ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.

Loading ...
Learning materials, instructional links.
- Photosynthesis (Google doc)
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis .The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O 2 ) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar). Herbivores then obtain this energy by eating plants, and carnivores obtain it by eating herbivores.
The process
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. The plant then releases the oxygen back into the air, and stores energy within the glucose molecules.
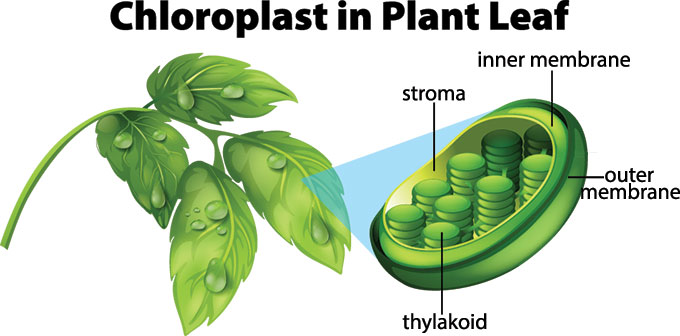
Chlorophyll
Inside the plant cell are small organelles called chloroplasts , which store the energy of sunlight. Within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast is a light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll , which is responsible for giving the plant its green color. During photosynthesis , chlorophyll absorbs energy from blue- and red-light waves, and reflects green-light waves, making the plant appear green.
Light-dependent Reactions vs. Light-independent Reactions
While there are many steps behind the process of photosynthesis, it can be broken down into two major stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reaction takes place within the thylakoid membrane and requires a steady stream of sunlight, hence the name light- dependent reaction. The chlorophyll absorbs energy from the light waves, which is converted into chemical energy in the form of the molecules ATP and NADPH . The light-independent stage, also known as the Calvin cycle , takes place in the stroma , the space between the thylakoid membranes and the chloroplast membranes, and does not require light, hence the name light- independent reaction. During this stage, energy from the ATP and NADPH molecules is used to assemble carbohydrate molecules, like glucose, from carbon dioxide.
C3 and C4 Photosynthesis
Not all forms of photosynthesis are created equal, however. There are different types of photosynthesis, including C3 photosynthesis and C4 photosynthesis. C3 photosynthesis is used by the majority of plants. It involves producing a three-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid during the Calvin Cycle, which goes on to become glucose. C4 photosynthesis, on the other hand, produces a four-carbon intermediate compound, which splits into carbon dioxide and a three-carbon compound during the Calvin Cycle. A benefit of C4 photosynthesis is that by producing higher levels of carbon, it allows plants to thrive in environments without much light or water. The National Geographic Society is making this content available under a Creative Commons CC-BY-NC-SA license . The License excludes the National Geographic Logo (meaning the words National Geographic + the Yellow Border Logo) and any images that are included as part of each content piece. For clarity the Logo and images may not be removed, altered, or changed in any way.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
March 20, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
It’s a wonderful world — and universe — out there.
Come explore with us!
Science News Explores
Explainer: how photosynthesis works.
Plants make sugar and oxygen with the power of water, carbon dioxide and sunlight

Green plants take in light from the sun and turn water and carbon dioxide into the oxygen we breathe and the sugars we eat.
Jeja/E+/Getty Images
Share this:
- Google Classroom
By Bethany Brookshire
October 28, 2020 at 6:30 am
Take a deep breath. Then thank a plant. If you eat fruit, vegetables, grains or potatoes, thank a plant too. Plants and algae provide us with the oxygen we need to survive, as well as the carbohydrates we use for energy. They do it all through photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process of creating sugar and oxygen from carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. It happens through a long series of chemical reactions. But it can be summarized like this: Carbon dioxide, water and light go in. Glucose, water and oxygen come out. (Glucose is a simple sugar.)
Photosynthesis can be split into two processes. The “photo” part refers to reactions triggered by light. “Synthesis” — the making of the sugar — is a separate process called the Calvin cycle.
Both processes happen inside a chloroplast. This is a specialized structure, or organelle, in a plant cell. The structure contains stacks of membranes called thylakoid membranes. That’s where the light reaction begins.
Let the light shine in
When light hits a plant’s leaves, it shines on chloroplasts and into their thylakoid membranes. Those membranes are filled with chlorophyll , a green pigment. This pigment absorbs light energy. Light travels as electromagnetic waves . The wavelength — distance between waves — determines energy level. Some of those wavelengths are visible to us as the colors we see . If a molecule, such as chlorophyll, has the right shape, it can absorb the energy from some wavelengths of light.
Chlorophyll can absorb light we see as blue and red. That’s why we see plants as green. Green is the wavelength plants reflect, not the color they absorb.
While light travels as a wave, it also can be a particle called a photon . Photons have no mass. They do, however, have a small amount of light energy.
When a photon of light from the sun bounces into a leaf, its energy excites a chlorophyll molecule. That photon starts a process that splits a molecule of water. The oxygen atom that splits off from the water instantly bonds with another, creating a molecule of oxygen, or O 2 . The chemical reaction also produces a molecule called ATP and another molecule called NADPH. Both of these allow a cell to store energy. The ATP and NADPH also will take part in the synthesis part of photosynthesis.
Notice that the light reaction makes no sugar. Instead, it supplies energy — stored in the ATP and NADPH — that gets plugged into the Calvin cycle. This is where sugar is made.
But the light reaction does produce something we use: oxygen. All the oxygen we breathe is the result of this step in photosynthesis, carried out by plants and algae (which are not plants ) the world over.
Give me some sugar
The next step takes the energy from the light reaction and applies it to a process called the Calvin cycle. The cycle is named for Melvin Calvin, the man who discovered it.
The Calvin cycle is sometimes also called the dark reaction because none of its steps require light. But it still happens during the day. That’s because it needs the energy produced by the light reaction that comes before it.
While the light reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes, the ATP and NADPH it produces end up in the stroma. This is the space inside the chloroplast but outside the thylakoid membranes.
The Calvin cycle has four major steps:
- carbon fixation : Here, the plant brings in CO 2 and attaches it to another carbon molecule, using rubisco. This is an enzyme , or chemical that makes reactions move faster. This step is so important that rubisco is the most common protein in a chloroplast — and on Earth. Rubisco attaches the carbon in CO 2 to a five-carbon molecule called ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (or RuBP). This creates a six-carbon molecule, which immediately splits into two chemicals, each with three carbons.
- reduction : The ATP and NADPH from the light reaction pop in and transform the two three-carbon molecules into two small sugar molecules. The sugar molecules are called G3P. That’s short for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GLIH- sur-AAL-duh-hide 3-FOS-fayt).
- carbohydrate formation : Some of that G3P leaves the cycle to be converted into bigger sugars such as glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ).
- regeneration : With more ATP from the continuing light reaction, leftover G3P picks up two more carbons to become RuBP. This RuBP pairs up with rubisco again. They are now ready to start the Calvin cycle again when the next molecule of CO 2 arrives.
At the end of photosynthesis, a plant ends up with glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), oxygen (O 2 ) and water (H 2 O). The glucose molecule goes on to bigger things. It can become part of a long-chain molecule, such as cellulose; that’s the chemical that makes up cell walls. Plants also can store the energy packed in a glucose molecule within larger starch molecules. They can even put the glucose into other sugars — such as fructose — to make a plant’s fruit sweet.
All of these molecules are carbohydrates — chemicals containing carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. (CarbOHydrate makes it easy to remember.) The plant uses the bonds in these chemicals to store energy. But we use the these chemicals too. Carbohydrates are an important part of the foods we eat, particularly grains, potatoes, fruits and vegetables.
More Stories from Science News Explores on Plants

To spy this palm’s blooms and fruits, start digging underground

Here’s why blueberries aren’t blue — but appear to be

Scientists Say: Marcescence

Pikmin ’s plant-animal mashups don’t exist — but sun-powered animals do

Scientists Say: Camouflage

Bits of trees can make and store energy for us to use

Bionic plants and electric algae may usher in a greener future

Some tree leaves are finding it too hot for photosynthesis
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Biology
Course: ap®︎/college biology > unit 3, photosynthesis.
- Intro to photosynthesis
- Breaking down photosynthesis stages
- Conceptual overview of light dependent reactions
- The light-dependent reactions
- The Calvin cycle
- Photosynthesis evolution
- Photosynthesis review
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
- Distance Learning
- Director's Circle
- Sustainability
- Smithsonian Science for the Classroom
- Smithsonian Science Stories
- STC Curriculum
- Smithsonian Science for Global Goals
- Explore Smithsonian
- Free Resources
- Smithsonian Science for Makerspaces
- Girls and Women in STEM
- Smithsonian Science for Computational Thinking
- Women in STEM eBook Series
- Space STEM Resources
- Space STEM Career Resources
- Smithsonian Science for NC and SC Classrooms
- Smithsonian Science Education Academies for Teachers
- Good Thinking!
- Quick Tips for Teachers
- English Learners in STEM
- Upcoming Events
- Action Planning Institute
- Building Awareness for Science Education
- Strategic Planning Institute
- Next Steps Institute
- STEM Diversity
- Zero Barriers in STEM
- Network for Emergent Socio-Scientific Thinking (NESST)
- Where We Are
- Smithsonian Science for Summer School (S4)
- Always Thinking Like A Scientist (ATLAS)
- STEM Literacy Project
- Success Stories
- France in Focus
- Smithsonian Science for Global Goals Research
- Smithsonian Youth STEM Exchange
- STEMvisions Blog
- What is Photosynthesis
When you get hungry, you grab a snack from your fridge or pantry. But what can plants do when they get hungry? You are probably aware that plants need sunlight, water, and a home (like soil) to grow, but where do they get their food? They make it themselves!
Plants are called autotrophs because they can use energy from light to synthesize, or make, their own food source. Many people believe they are “feeding” a plant when they put it in soil, water it, or place it outside in the Sun, but none of these things are considered food. Rather, plants use sunlight, water, and the gases in the air to make glucose, which is a form of sugar that plants need to survive. This process is called photosynthesis and is performed by all plants, algae, and even some microorganisms. To perform photosynthesis, plants need three things: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
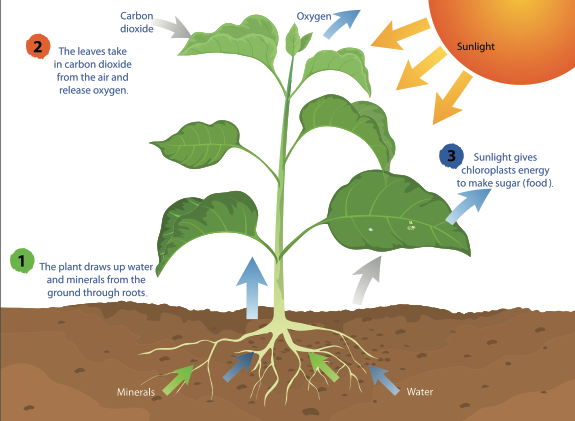
Just like you, plants need to take in gases in order to live. Animals take in gases through a process called respiration. During the respiration process, animals inhale all of the gases in the atmosphere, but the only gas that is retained and not immediately exhaled is oxygen. Plants, however, take in and use carbon dioxide gas for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide enters through tiny holes in a plant’s leaves, flowers, branches, stems, and roots. Plants also require water to make their food. Depending on the environment, a plant’s access to water will vary. For example, desert plants, like a cactus, have less available water than a lilypad in a pond, but every photosynthetic organism has some sort of adaptation, or special structure, designed to collect water. For most plants, roots are responsible for absorbing water.
The last requirement for photosynthesis is an important one because it provides the energy to make sugar. How does a plant take carbon dioxide and water molecules and make a food molecule? The Sun! The energy from light causes a chemical reaction that breaks down the molecules of carbon dioxide and water and reorganizes them to make the sugar (glucose) and oxygen gas. After the sugar is produced, it is then broken down by the mitochondria into energy that can be used for growth and repair. The oxygen that is produced is released from the same tiny holes through which the carbon dioxide entered. Even the oxygen that is released serves another purpose. Other organisms, such as animals, use oxygen to aid in their survival.
If we were to write a formula for photosynthesis, it would look like this:
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + Light energy → C 6 H 12 O 6 (sugar) + 6O 2
The whole process of photosynthesis is a transfer of energy from the Sun to a plant. In each sugar molecule created, there is a little bit of the energy from the Sun, which the plant can either use or store for later.
Imagine a pea plant. If that pea plant is forming new pods, it requires a large amount of sugar energy to grow larger. This is similar to how you eat food to grow taller and stronger. But rather than going to the store and buying groceries, the pea plant will use sunlight to obtain the energy to build sugar. When the pea pods are fully grown, the plant may no longer need as much sugar and will store it in its cells. A hungry rabbit comes along and decides to eat some of the plant, which provides the energy that allows the rabbit to hop back to its home. Where did the rabbit’s energy come from? Consider the process of photosynthesis. With the help of carbon dioxide and water, the pea pod used the energy from sunlight to construct the sugar molecules. When the rabbit ate the pea pod, it indirectly received energy from sunlight, which was stored in the sugar molecules in the plant.

Humans, other animals, fungi, and some microorganisms cannot make food in their own bodies like autotrophs, but they still rely on photosynthesis. Through the transfer of energy from the Sun to plants, plants build sugars that humans consume to drive our daily activities. Even when we eat things like chicken or fish, we are transferring energy from the Sun into our bodies because, at some point, one organism consumed a photosynthetic organism (e.g., the fish ate algae). So the next time you grab a snack to replenish your energy, thank the Sun for it!
This is an excerpt from the Structure and Function unit of our curriculum product line, Science and Technology Concepts TM (STC). Please visit our publisher, Carolina Biological , to learn more.
[BONUS FOR TEACHERS] Watch "Photosynthesis: Blinded by the Light" to explore student misconceptions about matter and energy in photosynthesis and strategies for eliciting student ideas to address or build on them.
Related Tags
View the discussion thread.
- Behind the Scenes
Popular Posts
- It’s All About the Tilt: Seasons Misconceptions Debunked
- Are All Snowflakes Really Different? The Science of Winter
- What Are Clouds?
- What is the Winter Solstice?
Featured Authors
- Brian Mandell, PhD
- Ashley Deese
- Kate Echevarria
- Katya Vines, PhD
- Jean Flanagan
- October (1)
- November (1)
- December (2)
- January (1)
- February (2)
- September (3)
- October (7)
- November (4)
- December (3)
- January (4)
- February (4)
- September (4)
- October (2)
- November (2)
- December (1)
- January (3)
- September (6)
- October (3)
- January (2)
- October (6)
- November (5)
- December (4)
- February (6)
- September (2)
- February (1)
- December (5)
- September (1)
- October (5)
- February (5)
- Terms of Use
- Google Plus
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Photosynthesis Process
The process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process of capturing light energy and transforming it into chemical energy. Green plants and several other organisms use light energy and convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. In this process, oxygen is produced as a by-product. This process can be seen in green plants and photosynthetic bacteria. They use electromagnetic radiation and convert it into chemical energy. With the help of water and sunlight, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and turn it into oxygen and carbohydrates.
The process provides not only energy needed but also helps in forming biomolecules. This reaction is an oxidation-reduction reaction that uses sunlight and nitrogen available in the atmosphere. It is the basic element in the food cycle. All the other organisms derive their energy from green plants and other photosynthetic bacteria. Hence, these plants are called autotrophs as they prepare their own food with the help of naturally available elements. One of the essential requirements for this process is a pigment called “chlorophyll”. This pigment is present in green plants and some bacteria. It helps in tapping sunlight and starting the entire process.
This process of converting light energy to other forms differs in plants and other bacteria. In the case of plants, water is used to form energy in the form of glucose and oxygen. On the other hand, in the case of bacteria, hydrogen sulphide replaces the water along with carbon dioxide to release carbohydrates, sulfur, and water molecules. Some of the photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll, phycobilins, bacteriorhodopsin, carotenoids. Chlorophyll is present in most green plants and helps in receiving sunlight and converting it into energy and glucose. They have single and double bonds alternatively, this makes them effective photoreceptors. Bacteriorhodopsin is another photosynthetic pigment that is generally present in Halobacteria. Phycobilins are present in cyanobacteria and red algae .
The photosynthesis process step by step conducts these reactions and maintains the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. However, photosynthesis in plant leaves usually occurs in two ways. These are light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions or dark reactions.
Light-Dependant Reaction
This process happens in the thylakoid membrane and needs a constant supply of photons or light energy. Chlorophylls use this energy and produce ATP and NADPH. Water molecules are transformed into oxygen through this process.
Light-Independent Reaction
This reaction happens in the stroma and can take place in the absence of light. It takes up ATP and NADPH produced from the light reaction to break down carbon dioxide. This process helps in forming three types of carbon sugars that create glucose.
Let’s understand the photosynthesis process step by step!
Step by Step Procedure of Photosynthesis
Fig: Process of photosynthesis
Plant leaves absorb the photons from sunlight that excite chlorophyll and activate electrons. In the first step, the water absorbed by plant roots is split into oxygen and hydrogen ions.
Then the excited electrons from ATP and NADPH. This process happens through the electron chain. Likewise, in this process, oxygen is released into the atmosphere through leaves.
In the next step, the energy from the light reaction transforms carbon dioxide into glucose. This whole process takes place in several stages. The series of reactions start with 3-Ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) and ends with the same molecule forming glucose.
The Rubisco enzyme is an essential component of this Calvin Cycle that initiates all the reactions.
All the significant reactions of the photosynthesis process generally take place during the daytime in the chloroplasts of leaves.
Following is the fundamental equation of photosynthesis
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O (+ light energy) → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2
This is the overall overview of how the photosynthesis process step by step takes place.
Factors that Affect Photosynthesis
Following is the list of factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Temperature and Light Intensity
Generally, with higher light and temperature intensity, the rate of photosynthesis increases. However, after a specific intensity of light, this rate saturates. It solely depends on the growing condition and species of the plants.
Water
The rate of photosynthesis depends on a steady water supply. A minimal amount of water is required to conduct the reactions. The maximum amount of water transpires through the stomata of leaves.
In arid areas, therefore, the opening and closing of stomata are limited. This allows reserving the water supply and overall temperature of leaves.
Carbon Dioxide
The concentration of carbon dioxide influences mainly the dark reactions of photosynthesis. Hence, this rate increases with the increased supply of carbon dioxide.
A few minerals like potassium, iron, magnesium, phosphate, etc. are essential for plant growth. They also hasten the rate of photosynthesis of plants.
Apart from that, a few other factors like environment , species, etc. affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Introduce energy and fixed carbon into the ecosystem.
Reduce a large quantity of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Produces oxygen that sustains all life.
Photosynthesis happens in the autotrophs, so they indirectly introduce energy into the ecosystem and that energy travels to other trophic levels
It is very important also for the heterotrophs which are dependent on autotrophs for energy.
It helps to maintain a healthy relationship between animals, plants, and humans making them mutually dependent.
Sunlight becomes the primary source of energy in the world and facilitates photosynthesis.
Pop Quiz
Photosynthesis is a/an _______________ process.
_______________ colour of light is responsible for photosynthesis in bacteria.
Which metal is present in both chlorophyll “a” and “b”?
Manganese
Chlorophyll is the structural unit of photosynthesis. True/False.
Answers: 1- Anabolic, 2-Red, 3-a), 4- False.
For more information regarding the photosynthesis process step by step, go through the course materials available on our website! You can also join live online classes via Vedantu’s app. Get a proper explanation of the concepts of photosynthesis from the top experts and develop your knowledge foundation properly. Find excellent study material regarding other concepts of biology and become more confident in this subject.
FAQs on Photosynthesis Process
1. What is the Process of Photosynthesis in Plants?
Photosynthesis is the process using which green plants and some other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy. It is a chemical process that happens in plants in general and some kinds of microorganisms. It absorbs sunlight and electromagnetic energy from the surroundings and converts them into chemical energy. This chemical energy produced from photosynthesis is stored in plants on the roots, fruits, etc. Humans and other animals consume these stored materials and finish the loop of the food chain.
This process is the base of the entire food chain. The energy produced here is transferred to the trophic levels above. At the basic level, photosynthesis takes place in the cell organelles known as chloroplasts. It has a pigment called chlorophyll, which gives green colour to the leaves.
2. What Does Photosynthesis Produce?
During photosynthesis, green plants capture light energy and use it in converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. It is a chemical process that generally takes place in plants and sometimes in a few microorganisms like cyanobacteria, red algae. This process uses the natural elements available in the surroundings like sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrates, oxygen, and glucose. This glucose and carbohydrates are stored in different parts of the plants like roots, fruits, etc. Some of the stored carbohydrates are used by the plants to live and grow. The excess energy is converted to storage and they are consumed by other organisms. Heterotrophs consume food from green plants.
3. Why is Photosynthesis Important?
The most crucial aspect of photosynthesis is that it is the primary source of oxygen and food that makes life possible on the earth. The food produced and stored in the plants is the foundation of the food chain of an ecosystem.
4. What happens when photosynthesis does not occur?
Photosynthesis is a process that converts light and electromagnetic energy into chemical energy. It is the basic reaction on which the entire world depends. Autotrophs generally perform the photosynthesis process. They are the living organisms that make their own food with the natural elements surrounding them. For example, plants and certain microorganisms perform photosynthesis. This further leads to the energy transfer in the next trophic levels. Heterotrophs depend upon autotrophs to meet their energy needs. So if the process of photosynthesis does not take place, the energy cycle will break. Plants can produce any glucose neither for themselves nor for others. We can live only for some days with already existing food and resources. So it is very important to protect all the natural elements involved in this process of photosynthesis.
5. What is the role played by chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll is a pigment present in green plants in the chloroplast. They help in converting light energy to chemical energy and glucose. Chlorophyll uses carbon dioxide, water, and light energy to make carbohydrates. This pigment is present in green plants, cyanobacteria, and some algae. It has magnesium ions closed in a large ring made up of chlorine. Apart from this pigment, many other elements like water, rhizobium bacteria help in the process of photosynthesis. For example, the rhizobium bacteria helps in photosynthetic activity by growing in anaerobic conditions and facilitating the process. It helps in fixing nitrogen from the atmosphere. This will avoid the usage of artificial and synthetic chemical fertilizers and improve soil fertility naturally.
Biology • Class 11

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


Photosynthesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 35968

- Chung (Peter) Chieh
- University of Waterloo
Discussion Questions
How is light energy harvested in photosynthesis and what is the reaction center?
Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy ( E = h v ) to chemical energy and storing it in the chemical bonds of sugar-like molecules. This process occurs in plants and some algae (Kingdom Protista). Plants need only light energy, CO 2 , and H 2 O to make sugar. The process of photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts (chloro = green; plasti = formed, molded), specifically using chlorophyll (phyll = leaf), the green pigment involved in photosynthesis.
As early as 1640, people have demonstrated that photosynthesis was a means of converting carbon dioxide in the air into plant material. Thus, photosynthesis has been studied by many scientists, and there are many sites related to photosynthesis. Some of these sites describe their recent recent research activities, whereas others are for educational purposes. Even books and journals are introduced in this link.
The photosynthesis is a very complicated process, and we can only give an introduction here. Photosynthesis reduces carbon dioxide into carbohydrates,
\[\ce{6 CO2 + 12 H2O + hv -> C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O}\]
Thus, both electrons and energy are required. The electrons come from water molecules, and the energy is first absorbed by pigments known as chlorophylls and carotenoids. The former absorb blue (wavelength 430 nm) and red (wavelength 670 nm) light and the later absorbe blue-green light (wavelenghts between 400 and 500 nm). Green and yellow light are not absorbed. Reflection of these types of light makes plants appear green.
There are many varieties of pigments. They are bonded to proteins which provide pigment molecules with the appropriate orientation and position with respect to each other. After absorption by pigment, light energy is transferred to chlorophylls that are bonded to special proteins. Pigments and protein involved with this actual primary electron transfer event together are called the reaction center . A large number of pigment molecules (100-5000), collectively referred to as antenna , "harvest" light and transfer the light energy to the same reaction center. The purpose is to maintain a high rate of electron transfer in the reaction center, even at lower light intensities.
What are produced and consumed in plants respiration?
Photosynthesis is responsible for the production of oxygen and carbohydrates in plants. All living organisms respire, and so do plants. In the respiration, oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide is produced.
respiration takes place all the time, but respiration is masked by higher rate of photosynthesis when the light intensities is high.
What is the Calvin-Benson cycle?
Working with the green algae chlorella, Melvin Calvin and Andy Benson, at the University of California at Berkeley, elucidated the following pathway for the conversion of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates:
Contributors and Attributions
Chung (Peter) Chieh (Professor Emeritus, Chemistry @ University of Waterloo)
The Balanced Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Overall Chemical Reaction
Frank Krahmer / Getty Images
- Biochemistry
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Photosynthesis is the process in plants and certain other organisms that uses the energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) and oxygen.
Here is the balanced equation for the overall reaction:
6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2
Where: CO 2 = carbon dioxide H 2 O = water light is required C 6 H 12 O 6 = glucose O 2 = oxygen
Explanation
In words, the equation may be stated as: Six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules react to produce one glucose molecule and six oxygen molecules .
The reaction requires energy in the form of light to overcome the activation energy needed for the reaction to proceed. Carbon dioxide and water don't spontaneously convert into glucose and oxygen .
- What Are the Products of Photosynthesis?
- Chlorophyll Definition and Role in Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis Vocabulary Terms and Definitions
- Examples of Chemical Reactions in Everyday Life
- Calvin Cycle Steps and Diagram
- Examples of 10 Balanced Chemical Equations
- Photosynthesis Basics - Study Guide
- What Is the Primary Function of the Calvin Cycle?
- The Photosynthesis Formula: Turning Sunlight into Energy
- Chemosynthesis Definition and Examples
- Synthesis Reaction Definition and Examples
- Equation for the Reaction Between Baking Soda and Vinegar
- Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis
- Understanding Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
- How to Balance Chemical Equations
- Combustion Reactions in Chemistry
- Photosynthesis Equation, Process and Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Equation
Photosynthesis is the process through which plants, some bacteria, and some protistans use the energy from sunlight to produce glucose . This process also produces carbon dioxide and water as by-products. It releases adenosine triphosphate i.e. ATP by cellular respiration. Also, it forms oxygen. In this topic, we will explain the photosynthesis equation will be explained.

Photosynthesis
Plants generally receive credit for being the base of food chains. Plant-like protists and one-celled organisms containing chloroplasts, hence they make their own contribution to the food chain and the conversion of carbon dioxide to oxygen.
They all perform photosynthesis. The word photosynthesis literally breaks down into photos, which means light and synthesis means composition.
So, photosynthesis means to put together using light. In addition, plants, algae and plant-like protists use sunlight to put together carbon dioxide and water to make sugar.
The Process of Photosynthesis
This process uses the energy of the sun to make the reaction of carbon dioxide and water to form glucose. Carbon dioxide enters the plants through tiny pores in the bottoms of leaves.
Water enters by various means, usually roots, but also by osmosis. The energy of the sun, absorbed by the green chemical chlorophyll, fuels the chemical reaction.
Then it combines the carbon dioxide molecules with the water molecules to form glucose. The glucose can be stored in fruits, roots, and stems of plants.
It can be released through the reverse process of respiration , where oxygen is used to break down the glucose into carbon dioxide and water, and releasing the stored energy.
Stages of Photosynthesis
When chlorophyll absorbs light energy, an electron gains energy and is then excited. The excited electron is transferred to another molecule i.e. acceptor.
The chlorophyll molecule is oxidized further and has a positive charge. Photoactivation of chlorophyll, as a result, split the water molecules and transfer the energy to ATP.
Photosynthesis comprises of two stages. These are a light-dependent reaction and light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reaction uses energy captured from sunlight by the chloroplasts in plant leaves.
It then produces a supply of electrons for the light-independent reactions. The light-independent reactions use energy from the supply of electrons to reduce carbon dioxide and finally produce glucose.
Photosynthesis is a process in which green plants use light energy, carbon dioxide, and water. And it produces glucose, oxygen, and water. Therefore it converts light energy into chemical energy i.e. the glucose for use in the plants.
The reaction for photosynthesis is as given as follows:
\(6CO_{2} + 12H_{2}O \overset{Light}{\rightarrow} 6O_{2} + C_{6}H_{12}O_{6} + 6H_{2}O\)
The reaction is often reduced to:
\(6CO_{2} + 6H_{2}O \overset{Light}{\rightarrow} 6O_{2} + C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}\)
Now, we can break down each piece of the photosynthesis equation.
On the reactants side, we have:
6CO 2 has six molecules of carbon dioxide
12H 2 O has twelve molecules of water
Light Energy has Light from the sun
On the products side, we have:
C 6 H 12 O 6 is glucose
6O 2 is six molecules of oxygen
6H 2 O is six molecules of water
The plant uses Glucose as energy. It releases oxygen and water back into the atmosphere to help other living things. During photosynthesis, plants use light energy to combine carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose, oxygen, and water.
Photosynthesis is very important because it provides plants with the energy they need to survive. It also provides needed oxygen and water back into the atmosphere.
Products of Photosynthesis
Through cellular respiration, it converts the glucose into adenosine triphosphate i.e. ATP. In addition to glucose, this reaction also produces oxygen that the plants release into the atmosphere.
Solved Question for You
Q: Why Photosynthesis is important?
Ans: Photosynthesis is plants taking in water, carbon dioxide, and light to make glucose and oxygen. This is important because each and every living thing needs oxygen to survive. All producers make oxygen and glucose for the secondary consumers and then the carnivores eat animals that eat the plants.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Tertiary Consumer – Definition, Functions and Examples
- Tundra Region – Climate, Plants, Animals, Facts
- Temperate Grassland – Definition, Features, Facts
- What is Balanced Ecosystem?
- Trophic Levels – Definition and Examples
- Soil as a Detritus-Based Ecosystem
- Algal Bloom – Causes and Effects
- Aquatic Ecosystem – Definition and its Types
- Types of Grassland Ecosystems
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.23: Photosynthesis Summary
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 6469
Forty Wall Street, a Trump-owned building, stands in downtown Manhattan. Former President Trump says he can't secure a bond to appeal the $454 million penalty in his civil fraud case. But New York Attorney General Letitia James says she is prepared to seize the former president's assets, including the building at 40 Wall Street, if he is unable to pay. Spencer Platt/Getty Images hide caption
Forty Wall Street, a Trump-owned building, stands in downtown Manhattan. Former President Trump says he can't secure a bond to appeal the $454 million penalty in his civil fraud case. But New York Attorney General Letitia James says she is prepared to seize the former president's assets, including the building at 40 Wall Street, if he is unable to pay.
Former President Donald Trump needs to arrange a $454 million bond to comply with a New York court ruling in less than a week, but the presumptive Republican presidential nominee says he can't find a company to put up the bond.
Trump's lawyers are asking an appeals court to stay the judgment, but the clock is ticking.
How did Trump come to owe the state of New York some $454 million?

Trump ordered to pay over $355M for fraudulent business practices in New York
This is the ruling that Judge Arthur Engoron issued last month , after finding that Donald, Eric and Donald Trump Jr., along with Trump Organization employees, engaged in a decade-long conspiracy to lie about the value of their assets.
In New York, if you make money by persistently committing fraud, you owe the ill-gotten portion back to the state. In this case, Judge Engoron determined that Donald Trump made over $350 million more than he should have if he'd been honest and when you add in interest, you get to $454 million.
Why does Trump have to come up with the money now?
Trump doesn't have to actually pay that money now, but he has to get a company to make a guarantee to the court that they will pay the money if he loses his appeal. That's the bond part.
But to get a bond, you have to put up assets, and in a court filing Monday Trump lawyers said they'd approached 30 companies but that getting a bond was a "practical impossibility," because they'd need a billion dollars in cash, which they don't have.

Trump unable to post $450M bond in New York fraud case, his lawyers say
They submitted an affidavit from an insurance executive who had testified at trial, and whom the trial judge had already discredited.
Trump says he's a billionaire. Why can't he just come up with the money himself?
Trump said during a deposition for this case, taken about a year ago, that he had plenty of cash. He said, "I believe we have substantially in excess of $400 million in cash ." And, he added, it's "going up very substantially every month."
News organizations have estimated that Trump actually has about $300 million in liquid assets — but he already had to set aside $100 million or so to put up a bond to pay the verdict in the E. Jean Carroll civil case . The rest of his money is largely tied up in buildings and golf courses, and while he could sell a property, that can't happen right away. Trump said Tuesday that would be a "fire sale," though he said many times during the trial he could always find a buyer to pay top dollar.

Jury orders Trump to pay $83 million for defaming columnist E. Jean Carroll
While Trump's political action committees have spent millions of dollars on his legal fees, they're unlikely to be of help to him in this case because of campaign finance laws .
Trump has accused the judge in the case of trying to take away his rights, posting on social media that any assets he may be forced to sell would be gone even if he ultimately wins his appeal.
That's a concern that any defendant could raise, whether they're liable for $450 or $450 million, says Adam Pollock, a former assistant attorney general in New York.
"But if you want to bond the appeal — stop enforcement of the judgment — you have to put up the full amount," he told Morning Edition . "That's what the law says. And that's a policy decision that Albany has made."
The deadline is Monday. What does Trump do if the appeals court doesn't rule his way?
He can appeal to New York's highest court and ask that court to stay the judgment. If they don't, he can ask a benefactor or he could try and stall some more until he comes into money from the upcoming sale of his social media company, or he could — though it has many disadvantages — declare bankruptcy.
But New York Attorney General Letitia James has been clear: If Trump doesn't pay, she will move to seize his assets.
"If he does not have funds to pay off the judgment, then we will seek judgment enforcement mechanisms in court," she said. "And we will ask the judge to seize his assets."
Trump's noncash assets run to $3 billion, Forbes estimates, so there's plenty of value there. The law limits the AG to seizing properties that were a part of the case, but there's about two dozen of those, everything from the Doral Golf Club to 40 Wall Street to Trump Tower. She's not limited to New York properties, though there are extra steps if she chooses to go out of state.
She could, in theory, send a sheriff or a marshal to enforce the judgment, and that brings on another legal process with many more opportunities for delay.
Can Trump be forced to pay up?
James can begin enforcement of the judgment immediately after the 30-day grace period expires next week, says Pollock. And there are several devices she can use to try to get him to pay.
For one, he says, she could serve Trump a restraining notice that would restrict his spending in other areas until he pays his bond.
"The restraining notice would say: 'Don't spend money, don't fill up your jet at the pump, until you pay the state of New York, or you'll be held in contempt of court,' " Pollock says. "And my impression is that ... Engoran, the judge here in New York, would be quick to hold him in contempt of court."
He says it's theoretically possible that James' could consider settling, especially if Trump were to write a check for something like $250 million. But short of that, he doesn't see any reason for her to proactively lower his bond, especially since she has the tools to go into banks and drain his accounts.
"The entire trial was effectively a roadmap to his financial assets," Pollock adds. "She can now send out a sheriff or a marshal of the city of New York to go walk into a financial institution holding what's known as an execution and empty his bank account short of $3,000, which is the statutory floor."
Pollock acknowledges that Trump has said he doesn't have $450 million in cash. But if he wants to stave off enforcement, "he needs to find a way to raise it."
- Letitia James
- court ruling
- Donald Trump
- Chemistry Formulas
Photosynthesis Formula
Photosynthesis is the process of converting the energy in which solar energy is converted into the form of light which is used in the production of carbohydrate molecules.
Solved Examples
Here are a few solved problems on Photosynthesis .
Problem 1: Write the complete balanced reaction for Photosynthesis both in symbol and word equation.
The balanced reaction for photosynthesis in word form is
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + oxygen.
The balanced reaction for photosynthesis in symbol form is
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
This information was really helpful to me thanks
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
photosynthesis, the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is captured and used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds.. It would be impossible to overestimate the importance of photosynthesis in the maintenance of life on Earth.
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process by which, phototrophic organisms including plants, uses sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to synthesize organic compounds. Login. Study Materials. ... Write down the Photosynthesis Equation. 6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2. Register at BYJU'S Biology to explore more photosynthesis notes or notes for ...
Photosynthesis (Google doc) Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis .The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O 2) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar). Herbivores then obtain this energy by eating plants, and carnivores obtain it by eating ...
Photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars. In a process driven by light energy, glucose molecules (or other sugars) are constructed from water and carbon dioxide, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. The glucose molecules provide organisms with two crucial resources: energy and ...
Photosynthesis is the process of creating sugar and oxygen from carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. It happens through a long series of chemical reactions. But it can be summarized like this: Carbon dioxide, water and light go in. Glucose, water and oxygen come out. (Glucose is a simple sugar.) Photosynthesis can be split into two processes.
The chemical equation for the entire process can be seen below. Photosynthesis Equation. 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + Light -> C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 + 6 H 2 O. Above is the overall reaction for photosynthesis. Using the energy from light and the hydrogens and electrons from water, the plant combines the carbons found in carbon dioxide into more complex ...
A diagram represents the process of photosynthesis. The top left corner of the diagram shows the sun. Light waves labeled sunlight point from the sun to a green plant in the center of the diagram. A circle labeled sugars magnifies a point on a leaf. The magnified circle shows two line segments with hexagons spaced along them, which represent ...
In general outline, photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration: while photosynthesis is a process of reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates, cellular respiration is the oxidation of carbohydrates or other nutrients to carbon dioxide. Nutrients used in cellular respiration include carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids.
Photosynthesis involves two stages: the light-dependent reactions, which require sunlight and water to produce oxygen, ATP, and NADPH, and the light-independent reactions (or "dark reactions"), which use the products of the light-dependent reactions along with carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrates. Created by Sal Khan.
photosynthesis: the process by which plants and other photoautotrophs generate carbohydrates and oxygen from carbon dioxide, water, and light energy in chloroplasts. photoautotroph: an organism that can synthesize its own food by using light as a source of energy. chemoautotroph: a simple organism, such as a protozoan, that derives its energy ...
The process of photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoids of chloroplasts. The process of cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria. The reactants of photosynthesis are light energy, carbon dioxide, and water. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. The reactants of cellular respiration are glucose and oxygen.
Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert light energy from the sun to chemical energy. During the process of photosynthesis, plants capture light energy and use it to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and glucose. Lets have a look at the process of photosynthesis and also explore its importance.
If we were to write a formula for photosynthesis, it would look like this: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + Light energy → C 6 H 12 O 6 (sugar) + 6O 2 The whole process of photosynthesis is a transfer of energy from the Sun to a plant. In each sugar molecule created, there is a little bit of the energy from the Sun, which the plant can either use or store ...
All the significant reactions of the photosynthesis process generally take place during the daytime in the chloroplasts of leaves. Following is the fundamental equation of photosynthesis. 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) → C6H12O6 + 6O2. This is the overall overview of how the photosynthesis process step by step takes place.
Photosynthesis is really important for the plant because it provides the plant with food: some of the glucose is used immediately, to give the plant energy in the process of respiration. some of ...
Process of Photosynthesis Step by Step. The sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll in the leaves of the plants. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through structures called the stomata, which are usually found on the underside of the leaves. Water is absorbed through the roots of the plant. The light-dependent reaction occurs during the day.
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy (E = h v) to chemical energy and storing it in the chemical bonds of sugar-like molecules.This process occurs in plants and some algae (Kingdom Protista). Plants need only light energy, CO 2, and H 2 O to make sugar. The process of photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts (chloro = green; plasti = formed, molded ...
photosynthesis, Process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light into chemical energy.In green plants, light energy is captured by chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of the leaves and used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds (simple and complex sugars) that are the basis of both plant and animal life.
Learn how to write the overall chemical reaction for photosynthesis and explain the chemical process by which plants form glucose and oxygen. ... Photosynthesis is the process in plants and certain other organisms that uses the energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) and oxygen.
Photosynthesis Equation. Photosynthesis is a process in which green plants use light energy, carbon dioxide, and water. And it produces glucose, oxygen, and water. Therefore it converts light energy into chemical energy i.e. the glucose for use in the plants. The reaction for photosynthesis is as given as follows: 6CO2 + 12H2O →Light 6O2 ...
The process of photosynthesis is commonly written as: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2.This means that the reactants, six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules, are converted by light energy captured by chlorophyll (implied by the arrow) into a sugar molecule and six oxygen molecules, the products. The sugar is used by the organism, and the oxygen is released as a by-product.
What is photosynthesis? The process of using the energy in sunlight to make food (glucose). But of course it is much more complex than that simple statement. Photosynthesis is a multistep biochemical pathway that uses the energy in sunlight to fix carbon dioxide, transferring the energy into carbohydrates, and releasing oxygen in the process.
Forty Wall Street, a Trump-owned building, stands in downtown Manhattan. Former President Trump says he can't secure a bond to appeal the $454 million penalty in his civil fraud case.
Men's NCAA Tournament 2024: Power Ranking All 68 Teams
Photosynthesis is the process of converting the energy in which solar energy is converted into the form of light which is used in the production of carbohydrate molecules. Solved Examples. Here are a few solved problems on Photosynthesis. Problem 1: Write the complete balanced reaction for Photosynthesis both in symbol and word equation. Sol ...