/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="short research statement sample"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Research statement, what is a research statement.
The research statement (or statement of research interests) is a common component of academic job applications. It is a summary of your research accomplishments, current work, and future direction and potential of your work.
The statement can discuss specific issues such as:
- funding history and potential
- requirements for laboratory equipment and space and other resources
- potential research and industrial collaborations
- how your research contributes to your field
- future direction of your research
The research statement should be technical, but should be intelligible to all members of the department, including those outside your subdiscipline. So keep the “big picture” in mind. The strongest research statements present a readable, compelling, and realistic research agenda that fits well with the needs, facilities, and goals of the department.
Research statements can be weakened by:
- overly ambitious proposals
- lack of clear direction
- lack of big-picture focus
- inadequate attention to the needs and facilities of the department or position

Why a Research Statement?
- It conveys to search committees the pieces of your professional identity and charts the course of your scholarly journey.
- It communicates a sense that your research will follow logically from what you have done and that it will be different, important, and innovative.
- It gives a context for your research interests—Why does your research matter? The so what?
- It combines your achievements and current work with the proposal for upcoming research.
- areas of specialty and expertise
- potential to get funding
- academic strengths and abilities
- compatibility with the department or school
- ability to think and communicate like a serious scholar and/or scientist
Formatting of Research Statements
The goal of the research statement is to introduce yourself to a search committee, which will probably contain scientists both in and outside your field, and get them excited about your research. To encourage people to read it:
- make it one or two pages, three at most
- use informative section headings and subheadings
- use bullets
- use an easily readable font size
- make the margins a reasonable size
Organization of Research Statements
Think of the overarching theme guiding your main research subject area. Write an essay that lays out:
- The main theme(s) and why it is important and what specific skills you use to attack the problem.
- A few specific examples of problems you have already solved with success to build credibility and inform people outside your field about what you do.
- A discussion of the future direction of your research. This section should be really exciting to people both in and outside your field. Don’t sell yourself short; if you think your research could lead to answers for big important questions, say so!
- A final paragraph that gives a good overall impression of your research.
Writing Research Statements
- Avoid jargon. Make sure that you describe your research in language that many people outside your specific subject area can understand. Ask people both in and outside your field to read it before you send your application. A search committee won’t get excited about something they can’t understand.
- Write as clearly, concisely, and concretely as you can.
- Keep it at a summary level; give more detail in the job talk.
- Ask others to proofread it. Be sure there are no spelling errors.
- Convince the search committee not only that you are knowledgeable, but that you are the right person to carry out the research.
- Include information that sets you apart (e.g., publication in Science, Nature, or a prestigious journal in your field).
- What excites you about your research? Sound fresh.
- Include preliminary results and how to build on results.
- Point out how current faculty may become future partners.
- Acknowledge the work of others.
- Use language that shows you are an independent researcher.
- BUT focus on your research work, not yourself.
- Include potential funding partners and industrial collaborations. Be creative!
- Provide a summary of your research.
- Put in background material to give the context/relevance/significance of your research.
- List major findings, outcomes, and implications.
- Describe both current and planned (future) research.
- Communicate a sense that your research will follow logically from what you have done and that it will be unique, significant, and innovative (and easy to fund).
Describe Your Future Goals or Research Plans
- Major problem(s) you want to focus on in your research.
- The problem’s relevance and significance to the field.
- Your specific goals for the next three to five years, including potential impact and outcomes.
- If you know what a particular agency funds, you can name the agency and briefly outline a proposal.
- Give broad enough goals so that if one area doesn’t get funded, you can pursue other research goals and funding.
Identify Potential Funding Sources
- Almost every institution wants to know whether you’ll be able to get external funding for research.
- Try to provide some possible sources of funding for the research, such as NIH, NSF, foundations, private agencies.
- Mention past funding, if appropriate.
Be Realistic
There is a delicate balance between a realistic research statement where you promise to work on problems you really think you can solve and over-reaching or dabbling in too many subject areas. Select an over-arching theme for your research statement and leave miscellaneous ideas or projects out. Everyone knows that you will work on more than what you mention in this statement.
Consider Also Preparing a Longer Version
- A longer version (five–15 pages) can be brought to your interview. (Check with your advisor to see if this is necessary.)
- You may be asked to describe research plans and budget in detail at the campus interview. Be prepared.
- Include laboratory needs (how much budget you need for equipment, how many grad assistants, etc.) to start up the research.
Samples of Research Statements
To find sample research statements with content specific to your discipline, search on the internet for your discipline + “Research Statement.”
- University of Pennsylvania Sample Research Statement
- Advice on writing a Research Statement (Plan) from the journal Science
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Graduate School Applications: Writing a Research Statement

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The research statement is a common component of a potential candidate’s application for post-undergraduate study. This may include applications for graduate programs, post-doctoral fellowships, or faculty positions. The research statement is often the primary way that a committee determines if a candidate’s interests and past experience make them a good fit for their program/institution.
What is a Research Statement?
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete.
What Should It Look Like?
Research statements are generally one to two single-spaced pages. You should be sure to thoroughly read and follow the length and content requirements for each individual application.
Your research statement should situate your work within the larger context of your field and show how your works contributes to, complicates, or counters other work being done. It should be written for an audience of other professionals in your field.
What Should It Include?
Your statement should start by articulating the broader field that you are working within and the larger question or questions that you are interested in answering. It should then move to articulate your specific interest.
The body of your statement should include a brief history of your past research . What questions did you initially set out to answer in your research project? What did you find? How did it contribute to your field? (i.e. did it lead to academic publications, conferences, or collaborations?). How did your past research propel you forward?
It should also address your present research . What questions are you actively trying to solve? What have you found so far? How are you connecting your research to the larger academic conversation? (i.e. do you have any publications under review, upcoming conferences, or other professional engagements?) What are the larger implications of your work?
Finally, it should describe the future trajectory on which you intend to take your research. What further questions do you want to solve? How do you intend to find answers to these questions? How can the institution to which you are applying help you in that process? What are the broader implications of your potential results?
Note: Make sure that the research project that you propose can be completed at the institution to which you are applying.
Other Considerations:
- What is the primary question that you have tried to address over the course of your academic career? Why is this question important to the field? How has each stage of your work related to that question?
- Include a few specific examples that show your success. What tangible solutions have you found to the question that you were trying to answer? How have your solutions impacted the larger field? Examples can include references to published findings, conference presentations, or other professional involvement.
- Be confident about your skills and abilities. The research statement is your opportunity to sell yourself to an institution. Show that you are self-motivated and passionate about your project.
Writing a Research Statement
What is a research statement.
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete.
The research statement is a common component of a potential student's application for post-undergraduate study. The research statement is often the primary way for departments and faculty to determine if a student's interests and past experience make them a good fit for their program/institution.
Although many programs ask for ‘personal statements,' these are not really meant to be biographies or life stories. What we, at Tufts Psychology, hope to find out is how well your abilities, interests, experiences and goals would fit within our program.
We encourage you to illustrate how your lived experience demonstrates qualities that are critical to success in pursuing a PhD in our program. Earning a PhD in any program is hard! Thus, as you are relaying your past, present, and future research interests, we are interested in learning how your lived experiences showcase the following:
- Perseverance
- Resilience in the face of difficulty
- Motivation to undertake intensive research training
- Involvement in efforts to promote equity and inclusion in your professional and/or personal life
- Unique perspectives that enrich the research questions you ask, the methods you use, and the communities to whom your research applies
How Do I Even Start Writing One?
Before you begin your statement, read as much as possible about our program so you can tailor your statement and convince the admissions committee that you will be a good fit.
Prepare an outline of the topics you want to cover (e.g., professional objectives and personal background) and list supporting material under each main topic. Write a rough draft in which you transform your outline into prose. Set it aside and read it a week later. If it still sounds good, go to the next stage. If not, rewrite it until it sounds right.
Do not feel bad if you do not have a great deal of experience in psychology to write about; no one who is about to graduate from college does. Do explain your relevant experiences (e.g., internships or research projects), but do not try to turn them into events of cosmic proportion. Be honest, sincere, and objective.
What Information Should It Include?
Your research statement should describe your previous experience, how that experience will facilitate your graduate education in our department, and why you are choosing to pursue graduate education in our department. Your goal should be to demonstrate how well you will fit in our program and in a specific laboratory.
Make sure to link your research interests to the expertise and research programs of faculty here. Identify at least one faculty member with whom you would like to work. Make sure that person is accepting graduate students when you apply. Read some of their papers and describe how you think the research could be extended in one or more novel directions. Again, specificity is a good idea.
Make sure to describe your relevant experience (e.g., honors thesis, research assistantship) in specific detail. If you have worked on a research project, discuss that project in detail. Your research statement should describe what you did on the project and how your role impacted your understanding of the research question.
Describe the concrete skills you have acquired prior to graduate school and the skills you hope to acquire.
Articulate why you want to pursue a graduate degree at our institution and with specific faculty in our department.
Make sure to clearly state your core research interests and explain why you think they are scientifically and/or practically important. Again, be specific.
What Should It Look Like?
Your final statement should be succinct. You should be sure to thoroughly read and follow the length and content requirements for each individual application. Finally, stick to the points requested by each program, and avoid lengthy personal or philosophical discussions.
How Do I Know if It is Ready?
Ask for feedback from at least one professor, preferably in the area you are interested in. Feedback from friends and family may also be useful. Many colleges and universities also have writing centers that are able to provide general feedback.
Of course, read and proofread the document multiple times. It is not always easy to be a thoughtful editor of your own work, so don't be afraid to ask for help.
Lastly, consider signing up to take part in the Application Statement Feedback Program . The program provides constructive feedback and editing support for the research statements of applicants to Psychology PhD programs in the United States.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Research Statement
Last Updated: May 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 64,094 times.
The research statement is a very common component of job applications in academia. The statement provides a summary of your research experience, interests, and agenda for reviewers to use to assess your candidacy for a position. Because the research statement introduces you as a researcher to the people reviewing your job application, it’s important to make the statement as impressive as possible. After you’ve planned out what you want to say, all you have to do is write your research statement with the right structure, style, and formatting!
Research Statement Outline and Example

Planning Your Research Statement

- For example, some of the major themes of your research might be slavery and race in the 18th century, the efficacy of cancer treatments, or the reproductive cycles of different species of crab.
- You may have several small questions that guide specific aspects of your research. Write all of these questions out, then see if you can formulate a broader question that encapsulates all of these smaller questions.

- For example, if your work is on x-ray technology, describe how your research has filled any knowledge gaps in your field, as well as how it could be applied to x-ray machines in hospitals.
- It’s important to be able to articulate why your research should matter to people who don’t study what you study to generate interest in your research outside your field. This is very helpful when you go to apply for grants for future research.

- Explain why these are the things you want to research next. Do your best to link your prior research to what you hope to study in the future. This will help give your reviewer a deeper sense of what motivates your research and why it matters.

- For example, if your research was historical and the documents you needed to answer your question didn’t exist, describe how you managed to pursue your research agenda using other types of documents.

- Some skills you might be able to highlight include experience working with digital archives, knowledge of a foreign language, or the ability to work collaboratively. When you're describing your skills, use specific, action-oriented words, rather than just personality traits. For example, you might write "speak Spanish" or "handled digital files."
- Don’t be modest about describing your skills. You want your research statement to impress whoever is reading it.
Structuring and Writing the Statement

- Because this section summarizes the rest of your research statement, you may want to write the executive summary after you’ve written the other sections first.
- Write your executive summary so that if the reviewer chooses to only read this section instead of your whole statement, they will still learn everything they need to know about you as an applicant.
- Make sure that you only include factual information that you can prove or demonstrate. Don't embellish or editorialize your experience to make it seem like it's more than it is.

- If you received a postdoctoral fellowship, describe your postdoc research in this section as well.
- If at all possible, include research in this section that goes beyond just your thesis or dissertation. Your application will be much stronger if reviewers see you as a researcher in a more general sense than as just a student.

- Again, as with the section on your graduate research, be sure to include a description of why this research matters and what relevant skills you bring to bear on it.
- If you’re still in graduate school, you can omit this section.

- Be realistic in describing your future research projects. Don’t describe potential projects or interests that are extremely different from your current projects. If all of your research to this point has been on the American civil war, future research projects in microbiology will sound very farfetched.

- For example, add a sentence that says “Dr. Jameson’s work on the study of slavery in colonial Georgia has served as an inspiration for my own work on slavery in South Carolina. I would welcome the opportunity to be able to collaborate with her on future research projects.”

- For example, if your research focuses on the history of Philadelphia, add a sentence to the paragraph on your future research projects that says, “I believe based on my work that I would be a very strong candidate to receive a Balch Fellowship from the Historical Society of Pennsylvania.”
- If you’ve received funding for your research in the past, mention this as well.

- Typically, your research statement should be about 1-2 pages long if you're applying for a humanities or social sciences position. For a position in psychology or the hard sciences, your research statement may be 3-4 pages long.
- Although you may think that having a longer research statement makes you seem more impressive, it’s more important that the reviewer actually read the statement. If it seems too long, they may just skip it, which will hurt your application.
Formatting and Editing

- For example, instead of saying, “This part of my research was super hard,” say, “I found this obstacle to be particularly challenging.”

- For example, if your research is primarily in anthropology, refrain from using phrases like “Gini coefficient” or “moiety.” Only use phrases that someone in a different field would probably be familiar with, such as “cultural construct,” “egalitarian,” or “social division.”
- If you have trusted friends or colleagues in fields other than your own, ask them to read your statement for you to make sure you don’t use any words or concepts that they can’t understand.

- For example, when describing your dissertation, say, “I hypothesized that…” When describing your future research projects, say, “I intend to…” or “My aim is to research…”

- At the same time, don’t make your font too big. If you write your research statement in a font larger than 12, you run the risk of appearing unprofessional.

- For instance, if you completed a postdoc, use subheadings in the section on previous research experience to delineate the research you did in graduate school and the research you did during your fellowship.

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/graduate_school_applications/writing_a_research_statement.html
- ↑ https://www.cmu.edu/student-success/other-resources/handouts/comm-supp-pdfs/writing-research-statement.pdf
- ↑ https://postdocs.cornell.edu/research-statement
- ↑ https://gradschool.cornell.edu/academic-progress/pathways-to-success/prepare-for-your-career/take-action/research-statement/
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/executivesummary
- ↑ https://www.niu.edu/writingtutorial/style/formal-and-informal-style.shtml
- ↑ https://www.unl.edu/gradstudies/connections/writing-about-your-research-verb-tense
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/editing-and-proofreading-techniques
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Apr 24, 2022
Did this article help you?
Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

- Get Curious
- Talk to People
- Take Action
- Inspire Others
- Events and Outcomes
- JHU At-A-Glance
- Students and Schools
- Ready to Hire?
- Mentor Students
- Hire Students
- “When U Grow Up” Podcast
Writing an Effective Research Statement
- Share This: Share Writing an Effective Research Statement on Facebook Share Writing an Effective Research Statement on LinkedIn Share Writing an Effective Research Statement on X
Your browser doesn't support HTML video.
A research statement is a summary of research achievements and a proposal for upcoming research. It often includes both current aims and findings, and future goals. Research statements are usually requested as part of a relevant job application process, and often assist in the identification of appropriate applicants. Learn more about how to craft an effective research statement.

Faculty Application: Research Statement
Criteria for success.
- Clearly articulate your brand.
- Demonstrate the impact of your past work.
- Show that you are credible to carry out your proposed future research.
- Articulate the importance of your research vision.
- Match the standards within the department to which you are applying.
- Show that you are a good fit for the position.
- Polish. Avoid typos.
Structure Diagram
The typical structure and length of research statements vary widely across fields. If you are unsure of what is typical in the field where you are applying, be sure to check with someone who is familiar with the standards.
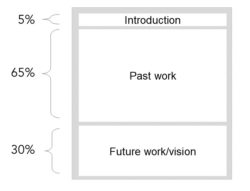
In electrical engineering and computer science, research statements are usually around three pages long with a focus on past and current work, often following the structure in the diagram below.
Identify Your Purpose
Your cover letter and CV outline your past work and hint at a general direction of your future work but do not go into detail. Therefore, the purpose of a research statement is to emphasize the importance of your past work and describe your research vision. Both your past/current work and future work presented in the research statement should reflect your branding statement .
In EECS, faculty research statements focus on past/current work. However, it is important to also include your vision for the future, which should build on your previous work. This statement should convince the committee that your future work is important, relevant, and feasible. The future work section should go beyond direct extensions of your doctoral or postdoctoral work; it should cover a 5-10 year span. Proposed future work should show scientific growth and convince the committee that you propose strong research directions for your future group. Your research statement can also include possible funding sources and collaborations.
Analyze Your Audience
Your audience is a faculty search committee, which is made up of professors from across the department, not just the ones in your research area. A typical search committee member is probably very busy reviewing lots of applications, and hence may not read your statement in depth until you make it to later rounds of the hiring process.
Knowing details of the job posting and what the faculty search committee is looking for will help you tailor your statement. If the call is for a specific research area (e.g., language processing, bioinformatics, algorithms, machine learning, systems), it is beneficial to motivate and emphasize the importance of your work in the language of that area whenever possible.
Structure your statement
Although there is usually no mandated structure for a research statement, it can be very helpful to a reader if the content flows naturally.
Use the hourglass concept. It makes a compelling introduction if a research statement presents motivation starting from the high-level picture and then zooms in to the main topic(s) of research. This is helpful for two reasons. First, a research statement is typically read by committee members from several research areas, so starting with a high-level picture gives members a gentle guidance to the meat of a work. Second, providing general motivation helps in showing how different pieces of research fit in a big puzzle.
After talking about specific results, the story typically zooms back out by discussing impact and future directions. It is best if future work has some concrete research directions and also widens up to touch on a broader perspective of research plans.
The diagram below summarizes the hourglass concept and provides one potential flow of content.
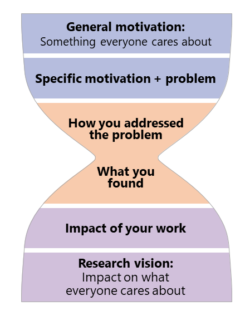
Use good formatting to help retain focus . A successful research statement is typically organized into three main parts: Introduction and motivation; past work/achievements; and vision/future work. Each of these parts can be divided into subsections.
In addition, you can help a reader focus their attention on the important content by:
- making each section/paragraph title tell a message;
- using bullet points and itemization while listing;
- using bold or italics to emphasize important keywords or sentences.
Some institutions set constraints on the format of research statements, primarily constraints on length . Make sure that your research statement is tailored to the guidelines. It is helpful to prepare two versions of your statement — a long one and a short one. The short version is usually the long one stripped of many details with the emphasis on high-level pictures and ideas.
Say who you are
Your research statement tells a story about you. Think who you want to be in the eyes of committee members (e.g., a programming languages person, a machine learning expert, a theory professor) and which of your achievements you want them to remember.
Make your research statement echo your branding one . A successful research statement builds a story around the author’s branding statement. A strong point is made if past and future work are echoes of the same brand.
Successful candidates outline their research agenda before stating actual results and after providing a background. Sometimes this is done even before giving background and motivation. In the latter case, the research agenda is typically stated briefly, and then reiterated with more context after providing the background.
Show credibility for your future work by your past work
Your past work is an excellent way to illustrate that you are fit for the future work you are proposing. Refer to some of your past work when outlining feasibility of your proposed future directions. Even if you aim to change your field of research, your past experience should still serve as a justification for why you are well suited for the new line of work.
Dedicate space to your strongest results . Describe your strongest results in the most detail. If you want to mention many papers, organize them into several themes. A successful statement communicates how obtained results affect a field or a research community. Impact of papers can be shown by awards, high number of citations, or follow up papers by other research groups. A reader will have limited time to go over your statement, so make sure that the reader’s attention is spent on your most impactful work. Note that your strongest results do not necessarily have to be your most recent ones; they can even be several years old. Nevertheless, it is still a good idea to also mention some of your recent work as it shows that you have been active lately as well.
Importantly, a research statement should be a coherent story about ideas and impact, not only an overview of published articles. Hence, it is often the case that a research statement does not discuss all papers published or all work done by the applicant.
Use figures to support important claims . Consider including figures . They can be used to support your claims about your results and/or in the future work section to illustrate your research plans. A well-made figure can help the reader quickly understand your work, but figures also take up a large amount of space. Use figures carefully, only to draw attention to the most important points.
Devote time!
Getting out a job application package takes an indefinitely long time (writing, addressing feedback, polishing, addressing feedback … aaaand polishing)! Start early and invest time.
Get feedback . Your application package will be read by committee members that are not necessarily in your research area. It is thus important to get feedback about your research statement from colleagues with different backgrounds and seniority. Note that it might take time for other people to share their feedback (remember, others are busy as well!), so plan ahead.
MIT EECS affiliates can also make an appointment with a Communication Fellow to obtain additional feedback on their statements.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Amy zhang research statement.
Submitted in 2018-2019 by Amy Zhang, now faculty at University of Washington 1 MB
Elena Glassman Research Statement
Submitted in 2017-2018 by Elena Glassman, now faculty at Harvard University 2 MB
Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Short research papers: how to write academic essays.
Jerz > Writing > Academic > Research Papers [ Title | Thesis | Blueprint | Quoting | Citing | MLA Format ]
This document focuses on the kind of short, narrowly-focused research papers that might be the final project in a freshman writing class or 200-level literature survey course.
In high school, you probably wrote a lot of personal essays (where your goal was to demonstrate you were engaged) and a lot of info-dump paragraphs (where your goal was to demonstrate you could remember and organize information your teacher told you to learn).
How is a college research essay different from the writing you did in high school?
This short video covers the same topic in a different way; I think the video and handout work together fairly well.
The assignment description your professor has already given you is your best source for understanding your specific writing task, but in general, a college research paper asks you to use evidence to defend some non-obvious, nuanced point about a complex topic.
Some professors may simply want you to explain a situation or describe a process; however, a more challenging task asks you to take a stand, demonstrating you can use credible sources to defend your original ideas.

- Choose a Narrow Topic
- Use Sources Appropriately
Avoid Distractions
Outside the classroom, if I want to “research” which phone I should buy, I would start with Google.
I would watch some YouTube unboxing videos, and I might ask my friends on social media. I’d assume somebody already has written about or knows about the latest phones, and the goal of my “research” is to find what the people I trust think is the correct answer.
An entomologist might do “research” by going into the forest, and catching and observing hundreds or thousands of butterflies. If she had begun and ended her research by Googling for “butterflies of Pennsylvania” she would never have seen, with her own eyes, that unusual specimen that leads her to conclude she has discovered a new species.
Her goal as a field researcher is not to find the “correct answer” that someone else has already published. Instead, her goal is to add something new to the store of human knowledge — something that hasn’t been written down yet.
As an undergraduate with a few short months or weeks to write a research paper, you won’t be expected to discover a new species of butterfly, or convince everyone on the planet to accept what 99.9% of scientists say about vaccines or climate change, or to adopt your personal views on abortion, vaping, or tattoos.
But your professor will probably want you to read essays published by credentialed experts who are presenting their results to other experts, often in excruciating detail that most of us non-experts will probably find boring.
Your instructor probably won’t give the results of a random Google search the same weight as peer-reviewed scholarly articles from academic journals. (See “ Academic Journals: What Are They? “)
The best databases are not free, but your student ID will get you access to your school’s collection of databases, so you should never have to pay to access any source. (Your friendly school librarian will help you find out exactly how to access the databases at your school.)
1. Plan to Revise
Even a very short paper is the result of a process.
- You start with one idea, you test it, and you hit on something better.
- You might end up somewhere unexpected. If so, that’s good — it means you learned something.
- If you’re only just starting your paper, and it’s due tomorrow, you have already robbed yourself of your most valuable resource — time.
Showcase your best insights at the beginning of your paper (rather than saving them for the end).
You won’t know what your best ideas are until you’ve written a full draft. Part of revision involves identifying strong ideas and making them more prominent, identifying filler and other weak material, and pruning it away to leave more room to develop your best ideas.
- It’s normal, in a your very first “discovery draft,” to hit on a really good idea about two-thirds of the way through your paper.
- But a polished academic paper is not a mystery novel. (A busy reader will not have the patience to hunt for clues.)
- A thesis statement that includes a clear reasoning blueprint (see “ Blueprinting: Planning Your Essay “) will help your reader identify and follow your ideas.
Before you submit your draft, make sure the title, the introduction, and the conclusion match . (I am amazed at how many students overlook this simple step.)
2. Choose a Narrow Topic
A short undergraduate research paper is not the proper occasion for you to tackle huge issues, such as, “Was Hamlet Shakespeare’s Best Tragedy?” or “Women’s Struggle for Equality” or “How to Eliminate Racism.” You won’t be graded down simply because you don’t have all the answers right away. The trick is to zoom in on one tiny little part of the argument .
Short Research Paper: Sample Topics
How would you improve each of these paper topics? (My responses are at the bottom of the page.)
- Environmentalism in America
- Immigration Trends in Wisconsin’s Chippewa Valley
- Drinking and Driving
- Local TV News
- 10 Ways that Advertisers Lie to the Public
- Athletes on College Campuses
3. Use Sources Appropriately
Unless you were asked to write an opinion paper or a reflection statement, your professor probably expects you to draw a topic from the assigned readings (if any).
- Some students frequently get this backwards — they write the paper first, then “look for quotes” from sources that agree with the opinions they’ve already committed to. (That’s not really doing research to learn anything new — that’s just looking for confirmation of what you already believe.)
- Start with the readings, but don’t pad your paper with summary .
- Many students try doing most of their research using Google. Depending on your topic, the Internet may simply not have good sources available.
- Go ahead and surf as you try to narrow your topic, but remember: you still need to cite whatever you find. (See: “ Researching Academic Papers .”)
When learning about the place of women in Victorian society, Sally is shocked to discover women couldn’t vote or own property. She begins her paper by listing these and other restrictions, and adds personal commentary such as:
Women can be just as strong and capable as men are. Why do men think they have the right to make all the laws and keep all the money, when women stay in the kitchen? People should be judged by what they contribute to society, not by the kind of chromosomes they carry.
After reaching the required number of pages, she tacks on a conclusion about how women are still fighting for their rights today, and submits her paper.
- during the Victorian period, female authors were being published and read like never before
- the public praised Queen Victoria (a woman!) for making England a world empire
- some women actually fought against the new feminists because they distrusted their motives
- many wealthy women in England were downright nasty to their poorer sisters, especially the Irish.
- Sally’s paper focused mainly on her general impression that sexism is unfair (something that she already believed before she started taking the course), but Sally has not engaged with the controversies or surprising details (such as, for instance, the fact that for the first time male writers were writing with female readers in mind; or that upperclass women contributed to the degradation of lower-class women).
On the advice of her professor, Sally revises her paper as follows:
Sally’s focused revision (right) makes specific reference to a particular source , and uses a quote to introduce a point. Sally still injects her own opinion, but she is offering specific comments on complex issues, not bumper-sticker slogans and sweeping generalizations, such as those given on the left.
Documenting Evidence
Back up your claims by quoting reputable sources . If you write”Recent research shows that…” or “Many scholars believe that…”, you are making a claim. You will have to back it up with authoritative evidence. This means that the body of your paper must include references to the specific page numbers where you got your outside information. (If your document is an online source that does not provide page numbers, ask your instructor what you should do. There might be a section title or paragraph number that you could cite, or you might print out the article and count the pages in your printout.)
Avoid using words like “always” or “never,” since all it takes is a single example to the contrary to disprove your claim. Likewise, be careful with words of causation and proof. For example, consider the claim that television causes violence in kids. The evidence might be that kids who commit crimes typically watch more television than kids who don’t. But… maybe the reason kids watch more television is that they’ve dropped out of school, and are unsupervised at home. An unsupervised kid might watch more television, and also commit more crimes — but that doesn’t mean that the television is the cause of those crimes.
You don’t need to cite common facts or observations, such as “a circle has 360 degrees” or “8-tracks and vinyl records are out of date,” but you would need to cite claims such as “circles have religious and philosophical significance in many cultures” or “the sales of 8-track tapes never approached those of vinyl records.”
Don’t waste words referring directly to “quotes” and “sources.”
If you use words like “in the book My Big Boring Academic Study , by Professor H. Pompous Windbag III, it says” or “the following quote by a government study shows that…” you are wasting words that would be better spent developing your ideas.
In the book Gramophone, Film, Typewriter , by Fredrich A. Kittler, it talks about writing and gender, and says on page 186, “an omnipresent metaphor equated women with the white sheet of nature or virginity onto which a very male stylus could inscribe the glory of its authorship.” As you can see from this quote, all this would change when women started working as professional typists.
The “it talks about” and “As you can see from this quote” are weak attempts to engage with the ideas presented by Kittler. “In the book… it talks” is wordy and nonsensical (books don’t talk).
MLA style encourages you to expend fewer words introducing your sources , and more words developing your own ideas. MLA style involves just the author’s last name, a space ( not a comma), and then the page number. Leave the author’s full name and the the title of the source for the Works Cited list at the end of your paper. Using about the same space as the original, see how MLA style helps an author devote more words to developing the idea more fully:
Before the invention of the typewriter, “an omnipresent metaphor” among professional writers concerned “a very male stylus” writing upon the passive, feminized “white sheet of nature or virginity” (Kittler 186). By contrast, the word “typewriter” referred to the machine as well as the female typist who used it (183).
See “ Quotations: Integrating them in MLA-Style Papers. ”
Stay On Topic
It’s fairly normal to sit and stare at the computer screen for a while until you come up with a title, then pick your way through your topic, offering an extremely broad introduction (see glittering generalities , below)..
- You might also type in a few long quotations that you like.
- After writing generalities and just poking and prodding for page or two, you will eventually hit on a fairly good idea .
- You will pursue it for a paragraph or two, perhaps throwing in another quotation.
- By then, you’ll realize that you’ve got almost three pages written, so you will tack on a hasty conclusion.
Hooray, you’ve finished your paper! Well, not quite…
- At the very least, you ought to rewrite your title and introduction to match your conclusion , so it looks like the place you ended up was where you were intending to go all along. You probably won’t get an A, because you’re still submitting two pages of fluff; but you will get credit for recognizing whatever you actually did accomplish.
- To get an A, you should delete all that fluff, use the “good idea” that you stumbled across as your new starting point , and keep going. Even “good writers” have to work — beefing up their best ideas and shaving away the rest, in order to build a whole paper that serves the good idea, rather than tacking the good idea on at the end and calling it a day.
See: Sally Slacker Writes a Paper , and Sally’s Professor Responds
Avoid Glittering Generalities
Key: Research Paper Topics
15 thoughts on “ Short Research Papers: How to Write Academic Essays ”
Hi, I was searching for some information on how to write quality academic paper when I came across your awesome article on Short Research Papers: How to Writer Academic Essays ( https://jerz.setonhill.edu/writing/academic1/short-research-papers/ ) Great stuff!!! I especially like the way you recommend sticking to the 4 basics of writing academic essays. Very few students have mastered how to avoid distractions and focus on a single topic. Many students think that the broad, sweeping statements could give them better grades but they are wrong.
However, I came across a few links that didn’t seem to be working for you. Want me to forward you the short list I jotted down? Cheers Elias
I see some broken links in the comments, but otherwise I’m not sure what you mean.
I found the part about not using my personal opinion or generalities to be very helpful. I am currently writing a 2 page paper and was having a hard time keeping it short. Now I know why. Thanks. Stick to the facts.
This seem to be old but very relevant. Most of what you have stated are things my professor has stated during class trying to prepare us to write a short thesis reading this information verses hearing it was very helpful. You have done an awesome job! I just hope I can take this and apply it to my papers!
Great Post! Thank u!
Thank you for all your effort and help. You´ve taught me a number of things, especially on what college professors´ look for in assigning students short research papers. I am bookmarking your page, and using it as a reference.
Thank you kindly. YOU´VE HELPED A LOST STUDENT FIND HER WAY!
I appreaciate all the help your web site has given to me. I have referred to it many times. I think there may be a typo under the headline of AVOID GLITTERING GENERALITIES: “Throughout the ages, mankind has found many uses for salt. Ancient tribes used it preserve meat;” This is in no way a slight – I thought you might want to know. Please forgive me if I am incorrect. Thank you again – you rock!
You are right — I’ll fix it the next time I’m at my desktop. Thank you!
i would like to say thank you for your detailed information even though it takes time to read as well as we’ve got learnings out from it . even though it’s holiday next week our teacher assigned us to make a short research paper in accordance of our selected topic ! I’m hoping that we can make it cause if we can’t make it, right away, for sure we will get a grade’s that can drop our jaws ! :) ♥ tnx ! keep it up ! ♪♪
Sorry I have not done this for years
Hello I am the mother of a high school student that needs help doing a paper proposal for her senior project. Her topic is Photography. To be honest I have done this for years and I am trying to help, but i am completely lost. What can you recommend since she told me a little late and the paper is due tomorrow 11/11/11.
This page is designed for college students, but I am sure your daughter’s teacher has assigned readings that will guide your daughter through her homework.
Any paper that your daughter writes herself, even if it is late, will be a valuable learning experience — showing her the value of managing her time better for the next time, and preparing her for the day when she will have to tackle grown-up problems on her own.
I am having a hard time with my government essay. I am 55 taking a college course for the first time, and I barely passed high school. Last year I took this course wrote the essay, and did many things wrong. It was all in the typing. I had good story line, excellent site words, and good points of arguments. It wasn’t right on paper. My format is off. Where can I find and print a format. also I need to learn site words.
Most teachers will provide a model to follow. If it’s not already part of the assignment instructions, you could ask your prof. Better yet, bring a near-complete draft to your prof’s office hours, a few days before the due date, and ask for feedback. Your school probably has a writing center or tutoring center, too.
I would like to thank you for such detailed information. I am not a native speaker and I am doing a research paper;so, as you may think, it is really a hard job for me. A friend of mine who saw my draft of Lit. Rev asked me what type of citation format i was using, MLA or APA and I was puzzeled; then I decided to check the net and came across to this! It is being such a help Elsa
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Research Statement

Anyone who went to college could actually relate to research, baby thesis or even the thesis paper itself. In every research design and research procedure, there has to be a research statement that serves as a summary writing of the whole research. It also talks about the achievements of the research as well as the upcoming research proposal to be executed in the near future.
Nursing Research Statement
Nursing research position statement.

Size: 244 KB
School Research Statement Examples
Graduate school research statement.

Size: 29 KB
Business School Research Statement

Size: 226 KB
Free School Research Statement

Size: 78 KB
Medical Research Statement Examples
Free medical research statement.

Size: 469 KB

BioMedical Research Statement

Size: 112 KB
Research Methodology Statements
Research methodology statement in pdf.

Size: 18 KB
Research Methodology and Problem Statement

Size: 405 KB
Preliminary Research Statement

Size: 102 KB
Personal Research Statement Example

Size: 73 KB
Business Research Statement Example

Size: 149 KB
Postdoctoral Research Statement
Size: 14 KB
Quantitative Research Statement

Size: 58 KB
Brief Research Statement Sample

Size: 382 KB
Short Research Statement

Size: 75 KB
Research Interests Statement Sample

Size: 79 KB
Graduate Research Statement

Size: 202 KB
Generic Research Statement

Size: 80 KB
Research Statement Example

Size: 103 KB
Research Statement Template

Size: 64 KB
Sample Research Statement

Research Job Application Statement

Research Statement Format

Research Problem Statement Template

- Google Docs
Size: 100 KB
What Is a Research Statement?
A research paper statement is a synthesis of your research achievement and proposals for the forthcoming research. It may also contain a discussion of specific issues about history, the current situation happening, recent political issues in the s and other industrial related collaborations.
How To Write an Effective Research Statement
Since a research statement has a potential to be read by many, one should bear in mind to be as credible and professional your research statement can be and in making your own research statement, one should call to mind his or her smart goals in achieving it.
Step 1: Make a Short Introduction of Yourself
You know that the smart goal of your research statement is to introduce yourself in a search committee, you have to call to mind by introducing yourself together with your research agenda . You have to carefully choose the words and ideas well, you get to sell yourself mainly in your introduction .
Step 2: Exhibit the Current Focus of the Research Statement
Exhibit the current focus of your research statement, which would be to state the problem that needs to be addressed. If the problem is to generalized, be sure to choose a specific problem to be handled first. Give a short explanation in the form of a concept statement .
Step 3: Go into Detail with Importance of Your Research
Indicate the things that would light up the interest of the reviewers of your research. Explain how would your research contribute much in the society and in the field where you are currently in. Convey that it would be helpful inside and outside of the field of your focus.
Step 4: Synthesize Your Research Business Proposal Goals
State the potentials of your work, this includes the ability to succeed in your current proposal. You must also set your short term goals , long term goals , smart goals , and career goals respectively.
How to format and organize research statements?
Research statements mainly act as the introductory of a researcher that mention his/her background and past experiences. Though it may sound boring, you can do some tricks in formatting your research statement. If you don’t know how, here are some tips and guidelines to keep a fascinating impression to your readers.
What are the contents of a research statement?
The following are the three elements in a research statement: research statement considerations for the recent study, research statement considerations for future study, and consideration for specific details.
What are the main types of research?
Certainly, there are lots of types of research papers or thesis proposal that fits according to what type of study you are currently focusing on. Here the two main types: qualitative research and quantitative research.
For the past years in the field of education, it is not only academic jobs and other related education-related jobs that require research statements for a job application (see also job application letter ). College students and graduate studies students need a strong and robust research statement, too. Always take note of the smart goals in each and every project you are working or anything you plan to do.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Graduate School
Research Interest Statement Samples That Worked

A good research interest statement sample can be hard to find. Still, it can also be a beneficial tool for writing one and preparing for a grad school application or post-graduate position. Your research interest statement is one of the key components of your application to get into grad school . In a few cases, admissions committees have used it instead of an interview, so it is important to write a strong essay. We’ve provided research interest statement samples for you in this blog post. We have also included several tips that will help you write a strong statement to help improve your chances of getting accepted into your dream program.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 13 min read
What is a research interest statement.
A research interest statement is essential for most graduate school, post-graduate, and academic job applications. Sometimes, it may be referred to it as a " statement of intent " or "description of research interests." While they are similar, research interest statement may require some additional information. Generally, your statement will pride a brief overview of your research background, including your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future research you'd like to complete, including any required equipment and collaborations. It is usually written in the form of a short essay. Still, of course, different graduate programs can have specific requirements, so make sure to check the program you are applying to and read the particular instructions that they give to ensure your research interest statement meets their requirements.
Your research statement plays a big role in the committee's decision. Ultimately, they are trying to figure out if you, as a person, and your research, would be a good fit for their program. A strong statement can help you convince them of this by showing your passion for research, your research interests and experience, the connection between your interests and the program, and the extent of your writing skills which is really important for paper and grant writing, and thus for earning money for your research!
Undergraduate programs are centered around classes, but graduate and post-graduate programs are all about your research and what your research contributes to your discipline of choice. That is why a research interest statement is so important, because it is essentially a way for you to share this information with the program that you have chosen.
Writing a strong statement can be helpful to you, as well. Having to explain your research and talk about your goals coherently will give you a chance to define your future research and career plans, as well as academic interests.
What Should Your Research Interest Statement Include?
The exact requirements of the research interest statement can vary depending on where you are applying and for what position. Most faculty positions will need you to produce a separate file for your statement, and most of the time, for an academic program, you can simply include your statement within your CV for graduate school .
Need to prepare your grad school CV? This video has helpful advice for you:
Unless otherwise stated by the program or faculty that you are applying to, your statement should be one to two pages long or between 600 and 1000 words. If you are including your description of interest statements on your resume, then it would be ideal to keep it between 400 and 600 words. Most programs will give you guidelines for the research interest statement so make sure you follow those. They rarely include a specific question or prompt but they might ask for a particular detail to be included in your interest statement. For example, a university’s requirements may look something like this: “In your statement of interest, you should detail your study and/or research interests and reasons for seeking admission. You must identify a faculty member from the Anthropology of Department with whom you are interested in being your advisor. The length of a statement of intent should be 2 pages in length (single-spaced, Times New Roman font size 12 point)”
Your statement should include a brief history of your past research. It should tell the committee what you have previously set out to answer with your research projects, what you found, and if it led to any academic publications or collaborations. It should also address your current research. What questions are you actively trying to solve? You will need to tell the committee if you’ve made any progress, what you have found, if you are connecting your research to the larger academic conversation and what the larger implications of your work actually are. Finally, you want to talk about the future of your research. What further questions do you want to solve? How do you intend to find answers to these questions? What are the broader implications of your potential results, and how can the institution you are applying to help you?
Before we show you some examples, let's go over a few essential things that you need to keep in mind while writing your research interest statement to make sure it is strong.
Preparation
Give Yourself Ample Time: Much like with other components of your application, like your CV or a graduate school interview question , preparation is the key to success. You should give yourself enough time to thoroughly research the program or faculty you are applying to, gather all the information or documents that can aid you in writing, and then write and rewrite as many times as you need to. Give yourself at least 6 weeks to draft, redraft, and finalize your statement. You may also want to consider investing in a graduate school admissions consultant as they have more experience writing these types of essays and may see things that you can’t.
Research the Program/Faculty: The purpose of your research interest statement is to tell the committee all about your research plans, how it will contribute to the field and convince them that not only is their institution is the best place for it, but that you will be an asset to them as a candidate. To do this, you need to know what kind of candidate they are looking for, what kind of research they have been interested in in the past, and if there is anything particular that they require in the research interest statement. Remember, expectations for research statements can vary among disciplines and universities, so it is essential that you write for the right audience.
The Format / Writing Style
Your research statement should be in an academic essay format. It needs to be concise, well-organized, and easy to read. For graduate school, PhD or post-doc positions, your research interest statement will usually be a part of your resume. We recommend that you stick to the following things when it comes to the format:
Limited Spots Available ","trustpilot":false}" :url=""https:\/\/bemoacademicconsulting.com\/grad-app-webinar-registration"" code="banner2" background-color="#000066" button-color="#ffffff" banner-image>
The Content
Introduction: This is a functional academic document, unlike college essays or personal statements, so you want to go straight to the point and focus on the key information that needs to be conveyed. You want to use this paragraph to tell the committee why you are writing this statement. In other words, you should clearly state what kind of research you are interested in pursuing at the institution in question and explain why you are drawn to the subject.
Body: This is your “why and how” paragraphs. In 2 or 3 paragraphs, you should expand on your interest, background, accomplishments, and plans in the field of research. Depending on your level of experience, you may use this time to talk about your previous or current research. If you do not have much experience, then you may use this paragraph to talk about any skills or academic achievements that could be relevant.
Conclusion: To conclude, you should restate your interest and tie it back to the research you intend to continue at the university. Be specific about the direction you’d like to take the research in, who you’d like to work with, and what the institution has that would help you. We also suggest including a concise statement that reiterates your unique suitability for the program, and what you can contribute to it and your chosen field.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Being Too Personal: Often, students will confuse the statement of purpose and the research interest statement or letter of intent. It is essential to understand the difference between these two documents because some programs will ask for both of these documents. There is quite a bit of overlap between the two essays, so they are very easy to mix up. Both documents ask applicants to focus on their research interests, relevant past academic & professional experiences, and their long-term goals in the field. However, a statement of purpose is more of a personal statement that describes your journey and overall suitability for a program. In contrast, a research interest statement is a more formal academic document specific to the research you intend to pursue in a program. It will include many details such as the faculty members you want to work with, the program facilities and resources you wish to use, etc.
Not Following Guidelines: As mentioned earlier, these statements can vary depending on the discipline and the faculty. It is crucial that you review all the institution's guidelines and follow them. Some schools will have a specific word count, others may simply give you a maximum and minimum word count. Others may even have a specific prompt or question that you will need to answer with your essay. You want to make sure that you are following the instructions provided by the program.
Using Too Much Jargon: Your statement will be read by people who are most likely knowledgeable, but they might not be from your specific field or specialty. We understand that it may not be possible to be clear about your research without using a few niche words, but try to keep them at a minimum and avoid using acronyms that are not well known outside of your specialty.
Having One Generic Statement: The requirements of your research statement are different from one school to another, and you should tailor your letter to the program you are writing to. We know that the research and experience you are talking about are still the same, but the qualities and aspects of that experience you play up should help you appeal to the school you are applying to. For example, if you are applying to a very collaborative program, you should highlight your collaborations and your experience working as part of a team.
Looking for tips on getting into grad school? This infographic is for you:
Research of Interest Statement Samples
Below are sample research interest statements for reference:
Research Statement of Interest 1
Jennifer Doe
As the child of an immigrant, I have always been fascinated by the relationship between identity, geographic territory, and economic development. With the rise of globalization, there is a broader effort in the social sciences to study the link between cultural identity, human mobility, and economic development in the contemporary world. I hope that my research will contribute to this as well. I am applying to the X University Global Anthropology program, as it is the best place for me to explore my research interests and channel them towards my long-term goals. I believe that my undergraduate education and the research experience it gave me have prepared me to undertake advanced research projects, thus making me an excellent candidate for this program.
I spent the first two years of undergraduate studies taking psychology courses. I went to university knowing that I wanted to learn about human behavior and culture. I was thirsty for information, but I did not know what kind of information just yet. It wasn’t until I took an elective anthropology class in my second year and started discussing identity in anthropology that something clicked. Unlike many other social sciences, anthropology explores the different ways that cultures affect human behavior and that connected right away with my experience as an immigrant. I have been passionate about the subject ever since, and I intend on spending my career exploring this topic further.
In the long run, I am interested in understanding how geography affects the construction of one’s cultural identity, especially when it comes to immigrants. Literature already exists on the topic, but most of it examines the upper levels of this process of social reproduction, concentrating on the roles of governments and associations in promoting ties between migrants and their homelands. Prof. Jane Doe Smith is one of the anthropologists researching the transnational migration experience, and I hope to have the opportunity to work with her at X University.
I was fortunate to be part of a summer research experience as an undergraduate, which took place in several west African countries, including Mali, Senegal, and Nigeria. Dr. Sam Smith was leading the research, and my time on his team allowed me to gain hands-on experience in research while living abroad. One of the things that I did almost daily was interview the subjects in a controlled environment, and sometimes I got to be a part of traditional ceremonies. I learnt how to observe without being intrusive and how to interact with clinical subjects. The experience only strengthened my curiosity and conviction that today more than ever, we need to understand what identity is and the different factors that can affect it.
I enrolled in several challenging research-oriented courses such as Applied Statistical Inference for the Behavioral Sciences, Principles of Measurement, and more throughout my degree. I was also able to work as a research lab assistant for one of my mentors, Mr. Jonathan Smith. I worked with him while he studied the relationship between identity, culture and “self.” My main duties were to assist in the creating of surveys and other assessment materials, administer written and verbal tests to participants, create literature reviews for potential resources, create summaries of findings for analysis and other office duties such as reserving testing rooms. This particular experience allowed me to get some hands-on experience with data collection, data analysis, report preparation and the creation of data summaries.
I know that there is a lot more that I can learn from the X University. I have seen the exemplary work in anthropology and other social studies done by the staff and alumni of this school. It has inspired and convinced me beyond the shadow of a doubt that pursuing my graduate studies in your program meets my personal, academic, and professional goals objectives.
My advanced research skills, passion for anthropology and clinical research, as well as my academic proficiency make me the ideal candidate for X University's Clinical Global Anthropology Master’s program. I believe that X University’s rigorous curriculum and facilities make it the perfect place for me, my long-term career goals and my research commitments.
Jamie Medicine
I am applying to the brain and development master's program of X university because it is one of the few universities that not only has a program that combines the two disciplines that I majored in my undergraduate studies: Psychology and Linguistics; but also because it is a program that I know would allow me to grow as a researcher, contribute to my chosen fields and achieve my long-term career goals. My research is motivated by two of my favorite things: language and music. To be more specific, hip-hop music. In 20xx, Rollingstone magazine published an article stating that hip hop was now more popular than rock and roll. The rise in popularity of this initially very niche genre has sparked a conversation in specific academic fields such as psychology, sociology, linguistics, and English about the use of language within it but also the effects that it can have on those who listen to it. I hope to one day contribute to that conversation by studying the relationship between hip-hop music and vocabulary development, and I believe that pursuing this particular research interest at X university is the best way for me to do that.
There are many potential places this research may lead me and many potential topics I may explore. Furthermore, there are many things that it would allow us to learn about the effect that music has on our brains and society at large.
I was fortunate enough to work under Dr. Jane D. Smith at the University of X for two years while conducting her recently published study on vocabulary instruction for children with a developmental language disorder. During my time in her lab, I interviewed participants and put together evaluation materials for them. I was also responsible for data entry, analysis, and summarizing. This experience gave me the skills and the knowledge that allowed me to exceed expectations for my final research project in undergraduate school.
One of my undergraduate degree requirements was to complete a small independent study under the supervision of a professor. I chose to study music's effect on children's vocabulary development. Several studies look for ways to decrease the million-word gap, and I wanted to see if this thing that I am so passionate about, music, had any effect at all. I compiled multiple literature reviews and analyzed their results, and I found that there is indeed a correlation between the number of words that a child spoke and the amount of music that they were exposed to.
This research is currently being explored on a larger scale by Prof. John Doe at X university and learning from him is one of the many reasons I have applied to this program. I took several research methodology courses throughout my degree, and I would love to enroll in the Applied Statistics for Psychology course he is currently teaching to build upon the foundational knowledge I already have. There are several other faculty members in the brain and language department with whom learning from would be a dream come true. In addition to that, working with them is a real possibility because the research they are currently doing and the research I hope to pursue are greatly matched.
I genuinely believe that X university has the curriculum and facilities that I need to meet my long-term goals and research commitments. I also believe that my academic achievements, eagerness to learn, and passion make me the perfect candidate for your program.
Interested in some tips to help you manage grad school once you're there? Check out this video :
It is essentially an essay that provides a brief overview of your research experience and goals. This includes your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future research you'd like to complete. It is also sometimes referred to as a "statement of intent" or "description of research interests."
This statement tells the admissions committee more about you as an applicant. It gives you the opportunity to tell them more about your research (past, present, and future) and show them that you are a good fit for their institution.
No. Some graduate school programs might ask for a statement of purpose and a writing sample instead, or they could ask for none of the above. You should always check the requirements of the specific program that you’re applying to.
Generally, your statement should be 400 to 1000 words or about two pages long. That said, most programs will give you guidelines so make sure you check those and follow them.
You certainly can but we do not recommend it. You should always tailor your statement to the program you are applying to. Remember that the aim is to convince the admissions committee that you are a good fit for their school so make sure you highlight the qualities and values that they care about.
We recommend that you doublecheck the information provided by your chosen program as they often have specific instructions for the format of the letter. If none exist, make sure that the format of your document is pleasing to the eye. Stick to easily legible fonts, a decent font size, spacing, margins, etc. Also, it is best to keep the content of the letter concise and professional.
We recommend giving yourself at least 6 weeks to write your statement. This will give you ample time to brainstorm, write a strong letter, read it again and edit it as many times as necessary. It also gives you enough time to get expert eyes on your letter and work with them to improve it if you wish.
No. Research interest statements are often required for post-graduate school applications and for other positions in academic faculties.
Absolutely! You can always reach out to admissions professionals, such as graduate school admissions consultants or grad school essays tutors .
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions.
Thank you for your excellent site
BeMo Academic Consulting
You are very welcome, Rasool!
Sadia Sultana
hello, thanks for providing guide line for Research Interest statement, the important aspect of scholarship application. Kindly guide me, What should be the title of the Research Statement. Thanks
Hi Sadia! Check the requirements of your school first. They might provide some info on whether a title is even needed.
Get Started Now
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
- Business Templates
- Sample Statements
FREE 6+ Short Research Statement Samples in PDF

Formal research is something we have been doing for a school related project or when the company requires us to do so such as market research . The point of research is to build knowledge through gathering of evidence for theories, and contribute to developing knowledge in a field of study. If you are about to conduct a research or is about to apply for a teaching job, a short research statement is a common component of academic job applications. Learn more about short research statement here in this article, and for templates you may want to check out our short research statement samples below:
Short Research Statement
6+ short research statement samples, 1. short academic career research statement, 2. short research personal statement, 3. short winning research statement, 4. short term anatomy research statement, 5. short term research statement, 6. sample short research statement, 7. short list research statement, what is a short research statement, how to write a short research statement, 1. introduction, 2. second to third paragraphs, 3. conclusion, what is the benefits of a research, what is a purpose statement, how long does a research study take.

Size: 382 KB

Size: 739 KB

Size: 164 KB

Size: 175 KB

Size: 66 KB

Size: 161 KB
A short research statement is a document that highlights your research growth: research experiences, interests, and plans. This includes a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete. When applying for an academic position, research productivity, focus and future are the most highly scrutinized in academic faculty appointments, particularly at research-intensive universities. This document is also needed should you intend to further your studies by joining graduate programs or post-doctoral studies.
The goal of the research statement is to introduce yourself to a search committee, which will probably contain professionals both in and outside your field, and get them interested in your work. It should be written for an audience of other professionals in your related field. A short research statement should be about 1 to 2 pages, 3 maybe the maximum. This should be brief and organized, and you should thoroughly read and follow the length and content requirements for each individual application. Your content should more or less include the following:
- Recent & Current Research: include preliminary results and how to build on results, provide a summary of your research and list major findings and outcomes.
- Future Research: discuss what are your short-term and long-term research goals, indicate how your research goals align with departmental goals and explain how your goals build on your recent research.
- Details: the research statement should be plan should be well-considered, realistic, and practical. And consider using preparatory data.
To get started, here are the components you will need for your short research statement.
The introduction which is the first paragraph of your research statement should summarize the contents of the research statement and include the information that is most important for departments to know. In this section introduce your research topic and interests in the context of your field.
In these sections, you should elaborate about your research project. Describe the significance of your projects for your field. Detail any publications initiated from your independent doctoral or postdoctoral research. Indicate plans to submit journals or future publication plans in greater detail. Describe the broader significance of your work. What ties your research projects together? What impact do you want to make on your field? If you’re writing a research statement for a teaching-oriented institution, you still can address some of the above questions, but make sure to connect them with your teaching.
A well-written conclusion provides you with several important opportunities to demonstrate your overall understanding of the research problem to the reader. This is by demonstrating the importance your ideas and introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem.
Conducting research is beneficial in a number of ways such as expanding knowledge and understanding of a chosen field, defining academic, career and personal interests, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills and increase business opportunities.
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Depending on the content and complexity of your topic, this may take up a day, weeks, a month or so.
The field of research has contributed in many important societal issues, science and development , environmental issues and in the progress of business organizations. A short research statement need not be fancy nor several pages long to make a point out of something. It should be written in sincerity of the research you have conducted in the past, are currently working on in the present and what you which to fulfill in the future. Overall, it has been beneficial in a lot areas and those who endeavor to take on it are very much respected and appreciated.
Related Posts
Free 11+ sample research plan, free 10+ marketing research proposal samples, free 10+ research paper proposal samples, free 10+ sample investment policy statement, free 10+ scientific research proposal samples, free 10+ compliance policy statement samples, free 10+ human resource statement of purpose samples, free 9+ sample goal statement, free 9+ sample research proposals, free 30+ research paper samples, free 10+ graduate statement of purpose samples, free 10+ dissertation problem statement samples, free 10+ sample confidentiality statement, free 10+ research disclosure statement samples, free 9+ grant problem statement samples, free 9+ one-page proposal samples, free 8+ research agenda samples, free 12+ sample research proposal, free 11+ statement of purpose samples.
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
How u.s. jews are experiencing the israel-hamas war.

Related: How U.S. Muslims are experiencing the Israel-Hamas war
American Jews report feeling a host of emotions – including sadness, anger, exhaustion and fear – in reaction to the Oct. 7 Hamas attack on Israel and the ensuing Israeli invasion of Gaza. Nine-in-ten say they think discrimination against Jews has risen in the United States since the Israel-Hamas war began. And three-quarters say they have felt personally offended by something they’ve seen in the news or on social media about the war .
But not all Jewish Americans are experiencing the conflict the same way. The survey, conducted Feb. 13-25, finds that younger and older Jews often view the war differently, mirroring patterns in the broader U.S. public. In both groups, younger adults tend to express much more negative attitudes toward Israel than older Americans do. U.S. Jews also differ by age when it comes to the level of connection they feel with Israel, as we found in our 2020 survey of Jewish Americans .
Pew Research Center conducted this survey to explore Americans’ views on the Israel-Hamas war, including what role the United States should play in the conflict. We surveyed a total of 12,693 U.S. adults from Feb. 13 to 25, 2024. Most of the respondents (10,642) are members of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel, an online survey panel recruited through national random sampling of residential addresses, which gives nearly all U.S. adults a chance of selection.
The remaining 2,051 respondents are members of three other survey panels – Ipsos’ KnowledgePanel, SSRS’s Opinion Panel, and NORC at the University of Chicago’s AmeriSpeak Panel – who were interviewed because they identify as Jewish or Muslim.
We “oversampled” (i.e., interviewed a disproportionately large number of) Jews and Muslims to provide more reliable estimates of their views on the topics covered in this survey. But these groups are not overrepresented in the national estimates reported here, because we adjusted for the oversampling in the weighting of the data. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education, religious affiliation and other categories. In total, 1,941 Jewish and 414 Muslim respondents participated in this survey.
While the sample design was identical for Jews and Muslims, the resulting sample sizes are different. There are two main reasons for this. The Jewish population in the United States is roughly double the size of the Muslim population . Consequently, national survey panels have roughly twice as many or more Jewish panelists as Muslim ones. In addition, decades of research on survey nonresponse has shown that some groups in the U.S. are more likely to participate in surveys than others. Generally speaking, Jewish adults are more likely to participate in surveys than Muslim adults.
The survey also included questions about where people were born and whether people identify as Arab or of Arab origin. Because of insufficient sample size, we are unable to analyze Arab Americans or Americans of Israeli or Palestinian descent separately.
In this survey, Jews and Muslims are defined as U.S. adults who answer a question about their current religion by saying they are Jewish or Muslim, respectively. Unlike our 2020 report on Jews in America , this report does not separately analyze the views of “Jews of no religion” (i.e., people who identify as Jewish culturally, ethnically or by family background but not by religion).
For more information on how we conducted this survey, refer to the ATP’s Methodology and the Methodology for this analysis. Here are the questions on views and knowledge of the Israel-Hamas war used in this analysis, and on perceptions of discrimination since the war began .
How and why the war is being fought
An overwhelming majority of Jewish American adults (93%) say that the way Hamas carried out its Oct. 7 attack was unacceptable.
But Jewish adults under 35 are divided over Israel’s military response: 52% say the way Israel has carried out the war has been acceptable, while 42% call it unacceptable, and 6% are unsure. Jews ages 50 and older are far more likely to say Israel’s conduct of the war has been acceptable (68%).
As for why the war is being fought in the first place, 77% of Jewish adults – including a majority in every age group – say Hamas’ reasons for fighting Israel are not valid. But Jewish adults under 35 are more likely than older Jews to say that Hamas’ reasons for fighting are valid: 31% of younger Jews take this position, compared with about one-in-ten of those ages 35 and older.
By comparison, 89% of Jewish Americans say Israel’s reasons for fighting Hamas are valid – far more than the 58% of all U.S. adults who say this . Younger Jews are less likely than their older counterparts to say Israel’s reasons for fighting Hamas are valid, though about eight-in-ten or more in every age group say this.
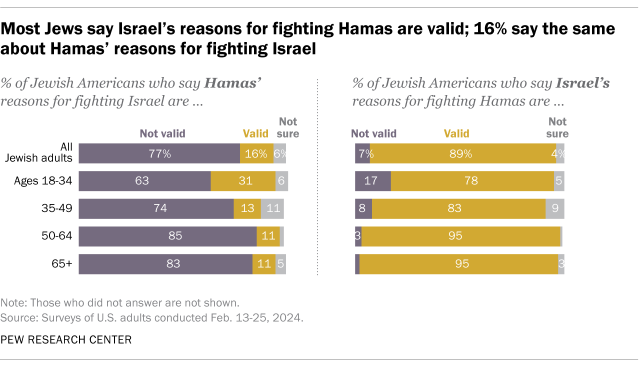
Views of the people and leadership involved in the war
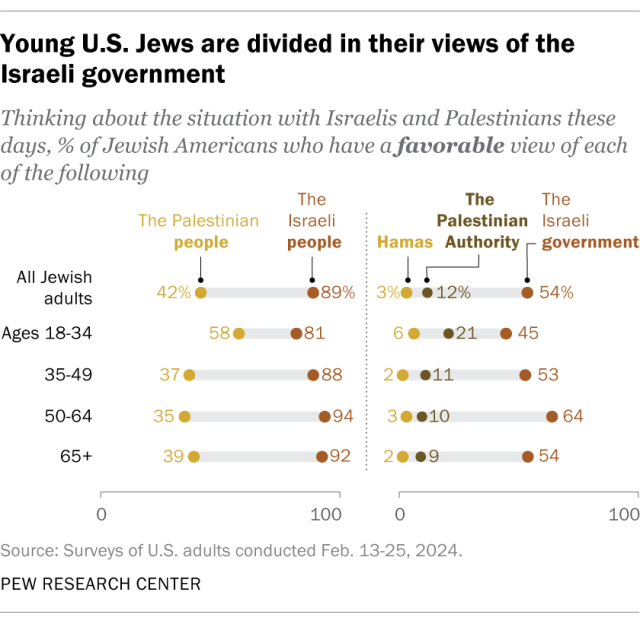
Around nine-in-ten U.S. Jews (89%) express a favorable view of the Israeli people, and 54% have a favorable view of the Israeli government. Jews are far more likely than the broader U.S. public to have a favorable view of the Israeli people (89% vs. 64%) and are also more likely than Americans overall to express a favorable opinion of Israel’s government (54% vs. 41%).
Four-in-ten American Jews have a favorable view of the Palestinian people – somewhat lower than the 50% of Americans overall who say the same. Very few Jewish Americans have a favorable opinion of Hamas, which has controlled Gaza, or the Palestinian Authority, which controls the West Bank (3% and 12%, respectively).
Jewish Americans are divided by party in their views of the Israeli government. Jews who identify as Republicans or lean toward the Republican Party are about twice as likely as Jews who identify as Democrats or lean Democratic to say they have a favorable view of the Israeli government (85% vs. 41%). (Among Jews, 68% identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party and 29% identify with or lean toward the Republican Party.) On the other hand, Jewish Democrats are more likely than Jewish Republicans to say they have a favorable view of the Palestinian people (52% vs. 20%) and the Palestinian Authority (14% vs. 9%).
Jewish Americans also differ by age in their views of the people and leadership involved in the conflict. Compared with older U.S. Jews, younger Jews express less favorable attitudes toward the Israeli people and more favorable views of the Palestinian people. Younger Jews also hold somewhat more positive views of the Palestinian Authority.
When it comes to the Israeli government, there are age differences among Jewish Americans, as there are among American overall . For example, 45% of Jews under 35 have a favorable view of the Israeli government, while 53% have an unfavorable view. Jews ages 50 to 64 are the only age group in which a majority express a favorable opinion of the Israeli government (64%).
What role should the U.S. play in the conflict?
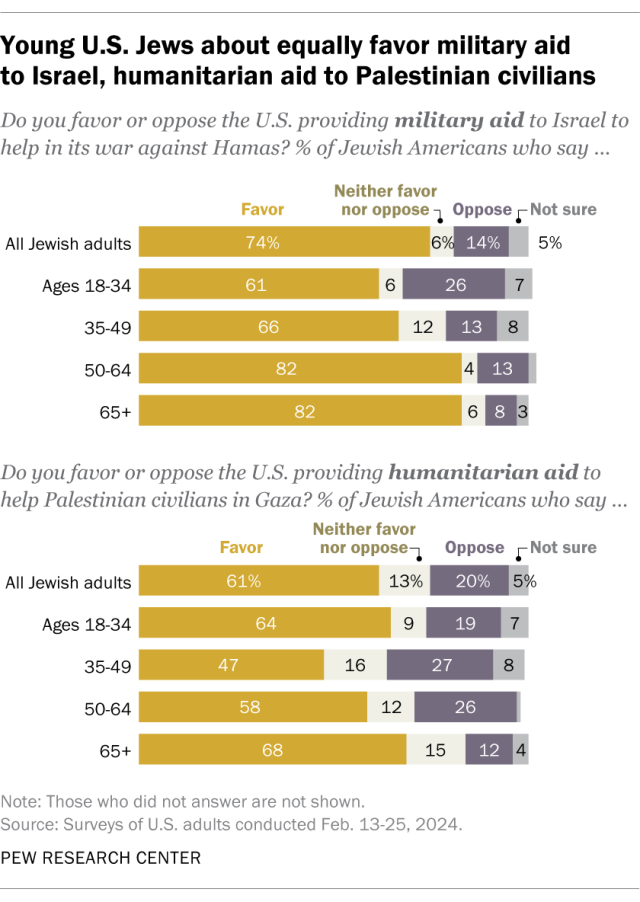
Most American Jews say the U.S. should play at least a minor role in diplomatically resolving the Israel-Hamas war. Majorities also favor providing military aid to Israel (74%) and humanitarian aid to Palestinian civilians in Gaza (61%). On all these questions, Jews tend to be more likely than U.S. adults as a whole to favor U.S. involvement .
Older Jews are more likely than their younger counterparts to say the U.S. should play a major diplomatic role in resolving the war: 54% of Jewish Americans ages 65 and older say this, compared with 33% of those ages 18 to 34. Older Jews are also more likely to favor the U.S. providing military aid to Israel to help in its war against Hamas (82% of those 50 and older vs. 61% of those 18 to 34).
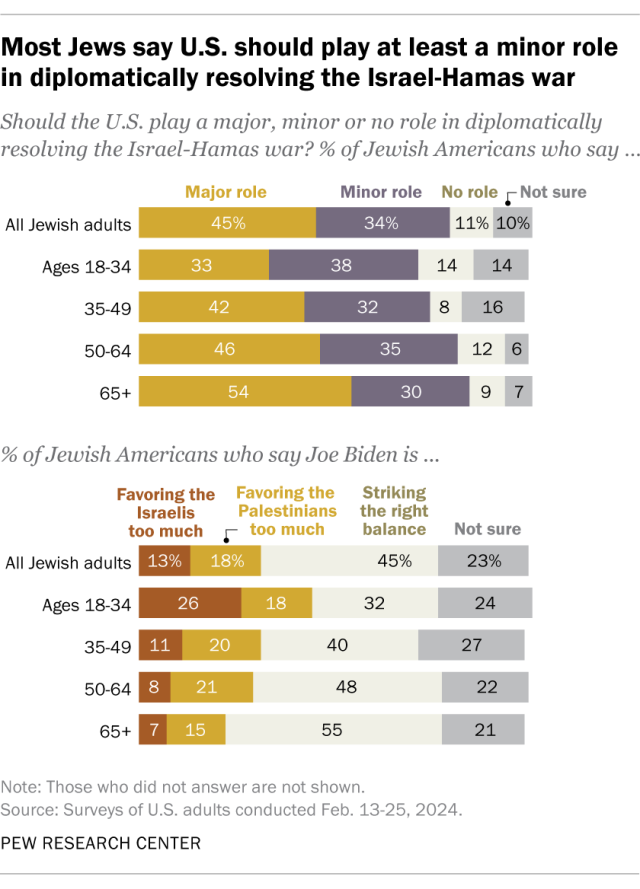
When it comes to how U.S. President Joe Biden is handling the conflict, relatively few Jewish adults under 50 (35%) say he is striking the right balance between Israelis and Palestinians. By comparison, 53% of Jews ages 50 and older say Biden is striking the right balance.
Discrimination, taking personal offense at speech or news about the Israel-Hamas war
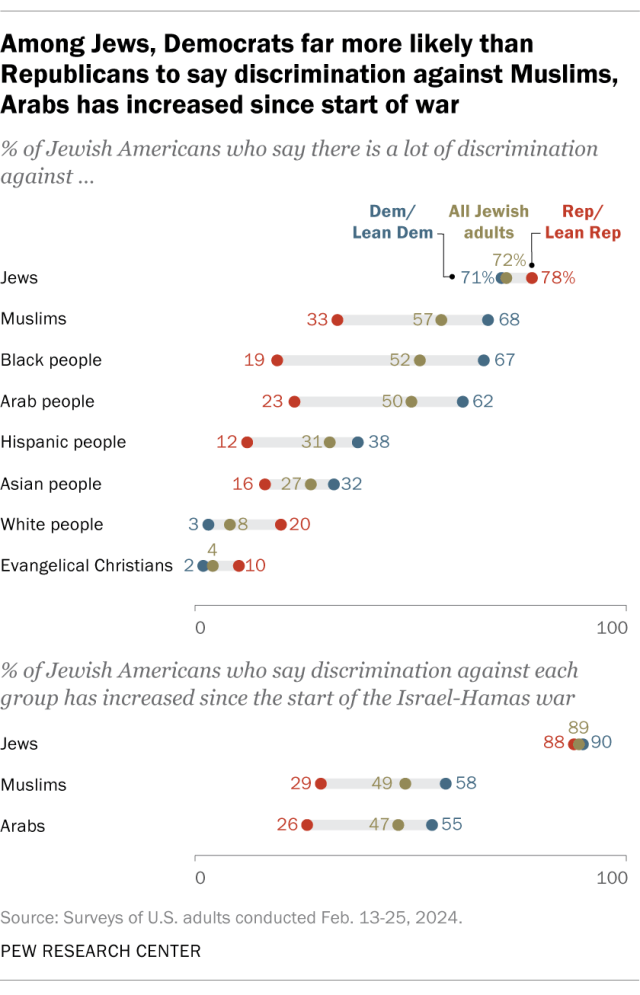
An overwhelming majority of Jewish Americans (94%) say there is at least some discrimination against Jews in America, including 72% who say there is a lot . Among Americans overall, a large majority (82%) also perceive at least some discrimination against American Jews.
Jewish Republicans and Democrats tend to perceive discrimination differently. Jewish Republicans are far less likely than Jewish Democrats to say that some groups – such as Muslims, Black people or Arab people – face a lot of discrimination in the U.S. today. Jewish Republicans are also far less likely than Jewish Democrats to say discrimination against Muslims and Arabs has increased since the start of the Israel-Hamas war.
Meanwhile, about three-quarters of U.S. Jews (74%) say they have felt offended because of something they saw on the news or social media about the Israel-Hamas war, and half have been offended by something someone has said around them about the war. A quarter say they have stopped talking to someone in person – or unfollowed or blocked someone online – because of that person’s comments about the conflict. Jews are far more likely than the U.S. public overall to say they have felt offended or stopped talking with someone under these circumstances .
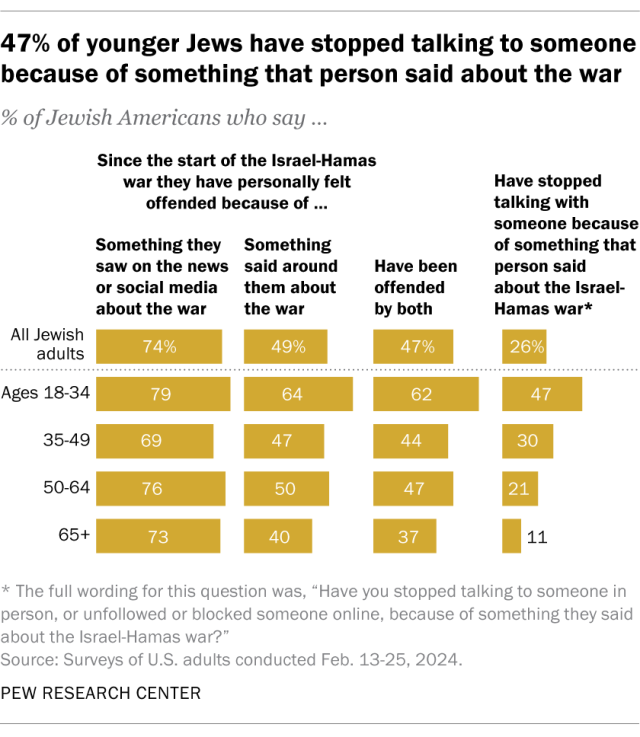
Younger Jews are especially likely to say they have felt offended, both by something they saw on social media or by something that was said around them. Six-in-ten Jewish Americans ages 18 to 34 say they have been offended by both (62%), while half or fewer among older age groups say the same.
Similarly, 47% of Jewish adults under the age of 35 say they have stopped talking to someone in person or online because of something that person said about the war. Jews ages 65 and older are the least likely to have done this (11%).

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Rising Numbers of Americans Say Jews and Muslims Face a Lot of Discrimination
How u.s. muslims are experiencing the israel-hamas war, striking findings from 2023, americans’ views of the israel-hamas war, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The document is, for the most part, short, well defined and robust. Samples & Examples. Academic Research Statement Examples guide researchers in organizing their thoughts, presenting their ideas effectively, and highlighting the significance of their work. To further enhance convenience, here are free downloadable templates that will enable ...
The research statement (or statement of research interests) is a common component of academic job applications. It is a summary of your research accomplishments, current work, and future direction and potential of your work. The statement can discuss specific issues such as: The research statement should be technical, but should be intelligible ...
state your short-term and long-term research goals Use the research statement only to describe your research. Your research statement is one of . a number of documents (e.g., personal statement, teaching statement, statement of diversity, resume/cv, cover letter, etc.) describing your academic career, so be discriminating and strategic
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete. The research statement is a common component of a potential candidate's application for post-undergraduate study.
A research statement is used when applying for academic faculty positions, and sometimes for research-intensive positions in think tanks or government. Because the academic job market is increasingly competitive, a common trend for hiring committees is to ask only for a cover letter and CV. If this is the case, you will need to condense your ...
This research statement is organized as follows: The first section discusses my work in the area of development economics/public policy, with a focus on my dissertation papers. The second section discusses my work in the area of contests/management from my postdoctoral work. Both sections include plans for future research in the respective areas.
o What are your short-term research goals (2-5 years)? o Discuss 2-3 feasible research ideas that interest you. o Explain how your goals build on (but are not necessarily direct extensions of) your recent work. ... Find sample research statements using a search engine, websites of professional organizations, etc. Finish a full draft.
UChicagoGRAD: Research Statements A well-written research statement should, most of all, convey a sense of focus in your research and scholarship and demonstrate your independence. In addition, it can: Formatting! 1" margins all around ! 11-12pt font ! Typically, 1-3 pages single spaced; if no length requirement is noted, UChicagoGRAD
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete. The research statement is a common component of a potential student's application for post-undergraduate study. The research statement is often the primary way ...
Four key components of a research statement. Background: Scientific interests and foundations. Skills: Research experience. Let your reader know how your interest developed and what you did outside of research to develop it (classes, workshops, books, etc.) Show the reader your research competency and what skills you bring to the table (write ...
Download Article. 1. Put an executive summary in the first section. Write 1-2 paragraphs that include a summary of your research agenda and its main focus, any publications you have, your plans for future research, and your ultimate career goals. Place these paragraphs at the very beginning of your research statement.
STEM or humanities fields--is a short formal account describing research interests, approaches, and future plans. Research statements for grants : Grantors are interested in providing funding for research: they also want the best bang for the money. Thus applicants who write research statements need to demonstrate that their research is
Form #2: Research Statement as Proposal. 1. Identify the gap or problem that your research will address a. Gap: what remains unknown about your topic b. Problem: issue for which you are developing a solution (more common in engineering, computer science) 2. Propose research questions, research aims, or problem statements 3.
A research statement is a summary of research achievements and a proposal for upcoming research. It often includes both current aims and findings, and future goals. Research statements are usually requested as part of a relevant job application process, and often assist in the identification of appropriate applicants. Learn more about how to ...
1. Be personal. This document is about you: who you are as a scientist, what interests you, where you see your research going in the future. Don't make it solely about the research (like you would a research manuscript or grant). Use "I" instead of "we". 2. Toot your own horn.
Make sure that your research statement is tailored to the guidelines. It is helpful to prepare two versions of your statement — a long one and a short one. The short version is usually the long one stripped of many details with the emphasis on high-level pictures and ideas. Say who you are. Your research statement tells a story about you.
A thesis statement that includes a clear reasoning blueprint (see " Blueprinting: Planning Your Essay ") will help your reader identify and follow your ideas. Before you submit your draft, make sure the title, the introduction, and the conclusion match. (I am amazed at how many students overlook this simple step.) 2.
Research Statements Career Advancement grad.uchicago.edu Usually 2 pages in length Research Statement and your name centered at the top Single spaced, with double spacing between paragraphs 1"margins and 11-12 pt. font Use subheadings for at-a-glance organization First-person point of view, with your research as the main character Frame your work appropriately, but do not
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Step 2: Exhibit the Current Focus of the Research Statement. Exhibit the current focus of your research statement, which would be to state the problem that needs to be addressed. If the problem is to generalized, be sure to choose a specific problem to be handled first. Give a short explanation in the form of a concept statement.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A good research interest statement sample can be hard to find. Still, it can also be a beneficial tool for writing one and preparing for a grad school application or post-graduate position. Your research interest statement is one of the key components of your application to get into grad school.In a few cases, admissions committees have used it instead of an interview, so it is important to ...
1. Short Academic Career Research Statement. 2. Short Research Personal Statement. 3. Short Winning Research Statement. 4. Short Term Anatomy Research Statement. 5.
American Jews report feeling a host of emotions - including sadness, anger, exhaustion and fear - in reaction to the Oct. 7 Hamas attack on Israel and the ensuing Israeli invasion of Gaza. Nine-in-ten say they think discrimination against Jews has risen in the United States since the Israel-Hamas war began. And three-quarters say they have ...