- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring

Global Health Care, Essay Example
Pages: 3
Words: 917
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Introduction
Global health care is a challenging phenomenon that supports the development of new perspectives and approaches to solving global health concerns, including nutrition, infectious disease, cancer, and chronic illness. It is important to address global health as a driving force in international healthcare expenditures because it represents an opportunity for clinicians throughout the world to collaborate and to address global health concerns to achieve favorable outcomes. Global healthcare in the modern era includes the utilization of technology to support different population groups and to address different challenges as related to global health problems that impact millions of people in different ways. These challenges demonstrate the importance of large-scale efforts to eradicate disease, to prevent illness, and to manage disease effectively through comprehensive strategies that encourage communication and collaboration across boundaries.
Global health care incorporates a number of critical factors into play so that people throughout the world are given a chance to live and to lead a higher quality of life. The World Health Organization (WHO) is of particular relevance because this organization supports global health initiatives and large-scale impact projects throughout the world (Sundewall et.al, 2009). The WHO recognizes the importance of developing strategies to address global health concerns by pooling resources in order to ensure that many population groups are positively impacted by these initiatives (Sundewall et.al, 2009). The WHO also collaborates with government bodies throughout the world to address specific concerns that are relevant to different population groups, such as infectious diseases, many of which ravage populations in a significant manner (Fineberg and Hunter, 2013). In this context, it is observed that global health has a significant impact on populations and their ability to thrive, given the high mortality rates of some diseases in less developed nations (Fineberg and Hunter, 2013). Therefore, it is expected that there will be additional frameworks in place to accommodate the needs of populations and the resources that are required to achieve favorable outcomes (Fineberg and Hunter, 2013).
In addition to the WHO, there are many other international organizations that support global health and disease in different ways. For example, The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) supports large-scale global health efforts to support the world’s children (imva.org, 2013). UNICEF works in conjunction with many governments and other sources of funding in order to accomplish its objectives related to child health and wellbeing (imva.org, 2013). UNICEF spends significant funds on many focus areas, including the preservation of child health, nutrition, emergency support, and sanitation in conjunction with local water supplies (imva.org, 2013). In addition, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) provides support in many areas, including a primary focus on healthcare in developing nations (imva.org, 2013).
Leininger’s Culture Care Theory is essential in satisfying the objectives of global health because it supports an understanding of the issues related to cultural diversity and how they impact healthcare practices throughout the world (Current Nursing, 2012). This theory embodies many of the differences that exist in modern healthcare practices and supports a greater understanding of the issues that are most relevant on a global scale (Current Nursing, 2012). This theory is applicable because it represents a call to action to consider cultural differences when providing care and treatment to different population groups, but not at the expense of the quality of care that is provided (Current Nursing, 2012). In many countries, the provision of care is largely dependent on cultural diversity and customs, which is essential to a thriving healthcare system; however, diversity must also incorporate the concept of providing maximum care for an individual in need of treatment (Current Nursing, 2012).
Professional nursing is highly relevant to global health because nurses address some of the most critical challenges in providing care and expanding access to treatment for millions of people throughout the world. However, it is also important for nurses working with global health initiatives to recognize the importance of these directives and to consider ways to improve quality of care without compromising principles or other factors in the process. These efforts will ensure that nurses maximize their knowledge and understanding of global health and its scope in order to achieve positive outcomes for people in desperate need of healthcare services throughout the world. Nurses must collaborate with small and large-scale organizations regarding global health issues so that population needs are targeted and are specific. These efforts will ensure that patients are treated in areas where healthcare access is severely limited.
Global health represents a significant set of challenges for clinicians throughout the world. It is important to recognize these concerns and to take the steps that are necessary to provide patients with the best possible outcomes to achieve optimal health. The scope of global health concerns is significant; therefore, it is important to address these concerns and to take the steps that are necessary to collaborate and promote initiatives to fight global health problems. When these objectives are achieved using the knowledge and expertise of nurses, it is likely that there will be many opportunities to treat patients and to educate them regarding positive health. With the assistance of large global organizations, nurses play an important role in shaping outcomes for women throughout the world.
Current Nursing (2012). Transcultural nursing. Retrieved from http://currentnursing.com/nursing_theory/transcultural_nursing.html
Fineberg, H.V., and Hunter, D. J. (2013). A global view of health – an unfolding series. T he New England Journal of Medicine, 368(1), 78-79.
Imva.org (2013). Bilateral agencies. Retrieved from http://www.imva.org/Pages/orgfrm.htm
Sundewall, J., Chansa, C., Tomson, G., Forsberg, B.C., and Mudenda, D. (2009). Global health initiatives and country health systems. The Lancet, 374, 1237.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Helping People: Compassion, Essay Example
Why Is There a Need to Breastfeed, Research Paper Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
- Open access
- Published: 07 April 2020
What is global health? Key concepts and clarification of misperceptions
Report of the 2019 GHRP editorial meeting
- Xinguang Chen 1 , 2 ,
- Hao Li 1 , 3 ,
- Don Eliseo Lucero-Prisno III 4 ,
- Abu S. Abdullah 5 , 6 ,
- Jiayan Huang 7 ,
- Charlotte Laurence 8 ,
- Xiaohui Liang 1 , 3 ,
- Zhenyu Ma 9 ,
- Zongfu Mao 1 , 3 ,
- Ran Ren 10 ,
- Shaolong Wu 11 ,
- Nan Wang 1 , 3 ,
- Peigang Wang 1 , 3 ,
- Tingting Wang 1 , 3 ,
- Hong Yan 3 &
- Yuliang Zou 3
Global Health Research and Policy volume 5 , Article number: 14 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
51k Accesses
26 Citations
8 Altmetric
Metrics details
The call for “W orking Together to Build a Community of Shared Future for Mankind” requires us to improve people’s health across the globe, while global health development entails a satisfactory answer to a fundamental question: “What is global health?” To promote research, teaching, policymaking, and practice in global health, we summarize the main points on the definition of global health from the Editorial Board Meeting of Global Health Research and Policy, convened in July 2019 in Wuhan, China. The meeting functioned as a platform for free brainstorming, in-depth discussion, and post-meeting synthesizing. Through the meeting, we have reached a consensus that global health can be considered as a general guiding principle, an organizing framework for thinking and action, a new branch of sciences and specialized discipline in the large family of public health and medicine. The word “global” in global health can be subjective or objective, depending on the context and setting. In addition to dual-, multi-country and global, a project or a study conducted at a local area can be global if it (1) is framed with a global perspective, (2) intends to address an issue with global impact, and/or (3) seeks global solutions to an issue, such as frameworks, strategies, policies, laws, and regulations. In this regard, global health is eventually an extension of “international health” by borrowing related knowledge, theories, technologies and methodologies from public health and medicine. Although global health is a concept that will continue to evolve, our conceptualization through group effort provides, to date, a comprehensive understanding. This report helps to inform individuals in the global health community to advance global health science and practice, and recommend to take advantage of the Belt and Road Initiative proposed by China.
“Promoting Health For All” can be considered as the mission of global health for collective efforts to build “a Community of Shared Future for Mankind” first proposed by President Xi Jinping of China in 2013. The concept of global health continues to evolve along with the rapid development in global health research, education, policymaking, and practice. It has been promoted on various platforms for exchange, including conferences, workshops and academic journals. Within the Editorial Board of Global Health Research and Policy (GHRP), many members expressed their own points of view and often disagreed with each other with regard to the concept of global health. Substantial discrepancies in the definition of global health will not only affect the daily work of the Editorial Board of GHRP, but also impede the development of global health sciences.
To promote a better understanding of the term “ global health” , we convened a special session in the 2019 GHRP Editorial Board Meeting on the 7th of July at Wuhan University, China. The session started with a review of previous work on the concept of global health by researchers from different institutions across the globe, followed by free brainstorms, questions-answers and open discussion. Individual participants raised many questions and generously shared their thoughts and understanding of the term global health. The session was ended with a summary co-led by Dr. Xinguang Chen and Dr. Hao Li. Post-meeting efforts were thus organized to further synthesize the opinions and comments gathered during the meeting and post-meeting development through emails, telephone calls and in-person communications. With all these efforts together, concensus have been met on several key concepts and a number of confusions have been clarified regarding global health. In this editorial, we report the main results and conclusions.
A brief history
Our current understanding of the concept of global health is based on information in the literature in the past seven to eight decades. Global health as a scientific term first appeared in the literature in the 1940s [ 1 ]. It was subsequently used by the World Health Organization (WHO) as guidance and theoretical foundation [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Few scholars discussed the concept of global health until the 1990s, and the number of papers on this topic has risen rapidly in the subsequent decade [ 5 ] when global health was promoted under the Global Health Initiative - a global health plan signed by the U.S. President Barack Obama [ 6 ]. As a key part of the national strategy in economic globalization, security and international policies, global health in the United States has promoted collaborations across countries to deal with challenging medical and health issues through federal funding, development aids, capacity building, education, scientific research, policymaking and implementation.
Based on his experience working with Professor Zongfu Mao, the lead Editors-in-Chief, who established the Global Health Institute at Wuhan University in 2011 and launched the GHRP in 2016, Dr. Chen presented his own thoughts surrounding the definition of global health to the 2019 GHRP Editorial Board Meeting. Briefly, Dr. Chen defined global health with a three-dimensional perspective.
First, global health can be considered as a guiding principle, a branch of health sciences, and a specialized discipline within the broader arena of public health and medicine [ 5 ]. As many researchers posit, global health first serves as a guiding principle for people who would like to contribute to the health of all people across the globe [ 5 , 7 , 8 ].
Second, Dr. Chen’s conceptualization of global health is consistent with the opinions of many other scholars. Global health as a branch of sciences focuses primarily on the medical and health issues with global impact or can be effectively addressed through global solutions [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Therefore, the goal of global health science is to understand global medical and health issues and develop global solutions and implications [ 7 , 9 , 15 , 17 , 18 , 19 ].
Third, according to Dr. Chen, to develop global health as a branch of science in the fields of public health and medicine, a specialized discipline must be established, including educational institutions, research entities, and academic societies. Only with such infrastructure, can the professionals and students in the global health field receive academic training, conduct global health research, exchange and disseminate research findings, and promote global health practices [ 5 , 15 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ].
Developmentally and historically, we have learned and will continue to learn global health from the WHO [ 1 , 4 , 24 , 25 ]. WHO’s projects are often ambitious, involving multiple countries, or even global in scope. Through research and action projects, the WHO has established a solid knowledge base, relevant theories, models, methodologies, valuable data, and lots of experiences that can be directly used in developing global health [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 ]. Typical examples include WHO’s efforts for global HIV/AIDS control [ 13 , 30 , 31 , 32 ], and the Primary Healthcare Programs to promote Health For All [ 33 , 34 ].
The definition of Global Health
From published studies in the international literature and our experiences in research, training, teaching and practice, our meeting reached a consensus-global health is a newly established branch of health sciences, growing out from medicine, public health and international health, with much input from the WHO. What makes global health different from them is that (1) global health deals with only medical and health issues with global impact [ 35 , 5 , 36 , 10 , 14 , 2 ] the main task of global health is to seek for global solutions to the issues with global health impact [ 7 , 18 , 37 ]; and (3) the ultimate goal is to use the power of academic research and science to promote health for all, and to improve health equity and reduce health disparities [ 7 , 14 , 15 , 18 , 38 ]. Therefore, global health targets populations in all countries and involves all sectors beyond medical and health systems, although global health research and practice can be conducted locally [ 39 ].
As a branch of medical and health sciences, global health has three fundamental tasks: (1) to master the spatio-temporal patterns of a medical and/or health issue across the globe to gain a better understanding of the issue and to assess its global impact [ 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 ]; (2) to investigate the determinants and influential factors associated with medical and health issues that are known to have global impact [ 15 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 ]; and (3) to establish evidence-based global solutions, including strategies, frameworks, governances, policies, regulations and laws [ 14 , 15 , 28 , 38 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 ].
Like public health, medicine, and other branches of sciences, global health should have three basic functions : The first function is to generate new knowledge and theories about global health issues, influential factors, and develop global solutions. The second function is to distribute the knowledge through education, training, publication and other forms of knowledge sharing. The last function is to apply the global health knowledge, theories, and intervention strategies in practice to solve global health problems.
Understanding the word “global”
Confusion in understanding the term ‘global health’ has largely resulted from our understanding of the word “global”. There are few discrepancies when the word ‘global’ is used in other settings such as in geography. In there, the world global physically pertains to the Earth we live on, including all people and all countries in the world. However, discrepancies appear when the word “global” is combined with the word “health” to form the term “global health”. Following the word “global” literately, an institution, a research project, or an article can be considered as global only if it encompasses all people and all countries in the world. If we follow this understanding, few of the work we are doing now belong to global health; even the work by WHO are for member countries only, not for all people and all countries in the world. But most studies published in various global health journals, including those in our GHRP, are conducted at a local or international level. How could this global health happen?
The argument presented above leads to another conceptualization: Global health means health for a very large group of people in a very large geographic area such as the Western Pacific, Africa, Asia, Europe, and Latin America. Along with this line of understanding, an institution, a research project or an article involving multi-countries and places can be considered as global, including those conducted in countries involved in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) [ 26 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 ]. They are considered as global because they meet our definitions of global health which focus on medical and health issues with global impact or look for global solutions to a medical or health issue [ 5 , 7 , 22 ].
One step further, the word ‘global’ can be considered as a concept of goal-setting in global health. Typical examples of this understanding are the goals established for a global health institution, for faculty specialized in global health, and for students who major or minor in global health. Although few of the global health institutions, scholars and students have conducted or are going to conduct research studies with a global sample or delivered interventions to all people in all countries, all of them share a common goal: Preventing diseases and promoting health for all people in the world. For example, preventing HIV transmission within Wuhan would not necessarily be a global health project; but the same project can be considered as global if it is guided by a global perspective, analyzed with methods with global link such as phylogenetic analysis [ 52 , 53 ], and the goal is to contribute to global implications to end HIV/AIDS epidemic.
The concept of global impact
Global impact is a key concept for global health. Different from other public health and medical disciplines, global health can address any issue that has a global impact on the health of human kind, including health system problems that have already affected or will affect a large number of people or countries across the globe. Three illustrative examples are (1) the SARS epidemic that occurred in several areas in Hong Kong could spread globally in a short period [ 11 ] to cause many medical and public health challenges [ 54 , 55 ]; (2) the global epidemic of HIV/AIDS [ 13 ]; and the novel coronavirus epidemic first broke out in December 2019 in Wuhan and quickly spread to many countries in the world [ 56 ].
Along with rapid and unevenly paced globalization, economic growth, and technological development, more and more medical and health issues with global impact emerge. Typical examples include growing health disparities, migration-related medical and health issues, issues related to internet abuse, the spread of sedentary lifestyles and lack of physical activity, obesity, increasing rates of substance abuse, depression, suicide and many other emerging mental health issues, and so on [ 10 , 23 , 36 , 42 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ]. GHRP is expecting to receive and publish more studies targeting these issues guided by a global health perspective and supports more researchers to look for global solutions to these issues.
The concept of global solution
Another concept parallel to global impact is global solution . What do we mean by global solutions? Different from the conventional understanding in public health and medicine, global health selectively targets issues with global impact. Such issues often can only be effectively solved at the macro level through cross-cultural, international, and/or even global collaboration and cooperation among different entities and stakeholders. Furthermore, as long as the problem is solved, it will benefit a large number of population. We term this type of interventions as a global solution. For example, the 90–90-90 strategy promoted by the WHO is a global solution to end the HIV/AIDS epidemic [ 61 , 62 ]; the measures used to end the SARS epidemic is a global solution [ 11 ]; and the ongoing measures to control influenza [ 63 , 64 ] and malaria [ 45 , 65 ], and the measures taken by China, WHO and many countries in the world to control the new coronaviral epidemic started in China are also great examples of global solutions [ 66 ].
Global solutions are also needed for many emerging health problems, including cardiovascular diseases, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, internet abuse, drug abuse, tobacco smoking, suicide, and other problems [ 29 , 44 ]. As described earlier, global solutions are not often a medical intervention or a procedure for individual patients but frameworks, policies, strategies, laws and regulations. Using social media to deliver interventions represents a promising approach in establishment of global solutions, given its power to penetrate physical barriers and can reach a large body of audience quickly.
Types of Global Health researches
One challenge to GHRP editors (and authors alike) is how to judge whether a research study is global? Based on the new definition of global health we proposed as described above, two types of studies are considered as global and will receive further reviews for publication consideration. Type I includes projects or studies that involve multiple countries with diverse backgrounds or cover a large diverse populations residing in a broad geographical area. Type II includes projects or studies guided by a global perspective, although they may use data from a local population or a local territory. Relative to Type I, we anticipate more Type II project and studies in the field of global health. Type I study is easy to assess, but caution is needed to assess if a project or a study is Type II. Therefore, we propose the following three points for consideration: (1) if the targeted issues are of global health impact, (2) if the research is attempted to understand an issue with a global perspective, and (3) if the research purpose is to seek for a global solution.
An illustrative example of Type I studies is the epidemic and control of SARS in Hong Kong [ 11 , 67 ]. Although started locally, SARS presents a global threat; while controlling the epidemic requires international and global collaboration, including measures to confine the infected and measures to block the transmission paths and measures to protect vulnerable populations, not simply the provisions of vaccines and medicines. HIV/AIDS presents another example of Type I project. The impact of HIV/AIDS is global. Any HIV/AIDS studies regardless of their scope will be global as long as it contributes to the global efforts to end the HIV/AIDS epidemic by 2030 [ 61 , 62 ]. Lastly, an investigation of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) in a country, in Nepal for example, can be considered as global if the study is framed from a global perspective [ 44 ].
The discussion presented above suggests that in addition to scope, the purpose of a project or study can determine if it is global. A pharmaceutical company can target all people in the world to develop a new drug. The research would be considered as global if the purpose is to improve the medical and health conditions of the global population. However, it would not be considered as global if the purpose is purely to pursue profit. A research study on a medical or health problem among rural-to-urban migrants in China [ 57 , 58 , 60 ] can be considered as global if the researchers frame the study with a global perspective and include an objective to inform other countries in the world to deal with the same or similar issues.
Think globally and act locally
The catchphrase “think globally and act locally” presents another guiding principle for global health and can be used to help determine whether a medical or public health research project or a study is global. First, thinking globally and acting locally means to learn from each other in understanding and solving local health problems with the broadest perspective possible. Taking traffic accidents as an example, traffic accidents increase rapidly in many countries undergoing rapid economic growth [ 68 , 69 ]. There are two approaches to the problem: (1) locally focused approach: conducting research studies locally to identify influential factors and to seek for solutions based on local research findings; or (2) a globally focused approach: conducting the same research with a global perspective by learning from other countries with successful solutions to issues related traffic accidents [ 70 ].
Second, thinking globally and acting locally means adopting solutions that haven been proven effective in other comparable settings. It may greatly increase the efficiency to solve many global health issues if we approach these issues with a globally focused perspective. For example, vector-borne diseases are very prevalent among people living in many countries in Africa and Latin America, such as malaria, dengue, and chikungunya [ 45 , 71 , 72 ]. We would be able to control these epidemics by directly adopting the successful strategy of massive use of bed nets that has been proven to be effective and cost-saving [ 73 ]. Unfortunately, this strategy is included only as “simple alternative measures” in the so-called global vector-borne disease control in these countries, while most resources are channeled towards more advanced technologies and vaccinations [ 16 , 19 , 74 ].
Third, thinking globally and acting locally means learning from each other at different levels. At the individual level, people in high income countries can learn from those in low- and mid-income countries (LMICs) to be physically more active, such as playing Taiji, Yoga, etc.; while people in LMICs can learn from those in high income countries to improve their hygiene, life styles, personal health management, etc. At the population level, communities, organizations, governments, and countries can learn from each other in understanding their own medical and health problems and healthcare systems, and to seek solutions for these problems. For example, China can learn from the United States to deal with health issues of rural to urban migrants [ 75 ]; and the United States can learn from China to build three-tier health care systems to deliver primary care and prevention measures to improve health equality.
Lastly, thinking globally and acting locally means opportunities to conduct global health research and to be able to exchange research findings and experiences across the globe; even without traveling to another country. For example, international immigrants and international students present a unique opportunity for global health research in a local city [ 5 , 76 ]. To be global, literature search and review remains the most important approach for us to learn from each other besides conducting collaborative work with the like-minded researchers across countries; rapid development in big data and machine learning provide another powerful approach for global health research. Institutions and programs for global health provides a formal venue for such learning and exchange opportunities.
Reframing a local research study as global
The purpose of this article is to promote global health through research and publication. Anyone who reads this paper up to this point might already be able to have a clear idea on how to reframe his/her own research project or article to be of global nature. There is no doubt that a research project is global if it involves multiple countries with investigators of diverse backgrounds from different countries. However, if a research project targets a local population with investigators from only one or two local institutions, can such project be considered as global?
Our answer to this question is “yes” even if a research study is conducted locally, if the researcher (1) can demonstrate that the issue to be studied or being studied has a global impact, or (2) eventually looks for a global solution although supported with local data. For example, the study of increased traffic accidents in a city in Pakistan can be considered as global if the researchers frame the problem from a global perspective and/or adopt global solutions by learning from other countries. On the other hand, a statistical report of traffic accidents or an epidemiological investigation of factors related to the traffic accidents at the local level will not be considered as global. Studies conducted in a local hospital on drug resistance to antibiotics and associated cost are global if expected findings can inform other countries to prevent abuse of antibiotics [ 77 ]. Lastly, studies supported by international health programs can be packaged as global simply by broadening the vision from international to global.
Is Global Health a new bottle with old wine?
Another challenge question many scholars often ask is: “What new things can global health bring to public health and medicine?” The essence of this question is whether global health is simply a collection of existing medical and health problems packaged with a new title? From our previous discussion, many readers may already have their own answer to this question that this is not true. However, we would like to emphasize a few points. First, global health is not equal to public health, medicine or both, but a newly emerged sub-discipline within the public health-medicine arena. Global health is not for all medical and health problems but for the problems with global impact and with the purpose of seeking global solutions. In other words, global health focuses primarily on mega medical and health problems that transcend geographical, cultural, and national boundaries and seeks broad solutions, including frameworks, partnerships and cooperation, policies, laws and regulations that can be implemented through governments, social media, communities, and other large and broad reaching mechanisms.
Second, global health needs many visions, methods, strategies, approaches, and frameworks that are not conventionally used in public health and medicine [ 5 , 18 , 22 , 34 ]. They will enable global health researchers to locate and investigate those medical and health issues with global impact, gain new knowledge about them, develop new strategies to solve them, and train health workers to deliver the developed strategies. Consequently, geography, history, culture, sociology, governance, and laws that are optional for medicine and public health are essential for global health. Lastly, it is fundamental to have a global perspective for anyone in global health, but this could be optional for other medical and health scientists [ 40 , 41 ].
Global Health, international health, and public health
As previously discussed, global health has been linked to several other related disciplines, particularly public health, international health, and medicine [ 3 , 5 , 7 , 18 , 22 ]. To our understanding, global health can be considered as an application of medical and public health sciences together with other disciplines (1) in tackling those issues with global impact and (2) in the effort to seek global solutions. Thus, global health treats public health sciences and medicine as their foundations, and will selectively use theories, knowledge, techniques, therapeutics and prevention measures from public health, medicine, and other disciplines to understand and solve global health problems.
There are also clear boundaries between global health, public health and medicine with regard to the target population. Medicine targets patient populations, public health targets health populations in general, while global health targets the global population. We have to admit that there are obvious overlaps between global health, public health and medicine, particularly between global health and international health. It is worth noting that global health can be considered as an extension of international health with regard to the scope and purposes. International health focuses on the health of participating countries with intention to affect non-participating countries, while global health directly states that its goal is to promote health and prevent and treat diseases for all people in all countries across the globe. Thus, global health can be considered as developed from, and eventually replace international health.
Challenges and opportunities for China to contribute to Global Health
To pursue A Community with a Shared Future for Mankind , China’s BRI , currently involving more than 150 countries across the globe, creates a great opportunity for Chinese scholars to contribute to global health. China has a lot to learn from other countries in advancing its medical and health technologies and to optimize its own healthcare system, and to reduce health disparities among the 56 ethnic groups of its people. China can also gain knowledge from other countries to construct healthy lifestyles and avoid unhealthy behaviors as Chinese people become more affluent. Adequate materials and money may be able to promote physical health in China; but it will be challenging for Chinese people to avoid mental health problems currently highly prevalent in many rich and developed countries.
To develop global health, we cannot ignore the opportunities along with the BRI for Chinese scholars to share China’s lessons and successful experience with other countries. China has made a lot of achievements in public health and medicine before and after the Open Door Policy [ 49 , 78 ]. Typical examples include the ups and downs of the 3-Tier Healthcare Systems, the Policy of Prevention First, and the Policy of Putting Rural Health as the Priority, the Massive Patriotic Hygiene Movement with emphasis on simple technology and broad community participation, the Free Healthcare System for urban and the Cooperative Healthcare System for rural residents. There are many aspects of these initiatives that other countries can emulate including the implementation of public health programs covering a huge population base unprecedented in many other countries.
There are challenges for Chinese scholars to share China’s experiences with others as encountered in practice. First of all, China is politically very stable while many other countries have to change their national leadership periodically. Changes in leadership may result in changes in the delivery of evidence- based intervention programs/projects, although the changes may not be evidence-based but politically oriented. For example, the 3-Tier Healthcare System that worked in China [ 79 , 80 ] may not work in other countries and places without modifications to suit for the settings where there is a lack of local organizational systems. Culturally, promotion of common values among the public is unique in China, thus interventions that are effective among Chinese population may not work in countries and places where individualism dominates. For example, vaccination program as a global solution against infectious diseases showed great success in China, but not in the United States as indicated by the 2019 measles outbreak [ 81 ].
China can also learn from countries and international agencies such as the United Kingdom, the United States, the World Health Organization, and the United Nations to successfully and effectively provide assistance to LMICs. As China develops, it will increasingly take on the role of a donor country. Therefore, it is important for Chinese scholars to learn from all countries in the world and to work together for a Community of Shared Future for Mankind during the great course to develop global health.
Promotion of global health is an essential part of the Working Together to Build a Community of Shared Future for Mankind. In this editorial, we summarized our discussions in the 2019 GHRP Editorial Board Meeting regarding the concept of global health. The goal is to enhance consensus among the board members as well as researchers, practitioners, educators and students in the global health community. We welcome comments, suggestions and critiques that may help further our understanding of the concept. We would like to keep the concept of global health open and let it evolve along with our research, teaching, policy and practice in global health.
Dunham GC. Today's global Frontiers in public health: I. a pattern for cooperative public health. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1945;35(2):89–95.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kickbusch I. Health promotion: a global perspective. Can J Public Health. 1986;77(5):321–6.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kickbusch I. Global + local = glocal public health. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1999;53(8):451–2.
Kickbusch I. Mapping the future of public health: action on global health. Can J Public Health. 2006;97(1):6–8.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chen X. Understanding the development and perception of global health for more effective student education. Yale J Biol Med. 2014;87(3):231–40.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bristol N. Obama's plans for US and global health. Lancet. 2008;372(9652):1797–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Koplan JP, Bond TC, Merson MH, Reddy KS, Rodriguez MH, Sewankambo NK, et al. Towards a common definition of global health. Lancet. 2009;373(9679):1993–5.
Peluso MJ, Encandela J, Hafler JP, Margolis CZ. Guiding principles for the development of global health education curricula in undergraduate medical education. Med Teach. 2012;34(8):653–8.
Brown TM, Cueto M, Fee E. The World Health Organization and the transition from international to global public health. Am J Public Health. 2006;96(1):62–72.
Friedrich MJ. Global obesity epidemic worsening. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2017;318(7):603.
Google Scholar
Hung LS. The SARS epidemic in Hong Kong: what lessons have we learned? J R Soc Med. 2003;96(8):374–8.
Institute of Medicine (US), Board on International Health. America's vital interest in global health: protecting our people, enhancing our economy, and advancing our international interests. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 1997.
Katz IT, Ehrenkranz P, El-Sadr W. The global HIV epidemic what will it take to get to the finish line? Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2018;319(11):1094–5.
Article Google Scholar
Kickbusch I. Global health diplomacy: how foreign policy can influence health. BMJ. 2011;342:d3154.
Ren R. The definition and characteristics of global health. Medicine & Philosophy. 2015;36(8A):1–3.
CAS Google Scholar
Strategies, The malERA Consultative Group on Integration. malERA: An updated research agenda for basic science and enabling technologies in malaria elimination and eradication. PLoS Med. 2017;14(11):e1002451.
Kickbusch I, Hein W, Silberschmidt G. Addressing global health governance challenges through a new mechanism: the proposal for a committee C of the world health assembly. J Law Med Ethics. 2010;38(3):550–63.
Merson MH, Black RE, Mills AJ. Global health: diseases, programs, systems and policies. Jones & Bartlett Learning, L.L.C: New York/Ontario/London; 2012.
The malERA Consultative Group on Integration Strategies. A research agenda for malaria eradication: cross-cutting issues for eradication. PLoS Med. 2011;8(1):e1000404.
Mao Z, Liu P, Xiang H. Reformation and renewal of the undergraduate education based on a global health perspective - an example of the College of Health at Wuhan University. Wuhan, China: Wuhan University Press; 2018.
Rowson M, Smith A, Hughes R, Johnson O, Maini A, Martin S, Yudkin JS, et al. The evolution of global health teaching in undergraduate medical curricula. Glob Health. 2012;8(1):35.
Rowson M, Willott C, Hughes R, Maini A, Martin S, Miranda JJ, Yudkin JS, et al. Conceptualising global health: theoretical issues and their relevance for teaching. Glob Health. 2012;8(1):36.
White SK. Public health at a crossroads: assessing teaching on economic globalization as a social determinant of health. Crit Public Health. 2012;22(3):281–95.
Khubchandani J, Simmons R. Going global: building a foundation for global health promotion research to practice. Health Promot Pract. 2012;13(3):293–7.
Kickbusch I, Silberschmidt G, Buss P. Global health diplomacy: the need for new perspectives, strategic approaches and skills in global health. Bull World Health Organ. 2007;85(3):230–2.
Agaku IT, Ayo-Yusuf OA, Vardavas CI, Connolly G. Predictors and patterns of cigarette and smokeless tobacco use among adolescents in 32 countries, 2007-2011. J Adolesc Health. 2014;54(1):47–53.
Nikaj S, Chaloupka FJ. The effect of prices on cigarette use among youths in the global youth tobacco survey. Nicotine Tob Res. 2014;16(S1):S16–23.
World Health Organization. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. Geneva, Switzerland World Health Organization; 2003.
Rao S, Aslam SK, Zaheer S, Shafique K. Anti-smoking initiatives and current smoking among 19643 adolescents in South Asia: findings from the global youth tobacco survey. Harm Reduct J. 2014;11(1):8.
Harman S. 15 years of 'War on AIDS': what impact has the global HIV/AIDS response had on the political economy of Africa? Rev Afr Polit Econ. 2015;42(145):467–76.
Raguin G, Girard PM. Toward a global health approach: lessons from the HIV and Ebola epidemics. Glob Health. 2018;14(1):1–4.
Stover J, Bertozzi S, Gutierrez JP, Walker N, Stanecki KA, Greener R, Ghys PD, et al. The global impact of scaling up HIV/AIDS prevention programs in low- and middle-income countries. Science. 2006;311(5766):1474–6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Amofah GK. Ghana. Selective versus comprehensive primary health care. Trop Dr. 1994;24(2):76–8.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Magnussen L, Ehiri J, Jolly P. Comprehensive versus selective primary health care: lessons for global health policy. Health Aff (Millwood). 2004;23(3):167–76.
Brown H. WHO puts cancer on global health agenda. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5(11):644.
Degenhardt L, Stockings E, Patton G, Hall WD, Lynskey M. The increasing global health priority of substance use in young people. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3(3):251–64.
Alonso PL, Brown G, Tanner M, Integratio, maIERA Consultative Grp. A Research Agenda for Malaria Eradication: Cross-Cutting Issues for Eradication. Plos Medicine. 2011;8(1):e1000399.
Stuckler D, McKee M. Five metaphors about global-health policy. Lancet. 2008;372(9633):95–7.
Beaglehole R, Bonita R. What is global health. Glob Health Action. 2010;3:5142.
Chen X, Chen DG. Statistical methods for global health and epidemiology. Basel, Switzerland: Springer; 2019.
Hao YT, Chen X. Research methods in global health (textbook). Beijing, China: People' Health Publication House; 2018.
Labonte R, Schrecker T. Globalization and social determinants of health: introduction and methodological background (part 1 of 3). Glob Health. 2007;3(1):5.
Labonte R, Schrecker T. Globalization and social determinants of health: the role of the global marketplace (part 2 of 3). Glob Health. 2007;3(1):6.
Aifah A, Iwelunmor J, Akwanalo C, Allison J, Amberbir A, Asante KP, Weber MB, et al. The Kathmandu declaration on global CVD/hypertension research and implementation science: a framework to advance implementation research for cardiovascular and other noncommunicable diseases in low- and middle-income countries. Glob Heart. 2019;14(2):103–7.
Feachem R, Sabot O. A new global malaria eradication strategy. Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1633–5.
Petersen PE. World health organization global policy for improvement of oral health--world health assembly 2007. Int Dent J. 2008;58(3):115–21.
Singh N. A new global malaria eradication strategy: implications for malaria research from an Indian perspective. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009;103(12):1202–3.
Grimm S. China-Africa cooperation: promises, pratice and prospects. Journal of Contemporary China. 2014;23(90):993–1011.
Tang K, Li ZH, Li WK, Chen L. China's silk road and global health. Lancet. 2017;390(10112):2595–601.
Witvliet MI, Arah OA, Stronks K, Kunst AE. A global study on lone mothers: exploring the associations of self-assessed general health with motherhood types and gender inequality in 32 countries. Womens Health Issues. 2014;24(2):e177–85.
Zhu S, Zhu W, Qian W, He Y, Huang J. A China - Vietnam collaboration for public health care: a preliminary study. Glob Health Res Policy. 2019;4(1):23.
Rife BD, Mavian C, Chen X, Ciccozzi M, Salemi M, Min J, Prosperi MC. Phylodynamic applications in 21(st) century global infectious disease research. Glob Health Res Policy. 2017;2(1):13.
Zhou S, Cella E, Zhou W, Kong WH, Liu MQ, Liu PL, Chen X, et al. Population dynamics of hepatitis C virus subtypes in injecting drug users on methadone maintenance treatment in China associated with economic and health reform. J Viral Hepat. 2017;24(7):551–60.
Lee A, Abdullah AS. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: a challenge for public health practice in Hong Kong. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2003;57(9):655–8.
Abdullah AS, Thomas GN, McGhee SM, Morisky DE. Impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) on travel and population mobility: implications for travel medicine practitioners. J Travel Med. 2004;11(2):107–11.
Li Q, Guan XH, Wu P, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020.
Chen XG, Yu B, Gong J, Wang PG, Elliott AL. Social capital associated with quality of life mediated by employment experiences: evidence from a random sample of rural-to-urban migrants in China. Soc Indic Res. 2018;139(1):327–46.
Guo Y, Chen XG, Gong J, Li F, Zhu CY, Yan YQ, Wang L. Association between spouse/child separation and migration-related stress among a random sample of rural-to-urban migrants in Wuhan China. Plos One. 2016;11(4):e0154252.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Sinyor M, Tse R, Pirkis J. Global trends in suicide epidemiology. Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 2017;30(1):1–6.
Yu B, Chen XG, Elliott AL, Wang Y, Li F, Gong J. Social capital, migration stress, depression and sexual risk behaviors among rural-to-urban migrants in China: a moderated mediation modeling analysis. Anxiety Stress and Coping. 2019;32(4):362–75.
Jamieson D, Kellerman SE. The 90 90 90 strategy to end the HIV pandemic by 2030: can the supply chain handle it? J Int AIDS Soc. 2016;19(1):20917.
Lima VD, St-Jean M, Rozada I, Shoveller JA, Nosyk B, Hogg RS, Montaner JSG, et al. Progress towards the United Nations 90-90-90 and 95-95-95 targets: the experience in British Columbia. Canada J Int AIDS Soc. 2017;20(3):e25011.
Friede M, Palkonyay L, Alfonso C, Pervikov Y, Torelli G, Wood D, Kieny MP. WHO initiative to increase global and equitable access to influenza vaccine in the event of a pandemic: supporting developing country production capacity through technology transfer. Vaccine. 2011;29(S1):A2–7.
Palkonyay L, Fatima H. A decade of adaptation: regulatory contributions of the World Health Organization to the global action plan for influenza vaccines (2006-2016). Vaccine. 2016;34(45):5414–9.
McCoy D, Kembhavi G, Patel J, Luintel A. The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation's grant-making programme for global health. Lancet. 2009;373(9675):1645–53.
World Health Organization. Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Geneva, Switzerland; 2020.
Abdullah AS, Tomlinson B, Cockram CS, Thomas GN. Lessons from the severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak in Hong Kong. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9(9):1042–5.
Ameratunga S, Hijar M, Norton R. Road-traffic injuries: confronting disparities to address a global-health problem. Lancet. 2006;367(9521):1533–40.
Naci H, Chisholm D, Baker TD. Distribution of road traffic deaths by road user group: a global comparison. Injury Prevention. 2009;15(1):55–9.
Kareem A. Review of global menace of road accidents with special reference to Malaysia- a social perspective. Malays J Med Sci. 2003;10(2):31–9.
Gubler DJ. The economic burden of dengue. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;86(5):743–4.
Wettstein ZS, Fleming M, Chang AY, Copenhaver DJ, Wateska AR, Bartsch SM, Kulkarni RP, et al. Total economic cost and burden of dengue in Nicaragua: 1996-2010. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;87(4):616–22.
Cheng H, Yang W, Kang W, Liu C. Large-scale spraying of bednets to control mosquito vectors and malaria in Sichuan. China Bull World Health Organ. 1995;73(3):321–8.
The malERA Consultative Group on Integration Strategies. A research agenda for malaria eradication: vector control. PLoS Med. 2011;8(1):e1000401.
Menzies NA, Hill AN, Cohen T, Salomon JA. The impact of migration on tuberculosis in the United States. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2018;22(12):1392–403.
Liu Y, Chen XG, Li SY, Bin Y, Wang Y, Yan H. Path analysis of acculturative stress components and their relationship with depression among international students in China. Stress Health. 2016;32(5):524–32.
Li H, Liu XL, Cui D, Wang Q, Mao Z, Gang L, Sun J, et al. Estimating the direct medical economic disease burden of healthcare associated infections in Chinese public tertiary hospitals. 2017;29(5):440-450. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2017;29(5):440–50.
Blumenthal D, Hsiao W. Lessons from the East - China's rapidly evolving health care system. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(14):1281–5.
Chen Z. Launch of the health-care reform plan in China. Lancet. 2009;373(9672):1322–4.
Liu XZ, Wang JL. An introduction to China’s health care system. J Public Health Policy. 1991;12(1):104–16.
Patel M, Lee AD, Redd SB, Clemmons NS, McNall RJ, Cohn AC, Gastanaduy PA. Increase in measles cases - United States, January 1-April 26, 2019. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(7):2127–30.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank those who had provided their comments for the improvement of the manuscript.
The work is funded by the journal development funds of Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Global Health Institute, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Xinguang Chen, Hao Li, Xiaohui Liang, Zongfu Mao, Nan Wang, Peigang Wang & Tingting Wang
Department of Epidemiology, University of Florida, Florida, USA
Xinguang Chen
School of Health Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Hao Li, Xiaohui Liang, Zongfu Mao, Nan Wang, Peigang Wang, Tingting Wang, Hong Yan & Yuliang Zou
Department of Global Health and Development, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, UK
Don Eliseo Lucero-Prisno III
Global Health Research Center, Duke Kunshan University, Kunshan, China
Abu S. Abdullah
Duke Global Health Institute, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, USA
School of Public Health, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Jiayan Huang
Consultant in Global Health, London, UK
Charlotte Laurence
School of Public Health, Guangxi Medical University, Guangxi, China
Global Health Research Center, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
School of Public Health, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Shaolong Wu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Chen XG wrote the manuscript. LI H organized the meeting, collecting the comments and editing the manuscript. Lucero-Prisno DE integrated all the comments together. Abdullah AS, Huang JY, Laurence C, Liang XH, Ma ZY, Ren R, Wu SL, Wang N, Wang PG and Wang Tt all participated in the discussion and comments of this manuscript. Laurence C and Liang XH both provided language editing. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hao Li .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The manuscript was sent to all the authors and they all agreed to submit it for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Chen, X., Li, H., Lucero-Prisno, D.E. et al. What is global health? Key concepts and clarification of misperceptions. glob health res policy 5 , 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-020-00142-7
Download citation
Received : 15 February 2020
Accepted : 09 March 2020
Published : 07 April 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-020-00142-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Global health
- Global impact
- Global solution
- Global health sciences
- Global health theory
- global health education
- Global health development
Global Health Research and Policy
ISSN: 2397-0642
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
How to build a better health system: 8 expert essays

We need to focus on keeping people healthy, not just treating them when they're sick Image: REUTERS/Rupak De Chowdhuri
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Global Future Council on Health and Healthcare
Introduction
By Francesca Colombo , Head, Health Division, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and Helen E. Clark , Prime Minister of New Zealand (1999-2008), The Helen Clark Foundation
Our healthy future cannot be achieved without putting the health and wellbeing of populations at the centre of public policy.
Ill health worsens an individual’s economic prospects throughout the lifecycle. For young infants and children, ill health affects their capacity to acumulate human capital; for adults, ill health lowers quality of life and labour market outcomes, and disadvantage compounds over the course of a lifetime.
And, yet, with all the robust evidence available that good health is beneficial to economies and societies, it is striking to see how health systems across the globe struggled to maximise the health of populations even before the COVID-19 pandemic – a crisis that has further exposed the stresses and weaknesses of our health systems. These must be addressed to make populations healthier and more resilient to future shocks.
Each one of us, at least once in our lives, is likely to have been frustrated with care that was inflexible, impersonal and bureaucratic. At the system level, these individual experiences add up to poor safety, poor care coordination and inefficiencies – costing millions of lives and enormous expense to societies.
This state of affairs contributes to slowing down the progress towards achieving the sustainable development goals to which all societies, regardless of their level of economic development, have committed.
Many of the conditions that can make change possible are in place. For example, ample evidence exists that investing in public health and primary prevention delivers significant health and economic dividends. Likewise, digital technology has made many services and products across different sectors safe, fast and seamless. There is no reason why, with the right policies, this should not happen in health systems as well. Think, for example, of the opportunities to bring high quality and specialised care to previously underserved populations. COVID-19 has accelerated the development and use of digital health technologies. There are opportunities to further nurture their use to improve public health and disease surveillance, clinical care, research and innovation.
To encourage reform towards health systems that are more resilient, better centred around what people need and sustainable over time, the Global Future Council on Health and Health Care has developed a series of stories illustrating why change must happen, and why this is eminently possible today. While the COVID-19 crisis is severally challenging health systems today, our healthy future is – with the right investments – within reach.
1. Five changes for sustainable health systems that put people first
The COVID-19 crisis has affected more than 188 countries and regions worldwide, causing large-scale loss of life and severe human suffering. The crisis poses a major threat to the global economy, with drops in activity, employment, and consumption worse than those seen during the 2008 financial crisis . COVID-19 has also exposed weaknesses in our health systems that must be addressed. How?
For a start, greater investment in population health would make people, particularly vulnerable population groups, more resilient to health risks. The health and socio-economic consequences of the virus are felt more acutely among disadvantaged populations, stretching a social fabric already challenged by high levels of inequalities. The crisis demonstrates the consequences of poor investment in addressing wider social determinants of health, including poverty, low education and unhealthy lifestyles. Despite much talk of the importance of health promotion, even across the richer OECD countries barely 3% of total health spending is devoted to prevention . Building resilience for populations also requires a greater focus on solidarity and redistribution in social protection systems to address underlying structural inequalities and poverty.
Beyond creating greater resilience in populations, health systems must be strengthened.
High-quality universal health coverage (UHC) is paramount. High levels of household out-of-pocket payments for health goods and services deter people from seeking early diagnosis and treatment at the very moment they need it most. Facing the COVID-19 crisis, many countries have strengthened access to health care, including coverage for diagnostic testing. Yet others do not have strong UHC arrangements. The pandemic reinforced the importance of commitments made in international fora, such as the 2019 High-Level Meeting on Universal Health Coverage , that well-functioning health systems require a deliberate focus on high-quality UHC. Such systems protect people from health threats, impoverishing health spending, and unexpected surges in demand for care.
Second, primary and elder care must be reinforced. COVID-19 presents a double threat for people with chronic conditions. Not only are they at greater risk of severe complications and death due to COVID-19; but also the crisis creates unintended health harm if they forgo usual care, whether because of disruption in services, fear of infections, or worries about burdening the health system. Strong primary health care maintains care continuity for these groups. With some 94% of deaths caused by COVID-19 among people aged over 60 in high-income countries, the elder care sector is also particularly vulnerable, calling for efforts to enhance control of infections, support and protect care workers and better coordinate medical and social care for frail elderly.
Third, the crisis demonstrates the importance of equipping health systems with both reserve capacity and agility. There is an historic underinvestment in the health workforce, with estimated global shortages of 18 million health professionals worldwide , mostly in low- and middle-income countries. Beyond sheer numbers, rigid health labour markets make it difficult to respond rapidly to demand and supply shocks. One way to address this is by creating a “reserve army” of health professionals that can be quickly mobilised. Some countries have allowed medical students in their last year of training to start working immediately, fast-tracked licenses and provided exceptional training. Others have mobilised pharmacists and care assistants. Storing a reserve capacity of supplies such as personal protection equipment, and maintaining care beds that can be quickly transformed into critical care beds, is similarly important.
Fourth, stronger health data systems are needed. The crisis has accelerated innovative digital solutions and uses of digital data, smartphone applications to monitor quarantine, robotic devices, and artificial intelligence to track the virus and predict where it may appear next. Access to telemedicine has been made easier. Yet more can be done to leverage standardised national electronic health records to extract routine data for real-time disease surveillance, clinical trials, and health system management. Barriers to full deployment of telemedicine, the lack of real-time data, of interoperable clinical record data, of data linkage capability and sharing within health and with other sectors remain to be addressed.
Fifth, an effective vaccine and successful vaccination of populations around the globe will provide the only real exit strategy. Success is not guaranteed and there are many policy issues yet to be resolved. International cooperation is vital. Multilateral commitments to pay for successful candidates would give manufacturers certainty so that they can scale production and have vaccine doses ready as quickly as possible following marketing authorisation, but could also help ensure that vaccines go first to where they are most effective in ending the pandemic. Whilst leaders face political pressure to put the health of their citizens first, it is more effective to allocate vaccines based on need. More support is needed for multilateral access mechanisms that contain licensing commitments and ensure that intellectual property is no barrier to access, commitments to technology transfer for local production, and allocation of scarce doses based on need.
The pandemic offers huge opportunities to learn lessons for health system preparedness and resilience. Greater focus on anticipating responses, solidarity within and across countries, agility in managing responses, and renewed efforts for collaborative actions will be a better normal for the future.
OECD Economic Outlook 2020 , Volume 2020 Issue 1, No. 107, OECD Publishing, Paris
OECD Employment Outlook 2020 : Worker Security and the COVID-19 Crisis, OECD Publishing, Paris
OECD Health at a Glance 2019, OECD Publishing, Paris
https://www.un.org/pga/73/wp-content/uploads/sites/53/2019/07/FINAL-draft-UHC-Political-Declaration.pdf
OECD (2020), Who Cares? Attracting and Retaining Care Workers for the Elderly, OECD Health Policy Studies, OECD Publishing, Paris
Working for Health and Growth: investing in the health workforce . Report of the High-Level Commission on Health Employment and Economic Growth, Geneva.
Colombo F., Oderkirk J., Slawomirski L. (2020) Health Information Systems, Electronic Medical Records, and Big Data in Global Healthcare: Progress and Challenges in OECD Countries . In: Haring R., Kickbusch I., Ganten D., Moeti M. (eds) Handbook of Global Health. Springer, Cham.
2. Improving population health and building healthy societies in times of COVID-19
By Helena Legido-Quigley , Associate Professor, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a stark reminder of the fragility of population health worldwide; at time of writing, more than 1 million people have died from the disease. The pandemic has already made evident that those suffering most from COVID-19 belong to disadvantaged populations and marginalised communities. Deep-rooted inequalities have contributed adversely to the health status of different populations within and between countries. Besides the direct and indirect health impacts of COVID-19 and the decimation of health systems, restrictions on population movement and lockdowns introduced to combat the pandemic are expected to have economic and social consequences on an unprecedented scale .
Population health – and addressing the consequences of COVID-19 – is about improving the physical and mental health outcomes and wellbeing of populations locally, regionally and nationally, while reducing health inequalities.¹ Moreover, there is an increasing recognition that societal and environmental factors, such as climate change and food insecurity, can also influence population health outcomes.
The experiences of Maria, David, and Ruben – as told by Spanish public broadcaster RTVE – exemplify the real challenges that people living in densely populated urban areas have faced when being exposed to COVID-19.¹
Maria is a Mexican migrant who has just returned from Connecticut to the Bronx. Her partner Jorge died in Connecticut from COVID-19. She now has no income and is looking for an apartment for herself and her three children. When Jorge became ill, she took him to the hospital, but they would not admit him and he was sent away to be cared for by Maria at home with their children. When an ambulance eventually took him to hospital, it was too late. He died that same night, alone in hospital. She thinks he had diabetes, but he was never diagnosed. They only had enough income to pay the basic bills. Maria is depressed, she is alone, but she knows she must carry on for her children. Her 10-year old child says that if he could help her, he would work. After three months, she finds an apartment.
David works as a hairdresser and takes an overcrowded train every day from Leganés to Chamberi in the centre of Madrid. He lives in a small flat in San Nicasio, one of the poorest working-class areas of Madrid with one of the largest ageing populations in Spain. The apartments are very small, making it difficult to be in confinement, and all of David’s neighbours know somebody who has been a victim of COVID-19. His father was also a hairdresser. David's father was not feeling well; he was taken to hospital by ambulance, and he died three days later. David was not able to say goodbye to his father. Unemployment has increased in that area; small local shops are losing their customers, and many more people are expecting to lose their jobs.
Ruben lives in Iztapalapa in Mexico City with three children, a daughter-in-law and five grandchildren. Their small apartment has few amenities, and no running water during the evening. At three o’clock every morning, he walks 45 minutes with his mobile stall to sell fruit juices near the hospital. His daily earnings keep the family. He goes to the central market to buy fruit, taking a packed dirty bus. He thinks the city's central market was contaminated at the beginning of the pandemic, but it could not be closed as it is the main source of food in the country. He has no health insurance, and he knows that as a diabetic he is at risk, but medication for his condition is too expensive. He has no alternative but to go to work every day: "We die of hunger or we die of COVID."
These real stories highlight the issues that must be addressed to reduce persistent health inequalities and achieve health outcomes focusing on population health. The examples of Maria, David and Ruben show the terrible outcomes COVID-19 has had for people living in poverty and social deprivation, older people, and those with co-morbidities and/or pre-existing health conditions. All three live in densely populated urban areas with poor housing, and have to travel long distances in overcrowded transport. Maria’s loss of income has had consequences for her housing security and access to healthcare and health insurance, which will most likely lead to worse health conditions for her and her children. Furthermore, all three experienced high levels of stress, which is magnified in the cases of Maria and David who were unable to be present when their loved ones died.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made it evident that to improve the health of the population and build healthy societies, there is a need to shift the focus from illness to health and wellness in order to address the social, political and commercial determinants of health; to promote healthy behaviours and lifestyles; and to foster universal health coverage.² Citizens all over the world are demanding that health systems be strengthened and for governments to protect the most vulnerable. A better future could be possible with leadership that is able to carefully consider the long-term health, economic and social policies that are needed.
In order to design and implement population health-friendly policies, there are three prerequisites. First, there is a need to improve understanding of the factors that influence health inequalities and the interconnections between the economic, social and health impacts. Second, broader policies should be considered not only within the health sector, but also in other sectors such as education, employment, transport and infrastructure, agriculture, water and sanitation. Third, the proposed policies need to be designed through involving the community, addressing the health of vulnerable groups, and fostering inter-sectoral action and partnerships.
Finally, within the UN's Agenda 2030 , Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3 sets out a forward-looking strategy for health whose main goal is to attain healthier lives and wellbeing. The 17 interdependent SDGs offer an opportunity to contribute to healthier, fairer and more equitable societies from which both communities and the environment can benefit.
The stories of Maria, David and Ruben are real stories featured in the Documentary: The impact of COVID19 in urban outskirts, Directed by Jose A Guardiola. Available here. Permission has been granted to narrate these stories.
Buck, D., Baylis, A., Dougall, D. and Robertson, R. (2018). A vision for population health: Towards a healthier future . [online] London: The King's Fund. [Accessed 20 Sept. 2020]
Wilton Park. (2020). Healthy societies, healthy populations (WP1734). Wiston House, Steyning. Retrieved from https://www.wiltonpark.org.uk/event/wp1734/ Cohen B. E. (2006). Population health as a framework for public health practice: a Canadian perspective. American journal of public health , 96 (9), 1574–1576.
3. Imagine a 'well-care' system that invests in keeping people healthy
By Maliha Hashmi , Executive Director, Health and Well-Being and Biotech, NEOM, and Jan Kimpen , Global Chief Medical Officer, Philips
Imagine a patient named Emily. Emily is aged 32 and I’m her doctor.
Emily was 65lb (29kg) above her ideal body weight, pre-diabetic and had high cholesterol. My initial visit with Emily was taken up with counselling on lifestyle changes, mainly diet and exercise; typical advice from one’s doctor in a time-pressured 15-minute visit. I had no other additional resources, incentives or systems to support me or Emily to help her turn her lifestyle around.
I saw Emily eight months later, not in my office, but in the hospital emergency room. Her husband accompanied her – she was vomiting, very weak and confused. She was admitted to the intensive care unit, connected to an insulin drip to lower her blood sugar, and diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. I talked to Emily then, emphasizing that the new medications for diabetes would only control the sugars, but she still had time to reverse things if she changed her lifestyle. She received further counselling from a nutritionist.
Over the years, Emily continued to gain weight, necessitating higher doses of her diabetes medication. More emergency room visits for high blood sugars ensued, she developed infections of her skin and feet, and ultimately, she developed kidney disease because of the uncontrolled diabetes. Ten years after I met Emily, she is 78lb (35kg) above her ideal body weight; she is blind and cannot feel her feet due to nerve damage from the high blood sugars; and she will soon need dialysis for her failing kidneys. Emily’s deteriorating health has carried a high financial cost both for herself and the healthcare system. We have prevented her from dying and extended her life with our interventions, but each interaction with the medical system has come at significant cost – and those costs will only rise. But we have also failed Emily by allowing her diabetes to progress. We know how to prevent this, but neither the right investments nor incentives are in place.
Emily could have been a real patient of mine. Her sad story will be familiar to all doctors caring for chronically ill patients. Unfortunately, patients like Emily are neglected by health systems across the world today. The burden of chronic disease is increasing at alarming rates. Across the OECD nearly 33% of those over 15 years live with one or more chronic condition, rising to 60% for over-65s. Approximately 50% of chronic disease deaths are attributed to cardiovascular disease (CVD). In the coming decades, obesity, will claim 92 million lives in the OECD while obesity-related diseases will cut life expectancy by three years by 2050.
These diseases can be largely prevented by primary prevention, an approach that emphasizes vaccinations, lifestyle behaviour modification and the regulation of unhealthy substances. Preventative interventions have been efficacious. For obesity, countries have effectively employed public awareness campaigns, health professionals training, and encouragement of dietary change (for example, limits on unhealthy foods, taxes and nutrition labelling).⁴,⁵ Other interventions, such as workplace health-promotion programmes, while showing some promise, still need to demonstrate their efficacy.

The COVID-19 crisis provides the ultimate incentive to double down on the prevention of chronic disease. Most people dying from COVID-19 have one or more chronic disease, including obesity, CVD, diabetes or respiratory problems – diseases that are preventable with a healthy lifestyle. COVID-19 has highlighted structural weaknesses in our health systems such as the neglect of prevention and primary care.
While the utility of primary prevention is understood and supported by a growing evidence base, its implementation has been thwarted by chronic underinvestment, indicating a lack of societal and governmental prioritization. On average, OECD countries only invest 2.8% of health spending on public health and prevention. The underlying drivers include decreased allocation to prevention research, lack of awareness in populations, the belief that long-run prevention may be more costly than treatment, and a lack of commitment by and incentives for healthcare professionals. Furthermore, public health is often viewed in a silo separate from the overall health system rather than a foundational component.
Health benefits aside, increasing investment in primary prevention presents a strong economic imperative. For example, obesity contributes to the treatment costs of many other diseases: 70% of diabetes costs, 23% for CVD and 9% for cancers. Economic losses further extend to absenteeism and decreased productivity.
Fee-for-service models that remunerate physicians based on the number of sick patients they see, regardless the quality and outcome, dominate healthcare systems worldwide. Primary prevention mandates a payment system that reimburses healthcare professionals and patients for preventive actions. Ministries of health and governmental leaders need to challenge skepticism around preventive interventions, realign incentives towards preventive actions and those that promote healthy choices by people. Primary prevention will eventually reduce the burden of chronic diseases on the healthcare system.
As I reflect back on Emily and her life, I wonder what our healthcare system could have done differently. What if our healthcare system was a well-care system instead of a sick-care system? Imagine a different scenario: Emily, a 32 year old pre-diabetic, had access to a nutritionist, an exercise coach or health coach and nurse who followed her closely at the time of her first visit with me. Imagine if Emily joined group exercise classes, learned where to find healthy foods and how to cook them, and had access to spaces in which to exercise and be active. Imagine Emily being better educated about her diabetes and empowered in her healthcare and staying healthy. In reality, it is much more complicated than this, but if our healthcare systems began to incentivize and invest in prevention and even rewarded Emily for weight loss and healthy behavioural changes, the outcome might have been different. Imagine Emily losing weight and continuing to be an active and contributing member of society. Imagine if we invested in keeping people healthy rather than waiting for people to get sick, and then treating them. Imagine a well-care system.
Anderson, G. (2011). Responding to the growing cost and prevalence of people with multiple chronic conditions . Retrieved from OECD.
Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. GBD Data Visualizations. Retrieved here.
OECD (2019), The Heavy Burden of Obesity: The Economics of Prevention, OECD Health Policy Studies, OECD Publishing, Paris.
OECD. (2017). Obesity Update . Retrieved here.
Malik, V. S., Willett, W. C., & Hu, F. B. (2013). Global obesity: trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nature Reviews Endocrinology , 9 (1), 13-27.
Lang, J., Cluff, L., Payne, J., Matson-Koffman, D., & Hampton, J. (2017). The centers for disease control and prevention: findings from the national healthy worksite program. Journal of occupational and environmental medicine , 59 (7), 631.
Gmeinder, M., Morgan, D., & Mueller, M. (2017). How much do OECD countries spend on prevention? Retrieved from OECD.
Jordan RE, Adab P, Cheng KK. Covid-19: risk factors for severe disease and death. BMJ. 2020;368:m1198.
Richardson, A. K. (2012). Investing in public health: barriers and possible solutions. Journal of Public Health , 34 (3), 322-327.
Yong, P. L., Saunders, R. S., & Olsen, L. (2010). Missed Prevention Opportunities The healthcare imperative: lowering costs and improving outcomes: workshop series summary (Vol. 852): National Academies Press Washington, DC.
OECD. (2019). The Heavy Burden of Obesity: The Economics of Prevention. Retrieved here .
McDaid, D., F. Sassi and S. Merkur (Eds.) (2015a), “Promoting Health, Preventing Disease: The Economic Case ”, Open University Press, New York.
OECD. (2019). The Heavy Burden of Obesity: The Economics of Prevention. Retrieved from OECD.
4. Why e arly detection and diagnosis is critical
By Paul Murray , Head of Life and Health Products, Swiss Re, and André Goy , Chairman and Executive Director & Chief of Lymphoma, John Theurer Cancer Center, Hackensack University Medical Center
Although healthcare systems around the world follow a common and simple principle and goal – that is, access to affordable high-quality healthcare – they vary significantly, and it is becoming increasingly costly to provide this access, due to ageing populations, the increasing burden of chronic diseases and the price of new innovations.
Governments are challenged by how best to provide care to their populations and make their systems sustainable. Neither universal health, single payer systems, hybrid systems, nor the variety of systems used throughout the US have yet provided a solution. However, systems that are ranked higher in numerous studies, such as a 2017 report by the Commonwealth Fund , typically include strong prevention care and early-detection programmes. This alone does not guarantee a good outcome as measured by either high or healthy life expectancy. But there should be no doubt that prevention and early detection can contribute to a more sustainable system by reducing the risk of serious diseases or disorders, and that investing in and operationalizing earlier detection and diagnosis of key conditions can lead to better patient outcomes and lower long-term costs.
To discuss early detection in a constructive manner it makes sense to describe its activities and scope. Early detection includes pre-symptomatic screening and treatment immediately or shortly after first symptoms are diagnosed. Programmes may include searching for a specific disease (for example, HIV/AIDS or breast cancer), or be more ubiquitous. Prevention, which is not the focus of this blog, can be interpreted as any activities undertaken to avoid diseases, such as information programmes, education, immunization or health monitoring.
Expenditures for prevention and early detection vary by country and typically range between 1-5% of total health expenditures.¹ During the 2008 global financial crisis, many countries reduced preventive spending. In the past few years, however, a number of countries have introduced reforms to strengthen and promote prevention and early detection. Possibly the most prominent example in recent years was the introduction of the Affordable Care Act in the US, which placed a special focus on providing a wide range of preventive and screening services. It lists 63 distinct services that must be covered without any copayment, co-insurance or having to pay a deductible.

Whilst logic dictates that investment in early detection should be encouraged, there are a few hurdles and challenges that need to be overcome and considered. We set out a few key criteria and requirements for an efficient early detection program:
1. Accessibility The healthcare system needs to provide access to a balanced distribution of physicians, both geographically (such as accessibility in rural areas), and by specialty. Patients should be able to access the system promptly without excessive waiting times for diagnoses or elective treatments. This helps mitigate conditions or diseases that are already quite advanced or have been incubating for months or even years before a clinical diagnosis. Access to physicians varies significantly across the globe from below one to more than 60 physicians per 10,000 people.² One important innovation for mitigating access deficiencies is telehealth. This should give individuals easier access to health-related services, not only in cases of sickness but also to supplement primary care.
2. Early symptoms and initial diagnosis Inaccurate or delayed initial diagnoses present a risk to the health of patients, can lead to inappropriate or unnecessary testing and treatment, and represents a significant share of total health expenditures. A medical second opinion service, especially for serious medical diagnoses, which can occur remotely, can help improve healthcare outcomes. Moreover, studies show that early and correct diagnosis opens up a greater range of curative treatment options and can reduce costs (e.g. for colon cancer, stage-four treatment costs are a multiple of stage-one treatment costs).³
3. New technology New early detection technologies can improve the ability to identify symptoms and diseases early: i. Advances in medical monitoring devices and wearable health technology, such as ECG and blood pressure monitors and biosensors, enable patients to take control of their own health and physical condition. This is an important trend that is expected to positively contribute to early detection, for example in atrial fibrillation and Alzheimers’ disease. ii. Diagnostic tools, using new biomarkers such as liquid biopsies or volatile organic compounds, together with the implementation of machine learning, can play an increasing role in areas such as oncology or infectious diseases.⁴
4. Regulation and Intervention Government regulation and intervention will be necessary to set ranges of normality, to prohibit or discourage overdiagnosis and to reduce incentives for providers to overtreat patients or to follow patients' inappropriate requests. In some countries, such as the US, there has been some success through capitation models and value-based care. Governments might also need to intervene to de-risk the innovation paradigm, such that private providers of capital feel able to invest more in the development of new detection technologies, in addition to proven business models in novel therapeutics.
OECD Health Working Papers No. 101 "How much do OECD countries spend on prevention" , 2017
World Health Organization; Global Health Observatory (GHO) data; https://www.who.int/gho/health_workforce/physicians_density/en/
Saving lives, averting costs; A report for Cancer Research UK, by Incisive Health, September 2014
Liquid Biopsy: Market Drivers And Obstacles; by Divyaa Ravishankar, Frost & Sullivan, January 21, 2019
Liquid Biopsies Become Cheap and Easy with New Microfluidic Device; February 26, 2019
How America’s 5 Top Hospitals are Using Machine Learning Today; by Kumba Sennaar, February 19, 2019
5. The business case for private investment in healthcare for all
Pascal Fröhlicher, Primary Care Innovation Scholar, Harvard Medical School, and Ian Wijaya, Managing Director in Lazard’s Global Healthcare Group
Faith, a mother of two, has just lost another customer. Some households where she is employed to clean, in a small town in South Africa, have little understanding of her medical needs. As a type 2 diabetes patient, this Zimbabwean woman visits the public clinic regularly, sometimes on short notice. At her last visit, after spending hours in a queue, she was finally told that the doctor could not see her. To avoid losing another day of work, she went to the local general practitioner to get her script, paying more than three daily wages for consultation and medication. Sadly, this fictional person reflects a reality for many people in middle-income countries.
Achieving universal health coverage by 2030, a key UN Sustainable Development Goal (SDG), is at risk. The World Bank has identified a $176 billion funding gap , increasing every year due to the growing needs of an ageing population, with the health burden shifting towards non-communicable diseases (NCDs), now the major cause of death in emerging markets . Traditional sources of healthcare funding struggle to increase budgets sufficiently to cover this gap and only about 4% of private health care investments focus on diseases that primarily affect low- and middle-income countries.
In middle-income countries, private investors often focus on extending established businesses, including developing private hospital capacity, targeting consumers already benefiting from quality healthcare. As a result, an insufficient amount of private capital is invested in strengthening healthcare systems for everyone.

Why is this the case? We discussed with senior health executives investing in Lower and Middle Income Countries (LMIC) and the following reasons emerged:
- Small market size . Scaling innovations in healthcare requires dealing with country-specific regulatory frameworks and competing interest groups, resulting in high market entry cost.
- Talent . Several LMICs are losing nurses and doctors but also business and finance professionals to European and North American markets due to the lack of local opportunities and a significant difference in salaries.
- Untested business models with relatively low gross margins. Providing healthcare requires innovative business models where consumers’ willingness to pay often needs to be demonstrated over a significant period of time. Additionally, relatively low gross margins drive the need for scale to leverage administrative costs, which increases risk.
- Government Relations. The main buyer of health-related products and services is government; yet the relationship between public and private sectors often lacks trust, creating barriers to successful collaboration. Add to that significant political risk, as contracts can be cancelled by incoming administrations after elections. Many countries also lack comprehensive technology strategies to successfully manage technological innovation.
- Complexity of donor funding. A significant portion of healthcare is funded by private donors, whose priorities might not always be congruent with the health priorities of the government.
Notwithstanding these barriers, healthcare, specifically in middle-income settings, could present an attractive value proposition for private investors:
- Economic growth rates . A growing middle class is expanding the potential market for healthcare products and services.
- Alignment of incentives . A high ratio of out-of-pocket payments for healthcare services is often associated with low quality. However, innovative business models can turn out of pocket payments into the basis for a customer-centric value proposition, as the provider is required to compete for a share of disposable income.
- Emergence of National Health Insurance Schemes . South Africa, Ghana, Nigeria and others are building national health insurance schemes, increasing a population’s ability to fund healthcare services and products .
- Increased prevalence of NCDs. Given the increasing incidence of chronic diseases and the potential of using technology to address these diseases, new business opportunities for private investment exist.
Based on the context above, several areas in healthcare delivery can present compelling opportunities for private companies.
- Aggregation of existing players.
- Leveraging primary care infrastructure. Retail companies can leverage their real estate, infrastructure and supply chains to deploy primary care services at greater scale than is currently the case.
- Telemedicine . Telecommunications providers can leverage their existing infrastructure and customer base to provide payment mechanisms and telehealth services at scale. As seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, investment in telemedicine can ensure that patients receive timely and continuous care in spite of restrictions and lockdowns.
- Cost effective diagnostics . Diagnostic tools operated by frontline workers and combined with the expertise of specialists can provide timely and efficient care.
To fully realize these opportunities, government must incentivise innovation, provide clear regulatory frameworks and, most importantly, ensure that health priorities are adequately addressed.
Venture capital and private equity firms as well as large international corporations can identify the most commercially viable solutions and scale them into new markets. The ubiquity of NCDs and the requirement to reduce costs globally provides innovators with the opportunity to scale their tested solutions from LMICs to higher income environments.
Successful investment exits in LMICs and other private sector success stories will attract more private capital. Governments that enable and support private investment in their healthcare systems would, with appropriate governance and guidance, generate benefits to their populations and economies. The economic value of healthy populations has been proven repeatedly , and in the face of COVID-19, private sector investment can promote innovation and the development of responsible, sustainable solutions.
Faith – the diabetic mother we introduced at the beginning of this article - could keep her client. As a stable patient, she could measure her glucose level at home and enter the results in an app on her phone, part of her monthly diabetes programme with the company that runs the health centre. She visits the nurse-led facility at the local taxi stand on her way to work when her app suggests it. The nurse in charge of the centre treats Faith efficiently, and, if necessary, communicates with a primary care physician or even a specialist through the telemedicine functionality of her electronic health system.
Improving LMIC health systems is not only a business opportunity, but a moral imperative for public and private leaders. With the appropriate technology and political will, this can become a reality.
6. How could COVID-19 change the way we pay for health services?
John E. Ataguba, Associate Professor and Director, University of Cape Town and Matthew Guilford, Co-Founder and Chief Executive Officer, Common Health
The emergence of the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2), causing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has challenged both developing and developed countries.
Countries have approached the management of infections differently. Many people are curious to understand their health system’s performance on COVID-19, both at the national level and compared to international peers. Alongside limited resources for health, many developing countries may have weak health systems that can make it challenging to respond adequately to the pandemic.
Even before COVID-19, high rates of out-of-pocket spending on health meant that every year, 800 million people faced catastrophic healthcare costs ,100 million families were pushed into poverty, and millions more simply avoided care for critical conditions because they could not afford to pay for it.
The pandemic and its economic fallout have caused household incomes to decline at the same time as healthcare risks are rising. In some countries with insurance schemes, and especially for private health insurance, the following questions have arisen: How large is the co-payment for a COVID-19 test? If my doctor’s office is closed, will the telemedicine consultation be covered by my insurance? Will my coronavirus care be paid for regardless of how I contracted the virus? These and other doubts can prevent people from seeking medical care in some countries.
In Nigeria, like many other countries in Africa, the government bears the costs associated with testing and treating COVID-19 irrespective of the individual’s insurance status. In the public health sector, where COVID-19 cases are treated, health workers are paid monthly salaries while budgets are allocated to health facilities for other services. Hospitals continue to receive budget allocations to finance all health services including the management and treatment of COVID-19. That implies that funds allocated to address other health needs are reduced and that in turn could affect the availability and quality of health services.
Although health workers providing care for COVID-19 patients in isolation and treatment centres in Nigeria are paid salaries that are augmented with a special incentive package, the degree of impact on the quality improvement of services remains unclear. The traditional and historical allocation of budgets does not always address the needs of the whole population and could result in poor health services and under-provision of health services for COVID-19 patients.
In some countries, the reliance on out-of-pocket funding is hardly better for private providers, who encounter brand risks, operational difficulties, and – in extreme cases – the risk of creating “debtor prisons” as they seek to collect payment from patients. Ironically, despite the huge demand for medical services to diagnose and treat COVID-19, large healthcare institutions and individual healthcare practitioners alike are facing financial distress.
Dependence on a steady stream of fee-for-service payments for outpatient consultations and elective procedures is leading to pay cuts for doctors in India , forfeited Eid bonuses for nurses in Indonesia , and hospital bankruptcies in the United States . In a recent McKinsey & Company survey, 77% of physicians reported that their business would suffer in 2020 , and 46% were concerned about their practice surviving the coronavirus pandemic.
COVID-19 is exposing how fee-for-service, historical budget allocation and out-of-pocket financing methods can hinder the performance of the health system. Some providers and health systems that deployed “value-based” models prior to the pandemic have reported that these approaches have improved financial resilience during COVID-19 and may support better results for patients. Nevertheless, these types of innovations do not represent the dominant payment model in any country.
How health service providers are paid has implications for whether service users can get needed health services in a timely fashion, and at an appropriate quality and an affordable cost. By shifting from fee-for-service reimbursements to fixed "capitation" and performance-based payments, these models incentivize providers to improve quality and coordination while also guaranteeing a baseline income level, even during times of disruption.
Health service providers could be paid either in the form of salaries, a fee for services they provide, by capitation (whether adjusted or straightforward), through global budgets, or by using a case-based payment system (for example, the diagnostics-related groups), among others. Because there are different incentives to consider when adopting any of the methods, they could be combined to achieve a specific goal. For example, in some countries, health workers are paid salaries , and some specific services are paid on a fee-for-service basis.
Ideally, health services could be purchased strategically , incorporating aspects of provider performance in transferring funds to providers and accounting for the health needs of the population they serve.
In this regard, strategic purchasing for health has been advocated and should be highlighted as crucial with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic. There is a need to ensure value in the way health providers are paid, inter alia to increase efficiency, ensure equity, and improve access to needed health services. Value-based payment methods, although not new in many countries, provide an avenue to encourage long-term value for money, better quality, and strategic purchasing for health, helping to build a healthier, more resilient world.
7. L essons in integrated care from the COVID-19 pandemic
Sarah Ziegler, Postdoctoral Researcher, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of Zurich, and Ninie Wang, Founder & CEO, Pinetree Care Group.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, people suffering non-communicable diseases (NCDs) have been at higher risk of becoming severely ill or dying. In Italy, 96.2% of people who died of COVID-19 lived with two or more chronic conditions.
Beyond the pandemic, cardiovascular disease, cancer, respiratory disease and diabetes are the leading burden of disease, with 41 million annual deaths. People with multimorbidity - a number of different conditions - often experience difficulties in accessing timely and coordinated healthcare, made worse when health systems are busy fighting against the pandemic.
Here is what happened in China with Lee, aged 62, who has been living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) for the past five years.
Before the pandemic, Lee’s care manager coordinated a multi-disciplinary team of physicians, nurses, pulmonary rehabilitation therapists, psychologists and social workers to put together a personalized care plan for her. Following the care plan, Lee stopped smoking and paid special attention to her diet, sleep and physical exercises, as well as sticking to her medication and follow-up visits. She participated in a weekly community-based physical activity program to meet other COPD patients, including short walks and exchange experiences. A mobile care team supported her with weekly cleaning and grocery shopping.
Together with her family, Lee had follow-up visits to ensure her care plan reflected her recovery and to modify the plan if needed. These integrated care services brought pieces of care together, centered around Lee’s needs, and provided a continuum of care that helped keep Lee in the community with a good quality of life for as long as possible.
Since the COVID-19 outbreak, such NCD services have been disrupted by lockdowns, the cancellation of elective care and the fear of visiting care service . These factors particularly affected people living with NCDs like Lee. As such, Lee was not able to follow her care plan anymore. The mobile care team was unable to visit her weekly as they were deployed to provide COVID-19 relief. Lee couldn’t participate in her community-based program, follow up on her daily activities, or see her family or psychologists. This negatively affected Lee’s COPD management and led to poor management of her physical activity and healthy diet.
The pandemic highlights the need for a flexible and reliable integrated care system to enable healthcare delivery to all people no matter where they live, uzilizing approaches such as telemedicine and effective triaging to overcome care disruptions.
Lee’s care manager created short videos to assist her family through each step of her care and called daily to check in on the implementation of the plan and answer questions. Lee received tele-consultations, and was invited to the weekly webcast series that supported COPD patient communities. When her uncle passed away because of pneumonia complications from COVID-19 in early April, Lee’s care manager arranged a palliative care provider to support the family through the difficult time of bereavement and provided food and supplies during quarantine. Lee could even continue with her physical activity program with an online training coach. There were a total of 38 exercise videos for strengthening and stretching arms, legs and trunk, which she could complete at different levels of difficulty and with different numbers of repetitions.
Lee’s case demonstrates that early detection, prevention, and management of NCDs play a crucial role in a global pandemic response. It shows how we need to shift away from health systems designed around single diseases towards health systems designed for the multidimensional needs of individuals. As part of the pandemic responses, addressing and managing risks related to NCDs and prevention of their complications are critical to improve outcomes for vulnerable people like Lee.
How to design and deliver successful integrated care
The challenge for the successful transformation of healthcare is to tailor care system-wide to population needs. A 2016 WHO Framework on integrated people-centered health services developed a set of five general strategies for countries to progress towards people-centered and sustainable health systems, calling for a fundamental transformation not only in the way health services are delivered, but also in the way they are financed and managed . These strategies call for countries to:
- Engage and empower people / communities: an integrated care system must mobilize everyone to work together using all available resources, especially when continuity of essential health and community services for NCDs are at risk of being undermined.
- Strengthen governance and accountability, so that integration emphasizes rather than weakens leadership in every part of the system, and ensure that NCDs are included in national COVID-19 plans and future essential health services.
- Reorient the model of care to put the needs and perspectives of each person / family at the center of care planning and outcome measurement, rather than institutions.
- Coordinate services within and across sectors, for example, integrate inter-disciplinary medical care with social care, addressing wider socio-economic, environmental and behavioral determinants of health.
- Create an enabling environment, with clear objectives, supportive financing, regulations and insurance coverage for integrated care, including the development and use of systemic digital health care solutions.
Whether due to an unexpected pandemic or a gradual increase in the burden of NCDs, each person could face many health threats across the life-course.
Only systems that dynamically assess each person’s complex health needs and address them through a timely, well-coordinated and tailored mix of health and social care services will be able to deliver desired health outcomes over the longer term, ensuring an uninterrupted good quality of life for Lee and many others like her.
- Wang B, Li R, Lu Z, Huang Y. Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: evidence from meta-analysis. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12: 6049–57.
- WHO. Noncommunicable diseases in emergencies. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016.
- WHO. COVID-19 significantly impacts health services for noncommunicable diseases. June 2020.
- Kluge HHP, Wickramasinghe K, Rippin HL, et al. Prevention and control of non-communicalbe diseases in the COVID-19 response. The Lancet. 2020. 395:1678-1680
- WHO. Framework on integrated people-centred health services. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016.
8 . Why access to healthcare alone will not save lives
Donald Berwick, President Emeritus and Senior Fellow, Institute for Healthcare Improvement; Nicola Bedlington, Special Adviser, European Patient Forum; and David Duong, Director, Program in Global Primary Care and Social Change, Harvard Medical School.
Joyce lies next to 10 other women in bare single beds in the post-partum recovery room at a rural hospital in Uganda. Just an hour ago, Joyce gave birth to a healthy baby boy. She is now struggling with abdominal pain. A nurse walks by, and Joyce tries to call out, but the nurse was too busy to attend to her; she was the only nurse looking after 20 patients.
Another hour passes, and Joyce is shaking and sweating profusely. Joyce’s husband runs into the corridor to find a nurse to come and evaluate her. The nurse notices Joyce’s critical condition - a high fever and a low blood pressure - and she quickly calls the doctor. The medical team rushes Joyce to the intensive care unit. Joyce has a very severe blood stream infection. It takes another hour before antibiotics are started - too late. Joyce dies, leaving behind a newborn son and a husband. Joyce, like many before her, falls victim to a pervasive global threat: poor quality of care.
Adopted by United Nations (UN) in 2015, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) are a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that all enjoy peace and prosperity by 2030. SDG 3 aims to ensure healthy lives and promote wellbeing for all. The 2019 UN General Assembly High Level Meeting on Universal Health Coverage (UHC) reaffirmed the need for the highest level of political commitment to health care for all.
However, progress towards UHC, often measured in terms of access, not outcomes, does not guarantee better health, as we can see from Joyce’s tragedy. This is also evident with the COVID-19 response. The rapidly evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted long-term structural inefficiencies and inequities in health systems and societies trying to mitigate the contagion and loss of life.
Systems are straining under significant pressure to ensure standards of care for both COVID-19 patients and other patients that run the risk of not receiving timely and appropriate care. Although poor quality of care has been a long-standing issue, it is imperative now more than ever that systems implement high-quality services as part of their efforts toward UHC.
Poor quality healthcare remains a challenge for countries at all levels of economic development: 10% of hospitalized patients acquire an infection during their hospitalization in low-and-middle income countries (LMIC), whereas 7% do in high-income countries. Poor quality healthcare disproportionally affects the poor and those in LMICs. Of the approximately 8.6 million deaths per year in 137 LMICs, 3.6 million are people who did not access the health system, whereas 5 million are people who sought and had access to services but received poor-quality care.
Joyce’s story is all too familiar; poor quality of care results in deaths from treatable diseases and conditions. Although the causes of death are often multifactorial, deaths and increased morbidity from treatable conditions are often a reflection of defects in the quality of care.
The large number of deaths and avoidable complications are also accompanied by substantial economic costs. In 2015 alone, 130 LMICs faced US $6 trillion in economic losses. Although there is concern that implementing quality measures may be a costly endeavor, it is clear that the economic toll associated with a lack of quality of care is far more troublesome and further stunts the socio-economic development of LMICs, made apparent with the COVID-19 pandemic.
Poor-quality care not only leads to adverse outcomes in terms of high morbidity and mortality, but it also impacts patient experience and patient confidence in health systems. Less than one-quarter of people in LMICs and approximately half of people in high-income countries believe that their health systems work well.
A lack of application and availability of evidenced-based guidelines is one key driver of poor-quality care. The rapidly changing landscape of medical knowledge and guidelines requires healthcare workers to have immediate access to current clinical resources. Despite our "information age", health providers are not accessing clinical guidelines or do not have access to the latest practical, lifesaving information.
Getting information to health workers in the places where it is most needed is a delivery challenge. Indeed, adherence to clinical practice guidelines in eight LMICs was below 50%, and in OECD countries, despite being a part of national guidelines, 19-53% of women aged 50-69 years did not receive mammography screening.4 The evidence in LMICs and HICs suggest that application of evidence-based guidelines lead to reduction in mortality and improved health outcomes.
Equally, the failure to change and continually improve the processes in health systems that support the workforce takes a high toll on quality of care. During the initial wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, countries such as Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore and Vietnam, which adapted and improved their health systems after the SARS and H1N1 outbreaks, were able to rapidly mobilize a large-scale quarantine and contact tracing strategy, supported with effective and coordinated mass communication.
These countries not only mitigated the economic and mortality damage, but also prevented their health systems and workforce from enduring extreme burden and inability to maintain critical medical supplies. In all nations, investing in healthcare organizations to enable them to become true “learning health care systems,” aiming at continual quality improvement, would yield major population health and health system gains.
The COVID-19 pandemic underscores the importance for health systems to be learning systems. Once the dust settles, we need to focus, collectively, on learning from this experience and adapting our health systems to be more resilient for the next one. This implies a need for commitment to and investment in global health cooperation, improvement in health care leadership, and change management.
With strong political and financial commitment to UHC, and its demonstrable effect in addressing crises such as COVID-19, for the first time, the world has a viable chance of UHC becoming a reality. However, without an equally strong political, managerial, and financial commitment to continually improving, high-quality health services, UHC will remain an empty promise.
1. United Nations General Assembly. Political declaration of the high-level meeting on universal health coverage. New York, NY2019.
2. Marmot M, Allen J, Boyce T, Goldblatt P, Morrison J. Health equity in England: the Marmot review 10 years on. Institute of Health Equity;2020.
3. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine: Committee on Improving the Quality of Health Care Globally. Crossing the global quality chasm: Improving health care worldwide. Washington, DC: National Academies Press;2018.
4. World Health Organization, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, World Bank Group. Delivering quality health services: a global imperative for universal health coverage. World Health Organization; 2018.
5. Kruk ME, Gage AD, Arsenault C, et al. High-quality health systems in the Sustainable Development Goals era: time for a revolution. The Lancet Global Health. 2018;6(11):e1196-e1252.
6. Ricci-Cabello I, Violán C, Foguet-Boreu Q, Mounce LT, Valderas JM. Impact of multi-morbidity on quality of healthcare and its implications for health policy, research and clinical practice. A scoping review. European Journal of General Practice. 2015;21(3):192-202.
7. Valtis YK, Rosenberg J, Bhandari S, et al. Evidence-based medicine for all: what we can learn from a programme providing free access to an online clinical resource to health workers in resource-limited settings. BMJ global health. 2016;1(1).
8. Institute of Medicine. Best Care at Lower Cost: The Path to Continuously Learning Health Care in America . Washington, DC: National Academies Press 2012.
Related topics:
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Physiol Genomics

The COVID-19 pandemic: a global health crisis
Casey a. pollard.
1 Department of Surgery, The University of Toledo, College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, Ohio
Michael P. Morran
2 The University of Toledo Advanced Microscopy and Imaging Center, The University of Toledo, College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, Ohio
Andrea L. Nestor-Kalinoski
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 was identified as the causative agent for a series of atypical respiratory diseases in the Hubei Province of Wuhan, China in December of 2019. The disease SARS-CoV-2, termed COVID-19, was officially declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization on March 11, 2020. SARS-CoV-2 contains a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome surrounded by an extracellular membrane containing a series of spike glycoproteins resembling a crown. COVID-19 infection results in diverse symptoms and morbidity depending on individual genetics, ethnicity, age, and geographic location. In severe cases, COVID-19 pathophysiology includes destruction of lung epithelial cells, thrombosis, hypercoagulation, and vascular leak leading to sepsis. These events lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and subsequent pulmonary fibrosis in patients. COVID-19 risk factors include cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and diabetes, which are highly prevalent in the United States. This population has upregulation of the angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptor, which is exploited by COVID-19 as the route of entry and infection. Viral envelope proteins bind to and degrade ACE2 receptors, thus preventing normal ACE2 function. COVID-19 infection causes imbalances in ACE2 and induces an inflammatory immune response, known as a cytokine storm, both of which amplify comorbidities within the host. Herein, we discuss the genetics, pathogenesis, and possible therapeutics of COVID-19 infection along with secondary complications associated with disease progression, including ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis. Understanding the mechanisms of COVID-19 infection will allow the development of vaccines or other novel therapeutic approaches to prevent transmission or reduce the severity of infection.
CORONAVIRUSES AND SARS-C o V-2 GENETICS
Coronaviruses are a well-studied group of viruses in the Coronaviridae family that are known for their ability to infect a variety of hosts due to their capacity to evolve in epidemiological situations, including crossing species barriers, mutagenesis, tissue tropism, and pathogenicity ( 10b , 14 , 83 ). Coronaviruses are round, enveloped virions roughly 80–220 nm in diameter that contain a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome of ∼26–32 kb surrounded by an extracellular membrane containing a casing of spike glycoproteins ( 32 , 80 ). The term corona in Latin translates to crown and was given to these viruses due to the presence of the spike casing that resembled a “crown-like structure” using electron microscopy ( 37 ).
Coronaviruses have been implicated in human disease as early as the late 1960s, where they were identified as the causative agents in respiratory illnesses that presented with mild symptoms associated with the common cold ( 32 ). Seven strains of human coronaviruses have been characterized, four of which are known to infect the upper respiratory tract and cause mild symptoms, while the three others are known for their severe disease-causing characteristics of the lower respiratory tract including the following: SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome), MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome), and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) ( 42 ). Since the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, data-sharing initiatives have led to the much needed generation of SARS-CoV-2 data, including complete reference genomes in the National Center for Biotechnology Information database ( {"type":"entrez-nucleotide","attrs":{"text":"NC_045512","term_id":"1798174254","term_text":"NC_045512"}} NC_045512 .2), which contains the 29,903 bp genomic sequence ( 83 ).
While it is known that the RNA polymerase of viruses lack proofreading capacity, the ensuing result is a high mutation rate with low replicative fidelity. In contrast, the coronaviruses possess an exonuclease proofreading capability that has resulted in the expansion and maintenance of one of the largest known viral genomes at ∼30 kb ( 17 , 60 ). The large viral genome of SARS-CoV-2 codes for four structural proteins including the envelope, membrane, nucleocapsid, and spike glycoprotein, which play a role in both molecular characterization and host cell entry ( 23 , 35 ). The SARS-CoV-2 genome also includes 16 nonstructural proteins and 9 accessory proteins required for replication and pathogenesis ( 23 , 35 , 60 ). While SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV are 75–80% identical ( 3 , 89 ), SARS-CoV-2 displays the highest sequence similarities with BatCoV at 96.2% ( 11 ). Global sequence comparison of SARS-CoV-2 isolates have expanded the literature and information known for this virus in a short period of time. Initial analysis of roughly 100 genomes of SARS-CoV-2 identified two major subtypes, designated L and S, which vary due to the presence of two linked single nucleotide polymorphisms ( 71 ). Interestingly, the L subtype is a derivative of the S type and was identified in ∼70% of the genomes compared with the S type in the remaining 30% ( 71 ). Phylogenic tree analysis of the L type suggests that the differences are related to a significantly higher mutation rate, which, consequently, results in higher transmission and/or replication rates ( 71 ). Furthermore, the SARS-CoV-2 virus has geographically diverse strains that seemingly vary in severity, mortality rate, and treatment options that were characterized using phylogenetic network analysis of 160 SARS-CoV-2 genomes ( 18 ). Three distinct viral clusters (A, B, and C) were identified with derivative subgroups, with cluster A sharing the closest similarity to the BatCoV genome. Clusters A and C are found predominantly in the Americas and Europe, while cluster C is found across East Asia ( 18 ).
INDIVIDUAL GENETIC PREDISPOSITION/SUSCEPTIBILITY
Throughout the progression of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is clear that not all infected patients are created equal. The diversity in symptoms, morbidity, genetics, age, and geographic location all play distinct roles in viral transmission. Understanding the genetic implications underlying severe COVID-19 infection requires complex biochemical and immunological studies. Previously identified immune-related genetic variants known to be associated with susceptibility to SARS-CoV ( 61 , 85 ), including mannose-binding lectin, basigin (CD147), C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), interleukin-12 and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes, might show promise due to the shared homology of the two viral genomes ( 41 , 69 , 73 , 78 ). Utilizing our current understanding of viral entry and pathophysiology in relation to viral infection has prompted research focused on host genetic factors that may help to mitigate differences in viral replication and the innate and adaptive immune responses triggered during viral infection ( 75 ). While angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptor expression seems promising as a genetic element that could relate to immunity, no polymorphisms or mutations in ACE2 related to spike protein binding resistance have been reported in populations ( 8 ). Although rare, ACE2 variants have been identified that alter the interaction between host cells and SARS-CoV-2 causing reduced affinity of SARS-CoV-2 binding ( 66 ). Along this same line of reasoning, the gene encoding the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) protease responsible for spike protein priming for viral entry has received much attention. Cell lines expressing high amounts of TMPRSS2 are highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection ( 43 ). In addition, it is known that TMPRSS2 has 2 isoforms 1 with and 1 without a 37 amino acid long cytoplasmic tail, which is thought to interact with viral spike proteins and promote viral spreading within the host ( 90 ).
Monoclonal antibodies against the spike protein of COVID-19 could play a pivotal role in blocking the virus attachment, fusion, and entry into host cells ( 67 , 72 ). Antibodies against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein or antibodies that bind to the ACE2 receptor have been discussed as potential therapeutics ( 67 , 72 ). Furthermore, recombinant RBD proteins have been shown to strongly bind to the ACE2 receptor in human and bat cells ( 67 ). There are also studies targeting glycocalyx loss as a therapeutic target of the spike protein. Importantly, blocking these initial steps in viral entry and replication could block the downstream cascade of COVID-19 pathophysiology. This would effectively decrease the morality rate of the current pandemic as it reduces the viral load in patients. Additionally, these antibodies could be potential candidates for COVID-19 antiviral and vaccine development ( 67 ). However, this therapeutic method would have very little impact on the case rate or the infectious propensity of the virus.
In addition, genetic alterations in immune response elements will be important in identifying possible gene candidates that could control host inflammatory responses that elicit the cytokine storm to help reduce secondary complications of infection by altering expression and activity of cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, interferons, and others ( 10 ). HLA is known to be one of the most polymorphic antigen systems in the body. In silico studies point out that all known HLA genotypes A, B, and C have affinity to bind SARS-CoV-2 peptides ( 50 ). Furthermore, predictive alleles have been found to have a binding capability that can infer susceptibility or possibly impart some T-cell-based immune response ( 50 ). Further studies have reviewed the genetic association of COVID-19 infection based on blood type ( 47 ) and sex, with the number of X chromosomes having an effect on susceptibility and progression of infection ( 20 ).
COVID-19 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 was originally identified as the causative agent for a series of atypical respiratory diseases in the Hubei Province of Wuhan, China in December of 2019. The disease SARS-CoV-2, which will be termed COVID-19 from herein, was officially declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020 ( 82b ). According to the WHO, there are 28,637,952 positive COVID-19 cases and 917,417 deaths worldwide as of September 14th, 2020 ( 82a ). As shown in Table 1 , the United States had 6,571,867 total cases resulting in 195,053 deaths, as of September 16th, 2020 according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention ( 10b ). Highly populated states like California, Texas, Florida, and New York have the highest total number of cases exceeding 400,000, while less populated rural states such as Vermont, Wyoming, and Maine have total case numbers below 5,000 ( 10b ). This reflects the predilection of the virus for more densely populated areas, allowing for higher rates of transmission in crowded areas compared with rural communities that are less densely populated. This can be seen in New York wherein the number of total deaths was 32,765 out numbering both California’s and Texas’s total deaths at 28,794 ( Table 1 ).
United States SARS-CoV-2 Statistics
The epidemiology of COVID-19 to date has been found to have disproportionate impacts on populations depending on sex and ethnicity. Table 1 highlights the differences in total cases and mortality by ethnicity, sex, and age. For example, in the United States ∼51.7% of total COVID-19 cases are female and 48.3% are male ( 10a ). In contrast, 54% of the total deaths in the United States are male compared with 46% female ( 10a ). The most significant predictor of poor outcome and mortality associated with COVID-19 is age. The mortality data in Table 1 include available data in nine different age brackets spanning 0–85 yr and above. Most notably, patients 50 yr and above in the United States have the highest mortality rates accounting for >94% of the total deaths due to COVID-19 ( Table 1 ; 10b , 10c ). In contrast, individuals 18–29 yr old have the highest percentage of total cases at 23.3% but only have a mortality rate of ∼0.5% ( 10b , 10c ). Older adults have higher rates of chronic health conditions that have been associated with poorer COVID-19 outcomes including hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and chronic kidney disease ( 62 ). These conditions place adults over 60 yr old at the highest risk of developing a complicated COVID-19 infection and mortality compared with younger cohorts without these conditions ( 62 ). Many patients with these conditions also take daily medications that interfere with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors for hypertension. This system has been implicated in COVID-19 infection and the virus’s ability to attach to host cells, causing dysregulated host cell responses, which subsequently results in worse outcomes ( 20 , 25 , 66 ).
Patients with COVID-19 often present with an array of symptoms that are similar to influenza that can make it difficult to diagnose. An epidemiological study of the first 41 patients infected with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China found that fatigue, cough, and fever were the most commonly reported symptoms ( 28 , 31 ). As a result, the general symptoms of COVID-19 are challenging to diagnose without reliable testing. Positive COVID-19 classifications include the following: asymptomatic, mild, moderate, severe, and critical. Asymptomatic patients test positive and exhibit no clinical symptoms while mild cases present with acute symptoms of respiratory tract infection and digestive complications. Moderate patients experience pneumonia, without noticeable hypoxemia, with lesions on chest computerized tomography (CT) scan. Severe patients experience pneumonia with detectable hypoxemia and CT lesions while critical patients experience acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) along with possible shock, encephalopathy, myocardial injury, coagulation dysfunction, heart failure, and acute kidney injury ( 86 ). In a study of 80 patients hospitalized for COVID-19, over 90% had detectable ground glass opacities present on CT scan ( 31 , 84 ). A correlation was also found with the degree of inflammation seen on chest CT and lymphopenia (low white blood cell count), days of symptoms, and fever ( 84 ). Although these symptoms are often informative in diagnosis, COVID-19 has an unpredictable clinical course. As a result, 13.8% of positive patients had severe cases that required an in-patient hospital stay, with 4.7% requiring intensive care unit hospitalization and 2.3% of cases resulting in death ( 31 ). Taken together, these factors make COVID-19 difficult to manage and hard for clinicians to diagnose and predict clinical outcomes. Furthermore, real-time generation of data using artificial intelligence is an absolute priority to combat the spread, diagnosis, treatment, and categorized susceptibility to COVID-19 ( 1 ).
Understanding the pathophysiology of COVID-19 is critical to improving patient outcomes and determining how we can overcome the current pandemic. A key component to the virus being able to enter host cells and replicate is the ACE2 receptor, which is highly expressed in alveolar epithelial cells of the lung as confirmed by RNA-seq ( 91 ). The viral glycoprotein spike casing found on the exterior of a virus particle is responsible for eliciting viral entry into susceptible host cells ( 27 ). The process of viral entry requires priming of the spike protein by host expressed TMPRSS2, which interacts with the spike protein and cleaves it into two functional subunits known as S1 and S2 ( 27 , 43 , 66 ). The S1 subunit directly interacts with the ACE2 receptor, leaving the S2 subunit to facilitate viral fusion with the host cell membrane ( Fig. 1 ; 25 , 27 , 41a ). Internalization and replication of virus subsequently cause degradation of membrane-bound ACE2 receptors ( 27 ), which in turn causes an increase in angiotensin II (ANG II) and the angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT 1 R) ( Fig. 1 ). Angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin to angiotensin I (ANG I). ANG I is cleaved via ACE to ANG II, wherein it can freely interact with AT 1 R and angiotensin type 2 receptor (AT 2 R). Excess ANG I and II are hydrolyzed by ACE2 to become the heptapeptides ANG-(1-9)/ANG-(1-7) ( Fig. 1 ). Reduced or bound ACE2 is unable to hydrolyze ANG I/II, which results in an inability of the counterbalancing effects of the Mas receptor (Mas-R) to protect against detrimental disease/immune complications. As a result of COVID-19 infection, decreases in ACE2 cause elevated activity in the ANG II/AT 1 R axis, resulting in an inflammatory immune response ( 76 ). This deficiency leads to many adverse outcomes for patients including interstitial fibrosis, myocardial hypertrophy, endothelial fibrosis, and increased inflammation ( 76 ). Additionally, thrombosis and hypercoagulation secondary to platelet activation after lung epithelial damage are seen in patients with severe infections ( 39 , 86 ). Further consequences of hypercoagulation include disseminated intravascular coagulation, pulmonary embolisms, cardiac complications, and an increased risk of death ( 39 , 70 ). Coagulation is induced as a protective physiological control in response to vascular leak but in turn elicits dangerous consequences in COVID-19 patients. Often the physiologic response mechanisms to vascular leak and permeability fail, which allows for enhanced viral invasion, thus amplifying the problem in host cells on two separate fronts ( 86 ).

Biological effects of COVID-19 infection on angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and GTPase signaling pathways. The COVID-19 virus can bind and interact with both shed ACE2 and the cell membrane-bound ACE2 receptor. COVID-19 particles utilize and degrade membrane bound ACE2 receptors to gain entry into host cells. Virus particles also bind shed ACE2 causing a reduction in free ACE2 thus preventing the hydrolysis of ANG I/II into ANG-(1-9)/ANG-(1-7), which results in an imbalanced renin-angiotensin system that becomes skewed toward the ANG II/angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT 1 R) axis. COVID-19 produces an inflammatory response, i.e., the cytokine storm, which triggers cellular activation through cytokine receptors (CRs). Upon infection, these interactions favor detrimental complications such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)/pulmonary fibrosis, vasoconstriction and alters cytoskeletal dynamics including cell proliferation, migration, and cytoskeletal composition. Intracellular elements such as Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 kinase and Rho GTPase-associated proteins play a significant role in controlling polymerization of F-actin, maintaining the density of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and modulating myofibroblast proliferation, and the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE AND COVID-19
The highest risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including ARDS, is diabetes, hypertension, and a history of heart disease ( 76 ). Although the primary target of COVID-19 is the lungs, it can also have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system. These comorbidities result in an upregulation of ACE2 on the cell surface of perivascular pericytes and cardiomyocytes, which is exploited by COVID-19 as the route of entry and infection ( 25 ). The leading cause of death in the United States is cardiovascular disease (CVD) causing more than 800,000 deaths in 2016 ( 20a ). A meta-analysis study in China found that COVID-19 causes acute cardiac injury in roughly 8.0% of patients, which poses concern for those that have a preexisting cardiac or metabolic condition ( 40 ). Cardiac injury may present as common arrhythmias, myocarditis, cardiogenic shock, and/or heart failure ( 24 , 49 ). Patients with prior cardiac history, including acute coronary syndrome and angina or myocardial infraction, have a higher risk for developing pneumonia and a decreased cardiac reserve that poses significant risks if they contract COVID-19 ( 40 , 88 ). The middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is in the same corona virus family as COVID-19, has similar clinical outcomes, and has been extensively studied in patients with these comorbid conditions ( 5 ). In an analysis of 637 MERS-CoV patient cases, 30% had cardiac diseases and 50% had hypertension or diabetes ( 5 , 88 ). These cardiovascular disorders are highly prevalent in the United States, placing this vulnerable population in a higher risk category for acquiring severe infection with COVID-19. Patients with CVD may not have the ability to maintain cardiovascular function upon COVID-19 infection, leading to an increase in metabolic demand, exacerbating cardiovascular conditions thus increasing their risk for severe outcomes ( 68 ).
COVID-19 AND ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
The host immune response to COVID-19 is similar to ARDS and therefore treatment modalities may be beneficial in treating COVID-19 patients. ARDS is defined clinically as bilateral neutrophilic infiltrates seen on imaging, acute hypoxia, and pulmonary edema ( 19 , 30 ). ARDS is caused by a dysregulated immune response with a fibroproliferative component due to excessive levels of cytokines, chemokines, and reactive oxygen species ( 30 ). ARDS-positive patients exhibit elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines including IFN-y, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-1 compared with patients with uncomplicated COVID-19 infections ( 12 ). A study in ARDS positive mice confirmed these findings, wherein bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from ARDS positive mice strains had higher levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with reduced levels of IL-10 in comparison with controls ( 57 ). Similarly, patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 infections have elevated cytokine profiles that are reflective of what defines a “cytokine storm.” The cytokine storm is a result of an uncontrolled immune response due to systemic inflammation and hemodynamic instability due to the abundance of proinflammatory cytokines that include IL-1, IL-6, IL-18, IFN-γ, and TNF-α ( Fig. 1 ) ( 65 ). As a result, new therapies are needed to thwart the immune response including nonconventional immunomodulation ( 22 ) to control the increase in proinflammatory cytokines that results in an accumulation of macrophages, neutrophils, and T cells from the circulation to the lung destroying the cell-cell interactions resulting in severe cases of ARDS. These findings suggest that patients suffering from ARDS and severe COVID-19 have a failed anti-inflammatory response that contributes to the excessive inflammatory damage caused by a host of proinflammatory cytokines wreaking havoc on lung tissue ( 58 ). Extensive damage to epithelial and endothelial cells of the lung triggers apoptotic destruction ( 12 ) leading to changes in the cellular junctions in alveolar tissue, thus increasing vascular permeability and ultimately alveolar fluid leak ( 30 ). Consequently, these cellular changes result in the pulmonary edema classically seen in ARDS patients ( 30 ), which is further complicated by an increase in dysregulated epithelial cell remodeling contributing to pulmonary fibrosis ( 12 ), a common cause of mortality in ARDS patients ( 30 ).
ABL1 AND VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (Abl1) is a widely expressed nonreceptor tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in controlling cell morphology, growth, and survival ( 79 , 82 ). Abl1 is activated through a variety of receptor interactions and factors including cytokines, DNA damage, and oxidative stress ( 77 ). Abl1 plays a major role in modulating cytoskeletal dynamics influencing cell proliferation, cell survival, endocytosis, membrane trafficking, and cell-cell junctions and is also implicated in solid tumor proliferation and survival ( 34 ). Abl1 signals proteins that are critical to extracellular matrix (ECM) function and composition including the formation of actin stress fibers. These fibers interact with F-actin, inducing filopodia, which can alter cell-cell junctions ( 59 , 79 , 82 ).
Inhibition of Abl1 leads to increased Rho-Rock signaling, actomyosin contractility, and destabilization of cell-cell adhesions leading to an increase in barrier disruption ( 16 , 59 , 87 ). There is a direct implication of Abl1 as a therapeutic target to regulate GTPases in an effort to control ARDS and fibrosis as a result of disrupted endothelial barrier function and vascular leak in the lungs of ARDS patients ( 45 , 82 , 87 ). This critical association can be detrimental in ARDS, pulmonary fibrosis, and in severe cases of COVID-19 infection when vascular leak becomes uncontrolled and leads to sepsis ( 30 ). Multiple studies have investigated therapies to preserve endothelial barrier function. This includes the therapeutic use of low molecular weight heparin to combat the degradation of heparin sulfate by heparinase, thus protecting the endothelial barrier ( 7 ). Furthermore, the drug imatinib, an Abl1 inhibitor, has been investigated for possible repurposing and use for lung injury patients ( 36 , 82 ). One study found that pretreatment with imatinib protected against acute lung injury in mice ( 36 ) and may have potential to be repurposed in patients suffering from ARDS and/or COVID-19. Case studies report that imatinib resolved pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis secondary to antibiotics ( 9 , 59 ). Selective targeting of Abl1-based therapeutics needs further investigation to avoid potential negative side effects. For example, studies have shown that inhibiting Abl1 leads to increased endothelial permeability because of F-actin alternations and is amplified in cells undergoing cyclic stretch secondary to mechanical ventilation ( 38 , 59 ). As a result, increased vascular permeability will lead to an acceleration in vascular leak, exacerbating outcomes in ARDS patients.
PULMONARY FIBROSIS AND GTPase SIGNALING
While much is known about the progression of COVID-19 and ARDS, the mechanism of pathophysiology and associated treatment strategies are still under investigation. One such area includes GTPase signaling and its role in the development of ARDS and subsequent pulmonary fibrosis. Pulmonary fibrosis is caused by excessive fibroblasts and ECM protein deposits in the lungs, referred to as scarring of the lungs ( 4 ). Myofibroblasts are derived from resident fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells in the lung that express high amounts of smooth muscle actin ( 29 ) and are major players in the production of excess collagen leading to progressive fibrosis in patients ( 6 ). The overall ECM composition and stiffness have a direct impact on the degree of fibroblast migration, proliferation, and differentiation ( 4 ). Studies have shown that denser ECM substrates in later stages of disease show higher fibroblast migration levels compared with decreased fibroblasts migration in less stiff substrates as seen in earlier stages ( 6 ). One pathway with therapeutic implications in these physiological processes is the Rho GTPase signaling cascade ( 6 , 82 ).
Rho GTPase signaling has vast cellular implications in the control of actin and myosin stress fiber formation, regulation of cell adhesion molecules, cell migration, and common cellular functions ( 81 ). In addition, Rho GTPases play significant roles in cytoskeletal actin remodeling by polymerization and de-polymerization of monomeric G-actin leading to the conversion of F-actin ( 29 ). Increases in F-actin fibers causes stiffening of the ECM in patients suffering from ARDS leading to decreased vascular compliance ( 33 ). ARDS patients often require some form of oxygen supplementation due to severe hypoxemia. These measures often lead to hyperoxia and cause acute lung injury compounding damage to the lungs ( 30 , 44 ). Interestingly, hyperoxia in mice was found to activate the Rho/ROCK GTPase pathway and led to an increase in cell stiffness secondary to F-actin increase. However, when these mice were treated with Y-27632, a Rho inhibitor, the cytoskeletal changes in stiffness were prevented ( 81 ). These results suggest a possible connection in the control of GTPase signaling and ARDS and/or fibrosis complications seen in patients who require supplemental oxygen. Therefore, therapeutically modulating the increased activity of the GTPase cascade could decrease the adverse effects of ARDS pathogenesis secondary to ECM remodeling events.
As previously discussed, the Rho GTPase pathway regulates ECM density ( 81 , 82 ). This leads to the conclusion that higher activation levels of Rho and associated downstream targets lead to a higher levels of fibroblast proliferation. The ACE2 cascade is protective against lung fibrosis through activation of Rho GTPase pathways, while ACE is damaging and stimulates fibrosis in lung endothelial cells ( 46 ). These findings correlate to the virus’s predilection for patients with a history of obesity, hypertension, and CVD as these chronic conditions have been found to have lower levels of ACE2 at baseline ( 76 ). Therefore, the interplay between the ACE2/ACE and the Rho GTPase pathway may be an important association that could be a target for therapeutics to block lung fibrosis that results in ARDS and a majority of the mortality in COVID-19 patients. A study performed by Haung et al. proved this association by showing blockade of the Rho GTPase pathway inhibits matrix stiffness and alters stress fiber formation in fibroblasts ( 29 ). Therefore, Rho is actively involved in the underlying mechanism of pulmonary fibrosis by controlling proteins critical to modulating the ECM. A few significant trials have tested this theory for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by using nintedanib, a multikinase inhibitor, and pirfenidone, a small molecule antifibrotic, both of which were shown to reduce loss of lung functioning in pulmonary fibrosis patients ( 6 ).
STRATEGIES FOR SARS-C o V-2 THERAPEUTICS
Controlling the extensive spread and progression of SARS-CoV-2 has proven very difficult and will require a multidisciplinary approach with global collaboration. While certain areas of interest in SARS-CoV-2 remain unknown, past coronavirus knowledge provides scientists with the foundation for the development and/or repurposing of therapeutic interventions and vaccine development. Since the spike protein of each individual type of coronavirus is unique, this protein is currently being targeted in vaccine development as an approach to block initial entry of the virus ( 2 , 63 ). Multiple vaccines have entered clinical trials, the first of which is an RNA-based vaccine, mRNA-1273 ( 26 ). This vaccine entered phase I clinical trials on March 16, 2020 in collaboration with the National Institutes of Health (NIH), utilizing 45 healthy participants ranging in ages from 18 to 55 yr old ( 2 ). Although science has provided the foundational studies on vaccine development, the time needed to assess the safety and efficacy of vaccine candidates is a major bottleneck in the overall process.
While vaccines are being tested and manufactured, novel therapeutic treatments for the control and clinical management of COVID-19 infection are needed. Numerous approaches for treatment have been anecdotally reviewed in mainstream media; however, there are currently no Food and Drug Administration-approved medications for the treatment of COVID-19 infections ( 13 ). Still, there are a number of medications under evaluation for their effectiveness as potential antivirals that are recommended for use in the National Institutes of Health COVID-19 treatment guidelines ( 13 ). A noteworthy example of a current therapeutic intervention includes the use of convalescent plasma therapy ( 15 , 64 ). In this process, plasma-containing-neutralizing antibodies, removed from a donor who has previously recovered from a SARS-CoV-2 infection, are administered to infected patients to impart protection. Another unique therapeutic method involves treatment with soluble recombinant human ACE2 to disrupt viral entry via the spike protein-ACE2 interaction. Initial testing with recombinant ACE2 in simian cell lines and engineered human tissues shows promise in reducing viral load in a dose-dependent fashion ( 48 ). Finally, due to the high sense of urgency in clinical treatment of COVID-19 infection, the repurposing of known antiviral drugs has been explored with extreme caution, and the rationale are outlined in the NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines ( 13 ). The treatment guidelines have the current recommendations either for or against the use of known antiviral drugs and the existing clinical trial data from the National Institutes of Health ( 13 ). Furthermore, implications for the use of some drugs have been identified using in silico databases that predict protein-protein interactions ( 23 , 74 ). Antiviral therapies contained in these studies include remdesivir, ivermectin, favipiravir, kaletra, and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin ( 13 , 23 , 74 ).
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose a serious public health threat to nations around the world, as effective antiviral therapeutics or vaccines are yet to be developed. The primary goal in the COVID-19 pandemic is to limit transmission and define clinical management that improves the cure rate and effectively reduces the overall mortality rate. To achieve this goal, a complete understanding of all aspects of coronaviruses is needed to prevent or lessen their threat to society in the future. A thorough understanding of the epidemiology, pathophysiology and pandemic response efforts to combat COVID-19 is an invaluable lesson to society providing a protocol to fight future pandemics should they occur. Most importantly, scientific insights gained in the fight against COVID-19 will provide the evidence needed to develop vaccines and antiviral therapeutics that target viral entry, immune response and activation, and clinical management of secondary complications associated with severe infections.
M.P.M. and A.L.N-K. acknowledge funding support from the University of Toledo University Research Funding Opportunities (URFO) Program - Interdisciplinary Research Initiation Award I-127366-01.
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
C.A.P., M.P.M., and A.L.N-K. prepared figures; C.A.P., M.P.M., and A.L.N-K. drafted manuscript; C.A.P., M.P.M., and A.L.N-K. edited and revised manuscript; C.A.P., M.P.M., and A.L.N-K. approved final version of manuscript.
An essay on a topic of international health importance
- PMID: 21167589
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62189-7
- Awards and Prizes
- Civil Disorders*
- Emergency Service, Hospital*
- Medical Staff, Hospital / psychology*
Global Health Issues: Essay Example
Global health essay: introduction.
A study conducted to investigate global health’s plight reveals that it is at its utmost disaster. The study shows that the new skills brought about by science and medicine have failed to meet the global population’s needs. Although outstanding enhancements have been prepared in the health condition globally over the last century, these improvements have not met the requirements of everyone. The reason behind this is the dissimilar living standards in different countries.
It is believed that the significant risk to the existing and developing health disaster tend to be those obliged to societal determinants confirmed to harmfully affect people’s health, including poverty and unsafe living and effective surroundings. Weak health schemes, worldwide deaths, and disparities in the health staff, among others, bring about global health disorders. (Schnurr et al. 398)
As one of the most alarming disasters in global health, hunger has done a lot in slowing down many countries in the world. Haiti, my country of birth, is one of the countries affected by global health issues. Haiti is believed to be a country that has never enjoyed freedom for a long time. Many may wonder why there is so much hunger in the country; the reason behind it is because of the poverty that has dominated the country.
Poverty in Haiti is exceptional due to poor governance, education, and the continued earthquakes (Shah para. 5). The lack of support in the agricultural sector has also contributed a lot towards hunger in the country, a position that Jacques Diouf, the Director General of FAO agrees with. Diouf states, “Economic and social reconstruction of the country needs a restoration of food production and massive investment in rural area” (Jere 1752). For this reason, you will find that almost everybody in Haiti is affected directly or indirectly.
The research shows that in the 21st century, hunger is the leading risk to health worldwide. A report published by the World Health Organization reveals that hunger kills more people than cancer, heart disease, AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis combined. It is also estimated that in every four children, one is underweight.
Due to the underweight condition, a child is likely to die from infectious diseases because of weakened immunity. According to one of the American researchers, “the hungry are the poorest of the poor, and enhancements in poverty don’t automatically reach them” (Dickenson 7) as it has been in Haiti. The impact of hunger can bring about poverty, malnutrition, and HIV/AIDS, among many more.
As many people know, poverty dramatically impacts the global health issue. The researcher has clearly proven that you may have nothing to eat if you are poor. Unlike in Haiti, many people are poor due to inadequate support from the government, which has not been stable for quite some time due to the alarming issues that arise in the country continually. It is believed that the most significant number of people in Haiti live below the poverty line causing the speedy growth of poverty in the country. (Jere, 1754)
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is not something new to the people of Haiti. Research shows that Haitians are chronically underfed due to insufficient food. Undernutrition affects the immune structure, mounting to the occurrences and sternness of diseases, and is an allied issue in approximately all children’s deaths. (Dickenson 8)
This disease will always withstand due to the lack of money caused by the country’s poor economy. In this case, many people indulge in prostitution in search of money, which is one of the most common ways of contracting HIV/AIDS. The behavior has spread rapidly due to poor governance, lack of enough to eat, and lack of education. In this situation, little is done to kick the disease out of the country. (Dickenson 9)
Current Aid Organizational
For these reasons, some organizations have come together to help this country from this alarming situation. These organizations are educating the people of Haiti, bringing about new technologies, and changing the drastically deteriorated economy. Some of these organizations include the Students for Global Citizenship Club (S4GC), Boston Aid Groups Lead, cell phones help aid groups, and the cholera struggle aid groups (Jere 1754).
Students for Global Citizenship Club (S4GC)
This organization has done a lot in promoting the responsiveness of Haitians regarding global matters and movements dealing with activism and volunteerism. The aim is to develop the lives of others. For this reason, the people of Haiti have learned how to help one another in times of need.
They have also learned the need to unite and form organizations that would take the country to great heights. Despite all the challenges Haitians face, they have something to enjoy after having centers that can now cater to their needs, especially regarding activism and leadership (Schnurr et al. 398).

Boston Aid Groups Lead
This organization has helped Haitians a lot by saving them during the earthquake. The organization also funded the victims of the earthquake. In doing so, the Haitians could not feel left behind from the comfort they received from this organization that was willing to heal their wounds even during these challenging times.
This organization has been doing wonders, even providing medical treatment for injured people during disasters. In these times of disaster, the organization remembers to advance nutritional aid and provide clean water for them to drink. It has developed and empowered the Haitians, so they can now better do the work by themselves. (Schnurr et al. 399)
Cell Phones Help Aid Group
Cell phones helped the Haitians a lot during this tough period. The main aim of this organization was to collect any relevant information that could assist the people whenever necessary. Any news that arose in the country was easily transmitted, and stern measures were taken immediately or before anything wrong happened.
This technology made the people feel connected, so they were eager to participate in the organization, finally leaving them with new knowledge. This technology simplified things since, previously, people could walk long distances to pass simple information. Now they have the chance to make use of the available technology, effectively saving on time and cost (Dickenson 10).
Cholera Intensifies Struggle for Aid Group
Due to the continued lack of proper diet, water pollution, and education, diseases had a wide path to enter the people of Haiti. This organization provided the most necessities in fighting any epidemic in the country. The organization was there to help stop the spread of disease, educate the people about appropriate hygiene, and humanize the dumping of unwanted waste. It was great for the country, making the people civilized by learning of all these (Schnurr et al. 399).
Illiteracy is among the leading issues associated with health problems. The level of illiteracy in Haiti is high, meaning that people cannot practice healthy eating habits. The discrepancy between the rich and poor is very high in Haiti. This discrepancy has led to increased health-related problems among poor citizens.
According to Kendall (293), Montrouis, Haiti has a club med that hosts the affluent people of the society and tourists. In contrast, just a few kilometers away, we have open markets characterized by raw meat, flies, homeless people, and malnourished families. It is a scenario of the rich bordering on the poor who live in adverse poverty and health-related issues. Haiti is not only the poorest state in the Western region but also cannot feed its citizens.
Due to that, people are exposed to malnutrition-related diseases like Marasmus and Kwashiorkor, among other conditions. According to Kendall (293), statistics show that an estimated 40 percent or more of the children in Haiti are chronically malnourished. The statistics also show that more than 80% of Haitians’ eating habits are poor, and they take less than 2,200 calories daily. The discrepancy is also seen in the income sector, where poor citizens are low-income earners who cannot afford food and medical services.
Healthcare quality is low in poor nations, and people hardly receive it. Most countries in the developing world are faced with this issue. The dissemination of healthcare facilities and healthcare is expensive to deliver to the people. The cost of medicine, medical care, insurance, and accessibility to the healthcare infrastructure are the drawbacks that hinder the delivery of adequate and quality healthcare.
Hospitals lack medical services providers and health doctors. According to Goldstein (41), Haiti is one of the poorest nations that provide low-quality and inadequate healthcare, and its citizens are affected by this. Statistics by the WHO estimate that for every 100,000 Haitians, only eight doctors and ten nurses (Goldstein 41) are available. It has been recorded as the lowest ratio in the healthcare sector in the world, and hence a global issue.
The scenario is worse even in other parts of the world, whereby most clinics, national hospitals, and even health doctors located in urban centers cannot be accessed easily by low-income earners and those living in rural areas. Rural dwellers have limited access to medical and healthcare facilities. A study done in Haiti by the World Health Organization has shown that rural dwellers in Haiti face this problem, and it has become a significant concern to aid and humanitarian organizations.
Low life expectancy has become a health issue in the world. Most nations, especially the ones with low economies, face low life expectancy. In Haiti, life expectancy is as low as 53 years for women and 50 for men (Goldstein 41). Infant mortality is also high, with many children dying before their first and fifth birthdays.
The report shows that of every 1000 children, 74 die before celebrating their first birthday. Their mothers also die, with more than 520 women dying during childbirth. It has been attributed to low income, while inaccessibility to healthcare facilities has also contributed to the observed scenario. A comparison of the situation in Haiti with that of the United States reveals an existing gap between the developing and the developed countries.
Sanitation has become a global health issue affecting most societies worldwide. In developing countries, sanitation facilities like sewerage and toilets and access to cleaner and safer water are not well accessed. This situation is attributed to some of the factors and issues discussed in this paper, like poverty, low income, the discrepancy between the poor and the rich, and the management of the economies of these countries. In Haiti, access to proper sanitation is worse, given that it is an island recently hit by a devastating earthquake.
Drinking water in Haiti is not clean and is mainly drawn from rivers polluted with industrial and human wastes (Goldstein 41). Diseases such as typhoid, cholera, and hookworm, among others, are therefore widespread in the country. The situation has affected the population and has become a concern to the humanitarian and aids organization. Malaria, a killer disease in Africa, is also a considerable concern in Haiti because of the poor drainage system and malnutrition known to weaken the body, making it vulnerable to disease.
Observations in Global Health Issues
In general, global health issues have a significant impact on many countries, especially Haiti. It is because the country has never enjoyed the fruits of its labor, unlike the other countries. Some of the impacts, like poverty, malnutrition, and HIV/AIDS, have contributed significantly to a slowdown in the country’s economic growth. Other impacts like poor sanitation facilities, poor quality healthcare facilities, discrepancies between the poor and the rich, and low life expectancy have been part of the health issues in Haiti.
The paper summarizes how with the help of humanitarian organizations, poor Haiti now has something to smile about. Research indicates that Haitians had nothing to smile about until these organizations stepped in. They have dramatically changed the country, leaving something they can smile for with them.
Health Issues Essay: Conclusion
Hunger is a global health issue that can leave someone with no joy at all. Hunger has proven to be the leading disaster as a global health issue of significant concern to governments, and the situation is no different in Haiti. The paper clearly shows how hunger has resulted in the spread of HIV/AIDs, malnutrition, and poverty, among others, in Haiti.
The paper also shows that the discrepancy between the poor and the rich contributes to poor health in Haiti. Quality of healthcare and healthcare facilities has also contributed to most global health issues like malnutrition, low maternity, and mortality rate. Sanitation that includes sewerage, toilet, and drinking water are common issues inhibited in the world and Haiti.
Works Cited
Dickenson, Nancy. Global Health Issues and Challenges. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 36.1 (2004): 6-10. Print.
Goldstein, Margaret J. Haiti in Pictures . Minneapolis: Lerner Publications Co. 2005. Print
Jere, Behrman, “The Economic Rationale for Investing in Nutrition in Developing Countries”, World Development 11. 11(npg): 1749-1993. Print.
Kendall, Diana, E. Sociology in Our Times . Belmont, CA: Thomson/Wadsworth, 2008. Print.
Labonte, Ronald. “Setting global health research priorities. Burden of disease and inherently global health issues should both be considered” , BMJ Journals 326. 7392 (2003 ):326- 722. Print.
Schnurr, Paula, Kaloupek, Danny, Sandra Bloom, Stuart Turner & Kaltman, Stacey. “Grand Challenges in Global Health”, Science journal 302.5644 (2003): 398-399.Print.
Shah, Anup. World Hunger and Poverty . 2010. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, April 24). Global Health Issues: Essay Example. https://studycorgi.com/global-health-issues/
"Global Health Issues: Essay Example." StudyCorgi , 24 Apr. 2020, studycorgi.com/global-health-issues/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'Global Health Issues: Essay Example'. 24 April.
1. StudyCorgi . "Global Health Issues: Essay Example." April 24, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/global-health-issues/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Global Health Issues: Essay Example." April 24, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/global-health-issues/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "Global Health Issues: Essay Example." April 24, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/global-health-issues/.
This paper, “Global Health Issues: Essay Example”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 22, 2024 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
- Open access
- Published: 08 August 2018
Migration and health: a global public health research priority
- Kolitha Wickramage 1 ,
- Jo Vearey 2 ,
- Anthony B. Zwi 3 ,
- Courtland Robinson 4 &
- Michael Knipper 5
BMC Public Health volume 18 , Article number: 987 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
45k Accesses
123 Citations
105 Altmetric
Metrics details
With 244 million international migrants, and significantly more people moving within their country of birth, there is an urgent need to engage with migration at all levels in order to support progress towards global health and development targets. In response to this, the 2nd Global Consultation on Migration and Health– held in Colombo, Sri Lanka in February 2017 – facilitated discussions concerning the role of research in supporting evidence-informed health responses that engage with migration.
Conclusions
Drawing on discussions with policy makers, research scholars, civil society, and United Nations agencies held in Colombo, we emphasize the urgent need for quality research on international and domestic (in-country) migration and health to support efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs aim to ‘leave no-one behind’ irrespective of their legal status. An ethically sound human rights approach to research that involves engagement across multiple disciplines is required. Researchers need to be sensitive when designing and disseminating research findings as data on migration and health may be misused, both at an individual and population level. We emphasize the importance of creating an ‘enabling environment’ for migration and health research at national, regional and global levels, and call for the development of meaningful linkages – such as through research reference groups – to support evidence-informed inter-sectoral policy and priority setting processes.
Peer Review reports
Migration and health are increasingly recognized as a global public health priority [ 1 ]. Incorporating mixed flows of economic, forced, and irregular migration, migration has increased in extent and complexity. Globally, it is estimated that there are 244 million international migrants and significantly more internal migrants – people moving within their country of birth [ 2 ]. Whilst the majority of international migrants move between countries of the ‘global south’ [ 2 ], these movements between low and middle-income countries remain a “blind spot” for policymakers, researchers and the media, with disproportionate political and policy attention focused on irregular migration to high-income countries. Migration is increasingly recognized as a determinant of health [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. However, the bidirectional relationship between migration and health remains poorly understood, and action on migration and health remains limited, negatively impacting not only those who migrate but also sending, receiving, and ‘left-behind’ communities [ 1 ].
In February 2017, an international group of researchers participated in the 2nd Global Consultation on Migration and Health held in Colombo, Sri Lanka with the objectives of sharing lessons learned, good practices, and research in addressing the relationship between migration and health [ 1 ]. Hosted by the International Organization for Migration (IOM), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the Sri Lankan government, the Global Consultation brought together governments, civil society, international organizations, and academic representatives in order to address migration and health. The Consultation facilitated engagement with the health needs of migrants, reconciling the focus on long-term economic and structural migration - both within and across international borders - with that of acute, large-scale displacement flows that may include refugees, asylum seekers, internally displaced persons and undocumented migrants.
The Consultation was organised around inputs on three thematic areas: Global Health [ 6 ]; Vulnerability and Resilience [ 7 ]; and, Development [ 8 ]. These inputs guided working group discussions exploring either policy, research, or monitoring in relation to migration and health. This paper reports on the outcomes of the research group after an extensive period of debate at the Consultation and over the subsequent 9 months. We identify key issues that should guide research practice in the field of migration and health, and outline strategies to support the development of evidence-informed policies and practices at global, regional, national, and local levels [ 9 ]. Debate and discussion at the Consultation, and below, were guided by two key questions:
What are the opportunities and challenges, and the essential components associated with developing a research agenda on migration and health?
What values and approaches should guide the development of a national research agenda and data collection system on migration and health?
Our discussions emphasized that international targets, such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Universal Health Coverage (UHC; Health target 3.8 of the SDGs), are unlikely to be achieved if the dynamics of migration are not better understood and incorporated in policy and programming. To address this, and in order to improve policy and programming, a renewed focus on enhancing our understanding of the linkages between both international and internal migration and health, as well as the outcomes and impacts arising from them, is urgently needed.
Migration and health research: Leave no-one behind
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) identify migration as both a catalyst and a driver for sustainable development. A clarion call of the SDGs is to ‘leave no-one behind’, irrespective of their legal status, in order to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) for all [ 10 ]. In many countries, however, equitable access to health services is considered as a goal only in relation to citizens. Additionally, internal migration is left out of programming and policy interventions designed to support UHC for all. While UHC aims at ensuring “everyone” can access affordable health systems without increasing the risk of financial ruin or impoverishment, the formulation of UHC remains unclear regarding non-nationals/non-citizens [ 11 ]. While many international declarations state that the right to health applies to all, including migrants and non-citizens, many national policies exclude these groups in whole or part [ 12 ].
In addition to international and internal migration, the health concerns associated with labour migration require attention; migrant workers are estimated to account for 150.3 million of the 244 million international migrants [ 2 ]. While labour migration leads to significant economic gains for countries of origin and destination, true developmental benefits are only realised with access to safe, orderly and humane migration practice [ 13 ]. Many migrant labourers work in conditions of precarious employment, within ‘difficult, degrading and dangerous’ jobs yet little is known about the health status, health outcomes, and resilience/vulnerability trajectories of these migrant workers and their ‘left behind’ families. Many undergo health assessments as a pre-condition for travel and migration, yet many such programs remain unlinked to national public health systems [ 14 ].
Our discussions highlighted the complex and heterogeneous nature of research on migration and health, with particular concerns raised around the emphasis on international rather than internal migration, in view of the greater volume of the latter. The need for a multilevel research agenda to guide appropriate action on international and internal migration, health, and development was highlighted. In order to account for immediate, long-term and inter-generational impacts on health outcomes, migration and health research should: (1) incorporate the different phases of migration (Fig. 1 ); (2) adopt a life-course approach; and, (3) integrate a social determinants of health (SDH) approach.
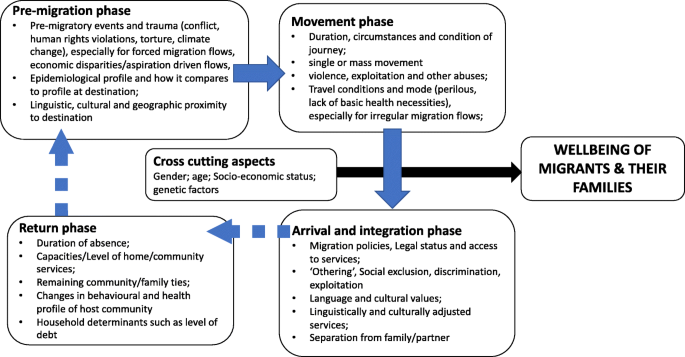
Factors influencing health and wellbeing of migrants and their families along the phases of migration
Unease was expressed about the increasingly polarised political viewpoints on migration, often propagated by nationalist and populist movements, which present real challenges to researchers. This may also be associated with a reluctance to finance research exploring discriminatory policies that limit the access of international migrants to health services and other positive determinants of health, including work and housing.
The increasing complexity of global, regional, and national migration trends, as well as disagreements about the correct way to define and label different types of migrants, create additional difficulties within an already tense and politically contested research domain. Associated with this are the particular challenges associated with collecting and utilising data on ‘irregular migrants’ – international migrants currently without the documentation required to legally be in a particular country. These undocumented migrants, often living in the shadows of society, are more vulnerable to poor health outcomes due to restrictive policies on access to health and social services, to safe working and living conditions, and/or a reluctance to access services for fear of arrest, detention and/or deportation [ 15 , 16 ]. Whilst arguments for improving access to health care for marginalised migrants are based on principles of equity, public health, and human rights, the importance of research on the economic implications of limiting access to care for international migrants was highlighted [ 2 ]. This challenging terrain generated a myriad of research questions during the group discussions (Table 1 ).
Towards a framework for advancing migration and health research
The consultation took into account the extensive research experience of the group (see Appendix ), as well as engagement with key literature and context-specific evidence [see, for example 1–7]. Discussion led to the development of a framework that brings together what we identify as the key components for advancing a global, multi-level, migration and health research agenda (Fig. 2 ). Two areas of focus to advance the migration and health research agenda were identified: (1) exploring health issues across various migrant typologies , and (2) improving our understanding of the interactions between migration and health . Advancing research in both areas is essential if we are to improve our understanding of how to respond to the complex linkages between both international and internal migration and health. This, we argue, can be achieved by moving away from an approach that exceptionalises migration and migrants, to one that integrates migration into overall health systems research, design, and delivery, and conceptualises this as a way to support the achievement of good health for all.
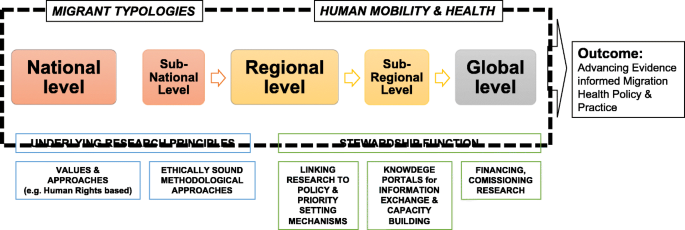
Advancing Migration and Health Research at National, Regional and Global Levels: a conceptual framework
Building from these focus areas, our framework outlines the essential components for the development and application of multi-level research on migration and health. First are key principles underlying research practice: promoting interdisciplinary, human rights oriented, ethically sound approaches for working with migrants. Second are multi-level stewardship functions needed to meaningfully link migration and health research to policy practice and priority setting, [ 17 ]. This includes establishing knowledge exchange mechanisms, financing, commissioning, and utilising research to guide evidence informed policies. This may better enable health systems to become ‘migration aware’ [ 18 ] or what the International Organization for Migration (IOM) terms ‘mobility competent’ - sensitive to health and migration [ 1 ].
Migration and health research: Two key focus areas
Migrant typologies.
To assist in understanding the associations between migration and health, our research must find ways to better capture and engage with complex, dynamic, and often intersecting migrant typologies. We must be careful not to cluster migrants and their associated lived experiences, to simple, reductionist categories such as internal versus cross-border or documented versus undocumented, or even refugee versus economic migrant [ 19 ]. However, we do need a way of categorising different migrant groups when, for example, exploring epidemiological profiles and associated burdens of disease. To do this, we need to develop a set of nuanced yet flexible typologies that are able to capture the contextually relevant factors affecting migrant experiences, at both the individual and population levels. As outlined in Table 2 , this will require careful consideration of multiple factors to assist us in improving our understandings of the ways in which diverse migrant groups are associated, or not, with various health and wellbeing outcomes. Definitions that are based on immigration status - such as ‘refugee’, ‘immigrant’ or ‘asylum seeker’ - will incorporate diverse sub-groups, often with different levels of health vulnerabilities and resiliencies based on their migration trajectory. For instance, a refugee entering a country with an offer of permanent resettlement or with a recognized temporary protected status, will have different opportunities and challenges than an asylum-seeker, or migrant worker, crossing a border possibly without documents or a clear pathway to needed healthcare and protections. Each of these migrating populations carry different health burdens (and resiliencies) from their country of origin, their social position and access to resources, and their migration experiences; and each will face different barriers and uncertainties as they seek access to services, support and integrate in host communities. The definitions of migrant groups adopted by states not only need clear elucidation but also need to reflect the context-specific conditions affecting health access and protection. In Europe, for example, the entitlements to health care for asylum seekers differ by country [ 20 ]. The Migrant Integration Policy Index (MIPEX) health strand was developed as a tool to monitor policies affecting migrant integration in 38 different countries [ 18 ]. It measures the equitability of policies relating to four issues: migrants’ entitlements to health services; accessibility of health services for migrants; responsiveness to migrants’ needs; and measures to achieve change. Such tools are important steps in assessing migrant integration and for implementing migrant-sensitive policies that are aligned with the person-centred UHC principles.
An awareness of this complexity underlies the need to document multiple migrant voices and migration experiences along the diverse trajectories when exploring associations between migration and health. This could, for instance, involve capturing the voices of children and other family members ‘left-behind’ as a result of labour migration, or of seasonal migrant workers. Research into the issues, policies and programmes that influence health and health literacy among migrant populations and the role that communities, households, industries, schools, and transnational networks play in promoting health also needs exploration.
Key challenges exist when attempting to use and compare migration data internationally, as a result of differences in the definition of who is an international migrant, non-national, or internal migrant; inconsistent data sources; and limited data coverage. A recent analysis of the availability, reliability and comparability of data on international migration flows in European countries noted that “comparing migration flows in various countries would be like comparing pears and apples” [ 21 ]. The use of standard indicators can result in unreliable data if migration dynamics are not considered. For example, measures of life expectancy are skewed if international migrants return to their home countries when they are seriously ill, but their departure is not accounted for in vital registration or other systems [ 21 ]. Reporting that is based on incomplete, poor quality or non-comparable population data that fails to measure and/or report migration can give rise to misleading conclusions and limits the validity of data interpretation.
Research at the nexus of migration and health
We recognise the bi-directionality of the relationship between migration and health. Our research should explore how different forms of migration influence health – at both individual and population levels - and how health status affects decisions to migrate and shapes post-migration experience. Migration trajectories can positively or negatively impact health outcomes, just as health status can affect migration outcomes; this two-way relationship should be better reflected in research. To support this, we must be sure to differentiate carefully between different migrant typologies – for example within or across international borders and for what purpose: work, family reunification, escape from persecution, flight from conflict or natural disaster, or to seek asylum. Each of these operates within substantially different contexts whether one takes the migrant and their health into account, or their rights and entitlements, or how they are seen by the dominant society or community to which they migrate. We recognise that being a migrant is not in itself a risk to health: it is the conditions associated with migration that may increase vulnerability to poor health [ 4 ]. Owing to the ways in which people move and the spaces they traverse or at which they arrive, migrants may reside in - or pass through - ‘spaces of vulnerability’ [ 22 ] – key spaces associated with potentially negative health outcomes – including along transport corridors, urban slums, construction sites, commercial farms, fishing communities, mines, and detention centres. Such spaces may contain a combination of social, economic and physical conditions that may increase the likelihood of exposure to violence and abuse and/or acquisition of communicable or non-communicable disease [ 22 ]. The daily stressors that may be experienced in these spaces are increasingly acknowledged to affect emotional wellbeing and mental health [ 23 ].
As migration is an ever-changing dynamic process, generating and maintaining timely and comparable migration data and improving relevant information systems is important. ‘Quick wins’ in obtaining migration and health data by integrating migration variables into existing national demographic and health surveys, for instance, were highlighted. National disease control programs such as tuberculosis, HIV and malaria control programs should also be encouraged to collect data on internal and international migration, especially in cross-border areas. Communicable disease control remains a key health concern associated with human migration. Our discussions recognised the importance of embracing systems-theory approach for improving understanding of how migration influences not only disease transmission but also health promotion, and health-care seeking behaviours. The importance of collecting such data with strict adherence to research ethics and human rights was emphasised.
Towards a multilevel migration and health research agenda
To effectively inform policies and programs on migration and health, it is essential to invest in evidence generation through research at local, national, regional, and global levels. Identified approaches include the establishment of research reference groups at each level to support, guide, and connect the development and application of research to support evidence-informed policy making at multiple levels. Mapping and analysis of key stakeholders, migration patterns, existing legal frameworks, data source, and research output via bibliometric analysis is needed. Multi-level migration and health policy and priority setting processes must be guided by interdisciplinary and multisectoral thinking in order to address the multiple determinants associated with the health of both internal and cross-border migrants.
Key constituencies need to be mobilised from academia, civil society, international organizations, the private sector including employer groups, trade unions and migrant worker networks. These groups may also play a role in commissioning or directly undertaking applied research in order to advance better outcomes for migrants and communities in both places of origin and destination. High-level political leadership and health and development champions should raise the visibility of migration and health research. It is important to utilise existing research structures and resources to support the development of a research agenda on migration and health, as well as to seek support for the development of dedicated research commissions on migration and health at multiple levels in order to harness evidence to drive policy-making and programme formation. For instance, the Government of Sri Lanka, with the technical cooperation of IOM, commissioned a National Migration Health Research Study in 2010 to explore health impacts of inbound, outbound, and internal migrant flows including those of left-behind migrant families. The research findings ultimately contributed to the formulation of an evidence-informed National Migration Health Policy and national action plan in 2013 [ 24 ]. The research was led through local research institutions and research process were linked to an inter-ministerial and inter-agency process chaired by the Minister of Health. This evidence informed policy making process also led to a number of national programs such as ‘the national border health program’ in 2013, revitalizing domestic legal frameworks on health security, and advancing health protection of migrant workers at regional inter-governmental initiatives such as the Colombo Process.
At the regional level, consultative processes are required to develop common approaches to migration and health, including communicable disease surveillance, monitoring of interventions, applied research collaboration across national borders and capacity building – particularly interdisciplinary postgraduate training. For instance, the Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (MBDS) Consortium is a sub-regional co-operation spearheaded by health ministries from member countries Cambodia, China, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam [ 25 ]. In relation to labour migration, regional processes – such as the Colombo Process [ 26 ] - should explore the management of overseas employment and contractual labour. In addition, migrant health-related concerns should be emphasised in the negotiation of free trade agreements that increase migration between states, such as the Post-2015 Health Development Agenda for a “ Healthy, Caring and Sustainable Community ” initiative of the Association of South-East Asian Nations (ASEAN) [ 27 ] and efforts to implement the “Health in all Policies” strategy of the European Union [ 7 ].
Methods to map human mobility for public health preparedness and response stemming from outbreaks and other health emergencies are needed in order to provide accurate information on population movements, for monitoring the progression of outbreaks, predicting future spread and allocating resources for surveillance and containment strategies. Human mobility was a critical factor in the spread of Ebola virus in the West African region.
A coordinated global research agenda on migration and health is urgently needed. Potential elements include collaboration with stakeholders involved in implementing global initiatives – such as the SDGs – to ensure that indicators and data collection strategies are sensitive to both internal and cross-border migration, and health related issues. Identification of datasets and data collection processes that can be adapted and mined for disaggregated health data related to migration are also crucial in advancing the evidence base. We support the development of a sustainable global reference group that can share research evidence, expertise and experience, develop methodological and ethical guidelines, undertake multi-country studies, provide training and build a global knowledge hub in migration and health. Such a group can also mobilise funders and development partners, collaborate with scientific and professional associations, and engage with journals and publishers to create awareness on the need to better promote migration and health research.
The ‘Migration, Health, and Development Research Initiative’ (MHADRI) is a global network of academics and other research partners who aim to advance migration and health research practice [ 28 ]. The research network was formed around the need to build a global alliance of migration and health researchers and provide a platform to share, collaborate, develop, mentor, advocate and disseminate inter-disciplinary research at the nexus of health and migration. A key goal of the network is to enable researchers from developing nations the opportunity to collaborate and promote research in the Global South. The network has grown to encompass 100 researchers globally, across diverse disciplines, geographic areas and stages of career. A global reference group would be well placed to develop good practice guides on data collection systems, research methods and ethics; research translation and dissemination; and, policy integration strategies.
Research principles
We identified core principles that should guide research on migration and health, and work with migrant populations: an ethically sound human rights approach to research that involves engagement across multiple disciplines. Researchers need to be sensitive when designing and disseminating research findings as data on migration and health may be misused, both at an individual and population level. Key questions related to how researchers can exercise their duty of care as they engage in research, and how we can promote careful use of data and research to make sure it does more good than harm. Activities associated with international migration sometimes take place in a climate of victim blaming, othering, and stigmatisation that prioritises purported national security concerns [ 29 ]. Pressing concerns were identified that relate to the ways in which researchers can navigate this increasingly challenging environment, and how trust can be established among different stakeholders – including with international migrant groups. Securitization agendas also affect the health of migrants by excluding, discriminating and/or blaming migrants as vectors of disease. Ethical approaches to research, with a clear commitment to universal human rights, are therefore paramount in a climate of increasingly restrictive immigration regimes.
Discussions also highlighted the challenges associated with the collection of data with and from migrant populations. These include sampling, biases, and practical barriers such as language and culture, as well as the challenges inherent in reaching people who are often highly marginalised and potentially criminalised. Particular attention needs to be given to ethical issues: protecting confidentiality and ensuring that participation in research does not have an adverse impact on migrants, especially irregular migrants, and that participants gain access to relevant services if required. The development of meaningful partnerships and respectful research practice with actors involved in the migration process will also improve the quality, reliability, legitimacy, and use of the data generated.
Contributions from a range of disciplines – such as anthropology, demography, sociology, law, political science, psychology, policy analysis, public health, and epidemiology – are required to unpack the complex relationships between migration and health. Approaches to “slow research” [ 30 ] may help increase the sensitivity of epistemologies and methods to local realities, intricate dynamics, and the multiple voices and perceptions of migrants, health professionals and other individuals involved [ 24 ]. However, the lack of dedicated research units, institutes or centres on migration and health - especially within lower-income country contexts - require existing researchers and scholars to consolidate and better engage with sub-regional, regional and global research networks to ensure capacity building, mentoring, and support. Sensitising the donor community to the migration and health agenda, especially those funding research, is paramount. Curriculum development and teaching support for building the next generation of migration and health researchers is critical to successfully building and sustaining future research on migration and health.
Stewardship elements
We discussed the importance of developing appropriate research translation and engagement activities in order to support key, identified stewardship functions [ 17 ] at the global, regional, national and local levels. Key gaps in stewardship related to the lack of major funding mechanisms for research at national, regional, and global levels, and the need to invest in capacity building for emerging researchers through training programs and support, especially for researchers in lower-income country settings. Collaboration is required to support relationships among researchers and with relevant stakeholders, particularly with migrant communities. This includes building inclusive migration and health research networks, developing communities of practice, and supporting collaborations with those working on other global health priorities. Our research also needs to include the experiences of service providers who engage with various migrant populations, such as those within the health care sectors, border management, law enforcement, and labour migration. The development of effective research translation and public engagement strategies for sharing research findings is critical: not only to shape multi-level policy processes but also public and political opinion.
There was clear consensus on our commitment to enhancing the quality and breadth of multi-level research evidence to support the development of improved responses to migration and health. The importance of an ‘enabling environment’ for migration and health research at local, national, regional and global levels was emphasised, as was the development of meaningful linkages – such as through research reference groups – to support evidence-informed and intersectoral policy and priority setting processes. Our research needs to be underpinned by a human rights approach to health and sound ethical practice. With adequate funding, capacity development, and support for academic freedom, we can improve the evidence base to guide policy and programming for migration and health at multiple levels and in so doing contribute to improving health for all.
Abbreviations
Association of South-East Asian Nations
International Organization for Migration, the UN Migration Agency
Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance
Migration, Health, and Development Research Initiative
Sustainable Development Goals
World Health Organization
IOM. Health of migrants: resetting the agenda. Report of the 2nd global consultation. Colombo, Sri Lanka, 21-23 February 2017. Geneva: IOM; 2017. https://www.iom.int/sites/default/files/our_work/DMM/Migration-Health/GC2_SriLanka_Report_2017_FINAL_22.09.2017_Internet.pdf
Google Scholar
IOM. Global Migration Trends Factsheet. Berlin: Global Migration Data Analysis Centre, IOM; 2017. http://gmdac.iom.int/global-migration-trends-factsheet . Accessed 13 Sep 2017.
Castañeda H, Holmes SM, Madrigal DS, Young M-ED, Beyeler N, Quesada J. Immigration as a social determinant of health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:375–92.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Davies A, Basten A, Frattini C. Migration: a social determinant of migrants’ health. Migr Health Eur Union. 2010;16:10–2.
Chung RY, Griffiths SM. Migration and health in the world: a global public health perspective. Public Health. 2018;158:64–5.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
IOM. Global Health - Thematic Discussion Paper. Geneva: IOM; 2017. https://www.iom.int/sites/default/files/our_work/DMM/Migration-Health/GC2_TDP_Global%20Health_FINAL_13.02.2017.pdf . Accessed 13 Sep 2017.
IOM. Vulnerability and Resilience - Thematic Discussion Paper. Geneva: IOM; 2017. https://www.iom.int/sites/default/files/our_work/DMM/Migration-Health/GC2_TDP_Vulnerability-and-Resilience_FINAL_13.02.2017.pdf . Accessed 13 Sep 2017.
IOM. Development - Thematic Discussion Paper. Geneva: IOM; 2017. https://www.iom.int/sites/default/files/our_work/DMM/Migration-Health/GC2_TDP_Development_FINAL_13.02.2017.pdf . Accessed 13 Sep 2017.
Bowen S, Zwi AB. Pathways to “evidence-informed” policy and practice: a framework for action. PLoS Med. 2005;2:e166.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
United Nations General Assembly: Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development, Resolution RES/70/1. New York; 2015.
Lougarre C. Using the right to health to promote universal health coverage. Health Hum Rights. 2016;18:35–48.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Abubakar I, Devakumar D, Madise N, Sammonds P, Groce N, Zimmerman C, et al. UCL–Lancet Commission on migration and health. Lancet. 2016;388:1141–2.
IOM. World Migration Report 2018. Geneva: IOM; 2018. https://publications.iom.int/system/files/pdf/wmr_2018_en.pdf . Accessed 2 July 2018
Wickramage K, Mosca D. Can migration health assessments become a mechanism for global public health good? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11:9954–63.
The Lancet. Adapting to migration as a planetary force. Lancet. 2015;386:1013.
Article Google Scholar
Willen SS, Knipper M, Abadía-Barrero CE, Davidovitch N. Syndemic vulnerability and the right to health. Lancet. 2017;389:964–77.
Saltman RB, Ferroussier-Davis O. The concept of stewardship in health policy. Bull World Health Organ. 2000;78:732–9.
PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Vearey J. Mobility, migration and generalised HIV epidemics: a focus on sub-Saharan Africa. In: Thomas F, editor. Handbook on Migration and Health: Edward Elgar Publishing, United Kingdom; 2016.
Hanefeld J, Vearey J, Lunt N, Bell S, Blanchet K, Duclos D, et al. A global research agenda on migration, mobility, and health. Lancet. 2017;389:2358–9.
IOM. Summary Report on the MIPEX Health Strand and Country Reports. Geneva: IOM; 2016.
Kupiszewska D, Kupiszewski M, Martí M, Ródenas C. Possibilities and limitations of comparative quantitative research on international migration flows. Brussels: European Commission; 2010.
Crush J (Ed. Spaces of Vulnerability: Migration and HIV/AIDS in South Africa (Migration Policy Series No. 24). 2002.
Vearey J. Healthy migration: a public health and development imperative for south(ern) Africa. S Afr Med J. 2014;104:663.
Wickramage K, Mosca D, Peiris D, Wickramage K, Mosca D, Peiris S, editors. Migration health research to advance evidence based policy and practice in Sri Lanka volume 1. Philippines: Institute of Medicine, 2017. Phillipines: Institute of Medicine; 2017.
Phommasack B, Jiraphongsa C, Ko Oo M, Bond KC, Phaholyothin N, Suphanchaimat R, et al. Mekong Basin disease surveillance (MBDS): a trust-based network. Emerg Health Threats J. 2013;6 https://doi.org/10.3402/ehtj.v6i0.19944 .
The Colombo Process Portal. http://colomboprocess.org /.
AESAN. ASEAN Post-2015 health development agenda. ASEAN; 2017. http://asean.org/storage/2017/02/APHDA-In-a-Nutshell.pdf . Accessed 13 Sep 2017.
Migration Health Research Portal. https://migrationhealthresearch.iom.int/mhadri . Accessed 13 Sept 2017.
Grove NJ, Zwi AB. Our health and theirs: forced migration, othering, and public health. Soc Sci Med. 2006;62:1931–42.
Adams V, Burke NJ, Whitmarsh I. Slow research: thoughts for a movement in Global Health. Med Anthropol. 2014;33:179–97.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Members of the research stream at the 2nd Global Consultation on Migration and Health who participated and contributed to the discussions (see Appendix ).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Migration Health Division, International Organization for Migration, United Nations Migration Agency, Geneva, Switzerland
Kolitha Wickramage
African Centre for Migration & Society, University of the Witwatersrand and Centre of African Studies, University of Edinburgh, PO Box 76, Wits, 2050, South Africa
Health, Rights and Development (HEARD@UNSW), School of Social Science, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, 2052, Australia
Anthony B. Zwi
Center for Humanitarian Health, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, MD, USA
Courtland Robinson
Institute of the History of Medicine, University Justus Liebig Giessen, Iheringstr. 6, 35392, Giessen, Germany
Michael Knipper
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to structuring and facilitating the research stream at the Global Consultation. KW, JV, AZ, CR, MK documented and synthesized the key themes emergent from the working groups and prepared ‘mind maps’. KW authored a section in the final report from the Global Consultation on behalf of the research stream, on which this article is based. JV wrote first draft of the article. KW and JV revised the article based on very helpful comments from two reviewers. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kolitha Wickramage .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Members of the research stream at the 2nd Global Consultation on Migration and Health
In alphabetical order:
Ibrahim Abubakar (Director, Institute for Global Health, University College London, United Kingdom)
Anjali Borhade (Associate Professor, Indian Institute of Public Health, India)
Chee-khoon Chan (Research Associate, University of Malaya, Malaysia)
Julia Puebla Fortier (Executive Director, Diversity Rx - Resources for Cross Cultural Health Care)
Charles Hui (Associate Professor of Paediatrics and Chief of Infectious Diseases, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario)
Michael Knipper (Associate Professor, Institute of the History of Medicine of the University of Giessen, Germany)
Michela Martini (Migration Health Regional Specialist, IOM Regional Office for Horn, East and Southern Africa, Nairobi, Kenya)
Moeketsi Modisenyane, National Department of Health, South Africa
Davide Mosca (Director, Migration Health Division, IOM, Geneva, Switzerland)
Kevin Pottie (Associate Professor, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario)
Bayard Roberts (Director, The Centre for Health and Social Change at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, United Kingdom)
William Courtland Robinson (Associate Professor, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, School of Public Health, USA)
Chesmal Siriwardhana (Associate Professor, London School for Hygiene and Tropical Medicine)
Ursula Trummer (Head, Center for Health and Migration, Vienna, Austria)
Jo Vearey (Associate Professor, African Centre for Migration & Society (ACMS), University of the Witwatersrand)
Kolitha Wickramage (Migration Health and Epidemiology Coordinator, IOM, Manila, Philippines)
Anthony Zwi (Professor of Global Health and Development, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wickramage, K., Vearey, J., Zwi, A.B. et al. Migration and health: a global public health research priority. BMC Public Health 18 , 987 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5932-5
Download citation
Received : 14 March 2018
Accepted : 02 August 2018
Published : 08 August 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5932-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Global health
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Skip to content
Worldwide CHOP Global Health Youth Essay Competition
Global health center.
Arabic | Spanish | French | Chinese
Call for youth stories

We invite you to draw from your personal experiences to submit an essay in response to the prompt:
“In the era of decolonizing global health, do high-income countries (HIC)* have an obligation to advance child health in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC)*?”
Eligibility
- To apply, you must be between the ages of 12 – 19 years old.
- Prior year winners are not eligible to apply.
- You can apply from anywhere in the world.
How it works
- Essays can be submitted in Arabic, Chinese, English, French, or Spanish.
- Essays must be double-spaced and typed in Times New Roman 12-point font.
- You are welcome to include an optional short video (1 min or less), poem, song (1 min or less), or visual art piece. Though the quality of these pieces will not be counted toward the review of your essay, they should enhance the message of your submission.
- Your submission must contain original content that speaks to your own ideas or experiences.
- Co-authorship is acceptable as long as all authors meet all eligibility criteria; however, only one submission per individual or group is permitted.
- Essays will be reviewed as they’re submitted and winners will be announced by Friday, Sept. 8, 2023. Winners will be selected based on their essay’s overall excellence excellence in response to the prompt.
- We will showcase these interviews at the 15th Annual CHOP Pediatric Global Health Conference (Friday, Sept. 29 – Saturday, Sept. 30th, 2023).
- There shall be three cash prizes: a First Prize of $150 , a Second Prize of $125 , and a Third Prize of $75 , in US dollars.
- Winners will also receive free access to any portions of the 15th Annual CHOP Pediatric Global Health Conference that will be live-streamed and/or recorded.

Irène Said Yes to Pediatrics
Irène Mathieu, MD, a resident in General Pediatrics and Global Health at CHOP, describes what led her to a residency in pediatrics.

Impact of Global Health Center
Each year over 5 million children worldwide die before their fifth birthday due to preventable and treatable illnesses. CHOP's Global Health Center is changing this.

Competence or Experience The Missing Voice in Pediatric Decision-Making
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
Photo ID 129550171© Katarzyna Bialasiewicz|Dreamstime.com
INTRODUCTION
One night in 2016, I fell sound asleep, then awoke to painkiller-induced, nightmarish hallucinations in the ICU. Despite being unable to identify myself or surroundings, I can clearly remember the discordant beeping of hospital monitors, acrid smell of saline wash, and taste of sickly sweet orange amoxicillin syrup. I was unaware that, the morning after I’d fallen asleep, I’d skied off an unmarked 30-foot cliff, breaking my legs, jaw, eye socket and nose, rupturing my right ear canal, and shattering nearly all of my teeth. Over the years that followed, I was fortunate enough to receive care from skilled, compassionate physicians. This not only allowed me to return to ski racing, but to dream of becoming a surgeon. Having grown older and thus more aware throughout my years as a pediatric patient, I’ve developed a nuanced understanding of what treatment made me feel heard.
In fact, I found the most radically varying aspect of my care to be the degree to which I was addressed as a conscious, capable individual versus an extension of my parents. This is unsurprising as the proper amount of authority lended to pediatric patients persists as highly disputed in bioethics. Over the course of this paper, several perspectives will be considered in order to evaluate the current position of the pediatric patient in medical decision-making. First, the ambiguity of maturity and reactions to pediatric autonomy will be considered through the Mature Minor Doctrine, especially important in the refusal of life-saving therapies. Next, the need for improved pain management, rooted in the misalignment of experienced and perceived pain in pediatric patients. Finally, this paper will prove, through the lenses of communitarianism and mosaic decision-making, the need for a more nuanced approach to pediatric care that structurally accounts for the patient’s voice without neglecting their place within a greater network. Therefore, there exists a great need for a more direct, balanced integration of pediatric patients’ as well as revisiting prevailing notions of where pediatric patients stand in relation to reason and experience.
To begin, Fleischman’s Pediatric Ethics opens with an exploration of what makes pediatric bioethics distinct. [1] Fleischman quickly runs into the most problematic of principles in the treatment of pediatric patients– autonomy. The ethical ambiguity of the degree of autonomy to offer pediatric patients and at what point in their lives is a central point of conflict. Many in favor of expanded authority point to the neurobiological similarity between young adults and late teenagers. [2] Furthermore, while parents are treated as natural decision-makers for their children, there are several cases of minors facing pressure to undergo medical treatment against their wishes. [3] , [4] In response to these concerns, the Mature Minor Doctrine was created, a common law exception to the parental consent requirement. The doctrine allows a minor “to refuse or consent to medical treatment if [they possess] sufficient maturity to understand and appreciate the benefits and risks of the proposed medical treatment.” [5] The doctrine has spurred extensive and impassioned bioethical discourse, especially in relation to the refusal of life-saving therapies.
In “Health Care Decisionmaking by Children'', Ross draws a clear distinction between the notion of competence, often cited in psychological justifications of the Mature Minor Doctrine, and sound judgment. [6] Her points against child liberationists can be simplified as follows: (a) children need time to develop virtues that preserve their life-time autonomy versus their present-day autonomy, (b) pediatric patients possess “limited world experience and so [their] decisions are not part of a well-conceived life plan,” [7] and (c) it serves parents and children alike for parents to make decisions in line with their view of a good life. I find all three points convincing, but each of them to be uniquely rooted in this same, critical lack of experience possessed by pediatric patients. I can attest to this. There were times where I suffered so desperately that I longed for relief by any means. I even told my mother that I was content only hearing out of one ear, willing to do anything to prevent another surgery. Now, I am fearful to imagine a world where, at my lowest, I had full autonomy.
Hence, the broad aversion to expanded pediatric autonomy is largely rooted in potential misuse, especially in the possibility of a unilateral, misinformed decision in favor of death via refusal of life-sustaining therapy. [8] , [9] Yet, one might argue, the desire for death has concrete rationale beyond lack of life experience— pain and suffering. As Foley describes, “The public's fear of pain and the media's portrayal that physician-assisted suicide and euthanasia are the only reliable options for pain relief… demand that health care delivery systems commit their efforts to improve pain relief at an institutional level.” [10] Indeed, the issue of insufficient pain management is all too common in pediatrics. One study comparing postoperative pain assessments surveyed 307 patients, 207 of whom were verbal. Across the board, nurses’ pain estimations produced significantly lower pain scores than parents and children, and were consistently closer to estimated pain scores of independent observers. [11] In another study, a total of 356 nurses across 22 Japanese PICUs were surveyed, and despite possessing a median of 4 years of experience, a mere 32.6% expressed confidence in their ability to accurately assess pain. [12] It is alarming and telling that even in verbal pediatric patients, pain is significantly underestimated by medical personnel, reflecting a real gap in pediatric patient-professional communication. I can, again, personally attest to this. In the children’s ward, I was offered only Tylenol for severe nerve pain in my legs that kept me awake most nights.
Relatedly, the spirited debate in response to the Mature Minor Doctrine is somewhat disproportionate. Despite the suggestion of various commentators that the law broadly recognizes the doctrine or that states are trending in its direction, only eight states have adopted a mature minor exception, and even these states condition this authority greatly. [13] With this in mind, a crucial issue is illuminated– an aversion to the pediatric patient voice altogether. As Flesichman writes, “Children should be informed about the nature of their condition, the proposed treatment plan, and the expected outcome… appropriate to their developmental levels.” [14] Hence, it is vital to curtail pediatric autonomy in complex and life-threatening choices, but it is worth seriously considering that the current landscape might excessively minimize or avoid pediatric patients’ expression, merely serving to inform them rather than account for their voice.
The experience that pediatric patients do possess, in the form of knowing their body, past medical experiences, and thus present pain-related needs, is systemically underrepresented. This is a pressing issue. Before considering expansion of the pediatric voice, though, it is first important to consider the manner in which the patient’s capacity is further complicated by their role within a larger community. It is worthwhile explicitly mentioning communitarianism, a prevailing school of thought in modern bioethics, defined by Callahan as “a way of… assum[ing] that human beings are social animals… and whose lives are lived out within deeply penetrating social, political, and cultural institutions and practices.” [15] Pediatric patients present a uniquely communitarian case as the perspectives of parents and the needs of patients’ families are vital considerations in offering care. The pediatric patient’s role in a larger family unit and community should be kept in focus so long as the well-being of the patient isn’t compromised, such as in potentially life-threatening religious preferences, as the obligation of the physician is, first and foremost, to the patient.
Nonetheless, the status quo demands a more thoughtful and structural accounting of the pediatric voice to ensure that they feel heard and empowered in complex decision-making and regular care alike. Hence, it is necessary to develop and evaluate clinical models and frameworks that directly account for the pediatric voice, that integrate pediatric patients’ input as continuous, regular, and required elements of treatment. For instance, there may be promise in a model similar to that of mosaic decision-making, a means of restoring the capacity of reemergent patients following brain injury. Rather than enabling complete surrogate authority, the model would enable a pediatric patient’s emergent voice to be accommodated but to not “speak beyond its range and capabilities” via group deliberation between surrogate and patient, a medical professional, and a patient advocate. [16] Opting for such a model would enable the active involvement of pediatric input without excessively empowering the patient in a manner that neglects their communitarian role and lack of experience.
In the heated response to the largely unenforced mature minor doctrine, one finds the invaluable and lacking factor of experience in pediatric patients, especially in decisions to withdraw or refuse life-sustaining medical treatments. In this same response, however, one finds a sharp aversion to the pediatric voice, reflected in pervasive under-medication. Deficits in pain management must be addressed to more effectively treat discomfort, an effort bolstered by a more structural accounting of the pediatric voice and thus pain-related needs. Finally, frameworks that regularly involve the pediatric patient perspective while valuing their communitarian importance and lacking experience, such as the mosaic model, hold real promise moving forward.
[1] Fleischman, Alan. Pediatric Ethics: Protecting the Interests of Children. (Oxford: Oxford University Press, September, 2016), p. 1-16.
[2] Coleman, Doriane & Rosoff, Philip. “The Legal Authority of Mature Minors to Consent to General Medical Treatment.” (Itasca: American Journal of Pediatrics, March 2013), p. 1.
[3] Hawkins, Susan. “Protecting the Rights and Interests of Competent Minors in Litigated Medical Treatment Disputes.” (New York: Fordham Law Review, March 1996), p. 1.
[4] Derish, Melinda & Heuvel, Kathleen. “Mature Minors Should Have the Right to Refuse Life-Sustaining Medical Treatment.” (Boston: The
Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics, January 2021), p. 1-14.
[5] Derish, Melinda & Heuvel, Kathleen. “Mature Minors Should Have the Right to Refuse Life-Sustaining Medical Treatment.” p. 7.
[6] Ross, Lainie. “Health Care Decisionmaking by Children. Is It in Their Best Interest?” (Garrison: The Hastings Center Report, November-December 1997), p. 1-5.
[7] Ross. “Health Care Decisionmaking by Children''. p. 5.
[8] Penkower, Jessica. “The Potential Right of Chronically Ill Adolescents to Refuse Life-Saving Medical Treatment - Fatal Misuse of the Mature Minor Doctrine.” (Chicago: DePaul Law Review, 1996), p. 1-8.
[9] Burk, Josh. “Mature Minors, Medical Choice, and the Constitutional Right to Martyrdom.” (Charlottesville: Virginia Law Review, September 2016), p. 1-15.
[10] Foley, Kathleen. “Pain Relief Into Practice: Rhetoric Without Reform.” (Alexandria: Journal of Clinical Oncology, 1995), p. 1-3
[11] Hla et. al. “Perception of Pediatric Pain: A Comparison of Postoperative Pain Assessments Between Child, Parent, Nurse, and Independent Observer.” (Melbourne: Pediatric Anesthesia. 2014) p. 1-5.
[12] Tsuboi et. al. “Nurses' perception of pediatric pain and pain assessment in the Japanese PICU.” (Tokyo: Pediatrics International, February 2023), p. 1-3, 10-12.
[13] Coleman, Doriane & Rosoff, Philip. “The Legal Authority of Mature Minors”. p. 1-3.
[14] Fleischman, Alan. Pediatric Ethics . p. 115.
[15] Callahan, Daniel. “Principlism and communitarianism.” (Garrison: The Hastings Center Report, October 2003), p. 2.
[16] Fins, Joseph. “Mosaic Decisionmaking and Reemergent Agency after Severe Brain Injury”. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, September 2017), p. 6.
Jonathan Tenenbaum
Third place winner of Voices in Bioethics' 2023 persuasive essay contest.
Disclaimer: These essays are submissions for the 2023 essay contest and have not undergone peer review or editing.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market Essay
What geographic or international health equity issues exist within and between countries participating in or attempting to establish regulations for the global medical tourism market?
Health equity implies the absence of unjust health differences among different social groups on different levels of the social ladder. Inequity in health isolates people on the basis of gender, poverty level, religion, and race. It is an ethical issue and is associated with human rights policies (Cattan & Tilford, 2006). The medical tourism market involves the provision of medical services to international patients.
Countries that practice medical tourism enhance their economic development though there is a certain risk. The risk involves sabotaging projects aimed at improving health equity both inside and outside the country. The rise in global health care systems has reduced their capability of meeting the goals of “Health for All” stated in the WHO Declaration of Alma Ata and safeguarding people’s rights to health.
The promotion of medical tourism may motivate the distribution of public resources to the private sector in order to support medical tourism (Hodges, Kimball & Turner, 2012). More so, medical tourism may lead to a transfer of professionals to the private health sector. This may result in a scarcity of health professionals in public health systems. Medical tourism also encourages the training of health professionals for more expensive and complex procedures, which attract medical tourists. This may reduce the provision of affordable and appropriate health services to local inhabitants. Medical tourism questions the credibility of health systems in the departure countries (Cattan & Tilford, 2006). This is because of the deviation of resources that are employed to take care of the sick in other countries at the cost of less privileged.
Do you believe that mental health is receiving an equal amount of attention as physical health worldwide?
Mental health is not receiving sufficient attention globally. Very few resources are allocated to the treatment of mental health as compared to physical health (Cattan & Tilford, 2006). Moreover, less funding is provided to do research in this sphere. This underfunding worsens during a recession because of the absence of a national tariff for mental health.
Mental health is not receiving much focus because of the stigma. Stigma is caused by heightened negligence among the general public and media about mental disorders. This is linked to fear of the mentally ill and the image painted by the media regarding associated risks and dangers. In addition, a bias against mental health exists in various medical centers.
People with mental disorders have low access to advanced treatment. More so, mental patients often have to wait for long months and years to get appropriate treatment. The long wait for medical care may cause the disease to advance to more severe stages, which can be difficult to treat. There is enough evidence that people with mental sickness are rejected on the basis that they are not severely sick to get emergency treatment.
The choice and ability to make decisions are not available for patients with mental health problems as they have little say on issues pertaining to their treatment (Cattan & Tilford, 2006). Admittedly, mental patients (and sometimes their caregivers) do not get sufficient (or adequate) attention and support from consultants as well as healthcare professionals on the best choices to make regarding their treatment.
Reference List
Cattan, M., & Tilford, S. (2006). Mental health promotion: A lifespan approach. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill International.
Hodges, J., Kimball, A., & Turner, L. (2012). Risks and challenges in medical tourism: Understanding the global market for health services. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, May 7). International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market. https://ivypanda.com/essays/international-healthcare-system/
"International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market." IvyPanda , 7 May 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/international-healthcare-system/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market'. 7 May.
IvyPanda . 2022. "International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market." May 7, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/international-healthcare-system/.
1. IvyPanda . "International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market." May 7, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/international-healthcare-system/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "International Healthcare: Medical Tourism Market." May 7, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/international-healthcare-system/.
- The Stigma of Mental Illness in Primary Health Care Physicians
- Mental Health Stigma From American Perspective
- Dyslexia Stigma among Saudi Nursing Students
- Goffman's definition of stigma is still useful in 2011
- Stigma Effects on Mental Health Treatment in Minorities
- Thyroid Disease and the Stigma Surrounding It: Weight Has Nothing to Do With It
- Stigma and Psychological Distress in HIV Caregivers
- People With Mental Illnesses: Stigma, Prejudice, and Discrimination
- Burden of Stigma in Mental Health Help Seeking
- Stigma Management in Society
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Treatments Analysis
- Pressure Ulcers as a Quality Issue in Healthcare
- Multivariate Analysis in Pulmonary Hypertension Study
- Recovery Time After Concussion: Study Methods
- Focus Group Research in Healthcare Organizations
Global Health Week 2024
GHP’s Global Health Week will be held April 22 to 26, 2024! Global Health Week 2024 will mark the 30th anniversary of the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) held in Cairo. The ICPD redefined population and development issues by emphasizing that the protection of individual human rights, including gender equity and reproductive health and rights, must be at the heart of population and development programs. During Global Health Week, we will analyze the ICPD’s progress and setbacks, discuss current and future priorities, and explore topics not addressed in Cairo, such as climate change and LGBTQIA+ issues.
Call for Abstracts!
Current Harvard students and postdoctoral fellows are invited to submit a poster presentation on global health and population studies. We particularly encourage submissions with topics related to population and development issues; however, we welcome submissions from many different disciplines and schools at Harvard University. Accepted posters will be displayed at the Global Health Week Symposium on Friday, April 26.
Submission deadline: Sunday, April 7, 2024 at 11:59pm Eastern
Abstract submission details are available here.
Questions should be directed to [email protected] .
Schedule of Events
Global health week symposium keynote address by dr. natalia kanem, md, mph, executive director of the un population fund (unfpa) additional panel speakers coming soon.
Friday, April 26 1:30 to 5:00pm with reception to follow Joseph B. Martin Conference Center (77 Avenue Louis Pasteur, Boston, MA 02115)
Registration information forthcoming.
News from the School

Building a better system for transgender health care

Report calls for regulations around dangerous pathogen research

Melissa Hoffer, Massachusetts' first climate chief, will deliver the May 2024 Convocation speech

Exploring mechanics of cancer progression
📕 Studying HQ
120+ healthcare argumentative essay topics [+outline], dr. wilson mn.
- August 3, 2022
- Essay Topics and Ideas , Samples
If you’re a nursing student, then you know how important it is to choose Great Healthcare argumentative essay topics.
After all, your essay will be graded on both the content of your argument and how well you defend it. That’s why it’s so important to choose topics that you’re passionate about and that you can research thoroughly.
What You'll Learn
Strong Healthcare argumentative essay topics
To help you get started, here are some strong Healthcare argumentative essay topics to consider:
- Is there a nurse shortage in the United States? If so, what are the causes, and what can be done to mitigate it?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of various types of Nurse staffing models?
- What are the implications of the current opioid epidemic on nurses and patients?
- Are there any ethical considerations that should be taken into account when providing care to terminally ill patients?
- What are the most effective ways to prevent or treat healthcare-acquired infections?
- Should nurses be allowed to prescribe medication? If so, under what circumstances?
- How can nurses best advocate for their patients’ rights?
- What is the role of nurses in disaster relief efforts?
- The high cost of healthcare in the United States.
- The debate over whether or not healthcare is a human right.
- The role of the government in providing healthcare.
- The pros and cons of the Affordable Care Act.
- The impact of healthcare on the economy.
- The problem of access to healthcare in rural areas.
- The debate over single-payer healthcare in the United States.
- The pros and cons of private health insurance.
- The rising cost of prescription drugs in the United States.
- The use of medical marijuana in the United States.
- The debates over end-of-life care and assisted suicide in the United States.
As you continue, thestudycorp.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.
Controversial Healthcare topics
There is no shortage of controversial healthcare topics to write about. From the high cost of insurance to the debate over medical marijuana, there are plenty of issues to spark an interesting and thought-provoking argumentative essay.
Here are some Controversial healthcare argumentative essay topics to get you started:
1. Is healthcare a right or a privilege?
2. Should the government do more to regulate the healthcare industry?
3. What is the best way to provide quality healthcare for all?
4. Should medical marijuana be legalized?
5. How can we control the rising cost of healthcare?
6. Should cloning be used for medical research?
7. Is it ethical to use stem cells from embryos?
8. How can we improve access to quality healthcare?
9. What are the implications of the Affordable Care Act?
10. What role should pharmaceutical companies play in healthcare?
11. The problems with the current healthcare system in the United States.
12. The need for reform of the healthcare system in the United States.
Great healthcare argumentative essay topics
Healthcare is a controversial and complex issue, and there are many different angles that you can take when writing an argumentative essay on the topic. Here are some great healthcare argumentative essay topics to get you started:
1. Should the government provide free or low-cost healthcare to all citizens?
2. Is private healthcare better than public healthcare?
3. Should there be more regulation of the healthcare industry?
4. Are medical costs too high in the United States?
5. Should all Americans be required to have health insurance?
6. How can the rising cost of healthcare be controlled?
7. What is the best way to provide healthcare to aging Americans?
8. What role should the government play in controlling the cost of prescription drugs?
9. What impact will the Affordable Care Act have on the healthcare system in the United States?
Hot healthcare argumentative essay topics
Healthcare is always a hot-button issue. Whether it’s the Affordable Care Act, single-payer healthcare, or something else entirely, there’s always plenty to debate when it comes to healthcare. Here are some great healthcare argumentative essay topics to help get you started.
1. Is the Affordable Care Act working?
2. Should the government do more to provide healthcare for its citizens?
3. Should there be a single-payer healthcare system in the United States?
4. What are the pros and cons of the Affordable Care Act?
5. What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare costs in the United States?
6. Is the Affordable Care Act sustainable in the long run?
7. What challenges does the Affordable Care Act face?
8. What are the potential solutions to the problems with the Affordable Care Act?
9. Is single-payer healthcare a good idea?
10. What are the pros and cons of single-payer healthcare?
Argumentative topics related to healthcare
Healthcare is always an ever-evolving issue. It’s one of those topics that everyone has an opinion on and is always eager to discuss . That’s why it makes for such a great topic for an argumentative essay . If you’re looking for some fresh ideas, here are some great healthcare argumentative essay topics to get you started.
1. Is our healthcare system in need of a complete overhaul?
3. Are rising healthcare costs making it difficult for people to access care?
4. Is our current healthcare system sustainable in the long term?
5. Should we be doing more to prevent disease and promote wellness?
6. What role should the private sector play in providing healthcare?
7. What can be done to reduce the number of errors in our healthcare system?
8. How can we make sure that everyone has access to quality healthcare?
9. What can be done to improve communication and collaboration between different parts of the healthcare system?
10. How can we make sure that everyone has access to the care they need when they need it?
Argumentative essay topics about health
There are many different stakeholders in the healthcare debate, and each one has their own interests and perspectives. Here are some great healthcare argumentative essay topics to get you started:
1. Who should pay for healthcare?
2. Is healthcare a right or a privilege?
3. What is the role of the government in healthcare?
4. Should there be limits on what treatments insurance companies must cover?
5. How can we improve access to healthcare?
6. What are the most effective methods of preventing disease?
7. How can we improve the quality of care in our hospitals?
8. What are the best ways to control costs in the healthcare system?
9. How can we ensure that everyone has access to basic care?
10. What are the ethical implications of rationing healthcare?
Medical argumentative essay topics
- Is healthcare a fundamental human right?
2. Should there be limits on medical research using human subjects?
3. Should marijuana be legalized for medicinal purposes?
4. Should the government do more to regulate the use of prescription drugs?
5. Is alternative medicine effective?
6. Are there benefits to using placebos in medical treatment?
7. Should cosmetic surgery be covered by health insurance?
8. Is it ethical to buy organs on the black market?
9. Are there risks associated with taking herbal supplements?
10. Is it morally wrong to end a pregnancy?
11. Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
12. Is it ethical to test new medical treatments on animals?
13. Should people with terminal illnesses have the right to end their lives?
14. Is it morally wrong to sell organs for transplantation?
15. Are there benefits to using stem cells from embryos in medical research?
16. Is it ethical to use human beings in medical experiments?
17. Should the government do more to fund medical research into cancer treatments?
18. Are there risks associated with genetic engineering of humans?
19. Is it ethical to clones humans for the purpose
Argumentative essays on mental illness
- Should there be more focus on mental health in schools?
- Are our current treatments for mental illness effective?
- Are mental health disorders more common now than they were in the past?
- How does social media impact mental health?
- How does trauma impact mental health?
- What are the most effective treatments for PTSD?
- Is therapy an effective treatment for mental illness?
- What causes mental illness?
- How can we destigmatize mental illness?
- How can we better support those with mental illness?
- Should insurance companies cover mental health treatments?
- What are the most effective treatments for depression?
- Should medication be used to treat mental illness?
- What are the most effective treatments for anxiety disorders?
- What are the most effective treatments for OCD?
- What are the most effective treatments for eating disorders?
- What are the most effective treatments for bipolar disorder?
- How can we better support caregivers of those with mental illness?
- What role does stigma play in mental illness?
![120+ healthcare argumentative essay topics [+outline] 1 120+ healthcare argumentative essay topics [+outline] 1](https://i0.wp.com/studyinghq.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/image-17-796x1030.png?resize=796%2C1030&ssl=1)
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Related Posts
- Term-Long Project Nursing Paper Example
- Case Study on Moral Status
- Applying the Concepts of Epidemiology and Nursing Research on Measles Nursing Paper Essay
- A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Nursing Research Paper
- 50 Potential Research Summary Topics
- Free Essays
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- How to Guides
- Essay Topics and Ideas
- Manage Orders
- Business StudyingHq
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. Global health care is a challenging phenomenon that supports the development of new perspectives and approaches to solving global health concerns, including nutrition, infectious disease, cancer, and chronic illness. It is important to address global health as a driving force in international healthcare expenditures because it ...
The increasing importance of global health. In addressing the place of global health in international affairs, I will be speaking about success, shocks, surprises, and moral vindication. The 21st century began well for public health. When the governments of 189 countries signed the Millennium Declaration in 2000, and committed themselves to ...
Our current understanding of the concept of global health is based on information in the literature in the past seven to eight decades. Global health as a scientific term first appeared in the literature in the 1940s [].It was subsequently used by the World Health Organization (WHO) as guidance and theoretical foundation [2,3,4].Few scholars discussed the concept of global health until the ...
Global health: current issues, future trends and foreign policy is a scholarly article that examines the challenges and opportunities of global health in the 21st century. It discusses the role of foreign policy in addressing health inequalities, promoting health security and advancing health diplomacy. The article also provides recommendations for future research and action in global health.
Health benefits aside, increasing investment in primary prevention presents a strong economic imperative. For example, obesity contributes to the treatment costs of many other diseases: 70% of diabetes costs, 23% for CVD and 9% for cancers. Economic losses further extend to absenteeism and decreased productivity.
The global vision that has brought improved travel and trade and increased interdependency among countries also calls for a common vision of health around the world. All countries are vulnerable to the ever-present threats of infectious disease, outbreaks, and epidemics. At the same time, there are opportunities for shared innovation and universal purpose as many countries that suffer from ...
Global mental health impact. The most common characteristics associated with the novel infectious COVID-19 include respiratory symptoms including cough, fever, respiratory problems, and, in ...
Global health has been getting much more attention lately, in settings as varied as the World Economic Forum, TIME Magazine, and even rock concerts—and for good reason. There is a new global determination to address the great disparity in health status between rich and poor people, communities, and nations, and this determination is reflected in explicit commitments of political will and ...
The global health policy landscape has evolved from the 20th century into the 21 st century, ... Frame analysis: an essay on the organization of the experience. [Google Scholar] 97. Benford R.D., Snow D.A. Framing processes and social movements: an overview and assessment. Annu Rev Sociol. 2000; 26:611-639. [Google Scholar]
Abstract. The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 was identified as the causative agent for a series of atypical respiratory diseases in the Hubei Province of Wuhan, China in December of 2019. The disease SARS-CoV-2, termed COVID-19, was officially declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization on March 11, 2020.
The main semantic result of this transition was a change in the epidemiological picture, which caused the need for mobilization and transformation of the healthcare system of developing countries. We will write a custom essay on your topica custom Essay on International Healthcare Systems and Mortality Rates. 808 writers online.
Defining Global Health: NPGH Fogarty Fellow Alumni Essays . Essay 1: Global health encompasses multiple concepts, derived from public health concepts and international health that were originally based in infectious disease control. However, the definition has evolved due to such factors as global trade, travel, and relations.
An essay on a topic of international health importance. An essay on a topic of international health importance. An essay on a topic of international health importance Lancet. 2011 Jan 22;377(9762):350-1. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62189-7. Epub 2010 Dec 15. PMID ...
Exclusively available on IvyPanda. The World Health Organization (WHO) is a focused agency of the United Nations (UN) that functions as a coordinating authority on global public health issues. When diplomats met to form the United Nations in 1945, one of the things they discussed an gave importance to was setting up a global health organization ...
This essay presents a survey of recent work in the history of international and global health from the mid-nineteenth to the early twenty-first centuries. It considers longstanding narratives alongside recent studies that have deployed approaches consonant with scholarship in the emerging global history of science and medicine.
Haiti, my country of birth, is one of the countries affected by global health issues. Haiti is believed to be a country that has never enjoyed freedom for a long time. Many may wonder why there is so much hunger in the country; the reason behind it is because of the poverty that has dominated the country. Poverty in Haiti is exceptional due to ...
Essay about Global Health and Diabetes. Global health is defined as "health problems, issues, or concerns that transcend national borders" (Institute of Medicine, 1997, p. 2). Koplan (2009) proposed a new definition for global health which he described as an "area for study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health ...
Global Health. The world is an increasingly shrinking place. Globalization has interconnected countries through trade and technology (De Cock, Simone, Davison, Slutsker, 2010). Today's economic turmoil is a great example of how is essentially one big web: one country's economic downturn has a domino effect on others.
In recent decades, public health policy and practice have been increasingly challenged by globalization, even as global financing for health has increased dramatically. This article discusses globalization and its health challenges from a vantage of political science, emphasizing increased global flows (of pathogens, information, trade, finance, and people) as driving, and driven by, global ...
Donaldson (2007, p.7) states that, "In today's globalised world, we can no longer consider the health of the UK in isolation. Chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, mental ill health, and alcohol- and tobacco-related illness - once deemed the preserve of industrialised nations - are now worldwide problems.
International Healthcare Policy Health And Social Care Essay. This assignment deals with the impact that social and cultural issues have on attitudes towards healthcare using their chosen nation as an example; I should evaluate healthcare policy in one national context and explain the influences on policy formation, including impacts of funding ...
With 244 million international migrants, and significantly more people moving within their country of birth, there is an urgent need to engage with migration at all levels in order to support progress towards global health and development targets. In response to this, the 2nd Global Consultation on Migration and Health- held in Colombo, Sri Lanka in February 2017 - facilitated discussions ...
Winners will be selected based on their essay's overall excellence excellence in response to the prompt. Selected winners will be invited for a recorded interview with the CHOP Global Health Center staff. We will showcase these interviews at the 15th Annual CHOP Pediatric Global Health Conference (Friday, Sept. 29 - Saturday, Sept. 30th, 2023).
Healthcare Issues, Systems, And Policies America, once the global leader in the health of its population and among the nations with the highest quality and most readily available healthcare services, has now fallen behind almost twenty other countries, including some that only became industrialized in the last third of the 20th century, and with substantial assistance from the United States.
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
The medical tourism market involves the provision of medical services to international patients. Countries that practice medical tourism enhance their economic development though there is a certain risk. The risk involves sabotaging projects aimed at improving health equity both inside and outside the country.
Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: APA. Moore, Sarah. (2021, September 15). The Impacts of War on Global Health.
Global Health Week 2024 will mark the 30th anniversary of the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) held in Cairo. The ICPD redefined population and development issues by emphasizing that the protection of individual human rights, including gender equity and reproductive health and rights, must be at the heart of ...
Russian Health Care Crisis. There has been wide variation among Russia's eighty-nine regions in terms of the severity and dynamics of the health and demographic crisis, remarked Judyth Twigg at a Kennan Institute lecture on 2 October 2000. Twigg, Assistant Professor, Department of Political Science and Public Administration at Virginia ...
11. The problems with the current healthcare system in the United States. 12. The need for reform of the healthcare system in the United States. Great healthcare argumentative essay topics. Healthcare is a controversial and complex issue, and there are many different angles that you can take when writing an argumentative essay on the topic.