
- EnGendering Data
- Seed Systems CoE


AGRICULTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN NEPAL: TRENDS, PROSPECTS, AND POLICY OPTIONS
BOOK LAUNCH November 11, 2020 | 4:30 PM – 6:00 PM (IST) / 6:00 AM - 7:3o AM EST
Agriculture is a vital sector of Nepal’s economy for food security, employment generation, and poverty reduction, but the sector’s performance over the past two and a half decades has been weak. Domestic food production has failed to keep pace with rising food demand, and the country has become a net importer of food, both staples and high-value commodities. The agriculture sector faces both structural and new challenges. Farmers, particularly smallholders, have poor access to technology, inputs, and credit. Improving farm incomes and livelihoods will require increasing smallholders’ participation in the production of high-value commodities, such as vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat, and eggs. It will also require measures to address the emerging challenge of climate change, given the high vulnerability of smallholders to floods, droughts, and other extreme weather events.
IFPRI South Asia has extensively worked in Nepal on a wide range of policy issues in collaboration with the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development, Government of Nepal, with support from USAID. The key outputs from this engagement are presented in a new book "Agricultural transformation in Nepal: Trends, prospects, and policy options" . The book addresses some of the key strategic questions related to agriculture in Nepal and suggests policy measures to improve the delivery of critical inputs and services to smallholders. It discusses how the new federal system and governance structure will affect the delivery of agricultural technology and services.
Download synopsis
IFPRI South Asia is pleased to invite participants to the virtual launch of the book on November 11, 2020.

Chief Guest Prof. Dr. Puspa Raj Kandel, Vice Chair of National Planning Commission, Government of Nepal
Chairs Dr. Johan Swinnen, Director General, IFPRI Dr. Yogendra K Karkee, Secretary, Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development, Government of Nepal
Moderator Dr. Muzna Alvi, Associate Research Fellow, IFPRI
Welcome Dr. Shahidur Rashid, Director, IFPRI SAR Dr. Swarnim Wagle, Chairman, IIDS
Discussants Dr. Usha Jha, Member, National Planning Commission, Government of Nepal Dr. Kusum Shakya, Dean, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences Dr. Loraine Ronchi, Practice Manager, South Asia Agriculture, The World Bank Dr. Poshraj Pandey, Chairman SAWTEE Dr. Chip Bury, Resilience and Food Security Advisor, USAID
Thapa, Ganesh, ed.; Kumar, Anjani, ed.; and Joshi, Pramod Kumar, ed. 2019. Agricultural transformation in Nepal: Trends, prospects, and policy options. Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9648-0
This work was undertaken as part of the CGIAR Research Program on Policies, Institutions, and Markets under it's research Flagship 2: Economywide Factors Affecting Agricultural Growth and Rural Transformation.

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Agricultural Transformation in Nepal: Trends, Prospects, and Policy Options

2019, Economic Journal of Development Issues
Related Papers
Nepalese Journal of Agricultural Sciences,
Bidur P Chaulagain
Nepal is in transition from conventional subsistence farming and livestock rearing to modern integrated farming system focusing on whole value chain. Due to inadequate scientific and technological knowledge among wider sector of farming communities Nepal has hitherto remained far behind in agricultural production, and has been shifted from a food grain exporter to importer country. About one third food grain and two third of other food commodities are now imported from other countries. These are the issues of most academic and socio-economic and technical researches in Nepal and other countries. This volume of the NepJAS consists of such original research and review articles. Few articles included in this volume are contributed from developed countries like USA, Russia, and China. There are altogether 30 articles published in this volume. This editorial summary presents gist of the major findings of those articles.
Bashu Dev Deshar
This paper is a review of agricultural degradation and its impacts on economy and environment in Nepal. It includes an overview of agriculture in Nepal and the changes that have taken place. This paper has basically been applied descriptive cum analytical research design to complete. Agricultural development has been sluggish, and has failed to keep pace with population growth. In recent years the yields of major food crops in Nepal have been lower than other South Asian countries and Nepal is now dependent on food imports. Land holding size per family and field sizes has both decreased markedly during recent years. If hill regions are considered independently, all cereal crops yields have stagnated in the last 30 years and gains in production that have been made. Crop productivity in the hills has declined due to land degradation. Of the 28% of Nepal land that is degraded, 10% is poorly managed sloping agriculture terraces. As yields and production of cereal crops have fallen, many...
BMC Journal of Scientific Research
Khom Kharel
Agriculture sector is the main components of economic development of developing countries likeNepal. This sector contributes boosting economy in terms of GDP, employment and food security,as more than 60% of Nepalese residents chose agriculture as their primary source of income. Theincrease in output and productivity in this sector is crucial for reducing poverty through long-term,high-growth economic growth. Increased agricultural production and output are important contrib-utors to the country's overall economic development. This study aims to look at how the agriculturesector contributes to the Nepalese economy's growth. Using data collected over a 20-year period,a simple linear regression model has applied to determine the economic impact of farm sector pro-duction on real GDP. The study finds a positive impact of agriculture sector on real GDP and othersectors. Though, agriculture sector has been facing diversified challenges improving its productionin Nepal.
Water Nepal
Ngamindra Dahal
bibek shahi
Nepal is culturally an agriculture based country. One third of GDP comes from agriculture and there are numerous opportunities in agriculture mainly because of varied agro-climate prevailed in the country. Niche specific commodities that have comparative advantage could be produced in fair quantity to meet the demand of huge market of neighboring India and China as purchasing capacity of people in those countries has improved markedly mainly for quality agriculture commodities. Trade deficit, food insecurity, income generation, poverty reduction, and employment generation could be addressed by turning present status of subsistence agriculture into robust, vibrant and commercial agriculture through technology led agro-industrialization. There are agro-commodities which are imported from India and other countries in huge quantity by the scarce hard currency earned through remittance. Evidence shows that almost 70% of the remittance is spent for agriculture commodities which have high potentiality to produce within the country even after local consumption. Such produce could be exported to other countries to mitigate trade imbalance, enhance export promotion and import reduction and promote graduating Nepal from LDC to DC within the stipulated time frame as proposed a couple of years ago by the government of Nepal. Nepal should come up with functional, pragmatic and implementable agriculture plan and policy to harness huge possibility of agriculture commercialization to meet the consumption demand per se within and outside the country. This paper highlights to address prospects and limitations of agriculture commercialization and suggests some way forward to make agriculture more vibrant and robust to address trade deficit, food and nutritional insecurity and livelihood enhancement of Nepalese as a whole thereby Nepal can tailor her pace of development with neighboring countries to meet the aspiration of Nepalese in the 21 st century. Methodology This is a policy paper giving emphasis on prospects and limitations of Nepalese agriculture as a whole. Discussions on different issues have been given by a thorough review of literatures available within and outside the country. Aside from this, practical experience of author who was involved in agriculture R&D of Nepal since four decades are also included in the pertinent issues encompassing agriculture systems in Nepal. Many of these
George Gitau
SAURABH KUMAR
Research Nepal Journal of Development Studies
Deepak Chaudhary
This paper analyzes agricultural development in terms of policy and implementation in Nepal. More than two-thirds populations in Nepal reside in the rural area and most of them depend on agriculture. Subsistence form of agriculture is common in Nepal. Rural Area and agriculture are interrelated; like two parts of the same coin. The contribution of agriculture to national Gross Domestic Product is remarkable; however, it is declining over the decades. In fact, the agricultural sector cannot attract young people; the trend of migration from rural to urban is significantly increasing. The poverty is exceedingly marked in rural Nepal. The Government of Nepal emphasizes agriculture development for poverty alleviation in order to alleviate poverty, rural development, and national economic growth through the policy level. However, available data and qualitative analysis reveal that the outcome from the agricultural sector is not satisfactory due to several factors. In such a situation, more than half of the population has been facing food insufficiency. Because of weak policy and implementation, the agriculture sector has been suffering poor outcome. In that way, the government of Nepal along with concerned authorities should effectively implement agriculture policies in order to reduce poverty and rural development. The agriculture-rural accommodating policies and successful performance are crucial for poverty alleviation and rural development.
RELATED PAPERS
Deepak kumar
SMP NEGERI 1 TROWULAN
Animal Behaviour
Malte Andersson
Nature Communications
John Joannopoulos
Ahmad Sulaeman
Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública
Oswaldo Tanaka
Edivaldo de Oliveira
Ingénierie des systèmes d'information
Salah Baina
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association)
Eiichi Saito
Aquatic Microbial Ecology
Cinzia Corinaldesi
Epidemiology
Sylvia Richardson
The American Journal of Geriatric Cardiology
Juan Enmanuel Ortiz Valdez
Journal of Water Resource and Protection
Blaise Koffi
Chemistry of Materials
chaiwon kwon
Malaysian Journal of Medical Research
diana arianti
Ankit Pati Tripathi
Journal of Animal and Poultry Production
Inas Ismail
uwaterloo成绩单制作 滑铁卢大学毕业证书
Advances in robotics & automation
Prof. Ebrahim A . Mattar
Remote Sensing
Steven Dewitte
Advances in Image and Video Processing
Dr. Md. Farhad Bulbul
Elaborate on texture in space
Paweł Niejadlik
Sibahle Magadla
Journal of Applied Physiology
antonio pedotti
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Agricultural Transformation in Nepal
Trends, Prospects, and Policy Options
- © 2019
- Ganesh Thapa 0 ,
- Anjani Kumar 1 ,
- P.K. Joshi 2
Visiting Scientist, International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), Patan, Nepal
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
Research Fellow, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), New Delhi, India
Former director, south asia office, international food policy research institute, new delhi, india.
- Provides a blueprint for sustainable and inclusive agricultural growth
- Covers a wide range of issues and presents policy options for the government and other stakeholders to address emerging challenges and to benefit from new opportunities
- Draws lessons for Nepal from the experiences of other countries such as India, Indonesia, Kenya, Malaysia, and South Africa
12k Accesses
44 Citations
29 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (20 chapters)
Front matter, introduction.
- Ganesh Thapa, Anjani Kumar, P. K. Joshi
Macro-issues in Agriculture
Structural transformation and growth: whither agriculture in nepal.
- Ramesh Paudel, Swarnim Waglé
The Role of Agriculture in Poverty Reduction in Nepal
- Ganesh Thapa, Raghav Gaiha, Katsushi Imai
Household Food Expenditure, Dietary Diversity, and Child Nutrition in Nepal
- Anjani Kumar, Ganesh B. Thapa, P. K. Joshi
Food Inflation in Nepal and Its Implications
- Ramesh Sharma
Climate Change Impact on Agricultural Sector of Nepal: Implications for Adaptation and Resilience Building
- Ganesh R. Joshi, Binaya Joshi
Productivity Growth and Its Drivers
Food demand system and projections to 2035: nepal.
- Praduman Kumar, Anjani Kumar, P. K. Joshi
Seed Sector Development in Nepal: Opportunities and Options for Improvement
- Devendra Gauchan
Use of Chemical Fertilizers in Nepal—Issues and Implications
- Hiroyuki Takeshima
Agricultural Mechanization in Nepal—Patterns, Impacts, and Enabling Strategies for Promotion
- Hiroyuki Takeshima, Madhusudan Bhattarai
Agricultural Research and Extension System in Nepal: An Organizational Review
- Suresh Chandra Babu, Ram Pratap Sah
- Agricultural Diversification
Agricultural Diversification in Nepal
- Champak Pokharel
Non-timber Forest Products (NTFP) and Agro-forestry Subsectors: Potential for Growth and Contribution in Agriculture Development
- Madhav Bahadur Karki, Chhote Lal Chowdhary
Impact of Migration and Remittances on Agriculture: A Micro–Macro-analysis
- Amina Maharjan, Beatrice Knerr

Agricultural Trade and Marketing
Trends, structure and drivers of nepal’s agricultural trade.
- Agriculture in Nepal
- Poverty Reduction
- Agriculture Productivity
- Agricultural Growth
- Agricultural Trade
- development policy
About this book
Editors and affiliations.
Ganesh Thapa
Anjani Kumar
About the editors
Bibliographic information.
Book Title : Agricultural Transformation in Nepal
Book Subtitle : Trends, Prospects, and Policy Options
Editors : Ganesh Thapa, Anjani Kumar, P.K. Joshi
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9648-0
Publisher : Springer Singapore
eBook Packages : Economics and Finance , Economics and Finance (R0)
Copyright Information : Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2019
Hardcover ISBN : 978-981-32-9647-3 Published: 06 December 2019
Softcover ISBN : 978-981-32-9650-3 Published: 03 January 2021
eBook ISBN : 978-981-32-9648-0 Published: 25 November 2019
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XLIII, 628
Number of Illustrations : 11 b/w illustrations, 79 illustrations in colour
Topics : Agricultural Economics , Development Economics , Development Policy
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Nepal’s Agricultural Landscape: Assessing the Government’s Stance
Technological developments and commercialization are key factors for long-term investment in the industry. the government can realize the immense potential to address the gap in technical skill development and commercialization to increase investment in agriculture., by mahotsav pradhan | december 14, 2023, economic development, 7 minute read.
Nepal is still largely an agrarian nation with around 62% of total population engaged in agriculture. The agriculture sector contributes to around one-third of the nation’s GDP and provides employment to two third of the population . But, the contribution to overall GDP has declined over time. Agriculture contributed to 36.64% of the GDP which then decreased to 23% by 2022. Similarly, the employment in agriculture has decreased from 73% in 2005 to 62% in 2021. Although the sector still contributes to a significant proportion of the overall GDP and a lot of population is engaged in agriculture, the government has allocated only NPR 58.98 billion (USD 445.21 million) for the agriculture sector in the fiscal year 2023/24 AD, out of a total size of NPR 1.751 trillion (USD 13.20 billion) which amounts to only 3.36% of total budget.
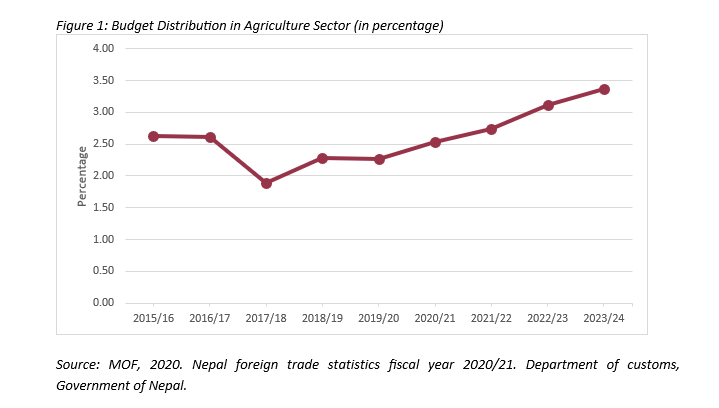
Current scenario of the government
Nepal is dependent on others for foods that it could produce on its own due to a lack of strong supportive policies despite having a lot of potential in this field. The priority of the government should be focused towards feeding the population with organic home-grown products, and reducing the increasing trade deficit through commercialization of products tailored to the climate and soil. But in reality, government investment, commercialization of agricultural practices, research and development, storage facilities are severely lacking.
Shrinking Workforce
The agriculture sector has remained stagnant over the years due to lack of attention from the government and the concerned stakeholders. The yield and crop production has decreased due to changing landscape, rainfall, and temperature directly leading to a rise in out-migration of workforce in search of better opportunities and income. According to the National Population Census 2021 preliminary result, 2.1 million Nepalis are living abroad which means one in every three households have at least one member absent or living outside of Nepal. Although there has been large increase in the in-flow of remittance, the hard-earned money is used up in buying foods to feed the families as it is actually cheaper to buy foods in the market than grow it in farms further widening the trade deficit. Nepal could save USD 2 billion (NPR 265 billion) every year if it could avoid the imports and decrease the agricultural trade deficit.
Inefficiency of FDIs and Business Development Strategies
SMEs in Nepal face difficulties in operation due to lack of adequate capital base, technology, information, and knowledge regarding marketing and opportunities. The government further adds up to it through high interest rates, high collateral requirements, information gap, and bureaucratic hurdles. According to Chandra Prasad Dhakal, President of FNCCI, Nepal invests only 1% of its total FDI on agriculture at present. The investors want security and return on their investment and Nepal must work towards providing an enabling environment in order to increase FDIs which would assist our farmers modernize farming with latest technologies.
Moreover, technological developments and commercialization are key factors for long-term investment in the industry. The government can realize the immense potential to address the gap in technical skill development and commercialization to increase investment in agriculture. Although agriculture contributes in the livelihood of significant proportion of the population, the potential for economic prosperity of the nation remains untapped due to poor business development strategies .
Investment Gap from BFIs
The agricultural sector of Nepal still falls far behind in being commercialized and mechanized due to a lack of significant investment. If we take a look into the data of agriculture census, the proportion of business holdings using agricultural credit to finance their farming is very low. Only 23% out of total holdings availed agricultural loan in 1991/92 AD. 24% of total holding availed for loan in 2001/02 AD which further decreased to 21.82% in 2010/11 AD.
The existing provision requires commercial banks to disburse minimum 15% of their total credit to agriculture sector. But the commercial and development banks are still below central bank’s mandate. Out of the total lending of commercial banks, only 13.1 percent (Rs.552.99 billion) lending has been in the agriculture sector.
Although number of financial institutions has increased in last two decades from 7 in 1990 to 111 as of mid-October 2023 , agricultural financing is not yet satisfactory. Agriculture Census data shows that the highest sources of loans have been actually from cooperatives (39%), relatives (14%), women’s group (14%), and others. Moreover, there are 1,414,997 holdings (34%) seeking additional loans of which 37% are doing so for livestock farming, followed by agriculture inputs (32%), irrigation (13%), and so on.
Inefficiency of aids
The agriculture and livestock department are a key area of a lot of foreign aid and funds from the World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB) and IFAD (International Fund for Agriculture Development). However, rampant corruption, inefficient planning, and incompetent inspections have hindered in Nepal’s development projects wasting scarce resources. The aids meant for under-privileged people and under-served regions have been diverted to contractors, middlemen, consultants, and excessive employee benefits. The Project for Agriculture Commercialisation and Trade (PACT) received NPR 5.1 billion (USD 38.49 million) from the World Bank to improve the farming business and raise rural income. But the World Bank’s own investigation found that a majority of the budget was enjoyed by the middlemen and “fake farmers”. However no legal action has been taken by the government against the perpetrators who siphoned off the funds.
Increasing agricultural trade deficit
Nepal is naturally gifted through agricultural diversity with varied topographical, altitudinal and temporal conditions. But now, Nepal is highly dependent on imports to sustain its daily foods due to a growing population and rising income. Nepal highly imports staples like rice, vegetables, and fruits that could have easily been produced in our own fertile lands. While Nepal’s population has more than tripled from 9.4 million to nearly 30 million in the past 60 years, paddy output has only increased from 1.8 tonnes per hectare to 3.8 tonnes . This resulted in Nepal’s grain import reaching NPR 80 billion (USD 603.77 million) where rice alone comprised of NPR 50 billion (USD 377.36 million). A third of all the remittances earned from foreign employment are used up in importing foods while Nepal exports only NPR 64 billion (USD 483.02 million) worth of food items.
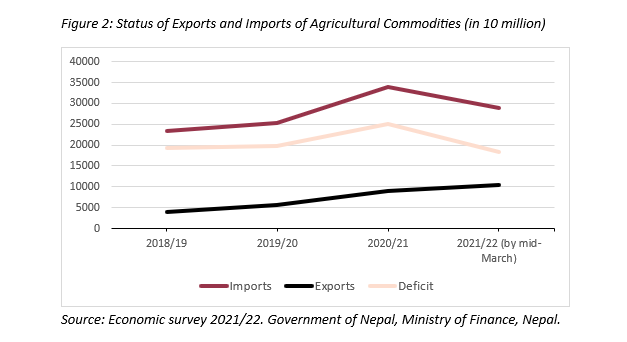
Nepal is a producer and exporter of tea and coffee, but it still imported NPR 9.5 billion (USD 71.70 million) worth of them. Half of the food imports are from India as the Indian farmers receive subsidies, seeds, fertilizers, technology, irrigation from their government which helps in producing crops at competitive prices. Hence, traditional Nepali variants are disappearing , replaced by cheaper, widely-available food variants.
Way forward
Nepal has a massive untapped opportunity in the agricultural sector and it can only be seized by establishing coordination between the government, banking sector, commercial agriculture, and business projects. Government investment is crucial in elevating rural livelihood and increasing agricultural productivity though agricultural support services, improved irrigation services for efficient water management, access to high-quality seeds, farm equipment, trainings in improved farming techniques, and value chain infrastructure. The government should further focus on sustainable practices of mixed farming systems (SIMFS) to decrease the increasing agricultural trade deficit. SIMFS has a positive effect on the environment also helping farmers to recover from droughts, floods, and even market failures . There must also be checks in the use of chemical fertilizers, investments in flood and erosion controls in the irrigation command areas, rural roads and bridges for connectivity and market access, and watershed conservation.
By improving the policy while also focusing on the efficient implementation of existing policies, Nepal can still improve the agricultural sector along with the overall economy of the country. It can be noted that despite the decline, the agricultural sector still has the highest share in the overall GDP and a large proportion of population are still dependent on it for their livelihood.

Mahotsav Pradhan holds a Bachelor’s degree in Economics (Honors) from the University of Delhi. Prior to joining Nepal Economic Forum as a Research Intern, he has worked as Foreign Exchange Intern at Nepal Rastra Bank. He has a keen interest in development economics, with a passion for exploring the dynamics of policy analysis and international finance.
<NEFTakes
Let's Write an Article for Blog
Agriculture in Nepal: An Essay with Comprehensive Analysis

Agriculture in Nepal: A Comprehensive Analysis
Agriculture is the backbone of Nepal’s economy, contributing to more than one-third of the country’s GDP and employing over 65% of the workforce. Nepal’s geographical and climatic diversity has provided a unique opportunity for agricultural production, with the potential to sustainably increase crop yields, livestock productivity, and export value. Despite these advantages, the sector faces several challenges, including limited access to modern inputs, poor infrastructure, and the impact of climate change. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of agriculture in Nepal and suggest ways to overcome these challenges.
Table of Contents

Agricultural Production in Nepal
Nepal’s agriculture sector is divided into two main sub-sectors: crop production and livestock production. The crop production sub-sector includes cereals, pulses, vegetables, fruits, and spices, while the livestock sub-sector includes cattle, buffalo, goat, sheep, and poultry. The country’s agricultural production is highly dependent on monsoon rainfall, which accounts for more than 80% of total precipitation. This makes Nepal’s agricultural production highly vulnerable to climate change, with the potential for droughts, floods, and other extreme weather events.
Also Read : Essay on Natural Resources in Nepal: An Overview
Despite these challenges, Nepal has made significant progress in agricultural production in recent years. The country’s cereal production has increased by 33% since 2000, while livestock productivity has also increased significantly. However, the sector still faces several challenges, including limited access to modern inputs, poor infrastructure, and low adoption of modern farming practices.

Challenges Facing Agriculture in Nepal
One of the primary challenges facing agriculture in Nepal is limited access to modern inputs. Farmers in Nepal lack access to quality seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and other modern inputs, which hinders their productivity and limits their potential for growth. The government has attempted to address this issue by subsidizing inputs and promoting private sector investment in the sector, but progress has been slow.
Another challenge facing agriculture in Nepal is poor infrastructure. The country’s rural areas lack basic infrastructure such as roads, electricity, and irrigation, which hinders farmers’ access to markets and limits their productivity. The government has attempted to address this issue by investing in infrastructure development, but progress has been slow due to the country’s rugged terrain and limited resources.

The impact of climate change is another challenge facing agriculture in Nepal. The country’s agriculture sector is highly vulnerable to extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and landslides. These events can cause significant damage to crops and livestock, leading to decreased yields and income for farmers. The government has attempted to address this issue by promoting climate-resilient farming practices, but progress has been slow due to limited resources and capacity.
Suggestions for Overcoming Challenges
To overcome the challenges facing agriculture in Nepal, several strategies can be adopted. Firstly, there needs to be an increased investment in agricultural research and development to promote the adoption of modern farming practices. This can include research into new crop varieties, improved irrigation systems, and better soil management practices.

Secondly, there needs to be an increased investment in rural infrastructure development to improve farmers’ access to markets and increase their productivity. This can include the construction of rural roads, electrification, and irrigation systems.
Finally, there needs to be an increased focus on climate-resilient farming practices to mitigate the impact of climate change on the agriculture sector. This can include the promotion of drought-tolerant crops, improved soil management practices, and better water management practices.
Also Read : Mahatma Gandhi: Inspiring a Movement for Change
Agriculture is a vital sector for Nepal’s economy, providing employment to over 65% of the workforce and contributing to more than one-third of the country’s GDP. However, the sector faces several challenges, including limited access to modern inputs, poor infrastructure, and the impact of climate change. To overcome these challenges, there can be done to promote agricultural research and development, invest in rural infrastructure development, and promote climate-resilient farming practices. By addressing these challenges, Nepal’s agriculture sector can continue to grow and contribute to the country’s economic development .
Related Posts

Essay on Natural Resources in Nepal: An Overview
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Nepal’s Agribusiness Transformation

Analysing the prospects and problems in Nepal’s agriculture development
The Covid-19 pandemic has presented Nepal with big opportunities to modernise its agriculture. But the transformation is fraught with challenges and a collaborative approach is needed to make it work.
--BY SANJEEV SHARMA
For Nepal, the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic has been severe and it is unlike past international crises when the events had little to no impact on the Himalayan country. But even in these gloomy times when the threat of the deadly pathogen looms large over the health of the citizens and the country’s economy, a silver lining has appeared on the dark clouds of uncertainty in that agriculture can help overcome many socio-economic problems that surround Nepal at present. With the global health emergency dampening the prospects of services and the manufacturing sectors, agriculture is suddenly being seen as the sector with the highest potential for investment and job creation. “We have introduced agriculture and animal husbandry programmes targeting unemployed youths and abroad returnees. They will be able to start agriculture enterprises in groups and get concessional agribusiness loans and will also get business insurance and facilitation to access the market,” says Minister for Agriculture and Livestock Development Ghanashyam Bhusal.
In a country like Nepal where the last few decades have seen agriculture becoming a much maligned activity, it is encouraging for farmers, foreign returnees and other people from rural areas who are looking to return to agriculture, and investors who are looking to invest in areas such as commercial farming and food processing. Some prominent business houses that had started agribusiness ventures prior to the pandemic are now expanding their activities in agriculture.
“The Covid-19 pandemic has brought agriculture into a vibrant discourse at the political, policy and operational levels, government and non-governmental sectors. As a result of the pandemic-induced economic crisis, many people who have returned to their villages and hometowns from local cities and overseas have taken up agriculture in various forms,” observes Yamuna Ghale who is a agriculture and food security analyst. According to her, due to restricted imported supplies, agriculture is being consequently viewed as an alternative not just for livelihoods but also as a profession. As of October 5, the official number of foreign returnees, who are mainly migrant workers, has reached 120,000. Similarly, people whose livelihood was affected by the pandemic-induced economic recession have also returned to their villages from cities across Nepal. Ghale says that Covid-19 thus has established agriculture as one of the most viable sectors for immediate engagement for people in the villages, including returnee migrants, for the adoption of urban farming and for finding innovative ways in agriculture inputs and food supply systems.
In what came as a big surprise to many, a latest government-commissioned study found the agriculture sector to be the most profitable sector in the country. According to the 2020 update of the National Economic Census 2018, the profit level in the agriculture sector is 55.7 percent largely outpacing the manufacturing sector which registers 14.7 percent. Businesspersons engaged in agribusiness also say that agribusiness offers good returns to investors. “Profitability in agriculture depends on crops that are cultivated and ownership of land. Nevertheless, the business of food is profitable in itself, so we should move towards food processing,” says Ananda Bagaria, managing director of Nimbus Holdings, adding, “Despite various problems, some industries such as sugar have been doing good business in the country.”
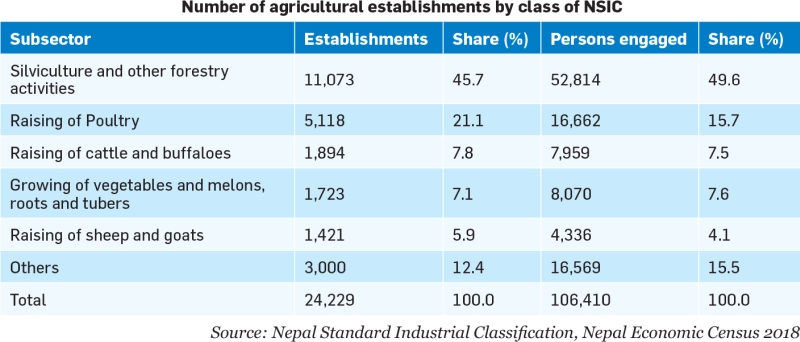
As per the National Census 2018, there are 24,229 business establishments in agriculture, fishing and forestry and this number accounts for 2.6 percent of the whole number of establishments in Nepal. Similarly, the contribution of the agriculture sector to the coutry’s GDP currently is 27.1 percent and the livelihood of two-thirds of the population is dependent on agricultural activities, according to the Economic Survey for FY2020/21 published by the Ministry of Finance.
Agriculture Development: Easier Said than Done Despite the newfound optimism, agriculture development remains elusive as the sector is fraught with numerous challenges. Political leaders, bureacrats and many experts seldom forget to use catchphrases like ‘agriculture revolution’, ‘employment generation’, ‘food self-sufficiency’ during speeches and discussions. “The agriculture sector has long been a scapegoat of ineffective policies. If we look closely at the budgets of the last 10 years, we can’t see any significant changes in the government’s priority when it comes to agriculture. “Time and again, terminologies like ‘commercialisation’ and ‘modernisation’ gain prominence in speeches and discussions,” says Bagaria.
Despite being called an agrarian economy, Nepal has to rely on imports to feed its people. The country’s food import bill in the fiscal year 2019/20 reached an all-time high of Rs 243 billion which was Rs 224 billion in FY2018/19. Import of rice topped the list with Rs 23.17 billion followed by fats and oils (Rs 50.24 billion), vegetables (Rs 33.05 billion), fruits (Rs 20.74 billion) and oil seeds (Rs 19.48 billion).
“If we look at the countries in the world having high agricultural output and compare the number of people employed per hectare of land in those nations and Nepal, then we can observe our real situation. The question here is what plans do we have to provide employment to people if we are to modernise the agriculture sector?” asks Bagaria, adding, “I think the answer lies in having a linkage between agriculture and manufacturing sectors. This also means creating a market for farm produce.”
Increased Production: Stagnant Productivity While there has been an increase in production of different types of crops and farm produce over the last few decades, the overall agricultural productivity has not been satisfactory. It is telling that in spite of the bumper harvests, the growth of rice productivity over the past five decades has stagnated at 1.5 percent. Nepal, which has one of the world’s highest per capita consumption of rice (137.5 kg) has not been able to feed its population which grew at a rate of 2.3 percent annually in those years. The Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development (MoALD) has estimated that the plantation of paddy will cover 1.37 million hectares across the country in the current fiscal year which was 1.55 million hectares in the last fiscal year. This indicates paddy acreage in Nepal will fall to its lowest in the last 20 years. The country’s paddy productivity is 3.5 metric tonnes per hectare which is among the lowest in the world and well below the global average of 4.7 metric tonnes per hectare.
In 2019, paddy production in Nepal reached an all-time high of 5.61 million metric tonnes followed by 5.55 million metric tonnes, which is expected to decrease this year due to severe disturbances caused by the Covid-19 pandemic alongwith the shortage of chemical fertilizers in the market. Despite the record harvests over the last few years, domestic production has not been met as the yearly demand for rice stands at 6.6 million metric tonnes. Tradionally, paddy has remained the most important crop for Nepal as rice is the most consumed staple diet across the country. According to official stastistics, the contribution of rice to agricultural gross domestic product (AGDP) of Nepal stands at 20 percent and nearly 8 percent to the country’s GDP.
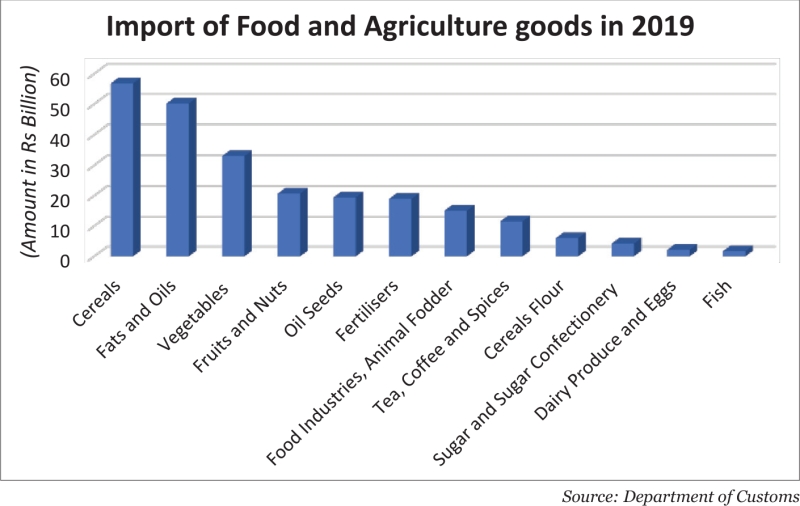
Similarly, Nepal also imports pulses worth billions in spite of being the fourth largest producer of lentils in the South Asia region. At annunalised rates, the production, production growth and procutivity of pulses stand at 319,770 metric tonnes, 2.47 percent and 1.67 percent respectively. In the last fiscal year, Nepal imported pulses worth Rs 18.20 billion which was Rs 13.52 billion in FY2018/19. A similar situation can be observed in the area of vegetables. Nepal produces 4.2 million metric tonnes of vegetables which does not meet the demand for 4.5 million metric tonnes. In FY2018/19, the country imported vegetables worth Rs 33.05 billion, an increase of Rs 4.40 billion from Rs 28.66 billion in FY2017/18. Meanwhile, Nepal also exports some 25,000 metric tonnes of vegetables every year.
Poultry is among the few areas in agriculture in which Nepal fares relatively better in terms of productivity. The production of chicken meat which was 16,662 metric tonnes in FY2008/2009 jumped to 60,402 metric tonnes in FY2017/18; the production of eggs totaled 1.51 billion in FY2017/18 which was 620 million in FY2008/2009. Meanwhile, the annual production of fish is about 83,897 metric tonnes. Still, the import of poultry meat and fish amounted to Rs 3 billion in FY2018/19 indicating that the increased production of poultry and aquaculture are insufficient to meet domestic demand. High value products such as tea and coffee also make up a sizeable portion of Nepal’s agro import. In FY2018/19, tea and coffee imports amounted to Rs 11 billion. The production of tea and coffee, meanwhile, was 25,205.85 metric tonnes and 530 metric tonnes respectively. Among the few export-oriented items, tea and coffee are considered to have big potential for Nepal; in the last fiscal year, the country’s tea and coffee exports were 15,700 metric tonnes and 45.81 metric tonnes respectively.
Agriculture Minister Bhusal says that the government has felt the need to shift its approach for agriculture development. “In the past, our focus was more on agriculture production and productivity. We will now focus on increasing farmers’ access to markets and ensuring a fair price for their products. For this, various work like implementation of minimum support price, study on market management, development of necessary market infrastructure, will be carried out,” informs Bhusal. “Similarly, all local levels will be linked to the market, the feasibility of national and international agricultural trade will be studied, and farmers will be informed about the programmes. For the purpose, a structure will be set up under MoALD for which we have also arranged a budget in the current fiscal year,” he adds.
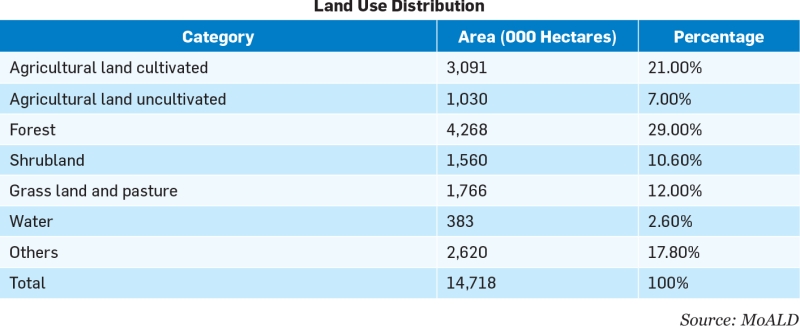
Shrinking Agricultural Land The loss of arable land due to unplanned urbanisation and infrastructure development is considered to be the major reason for declining agricultural productivity. According to data from the World Bank, arable land as a percentage of the total land area of Nepal declined to 14.75 percent in 2016 from 16.42 percent in 2001. Though there is no exact data about the loss of paddy fields, the government has estimated that 100,000 hectares of such land have been lost in the past decade. Similarly, lack of irrigation is also another hindrance when it comes to increasing agricultural productivity as nearly half of the arable land in the country has to rely on rain water for agriculture; official stastistics show that only 56 percent of the country’s total arable land is irrigated. In the meatime, of the 4.1 million hectares of arable land in Nepal, one million hectares is barren.
Land Use Distribution Experts stress on proper policies and actions related to land utilisation to address the problems. “Agricultural productivity is about land, labour, and resource management. The shrinking land availability could be managed through effective implementation of the land policy making best use of all the arable land, managing resource tenure including user rights, facilitation of land use process and making land related institutions user responsive mainly to women, small holders and other users such as private sectors in operating processing zones, ware houses, auction centres etc,” says Ghale.
Though politicians have long been using the agenda of ‘progressive’ land reform and increasing agricultural productivity as tools to meet their own political objectives, things have’t changed visbly on the ground. Entrepreneurs, however, hold a different opnion on the issues regarding land reform. “Issues in land reform are cited as hindrances to private investment in agriculture. But let us look at the sugar industry; land was fragmented even when sugar industries began to open in different parts of the country,” says Bagaria.

Agro Export: A Pipedream or Real Potential? For a long time, the government has given emphasis to the export of agricultural commodities. However, the export of agro produce has remained dismal as domestic production struggles to meet the surging internal demand for food items. The Nepal Trade Integration Strategy (NTIS) 2016 incorporated some agricultural goods including ginger, cardamom, tea, medicinal herbs and aromatic plants as high value exportable items. However, export performance of many agricultural goods listed in NTIS 2016 has remained below-par over the years. Except for tea and medicinal herbs, export of other agricultural goods has been satisfactory.
This situation has led stakeholders to urge the government to give emphasis to the substitution of food imports rather than increasing exports. “It was encouraging to hear the agriculture minister saying that we should stop dreaming of exports and rather talk about import substitution. His statement was trolled in social media. But if we see it positively, then he must have realised that we lack essential infrastructure for exports and we also don’t have any inherent advantage,” says Bagaria referring to a speech made by the Agriculture Minister Bhusal at the Federal Parliament a few months ago.
He sees a growing awareness among people in the government that substitution of food imports should be the government’s priority. According to him, there are 5 to 7 major crops and farm produce - paddy, wheat, maize, potato, livestock and milk - that contribute to 70-80 percent of Nepal’s agricultural GDP. “So, we need a complete turnaround in the production of these items. We need plans to substitute import of these items in the next five years. If we look at last year’s statistics, 5.5 million tonnes of paddy was imported,” says Bagaria, adding, “We need to look into why rice mills in Nepal are closed. These topics should be areas of focus in our discourse of agriculture sector development. We talk about agriculture zones and industrial districts, but there is also a need to talk about agro processing zones.”
Experts believe that there are heaps of challenges to overcome before the country can benefit from exporting agricultural commodities to the international market. “The challenges are related to planning with immediate short and long term vision in the agriculture sector with categorized services for food crops, cash crops and other valuable crops for export market development for employment, income and food security,” she mentions.
Meanwhile, businesspersons who have entered the agribusiness in recent years see big opportunities in exporting farm produce. “Tourism, hydropower and agriculture are three major sectors for Nepal to earn foreign currency and IMS Group is engaged in all these sectors. Hydropower is lacking in terms of energy export, whereas we don’t have sufficient infrastructure in tourism. So, agriculture can be the best sector for Nepal to earn foreign currency,” opines Deepak Malhotra, chairman of IMS Group.

Private Sector Participation The recent years have seen some business houses starting to invest in agribusiness. According to Malhotra his group saw big potential to invest in agriculture which will also help to lower the country’s dependency on import of food to some extent. IMS Agro, the agribusiness vertical of IMS Group has plans not only for domestic supply but also to export farm produce to Gulf nations including the United Arab Emirates and Qatar. Under a pilot project, IMS Agro started the cultivation of paddy, wheat, papaya, strawberry and lemon at its 25 bighas of land in Sunsari. “We will prepare a strategy to expand our market across the country from east to west next year,” shares Malhotra.
Many large business houses of today have their roots in agribusiness. From the Dugars, Golchhas, Khetans, Sharda Groups to Panchakanya Group, many business houses that have investments in various verticals started grain trading businesses moving later into food processing, industrial and other ventures. Over the years, many of them have reduced their presence in agriculture or left agribusiness altogether, but some business houses have ventured into farming high-value crops. For instance, Jyoti Group is into the production and export of coffee. The group which commenced commercial cultivation of coffee at Nirmalpokhari, Kaski in 2008 exports the processed Himalayan Arabica coffee beans to Japan. With the Himalayan Arabica coffee gaining a good market in the East Asian country, the group is expanding its coffee farming to Lamjung.
Over the last couple of years, Nepali coffee has gained popularity in the international markets. In 2016, the Himalayan Arabica Specialty Organic Coffee was named the Best Gourmet Coffee in the 2nd International Contest of Coffee organised in Paris in 2016. According to coffee exporters, the current 500,000 kgs annual production of Himalayan Arabica is insufficient to fulfill the increasing demand for Nepali coffee in the international market.
Similarly, another business group, Vaidya’s Organization of Industries and Trading Houses (VOITH) is also engaged in agro processing, tea production and animal feed production. Its subsidiary companies including Guranse Tea Estate, Mai-Illam Guranse Tea Industries and Nirvana Tea Processing and Packaging are in the business of exporting high-quality Nepali orthodox tea.
Credit Flow of Commercial Banks in Agriculture Golyan Group is among the new entrants in agriculture. Under the brand Mato, Golyan Agro over one year ago started to supply organic farm produce at affordable rates in the market. What began as a CSR initiative in Rangpur, Jhapa has grown to become a successful business model of perennial farming encompassing nearly 1,000 farmers from 25 villages. For the collection of farm produce and market management, Golyan Group has been collaborating with the Women Entreprenuers’ Association of Nepal (WEAN) in Jhapa. Mato already has a few stores and the group has plans to open at least 20 stores in Kathmandu this year aiming to operate 100 stores across the capital valley and to also expand branches in different parts of the country over the next few years.
“Among our entire investment portfolio, agribusiness will be the biggest in the next five years. We established ‘Mato’ to start a retail business creating a big market for organic farm produce. Eventually, there will be profit in agriculture, but the growth will not achieve greater heights by just supplying products to local markets,” said Pawan Kumar Golyan, chairman of Golyan Group, during a conversation with NewBiz in August, adding, “So, we have planned to start exporting farm produce when Mato will become a certified organic brand in the next three years. Currently, we are also engaged in small exports. During the lockdown, we exported water melons and a few other farm produce.”
Currently, Golyan Group is in the process of expanding its organic farming for which it has bought land totaling 300 bighas in different locations of Jhapa. Golyan agro which has already planted crops such as paddy, fruits including strawberry, lemon, watermelon, dragon fruit, papaya and seasonal vegetables also plans to cultivate medicinal herbs, bettlenuts and bamboo. Similarly, the company has planted local rice breed ‘Kalanamak’ in 190 bighas in Jhapa and Bardia districts collaborating with the local farmers. Golyan Agro plans to take up rice plantation in 1,000 bighas by next year. Besides this, the company is also preparing to produce plant seeds to end the dependency on imported seeds.
While these initiatives are commendable in terms of setting a new direction for Nepal’s agriculture development, much needs to be done from the government’s side to attract the private sector into agribusiness, say experts. “The foremost important need is to clarify and state the position in defining what kind of agriculture is to be promoted. The unbundling report is yet to be clarified for the provincial and local governments to take up their roles and responsibilities including the private sector. Likewise, policies related to the role of the private sector have to be defined explicitly,” states Ghale.
Leave a comment

No Laughing Matter
The sweet rewards of power.

Update: 2020-03-25 | Source: Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB)
Update : 2020-03-25
Source: Federation of Nepal Gold and Silver Dealers' Association

- _Grade VIII
- _ _Social Studies
- _ _(Grade XI- New Course)
- _ _ _Language Development
- _ _ _Literary Studies
- _ _ _ _Short Stories
- _ _ _ _Poems
- _ _(Grade XII- New Course)
- _Basic Level
- Moral Stories
- General Knowledge
- Information
Thursday, February 1, 2018

Importance of Agriculture in Nepal (Essay)

51 comments:

I recently found many useful information in your website especially this blog page. Among the lots of comments on your articles. Thanks for sharing. Sindh Irrigated Agriculture Progress
I will really appreciate the writer's choice for choosing this excellent article appropriate to my matter.Here is deep description about the article matter which helped me more. write my essay for me
A professional writer reads your writing and will completely fix all the grammatical errors, misspellings, and incorrect word choices. Some try correcting the proofs of service and will go a step further and publish the organization, clarity, and structure. If you consider sending each school paper that you write, to an essay editing service, before you were filming it, you might want to make sure that your editor understands your needs. Most teachers can develop a good idea of your tone and point of view during the semester. A professional editor will test your writing academic and conditions of publishing. essay writing service
Custom essay writing services are rampant on the web these days. Every time I turn around, it seems like there is a new website selling essays to unsuspecting college students around the world. essay writer service
A granja de galinhas deve ser um local iluminado e ventilado. Mas, ao mesmo tempo, deve proteger as galinhas da chuva, do sol excessivo no verão e do possível ataque de predadores. granja de galinhas
Agrarian science and agriculture, albeit identified with one another, are basically totally different from each other. Online Basmati Rice
Hello, I have browsed most of your posts. This post is probably where I got the most useful information for my research. Thanks for posting, maybe we can see more on this. Are you aware of any other websites on this subject. tutlance
The term agricultural marketing is comprised of two different words namely, agriculture and marketing. 'Agriculture', of course refers to the activities making use of natural resources for the welfare of society whereas 'Marketing' means looking after the marketing functions, channels and agencies etc. agronomie
The outcome has been two books and a DVD that have helped children accomplish a portion of the potential that sits inside us all. how to start a blog
Deutz Fahr Parts Catalog involves growing of crops such as fruits and vegetables and rearing of livestock to produce food for public consumption. Without agriculture our existence as humans and livestock would be threatened. Whether one is practicing agriculture in a small farm or in a large farm, agriculture provides many benefits to the society.
All these points will give you an outline to your essay writing. Do not stick to one point. This makes the reader disinterested in your writing. essay writing service
I found Hubwit as a transparent s ite, a social hub which is a conglomerate of Buyers and Sellers who are ready to offer online digital consultancy at decent cost. https://owlessay.net/write-my-paper/
Sustainable agriculture is often thought of in terms of environmental issues, but in this article, I define it more broadly, so as to encompass economic and human factors as well. I argue that the single most important factor in achieving truly sustainable agriculture is the leaving intact of ecosystems. I set the target goal of preserving 70% of all land as wild ecosystems. These intact wild ecosystems could provide immense economic benefits both for agriculture and for society as a whole, both in terms of direct and indirect effects. Mandi Bhav Today
Have your ideas first in your mind without putting them down on the paper. When you feel like writing them down, take notes on every idea, word and phrase that involves your mind and relates to the main topics your essay. http://www.northwesteliteindex.com/the-many-ways-to-find-cheap-essay-writers.html
Love to read it,Waiting For More new Update and I Already Read your Recent Post its Great Thanks. essay typer real?
I found so many interesting stuff in your blog especially its discussion. From the tons of comments on your articles, I guess I am not the only one having all the enjoyment here! keep up the good work... using an essay writing service
All the schools affiliated to the CBSE board are bound the exam system and need to teach the NCERT syllabus as per the guidelines specified by the board. Raipur Board 12th Model Paper 2021
Wow, What a Excellent post. I really found this to much informatics. It is what i was searching for.I would like to suggest you that please keep sharing such type of info.Thanks https://ejemplosmaterialesconstruccion.blogspot.com/
Where do essay writing services get their essays? Although many of these companies would like you to believe that they are creating essays with a qualified team of writers, most of these so-called essay writing services actually outsource their writing to India and other countries. dissertation help
Wow, cool post. I’d like to write like this too – taking time and real hard work to make a great article… but I put things off too much and never seem to get started. Thanks though. Descriptive Essay Writing Service
A fruitful decision of composing method ensures your accomplishment in getting A for exertion for your essay. check out the post right here
Last month, when i visited your blog i got an error on the mysql server of yours.*~,”* https://artdaily.com/news/131118/The-Algorithm-of-How-to-Buy-Essay-Online-Cheap#.X9x8q9gzZPb
To realize how to compose an essay above all else you ought to distinguish the sort of essay you are going to compose. At the point when we talk about the essay types, as a rule we manage the accompanying: "For and Against" Essays, Opinion Essays, Providing Solutions to Problems and Letters to the Editor. research paper writing rules
LIC Customer login as a new user, login to LIC India service portal to pay premium online and to manage all your insurance policies, activate new helpline services, check your loan and interest details in LIC login, check the premium subscriptions with calculator, subscribe for online term insurance available on registration at e Services portal. LIC india login All the premier services are available for LIC policy customer with one registered login at Life Insurance Corporation customer portal account, if your are agent or customer, you can access the LIC policy number services separately with Agent login and LIC customer login with new and old portal login.
is easy to value, and has a clear and evident track record to analyse, and as such agriculture investment ticks all of the relevant boxes to potentially become the ideal asset class for investors today. Europa-Road kombájn szállítás
At the point when you are writing for posts, attempt and give your perusers significant quality data. Recollect this is your crowd. These are individuals you are attempting to build up a compatibility with. Assignment Help
The main thrust behind the Hatch Act was the need of the country to enable the ranchers so they could improve efficiency and feed the developing populace. Since the mid nineteen sixties, agriculture has acquired a ton of significance in creating and created nations. targonca szállítás Europa-Road Kft.
A research paper help service is basically an academic paper writing help company or agency that helps students write academic papers. Such companies provide reference material. Several research writing services have come into existence over the past few decades. But students trust us the most, because of our unique quality timely delivery and rapid change.

Agriculture is one of the best and important department of any country and if you make your country prosperous, you should make this department strong and powerful. Assignment writing services .
It is imperative that we read blog post very carefully. I am already done it and find that this post is really amazing. buy assignment 2021
There are different types of such software available in the market so you can choose any one of them according to your requirements and need. Best Essay Writing Services UK
The individual touch that she provides for the new shades does much for Essie's ubiquity. Persistent course of observing new shades has kept Essie nail clean in the front line of the multitude of other comparative organizations. PhD Thesis Writing Services UK
Say It With Flowers Many people love flowers - to varying degrees at least - whether or not only as something special to some loved one. But there is however more to flowers than just a pretty gift. Many flowers are edible by humans and/or animals, or infused as a health drink. SPRING FLOWER GARDENING TIPS
These calculations are for reference purposes only. All figures are estimates only through tree value calculator and are not guaranteed as accurate. Always consult a professional financial

There are many different reasons why people should start growing garden vegetables - no matter how small. Let's examine some of these reasons so we'd know what to expect from this hobby.

थिद इस फुच्किंग कन्टट

The Assignment Helpline appreciates your blog; keep it up.We really enjoy reading your blog.This blog contains the aforementioned information on e-learning. financial management assignment
Agriculture is the main source of occupation and significant contributor in Indian economy in which rice and wheat are the major food grains of the world. Trade best quality rice variety in African and Gulf Country.
Writehw helps in the creation of the following: Website: https://writehw.com/ Phone: +1(857)399-2684 [email protected] -Brochures -Flyers -Business Cards -Infographics -Digital Posters -Logos -Invitation Cards
This blog is very nice as per our reading experience. you have deliver very good informative blogs and giving us good info. Perico Ripico Tours: Embark on an unforgettable adventure with breathtaking landscapes, expert guides, and unmatched hospitality. Immerse yourself in nature's wonders and create lifelong memories. A journey like no other! Best travel guide to Punta Cana
Wonderful articles, Your blog has offered with helpful data for working with. Every suggestion in the article is excellent. erp customization
Discover the the best websites for education that can help you with research statisticshelper
NMIMS solved assignment Buy NMIMS solved assignment Sep 2023. Get 100% plagiarism free NMIMS solved assignments sep 2023 with high quality content from us at cheap price Nmims Solved Assignment
If you have specific questions or inquiries about "suryaxetri" or the context it refers to, you can try reaching out to them directly through their website or contact information if available. Please note that the availability of reviews and information can vary widely depending on the specific aspect or context of "suryaxetri" you are interested in. When exploring websites, services, or individuals, it's essential to gather information from multiple sources and consider the relevance and credibility of the information you find. south jersey flsa lawyer
Visit their official website or social media profiles to find user reviews, testimonials, and information about their products, services, or offerings. If you have specific questions or need more information, contact them directly through their contact information. E-commerce platforms like Amazon and eBay can often provide customer reviews and ratings for their products. Check for online communities, forums, or social media groups related to the specific product or service you associate with "suryaxetri." Remember to specify the specific aspect or product you are looking for, as "suryaxetri" may encompass various offerings or topics. abogado de accidentes
You have provided a detailed account of agriculture in Nepal in this article. This article is very informative and useful for farmers. Thank you. NMIMS solved Assignment
A small business with four employees can use a dinstar fxs voip gateway to connect its analog phones to a VoIP PBX system.
Agriculture is a vital aspect of Nepal's economy and livelihoods, contributing significantly to the country's GDP and providing livelihoods, food security, and rural development. The majority of the population engages in farming activities, making agriculture a primary source of income for rural households. The sector encompasses a diverse range of crops, livestock, and agro-based industries, contributing to both domestic consumption and export earnings. Nepal's agrarian landscape offers employment opportunities for farmers, laborers, and agribusiness entrepreneurs, absorbing a large workforce, particularly in rural areas where alternative job opportunities are limited. Agriculture is the backbone of Nepal's food security, with the cultivation of various crops such as rice, wheat, maize, pulses, and vegetables ensuring a diverse and nutritious diet for the population. Promoting sustainable farming practices and technological advancements can enhance food production capabilities and mitigate risks associated with food shortages and price volatility. Investments in agricultural infrastructure, such as irrigation systems, roads, and storage facilities, improve farming efficiency and contribute to overall rural development. A thriving agricultural sector is essential for uplifting the standard of living in rural areas, as the majority of Nepal's population resides in these communities. Nepal's unique topography and climate make it vulnerable to environmental challenges, but sustainable agricultural practices are crucial for preserving natural resources, preventing soil erosion, and maintaining biodiversity. Encouraging eco-friendly farming techniques and promoting agroforestry can contribute to environmental conservation and resilience against climate change impacts. In conclusion, agriculture is not just a sector of the economy in Nepal; it is a way of life that sustains millions of people. Recognizing its importance and implementing policies that promote sustainable development is essential for the nation's prosperity, well-being, and preservation of its natural heritage. abogados divorcio arlington va
Agriculture is a vital component of Nepal's economy, providing livelihoods for the majority of the population and contributing a significant percentage of the country's GDP. It is also a primary source of employment, particularly in rural areas where farming activities are prevalent. Agriculture is crucial for food security, as the majority of the population relies on locally produced crops for sustenance. Rural development is directly linked to agriculture, with improved practices, infrastructure, and technology contributing to overall rural upliftment. Agricultural products like tea, rice, spices, and medicinal herbs contribute to Nepal's export earnings, providing an avenue for economic growth. Agriculture is deeply embedded in Nepal's culture and traditions, with many festivals and rituals linked to agricultural practices reflecting the agrarian way of life. Traditional agricultural practices contribute to biodiversity conservation by maintaining a variety of crops and livestock adapted to different regions. Agriculture is a source of income for many households, with improved practices, access to markets, and value addition to agricultural products increasing farmers' income. Sustainable agriculture is essential for the long-term well-being of the country, ensuring the conservation of natural resources, promoting resilience to climate change, and protecting the environment. abogado de accidentes de dui

Are you searching for online assignment help? if yes then connect Global assignment help and take 24/7 experts assistance for complete your assessment task . Assignmenttask.com is one stop solution for students. Place an order today.
Your blog contains excellent information, and I'm pleased to have found this post, which offers a wealth of useful insights. Thanks software development company in India
Email Subscription
Enter your email address:
Delivered by FeedBurner
Subscribe Our Youtube Channel
Total pageviews.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and conditions
Popular Posts

Copyright (c) 2021 Surya Xetri
- Projects & Operations
Nepal: Agriculture Commercialization and Trade

Sushila KC (center) from Lubhu VDC started vegetable farming through the Progressive Women's Group supported by PACT.
The Nepalese agricultural sector is dominated by the production of basic staple grains. About 82 percent of cultivated land is planted with cereal crops, but basic staple grains contribute only about 30 percent of agricultural Gross Domestic Product (DFP). Since the share of high-value crops in total cultivated area is still small, the desired process of agricultural diversification is struggling to be noticed at the aggregate level. The reliance on subsistence level agriculture hinders the growth and contributes less towards fighting poverty and food insecurity. Trade is subject to gluts and price crashes due to lack of information and services in the local market. Storage and transport facilities are poorly developed; and quality and value enhancement through grading and processing is not well conceptualized. In the absence of adequate marketing channels and opportunities, the incentive and financial capacity to invest in improved farm, value addition and processing techniques, water management or modern inputs is limited.
PACT aims to improve the competitiveness of smallholder farmers and agribusinesses within selected commodity value chains. The project supports the value chain actors by providing competitive matching grants based on eligible proposals from private entrepreneurs, farmer groups, cooperatives, traders and exporters, for technology support, agribusiness development, post-harvest facilities and market linkages. Matching grant contribution of 25-40 percent of the total agreed amount, depending upon the nature of application, has to come from grant recipient. Several steps of screening followed by detailed field verification take place before a grant is awarded. Results targets and milestones, which have to be achieved prior to the release of each installment, are set for each sub project selected. Overall, PACT’s support to the grant recipients is primarily cash contribution, with some technical support including for ensuring environmental and safeguards compliance, supervision and monitoring, as needed.
Furthermore, PACT has been supporting the rehabilitation of Kalimati fruits and vegetable market, and has also initiated the support for the construction of Fruit and Floriculture wholesale market in Kathmandu. Rehabilitation and reconstruction of several other fruits, vegetables, fisheries and livestock wholesale markets in Central, Eastern and Western development regions of Nepal has also been initiated. Through PACT's Agribusiness Innovation Center, the project connects emerging agro entrepreneurs and facilitates investments in agribusiness sector. This entails directly working with early stage enterprises and facilitation of their growth through a number of services like shared facilities and equipment, business development, technology, finance, mentoring and networking.
Additionally, the project aims to reduce existing obstacles to agriculture and food trade thereby increasing the ability of farmers and agribusiness to respond to sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) and food-quality standards to meet domestic and international market requirements.

PACT has been serving farmers and entrepreneurs in Nepal to build viable agribusinesses by helping them find new market opportunities.
Despite political instability leading to public strikes, transport closures and frequent changes in the leadership at the implementing agency, the project has been able to overcome the odds and demonstrate one of the most promising models of agricultural commercialization for Nepal.
In four years, PACT’s support has resulted in significant increase in volume, sales and productivity of the selected commodities value chains, majorly targeting high value fruits and vegetables, cereal crops, dairy and meat products. Procurement of laboratory equipment for the Department of Food Technology and Quality Control (DFTQC), Department of Livestock Services (DoLS) and Department of Agriculture (DoA), and the implementation of a food analysis training program, has improved the departments’ respective capacity to conduct monitoring and verification of quality standards. The project has generated high demand through advocacy to farmers and agribusinesses to increase investments and seek financing through the competitive grant scheme. As a result, there is demand for agribusiness support from all parts of the country, demand from the private sector to engage at a larger and more significant scale and demand for increased services for quality monitoring and certification for exports.
Impacts are also seen at a broader level, e.g. in the coffee sector where the national coffee producer association (NCPA) and 4 district coffee producer associations (DCPAs) from Lalitpur, Kavrepalanchowk, Kaski and Syangja received matching grants to expand coffee plantations, increase productivity, production and sales. The DCPA has seen a net increase in coffee area by 11 Ha within a year; certification of locally produced coffee by an Australian certifying agency (NASA) as organic coffee and a 60% increase in exports within a year. Similarly for cereal seed production the project reports an increase of production of over 150% due to investments which enabled local seed producers from the indigenous Tharu community to access technical advisory services and improved technology. The quality and standards support has resulted in an increased surveillance of the quality of food in Kathmandu and is directly responding to demands from consumer welfare organizations.
PACT has so far supported over 124 cooperatives, 65 farmer groups, 54 private entrepreneurs and 8 producer associations, reaching out to around 42,800 beneficiaries, of which over 42% are women.
Beneficiaries
30-year-old Sushila KC from Lubhu VDC of Lalitpur was a rural housewife who grew vegetables for her own family’s consumption. Now, Sushila belongs to the Pragatisheel Mahila Samuha (Progressive Womens’ Group), a group of women farmers who are supported by the local nursery with subsidized seeds and technical advice to increase vegetable production. Under PACT, 200 other farmers in the area are also participating in the program, planting tomatoes and other cash crops. They aim to sell vegetables worth 15 million rupees this year.
“I am grateful that I didn’t have to take out a loan to celebrate the festival of Dashain last year. I made a profit of 22,000 rupees in the months leading up to the festival, selling tomatoes and cauliflower.”
Bank Group Contribution
The PACT was approved by the IDA Board of Directors in June 04, 2009 with a commitment amount of $20 million. Later an additional financing of $40 million was approved in November 2012 that extended the project life to June 2018.
Moving Forward
PACT is moving forward to achieve its objective of engaging the organized/institutionalized small and medium scale farmers in profitable market-oriented agriculture activities. The project envisages a steady and commercialized agricultural future for Nepal with commodities eventually produced and marketed not only to cater the local markets but targeted towards export as well. To fulfil this strategic objective, the PACT is encouraging and supporting the local farmers and ensuring efficient and effective Sanitary and Phytosanitory services that have been a major hurdle in the past to market and trade Nepalese agricultural commodities. With its extended support to the private sector, value chain development and investments in agriculture, PACT aspires to shape a better future for commercialized agriculture in Nepal.

- Project Documents
- More Nepal Results
- World Bank in Nepal
- World Bank Nepal on Facebook
RELATED PROJECT
- Project for Agriculture Commercialization and Trade (PACT)
You have clicked on a link to a page that is not part of the beta version of the new worldbank.org. Before you leave, we’d love to get your feedback on your experience while you were here. Will you take two minutes to complete a brief survey that will help us to improve our website?
Feedback Survey
Thank you for agreeing to provide feedback on the new version of worldbank.org; your response will help us to improve our website.
Thank you for participating in this survey! Your feedback is very helpful to us as we work to improve the site functionality on worldbank.org.
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .

Home » Publications » Nepal » Commercialization of Agriculture in Nepal
Publications
Commercialization of agriculture in nepal, authors: samriddhi foundation, published date: august 2011.

Associated with low level of economic growth, Nepal is characterized as a country with a large portion of rural population, high poverty rate and subsistence agriculture. On various levels, all of these factors are interconnected. About eighty percent of the country’s population lives in rural areas and agriculture is their primary livelihood where the rural poverty rate is over three times that of urban areas, 35 percent compared to 10 percent (NARC, 2010). This poverty rate can be associated with the subsistence nature of the major means of livelihood in these areas, agriculture. Hence, the involvement of the majority of the population in agriculture is very important to analyze in context of social and economic development of Nepal. Agriculture, which employs two third of the country’s labor force and contributes to more than one third of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), is the main source of food, income and employment for the majority, especially for the rural population. Hence, agricultural sector is key in issues of economic growth, poverty alleviation, better living standard of the Nepalese people and overall Human Development.
In this context, Commercialization of agriculture has been proposed as a feasible option for economic growth and poverty alleviation. Since the formulation of the Fifth Five-Year Plan (1975–80), agriculture has been the highest priority because economic growth was dependent on both increasing the productivity of existing crops and diversifying the agricultural base for use as industrial inputs (Savada , M. A. , 1991). The adoption of the 20- year Agriculture Perspective Plan (APP) in 1997 reflects the emphasis the government has given on the agricultural sector and its commercialization.
However, despite all efforts to bring about revolutionary changes and growth in the agriculture sector of Nepal, the attempt has not fully translated into reality. Hence, from policy issues to institutional challenges to practical bottlenecks, this paper attempts to analyze various aspects of commercialization of Agriculture in Nepal.

Download “Commercialization of Agriculture in Nepal- English”
Samriddhi Foundation © 2006-2024. All rights reserved
krafted in Kathmandu by 13Colours.com

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The key outputs from this engagement are presented in a new book "Agricultural transformation in Nepal: Trends, prospects, and policy options". The book addresses some of the key strategic questions related to agriculture in Nepal and suggests policy measures to improve the delivery of critical inputs and services to smallholders.
2002/3, 2.52% of the total national budget was al-. located for agriculture which increased to 2.75% in. the year 2009/10 and 3.77% in 2014/15 ( MOF,2015 ). In the year 2020/21, the budget for the ...
This paper analyzes agricultural development in terms of policy and implementation in Nepal. More than two-thirds populations in Nepal reside in the rural area and most of them depend on agriculture. Subsistence form of agriculture is common in Nepal. Rural Area and agriculture are interrelated; like two parts of the same coin.
Nepal's agricultural transformation by 2030 and wishful thinking. The prime focus of the government at this stage is to develop competitiveness of smallholder farmers to enter into markets, generation of skilled labor in agriculture and to some extent establish effective value chains. A very low growth rate in the agricultural GDP and a ...
In the context of agriculture modernization, the country has brought various policy measures and programs before and after establishing democracy in 1990.Various policies and programs aimed, Nepal ...
Nepal, having an agro-based economy, improvement in agricultural productivity will provide an initial spur to industrialization (Gauchan, 2018). Nepal has an estimated 44.7% of agricultural ...
Chapter 1 Introduction Part I Macro-issues in Agriculture Chapter 2 Structural Transformation and Growth: Whither Agriculture in Nepal Chapter 3 The Role of Agriculture in Poverty Reduction in Nepal Chapter 4 Household Food Expenditure, Dietary Diversity, and Child Nutrition in Nepal [Publisher link] Chapter 5 Food Inflation in Nepal and Its Implications
This book addresses some key strategic questions related to agriculture in the context of major contemporary developments and emerging challenges in Nepal such as the changing role of agriculture with economic growth, structural transformation in reducing poverty, improving nutritional outcomes, and addressing the challenges of climate change.
and modernization of agriculture; and Planning for agricultural tools and an access to market with appropriate price for the produce. Since the first five-year plan implemented in 1956, modern agriculture development has been initiated for the country's economic ... Nepal Agriculture Perspective Plan, APP (1995-2015) was important in the context
which were having high potential for agricultural production. Fig 1: Map showing research districts and sites. (Paudel et al. 2012) This paper is drawn from twelve FGDs with women, men, elderly and the youth to draw insights on youth mobility, farmer's attraction to agriculture, feminization of agriculture and its
Agriculture contributed to 36.64% of the GDP which then decreased to 23% by 2022. Similarly, the employment in agriculture has decreased from 73% in 2005 to 62% in 2021. Although the sector still contributes to a significant proportion of the overall GDP and a lot of population is engaged in agriculture, the government has allocated only NPR 58 ...
Agriculture in Nepal: A Comprehensive Analysis. Agriculture is the backbone of Nepal's economy, contributing to more than one-third of the country's GDP and employing over 65% of the workforce. Nepal's geographical and climatic diversity has provided a unique opportunity for agricultural production, with the potential to sustainably ...
Modernization of Agriculture for a Prosperous Nepal" from 21st to 22nd Jestha 2077 (June 4-5, 2021) in Kathmandu. This conference is expected to help design future policies, plan and strategies of agricultural modernization for a Prosperous Nepal. Selected five thematic papers
Abstract. In this study, the policy provisions, including legislative and institutional arrangements, made for agricultural development in Nepal are evaluated. The gaps and constraints are identified and mechanisms to reduce the gaps and address constraints are proposed. This study is primarily based on the review of literatures accompanied ...
In FY2018/19, the country imported vegetables worth Rs 33.05 billion, an increase of Rs 4.40 billion from Rs 28.66 billion in FY2017/18. Meanwhile, Nepal also exports some 25,000 metric tonnes of vegetables every year. Poultry is among the few areas in agriculture in which Nepal fares relatively better in terms of productivity.
Agricultural Transformation in Nepal Trends, Prospects, and Policy Options Seed Sector Development in Nepal: Opportunities and Options for Improvement November 2022 DOI: 10.1007/978-981-32-9648
Drawing on studies by various researchers, it explores the positive outcomes of initiatives like the Agricultural Credit Guarantee Scheme (ACGS) and Prime Minister Agriculture Modernization Project (PMAMP), which have led to increased credit disbursements and adoption of modern agricultural practices.
Nepal is an agriculture country. About 66 percent Nepalese people are involved in agriculture as their occupation. The agriculture has contributed about 36% in the gross domestic product. It has an important role in the economic development of the country. It is the main source of foodstuffs.
The Project for Agriculture Commercialization and Trade (PACT) has been serving farmers and entrepreneurs in Nepal to build viable agribusinesses by helping them find new market opportunities, determine market demands and build strategic linkages to increase productivity and quality. Since 2009, the project has reached out to over 42,800 ...
65% population engaged in agriculture. Dominated by subsistence and small holder agriculture. GDP contribution of agriculture 27.59%. Trade deficit in agriculture $1.2 billion. Total agricultural land 28.8%. Arable land 15.1%. Irrigated area 65%. Year round 30-35%. Rice, wheat and maize based cropping pattern in dominant in hill and terai.
Agriculture in Nepal is the main stay of people. Population engaged in agriculture is 65.6% with. the cultivated agriculture land of 30, 91,000 ha and share of agriculture gross domestic product ...
Daily Updates of the Latest Projects & Documents. The development objective of the Agricultural Commercialization and Trade Project for Nepal is to improve the competitiveness of smallholder farmers and the agribusiness .
The adoption of the 20- year Agriculture Perspective Plan (APP) in 1997 reflects the emphasis the government has given on the agricultural sector and its commercialization. However, despite all efforts to bring about revolutionary changes and growth in the agriculture sector of Nepal, the attempt has not fully translated into reality.
President Ramchandra Poudel has outlined the government's comprehensive policies and programs for the fiscal year 2081/082. Presented at the Federal Parliament's joint meeting, these policies focus on transforming Nepal's agricultural sector to ensure self-sufficiency, modernization, and increased productivity. Achievements in the Current ...
Agricultural development strategy (ADS) -2015 have created a clear. roadmap for agricultural mechanization in Nepal. After the pro-. mulgation of the constitution of Nepal, agriculture development ...