Cultural Identity Essay
27 August, 2020
12 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
No matter where you study, composing essays of any type and complexity is a critical component in any studying program. Most likely, you have already been assigned the task to write a cultural identity essay, which is an essay that has to do a lot with your personality and cultural background. In essence, writing a cultural identity essay is fundamental for providing the reader with an understanding of who you are and which outlook you have. This may include the topics of religion, traditions, ethnicity, race, and so on. So, what shall you do to compose a winning cultural identity essay?


Cultural Identity Paper: Definitions, Goals & Topics

Before starting off with a cultural identity essay, it is fundamental to uncover what is particular about this type of paper. First and foremost, it will be rather logical to begin with giving a general and straightforward definition of a cultural identity essay. In essence, cultural identity essay implies outlining the role of the culture in defining your outlook, shaping your personality, points of view regarding a multitude of matters, and forming your qualities and beliefs. Given a simpler definition, a cultural identity essay requires you to write about how culture has influenced your personality and yourself in general. So in this kind of essay you as a narrator need to give an understanding of who you are, which strengths you have, and what your solid life position is.
Yet, the goal of a cultural identity essay is not strictly limited to describing who you are and merely outlining your biography. Instead, this type of essay pursues specific objectives, achieving which is a perfect indicator of how high-quality your essay is. Initially, the primary goal implies outlining your cultural focus and why it makes you peculiar. For instance, if you are a french adolescent living in Canada, you may describe what is so special about it: traditions of the community, beliefs, opinions, approaches. Basically, you may talk about the principles of the society as well as its beliefs that made you become the person you are today.
So far, cultural identity is a rather broad topic, so you will likely have a multitude of fascinating ideas for your paper. For instance, some of the most attention-grabbing topics for a personal cultural identity essay are:
- Memorable traditions of your community
- A cultural event that has influenced your personality
- Influential people in your community
- Locations and places that tell a lot about your culture and identity
Cultural Identity Essay Structure
As you might have already guessed, composing an essay on cultural identity might turn out to be fascinating but somewhat challenging. Even though the spectrum of topics is rather broad, the question of how to create the most appropriate and appealing structure remains open.
Like any other kind of an academic essay, a cultural identity essay must compose of three parts: introduction, body, and concluding remarks. Let’s take a more detailed look at each of the components:
Introduction
Starting to write an essay is most likely one of the most time-consuming and mind-challenging procedures. Therefore, you can postpone writing your introduction and approach it right after you finish body paragraphs. Nevertheless, you should think of a suitable topic as well as come up with an explicit thesis. At the beginning of the introduction section, give some hints regarding the matter you are going to discuss. You have to mention your thesis statement after you have briefly guided the reader through the topic. You can also think of indicating some vital information about yourself, which is, of course, relevant to the topic you selected.
Your main body should reveal your ideas and arguments. Most likely, it will consist of 3-5 paragraphs that are more or less equal in size. What you have to keep in mind to compose a sound ‘my cultural identity essay’ is the argumentation. In particular, always remember to reveal an argument and back it up with evidence in each body paragraph. And, of course, try to stick to the topic and make sure that you answer the overall question that you stated in your topic. Besides, always keep your thesis statement in mind: make sure that none of its components is left without your attention and argumentation.
Conclusion
Finally, after you are all finished with body paragraphs and introduction, briefly summarize all the points in your final remarks section. Paraphrase what you have already revealed in the main body, and make sure you logically lead the reader to the overall argument. Indicate your cultural identity once again and draw a bottom line regarding how your culture has influenced your personality.
Best Tips For Writing Cultural Identity Essay
Writing a ‘cultural identity essay about myself’ might be somewhat challenging at first. However, you will no longer struggle if you take a couple of plain tips into consideration. Following the tips below will give you some sound and reasonable cultural identity essay ideas as well as make the writing process much more pleasant:
- Start off by creating an outline. The reason why most students struggle with creating a cultural identity essay lies behind a weak structure. The best way to organize your ideas and let them flow logically is to come up with a helpful outline. Having a reference to build on is incredibly useful, and it allows your essay to look polished.
- Remember to write about yourself. The task of a cultural identity essay implies not focusing on your culture per se, but to talk about how it shaped your personality. So, switch your focus to describing who you are and what your attitudes and positions are.
- Think of the most fundamental cultural aspects. Needless to say, you first need to come up with a couple of ideas to be based upon in your paper. So, brainstorm all the possible ideas and try to decide which of them deserve the most attention. In essence, try to determine which of the aspects affected your personality the most.
- Edit and proofread before submitting your paper. Of course, the content and the coherence of your essay’s structure play a crucial role. But the grammatical correctness matters a lot too. Even if you are a native speaker, you may still make accidental errors in the text. To avoid the situation when unintentional mistakes spoil the impression from your essay, always double check your cultural identity essay.
A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

Cultural Diversity Essay & Community Essay Examples
If you’ve started to research college application requirements for the schools on your list, you might have come across the “cultural diversity essay.” In this guide, we’ll explore the cultural diversity essay in depth. We will compare the cultural diversity essay to the community essay and discuss how to approach these kinds of supplements. We’ll also provide examples of diversity essays and community essay examples. But first, let’s discuss exactly what a cultural diversity essay is.
The purpose of the cultural diversity essay in college applications is to show the admissions committee what makes you unique. The cultural diversity essay also lets you describe what type of “ diversity ” you would bring to campus.
We’ll also highlight a diversity essay sample for three college applications. These include the Georgetown application essay , Rice application essay , and Williams application essay . We’ll provide examples of diversity essays for each college. Then, for each of these college essays that worked, we will analyze their strengths to help you craft your own essays.
Finally, we’ll give you some tips on how to write a cultural diversity essay that will make your applications shine.
But first, let’s explore the types of college essays you might encounter on your college applications.
Types of College Essays

College application requirements will differ among schools. However, you’ll submit one piece of writing to nearly every school on your list—the personal statement . A strong personal statement can help you stand out in the admissions process.
So, how do you know what to write about? That depends on the type of college essay included in your college application requirements.
There are a few main types of college essays that you might encounter in the college admissions process. Theese include the “Why School ” essay, the “Why Major ” essay, and the extracurricular activity essay. This also includes the type of essay we will focus on in this guide—the cultural diversity essay.
“Why School” essay
The “Why School ” essay is exactly what it sounds like. For this type of college essay, you’ll need to underscore why you want to go to this particular school.
However, don’t make the mistake of just listing off what you like about the school. Additionally, don’t just reiterate information you can find on their admissions website. Instead, you’ll want to make connections between what the school offers and how you are a great fit for that college community.
“Why Major” essay
The idea behind the “Why Major ” essay is similar to that of the “Why School ” essay above. However, instead of writing about the school at large, this essay should highlight why you plan to study your chosen major.
There are plenty of directions you could take with this type of essay. For instance, you might describe how you chose this major, what career you plan to pursue upon graduation, or other details.
Extracurricular Activity essay
The extracurricular activity essay asks you to elaborate on one of the activities that you participated in outside of the classroom.
For this type of college essay, you’ll need to select an extracurricular activity that you pursued while you were in high school. Bonus points if you can tie your extracurricular activity into your future major, career goals, or other extracurricular activities for college. Overall, your extracurricular activity essay should go beyond your activities list. In doing so, it should highlight why your chosen activity matters to you.
Cultural Diversity essay
The cultural diversity essay is your chance to expound upon diversity in all its forms. Before you write your cultural diversity essay, you should ask yourself some key questions. These questions can include: How will you bring diversity to your future college campus? What unique perspective do you bring to the table?
Another sub-category of the cultural diversity essay is the gender diversity essay. As its name suggests, this essay would center around the author’s gender. This essay would highlight how gender shapes the way the writer understands the world around them.
Later, we’ll look at examples of diversity essays and other college essays that worked. But before we do, let’s figure out how to identify a cultural diversity essay in the first place.
How to identify a ‘cultural diversity’ essay

So, you’re wondering how you’ll be able to identify a cultural diversity essay as you review your college application requirements.
Aside from the major giveaway of having the word “diversity” in the prompt, a cultural diversity essay will ask you to describe what makes you different from other applicants. In other words, what aspects of your unique culture(s) have influenced your perspective and shaped you into who you are today?
Diversity can refer to race, ethnicity, first-generation status, gender, or anything in between. You can write about a myriad of things in a cultural diversity essay. For instance, you might discuss your personal background, identity, values, experiences, or how you’ve overcome challenges in your life.
However, don’t feel limited in what you can address in a cultural diversity essay. The words “culture” and “diversity” mean different things to different people. Above all, you’ll want your diversity essays for college to be personal and sincere.
How is a ‘community’ essay different?

A community essay can also be considered a cultural diversity essay. In fact, you can think of the community essay as a subcategory of the cultural diversity essay. However, there is a key difference between a community essay and a cultural diversity essay, which we will illustrate below.
You might have already seen some community essay examples while you were researching college application requirements. But how exactly is a community essay different from a cultural diversity essay?
One way to tell the difference between community essay examples and cultural diversity essay examples is by the prompt. A community essay will highlight, well, community . This means it will focus on how your identity will shape your interactions on campus—not just how it informs your own experiences.
Two common forms to look out for
Community essay examples can take two forms. First, you’ll find community essay examples about your past experiences. These let you show the admissions team how you have positively influenced your own community.
Other community essay examples, however, will focus on the future. These community essay examples will ask you to detail how you will contribute to your future college community. We refer to these as college community essay examples.
In college community essay examples, you’ll see applicants detail how they might interact with their fellow students. These essays may also discuss how students plan to positively contribute to the campus community.
As we mentioned above, the community essay, along with community essay examples and college community essay examples, fit into the larger category of the cultural diversity essay. Although we do not have specific community essay examples or college community essay examples in this guide, we will continue to highlight the subtle differences between the two.
Before we continue the discussion of community essay examples and college community essay examples, let’s start with some examples of cultural diversity essay prompts. For each of the cultural diversity essay prompts, we’ll name the institutions that include these diversity essays for college as part of their college application requirements.
What are some examples of ‘cultural diversity’ essays?
Now, you have a better understanding of the similarities and differences between the cultural diversity essay and the community essay. So, next, let’s look at some examples of cultural diversity essay prompts.
The prompts below are from the Georgetown application, Rice application, and Williams application, respectively. As we discuss the similarities and differences between prompts, remember the framework we provided above for what constitutes a cultural diversity essay and a community essay.
Later in this guide, we’ll provide real examples of diversity essays, including Georgetown essay examples, Rice University essay examples, and Williams supplemental essays examples. These are all considered college essays that worked—meaning that the author was accepted into that particular institution.
Georgetown Supplementals Essays

Later, we’ll look at Georgetown supplemental essay examples. Diversity essays for Georgetown are a product of this prompt:
As Georgetown is a diverse community, the Admissions Committee would like to know more about you in your own words. Please submit a brief essay, either personal or creative, which you feel best describes you.
You might have noticed two keywords in this prompt right away: “diverse” and “community.” These buzzwords indicate that this prompt is a cultural diversity essay. You could even argue that responses to this prompt would result in college community essay examples. After all, the prompt refers to the Georgetown community.
For this prompt, you’ll want to produce a diversity essay sample that highlights who you are. In order to do that successfully, you’ll need to self-reflect before putting pen to paper. What aspects of your background, personality, or values best describe who you are? How might your presence at Georgetown influence or contribute to their diverse community?
Additionally, this cultural diversity essay can be personal or creative. So, you have more flexibility with the Georgetown supplemental essays than with other similar diversity essay prompts. Depending on the direction you go, your response to this prompt could be considered a cultural diversity essay, gender diversity essay, or a college community essay.
Rice University Essays

The current Rice acceptance rate is just 9% , making it a highly selective school. Because the Rice acceptance rate is so low, your personal statement and supplemental essays can make a huge difference.
The Rice University essay examples we’ll provide below are based on this prompt:
The quality of Rice’s academic life and the Residential College System are heavily influenced by the unique life experiences and cultural traditions each student brings. What personal perspective would you contribute to life at Rice?
Breaking down the prompt.
Like the prompt above, this cultural diversity essay asks about your “life experiences,” “cultural traditions,” and personal “perspectives.” These phrases indicate a cultural diversity essay. Keep in mind this may not be the exact prompt you’ll have to answer in your own Rice application. However, future Rice prompts will likely follow a similar framework as this diversity essay sample.
Although this prompt is not as flexible as the Georgetown prompt, it does let you discuss aspects of Rice’s academic life and Residential College System that appeal to you. You can also highlight how your experiences have influenced your personal perspective.
The prompt also asks about how you would contribute to life at Rice. So, your response could also fall in line with college community essay examples. Remember, college community essay examples are another sub-category of community essay examples. Successful college community essay examples will illustrate the ways in which students would contribute to their future campus community.
Williams Supplemental Essays

Like the Rice acceptance rate, the Williams acceptance rate is also 9% . Because the Williams acceptance rate is so low, you’ll want to pay close attention to the Williams supplemental essays examples as you begin the writing process.
The Williams supplemental essays examples below are based on this prompt:
Every first-year student at Williams lives in an Entry – a thoughtfully constructed microcosm of the student community that’s a defining part of the Williams experience. From the moment they arrive, students find themselves in what’s likely the most diverse collection of backgrounds, perspectives, and interests they’ve ever encountered. What might differentiate you from the 19 other first-year students in an Entry? What perspective would you add to the conversation with your peer(s)?
Reflecting on the prompt.
Immediately, words like “diverse,” “backgrounds,” “perspectives,” “interests,” and “differentiate” should stand out to you. These keywords highlight the fact that this is a cultural diversity essay. Similar to the Rice essay, this may not be the exact prompt you’ll face on your Williams application. However, we can still learn from it.
Like the Georgetown essay, this prompt requires you to put in some self-reflection before you start writing. What aspects of your background differentiate you from other people? How would these differences impact your interactions with peers?
This prompt also touches on the “student community” and how you would “add to the conversation with your peer(s).” By extension, any strong responses to this prompt could also be considered as college community essay examples.
Community Essays
All of the prompts above mention campus community. So, you could argue that they are also examples of community essays.
Like we mentioned above, you can think of community essays as a subcategory of the cultural diversity essay. If the prompt alludes to the campus community, or if your response is centered on how you would interact within that community, your essay likely falls into the world of college community essay examples.
Regardless of what you would classify the essay as, all successful essays will be thoughtful, personal, and rich with details. We’ll show you examples of this in our “college essays that worked” section below.
Which schools require a cultural diversity or community essay?
Besides Georgetown, Rice, and Williams, many other college applications require a cultural diversity essay or community essay. In fact, from the Ivy League to HBCUs and state schools, the cultural diversity essay is a staple across college applications.
Although we will not provide a diversity essay sample for each of the colleges below, it is helpful to read the prompts. This will build your familiarity with other college applications that require a cultural diversity essay or community essay. Some schools that require a cultural diversity essay or community essay include New York University , Duke University , Harvard University , Johns Hopkins University , and University of Michigan .
New York University

NYU listed a cultural diversity essay as part of its 2022-2023 college application requirements. Here is the prompt:
NYU was founded on the belief that a student’s identity should not dictate the ability for them to access higher education. That sense of opportunity for all students, of all backgrounds, remains a part of who we are today and a critical part of what makes us a world class university. Our community embraces diversity, in all its forms, as a cornerstone of the NYU experience. We would like to better understand how your experiences would help us to shape and grow our diverse community.
Duke university.

Duke is well-known for its community essay:
What is your sense of Duke as a university and a community, and why do you consider it a good match for you? If there’s something in particular about our offerings that attracts you, feel free to share that as well.

A top-ranked Ivy League institution, Harvard University also has a cultural diversity essay as part of its college application requirements:
Harvard has long recognized the importance of student body diversity of all kinds. We welcome you to write about distinctive aspects of your background, personal development, or the intellectual interests you might bring to your Harvard classmates.
Johns hopkins university.

The Johns Hopkins supplement is another example of a cultural diversity essay:
Founded in the spirit of exploration and discovery, Johns Hopkins University encourages students to share their perspectives, develop their interests, and pursue new experiences. Use this space to share something you’d like the admissions committee to know about you (your interests, your background, your identity, or your community), and how it has shaped what you want to get out of your college experience at Hopkins.
University of michigan.

The University of Michigan requires a community essay for its application:
Everyone belongs to many different communities and/or groups defined by (among other things) shared geography, religion, ethnicity, income, cuisine, interest, race, ideology, or intellectual heritage. Choose one of the communities to which you belong and describe that community and your place within it.
Community essay examples.
The Duke and Michigan prompts are perfect illustrations of community essay examples. However, they have some critical differences. So, if you apply to both of these schools, you’ll have to change the way you approach either of these community essays.
The Duke prompt asks you to highlight why you are a good match for the Duke community. You’ll also see this prompt in other community essay examples. To write a successful response to this prompt, you’ll need to reference offerings specific to Duke (or whichever college requires this essay). In order to know what to reference, you’ll need to do your research before you start writing.
Consider the following questions as you write your diversity essay sample if the prompt is similar to Duke University’s
- What values does this college community have?
- How do these tie in with what you value?
- Is there something that this college offers that matches your interests, personality, or background?
On the other hand, the Michigan essay prompt asks you to describe a community that you belong to as well as your place within that community. This is another variation of the prompt for community essay examples.
To write a successful response to this prompt, you’ll need to identify a community that you belong to. Then, you’ll need to think critically about how you interact with that community.
Below are some questions to consider as you write your diversity essay sample for colleges like Michigan:
- Out of all the communities you belong to, which can you highlight in your response?
- How have you impacted this community?
- How has this community impacted you?
Now, in the next few sections, we’ll dive into the Georgetown supplemental essay examples, the Rice university essay examples, and the Williams supplemental essays examples. After each diversity essay sample, we’ll include a breakdown of why these are considered college essays that worked.
Georgetown Essay Examples

As a reminder, the Georgetown essay examples respond to this prompt:
As Georgetown is a diverse community, the Admissions Committee would like to know more about you in your own words. Please submit a brief essay, either personal or creative, which you feel best describes you.
Here is the excerpt of the diversity essay sample from our Georgetown essay examples:
Georgetown University Essay Example
The best thing I ever did was skip eight days of school in a row. Despite the protests of teachers over missed class time, I told them that the world is my classroom. The lessons I remember most are those that took place during my annual family vacation to coastal Maine. That rural world is the most authentic and incredible classroom where learning simply happens and becomes exponential.
Years ago, as I hunted through the rocks and seaweed for seaglass and mussels, I befriended a Maine local hauling her battered kayak on the shore. Though I didn’t realize it at the time, I had found a kindred spirit in Jeanne. Jeanne is a year-round resident who is more than the hard working, rugged Mainer that meets the eye; reserved and humble in nature, she is a wealth of knowledge and is self-taught through necessity. With thoughtful attention to detail, I engineered a primitive ramp made of driftwood and a pulley system to haul her kayak up the cliff. We diligently figured out complex problems and developed solutions through trial and error.
After running out of conventional materials, I recycled and reimagined items that had washed ashore. We expected to succeed, but were not afraid to fail. Working with Jeanne has been the best classroom in the world; without textbooks or technology, she has made a difference in my life. Whether building a basic irrigation system for her organic garden or installing solar panels to harness the sun’s energy, every project has shown me the value of taking action and making an impact. Each year brings a different project with new excitement and unique challenges. My resourcefulness, problem solving ability, and innovative thinking have advanced under her tutelage.
While exploring the rocky coast of Maine, I embrace every experience as an unparalleled educational opportunity that transcends any classroom environment. I discovered that firsthand experience and real-world application of science are my best teachers. In school, applications of complex calculations and abstract theories are sometimes obscured by grades and structure. In Maine, I expand my love of science and renourish my curious spirit. I am a highly independent, frugal, resilient Mainer living as a southern girl in NC.
Why this essay worked
This is one of the Georgetown supplemental essay examples that works, and here’s why. The author starts the essay with an interesting hook, which makes the reader want to learn more about this person and their perspective.
Throughout the essay, the author illustrates their intellectual curiosity. From befriending Jeanne and creating a pulley system to engineering other projects on the rocky coast of Maine, the author demonstrates how they welcome challenges and work to solve problems.
Further, the author mentions values that matter to them—taking action and making an impact. Both facets are also part of Georgetown’s core values . By making these connections in their essay, the author shows the admissions committee exactly how they would be a great fit for the Georgetown community.
Finally, the author uses their experience in Maine to showcase their love of science, which is likely the field they will study at Georgetown. Like this writer, you should try to include most important parts of your identity into your essay. This includes things like life experiences, passions, majors, extracurricular activities for college, and more.
Rice University Essay Examples

The Rice University essay examples are from this prompt:
The quality of Rice’s academic life and the Residential College System are heavily influenced by the unique life experiences and cultural traditions each student brings. What personal perspective would you contribute to life at Rice? (500-word limit)
Rice university essay example.
Like every applicant, I also have a story to share. A story that makes me who I am and consists of chapters about my life experiences and adventures. Having been born in a different country, my journey to America was one of the most difficult things I had ever experienced. Everything felt different. The atmosphere, the places, the food, and especially the people. Everywhere I looked, I saw something new. Although it was a bit overwhelming, one thing had not changed.
The caring nature of the people was still prevalent in everyday interactions. I was overwhelmed by how supportive and understanding people were of one another. Whether it is race, religion, or culture, everyone was accepted and appreciated. I knew that I could be whoever I wanted to be and that the only limitation was my imagination. Through hard work and persistence I put my all in everything that I did. I get this work ethic from my father since he is living proof that anything can be accomplished with continued determination. Listening to the childhood stories he told me, my dad would reminisce about how he was born in an impoverished area in a third world country during a turbulent and unpredictable time.
Even with a passion for learning, he had to work a laborious job in an attempt to help his parents make ends meet. He talked about how he would study under the street lights when the power went out at home. His parents wanted something better for him, as did he. Not living in America changed nothing about their work ethic. His parents continued to work hard daily, in an attempt to provide for their son. My dad worked and studied countless hours, paying his way through school with jobs and scholarships. His efforts paid off when he finally moved to America and opened his own business. None of it would have been possible without tremendous effort and dedication needed for a better life, values that are instilled within me as well, and this is the perspective that I wish to bring to Rice.
This diversity essay sample references the author’s unique life experiences and personal perspective, which makes it one example of college essays that worked. The author begins the essay by alluding to their unique story—they were born in a different country and then came to America. Instead of facing this change as a challenge, the author shows how this new experience helped them to feel comfortable with all kinds of people. They also highlight how their diversity was accepted and appreciated.
Additionally, the author incorporates information about their father’s story, which helps to frame their own values and where those values came from. The values that they chose to highlight also fall in line with the values of the Rice community.
Williams Supplemental Essay Examples

Let’s read the prompt that inspired so many strong Williams supplemental essays examples again:
Every first-year student at Williams lives in an Entry—a thoughtfully constructed microcosm of the student community that’s a defining part of the Williams experience. From the moment they arrive, students find themselves in what’s likely the most diverse collection of backgrounds, perspectives and interests they’ve ever encountered. What might differentiate you from the 19 other first-year students in an entry? What perspective(s) would you add to the conversation with your peers?
Williams college essay example.
Through the flow in my head
See you clad in red
But not just the clothes
It’s your whole being
Covering in this sickening blanket
Of heat and pain
Are you in agony, I wonder?
Is this the hell they told me about?
Have we been condemned?
Reduced to nothing but pain
At least we have each other
In our envelopes of crimson
I try in vain
“Take my hands” I shriek
“Let’s protect each other,
You and me, through this hell”
My body contorts
And deforms into nothingness
You remain the same
Clad in red
With faraway eyes
You, like a statue
Your eyes fixed somewhere else
You never see me
Just the red briefcase in your heart
We aren’t together
It’s always been me alone
While you stand there, aloof, with the briefcase in your heart.
I wrote this poem the day my prayer request for the Uighur Muslims got denied at school. At the time, I was stunned. I was taught to have empathy for those around me. Yet, that empathy disappears when told to extend it to someone different. I can’t comprehend this contradiction and I refuse to.
At Williams, I hope to become a Community Engagement Fellow at the Davis Center. I hope to use Williams’ support for social justice and advocacy to educate my fellow classmates on social issues around the world. Williams students are not just scholars but also leaders and changemakers. Together, we can strive to better the world through advocacy.
Human’s capability for love is endless. We just need to open our hearts to everyone.
It’s time to let the briefcase go and look at those around us with our real human eyes.
We see you now. Please forgive us.
As we mentioned above, the Williams acceptance rate is incredibly low. This makes the supplemental essay that much more important.
This diversity essay sample works because it is personal and memorable. The author chooses to start the essay off with a poem. Which, if done right, will immediately grab the reader’s attention.
Further, the author contextualizes the poem by explaining the circumstances surrounding it—they wrote it in response to a prayer request that was denied at school. In doing so, they also highlight their own values of empathy and embracing diversity.
Finally, the author ends their cultural diversity essay by describing what excites them about Williams. They also discuss how they see themselves interacting within the Williams community. This is a key piece of the essay, as it helps the reader understand how the author would be a good fit for Williams.
The examples provided within this essay also touch on issues that are important to the author, which provides a glimpse into the type of student the author would be on campus. Additionally, this response shows what potential extracurricular activities for college the author might be interested in pursuing while at Williams.
How to Write a Cultural Diversity Essay
You want your diversity essay to stand out from any other diversity essay sample. But how do you write a successful cultural diversity essay?
First, consider what pieces of your identity you want to highlight in your essay. Of course, race and ethnicity are important facets of diversity. However, there are plenty of other factors to consider.
As you brainstorm, think outside the box to figure out what aspects of your identity help make up who you are. Because identity and diversity fall on a spectrum, there is no right or wrong answer here.
Fit your ideas to the specific school
Once you’ve decided on what you want to represent in your cultural diversity essay, think about how that fits into the college of your choice. Use your cultural diversity essay to make connections to the school. If your college has specific values or programs that align with your identity, then include them in your cultural diversity essay!
Above all, you should write about something that is important to you. Your cultural diversity essay, gender diversity essay, or community essay will succeed if you are passionate about your topic and willing to get personal.
Additional Tips for Community & Cultural Diversity Essays

1. Start Early
In order to create the strongest diversity essay possible, you’ll want to start early. Filling out college applications is already a time-consuming process. So, you can cut back on additional stress and anxiety by writing your cultural diversity essay as early as possible.
2. Brainstorm
Writing a cultural diversity essay or community essay is a personal process. To set yourself up for success, take time to brainstorm and reflect on your topic. Overall, you want your cultural diversity essay to be a good indication of who you are and what makes you a unique applicant.
3. Proofread
We can’t stress this final tip enough. Be sure to proofread your cultural diversity essay before you hit the submit button. Additionally, you can read your essay aloud to hear how it flows. You can also can ask someone you trust, like your college advisor or a teacher, to help proofread your essay as well.
Other CollegeAdvisor Essay Resources to Explore
Looking for additional resources on supplemental essays for the colleges we mentioned above? Do you need help with incorporating extracurricular activities for college into your essays or crafting a strong diversity essay sample? We’ve got you covered.
Our how to get into Georgetown guide covers additional tips on how to approach the supplemental diversity essay. If you’re wondering how to write about community in your essay, check out our campus community article for an insider’s perspective on Williams College.
Want to learn strategies for writing compelling cultural diversity essays? Check out this Q&A webinar, featuring a former Georgetown admissions officer. And, if you’re still unsure of what to highlight in your community essay, try getting inspiration from a virtual college tour .
Cultural Diversity Essay & Community Essay Examples – Final Thoughts
Your supplemental essays are an important piece of the college application puzzle. With colleges becoming more competitive than ever, you’ll want to do everything you can to create a strong candidate profile. This includes writing well-crafted responses for a cultural diversity essay, gender diversity essay, or community essay.
We hope our cultural diversity essay guide helped you learn more about this common type of supplemental essay. As you are writing your own cultural diversity essay or community essay, use the essay examples from Georgetown, Rice, and Williams above as your guide.
Getting into top schools takes a lot more than a strong resume. Writing specific, thoughtful, and personal responses for a cultural diversity essay, gender diversity essay, or community essay will put you one step closer to maximizing your chances of admission. Good luck!
CollegeAdvisor.com is here to help you with every aspect of the college admissions process. From taking a gap year to completing enrollment , we’re here to help. Register today to receive one-on-one support from an admissions expert as you begin your college application journey.

This essay guide was written by senior advisor, Claire Babbs . Looking for more admissions support? Click here to schedule a free meeting with one of our Admissions Specialists. During your meeting, our team will discuss your profile and help you find targeted ways to increase your admissions odds at top schools. We’ll also answer any questions and discuss how CollegeAdvisor.com can support you in the college application process.
Personalized and effective college advising for high school students.
- Advisor Application
- Popular Colleges
- Privacy Policy and Cookie Notice
- Student Login
- California Privacy Notice
- Terms and Conditions
- Your Privacy Choices
By using the College Advisor site and/or working with College Advisor, you agree to our updated Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy , including an arbitration clause that covers any disputes relating to our policies and your use of our products and services.

How to Write an Essay about Your Culture

Do you need to write an essay about your culture but don’t know where to start? You’ve come to the right place! I’m Constance, and I’ll show you how to write an essay about your culture. I’ll guide you step by step, and we’ll write a sample essay together. Let’s dive in.
Writing an essay about your culture includes 5 steps:
Step 1. Plan how many words you want in each paragraph.
When you know the exact number of words you need for an essay, planning the word count for each paragraph will be much easier.
For example, a 300-word essay typically consists of five paragraphs and three key elements:
- The introductory paragraph.
- Three body paragraphs.
- The conclusion, or the concluding paragraph.
Here’s a simple way to distribute 300 words across the five paragraphs in your essay:
You’ll get 300 when you add up these numbers.
Step 2. Decide on what your main and supporting points will be.
First, you must take a stand, meaning you must decide on your main point. What do you really want to say about your culture? Whatever you want to say, that becomes your thesis.
For example, “My culture is very rich.” That is enough to get started. You’ll get a better idea of how to expand or tweak your thesis after the next step.
Next, divide your topic using the Power of Three to prove the point that your culture is rich using three supporting ideas.
The Power of Three effectively divides an essay’s main idea into its supporting points. It means your main idea is true because of the three reasons you will provide in the body. So, it is a three-part structure that helps produce your body paragraphs .
Let’s try it for an essay about Filipino culture!
For example, here are three supporting ideas explaining the richness of Filipino culture:
- The Philippines has incredible food .
- Traditional Filipino clothing reflects the country’s heritage.
- Family values in the Philippines are essential.
Great! Now we have everything we need to write an essay about Filipino culture. We’re all set for the next step!
Step 3. Write your introductory paragraph.
Here are the key components of an introductory paragraph you need to remember in writing your essay:
Our first sentence is the introduction, which should pull our reader into the world we want to portray in our essay.
And the rest of the introductory paragraph is our thesis statement. It includes our main idea and three supporting points.
Example of an introductory paragraph about culture
“Having been colonized for centuries, the Philippines boasts a vast heritage. It has a rich culture characterized by food, clothing, and family values. Filipino culture has delicious food inherited from diverse parts of the world and periods of conquest. Traditional Filipino clothing reflects the country’s history, as well. And Filipinos prize their family values probably above all else.”
Look at how the introductory paragraph goes from a general statement to specific ideas that support our main idea.
Our introductory sentence is a general statement that serves as the opening in our essay. It briefly sets the essay’s context. Next comes the thesis statement — our main idea. Finally, we have three supporting ideas for our thesis.
Step 4. Write your essay’s body paragraphs.
Again, a 300-word essay typically has three body paragraphs containing your three supporting ideas. Here’s how to structure a body paragraph:

Looking back at our word count plan, we know that our body paragraphs should have roughly 70 words each. Remember your word plan as you write.
Body Paragraph 1
“The Philippines boasts a diverse food culture. It reflects indigenous flavors and foreign influences, such as American, Spanish, Indian, and Chinese. Whether it’s a typical or special day, Filipinos love eating these various dishes with rice, a staple. For example, rice goes well with curry, noodles, and adobo. It is also common to see various foods like pizza, pancit, lumpia, paella, (Filipino-style) sweet spaghetti, cakes, and ice cream at parties.”
As you can see, the first sentence in this body paragraph is a topic sentence . It gives context to the paragraph and briefly summarizes it.
The second sentence explains why the Philippine food culture is considered diverse.
The remaining sentences illustrate your main point (topic sentence) by providing examples, starting with rice in sentence 3.
Body Paragraph 2
“Traditional Filipino clothing reflects Philippine cultural heritage. Although Filipinos now conform to current fashion trends in their everyday lives, the traditional clothing style is often used during celebrations. The traditional fashion sense exhibits influences from indigenous tribes, Chinese immigration waves, the Spaniards, and Americans, portraying the chronology of Philippine historical events. For example, the Philippines’ national costume, the baro’t saya, is an elegant blend of Spanish and Filipino clothing styles. Even some modernized forms of clothing also display other global influences.”
Just like Body Paragraph 1, this paragraph follows the same structure outlined in the diagram. It proceeds from a general statement to more specific points :
- The topic sentence.
- An explanation.
Body Paragraph 3
“Family values are vital in the Philippines. The daily lives of most Filipinos revolve around close and extended family, making them known for their family-oriented lifestyle even when they’re overseas. It’s common for children to live with their parents after reaching legal age; some even stay after getting married or obtaining a job. Filipinos also cherish their extended families (aunts, uncles, grandparents, and cousins) and hanging out or celebrating significant events together.”
Once again, this paragraph follows the body paragraph structure. Now, we’re all set for the final step — the conclusion.
Step 5. Write the conclusion.
The easiest way to write a concluding paragraph for your essay on your culture is to restate your main idea and its supporting points using different words. You can even paraphrase your introduction — a time-proven method!
Let’s write the conclusion for our essay.
“Because of its history, the Philippines has a rich, diverse culture rooted in a vast heritage. Filipino cuisine is a blend of indigenous and foreign flavors. The nation’s history is reflected in its traditional clothing. And family values display a distinct Filipino trait.”
Note that this conclusion uses different words to restate the points we’ve already made, including those in the body paragraphs.
Hope this was helpful. Now go ahead and write an essay about your culture!
Tutor Phil is an e-learning professional who helps adult learners finish their degrees by teaching them academic writing skills.
You Might Like These Next...
How to Write a 300 Word Essay - Simple Tutorial
https://youtu.be/qXST2gJbkhw If you need to write a 300-word essay, you’ve come to the right place. I’m Tutor Phil, and in this tutorial I’ll guide you through the process step by...
Essay Writing for Beginners: 6-Step Guide with Examples
https://youtu.be/w6yanrc1a_g If you need to write an essay, whether for a college course or to pass a writing test, this guide will take you through the process step-by-step. Even if you have...
What Is Culture Essay Writing – Expert’s Guide
- Essay Tips&Tricks
- Essay Writing Guides

Culture is an important component of human life, which helps to find like-minded people. We should not forget that culture can be expressed in different situations, such as food, music, outlook on life, and even clothing. It is important to understand that despite differences in different cultures, you should always respect and be friendly to others.
Culture Essay Explained
To begin with, let’s figure out what a culture essay is. Simply put, this is a kind of description of a culture, starting from your thoughts and opinions. In society, culture helps to understand what norms exist for people. You can write culture essays on completely different topics related to culture because it manifests itself in all components of our lives. These are dances, art, technology, and even music.
Culture determines what is acceptable and what is unacceptable in any society. Based on this, it can be understood that a culture essay is a popular writing style because it can describe your personal opinion about culture and express your thoughts and views.
What Is the Importance of Culture in Human Life?
Culture plays a very important role in our life. It helps people to ensure social well-being in society and find like-minded people. Culture in society is one of the main life factors that help people express their education and development. You can understand a cultured person or not by the way he communicates with people in society.
For many people, culture is as important a factor as their personal lives and family values. Watching people, you might notice that people who adhere to the same culture immediately have an inextricable connection and many common interests because such people are connected not only by common views on the world but also by tastes in food, traditions, and much more.
How to Write a Culture Essay Outline
To write a successful culture essay, it is important to understand where to start and stick to a clear plan. A writing plan should be in each piece so the reader can understand and navigate the article’s essence.
This is especially true for a research paper and an argumentative essay because, in such reports, you must specifically describe the subject of research and argue your conclusions. But writing structure is just as important for culture essays, so here are the important steps in writing a plan:
First, you need to consider the introduction because it is regarded as one of the most important parts of the essay. Here you should present the most important information discussed in the main part so that the reader is interested and wants to read the text further.
Create a short thesis with which you will convey the essence of the essay to the audience and briefly express your opinion on this topic.
Work on the basic information you will be using. It is very important to write about those things that are interesting to you and that you understand. Suppose this is a new topic for you. In that case, it is best to check the integrity of the information on several sources several times so as not to misinform the reader and arouse the desired interest in your article.
Write your findings. In many essay examples, the author writes his conclusion based on personal experience and thoughts. Never try to write similarly. For a successful culture essay conclusion, noting how you feel and conveying your emotions from personal experience and knowledge is important.
Writing an Introduction to a Culture Essay
The introduction is one of the most important parts of any essay. When starting to write an introduction, you should already understand what you will talk to the reader about in the future. It is important to remember that the information you use in this section should be discussed in the main part and be argued with facts and supported by your real-life examples.
Writing an introduction is often difficult and energy-consuming for a writer because this paragraph should contain only the most important information from your text that will be able to interest the reader.
To make it easier, you can write the introduction after you’ve completed the main text, but it’s important to decide on the topic and abstract first. For example, at the beginning of the culture essay, you need to tell the audience about the issue you will be discussing and then familiarize the readers with the thesis.
Next, talk with the reader about your opinion on this topic and tell a little about yourself so that people can imagine the person who writes about the issue of interest to them.
Writing a Body of a Culture Essay
The body of your culture essay should introduce the reader to the culture you are researching. Therefore, it is important to convey all the emotions when writing so that people have a clear picture and understanding of the culture. A culture essay is a combination of a descriptive essay and an argumentative essay where you also describe and argue your opinion on a given topic.
The body of your essay may include several paragraphs and headings. In each paragraph, you will describe different aspects of this culture and your arguments for them. This section should explain to the reader why you have chosen this particular topic for writing so that people clearly understand your interest in the topic of culture.
Using personal examples and arguments from your life best draws the reader. It is important to write in a language understandable to the reader. Try to use simple, uncomplicated phrases with which you will arouse confidence and pleasant emotions in your audience. Imagine that you are talking to a reader. Writing an essay is a simple and accessible language that will help connect the reader and keep them interested.
Writing a Conclusion for a Culture Essay
After you have written the main part of your essay, you should summarize all of the above. To do this, you must analyze all the information and briefly state it to the reader. It is important not to deviate from your opinion and only try to back it up with appropriate phrases. In conclusion, you can once again repeat your statement about this culture or emphasize its main nuances.
In many essay examples, the authors write a huge paragraph with conclusions, touching on other topics there that have nothing to do with this, so you shouldn’t do it because, in conclusion, the main thing is to write it short and clear so that the reader can immediately understand the whole essence of what you wrote on this section.
Try to choose the right words and not pour water just like that. The main thing in this paragraph is the logical compilation of the results of all of the above.
The Most Interesting Cultural Topics
Culture essays are one of the best ways to do personal research about culture. In this kind of descriptive essay, you can analyze a huge number of topics and traditions of a particular culture and learn about the cultural origins of different types of people.
When choosing a topic for writing a culture essay, you need to be very serious and try to select the case that you will be interested in discussing, and you can describe all aspects of culture in such colors so that the reader can share your point of view and get carried away reading the article. So here are some interesting topics to talk about in your culture essay:
- Similarities between different cultures
- The influence of religion on culture
- The difference between the cultures of other continents
- Gender characteristics and the impact of cultures on them
- The role of culture in the personal growth of a person
- Popular cultures
- How is the Internet changing culture?
Tips for Writing a Successful Culture Essay
It’s no secret that before you start writing an essay, you need to create a so-called draft, in which you indicate for yourself all the most important points of the article and determine the sequence in which information is presented.
In a culture essay, it is important to adhere to the structure for the reader to understand what you are writing about. Here are some tips on how to make your essay successful and interesting:
Be Responsible in Your Topic Selection Process
The cultural topic is very relevant and extensive, so you should have no problem choosing. However, suppose you cannot decide which topic you would like to consider. In that case, you have the opportunity to look at a list of interesting and relevant issues on the Internet and then write an essay with a personal opinion on this matter. You can read other essay examples, but the main thing is not to use another author’s opinion in your article; this essay should be written based on personal experience and your own opinion.
Choosing a topic can seem quite complicated because you have to decide what you will have to communicate with your readers about, having previously studied all the nuances and made certain personal conclusions about it.
Make Sure to Express Your Unique Views
Culture essay aims to express personal views and thoughts on the topic you are discussing. Therefore, try to describe your opinion and understanding of this topic as clearly and reasonably as possible.
Despite this, you can use knowledge and information from other sources, but if you use it in your text, it is important to indicate exactly where you got this information from so that no plagiarism is detected during the critical writing report assessment, which is very important for an essay of this kind.
Avoid Repetition
For example, if you use the same phrase several times in the text, the best option would be to rephrase it so that it does not change its meaning but sounds different at the same time.
Use Only Proven Information
Imagine that you are writing a research paper and carefully studying the chosen topic. In no case do not use fictitious facts in the text. Instead, only reliable information should be supported by your arguments.
Utilize Linear Writing Style
Use the linear writing style of the culture essay. This will help the reader to read your article in a logical and structured way continuously.
Write a Clear Thesis and Stick To Your Position Throughout the Essay
Write in plain language that is easy for the reader to understand. Do not use complicated terms and phrases. The reader should feel as if you are talking to him.
Example of a Culture Essay and Essay Writing Services
We will look at the culture essay, which reveals the meaning of culture and how it changes and develops in the modern world. This one of the decent essay examples discusses how culture affects our lives and explains how different cultures exist worldwide.
Introduction
1.1 Definition of the term “Culture”
1.2 A story about the origin of culture and its development
1.3 Thesis: Culture is one of the main factors in our life and the lives of every person. Although culture changes over time, it remains in each of us
- What does culture mean?
2.1 Culture reflects the inner qualities of a person
2.2 Culture develops according to the development in our life
- Differences between different cultures
3.1 What are the differences, and why do you need to understand cultural differences
- What is the purpose of culture in human life?
Culture is a kind of collection of all parts of society. This is a huge complex of different beliefs and thoughts of people that were created over time. Culture can change depending on the other factors that influence it, as it keeps up with the times, and we all know that concepts and views can change over time. Each country has its own culture and traditions, and people in different countries express themselves in this way.
Having studied the culture of another country, you can understand the way of thinking of the people who live there and understand their values. To understand a person of another nation, it is enough to study his culture in detail.
Since culture is an indicator of human fulfillment, it can change at different times and places and remain individual for each nation.
What Does Culture Mean?
Culture describes the concepts and attitudes of people in different groups. People themselves create their own culture, this does not happen immediately, but after a long time, despite this, it exists. Other groups of people can be of the same culture, but they will still have completely different views on life and concepts. In the process of life, a person’s opinions and thoughts may change, but faith in one’s culture remains unchanged.
Differences Between Different Cultures
The differences between different cultures can depend on many factors, personal moral principles, political views, and even differences in musical tastes or food tastes. For example, in many countries, people do not eat pork meat, while in others, it is the norm. Therefore, when communicating in or coming into a society where there are people of other cultural concepts, it is important to consider other people’s interests so that respect appears in the group.
Understanding cultural differences of this kind will help to find mutual understanding among people and make them a single whole. Each person must respect the culture and views of other people, and only then will understanding and love reign in our world.
What Is the Purpose of Culture in Human Life?
Culture is important in all moments of human life, especially when you are in society. For example, when you come to a new job, you find yourself in a team where everyone has different thoughts and views. Therefore, it is important to respect the opinions of other people and in no case try to prove your point of view to others. Culture is also very important because, to some extent, it helps to find like-minded people and create a warm and friendly atmosphere in society.
If you have any difficulties writing a culture essay, you can always turn to essay writing service , where you will meet real professionals who will answer all your questions and do the hard work for you at an excellent price and in a short time. Moreover, you can be sure that each author has a degree in the field of culture, and your essay will be written with high quality and success.
Business Essay and the Best Way of Its Writing
Business is an essential aspect of today’s evolving world. It is a lucrative industry that impacts many sectors, including education. Business-related courses are popular as many students are pursuing the… Read More
- Academic Writing Tips

All About Persuasive Essay Writing
Writing a persuasive essay requires expressing your viewpoint and convincing readers of its rightfulness. Many struggle with completing this type of written assignment because of a lack of proper writing… Read More

How to write an anthropology essay perfectly?
Stuck with an anthropology essay with no help in sight? Anthropology essay writing is not a simple task. Not many college students can handle such a paper. An anthropology essay… Read More

Table of contents
Essays About Culture and Society: Top 5 Examples
Culture and society are complicated topics that can’t exist without each other. See our essays about culture and society examples and prompts for your writing.
Writing essays about culture and society is common among those taking social and cultural studies. As its name suggests, this field explores past and present customs and beliefs within society. This area offers career opportunities in education, medicine, human resources, and others. Creating an essay about this subject requires cultural and social knowledge gained through reliable sources and personal experience.
5 Essay Examples
1. the concept of culture and society by alex adkins, 2. native american culture and society by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 3. society, culture, and civilization essay by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 4. cultural norms and society by lucille horton, 5. the impact of culture & society on the children’s development by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 1. defining culture and society, 2. the importance of culture and society, 3. culture and society: the medieval era, 4. the american culture and society today, 5. the influence of korean culture on today’s society, 6. how media influences culture and society, 7. culture and society: lgbtqia+.
“Culture, as often defined in most sociology textbooks, is the way of life of a society. It is the sum of the ideas, beliefs, behaviors, norms, traditions, and activities shared by a particular group of people. According to Giddens (1989), any society cannot exist without a culture.”
Adkin’s essay contains several passages explaining the concept, role, and importance of culture and society. He describes culture as a vital aspect of society, referring to it as the one that binds its citizens. To further discuss the role of culture in society, Adkin mentions Japanese and Chinese cultures to prove that culture sets the difference between societies.
As for society, Adkin says that culture builds and facilitates social institutions to interact with each other. These include family, religion, government, etc., which are responsible for the development of an individual and the type of society. He explains that society changes because of culture. As a person grows up, they are exposed to different situations and realizations that give them new perspectives affecting their cultural heritage.
Looking for more? Check out these essays about culture shock .
“Native Americans are the native people of the North, Central, and South America. There are many types of Native Americans such as Arikara, Iroquois, Pawnee, Sioux, Apache, Eskimo, Cree, Choctaw, Comanche, etc. Cherokee people have a diverse society and culture.”
While the author lists various types of Native American societies, they focus on one prominent tribe from the Iroquoian lineage, the Cherokee. The author shares fascinating facts about the tribe.
The author describes why the Cherokee refer to themselves as cavemen, and Cherokee women are powerful but still equal to men, explaining their matrilineal society. As one of the civilized tribes in America, the Cherokees are a diverse society that accepts other tribes, but they cannot marry someone from the same clan. Cherokee culture includes the Booger mask dance and the Iroquoian language.
“Society can comprise people groups that have not developed civilization yet, as it concerns any relationship of the individuals. Culture is prior to civilization since it shapes the communities, making them highly adaptive to the specific conditions in which they live. Civilization is dependent on both concepts because it absolutizes societal norms and traditions and elevates material culture and virtues to the most complicated stage.”
To understand the concept of man, the author describes society as a group of families conforming to a particular set of customs and practices known as culture. On the other hand, civilization results from prolonged and continuous changes in culture and society. The writer believes that although they are different from each other, these three constructs are interrelated and essential to complete the whole sequence of the modern human experience.
Looking for more? Check out these essays about globalization .
“Different countries have different cultures. This is because different countries are composed of multitudes of different norms. Norms are commonly established when a majority of the society’s population practice a particular or common habit of living.”
In this essay, the writer defines society as an association, culture as a collection of characteristics, and norms as standard practices. Since society is defined by culture, historical events, and norms that define culture, and culture is the most potent aspect of civilization, Horton views cultural norms as the primary support of society.
The essay also includes examples that explain the topic, such as comparing East and West cultures. Horton believes that while everyone has a different culture, understanding a person’s culture before making a comment or judgment is essential.
“Culture plays an essential job in affecting this improvement, and what is viewed as ‘typical’ advancement change incredibly starting with one culture then onto the next. The general public and culture in which one grows up impact everything from formative developments and child rearing styles to what sorts of hardship one will probably confront.”
In this essay, the author uses their personal experiences to show the real impact of cultural traditions and values on the thought process and worldview as a child grows. As a Muslim, the writer was introduced to various rites and rituals at a young age, such as fasting. They believe this ritual teaches them to control their desires and care for the poor. Ultimately, society significantly impacts youth, but learning about social and cultural differences helps people, especially parents, to guide their child’s developmental process.
7 Prompts for Essays About Culture and Society
The Oxford Dictionary defines culture as a group’s customs, beliefs, and way of life, while society is people living in a community. Use this prompt and be creative in explaining the meaning of culture and society. Explore and use various dictionaries and add quotations from studies and books such as ” Culture and Society, 1780-1950 .” Then, define culture and society by picking the common ideas gathered through this compiled knowledge.

Culture is vital to society because one cannot function without the other. For this prompt, delve into the specifics of this connection. Depending on your approach, you can divide the body of your paper into three sections to separate and discuss their importance: culture, society, and culture and society. In the third section, explain the possible impact if one of them does not work correctly. Conclude your essay by summarizing and answering the question, “what is the importance of culture and society?”.
Culture and society constantly change for various reasons, including new technological inventions. For this prompt, identify and discuss the main features and significant influences of the medieval era. Explain the reasons for its changes and why society evolved to new societal norms and cultural changes. Consider whether there’s a chance to bring the positive parts of old cultures and societies to the modern day.
Today, culture in the US is a diverse mix of practices, beliefs, and traditions. This is due to the large number of people immigrating to the US from different countries worldwide. As a culturally diverse country, use this prompt to discuss America’s social and cultural characteristics, such as language, cuisine, music, religious beliefs, and more. Then, explain how Americans keep up with these changes in their normal culture.
Are you interested in writing about diversity? Check out our guide on how to write an essay about diversity .

If you love music, you’ve probably heard of KPOP or BTS . Korean pop music is just one part of South Korean culture that has traveled globally. In this prompt, discuss the aspects of Korean culture that are prevalent today worldwide. Research when and where these cultural trends began and why they became popular in other parts of the world. To create an engaging essay, conduct interviews with your classmates to ask if they know anything about Korean culture.
Do you want to write about music instead? Check out our essays about music topic guide !
Any form of media, such as print media, music, and the internet, dramatically influences culture and society. For example, streaming platforms like Netflix and Disney+ are hugely influential in today’s society, particularly among young people. In this essay, discuss today’s most popular forms of media and look at how they can influence culture and society. This could be as simple as influencing slang language, fashion, or popular careers such as becoming an influencer.
Recent studies show that the US has shifted its attitude toward the LGBTQIA+ community. With a rise in Americans who embrace new perspectives and now recognize same-sex marriage and parenthood. To effectively discuss the topic, including current issues within the LGBTQIA+ community, such as violence and bullying, and research the steps taken by government organizations to combat it.

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents

Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Democratic societies are often characterized by extensive pluralism of religions, cultures, ethnicities, and worldviews, on the basis of which citizens make claims against their state. Democratic states are additionally characterized by a commitment to treat all citizens equally, and so they require fair and just ways to wade through and respond to these claims. This entry considers cultural claims in particular.
Cultural claims are ubiquitous in political and legal spaces. Not only do individuals and groups both make cultural claims against the state, often for legal or political accommodations, but the state often explains its choices in terms of protecting particular aspects of its culture. This entry will first examine the ways in which “culture” is defined by political and moral philosophers: culture-as-encompassing group, culture-as-social-formation, culture-as-narrative/dialogue, and culture-as-identity. Over the course of this discussion, the “essentialist” challenge will be introduced: an essentialist account of culture is one that treats certain key characteristics of that culture as defining it and correspondingly all of its members must share certain key traits in order to be treated as members (for more, see Phillips 2010). In particular, the entry goes on to note that early conceptions of culture-as-encompassing groups are criticized for being essentialist, and later conceptions are attempts to reformulate culture in ways that avoid the essentialist challenge.
Following an articulation of these main ways of understanding culture, the entry turns to an assessment of distinct (though occasionally overlapping) types of cultural claims that are pressed against the state by minority groups: exemption claims, assistance claims, self-determination claims, recognition claims, preservation claims (and claims against coerced cultural loss), defensive claims in legal settings, and exclusive use claims (claims against cultural appropriation). There are both justifications for, and objections to, these claims, and they often hinge on how “culture” is understood. In many cases, the disputes about the justifiability of these claims hinge on competing understandings of what culture is, and especially, how valuable it is to those who are members, as will be shown below. Finally, the entry will close with an assessment of cases where a majority community makes cultural claims to justify actions, mainly in the context of controlling immigration and, in some cases, refusing entry to potential migrants all together, as well as the cultural demands it makes of those who are admitted, and the range of justifications and objections offered in these cases. This section considers the content of the majority culture, to which newcomers are asked to adhere, as well as how forcibly they can be “asked” to do so.
1.1 Culture-as-encompassing-group
1.2 culture-as-social-formation, 1.3 culture-as-dialogue, 1.4 culture-as-identity (or identity rather than culture), 2.1 exemption rights, 2.2 assistance rights, 2.3 self-determination rights, 2.4 recognition rights, 2.5 cultural preservation rights, 2.6 rights against cultural loss, 2.7 cultural defense rights, 2.8 exclusive cultural use rights (or rights against cultural appropriation), 3.1 cultural continuity and exclusion rights, 3.2 cultural continuity and integration enforcement rights, 4. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries, 1. defining culture.
Defining the term “culture” is very challenging: it has been described as both a “notoriously overbroad concept” (Song 2009: 177) and a “notoriously ambiguous concept” (Eisenberg 2009: 7). It is deployed in multiple ways: as the entry will go on to consider in more length, the term “culture” can refer to the set of norms, practices and values that characterize minority and majority groups, for example by noting that the Hasidic Jewish communities in New York practice a unique “culture”, or by describing Italian or Senegalese culture. But it is also used in other ways, for example, to refer to “bro” culture or “hipster” culture, or the culture of British football fans. Moreover, any one person can be a member of multiple cultures—someone (like this writer!) can be a member of the Canadian culture, the Ottawan culture, the Jewish culture, and the academic culture at the same time. Contextual considerations will explain why the norms, practices, and values that define each of these cultures become relevant at a particular moment. Moreover, only some of these cultures have political and legal relevance; only those that do are the focus of this entry.
In the political and legal spheres, there is widespread disagreement about what culture is , and the next section is focused on elaborating these distinct views of culture. There is however considerable agreement that whatever it is, it matters to people and the meaning and value it provides to the lives of individuals are among the most important reasons, if not the most important ones, to defend and protect it in legal and political spaces. This value is why it is important to attempt to discover what culture is and correspondingly why, and which aspects of it in particular, should or should not be protected in the public sphere. Notice that the observation that cultures are valuable to people, and indeed that they bring value to the lives of individuals, is not the same as saying that individual cultural practices are all good. Any defensible account of culture must take seriously the importance of culture in general without defending all of its instantiations. There are four main ways in which culture has been interpreted: as an encompassing group, as social formation, in dialogic terms, and in identity terms.
One way to think about culture is as a kind of all-encompassing whole, which shapes all or most dimensions of our lives. It is perhaps Will Kymlicka’s formulation of a “societal culture” that is most responsible for generating serious reflection on the nature of culture understood in this way. A societal culture
provides its members with meaningful ways of life across the full range of human activities, including social, educational, religious, recreational and economic life, encompassing both public and private spheres. (Kymlicka 1996: 76)
Kymlicka explains that a vibrant societal culture provides a “context for choice”, i.e., it provides the resources that individuals rely on to make sense of their world and the choices it offers. On this account, nation-states are well-described as having a societal culture, as are Indigenous groups and sub-state national minority groups (for example, the Catalans or the Tibetans); immigrant groups which sustain a range of cultural practices and norms even as they integrate into a larger “societal culture” are not.
Kymlicka is not alone in offering an encompassing account of culture. Michael Walzer too offers such an account, proposing that we understand political communities as “communities of character”, in which members are bound by a “world of common meanings” (Walzer 1983: 28). Avishai Margalit and Joseph Raz also describe so-called “encompassing” groups, in which their members
find in them a culture which shapes to a large degree their tastes and opportunities, and which provides an anchor for their self-identification and the safety of effortless secure belonging. (Margalit & Raz 1990: 448)
Avishai Margalit and Moshe Halbertal say of an encompassing group that its culture “covers various important aspects of life”, and in so saying, they offer as an example the Ultra-Orthodox Jewish culture:
it defines people’s activities (such as Torah study in Ultra-Orthodox culture), determines occupation (such as circumciser), and defines important relationships (such as marriage). It affects everything people do: cooking, architectural style, common language, literary and artistic traditions, music, customs, dress, festivals, ceremonies…the culture influences its members’ taste, the types of options they have and the meaning of these options, and the characteristics they consider significant in their evaluation of themselves and others. (Margalit & Halbertal 1994: 498)
Whereas Kymlicka emphasizes the freedom that is offered by a robust societal culture, Margalit and Halbertal speak of its role in securing members’ “personality identity” (Margalit & Halbertal 1994: 502) and Walzer of its importance in shaping a “collective consciousness”. Although these scholars justify the protection of a robust culture for many reasons, they agree that what culture does, fundamentally, is offer a background value system that helps members select among options and interpret their value, including for example with respect to certain forms of employment, or education, or family structure and child-rearing. Walzer captures the way in which culture informs how even the most basic of things are understood:
a single necessary good, and one that is always necessary—food, for example—carries different meanings in different places. Bread is the staff of life, the body of Christ, the symbol of the Sabbath, the means of hospitality, and so on. (Walzer 1983: 8)
Much is illuminated by these accounts of culture, including especially why depleted societal cultures may be less able to provide the context for choice that Kymlicka emphasizes, or why one’s “personality identity” may thereby be threatened: if a cultural group’s educational, political, or economic systems are weakened, their capacity to support members to make sense of the world, and choose among options, is likewise weakened. Moreover, this account illustrates the wrong of undermining the cultures of others: if a culture is undermined, the choices available to its members are thereby reduced. We can see this with respect to Indigenous culture in many states: where states have actively attempted to erase Indigenous culture, the result has been severe social dislocation and alienation among Indigenous peoples whose context for choice has been substantially weakened.
However, multiple objections have been launched at this way of understanding culture, most of which are variants on what is termed the “essentialist” objection; notice, though, that the views described above are not believed by their holders to be essentialist. The essentialist objection targets what it sees as an assumption that members of a culture will hold the same set of practices, norms, and values to be important, and in the same measure. But, say critics, this assumption does not hold: in any actual culture, members will be differently committed to its defining practices and norms, and indeed, there will necessarily be disagreement around which of its practices and norms are defining in the first place. The essentialist objection says, roughly, that treating culture as encompassing wrongly does one of the following things: 1) it proclaims that certain features of a culture are at its core and therefore immutable, on pain of dissolving the culture (Eisenberg 2009: 120), and correspondingly that cultures are necessarily bounded and determinate rather than contested and fluid (Moore 2019; Patten 2014: 38); 2) having identified these features as at a culture’s core, it excludes those who believe themselves to be members but do not conform to, display, or respect these features (Parvin 2008: 318–19); and, 3) it ignores the reality that most people in a liberal society “draw their identity from a multiplicity of roles and communities and memberships at any one time” (Parvin 2008: 321), which can variously have social salience, depending on the context, both independently of, and sometimes in conjunction with, cultural identities (Moore 2019). In summary, a too-encompassing account of what culture is for its members runs the risk of treating the boundaries of a culture as if they are determinate, unshifting, and as though its members display no variance (and perhaps cannot display variance) in their commitment to the culture as a whole and its defining practices.
The alternative accounts of culture that are considered below are all, at least in part, intended to respond to the essentialist challenge; their objective is, in other words, to generate a plausible account of what culture is , and correspondingly what it means to be a member of a particular cultural group, that can be deployed to make sense of legal and political controversies, and ideally adjudicate among them, without succumbing to the essentialist challenge. A caveat: the views of culture treated below should be understood as “ideal types”, characterized so as to understand its key features, how it is differentiated from other views, and why it does not fall victim (in its own estimation) to the essentialist challenge.
One attempt to reconceive culture in a way that responds to the essentialist challenge, but which retains a view of culture as largely encompassing, proposes that cultures are defined by their members’ shared experience of social formation (Patten 2014: 39). On this “social lineage” account of culture, what makes a culture is that its members are subject to a “set of formative conditions that are distinct from the formative conditions that are imposed on others” (Patten 2014: 51). The experience of being subjected to common institutions, understood broadly to include shared educational spaces, languages, media, as well as shared historical traditions and stories, overlapping familial structures, and so on, shapes a sense among cultural group members that they share a distinct way of seeing the world, and that certain assumptions that they possess are shared by, or at least understood by, others. This view emphasizes a culture’s historical trajectory, but does not require that its defining norms, values and practices are unchanging over time. On the contrary,
internal variation is possible because subjection to a common set of formative influences does not imply that people will end up with a homogeneous set of beliefs or values. (Patten 2014: 52)
As a result, cultures are sites in which members can contest and deliberate their meaning with enough shared assumptions about the way the world works that they can recognize each other as engaged in the same project.
Patten writes of the institutions to which cultural group members are subject that they are at least to some degree “isolated from the institutions and practices that work to socialize outsiders” (Patten 2014: 52), and thus serve to distinguish one culture from another. On this view, significant emphasis is placed on who is controlling the levers of the institutions that shape members’ formation: that is, it matters that members are in control of the institutions to which they, themselves, are subject, so that they can plausibly shape their own social experience, and the experience of younger members, in fundamental ways. Where the control over this social formation is denied, a culture’s members are thereby harmed; when it is coercively denied, there is very likely an injustice demanding remedy.
By focusing on the shared experience of subjection to common cultural institutions, this account avoids the accusation that what defines a culture is the stability of its basic norms and values over time: culture is not, on this view, a static entity. Instead, what matters is that cultural group members believe themselves to be members of a cultural group, and that this belief’s foundation is in the experience of common cultural institutions, rather than in the specific practices that are central to the group. These central practices can change fundamentally, without the cultural group itself dissolving. However, this view is subject to criticism by scholars who worry that those who control the levers of formation do not represent the views of all members (Phillips 2018), that instead they are using their relative positions of power to create and enforce cultural norms and practices that do not command (or would not command, without coercion) widespread agreement.
The latter objection—that a so-called culture is the product of some but not all of its members leads some scholars to rearticulate culture in terms of the ways in which it is constructed via dialogue among members and their engagement with each other. The purpose of emphasizing that a culture’s members are the source of its main practices, values and norms, is to emphasize that a culture is not “given” to its members from above, as a fixed and unalterable entity. Rather, members of a culture are, in a fundamental way, its authors. Here is James Tully explaining this: cultures are
continuously contested, imagined and reimagined, transformed and negotiated, both by their members and through their interactions with others. (Tully 1995: 11)
Seyla Benhabib similarly emphasizes the narrative aspect of cultures, noting that insiders
experience their traditions, stories, rituals and symbols, tools, and material living conditions through shared, albeit contested and contestable, narrative accounts. (Benhabib 2002: 5)
That there is contestation among members, and that its main elements are under constant negotiation, does not render a culture any less meaningful for its members. What may seem confusing is the idea that a contestable and constantly shifting culture warrants protection; perhaps protection means artificially halting the natural changes that a culture would undergo, by protecting elements of it at a moment in time. But defenders of this view demand protection in the form of ensuring that the forums in which culture is negotiated, shared and transmitted, are sustained in robust and inclusive ways, and without unwanted interference by forces external to the culture. As with the culture-as-formation account, the emphasis is on the capacity of group members to shape the norms and practices that are central, rather than with the norms and practices themselves.
How does this view respond to the worry about asymmetrical power distribution within a cultural group? Focusing on the ways in which a culture’s central characteristics are determined via negotiation among members is an attempt to be attentive to the power structures that shape whose voice is heard during these negotiations, in minority and majority cultures (Dhamoon 2006). In many, and indeed perhaps in most, cultures, historically the dominant voices have been male, and one impact of that has generally been a gendered view of the how best to organize cultural life, that has reduced the rights of women (and other minorities) in myriad ways, often to their disadvantage as well as against their will. For some, the oppression of less powerful members by those who hold the levers of power generates at least partial skepticism about the value of protecting or accommodating culture in liberal, democratic states, especially in cases where it may seem that “multiculturalism is bad for women” (Okin 1999). On this view, cultural practices that undermine the rights of women (and other minorities) should not be tolerated in liberal democratic states.
The recognition that many cultural practices are disadvantageous to women (and other minorities) does not propel all political theorists to adopt a skeptical attitude towards them in all cases. For some, it is an opportunity to see that cultures can be valued even by those who are putatively oppressed, even as they work from the inside to influence the direction of their culture, towards less oppressive norms and practices. For example, although often sidelined from their centres of power, many women value their cultures in ways that press them not to exit, but rather to engage in processes of reforming inegalitarian practices and norms, from within (Deveaux 2007). This way of thinking about culture and its contents celebrates, and encourages, moves to “democratize” the mechanisms by which a cultural group’s main norms, values and practices are adopted, and defends public cultures that are genuinely open to multiple voices (Lenard 2012).
This narrative or dialogic account of culture thus responds well to the essentialist challenge, by denying that the defining features of a culture must be static and equally valuable to all members of a cultural group. But, it must respond to another challenge, namely, the individuation challenge (Moore 2019). If an account of culture is going to be robust enough to define the entities that should be entitled to additional political and legal consideration in various ways, including with respect to additional rights protections or exemptions from certain legal and political requirements, it must also be able to identify with some specificity the boundaries of a particular, discrete, culture and who legitimately counts as a member for the purposes of respecting the political and legal claims made as a result. But this can be a challenge to accomplish.
To see why, consider Benhabib’s account of the ways in which cultures are observed from the outside, and the way they are experienced from the inside. The observer is largely responsible, she says, for imposing “unity and coherence on cultures”, whereas from the inside, its participants
One effect of understanding the culture in this way is that while many of its members will hold deeply to the central values and take deep satisfaction in participating in the central cultural traditions, many others will dip in and out of its central practices, and pick and choose among its central values and norms. So, just who counts as a member is blurry, and this blurriness may appear to be a problem when membership is said to confer rights and privileges that are not available to non-members. There is an inevitable tension between the need to individuate cultures for political reasons and the boundaries of cultures which are inevitably poorly demarcated. Only context will enable us to resolve the political questions that will thereby emerge.
To answer the challenge of how to identify a culture, and its members, one proposal focuses on the subjective component associated with belonging to a cultural group. Take this example, described by Margaret Moore: although there is deep division in Northern Ireland between Catholics and Protestants, the differences are neither religious (the conflict is not about distinctive interpretations of a religious text, and religious figures are not targeted for violence), nor cultural, since surveys of cultural values of both communities reveal considerable overlap among the values that competing communities hold (Moore 1999: 35). She says, rather, a focus on shared identities among rival groups makes more sense of the conflict. A largely or partly identity-focused view highlights that one key dimension of culture is the way in which it shapes the identity of cultural group members. As well, such a view highlights that culture is a thing to which many people will have important connections, but which will be defining for them in multiple and distinct ways. An identity-focused view has clear merits: for example, it can explain why individuals remain nominally attached to a culture, even though its centrally defining features shift historically over time, and even if they do not engage with some of its more traditional aspects.
Additionally, an identity-focused view can accommodate identities that are not obviously culturally based, for example, including LGBTQ+ identities (Eisenberg 2009: 20; for a discussion of cultural/identity claims in an LGBTQ+ context, see Ghosh 2018: chapter 4). Indeed, an identity-focused view aims to circumvent the difficulty of identifying what specific material is legitimately cultural material. As noted above, scholars of minority cultures frequently note that there is a wide variety of claims made by a wide variety of groups, and these groups are defined by an assortment of distinct characteristics, including race, ethnicity, religion and sexuality. Say its defenders, a focus on identity rather than culture may be preferable because
the term identity covers more ground in the sense that it can refer to religious, linguistic, gendered, Indigenous and other dimensions of self-understanding. (Eisenberg 2009: 2)
2. Minority Cultural Rights Claims
The four views of culture described above inform the cultural claims that both individuals and groups make against the state. The specific threats that individuals and groups face, and which demand a kind of protection, are distinct, as are the responses that states may have in response to the claims made by individuals and groups (Eisenberg 2009: 20–21). In some cases, claims are made for accommodations for all members of a group qua group; in others, claims are made with respect to particular individuals; and there may well be connection among these. For example, a group may demand language protection policies, or an individual may claim a right to speak her mother tongue in legal proceedings. These rights are related to each other, and may be in some cases derived from one another: one reason an individual has a right to speak her mother tongue in legal proceedings may be because the state has recognized her language as an official language either of the state, or of a sub-state jurisdiction, for example. As a matter of accommodation , it will be important in what follows to notice when claims are made for accommodations that apply to individuals and when they are accommodations that apply to groups; although some philosophers are keen to assess whether cultural rights are best understood as individual or group rights (Casals 2006), the analysis below proceeds by assuming that they can be both (following Levy 2000: 125).
Notice as well that the term “accommodation” is a kind of catch-all to include the wide range of claims an individual or group can make against a state on the basis of culture. Political philosophers have attempted to distinguish among these claims in myriad ways, in order to make sense of them. Many such rights are claimed by immigrant groups (typically) to a state, who require certain accommodations from the state in order to better integrate into that state. In the larger debate around the value of multiculturalism, there is considerable discussion about which sorts of accommodations encourage the integration of, especially, culturally distinct newcomers, and which sorts permit or even encourage their separation from the larger society (e.g., Sniderman & Hagendoorn 2007). Some scholars worry, as well, that a focus on how best to accommodate cultural minority groups travels with ignoring (perhaps wilfully) more important questions of redistribution to those who are less well off (Barry 2001; Fraser 1995). In general, however, multicultural theorists agree that accommodation rights are most defensible when they support the integration of minorities in general, and newcomers in particular, as well as when they are aimed at remedying persistent inequalities between majority and minority groups.
It is worth noting that not everyone readily agrees that “culture” should be treated as a source of distinct legal and political claims, however. For example, Sarah Song points out that so-called “multicultural” claims are often in fact claims to accommodate a wide range of groups, including racial, religious and ethnic groups. Many political theorists of cultural rights appear to believe that there are distinct and recognizable cultural groups, making distinctive cultural claims, whereas in their example-giving they rely on a “wide range of examples involving religion, language, ethnicity, nationality, and race” (Song 2009: 177). Rarely is “culture” alone the basis for a claim against a state. Rather, says Song, so-called cultural claims are in fact often demands for other well-understood and defensible democratic goods. Most such demands are for religious accommodations, well-defended by standard liberal defenses of freedom of conscience; others are demands for reparations for past and ongoing wrong, in the form of affirmative action; others yet are demands for democratic inclusion, often rooted in a morally problematic history of deliberate exclusion. Once the reasons for these “cultural” demands are revealed clearly, we will often find democratically defensible reasons to respect and accommodate them, without needing to resort to relying on culture as a distinct entity, giving rise to a distinct set of rights-claims. The result is that the controversy associated with properly defining cultures and identifying their members can be avoided in many instances. However, this analysis can make it difficult to treat cases where something called “culture” interacts with, or supplements, religious, ethnic, and racial claims.
Take the case of the choice, made by referendum, to ban minarets on mosques in Switzerland. The defensibility of the ban has been the subject of deliberation among political philosophers, and one key point of contention has been whether and to what extent minarets are religiously required by Islam. Many interpreters propose that, since minarets are not obligatory according to Islamic religious requirements, the choice to ban them is regrettable (because of what it says about the public place of Islam in Switzerland), but it does not violate the religious freedom of practising Muslims in Switzerland, and as a result is permissible (Miller 2016). In making this claim, however, what is ignored is the cultural significance of minarets. Without a recognition of the distinct place of culture in certain claims, a full understanding of the minaret case cannot be reached. The same challenge can be seen in deliberations around whether Muslim women should be permitted to wear face coverings in public spaces. Some commentators suggest that, because (according to some interpretations) Islamic texts do not appear to require face coverings, women can be denied the right to engage in this practice, without violating their religious freedom. In making this argument, its defenders notice that the choice to cover faces is in effect a (mere) cultural interpretation of Islamic requirements, as evidenced by the fact that only some communities of practising Muslims engage in the practice. For some scholars, it is essential to separate religious from cultural claims—liberal democratic states take religious claims very seriously as matters of conscience, and have a long history of zealously protecting religious freedom. So, having determined that a claim is not one of religious freedom, such scholars believe they can comfortably deny the request for permission to cover faces in public spaces. However, ignoring the cultural dimensions of the claim—or treating them as though they are obviously of less significance than the underlying religious claim—fails to treat the case properly. In particular, it fails to take seriously that religious obligations necessarily have cultural interpretations, that a full recognition of religious freedom entails recognizing their cultural interpretations, and that specifically cultural legal and political accommodation (of a religious commitment) will thereby be called for.
In what follows, distinct types of cultural claims, made against a state’s major institutions, will be examined. These claims are, as will be seen, sometimes made by individuals and sometimes by groups. Where relevant, the analysis will highlight whether the concept of culture that is being deployed is culture-as-encompassing group, culture-as-social-formation, culture-as-narrative, or culture-as-identity. The analysis will not always be neat. In some cases, there will be multiple defenses of a cultural right, which rely on distinct understandings of culture.
Perhaps the most familiar type of cultural claim made against the state is in the form of request for exemptions from rules and regulations that typically apply to all citizens. Exemption rights respond to the fact that, in liberal democracies, laws and practices are meant—genuinely—to treat all citizens equally, but that there are some which inadvertently impose disadvantage on certain minorities. The worry to be resolved is that minority citizens are unintentionally or accidentally burdened by the normal application of certain laws (Levy 2000: 130), in ways that treat them unfairly, which can be resolved by exemptions from certain laws and normal practices (Quong 2006; Gutmann 2003). The extension of exemption rights then is understood as a
a recognition of that difference, as an attempt not to unduly burden the minority culture or religion en route to the laws’ legitimate goals. (Levy 2000: 130)
For example, some Sikhs request exemption from laws that require wearing motorcycle or construction-site helmets. Although Sikhism is a religion, Sikhs describe the requirement that they wear a turban not quite as a religious requirement, but rather as a symbol of their faith and commitment to Sikh values, as well as an expression of their identity (Sikh Faith FAQs in Other Internet Resources ). Without exemption from these laws, Sikhs would be excluded from taking advantage of opportunities that are meant to be available to all citizens on an equal basis. The same is true of Indigenous communities, who have requested exemptions from generally applicable laws that limit hunting and fishing, explaining that such limits undermine their traditional way of life, or make it hard (or impossible) for them to sustain themselves (Levy 2000: 128). Before Sunday-closing laws were abandoned in Canada and the United States, religious minorities were occasionally granted exemptions from them. In these cases, as described above and without legally provided exemptions, people (usually minorities) must choose between participating in opportunities that should be available to all citizens on an equal basis or to respect their (cultural) understanding of what their religion requires of them.
The request for exemption can be lightly distinguished from the request for rule modification. As indicated, exemption requests are, as they sound, requests that individuals be exempted from certain requirements that are meant to apply to all citizens equally; modification requests ask for changes in existing, majority, practices to accommodate certain other, minority, practices. Sikhs sometimes request exemption from laws that would, otherwise, require them to remove their turban as above; in other cases, they request uniform modifications, so that turbans are treated as one among several available head coverings for those carrying out a specific role. The same is true of uniform modification requests made by Muslim women who cover their faces or heads, and Jewish men who wear yarmulkes, where uniforms have traditionally required an uncovered head or face, or where they have required particular head coverings (as in the Sikh case, they may also be presented as requests for exemptions). Similarly, when observant Muslims request short breaks in their work day to pray at specific times of day, or when Jewish and Muslim students ask for changes in the provision of foods (to accommodate kosher and halal obligations) in school cafeterias, the request is for modification rather than exemption.
In most cases, the early failure of a legitimate law to modify or exempt new practices is unintentional. That is, the laws or practices in place were not adopted intentionally with the purpose of excluding, but were rather adopted under the assumption that they treat the existing population fairly. But widespread immigration has diversified many populations in substantial ways. Immigrants often travel with practices and norms that are, when they arrive, unfamiliar to the states they are joining, and as a result states are asked to modify certain laws, and exempt newcomers from certain others. There may be cases where there are legitimate public reasons to persist in applying certain laws in spite of the disadvantage they generate for newcomers. As well, there are cases where states persist in demanding obedience to laws and practices that clearly disadvantage newcomers attempting to integrate, but where there are no good mitigating factors to justify persisting in the imposing of disadvantage (as when the Danish town of Randers passed a law requiring that pork be served “on an equal footing with other foods” in school cafeterias). In these latter cases, the exclusionary impact of the laws is no longer inadvertent, and they are generally condemnable for perpetuating unnecessary and unjustified exclusion from political, economic and social spaces.
It is not always the case that individuals or groups claiming cultural rights to exemption and modification are immigrants, but that is often the case. Indigenous communities ask for exemptions, as do certain orthodox religious communities. These cases will be discussed below in the section focused on cultural preservation.
Demands for assistance call on the state to preserve the conditions under which various elements of a culture can persist and even thrive, especially minority languages, or to promote and protect cultural associations in various ways, including by offering financial support to artists from within these cultural groups, or by providing resources to permit the production and distribution of ethnic-language media. The justification for assistance rights is the same as for exemption and modification requests: it is to prevent persistent unfairness in access to rights or goods that are meant to be available for all citizens on an equal basis. In the case of assistance rights, cultural minority groups argue that the majority group has access to these goods already, for example to a robust language or media space, and so they request state resources to secure these goods for cultural minorities as well. Here, whereas the justification overlaps with the one offered to defend exemption and modification rights—to generate fairness—the understanding of culture that underpins the demand for these rights is distinct. Typically, exemption and modification claims treat culture-as-identity or dialogue, whereas in the case of assistance claims, the background understanding of culture is often culture-as-social-formation or culture-as-encompassing group; the culture is treated as a whole that requires assistance to protect each of its central parts, in order to do the job of shaping members well.
Self-determination rights are those that confer substantial control to sub-state jurisdictions over a particular territory and in particular the right to run the major institutions on that territory. A self-determining community is one that, because of control over major institutions in a territory, is capable of making and enforcing decisions, without interference by outsiders, in multiple policy spaces (I. M. Young 2004). The justification for self-determination rights is sometimes based on reparation or corrective justice, for example where past state actions have undermined the capacity for a particular cultural group to be self-determining in the first place (Song 2009: 184). In other cases, the demand for self-determination is justified with respect to the importance of protecting the autonomy of a culturally distinct sub-state jurisdiction, that is, its capacity to run its own affairs in ways that are consonant with its particular cultural preferences. The right to self-determination typically relies on an understanding of culture-as-encompassing group, or culture-as-social-formation, suggesting that without significant control over the major institutions that govern the lives of citizens, the relevant group will not be able to be self-determining.
The right to self-determination is typically attributed to states, so its meaning in the context of minority communities operating at the sub-state level is not always clear. Among sub-state jurisdictions, the right is often claimed by Indigenous groups as well as sub-state national groups, like the Basques and the Scottish, whose “societal culture” is manifestly distinct from the majority’s societal culture. The demand for self-determination is a demand to make choices about how children are educated, what language is spoken by the relevant political authorities, and how the public space should be organized. The right claimed has at least three manifestations: 1) the right, at a minimum, to “maintain a comprehensive way of life within the larger society without interference”; 2) the right to recognition by the majority for its way of life, and 3) the right to active backing by the majority to affirmatively support the relevant way of life so that “the culture can flourish” (Margalit & Halbertal 1994: 498). These three interpretations make distinct demands on the state, running from simple non-interference to active participation in sustaining the conditions for self-determination. As a result, the larger state is sometimes tasked with assessing the extent to which it wants to direct its resources to supporting a particular request for self-determination, focused on whether associated claims to cultural preservation are warranted. These will be considered below.
The demand for formal recognition in legal and political documents often travels with the demand for self-determination, and is grounded in a desire to have the majority mark its commitment to the full and equal respect of a cultural minority group (Mcbride 2009). In the Canadian case, the Québécois have long fought for recognition as a nation, with a “distinct society”. Attempts to recognize Québec’s status in the Canadian constitution have repeatedly failed, though a motion that read “That this House recognize that the Québécois form a nation within a united Canada” was approved (with considerable controversy, however) by the House of Commons in 2006. The demand for recognition in this case is a demand for respect as an equal, national, founding partner of the Canadian state.
In the case of Indigenous communities as well, the right to self-determination often includes not only the demand to exercise authority over specific jurisdictions, but also for recognition. They seek recognition, for example, as original inhabitants of a particular state, or as nations in their own right, or as having been the victims of various crimes at the hands of colonizers, including the violation of early treaties between them, as well as demands for state support in sustaining and, in many cases, rebuilding communities that were actively devastated by colonizing/settler governments. In Canada, and other colonizing states, for example, it has become common to read land acknowledgement statements in advance of events (including as part of the “announcements” read at the beginning of a school day), recognizing that events and proceedings are taking place on unceded Indigenous land. Similarly, Australian Indigenous communities have long argued for official recognition in the Australian constitution. From the perspective of Australian Indigenous communities, the hope, and indeed the expectation, is that official recognition will give rise to additional rights and benefits, for example to greater voice and political access to members of the minority. The hope for additional rights and benefits is present in some, but not all, cases of recognition claims (for example, it largely was not present in the case of Québec).
Recognition comes in other forms beyond acknowledgement in legal and political documents, that are intended to confirm respect for minority groups. In some states, the languages of minority groups can be officially recognized as national languages. For example, the Romansh language in Switzerland is officially recognized as a national language, even though its speakers make up less than 1% of the country’s total population. By contrast, Turkish laws that banned the speaking of Kurdish in public spaces were an attempt to deny recognition to a national minority (lifted finally in 1991). As with demands for official recognition in binding constitutional documents, these sorts of recognition demonstrate respect for minority communities as well as a commitment to treating them as full and equal members of the larger state.
Cultural preservation rights are those that groups claim as key to sustaining a cultural group as a cultural group. This right is sometimes described as a right to the “survival of a culturally-specific people” (Gutmann 2003: 75). In some cases, the justification is based on the claim that certain forms of exposure to and engagement with the wider community will result in the erosion of a culture that is valued by its members. In others, the justification is historical, as in where orthodox religious groups, fleeing religious persecution in Europe, agreed to settle new land in Canada and the United States in exchange for religious freedom. In others, the central justification is that cultural diversity is valuable and worth preserving, in and of itself (Parekh 2000). (In some cases, cultural preservation rights are claimed as recompense for past wrong; this claim is considered separately, below.) Demands for cultural preservation are most controversial where they are made by illiberal groups, as will be detailed shortly.
It is worth dwelling here for a moment to notice that there are two ways to interpret cultural preservation: it could mean the preservation of a group as a distinct cultural entity or it could mean the preservation of certain practices and values that are believed, at a moment in time, to be central to the culture. Rights to cultural preservation come in multiple formats, including demands for exemption, parental autonomy, respect for internal conflict resolution mechanisms (in family law, mainly), and control over membership. These rights are justified with respect to preserving culture, and typically rely on an understanding of culture-as-encompassing groups or culture-as-social-formation, just as does the more general right to self-determination with which they often travel.
Many minority illiberal groups ask only for rights of forbearance against the state in which they live (Spinner-Halev 2000). In response, a state may permit an illiberal cultural group to be “left alone”, on the idea that so long as it can persist without state support of any kind, it may do so. A state may be asked to do more, however, to preserve the culture.
For example, a state may be asked to exempt community members from certain requirements that are typically demanded of all citizens, including mandatory schooling and child labour laws. Consider this example: many orthodox Amish communities live a life that is largely segregated from the wider community. They live a religiously structured way of life which dictates whom members marry, how they raise children, how they produce an economy that permits their way of life to continue. In most cases, they demand neither recognition nor additional financial support in order to protect their communities’ way of life. They had previously demanded only non-interference, for the most part. But, in the 1970s, some American Amish communities demanded, and were granted, the right to withdraw their children from mandatory education at the age of 14, arguing that where their children were required to remain in school until the age of 16, they were more likely to exit the community. This high rate of exit would, they argued, result in the failure of the Amish way of life to persist over time (Burtt 1994). The right of exemption the Amish claimed was, in this case, derivative of the larger demand for cultural self-preservation; without the exemption, they said, the culture itself might fade away.
A state may also be asked to respect certain domains of legal authority, perhaps most frequently in the domain of family law. Minority communities often regulate the conditions of marriage, and custody of children, as well as divorce, and request the legal authority to do so. Respecting the legal authority of minority communities to exercise jurisdiction in family law is the kind of request that often troubles critics of cultural minority rights, since it may entrench disadvantages to women, for example in divorce settlements or custody agreements (Shachar 2001; Bakht 2007). In general, then, states that acknowledge the legal authority of minority communities in the space of family law also demand that those who are participating in these adjudication proceedings do so willingly; majority states therefore often retain permission for themselves to interefere in these proceedings, in support of those who may be inadequately protected. The state must attempt a balance here, between offering its support to the most vulnerable members of a minority group (for example to ensure that their constitutional rights are protected) and interference of a kind that is inattentive to the rightful claims of minority groups to persist over time, in part by exercising its authority in key spaces.
Another common form of cultural preservation rights are exclusion rights, that is, the right of a cultural group to refuse to admit others to territory or membership, because of a worry that more generous terms of admission threatens to undermine it by, in effect, diluting it. Just as states have the putative right to control their borders (discussed below in section 3), and who can claim membership rights even after admission, so do some sub-state jurisdictions claim this double right of exclusion, citing the importance of cultural preservation. Indigenous communities have sometimes claimed the right to exclude non-Indigenous individuals from settling on their territories or the right to exclude others (for example non-Indigenous spouses of Indigenous persons) from certain membership benefits, including the right to vote (or otherwise have a say) for those who will govern. State courts have been asked to adjudicate the rightful authority of Indigenous communities to make these determinations (see Song 2005).
The cultural preservation rights described above pose a difficult challenge, connected to the critiques of treating culture as an encompassing group: any claim for cultural preservation, say some critics, translates in effect into problematic claims of control over members, which, moreover, are typically most restrictive for women and LGBTQ+ members of a cultural group. This is a challenge posed most forcefully where rights of cultural preservation are demanded by so-called illiberal groups like the Amish, and where they are (in the eyes of critics) imposed on children against their will. Illiberal groups are those which deny certain key liberal values, like autonomy and equality; in many cases, these communities are supported by educational systems that discourage autonomous choice-making, by avoiding the teaching of skills and capacities that typically enable it, and by enforcing hierarchical rules that elevate some members over others in ways that egalitarians find uncomfortable. The worry is that the community wants not only to preserve itself as a distinct cultural group, but also that it wants to protect a kind of cultural homogeneity that leaves no room for contestation or dissent over its central values and practices. These latter hierarchical rules often render women vulnerable to more powerful men, who may demand various forms of sexual subservience to them, who relegate them to the home to care for children, and who impose rigid codes of behaviour on them, for which harsh penalties are meted out in cases of violation. These kinds of so-called “cultural practices” are, for some critics, such that they render any form of state support in protecting minority cultural groups largely indefensible (Okin 1999).
A worry that runs through objections to these many cultural preservation rights is that women may not be willing participants in these cultures, and therefore that respecting cultural preservation rights consigns women to lives they would not choose, do not want, and cannot escape. But for many it is a mistake to assume that women members are such only under duress, since many will deeply value the community itself and respect the norms and values that it seeks to protect, even if they reject certain among them. In these cases, and where political theorists consider them, there is an attempt to move from treating culture in encompassing terms towards treating it in dialogic and narrative terms. Cultures, even oppressive (to liberals) minority cultures, are subject to change, and perhaps the best source of change is deeply committed members who willingly endorse key values but reject others, including those that do not respect the equal rights of women. Monique Deveaux’s account of female adult participants in customary marriages in South Africa, who accept some elements of their culture, but who aim to gain a voice at the table to shift others, treats culture in dialogic terms (Deveaux 2007). Here, the key motivating thought is that cultures can and do shift over time, in response to how its members engage in it, and what matters is not the change itself, but who or what is its source. On this view, the objective of cultural preservation rights is not to preserve culture per se , a challenge that would prove impossible in any case, but rather the right to protect the ability of group members to shape their culture and to protect it against unwelcome sources of change.
Others argue that so long as women, and any others subject to rigid cultural demands, possess a right (or the capacity) to exit the community, their choice to remain should be treated as such (Kukathas 1992). For those who hold this view, efforts to render the right to exit genuinely exercisable are tremendously important (Kukathas 2012; Holzleithner 2012). In so doing, a state must make a choice about the resources it provides to those members who may desire to exit, but who do not have the means to establish themselves in the larger society. In some orthodox religious communities, property is owned in common and individual members do not have any personal property or resources; as a result, exiters have nothing on which to rely while they establish their new lives. In others, members are poorly educated, and unfamiliar with life outside of their own communities, and so exit without the capacity to sustain themselves in the larger society. So, receiving states can offer support to exiters in various ways, for example by providing shelters to exiting women (and men), in which education is provided so that they may eventually attain self-sufficiency as a member of mainstream society. The choice to support exiters may seem to undermine a culture’s capacity for self-preservation. But supporting exiters is not well-understood as denying cultural preservation rights; rather, the choice to do so stems from a state’s commitment to protecting the rights of all of its members, including the most vulnerable, as best as it can do.
The right to cultural preservation described above should be distinguished from the slightly different right against coerced cultural loss, which focuses on preservation in cases where the potential loss is the result of coercion by outside forces against which a cultural group is relatively powerless. Of course, cultural change is inevitable in some form, as highlighted above, and especially if one holds a culture-as-dialogue view, cultures are in fact never static. Rather, practices, norms, and values that are defining of a culture at one time may cease to be centrally defining of that culture, for a whole range of reasons including economic, environmental, and political. So, in fact, some amount of cultural loss is inevitable, and moreover, it is not always to be regretted. Sometimes, it is a normal response to external factors that are beyond a culture’s control, and sometimes it is welcome because the changes result in the better protection of human rights or more inclusive cultural traditions and practices. A cultural group may choose to shift their central modes of production in response to changing environmental factors, for example. So, as Samuel Scheffler has argued, the strong preservationist view of culture—that cultures should be insulated from all forms of change—must be rejected (Scheffler 2007).
Yet, especially minority cultures may sometimes have a reasonable claim that they are not able to protect themselves against unwanted cultural change, or that they are not able to control the pace of change. They may thereby be entitled to forms of state support, to help them create the conditions under which they can resist unwanted cultural change. When linguistic minorities request state support to persist in educating children in a minority language, for example, sometimes the justification is in the name of protecting against the erosion of the language in the face of pressure to adopt or become fluent in the majority language.
In other cases, majorities are actively focused on undermining minority cultures, often over years and even decades. Colonial states have pursued genocidal policies against Indigenous communities for example, with the expressed purpose of undermining their capacity to survive as distinct peoples. In assessing cases of cultural loss, then, a key factor is whether the shift is forced upon minority groups, not necessarily by changing environmental or economic conditions, but by agents who intend to undermine the culture, by actively disvaluing it and thereby acting so as to undermine the conditions for its robust continuity. External, malicious, factors that engender cultural change that would not otherwise be expected, make the change not only regrettable, but generate a case for reparations, for example with respect to Indigenous communities, where there is “evidence of a history of dispossession, discrimination, or subordination” (Phillips 2018: 97).
In legal environments, wrong-doers sometimes deploy a cultural defense, explaining that minority cultural norms and values, which are in tension with those of the majority, are causally relevant in explaining why they committed a wrong. A cultural defense has, thereby, sometimes been treated as a relevant mitigating factor in assigning punishment. The right to offer a cultural defense is typically justified with respect to the importance of recognizing that minorities do not always operate according to the same values and norms that are represented in the majority’s legal system, and that these differences are entitled to some consideration in legal spaces. Earlier court decisions accepted explanations that, for example, men who murdered their unfaithful partners were moved to do so by a combination of shame and rage associated with cultural norms. For example, men who claimed that “gang rape” (known culturally as marriage by capture) was mandated by Hmong culture as a way to secure a wife, in which women were not only complicit but in fact willing partners, are no longer understood to have a defense in legal suits accusing them of rape (Song 2005). However, the power of “cultural” explanations in mainstream legal spaces has decreased over time, as states have come to see how many of these defenses are in fact cover for patriarchal, misogynist attitudes that persist, both in some minority communities and in the wider community.
“Cultural” defenses of crime often amount to treating culture as though it were a homogeneous whole, and as though perpetrators of crime rather than its victims have a lock on its interpretation. But “respect for culture cannot mean deference to whatever the established authorities of culture deem right” (Gutmann 2003: 46). Additionally, a generic imperative to “respect culture” in legal spaces can ignore the differences among types of cultural expectations, which can range from permissible acts, to encouraged acts and required acts, only some of which may justifiably be treated as legally relevant (Vitikainen 2015: 162). As well, it can permit and encourage the representation of minority (especially non-western) cultures as stereotypes, and “mobilizes culture in ways that encourage absurdly large generalizations about people from particular cultural groups” (Phillips 2007: 81 & 99). The danger represented by an uncritical acceptance of the cultural defense is in a treatment of culture as so encompassing that it treats its members as incapable of autonomous decision-making. But, say critics of the cultural defense, this is a mistake—along with many other factors, culture can be part of an explanation for engaging in wrong-doing, but should “never be mistaken for the whole truth” (Phillips 2007: 98).
A final cultural right that is claimed by some is the right to control cultural artifacts or expressions, or the use of cultural content in general (Matthes 2016). This is the right that is at issue in recent controversies focused on cultural appropriation, defined as the use, by a non-member, of “something of cultural value, usually a symbol or a practice, to others” (Lenard & Balint 2020). Familiar examples of actions that have been accused of engaging in cultural appropriation include the wearing of dreadlocks by whites; the donning of Indigenous clothing as Halloween costumes; the use of turbans in high fashion; the teaching of yoga by instructors who do not have South Asian backgrounds. In all of these cases, a non-member is accused of “appropriating” a particular cultural practice or symbol that is not their own. On this view, cultures have exclusive rights to use their cultural “products” as they see fit, often because that practice is understood to be central to their identity. This perspective is controversial, and often mocked, by those who observe that history just is the mingling and sharing of cultural practices and symbols, including in the spaces of cuisine, the arts, dress and spiritual practices; their mocking treats the rights claim as relying on an understanding of culture that is unchanging and immutable over time, which is historically inaccurate and, furthermore, undesirable. Correspondingly, key cultural artifacts are best understood as belonging to “humanity”: “it isn’t peoples who experience and value art: it’s men and women” (Appiah 2009).
The right claimed—to full or exclusive use of defining cultural practices or symbols—is perhaps not best enforced by the state, though states can and do engage in practices that are attentive to the harms allegedly caused by cultural appropriation. For example, centralized support for the arts, in the form of grants to produce artistic endeavours, can be sensitive to who is asking for support to produce what , and can direct funding towards artists from a particular tradition who aim to produce culturally specific products, and correspondingly refuse (unless very good reason is offered) to support endeavours by cultural outsiders to produce “insider” art (Rowell 1995; J. O. Young 2008). The right claimed is relatively stronger where a particular cultural community is the victim of a power imbalance, where the cultural community has expressly requested that a particular practice or symbol be “left alone” by a majority community, and where members of the majority community are profiting on the basis of its use of the particular symbol or practice (Lenard & Balint 2020). As in other cases, the right claimed by a cultural group is strongest where there are persistent inequalities between the minority claimant and the majority group.
3. Majority Cultural Rights Claims
Section 2 considered the cultural rights claims that are, usually, made by minority groups. Majority groups make cultural claims as well, in particular with respect to excluding others from their territory as well as with respect to what can be demanded of those who are admitted.
One domain in which majority communities claim a cultural right is in the space of immigration. For some, the right of states to shape their culture can legitimately serve as a reason to exclude others, in general and sometimes specific others. This view is often attributed to Michael Walzer, who argues that the right of a state to control its borders is intimately connected to its capacity to
defend the liberty and welfare, the politics and culture of a group of people committed to one another and to their common life. (Walzer 1983: 39, emphasis added)
The right of a state to control its culture is therefore an essential one to protect its “collective consciousness”, as noted in Section 1.
This claim has encountered pushback from many scholars, for multiple reasons. One reason is that the claim that a state may exclude would-be migrants for cultural reasons has too often been, in fact, an attempt to enact discriminatory legislation aimed at excluding migrants whose beliefs and practices are said to be incompatible with, or even undermining of, the values and norms that define the majority’s culture. Exclusion based on so-called cultural reasons has often been a claim that a state prefers to remain culturally, religiously, ethnically, and racially homogeneous. Historically, states engaged explicitly in such discriminatory practices, which have now been repudiated, including for example variants of Asian Exclusion Acts which were in operation in North America in the early 1900s.
The same accusation is also merited in several recent cases, such as the implementation of the so-called Muslim Ban in the United States, or with respect to proposals during the height of the crisis in Syria (2015) in some countries to prioritize Christian over Muslim refugees (Song 2018). Among political theorists of immigration, there is however widespread repudiation of discriminatory immigration policies, both explicitly and implicitly, even among those who defend the general right of states to exclude would-be migrants and refugees, for many reasons including to preserve culture (Miller 2005).
A second source of pushback stems from a more general skepticism that a majority’s culture, even if genuinely valuable to its members, should be treated as sufficiently so to warrant excluding migrants, especially necessitous ones (the language of necessity is borrowed from Song 2018). Even if it is conceded that culture is valuable to a majority, many scholars believe that its protection cannot warrant excluding those in severe need of safety or subsistence.
Yet, say those who defend the view that culture can, at least in some cases, serve to exclude migrants, there is a case to be made for treating the state as possessing the right to cultural continuity (Miller 2005). This claimed right looks very much like the right to cultural preservation (or against cultural loss) described above, and it highlights not so much the sentimental dimensions of a majority’s attachment to its culture, but rather its pragmatic interpretation. On this view, any particular state is defined by a “shared public culture” which, because shared, underpins the trust that democratic states rely on to pursue political and social objectives in common. No particular value that makes up a shared public culture is valuable in and of itself. Rather, it is the combination of a set of values, norms, and practices, that produces “our” culture that is valuable, and in its presence, trust is higher; as a result, so is the willingness to cooperate to support policies that require some sacrifice, including for example, commitment to redistributive social policies that are especially to the benefit of those who are least well-off (e.g., see the essays in Gustavsson & Miller 2019). So, according to those who defend these views, a state that seeks to exert control over admission citing “cultural” reasons is neither racist nor discriminatory, but rather is seeking controlled admission (rather than closed borders) so that newcomers can, over a sufficient time period, come to adopt enough of the set of defining values, norms, and practices, to be able to warrant and extend the trust that underpins the policies that instantiate these objectively valued goods.
States that defend the right of cultural continuity at the level of admission to a state typically also deploy the right to adopt and enforce “integration” policies that encourage newcomers to adopt majority norms and values, arguing that the faster such adoption happens, the more rapid admission itself can be. Integration policies ask newcomers to adopt the norms and practices of the majority community, whereas accommodation policies ask the majority to accommodate practices that are distinct from those that define the majority’s culture. On this conventional multicultural view, the process by which migrants are admitted to the territory, and then to membership, is a “two-way” street, requiring that both newcomers and the host state adapt in response to each other (Kymlicka 1998).
Is the demand that newcomers integrate culturally reasonable? Is it reasonable, that is, to ask immigrants to adopt the norms, values, and practices that are central to the culture they have joined (l will leave aside the question of economic and political integration, here)? Notice that in the political and sociological literature in immigration incorporation, integration (culturally) is typically distinguished from assimilation, where the former focuses on welcoming newcomers with the distinct sets of norms and values that travel with them (and so accommodating them where possible), and the latter demands that immigrants adopt as fully as possible the set of norms and values that are central to the host society (Brubaker 2001; see also Modood 2007). In the political theory literature on multiculturalism, however, it is widely accepted that a demand for full assimilation is normatively problematic (it requires too much of immigrants, to abandon their histories and identities, as part of joining a new community), but that some form of encouragement to integrate is permissible.
Whether the integration demands are permissible depends on at least two connected things, however: first, on the content of the shared public culture and, second, on the accessibility of the venues in which the content of this public culture is deliberated. The space in which a culture is deliberated is amorphous as well as expansive. The source of key norms, practices, and values is multi-fold: some are historical, some are deliberately adopted through political processes, some are accidentally adopted in response to contingent circumstances. The demand that newcomers integrate, in the sense of adopt the norms and practices of the majority culture to at least a reasonable extent is more defensible in cases where access to spaces in which they are deliberated is public and therefore open to many voices. The precise meaning of “accessibility” to spaces that are not clearly defined, and entry to which is not monitored or policed in any formal way, is challenging to pin down. But the key point is that to the extent that cultures welcome and take seriously new voices—in public media, in political spaces, and so on—they can be described as publicly accessible. So, there is a connection between the legitimacy of demanding adherence to majority culture norms and practices, as part of the process of integration, and the genuine access that newcomers have to the spaces in which they are deliberated.
In considering the second question, with respect to the content of a majority’s shared public culture, I borrow from the literature in the political theory of nationalism (though I do not believe that the language of nationalism itself is essential to appreciate its relevance to the discussion here). A culture can be defined by features that are more or less inclusive. Where cultures are defined by characteristics that are typically used to describe ethnic nations, including shared history, religion, ethnicity/race, newcomers are less easily able to join them and be recognized as full members. Where cultures are defined by characteristics that are typically used, on the other hand, to describe civic nations, including shared commitment to political institutions and, usually, a commitment to liberal democratic principles, then they are more welcoming for newcomers. In the language adopted earlier in this entry, cultures that are defined by exclusive features are more likely to treat culture as encompassing, whereas cultures that adopt inclusive features, and emphasize accessibility to the forums in which its content is deliberated, treat culture in dialogic or identity terms. This need not be the case, though, since those who treat culture in dialogic terms may nevertheless believe that key elements of history or religion are central to it (though they are open to deliberation about the appropriateness of these elements as central) and similarly identities can be formulated on the basis of exclusionary features.
Another way to define inclusivity focuses attention on the extent to which a culture’s main norms, practices, and values can be adopted by newcomers without their giving up something they value (Lenard 2019). Key here is to define the permissible contours of an inclusive culture that, at the same time, can serve to distinguish it from others in ways that resolve what philosophers have called the “particularity” problem. If cultures are defined only by commitment to liberal democratic principles and the institutions that instantiate them, then a person will necessarily be committed to any state that is so defined. But this conclusion does not make sense of the reality that many citizens are attached to their state’s interpretation of these values—fundamental, abstract, liberal democratic principles are adopted, respected, and instantiated, in other words, in a culturally specific way. It is important, then, to delineate the boundary of permissible cultural content, which can include recognition of key historical moments, or political conversations, or cultural icons. No state can demand of newcomers that their emotional commitment be to their new state; but it can reasonably impart information about learnable key cultural markers, encourage newcomers to adopt the associated practices and norms, and hope that over time their emotional identification shifts to the host state, at least partially (Carens 2005). Under the condition that the public cultural content of a host state is reasonably accessible, and that the forums in which it is deliberated are likewise reasonably accessible, then the host state can permissibly encourage the integration of newcomers. This right is perhaps best understood as derivative of the right to cultural continuity that states claim in relation to immigration, which can permissibly be claimed if and only if the accessibility conditions described above are met.
Not all scholars agree on this point, of course, and some reject entirely the suggestion that newcomers can be asked to make accommodations to the culture of the state that they have joined. Those who adopt variants on this view treat the majority’s culture as nearly always homogeneous and oppressive in ways that are disrespectful of newcomers, and treat the demand for integration along at least some dimensions as “cleaned up” variations on the discriminatory and racist immigration policies of the past (Abizadeh 2002). This is a real worry. When the Netherlands demanded that potential migrants from majority Muslim countries watch a video and pass a test merely to gain entry to its territory—a video that showed gay men kissing and a topless woman—it was widely excoriated for its discriminatory intent, rather than (as was claimed) an attempt to ensure that migrants could adopt the liberal values that supposedly characterized the country’s culture. More generally, the mechanisms of encouraging the learning and adoption of the majority culture’s values, in addition to its actual content as delineated above, as well as the consequences for failure to do so, must be scrutinized for their reasonableness. This assessment is a tricky business, certainly, made trickier because in many (if not most) immigration situations, the potential newcomer is in a situation of vulnerability in relation to the host state: their interest in gaining entry is very strong and so in many cases, they will accept heavy-handed attempts to coerce their integration without complaint.
Both minority groups (many of which are immigrant groups) and majority groups claim that “culture” is important and deserving of accommodation in multiple ways. This entry began with an examination of the multiple ways in which culture has been understood, to unpack the ways in which it is deployed when specific cultural rights are claimed. It is important to notice that these cultural claims, on both sides, are often made in relation to each other: a minority group demands a particular cultural right and the majority responds by claiming a different cultural right. In many cases, the choice to respect or ignore claimed cultural rights is framed in terms of the impact that doing so will have on the culture of the majority, for example, by stating that a particular practice for which accommodation is requested is incompatible with the majority culture in general, or sometimes more specifically with a particular practice or norm that is believed to be particularly important. The latter claim was made, for example, in France, during “l’affaire du foulard”—the right to cover one’s head as a manifestation of Islamic (or Jewish) religious commitment was denied for the way in which it compromised the French’s commitment to laicity (Laborde 2008; Benhabib 2004).
This entry has attempted to offer the resources that are essential to adjudicating these conflicts, in ways that take seriously both those who demand cultural rights and those who resist respecting them. Hopefully, future political theory can make use of this taxonomy to identify satisfactory conclusions to these conflicts when they arise.
- Abizadeh, Arash, 2002, “Does Liberal Democracy Presuppose a Cultural Nation? Four Arguments”, American Political Science Review , 96(3): 495–509. doi:10.1017/S000305540200028X
- Appiah, Kwame Anthony, 2009, “Whose Culture Is It, Anyway?”, in Cultural Heritage Issues: The Legacy of Conquest, Colonization and Commerce , edited by James A. R. Nafziger and Ann Nicgorski, Leiden: Brill, 207–21.
- Bakht, Natasha, 2007, “Religious Arbitration in Canada: Protecting Women by Protecting Them from Religion”, Canadian Journal of Women and the Law , 19(1): 119–144.
- Barry, Brian, 2001, Culture and Equality: An Egalitarian Critique of Multiculturalism , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Benhabib, Seyla, 2002, The Claims of Culture: Equality and Diversity in the Global Era , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 2004, The Rights of Others: Aliens, Residents, and Citizens , Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511790799
- Borchers, Dagmar and Annamari Vitikainen (eds.), 2012, On Exit: Interdisciplinary Perspectives on the Right of Exit in Liberal Multicultural Societies , Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter. doi:10.1515/9783110270860
- Brubaker, Rogers, 2001, “The Return of Assimilation? Changing Perspectives on Immigration and Its Sequels in France, Germany, and the United States”, Ethnic and Racial Studies , 24(4): 531–548. doi:10.1080/01419870120049770
- Burtt, Shelley, 1994, “Religious Parents, Secular Schools: A Liberal Defense of an Illiberal Education”, The Review of Politics , 56(1): 51–70. doi:10.1017/S0034670500049500
- Carens, Joseph, 2005, “The Integration of Immigrants”, Journal of Moral Philosophy , 2(1): 29–46. doi:10.1177/1740468105052582
- Casals, Neus Torbisco, 2006, Group Rights as Human Rights: A Liberal Approach to Multiculturalism , (Law and Philosophy Library 75), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers. doi:10.1007/1-4020-4209-4
- Deveaux, Monique, 2007, Gender and Justice in Multicultural Liberal States , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199289790.001.0001
- Dhamoon, Rita, 2006, “Shifting From ‘Culture’ to ‘the Cultural’: Critical Theorizing of Identity/Difference Politics”, Constellations , 13(3): 354–373. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8675.2006.00406.x
- Eisenberg, Avigail, 2009, Reasons of Identity: A Normative Guide to the Political and Legal Assessment of Identity Claims , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199291304.001.0001
- Fraser, Nancy, 1995, “Recognition or Redistribution? A Critical Reading of Iris Young’s Justice and the Politics of Difference ”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 3(2): 166–180. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9760.1995.tb00033.x
- Ghosh, Cyril, 2018, De-Moralizing Gay Rights: Some Queer Remarks on LGBT+ Rights Politics in the US , Cham, Switzerland: Palgrave Macmillan. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-78840-1
- Gustavsson, Gina and David Miller (eds.), 2019, Liberal Nationalism and Its Critics: Normative and Empirical Questions , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198842545.001.0001
- Gutmann, Amy, 2003, Identity in Democracy , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Holzleithner, Elisabeth, 2012, “Interrogating Exit in Multiculturalist Theorizing: Conditions and Limitations”, in Borchers and Vitikainen 2012: 13–33. doi:10.1515/9783110270860.13
- Kukathas, Chandran, 1992, “Are There Any Cultural Rights?”, Political Theory , 20(1): 105–139. doi:10.1177/0090591792020001006
- –––, 2012, “Exit, Freedom and Gender”, in Borchers and Vitikainen 2012: 34–56. doi:10.1515/9783110270860.34
- Kymlicka, Will, 1996, Multicultural Citizenship: A Liberal Theory of Minority Rights , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1998, Finding Our Way: Rethinking Ethnocultural Relations in Canada , Toronto: Oxford University Press.
- Laborde, Cecile, 2008, Critical Republicanism: The Hijab Controversy and Political Philosophy , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199550210.001.0001
- Lenard, Patti Tamara.,2012, Trust, Democracy and Multicultural Challenges , University Park, PA: Pennsylvania University State Press.
- –––, 2019, “Inclusive Identities: The Foundation of Trust in Multicultural Communities”, in Gustavsson and Miller 2019: 155–171. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198842545.003.0009
- Lenard, Patti Tamara and Peter Balint, 2020, “What Is (the Wrong of) Cultural Appropriation?”, Ethnicities , 20(2): 331–52. doi:10.1177/1468796819866498
- Levy, Jacob, 2000, Multiculturalism of Fear , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/0198297122.001.0001
- Margalit, Avishai and Moshe Halbertal, 1994, “Liberalism and the Right to Culture”, Social Research: An International Quarterly , 61(3): 491–510.
- Margalit, Avishai and Joseph Raz, 1990, “National Self-Determination”:, Journal of Philosophy , 87(9): 439–461. doi:10.2307/2026968
- Matthes, Erich Hatala, 2016, “Cultural Appropriation Without Cultural Essentialism?”, Social Theory and Practice , 42(2): 343–366. doi:10.5840/soctheorpract201642219
- Mcbride, Cillian, 2009, “Demanding Recognition: Equality, Respect, and Esteem”, European Journal of Political Theory , 8(1): 96–108. doi:10.1177/1474885108096962
- Miller, David, 2005, “Immigration: The Case for Limits”, in Contemporary Debates in Applied Ethics , Andrew Cohen and Christopher Wellman (eds), Malden: Blackwell Publishers, 193–207.
- –––, 2016, “Majorities and Minarets: Religious Freedom and Public Space”, British Journal of Political Science , 46(2): 437–456. doi:10.1017/S0007123414000131
- Modood, Tariq, 2007, Multiculturalism: A Civic Idea , Cambridge, UK: Polity Press.
- Moore, Margaret, 1999, “Beyond the Cultural Argument for Liberal Nationalism”, Critical Review of International Social and Political Philosophy , 2(3): 26–47. doi:10.1080/13698239908403282
- –––, 2019, “Liberal Nationalism and the Challenge of Essentialism”, in Gustavsson and Miller 2019: 188–202. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198842545.003.0011
- Okin, Susan Moller, 1999, Is Multiculturalism Bad for Women? Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Parekh, Bhikhu, 2000, Rethinking Multiculturalism: Cultural Diversity and Political Theory , Basingstoke: Macmillan Press.
- Parvin, Phil, 2008, “What’s Special About Culture? Identity, Autonomy, and Public Reason”, Critical Review of International Social and Political Philosophy , 11(3): 315–233. doi:10.1080/13698230802276447
- Patten, Alan, 2014, Equal Recognition: The Moral Foundations of Minority Rights , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Phillips, Anne, 2007, Multiculturalism without Culture , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 2010, “What’s Wrong with Essentialism?”, Distinktion: Journal of Social Theory , 11(1): 47–60. doi:10.1080/1600910X.2010.9672755
- –––, 2018, “What Makes Culture Special?”, Political Theory , 46(1): 92–98. doi:10.1177/0090591717696023
- Quong, Jonathan, 2006, “Cultural Exemptions, Expensive Tastes, and Equal Opportunities”, Journal of Applied Philosophy , 23(1): 53–71. doi:10.1111/j.1468-5930.2006.00320.x
- Rowell, John, 1995, “The Politics of Cultural Appropriation”, Journal of Value Inquiry , 29(1): 137–142.
- Scheffler, Samuel, 2007, “Immigration and the Significance of Culture”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 35(2): 93–125. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2007.00101.x
- Shachar, Ayelet, 2001, Multicultural Jurisdictions: Cultural Differences and Women’s Rights , Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511490330
- Sniderman, Paul M. and Louk Hagendoorn, 2007, When Ways of Life Collide , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Song, Sarah, 2005, “Majority Norms, Multiculturalism, and Gender Equality”, American Political Science Review , 99(4): 473–489. doi:10.1017/S0003055405051828
- –––, 2009, “The Subject of Multiculturalism: Culture, Religion, Language, Ethnicity, Nationality, and Race?”, in New Waves in Political Philosophy , Boudewijn de Bruin and Christopher F. Zurn (eds.), London: Palgrave Macmillan UK, 177–197. doi:10.1057/9780230234994_10
- –––, 2018, Immigration and Democracy , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190909222.001.0001
- Spinner-Halev, Jeff, 2000, Surviving Diversity: Religion and Democratic Citizenship , Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Tully, James, 1995, Strange Multiplicity: Constitutionalism in the Age of Diversity , Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Vitikainen, Annamari, 2015, The Limits of Liberal Multiculturalism: Towards an Individuated Approach to Cultural Diversity , London: Palgrave Macmillan UK. doi:10.1057/9781137404626
- Walzer, Michael, 1983, Spheres of Justice: A Defense of Pluralism and Equality , New York: Basic Books.
- Young, Iris Marion, 2004, “Two Concepts of Self-Determination”, in Ethnicity, Nationalism, and Minority Rights , Stephen May, Tariq Modood, and Judith Squires (eds.), Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 176–196. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511489235.009
- Young, James O., 2008, Cultural Appropriation and the Arts , Malden, MA: Blackwell.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Sikh Faith FAQs , World Sikh Organization of Canada.
citizenship | cultural heritage, ethics of | culture: and cognitive science | identity | multiculturalism | rights: group
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Matthias Hoesch, Margaret Moore, and Stéfanie Morris for comments on an earlier draft of this entry.
Copyright © 2020 by Patti Tamara Lenard < Patti . Lenard @ uottawa . ca >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
3.1 What Is Culture?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you should be able to:
- Differentiate between culture and society
- Explain material versus nonmaterial culture
- Discuss the concept of cultural universals as it relates to society
- Compare and contrast ethnocentrism and xenocentrism
Humans are social creatures. According to Smithsonian Institution research, humans have been forming groups for almost 3 million years in order to survive. Living together, people formed common habits and behaviors, from specific methods of childrearing to preferred techniques for obtaining food.
Almost every human behavior, from shopping to marriage, is learned. In the U.S., marriage is generally seen as an individual choice made by two adults, based on mutual feelings of love. In other nations and in other times, marriages have been arranged through an intricate process of interviews and negotiations between entire families. In Papua New Guinea, almost 30 percent of women marry before the age of 18, and 8 percent of men have more than one wife (National Statistical Office, 2019). To people who are not from such a culture, arranged marriages may seem to have risks of incompatibility or the absence of romantic love. But many people from cultures where marriages are arranged, which includes a number of highly populated and modern countries, often prefer the approach because it reduces stress and increases stability (Jankowiak 2021).
Being familiar with unwritten rules helps people feel secure and at ease. Knowing to look left instead of right for oncoming traffic while crossing the street can help avoid serious injury and even death. Knowing unwritten rules is also fundamental in understanding humor in different cultures. Humor is common to all societies, but what makes something funny is not. Americans may laugh at a scene in which an actor falls; in other cultures, falling is never funny. Most people want to live their daily lives confident that their behaviors will not be challenged or disrupted. But even an action as seemingly simple as commuting to work evidences a great deal of cultural propriety, that is, there are a lot of expected behaviors. And many interpretations of them.
Take the case of going to work on public transportation. Whether people are commuting in Egypt, Ireland, India, Japan, and the U.S., many behaviors will be the same and may reveal patterns. Others will be different. In many societies that enjoy public transportation, a passenger will find a marked bus stop or station, wait for the bus or train, pay an agent before or after boarding, and quietly take a seat if one is available. But when boarding a bus in Cairo, Egypt, passengers might board while the bus is moving, because buses often do not come to a full stop to take on patrons. In Dublin, Ireland, bus riders would be expected to extend an arm to indicate that they want the bus to stop for them. And when boarding a commuter train in Mumbai, India, passengers must squeeze into overstuffed cars amid a lot of pushing and shoving on the crowded platforms. That kind of behavior might be considered rude in other societies, but in Mumbai it reflects the daily challenges of getting around on a train system that is taxed to capacity.
Culture can be material or nonmaterial. Metro passes and bus tokens are part of material culture, as are the buses, subway cars, and the physical structures of the bus stop. Think of material culture as items you can touch-they are tangible . Nonmaterial culture , in contrast, consists of the ideas, attitudes, and beliefs of a society. These are things you cannot touch. They are intangible . You may believe that a line should be formed to enter the subway car or that other passengers should not stand so close to you. Those beliefs are intangible because they do not have physical properties and can be touched.
Material and nonmaterial aspects of culture are linked, and physical objects often symbolize cultural ideas. A metro pass is a material object, but it represents a form of nonmaterial culture, namely, capitalism, and the acceptance of paying for transportation. Clothing, hairstyles, and jewelry are part of material culture, but the appropriateness of wearing certain clothing for specific events reflects nonmaterial culture. A school building belongs to material culture symbolizing education, but the teaching methods and educational standards are part of education’s nonmaterial culture.
As people travel from different regions to entirely different parts of the world, certain material and nonmaterial aspects of culture become dramatically unfamiliar. What happens when we encounter different cultures? As we interact with cultures other than our own, we become more aware of the differences and commonalities between others and our own. If we keep our sociological imagination awake, we can begin to understand and accept the differences. Body language and hand gestures vary around the world, but some body language seems to be shared across cultures: When someone arrives home later than permitted, a parent or guardian meeting them at the door with crossed arms and a frown on their face means the same in Russia as it does in the U.S. as it does in Ghana.
Cultural Universals
Although cultures vary, they also share common elements. Cultural universals are patterns or traits that are globally common to all societies. One example of a cultural universal is the family unit: every human society recognizes a family structure that regulates sexual reproduction and the care of children. Even so, how that family unit is defined and how it functions vary. In many Asian cultures, for example, family members from all generations commonly live together in one household. In these cultures, young adults continue to live in the extended household family structure until they marry and join their spouse’s household, or they may remain and raise their nuclear family within the extended family’s homestead. In the U.S., by contrast, individuals are expected to leave home and live independently for a period before forming a family unit that consists of parents and their offspring. Other cultural universals include customs like funeral rites, weddings, and celebrations of births. However, each culture may view and conduct the ceremonies quite differently.
Anthropologist George Murdock first investigated the existence of cultural universals while studying systems of kinship around the world. Murdock found that cultural universals often revolve around basic human survival, such as finding food, clothing, and shelter, or around shared human experiences, such as birth and death or illness and healing. Through his research, Murdock identified other universals including language, the concept of personal names, and, interestingly, jokes. Humor seems to be a universal way to release tensions and create a sense of unity among people (Murdock, 1949). Sociologists consider humor necessary to human interaction because it helps individuals navigate otherwise tense situations.
Sociological Research
Is music a cultural universal.
Imagine that you are sitting in a theater, watching a film. The movie opens with the protagonist sitting on a park bench with a grim expression on their face. The music starts to come in. The first slow and mournful notes play in a minor key. As the melody continues, the heroine turns her head and sees a man walking toward her. The music gets louder, and the sounds don’t seem to go together – as if the orchestra is intentionally playing the wrong notes. You tense up as you watch, almost hoping to stop. The character is clearly in danger.
Now imagine that you are watching the same movie – the exact same footage – but with a different soundtrack. As the scene opens, the music is soft and soothing, with a hint of sadness. You see the protagonist sitting on the park bench with a grim expression. Suddenly, the music swells. The woman looks up and sees a man walking toward her. The notes are high and bright, and the pace is bouncy. You feel your heart rise in your chest. This is a happy moment.
Music has the ability to evoke emotional responses. In television shows, movies, commercials, and even the background music in a store, music has a message and seems to easily draw a response from those who hear it – joy, sadness, fear, victory. Are these types of musical cues cultural universals?
In 2009, a team of psychologists, led by Thomas Fritz of the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, Germany, studied people’s reactions to music that they’d never heard (Fritz et al., 2009). The research team traveled to Cameroon, Africa, and asked Mafa tribal members to listen to Western music. The tribe, isolated from Western culture, had never been exposed to Western culture and had no context or experience within which to interpret its music. Even so, as the tribal members listened to a Western piano piece, they were able to recognize three basic emotions: happiness, sadness, and fear. Music, the study suggested, is a sort of universal language.
Researchers also found that music can foster a sense of wholeness within a group. In fact, scientists who study the evolution of language have concluded that originally language (an established component of group identity) and music were one (Darwin, 1871). Additionally, since music is largely nonverbal, the sounds of music can cross societal boundaries more easily than words. Music allows people to make connections, where language might be a more difficult barricade. As Fritz and his team found, music and the emotions it conveys are cultural universals.
Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism
Although human societies have much in common, cultural differences are far more prevalent than cultural universals. For example, while all cultures have language, analysis of conversational etiquette reveals tremendous differences. In some Middle Eastern cultures, it is common to stand close to others in conversation. Americans keep more distance and maintain a large “personal space.” Additionally, behaviors as simple as eating and drinking vary greatly from culture to culture. Some cultures use tools to put the food in the mouth while others use their fingers. If your professor comes into an early morning class holding a mug of liquid, what do you assume they are drinking? In the U.S., it’s most likely filled with coffee, not Earl Grey tea, a favorite in England, or Yak Butter tea, a staple in Tibet.
Some travelers pride themselves on their willingness to try unfamiliar foods, like the late celebrated food writer Anthony Bourdain (1956-2017). Often, however, people express disgust at another culture's cuisine. They might think that it’s gross to eat raw meat from a donkey or parts of a rodent, while they don’t question their own habit of eating cows or pigs.
Such attitudes are examples of ethnocentrism , which means to evaluate and judge another culture based on one’s own cultural norms. Ethnocentrism is believing your group is the correct measuring standard and if other cultures do not measure up to it, they are wrong. As sociologist William Graham Sumner (1906) described the term, it is a belief or attitude that one’s own culture is better than all others. Almost everyone is a little bit ethnocentric.
A high level of appreciation for one’s own culture can be healthy. A shared sense of community pride, for example, connects people in a society. But ethnocentrism can lead to disdain or dislike of other cultures and could cause misunderstanding, stereotyping, and conflict. Individuals, government, non-government, private, and religious institutions with the best intentions sometimes travel to a society to “help” its people, because they see them as uneducated, backward, or even inferior. Cultural imperialism is the deliberate imposition of one’s own cultural values on another culture.
Colonial expansion by Portugal, Spain, Netherlands, and England grew quickly in the fifteenth century was accompanied by severe cultural imperialism. European colonizers often viewed the people in these new lands as uncultured savages who needed to adopt Catholic governance, Christianity, European dress, and other cultural practices.
A modern example of cultural imperialism may include the work of international aid agencies who introduce agricultural methods and plant species from developed countries into areas that are better served by indigenous varieties and agricultural approaches to the particular region. Another example would be the deforestation of the Amazon Basin as indigenous cultures lose land to timber corporations.
When people find themselves in a new culture, they may experience disorientation and frustration. In sociology, we call this culture shock . In addition to the traveler’s biological clock being ‘off’, a traveler from Chicago might find the nightly silence of rural Montana unsettling, not peaceful. Now, imagine that the ‘difference’ is cultural. An exchange student from China to the U.S. might be annoyed by the constant interruptions in class as other students ask questions—a practice that is considered rude in China. Perhaps the Chicago traveler was initially captivated with Montana’s quiet beauty and the Chinese student was originally excited to see a U.S.- style classroom firsthand. But as they experience unanticipated differences from their own culture, they may experience ethnocentrism as their excitement gives way to discomfort and doubts about how to behave appropriately in the new situation. According to many authors, international students studying in the U.S. report that there are personality traits and behaviors expected of them. Black African students report having to learn to ‘be Black in the U.S.’ and Chinese students report that they are naturally expected to be good at math. In African countries, people are identified by country or kin, not color. Eventually, as people learn more about a culture, they adapt to the new culture for a variety of reasons.
Culture shock may appear because people aren’t always expecting cultural differences. Anthropologist Ken Barger (1971) discovered this when he conducted a participatory observation in an Inuit community in the Canadian Arctic. Originally from Indiana, Barger hesitated when invited to join a local snowshoe race. He knew he would never hold his own against these experts. Sure enough, he finished last, to his mortification. But the tribal members congratulated him, saying, “You really tried!” In Barger’s own culture, he had learned to value victory. To the Inuit people, winning was enjoyable, but their culture valued survival skills essential to their environment: how hard someone tried could mean the difference between life and death. Over the course of his stay, Barger participated in caribou hunts, learned how to take shelter in winter storms, and sometimes went days with little or no food to share among tribal members. Trying hard and working together, two nonmaterial values, were indeed much more important than winning.
During his time with the Inuit tribe, Barger learned to engage in cultural relativism . Cultural relativism is the practice of assessing a culture by its own standards rather than viewing it through the lens of one’s own culture. Practicing cultural relativism requires an open mind and a willingness to consider, and even adapt to, new values, norms, and practices.
However, indiscriminately embracing everything about a new culture is not always possible. Even the most culturally relativist people from egalitarian societies—ones in which women have political rights and control over their own bodies—question whether the widespread practice of female genital mutilation in countries such as Ethiopia and Sudan should be accepted as a part of cultural tradition. Sociologists attempting to engage in cultural relativism, then, may struggle to reconcile aspects of their own culture with aspects of a culture that they are studying. Sociologists may take issue with the practices of female genital mutilation in many countries to ensure virginity at marriage just as some male sociologists might take issue with scarring of the flesh to show membership. Sociologists work diligently to keep personal biases out of research analysis.
Sometimes when people attempt to address feelings of ethnocentrism and develop cultural relativism, they swing too far to the other end of the spectrum. Xenocentrism is the opposite of ethnocentrism, and refers to the belief that another culture is superior to one’s own. (The Greek root word xeno-, pronounced “ZEE-no,” means “stranger” or “foreign guest.”) An exchange student who goes home after a semester abroad or a sociologist who returns from the field may find it difficult to associate with the values of their own culture after having experienced what they deem a more upright or nobler way of living. An opposite reaction is xenophobia, an irrational fear or hatred of different cultures.
Perhaps the greatest challenge for sociologists studying different cultures is the matter of keeping a perspective. It is impossible for anyone to overcome all cultural biases. The best we can do is strive to be aware of them. Pride in one’s own culture doesn’t have to lead to imposing its values or ideas on others. And an appreciation for another culture shouldn’t preclude individuals from studying it with a critical eye. This practice is perhaps the most difficult for all social scientists.
Sociology in the Real World
Overcoming culture shock.
During her summer vacation, Caitlin flew from Chicago, Illinois to Madrid, Spain to visit Maria, the exchange student she had befriended the previous semester. In the airport, she heard rapid, musical Spanish being spoken all around her.
Exciting as it was, she felt isolated and disconnected. Maria’s mother kissed Caitlin on both cheeks when she greeted her. Her imposing father kept his distance. Caitlin was half asleep by the time supper was served—at 10 p.m. Maria’s family sat at the table for hours, speaking loudly, gesturing, and arguing about politics, a taboo dinner subject in Caitlin’s house. They served wine and toasted their honored guest. Caitlin had trouble interpreting her hosts’ facial expressions, and did not realize she should make the next toast. That night, Caitlin crawled into a strange bed, wishing she had not come. She missed her home and felt overwhelmed by the new customs, language, and surroundings. She’d studied Spanish in school for years—why hadn’t it prepared her for this?
What Caitlin did not realize was that people depend not only on spoken words but also on body language, like gestures and facial expressions, to communicate. Cultural norms and practices accompany even the smallest nonverbal signals (DuBois, 1951). They help people know when to shake hands, where to sit, how to converse, and even when to laugh. We relate to others through a shared set of cultural norms, and ordinarily, we take them for granted.
For this reason, culture shock is often associated with traveling abroad, although it can happen in one’s own country, state, or even hometown. Anthropologist Kalervo Oberg (1960) is credited with first coining the term “culture shock.” In his studies, Oberg found that most people are excited at first to encounter a new culture. But bit by bit, they become stressed by interacting with people from a different culture who speak another language and use different regional expressions. There is new food to digest, new daily schedules to follow, and new rules of etiquette to learn. Living with this constant stress can make people feel incompetent and insecure. People react to frustration in a new culture, Oberg found, by initially rejecting it and glorifying one’s own culture. An American visiting Italy might long for a “real” pizza or complain about the unsafe driving habits of Italians.
It helps to remember that culture is learned. Everyone is ethnocentric to an extent, and identifying with one’s own country is natural. Caitlin’s shock was minor compared to that of her friends Dayar and Mahlika, a Turkish couple living in married student housing on campus. And it was nothing like that of her classmate Sanai. Sanai had been forced to flee war-torn Bosnia with her family when she was fifteen. After two weeks in Spain, Caitlin had developed more compassion and understanding for what those people had gone through. She understood that adjusting to a new culture takes time. It can take weeks or months to recover from culture shock, and it can take years to fully adjust to living in a new culture.
By the end of Caitlin’s trip, she had made new lifelong friends. Caitlin stepped out of her comfort zone. She had learned a lot about Spain, but discovered a lot about herself and her own culture.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Tonja R. Conerly, Kathleen Holmes, Asha Lal Tamang
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Sociology 3e
- Publication date: Jun 3, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/3-1-what-is-culture
© Jan 18, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Essay on Importance of Culture and Tradition
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance of Culture and Tradition in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance of Culture and Tradition
Introduction.
Culture and tradition are vital aspects of our lives. They define our identity, guide our behavior, and connect us to our history.
The Role of Culture
Culture is the shared values, beliefs, and customs of a group. It shapes our thinking and decisions, making us unique.
Significance of Traditions
Traditions are practices passed down generations. They foster unity and continuity, strengthening our bond with our ancestors.
In essence, culture and tradition are the backbone of our society. They provide a sense of belonging and help preserve our heritage.
250 Words Essay on Importance of Culture and Tradition
Understanding culture and tradition.
Culture and tradition are the pillars of any society, shaping the identity and character of individuals and communities. They are the collective manifestation of shared behaviors, beliefs, and values, passed down through generations.
Culture is the lens through which we perceive and evaluate what is around us. It influences our perspectives, attitudes, and behaviors, serving as a roadmap for both individual and community behaviors. It fosters a sense of belonging and security, reinforcing societal norms and expectations.
Significance of Tradition
Traditions, on the other hand, are specific practices or customs that are perpetuated across generations. They provide a sense of continuity and connection to our past. Traditions can foster unity, create positive memories, and build strong relationships within communities.
Culture, Tradition, and Identity
Both culture and tradition are integral to identity formation. They define our roots and give us a sense of belonging. They shape our worldview and influence our values, thus impacting our decisions and actions.
Preserving Culture and Tradition
In an increasingly globalized world, there’s a risk of cultural erosion. It is essential to preserve culture and tradition, not as unchangeable relics of the past, but as dynamic entities that evolve while retaining their core essence. This preservation promotes diversity and enriches global understanding.
In conclusion, culture and tradition are not just about the past. They are living, dynamic aspects of social life that play a critical role in shaping our present and future. Their importance lies in their capacity to promote social cohesion, personal identity, and mutual understanding.
500 Words Essay on Importance of Culture and Tradition
Culture and tradition are integral aspects of human life. They provide a sense of identity, belonging, and continuity, shaping our perceptions and behaviors. As we delve into the significance of culture and tradition, we unravel the profound influences they have on individual and societal development.
The Essence of Identity and Belonging
Culture and tradition are the bedrock of our identity. They offer a unique lens through which we view and interpret the world. Our cultural heritage, expressed through language, art, rituals, and social norms, shapes our worldview and forms our unique identity. This identity, in turn, fosters a sense of belonging, a vital aspect of our psychological well-being.
Preservation of Historical Continuity
Traditions serve as a bridge between the past, present, and future, ensuring historical continuity. They preserve and pass on the wisdom, knowledge, and experiences of previous generations. This continuity provides a sense of stability and predictability, which is essential in a rapidly changing world.
Contribution to Social Cohesion
Culture and tradition play a crucial role in promoting social cohesion. Shared cultural practices and beliefs create a sense of unity and mutual understanding among individuals. They provide a common ground for communication, reducing conflicts, and fostering peaceful coexistence.
Role in Moral and Ethical Development
Culture and tradition also play a significant role in moral and ethical development. They instill values, norms, and moral codes that guide individual behavior and social interactions. These ethical frameworks help maintain social order and harmony, promoting cooperative and responsible behavior.
Challenges and Evolution
Despite their importance, culture and tradition are not static; they evolve over time. Societies must balance the preservation of cultural heritage with the need for adaptation and progress. Unquestioned adherence to outdated traditions can hinder societal growth and development. Conversely, the complete abandonment of cultural practices can lead to a loss of identity and historical continuity.
In essence, culture and tradition are not merely relics of the past but dynamic and evolving aspects of human societies. They provide identity, ensure historical continuity, promote social cohesion, and guide moral development. However, it is equally important to critically engage with our cultural practices and traditions, ensuring they evolve in ways that are inclusive, progressive, and responsive to changing societal needs. The importance of culture and tradition, therefore, lies not just in preservation but also in thoughtful evolution.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Odisha Culture
- Essay on Maharashtra Culture
- Essay on College Life Experience
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
One Comment
It’s was really good……. I loved the essay
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding Essay
Introduction, nature and origins of agriculture, agriculture: essential constituents, people belonging to the culture, impact and further evolution, reference list.
Agriculture is typically defined as “science, art, or practice of cultivating the soil, producing crops, and raising livestock and in varying degrees the preparation and marketing of the resulting products” (Shelach-Lavi, 2015, p. 46).
Culture vs. Discipline
One might argue that agriculture should be viewed as discipline as opposed to culture since it focuses mainly on one aspect of people’s lives, i.e., food. However, agriculture should also be viewed as a cultural phenomenon as it defines the lifestyle of the people participating its processes. Culture, in its turn, is defined as “that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, arts, morals, law, custom, and many other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society” (Whitney & Larson, 2014). Seeing that agriculture shapes the society and defines the course of its further development, promoting the ideas of environmentalism and sustainability, it will be reasonable to assume that agriculture belongs to the domain of cultures.
Back to the Fertile Crescent
The art of growing plants, in fact, has one of the longest histories among the rest of the existing cultures. Resulting from the basic human needs, i.e., the necessity to eat, agriculture emerged in the area known nowadays as the Fertile Crescent. Starting as an attempt to create food reserves for the future, agriculture slowly developed into the art of growing food.
Defining Markets and Trade
While the subject matter primarily revolved around growing plants and working in the field, it slowly started shaping the economy. The effects of the phenomenon under analysis can be traced nowadays in the relationships that agrarian societies build with the rest of the states.
Food and Politics
Although the connection between growing food and entering the political arena might seem somewhat farfetched, one must agree that trade relationships, in general, and food trade, in particular, defined the course of political relationships between states at some point of the global development.
Culture of Food
At the very start of agriculture development, the domain was primarily related to food and the related concepts. There is no need to stress that food is the primary product of the agricultural activities. Therefore, the members thereof consider food as not merely something to fill their stomach with but as a crucial resource, the production of which requires a significant effort and care.
Significance of Natural Resources
The emphasis on nature as the source of products that life depends on is another essential characteristic trait of agriculture. As a culture, it clearly puts a very strong stress on the need to appreciate natural resources.
Connection with Nature
In the present days, the phenomenon under analysis is typically viewed through the lens of sustainability. Agriculture requires a perfect knowledge of a range of plants, good understanding of the natural processes so that the emergent issues such as drought could be addressed properly, etc. Moreover, the members of an agricultural community traditionally stress the significance of exhaustible natural resources as something to be cherished and taken good care of.
The tools that are typically associated with the culture in question have undergone sufficient changes since their invention. At first, agricultural tools implies primarily manual labor. Thus, the use of hand tools such as a hand hay was typical. However, with the technological breakthrough of the 20 th century, machinery is used for these purposes (e.g., tractors, cultivators, sprinkler systems, etc.).
Among the key activities in agriculture, soil cultivation, planting, irrigation, and harvesting deserve to be mentioned. Each of the procedures listed above addresses a certain stage of growing a plant and is primarily carried out with the help of machinery, especially in large agricultural communities.
Reasons Behind the Choice
As a rule, the choice to accept agriculture as a lifestyle is defined by one’s geographical location. Living in the rural area that does not invite one to become a member of any other culture and requires that one should consider agricultural activities as the main source of income are usually the choice factors.
Key Characteristics
In lieu of the recent environment-related issues, particularly, the use of finite sources and the appropriate allocation of resources, environmental awareness and responsibility can be viewed as the essential traits of a farmer.
In addition, talking about farmers as the most common type of agriculturists, one must mention the fact that the given denizens of the state population tend to have a very good sense of togetherness and community. Every single member thereof has strong ties to the rest of the members. The specified phenomenon can be explained by the fact that most agricultural processes must be carried out in a team. Consistent participation in team-related activities, in its turn, creates a sense of togetherness and invites the participants to build strong relationships based on cooperation, commitment, and appreciation for traditions.
Claiming that people belonging to the culture under discussion defy innovations, however, would be wrong. On the contrary, farmers working in the rural areas tend to mix technological innovations and the latest ideas with the traditional approach so that the two concepts could be compatible. The delicate balance, which the task above requires to maintain, allows agriculturalists to remain an integral part of the global community, at the same time being committed to their traditions and culture.
Sustainability in Agriculture
Although the focus of agriculture has always been on natural resources, it has only been comparatively recently that the issue of resource replenishment, the problem of finite resources, and the concept of sustainability were brought up.
In fact, the culture has spurred the growth of biodiversity. Seeing that agriculture encourages sustainable use of resources, it can be considered significant for preventing different environments and habitats from being destroyed. The processes above align with the essential principles of biodiversity promotion, according to the existing definition thereof:
Agricultural biodiversity is a broad term that includes all components of biological diversity of relevance to food and agriculture, and all components of biological diversity that constitute the agricultural ecosystems, also named agro-ecosystems: the variety and variability of animals, plants and micro-organisms, at the genetic, species and ecosystem levels, which are necessary to sustain key functions of the agro-ecosystem, its structure and processes. ( What is agricultural biodiversity? , 2016, par. 1)
Therefore, when considering the impact of agriculture as a cultural phenomenon, one must mention that, in the context of the contemporary green movement, it addresses some of the most topical environmentalism issues. Particularly, the concept of sustainability as the most plausible tool for managing resources use deserves to be brought up.
Agriculture vs. Urbanism: Coexistence as a Solution
As it has been explained above, the current trends in technology and development, in general, affect agriculture on many levels to a considerable extent. Among the trends that are currently shaping the subject matter significantly, the concept of urbanism deserves to be brought up. The phenomenon above is traditionally defined as the process of industrial expansion. It, therefore, implies that urban areas should be expanded and that the rural ones should shrink. Although the identified process may be viewed as positive for economics as it provides opportunities for business growth, it is likely to have a deplorable effect on the development of agriculture unless carried out with the basic principles of sustainability in mind.
Despite the fact that agricultural areas are currently shrinking, the land that is used for the purposes of growing food and carrying out other agricultural activities is still very large. According to the latest estimations, the overall amount of agricultural land made 38% in 2015 ( Agricultural land (% of land area) , 2016). Furthermore, the correlation between the rural and the urban areas has been practically the same (around 36–38%) over the past decade. Although the area above is not populated just as densely as urban areas are, the overall number of people working in the field of agriculture, no pun intended, is still very large. Therefore, although the problem of urbanization as a threat to agriculture remains an issue, there is still time to develop the strategy that will allow retaining this culture.
Technological Innovations
Although the transfer into the digital environment has not yet affected agriculture to a considerable extent, it is expected that agrarian societies will have to suffer significant changes. In case the ideas of environmentalism remain influential in the future society, it can be expected that the digital innovations emerging as a result of the technological progress will be used to enhance the further development of agriculture.
In fact, the adoption of the current IT tools and especially the use of modern media, including social networks should be viewed as an important step in making the discussed culture popular among the rest of the people. Shedding more light on different aspects of agriculture, its proponents will help people understand the goals and objectives thereof. Consequently, extensive support from the rest of the world can be expected by the members of agricultural communities.
Although agriculture is typically interpreted as the process of growing different types of crops, fruit, and vegetables, it can, in fact, be viewed as a unique culture aimed at maintaining balance in the use of natural resources. A large number of people support the ideas that the philosophy of agriculture is based on.
The culture is mostly represented by farmers living in the rural areas. Because of the unique lifestyle, agriculturists have built a strong culture based on the idea of sustainable use of resources and the promotion of support across the community. The emphasis on togetherness that can be traced in the designated setting easily allows assuming that agriculture as a specimen of the contemporary cultural movements needs to be encouraged.
At present, however, the culture above needs significant support. The emphasis on urbanization and the following use of large areas of land hampers agricultural development. Therefore, raising awareness has to be viewed as the next step in making agriculture more resilient to negative external factors.
Agricultural land (% of land area) . (2016)
Shelach-Lavi, G. (2015). The archaeology of early China . Boston, MA: Cambridge University Press.
What is agricultural biodiversity? (2016).
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 26). Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding. https://ivypanda.com/essays/culture-and-agriculture-nature-and-significance-understanding/
"Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding." IvyPanda , 26 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/culture-and-agriculture-nature-and-significance-understanding/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding'. 26 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding." January 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/culture-and-agriculture-nature-and-significance-understanding/.
1. IvyPanda . "Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding." January 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/culture-and-agriculture-nature-and-significance-understanding/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Culture and Agriculture: Nature and Significance Understanding." January 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/culture-and-agriculture-nature-and-significance-understanding/.
- The Free Exercise Thereof: Freedom of Religion in the First Amendment
- Farmers and Their Role in the American Agriculture
- Social Capital in Agriculture and Rural Development
- Effects of Industrialized Agriculture
- Urban Agriculture and Localization
- Urban Agriculture Effects on Economy
- Essay on Sustainable Agriculture
- Farmer Definition and Culture
- Urban Agriculture in Chicago: Pros and Cons
- Big Data and Agriculture
- Agricultural Nutrient Pollution and Its Reduction
- British Growing Peanuts in Tanzania
- Soil Erosion, Its Factors and Preventive Measures
- Osmosis in Living Organism: Germination Experiment
- Urban Agricultural Impact on Human Life
Essay on Indian Culture for Students and Children
500+ words essay on indian culture.
India is a country that boasts of a rich culture. The culture of India refers to a collection of minor unique cultures. The culture of India comprises of clothing, festivals, languages, religions, music, dance, architecture, food, and art in India. Most noteworthy, Indian culture has been influenced by several foreign cultures throughout its history. Also, the history of India’s culture is several millennia old.
Components of Indian Culture
First of all, Indian origin religions are Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism . All of these religions are based on karma and dharma. Furthermore, these four are called as Indian religions. Indian religions are a major category of world religions along with Abrahamic religions.
Also, many foreign religions are present in India as well. These foreign religions include Abrahamic religions. The Abrahamic religions in India certainly are Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Besides Abrahamic religions, Zoroastrianism and Bahá’í Faith are the other foreign religions which exist in India. Consequently, the presence of so many diverse religions has given rise to tolerance and secularism in Indian culture.
The Joint family system is the prevailing system of Indian culture . Most noteworthy, the family members consist of parents, children, children’s spouses, and offspring. All of these family members live together. Furthermore, the eldest male member is the head of the family.
Arranged marriages are the norm in Indian culture. Probably most Indians have their marriages planned by their parents. In almost all Indian marriages, the bride’s family gives dowry to bridegroom. Weddings are certainly festive occasions in Indian culture. There is involvement of striking decorations, clothing, music, dance, rituals in Indian weddings. Most noteworthy, the divorce rates in India are very low.
India celebrates a huge number of festivals. These festivals are very diverse due to multi-religious and multi-cultural Indian society. Indians greatly value festive occasions. Above all, the whole country joins in the celebrations irrespective of the differences.
Traditional Indian food, arts, music, sports, clothing, and architecture vary significantly across different regions. These components are influenced by various factors. Above all, these factors are geography, climate, culture, and rural/urban setting.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Perceptions of Indian Culture
Indian culture has been an inspiration to many writers. India is certainly a symbol of unity around the world. Indian culture is certainly very complex. Furthermore, the conception of Indian identity poses certain difficulties. However, despite this, a typical Indian culture does exist. The creation of this typical Indian culture results from some internal forces. Above all, these forces are a robust Constitution, universal adult franchise, secular policy , flexible federal structure, etc.
Indian culture is characterized by a strict social hierarchy. Furthermore, Indian children are taught their roles and place in society from an early age. Probably, many Indians believe that gods and spirits have a role in determining their life. Earlier, traditional Hindus were divided into polluting and non-polluting occupations. Now, this difference is declining.
Indian culture is certainly very diverse. Also, Indian children learn and assimilate in the differences. In recent decades, huge changes have taken place in Indian culture. Above all, these changes are female empowerment , westernization, a decline of superstition, higher literacy , improved education, etc.
To sum it up, the culture of India is one of the oldest cultures in the World. Above all, many Indians till stick to the traditional Indian culture in spite of rapid westernization. Indians have demonstrated strong unity irrespective of the diversity among them. Unity in Diversity is the ultimate mantra of Indian culture.
FAQs on Indian Culture
Q1 What are the Indian religions?
A1 Indian religions refer to a major category of religion. Most noteworthy, these religions have their origin in India. Furthermore, the major Indian religions are Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism.
Q2 What are changes that have taken place in Indian culture in recent decades?
A2 Certainly, many changes have taken place in Indian culture in recent decades. Above all, these changes are female empowerment, westernization, a decline of superstition, higher literacy, improved education, etc.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Hispanic — Hispanic And Hispanic Culture
Hispanic and Hispanic Culture
- Categories: Hispanic
About this sample

Words: 763 |
Published: Mar 14, 2024
Words: 763 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
6 pages / 2857 words
5 pages / 2072 words
5 pages / 2295 words
5 pages / 2359 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Hispanic
Black African Americans and Hispanic/Latinos are two distinct cultural groups with rich histories and unique identities. Understanding the historical, cultural, linguistic, and socioeconomic factors that shape these communities [...]
Bartolome de las Casas once stated, “Upon this herd of gentle sheep, the Spaniards descended like starving wolves and tigers and lions. ” Las Casas believed that Natives were peaceful and non-deserving of the torment and [...]
Introduction to the Quinceañera celebration in Spanish culture Definition of Quinceañera and its cultural significance Exploration of the origins of Quinceañeras Evolution of the celebration from pre-Hispanic [...]
Do people already assume you speak Spanish because you are of Hispanic descent? Do they judge when they find out you don't? If you don’t understand your culture would that make you any less of a member to your ethnic group. [...]
Frederick Douglass accuses the portrayal of the independent, just, free and individualistic American identity as “inhuman mockery”, falsely advertising that not all people that reside in America possessed the same liberties and [...]
Carlos Bulosan’s America Is in the Heart meditates on the place of Filipino writers within American literature. In America Is in the Heart, there are two “types” of writers that are presented: “American writers” and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Find anything you save across the site in your account
By Lauren Oyler

In her short story “Five Signs of Disturbance,” Lydia Davis writes of a woman who is “frightened”:
She cannot always decide whether what seems to her a sign of disturbance should be counted as such, since it is fairly normal for her, such as talking aloud to herself or eating too much, or whether it should be counted because to someone else it might seem at least somewhat abnormal, and so, after thinking of ten or eleven signs, she wavers between counting five and seven signs as real signs of disturbance and finally settles on five, partly because she cannot accept the idea that there could be as many as seven.
I would have thought it’s normal to be weird about a few things, but being confronted with such a perspective always makes me doubt myself. I, too, wonder constantly if the things I do and experience are normal. But I have many more signs of disturbance than ten or eleven. I think.
I could say I’m sleeping badly, but it’s worse than that—I’m sleeping incorrectly. When I lie down, I don’t actually rest my head on the pillow; instead, I hold it slightly aloft, so that it touches the pillow but, instead of sinking into the soft material, remains hovering above it. To an observer I would seem to be lying down normally. I tell myself to relax—among other issues, I’m worried I’ll develop a thick neck. When I do, I’m shocked at how much I had just moments before been not relaxing. This is sleep , I think. This is what going to sleep actually feels like . But soon I find my head has risen above the pillow again, and I must admit to myself that I don’t know what going to sleep actually feels like.
From this you’d think I have trouble falling asleep; not so. I’m usually exhausted. But I almost always wake up too soon. Sometimes for no reason; sometimes by a tingling in my ring and pinky fingers, which I experience because I hold my arms tense in sleep, often with my hands in fists so tight that they leave marks from my nails on my palm. I learned the tingling is caused by the ulnar nerve, from a masseuse who observed my posture; she also intuited that I had been born via C-section and was thus likely dealing with an original sense of having been forcibly removed from a place of safety. The clenching, broadly, leads me to grind my teeth, which I have done for at least ten years, and the grinding, probably, leads to the tinnitus, which is relatively new. One of these things might also be at fault for what’s known as exploding head syndrome: at night, I sometimes see flashes of light behind my closed eyes, as if there are fireworks outside my window, and hear mechanical sounds that aren’t there. Despite its spectacular name, the condition is “prognostically benign,” accompanied by no pain or immediate threat to health. The fear I experience along with these hallucinations inspires a series of logical justifications: it’s all in my head, which is, of course, exactly the problem.
Trouble sleeping is certainly normal, but it doesn’t help the project of being awake. While socializing, I am cheerful, gossipy, and quite fun until I’m sleepy, but sometimes I catch myself doing artistic things with my hands and posture—fidgeting, wringing, clenching—even as I engage charmingly (I hope) with my interlocutors. Other times, I will look down from a conversation and notice, Oh, the fist again; because I can laugh at myself, I hold it up to show my friend, as if it contains a surprise. I do not pick or bite my nails, but in groups or alone, at home or out, I cannot keep my shoulders down. (Large deltoids—almost as bad as a thick neck.) Twice now, at parties, men have come up behind me and attempted to physically correct my posture, followed by a little lecture. Never mind the cell-phone addiction, the laptop that sits on the table so that I must look down on it, the ambient tension of contemporary life, when I must be on guard against men who randomly correct my posture. The slouch, they say, is the result of my failure to accept myself as a tall woman.
I honestly don’t think that’s it, but should you really take my word for it? I sometimes feel strange pains in various parts of my body, just fleeting ones, which I then waste a lot of time thinking about. I have occasionally fainted for no reason, and more than once broken out in hives. I get sweaty, feel anxious about being sweaty—about the sweat becoming visible to others, disgusting them—and get sweatier. After I go in the sun, I experience what I call a sunburn neurosis, my skin burning and tingling, though I remain, owing to anxious sunscreen application, as white as a Victorian ghost; I haven’t had a sunburn since I was a teen-ager. Acid reflux can last for weeks. I often find it difficult to eat because I am nauseated due to stress.
I don’t have any phobias, but I do feel afraid. When I’m particularly stressed, I sense movement out of the corner of my eye and jump, like an animal preparing to fend off attack; there’s nothing there. I hold my breath, make little noises, sing little songs, shake. Sometimes I perform feats of what might look from the outside like symptoms of very mild obsessive-compulsive disorder: checking more than twice that the front door is locked; changing the combination on a locker at the gym or a museum multiple times, because I am afraid someone saw me set it. I am hesitant to even mention this one, knowing, because of my years-long Internet addiction—which I would attribute to, among other things, an attempt to escape my anxious, spiralling thoughts, or maybe to externalize them—that if someone claims they “are O.C.D.” about facts of life, such as cleaning the kitchen, people get mad: perfectionism, neuroticism, and thoroughness are not O.C.D. In my defense, I never clean the kitchen.
My work suffers, of course. How could it not? I’m sadly not a perfectionist but, rather, an avoider and a regretter. There are periods when I will respond to e-mails at a reasonable pace, and then there’s the e-mail about a potentially lucrative project that I ignored for months. I haven’t even opened it; I don’t know what it says. Since childhood, I’ve had versions of “the packing dream,” in which I am surrounded by clothes strewn chaotically around the room, and I cannot choose what to bring on a trip. I may have enough time to finish packing, or I may already be too late. Whatever the scenario, it’s never one of those dreams about physical impediments, in which you try to move but can’t; the obstacle is always only my own mind, my own incapability, and that is the torment—that I’ve done this to myself. (I have never actually missed a flight.) As for work, I always manage to “get it done,” though I don’t know how. It’s probably a reasonable enough fear of failure—or fear of failing to achieve the impossibly ambitious vision in my mind—that is my obstacle. Even worse is the possibility, floated by sanguine meditators and accepters of things-as-they-are, that I may need the anxiety, and the promise of eventual relief from it, to do anything at all.
What about panic attacks? I’ve never had the kind of panic attack that people mistake for a medical emergency, but sometimes I become very still, sort of unable to move, for, I don’t know, ten to twenty minutes to an hour, and my muscles are sore the next day. There are the usual racing thoughts: love, squandered potential, unlikely vanities, loss of income. Injustices committed against me; chores. Will I get cancer? Knowing that everyone worries they have cancer helps only a little bit. My ultimate anxiety is not that a certain fear will come true. Rather, I experience panic as mostly meta: the horror of being trapped, in this mind-set, for the rest of my life.
Naturally, I am not merely anxious; I am also very sad. The two are, for me, inextricable: I get anxious that I’ll get sad and sad that I’m so anxious. It’s harder to describe the depression, and the fear of it, because fewer physical symptoms are involved. Weeping, that telltale sign of sadness, is usually cathartic, a response to a specific buildup of identifiable issues, and thus not involved in what I can’t help but think of as the true suffering, which recedes and returns, recedes and returns. People often talk about being unable to get out of bed in the morning. What if you can get out of bed—after about an hour and a half of lying awake in it, thinking about how you should get out of bed? What if you can get out of bed but find it beckons you back throughout the day? What if you are, owing to your difficulty sleeping, just tired? Which comes first, exhaustion or depression? Does it matter?
Even knowing that “normal” is a nefarious construct, used to shame and control, there’s something about these symptoms that makes me want to know how many people have them; they mean nothing to me alone because none of them is so unusual as to cause alarm, or even merit comment, and so they might mean anything. Is it really such a big deal? I don’t know where to put the emphasis, how to tell it, and this is particularly disturbing because knowing where to put the emphasis is my vocation, which is also bound up with, I’ll admit, my “sense of self.” “You don’t seem anxious,” friends will say, surprised at my competent narration. This is not the response I want. How competent could it be if no one believes what I’m telling them?
I can shift the blame. As with anything that matters, the language we use to describe “mental illness” is all wrong. Mental illness is “real,” as real as a tumor, but not the same kind of real as a tumor. Its effects are measurable, in blood pressure or hours slept, or noticeable, in weird hand gestures or an erratic mode of speaking, but mental illness has no shape or volume; its size cannot be conveyed through comparisons to fruits and vegetables. It becomes real in the description of its effects, in the naming of everything around it, rather than in attempts to define it, though we have many words and phrases that approach the task. “Disturbance” is funny, and accurate, because it refers both to the internal condition and what it produces: behavior that might unsettle oneself or others. I become “nervous” in small-stakes situations of short or predetermined time frames; “nervousness” no longer describes the anxious disposition, as it did in the past, but the feeling of being anxious about a specific thing that is usually imminent. I’m “neurotic” because I know the basics of psychoanalysis and am a fast-talking big-city professional; I’m “neurasthenic” because I know the word. My mother used to call herself, as well as me, a “worrywart”; to “worry” is to fidget with something in the mind. “Panic” is acute, “attack” is very acute, and a “fit” is a cute version of a “panic attack”; “throwing a fit” is what children do and what adults do when they are “freaking out” while simultaneously making childish demands. Like “freaking out,” “going insane” is applicable as a joke in retrospect, though it became too popular on the Internet and lost its edge, particularly because the sort of people who said it were just the sort who ought to be arguing that the usage stigmatizes people with mental illnesses. I still indulge in “crazy,” which is classic, and permitted, I think, because I am. “Distressed” is the joke version of nervous, though someone “in distress” is being euphemized, as is someone “behaving erratically.” A “crisis” is both intense and prolonged; a “spiral” is a crisis about one issue, characterized by repetitive and catastrophic thinking, and “spiralling” may feature prominently in crises, but in a slightly funny way. I fear having a true “breakdown,” which suggests, to me, among other things, a failure of speech, but I also fantasize about having a true breakdown for the same reason. I am rarely, if ever, “hysterical”; that’s sexist. “Mentally ill” is, of course, insufficient, though when I have seen other people “in crisis” I have thought I actually understand the term. The concept of “mental health,” did you know, comes from Plato, who said that it could be cultivated through the elimination of passion by reason. Today, good mental health means something like the elimination of both passion and reason.
Unless I’m about to appear onstage, in which case I am “nervous,” I describe myself as “anxious” so that people know I’m serious: this is not a passing worry but a constant state, and if I were to seek a medical diagnosis I would get one, handily. The question “Why don’t you?” naturally arises. The answer is that I do not feel it would help, and might even create more problems than it solves. In medicine, the problem of language is a problem of classification; I do not seek a diagnosis, probably, because I do not want to be trapped in a single term. (I hate being trapped, you might have noticed.) Like everyone else’s, my mind dabbles in an array of mental illnesses to create a bespoke product, and I find all the terms I know either ludicrously broad or ludicrously specific. I learned from Scott Stossel’s upsettingly thorough 2014 book, “ My Age of Anxiety: Fear, Hope, Dread, and the Search for Peace of Mind ,” that the term “generalized anxiety disorder” was conceived at a dinner party, in the nineteen-seventies, held among members of a task force working on the DSM-III . According to David Sheehan, a psychiatrist who was there, they were all drunk, wondering how to classify a colleague who “didn’t suffer from panic attacks but who worried all the time . . . just sort of generally anxious.” “For the next thirty years,” Sheehan continues, “the world collected data” on the group’s drunken musing. The point of this anecdote, Stossel establishes, is not to say that generalized anxiety disorder isn’t real but to demonstrate how somewhat arbitrary decisions made by powerful people can shape how we see ourselves. I also don’t mean to suggest that the ideas that we have while drunk are bad—more that drunkenness can give us an admirable economy and frankness, and encourage us to just pick something and go with it, something that some of us, sober, really struggle to do.
An essay like this is supposed to have a narrative. Where does my anxiety come from? Famously, it’s overdetermined. First, my parents: they passed down bad genes, and then they might not have raised me right. To go further I’d have to discuss the ways that they might not have been raised right, and then discuss the ways that they might not have raised me right. Although, like everyone, I have a list of these in the Notes app on my phone, and I update it every few days when a new injustice committed against my past innocence reveals itself, I am hesitant to go down this path, which narrows to a tunnel, which is eventually pitch-dark. The packing dream, a desire to escape my humble origins; the sunburn neurosis, from my mother’s warnings. I am the way I am because my father did this, or my mother didn’t do that. Not a very satisfying conclusion.
What about society? That’s what’s fucked up. In the early two-thousands, a group of academics in Chicago formed a collective called the Feel Tank—an alternative to the think tank, though of course they also opposed “the facile splitting of thinking and feeling.” According to their manifesto, they sought “to understand the economic and the nervous system of contemporary life” by being “interested in the potential for ‘bad feelings’ like hopelessness, apathy, anxiety, fear, numbness, despair and ambivalence to constitute and be constituted as forms of resistance.” One of their early slogans was “Depressed? . . . It might be political.”
Here the concept of normality truly collapses: what is normal—financial precarity, an inability to plan for the future, war—is not good at all. Feel Tank Chicago was established as part of the “affective turn” in the academic humanities, which began in the nineties; this approach to understanding emotions as shaped by power structures has become wildly influential, though it’s not new. For example: the concept of Americanitis, popularized by William James at the end of the nineteenth century, described “the high-strung, nervous, active temperament of the American people,” according to an 1898 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association . The causes—advances in technology and accompanying pressures of capitalism—were much the same as they are today. Wherever the contemporary occurs, anxiety and depression are seen as natural reactions to it, and performances of profound mental discord in response to the news will be familiar to anyone on social media.
If conventional understandings of mental illness tend to make it about you—the chemicals in your brain or the particular contours of your childhood—this conception wonders if you can harness its power to make things better for everyone. Nice. But there’s something a little simplistic about the way one can attribute all feelings of negativity, disconnection, or anxiety to what amounts to a higher power, as anyone who’s read those social-media laments will know. Doesn’t this encourage more bad feelings: solipsism, nihilism, futility? Looking for something to blame may feel better than beating oneself up, but it doesn’t feel good . In her 2012 book, “ Depression: A Public Feeling ,” Ann Cvetkovich describes the Public Feelings Project—Feel Tank Chicago described themselves as a “cell” of this larger group—as an attempt to “depathologize negative feelings so that they can be seen as a possible resource for political action,” but without suggesting “that depression is thereby converted into a positive experience.”
Indeed, the encouragement to understand our suffering as determined by external conditions does not seem to ease it. The comfort of believing you are normal is that you have company in misery and that your condition seems less likely to become worse. But if “normal” is, by definition, something that is getting worse all the time, then your condition is a form of solidarity—not necessarily a source of solace. (And if you derive solace from the solidarity, do you really want to sacrifice the quality that grants you access to it?) For my purposes—which are, I suppose, to understand whether and how I am abnormal without annoying the reader—stories that foreground their protagonists’ participation in public feeling tend to be unsatisfying. If my suffering has nothing do with me, if it’s the expression of social and political conditions, why should the reader, or well-meaning friend, care? This is why narratives that compete directly with the idea of collective feeling and collective resistance, conservative tales of bootstrapping and hard work, are so compelling: they make a lot more sense.
Until the revolution that would be our relief comes, we must “do the work” to get better ourselves. “Have you tried talking to someone?” people ask, when I mention my various issues. Are you that somebody? No: they mean that, in addition to the natural sleep aids, the regular exercise, the healthy diet, the cultivation of hobbies, the having of friends, the practicing of meditation, and the occasional massage, I should go to therapy.
I have tried talking to someone; it’s fine. The responses I get when I utter the magic words “my therapist” are more thought-provoking than any of the personal revelations I’ve uncovered with him so far, though the idea is that you need to do it for years for the benefits to accrue. “I’m proud of you,” friends say. As if it is so difficult to think seriously about myself for hours a day—as if that weren’t what I was doing with my anxiety anyway. These friends will talk about my problems with me endlessly, as long as I am “in therapy.” If I am not, or if I express my doubts about the possibility of transcending the workings of my own mind by paying someone to guide me through the process, the response is unanimous: I must find a new therapist, someone who is “right” for me. They wonder, gently, gently: Is it possible that I, so high-achieving, am unconsciously telling the therapist what I think he wants to hear—deceiving him by being adequately emotional, apparently reflective, in order to give true self-knowledge the slip? Should I not find someone meaner, nicer, female, more intellectual, less intellectual, someone who will not fall for my tricks?
Or: I must try a different therapeutic approach. A bit of research quickly reveals an expanse of options: somatic-experiencing therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, dialectical behavioral therapy, integrative therapy, gestalt therapy, humanistic therapy, psychodynamic therapy, exposure therapy, shock therapy, biofeedback, counselling, coaching, one of the innumerable schools of psychoanalysis. At a wedding, I was strongly recommended E.M.D.R., or “eye-movement desensitization and reprocessing” therapy, in which eye movement is stimulated in an attempt to retrain the brain to respond to trauma. Some of these styles of therapy are more or less the same thing, just with different names, but, given the nature of the enterprise, you have to assume that the selection of one name or another, or a combination of names, indicates subtle differences in method that surely multiply to create different outcomes. Whether you’re supposed to think about outcomes is a key differentiating factor in therapeutic approaches.
A psychiatrist might prescribe medication, a fraught topic. It’s hard to write about medication without having taken it oneself, which I have so far resisted. I’ve tried a couple of popular pharmaceuticals recreationally and find I am more afraid of them than I am of illegal club drugs; they really work. While I have no idea what it’s like to be on psychiatric medication long term, no one else can say what it’s like, either; the medications famously interact with each person differently, so there is no way to understand them as an experience except through trial and error. The possible side effects are sometimes just as bad as the symptoms they’re supposed to alleviate. The process of stopping these medications, which many patients want to do , is criminally under-studied and requires a painful period of weaning that comes with prohibitively bad side effects, too. (To start antidepressants is to sign up for some future moment when you won’t want to take them anymore, and to have to decide whether you want to experience “brain zaps” in order to stop.)
At the same time, they often help. Criticize what you believe to be the craven overprescription of psychiatric medication in the United States and someone on the Internet will take personal offense: Wellbutrin saved my life! At the end of Sheila Heti’s 2018 novel, “ Motherhood ,” the narrator begins taking antidepressants, and all her problems—primarily her vacillation about the question of whether to have a child, which constitutes the entire novel, along with a debilitating, weeping sadness around her period—are suddenly solved, with what the critic Willa Paskin called a “lexapro-ex-machina.” The abruptness of the ironic conclusion is itself a comment on the role that psychiatric medication plays in North American life, but this plot point, one of the book’s very few, also demonstrates the way philosophical searching ceases when the anguish that propels it is no longer there. Medication allows Heti’s narrator to ignore the upsetting reality that she could go on trying to decide, or regretting, forever. There is no arc, nor character development, nor point, without anticlimactic intervention.
I once attended a session of what I called jaw yoga, hoping to “manage” my bruxism. It was conducted by a Greek woman named Angela who described herself as a dancer, choreographer, and yoga coach; she was also, incredibly, an actual dentist. At the union of these disparate interests was a passionate belief that the jaw had been neglected in the world of dance and that the rest of the body had been neglected in the world of dentistry. “Once you are grinding and pressing the teeth, your cranium and shoulders, hips, knees and feet are reacting to this pressure,” her course description read, beneath a photo of her lying on her stomach, cupping her jaw in her hands. “Once the skeleton is affected, also the organs are reacting. A chain reaction of organs and emotions is put in motion.” She told us how to identify the various parts of the jaw and ended the class by singing along to a recording of “All You Need Is Love.” As we left, she passed out business cards that read “You are the point.”
It didn’t work, though maybe I should have attended more sessions. A resistance to helping oneself is often a simple denial of reality: I don’t want it to be true that I need help, not because I would like to imagine myself as strong and never in need—a common explanation—but because I do not want to have these problems that are notoriously difficult to solve, about which there is no professional agreement. I do not want to embark on a years-long project dedicated to my own mind. I have other things to think about.
A final worry: Am I being confessional? The great trick of declaring outsized anguish, of being publicly and clinically wrecked by one’s feelings, is that once you do it your feelings set the limits, and no one wants to hurt them. The confession is a simple form of writing. It does not contextualize, illuminate, or complicate. Its main purpose is not the creation of aesthetic beauty out of the materials at hand (life, pain) but selfishness: relieving the confessor’s desire to confess. The form travels in one direction, from me to you, offering no path to analysis, critique, or, God forbid, argument. If the feelings are unique, the confession is justified; if they’re normal, it is, too. One yearns for the breakthrough, the epiphany, the point, that will make sense of it all, and thus cure it. But catharsis for me is boring for you. ♦
This is drawn from “ No Judgment .”
New Yorker Favorites
The repressive, authoritarian soul of “ Thomas the Tank Engine .”
Why the last snow on Earth may be red .
Harper Lee’s abandoned true-crime novel .
How the super-rich are preparing for doomsday .
What if a pill could give you all the benefits of a workout ?
A photographer’s college classmates, back then and now .
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Shayla Love
By Sunita Puri
By Leslie Jamison

By Cal Newport

Kinkela essay published in ‘A Cultural History of Insects in the Modern Age’

Dr. David Kinkela
“Food and Insects,” an essay written by Department of History Professor David Kinkela, has been published in “A Cultural History of Insects in the Modern Age.”
Each of the work’s six hardcover volumes covers the same topics, so readers can either study a period/volume or follow a topic across history. Dr. Kinkela’s essay appears in the Modern Age volume (1920 to the present).
“I looked at music, film, television and new movies, and how ideas of insects and food production were depicted in particular cultural forms,” Dr. Kinkela explained. For example: the bool weevil, a beetle, in the traditional blues song “Bool Weevil Blues.”
Other areas explored include monster movies of the 1950s, how gigantic insects were depicted on movie screens in that same era and the rhetoric around organic and industrial farming and pest control in the agricultural system. “I also discovered a great ‘Saturday Night Live’ skit, showing killer bees invading the U.S., with John Belushi and Dan Aykroyd,” Kinkela noted. Also found was “The Bee Movie,” voiced by comedian Jerry Seinfeld.
Kinkela incorporates research that he compiled for essay in two courses that he teaches: HIST 352: U.S. Environmental History and HIST 310: World Environmental History.
“A Cultural History of Insects” reveals people’s relationship with insects – in life and in death – and is published by Bloombury Academic Presson.
- Department of History
- College of Liberal Arts and Sciences
You May Also Like

Hegna co-authors paper on the early fossil record of clam shrimp
The Devonian (about 355-415 million years ago) was when the clam shrimp — a still-living group of crustaceans that can be found in western NY — first appeared in the fossil record.

Lim interviewed for new book that explores technology success stories in performing arts
A new theatre design resource, “Raising the Curtain: Technology Success Stories from Performing Arts Leaders and Artists,” features information and insight by Scenic Design Associate Professor Czerton Lim.

Fredonia music faculty, alumna commissioned to write music in celebration of total solar eclipse
School of Music Lecturer and alumnus Andrew Martin Smith and former adjunct lecturer Jamie Leigh Sampson were commissioned by the Toledo Alliance for the Performing Arts to collaborate in the creation of new musical compositions in celebration of the total solar eclipse crossing North America.
After a writer expressed sympathy for Israelis in an essay, all hell broke loose at a literary journal

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
What are the limits of empathy in war?
That’s the question that Joanna Chen, a liberal writer and translator who is Jewish and lives in Israel, probed in an essay about her struggles since Oct. 7 to connect with Palestinians.
“It is not easy to tread the line of empathy, to feel passion for both sides,” she wrote in the literary journal Guernica , explaining that she briefly stopped her volunteer work driving Palestinian children to Israeli hospitals for lifesaving medical care.
“How could I continue after Hamas had massacred and kidnapped so many civilians,” she asked, noting that the dead included a fellow volunteer, a longtime peace activist named Vivian Silver. “And I admit, I was afraid for my own life.”

The essay, titled “From the Edges of a Broken World,” provoked an uproar in the activist literary world. Over the weekend, more than a dozen of the publication’s staff resigned in protest — and Guernica removed the essay from its website.
“Guernica regrets having published this piece, and has retracted it,” the magazine said in a statement . “A more fulsome explanation will follow.”
Among those who quit was the co-publisher, Madhuri Sastry, who wrote on X that the essay was “a hand-wringing apologia for Zionism and the ongoing genocide in Palestine.”
Sastry also called for the resignation of the editor in chief, Jina Moore Ngarambe, a veteran foreign correspondent. Ngarambe did not respond to requests for comment.
In a statement to The Times on Tuesday, Chen said: “Removing any stories and silencing any voices is the opposite of progress and the opposite of literature.”
“Today, people are afraid to listen to voices that do not perfectly mirror their own,” she said. “But ignorance begets hatred. My essay is an opening to a dialogue that I hope will emerge when the shouting dies down.”
The retraction of the essay comes as a new generation of activists in the literary world frames the conflict in the Middle East as a black-and-white battle between two sides — oppressor and oppressed — and pressures institutions to boycott Israeli or Zionist writers.

World & Nation
U.S. college campuses have embraced the Palestinian cause like never before. The story began decades ago
The Palestinian cause — and hostility toward Israel — has shifted from the sidelines of student activism to a robust political movement at U.S. colleges.
Dec. 7, 2023
In January, protesters from Writers Against the War on Gaza disrupted a PEN America event in Los Angeles featuring actor Mayim Bialik, who supports Israel and opposes a cease-fire. Last month, the Jewish Book Council, a nonprofit that promotes Jewish writers and stories, launched an initiative for authors, publishers, agents and others to report antisemitic incidents in the world of publishing — from “getting review-bombed because their book includes Jewish content” to “threats of intimidation and violence.”
For many activists, giving voice to opposing points of view or conveying empathy for Israeli victims of Hamas amounts to both-sidesism that glosses over power imbalances. Israel says that Hamas killed about 1,200 people on Oct. 7, prompting an invasion that authorities in Gaza say has killed more than 31,000 people.
On X, Guernica’s former fiction editor, Ishita Marwah, slammed Chen’s essay as a “rank piece of genocide apologia” and condemned Guernica as “a pillar of eugenicist white colonialism masquerading as goodness.”
Grace Loh Prasad, a Taiwanese-born writer based in the Bay Area who published an excerpt of her new memoir in Guernica last week, wrote : “I am alarmed & upset that my writing has appeared alongside an essay that attempts to convey empathy for a colonizing, genocidal power.”
Hua Xi, Guernica’s former interviews editor, singled out a passage in which Chen describes a neighbor telling her she tried to calm her children who were frightened by the sound of military planes flying over their house: I tell them these are good booms.
Chen writes: “ She grimaced, and I understood the subtext, that the Israeli army was bombing Gaza.”
For Xi, quoting an Israeli calling bombs “good booms” undermines Guernica’s “premise that they are holding space for Palestinian writers.”
Rather than just disagree, these activists are calling for the silencing of voices they view as harmful.
On social media, an activist accused Chen of “both-sidesing genocide.” Another condemned Chen, who was born in Britain and moved to Israel with her parents when she was 16, as “a settler who has settler genocidal friends and raised settler genocidal children.”
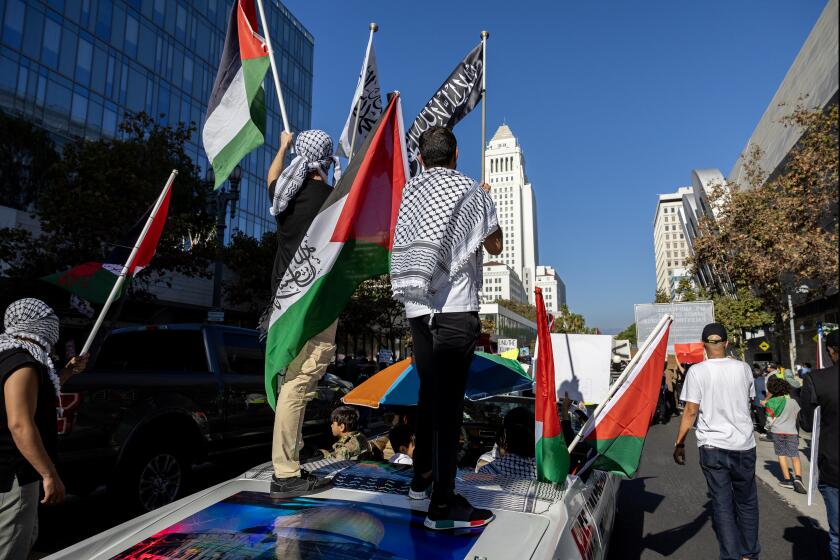

‘This is not a pro-Hamas protest’: Palestinian Americans fight charges of antisemitism
The Palestinian cause has never had so much support. But some Palestinian Americans say the movement has a messaging problem.
Dec. 21, 2023
Established in 2004 amid the U.S. invasion of Iraq, Guernica was founded as an unabashedly antiwar, anti-imperialist publication, according to one of its founders, Josh Jones.
The journal took its name from a Lower East Side bar where two of the founders participated in a reading series, and Picasso’s iconic painting depicting the horror of the 1937 bombing of the Basque town in northern Spain.
Guernica’s leaders did not always agree on what it meant to be antiwar — particularly as a growing wave of pro-Palestinian activists called for not platforming pro-Israeli voices.
Sastry wrote on X that over the last few months she urged Guernica’s leaders to “commit to cultural boycotts” organized by pro-Palestinian activists. They disagreed, she wrote, telling staff in an email that “Guernica’s political projects can be found in what we publish.”
For the record:
8:23 a.m. March 13, 2024 An earlier version of this article said Madhuri Sastry flagged concerns about a Joanna Chen story published in Guernica’s “Voices on Palestine” compilation. The story was published but not included in the collection.
But Sastry did not always like what the magazine published. Even before this week, she said, she raised concerns about a previous story by Chen that was being considered for the magazine’s “Voices on Palestine” compilation. It was ultimately excluded.
At the same time, Guernica’s editors received complaints that their magazine lacked a complexity of voices and was too pro-Palestinian.
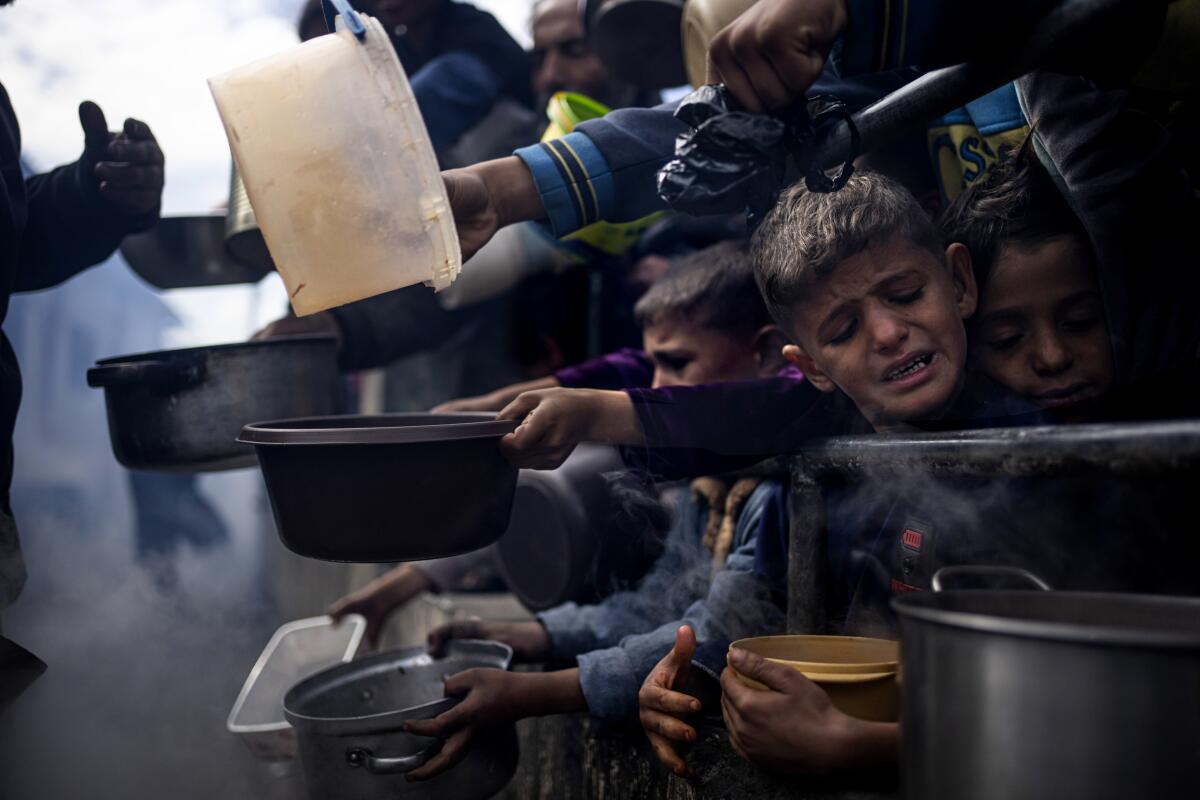

Emily Fox Kaplan, an essayist and journalist who is Jewish and has written for Guernica since 2020, wrote on X that “the only mistake Guernica made was not publishing a wide variety of voices” on the Israel-Palestinian issue “from day one.”
“The problem, when it really comes down to it, is that it presents an Israeli as human,” Kaplan wrote of Chen’s essay. “The people who are losing their minds about this want to believe that there are no civilians in Israel. They want a simple good guys/bad guys binary, and this creates cognitive dissonance.”
Other writers accused activists who attacked Chen’s essay of “bareknuckled antisemitism” and Guernica of “ taking its cue from Joe McCarthy and MAGA book burners .”
“God forbid someone might think Israelis are complex human beings, and not just demons,” said Lahav Harkov, a senior political correspondent at Jewish Insider.
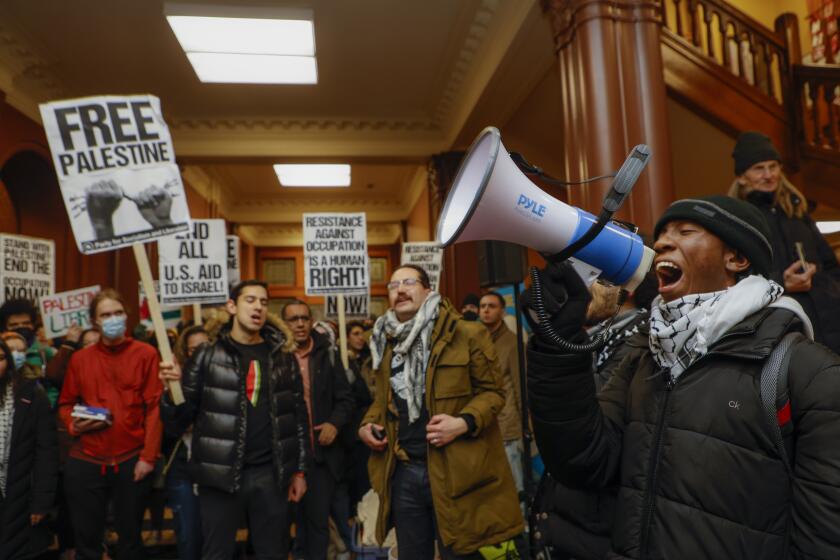

The antisemitic cartoon roiling Harvard? It’s not the first time it caused a firestorm
Activists set out to highlight the links between Black and Palestinian liberation. They dredged up a historic dispute over an antisemitic cartoon.
Feb. 23, 2024
Chen said in her statement to The Times that she did not realize the essay was sparking more than usual criticism until Saturday evening when a friend texted to alert her that one of the Guernica editors had resigned. She reached out to the editor in chief that evening and they spoke briefly Sunday morning.
“Since then, nothing,” she said.
“Guernica claims to be ‘a home for singular voices, incisive ideas, and critical questions’ but apparently there is no longer space in this home for a real conversation,” Chen said. “But I do not regard this as a missed opportunity: my words are being read and the door is still, in fact, open.”
Her essay, which is available on the Internet archive , Wayback Machine, offers a personal account of living in Israel before and after Oct. 7.
She wrote that she struggled to assimilate when she moved to Israel. Two years later, at 18, she chose not to serve in the Israel Defense Forces. Besides her volunteer work with Road to Recovery, which provides transportation for Palestinian children to hospitals, she describes donating blood to the people of Gaza. She also translated and edited the poems of Palestinian poets, believing their voices were “just as important” as the voices she translated from Hebrew.
After Oct. 7, Chen wrote, “I listened to interviews with survivors; I watched videos of atrocities committed by Hamas in southern Israel and reports about the rising number of innocent civilians killed in a devastated Gaza.”
She described holding a space in her mind for the victims in both Israel and Gaza: “At night, I lay in bed on my back in the dark, listening to rain against the window. I wondered if the Israeli hostages underground, the children and women, had any way of knowing the weather had turned cold, and I thought of the people of Gaza, the children and women, huddled inside tents supplied by the UN or looking for shelter.”
When a fellow volunteer expressed anger that Palestinians she had helped did not reach out after Oct. 7, Chen did not take sides.
“The Palestinians in the West Bank were struggling with their own problems: closure, the inability to work, the threat of widescale arrests being made by the Israeli army, and harassment by settlers,” she wrote. “No one was safe.”
Two weeks after Oct. 7, Chen writes, she resumed volunteering for Road to Recovery, ignoring her family’s fears for her safety, and drove a Palestinian boy and his father to an Israeli hospital. When they exited her car and the child’s father thanked her, she wrote, she wanted to tell him: “ No, thank you for trusting me with your child. Thank you for reminding me that we can still find empathy and love in this broken world.”
For activists who object to the very existence of Israel, Chen’s liberal framing — and refusal to take a stance — is inherently problematic: They say that the focus on finding empathy and love in a broken world ultimately justifies the status quo.
In her critique of the essay, April Zhu, former senior editor for interviews, wrote the essay starts “from a place that ostensibly acknowledges the ‘shared humanity’ of Palestinians and Israelis, yet fails or refuses to trace the shape of power — in this case, a violent, imperialist, colonial power — that makes the systematic and historic dehumanization of Palestinians ... a non-issue.”
Some argued that Chen’s liberal perspective was more problematic than any conservative voice.
“I find open warmongering less nauseating than this sort of self-pitying faux-bleeding heart claptrap,” wrote an independent filmmaker from L.A. “The fascist propagandist is at least honest. The liberal propagandist never shuts up about how tormented they are by the terrible *complexity* of it all. Get over yourself.”
More to Read

Letters to the Editor: ‘War is hell’ is an awful excuse to keep killing Palestinians
Feb. 29, 2024

Opinion: How the fight against antisemitism is now used to promote an ‘anti-woke’ agenda
Jan. 24, 2024

Israel’s media mostly keep Gaza’s human toll out of sight
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Jenny Jarvie is a national correspondent for the Los Angeles Times based in Atlanta.
More From the Los Angeles Times
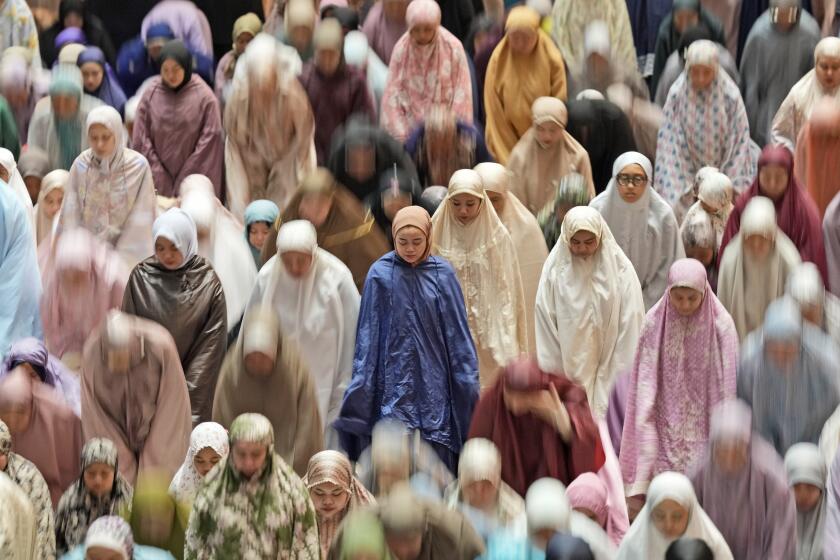

What is Ramadan and how do Muslims observe the Islamic holy month?
March 15, 2024

The first ship to use a new sea route delivers aid to Gaza, Israeli military says

Proposed U.S. resolution would back global efforts for an immediate and sustained cease-fire in Gaza

Biden backs Schumer after senator calls for new elections in Israel
Get JTA's Daily Briefing in your inbox
I accept the JTA Privacy Policy .
By submitting the above I agree to the privacy policy and terms of use of JTA.org
Guernica magazine retracts Israeli writer’s coexistence essay that co-publisher called an ‘apologia for Zionism’
( JTA ) — Amid criticism from staff members and others, a prestigious literary magazine has retracted an essay by an Israeli writer and translator wrestling with her attempts to find mutual understanding with Palestinians after Oct. 7.
Guernica magazine did not explain the retraction over the weekend but said it “regrets having published” the essay by Joanna Chen, titled “From The Edges Of A Broken World.”
The retraction came after multiple members of the journal’s volunteer staff resigned publicly over the essay.
Madhuri Sastry, a human-rights worker and researcher formerly of the American Red Cross, quit as co-publisher on Sunday after calling the essay “a hand-wringing apologia for Zionism and the ongoing genocide in Palestine.” She also called for the resignation of the magazine’s editor-in-chief, Jina Ngarambe.
As many as 15 other editors and staffers also resigned, according to a review of recent changes to the magazine’s masthead, many after making their own public statements decrying the essay and Guernica’s choice to print it. Ishita Marwah, Guernica’s departing fiction editor, for example, wrote that publishing the piece made the magazine “a pillar of eugenicist white colonialism masquerading as goodness.”
The Guernica page that used to house Chen’s essay now reads, “Guernica regrets having published this piece, and has retracted it. A more fulsome explanation will follow.”
Chen did not immediately return a request for comment on Sunday.
The retraction comes amid widespread tensions within the literary community over the Israel-Hamas war. A number of independent literary magazines like Guernica have prioritized pro-Palestinian narratives, and Jewish and pro-Israel authors have been targeted with online criticism. The situation is so acute that the Jewish Book Council, a nonprofit that promotes Jewish writers and stories, recently launched an initiative to track antisemitism in the literary world .
Guernica’s case stands out because Chen, and her essay, are deeply critical of the present situation in Israel. Chen, a writer and translator of both Hebrew and Arabic work who moved to Israel from the United Kingdom as a teenager, wrote for Guernica in 2015 about her efforts not to build on land from which Palestinians had been displaced. In the retracted essay, she details her commitment to coexistence and frets over the ways in which Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack on Israel has challenged it.
Chen writes that she did not serve in the Israel Defense Forces, and describes how she worked as a volunteer for Road to Recovery, an organization in which Israelis provide transport for Palestinians who are seeking medical care, both before and after Hamas’ attack (while briefly pausing in the immediate aftermath). She also recalls an experience donating blood to Palestinians during Israel’s 2014 war in Gaza, for which she received blowback from other Israelis. But she says the bridges she had been working to build felt impossible to complete after Oct. 7.
“It is not easy to tread the line of empathy, to feel passion for both sides,” Chen writes in the piece, which also includes translated excerpts from Hebrew- and Arabic-language poems. It remains available online through the Internet Archive .
Of two Gaza-based poets whose work she previously played a role in translating, Chen wrote, “Their voices are important ones, and I want the English-speaking world to listen to them as much as I want the world to listen to the voices I translate from Hebrew.”
Almost as soon as the piece appeared online, it began drawing criticism from within the Guernica staff. Founded in 2004 partly in response to the Iraq War and named after Pablo Picasso’s famous anti-war painting, the nonprofit magazine has long married literary bona fides and left-wing politics. Having published writers such as Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie, George Saunders and Jesmyn Ward, it identifies its focus as “the intersection of art and politics.”
The publication of Chen’s piece, Sastry said in her statement, violated the magazine’s “anti-imperialist” spirit. She wrote that she had initially pushed the magazine to support a cultural boycott of Israel but was told that the publication’s politics should be expressed “solely through our editorial choices and position.” Now, she said, an editorial process she sees as opaque had led to the publication of a piece she could not support.
“I am deeply ashamed to see this piece in Guernica’s pages, and sincerely apologize to the writers, readers and supporters who feel betrayed by this decision,” the co-publisher tweeted.
Sastry did not provide examples of what she found objectionable about the piece, except to note that it “attempts to soften the violence of colonialism and genocide.” But several other departing editors offered more specific critiques.
“It starts from the outside, from a place that ostensibly acknowledges the ‘shared humanity’ of Palestinians and Israelis, yet fails or refuses to trace the shape of power — in this case, a violent, imperialist, colonial power — that makes the systematic and historic dehumanization of Palestinians (the tacit precondition for why she may feel a need at all to affirm ‘shared humanity’ in the first place) a non-issue,” senior editor April Zhu wrote in a statement published Saturday.
Joshua Gutterman Tranen, an anti-Zionist Jewish writer who has published in Guernica in the past, specifically pointed out a passage he found objectionable in which Chen briefly pauses her volunteer work after Oct. 7, writing, “How could I continue after Hamas had massacred and kidnapped so many civilians, including Road to Recovery members, such as Vivian Silver, a longtime Canadian peace activist? And I have to admit, I was afraid for my own life.”
“The moment in the Guernica essay where the Israeli writer — who never considers why Palestinian children don’t have access to adequate healthcare b/c of colonization and apartheid — says she has to stop assisting them getting medical support because of ‘Hamas,’” Tranen tweeted. “This is genocidal.”
Israel strenuously rejects the charge that it is committing genocide, saying it takes measures to avoid killing civilians. Its supporters, including a cohort of Black Jews who have vocally defended Israel online in recent months, dispute that it is a “white” country, noting that a large portion of its Jewish population has roots in the Middle East and North Africa.
Chen’s essay is not the first time progressive Jews and Israelis have been condemned for being insufficiently critical of Israel. The official movement to boycott Israel, for example, called for a boycott of Standing Together , an Israeli-Palestinian coexistence group that opposes the war, saying that the group promotes “normalization” of Israel. And when Haymarket Books, a left-wing publisher, recently announced a book co-authored by longtime leaders of the anti-Zionist group Jewish Voice for Peace, it drew sharp criticism on Instagram — in part because one author, who supports boycotting Israel, is married to an Israeli and has family members in Israel.
For some Jews who have questioned their place in progressive and literary spaces since Oct. 7, Guernica’s retraction offered new evidence of a toxic discourse in which no Israeli or Jew can pass muster.
“THIS is what was beyond the pale? This essay of nuance, lived experiences, fears, hopes, and continuing to strive in her own way for peace?” tweeted Sara Yael Hirschhorn, a historian of modern Israel who has written about her own struggle to sustain her liberal Zionist outlook after the attack, after reading the retracted piece. “Obviously this is just a bigoted decision about an Israeli and Jewish author … This virtual burning of books is bareknuckled antisemitism.”
Emily Fox Kaplan, a Jewish writer who had shared the essay before it was retracted, wrote that she saw the criticism of Chen’s essay as part of a much wider dynamic.
“The problem, when it really comes down to it, is that it presents an Israeli as human,” she tweeted. “The people who are losing their minds about this want to believe that there are no civilians in Israel. They want a simple good guys/bad guys binary, and this creates cognitive dissonance.”
Some non-Jewish writers also lamented the piece’s retraction.
“Anyone who wants to seriously grapple with war had better be prepared for far more shocking opinions than are found in this thoughtful essay by a translator and writer living in Israel,” tweeted Phil Klay, a U.S. military veteran whose writing draws on his war experiences. “Shame on @GuernicaMag for pulling it down.”
Matt Gallagher, a war correspondent who is also a veteran and who opposes the Israel-Hamas war, said his own work had benefited from reading thoughtful authors whose perspectives were different from his own.
“If you want the war in Gaza to end, as I do,” he tweeted , “shouting down calm Israeli voices mulling the ruin of it all isn’t going to help.”
Share this:
Recommended from jta.

11-month-old Binyomin Kuravsky was killed by a faulty radiator — and now his parents demand accountability from the city

Freed hostage says NY Jewish community ‘gives us strength’ as thousands rally to mark 150 days since Oct. 7

NYPD reports 17 antisemitic crimes in February, as Oct. 7 surge appears to taper off

ADL chief defends honoring Jared Kushner, acknowledges blowback at annual summit

Columbia U antisemitism task force says Jews experiencing ‘isolation and pain’ on campus
Jump to navigation
CFP Preternatural in Popular Culture (6/15/2024; NEPCA Online and Dudley, MA 10/3-5/2024)
Call for Papers: Preternatural in Popular Culture
Monsters & the Monstrous Area of the Northeast Popular Culture Association
2024 Annual Conference of the Northeast Popular Culture Association
Nichols College (Dudley, MA) and Zoom, 3-5 October 2024
Proposals due by 15 June 2024
The Monsters & the Monstrous Area of the Northeast Popular Culture Association (NEPCA) invites submissions under the general theme of the Preternatural in Popular Culture.
For this year, submissions should focus on creatures and/or creations that exist above, beyond, and/or outside the natural world and the ways these entities are represented in popular culture (anime, comics, fiction, film, manga, streaming video, television, etc.) from across time and space.
The Monsters & the Monstrous Area is among NEPCA’s largest areas, and we often have blocks of sessions running across the full event. To best accommodate everyone, single presentation submissions are preferred over panel submissions.
Please direct any questions or concerns to Michael A. Torregrossa, Monsters & the Monstrous Area Chair, at [email protected] , and check out our blog Popular Preternaturaliana: Studying the Monstrous in Popular Culture for ideas and past sessions. The blog can be accessed at https://popularpreternaturaliana.blogspot.com/ .
Conference Information
The 2024 Northeast Popular Culture Association (NEPCA) will host its annual conference this fall as a hybrid conference from Thursday, 3 October, through Saturday, 5 October. Presenters will be required to become members of NEPCA for the year.
Virtual sessions will take place on Thursday evening and Friday morning via Zoom, and in-person sessions will take place on Friday evening and Saturday morning at Nichols College, in Dudley, Massachusetts.
For more information about the conference and to submit a proposal, please visit our NEPCA’s dedicated Conference site at https://nepca.blog/2024-conference-page/ . Be prepared to answer the following questions about your proposal:
- Proposal Type (Single Presentation or Panel)
- Modality (in person or virtual)
- Subject Area
- Working Title
- Academic Affiliation (if any)
- Abstract (250 words)
- Short bio (50-200 words)
- Accommodations
- Preferences for when to present
The submissions site will be open until 11:59 PM (EDT) on 15 June 2024.
- Contributors
- Mission and Values
- Submissions
- The Regulatory Review In Depth

Safety Culture vs. Safety Systems in U.S. Transportation
Roslyn layton.

Regulators should focus on forging a safety culture to reduce automotive accidents and fatalities.
Transportation safety is a critical topic of policy research. As a function of population growth and miles traveled, U.S. transportation safety demonstrates a significant reduction in the number of fatalities during the last 30 years. This progress likely reflects “ safety culture ,” or the set of beliefs, practices, norms, and rules which mediate transportation.
For example, air travel deaths have plummeted by two-thirds, even though total miles traveled have increased by 42 percent over the last 30 years. Today, the few aviation-related deaths that occur each year happen on private, not scheduled commercial, flights.
Some scholars attribute the gains in air safety to the confidential, voluntary, and non-punitive Aviation Safety Reporting System , although the relationship between reporting and reduced accidents is unclear . But research suggests more clearly that these gains from learned practices as a psychological or social concept can improve safety, particularly in workplaces facilitated by manager commitment and employee involvement.
Such safety culture dynamics underpin the operation of railroads and are credited with reducing risk of accidents in the Swedish rail sector by 81 percent. The Bureau of Transportation Statistics observes that most rail fatalities are related to trespassing, something beyond the control of rail operators.
Although air travel and rail transport are increasingly and impressively safe, a disturbing trend of increasing fatalities, both for pedestrians and motorists, has emerged on roadways. As data compiled by the U.S. Department of Transportation demonstrates , the United States has experienced a significant long-term improvement for air and rail fatalities, but stasis for highway travel. The trend shows that transport deaths have held constant, even though the U.S. population has increased by one-third. However, highway deaths still account for the overwhelming total: 94 percent in 1991, and 95 percent in 2021.
It could be argued that the number of highway deaths is lower because population and miles traveled have increased by one-third. But the data suggest a bleak picture when it comes to motorcycles and light trucks. The death levels associated with these vehicles have increased in real numbers. According to a 2022 U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study , the United States has the worst performance among developed nations as measured in traffic deaths per 100,000 people.
Further data on motorcycles from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) shows that there are typically about 8.5 million registered motorcycles in the United States. 2021 was the worst year in recorded U.S. history for motorcycle safety: 5,932 deaths, and some 82,000 injuries.
A variety of explanations for this increase in fatalities and injuries are possible. NHTSA notes that alcohol impairment remains a problem across the board for motor vehicle death, with the presence of higher blood alcohol noted in 27 percent of motorcycle deaths, with a whopping 41 percent of motorcyclists in single-vehicle crashes being alcohol impaired. By contrast, increased blood alcohol levels are noted in 23 percent of passenger cars deaths, 19 percent of light trucks, and 3 percent of large truck deaths. NHTSA also reports that 36 percent of motorcyclists in fatal accidents lack a valid drivers’ license. Furthermore, there is no federal helmet law, so each state sets its own requirement.
A National Institutes of Health model suggests that marijuana legalization across the United States is associated with an 18 percent increase in automobile injuries and a 4 percent increase in fatalities depending on the state. Another explanation is that the growing number of motor vehicles is associated with pedestrian death.
Building a safety culture relies on learned behaviors, enforcement, monitoring, and responsibility. It requires aligning public policy with the operations of America’s industrial sectors for air, rail, and public transit, so policymakers can oversee objectives and hold individuals accountable. Outside of commercial truck drivers, U.S. motorists are not part of a workforce safety culture. Drivers are not employees conforming to standards set by bosses.
U.S. roadways are governed effectively under what the Transportation Department calls a “ safe system approach .” This is a risk management paradigm which attempts to prevent and minimize adverse outcomes through protective and preventative measures. Rather than hold humans accountable, this approach accepts that people are flawed and attempts to design systems to compensate for their inevitable errors. One example of the safe systems approach is reflected in the Honoring Abbas Family Legacy to Terminate Drunk Driving Act , which requires cars to be equipped with sensors that disable the car in the event of a driver with excessive alcohol levels.
An example of safety culture in motoring, by contrast, could include drivers’ licensing and training requirements which attempt to regulate behavior for preferred outcomes. In these respects, the United States has lower age minimums and fewer training requirements than most countries and the highest acceptable legal level for blood alcohol. Of course, there are likely elements of culture and systems approaches in any sector.
The troubling, increasing rate of motor vehicle death receives relatively little focus, whereas discrete transport mishaps—such as air door blowouts mid-flight—garner more policy and press attention, even though no deaths occurred. This is not to dismiss fear or injury, but focus does matter in reducing fatality. A case in point is the Ohio train derailment in 2023, which prompted the Railway Safety Act of 2023 , even though no one died. The bill’s provisions for minimum crew size, maximum life of tank cars, and fees for rail carriers have nothing to do with the cause of the derailment: a faulty wheel bearing. In any event, the rail industry has committed to continue to foster safety culture which is more likely to ensure that derailments are reduced and eliminated in the future.

Roslyn Layton is a Senior Fellow at the National Security Institute at George Mason University’s Antonin Scalia Law School.
Related Essays

Solving the Pedestrian Safety Crisis
Scholar explains how NHTSA can regulate to ensure pedestrian safety.

Americans Shortchanged in Pandemic Coin Dearth
The Federal Reserve’s response to coin circulation disruptions has created a coin shortage.

Closing Gaps in Energy Cybersecurity
GAO finds that the Energy Department needs to do more to address cybersecurity risks.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
First and foremost, a cultural identity essay is the one where you share your vision of the world and personality. Below is an example that you might consider when writing your next cultural identity essay. I was born in Italy to a German family. My mother comes from the capital of Germany - Berlin, while my father was born and raised in a ...
14 Prompts on Essays about Culture and Identity. You can discuss many things on the subject of culture and identity. To give you a starting point, here are some prompts to help you write an exciting essay about culture. If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips and our round-up of the best essay checkers. 1.
Culture essays present excellent opportunities for conducting extensive research. They allow students to analyze acute global problems and investigate the topic of diversity, customs, and traditions, as well as the significance of individuals' cultural backgrounds. You can choose one of the many topics for your culture essay.
Writing a cultural diversity essay or community essay is a personal process. To set yourself up for success, take time to brainstorm and reflect on your topic. Overall, you want your cultural diversity essay to be a good indication of who you are and what makes you a unique applicant. 3. Proofread. We can't stress this final tip enough.
Writing an essay about your culture includes 5 steps: Step 1. Plan how many words you want in each paragraph. When you know the exact number of words you need for an essay, planning the word count for each paragraph will be much easier. For example, a 300-word essay typically consists of five paragraphs and three key elements:
Every student exploring cultural and other social studies may face the task of writing a thematic essay. This type of educational activity is an independent reflection of a person on a scientific problem, using ideas, cultural backgrounds, associative images from other areas of their own culture, personal experience, and social practice.
Culture shock essay has strong elements of narrative and personal essays. Even if you are writing a definition of culture shock, it begs some anecdotal evidence to illustrate those experiences.
Culture is a body of characteristics such as beliefs, social norms and ethnic background shared in a region by a population of people. Development and discipline can be influenced by culture. Culture contains values, norms, prejudice, social influence and human activity. Values and beliefs hold high importance.
In society, culture helps to understand what norms exist for people. You can write culture essays on completely different topics related to culture because it manifests itself in all components of our lives. These are dances, art, technology, and even music. Culture determines what is acceptable and what is unacceptable in any society.
In this essay, we will delve into the concept of culture, examining how it is influenced by factors such as geography, history, religion, and language. We will also analyze the major elements of culture, including symbols, language , norms, values, and artifacts, and explore how these elements profoundly impact the way people think, communicate ...
5 Essay Examples. 1. The Concept of Culture and Society by Alex Adkins. "Culture, as often defined in most sociology textbooks, is the way of life of a society. It is the sum of the ideas, beliefs, behaviors, norms, traditions, and activities shared by a particular group of people. According to Giddens (1989), any society cannot exist without ...
Culture is a dynamic and multifaceted concept that is deeply woven into the fabric of human societies. It shapes our beliefs, values, customs, language, and the way we interact with one another.In this essay, we will explore the essence of culture, delving into what it encompasses and why it holds such paramount importance in our lives and the world at large.
Rather, it is the combination of a set of values, norms, and practices, that produces "our" culture that is valuable, and in its presence, trust is higher; as a result, so is the willingness to cooperate to support policies that require some sacrifice, including for example, commitment to redistributive social policies that are especially ...
This essay examines the meaning of culture and provides several possible titles and topics that may be used as starting points for developing a paper on culture. It discusses the definition of culture, how culture is developed, and how cultures change. It shows how cultural identity and cultural differences are formed and how culture diversity is a fact of life.
Culture plays a key role in shaping individuals' socialization processes and identity formation. The values, beliefs, and practices of one's culture influence the development of self-concept and identity. Furthermore, culture interacts with social institutions such as family, education, and religion to form individuals' values and beliefs ...
Culture can be material or nonmaterial. Metro passes and bus tokens are part of material culture, as are the buses, subway cars, and the physical structures of the bus stop. Think of material culture as items you can touch-they are tangible. Nonmaterial culture, in contrast, consists of the ideas, attitudes, and beliefs of a society. These are ...
The overall culture of America include beliefs, arts, traditions, values, customs, innovations and ideals drawn from the locals and from foreigners across the boarders. American culture in a mixture of ideas and ideals from varied quarters, factors like democracy, civil liberty, Christianity, traditions, moral elements and entertainment have ...
Culture . . . is that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, art, morals, law, custom, and any other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society. In Anthropology (1881) Tylor made it clear that culture, so defined, is possessed by man alone.
Essay Writing Service. Different people define culture in different ways, for example "Culture: learned and shared human patterns or models for living; day- to-day living patterns, these patterns and models pervade all aspects of human social interaction. Culture is mankind's primary adaptive mechanism"1.
100 Words Essay on Importance of Culture and Tradition Introduction. Culture and tradition are vital aspects of our lives. They define our identity, guide our behavior, and connect us to our history. The Role of Culture. Culture is the shared values, beliefs, and customs of a group. It shapes our thinking and decisions, making us unique.
Culture is a complex system of values, beliefs, social customs, and material objects shared by a group distinguished by physical geographical boundaries (Rubenstein, 2016). Several components of culture include: land, people, values, beliefs, attitudes, traditions, daily life, night life, food, communication, government and business.
Culture, in its turn, is defined as "that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, arts, morals, law, custom, and many other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society" (Whitney & Larson, 2014). Seeing that agriculture shapes the society and defines the course of its further development, promoting the ideas of ...
500+ Words Essay on Indian Culture. India is a country that boasts of a rich culture. The culture of India refers to a collection of minor unique cultures. The culture of India comprises of clothing, festivals, languages, religions, music, dance, architecture, food, and art in India. Most noteworthy, Indian culture has been influenced by ...
In this essay, we will delve into the complexities and nuances of Hispanic culture, exploring its influences on art, music, cuisine, and more. By examining the unique characteristics that define Hispanic culture, we will gain a deeper understanding of its impact on society and the world at large.
Lauren Oyler writes about living with anxiety and whether whether "normal" means anything when we all dabble in an array of diagnoses.
Dr. Kinkela's essay appears in the Modern Age volume (1920 to the present). "I looked at music, film, television and new movies, and how ideas of insects and food production were depicted in particular cultural forms," Dr. Kinkela explained. For example: the bool weevil, a beetle, in the traditional blues song "Bool Weevil Blues."
A Jewish writer described her attempts after Oct. 7 to find empathy across the Israeli-Palestinian divide. Her essay triggered mass resignations and a retraction.
"The moment in the Guernica essay where the Israeli writer — who never considers why Palestinian children don't have access to adequate healthcare b/c of colonization and apartheid — says ...
2024 Annual Conference of the Northeast Popular Culture Association Nichols College (Dudley, MA) and Zoom, 3-5 October 2024 Proposals due by 15 June 2024 The Monsters & the Monstrous Area of the Northeast Popular Culture Association (NEPCA) invites submissions under the general theme of the Preternatural in Popular Culture.
An example of safety culture in motoring, by contrast, could include drivers' licensing and training requirements which attempt to regulate behavior for preferred outcomes. In these respects, the United States has lower age minimums and fewer training requirements than most countries and the highest acceptable legal level for blood alcohol ...