Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan
By Andy Marker | July 29, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up expert-tested financial templates for your business plan, all of which are free to download in Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find the essential financial statement templates, including income statement templates , cash flow statement templates , and balance sheet templates . Plus, we cover the key elements of the financial section of a business plan .

Financial Plan Templates
Download and prepare these financial plan templates to include in your business plan. Use historical data and future projections to produce an overview of the financial health of your organization to support your business plan and gain buy-in from stakeholders
Business Financial Plan Template
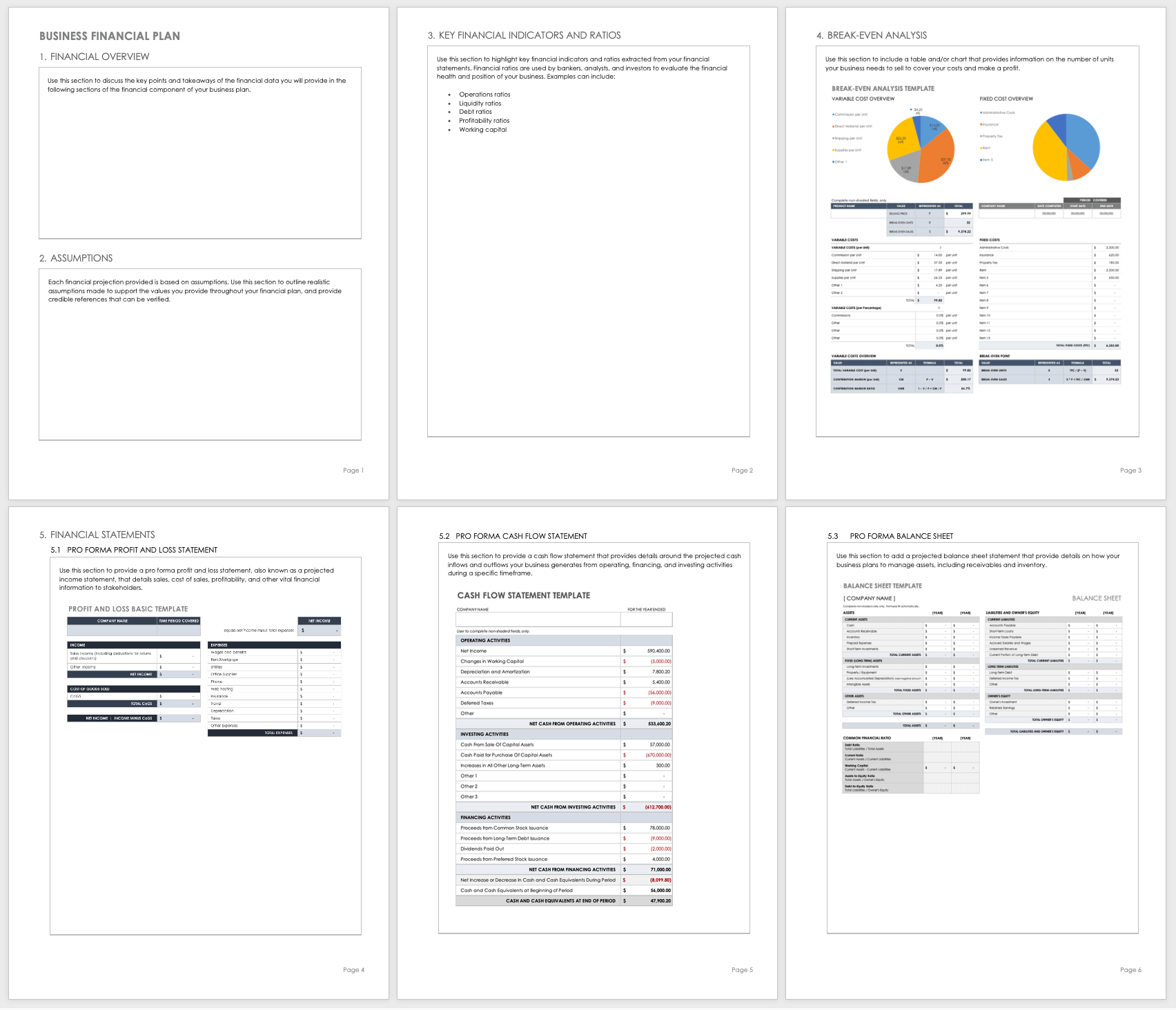
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Download Financial Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Financial Plan Projections Template for Startups
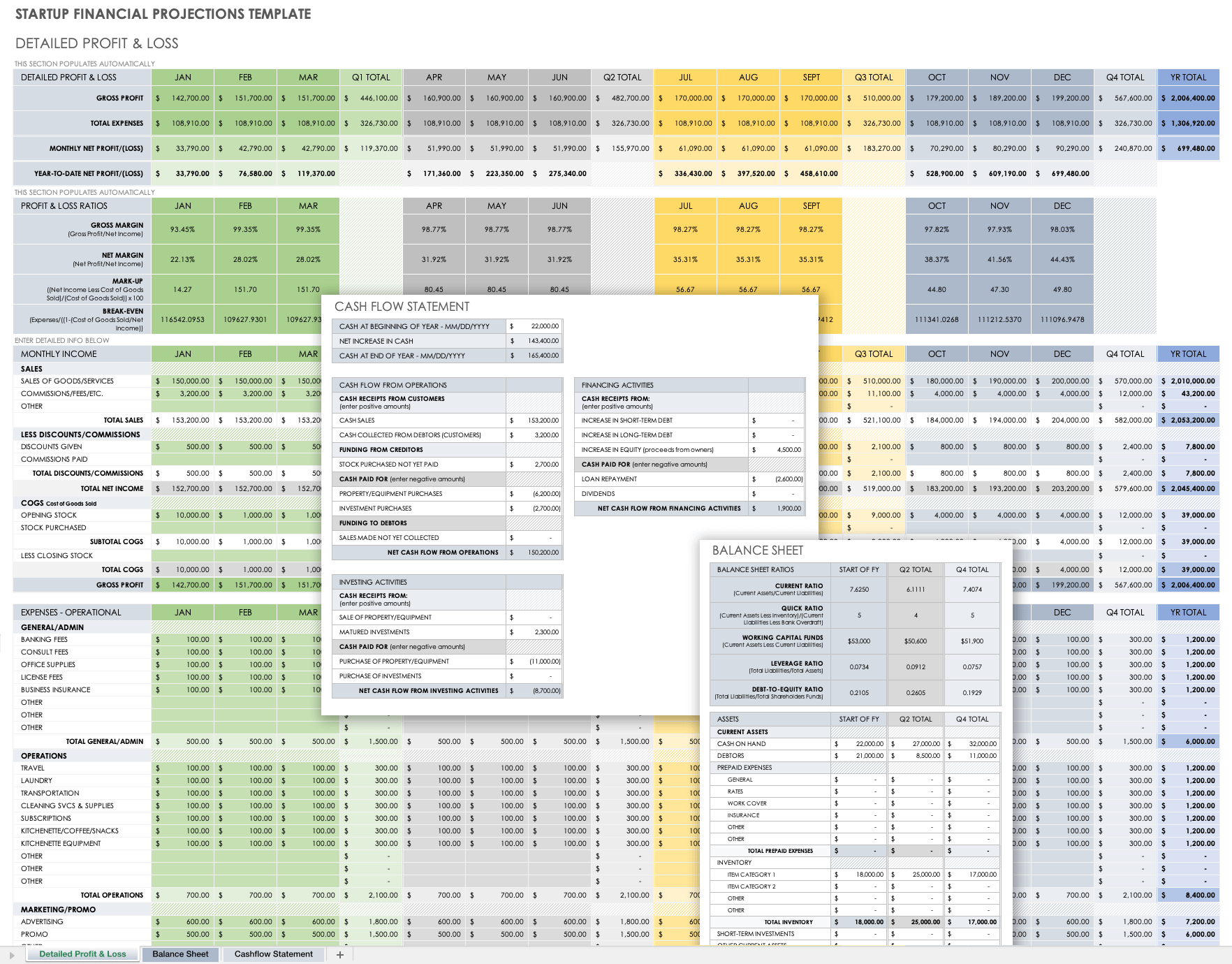
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business.
Download Startup Financial Projections Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Income Statement Templates for Business Plan
Also called profit and loss statements , these income statement templates will empower you to make critical business decisions by providing insight into your company, as well as illustrating the projected profitability associated with business activities. The numbers prepared in your income statement directly influence the cash flow and balance sheet forecasts.
Pro Forma Income Statement/Profit and Loss Sample
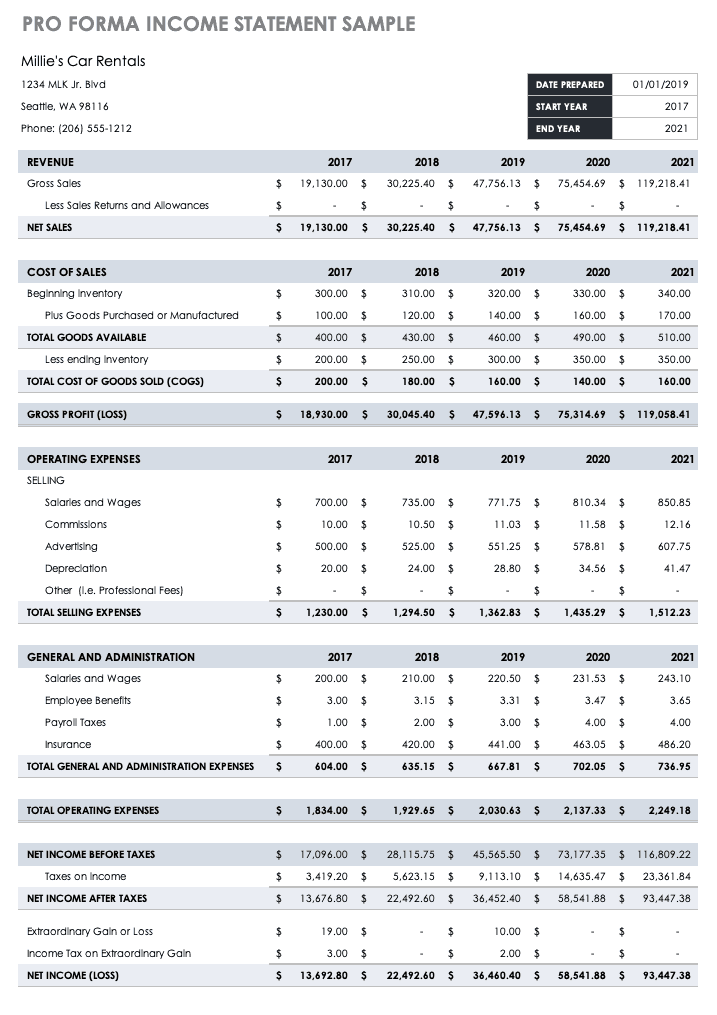
Use this pro forma income statement template to project income and expenses over a three-year time period. Pro forma income statements consider historical or market analysis data to calculate the estimated sales, cost of sales, profits, and more.
Download Pro Forma Income Statement Sample - Excel
Small Business Profit and Loss Statement
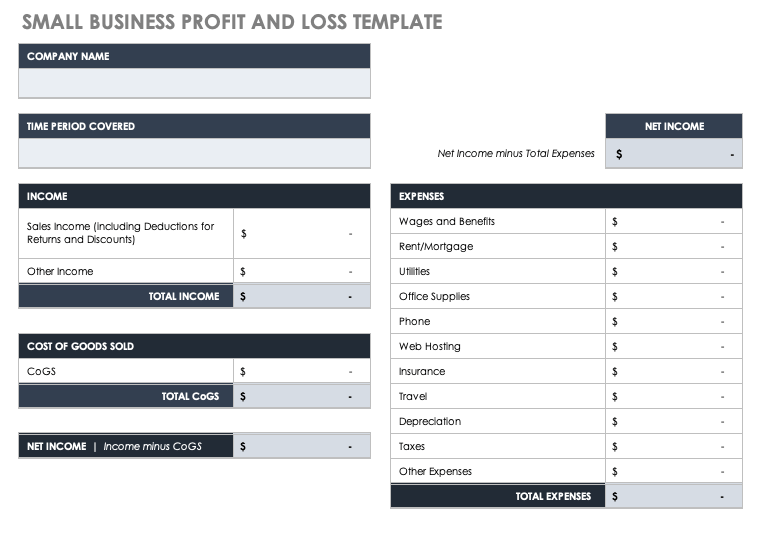
Small businesses can use this simple profit and loss statement template to project income and expenses for a specific time period. Enter expected income, cost of goods sold, and business expenses, and the built-in formulas will automatically calculate the net income.
Download Small Business Profit and Loss Template - Excel
3-Year Income Statement Template
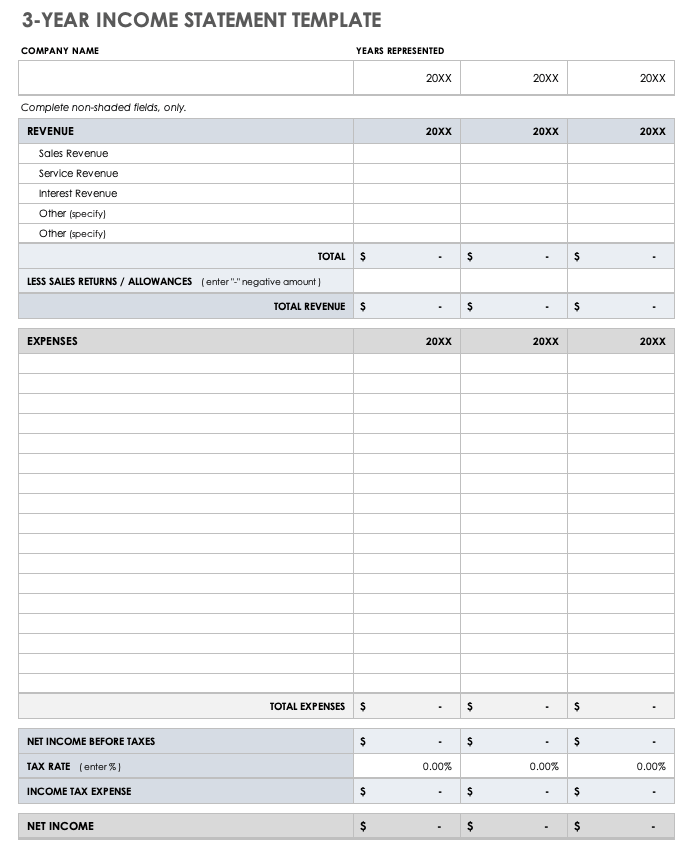
Use this income statement template to calculate and assess the profit and loss generated by your business over three years. This template provides room to enter revenue and expenses associated with operating your business and allows you to track performance over time.
Download 3-Year Income Statement Template
For additional resources, including how to use profit and loss statements, visit “ Download Free Profit and Loss Templates .”
Cash Flow Statement Templates for Business Plan
Use these free cash flow statement templates to convey how efficiently your company manages the inflow and outflow of money. Use a cash flow statement to analyze the availability of liquid assets and your company’s ability to grow and sustain itself long term.
Simple Cash Flow Template

Use this basic cash flow template to compare your business cash flows against different time periods. Enter the beginning balance of cash on hand, and then detail itemized cash receipts, payments, costs of goods sold, and expenses. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate total cash payments, net cash change, and the month ending cash position.
Download Simple Cash Flow Template
12-Month Cash Flow Forecast Template
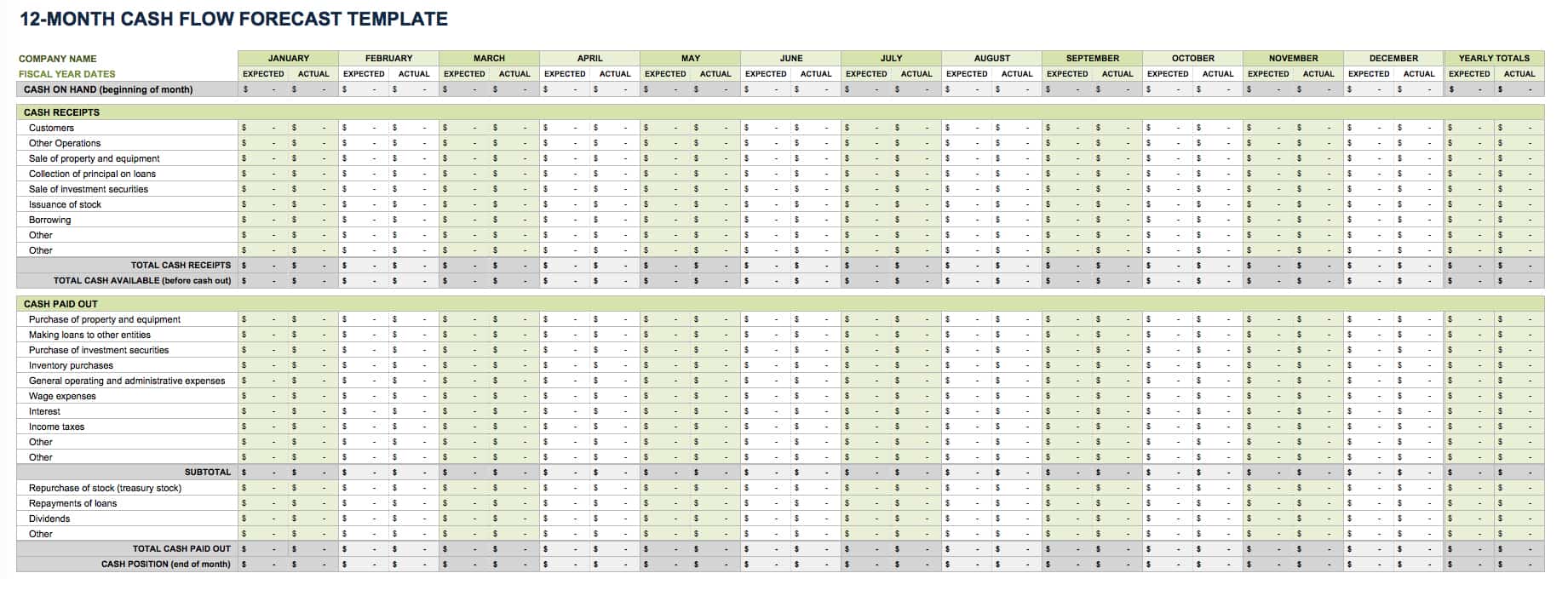
Use this cash flow forecast template, also called a pro forma cash flow template, to track and compare expected and actual cash flow outcomes on a monthly and yearly basis. Enter the cash on hand at the beginning of each month, and then add the cash receipts (from customers, issuance of stock, and other operations). Finally, add the cash paid out (purchases made, wage expenses, and other cash outflow). Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate your cash position for each month with.
Download 12-Month Cash Flow Forecast
3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template Set
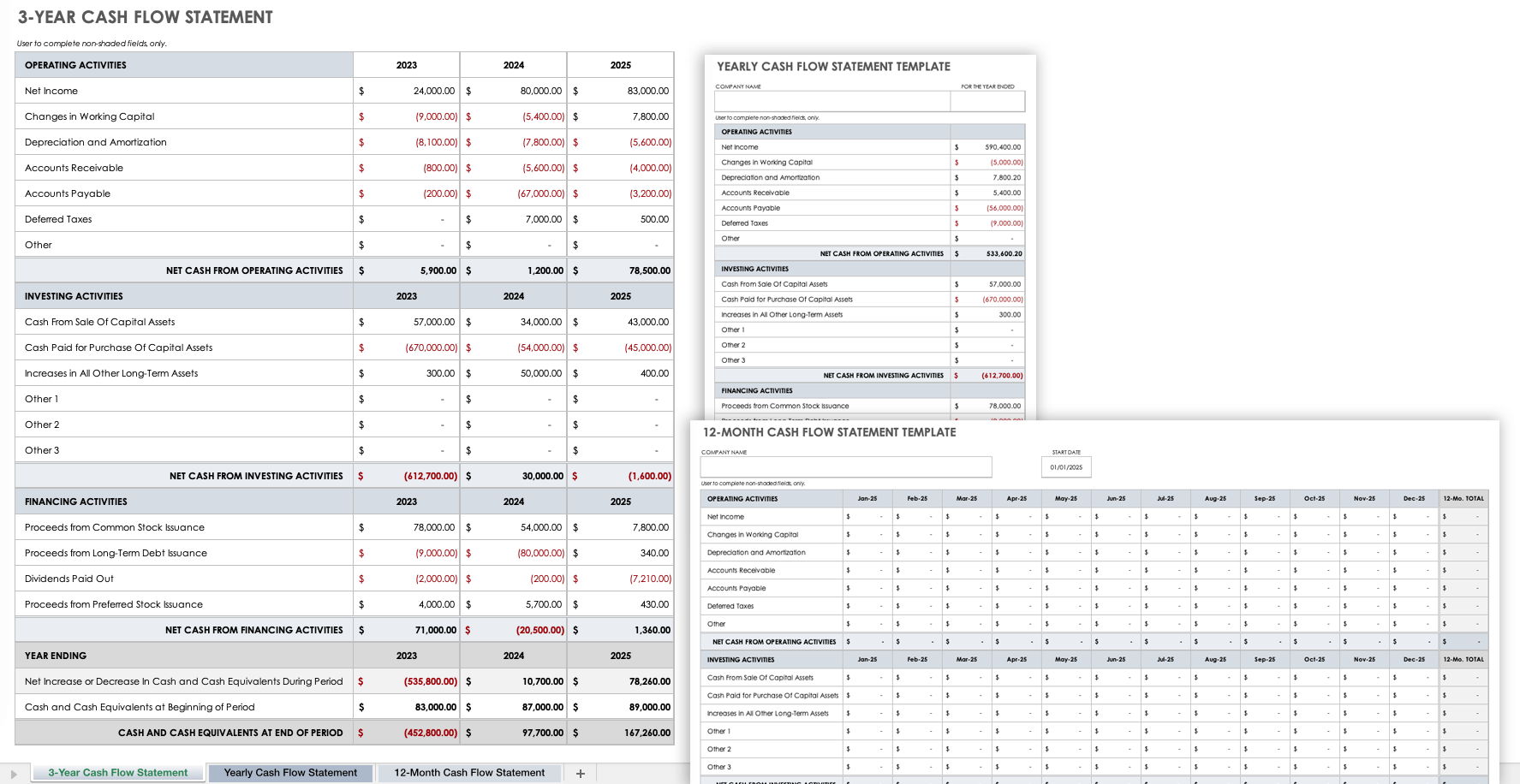
Use this cash flow statement template set to analyze the amount of cash your company has compared to its expenses and liabilities. This template set contains a tab to create a monthly cash flow statement, a yearly cash flow statement, and a three-year cash flow statement to track cash flow for the operating, investing, and financing activities of your business.
Download 3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template
For additional information on managing your cash flow, including how to create a cash flow forecast, visit “ Free Cash Flow Statement Templates .”
Balance Sheet Templates for a Business Plan
Use these free balance sheet templates to convey the financial position of your business during a specific time period to potential investors and stakeholders.
Small Business Pro Forma Balance Sheet
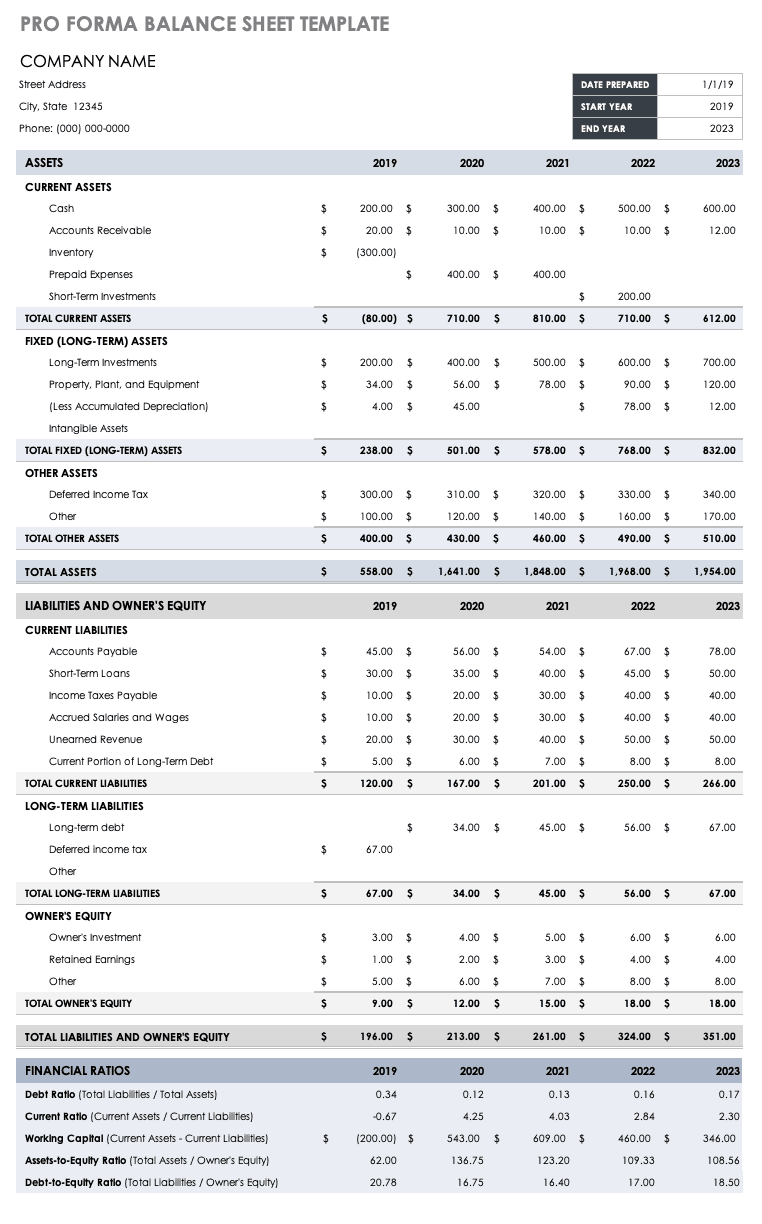
Small businesses can use this pro forma balance sheet template to project account balances for assets, liabilities, and equity for a designated period. Established businesses can use this template (and its built-in formulas) to calculate key financial ratios, including working capital.
Download Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template
Monthly and Quarterly Balance Sheet Template
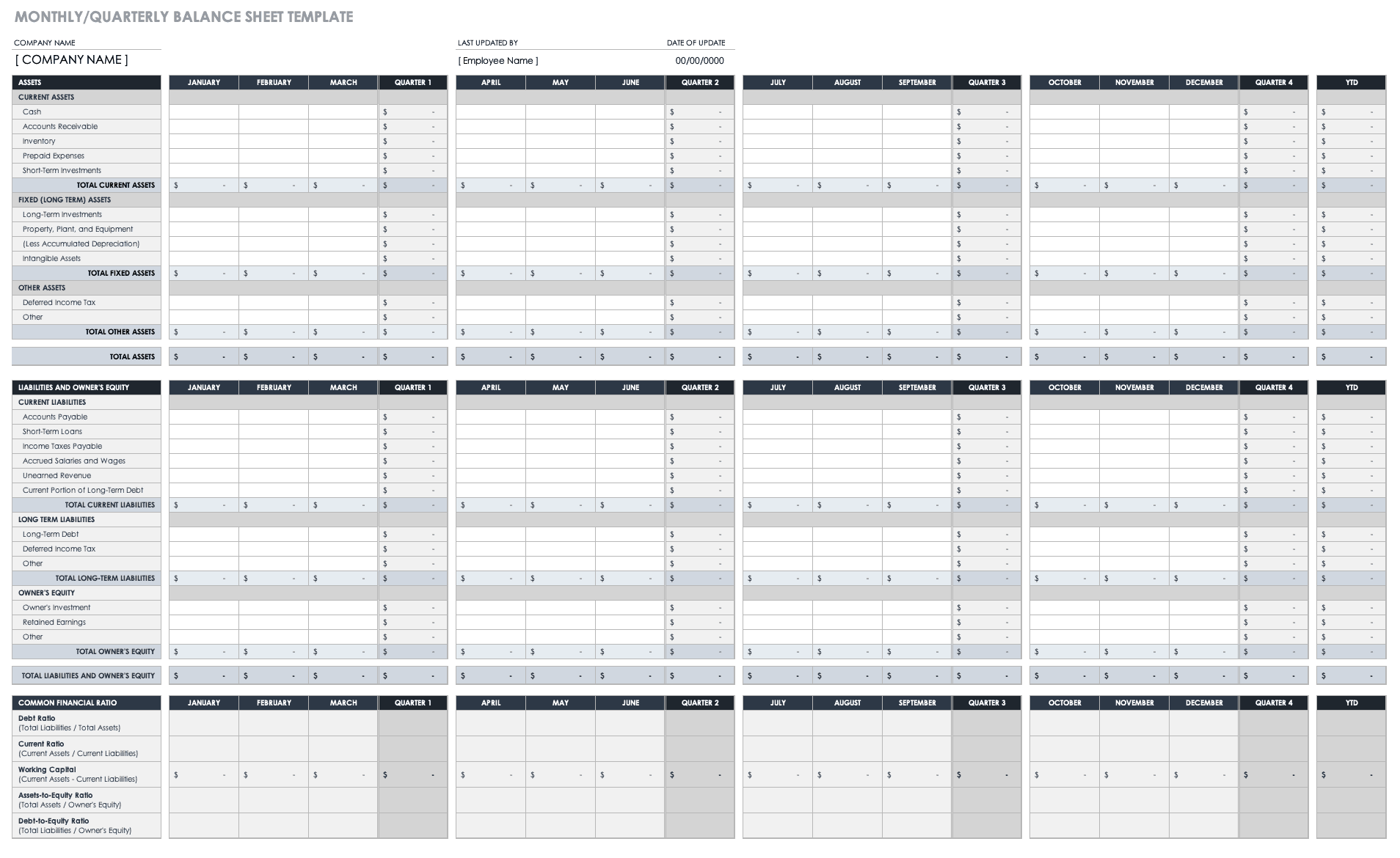
Use this balance sheet template to evaluate your company’s financial health on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can also use this template to project your financial position for a specified time in the future. Once you complete the balance sheet, you can compare and analyze your assets, liabilities, and equity on a quarter-over-quarter or year-over-year basis.
Download Monthly/Quarterly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
Yearly Balance Sheet Template
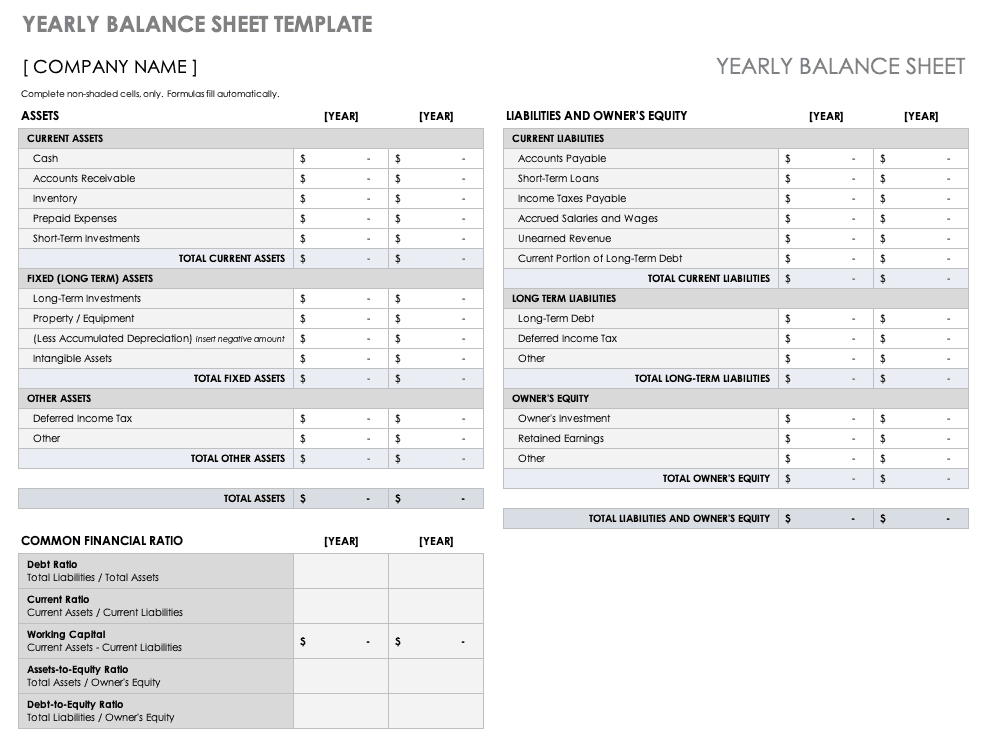
Use this balance sheet template to compare your company’s short and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity year-over-year. This template also provides calculations for common financial ratios with built-in formulas, so you can use it to evaluate account balances annually.
Download Yearly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
For more downloadable resources for a wide range of organizations, visit “ Free Balance Sheet Templates .”
Sales Forecast Templates for Business Plan
Sales projections are a fundamental part of a business plan, and should support all other components of your plan, including your market analysis, product offerings, and marketing plan . Use these sales forecast templates to estimate future sales, and ensure the numbers align with the sales numbers provided in your income statement.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
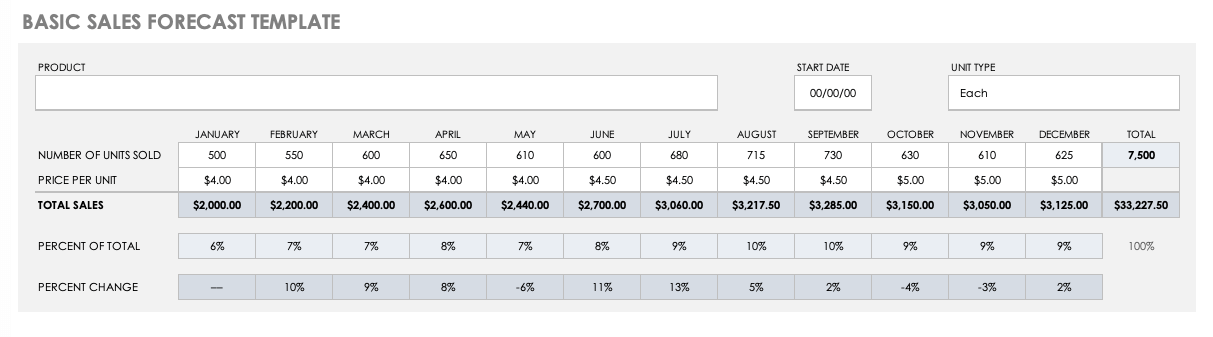
Use this basic forecast template to project the sales of a specific product. Gather historical and industry sales data to generate monthly and yearly estimates of the number of units sold and the price per unit. Then, the pre-built formulas will calculate percentages automatically. You’ll also find details about which months provide the highest sales percentage, and the percentage change in sales month-over-month.
Download Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
12-Month Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
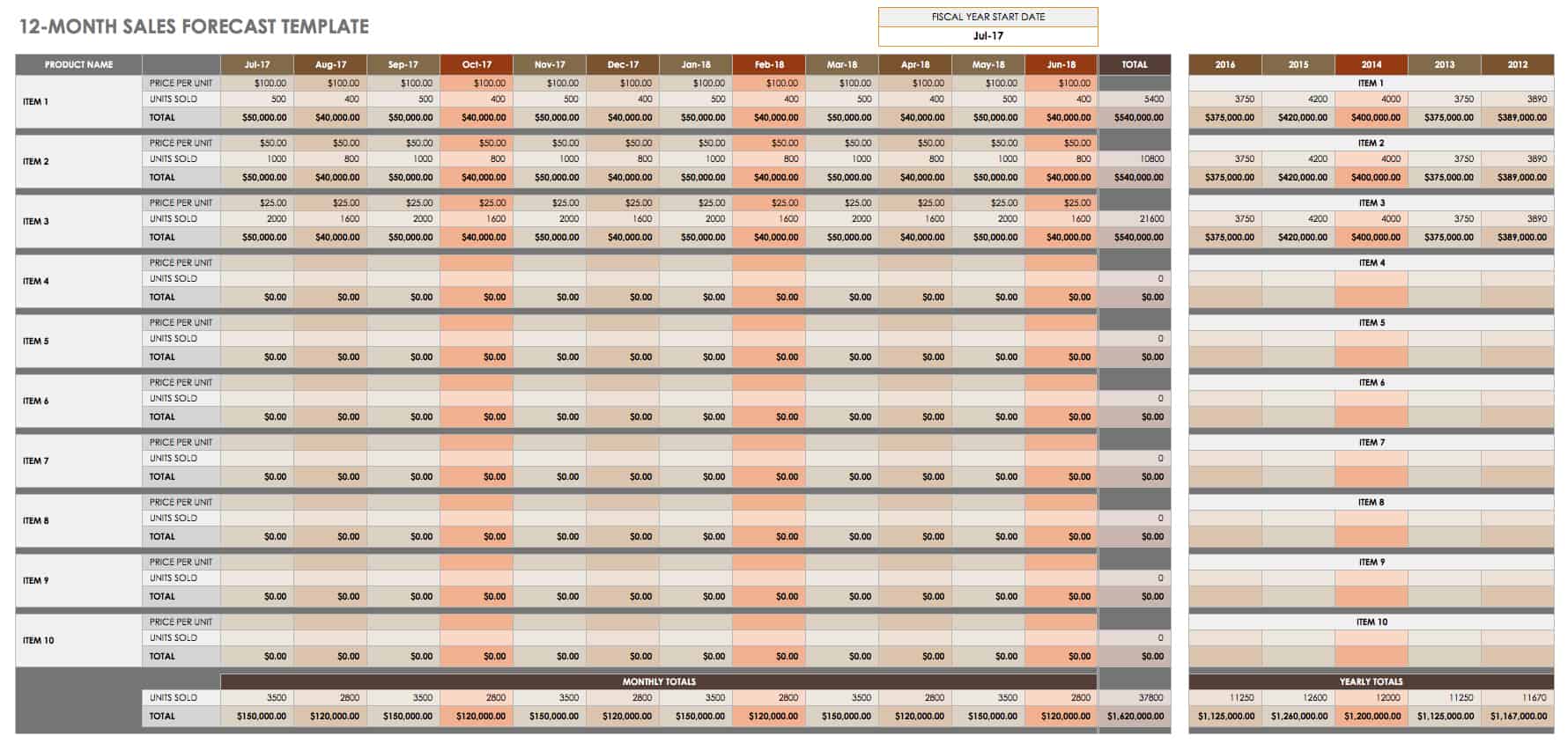
Use this sales forecast template to project the future sales of a business across multiple products or services over the course of a year. Enter your estimated monthly sales, and the built-in formulas will calculate annual totals. There is also space to record and track year-over-year sales, so you can pinpoint sales trends.
Download 12-Month Sales Forecasting Template for Multiple Products
3-Year Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
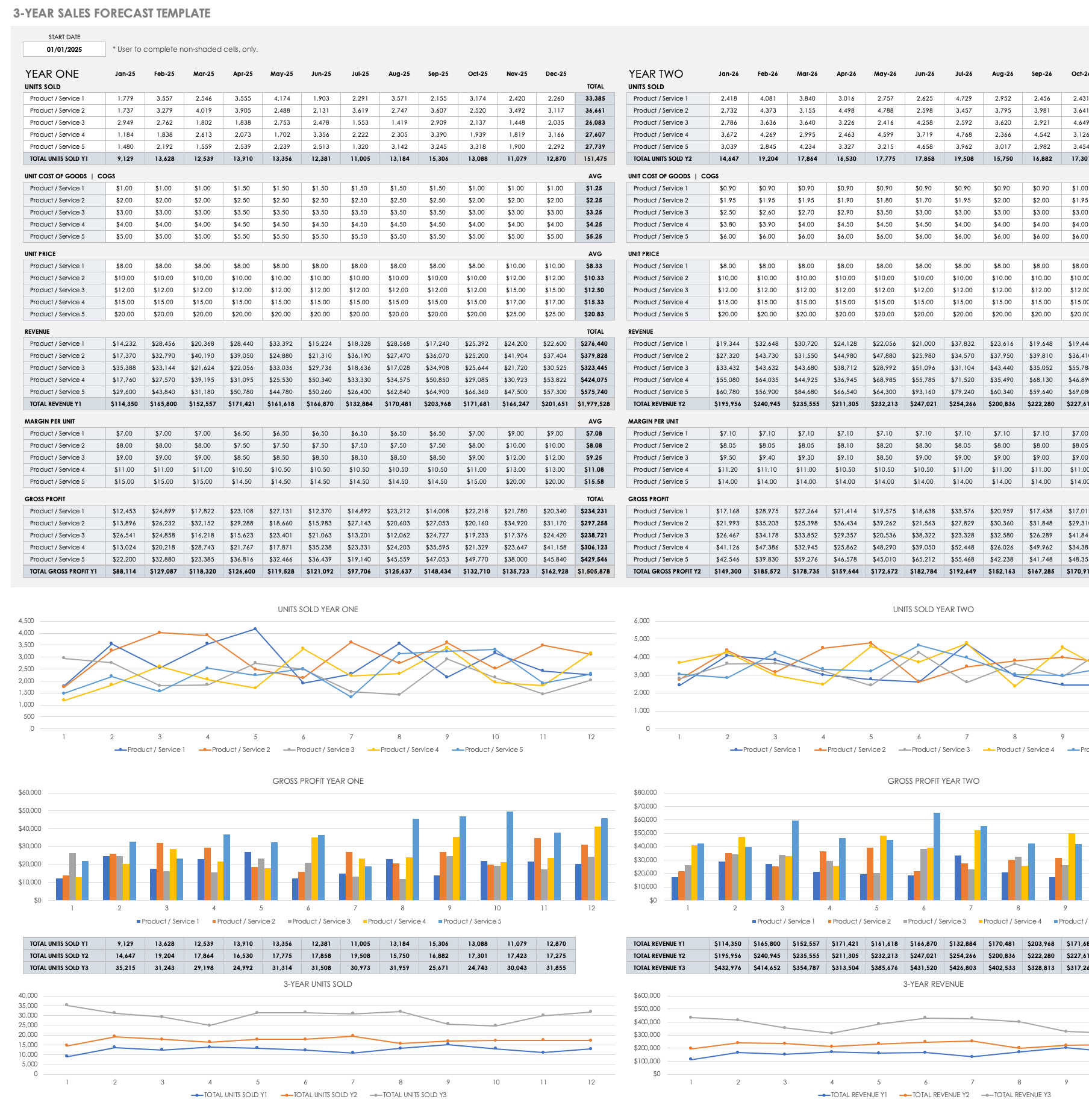
Use this sales forecast template to estimate the monthly and yearly sales for multiple products over a three-year period. Enter the monthly units sold, unit costs, and unit price. Once you enter those values, built-in formulas will automatically calculate revenue, margin per unit, and gross profit. This template also provides bar charts and line graphs to visually display sales and gross profit year over year.
Download 3-Year Sales Forecast Template - Excel
For a wider selection of resources to project your sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Break-Even Analysis Template for Business Plan
A break-even analysis will help you ascertain the point at which a business, product, or service will become profitable. This analysis uses a calculation to pinpoint the number of service or unit sales you need to make to cover costs and make a profit.
Break-Even Analysis Template
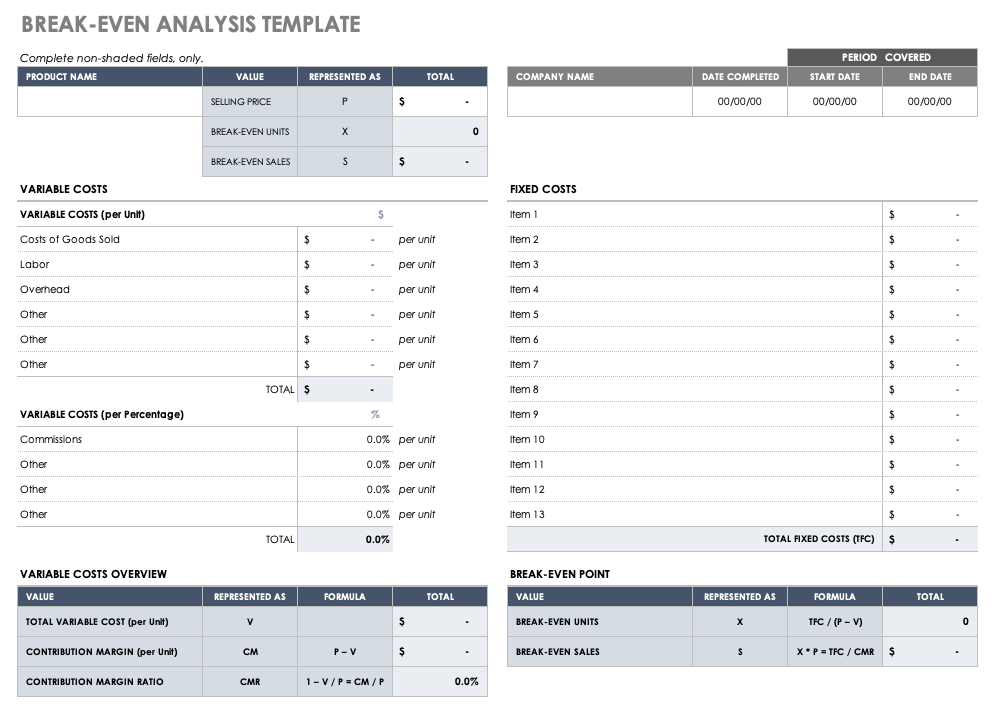
Use this break-even analysis template to calculate the number of sales needed to become profitable. Enter the product's selling price at the top of the template, and then add the fixed and variable costs. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate the total variable cost, the contribution margin, and break-even units and sales values.
Download Break-Even Analysis Template
For additional resources, visit, “ Free Financial Planning Templates .”
Business Budget Templates for Business Plan
These business budget templates will help you track costs (e.g., fixed and variable) and expenses (e.g., one-time and recurring) associated with starting and running a business. Having a detailed budget enables you to make sound strategic decisions, and should align with the expense values listed on your income statement.
Startup Budget Template
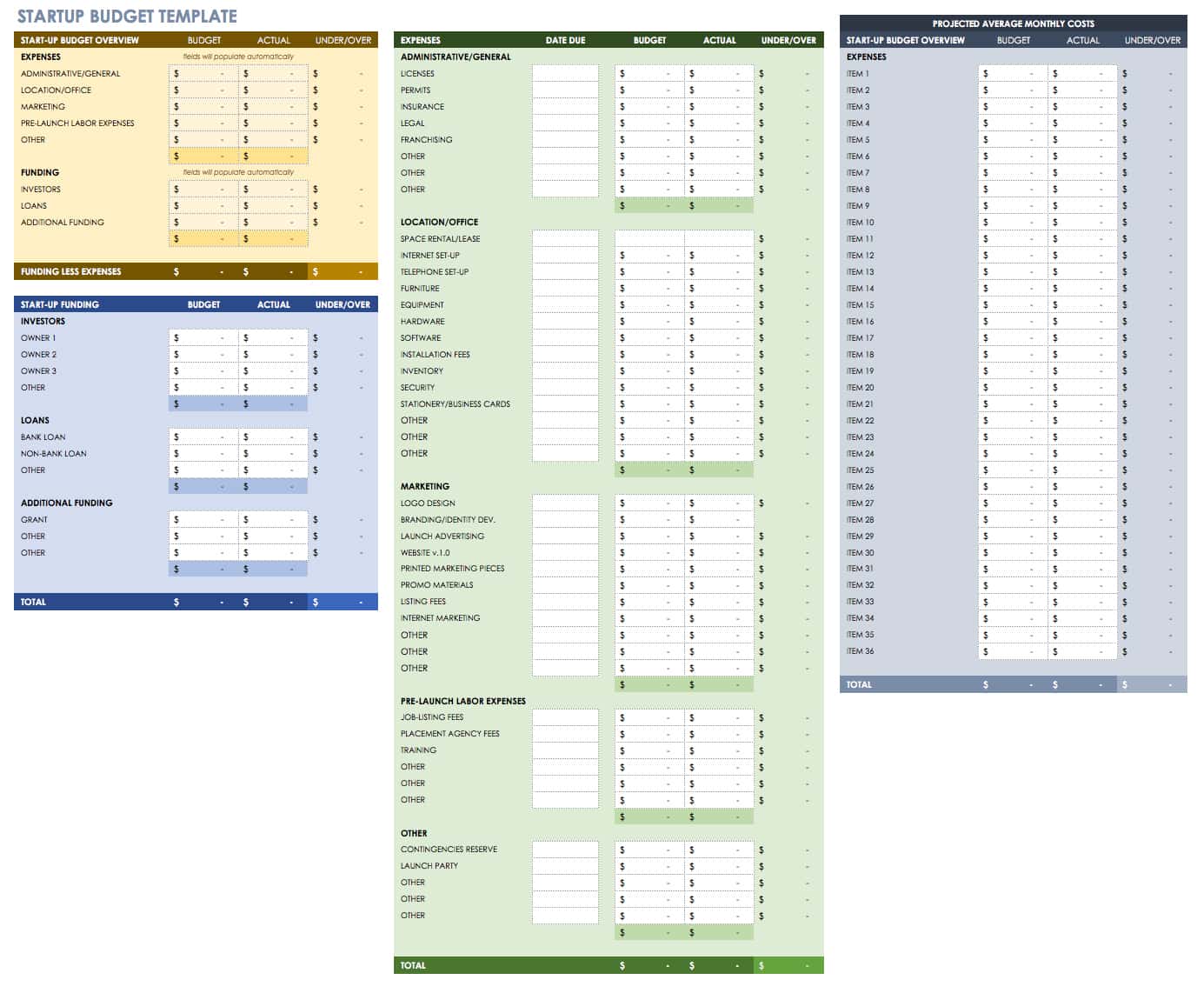
Use this startup budget template to track estimated and actual costs and expenses for various business categories, including administrative, marketing, labor, and other office costs. There is also room to provide funding estimates from investors, banks, and other sources to get a detailed view of the resources you need to start and operate your business.
Download Startup Budget Template
Small Business Budget Template
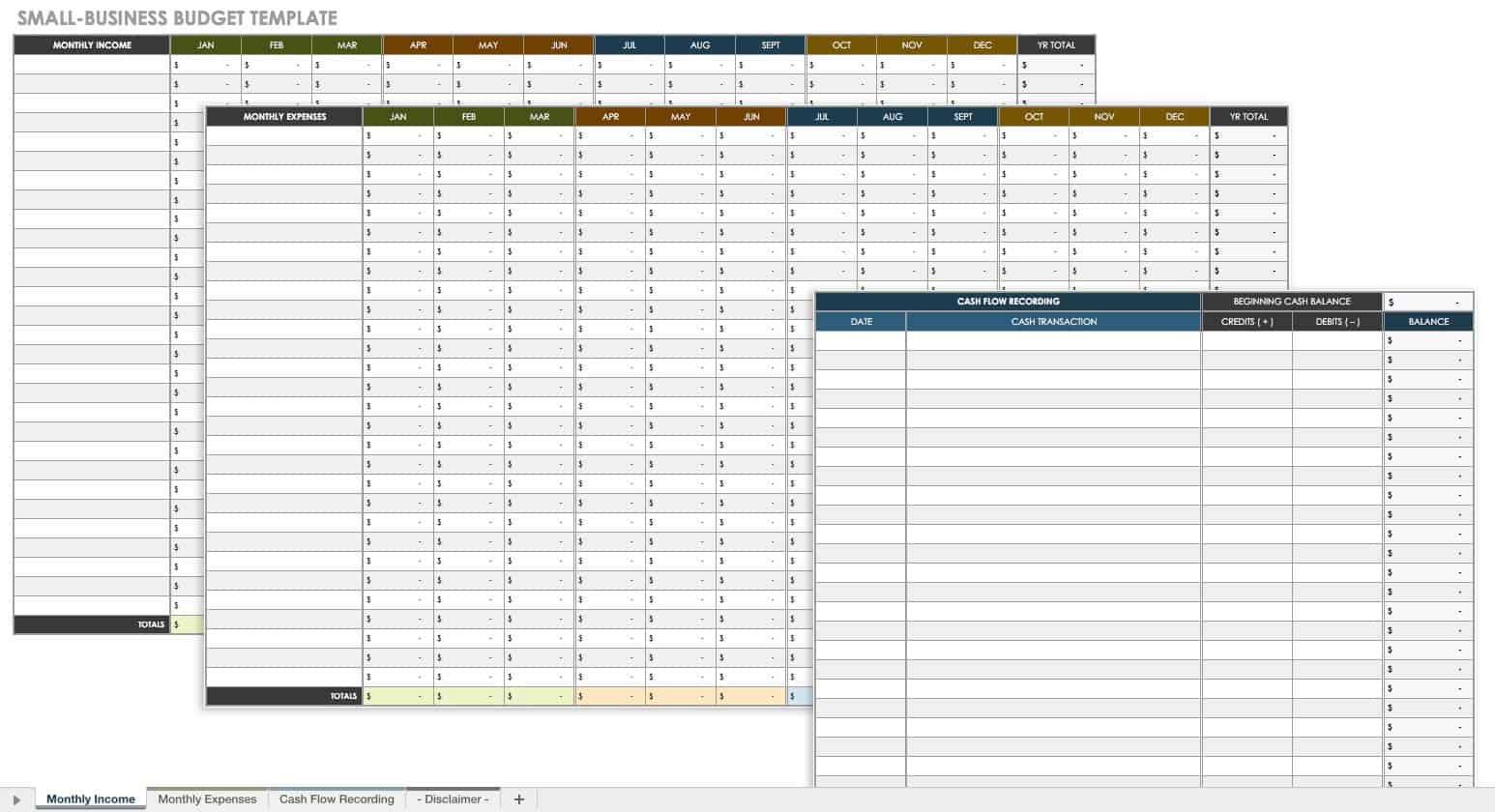
This business budget template is ideal for small businesses that want to record estimated revenue and expenditures on a monthly and yearly basis. This customizable template comes with a tab to list income, expenses, and a cash flow recording to track cash transactions and balances.
Download Small Business Budget Template
Professional Business Budget Template

Established organizations will appreciate this customizable business budget template, which contains a separate tab to track projected business expenses, actual business expenses, variances, and an expense analysis. Once you enter projected and actual expenses, the built-in formulas will automatically calculate expense variances and populate the included visual charts.
Download Professional Business Budget Template
For additional resources to plan and track your business costs and expenses, visit “ Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company .”
Other Financial Templates for Business Plan
In this section, you’ll find additional financial templates that you may want to include as part of your larger business plan.
Startup Funding Requirements Template
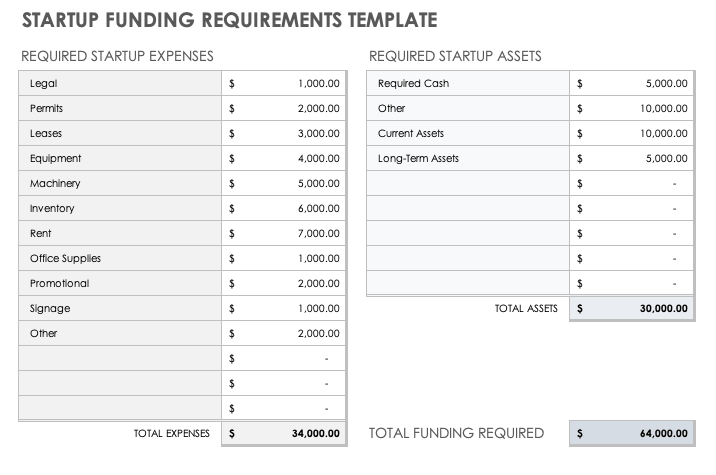
This simple startup funding requirements template is useful for startups and small businesses that require funding to get business off the ground. The numbers generated in this template should align with those in your financial projections, and should detail the allocation of acquired capital to various startup expenses.
Download Startup Funding Requirements Template - Excel
Personnel Plan Template
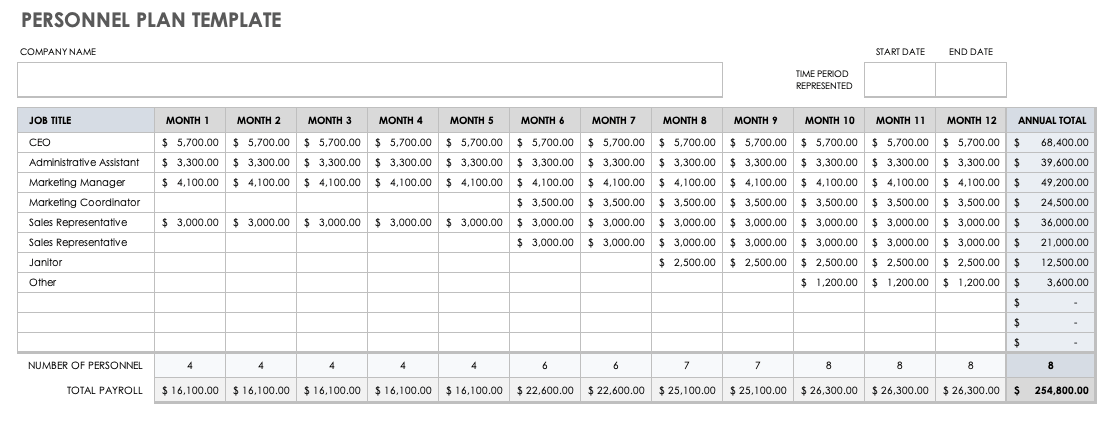
Use this customizable personnel plan template to map out the current and future staff needed to get — and keep — the business running. This information belongs in the personnel section of a business plan, and details the job title, amount of pay, and hiring timeline for each position. This template calculates the monthly and yearly expenses associated with each role using built-in formulas. Additionally, you can add an organizational chart to provide a visual overview of the company’s structure.
Download Personnel Plan Template - Excel
Elements of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Whether your organization is a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, the financial plan is the cornerstone of any business plan. The financial section should demonstrate the feasibility and profitability of your idea and should support all other aspects of the business plan.
Below, you’ll find a quick overview of the components of a solid financial plan.
- Financial Overview: This section provides a brief summary of the financial section, and includes key takeaways of the financial statements. If you prefer, you can also add a brief description of each statement in the respective statement’s section.
- Key Assumptions: This component details the basis for your financial projections, including tax and interest rates, economic climate, and other critical, underlying factors.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculation helps establish the selling price of a product or service, and determines when a product or service should become profitable.
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement, this section details the sales, cost of sales, profitability, and other vital financial information to stakeholders.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: This area outlines the projected cash inflows and outflows the business expects to generate from operating, financing, and investing activities during a specific timeframe.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: This document conveys how your business plans to manage assets, including receivables and inventory.
- Key Financial Indicators and Ratios: In this section, highlight key financial indicators and ratios extracted from financial statements that bankers, analysts, and investors can use to evaluate the financial health and position of your business.
Need help putting together the rest of your business plan? Check out our free simple business plan templates to get started. You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy. If you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering startup business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Plan Financials and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- Subscribers For Subscribers
- ELN Write for Entrepreneur
- Store Entrepreneur Store
- Spotlight Spotlight
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors
How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan Your income statement shows investors if you are making money. Here's everything you'll need to create one.
By Eric Butow • Oct 27, 2023
Key Takeaways
- An income statement is your business's bottom line: your total revenue from sales minus all of your costs.
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 2 / 11 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 5: Organizing Operations and Finances series.
Financial data is always at the back of the business plan, but that doesn't mean it's any less important than up-front material such as the description of the business concept and the management team. Astute investors look carefully at the charts, tables, formulas, and spreadsheets in the financial section because they know that this information is like the pulse, respiration rate, and blood pressure in a human being. It shows the condition of the patient. In fact, you'll find many potential investors taking a quick peek at the numbers before reading the plan.
Related: How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
Financial statements come in threes: income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Taken together they provide an accurate picture of a company's current value, plus its ability to pay its bills today and earn a profit going forward. This information is very important to business plan readers.
Why You Need an Income Statement
In his article, How to Do a Monthly Income Statement Analysis That Fuels Growth , Noah Parsons writes: "In short, you use your income statement to fuel a greater analysis of the financial standing of your business. It helps you identify any top-level issues or opportunities that you can then dive into with forecast scenarios and by looking at elements of your other financial documentation.
Related: How to Make a Balance Sheet
You want to leverage your income statement to understand if you're performing better, worse or as expected. This is done by comparing it to your sales and expense forecasts through a review process known as plan vs actuals comparison. You then update projections to match actual performance to better showcase how your business will net out moving forward."
What Is In an Income Statement
An income statement shows whether you are making any money. It adds up all your revenue from sales and other sources, subtracts all your costs, and comes up with the net income figure, also known as the bottom line.
Related: How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
Income statements are called various names—profit and loss statement (P&L) and earnings statement are two common alternatives. They can get pretty complicated in their attempt to capture sources of income, such as interest, and expenses, such as depreciation. But the basic idea is pretty simple: If you subtract costs from income, what you have left is profit.
To figure out your income statement, you need to gather a bunch of numbers, most of which are easily obtainable. They include your gross revenue, which is made up of sales and any income from interest or sales of assets; your sales, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses; what you paid out in interest and dividends, if anything; and your corporate tax rate. If you have those, you're ready to go.
Related: Tips and Strategies for Using the Balance Sheet as Your Franchise Scorecard
Sales and Revenue
Revenue is all the income you receive from selling your products or services as well as from other sources such as interest income and sales of assets.
Gross Sales
Your sales figure is the income you receive from selling your product or service. Gross sales equals total sales minus returns. It doesn't include interest or income from sales of assets.
Interest and Dividends
Most businesses have a little reserve fund they keep in an interest-bearing bank or money market account. Income from this fund, as well as from any other interest-paying or dividend-paying securities they own, shows up on the income statement just below the sales figure.
Related: How to Measure Franchise Success With Your Income Statement
Other Income
If you finally decide that the branch office out on County Line Road isn't ever going to turn a decent profit, and you sell the land, building, and fixtures, the income from that sale will show up on your income statement as "other income." Other income may include sales of unused or obsolete equipment or any income-generating activity that's not part of your main line of business.
Costs come in all varieties—that's no secret. You'll record variable costs, such as the cost of goods sold, as well as fixed costs—rent, insurance, maintenance, and so forth. You'll also record costs that are a little trickier, the prime example being depreciation.
Related: How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold, or COGS, includes expenses associated directly with generating the product or service you're selling. If you buy smartphone components and assemble them, your COGS will include the price of the chips, screen, and other parts, as well as the wages of those doing the assembly. You'll also include supervisor salaries and utilities for your factory. If you're a solo professional service provider, on the other hand, your COGS may amount to little more than whatever salary you pay yourself and whatever technology you may use for your business.
Related: My Company Hears Hundreds of Pitches Every Year — Here's What Investors Are Actually Looking For.
Sales, General, and Administrative Costs
You have some expenses that aren't closely tied to sales volume, including salaries for office personnel, salespeople compensation, rent, insurance, and the like. These are split out from the sales-sensitive COGS figure and included on a separate line.
Depreciation
Depreciation is one of the most baffling pieces of accounting wizardwork. It's a paper loss, a way of subtracting over time the cost of a piece of equipment or a building that lasts many years even though it may get paid for immediately.
Related: 10 Mistakes to Avoid When Pitching Investors (Infographic)
Depreciation isn't an expense that involves cash coming out of your pocket. Yet it's a real expense in an accounting sense, and most income statements will have an entry for depreciation coming off the top of pretax earnings. It refers to an ongoing decrease in asset value.
If you have capital items that you are depreciating, such as an office in your home or a large piece of machinery, your accountant will be able to set up a schedule for depreciation. Each year, you'll take a portion of the purchase price of that item off your earnings statement. Although it hurts profits, depreciation can reduce future taxes.
Paying the interest on loans is another expense that gets a line all to itself and comes out of earnings just before taxes are subtracted. This line doesn't include payments against the principal. Because these payments result in a reduction of liabilities—which we'll talk about in a few pages in connection with your balance sheet—they're not regarded as expenses on the income statement.
Related: How to Craft a Business Plan That Will Turn Investors' Heads
The best thing about taxes is that they're figured last, on the profits that are left after every other thing has been taken out. Tax rates vary widely according to where your company is located, how and whether state and local taxes are figured, and your special tax situation. Use previous years as a guidepost for future returns. If you are just opening your business, work carefully with your accountant to set up a system whereby you can pay the necessary taxes at regular intervals.
Buzzword: EBIT
EBIT stands for earnings before interest and taxes. It is an indicator of a company's profitability, calculated as revenue minus expenses, excluding tax and interest.
Related: Don't Make This Huge Mistake on Your Financial Model
Important Plan Note
Don't confuse sales with receipts. Your sales figure represents sales booked during the period, not necessarily money received. If your customers buy now and pay later, there may be a significant difference between sales and cash receipts.
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
How to prepare an income statement for a small business

What’s an income statement?
Why is an income statement important, your reporting period, the type of income statement you need, how to create a single-step income statement, how to create a multi-step income statement, one step at a time, small business income statement template, example of a single-step income statement, example of a multi-step income statement, keep your business organized for easy reporting.
An income statement details revenue and expenses to provide insights into a business’s financial performance during a period of time.
Read on to learn what an income statement is, what it includes, why it’s important, and how to make an income statement for your small business. We’ve even included a free small business income statement template you can use.
Also referred to as a profit and loss (P&L) statement, an income statement is one of three main financial reports a business of any size needs to prepare, alongside the balance sheet and cash flow statement .
An income statement gives insights into your business’s operations, how efficiently it is being managed, what departments are underperforming, and how well it’s doing compared to the competition.
The income statement calculates the company’s net income or net profit by taking into account its earnings, gains, expenses, and losses over a period. A balance sheet, on the other hand, only lists the fiscal situation on a specific date.
Unlike a cash flow statement, an income statement includes the full sums of all sales and purchases, whether they were done in cash or credit. This means that an expense is listed in full, even if you’re paying for it in installments or with net terms after the end of the reporting period. The same goes for revenue, which is listed whether it was collected yet or not.
A properly prepared income statement gives business owners a clear picture of the company’s financial position.
Using the income statement, a business owner can adjust their business plan according to the company’s actual performance. They can also explore which business activities produce the most revenue and profit
to assess their viability and contribution to the business’s overall health.
An income statement is also a viable tool for figuring out the balance between expense management and additional investment. In other words, which expenses can be cut back and where you should invest more. And, it helps find areas for improvement, for example, a business activity that has potential but is suffering from inefficiencies.
What’s included in an income statement
When you prepare an income statement, there are four main categories to take into account: revenue, gains, expenses, and losses.
These are used to calculate the company’s gross profit Profit Profit is the earnings that remain after you deduct expenses from revenues. Net profit is what’s left when all types of expenses are deducted from sales. Gross profit is what’s left after deducting the costs associated with making and selling the products, or the costs associated with providing services. and net income for the reporting period.
Revenue includes:
- Operating revenue. This refers to revenue directly linked to sales from your primary business activities. Depending on your industry and specialties these can be goods, services, or both. For example, if you own a coffee shop, all the coffee, pastries, and teas you sell at the shop, go into your operating revenue.
- Non-operating revenue. Recurring revenue driven from secondary non-core activity. This can be for example, from interest on your savings in the bank, renting out unused space, selling branded merchandise, or ad space in public areas of your establishment. If we go back to the coffee shop example, the money from ads hanging in the bathroom or from selling reusable takeaway cups goes under non-operating revenue.
- Returns and concessions. This item has a negative value as it represents sales that have been canceled for whatever reason and need to be deducted from your revenue.
Unlike revenue, gains refer to non-recurring income. It is typically generated not from the sale of goods or services but from other non-core business activities such as the sale of a branch, property, and used equipment or winning a lawsuit or insurance claim.
These are relatively rare activities, especially for a small business, so they may not apply for every period.
All money spent during the reporting period including:
- Cost of goods (COGS) . The total costs directly associated with producing or acquiring goods for sale or providing a service.
- Operating expenses. Costs directly linked to sales related to your primary business activity. This includes marketing, payroll, packaging, etc.
- Non-operating expenses. All expenses not directly related to the core activity but essential to the general management of the company. For example, cleaning, rent, overhead, office supplies, etc.
- Income tax. The total amount of taxes owed for the business’s income during the reporting period.
- Interest. The total amount of interest your business incurred for loans and other forms of debt over the period.
Losses can include:
- Depreciation. The lost value of assets over time due to wear and tear, outdated technology, or other factors. Depreciation is a percentage of the asset’s original cost that is deducted every year to reflect this decline.
- Legal remedies. Losses that occur when a company loses a court case or reaches a settlement requiring it to pay another party.
How to create an income statement
Before you can start preparing your income statement, you first need to figure out two things:
Income statements are usually produced for a 12-month period but some companies may choose shorter time spans, for example, quarterly or even monthly statements.
A longer reporting period gives a better picture of your business performance without the fleeting effects of seasonality.
A shorter period, on the other hand, gives you more oversight for quickly adjusting your strategy according to the performance. During times of transition, it may be beneficial to produce more frequent reports.
When deciding your reporting period, also examine when it should begin or end. For simplicity, many businesses choose to do annual reports beginning January 1st and ending December 31st.
However, companies sometimes define their fiscal year independently from the calendar year. This means, for example, that their annual report may cover a year ending on June 30th instead.
Regardless of what you choose, it’s important to clearly state your reporting period at the top of your income statement.
There are two types of income statements:
A single-step income statement in which all expenses and losses are bundled together and deducted from all revenues and gains.
A multi-step income statement in which you separate operating income and expenses from non-operating income and expenses to get a better picture of the performance of your various business activities.
Generally speaking, a single-step income statement is usually enough for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that have a simple business structure and a single core activity.
A multi-step statement would be a better fit for larger businesses with diverse business activities and multiple departments.
That said, if your SMB is looking to secure a loan or any other type of financing, you may be required to produce a multi-step statement as well.
Contrary to what the phrase single-step might suggest, there are a few steps you need to take to prepare your income statement:
- Add up all your revenue and gains.
- Add up all your expenses and losses.
- Deduct your expenses and losses from your revenue and gains to reach your income before tax and interest (EBIT).
- Add up your tax and interest.
- Deduct tax and interest from EBIT to reach net profit.
As you’ve probably already figured out, a multi-step statement has a lot more steps.
Here’s how to do an income statement using the multi-step method:
Step 1: Operating revenue Add up all your revenue from sales during the reporting period and deduct your returns and concessions.
Step 2: Cost of goods sold (COGS)
Add up all expenses directly related to the manufacturing or acquisition of goods sold or the provision of services to determine your COGS.
Step 3: Gross profit
Deduct your COGS from the operating revenue.
Step 4: Operating expenses
Add up all operating costs incurred in the reported period. Remember that this should not include COGS, which are already accounted for.
Step 5: Total operating income
Deduct the operational expenses from your gross profit.
Step 6: Non-operating revenue
Add up all income from non-core activities.
Step 7: Non-operating expenses
Add up all expenses for non-core activities.
Step 8: Non-operating income
Subtract non-operating expenses from non-operating revenue.
Step 9: Gains and losses
Add up all your gains then deduct your losses.
Step 10: Income before tax and interest (EBIT)
Add gains and losses to non-operating income and operating income to reach your EBIT.
Step 11: Taxes and interest
Add up the income tax for the reporting period and the interest incurred for debt during that time.
Step 12: Net profit
Subtract the taxes and interest from your EBIT to reach net profit.
Handling financial statements can be overwhelming for anyone, especially small business owners who are more passionate about serving their customers than about spreadsheets and numbers.
To save you time, we’ve prepared an income statement template for small businesses to leverage.
It comes in a spreadsheet format (.xlsx) that you can open with Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or any other compatible spreadsheet program you’re used to.
In the file, you’ll find two sheets to choose from: one for a single-step income statement and the other for a multi-step statement. All you have to do is fill out your company’s information. We’ve already put in the formulas so all the calculations are done automatically.
Feel free to change the description of the items to fit your business. You can also add or delete lines as needed.
Download the free small business income statement template here.
Income statement examples
In case you’re confused, here are examples of what an income statement using both methods would look like for a pet supply store called Rocky’s Pet Supplies.
We used Melio’s income statement template to create both versions. As you can see, the numbers are the same but the way they are presented is quite different.
Here’s what Rocky’s Pet Supplies’ single-step income statement for 2023 looks like.

Here’s what Rocky’s Pet Supplies’ multi-step income statement for 2023 looks like.

Using an online payment platform like Melio to pay your business bills makes it easy to find all your expenses when it’s time to make an income statement. Sign up for Melio today to start sending digital payments to all your vendors.
P.S. Don’t forget to pick up our small business income statement template.
*This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and is not intended as financial advice. **Melio does not provide legal, tax or accounting advice, and you should consult with a professional advisor before making any financial decisions.

Choosing the right suppliers and vendors to work with
Learn why choosing the right vendors is so important—and how to find the right ones.

Some end-of-year tax magic: deduct today, pay in 2023
How can you reap tax benefits for your end-of-year purchases and put off payments until next year? Hint: It’s not a loan and it’s already in your wallet.

Bookkeeping 101: What’s an EFT payment?
If your business is trying to move past paper-based payment methods, you’ve probably already used electronic fund transfers without even knowing it.
YOUR PRIVACY RIGHTS.
Do Not Sell Or Share My Personal Information.
To submit a request to opt out of sale/sharing of your personal information, please submit the form below.
If you are a resident of California, you have the right to opt-out of the selling or sharing of your personal information. To exercise this right, please provide your State and Country of residency. Please note that when you submit an opt-out we do not know who you are within our systems, and your opt-out will apply only to information collected from tracking technologies on the specific browser from which you opt-out. If you delete or reset your cookies, or use a different browser or device, you will need to reconfigure your settings. If you want the opt-out to apply to information we have about you in our systems, such as your email address, please also provide your full name, email address, and phone number. Any information you provide below will not be used, disclosed, or retained for any purpose other than processing the request to opt-out of sale/sharing.
You can learn more about your rights in our Privacy Policy .
Something went wrong, please try again.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
We received your request.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056
Income Statement Templates
Get in-depth insight of your business performance with income statement. download these easy to use example income statement templates..

What is Income Statement?
An income statement gives an overview of a company’s income and expenses. It is a type of financial statement used to evaluate the company’s performance in the short term. Since most other financial statements are prepared annually or biannually, an income statement is also created monthly or quarterly. An income statement is also called a profit and loss statement, earnings statement, or statement of operations.
An income statement helps managers and investors make decisions in the short term. It helps assess the company’s growth trajectory.
The income statement is primarily used for measuring profitability, not cash flow.
Why use an income Statement
An Income Statement is prepared monthly and quarterly. Unlike other financial statements and reports, the income statement gives business profitability information on a monthly basis. A monthly report can help identify immediate threats and opportunities and a business can avoid nose dive.
You can also use this income statement template in financial planning of your business plan . Having a template for income statement will save you time and hassle in writing your business plan .
Investors may also ask for income statements in addition to the balance sheet and other financial reports. The reason is the same as the income statement focuses more on the short term.
Income Statement Template for Business Plan
A forecast income statement is an essential part of a business plan. Along with cash flow statement and balance sheet, income statement makes the financial planning part of the business plan.
This income statement template for business plan can be used without any additional changes; download income statement template, populate it with forecast numbers and your income statement for business plan is ready.
Download Free Income Income Statement Templates
There are two basic types of income statements, Single-step income statements, and multi-step income statements. Here is a short side-by-side comparison of the two. When you are unsure about it, use Single Step Income Statement.
We have prepared these three income statement templates. You can also download income statement excel format. You can also use the income statement template for business plan.
Basic Single Step Income Statement
Traditional Income Statement
Multi-step income statement

Download single or simple income statement template in excel format here. Put in your business numbers in the templates and see how your business is doing!
Download Single Step Income Statement Template Excel
Traditional income statement is easy to use. Download the traditional income statement template and make financial statement for your business.
Download Traditional Income Statement Template
Multi Step Income Statement gives an in-depth analysis of your business. Download this free multi step income statement template to look closely into your business performance.
Download Multi Step Income Statement Template
Comparison of Single Step Income Statement vs Multi Step Income Statement
A single step income statement is prepared with simple accounting equation that subtracts ‘losses and expenses’ from ‘revenues and gains’. Whereas the multi step income statements also include the the expenses and revenues from non-operational resources and follows a three step approach to calculate net income. An example of income statement will include all the list items mentioned here.
Income Statement Formula
In one line, the income statement formula is:
“ total revenues – total expanses= Net income”
An income statement gives a comparison and overview of the company’s revenue and expenses. It helps understand the business growth trajectory in the short term.
If your business’s revenues are greater than the expenses, your company is making a profit. Whereas, if your expenses are more than your revenues, your company needs to look closely into the income statement and take the necessary steps for making it profitable again.
The income statement displays the net profitability of a business. It serves as a tool for investors and owners and it shows the company’s profitability.
An income statement is a better financial report for checking the performance of a business in the short run.
What goes on an income statement?
For most businesses, the income statement items will be different. However, the structure stays the same. Most templates can be used for any industry after a few changes. You will find these list items on any income statement example.
- Cost of Goods Manufactured
- Gross Margin
- Amortization
- Depreciation
- Rent expense
- Salaries and Wages
- Phone and internet
- Operating Income (EBIT)
- Interest Expense
- Earnings Before Tax (EBT)
How to Prepare an Income Statement?
We have provided simple income statement templates and you can use them as guidelines for preparing an income statement. Our templates are compatible with Microsoft Excel; you can download and use them for your business.
The following steps will be helpful for you in preparing an income statement.
1. Select a Reporting Period
An income report shows revenues and expenses for a certain time period. You can choose any time period from one month to many years.
Mostly income statement is created on a monthly, quarterly, bi-annually, or yearly basis. Most companies create monthly income statements to keep a close eye on their performance.
2. Prepare a Trial Balance Report
You will need to create a standard trial balance report for creating an income report. A trial balance report gives end balance numbers for each account which is necessary for the income statement. If you are using an accounting tool, you can easily prepare and print out the trial balance report in a few clicks.
3. Calculate Revenue
Next, you will need to calculate all the revenues your firm has earned in the selected time period. Revenues will include everything you have earned from selling your goods or services in the reporting period, whether you have received the payment or not.
4. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold includes the labor cost, materials cost, and overhead costs you have made in offering your goods or services.
From your trial balance, add the ‘cost of goods sold items and put the number on the income statement below revenue line items.
5. Calculate Gross Margin
Subtract ‘cost of goods sold’ from ‘Revenues’ and you will have your Gross Margin number.
6. Include Operating Expenses
Take all the operating expenses line items from your trial balance and put the final number in ‘selling and administrative expanses’ in the income statement.
7. Calculate your Income
When you take out the ‘selling and administrative’ expanses from ‘Gross Income’, you will get your income before taxes.
8. Include Income Tax
Find your state’s tax rate, multiply it with your pretax income and you will get the income amount you will have to pay. The income tax number will go below the pretax income in the income statement.
Pro Tips: learn how to to calculate income tax with our income tax calculator .
9. Calculate Net Income
Take out the income tax from pretax income and you will get your net income. Your net income will give you an overview of your business performance and profitability.
10. Finalize the Income Statement
Add the ‘Income Statement’ in the header of the income statement report for easier identification. Your income statement is complete now.
In case you are using income statement template in a business plan, you will put the expected, forecast numbers in the template to prepare the income statement.
Need help creating other essential business reports?
Download our 15+ designer approved business templates for free and make your clients feel impressed.
A Profit and loss statement (P&L statement) is also called an income statement. An income statement or P&L statement is the summary of revenues, expenses, cost of goods sold, administrative expenses, and taxes for a specific time period.
Income statement and balance sheet are not the same. Both of these reports give important information about the business; an income statement gives a profit and loss assessment of a business while balance sheets tell about the financial situation of a business at a certain point in time.
Income statement can be prepared for both cash and accrual-based accounting. However, the revenues and expenses calculation method will be different as we will only be recording the revenues received and expenses made.
Income Statement shows the current profitability of a business. It details the revenues and expenses of a business. The income statement can be negative if the expenses and costs are more than the total revenue.
An income statement includes the following expenses.
Cost of goods sold- the expenses you incur for the materials and labor.
Selling, General and Administrative Expanses-this head include all indirect expenses, advertising expenses, overhead expenses, rentals, etc.
Depreciation and Amortization- Depreciation shows the decrease in the value of tangible assets like machinery, automobiles, etc; amortization is the decrease in the value of intangible assets like patents and trademarks.
Research and Development-If your business has a research and development facility, you will need to add these costs to the income statement.
There are two basic types of income statements; single-step income statements and multistep income statements. A multistep income statement has more details and includes incomes and expenses.
Get in Touch
Contact us today for a free consultation, related articles, quick links.

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077


Simple Income Statement Template (In Excel)

When creating your business plan, you’ll need to include a comprehensive income statement. An income statement, also commonly referred to as a profit and loss statement, is essentially a snapshot of your business’s profitability or the profits generated from operations over a certain period of time. It contains the company’s revenues, total operating expenses, and net income over a specific time period.
This information is important to potential lenders or investors, as it will show them how the company is performing. It can also help identify areas of improvement and track income and expenses over time. So if you’re in the midst of creating your business plan, you need to include an income statement to show investors and other shareholders the state of your finances.
What is a Pro Forma Income Statement?
A pro forma income statement is an advance income statement projection that is used to estimate a company’s financial performance in the future. It is prepared before the actual income statement is finalized and takes into account changes in market conditions, as well as any planned investments or expenses. The pro forma statement contains estimated figures that are not yet finalized, allowing businesses to plan ahead and make more informed decisions when it comes to their finances.
The pro forma statement typically includes projected sales revenues and expenses, such as costs of goods sold, operating expenses, and interest expenses. The goal of a pro forma income statement is to provide companies with an idea of how their business will perform financially in the future so they can adjust their budget according to the estimated outcomes. A pro forma can also be used to compare different scenarios and forecast potential challenges or opportunities for a business moving forward.
In addition, a pro forma statement can be used by investors as a tool for analyzing a company’s performance over time, as well as its ability to meet short-term goals or take on new projects. This allows investors to gain insights that are not easily visible when solely focusing on historical data points or industry averages. By taking into account current trends and accurate assumptions about the future, a pro forma provides valuable information that can help investors make better investment decisions.
Why You Need an Income Statement For Your Business
There are several reasons why your business needs an income statement:
- Helps you get funding: First and foremost, an income statement is essential for obtaining financing from potential investors. Without an income statement in your business plan, it is almost impossible to receive funding for your business, as investors will want to know exactly how much money your business has earned or lost in order to make an investment decision. By having a clear and up-to-date profit and loss statement in your business plan, you can provide potential investors with the vital information they will need in order to make an informed decision.
- Helps monitor financial performance: An income statement provides owners and investors with important insights into a business’s financial performance over a given period of time. This allows the owner to track revenue and expenses, as well as any gross profit or loss that may have been incurred throughout the year. These insights can then be used to make better business decisions in the future, such as hiring additional staff or investing in new equipment.
- Improves decision-making: By having an income statement in place, a business is able to make more informed decisions on how to best allocate its resources. This can be especially helpful when attempting to determine the impact that certain expenses may have on a company’s bottom line. With the help of an income statement, businesses can better understand which investments or expenditures are necessary for the long-term health of the organization.
- Completes your business plan: You need a business plan for several reasons, including raising capital, obtaining a loan, or even just formalizing your business concept. An income statement is an essential component of any business plan, as it provides investors, lenders, and other shareholders with the necessary information to make an informed decision about your business.
Finish Your Financial Model and Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your financial model and business plan?
Components of a Simple Small Business Income Statement
When working on your income statement, there are several essential components that you need to include to get an accurate picture of your financials. These components include:
Revenue is the amount of money your business earns from its sales. This includes all income generated through the sale of products and services, as well as any other fees your company may collect.
Expenses are all costs associated with running a business. These business expenses include things like labor costs, materials, rent or utilities, marketing expenses, insurance costs, taxes and any other operating expenses specific to your type of business.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of goods sold (COGS) refers to the amount of money spent on producing the goods or services that your company sells. This includes all direct expenses associated with the production and delivery of products and services, such as the cost of raw materials, labor costs, and shipping and handling fees.
Non-Operating Income And Expenses
Non-operating income and expenses refer to sources of income or costs that are not directly related to the core operations of your business. This could include things like interest income, dividends, or gains from investments. It could also include any non-operational expenses such as legal fees or accounting services.
Gains And Losses
Gains and losses refer to amounts earned or spent outside of the core operations of your business. This could include any gains or losses due to currency exchange rates, investments, or other activities not related to the day-to-day running of your business.
The net income is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. This number will tell you whether or not your business has earned a net profit or incurred a loss in the given period of time. It’s important to note that in some cases, there may be additional expenses, such as depreciation charges, that should be taken into account when calculating net income.
Get our free income statement template download to help you create your own.
Download our Sample Income Statement
How To Create a Basic Income Statement For Small Businesses
Now that you know what you need to include in your income statement, you’re ready to create one. Creating an income statement for your small business is quite simple. All you need is a simple spreadsheet, like Microsoft Excel, to get started. Below are the steps you should take to create your income statement:
- Choose Your Period: First, you have to decide on the time frame for your income statement. This could be monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Gather Your Data: The next step is to collect all of your data for the given period. This includes sales and revenue figures, as well as costs associated with running your business, such as expenses, COGS, and non-operating income and expenses.
- Arrange Your Spreadsheet: Before inputting your data, you need to organize your income statement so that it’s easy to read and understand. That means creating separate categories, such as revenue, expenses, gains and losses, etc. and putting them in separate columns or rows.
- Input Formulas: Once you have your spreadsheet organized, you need to input formulas to calculate total revenue, total expenses, net income, and other components of your statement. It’s easiest to do this before inputting all your data.
- Input Your Data: Once you have everything organized into categories, it’s time to enter your data into the spreadsheet. It’s best to start with one category at a time. For example, first, input all your revenue data, then move on to expenses, etc.
- Calculate Your Net Income: Once all of your data is entered in, you can calculate your net income by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. This will give you an accurate picture of how your business has performed over the given period of time.
- Save & Review: Once you’ve calculated your net income, save the spreadsheet and review it to ensure that all of your numbers are accurate. You’ll want to save this as your own income statement template so you can use it again in the future. It is recommended that you update your income statement at least once a year.
Other Financial Statements
The income statement is not the only financial statement that is important for your small business. Other financial statements, such as a balance sheet and cash flow statement, are also essential to understanding the company’s financial health.
The balance sheet is a snapshot of the financial position of your business at a given point in time, showing assets, liabilities, and capital. It’s a useful tool for understanding the overall financial situation of your business. It’s very similar to the income statement, but the difference is that the balance sheet shows a static point in time, whereas the income statement shows the financials over a period of time.
The cash flow statement is another important financial document that tracks the flow of money into and out of your business. It shows how much cash has been generated, as well as how much is being spent. This document can be used to understand the financial health of your business and make sound decisions about investing and other financial activities. However, unlike the income statement or balance sheet, it does not track any non-cash transactions such as depreciation, investment gains, or other activities not related to the day-to-day running of your business.

OR, Let Us Develop Your Financial Model For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed financial models for thousands of companies that have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s financial modeling services can create your financial plan for you.

Income Statement Template
Your business plan should include a three-year forecast of your income statement..
Refer to the sample income statement in the tab below while reviewing this section as a guideline or income statement template for your own business. The income statement shows revenue and expenses, usually by month. At the bottom, total expenses are subtracted from total revenue to arrive at Net Ordinary Income—which is essentially profit, though in an actual business there will be some accounting and tax adjustments made to arrive at true profit. That’s why profit is often referred to as “the bottom line.” Your business plan should include a three-year forecast of your income statement. Here’s a closer look at some specifics of the income statement, and guidance on how to prepare your own income statement.
Sample Income Statement
Finish your business plan in one day., getting started.
It’s much easier to think ahead for one year than it is for three. So, start with a one-year view. After putting together a reasonably thorough view of year one, it will be relatively easy to create years two and three by thinking of the changes that are expected to occur in the following years.
Notice how the income statement template is organized. Each column is labeled and represents a time period (usually a month) with totals for the year in the far right column.
Review from top to bottom the leftmost column of the sample income statement, to see all the categories of revenue and expenses, plus some subtotals for organization.
Again, looking at the sample income statement, notice that a separate line is used for each major revenue category. The sample company includes lines for Programming Services, Software Sales and Network Maintenance. Think of the significant distinctions in your areas of revenue and create your own categories. Remember at this point to keep it simple. As you put together your income forecast, think carefully about the timing (when sales will begin) and growth rates you project. You will be asked if the business is ready to support the sales you are forecasting and whether you will have done in advance the necessary things to drive the level of sales you’re predicting in the time periods shown.
Cost of Goods Sold
Moving down the left column, look at the Cost of Goods Sold section, which is right below our Income categories. For companies selling products, the cost of the products being sold goes into this section. In our sample company, notice that in February they forecasted software income of $250, and there is a corresponding cost of goods sold of $150. This represents a product they purchase for $150 and resell for $250.
Some service businesses have costs associated with the services they sell. These would be treated in the same way, but would be called ‘costs of sales’ instead of costs of goods sold. Even sales commissions are sometimes included in the cost of sales category, both for product businesses and service businesses.
Whether it’s a cost of goods sold or cost of sales, this section should include outside expenses that are incurred whenever a sale takes place.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is completely different from the more common term “profit.” Gross profit is the total revenue, minus the cost of goods sold or the cost of sales. If your business sells furniture and you buy a desk for $300 and sell it for $500, your gross profit is $200. If you are a consultant and you invoice a customer for $500 and you have no cost of goods sold, your gross profit is the same as your sales ($500 sales minus $0 cost of sales = $500 gross profit).
The sample company sells mostly services, with some software sales. So their gross profit is quite high. Look, for example, at July and notice that they have $24,500 in total sales and cost of goods sold of $1,200. Why so low? Because the cost of goods sold is for software they purchase and resell. In July they had software sales of only $2,000. If we were to break it down further (this is not shown on the sample statement) they had software gross margin of $800 ($2,000 sales minus $1,200 cost of goods = $800 gross profit.)
Businesses that sell mostly products need to watch their gross profit carefully. What matters in this type of business is not how much you sell, but how much you keep—that’s gross profit.
The expenses for the sample company are broken down into 14 categories. The major categories are self-explanatory (payroll expense, rent, etc.). When creating the list of expense categories for your business, keep it simple, using as few as 5 and no more than 20. It’s not critical whether you include the cost for small expenses in their own category, such as “office supplies,” or in a more general category such as “Office Expenses” (which would also include telephone, Internet and similar expenses).. The important thing is that all of your expenses are accounted for in one category or another.
Pay special attention to payroll costs, marketing costs and rent. These are likely to be your largest expenses. In your business plan you have probably addressed adding staff and marketing activities. Be sure that the income statement reflects the expense for these things in the time period when you said you were going to initiate the activity (or in advance, to allow for preparation time). Also make sure that your rent keeps pace with your payroll or headcount. You would expect to need more office space for 10 employees than for 3. There will be other corresponding expenses that grow with head count.
Look carefully at your revenue, payroll expense and overall expenses to be sure they are all moving in a logical pattern. If you study this carefully , you will get in tune with what it’s going to take to grow your business. You’ll soon find that you’re “living your business” on paper and able to make changes and decisions that will have a significant impact on your business. That’s what it’s about!
Net Ordinary Income. Net ordinary income is what is left when you subtract all of the expenses from all of the income:
Total Income – Cost of Goods Sold – Total Expenses = Net Ordinary Income
Since gross profit already subtracts the cost of goods sold from income, another way to calculate net ordinary income is:
Gross Profit – Total Expenses = Net Ordinary Income
So for year one in our sample company, the Total Income was $236,000, gross profit was $226,100, total expenses $204,597 and Net Ordinary Income was $21,503.
Wait a minute—isn’t that profit? Almost. If these become your actual numbers, your accountant will add a few more lines to take into account taxes, depreciation and a few of those other details we said were not critical for small-business-plan financial statements. For your business plan, rather than forecast profit, stop here at Net Ordinary Income.
Take your time to study our income statement template and get comfortable with it. For additional perspective, you might want to review the Wikipedia article on income statements which is linked here .
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Prepare an Income Statement

- 09 Dec 2021
When it comes to financial statements , each communicates specific information and is needed in different contexts to understand a company’s financial health.
The income statement is one of the most important financial statements because it details a company’s income and expenses over a specific period. This document communicates a wealth of information to those reading it—from key executives and stakeholders to investors and employees. Being able to read an income statement is important, but knowing how to generate one is just as critical.
Here’s an overview of the information found in an income statement, along with a step-by-step look at the process of preparing one for your organization.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is an Income Statement?
An income statement is a financial report detailing a company’s income and expenses over a reporting period. It can also be referred to as a profit and loss (P&L) statement and is typically prepared quarterly or annually.
Income statements depict a company’s financial performance over a reporting period. Because the income statement details revenues and expenses, it provides a glimpse into which business activities brought in revenue and which cost the organization money—information investors can use to understand its health and executives can use to find areas for improvement.
Related: How to Read & Understand an Income Statement
An income statement typically includes the following information:
- Revenue: How much money a business took in during a reporting period
- Expenses: How much money a business spent during a reporting period
- Costs of goods sold (COGS): The total costs associated with component parts of whatever product or service a company makes and sells
- Gross profit: Revenue minus costs of goods sold
- Operating income: Gross profit minus operating expenses
- Income before taxes: Operating income minus non-operating expenses
- Net income: Income before taxes
- Earnings per share (EPS): Net income divided by the total number of outstanding shares
- Depreciation: Value lost by assets, such as inventory, equipment, and property, over time
- EBITDA: Earnings before interest, depreciation, taxes, and amortization
Related: 13 Financial Performance Measures Managers Should Monitor
Steps to Prepare an Income Statement
1. choose your reporting period.
Your reporting period is the specific timeframe the income statement covers. Choosing the correct one is critical.
Monthly, quarterly, and annual reporting periods are all common. Which reporting period is right for you depends on your goals. A monthly report, for example, details a shorter period, making it easier to apply tactical adjustments that affect the next month’s business activities. A quarterly or annual report, on the other hand, provides analysis from a higher level, which can help identify trends over the long term.
2. Calculate Total Revenue
Once you know the reporting period, calculate the total revenue your business generated during it.
If you prepare the income statement for your entire organization, this should include revenue from all lines of business. If you prepare the income statement for a particular business line or segment, you should limit revenue to products or services that fall under that umbrella.
3. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Next, calculate the total cost of goods sold for any product or service that generated revenue for your business during the reporting period. This encompasses direct and indirect costs of producing and selling products or services, including:
- Direct labor expenses
- Material expenses
- Parts or component expenses
- Distribution costs
- Any expense directly tied to the production of your product or service
4. Calculate Gross Profit
The next step is to determine gross profit for the reporting period. To calculate this, simply subtract the cost of goods sold from revenue.

5. Calculate Operating Expenses
Once you know gross profit, calculate operating expenses (OPEX).
Operating expenses are indirect costs associated with doing business. These differ from cost of goods sold because they’re not directly associated with the process of producing or distributing products or services. Examples of expenses that fall under the OPEX category include:
- Office supplies
6. Calculate Income
To calculate total income, subtract operating expenses from gross profit. This number is essentially the pre-tax income your business generated during the reporting period. This can also be referred to as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
7. Calculate Interest and Taxes
After calculating income for the reporting period, determine interest and tax charges.
Interest refers to any charges your company must pay on the debt it owes. To calculate interest charges, you must first understand how much money you owe and the interest rate being charged. Accounting software often automatically calculates interest charges for the reporting period.
Next, calculate your total tax burden for the reporting period. This includes local, state, and federal taxes, as well as any payroll taxes.
8. Calculate Net Income
The final step is to calculate net income for the reporting period. To do this, subtract interest and then taxes from your EBIT. The number remaining reflects your business’s available funds, which can be used for various purposes, such as being added to a reserve, distributed to shareholders, utilized for research and development, or to fuel business expansion.
Income Statement Example
Below is an example income statement for a fictional company. As you can see at the top, the reporting period is for the year that ended on Sept. 28, 2019.
Go to the alternative version .
During the reporting period, the company made approximately $4.4 billion in total sales. It cost the business approximately $2.7 billion to achieve those sales. As a result, gross profit was about $1.6 billion.
Next, $560.4 million in selling and operating expenses and $293.7 million in general administrative expenses were subtracted. This left the company with an operating income of $765.2 million. To this, additional gains were added and losses subtracted, including $257.6 million in income tax.
At the bottom of the income statement, it’s clear the business realized a net income of $483.2 million during the reporting period.

A Critical Skill for Business Leaders
Although the income statement is typically generated by a member of the accounting department at large organizations, knowing how to compile one is beneficial to a range of professionals.
Whether you’re an individual contributor, a member of the leadership team in a non-accounting role, or an entrepreneur who wears many hats, learning how to create an income statement can provide a deeper understanding of the financial metrics that matter to your business. It can also help improve your financial analysis capabilities .
Do you want to take your career to the next level? Consider enrolling in Financial Accounting —one of three courses comprising our Credential of Readiness (CORe) program —which can teach you the key financial topics you need to understand business performance and potential. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .
Data Tables
Company b income statement.
For Year Ended September 28, 2019 (In thousands)
Go back to the article .

About the Author
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Taking Stock of Expenses
The income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet.
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders' equity. It also should include a brief explanation and analysis of these four statements.
Think of your business expenses as two cost categories: your start-up expenses and your operating expenses. All the costs of getting your business up and running should be considered start-up expenses. These may include:
- Business registration fees
- Business licensing and permits
- Starting inventory
- Rent deposits
- Down payments on a property
- Down payments on equipment
- Utility setup fees
Your own list will expand as soon as you start to itemize them.
Operating expenses are the costs of keeping your business running . Think of these as your monthly expenses. Your list of operating expenses may include:
- Salaries (including your own)
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Telecommunication expenses
- Raw materials
- Distribution
- Loan payments
- Office supplies
- Maintenance
Once you have listed all of your operating expenses, the total will reflect the monthly cost of operating your business. Multiply this number by six, and you have a six-month estimate of your operating expenses. Adding this amount to your total startup expenses list, and you have a ballpark figure for your complete start-up costs.
Now you can begin to put together your financial statements for your business plan starting with the income statement.
The income statement shows your revenues, expenses, and profit for a particular period—a snapshot of your business that shows whether or not your business is profitable. Subtract expenses from your revenue to determine your profit or loss.
While established businesses normally produce an income statement each fiscal quarter or once each fiscal year, for the purposes of the business plan, an income statement should be generated monthly for the first year.
Not all of the categories in this income statement will apply to your business. Eliminate those that do not apply, and add categories where necessary to adapt this template to your business.
If you have a product-based business, the revenue section of the income statement will look different. Revenue will be called sales, and you should account for any inventory.
The cash flow projection shows how cash is expected to flow in and out of your business. It is an important tool for cash flow management because it indicates when your expenditures are too high or if you might need a short-term investment to deal with a cash flow surplus. As part of your business plan, the cash flow projection will show how much capital investment your business idea needs.
For investors, the cash flow projection shows whether your business is a good credit risk and if there is enough cash on hand to make your business a good candidate for a line of credit, a short-term loan , or a longer-term investment. You should include cash flow projections for each month over one year in the financial section of your business plan.
Do not confuse the cash flow projection with the cash flow statement. The cash flow statement shows the flow of cash in and out of your business. In other words, it describes the cash flow that has occurred in the past. The cash flow projection shows the cash that is anticipated to be generated or expended over a chosen period in the future.
There are three parts to the cash flow projection:
- Cash revenues: Enter your estimated sales figures for each month. Only enter the sales that are collectible in cash during each month you are detailing.
- Cash disbursements: Take the various expense categories from your ledger and list the cash expenditures you actually expect to pay for each month.
- Reconciliation of cash revenues to cash disbursements: This section shows an opening balance, which is the carryover from the previous month's operations. The current month's revenues are added to this balance, the current month's disbursements are subtracted, and the adjusted cash flow balance is carried over to the next month.
The balance sheet reports your business's net worth at a particular point in time. It summarizes all the financial data about your business in three categories:
- Assets : Tangible objects of financial value that are owned by the company.
- Liabilities: Debt owed to a creditor of the company.
- Equity: The net difference when the total liabilities are subtracted from the total assets.
The relationship between these elements of financial data is expressed with the equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity .
For your business plan , you should create a pro forma balance sheet that summarizes the information in the income statement and cash flow projections. A business typically prepares a balance sheet once a year.
Once your balance sheet is complete, write a brief analysis for each of the three financial statements. The analysis should be short with highlights rather than in-depth analysis. The financial statements themselves should be placed in your business plan's appendices.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Business Plan in Under an Hour

15 Min. Read
How to Write a Cannabis Business Plan + Free Sample Plan

11 Min. Read
How to Create a Sales Forecast

7 Min. Read
How to Write an Online Boutique Clothing Store Business Plan + Example Templates
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- HR & Payroll

Complete Guide to Income Statements [+ examples and templates]

According to the statistics from the Small Business Administration, there are $30.2 million of small businesses across the United States of America, which accounts for 99.9% of all companies in the United States. And each one of them, including your business, need to prepare an income statement!

Why you should prepare an Income Statement
The income statement is a comprehensive breakdown of your company's operating and non-operating expenses and revenue. This financial statement tells you, in a glance:
a. where the business is earning money, b. where the business is spending the money, and c. if the business is running profitably
An income statement is what any potential investor will ask for as one of the first documents if they are serious about investing in your business. Any financial audit will require an income statement which will be studied and analyzed.
In addition to the above, a well prepared income statement speaks about the business and financial maturity of an organization. Which is why we will be going over income statements in great detail in rest of the article.
What we will cover
Different nomenclatures.
- Types of income statement (Single and Multi Step)
- Multi-step income statements
- Understanding Chart of Accounts
- Examples from different industries
- Examples from the Big Four Tech Companies
- Where to study/source them from?
- Income Statement Excel Samples (Free Download)
The terms P&L statement, Profit and Loss Statement and Income Statement are used interchangeably. The income statement is sometimes also known as statement of revenue or earning statement.
Types of Income Statement
There are two primary methods followed to prepare income statements: a. Single Step b. Multi Step
A) Single Step Income Statement
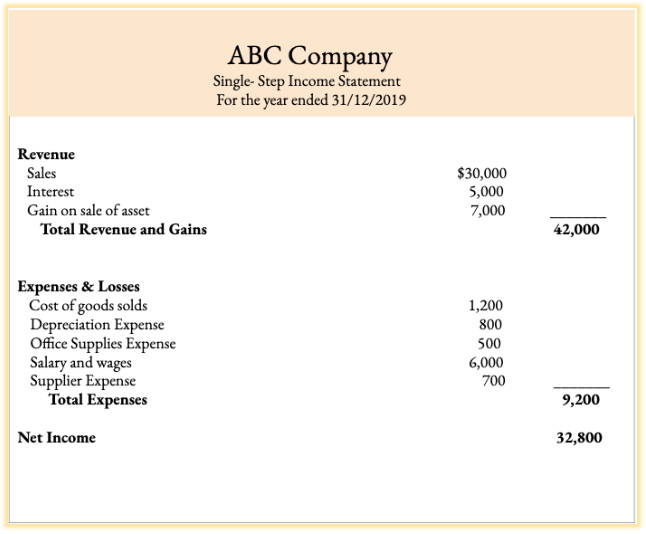
A single step statement lists every detail in a single column, and provides the summation of the rows. All the revenue is clubbed together, as are all the expenses. It does not delve into breakdown of operating costs or cost of goods sold or any sub categories.
The net income is calculated by subtracting the Total Expenses from Total Revenue. This is the only calculation used in a single step statement.
Net Income = Total Revenue - Total Expense
Although the single-step income statement is easier to prepare and understand, it does not provide comprehensive information of the company's gross profits or operations. Which is why, if a business plans to raise fund or apply for bank loans, then it must prepare a Multi Step Income Statement.
B) Multi-Step Income Statement
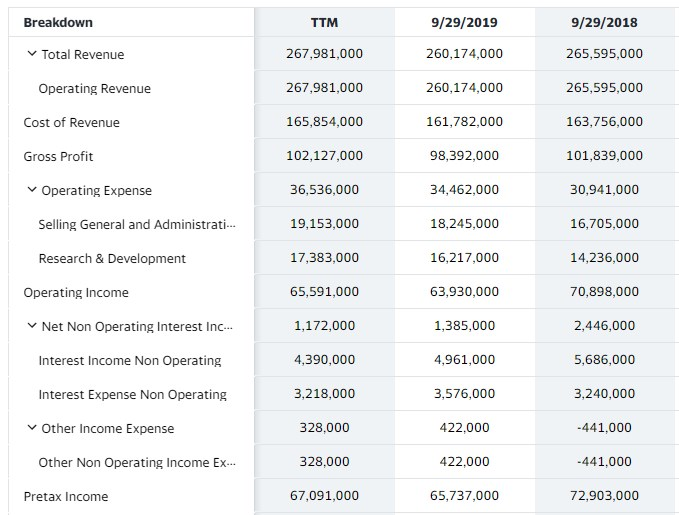
A multi step statement, as the name suggests, is broken down into various steps and provides a detailed overview of operating and non-operating revenue and expenses. It also shows the gross profit (or gross margin) as well as the net income.
The calculations involved in a typical multi step statement are as follows:
Gross Profit = Operating Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold
Operating Income = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses
Non Operating Income = Non Operating Revenue - Non Operating Expenses
Net Income Before Taxes = Operating Income + Non Operating Income
Net Income After Taxes = Net Income Before Taxes - Taxes
Some key points to note
Sales revenue is obtained from the selling activities of the company’s products, whereas the cost of goods sold is the expense incurred directly from producing the goods.
To compute the net sales, you will have to subtract the total revenue from any sales returns or sales allowances.
The gross profit gives you the idea of how much the sales covered the direct cost of producing the goods.
The derivation of operating income comes from the subtraction of the gross profit from the operating expenses. The operating costs are the cost to run the business.
Here are some of the examples of operating expenses:
A. Selling Expense
Marketing and Advertising
Any expense that relates to promoting, advertising, and campaigns held to raise awareness of the products or to sell the products.
Distribution Expense
The cost incurred to deliver the products from one place to another. It can be the freight cost incurred from sending the goods to the end consumers.
Sales Commission
The cost incurred for hiring salesperson to sell the products and paying additional fees to them once they reach their sales target.
B. Administrative Expense
Office rental
The expense related to renting office building to business operations.
Wages and Salaries
The cost incurred for hiring employees in the company to perform specific business tasks.
Office Supplies
Any expense related to office supplies such as providing stationery for every employee, papers, and ink for printing, to printer’s toner.
Depreciation of Office Equipment
The allocation of the cost of the office equipment such as desktops, printers, and other office equipment within its useful life.
Closer to the end of the income Statement, you should arrive at the company's net income. The net income is the sum of the operating income and non-operating income, after deducting interest expense and tax.
Non-operating income is the gain or loss from any sources not related to the core business activities. Here are some examples of non-operating income activities:
Gain or Loss from Investments
To compute the capital gain or loss, subtract the selling price of the investment products from the purchase price. Some of the investing activities performed by the company include investment in shares, property, index funds, or bonds.
Foreign Exchange Gain/Loss
The foreign currency gain and loss is the difference between converting the foreign currency to base currency, when the company sells goods and services in a foreign currency, by referring to the prevailing exchange rate.
Sales of Assets
Income generated from selling the company’s assets includes plant, property, trade names, leaseholds, or any inventory.
Of course, one might wonder where all these categories and sub categories are defined. This is what we will explore in the next section on Chart Of Accounts , where all these details are stored.
Charts of Accounts

In accounting, Chart of Accounts is a list of all the financial accounts used by the organization that comprises of reports used in both the general ledger and the Profit and Loss statements. All the categories and sub categories one sees in an income statement are from the chart of accounts.
The Chart of Accounts usually consists of the 5 different types of accounts - Assets , Liabilities , Revenue , Expenses , and Equity . It's then broken down into more categories and sub-categories.
Not every company shares the same Charts of Accounts, and it can vary depending on the nature of your business.
Typically, businesses assign a specific code to each of the accounts to identify the records conveniently. The account's code could be in numerical, alphabetical or alphanumerical format based on the organization's preferences.
The image shown above is Deskera Books' Chart of Accounts by default. Small businesses can create the account code and tag each of the account to the respective category.
Income Statement Examples from Different Industries
As we have already walk through the types of income statement earlier, let us now view and analyze the multi-step statements generated by a few public listed companies from different industries.
The industries that we will cover below are:
1. Merchandising industry
2. Manufacturing industry
3. Services industry
4. E-commerce industry
Merchandising Industry
Merchandising industry are the companies that sell final products to the end consumers. Based on the study done by Statista, the top merchandise products in the U.S are the home and school office supplies, which amounted to 4.21 billion U.S dollars.
Let's check out the the income statement from 3M corporation, one of the most popular home and school supplies' companies in the world.
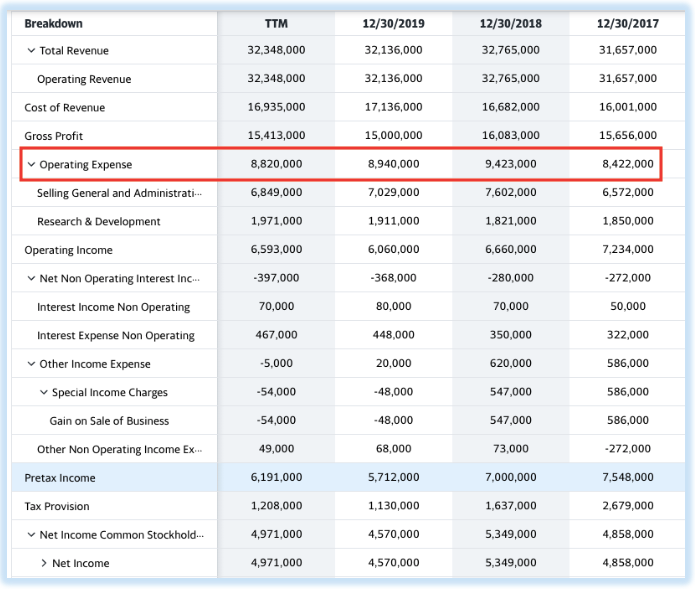
Based on 3M's income statement, you can view the breakdown of the operating expense and operating income into different sub-categories. For instance, the operating expense incurred by 3M Corporation includes selling, general and administrative expense and Research and Development Expense.
The selling, general, and administrative expense is the most prevalent type of expense incurred by all businesses. On top of that, 3M companies also invest their funds in the Research and Development field. They have thousands of researchers scientists and researchers from all over the world to carry out their R&D activities.
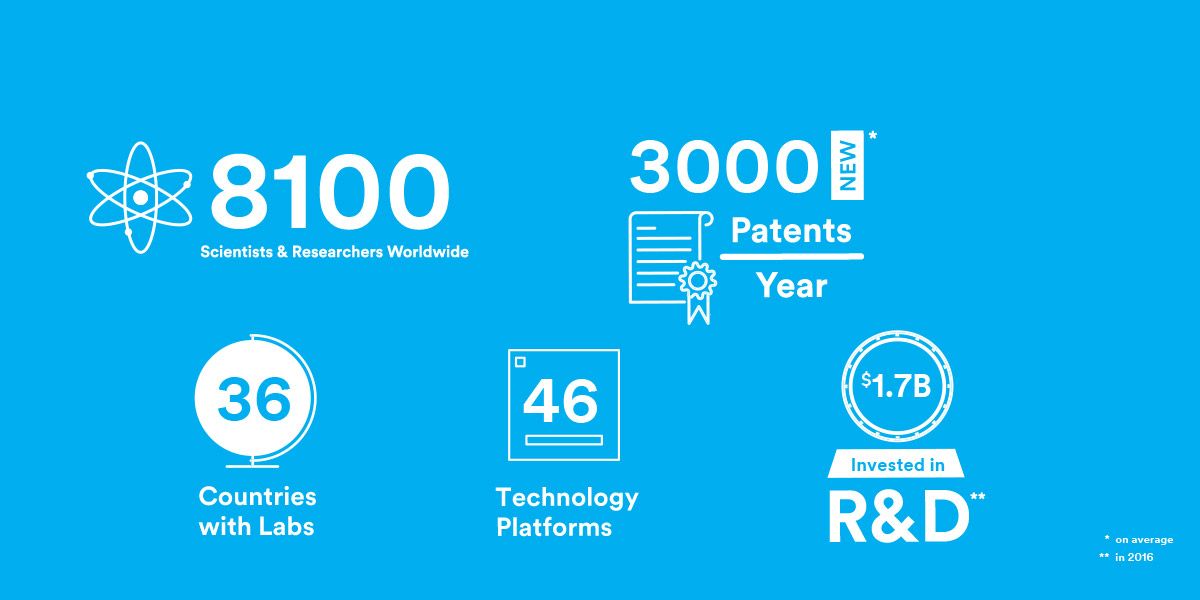
Due to extensive research, the company produces more than 3,000 patents each year. Aside from that, they have various patents to industries, such as the healthcare, automotive, technology, and the electronics industry. And we can determine this by one look at the income statement!
Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry involves processing raw materials using colossal machine, tools, chemicals, or formulation to produce the finished product. According to the study done by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, manufacturing is part of the component of gross domestic product, which was worth $2.33 trillion back in 2018.
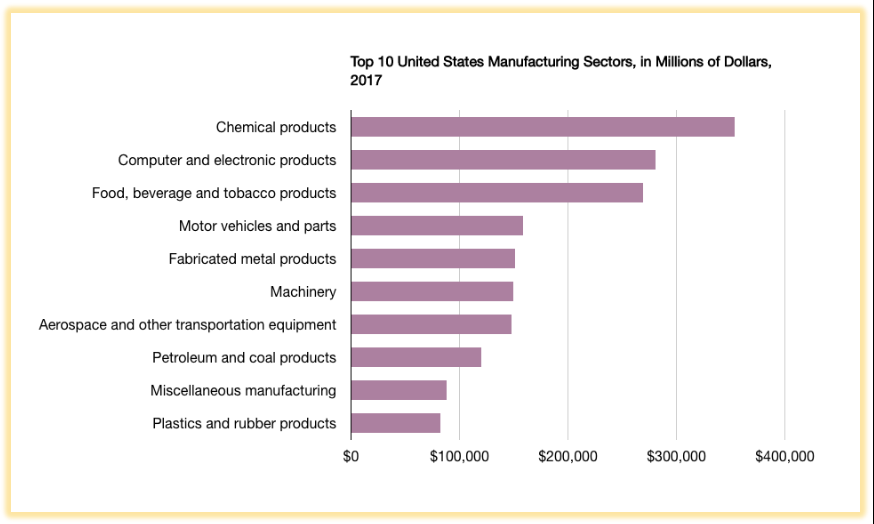
Intel is the biggest semiconductor chip manufacturer in the world. Intel manufactures network interface controllers, processors, and other computing devices that are in high demand. It also supplies microprocessors to other big companies such as Apple, Dell, and Lenovo.
So, let’s have a look at the income statement prepared by Intel Corporation.
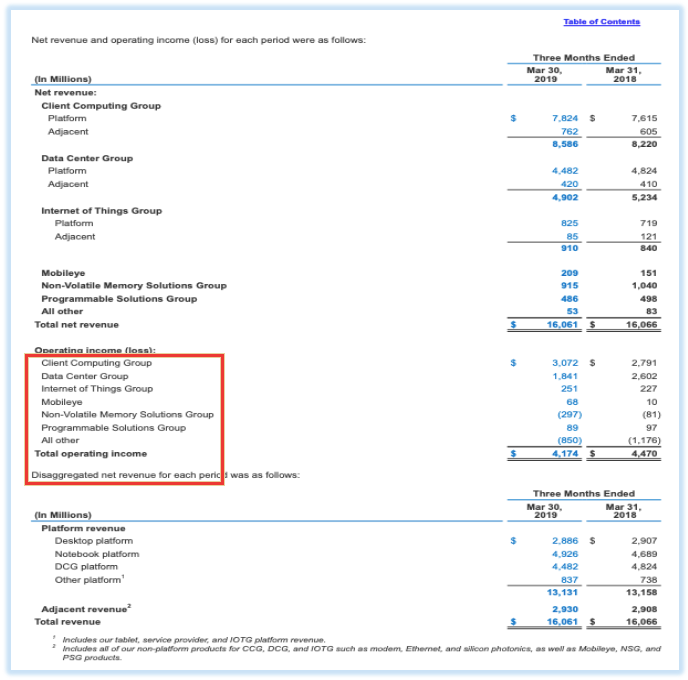
Intel’s income statement shows the breakdown of its operating income into a few groups. As the company is enormous, Intel manages its business by segmenting the processes into different groups.
You can also note that Intel has a various stream of operating income from a few different groups as shown above such as;
• Client Computing Group
• Data Center Group
• Internet of Things Group
• Non-volatile Memory Solutions Group
• Programmable Solutions Group
• All other
These are the various business units that contribute to Intel’s total operating income as a whole.
The accounts used in the preparation of the income statement are different for different companies. Some of the companies do not have a variety of business units. Therefore, they derive their operating income only from one business unit.
Service Industry
Also known as the tertiary sector, the service sector comprises education, healthcare, social worker, computer services, communications, banks, and the hotel industry. As the name suggests, the services industry does not provide any tangible products to the final consumers as they only offer services as the final goods.
Today, we will look at Wyndham Hotels, and Resorts's income statement in the United States.
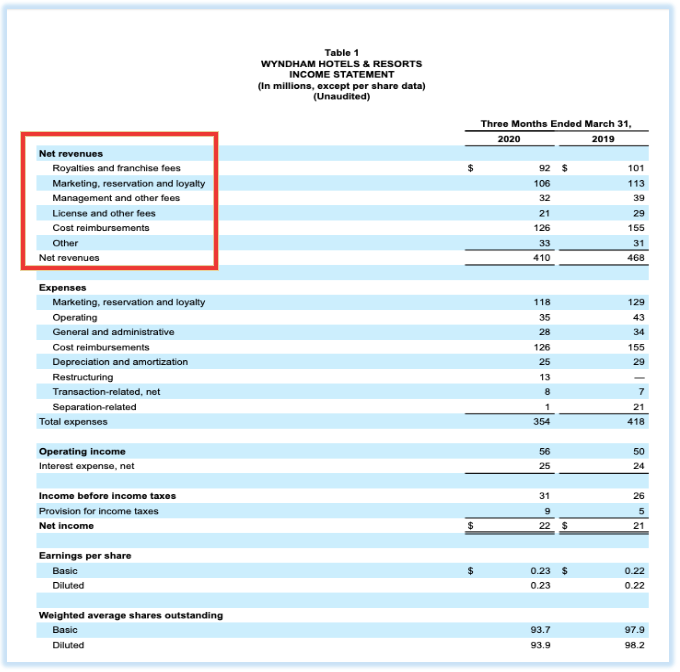
The income statement shown above is the Wyndham Hotels and Resorts’ income statement for the first quarter, 31st March 2020 and 2019 (unaudited).
Based on the analysis of this income statement, you can see that there is no cost of goods sold involved to compute the net revenue.
The reason there is no cost of goods sold account involved is that the service industry does not produce any end products. The primary source of revenue is from the service they provide to the end customers.
The net revenues for Wyndham Hotels and Resorts derive from royalties and franchise fees, marketing reservation and loyalty fees, management, and other fees, license and additional fees, cost reimbursement, and others.
E-Commerce Industry
The e-commerce industry is a multi-billion dollar worth and one of the fastest growing sectors in the world. As we progress towards digitization, more businesses are starting to sell their products and services online.
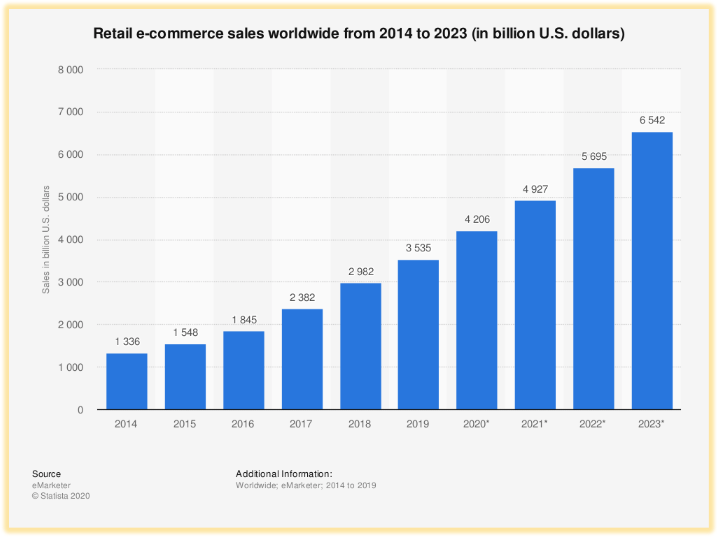
E-commerce sales reached $3.5 trillion in 2019, and pre-Covid-19 predictions show that the number will grow to $6.54 trillion in 2023.
Let us have a look how the biggest eCommerce player in the world, Amazon, prepares its income statement.
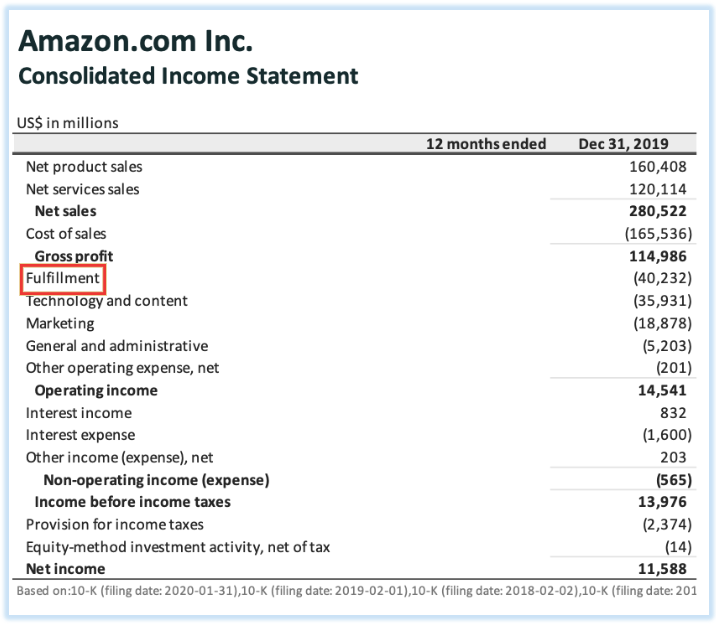
The net sales of Amazon, the largest e-commerce company, derives mainly from its online store.
Apart from online stores, Amazon also generated revenue from its physical stores as they used to have brick and mortar stores before transforming into the e-commerce business . The company's revenue also comes from other sources, such as third-party seller services, subscription services, AWS, and others.
One of the operating expenses of Amazon is the fulfillment expense. A smaller e-Commerce company can avoid high fulfillment costs if they use dropshipping. You can find out how Deskera Books could help with your business with inbuilt support for dropshipping .
Examples of income statement from the Big Four Tech Company
Any discussion on financial statements would be incomplete without taking a look at the financial statements from the big tech companies. We already looked at Amazon in the section above, and here are the others.
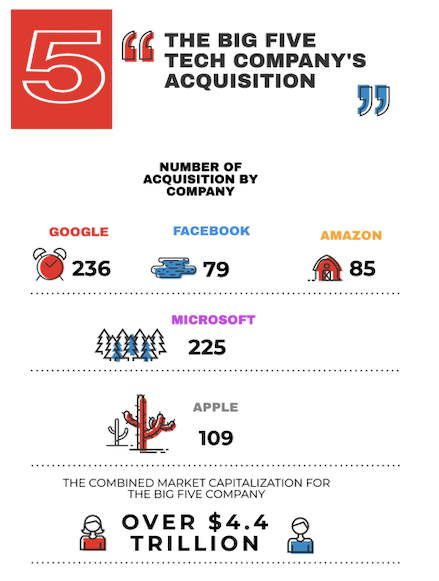
The most popular Big Five tech companies are Apple, Google (Alphabet), Facebook, Amazon, and Microsoft. These giant companies are also known as "FAAMG." Based on the source from Visual Capitalist , the combined market capitalization for the Big Five giant tech company are worth more than $4.4 trillion!
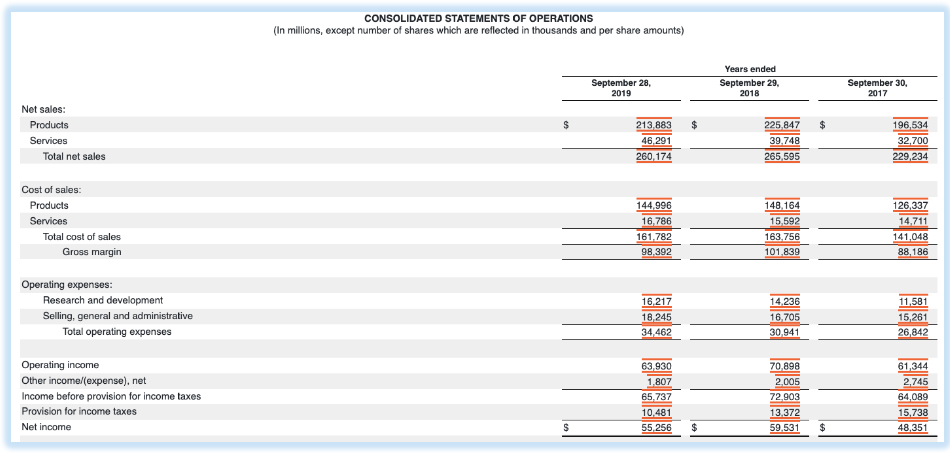
The income statement shown above is the financial report prepared by Apple Inc.
Based on the report, the company's net sales are the summation of the sales from the products and services they provide to their customers. The gross margin can be computed by subtracting the total cost of sales from the total net sales.
The operating expenses incurred are similar to other companies such as Apple allocated expenses to selling, general and administrative tasks and also Research and Development.
The net income of Apple Inc for the month year ended September 28, 2019 is a total of $55,256 millions!
Facebook is one of the popular social media platforms for social networking and also advertising. Founded by Mark Zuckerberg in early 2004, Facebook has about 2.6 billion users worldwide today.
Let us take a look at Facebook's income statement.
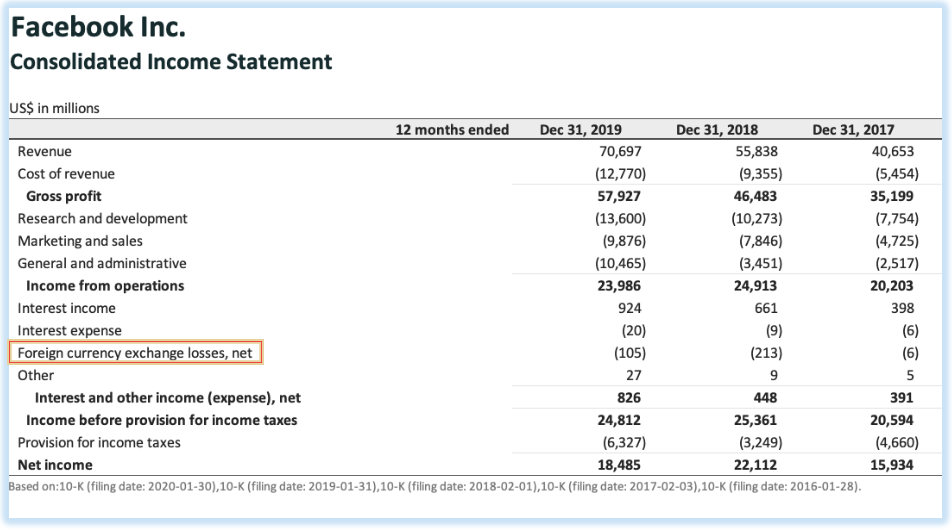
Facebook's operating expense includes Research and Development, Marketing and Sales, and General and Administrative tasks.
Facebook's exposure to foreign currency risk is due to the fluctuations in their net income from the transaction gain and losses related to certain current assets and current liabilities, denominated in other currencies.
The foreign currency losses in the year 2017 is US$6 million, US$213 million in the year 2018, and US$105 million in 2019, as shown based on the income statement report.
As per the report, the net income for Facebook decreased from US$ 22,112 million in 2018 to US$18,485 million for the year 2019.
Microsoft is one of the Big Five Tech Company that needs no introduction. Microsoft is also known worldwide for its consumer electronics such as computers, laptops, computer software, and other related services.
Let's take a look at Microsoft's income statement.
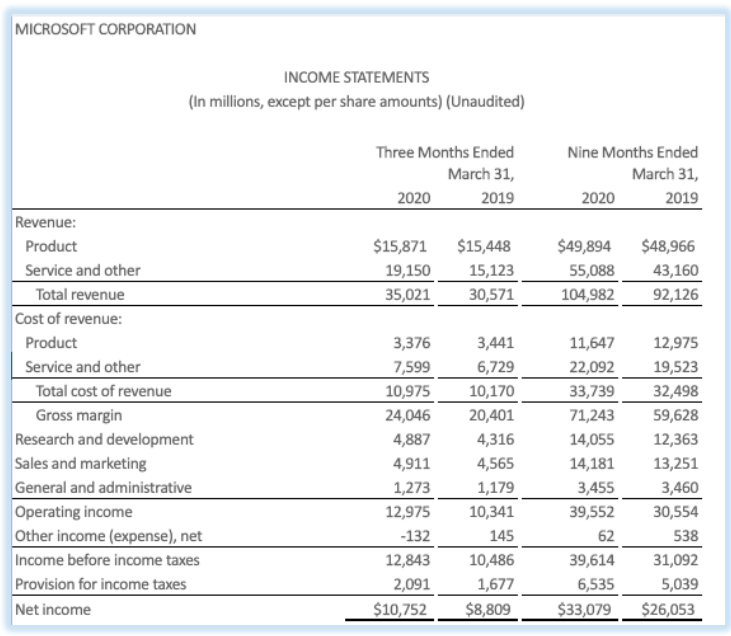
Microsoft derives its revenue from both the sales of products and services. By deducting the cost of revenue for products, services, and others, the gross margin for three months ended March 31, 2020, is a total of $24,046 million.
The operating expenses involve three accounts, including Research and Development, Sales and Marketing, and General and Administrative.
Microsoft Corporation pays a total of $2,091 million in income taxes for the three months ended, March 31, 2020. After subtracting the income tax, the net income stands at $10,752 million.
The parent company of Google is Alphabet Inc. Alphabet Inc is a multinational technology company that provides internet-related services and products. Some of the products and services from Alphabet Inc include the search engine, online advertising technologies, hardware, and cloud computing software.
Let us dive deeper into the income statement prepared by Alphabet Inc.
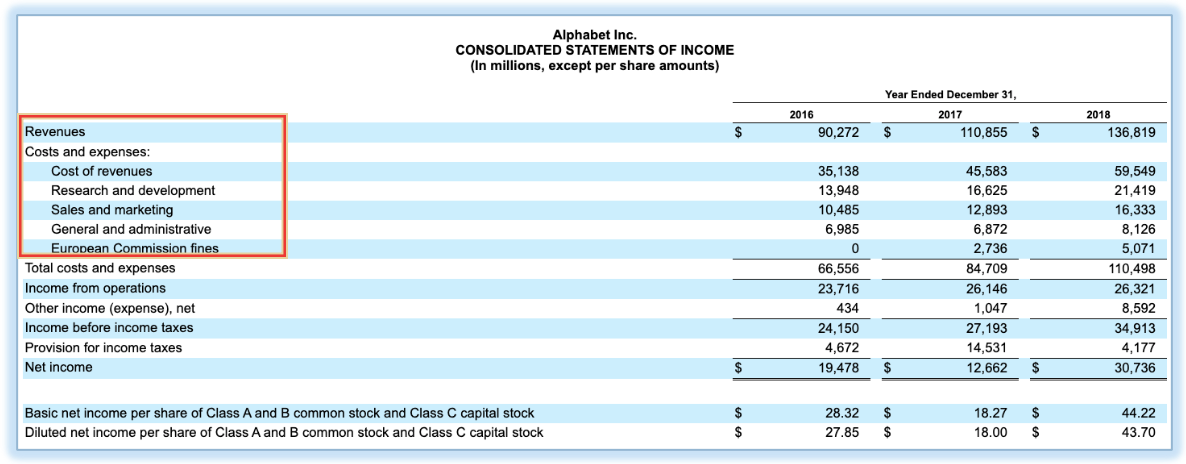
Based on the consolidated income statement from Alphabet Inc, you notice that the costs of revenue and operating expenses are combined without breaking down into two separate accounts. For the previous company mentioned above, most of the companies separate the cost of goods sold account from the operating expense account instead of lumping them together.
The company then fetched its income from operations by deducting the revenue from the total costs and expenses. They did not highlight the gross margin figure and dive straight to the income from the operations account.
An unusual account/heading that shows up here is the European Commission Fines.
According to the European Commission , the EC has fined Google for breaching the European anti-trust rules. The infringement is due to the restrictive clauses in their contracts with third-party websites that prevent competitors from placing search advertisements on these websites. Therefore, Alphabet Inc has to pay the fines imposed on them.
How to See Income Statements Online
If you are keen to study the income statement of public listed companies, then this section is for you.
Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance is a popular tool that most University students used to extract financial data from the public listed company for their research.
First of all, go to the Yahoo website.
Once you have landed on Yahoo website, you can hover your mouse towards the Finance section and click on it.
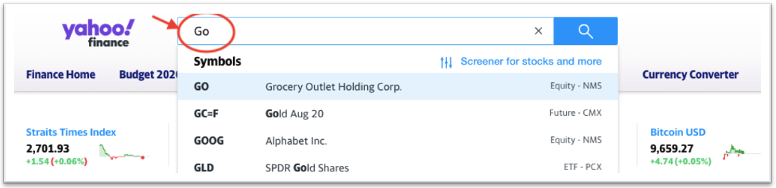
You can use the search bar to find the financial reporting for all the public listed companies in the world.
For instance, if you search Go in the search bar, there will be a list companies close the company's name "Go" appear in the drop-down selection. Choose the relevant company that you are looking for.
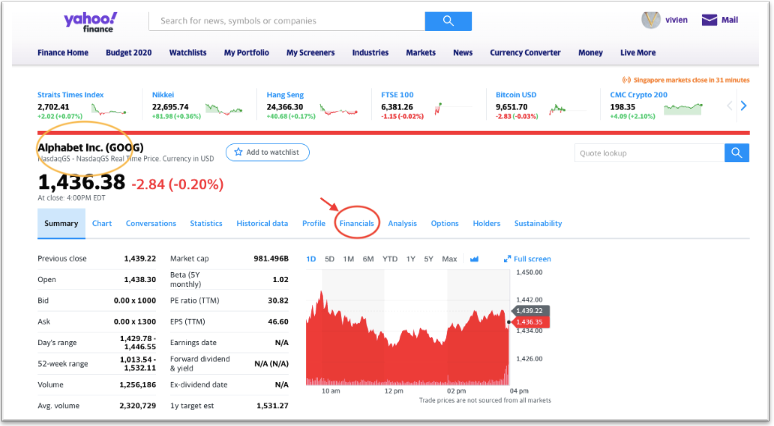
Once you have selected the right company, the company name will appear at the top right of the page. For instance, you can view the company's name Alphabet Inc. (GOOG) based on the image above, to confirm it's the right company. Click on the Financials section.
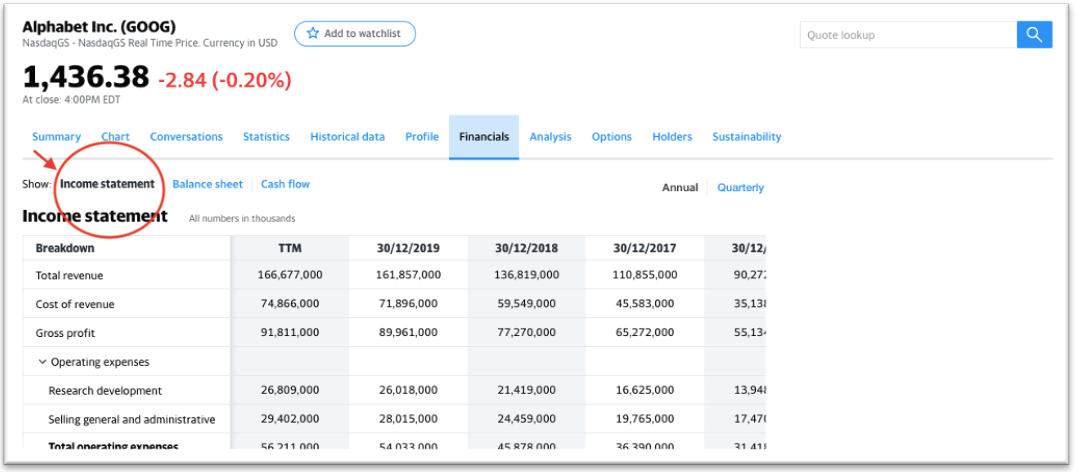
In this page, small business should be able to view the company’s financial reporting, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and also cash flow statement for few years. Switch to Quarterly report, if you wish to view the quarterly report instead.
Besides Yahoo Finance, you can also utilize the EDGAR website to download the public listed companies in the United States.
EDGAR is the short form of Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval. It is created by the Securities and Exchange Commission in America to increase the efficiency and accessibility of corporate filing. All the publicly traded companies in America are required to file their reports compliant with SEC.
To use this, first of all, go to the EDGAR website.
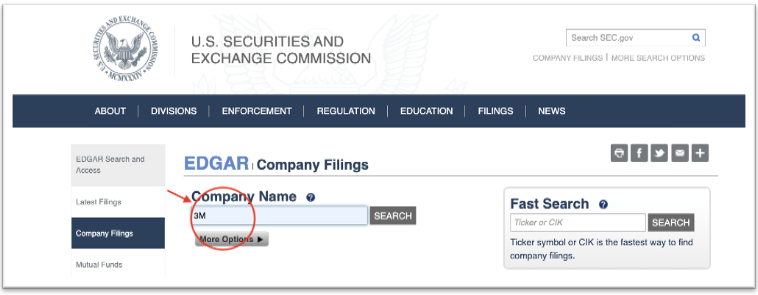
Make sure that you’re on the company's filing page. Next, enter the company name you are looking for and click on the Search button.
A list of the company's names will appear. Click on the numbering link on the first column of the company's financial data that you wish to view. Next, you should be able to see all the types of filing done by the company.
You can search for the company's annual report using the filter selection, as shown above.
Enter the filing types in the search box. If you wish to view the annual report, enter 10-Q and 10-K for quarterly and yearly annual report. Click on the Documents button under the Format column.
Lastly, to view the company annual report, click on the numbering link under the Document column.

Lastly, you should be able to view the company's annual report for the year you have indicated. In this report, you should have comprehensive details of the company's performance.
Also, you can view the company's consolidated income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flow in this annual report.
Free Income Statement Template Download
Most people have a hard time preparing and generating financial statements from scratch. Which is why we have prepared some easy to use excel templates for you to download and use.
In the long run though, it is advisable to move away from excel and use an online accounting software to auto generate your income statement. Deskera Books can do this easily for you. You just have to record your transactions and a multi-step income statement is generated for you by the system.

Guide to Understanding Accounts Receivable Days (A/R Days)

Everything You Need to Know About Professional Tax in Andhra Pradesh

Andhra Pradesh forms XXVI Letter of Appointment
Hey! Try Deskera Now!
Everything to Run Your Business
Get Accounting, CRM & Payroll in one integrated package with Deskera All-in-One .
Original text

Access our collection of user-friendly templates for business planning, finance, sales, marketing, and management, designed to assist you in developing strategies for either launching a new business venture or expanding an existing one.
You can use the templates below as a starting point to create your startup business plan or map out how you will expand your existing business. Then meet with a SCORE mentor to get expert business planning advice and feedback on your business plan.
If writing a full business plan seems overwhelming, start with a one-page Business Model Canvas. Developed by Founder and CEO of Strategyzer, Alexander Osterwalder, it can be used to easily document your business concept.
Download this template to fill out the nine squares focusing on the different building blocks of any business:
- Value Proposition
- Customer Segments
- Customer Relationships
- Key Activities
- Key Resources
- Key Partners
- Cost Structure
- Revenue Streams
For help completing the Business Model Canvas Template, contact a SCORE business mentor for guidance
From creating a startup budget to managing cash flow for a growing business, keeping tabs on your business’s finances is essential to success. The templates below will help you monitor and manage your business’s financial situation, create financial projections and seek financing to start or grow your business.
This interactive calculator allows you to provide inputs and see a full estimated repayment schedule to plan your capital needs and cash flow.
A 12-month profit and loss projection, also known as an income statement or statement of earnings, provides a detailed overview of your financial performance over a one-year period. This projection helps you anticipate future financial outcomes by estimating monthly income and expenses, which facilitates informed decision-making and strategic planning.
If you’re trying to get a loan from a bank, they may ask you for a personal financial statement. You can use this free, downloadable template to document your assets, liabilities and net worth.
A Personal Financial Statement is a
Marketing helps your business build brand awareness, attract customers and create customer loyalty. Use these templates to forecast sales, develop your marketing strategy and map out your marketing budget and plan.
How healthy is your business? Are you missing out on potential growth opportunities or ignoring areas of weakness? Do you need to hire employees to reach your goals? The following templates will help you assess the state of your business and accomplish important management tasks.
Whether you are starting your business or established and looking to grow, our Business Healthcheck Tool will provide practical information and guidance.
Learn how having a SCORE mentor can be a valuable asset for your business. A SCORE mentor can provide guidance and support in various areas of business, including finance, marketing, and strategy. They can help you navigate challenges and make important decisions based on their expertise and experience. By seeking out a SCORE mentor, you can gain the guidance and support you need to help grow your business and achieve success.
SCORE offers free business mentoring to anyone that wants to start, currently owns, or is planning to close or sell a small business. To initiate the process, input your zip code in the designated area below. Then, complete the mentoring request form on the following page, including as much information as possible about your business. This information is used to match you with a mentor in your area. After submitting the request, you will receive an email from your mentor to arrange your first mentoring session.
Copyright © 2024 SCORE Association, SCORE.org
Funded, in part, through a Cooperative Agreement with the U.S. Small Business Administration. All opinions, and/or recommendations expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SBA.
Be Stress Free and Tax Ready 🙌 70% Off for 4 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
70% Off for 4 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
Free Income Statement Template
As a business owner, you know how important it is to keep your numbers in check. Knowing how much revenue is coming in, how much money is going out, and how much profit you are making is essential to making smart business decisions.That’s why you need an accounting system that helps you stay organized. With the free Income Statement template from FreshBooks, you have everything you need to track your income and more.
Simply download the template in your chosen format, customize and save. You’ll have a complete sheet to save for your records and a simple way to stay on top of your numbers.
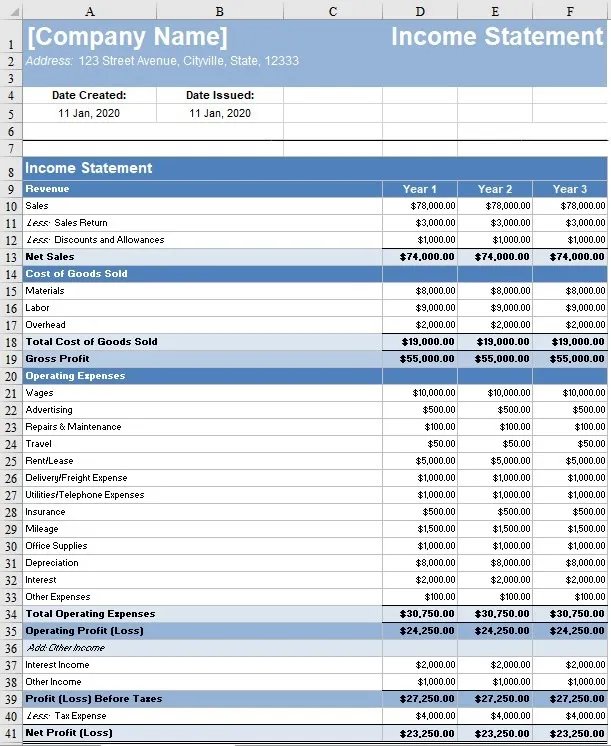
Get a Free Invoice Statement Template
If you want your business to thrive, you’ll need a straightforward way to track ytehour numbers. Good news is, the free invoice statement template from FreshBooks is here to help you get a grasp on your bookkeeping.
You can download your free income statement template in the format that suits you best. If you like using spreadsheets, you can use the free Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets invoice statement to get started.
With the free income statement excel template, you’ll gain access to a helpful income statement formula. This can be hugely rewarding if you don’t have the time or means to structure one yourself.
The blank income statement has customizable fields for you to plug in your revenue and expenses. From there, you can calculate your profit or loss for the given period. A profit or loss statement is a crucial component of understanding a company’s financial health and can assist when making important decisions on how to run a business.
Some business owners even create monthly income, quarterly or yearly statements. No matter how often you want to calculate your profit or loss, the FreshBooks income statement example will be a helpful resource for you.
Available for download in .DOC, .PDF, .WORD, Google Docs and Google Sheets.
Featured In
Want to learn more about growing your business, track your income with freshbooks.
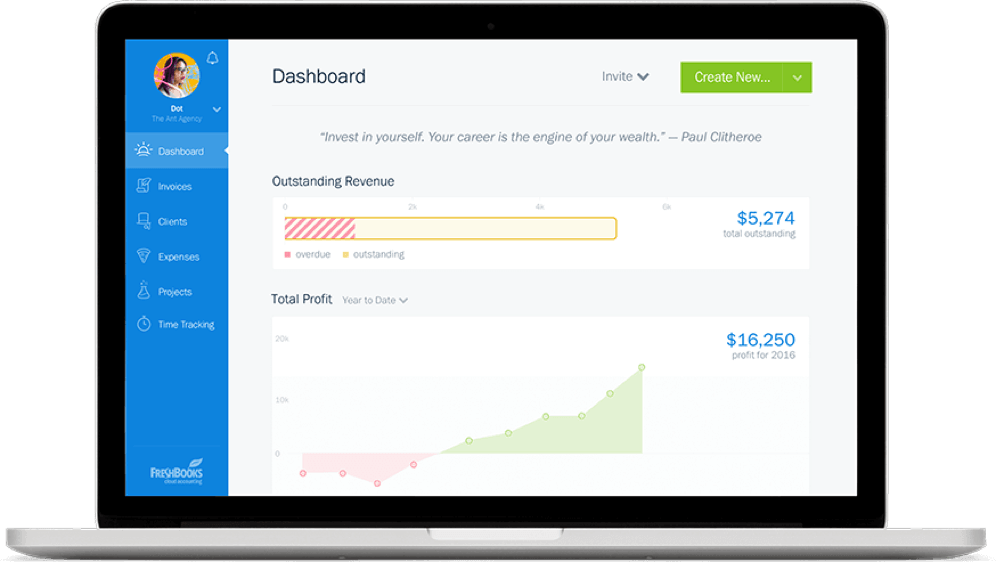
Take bookkeeping into your own hands with FreshBooks income statements.
Free Income Statement Example
Download As:
What is an Invoice Statement?
Why use an income statement.
- How Do I Fill In an Invoice Statement?
Frequently Asked Questions
Benefits of freshbooks accounting, get started with freshbooks.

An invoice statement is an accounting report that is used to list your net income or business expenses, which would be either profit or loss. This statement is also commonly referred to as a “profit and loss report” or “P&L” statement.
You can generate an invoice statement whenever you choose, but they are typically used to report your business’s financial activity during a designated accounting period, such as per month, quarter, or year.
The invoice statement template serves as a great guideline to make sure you’re including all of the proper information on your income and expense statement.

“I’ve been using FreshBooks for 6 years and love how the design, functionality, and platform has grown with me.”
Kathleen Shannon
Co-Host of Being Boss
Are you ready to take control of your business accounting? The cloud accounting software from FreshBooks will get you there. Create invoices and other business reports with ease as you take your accounting on the go.
Access FreshBooks from your smartphone, tablet, or laptop as long as you have a wifi connection. Accounting has never been more convenient.
“FreshBooks has helped me to simplify my bookkeeping without the stress”
The success of your business depends on you making informed decisions. That’s why having your business financials organized and on-hand is one of the best things you can do to get started on the right track.
An income statement will show you exactly what your net profit is and will help you determine whether you need to decrease your costs or increase your revenue to stay in the black. Sound simple? Use the FreshBooks income and expense template to get started.
Take Control of Your Accounting with FreshBooks
How do i fill in an income statement.
Want to create your own Income Statement in minutes? Simply download the financial statement template and follow the steps below to get started.
Choose a File Format
Choose one of our invoice statement template formats.
Download Template
Once you’ve chosen which template to use, download it to your device.
Add Your Branding
Add your business name and logo at the top. Change the fonts to match your branding.
Fill in Revenue
Create revenue subcategories. Fill them in and calculate total revenue.
Fill in Expenses
Customize the expense subcategories and fill them in. Calculate the total costs.
Calculate Net Income
Determine whether you’ve made a profit or a loss. Subtract expenses from revenue.
Check Out Our Other Accounting Sheets
There is more to accounting than determining if you’ve turned a profit. You need to see where each dollar has come from or gone to. That’s why FreshBooks provides a number of other sample accounting sheets.
- Profit and Loss Templates
- Expense Report Templates
- Simple Balance Sheet Templates
- General Ledger Templates
- Income Statement Templates
- Billing Statement Templates
- Bank Reconciliation Templates
Income statements are used to compare your revenue to your expenses to determine if you have made a profit or a loss. Creating income statements will help you track your income, net profit and more to keep you organized.
When creating your own income statement, you’ll want to include a breakdown of your revenue, expenses, and net income.
The income and expense statement template from FreshBooks includes blank, easy-to-use fields for all of the information that you need to include.
Net income is calculated by subtracting expenses from income. If the number is positive, you have a profit and if it’s negative, you have a loss.
Most definitely. FreshBooks has other free resources, such as general ledger templates, expense reports and more.
Our free accounting resources, including the free income statement format, are designed for business owners looking to take a do-it-yourself approach to accounting. But the FreshBooks cloud accounting software is a much more powerful and efficient resource that’s designed to help businesses save money and time on their bookkeeping.
The resources that are included in the FreshBooks cloud accounting software are a lifesaver for business owners who want a thorough understanding of their company’s finances. Keeping your accounts organized is a fundamental part of any healthy business plan, and that’s where a practical, fully customizable bookkeeping resource comes in.
FreshBooks offers cleverly-designed accounting reporting features that can help any business easily keep track of their finances, including their revenue and losses. You’ll gain unlimited access to practical financial templates that are the backbone of business planning and will help you keep track of your critical business activities.
If you’re looking for more free templates to help keep your business running as smoothly as possible, check out some of the other free templates on the FreshBooks website.
An income statement or balance sheet is a necessary financial document that tracks how much money is coming in and out of a business, and with the free balance sheet template from FreshBooks, every dollar will be accounted for.
A small business income statement showcases a company’s revenue and expense over the course of a specific time frame. FreshBooks provides a specialized small business income statement template, perfect for any small business owner who requires accuracy and is looking for efficiency in their accounting.
Take control of your finances and automate your bookkeeping with FreshBooks. You can get back to business and start running your company the way it deserves.
Ready to automate your bookkeeping?
Detailed Reports
Cloud storage, automated invoicing, co-working portal, accounting on the go, no binding contracts.
If you’re ready to take control and automate your bookkeeping, it is time to sign up for FreshBooks. Try risk-free for 30 days.
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download and prepare free financial templates for your business plan, including income statement templates, cash flow statement templates, balance sheet templates, and more. Learn the key elements of the financial section of a business plan and how to use them to project your financial health and performance.
An income statement is your business's bottom line: your total revenue from sales minus all of your costs. Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own. This is part 2 / 11 of ...
Add up all your gains then deduct your losses. Step 10: Income before tax and interest (EBIT) Add gains and losses to non-operating income and operating income to reach your EBIT. Step 11: Taxes and interest. Add up the income tax for the reporting period and the interest incurred for debt during that time.
Along with cash flow statement and balance sheet, income statement makes the financial planning part of the business plan. This income statement template for business plan can be used without any additional changes; download income statement template, populate it with forecast numbers and your income statement for business plan is ready.
With Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template, which includes a completely automated financial model (income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), you can finish your business plan and financial model in just 8 hours or less. Components of a Simple Small Business Income Statement.
The income statement (also called a profit and loss statement) summarizes a business' revenues and operating expenses over a time period to calculate the net income for the period.. Below are two types of income statement templates. #1 Annual income statement template. If you are analyzing the financial information for a company that spans several years, you may wish to use an annual income ...
Financial Templates for Your Business Plan Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow, and More . ... Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement. Shows the company's revenue, expenses, and profit or loss. Key formula: Total Revenue - Total Expenses = Profit or Loss. This is an important financial statement that you should ...
Income Statement Template Your business plan should include a three-year forecast of your income statement. Income Statement Template. Refer to the sample income statement in the tab below while reviewing this section as a guideline or income statement template for your own business. The income statement shows revenue and expenses, usually by ...
Free business plan template. A fill-in-the-blank template designed for business owners. Download Now. Sample Plans. ... Download Now: Free Income Statement Template. Creating a financial plan is often the most intimidating part of writing a business plan. It's also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial ...
Steps to Prepare an Income Statement. 1. Choose Your Reporting Period. Your reporting period is the specific timeframe the income statement covers. Choosing the correct one is critical. Monthly, quarterly, and annual reporting periods are all common. Which reporting period is right for you depends on your goals.
Free business plan template. A fill-in-the-blank template designed for business owners. Download Now. Sample Plans. ... Typically, an income statement is a list of revenue and expenses, with the company's net profit listed at the end (check out the section on income statement examples below to see what it looks like).
Include Financial Statements in Your Business Plan. You will need a complete startup business plan to take to a bank or other business lender. The financial statements are a key part of this plan. Give the main points in the executive summary and include all the statements in the financial section. 09 of 09.
The Income Statement. The Cash Flow Projection. The Balance Sheet. Photo: Jetta Productions Inc/Getty Images. Was this page helpful? Learn how to write the financial plan section of your business plan: income statement, cash flow projections, and balance sheet (templates included).
Business Plan Template. Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. ... Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection. Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits.
Download Now: Free Business Plan Template. Writing a business plan doesn't have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you'll learn how to write a business plan that's detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
Download free income statement templates in excel. Get ready-to-use income statement templates. In addition to the above, a well prepared income statement speaks about the business and financial maturity of an organization. Which is why we will be going over income statements in great detail in rest of the article.
Join over 7 million customers globally and find the QuickBooks plan that works for you. See plans & pricing. Important offers, pricing details and disclaimers. The income statement gives you a snapshot view of your business's financial performance and profitability. Download our free income statement template today!
Download our free business plan template for your established business as a Word doc. A business plan for an established business serves as a roadmap guiding the growth and continued success of your business throughout its next stages. ... A 12-month profit and loss projection, also known as an income statement or statement of earnings ...
With the free Income Statement template from FreshBooks, you have everything you need to track your income and more. Simply download the template in your chosen format, customize and save. You'll have a complete sheet to save for your records and a simple way to stay on top of your numbers. Create Income Statement.