries from the United Nations Development Program, data collected by other researchers (often used in meta-analytic studies), or publicly available third-party data, such as financial data from stock markets or real-time auction data from eBay. This is in contrast to most other research designs where collecting primary data for research is part of the researcher’s job. Secondary data analysis may be an effective means of research where primary data collection is too costly or infeasible, and secondary data is available at a level of analysis suitable for answering the researcher’s questions. The limitations of this design are that the data might not have been collected in a systematic or scientific manner and hence unsuitable for scientific research, since the data was collected for a presumably different purpose, they may not adequately address the research questions of interest to the researcher, and interval validity is problematic if the temporal precedence between cause and effect is unclear.
Case research is an in-depth investigation of a problem in one or more real-life settings (case sites) over an extended period of time. Data may be collected using a combination of interviews, personal observations, and internal or external documents. Case studies can be positivist in nature (for hypotheses testing) or interpretive (for theory building). The strength of this research method is its ability to discover a wide variety of social, cultural, and political factors potentially related to the phenomenon of interest that may not be known in advance. Analysis tends to be qualitative in nature, but heavily contextualised and nuanced. However, interpretation of findings may depend on the observational and integrative ability of the researcher, lack of control may make it difficult to establish causality, and findings from a single case site may not be readily generalised to other case sites. Generalisability can be improved by replicating and comparing the analysis in other case sites in a multiple case design .
Focus group research is a type of research that involves bringing in a small group of subjects (typically six to ten people) at one location, and having them discuss a phenomenon of interest for a period of one and a half to two hours. The discussion is moderated and led by a trained facilitator, who sets the agenda and poses an initial set of questions for participants, makes sure that the ideas and experiences of all participants are represented, and attempts to build a holistic understanding of the problem situation based on participants’ comments and experiences. Internal validity cannot be established due to lack of controls and the findings may not be generalised to other settings because of the small sample size. Hence, focus groups are not generally used for explanatory or descriptive research, but are more suited for exploratory research.
Action research assumes that complex social phenomena are best understood by introducing interventions or ‘actions’ into those phenomena and observing the effects of those actions. In this method, the researcher is embedded within a social context such as an organisation and initiates an action—such as new organisational procedures or new technologies—in response to a real problem such as declining profitability or operational bottlenecks. The researcher’s choice of actions must be based on theory, which should explain why and how such actions may cause the desired change. The researcher then observes the results of that action, modifying it as necessary, while simultaneously learning from the action and generating theoretical insights about the target problem and interventions. The initial theory is validated by the extent to which the chosen action successfully solves the target problem. Simultaneous problem solving and insight generation is the central feature that distinguishes action research from all other research methods, and hence, action research is an excellent method for bridging research and practice. This method is also suited for studying unique social problems that cannot be replicated outside that context, but it is also subject to researcher bias and subjectivity, and the generalisability of findings is often restricted to the context where the study was conducted.
Ethnography is an interpretive research design inspired by anthropology that emphasises that research phenomenon must be studied within the context of its culture. The researcher is deeply immersed in a certain culture over an extended period of time—eight months to two years—and during that period, engages, observes, and records the daily life of the studied culture, and theorises about the evolution and behaviours in that culture. Data is collected primarily via observational techniques, formal and informal interaction with participants in that culture, and personal field notes, while data analysis involves ‘sense-making’. The researcher must narrate her experience in great detail so that readers may experience that same culture without necessarily being there. The advantages of this approach are its sensitiveness to the context, the rich and nuanced understanding it generates, and minimal respondent bias. However, this is also an extremely time and resource-intensive approach, and findings are specific to a given culture and less generalisable to other cultures.
Selecting research designs
Given the above multitude of research designs, which design should researchers choose for their research? Generally speaking, researchers tend to select those research designs that they are most comfortable with and feel most competent to handle, but ideally, the choice should depend on the nature of the research phenomenon being studied. In the preliminary phases of research, when the research problem is unclear and the researcher wants to scope out the nature and extent of a certain research problem, a focus group (for an individual unit of analysis) or a case study (for an organisational unit of analysis) is an ideal strategy for exploratory research. As one delves further into the research domain, but finds that there are no good theories to explain the phenomenon of interest and wants to build a theory to fill in the unmet gap in that area, interpretive designs such as case research or ethnography may be useful designs. If competing theories exist and the researcher wishes to test these different theories or integrate them into a larger theory, positivist designs such as experimental design, survey research, or secondary data analysis are more appropriate.
Regardless of the specific research design chosen, the researcher should strive to collect quantitative and qualitative data using a combination of techniques such as questionnaires, interviews, observations, documents, or secondary data. For instance, even in a highly structured survey questionnaire, intended to collect quantitative data, the researcher may leave some room for a few open-ended questions to collect qualitative data that may generate unexpected insights not otherwise available from structured quantitative data alone. Likewise, while case research employ mostly face-to-face interviews to collect most qualitative data, the potential and value of collecting quantitative data should not be ignored. As an example, in a study of organisational decision-making processes, the case interviewer can record numeric quantities such as how many months it took to make certain organisational decisions, how many people were involved in that decision process, and how many decision alternatives were considered, which can provide valuable insights not otherwise available from interviewees’ narrative responses. Irrespective of the specific research design employed, the goal of the researcher should be to collect as much and as diverse data as possible that can help generate the best possible insights about the phenomenon of interest.
Social Science Research: Principles, Methods and Practices (Revised edition) Copyright © 2019 by Anol Bhattacherjee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research: The Differences Explained
From Scribbr
Empirical Research
What is empirical research.
"Empirical research is research that is based on observation and measurement of phenomena, as directly experienced by the researcher. The data thus gathered may be compared against a theory or hypothesis, but the results are still based on real life experience. The data gathered is all primary data, although secondary data from a literature review may form the theoretical background."
Characteristics of Empirical Research
Emerald Publishing's guide to conducting empirical research identifies a number of common elements to empirical research:
A research question , which will determine research objectives.
A particular and planned design for the research, which will depend on the question and which will find ways of answering it with appropriate use of resources.
The gathering of primary data , which is then analysed.
A particular methodology for collecting and analysing the data, such as an experiment or survey.
The limitation of the data to a particular group, area or time scale, known as a sample [emphasis added]: for example, a specific number of employees of a particular company type, or all users of a library over a given time scale. The sample should be somehow representative of a wider population.
The ability to recreate the study and test the results. This is known as reliability .
The ability to generalize from the findings to a larger sample and to other situations.
If you see these elements in a research article, you can feel confident that you have found empirical research. Emerald's guide goes into more detail on each element.
Emerald Publishing (n.d.). How to... conduct empirical research. https://www.emeraldgrouppublishing.com/how-to/research-methods/conduct-empirical-research-l
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative
- Data Collection Methods
- Analyzing Data
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge.
Quantitative research
Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Qualitative research
Common qualitative methods include interviews with open-ended questions, observations described in words, and literature reviews that explore concepts and theories.
Streefkerk, R. (2022, February 7). Qualitative vs. quantitative research: Differences, examples & methods. Scibbr. https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-quantitative-research/
Quantitative and qualitative data can be collected using various methods. It is important to use a data collection method that will help answer your research question(s).
Many data collection methods can be either qualitative or quantitative. For example, in surveys, observations or case studies , your data can be represented as numbers (e.g. using rating scales or counting frequencies) or as words (e.g. with open-ended questions or descriptions of what you observe).
However, some methods are more commonly used in one type or the other.
Quantitative data collection methods
- Surveys : List of closed or multiple choice questions that is distributed to a sample (online, in person, or over the phone).
- Experiments : Situation in which variables are controlled and manipulated to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations: Observing subjects in a natural environment where variables can’t be controlled.
Qualitative data collection methods
- Interviews : Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
- Focus groups: Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
- Ethnography : Participating in a community or organization for an extended period of time to closely observe culture and behavior.
- Literature review : Survey of published works by other authors.

When to use qualitative vs. quantitative research
A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is:
- Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis)
- Use qualitative research if you want to understand something (concepts, thoughts, experiences)
For most research topics you can choose a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach . Which type you choose depends on, among other things, whether you’re taking an inductive vs. deductive research approach ; your research question(s) ; whether you’re doing experimental , correlational , or descriptive research ; and practical considerations such as time, money, availability of data, and access to respondents.
Streefkerk, R. (2022, February 7). Qualitative vs. quantitative research: Differences, examples & methods. Scibbr. https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-quantitative-research/
Qualitative or quantitative data by itself can’t prove or demonstrate anything, but has to be analyzed to show its meaning in relation to the research questions. The method of analysis differs for each type of data.
Analyzing quantitative data
Quantitative data is based on numbers. Simple math or more advanced statistical analysis is used to discover commonalities or patterns in the data. The results are often reported in graphs and tables.
Applications such as Excel, SPSS, or R can be used to calculate things like:
- Average scores
- The number of times a particular answer was given
- The correlation or causation between two or more variables
- The reliability and validity of the results
Analyzing qualitative data
Qualitative data is more difficult to analyze than quantitative data. It consists of text, images or videos instead of numbers.
Some common approaches to analyzing qualitative data include:
- Qualitative content analysis : Tracking the occurrence, position and meaning of words or phrases
- Thematic analysis : Closely examining the data to identify the main themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying how communication works in social contexts
Comparison of Research Processes
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research design : qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (Fifth). SAGE Publications.
- << Previous: Literature Review Research
- Next: Research Design By Discipline >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Research Design: What it is, Elements & Types

Can you imagine doing research without a plan? Probably not. When we discuss a strategy to collect, study, and evaluate data, we talk about research design. This design addresses problems and creates a consistent and logical model for data analysis. Let’s learn more about it.
What is Research Design?
Research design is the framework of research methods and techniques chosen by a researcher to conduct a study. The design allows researchers to sharpen the research methods suitable for the subject matter and set up their studies for success.
Creating a research topic explains the type of research (experimental, survey research , correlational , semi-experimental, review) and its sub-type (experimental design, research problem , descriptive case-study).
There are three main types of designs for research:
- Data collection
- Measurement
- Data Analysis
The research problem an organization faces will determine the design, not vice-versa. The design phase of a study determines which tools to use and how they are used.
The Process of Research Design
The research design process is a systematic and structured approach to conducting research. The process is essential to ensure that the study is valid, reliable, and produces meaningful results.
- Consider your aims and approaches: Determine the research questions and objectives, and identify the theoretical framework and methodology for the study.
- Choose a type of Research Design: Select the appropriate research design, such as experimental, correlational, survey, case study, or ethnographic, based on the research questions and objectives.
- Identify your population and sampling method: Determine the target population and sample size, and choose the sampling method, such as random , stratified random sampling , or convenience sampling.
- Choose your data collection methods: Decide on the data collection methods , such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments, and select the appropriate instruments or tools for collecting data.
- Plan your data collection procedures: Develop a plan for data collection, including the timeframe, location, and personnel involved, and ensure ethical considerations.
- Decide on your data analysis strategies: Select the appropriate data analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis , content analysis, or discourse analysis, and plan how to interpret the results.
The process of research design is a critical step in conducting research. By following the steps of research design, researchers can ensure that their study is well-planned, ethical, and rigorous.
Research Design Elements
Impactful research usually creates a minimum bias in data and increases trust in the accuracy of collected data. A design that produces the slightest margin of error in experimental research is generally considered the desired outcome. The essential elements are:
- Accurate purpose statement
- Techniques to be implemented for collecting and analyzing research
- The method applied for analyzing collected details
- Type of research methodology
- Probable objections to research
- Settings for the research study
- Measurement of analysis
Characteristics of Research Design
A proper design sets your study up for success. Successful research studies provide insights that are accurate and unbiased. You’ll need to create a survey that meets all of the main characteristics of a design. There are four key characteristics:

- Neutrality: When you set up your study, you may have to make assumptions about the data you expect to collect. The results projected in the research should be free from research bias and neutral. Understand opinions about the final evaluated scores and conclusions from multiple individuals and consider those who agree with the results.
- Reliability: With regularly conducted research, the researcher expects similar results every time. You’ll only be able to reach the desired results if your design is reliable. Your plan should indicate how to form research questions to ensure the standard of results.
- Validity: There are multiple measuring tools available. However, the only correct measuring tools are those which help a researcher in gauging results according to the objective of the research. The questionnaire developed from this design will then be valid.
- Generalization: The outcome of your design should apply to a population and not just a restricted sample . A generalized method implies that your survey can be conducted on any part of a population with similar accuracy.
The above factors affect how respondents answer the research questions, so they should balance all the above characteristics in a good design. If you want, you can also learn about Selection Bias through our blog.
Research Design Types
A researcher must clearly understand the various types to select which model to implement for a study. Like the research itself, the design of your analysis can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative.
Qualitative research
Qualitative research determines relationships between collected data and observations based on mathematical calculations. Statistical methods can prove or disprove theories related to a naturally existing phenomenon. Researchers rely on qualitative observation research methods that conclude “why” a particular theory exists and “what” respondents have to say about it.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is for cases where statistical conclusions to collect actionable insights are essential. Numbers provide a better perspective for making critical business decisions. Quantitative research methods are necessary for the growth of any organization. Insights drawn from complex numerical data and analysis prove to be highly effective when making decisions about the business’s future.
Qualitative Research vs Quantitative Research
Here is a chart that highlights the major differences between qualitative and quantitative research:
In summary or analysis , the step of qualitative research is more exploratory and focuses on understanding the subjective experiences of individuals, while quantitative research is more focused on objective data and statistical analysis.
You can further break down the types of research design into five categories:
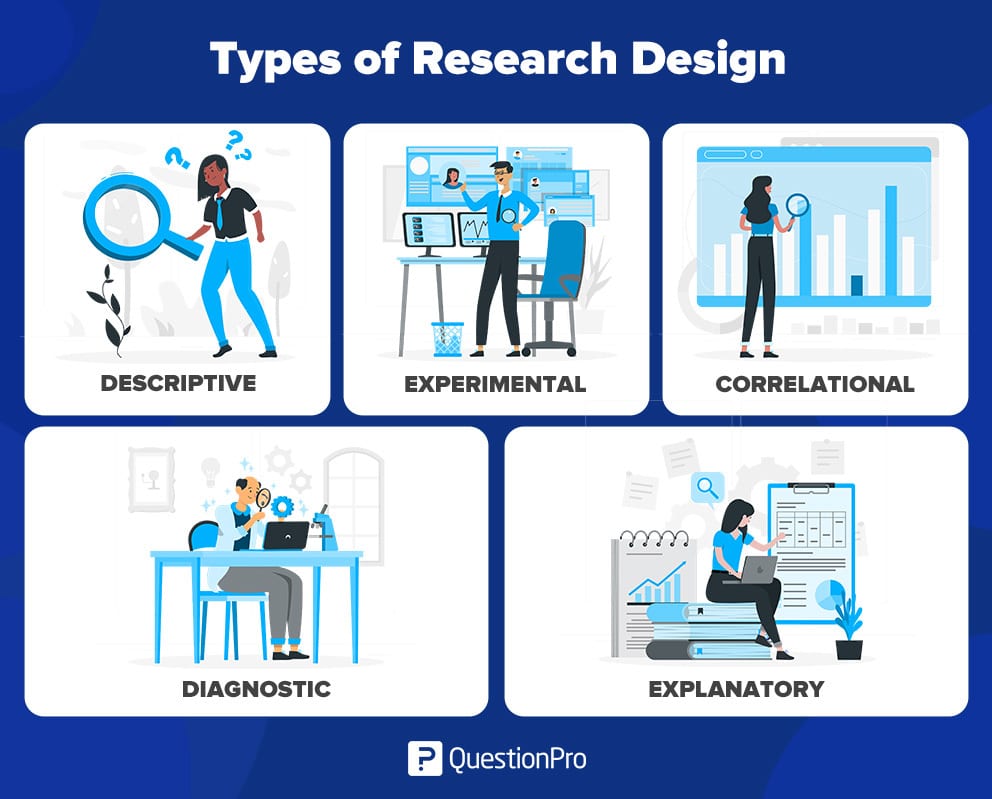
1. Descriptive: In a descriptive composition, a researcher is solely interested in describing the situation or case under their research study. It is a theory-based design method created by gathering, analyzing, and presenting collected data. This allows a researcher to provide insights into the why and how of research. Descriptive design helps others better understand the need for the research. If the problem statement is not clear, you can conduct exploratory research.
2. Experimental: Experimental research establishes a relationship between the cause and effect of a situation. It is a causal research design where one observes the impact caused by the independent variable on the dependent variable. For example, one monitors the influence of an independent variable such as a price on a dependent variable such as customer satisfaction or brand loyalty. It is an efficient research method as it contributes to solving a problem.
The independent variables are manipulated to monitor the change it has on the dependent variable. Social sciences often use it to observe human behavior by analyzing two groups. Researchers can have participants change their actions and study how the people around them react to understand social psychology better.
3. Correlational research: Correlational research is a non-experimental research technique. It helps researchers establish a relationship between two closely connected variables. There is no assumption while evaluating a relationship between two other variables, and statistical analysis techniques calculate the relationship between them. This type of research requires two different groups.
A correlation coefficient determines the correlation between two variables whose values range between -1 and +1. If the correlation coefficient is towards +1, it indicates a positive relationship between the variables, and -1 means a negative relationship between the two variables.
4. Diagnostic research: In diagnostic design, the researcher is looking to evaluate the underlying cause of a specific topic or phenomenon. This method helps one learn more about the factors that create troublesome situations.
This design has three parts of the research:
- Inception of the issue
- Diagnosis of the issue
- Solution for the issue
5. Explanatory research : Explanatory design uses a researcher’s ideas and thoughts on a subject to further explore their theories. The study explains unexplored aspects of a subject and details the research questions’ what, how, and why.
Benefits of Research Design
There are several benefits of having a well-designed research plan. Including:
- Clarity of research objectives: Research design provides a clear understanding of the research objectives and the desired outcomes.
- Increased validity and reliability: To ensure the validity and reliability of results, research design help to minimize the risk of bias and helps to control extraneous variables.
- Improved data collection: Research design helps to ensure that the proper data is collected and data is collected systematically and consistently.
- Better data analysis: Research design helps ensure that the collected data can be analyzed effectively, providing meaningful insights and conclusions.
- Improved communication: A well-designed research helps ensure the results are clean and influential within the research team and external stakeholders.
- Efficient use of resources: reducing the risk of waste and maximizing the impact of the research, research design helps to ensure that resources are used efficiently.
A well-designed research plan is essential for successful research, providing clear and meaningful insights and ensuring that resources are practical.
QuestionPro offers a comprehensive solution for researchers looking to conduct research. With its user-friendly interface, robust data collection and analysis tools, and the ability to integrate results from multiple sources, QuestionPro provides a versatile platform for designing and executing research projects.
Our robust suite of research tools provides you with all you need to derive research results. Our online survey platform includes custom point-and-click logic and advanced question types. Uncover the insights that matter the most.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 20 Employee Engagement Software Solutions
May 3, 2024

15 Best Customer Experience Software of 2024
May 2, 2024

Journey Orchestration Platforms: Top 11 Platforms in 2024

Top 12 Employee Pulse Survey Tools Unlocking Insights in 2024
May 1, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
Research Design and Methods An Applied Guide for the Scholar-Practitioner
- Gary J. Burkholder - Walden University, USA
- Kimberley A. Cox - Walden University, USA
- Linda M. Crawford - Walden University, USA
- John H. Hitchcock - Abt Associates Inc., USA
- Description
Research Design and Methods: An Applied Guide for the Scholar-Practitioner is written for students seeking advanced degrees who want to use evidence-based research to support their practice. This practical and accessible text addresses the foundational concepts of research design and methods; provides a more detailed exploration of designs and approaches popular with graduate students in applied disciplines; covers qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods designs; discusses ethical considerations and quality in research; and provides guidance on writing a research proposal.
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
Supplements
- Editable, chapter-specific Microsoft® PowerPoint® slides offer you complete flexibility in easily creating a multimedia presentation for your course.
- Lecture Notes , including Outline and Objectives, which may be used for lecture and/or student handouts.
- Case studies from SAGE Research Methods accompanied by critical thinking/discussion questions.
- Tables and figures from the printed book are available in an easily-downloadable format for use in papers, hand-outs, and presentations.
“The chapters in this text are logically and clearly organized around levels of understanding that are intuitive and easy to follow. They offer dynamic examples that will keep students engaged. Readers will learn to connect theory and practice, helping them become better researchers, and better consumers of research.”
“ Research Design and Methods: An Applied Guide for the Scholar-Practitioner is a must-read for both new and seasoned researchers. Every topic in the text is comprehensively explained with excellent examples.”
“This text provides clear and concise discussions of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods research for the new scholar-practitioner. The use of questioning and visuals affords students the opportunity to make connections and reflect on their learning.”
“The edited nature of this book provides a multitude of rich perspectives from well-respected authors. This book is a must-have for introductory research methods students.”
“This is an excellent read for anyone interested in understanding research, the book provides good clarity and practical examples…. It is a pragmatic book that translates research concepts into practice.”
Clear chapters. Acessible format
It contains most of what I needed for my Research Methods class. Very good book!
Current book looks better to teach.
A user-friendly, relevant, and applicable resource for all scholar-practitioners.
- The authors are highly experienced experts in the field who are skilled in translating difficult concepts into straightforward examples.
- The text is comprehensive in its coverage of research design and methods across multiple courses , working well as a beginning or intermediate text for a research design course or as a supplementary text in related courses.
- Complementary chapters on qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods data analysis show readers how to holistically apply what they’ve learned about research design to data analysis.
- A chapter on writing a research proposal ensures that readers develop their skills for formulating their research ideas in proposal form.
- Questions for Reflection, and Key Sources for further reading are included at the end of each chapter.
Sample Materials & Chapters
3: Conceptual and Theoretical Frameworks in Research
16: Applied Research: Action Research
For instructors
Select a purchasing option, related products.


Chapter 2. Research Design
Getting started.
When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a “research proposal” that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question. I highly recommend you think about designing your own research study as you progress through this textbook. Even if you don’t have a study in mind yet, it can be a helpful exercise as you progress through the course. But how to start? How can one design a research study before they even know what research looks like? This chapter will serve as a brief overview of the research design process to orient you to what will be coming in later chapters. Think of it as a “skeleton” of what you will read in more detail in later chapters. Ideally, you will read this chapter both now (in sequence) and later during your reading of the remainder of the text. Do not worry if you have questions the first time you read this chapter. Many things will become clearer as the text advances and as you gain a deeper understanding of all the components of good qualitative research. This is just a preliminary map to get you on the right road.

Research Design Steps
Before you even get started, you will need to have a broad topic of interest in mind. [1] . In my experience, students can confuse this broad topic with the actual research question, so it is important to clearly distinguish the two. And the place to start is the broad topic. It might be, as was the case with me, working-class college students. But what about working-class college students? What’s it like to be one? Why are there so few compared to others? How do colleges assist (or fail to assist) them? What interested me was something I could barely articulate at first and went something like this: “Why was it so difficult and lonely to be me?” And by extension, “Did others share this experience?”
Once you have a general topic, reflect on why this is important to you. Sometimes we connect with a topic and we don’t really know why. Even if you are not willing to share the real underlying reason you are interested in a topic, it is important that you know the deeper reasons that motivate you. Otherwise, it is quite possible that at some point during the research, you will find yourself turned around facing the wrong direction. I have seen it happen many times. The reason is that the research question is not the same thing as the general topic of interest, and if you don’t know the reasons for your interest, you are likely to design a study answering a research question that is beside the point—to you, at least. And this means you will be much less motivated to carry your research to completion.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study? What are the advantages of qualitative research methods for studying mentorship?
Qualitative research methods are a huge opportunity to increase access, equity, inclusion, and social justice. Qualitative research allows us to engage and examine the uniquenesses/nuances within minoritized and dominant identities and our experiences with these identities. Qualitative research allows us to explore a specific topic, and through that exploration, we can link history to experiences and look for patterns or offer up a unique phenomenon. There’s such beauty in being able to tell a particular story, and qualitative research is a great mode for that! For our work, we examined the relationships we typically use the term mentorship for but didn’t feel that was quite the right word. Qualitative research allowed us to pick apart what we did and how we engaged in our relationships, which then allowed us to more accurately describe what was unique about our mentorship relationships, which we ultimately named liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021) . Qualitative research gave us the means to explore, process, and name our experiences; what a powerful tool!
How do you come up with ideas for what to study (and how to study it)? Where did you get the idea for studying mentorship?
Coming up with ideas for research, for me, is kind of like Googling a question I have, not finding enough information, and then deciding to dig a little deeper to get the answer. The idea to study mentorship actually came up in conversation with my mentorship triad. We were talking in one of our meetings about our relationship—kind of meta, huh? We discussed how we felt that mentorship was not quite the right term for the relationships we had built. One of us asked what was different about our relationships and mentorship. This all happened when I was taking an ethnography course. During the next session of class, we were discussing auto- and duoethnography, and it hit me—let’s explore our version of mentorship, which we later went on to name liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021 ). The idea and questions came out of being curious and wanting to find an answer. As I continue to research, I see opportunities in questions I have about my work or during conversations that, in our search for answers, end up exposing gaps in the literature. If I can’t find the answer already out there, I can study it.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
When you have a better idea of why you are interested in what it is that interests you, you may be surprised to learn that the obvious approaches to the topic are not the only ones. For example, let’s say you think you are interested in preserving coastal wildlife. And as a social scientist, you are interested in policies and practices that affect the long-term viability of coastal wildlife, especially around fishing communities. It would be natural then to consider designing a research study around fishing communities and how they manage their ecosystems. But when you really think about it, you realize that what interests you the most is how people whose livelihoods depend on a particular resource act in ways that deplete that resource. Or, even deeper, you contemplate the puzzle, “How do people justify actions that damage their surroundings?” Now, there are many ways to design a study that gets at that broader question, and not all of them are about fishing communities, although that is certainly one way to go. Maybe you could design an interview-based study that includes and compares loggers, fishers, and desert golfers (those who golf in arid lands that require a great deal of wasteful irrigation). Or design a case study around one particular example where resources were completely used up by a community. Without knowing what it is you are really interested in, what motivates your interest in a surface phenomenon, you are unlikely to come up with the appropriate research design.
These first stages of research design are often the most difficult, but have patience . Taking the time to consider why you are going to go through a lot of trouble to get answers will prevent a lot of wasted energy in the future.
There are distinct reasons for pursuing particular research questions, and it is helpful to distinguish between them. First, you may be personally motivated. This is probably the most important and the most often overlooked. What is it about the social world that sparks your curiosity? What bothers you? What answers do you need in order to keep living? For me, I knew I needed to get a handle on what higher education was for before I kept going at it. I needed to understand why I felt so different from my peers and whether this whole “higher education” thing was “for the likes of me” before I could complete my degree. That is the personal motivation question. Your personal motivation might also be political in nature, in that you want to change the world in a particular way. It’s all right to acknowledge this. In fact, it is better to acknowledge it than to hide it.
There are also academic and professional motivations for a particular study. If you are an absolute beginner, these may be difficult to find. We’ll talk more about this when we discuss reviewing the literature. Simply put, you are probably not the only person in the world to have thought about this question or issue and those related to it. So how does your interest area fit into what others have studied? Perhaps there is a good study out there of fishing communities, but no one has quite asked the “justification” question. You are motivated to address this to “fill the gap” in our collective knowledge. And maybe you are really not at all sure of what interests you, but you do know that [insert your topic] interests a lot of people, so you would like to work in this area too. You want to be involved in the academic conversation. That is a professional motivation and a very important one to articulate.
Practical and strategic motivations are a third kind. Perhaps you want to encourage people to take better care of the natural resources around them. If this is also part of your motivation, you will want to design your research project in a way that might have an impact on how people behave in the future. There are many ways to do this, one of which is using qualitative research methods rather than quantitative research methods, as the findings of qualitative research are often easier to communicate to a broader audience than the results of quantitative research. You might even be able to engage the community you are studying in the collecting and analyzing of data, something taboo in quantitative research but actively embraced and encouraged by qualitative researchers. But there are other practical reasons, such as getting “done” with your research in a certain amount of time or having access (or no access) to certain information. There is nothing wrong with considering constraints and opportunities when designing your study. Or maybe one of the practical or strategic goals is about learning competence in this area so that you can demonstrate the ability to conduct interviews and focus groups with future employers. Keeping that in mind will help shape your study and prevent you from getting sidetracked using a technique that you are less invested in learning about.
STOP HERE for a moment
I recommend you write a paragraph (at least) explaining your aims and goals. Include a sentence about each of the following: personal/political goals, practical or professional/academic goals, and practical/strategic goals. Think through how all of the goals are related and can be achieved by this particular research study . If they can’t, have a rethink. Perhaps this is not the best way to go about it.
You will also want to be clear about the purpose of your study. “Wait, didn’t we just do this?” you might ask. No! Your goals are not the same as the purpose of the study, although they are related. You can think about purpose lying on a continuum from “ theory ” to “action” (figure 2.1). Sometimes you are doing research to discover new knowledge about the world, while other times you are doing a study because you want to measure an impact or make a difference in the world.
Basic research involves research that is done for the sake of “pure” knowledge—that is, knowledge that, at least at this moment in time, may not have any apparent use or application. Often, and this is very important, knowledge of this kind is later found to be extremely helpful in solving problems. So one way of thinking about basic research is that it is knowledge for which no use is yet known but will probably one day prove to be extremely useful. If you are doing basic research, you do not need to argue its usefulness, as the whole point is that we just don’t know yet what this might be.
Researchers engaged in basic research want to understand how the world operates. They are interested in investigating a phenomenon to get at the nature of reality with regard to that phenomenon. The basic researcher’s purpose is to understand and explain ( Patton 2002:215 ).
Basic research is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works. Grounded Theory is one approach to qualitative research methods that exemplifies basic research (see chapter 4). Most academic journal articles publish basic research findings. If you are working in academia (e.g., writing your dissertation), the default expectation is that you are conducting basic research.
Applied research in the social sciences is research that addresses human and social problems. Unlike basic research, the researcher has expectations that the research will help contribute to resolving a problem, if only by identifying its contours, history, or context. From my experience, most students have this as their baseline assumption about research. Why do a study if not to make things better? But this is a common mistake. Students and their committee members are often working with default assumptions here—the former thinking about applied research as their purpose, the latter thinking about basic research: “The purpose of applied research is to contribute knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment. While in basic research the source of questions is the tradition within a scholarly discipline, in applied research the source of questions is in the problems and concerns experienced by people and by policymakers” ( Patton 2002:217 ).
Applied research is less geared toward theory in two ways. First, its questions do not derive from previous literature. For this reason, applied research studies have much more limited literature reviews than those found in basic research (although they make up for this by having much more “background” about the problem). Second, it does not generate theory in the same way as basic research does. The findings of an applied research project may not be generalizable beyond the boundaries of this particular problem or context. The findings are more limited. They are useful now but may be less useful later. This is why basic research remains the default “gold standard” of academic research.
Evaluation research is research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. We already know the problems, and someone has already come up with solutions. There might be a program, say, for first-generation college students on your campus. Does this program work? Are first-generation students who participate in the program more likely to graduate than those who do not? These are the types of questions addressed by evaluation research. There are two types of research within this broader frame; however, one more action-oriented than the next. In summative evaluation , an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made. Should we continue our first-gen program? Is it a good model for other campuses? Because the purpose of such summative evaluation is to measure success and to determine whether this success is scalable (capable of being generalized beyond the specific case), quantitative data is more often used than qualitative data. In our example, we might have “outcomes” data for thousands of students, and we might run various tests to determine if the better outcomes of those in the program are statistically significant so that we can generalize the findings and recommend similar programs elsewhere. Qualitative data in the form of focus groups or interviews can then be used for illustrative purposes, providing more depth to the quantitative analyses. In contrast, formative evaluation attempts to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness). Formative evaluations rely more heavily on qualitative data—case studies, interviews, focus groups. The findings are meant not to generalize beyond the particular but to improve this program. If you are a student seeking to improve your qualitative research skills and you do not care about generating basic research, formative evaluation studies might be an attractive option for you to pursue, as there are always local programs that need evaluation and suggestions for improvement. Again, be very clear about your purpose when talking through your research proposal with your committee.
Action research takes a further step beyond evaluation, even formative evaluation, to being part of the solution itself. This is about as far from basic research as one could get and definitely falls beyond the scope of “science,” as conventionally defined. The distinction between action and research is blurry, the research methods are often in constant flux, and the only “findings” are specific to the problem or case at hand and often are findings about the process of intervention itself. Rather than evaluate a program as a whole, action research often seeks to change and improve some particular aspect that may not be working—maybe there is not enough diversity in an organization or maybe women’s voices are muted during meetings and the organization wonders why and would like to change this. In a further step, participatory action research , those women would become part of the research team, attempting to amplify their voices in the organization through participation in the action research. As action research employs methods that involve people in the process, focus groups are quite common.
If you are working on a thesis or dissertation, chances are your committee will expect you to be contributing to fundamental knowledge and theory ( basic research ). If your interests lie more toward the action end of the continuum, however, it is helpful to talk to your committee about this before you get started. Knowing your purpose in advance will help avoid misunderstandings during the later stages of the research process!
The Research Question
Once you have written your paragraph and clarified your purpose and truly know that this study is the best study for you to be doing right now , you are ready to write and refine your actual research question. Know that research questions are often moving targets in qualitative research, that they can be refined up to the very end of data collection and analysis. But you do have to have a working research question at all stages. This is your “anchor” when you get lost in the data. What are you addressing? What are you looking at and why? Your research question guides you through the thicket. It is common to have a whole host of questions about a phenomenon or case, both at the outset and throughout the study, but you should be able to pare it down to no more than two or three sentences when asked. These sentences should both clarify the intent of the research and explain why this is an important question to answer. More on refining your research question can be found in chapter 4.
Chances are, you will have already done some prior reading before coming up with your interest and your questions, but you may not have conducted a systematic literature review. This is the next crucial stage to be completed before venturing further. You don’t want to start collecting data and then realize that someone has already beaten you to the punch. A review of the literature that is already out there will let you know (1) if others have already done the study you are envisioning; (2) if others have done similar studies, which can help you out; and (3) what ideas or concepts are out there that can help you frame your study and make sense of your findings. More on literature reviews can be found in chapter 9.
In addition to reviewing the literature for similar studies to what you are proposing, it can be extremely helpful to find a study that inspires you. This may have absolutely nothing to do with the topic you are interested in but is written so beautifully or organized so interestingly or otherwise speaks to you in such a way that you want to post it somewhere to remind you of what you want to be doing. You might not understand this in the early stages—why would you find a study that has nothing to do with the one you are doing helpful? But trust me, when you are deep into analysis and writing, having an inspirational model in view can help you push through. If you are motivated to do something that might change the world, you probably have read something somewhere that inspired you. Go back to that original inspiration and read it carefully and see how they managed to convey the passion that you so appreciate.
At this stage, you are still just getting started. There are a lot of things to do before setting forth to collect data! You’ll want to consider and choose a research tradition and a set of data-collection techniques that both help you answer your research question and match all your aims and goals. For example, if you really want to help migrant workers speak for themselves, you might draw on feminist theory and participatory action research models. Chapters 3 and 4 will provide you with more information on epistemologies and approaches.
Next, you have to clarify your “units of analysis.” What is the level at which you are focusing your study? Often, the unit in qualitative research methods is individual people, or “human subjects.” But your units of analysis could just as well be organizations (colleges, hospitals) or programs or even whole nations. Think about what it is you want to be saying at the end of your study—are the insights you are hoping to make about people or about organizations or about something else entirely? A unit of analysis can even be a historical period! Every unit of analysis will call for a different kind of data collection and analysis and will produce different kinds of “findings” at the conclusion of your study. [2]
Regardless of what unit of analysis you select, you will probably have to consider the “human subjects” involved in your research. [3] Who are they? What interactions will you have with them—that is, what kind of data will you be collecting? Before answering these questions, define your population of interest and your research setting. Use your research question to help guide you.
Let’s use an example from a real study. In Geographies of Campus Inequality , Benson and Lee ( 2020 ) list three related research questions: “(1) What are the different ways that first-generation students organize their social, extracurricular, and academic activities at selective and highly selective colleges? (2) how do first-generation students sort themselves and get sorted into these different types of campus lives; and (3) how do these different patterns of campus engagement prepare first-generation students for their post-college lives?” (3).
Note that we are jumping into this a bit late, after Benson and Lee have described previous studies (the literature review) and what is known about first-generation college students and what is not known. They want to know about differences within this group, and they are interested in ones attending certain kinds of colleges because those colleges will be sites where academic and extracurricular pressures compete. That is the context for their three related research questions. What is the population of interest here? First-generation college students . What is the research setting? Selective and highly selective colleges . But a host of questions remain. Which students in the real world, which colleges? What about gender, race, and other identity markers? Will the students be asked questions? Are the students still in college, or will they be asked about what college was like for them? Will they be observed? Will they be shadowed? Will they be surveyed? Will they be asked to keep diaries of their time in college? How many students? How many colleges? For how long will they be observed?
Recommendation
Take a moment and write down suggestions for Benson and Lee before continuing on to what they actually did.
Have you written down your own suggestions? Good. Now let’s compare those with what they actually did. Benson and Lee drew on two sources of data: in-depth interviews with sixty-four first-generation students and survey data from a preexisting national survey of students at twenty-eight selective colleges. Let’s ignore the survey for our purposes here and focus on those interviews. The interviews were conducted between 2014 and 2016 at a single selective college, “Hilltop” (a pseudonym ). They employed a “purposive” sampling strategy to ensure an equal number of male-identifying and female-identifying students as well as equal numbers of White, Black, and Latinx students. Each student was interviewed once. Hilltop is a selective liberal arts college in the northeast that enrolls about three thousand students.
How did your suggestions match up to those actually used by the researchers in this study? It is possible your suggestions were too ambitious? Beginning qualitative researchers can often make that mistake. You want a research design that is both effective (it matches your question and goals) and doable. You will never be able to collect data from your entire population of interest (unless your research question is really so narrow to be relevant to very few people!), so you will need to come up with a good sample. Define the criteria for this sample, as Benson and Lee did when deciding to interview an equal number of students by gender and race categories. Define the criteria for your sample setting too. Hilltop is typical for selective colleges. That was a research choice made by Benson and Lee. For more on sampling and sampling choices, see chapter 5.
Benson and Lee chose to employ interviews. If you also would like to include interviews, you have to think about what will be asked in them. Most interview-based research involves an interview guide, a set of questions or question areas that will be asked of each participant. The research question helps you create a relevant interview guide. You want to ask questions whose answers will provide insight into your research question. Again, your research question is the anchor you will continually come back to as you plan for and conduct your study. It may be that once you begin interviewing, you find that people are telling you something totally unexpected, and this makes you rethink your research question. That is fine. Then you have a new anchor. But you always have an anchor. More on interviewing can be found in chapter 11.
Let’s imagine Benson and Lee also observed college students as they went about doing the things college students do, both in the classroom and in the clubs and social activities in which they participate. They would have needed a plan for this. Would they sit in on classes? Which ones and how many? Would they attend club meetings and sports events? Which ones and how many? Would they participate themselves? How would they record their observations? More on observation techniques can be found in both chapters 13 and 14.
At this point, the design is almost complete. You know why you are doing this study, you have a clear research question to guide you, you have identified your population of interest and research setting, and you have a reasonable sample of each. You also have put together a plan for data collection, which might include drafting an interview guide or making plans for observations. And so you know exactly what you will be doing for the next several months (or years!). To put the project into action, there are a few more things necessary before actually going into the field.
First, you will need to make sure you have any necessary supplies, including recording technology. These days, many researchers use their phones to record interviews. Second, you will need to draft a few documents for your participants. These include informed consent forms and recruiting materials, such as posters or email texts, that explain what this study is in clear language. Third, you will draft a research protocol to submit to your institutional review board (IRB) ; this research protocol will include the interview guide (if you are using one), the consent form template, and all examples of recruiting material. Depending on your institution and the details of your study design, it may take weeks or even, in some unfortunate cases, months before you secure IRB approval. Make sure you plan on this time in your project timeline. While you wait, you can continue to review the literature and possibly begin drafting a section on the literature review for your eventual presentation/publication. More on IRB procedures can be found in chapter 8 and more general ethical considerations in chapter 7.
Once you have approval, you can begin!
Research Design Checklist
Before data collection begins, do the following:
- Write a paragraph explaining your aims and goals (personal/political, practical/strategic, professional/academic).
- Define your research question; write two to three sentences that clarify the intent of the research and why this is an important question to answer.
- Review the literature for similar studies that address your research question or similar research questions; think laterally about some literature that might be helpful or illuminating but is not exactly about the same topic.
- Find a written study that inspires you—it may or may not be on the research question you have chosen.
- Consider and choose a research tradition and set of data-collection techniques that (1) help answer your research question and (2) match your aims and goals.
- Define your population of interest and your research setting.
- Define the criteria for your sample (How many? Why these? How will you find them, gain access, and acquire consent?).
- If you are conducting interviews, draft an interview guide.
- If you are making observations, create a plan for observations (sites, times, recording, access).
- Acquire any necessary technology (recording devices/software).
- Draft consent forms that clearly identify the research focus and selection process.
- Create recruiting materials (posters, email, texts).
- Apply for IRB approval (proposal plus consent form plus recruiting materials).
- Block out time for collecting data.
- At the end of the chapter, you will find a " Research Design Checklist " that summarizes the main recommendations made here ↵
- For example, if your focus is society and culture , you might collect data through observation or a case study. If your focus is individual lived experience , you are probably going to be interviewing some people. And if your focus is language and communication , you will probably be analyzing text (written or visual). ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:16 ). ↵
- You may not have any "live" human subjects. There are qualitative research methods that do not require interactions with live human beings - see chapter 16 , "Archival and Historical Sources." But for the most part, you are probably reading this textbook because you are interested in doing research with people. The rest of the chapter will assume this is the case. ↵
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and research design that focuses on an individual case (e.g., setting, institution, or sometimes an individual) in order to explore its complexity, history, and interactive parts. As an approach, it is particularly useful for obtaining a deep appreciation of an issue, event, or phenomenon of interest in its particular context.
The controlling force in research; can be understood as lying on a continuum from basic research (knowledge production) to action research (effecting change).
In its most basic sense, a theory is a story we tell about how the world works that can be tested with empirical evidence. In qualitative research, we use the term in a variety of ways, many of which are different from how they are used by quantitative researchers. Although some qualitative research can be described as “testing theory,” it is more common to “build theory” from the data using inductive reasoning , as done in Grounded Theory . There are so-called “grand theories” that seek to integrate a whole series of findings and stories into an overarching paradigm about how the world works, and much smaller theories or concepts about particular processes and relationships. Theory can even be used to explain particular methodological perspectives or approaches, as in Institutional Ethnography , which is both a way of doing research and a theory about how the world works.
Research that is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
Research that contributes knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment.
Research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. There are two kinds: summative and formative .
Research in which an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made, often for the purpose of generalizing to other cases or programs. Generally uses qualitative research as a supplement to primary quantitative data analyses. Contrast formative evaluation research .
Research designed to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness); relies heavily on qualitative research methods. Contrast summative evaluation research
Research carried out at a particular organizational or community site with the intention of affecting change; often involves research subjects as participants of the study. See also participatory action research .
Research in which both researchers and participants work together to understand a problematic situation and change it for the better.
The level of the focus of analysis (e.g., individual people, organizations, programs, neighborhoods).
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A fictional name assigned to give anonymity to a person, group, or place. Pseudonyms are important ways of protecting the identity of research participants while still providing a “human element” in the presentation of qualitative data. There are ethical considerations to be made in selecting pseudonyms; some researchers allow research participants to choose their own.
A requirement for research involving human participants; the documentation of informed consent. In some cases, oral consent or assent may be sufficient, but the default standard is a single-page easy-to-understand form that both the researcher and the participant sign and date. Under federal guidelines, all researchers "shall seek such consent only under circumstances that provide the prospective subject or the representative sufficient opportunity to consider whether or not to participate and that minimize the possibility of coercion or undue influence. The information that is given to the subject or the representative shall be in language understandable to the subject or the representative. No informed consent, whether oral or written, may include any exculpatory language through which the subject or the representative is made to waive or appear to waive any of the subject's rights or releases or appears to release the investigator, the sponsor, the institution, or its agents from liability for negligence" (21 CFR 50.20). Your IRB office will be able to provide a template for use in your study .
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

What Is Research Methodology? Types, Process, Examples In Research Design
Research methodology is the backbone of any successful study, providing a structured approach to collecting and analysing data. It encompasses a broad spectrum of methods, each with specific processes and applications, tailored to answer distinct research questions.
This article will explore various types of research methodologies, delve into their processes, and illustrate with examples how they are applied in real-world research.
Understanding these methodologies is essential for any researcher aiming to conduct thorough and impactful studies.
Types Of Research Methodology
Research methodology contains various strategies and approaches to conduct scientific research, each tailored to specific types of questions and data.
Think of research methodology as the master plan for your study. It guides you on why and how to gather and analyse data, ensuring your approach aligns perfectly with your research question.
This methodology includes deciding between qualitative research, which explores topics in depth through interviews or focus groups, or quantitative research, which quantifies data through surveys and statistical analysis.

There is even an option to mix both, and approach called the mixed method.
If you’re analysing the lived experiences of individuals in a specific setting, qualitative methodologies allow you to capture the nuances of human emotions and behaviours through detailed narratives.
Quantitative methodologies would enable you to measure and compare these experiences in a more structured, numerical format.
Choosing a robust methodology not only provides the rationale for the methods you choose but also highlights the research limitations and ethical considerations, keeping your study transparent and grounded.
It’s a thoughtful composition that gives research its direction and purpose, much like how an architect’s plan is essential before the actual construction begins.
Qualitative Research Methodology
Qualitative research dives deep into the social context of a topic. It collects words and textual data rather than numerical data.
Within the family, qualitative research methodologies can be broken down into several approaches:
Ethnography: Deeply rooted in the traditions of anthropology, you immerse yourself in the community or social setting you’re studying when conducting an ethnography study.
Case Study Research: Here, you explore the complexity of a single case in detail. This could be an institution, a group, or an individual. You might look into interviews, documents, and reports, to build a comprehensive picture of the subject.
Grounded Theory: Here, you try to generate theories from the data itself rather than testing existing hypotheses. You might start with a research question but allow your theories to develop as you gather more data.
Narrative Research: You explore the stories people tell about their lives and personal experiences in their own words. Through techniques like in-depth interviews or life story collections, you analyse the narrative to understand the individual’s experiences.
Discourse Analysis: You analyse written or spoken words to understand the social norms and power structures that underlie the language used. This method can reveal a lot about the social context and the dynamics of power in communication.
These methods help to uncover patterns in how people think and interact. For example, in exploring consumer attitudes toward a new product, you would likely conduct focus groups or participant observations to gather qualitative data.
This method helps you understand the motivations and feelings behind consumer choices.
Quantitative Research Methodology

Quantitative research relies on numerical data to find patterns and test hypotheses. This methodology uses statistical analysis to quantify data and uncover relationships between variables.
There are several approaches in quantitative research:
Experimental Research: This is the gold standard when you aim to determine causality. By manipulating one variable and controlling others, you observe changes in the dependent variables.
Survey Research: A popular approach, because of its efficiency in collecting data from a large sample of participants. By using standardised questions, you can gather data that are easy to analyse statistically.
Correlational Research: This approach tries to identify relationships between two or more variables without establishing a causal link. The strength and direction of these relationships are quantified, albeit without confirming one variable causes another.
Longitudinal Studies: You track variables over time, providing a dynamic view of how situations evolve. This approach requires commitment and can be resource-intensive, but the depth of data they provide is unparalleled.
Cross-sectional Studies: Offers a snapshot of a population at a single point in time. They are quicker and cheaper than longitudinal studies.
Mixed Research Methodology

Mixed methods research combines both approaches to benefit from the depth of qualitative data and the breadth of quantitative analysis.
You might start with qualitative interviews to develop hypotheses about health behaviours in a community. Then, you could conduct a large-scale survey to test these hypotheses quantitatively.
This approach is particularly useful when you want to explore a new area where previous data may not exist, giving you a comprehensive insight into both the empirical and social dimensions of a research problem.
Factors To Consider When Deciding On Research Methodology
When you dive into a research project, choosing the right methodology is akin to selecting the best tools for building a house.
It shapes how you approach the research question, gather data, and interpret the results. Here are a couple of crucial factors to keep in mind.
Research Question Compatibility
The type of research question you pose can heavily influence the methodology you choose. Qualitative methodologies are superb for exploratory research where you aim to understand concepts, perceptions, and experiences.
If you’re exploring how patients feel about a new healthcare policy, interviews and focus groups would be instrumental.
Quantitative methods are your go-to for questions that require measurable and statistical data, like assessing the prevalence of a medical condition across different regions.
Data Requirements
Consider what data is necessary to address your research question effectively. Qualitative data can provide depth and detail through:
- images, and
This makes qualitative method ideal for understanding complex social interactions or historical contexts.
Quantitative data, however, offers the breadth and is often numerical, allowing for a broad analysis of patterns and correlations.
If your study aims to investigate both the breadth and depth, a mixed methods approach might be necessary, enabling you to draw on the strengths of both qualitative and quantitative data.
Resources and Constraints
While deciding on research methodology, you must evaluate the resources available, including:
- funding, and
Quantitative research often requires larger samples and hence, might be more costly and time-consuming.
Qualitative research, while generally less resource-intensive, demands substantial time for data collection and analysis, especially if you conduct lengthy interviews or detailed content analysis.
If resources are limited, adapting your methodology to fit these constraints without compromising the integrity of your research is crucial.
Skill Set and Expertise
Your familiarity and comfort level with various research methodologies will significantly affect your choice.
Conducting sophisticated statistical analyses requires a different skill set than carrying out in-depth qualitative interviews.
If your background is in social science, you might find qualitative methods more within your wheelhouse; whereas, a postgraduate student in epidemiology might be more adept at quantitative methods.
It’s also worth considering the availability of workshops, courses, or collaborators who could complement your skills.
Ethical and Practical Considerations
Different methodologies raise different ethical concerns.
In qualitative research, maintaining anonymity and dealing with sensitive information can be challenging, especially when using direct quotes or detailed descriptions from participants.

Quantitative research might involve considerations around participant consent for large surveys or experiments.
Practically, you need to think about the sampling design to ensure it is representative of the population studied. Non-probability sampling might be quicker and cheaper but can introduce bias, limiting the generalisability of your findings.
By meticulously considering these factors, you tailor your research design to not just answer the research questions effectively but also to reflect the realities of your operational environment.
This thoughtful approach helps ensure that your research is not only robust but also practical and ethical, standing up to both academic scrutiny and real-world application.
What Is Research Methodology? Answered
Research methodology is a crucial framework that guides the entire research process. It involves choosing between various qualitative and quantitative approaches, each tailored to specific research questions and objectives.
Your chosen methodology shapes how data is gathered, analysed, and interpreted, ultimately influencing the reliability and validity of your research findings.
Understanding these methodologies ensures that researchers can effectively write research proposal, address their study’s aims and contribute valuable insights to their field.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider
Cookie consent
We use our own and third-party cookies to show you more relevant content based on your browsing and navigation history. Please accept or manage your cookie settings below. Here's our cookie policy

- Form Builder Signups and orders
- Survey maker Research and feedback
- Quiz Maker Trivia and product match
- Find Customers Generate more leads
- Get Feedback Discover ways to improve
- Do research Uncover trends and ideas
- Marketers Forms for marketing teams
- Product Forms for product teams
- HR Forms for HR teams
- Customer success Forms for customer success teams
- Business Forms for general business
- Form templates
- Survey templates
- Quiz templates
- Poll templates
- Order forms
- Feedback forms
- Satisfaction surveys
- Application forms
- Feedback surveys
- Evaluation forms
- Request forms
- Signup forms
- Business surveys
- Marketing surveys
- Report forms
- Customer feedback form
- Registration form
- Branding questionnaire
- 360 feedback
- Lead generation
- Contact form
- Signup sheet
- Help center Find quick answers
- Contact us Speak to someone
- Our blog Get inspired
- Our community Share and learn
- Our guides Tips and how-to
- Updates News and announcements
- Brand Our guidelines
- Partners Browse or join
- Careers Join our team
- → The 6-Step Guide to Market Research P...
The 6-Step Guide to Market Research Processes
Looking for a step-by-step guide to market research processes? Learn more about the marketing research process and methods to gather data—and make the most of it.

Latest posts on Tips
Typeform | 05.2024
Typeform | 04.2024
Say what you will about McDonald’s, but one of the things most respected about their brand is the international menu concept.
From maple and bacon poutine in Canada and gazpacho in Spain to India’s McPaneer Royale, McDonald’s knows how to give the people what they want.
And how do they inject local appeal in a global brand? By gaining a deep understanding of the consumers in every target market they plan to enter.
If you’re thinking about doing consumer insights research, you should be familiar with market research processes. Let’s start with the basics. What is market research, and how is it different from marketing research?
What is market research?
People often confuse market research and marketing research. Aren’t they just different words for the same thing?
ESOMAR, the global research and data association, and the American Marketing Association would disagree. Here’s the gist:
Market research emphasizes the process of collecting consumer data , while marketing research refers to the product of that information and/or a function within an organization.
Essentially, you might be looking for a marketing researcher to conduct market research. Market research will help you answer questions about your customers, your competitors, or current and potential markets.
The 6-step marketing research process

Market research can seem like a mystery.
However, market research processes are quite systematic—well, in theory. In practice, the steps involve exploration, creativity, and abstraction.
Here are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Identify the problem
Researchers are curious people. That’s why every research project starts with a question.
What is the part of your business you want to know more about? Identifying the problem is the most important step in market research processes. It’s going to determine every step you take in the future—of market research, anyway.
Not sure where to start? Here are a few tips:
Look for marketing challenges or opportunities. Maybe your brand awareness could use a boost. You've noticed declining customer loyalty, or you’re considering opportunities in emerging markets.
Frame it as a question. Why is customer loyalty decreasing? How can we enter the market for luxury hotels? What does our customer’s typical path to purchase look like?
Determine what type of problem you have. In market research, a problem can be ambiguous, clearly defined, or somewhere in the middle. Do you know the variables and factors influencing what you want to measure? This is important as it'll influence your overall research design, which is up next.
2. Design the research
There are three types of research designs. The design you choose will be informed by how well-defined your problem is.
If you don’t know much about the problem, you need:
Exploratory research: If you don’t know the major variables or factors at play, your research is ambiguous. Exploratory research can help you develop a hypothesis or ask a more precise question. If you have a vague idea about what’s important to solve the problem, you need:
Descriptive research: Descriptive research does what it says on the box— it describes a certain phenomenon or the characteristics of a population. It can build on exploratory research but doesn’t give insight into the how, when, or why. Descriptive research is useful for parsing out market segments and measuring performance. Consequently, you need a pretty good idea of what you’re measuring and how it'll be measured. If you want to know how cause and effect are linked, you need:
Causal research: Market researchers conduct causal research when they want to understand the relationships between two or more variables. Simply put, causal research helps you understand cause and effect.
3. Choose your sample and market research methods
Data is the essence of market research. At the end of these market research processes, data is analyzed, interpreted, and turned into information and actionable insights.
Data can be qualitative or quantitative . Qualitative data can take many forms, from descriptions to audio and video. Quantitative data is typically presented in values and figures.
When choosing your sample, you must select the population you want to study. A population is a group with some shared characteristics that you’re interested in gathering data from. It can be broad (Canadians) or narrow (independent gym owners in Chicago).
No matter how small or large your population, you’ll unlikely be able to work with everyone.
The key to choosing a good sample is that it is representative. That means the people you select to participate (the sample) should reflect the larger group you’re studying.
4. Get the data
There are two forms of data you can collect: primary and secondary data.
Primary data is gathered specifically for your project. Secondary data has already been collected, either internally or externally through government agencies, consulting or market research firms, websites, social networks, and so on.
Depending on your research design, you may want to check internally for secondary data. For example, let’s say you’re trying to understand the annual purchase cycle for your business. You'd gather sales and reports and company records—that's secondary data.
But of course, secondary data still needs to be prepared for analysis
There are two ways to collect primary data: directly or indirectly. Direct data collection is just that—you are speaking to your participants directly. That can be through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and so on. Indirect data collection typically means observation. Think in-store observation, shelf experiments, or website heatmaps.
5. Analyze the data
Data analysis is a process of looking for patterns in data and trying to understand why those patterns exist. Data can be analyzed quantitatively or qualitatively.
Quantitative data analysis is a process more complicated than can be described here. Unless you’re a math whiz, you’ll probably just use a data analysis software like SPSS or StatCrunch.
Qualitative data analysis typically involves coding—but not the computer programming kind, don’t you worry. This type of coding can be done by hand or using software such as NVivo. It involves looking for themes, concepts, and words that are repeated throughout the data.
6. Interpret and present the insights
Interpretation involves answering the question: What does the data tell me about what I wanted to know?
That’s where themes and patterns come in. You can describe trends and present them using figures or descriptions drawn from your participants.
Part of interpretation is using what you know about customers, businesses, or markets to provide recommendations for how to move forward. These data-driven suggestions should offer a solution to the initial problem. The results of the research can also bring to light a problem you weren’t even aware you had.
Overview of market research methods

Market researchers are able to draw on a large toolbox of market research methods. Typically, they fall into the qualitative or quantitative category because of the type of data they produce.
Focus groups
Best for: Exploratory research
Type of method: Qualitative
A market research technique that involves a group discussion about certain topics led by a moderator to uncover the thoughts and opinions of participants.
In-depth interviews
Best for: Descriptive research
An interview that's conducted with an individual aimed at getting deeper insights about attitudes, motivations, or experiences.
Ethnography
Best for: Descriptive research
Also known as participant observation, it involves spending time with participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a lab setting).
Observational
Carefully watch people to understand what they’re doing. It allows you to learn about consumer or employee behavior but not the motivation behind it.
Discourse analysis
Best for: Exploratory or descriptive research
This is a fancy way of saying “analyzing what people say.” Social listening is a form of discourse analysis. Examining customer reviews, help transcripts, social media comments, and more are all forms of discourse analysis.
Type of method: Quantitative
Surveys are the crux of market research. They involve collecting facts, figures, and opinions using a questionnaire. Surveys can also yield qualitative data if participants write out answers. Surveys may seem simple, but there are a lot of factors that can turn good intentions into bad data—be sure to read our tips on the right question types to ask .
Structured observation
Observation research can also be quantitative if you are observing participants without direct involvement and assigning values to certain behaviors.
A/B testing
Also called split testing, this is a way to compare responses to a variation of a single variable to see which performs better. For example, presenting users with two versions of an ad to see which gets more clicks.
Best for: Causal research
Marketing experimentation typically involves manipulating a variable to see how it influences behavior. It can be conducted in a lab or in the field.
Examples of market research

Time to put this into practice. Let’s look at market research examples of various types of research designs.
Exploratory market research
Mobile phone company HTC wanted to understand how they could improve the user experience of their phones. This problem required exploratory research because there wasn’t a specific feature they wanted to test. They simply wanted to learn more from their customers.
With market research, they observed how participants interacted with their phones. They looked for challenges people had with everyday usage. After analyzing these pain points, they added new functions to their next model that made the phones easier to use.
Descriptive market research
Company ABC wants to understand how large the market for vegan cheese is in Canada. They have a somewhat defined research problem: What is the potential market share for vegan cheese?
In order to provide an answer, market researchers will have to describe various characteristics: who the customers are, why they buy vegan cheese, competitor market penetration, and potential opportunities.
This requires mixed-method research. The researchers might collect secondary data on the number of vegans in Canada or how much vegan cheese is sold in the country and through which companies. They may also conduct focus groups to understand what motivates people to buy vegan cheese.
Once complete, they'll be able to present statistics on vegans in Canada and estimate Company ABC’s potential market share.
Causal market research
Causal research requires keeping variables and conditions the same, save for the one you are testing. German marketing and sensory research company iSi is a company that runs both field and lab experiments.
They worked with a chocolate bar company to design an experiment that tested 12 different chocolate bar recipes.
The consumers sequentially tested the recipes and provided ratings (quantitative data) and descriptions (qualitative data) of each one. The result was that consumers were most satiated by “a firm, tough texture and a higher amount of caramel and peanuts.”
Discovering market research processes
One thing to remember is that market research is an iterative process. You can keep using what you learn to conduct better studies and evaluate the changing market conditions and the whims of consumers.
Ready to tackle the market research process? Build a market research survey with Typeform—choose from one of our customizable templates to gather beautifully designed data.

About the author
We're Typeform - a team on a mission to transform data collection by bringing you refreshingly different forms.
Liked that? Check these out:

Decoding Lead Generation Lingo: A Back-to-Basics Guide
The world of lead generation is full of acronyms and jargon. If you’re struggling to keep up, this back-to-basics guide will set you and your team on the right path.
Typeform | 12.2023

The 8 types of market research and how to use them
There are eight types of marketing research you can try to stay ahead of the competition. Learn more about marketing research methods and how to use them.

Survey design: Best practices and 15 expert tips
Beautiful surveys perform better. Read our 15 top tips to make more effective surveys and create a bigger impact with your business.
Lydia Kentowski | 01.2024
Research progress of epileptic seizure prediction methods based on EEG
- Review Paper
- Published: 07 May 2024
Cite this article

- Zhongpeng Wang 1 , 2 ,
- Xiaoxin Song ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0008-0176-2310 1 ,
- Long Chen 1 , 2 ,
- Jinxiang Nan 1 ,
- Yulin Sun 1 ,
- Meijun Pang 1 , 2 ,
- Kuo Zhang 1 , 2 ,
- Xiuyun Liu 1 , 2 &
- Dong Ming 1 , 2
At present, at least 30% of refractory epilepsy patients in the world cannot be effectively controlled and treated. The suddenness and unpredictability of seizures greatly affect the physical and mental health and even the life safety of patients, and the realization of early prediction of seizures and the adoption of interventions are of great significance to the improvement of patients’ quality of life. In this paper, we firstly introduce the design process of EEG-based seizure prediction methods, introduce several databases commonly used in the research, and summarize the commonly used methods in pre-processing, feature extraction, classification and identification, and post-processing. Then, based on scalp EEG and intracranial EEG respectively, we reviewed the current status of epileptic seizure prediction research from five commonly used feature analysis methods, and make a comprehensive evaluation of both. Finally, this paper describes the reasons why the current algorithms cannot be applied to the clinic, summarizes their limitations, and gives corresponding suggestions, aiming to provide improvement directions for subsequent research. In addition, deep learning algorithms have emerged in recent years, and this paper also compares the advantages and disadvantages of deep learning algorithms with traditional machine learning methods, in the hope of providing researchers with new technologies and new ideas and making significant breakthroughs in the field of epileptic seizure prediction.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Aarabi A, Fazel-Rezai R, Aghakhani Y (2009) EEG seizure prediction: measures and challenges. In: 2009 Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 03–06 September 2009
Aarabi A, He B (2017) Seizure prediction in patients with focal hippocampal epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol 128(7):1299–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.04.026
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Abbasi B, Goldenholz DM (2019) Machine learning applications in epilepsy. Epilepsia 60(10):2037–2047. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16333
Acharya UR, Vinitha Sree S, Swapna G, Martis RJ, Suri JS (2013) Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: a review. Knowl-Based Syst 45:147–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2013.02.014
Article Google Scholar
Acharya UR, Hagiwara Y, Adeli H (2018a) Automated seizure prediction. Epilepsy Behav 88:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.09.030
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Acharya UR, Oh SL, Hagiwara Y, Tan JH, Adeli H (2018b) Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 100:270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.09.017
Alexandre Teixeira C, Direito B, Bandarabadi M, Le Van QM, Valderrama M, Schelter B, Schulze-Bonhage A, Navarro V, Sales F, Dourado A (2014) Epileptic seizure predictors based on computational intelligence techniques: a comparative study with 278 patients. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 114(3):324–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.02.007
Alotaiby TN, Alshebeili SA, Alotaibi FM, Alrshoud SR (2017) Epileptic seizure prediction using CSP and LDA for scalp EEG signals. Comput Intell Neurosci 2017:1240323. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1240323
Bandarabadi M, Teixeira CA, Rasekhi J, Dourado A (2015) Epileptic seizure prediction using relative spectral power features. Clin Neurophysiol 126(2):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2014.05.022
Beniczky S, Karoly P, Nurse E, Ryvlin P, Cook M (2021) Machine learning and wearable devices of the future. Epilepsia 62(Suppl 2):S116–S124. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16555
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer New York, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-45528-0
Book Google Scholar
Blanco S, Garay A, Coulombie D (2013) Comparison of frequency bands using spectral entropy for epileptic seizure prediction. ISRN Neurol 2013:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/287327
Bonn E a U. Epileptologie Bonn / Forschung / AG Lehnertz / EEG Data Download n.d. https://www.ukbonn.de/epileptologie/?idcat=193&lang=3
Brázdil M, Pail M, Halámek J, Plešinger F, Cimbálník J, Roman R, Klimeš P, Daniel P, Chrastina J, Brichtová E, Rektor I, Worrell GA, Jurák P (2017) Very high-frequency oscillations: Novel biomarkers of the epileptogenic zone. Ann Neurol 82(2):299–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25006
Burges CJC (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Disc 2(2):121–167. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009715923555
Chen H, Ji T, Zhan X, Liu X, Yu G, Wang W, Jiang Y, Zhou X-H, Ullah I (2022) An explainable statistical method for seizure prediction using brain functional connectivity from EEG. Comput Intell Neurosci 2022:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2183562
Chu H, Chung CK, Jeong W, Cho KH (2017) Predicting epileptic seizures from scalp EEG based on attractor state analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 143:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.03.002
Competition RP (2014) American Epilepsy Society seizure prediction challenge. https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/seizure-prediction/data
Cui S, Duan L, Qiao Y, Xiao Y (2018) Learning EEG synchronization patterns for epileptic seizure prediction using bag-of-wave features. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput (prepublish). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1000-3
D’Alessandro M, Esteller R, Vachtsevanos G, Hinson A, Echauz J, Litt B (2003) Epileptic seizure prediction using hybrid feature selection over multiple intracranial EEG electrode contacts: a report of four patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50(5):603–615. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2003.810706
Delamont RS, Walker MC (2011) Pre-ictal autonomic changes. Epilepsy Res 97(3):267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.10.016
Detti P, Vatti G, Zabalo Manrique de Lara G (2020) EEG synchronization analysis for seizure prediction: a study on data of noninvasive recordings. Processes 8(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070846
Direito B, Teixeira CA, Sales F, Castelo-Branco M, Dourado A (2017) A realistic seizure prediction study based on multiclass SVM. Int J Neural Syst 27(3):1750006. https://doi.org/10.1142/s012906571750006x
Duun-Henriksen J, Kjaer TW, Madsen RE, Remvig LS, Thomsen CE, Sorensen HB (2012) Channel selection for automatic seizure detection. Clin Neurophysiol 123(1):84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2011.06.001
Elger CE, Lehnertz K (1998) Seizure prediction by non-linear time series analysis of brain electrical activity. Eur J Neurosci 10(2):786–789. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00090.x
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
EPMoghaddam D, Sheth SA, Haneef Z, Gavvala J, Aazhang B (2022) Epileptic seizure prediction using spectral width of the covariance matrix. J Neural Eng 19(2). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ac6063
Fei K, Wang W, Yang Q, Tang S (2017) Chaos feature study in fractional Fourier domain for preictal prediction of epileptic seizure. Neurocomputing 249:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.04.019
Freiburg UO (2003) Seizure prediction project Freiburg. https://epilepsy.uni-freiburg.de/
Freiman TM, Eismann-Schweimler J, Frotscher M (2011) Granule cell dispersion in temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with changes in dendritic orientation and spine distribution. Exp Neurol 229(2):332–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.02.017
Gao Y, Liu A, Wang L, Qian R, Chen X (2023) A self-interpretable deep learning model for seizure prediction using a multi-scale prototypical part network. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 31:1847–1856. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2023.3260845
Ghosh A, Sarkar A, Das T, Basak P (2017) Pre-ictal epileptic seizure prediction based on ECG signal analysis. In: 2017 2nd International conference for convergence in technology (I2CT), Mumbai, India, 07–09 April 2017
Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng CK, Stanley HE (2000) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):E215–E220. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215
Han C, Peng F, Chen C, Li W, Zhang X, Wang X, Zhou W (2021) Research progress of epileptic seizure predictions based on electroencephalogram signals. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 38(6):1193–1202. https://doi.org/10.7507/1001-5515.202105052
Hao J, Cui Y, Niu B, Yu L, Lin Y, Xia Y, Yao D, Guo D (2021) Roles of very fast ripple (500–1000[Formula: see text]Hz) in the hippocampal network during status epilepticus. Int J Neural Syst 31(4):2150002. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065721500027
Hassan AR, Subasi A (2016) Automatic identification of epileptic seizures from EEG signals using linear programming boosting. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 136:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.08.013
Honghong H, Feng Z, Liangfu L, Xiaopeng S (2023) A review of the application of neural networks in epileptic seizure prediction. J Front Comput Sci Technol 17(11):2543–2556. https://doi.org/10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2302001
Howbert JJ, Patterson EE, Stead SM, Brinkmann B, Vasoli V, Crepeau D, Vite CH, Sturges B, Ruedebusch V, Mavoori J, Leyde K, Sheffield WD, Litt B, Worrell GA (2014) Forecasting seizures in dogs with naturally occurring epilepsy. PLoS ONE 9(1):e81920. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081920
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Iasemidis LD, Sackellares JC, Zaveri HP, Williams WJ (1990) Phase space topography and the Lyapunov exponent of electrocorticograms in partial seizures. Brain Topogr 2(3):187–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01140588
Iasemidis LD, Deng-Shan S, Chaovalitwongse W, Sackellares JC, Pardalos PM, Principe JC, Carney PR, Prasad A, Veeramani B, Tsakalis K (2003) Adaptive epileptic seizure prediction system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50(5):616–627. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2003.810689
Ibrahim F, Abd-Elateif El-Gindy S, El-Dolil SM, El-Fishawy AS, El-Rabaie E-SM, Dessouky MI, Eldokany IM, Alotaiby TN, Alshebeili SA, Abd El-Samie FE (2019) A statistical framework for EEG channel selection and seizure prediction on mobile. Int J Speech Technol 22(1):191–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-09565-7
Islam MS, El-Hajj AM, Alawieh H, Dawy Z, Abbas N, El-Imad J (2020) EEG mobility artifact removal for ambulatory epileptic seizure prediction applications. Biomed Signal Process Control 55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101638
Jacobs J, LeVan P, Chander R, Hall J, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2008) Interictal high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) are an indicator of seizure onset areas independent of spikes in the human epileptic brain. Epilepsia 49(11):1893–1907. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01656.x
Jacobs J, Zijlmans M, Zelmann R, Chatillon CE, Hall J, Olivier A, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2010) High-frequency electroencephalographic oscillations correlate with outcome of epilepsy surgery. Ann Neurol 67(2):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21847
Jemal I, Mitiche A, Mezghani N (2021) A study of EEG feature complexity in epileptic seizure prediction. Appl Sci 11(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041579
Khan H, Marcuse L, Fields M, Swann K, Yener B (2018) Focal onset seizure prediction using convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(9):2109–2118. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2017.2785401
Klatt J, Feldwisch-Drentrup H, Ihle M, Navarro V, Neufang M, Teixeira C, Adam C, Valderrama M, Alvarado-Rojas C, Witon A, Le Van QM, Sales F, Dourado A, Timmer J, Schulze-Bonhage A, Schelter B (2012) The EPILEPSIAE database: an extensive electroencephalography database of epilepsy patients. Epilepsia 53(9):1669–1676. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03564.x
Le Douget JE, Fouad A, Maskani Filali M, Pyrzowski J, Le Van QM (2017) Surface and intracranial EEG spike detection based on discrete wavelet decomposition and random forest classification. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2017:475–478. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2017.8036865
Lekshmy HO, Panickar D, Harikumar S (2022) Comparative analysis of multiple machine learning algorithms for epileptic seizure prediction. J Phys Conf Ser 2161(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2161/1/012055
Li S, Zhou W, Yuan Q, Liu Y (2013) Seizure prediction using spike rate of intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 21(6):880–886. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2013.2282153
Li Y, Liu Y, Guo YZ, Liao XF, Hu B, Yu T (2022) Spatio-temporal-spectral hierarchical graph convolutional network with semisupervised active learning for patient-specific seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Cybern 52(11):12189–12204. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2021.3071860
Litt B, Echauz J (2002) Prediction of epileptic seizures. Lancet Neurol 1(1):22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(02)00003-0
Lu L, Zhang F, Wu Y, Ma S, Zhang X, Ni G (2022) A multi-frame network model for predicting seizure based on sEEG and iEEG data. Front Comput Neurosci 16:1059565. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2022.1059565
Maimaiti B, Meng H, Lv Y, Qiu J, Zhu Z, Xie Y, Li Y, Yu C, Zhao W, Liu J, Li M (2022) An overview of EEG-based machine learning methods in seizure prediction and opportunities for neurologists in this field. Neuroscience 481:197–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.11.017
Mirowski P, Madhavan D, LeCun Y, Kuzniecky R (2009) Classification of patterns of EEG synchronization for seizure prediction. Clin Neurophysiol 120(11):1927–1940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.09.002
Mormann F, Lehnertz K, David P, Elger CE (2000) Mean phase coherence as a measure for phase synchronization and its application to the EEG of epilepsy patients. Physica D 144(3–4):358–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2789(00)00087-7
Mormann F, Kreuz T, Rieke C, Andrzejak RG, Kraskov A, David P, Elger CE, Lehnertz K (2005) On the predictability of epileptic seizures. Clin Neurophysiol 116(3):569–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2004.08.025
Nabil D, Benali R, Reguig FB (2020) Epileptic seizure recognition using EEG wavelet decomposition based on nonlinear and statistical features with support vector machine classification. Biomed Eng Biomed Tech 65(2):133–148. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2018-0246
Netoff T, Park Y, Parhi K (2009) Seizure prediction using cost-sensitive support vector machine. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009:3322–3325. https://doi.org/10.1109/iembs.2009.5333711
Ngamga EJ, Bialonski S, Marwan N, Kurths J, Geier C, Lehnertz K (2016) Evaluation of selected recurrence measures in discriminating pre-ictal and inter-ictal periods from epileptic EEG data. Phys Lett A 380(16):1419–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2016.02.024
Article CAS Google Scholar
Osmond E, Billetop A, Jary S, Likeman M, Thoresen M, Luyt K (2014) Neonatal seizures: magnetic resonance imaging adds value in the diagnosis and prediction of neurodisability. Acta Paediatr 103(8):820–826. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.12583
Oyrer J, Maljevic S, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF, Petrou S, Reid CA (2018) Ion channels in genetic epilepsy: from genes and mechanisms to disease-targeted therapies. Pharmacol Rev 70(1):142–173. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.014456
Parhi KK, Zhang Z (2019) Discriminative ratio of spectral power and relative power features derived via frequency-domain model ratio with application to seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 13(4):645–657. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbcas.2019.2917184
Park Y, Luo L, Parhi KK, Netoff T (2011) Seizure prediction with spectral power of EEG using cost-sensitive support vector machines. Epilepsia 52(10):1761–1770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03138.x
Patel AD, Moss R, Rust SW, Patterson J, Strouse R, Gedela S, Haines J, Lin SM (2016) Patient-centered design criteria for wearable seizure detection devices. Epilepsy Behav 64(Pt A):116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.09.012
Peters B (2022) Risks and complications of seizures. https://www.verywellhealth.com/risks-and-complications-of-seizures-4685790
Qin Y, Zheng H, Chen W, Qin Q, Han C, Che Y (2020). Patient-specific seizure prediction with scalp EEG using convolutional neural network and extreme learning machine. In: 2020 39th Chinese control conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020
Rajkomar A, Dean J, Kohane I (2019) Machine learning in medicine. N Engl J Med 380(14):1347–1358. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1814259
Rasekhi J, Mollaei MR, Bandarabadi M, Teixeira CA, Dourado A (2013) Preprocessing effects of 22 linear univariate features on the performance of seizure prediction methods. J Neurosci Methods 217(1–2):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.03.019
Savadkoohi M, Oladunni T, Thompson L (2020) A machine learning approach to epileptic seizure prediction using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signal. Biocybern Biomed Eng 40(3):1328–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2020.07.004
Schelter B, Winterhalder M, Maiwald T, Brandt A, Schad A, Schulze-Bonhage A, Timmer J (2006) Testing statistical significance of multivariate time series analysis techniques for epileptic seizure prediction. Chaos 16(1):013108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2137623
Schulze-Bonhage A, Sales F, Wagner K, Teotonio R, Carius A, Schelle A, Ihle M (2010) Views of patients with epilepsy on seizure prediction devices. Epilepsy Behav 18(4):388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2010.05.008
Shahidi Zandi A, Tafreshi R, Javidan M, Dumont GA (2013) Predicting epileptic seizures in scalp EEG based on a variational Bayesian Gaussian mixture model of zero-crossing intervals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(5):1401–1413. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2012.2237399
Sharif B, Jafari AH (2017) Prediction of epileptic seizures from EEG using analysis of ictal rules on Poincaré plane. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 145:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.04.001
Slimen IB, Boubchir L, Seddik H (2020) Epileptic seizure prediction based on EEG spikes detection of ictal-preictal states. J Biomed Res 34(3). https://doi.org/10.7555/jbr.34.20190097
Sun Y, Jin W, Si X, Zhang X, Cao J, Wang L, Yin S, Ming D (2022) Continuous seizure detection based on transformer and long-term iEEG. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(11):5418–5427. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2022.3199206
Sun B, Lv J-J, Rui L-G, Yang Y-X, Chen Y-G, Ma C, Gao Z-K (2021) Seizure prediction in scalp EEG based channel attention dual-input convolutional neural network. Physica A Stat Mech Appl 584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2021.126376
Tamanna T, Rahman M A, Sultana S, Haque M H, Parvez MZ (2021) Predicting seizure onset based on time-frequency analysis of EEG signals. Chaos Solitons Fractals 145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110796
Tomlinson SB, Porter BE, Marsh ED (2017) Interictal network synchrony and local heterogeneity predict epilepsy surgery outcome among pediatric patients. Epilepsia 58(3):402–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13657
Truong ND, Nguyen AD, Kuhlmann L, Bonyadi MR, Yang J, Ippolito S, Kavehei O (2018) Convolutional neural networks for seizure prediction using intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram. Neural Netw 105:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.018
Tsiouris Κ, Pezoulas VC, Zervakis M, Konitsiotis S, Koutsouris DD, Fotiadis DI (2018) A long short-term memory deep learning network for the prediction of epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 99:24–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.05.019
Usman SM, Khalid S, Akhtar R, Bortolotto Z, Bashir Z, Qiu H (2019a) Using scalp EEG and intracranial EEG signals for predicting epileptic seizures: review of available methodologies. Seizure 71:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2019.08.006
Usman SM, Khalid S, Akhtar R, Bortolotto Z, Bashir Z, Qiu HY (2019b) Using scalp EEG and intracranial EEG signals for predicting epileptic seizures: review of available methodologies. Seizure-Eur J Epilepsy 71:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2019.08.006
Usman SM, Latif S, Beg A (2019c) Principle components analysis for seizures prediction using wavelet transform. Int J Adv Appl Sci 6(3):50–55. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2019.03.008
Varotto G, Tassi L, Franceschetti S, Spreafico R, Panzica F (2012) Epileptogenic networks of type II focal cortical dysplasia: a stereo-EEG study. Neuroimage 61(3):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.090
Velmurugan J, Nagarajan SS, Mariyappa N, Mundlamuri RC, Raghavendra K, Bharath RD, Saini J, Arivazhagan A, Rajeswaran J, Mahadevan A, Malla BR, Satishchandra P, Sinha S (2019) Magnetoencephalography imaging of high frequency oscillations strengthens presurgical localization and outcome prediction. Brain 142(11):3514–3529. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz284
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T, Baram TZ (2011a) The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 7(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.178
Vezzani A, Maroso M, Balosso S, Sanchez MA, Bartfai T (2011b) IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling in infection, inflammation, stress and neurodegeneration couples hyperexcitability and seizures. Brain Behav Immun 25(7):1281–1289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.03.018
Wang G, Wang D, Du C, Li K, Zhang J, Liu Z, Tao Y, Wang M, Cao Z, Yan X (2020a) Seizure Prediction Using Directed Transfer Function and Convolution Neural Network on Intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(12):2711–2720. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2020.3035836
Wang Y, Shi Y, Cheng Y, He Z, Wei X, Chen Z, Zhou Y (2023) A spatiotemporal graph attention network based on synchronization for epileptic seizure prediction. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 27(2):900–911. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2022.3221211
Wang Y, Zhou D, Yang X, Xu X, Ren L, Yu T, Zhou W, Shao X, Yang Z, Wang S, Cao D, Liu C, Kwan SY, Xiang J (2020b) Expert consensus on clinical applications of high-frequency oscillations in epilepsy. Acta Epileptol 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42494-020-00018-w
WHO (2023) World Health Organization. Epilepsy. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy
Williamson JR, Bliss DW, Browne DW, Narayanan JT (2012) Seizure prediction using EEG spatiotemporal correlation structure. Epilepsy Behav 25(2):230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.07.007
Wong M, Guo D (2013) Dendritic spine pathology in epilepsy: cause or consequence? Neuroscience 251:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.048
Wu G, Li Z, Zhang Y, Dong X, Ye L (2019) Study of feature extraction algorithms for epileptic seizure prediction based on SVM. In: Communications, signal processing, and systems pp 2370–2377. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6571-2_289
Wu J, Zhou T, Li T (2020) Detecting epileptic seizures in EEG signals with complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting. Entropy (Basel), 22(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020140
Xiang J, Li C, Li H, Cao R, Wang B, Han X, Chen J (2015) The detection of epileptic seizure signals based on fuzzy entropy. J Neurosci Methods 243:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.01.015
Yang S, Li B, Zhang Y, Duan M, Liu S, Zhang Y, Feng X, Tan R, Huang L, Zhou F (2020) Selection of features for patient-independent detection of seizure events using scalp EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 119:103671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103671
Yang X, Zhao J, Sun Q, Lu J, Ma X (2021) An effective dual self-attention residual network for seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:1604–1613. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2021.3103210
Yu Z, Nie W, Zhou W, Xu F, Yuan S, Leng Y, Yuan Q (2018) Epileptic seizure prediction based on local mean decomposition and deep convolutional neural network. J Supercomput 76(5):3462–3476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2600-6
Yuan S, Zhou W, Chen L (2018) Epileptic seizure prediction using diffusion distance and Bayesian linear discriminate analysis on intracranial EEG. Int J Neural Syst 28(1):1750043. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065717500435
Zelig D, Goldberg I, Shor O, Ben Dor S, Yaniv-Rosenfeld A, Milikovsky DZ, Ofer J, Imtiaz H, Friedman A, Benninger F (2022) Paroxysmal slow wave events predict epilepsy following a first seizure. Epilepsia 63(1):190–198. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.17110
Zhang Y, Yang S, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Han B, Zhou F (2018) Integration of 24 feature types to accurately detect and predict seizures using scalp EEG signals. Sensors (Basel), 18(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051372
Zheng Y, Wang G, Li K, Bao G, Wang J (2014) Epileptic seizure prediction using phase synchronization based on bivariate empirical mode decomposition. Clin Neurophysiol 125(6):1104–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2013.09.047
Zhu J, Lin H, Su C, Shen Q, Jiang D (2003) The roles of different components of EEGs for seizure prediction-wavelet energy evaluation. Acta Bioch Bioph Sin 01:73–78
Google Scholar
Zurich (2018) The SWEC-ETHZ iEEG database and algorithms. http://ieeg-swez.ethz.ch/
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2022YFF1202304; in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62376190, Grant 81925020, and Grant 82001939; and in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin under Grant 22JCYBJC01430.
National Natural Science Foundation of China 62376190, Zhongpeng Wang, 81925020, Dong Ming, 82001939, Long Chen
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Academy of Medical Engineering and Translational Medicine, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, China
Zhongpeng Wang, Xiaoxin Song, Long Chen, Jinxiang Nan, Yulin Sun, Meijun Pang, Kuo Zhang, Xiuyun Liu & Dong Ming
Haihe Laboratory of Brain-Computer Interaction and Human-Machine Integration, Tianjin, 300392, China
Zhongpeng Wang, Long Chen, Meijun Pang, Kuo Zhang, Xiuyun Liu & Dong Ming
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Long Chen or Xiuyun Liu .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Data Availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, Z., Song, X., Chen, L. et al. Research progress of epileptic seizure prediction methods based on EEG. Cogn Neurodyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10109-w
Download citation
Received : 20 September 2023
Revised : 09 March 2024
Accepted : 14 March 2024
Published : 07 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10109-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Seizure prediction
- Intracranial EEG (iEEG)
- Feature extraction
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
Online Survey Software
Discover what your customers and employees are really thinking.
Survey software gets answers to your most important customer, employee, marketing and product questions. It can handle everything from simple customer feedback questionnaires to detailed research projects for the world’s biggest brands.
Buy Online Free Trial

Today's reality—sound familiar?
2.6x more success could have been realized in marketing campaigns with better research & insights., 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy in place., 13% of marketing spend is wasted for reasons that could have been addressed through better market research., with online survey software you can:.
- Eliminate manual data collection
- Get real-time, actionable insights
- Reach more people, faster and easier
- Get better, more honest responses
- Create professional surveys without any experience
Ready to take your market research to the next level?
Answers and insights from your audience, wherever they are.
Wherever you need to gather data, survey software can help. From a simple survey link you can paste anywhere, to advanced integrations with your CRM, to email, social, website, QR code, SMS and offline surveys, we’ll help you reach your target respondents, no matter where they are.
Drag-and-drop simplicity for even the most advanced surveys
Choose from 23 question types (including video/audio responses) and use advanced logic, branching, quotas, API integrations into Zendesk and email triggers to build and launch your project. It’s all done in an intuitive drag-and-drop software interface that makes even the most sophisticated surveys easy to create, launch and analyze.
Next-level survey reports and dashboards
Make better decisions with advanced reports and dashboards you can share in seconds. Choose from over 30 different graph types, share reports online, or export survey data to popular formats like CSV, TSV, Excel, SPSS and more.
Built-in intelligence with every type of survey
Leverage advanced analysis, including video feedback summarization powered by generative AI, crosstabs, and statistical analysis tools. Automatically review survey design to ensure methodology best practices, response quality, and compliance with internal policies and PII.
You’re in good company
Qualtrics has helped us bring some exciting new products to life, and ensured that we’re communicating the benefits in a way that resonates
Qualtrics enabled us to break silos that previously existed, helping us share customer insights across the group and reach our goals quicker
Survey software FAQs
A survey is a method of gathering information using relevant questions from a sample of people with the aim of understanding populations as a whole. Surveys provide a critical source of data and insights for everyone engaged in the information economy, from businesses to media, to government and academics.
Survey software is a tool used to design, send and analyze surveys online. It’s the primary method of collecting feedback at scale whether that’s a simple questionnaire or a detailed study such as customer or employee feedback as part of a more structured experience management program. Cloud-based survey technology has revolutionized the ability to get data, quickly, from a large number of respondents by automating the process of sending out surveys across a variety of channels from websites and mobile to apps, email and even chatbots.
Surveys provide quick, quantitative data on a wide audience’s opinions, preferences, and experiences. They are cost-effective, easy to administer, and can reach a large population. They also allow for anonymity, increasing the chance of honest responses, and their standardized format makes it easy to aggregate and analyze data for clear insights into trends and patterns.
To create a survey , define the objectives, choose target participants, design clear and concise questions, select a survey tool or platform, and ensure the layout is logical. Test the survey, distribute it, and collect responses. Remember to keep it as brief as possible while gathering the necessary information.
To write survey questions , be clear and specific to avoid confusion. Use simple, unbiased language, and opt for closed-ended questions for easier analysis. Ensure questions are relevant to your objectives, and avoid leading or loaded questions that could influence answers. Pretest your questions to catch any issues and revise as needed for clarity and objectivity.
Now used by more than 18,000+ brands, and supporting more than 1.3 billion surveys a year, Qualtrics empowers organizations to gather invaluable customer insights and take immediate, game-changing action – with zero coding required. The Qualtrics survey tool makes it easy to get answers to your most important marketing, branding, customer, and product questions, with easy-to-use tools that can handle everything from simple customer feedback questionnaires to detailed research projects.
Qualtrics Strategic Research pricing is based on interactions including number of survey responses and minutes of video feedback. Our special online pricing offer starts at $420 per month and can be purchased here . Alternatively, you can get started with a free account with basic functionality, or get 30 days access to advanced features with a free trial .
Yes, we offer a free account option with basic survey functionality.
You might also like
7 Tips for Writing Great Questions
The Qualtrics Hand Book Of Question Design
Qualitative research design handbook
2024 Research Trends Report
How AI will Reinvent the Market Research Industry
Quantitative and qualitative research design
Request Demo
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Main navigation
- How to apply
- Secondment jobs
- Working for the OSCE

International consultant on good governance and anti-corruption research design and methods
🔍 taj - osce programme office in dushanbe, dushanbe.
Background:
The OSCE within its second dimension on environmental and economic issues assists the governments of participating States in strengthening their national anti-corruption practices, advising on improving the relevant institutional framework and building up national capacities. The OSCE participating States have recognized that “corruption represents one of the major impediments to the prosperity and sustainable development of the participating States that undermines their stability and security and threatens the OSCE’s shared values” (see Ministerial Council Decision No. 11/04). In line with the OSCE documents, specifically Ministerial Council Decision No. 6/20 and Ministerial Council Declaration No. 3/18, the role of women and youth is of vital importance for achieving results in combating corruption. On the basis of its mandate, the OSCE Programme Office in Dushanbe (POiD) supports all efforts aimed at decreasing the risks emanating from corruption and further strengthening capacities to effectively combat corruption at all levels.
Corruption is still a major challenge for Tajikistan, recognised by the National Development Strategy of Tajikistan until 2030. In September 2021, Tajikistan adopted the National Anti-Corruption Strategy 2021-2030 and the Action Plan for the implementation of the Strategy for the period 2021-2025. The main goals and objectives of the implementation of the National Anti-Corruption Strategy are to increase the anti-corruption awareness of the population and create an atmosphere of intolerance to corruption, eliminate the causes and conditions conducive to corruption, and in general reduce the intensity of corruption.
- In order to combine efforts in implementation of the National Anti-Corruption Strategy for the period until 2030 and the related Action Plan for 2021-2025, the POiD will support the Agency for State Financial Control and Fight against Corruption (Anti-Corruption Agency), in organizing a comprehensive sociological survey with target of 10,000 respondents (citizens) on the state of corruption and the effectiveness of measures to prevent and combat it. This activity will be conducted in co-operation with relevant ministries and agencies (see item number 69 of the Action Plan to implement the National AC Strategy) and the Coalition of Civil-Society Organisations of Tajikistan on Transparency and Anti-Corruption (Coalition). The results of the survey will be used to establish the level of corruption in the respective branches of government and to determine and adjust anti-corruption policies in the Republic of Tajikistan;
- A two-day workshop for civil society on how to conduct and design research related to alternative monitoring is planned. The workshop is part of the POiD’s efforts, in co-operation with the Coalition and with the backing of the Anti-Corruption Agency, to support and strengthen the monitoring role of civil society. To increase the participation of women and youth in the fight against corruption, the POiD is supporting a nationwide awareness-raising campaign in the form of lectures and panel discussions on aspects of combating corruption, in which the international consultant will participate. The awareness-raising campaign is run in co-operation with the Anti-Corruption Agency, the Coalition or any other national partners.
Objective of Assignment:
1. The international consultant will provide guidance and support in the development of the methodology and draft questionnaires based on international best practices for a comprehensive sociological survey on the state of corruption and the effectiveness of measures to prevent and combat it; 2. The international consultant will conduct a two-day workshop on research methods related to alternative monitoring for participants from civil society to familiarize civil society activists in a structured way with research design and methods of qualitative and quantitative research on good governance and anti-corruption issues; 3. The international consultant will contribute to the anti-corruption awareness-raising campaign with special focus on youth and women.
Duration of Assignment:
9.5 days
Tasks and Responsibilities: Under the overall supervision of the Good Governance Officer, the successful candidate will be tasked with the following duties:
- Conducting introductory/preparatory meetings with the Anti-Corruption Agency, Coalition, OSCE POiD to discuss details of the sociological survey, development of the survey methodology and draft questionnaires, guidance process (0.5 day on-site, May 2024). Designing the schedule of the guidance process (0.5 day on-site, May 2024);
- Reviewing, advising and commenting on draft methodology and questionnaire based on best international practices, per E-Mail communication and, if appropriate, telecommunication, in Russian language (1 day on-site, 1 day on distance, May 2024);
- Addressing feedback, replying to questions/comments from Anti-Corruption Agency, Coalition, OSCE POiD, providing review on final methodology and questionnaire, per E-Mail communication and, if appropriate, telecommunication, in Russian language (1.5 days, May - June 2024);
- Developing training materials for the two-day workshop on research methods related to alternative monitoring for participants from civil society in Russian language (agenda, handout materials, presentation, pre- and post-tests) (2 days, May 2024);
- Conducting the two-day workshop on research methods related to alternative monitoring for participants from civil society in Dushanbe in Russian language (2 days on-site, May 2024);
- Delivering a two-hour public lecture or participate in a panel discussion on sociological research on good governance and corruption within the framework of the anti-corruption awareness-raising campaign (0.5 day on-site, May 2024);
- Drafting a technical report on activities conducted (0.5 day, June 2024).
Deliverables:
- Introductory /preparatory meetings with the ACA, Coalition, OSCE POiD is conducted;
- Schedule of guidance is discussed, agreed and drafted;
- First round of comments to draft methodology and questionnaire is provided;
- Questions, comments, feedbacks were addressed; review of final drafts of the methodology and questionnaire were provided;
- Training materials are prepared and submitted (agenda, handout materials, presentation, pre- and post-tests);
- Conducted two-day workshop on research methods related to alternative monitoring for participants from civil society in Dushanbe in Russian language;
- Delivered a two-hour public lecture or participated in a panel discussion on sociological research on good governance and corruption within the framework of the anti-corruption awareness-raising campaign;
- Technical report about conducted activities, including a list of contacts and, if applicable, comprehensive documentation attached.
For more detailed information on the structure and work of the OSCE Programme Office in Dushanbe, please see: http://www.osce.org/programme-office-in-dushanbe
Necessary Qualifications:
- Advanced university degree in law, economy, public administration, social sciences or related field;
- At least 6 years of professional experience in good governance, including minimum 4 years of practical experience in designing and/or conducting research and surveys on anti-corruption or good governance issues;
- Experience in conducting trainings, workshops, courses on good governance issues or combating corruption;
- Professional experience in designing and/or conducting large-scale surveys will be an asset;
- Professional experience in the context of Tajikistan or any other post-Soviet country will be an asset;
- Excellent analytical and writing skills, proved by authorship of analytical report and/or publications
- Excellent written and spoken Russian and English;
- Demonstrated gender awareness and sensitivity, and an ability to integrate a gender perspective into tasks and activities;
- Ability and willingness to work as a member of team, with people of different cultural, and religious backgrounds, different gender, and diverse political views, while maintaining impartiality and objectivity;
- Computer literate with practical experience using Microsoft applications.
Remuneration Package:
Remuneration will be based on the selected consultant's/expert's qualifications, experience, the tasks and deliverables for this position and in accordance with the OSCE established rates.
If you wish to apply for this position, please use the OSCE's online application link found under https://vacancies.osce.org/ .
The OSCE retains the discretion to re-advertise/re-post the vacancy, to cancel the recruitment or to offer an appointment with a modified job description or for a different duration.
Only those candidates who are selected to participate in the subsequent stages of recruitment will be contacted.
The OSCE is committed to diversity and inclusion within its workforce, and encourages qualified female and male candidates from all religious, ethnic and social backgrounds to apply to become a part of the Organization.
Candidates should be aware that OSCE officials shall conduct themselves at all times in a manner befitting the status of an international civil servant. This includes avoiding any action which may adversely reflect on the integrity, independence and impartiality of their position and function as officials of the OSCE. The OSCE is committed to applying the highest ethical standards in carrying out its mandate. For more information on the values set out in OSCE Competency Model, please see https://jobs.osce.org/resources/document/our-competency-model .
Please be aware that the OSCE does not request payment at any stage of the application and review process.
- Issued by: OSCE Programme Office in Dushanbe
- Requisition ID: TAJ000222
- Contract Type: Special Service Agreement (SSA) / Consultant
- Grade: No grade
- Job Type: Consultant
- Number of posts: 1
- Location: TAJ - OSCE Programme Office in Dushanbe, Dushanbe
- Issue Date: May 1, 2024
- Closing Date: May 22, 2024
- Education Level: Master's Degree (Second-level university degree or equivalent)
- Job Field: Economic & Environmental Affairs
Previous Job Searches
Create and manage profiles for future opportunities.
My Submissions
Track your opportunities.
Similar Listings
TAJ - OSCE Programme Office in Dushanbe, Dushanbe
📁 Economic & Environmental Affairs
Requisition #: TAJ000204
Requisition #: TAJ000205
Can I receive notifications about my jobs?
Sure star your jobs to receive notifications., starring jobs:.
Only need to see the jobs you"re responsible for? Star them!
By starring jobs, you"ll receive notifications when activity occurs on them. You can also filter directly to them when on the site.
Automatic Job Starring:
If you send a Recruiter Campaign from your account, the Social Sourcing system will automatically star the jobs you selected for that message. Therefore, you will be alerted immediately of any activity happening on those jobs.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Research Design. Definition: Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall aims and approach; The type of research design you'll use; Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects; Your data collection methods; The procedures you'll follow to ...
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data. Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive, correlational, experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs. Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological ...
Research design methods refer to the systematic approaches and techniques used to plan, structure, and conduct a research study. The choice of research design method depends on the research questions, objectives, and the nature of the study. Here are some key research design methods commonly used in various fields: 1.
Research design is a plan to answer your research question. A research method is a strategy used to implement that plan. Research design and methods are different but closely related, because good research design ensures that the data you obtain will help you answer your research question more effectively.
Research Design and Research Methods 47 research design link your purposes to the broader, more theoretical aspects of procedures for conducting Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research, while the following section will examine decisions about research methods as a narrower, more technical aspect of procedures.
There are various types of research design, each suited to different research questions and objectives: • Quantitative Research: Focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis to quantify relationships and patterns. Common methods include surveys, experiments, and observational studies. • Qualitative Research: Emphasizes understanding ...
Research study design is a framework, or the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research problem. Research study designs are of many types, each with its advantages and limitations. The type of study design used to answer a particular research question is determined by the ...
NOTE: Use the SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases and the SAGE Research Methods Videos databases to search for scholarly resources on how to apply specific research designs and methods. The Research Methods Online database contains links to more than 175,000 pages of SAGE publisher's book, journal, and reference content on quantitative ...
Research design is a comprehensive plan for data collection in an empirical research project. It is a 'blueprint' for empirical research aimed at answering specific research questions or testing specific hypotheses, and must specify at least three processes: the data collection process, the instrument development process, and the sampling process.
Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions. This type of research can be used to establish generalizable facts about a topic. Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Research design is the framework of research methods and techniques chosen by a researcher to conduct a study. The design allows researchers to sharpen the research methods suitable for the subject matter and set up their studies for success. Creating a research topic explains the type of research (experimental,survey research,correlational ...
The Sixth Edition of the bestselling Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches provides clear and concise instruction for designing research projects or developing research proposals. This user-friendly text walks readers through research methods, from reviewing the literature to writing a research question and stating a hypothesis to designing the study.
Research Design and Methods: An Applied Guide for the Scholar-Practitioner is written for students seeking advanced degrees who want to use evidence-based research to support their practice. This practical and accessible text addresses the foundational concepts of research design and methods; provides a more detailed exploration of designs and approaches popular with graduate students in ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Chapter 2. Research Design Getting Started. When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a "research proposal" that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question.
Mixed method research design is an integration of qualitative and quantitative research an d . data in a research study. According to Burke-Johnson et al., (2007) this is an e mpirical .
Although the existence of multiple approaches is a powerful source in the development of a research design, new public administration (PA) researchers and students may see it as a source of confusion because there is a lack of clarity in the literature about the approaches to research design, research methods, and research methodology in the ...
Quantitative dominant [or quantitatively driven] mixed methods research is the type of mixed research in which one relies on a quantitative, postpositivist view of the research process, while concurrently recognizing that the addition of qualitative data and approaches are likely to benefit most research projects. (p.
Design research is the process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting data and insights to inspire, guide and provide context for designs. It's a research discipline that applies both quantitative and qualitative research methods to help make well-informed design decisions. Not to be confused with user experience research - focused on the ...
Research methodology is the backbone of any successful study, providing a structured approach to collecting and analysing data. It encompasses a broad spectrum of methods, each with specific processes and applications, tailored to answer distinct research questions.
Learn more about the marketing research process and methods to gather data—and make the most of it. Cookie consent. ... This is important as it'll influence your overall research design, which is up next. 2. Design the research. There are three types of research designs. The design you choose will be informed by how well-defined your problem is.
The first section of this chapter describes the four steps of the design process of the seizure prediction method. "Research of epileptic seizure prediction based on iEEG" and "Research of epileptic seizure prediction based on scalp EEG" will present the iEEG-based and scalp EEG-based seizure prediction methods according to different feature types.
The introduction of genome engineering technology has transformed biomedical research, making it possible to make precise changes to genetic information. However, creating an efficient gene-editing system requires a deep understanding of CRISPR technology, and the complex experimental systems under investigation. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in various tasks, they ...
Survey software is a tool used to design, send and analyze surveys online. It's the primary method of collecting feedback at scale whether that's a simple questionnaire or a detailed study such as customer or employee feedback as part of a more structured experience management program.
In this paper, we present the design and analysis of a tunable broadband terahertz absorber based on periodic graphene ring arrays. Due to plasmon hybridization modes excited in the graphene ring ...
The international consultant will conduct a two-day workshop on research methods related to alternative monitoring for participants from civil society to familiarize civil society activists in a structured way with research design and methods of qualitative and quantitative research on good governance and anti-corruption issues; 3. The ...