- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)

How to Write a Critique Paper: Guide + Steps & Tips
Critical thinking is an essential life skill taught in academia. Critique essays help us develop this skill. However, it’s challenging to figure out how to write one independently. Our team has created this comprehensive guide to teach you how to express opinions in an academically correct manner. Here, you’ll discover step-by-step guidelines to help you write an essay. We’ve also addressed the proper essay critique format structure and provided several practical examples of how it should look. So, if you are interested and wish to learn more, start reading ASAP!
📃 What Is a Critique Paper?
- 🔍 Critique Essay Types
- 🥇 Critique Essay Topics
- 🗝 How to Write a Critique Paper
- 📝 Format & Structure
- 🏆 Critique Paper Examples
🔗 References
A critique paper is a piece of writing that provides an in-depth analysis of another work. These include books, poems, articles, songs, movies, works of art, or podcast episodes. Aside from these, a critique may also cover arguments, concepts, and artistic performances. For example, a student may evaluate a book they’ve read or the merit of the First Amendment.
In a critique essay , one addresses the subject of the analysis, its source, intent, and purpose, in addition to its structure and content. You may present your own opinion on the analyzed work or include alternative points of view. Your paper can consist of an interpretation of what a piece of work means and an assessment of its worth.
🔍 Discover All Critique Essay Types
Now, we will detail everything you need to know about the main types of critique papers. Use the table below to determine which one will suit your essay best.

🥇 19 Best Critique Essay Topics
This segment has some of the best topics for critical essays that you can use in your assignments. Make sure to look through them and find some inspiration! Some of them are sure to catch your attention.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the justice system in curbing drug use.
- Why are people reluctant to change their views on the Second Amendment?
- Critical review of the moral lessons in contemporary young adult novels.
- Is critical thinking still relevant in the modern world?
- Analyze the health effects of fast food on the human body.
- Describe the effects of racism on underrepresented groups.
- Build a case for the causes of the homeless crisis in the US.
- Unraveling motivational factors: a critique of psychological theories in the workplace.
- Analyze the shifting of gender roles in modern society.
- What is the impact of corruption on the economy?
- The impact of setting and atmosphere on the reader’s experience of a book.
- Investigate the role of mass media in decreasing racial tension in the US.
- Analyze the use of symbolism and imagery in Edgar Allan Poe’s short stories.
- Ethical dilemmas in medical study: critical analysis of journal articles on human trials.
- Which themes are the most common in current TV shows?
- Explain how fashion choices impact one’s identity.
- Build a case for a free higher education.
- What are the effects of social media on human communication?
- From page to screen: A comparative critique of the book and movie versions of The Lord of the Rings.
🗝 How to Write a Critique Paper: 5 Key Steps
We recognize that tackling a critique paper without proper guidance can be time-consuming and daunting. That’s why we have outlined the steps you should take to make a detailed plan for your future essay. These five steps will guide you in analyzing work successfully and creating quality papers.

- Explore the work. Before writing your essay, carefully examine the text you will be critiquing. Take notes relevant to your paper’s topic along the way. Pay attention to details and try noting the strengths and weaknesses of a piece of work.
- Conduct research. Aside from inspecting the work itself, you should also thoroughly study the surrounding context. Learn everything relevant about its author, background, and cultural and historical factors. So, you will receive essential information about the research subject, allowing you to understand it better.
- Create a thesis statement. This part usually includes a concise summary of the analysis of the work and conducted research. Students must carefully write their thesis statements to present their main argument or the work’s brief evaluation.
- Write the critical paper. After you have composed a solid thesis statement, it’s time to write your essay. Begin by providing background data in the introductory paragraph. Follow with analysis and evidence that supports the paper’s intent. Finish with a conclusion that gives a summary of the key points and reinforcing the thesis statement.
- Edit and revise to perfection. When you have the first draft, carefully review and edit its segments. See if the paper is structurally sound, easy to follow, and has a coherent format. Good writing provides its arguments logically, with clear connections between evidence and analysis. Pay close attention to segments that make you stumble and reread all sentences twice.
📝 Critique Paper Format & Structure
Before attempting to write your critique essay, you should familiarize yourself with its structure and form. We’ll examine each part in-depth and describe which elements they should have. It will give you an idea of how to structure your essay correctly.
Examining each component is essential after you get acquainted with the basic structure of a critique paper. We have detailed for you below.
Critique Essay: Introduction
You probably already know how essential the introduction is in a critique paper. This is why it’s vital to understand its proper structure. One should consider all elements that must be present in this part of the paper.
- Provide the name of the critiqued work, when it was first published, and by whom.
- Describe the thesis statement or the main idea of the paper.
- Give the context of the work, political or social, and its importance in a discipline or an academic field.
- Finish with a sentence that briefly evaluates the examined work and transitions into the main body.
Critique Essay: Main Body
We’ve finally arrived at the analysis, the most crucial part of creating a critique. Here, we’ll look at the structure of the main body paragraphs . This part of the article will explain what to include in your critical paper.
The body starts with a summary that explains:
- The main points of the work.
- How the points were achieved through characters, symbols, and various techniques.
- The aim of the research, how it was conducted, and based on what.
The rest of the body is a detailed critical evaluation of the work that includes:
- A systematic and thorough approach to assessing different elements.
- An assessment of the author’s ability or lack thereof to achieve their goals with these components.
- Supporting evidence for your arguments and evaluation.

Critique Essay: Conclusion
Lastly, let’s consider the conclusion of your critique paper. It is the time to summarize and reiterate what you have discussed in your work. An essay conclusion should contain the following elements:
- A concise statement that summarizes the entire work.
- A rundown of key points identified and covered in the evaluation.
- If necessary, the conclusion may provide recommendations for others interested in getting acquainted with the work.
🏆 Great Critique Paper Examples
We believe a good sample is one of the best aids in writing a quality essay. After all, theory can be insufficient and it’s best to see something done in practice. We’ve provided several great essay examples below for you to consider.
- Critique Against Orwell’s Style in “Animal Farm.” Orwell’s Animal Farm is a witty commentary on society and the cycle of power. To this day, the work is one of the strongest anti-Stalinist novels. Despite its themes, one of his most famous novels is often criticized for its mediocre writing style. This essay wants to advocate for this opinion through literary analysis.
- Critique of an Adidas Promotional Strategy. Adidas is one of the world’s most fabulous clothes, shoes, and equipment producers. The corporation registers hundreds of patterns on new tech for its products every year. But this doesn’t mean that Adidas does everything right. This paper demonstrates the unethical practices the company uses in its advertising campaigns.
- A Reader Response Critique of “A Rose for Emily.” Written in 1892, The Yellow Wallpaper is a short story by Charlotte Perkins Gilman. It talks about the role of women in the late 1800s. Back then, they were regarded as passive individuals who couldn’t think independently. This paper critically examines the text’s effectiveness as a psychological horror story.
- Organizational Personnel Policy Critique. Personnel management covers many aspects of a company’s daily operations. It helps create a harmonious work environment that benefits all participants. However, some of the current policies are outdated and need to be adjusted. This paper critically analyzes policies that drive and evaluate performance. It also shows which changes can be applied to standard HR guidelines.
We are confident that our tips and instructions will make it easier for you to achieve great results. Besides, you can try our helpful essay topic maker to come up with writing ideas! Consider forwarding this article to your friends who may be looking for a quality guide on critical papers.
- What Makes a Critique a Critique? – Tara Horkoff, Writing for Success, OpenTextBC
- How to write a critique – CiteWrite, Queensland University of Technology
- Writing a Critique – Tiffin University, Pfeiffer Library
- Writing a Critique Paper: Seven Easy Steps – Patrick A. Regoniel, Simple Educate
- How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay – Dan Brown, MasterClass
How to Write Critical Reviews
When you are asked to write a critical review of a book or article, you will need to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. In other words, you will be examining another person’s thoughts on a topic from your point of view.
Your stand must go beyond your “gut reaction” to the work and be based on your knowledge (readings, lecture, experience) of the topic as well as on factors such as criteria stated in your assignment or discussed by you and your instructor.
Make your stand clear at the beginning of your review, in your evaluations of specific parts, and in your concluding commentary.
Remember that your goal should be to make a few key points about the book or article, not to discuss everything the author writes.
Understanding the Assignment
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work–deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole.
Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain points and prevent you from merely summarizing what the author says. Assuming the role of an analytical reader will also help you to determine whether or not the author fulfills the stated purpose of the book or article and enhances your understanding or knowledge of a particular topic.
Be sure to read your assignment thoroughly before you read the article or book. Your instructor may have included specific guidelines for you to follow. Keeping these guidelines in mind as you read the article or book can really help you write your paper!
Also, note where the work connects with what you’ve studied in the course. You can make the most efficient use of your reading and notetaking time if you are an active reader; that is, keep relevant questions in mind and jot down page numbers as well as your responses to ideas that appear to be significant as you read.
Please note: The length of your introduction and overview, the number of points you choose to review, and the length of your conclusion should be proportionate to the page limit stated in your assignment and should reflect the complexity of the material being reviewed as well as the expectations of your reader.
Write the introduction
Below are a few guidelines to help you write the introduction to your critical review.
Introduce your review appropriately
Begin your review with an introduction appropriate to your assignment.
If your assignment asks you to review only one book and not to use outside sources, your introduction will focus on identifying the author, the title, the main topic or issue presented in the book, and the author’s purpose in writing the book.
If your assignment asks you to review the book as it relates to issues or themes discussed in the course, or to review two or more books on the same topic, your introduction must also encompass those expectations.
Explain relationships
For example, before you can review two books on a topic, you must explain to your reader in your introduction how they are related to one another.
Within this shared context (or under this “umbrella”) you can then review comparable aspects of both books, pointing out where the authors agree and differ.
In other words, the more complicated your assignment is, the more your introduction must accomplish.
Finally, the introduction to a book review is always the place for you to establish your position as the reviewer (your thesis about the author’s thesis).
As you write, consider the following questions:
- Is the book a memoir, a treatise, a collection of facts, an extended argument, etc.? Is the article a documentary, a write-up of primary research, a position paper, etc.?
- Who is the author? What does the preface or foreword tell you about the author’s purpose, background, and credentials? What is the author’s approach to the topic (as a journalist? a historian? a researcher?)?
- What is the main topic or problem addressed? How does the work relate to a discipline, to a profession, to a particular audience, or to other works on the topic?
- What is your critical evaluation of the work (your thesis)? Why have you taken that position? What criteria are you basing your position on?
Provide an overview
In your introduction, you will also want to provide an overview. An overview supplies your reader with certain general information not appropriate for including in the introduction but necessary to understanding the body of the review.
Generally, an overview describes your book’s division into chapters, sections, or points of discussion. An overview may also include background information about the topic, about your stand, or about the criteria you will use for evaluation.
The overview and the introduction work together to provide a comprehensive beginning for (a “springboard” into) your review.
- What are the author’s basic premises? What issues are raised, or what themes emerge? What situation (i.e., racism on college campuses) provides a basis for the author’s assertions?
- How informed is my reader? What background information is relevant to the entire book and should be placed here rather than in a body paragraph?
Write the body
The body is the center of your paper, where you draw out your main arguments. Below are some guidelines to help you write it.
Organize using a logical plan
Organize the body of your review according to a logical plan. Here are two options:
- First, summarize, in a series of paragraphs, those major points from the book that you plan to discuss; incorporating each major point into a topic sentence for a paragraph is an effective organizational strategy. Second, discuss and evaluate these points in a following group of paragraphs. (There are two dangers lurking in this pattern–you may allot too many paragraphs to summary and too few to evaluation, or you may re-summarize too many points from the book in your evaluation section.)
- Alternatively, you can summarize and evaluate the major points you have chosen from the book in a point-by-point schema. That means you will discuss and evaluate point one within the same paragraph (or in several if the point is significant and warrants extended discussion) before you summarize and evaluate point two, point three, etc., moving in a logical sequence from point to point to point. Here again, it is effective to use the topic sentence of each paragraph to identify the point from the book that you plan to summarize or evaluate.
Questions to keep in mind as you write
With either organizational pattern, consider the following questions:
- What are the author’s most important points? How do these relate to one another? (Make relationships clear by using transitions: “In contrast,” an equally strong argument,” “moreover,” “a final conclusion,” etc.).
- What types of evidence or information does the author present to support his or her points? Is this evidence convincing, controversial, factual, one-sided, etc.? (Consider the use of primary historical material, case studies, narratives, recent scientific findings, statistics.)
- Where does the author do a good job of conveying factual material as well as personal perspective? Where does the author fail to do so? If solutions to a problem are offered, are they believable, misguided, or promising?
- Which parts of the work (particular arguments, descriptions, chapters, etc.) are most effective and which parts are least effective? Why?
- Where (if at all) does the author convey personal prejudice, support illogical relationships, or present evidence out of its appropriate context?
Keep your opinions distinct and cite your sources
Remember, as you discuss the author’s major points, be sure to distinguish consistently between the author’s opinions and your own.
Keep the summary portions of your discussion concise, remembering that your task as a reviewer is to re-see the author’s work, not to re-tell it.
And, importantly, if you refer to ideas from other books and articles or from lecture and course materials, always document your sources, or else you might wander into the realm of plagiarism.
Include only that material which has relevance for your review and use direct quotations sparingly. The Writing Center has other handouts to help you paraphrase text and introduce quotations.
Write the conclusion
You will want to use the conclusion to state your overall critical evaluation.
You have already discussed the major points the author makes, examined how the author supports arguments, and evaluated the quality or effectiveness of specific aspects of the book or article.
Now you must make an evaluation of the work as a whole, determining such things as whether or not the author achieves the stated or implied purpose and if the work makes a significant contribution to an existing body of knowledge.
Consider the following questions:
- Is the work appropriately subjective or objective according to the author’s purpose?
- How well does the work maintain its stated or implied focus? Does the author present extraneous material? Does the author exclude or ignore relevant information?
- How well has the author achieved the overall purpose of the book or article? What contribution does the work make to an existing body of knowledge or to a specific group of readers? Can you justify the use of this work in a particular course?
- What is the most important final comment you wish to make about the book or article? Do you have any suggestions for the direction of future research in the area? What has reading this work done for you or demonstrated to you?

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
Critique Essay: Your Comprehensive Guide to Writing A+ Critique Essays

Table of Contents
Just like a concept essay , a critique essay is an essential assignment that examines another author’s work to analyze and interpret it. This task is common in college, and it’s also called an analytical essay .
But how do you handle this task and score excellent grades? This guide delves into all the details of composing an A+ critical paper. Read to learn more.
What Is a Critique Essay?
Let’s set the ball rolling by defining a critique essay . It is an academic assignment that summarizes a text and critically evaluates its validity. It aims to evaluate a given text’s impact in a specific discipline and shows whether the evaluated text achieved its intended goal or didn’t.
This assignment needs careful study of the texts before summarizing and critically analyzing them. Your main task is to understand the piece and present your critical assessment. Your final verdict can be negative or positive, depending on the work’s quality and analysis. We can summarize this paper in the following four terms.
- A description that gives readers a sense of the writer’s overall goal with their publications.
- An analysis that examines how the text’s structure and language convey its meaning.
- An interpretation that states each of the work’s parts’ significance.
- An assessment that judges the piece’s overall worth or value.
Types of Critique Essays
Critique essays come in three main forms, as discussed below.
- Descriptive
This essay examines a text or other works. It primarily focuses on a work’s specific features. Comparing and contrasting your analysis subject to a classic example of its genre is also possible.
- Evaluative
This analytical essay estimates a work’s value. It shows if it’s as good as you expected based on the recommendations or if you feel it wasted your time.
- Interpretive
Interpretive essays give your readers answers relating to a work’s meaning. To achieve this goal, you must choose a technique for establishing that meaning. For instance, you may read, watch, or observe your analysis subject before floating arguments.
Critique Essay Outline
Writing an excellent critique essay is difficult without an outline. An outline is the only way to save writing time and organize your ideas where they should fit. This step requires you to determine the evidence and arguments you will evaluate. These arguments support and validate your thesis statement.
Additionally, your paper’s outline shows you how your essay will look. After creating the wireframe, you may adjust it or add more details to make your writing more effective. Your skeleton takes the traditional five-paragraph essay format.
Introduction
Your work needs an introduction paragraph. This section opens with an introductory phrase about the work you are analyzing. It tells the reader what you will critique, who the author is, and provide its publication date. The intro specifies the work’s core argument. Its third sentence contains your thesis statement.
Your work requires a summary paragraph to show the reader what you discussed in the body paragraphs. This section follows your introduction and leads to a detailed discussion.
Your main body comprises three to five paragraphs or more if necessary. Each section addresses a given text dimension, like bias, tone, style, or organization. Moreover, every paragraph confirms your thesis statement regarding the piece’s effectiveness. Each body paragraph opens with a topic sentence summarizing the subsection. Next, you introduce your evidence and close the chapter by referring to the thesis.
Your conclusion gives your final verdict on a given piece’s effectiveness. This strong conclusion paragraph summarizes your main ideas and paraphrases your thesis statement to confirm that everything you discussed confirmed it.
How to Start a Critique Essay
Starting your critique essay is easy if you follow the correct process. This discussion explores how to commence this assignment.
Critical Reading
- Read the Literary Piece Carefully
Your journey starts by reading the piece you have to critique to understand it. Your careful reading should immerse you into the author’s world and imagine why they drafted their work. Also, take note and underscore essential facts. Your assignment must also highlight which literary tools succeeded in achieving the material’s goal. Lastly, determine what you dislike about the piece, such as incompleteness, gaps, or inconsistencies.
- Formulate the Author’s Thesis
Use the text you read to formulate the author’s thesis or primary arguments. You can find this argument in the paper’s introduction. If you are handling literary work, create one of the key themes because the thesis isn’t clear.
- Summarize the Analyzed Text
You need one paragraph to summarize your paper’s content and give the reader a gist of what you covered. It should come between the introduction and the three body paragraphs.
Analyze the Text
Analyze your text before composing your assignment. Your analysis should lead you to the following critical questions:
- How did your emotions respond to the text, and which methods, images, or ideas made you feel so?
- Based on the author’s background, which experiences made them formulate such a thesis?
- What other significant works has the author produced to demonstrate their general thought direction?
- Have you used the concepts correctly in the text?
- Are your references reliable, and do they adequately prove the author’s judgment?
Write Your Critical Essay
Lastly, draft your critique essay by writing a brief overview of the text you are examining. Next, formulate your thesis statement reflecting your stand on the work you are critiquing. Afterward, write a summary paragraph that captures the paper’s essence. Below are essential questions to ask and answer to ensure you did the correct thing:
- Who created the piece you are critiquing?
- Did you present your work objectively or subjectively?
- What is your work’s aim, and were they attained?
- What methods, styles, and media did the author use, and did they achieve their goal?
- What assumptions underlie the work, and how do they influence its validity?
- What forms of evidence or persuasion did you use, and is your evidence interpreted fairly?
- How is the material structured?
- Does the work favor a specific interpretation or viewpoint, and how effective is it?
- Does the work promote an understanding of vital ideas or theories?
- How does the piece resonate or fail to resonate with primary concepts or other works in its discipline?
Example of Critique Essay On Articles
An article-related critique essay is a paper that evaluates an article to determine its effectiveness in attaining a goal. An article could comprise opinions, personal experiences, and external research. This essay entertains, informs, persuades, or educates readers. An article critique differs from a summary because a summary doesn’t offer a critical analysis. A critique, in its turn, resembles a review because it evaluates the author’s ability to fulfill its stated purpose. Your article critique must back its claims regarding an issue through evidence in the text and other external sources.
A Sample Article Critique Paper
Nothing teaches better than an excellent model of what you are learning. Here’s a sample article critique paper.
The Education Sector Cannot Solve Problems It Doesn’t Acknowledge (David and Nelson, 2021). New York, a state in the United States of America, fully understands this problem and has formulated initiatives and policies to improve equity in public schools at all levels. Education policymakers have implemented an All-Inclusive Response Strategy(ARS) to achieve this noble goal. The practical goal of this strategy is to ensure that all New York children enjoy inclusive education. This approach seeks to eliminate biases, barriers, or power dynamics that discourage students’ learning potential. Acknowledging educational challenges and committing to developing solutions is the most critical step school administrators can take to support the education system. However, these principal players should formulate proper thought, research, and policy guidelines to ensure their policies and strategies include all the potential issues and leave enough room for improvement.
The procedures also proposed religious tolerance and accommodation, anti-discrimination, and all forms of harassment. This inclusive policy must have sound techniques for how other stakeholders will implement, review, and monitor it henceforth. Fortunately, New York has succeeded on this front. This article evaluates how well this equity program was executed in the state as it endeavors to promote equity and inclusivity in its public schools…
Do you still have questions regarding a critique essay ? This section answers some of the most frequently asked questions in this essay.
What are the five parts of a critique essay ?
A perfect critique paper comprises five sections, namely: the introduction, the summary paragraph, the first paragraph, the second paragraph, the third paragraph, and the conclusion.
What is an example of a critique?
A critique essay example should meet all assignment requirements. It also comprises all the essential components, as mentioned in question one.
What are the four rules of critique?
The four rules governing a good critique essay are as follows:
- An effective introduction that provides a quick background review, defines the necessary terminology, and ends with a thesis.
- A summary that gives a broad overview of what the source discusses.
- A critique that shows your personal opinion, supported by evidence.
A conclusion that summarizes your main ideas, reminds your readers of your thesis, and concludes the paper.

105 Microeconomics Research Topics

50 Top-Notch Economics Research Topics

5 Types of Expository Essays – The 2024’s Guide
How to Write a Critique Paper: Format, Tips, & Critique Essay Examples
A critique paper is an academic writing genre that summarizes and gives a critical evaluation of a concept or work. Or, to put it simply, it is no more than a summary and a critical analysis of a specific issue. This type of writing aims to evaluate the impact of the given work or concept in its field.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
Want to learn more? Continue reading this article written by Custom-writing experts! It contains:
- best tips on how to critique an article or a literary work,
- a critique paper example with introduction, body, and conclusion.
💁 What Is a Critique Paper?
- 👣 Critical Writing Steps
👀 Critical Essay Types
📝 critique paper format, 📑 critique paper outline, 🔗 references.
A critique is a particular academic writing genre that requires you to carefully study, summarize, and critically analyze a study or a concept. In other words, it is nothing more than a critical analysis. That is all you are doing when writing a critical essay: trying to understand the work and present an evaluation. Critical essays can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves.
👣 How to Write a Critique Essay: Main Steps
Starting critique essays is the most challenging part. You are supposed to substantiate your opinion with quotes and paraphrases, avoiding retelling the entire text. A critical analysis aims to find out whether an article or another piece of writing is compelling. First, you need to formulate the author’s thesis: what was the literary work supposed to convey? Then, explore the text on how this main idea was elaborated. Finally, draft your critique according to the structure given below.

Step 1: Critical Reading
1.1. Attentively read the literary work. While reading, make notes and underline the essentials.
- Try to come into the author’s world and think why they wrote such a piece.
- Point out which literary devices are successful. Some research in literary theory may be required.
- Find out what you dislike about the text, i.e., controversies, gaps, inconsistency, or incompleteness.
1.2. Find or formulate the author’s thesis.
- What is the principal argument? In an article, it can be found in the first paragraph.
- In a literary work, formulate one of the principal themes, as the thesis is not explicit.
- If you write a critique of painting, find out what feelings, emotions, or ideas, the artist attempted to project.
1.3. Make a summary or synopsis of the analyzed text.
- One paragraph will suffice. You can use it in your critique essay, if necessary.
- The point is to explore the gist.
Step 2: Analyzing the Text
After the reading phase, ask yourself the following questions :
- What was your emotional response to the text? Which techniques, images, or ideas made you feel so?
- Find out the author’s background. Which experiences made them raise such a thesis? What other significant works have they written that demonstrate the general direction of thought of this person?
- Are the concepts used correctly in the text? Are the references reliable, and do they sufficiently substantiate the author’s opinion?
Step 3: Drafting the Essay
Finally, it is time to draft your essay. First of all, you’ll need to write a brief overview of the text you’re analyzing. Then, formulate a thesis statement – one sentence that will contain your opinion of the work under scrutiny. After that, make a one-paragraph summary of the text.
You can use this simple template for the draft version of your analysis. Another thing that can help you at this step is a summary creator to make the creative process more efficient.
Critique Paper Template
- Start with an introductory phrase about the domain of the work in question.
- Tell which work you are going to analyze, its author, and year of publication.
- Specify the principal argument of the work under study.
- In the third sentence, clearly state your thesis.
- Here you can insert the summary you wrote before.
- This is the only place where you can use it. No summary can be written in the main body!
- Use one paragraph for every separate analyzed aspect of the text (style, organization, fairness/bias, etc.).
- Each paragraph should confirm your thesis (e.g., whether the text is effective or ineffective).
- Each paragraph shall start with a topic sentence, followed by evidence, and concluded with a statement referring to the thesis.
- Provide a final judgment on the effectiveness of the piece of writing.
- Summarize your main points and restate the thesis, indicating that everything you said above confirms it.
You can evaluate the chosen work or concept in several ways. Pick the one you feel more comfortable with from the following:
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
- Descriptive critical essays examine texts or other works. Their primary focus is usually on certain features of a work, and it is common to compare and contrast the subject of your analysis to a classic example of the genre to which it belongs.
- Evaluative critical essays provide an estimate of the value of the work. Was it as good as you expected based on the recommendations, or do you feel your time would have been better spent on something else?
- Interpretive essays provide your readers with answers that relate to the meaning of the work in question. To do this, you must select a method of determining the meaning, read/watch/observe your analysis subject using this method, and put forth an argument.
There are also different types of critiques. The University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, in the article “ Writing critiques ,” discusses them as well as the appropriate critique language.
Critique Paper Topics
- Critique of the article Is Google Making Us Stupid? by Nicholas Carr .
- Interpret the symbolism of Edgar Alan Poe’s The Black Cat .
- Examine the topicality of the article Impact of Racial/Ethnic Differences on Child Mental Health Care .
- Critical essay on Alice Walker’s short story Everyday Use .
- Discuss the value of the essay The Hanging by George Orwell .
- A critique on the article Stocks Versus Bonds : Explaining the Equity Risk Premium .
- Explore the themes Tennessee Williams reveals in The Glass Menagerie.
- Analyze the relevance of the article Leadership Characteristics and Digital Transformation .
- Critical evaluation of Jonathan Harvey’s play Beautiful Thing .
- Analyze and critique Derek Raymond’s story He Died with His Eyes Open .
- Discuss the techniques author uses to present the problem of choice in The Plague .
- Examine and evaluate the research article Using Evidence-Based Practice to Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia .
- Explore the scientific value of the article Our Future: A Lancet Commission on Adolescent Health and Wellbeing .
- Describe the ideas E. Hemingway put into his A Clean, Well-Lighted Place .
- Analyze the literary qualities of Always Running La Vida Loca: Gang Days in L. A .
- Critical writing on The Incarnation of Power by Wright Mills .
- Explain the strengths and shortcomings of Tim Kreider’s article The Busy Trap .
- Critical response to Woolf’s novel Mrs. Dalloway .
- Examine the main idea of Richard Godbeer’s book Escaping Salem .
- The strong and weak points of the article The Confusion of Tongues by William G. Bellshaw .
- Critical review of Gulliver’s Travels .
- Analyze the stylistic devices Anthony Lewis uses in Gideon’s Trumpet.
- Examine the techniques Elie Wiesel uses to show relationship transformation in the book Night .
- Critique of the play Fences by August Wilson .
- The role of exposition in Achebe’s novel Things Fall Apart.
- The main themes John Maxwell discusses in his book Disgrace .
- Critical evaluation of Ray Bradbury’s Fahrenheit 451 .
- The ideas and concept of the book The Vegetarian Imperative .
- Different points of view on one historical figure in the book Two Lives of Charlemagne .
Since the APA critique paper format is one of the most common, let’s discuss it in more detail. Check out the information below to learn more:
The APA Manual recommends using the following fonts:
- 11-point Calibri,
- 11-point Arial,
- 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode,
- 12-point Times New Roman,
- 11-point Georgia,
- 10-point Computer Modern.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Add 1-inch margins on all sides.
📌 Page numbers
Page numbers should appear at the top right-hand corner, starting with the title page.
📌 Line spacing
The entire document, including the title page and reference list, should be double-spaced.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
📌 Title page
The title page should include the following information:
- page number 1 in the top right-hand corner of the page header,
- paper title,
- the student’s name,
- the name of the department and the college or university,
- course number and name,
- the instructor’s name,
- due date (the date format used in your country).
📌 Critique paper title
The title of your critique paper should be no more than 12 words. In addition, it should be centered and typed in bold using title case.
📌 In-text citations
For the in-text citation, provide the author’s last name and publication year in brackets. If you are using direct citation, add the page number after the year.
📌 References
The last page of your paper should include a list of all sources cited in your essay. Here’s a general format of book and journal article citations you should use:
Book: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Book title: Subtitle . Publisher.
Journal article: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Title of the article. Journal Title, volume (issue number), start page–end page.
The main parts of good critical response essays are:
- Introduction. The introduction is the most essential part of the critical response. It should be concise and include the author and title of the work being analyzed, its main idea, and a strong thesis statement.
- Summary. This should be brief and to the point. Only the author’s/creator’s main ideas and arguments should be included.
- Analysis/interpretation. Discuss what the author’s/creator’s primary goal was and determine whether this goal was reached successfully. Use the evidence you have gathered to argue whether or not the author/creator achieved was adequately convincing (remember there should be no personal bias in this discussion).
- Evaluation/response. At this point, your readers are ready to learn your objective response to the work. It should be professional yet entertaining to read. Do not hesitate to use strong language. You can say that the work you analyzed was weak and poorly-structured if that is the case, but keep in mind that you have to have evidence to back up your claim.
- Conclusion. The last paragraph of your work should restate the thesis statement, summarize the key points, and create a sense of closure for the readers.
Critique Paper Introduction
The introduction is setting the stage for your analysis. Here are some tips to follow when working on it:
- Provide the reader with a brief synopsis of the main points of the work you are critiquing .
- State your general opinion of the work , using it as your thesis statement. The ideal situation is that you identify and use a controversial thesis.
- Remember that you will uncover a lot of necessary information about the work you are critiquing. You mustn’t make use of all of it, providing the reader with information that is unnecessary in your critique. If you are writing about Shakespeare, you don’t have to waste your or your reader’s time going through all of his works.
Critique Paper Body
The body of the critique contains the supporting paragraphs. This is where you will provide the facts that prove your main idea and support your thesis. Follow the tips below when writing the body of your critique.
- Every paragraph must focus on a precise concept from the paper under your scrutiny , and your job is to include arguments to support or disprove that concept. Concrete evidence is required.
- A critical essay is written in the third-person and ensures the reader is presented with an objective analysis.
- Discuss whether the author was able to achieve their goals and adequately get their point across.
- It is important not to confuse facts and opinions . An opinion is a personal thought and requires confirmation, whereas a fact is supported by reliable data and requires no further proof. Do not back up one idea with another one.
- Remember that your purpose is to provide the reader with an understanding of a particular piece of literature or other work from your perspective. Be as specific as possible.
Critique Paper Conclusion
Finally, you will need to write a conclusion for your critique. The conclusion reasserts your overall general opinion of the ideas presented in the text and ensures there is no doubt in the reader’s mind about what you believe and why. Follow these tips when writing your conclusion:
- Summarize the analysis you provided in the body of the critique.
- Summarize the primary reasons why you made your analysis .
- Where appropriate, provide recommendations on how the work you critiqued can be improved.
For more details on how to write a critique, check out the great critique analysis template provided by Thompson Rivers University.
If you want more information on essay writing in general, look at the Secrets of Essay Writing .
Example of Critique Paper with Introduction, Body, and Conclusion
Check out this critical response example to “The Last Inch” by James Aldridge to show how everything works in practice:
Introduction
In his story “The Last Inch,” James Aldridge addresses the issue of the relationship between parents and children. The author captured the young boy’s coming into maturity coinciding with a challenging trial. He also demonstrated how the twelve-year-old boy obtained his father’s character traits. Aldridge’s prose is both brutal and poetic, expressing his characters’ genuine emotions and the sad truths of their situations.
Body: Summary
The story is about Ben Ensley, an unemployed professional pilot, who decides to capture underwater shots for money. He travels to Shark Bay with his son, Davy. Ben is severely injured after being attacked by a shark while photographing. His last hope of survival is to fly back to the little African hamlet from where they took off.
Body: Analysis
The story effectively uses the themes of survival and fatherhood and has an intriguing and captivating plot. In addition, Ben’s metamorphosis from a failing pilot to a determined survivor is effectively presented. His bond with his son, Davy, adds depth and emotional importance to the story. At the same time, the background information about Ben’s past and his life before the shark attack could be more effectively integrated into the main story rather than being presented as separate blocks of text.
Body: Evaluation
I find “The Last Inch” by James Aldridge a very engaging and emotional story since it highlights the idea of a father’s unconditional love and determination in the face of adversity. I was also impressed by the vivid descriptions and strong character development of the father and son.
Conclusion
“The Last Inch” by James Aldridge is an engaging and emotional narrative that will appeal to readers of all ages. It is a story of strength, dedication, and the unbreakable link between father and son. Though some backstory could be integrated more smoothly, “The Last Inch” impresses with its emotional punch. It leaves the readers touched by the raw power of fatherly love and human will.
📚 Critique Essay Examples
With all of the information and tips provided above, your way will become clearer when you have a solid example of a critique essay.
Below is a critical response to The Yellow Wallpaper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
When speaking of feminist literature that is prominent and manages to touch on incredibly controversial issues, The Yellow Wallpaper is the first book that comes to mind. Written from a first-person perspective, magnifying the effect of the narrative, the short story by Charlotte Perkins Gilman introduces the reader to the problem of the physical and mental health of the women of the 19th century. However, the message that is intended to concern feminist ideas is rather subtle. Written in the form of several diary entries, the novel offers a mysterious plot, and at the same time, shockingly realistic details.
What really stands out about the novel is the fact that the reader is never really sure how much of the story takes place in reality and how much of it happens in the psychotic mind of the protagonist. In addition, the novel contains a plethora of description that contributes to the strain and enhances the correlation between the atmosphere and the protagonist’s fears: “The color is repellent, almost revolting; a smoldering unclean yellow, strangely faded by the slow-turning sunlight” (Gilman).
Despite Gilman’s obvious intent to make the novel a feminist story with a dash of thriller thrown in, the result is instead a thriller with a dash of feminism, as Allen (2009) explains. However, there is no doubt that the novel is a renowned classic. Offering a perfect portrayal of the 19th-century stereotypes, it is a treasure that is certainly worth the read.
If you need another critique essay example, take a look at our sample on “ The Importance of Being Earnest ” by Oscar Wilde.
And here are some more critique paper examples for you check out:
- A Good Man Is Hard to Find: Critique Paper
- Critique on “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
- “When the Five Rights Go Wrong” Article Critique
- Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey — Comparison & Critique
- “The TrueBlue Study”: Qualitative Article Critique
- Ethical Conflict Associated With Managed Care: Views of Nurse Practitioners’: Article Critique
- Benefits and Disadvantages of Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress: Article Critique
- Reducing Stress in Student Nurses: Article Critique
- Management of Change and Professional Safety – Article Critique
- “Views of Young People Towards Physical Activity”: Article Critique
Seeing an example of a critique is so helpful. You can find many other examples of a critique paper at the University of Minnesota and John Hopkins University. Plus, you can check out this video for a great explanation of how to write a critique.
- Critical Analysis
- Writing an Article Critique
- The Critique Essay
- Critique Essay
- Writing a Critique
- Writing A Book Critique
- Media Critique
- Tips for an Effective Creative Writing Critique
- How to Write an Article Critique
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

What is a creative essay, if not the way to express yourself? Crafting such a paper is a task that allows you to communicate your opinion and tell a story. However, even using your imagination to a great extent doesn’t free you from following academic writing rules. Don’t even get...

A compare and contrast essay — what is it? In this type of paper, you compare two different things or ideas, highlighting what is similar between the two, and you also contrast them, highlighting what is different. The two things might be events, people, books, points of view, lifestyles, or...

What is an expository essay? This type of writing aims to inform the reader about the subject clearly, concisely, and objectively. The keyword here is “inform”. You are not trying to persuade your reader to think a certain way or let your own opinions and emotions cloud your work. Just stick to the...
![what is critique essay Short Story Analysis: How to Write It Step by Step [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-sits-end-trolltunga-before-mountains-284x153.jpg)
Have you ever tried to write a story analysis but ended up being completely confused and lost? Well, the task might be challenging if you don’t know the essential rules for literary analysis creation. But don’t get frustrated! We know how to write a short story analysis, and we are...

Have you ever tried to get somebody round to your way of thinking? Then you should know how daunting the task is. Still, if your persuasion is successful, the result is emotionally rewarding. A persuasive essay is a type of writing that uses facts and logic to argument and substantiate...
![what is critique essay Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![what is critique essay Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![what is critique essay Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens, and even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How to write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How to make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this and use the following three simple principles and 15 creative...

A life experience essay combines the elements of narration, description, and self-reflection. Such a paper has to focus on a single event that had a significant impact on a person’s worldview and values. Writing an essay about life experience prompts students to do the following: evaluate their behavior in specific...

Who has made a significant impact in your life and why? Essay on the topic might be challenging to write. One is usually asked to write such a text as a college admission essay. A topic for this paper can be of your choice or pre-established by the institution. Either...
May I know who’s the author? For my citation activity.

Hello, Kriszha! You can reference it as a web source/web page.
Wow…great work… kindly can you assist me in writing a critique about indiscipline in a school
Hello, Vivian! Our experts will help you with any task
That’s an interesting demonstration I watched. However, my weakness is that I’m very poor in language and analysing issues.
Thanks for the feedback, Adamu!
Hi, can you help me for my assignment about article critiquing?
Hello, Vivian! Our experts will help you with any task!
I need your help if you can send me a full written dissertation..thank you
Hello! Our experts will help you with any task!
This is gud
Thanks for stopping by!
Can you help me to my activities
Hello, Sandara! Our experts will help you with any task!
Thank you so much! This really helped me!
Glad to help, Maya! Thank you for stopping by!

Writing Critiques
Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people’s work in their academic area. Search for a “manuscript reviewer guide” in your own discipline to guide your analysis of the content. Use this handout as an orientation to the audience and purpose of different types of critiques and to the linguistic strategies appropriate to all of them.
Types of critique
Article or book review assignment in an academic class.
Text: Article or book that has already been published Audience: Professors Purpose:
- to demonstrate your skills for close reading and analysis
- to show that you understand key concepts in your field
- to learn how to review a manuscript for your future professional work
Published book review
Text: Book that has already been published Audience: Disciplinary colleagues Purpose:
- to describe the book’s contents
- to summarize the book’s strengths and weaknesses
- to provide a reliable recommendation to read (or not read) the book
Manuscript review
Text: Manuscript that has been submitted but has not been published yet Audience: Journal editor and manuscript authors Purpose:
- to provide the editor with an evaluation of the manuscript
- to recommend to the editor that the article be published, revised, or rejected
- to provide the authors with constructive feedback and reasonable suggestions for revision
Language strategies for critiquing
For each type of critique, it’s important to state your praise, criticism, and suggestions politely, but with the appropriate level of strength. The following language structures should help you achieve this challenging task.
Offering Praise and Criticism
A strategy called “hedging” will help you express praise or criticism with varying levels of strength. It will also help you express varying levels of certainty in your own assertions. Grammatical structures used for hedging include:
Modal verbs Using modal verbs (could, can, may, might, etc.) allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This text is inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field. This text may be inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field.
Qualifying adjectives and adverbs Using qualifying adjectives and adverbs (possible, likely, possibly, somewhat, etc.) allows you to introduce a level of probability into your comments. Compare:
Readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will probably find the theoretical model somewhat difficult to understand completely.
Note: You can see from the last example that too many qualifiers makes the idea sound undesirably weak.
Tentative verbs Using tentative verbs (seems, indicates, suggests, etc.) also allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This omission shows that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission indicates that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission seems to suggest that the authors are not aware of the current literature.
Offering suggestions
Whether you are critiquing a published or unpublished text, you are expected to point out problems and suggest solutions. If you are critiquing an unpublished manuscript, the author can use your suggestions to revise. Your suggestions have the potential to become real actions. If you are critiquing a published text, the author cannot revise, so your suggestions are purely hypothetical. These two situations require slightly different grammar.
Unpublished manuscripts: “would be X if they did Y” Reviewers commonly point out weakness by pointing toward improvement. For instance, if the problem is “unclear methodology,” reviewers may write that “the methodology would be more clear if …” plus a suggestion. If the author can use the suggestions to revise, the grammar is “X would be better if the authors did Y” (would be + simple past suggestion).
The tables would be clearer if the authors highlighted the key results. The discussion would be more persuasive if the authors accounted for the discrepancies in the data.
Published manuscripts: “would have been X if they had done Y” If the authors cannot revise based on your suggestions, use the past unreal conditional form “X would have been better if the authors had done Y” (would have been + past perfect suggestion).
The tables would have been clearer if the authors had highlighted key results. The discussion would have been more persuasive if the authors had accounted for discrepancies in the data.
Note: For more information on conditional structures, see our Conditionals handout .

Make a Gift
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center Writing to Critique
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
When you hear that your writing assignment is a “critique,” here’s what you do: instantly substitute the word “evaluation.” You see, essentially, that’s what a critique is—an e-value-ation. You rate the value of something. The value can be positive, negative or, most likely, a mix of the two.
Evaluating or critiquing is something that you do every day, whether you are aware of it or not. You do it personally—is this the right outfit for today’s video? I can’t believe my spouse did our townhouse totally in beige.
But you also do it professionally: Will my team’s plans for the new product launch work? Should I hire or promote this person? What’s the best notebook computer for the sales team? All of those contain an evaluation. As a matter of fact, your ability to think critically (in an evaluative fashion) and to offer compelling reasons and evidence for your evaluations is one of the most valued skills in the workplace and will play a crucial role in your career advancement.
Let’s take a look at the typical parts of a critique or evaluation essay and get to know what should be done in each one:
Introduction
Unlike the introduction to most of the essays you write in school, where the main purpose is simply to introduce the thesis, the introduction of a critique or evaluation essay is more complex.
First, you must introduce the author and the title of the work being critiqued. This information is often in the first sentence of a critique’s introduction, but so long as the info is at or near the top you are fine.
Second, state the author’s main point (whether in the entire work or the section of the work you are critiquing). The main point is sometimes called the “take away”—what the author wants the reader to remember or do after reading.
Third, state in 1-2 sentences your overall evaluation of the work you are critiquing. If “overall evaluation” sounds like your conclusion, bingo, you are correct. So, it may be wise to leave this portion of your intro unwritten until you have finished your first draft.
Fourth, be sure to add any background information the reader needs to place the author’s work in context. What overall topic is the work related to? Is there a controversy involved? Be sure to set the stage since your reader has not read the work.
After the introduction comes part two: the summary of the work or that part of the work under consideration. When writing this summary, you are an objective reporter providing an unbiased statement of two things:
- the author’s overall point or take-away
- the main supports offered for that point
And like a good reporter, your language should be untainted by your own views and certainly be written in the third person—no I’s or you’s. Your goal: After someone reads a good summary (also called an abstract), that reader should know the author’s thesis and main points without detecting any of your opinion.
Part three is the evaluation. This is where you transition from being a reporter to being a judge. Just like a judge at a gymnastics meet, you weigh the strong points and the weak points of the performance, then provide an overall rating. Also, just like at a gymnastics meet, you have a scorecard of criteria that you use to make this judgment, this rating. However, instead of mount and dismount, flexibility and strength, your criteria are more likely to be items like this:
- Accuracy of information
- Presence or lack of definition of key terms
- Hidden assumptions
- Clarity of language
- Fairness—the author weighed both sides without undue bias
- Logic and Organization—do the main points link together in a meaningful way and add up to a valid argument? Are there gaps in the argument?
- Fallacies—these refer to such argument no-no’s as name calling, hasty generalization, oversimplification, substituting emotional language for fact or logic, or the black/white or either/or fallacy, the bandwagon appeal (everybody is doing it, so it must be OK), and so on.
Part four is the response. Now it’s your turn. You are no longer a reporter or a judge. You are you, providing your personal take on this work. How do you do that? Simple: Ask yourself questions like these:
- What do I agree and disagree with?
- What does the author get right, what does she/he get wrong, in my opinion?
- What ultimate merit does this work have—some, a little, none?
- Would I recommend this work as a source on this topic or should it be avoided—why or why not?
The response section is also where you would use outside sources to back up your opinion of this work and its merits or demerits. In that sense, your response section is like a miniature essay, where your thesis is your opinion of the work and your main points support your opinion.
Part five is the wrap up. It doesn’t have to be long. Your main tasks are to:
- Remind your audience of the overall importance of the topic—bring the reader back to ground zero, the topic at hand.
- Bring together your assessment or rating of the work, together with your personal response to it. In doing so, focus on overall strengths and weaknesses. Then use both to state what you believe is the ultimate success of the work .
So there you are—the mysteries of the “critique” demystified. You simply
- Introduce the work
- Summarize the work
- Rate the work based on a set of clear criteria
- Respond to the work in a personal way
- Wrap it up by talking about overall success failure of the work and the importance of the topic it tries to address.
Do those things—in that order—and you will end up with a critique that is sound and meaningful.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
How to Structure and Write an Effective Critique Paper
Critique papers are an essential part of academic writing, especially in the fields of humanities and social sciences. They involve analyzing a piece of work and objectively evaluating its strengths and weaknesses. Writing a critique paper can be challenging, requiring careful reading, research, and analysis. Yet, it is possible to produce a high-quality essay with careful planning and attention to detail.
This article will teach you how to write an article critique by explaining the types of critique essays, their structure, and the steps involved in how to write a critique essay. The article also provides essay tips for producing a well-written and effective critique.
What is a Critique Paper?
A critique paper is an academic paper as a response to a body of work, such as a play, concept, scholarly article, poetry, book, or research paper. Its purpose is to objectively assess the work in question, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. But also to provide a detailed analysis of its content, structure, and methodology.
This kind of essay can be one of the trickiest assignments, and not everyone can produce a well-scrutinized, original piece of writing. That’s why many students reach for assistance from analytical essay writing services that guarantee to handle the job with the help of professional writers and experts. These services proved to be of high quality and effective support to many schoolers who chose to try them in a variety of different disciplines.
Knowing how to write an article critique requires careful reading, analysis, and an evaluative approach. A well-written critique paper example demonstrates the writer’s ability to analyze and evaluate works. It should also be organized logically, guiding the reader through the analysis. Additionally, writers should be aware of their biases and assumptions and strive to critique objectively. On a final note, it’s essential to review the guidelines and follow the required structure. This is to ensure that the article critique meets the assignment’s expectations.
Types of Critical Essays
There are several types of essays of this kind, each with its approach and focus. To follow we have a list of the most common ones.
Descriptive
A descriptive critical essay combines elements of descriptive writing with a thorough analysis. In this type of essay, the writer describes a particular work in detail and then evaluates it based on certain criteria. They can provide a deep and insightful understanding of the work using sensory details and descriptive language.
An evaluative essay consists of a personal judgment to evaluate the value or effectiveness of a particular work or idea. In this type of essay, the writer analyzes the work and expresses their opinion on its merits or shortcomings. At the same time, they must avoid personal bias and focus on facts rather than one’s opinions or feelings. However, it’s also essential to provide a personal perspective and interpretation of the work as long as it’s supported by evidence.
Interpretive
This type of essay involves analyzing and interpreting the meaning and significance of the work being evaluated. It delves deeper into the themes, symbolism, and underlying conveyed messages. When writing an interpretive essay, it’s important to be clear and concise. Avoid confusing the reader by using jargon or unnecessarily complex language.
Structure of Critique Paper
The structure of a typical critique essay example includes an introduction, a summary, an analysis, and a conclusion. The paper format is a crucial element. Just like when you write your research papers , a critique benefits from a clear one to guide the reader. Therefore, work on defining the critique essay outline before starting the writing process. One of the most common formatting styles to adopt is the APA format (APA: American Psychological Association), which has specific rules and guidelines. And keep in mind that some specific elements should be included in each section:
Introduction: The introduction’s function is to provide background relevant information. It should also include the thesis statement, which is the writer’s main argument or position on the topic. The thesis statement should be clear and specific and presented in a way that engages the reader.
Summary: The summary provides an overview of the text. It must be objective, unbiased, and accurately summarize the piece’s main points. The summary has to be brief and to the point and should only include the most important details of the work.
Analysis: The analysis is where the writer provides their evaluation of the text being critiqued. This section is the most detailed and extensive part of the paper, containing the facts that prove your main argument and support your thesis. The analysis should focus on the thesis statement and provide a clear and logical argument.
Conclusion: In the conclusion, the paper’s main points are summarized, and the thesis statement is restated to emphasize the writer’s main position. It should provide a final evaluation of the work and include recommendations for improvement.
Essential Steps to Write a Critique Essay
Critique writing requires a thoughtful and detailed approach. You can find below the essential steps to follow:
Read and observe the work:
Before beginning the essay, you should read and observe the work, taking notes on its relevant elements. It is crucial to pay attention to details and to identify both strengths and weaknesses.
Conduct research:
In addition to analyzing the work, you need to research the author, director, or artist and the work’s historical and cultural context. This step can be time and effort-consuming. That’s why as a student who’s probably stuck with many assignments, you can consider to pay for research paper , which will solve the problem most efficiently. The research can provide valuable insights into the work and help you develop a more informed critique.
Develop a thesis statement:
Based on the analysis of the work and any research conducted, you should develop a clear and specific thesis statement that accurately presents your main argument or evaluation of the piece.
Write your critique:
Once you have your thesis statement, you can begin writing your critique essay. Begin by providing some background information on the work in an introduction. In the body of your essay, provide evidence and analysis to support your evaluation. Use specific examples and quotes from the text to support your arguments. Consider including external sources to provide additional context or compare the work to similar works. Finally, end your essay with a conclusion summarizing your main points and restating your thesis statement.
Revise and edit:
After completing the first draft of your essay, you should revise and edit it carefully. Pay attention to your argument’s structure, clarity, and coherence. Also, ensure that your essay logically progresses from one concept to the next. It’s important to note that when you format an essay , considerations may vary depending on the assignment’s specific requirements. Some may require additional sections, such as a discussion of the author’s background or a comparison to other works.
How to start a critique paper?
Starting a critique paper requires careful consideration and preparation. It is important to read and understand the subject thoroughly, including its purpose, structure, and context. Once you have a clear understanding of the subject, you should identify specific criteria to use in your evaluation, such as style, structure, effectiveness, relevance, and accuracy. Taking notes on the subject’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement will help you organize your thoughts, and creating an outline that includes the introduction, analysis, and conclusion will ensure a well-structured paper. Finally, a strong thesis statement that clearly states your evaluation of the subject and the criteria you will use to evaluate it is crucial to the success of your critique paper.
How can I write a critique paper on a research article?
To write a critique paper on a research article, it is essential to consider key areas such as the research question and hypothesis, methodology, results, and overall evaluation. Firstly, determine whether the research question is clear, relevant, and testable. Secondly, evaluate the methodology used in the study to determine whether it’s appropriate for the research question. Thirdly, analyze the results presented in the research article to determine whether they are consistent with the research question and hypothesis. Lastly, evaluate the overall quality and contribution of the research article to the field. By considering these areas, you can provide a comprehensive critique of the research article.
What is the difference between summarizing and critiquing an article?
Many students struggle to distinguish between the two. They often summarize the work, neglecting to adopt a personal approach and use analytical skills. In such cases, custom essay writing service Edusson is the best option to handle the job for you. It also helps you improve your critical thinking and practical skills.
Related posts:
- 6 Step Process for Essay Writing
- How to Write a Diagnostic Essay (Without Fail)
- The Full Guide to Writing Comparison Essays with Point-by-Point Method
- Footnotes 101: A Guide to Proper Formatting
Improve your writing with our guides

How to Write a Scholarship Essay


Definition Essay: The Complete Guide with Essay Topics and Examples

Critical Essay: The Complete Guide. Essay Topics, Examples and Outlines
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.


IOE Writing Centre
- Writing a Critical Review

Writing a Critique

A critique (or critical review) is not to be mistaken for a literature review. A 'critical review', or 'critique', is a complete type of text (or genre), discussing one particular article or book in detail. In some instances, you may be asked to write a critique of two or three articles (e.g. a comparative critical review). In contrast, a 'literature review', which also needs to be 'critical', is a part of a larger type of text, such as a chapter of your dissertation.
Most importantly: Read your article / book as many times as possible, as this will make the critical review much easier.
1. Read and take notes 2. Organising your writing 3. Summary 4. Evaluation 5. Linguistic features of a critical review 6. Summary language 7. Evaluation language 8. Conclusion language 9. Example extracts from a critical review 10. Further resources
Read and Take Notes
To improve your reading confidence and efficiency, visit our pages on reading.
Further reading: Read Confidently
After you are familiar with the text, make notes on some of the following questions. Choose the questions which seem suitable:
- What kind of article is it (for example does it present data or does it present purely theoretical arguments)?
- What is the main area under discussion?
- What are the main findings?
- What are the stated limitations?
- Where does the author's data and evidence come from? Are they appropriate / sufficient?
- What are the main issues raised by the author?
- What questions are raised?
- How well are these questions addressed?
- What are the major points/interpretations made by the author in terms of the issues raised?
- Is the text balanced? Is it fair / biased?
- Does the author contradict herself?
- How does all this relate to other literature on this topic?
- How does all this relate to your own experience, ideas and views?
- What else has this author written? Do these build / complement this text?
- (Optional) Has anyone else reviewed this article? What did they say? Do I agree with them?
^ Back to top
Organising your writing
You first need to summarise the text that you have read. One reason to summarise the text is that the reader may not have read the text. In your summary, you will
- focus on points within the article that you think are interesting
- summarise the author(s) main ideas or argument
- explain how these ideas / argument have been constructed. (For example, is the author basing her arguments on data that they have collected? Are the main ideas / argument purely theoretical?)
In your summary you might answer the following questions: Why is this topic important? Where can this text be located? For example, does it address policy studies? What other prominent authors also write about this?
Evaluation is the most important part in a critical review.
Use the literature to support your views. You may also use your knowledge of conducting research, and your own experience. Evaluation can be explicit or implicit.
Explicit evaluation
Explicit evaluation involves stating directly (explicitly) how you intend to evaluate the text. e.g. "I will review this article by focusing on the following questions. First, I will examine the extent to which the authors contribute to current thought on Second Language Acquisition (SLA) pedagogy. After that, I will analyse whether the authors' propositions are feasible within overseas SLA classrooms."
Implicit evaluation
Implicit evaluation is less direct. The following section on Linguistic Features of Writing a Critical Review contains language that evaluates the text. A difficult part of evaluation of a published text (and a professional author) is how to do this as a student. There is nothing wrong with making your position as a student explicit and incorporating it into your evaluation. Examples of how you might do this can be found in the section on Linguistic Features of Writing a Critical Review. You need to remember to locate and analyse the author's argument when you are writing your critical review. For example, you need to locate the authors' view of classroom pedagogy as presented in the book / article and not present a critique of views of classroom pedagogy in general.
Linguistic features of a critical review
The following examples come from published critical reviews. Some of them have been adapted for student use.
Summary language
- This article / book is divided into two / three parts. First...
- While the title might suggest...
- The tone appears to be...
- Title is the first / second volume in the series Title, edited by...The books / articles in this series address...
- The second / third claim is based on...
- The author challenges the notion that...
- The author tries to find a more middle ground / make more modest claims...
- The article / book begins with a short historical overview of...
- Numerous authors have recently suggested that...(see Author, Year; Author, Year). Author would also be once such author. With his / her argument that...
- To refer to title as a...is not to say that it is...
- This book / article is aimed at... This intended readership...
- The author's book / article examines the...To do this, the author first...
- The author develops / suggests a theoretical / pedagogical model to…
- This book / article positions itself firmly within the field of...
- The author in a series of subtle arguments, indicates that he / she...
- The argument is therefore...
- The author asks "..."
- With a purely critical / postmodern take on...
- Topic, as the author points out, can be viewed as...
- In this recent contribution to the field of...this British author...
- As a leading author in the field of...
- This book / article nicely contributes to the field of...and complements other work by this author...
- The second / third part of...provides / questions / asks the reader...
- Title is intended to encourage students / researchers to...
- The approach taken by the author provides the opportunity to examine...in a qualitative / quantitative research framework that nicely complements...
- The author notes / claims that state support / a focus on pedagogy / the adoption of...remains vital if...
- According to Author (Year) teaching towards examinations is not as effective as it is in other areas of the curriculum. This is because, as Author (Year) claims that examinations have undue status within the curriculum.
- According to Author (Year)…is not as effective in some areas of the curriculum / syllabus as others. Therefore the author believes that this is a reason for some school's…
Evaluation language
- This argument is not entirely convincing, as...furthermore it commodifies / rationalises the...
- Over the last five / ten years the view of...has increasingly been viewed as 'complicated' (see Author, Year; Author, Year).
- However, through trying to integrate...with...the author...
- There are difficulties with such a position.
- Inevitably, several crucial questions are left unanswered / glossed over by this insightful / timely / interesting / stimulating book / article. Why should...
- It might have been more relevant for the author to have written this book / article as...
- This article / book is not without disappointment from those who would view...as...
- This chosen framework enlightens / clouds...
- This analysis intends to be...but falls a little short as...
- The authors rightly conclude that if...
- A detailed, well-written and rigorous account of...
- As a Korean student I feel that this article / book very clearly illustrates...
- The beginning of...provides an informative overview into...
- The tables / figures do little to help / greatly help the reader...
- The reaction by scholars who take a...approach might not be so favourable (e.g. Author, Year).
- This explanation has a few weaknesses that other researchers have pointed out (see Author, Year; Author, Year). The first is...
- On the other hand, the author wisely suggests / proposes that...By combining these two dimensions...
- The author's brief introduction to...may leave the intended reader confused as it fails to properly...
- Despite my inability to...I was greatly interested in...
- Even where this reader / I disagree(s), the author's effort to...
- The author thus combines...with...to argue...which seems quite improbable for a number of reasons. First...
- Perhaps this aversion to...would explain the author's reluctance to...
- As a second language student from ...I find it slightly ironic that such an anglo-centric view is...
- The reader is rewarded with...
- Less convincing is the broad-sweeping generalisation that...
- There is no denying the author's subject knowledge nor his / her...
- The author's prose is dense and littered with unnecessary jargon...
- The author's critique of...might seem harsh but is well supported within the literature (see Author, Year; Author, Year; Author, Year). Aligning herself with the author, Author (Year) states that...
- As it stands, the central focus of Title is well / poorly supported by its empirical findings...
- Given the hesitation to generalise to...the limitation of...does not seem problematic...
- For instance, the term...is never properly defined and the reader left to guess as to whether...
- Furthermore, to label...as...inadvertently misguides...
- In addition, this research proves to be timely / especially significant to... as recent government policy / proposals has / have been enacted to...
- On this well researched / documented basis the author emphasises / proposes that...
- Nonetheless, other research / scholarship / data tend to counter / contradict this possible trend / assumption...(see Author, Year; Author, Year).
- Without entering into detail of the..., it should be stated that Title should be read by...others will see little value in...
- As experimental conditions were not used in the study the word 'significant' misleads the reader.
- The article / book becomes repetitious in its assertion that...
- The thread of the author's argument becomes lost in an overuse of empirical data...
- Almost every argument presented in the final section is largely derivative, providing little to say about...
- She / he does not seem to take into consideration; however, that there are fundamental differences in the conditions of…
- As Author (Year) points out, however, it seems to be necessary to look at…
- This suggest that having low…does not necessarily indicate that…is ineffective.
- Therefore, the suggestion made by Author (Year)…is difficult to support.
- When considering all the data presented…it is not clear that the low scores of some students, indeed, reflects…
Conclusion language
- Overall this article / book is an analytical look at...which within the field of...is often overlooked.
- Despite its problems, Title offers valuable theoretical insights / interesting examples / a contribution to pedagogy and a starting point for students / researchers of...with an interest in...
- This detailed and rigorously argued...
- This first / second volume / book / article by...with an interest in...is highly informative...
Example extracts from a critical review
Writing critically.
If you have been told your writing is not critical enough, it probably means that your writing treats the knowledge claims as if they are true, well supported, and applicable in the context you are writing about. This may not always be the case.
In these two examples, the extracts refer to the same section of text. In each example, the section that refers to a source has been highlighted in bold. The note below the example then explains how the writer has used the source material.
There is a strong positive effect on students, both educationally and emotionally, when the instructors try to learn to say students' names without making pronunciation errors (Kiang, 2004).
Use of source material in example a:
This is a simple paraphrase with no critical comment. It looks like the writer agrees with Kiang. (This is not a good example for critical writing, as the writer has not made any critical comment).
Kiang (2004) gives various examples to support his claim that "the positive emotional and educational impact on students is clear" (p.210) when instructors try to pronounce students' names in the correct way. He quotes one student, Nguyet, as saying that he "felt surprised and happy" (p.211) when the tutor said his name clearly . The emotional effect claimed by Kiang is illustrated in quotes such as these, although the educational impact is supported more indirectly through the chapter. Overall, he provides more examples of students being negatively affected by incorrect pronunciation, and it is difficult to find examples within the text of a positive educational impact as such.
Use of source material in example b:
The writer describes Kiang's (2004) claim and the examples which he uses to try to support it. The writer then comments that the examples do not seem balanced and may not be enough to support the claims fully. This is a better example of writing which expresses criticality.
^Back to top
Further resources
You may also be interested in our page on criticality, which covers criticality in general, and includes more critical reading questions.
Further reading: Read and Write Critically
We recommend that you do not search for other university guidelines on critical reviews. This is because the expectations may be different at other institutions. Ask your tutor for more guidance or examples if you have further questions.
IOE Writing Centre Online
Self-access resources from the Academic Writing Centre at the UCL Institute of Education.
Anonymous Suggestions Box
Information for Staff
Academic Writing Centre
Academic Writing Centre, UCL Institute of Education [email protected] Twitter: @AWC_IOE Skype: awc.ioe
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Masterlinks
- About Hunter
- One Stop for Students
- Make a Gift
- Access the Student Guide
- Apply to Become a Peer Tutor
- Access the Faculty Guide
- Request a Classroom Visit
- Refer a Student to the Center
- Request a Classroom Workshop
- The Writing Process
- The Documented Essay/Research Paper
- Writing for English Courses
- Writing Across the Curriculum
- Grammar and Mechanics
- Business and Professional Writing
- CUNY TESTING
- | Workshops
- Research Information and Resources
- Evaluating Information Sources
- Writing Tools and References
- Reading Room
- Literary Resources
- ESL Resources for Students
- ESL Resources for Faculty
- Teaching and Learning
- | Contact Us
To critique a piece of writing is to do the following:
- describe: give the reader a sense of the writer’s overall purpose and intent
- analyze: examine how the structure and language of the text convey its meaning
- interpret: state the significance or importance of each part of the text
- assess: make a judgment of the work’s worth or value
FORMATTING A CRITIQUE
Here are two structures for critiques, one for nonfiction and one for fiction/literature.
The Critique Format for Nonfiction
Introduction
- name of author and work
- general overview of subject and summary of author's argument
- focusing (or thesis) sentence indicating how you will divide the whole work for discussion or the particular elements you will discuss
- objective description of a major point in the work
- detailed analysis of how the work conveys an idea or concept
- interpretation of the concept
- repetition of description, analysis, interpretation if more than one major concept is covered
- overall interpretation
- relationship of particular interpretations to subject as a whole
- critical assessment of the value, worth, or meaning of the work, both negative and positive
The Critique Format for Fiction/Literature
- brief summary/description of work as a whole
- focusing sentence indicating what element you plan to examine
- general indication of overall significance of work
- literal description of the first major element or portion of the work
- detailed analysis
- interpretation
- literal description of second major element
- interpretation (including, if necessary, the relationship to the first major point)
- overall interpretation of the elements studied
- consideration of those elements within the context of the work as a whole
- critical assessment of the value, worth, meaning, or significance of the work, both positive and negative
You may not be asked in every critique to assess a work, only to analyze and interpret it. If you are asked for a personal response, remember that your assessment should not be the expression of an unsupported personal opinion. Your interpretations and your conclusions must be based on evidence from the text and follow from the ideas you have dealt with in the paper.
Remember also that a critique may express a positive as well as a negative assessment. Don't confuse critique with criticize in the popular sense of the word, meaning “to point out faults.”
Document Actions
- Public Safety
- Website Feedback
- Privacy Policy
- CUNY Tobacco Policy

How to Write a Good Critique Essay

How to Write a Close Reading Essay
The word "criticize," has by definition and perception largely negative connotations attached. Students may dread having their creative writing critiqued in a group setting. However, a fair assessment of any text, object, place or experience deeply analyzes all component parts and then renders judgment. When writing a critique essay, your readers need to understand how and why you arrived at your conclusion. A thorough and analytic critique provides them with an understanding of the critic’s values.
Describe Author and Work
Describe the work and its creator in the first paragraph. Do not assume that readers know the work or author prior to reading the critique. It is necessary to place the work in context so the reader has a sense of what is happening. Determine if the text is a first outing for the author or the latest in a long series. Does the author have a reputation or expertise in a certain field? Is the work controversial or well-known or little-known, and why? What is the intended audience for this work? By answering these questions, the reader has a stronger base of information to add clarity to the rest of the critique.
Write an accurate summary of the work’s main ideas in the second paragraph. Do not mingle your own evaluation with this summary. Instead, use the summary to explain the most important ideas the author tried to convey in the entire work and any other literary details that might guide or enlighten your reader.
In this section, critique the author’s presentation. Ask yourself a series of questions as you write the critique. Did the author present accurate and relevant data in a logical manner? Did the author clearly define important terms or jargon? Did the author offer sound interpretations? Focus in this paragraph, on whether the author achieved his or her purpose for creating the piece of writing.
State Your Opinion
Here, you will state both your own agreements and disagreements with the author. Develop your ideas by explaining why you agree and disagree with the author’s ideas. To further support your critique, cite other critics who support your interpretation.
In the last paragraphs, compose the conclusion that restates the main agreements and objections to the work. This conclusion is often the shortest paragraph in the critique but may also be the most important as it sums up the entire critique. In the closing, do not mention any new idea that does not already appear in the body paragraphs. The final paragraph is included to give an overview of the entire essay by restating its main ideas.
Related Articles

How to Write an Introduction to an Analytical Essay

How to Write Prose Commentary

Guidelines for a Reflection & Summary Paper

How to Write a Summary of an Autobiography

How to Write a Dissertation Summary

How to Construct a Rationale Statement

How to Write a Thesis Statement for "Robinson Crusoe"

How to Write an Eighth Grade Book Report
- Goshen College: Essay Critique Guidelines
- Massey University: Article Critique
- Writing Forward: How to Critique Other Writers' Works
- College Essay Tips: How To Write A Critique Essay for College
- Document in instructor-recommended citation style all quotes, paraphrases and summaries.
- Write a detailed summary of the text before writing the critique.
Patricia Hunt first found her voice as a fiction and nonfiction writer in 1974. An English teacher for over 27 years, Hunt's works have appeared in "The Alaska Quarterly Review," "The New Southern Literary Messenger" and "San Jose Studies." She has a Master of Fine Arts in creative writing from American University and a doctorate in studies of America from the University of Maryland.

Writing a Critique
About this guide.
- What Is a Critique?
- Getting Started
- Components of a Critique Essay
This guide provides an overview of critiques and how to write them. The contents include the following:
- What is a Critique? An overview of the standard critique essay.
- Getting Started Tips to set yourself up for success when writing a critique
- Components of a Critique Essay The components of a critique essay and how to write them
- Examples Example critique articles
- Get Help Provides links to additional resources that were not otherwise mentioned.
Rate this guide!
- Next: What Is a Critique? >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/critique

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.1: What’s a Critique and Why Does it Matter?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 6510

- Steven D. Krause
- Eastern Michigan University
Critiques evaluate and analyze a wide variety of things (texts, images, performances, etc.) based on reasons or criteria. Sometimes, people equate the notion of “critique” to “criticism,” which usually suggests a negative interpretation. These terms are easy to confuse, but I want to be clear that critique and criticize don’t mean the same thing. A negative critique might be said to be “criticism” in the way we often understand the term “to criticize,” but critiques can be positive too.
We’re all familiar with one of the most basic forms of critique: reviews (film reviews, music reviews, art reviews, book reviews, etc.). Critiques in the form of reviews tend to have a fairly simple and particular point: whether or not something is “good” or “bad.”
Academic critiques are similar to the reviews we see in popular sources in that critique writers are trying to make a particular point about whatever it is that they are critiquing. But there are some differences between the sorts of critiques we read in academic sources versus the ones we read in popular sources.
- The subjects of academic critiques tend to be other academic writings and they frequently appear in scholarly journals.
- Academic critiques frequently go further in making an argument beyond a simple assessment of the quality of a particular book, film, performance, or work of art. Academic critique writers will often compare and discuss several works that are similar to each other to make some larger point. In other words, instead of simply commenting on whether something was good or bad, academic critiques tend to explore issues and ideas in ways that are more complicated than merely “good” or “bad.”
The main focus of this chapter is the value of writing critiques as a part of the research writing process. Critiquing writing is important because in order to write a good critique you need to critically read : that is, you need to closely read and understand whatever it is you are critiquing, you need to apply appropriate criteria in order evaluate it, you need to summarize it, and to ultimately make some sort of point about the text you are critiquing.
These skills-- critically and closely reading, summarizing, creating and applying criteria, and then making an evaluation-- are key to The Process of Research Writing, and they should help you as you work through the process of research writing.
In this chapter, I’ve provided a “step-by-step” process for making a critique. I would encourage you to quickly read or skim through this chapter first, and then go back and work through the steps and exercises describe.
Selecting the right text to critique
The first step in writing a critique is selecting a text to critique. For the purposes of this writing exercise, you should check with your teacher for guidelines on what text to pick. If you are doing an annotated bibliography as part of your research project (see chapter 6, “The Annotated Bibliography Exercise”), then you are might find more materials that will work well for this project as you continuously research.
Short and simple newspaper articles, while useful as part of the research process, can be difficult to critique since they don’t have the sort of detail that easily allows for a critical reading. On the other hand, critiquing an entire book is probably a more ambitious task than you are likely to have time or energy for with this exercise. Instead, consider critiquing one of the more fully developed texts you’ve come across in your research: an in-depth examination from a news magazine, a chapter from a scholarly book, a report on a research study or experiment, or an analysis published in an academic journal. These more complex essays usually present more opportunities for issues to critique.
Depending on your teacher’s assignment, the “text” you critique might include something that isn’t in writing: a movie, a music CD, a multimedia presentation, a computer game, a painting, etc. As is the case with more traditional writings, you want to select a text that has enough substance to it so that it stands up to a critical reading.
Exercise 7.1
Pick out at least three different possibilities for texts that you could critique for this exercise. If you’ve already started work on your research and an annotated bibliography for your research topic, you should consider those pieces of research as possibilities. Working alone or in small groups, consider the potential of each text. Here are some questions to think about:
- Does the text provide in-depth information? How long is it? Does it include a “works cited” or bibliography section?
- What is the source of the text? Does it come from an academic, professional, or scholarly publication?
- Does the text advocate a particular position? What is it, and do you agree or disagree with the text?
What Is a Critique in Composition?
Tips on Writing a Peer Review
Hero Images/Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A critique is a formal analysis and evaluation of a text , production, or performance—either one's own (a self-critique ) or someone else's. In composition , a critique is sometimes called a response paper . When written by another expert in the field, a critique can also be called a peer review . Peer reviews are done to decide whether to accept an article for publication in a scholarly journal or, in an education setting, can be done in groups of students who offer feedback to each other on their papers ( peer response ).
Critiques differ from reviews (these are also different from peer reviews) in that critiques offer more depth to their analysis. Think of the difference between a scholarly article examining a work of literature in a journal (critique) and the kinds of topics that would be covered there vs. a few-hundred-word review of a book in a newspaper or magazine for the lay audience, for readers to decide whether they should purchase it.
Compare the term critique with critical analysis , critical essay , and evaluation essay .
Critiquing criteria are the standards, rules, or tests that serve as the bases for judgments.
Critiquing a Paper
A critique starts out with a summary of the topic of the paper but differs from a straight summary because it adds the reviewer's analysis.
If a critique is happening to the first draft of a paper, the issues brought by the reviewers need to be large-scale issues with the premise or procedure of obtaining the results—in the case of a scientific paper peer review—and arguments, such as flaws in logic or source material and fallacies, rather than be criticisms on a line level (grammar and the like). Ambiguity and irony presented in the paper could be targets as well.
"The critique is the process of objectively and critically evaluating a research report's content for scientific merit and application to practice, theory, and education, write Geri LoBiondo-Wood and Judith Haber. "It requires some knowledge of the subject matter and knowledge of how to critically read and use critiquing criteria." ("Nursing Research: Methods and Critical Appraisal for Evidence-Based Practice." Elsevier Health Sciences, 2006)
A critique should also point out what works well, not just the flaws in the paper.
"A critique should emphasize first what the article contributes to the field and then identify the shortcomings or limitations," write authors H. Beall and J. Trimbur. "In other words, a critique is a balanced appraisal, not a hatchet job." ("How to Read a Scientific Article." In "Communicating Science: Professional Contexts," ed. by Eileen Scanlon et al. Taylor & Francis, 1998)
The Purpose of a Critique
Arguments by the reviewer also need to be backed up with evidence. It isn't enough just to say that the paper in question is flawed but also how it's flawed and why—what's the proof that the argument won't hold up?
"It is important to be clear about what a critique is supposed to accomplish," write authors C. Grant Luckhardt and William Bechtel. They continue:
A critique is not the same as a demonstration that the conclusion of someone's argument is false. Imagine that someone has circulated a memorandum arguing that your company retain your current legal counsel. You, however, are convinced that it is time for a change, and want to demonstrate that....It is important to note here that you can prepare such a demonstration without mentioning any of your colleague's arguments or rebutting them. A critique of your colleague's demonstration, in contrast, requires you to examine the arguments in the demonstration and show that they fail to establish the conclusion that the current legal counsel should be retained. "A critique of your colleague's demonstration does not show that its conclusion is wrong. It only shows that the arguments advanced do not establish the conclusion it is claimed they do." ("How to Do Things With Logic." Lawrence Erlbaum, 1994)
Self-Critiques in Creative Writing
A related term to critiquing used frequently in scholarly Bible study is exegesis, though it doesn't apply only to Bible scholarship.
"An exegesis (in a creative writing discourse )...is a scholarly piece of writing with a focus on textual analysis and comparison using literature which relates to your creative writing project. Usually an exegesis is longer than a critique and reads more like a dissertation. There tends to be greater emphasis on your chosen comparative text than on your own creative writing project, with a clear thesis linking the two. "The good news is, once you learn how to write a critique on your creative process, you will find that it actually helps you to better understand your creative writing." (Tara Mokhtari, The Bloomsbury Introduction to Creative Writing . Bloomsbury, 2015)
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- Definition and Examples of Explication (Analysis)
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Critical Essay
- How to Write an Abstract
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- How To Write a Top-Scoring ACT Essay for the Enhanced Writing Test
- The Way Peer Review Works in the Social Sciences
- GMAT Sample Questions, Answers and Explanations
- Critical Analysis in Composition
- How to Write a Response Paper
- Peer Response (Composition)
- Full-Text Sociology Journals Online
- What Does Argumentation Mean?
- What Is a Literature Review?
- 3 Changes That Will Take Your Essay From Good To Great
Definition of Critique
Critique is a literary technique that means to critically evaluate a piece of literary work, or a political or philosophical theory in detail. A critique could be a critical essay , an article evaluating a literary piece, or a review. It may be just like a summary that identifies the central issue, raises questions, takes notice of theoretical and experimental approaches, and reviews the significance of the results. Apart from that, its purpose is to highlight both the shortcomings as well as strengths of a literary piece or a work of art. Moreover, critical evaluation or assessment requires sufficient knowledge about the subject matter.
Examples of Critique in Literature
Example #1: the guardian (by philip hope-wallace).
In The Guardian , critic Philip Hope-Wallace has portrayed Beckett’s play , Waiting for Godot, as “inexplicit and deliberately fatuous.” He also claimed this play to have “bored some people acutely. [while] Others found it a witty and poetic conundrum .” Godot would possibly be a God, and the dresses of tramps are like Chaplinesque zanies in a circus. Both speak futile cross talks like music hall exchanges. This play bored audience acutely, while others consider it as a poetic and witty conundrum. Finally, he calls the play a dramatic vacuum. It is without any plot , climax , denouement , beginning, middle and end.
Example #2: The Washington Post (By The Washington Post)
A famous writer, Jonathan Yardley, gives a complete analysis of F. Scott Fitzgerald’s popular novel , The Great Gatsby in The Washington Post . He calls the novel an enormous achievement in Fitzgerald’s career. It is his masterwork and seems that no other American novel could ever come close to its literary artistry.
This novel is very popular, and its every passage is famous, thus there is no need to retrace its details and familiar background. Fitzgerald has written it with unusual subtlety and sustained that tone in the entire novel. In the end, he says that this novel is “the most beautiful, compelling and true in all of American literature.” Then he says, “If from all of our country’s books I could have only one, The Great Gatsby , would be it.”
Example #3: Hamlet: Poem Unlimited (By Harold Bloom)
In his book, Hamlet : Poem Unlimited , Harold Bloom declares William Shakespeare ’s Hamlet as “unlimited,” coming “of no genre ,” because its greatness “… competes only with the world’s scriptures.” This amazing significance cannot emerge from a work, which is about tendentious and politicized things.
Bloom abandons the idea that Prince Hamlet ’s double shock of his father’s death and his mother’s second marriage has brought a drastic change in Hamlet. The truth, however, is that “Something in Hamlet dies before the play opens.” In fact, the theme or central idea of this play is “Hamlet’s consciousness of his own consciousness, unlimited yet at war with itself.” Thus, the play is about awakening of self-awareness, and Hamlet fights with “his desire to come to an end of playacting.”
Example #4: The Daily Telegraph (By Victoria Lambert)
Victoria Lambert, in The Daily Telegraph, writes her critical reviews on Jane Austen ’s novel, Pride and Prejudice . She describes the novel as surprisingly comforting as much as iconoclastic. It is a great story that challenges the people’s perceptions, and also draws a line through their thoughts and female history.
Certainly, there is an enjoyment of the Georgian grace, a world where we can solve problems by a ball invitation, a new gown, and scrumptious gossip. The social life at Hampshire Vicarage, its complex social mores, obsessions with money and class, its picnics and parities, draw the readers – especially females – to a point of obsession. The critics appreciate Austen’s overall depiction of the way money rules a society. She also admits Austen’s ability to describe the human heart in detail, setting her literary pulse racing.
Function of Critique
Critiques vary widely, ranging from giving reviews of books, as these reviews might determine whether a book is going to be popular or not, to rhetorical analysis of articles and pieces of artwork. Its advantage is that, despite negative criticism and reviews, many books win commercial success. Sometimes a critic serves as a scholarly detective, authenticating unknown books and unearthing master pieces. Thus, obscure scholarly skills could work as a most basic criticism, bringing literary pieces to public attention.
Besides, a critique may antagonize the author. Many authors do not feel that literature needs investigators, and advocates are not happy when they hear that their works are imitative, incomplete, or have unintended meanings. However, most critiques are useful, as they help improve the works of authors.
Post navigation
Writing a Critique Paper: Seven Easy Steps
Were you assigned or asked by your professor to write a critique paper? It’s easy to write one. Just follow the following four steps in writing a critique paper and three steps in presenting it, then you’re ready to go.
One of the students’ requirements I specified in the course module is a critique paper. Just so everyone benefits from the guide I prepared for that class, I share it here.
To standardize the format they use in writing a critique paper, I came up with the following steps to make their submissions worthwhile.
Since they are graduate students, more is expected of them. Hence, most of the verbs I use in writing the lesson’s objectives reside in the domain of higher thinking skills or HOTS. Developing the students’ critical thinking skills will help them analyze future problems and propose solutions that embody environmental principles thus resonate desirable outcomes aligned with the goal of sustainable development.
Table of Contents
Step-by-step procedure in writing a critique paper.
I quickly wrote this simple guide on writing a critique paper to help you evaluate any composition you want to write about. It could be a book, a scientific article, a gray paper, or whatever your professor assigns. I integrated the essence of the approach in this article.
The critique paper essentially comprises two major parts, namely the:
1) Procedure in Writing a Critique Paper, and the
2) Format of the Critique Paper.
First, you will need to know the procedure that will guide you in evaluating a paper. Second, the format of the critique paper refers to how you present it so that it becomes logical and scholarly in tone.
The Four Steps in Writing a Critique Paper
Here are the four steps in writing a critique paper:
To write a good critique paper, it pays to adhere to a smooth flow of thought in your evaluation of the piece. You will need to introduce the topic, analyze, interpret, then conclude it.
Introduce the Discussion Topic
Introduce the topic of the critique paper. To capture the author’s idea, you may apply the 5Ws and 1H approach in writing your technical report.
That means, when you write your critique paper, you should be able to answer the Why , When , Where , What , Who , and How questions. Using this approach prevents missing out on the essential details. If you can write a critique paper that adheres to this approach, that would be excellent.
Here’s a simplified example to illustrate the technique:
The news article by John Doe was a narrative about a bank robbery. Accordingly, a masked man (Who) robbed a bank (What) the other day (When) next to a police station (Where) . He did so in broad daylight (How) . He used a bicycle to escape from the scene of the crime (How) . In his haste, he bumped into a post. His mask fell off; thus, everyone saw his face, allowing witnesses to describe him. As a result, he had difficulty escaping the police, who eventually retrieved his loot and put him in jail because of his wrongdoing (Why) .
Hence, you give details about the topic, in this case, a bank robbery. Briefly describe what you want to tell your audience. State the overall purpose of writing the piece and its intention.
Is the essay written to inform, entertain, educate, raise an issue for debate, and so on? Don’t parrot or repeat what the writer wrote in his paper. And write a paragraph or a few sentences as succinctly as you can.
Analyze means to break down the abstract ideas presented into manageable bits.
What are the main points of the composition? How was it structured? Did the view expressed by the author allow you, as the reader, to understand?
In the example given above, it’s easy to analyze the event as revealed by the chain of events. How do you examine the situation?
The following steps are helpful in the analysis of information:
- Ask yourself what your objective is in writing the critique paper. Come up with a guidepost in examining it. Are you looking at it with some goal or purpose in mind? Say you want to find out how thieves carry out bank robberies. Perhaps you can categorize those robberies as either planned or unplanned.
- Find out the source, or basis, of the information that you need. Will you use the paper as your source of data, or do you have corroborating evidence?
- Remove unnecessary information from your data source. Your decision to do so depends on your objective. If there is irrelevant data, remove it from your critique.
We can use an analogy here to clearly explain the analysis portion.
If you want to split a log, what would you do? Do you use an ax, a chainsaw, or perhaps a knife? The last one is out of the question. It’s inappropriate.
Thus, it would be best if you defined the tools of your analysis. Tools facilitate understanding and allow you to make an incisive analysis.
Read More : 5 Tools in Writing the Analysis Section of the Critique Paper
Now, you are ready to interpret the article, book, or any composition once the requisites of analysis are in place.
Visualize the event in your mind and interpret the behavior of actors in the bank robbery incident. You have several actors in that bank heist: the robber, the police, and the witnesses of the crime.
While reading the story, it might have occurred to you that the robber is inexperienced. We can see some discrepancies in his actions.
Imagine, his mode of escape is a bicycle. What got into him? Maybe he did not plan the robbery at all. Besides, there was no mention that the robber used a gun in the heist.
That fact confirms the first observation that he was not ready at all. Escaping the scene of the crime using a bicycle with nothing to defend himself once pursued? He’s insane. Unimaginable. He’s better off sleeping at home and waiting for food to land on his lap if food will come at all.
If we examine the police’s response, they were relatively quick. Right after the robber escaped the crime scene, they appeared to remedy the situation. The robber did not put up a fight.
What? With bare knuckles? It makes little sense.
If we look at the witnesses’ behavior, we can discern that perhaps they willingly informed the police of the bank robber’s details. They were not afraid. And that’s because the robber appears to be unarmed. But there was no specific mention of it.
Narrate the importance of each of the different sections or paragraphs. How does the write-up contribute to the overall picture of the issue or problem being studied?
Assess or Evaluate
Finally, judge whether the article was a worthwhile account after all. Did it meet expectations? Was it able to convey the information most efficiently? Or are there loopholes or flaws that should have been mentioned?
Format of Presenting the Critique Paper
The logical format in writing a critique paper comprises at least three sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. This approach is systematic and achieves a good flow that readers can follow.
Introduction
Include the title and name of the author in your introduction. Make a general description of the topic being discussed, including the author’s assumptions, inferences, or contentions. Find out the thesis or central argument , which will be the basis of your discussion.
The robbery example appears to be inappropriate to demonstrate this section, as it is so simple. So we level up to a scientific article.
In any scientific article, there is always a thesis that guides the write-up. A thesis is a statement that expresses what the author believes in and tries to test in his study. The investigation or research converges (ideally) to this central theme as the author’s argument.
You can find the thesis in the paper’s hypothesis section. That’s because a hypothesis is a tentative thesis. Hypo means “below or under,” meaning it is the author’s tentative explanation of whatever phenomenon he tackles.
If you need more information about this, please refer to my previous post titled “ How to Write a Thesis .”
How is the introduction of a critique paper structured? It follows the general guidelines of writing from a broad perspective to more specific concerns or details. See how it’s written here: Writing a Thesis Introduction: from General to Specific .
You may include the process you adopted in writing the critique paper in this section.
The body of the paper includes details about the article being examined. It is here where you place all those musings of yours after applying the analytical tools .
This section is similar to the results and discussion portion of a scientific paper. It describes the outcome of your analysis and interpretation.
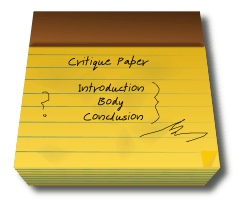
In explaining or expressing your argument, substantiate it by citing references to make it believable. Make sure that those references are relevant as well as timely. Don’t cite references that are so far out in the past. These, perhaps, would not amount to a better understanding of the topic at hand. Find one that will help you understand the situation.
Besides, who wants to adopt the perspective of an author who has not even got hold of a mobile phone if your paper is about using mobile phones to facilitate learning during the pandemic caused by COVID-19 ? Find a more recent one that will help you understand the situation.
Objectively examine the major points presented by the author by giving details about the work. How does the author present or express the idea or concept? Is he (or she) convincing the way he/she presents his/her paper’s thesis?
Well, I don’t want to be gender-biased, but I find the “he/she” term somewhat queer. I’ll get back to the “he” again, to represent both sexes.
I mention the gender issue because the literature says that there is a difference in how a person sees things based on gender. For example, Ragins & Sundstrom (1989) observed that it would be more difficult for women to obtain power in the organization than men. And there’s a paper on gender and emotions by Shields et al. (2006) , although I wouldn’t know the outcome of that study as it is behind a paywall. My point is just that there is a difference in perspective between men and women. Alright.
Therefore, always find evidence to support your position. Explain why you agree or disagree with the author. Point out the discrepancies or strengths of the paper.
Well, everything has an end. Write a critique paper that incorporates the key takeaways of the document examined. End the critique with an overall interpretation of the article, whatever that is.
Why do you think is the paper relevant in the course’s context that you are taking? How does it contribute to say, the study of human behavior (in reference to the bank robbery)? Are there areas that need to be considered by future researchers, investigators, or scientists? That will be the knowledge gap that the next generation of researchers will have to look into.
If you have read up to this point, then thank you for reading my musings. I hope that helped you clarify the steps in writing a critique paper. A well-written critique paper depends on your writing style.
Read More : How to Write an Article with AI: A Guide to Using AI for Article Creation and Refinement
Notice that my writing style changes based on the topic that I discuss. Hence, if your professor assigns you a serious, rigorous, incisive, and detailed analysis of a scientific article, then that is the way to go. Adopt a formal mode in your writing.
Final Tip : Find a paper that is easy for you to understand. In that way, you can clearly express your thoughts. Write a critique paper that rocks!
Related Reading
Master Content Analysis: An All-in-One Guide
Ragins, B. R., & Sundstrom, E. (1989). Gender and power in organizations: A longitudinal perspective. Psychological bulletin , 105 (1), 51.
Shields, S. A., Garner, D. N., Di Leone, B., & Hadley, A. M. (2006). Gender and emotion. In Handbook of the sociology of emotions (pp. 63-83). Springer, Boston, MA.
© 2020 November 20 P. A. Regoniel
Related Posts

Three Tips on How to Write a Good Statistical Question
Five tips for research paper presentation, how to write the conceptual framework in a research proposal, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a faculty member of the graduate school, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
Thank you..for your idea ..it was indeed helpful
Glad it helped you Preezy.
This is extremely helpful. Thank you very much!
Thanks for sharing tips on how to write critique papers. This article is very informative and easy to understand.
Welcome. Thank you for your appreciation.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Researching
51 Critiquing a Text
Let’s review:
- When we summarize a text, we capture its main points.
- When we analyze a text, we consider how it has been put together—we dissect it, more or less, to see how it works
When we critique a text, we evaluate it, asking it questions. Critique shares a root with the word “criticize.” Most of us tend to think of criticism as being negative or mean, but in the academic sense, doing a critique is a constructive way to better explore and understand the material we’re working with. The word critique’s origin means “to evaluate,” and through our critique, we do a deep evaluation of a text.
When we critique a text, we interrogate it. Our own opinions and ideas become part of our textual analysis. We question the text, we argue with it, and we delve into it for deeper meanings.
Ideas to Consider when Critiquing a Text
- How did you respond to the piece? Did you like it? Did it appeal to you? Could you identify with it?
- Do you agree with the main ideas in the text?
- Did you find any errors in reasoning? Any gaps in the discussion?
- Did the organization make sense?
- Was evidence used correctly, without manipulation? Has the writer used appropriate sources for support?
- Is the author objective? Biased? Reasonable? (Note that the author might just as easily be subjective, unbiased, and unreasonable! Every type of writing and tone can be used for a specific purpose. By identifying these techniques and considering why the author is using them, you begin to understand more about the text.)
- Has the author left anything out? If yes, was this accidental? Intentional?
- Are the text’s tone and language text appropriate?
- Are all of the author’s statements clear? Is anything confusing?
- What worked well in the text? What was lacking or failed completely?
- What is the cultural context [1] of the text?
These are only a few ideas relating to critique, but they’ll get you started. When you critique, try working with these statements, offering explanations to support your ideas. Bring in content from the text (textual evidence) to support your ideas.
Text Attributions
- This chapter was adapted from “ Critiquing a Text ” in The Word on College Reading and Writing by Carol Burnell, Jaime Wood, Monique Babin, Susan Pesznecker, and Nicole Rosevear, which is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence . Adapted by Allison Kilgannon.
- Cultural context is way of asking who is affected by the ideas and who stands to lose or gain if the ideas take place. When you think about this, think of all kinds of social and cultural variables, including age, gender, occupation, education, race, ethnicity, religion, economic status, and so forth. ↵
Advanced English Copyright © 2021 by Allison Kilgannon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- English Grammar
- Writing Paragraphs
How to Write a Critique in Five Paragraphs
Last Updated: January 20, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diane Stubbs . Diane Stubbs is a Secondary English Teacher with over 22 years of experience teaching all high school grade levels and AP courses. She specializes in secondary education, classroom management, and educational technology. Diane earned a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Delaware and a Master of Education from Wesley College. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 972,890 times.
A critique is usually written in response to a creative work, such as a novel, a film, poetry, or a painting. However, critiques are also sometimes assigned for research articles and media items, such as news articles or features. A critique is slightly different than a traditional 5-paragraph theme, as it is usually focused on the overall effectiveness and usefulness of the work it is critiquing, rather than making a strictly analytical argument about it. Organizing your critique into 5 paragraphs can help you structure your thoughts.
Laying the Groundwork

- Does the creator clearly state her/his main point or goal? If not, why do you think that is?
- Who do you think is the creator’s intended audience? This can be crucial to determining the success of a work; for example, a movie intended for young children might work well for its intended audience but not for adult viewers.
- What reactions do you have when reading or viewing this work? Does it provoke emotional responses? Do you feel confused?
- What questions does the work make you think of? Does it suggest other avenues of exploration or observation to you?

- For example, if you're critiquing a research article about a new treatment for the flu, a little research about other flu treatments currently available could be helpful to you when situating the work in context.
- As another example, if you're writing about a movie, you might want to briefly discuss the director's other films, or other important movies in this particular genre (indie, action, drama, etc.).
- Your school or university library is usually a good place to start when conducting research, as their databases provide verified, expert sources. Google Scholar can also be a good source for research.
Writing the Introductory Paragraph

- For a work of fiction or a published work of journalism or research, this information is usually available in the publication itself, such as on the copyright page for a novel.
- For a film, you may wish to refer to a source such as IMDb to get the information you need. If you're critiquing a famous artwork, an encyclopedia of art would be a good place to find information on the creator, the title, and important dates (date of creation, date of exhibition, etc.).

- For example, if you’re assessing a research article in the sciences, a quick overview of its place in the academic discussion could be useful (e.g., “Professor X’s work on fruit flies is part of a long research tradition on Blah Blah Blah.”)
- If you are evaluating a painting, giving some brief information on where it was first displayed, for whom it was painted, etc., would be useful.
- If you are assessing a novel, it could be good to talk about what genre or literary tradition the novel is written within (e.g., fantasy, High Modernism, romance). You may also want to include details about the author’s biography that seem particularly relevant to your critique.
- For a media item, such as a news article, consider the social and/or political context of the media outlet the item came from (e.g., Fox News, BBC, etc.) and of the issue it is dealing with (e.g., immigration, education, entertainment).

- The authors of research articles will often state very clearly in the abstract and in the introduction to their work what they are investigating, often with sentences that say something like this: "In this article we provide a new framework for analyzing X and argue that it is superior to previous methods because of reason A and reason B."
- For creative works, you may not have an explicit statement from the author or creator about their purpose, but you can often infer one from the context the work occupies. For example, if you were examining the movie The Shining, you might argue that the filmmaker Stanley Kubrick's goal is to call attention to the poor treatment of Native Americans because of the strong Native American themes present in the movie. You could then present the reasons why you think that in the rest of the essay.

- For example, if you were writing about The Shining, you could summarize the main points this way: "Stanley Kubrick uses strong symbolism, such as the placement of the movie's hotel on an Indian burial ground, the naming of the hotel "Overlook," and the constant presence of Native American artwork and representation, to call viewers' attention to America's treatment of Native Americans in history."

- For a research article, you will probably want to focus your thesis on whether the research and discussion supported the authors' claims. You may also wish to critique the research methodology, if there are obvious flaws present.
- For creative works, consider what you believe the author or creator's goal was in making the work, and then present your assessment of whether or not they achieved that goal.
Writing the 3 Body Paragraphs

- If you have three clear points about your work, you can organize each paragraph by point. For example, if you are analyzing a painting, you might critique the painter’s use of color, light, and composition, devoting a paragraph to each topic.
- If you have more than three points about your work, you can organize each paragraph thematically. For example, if you are critiquing a movie and want to talk about its treatment of women, its screenwriting, its pacing, its use of color and framing, and its acting, you might think about the broader categories that these points fall into, such as “production” (pacing, color and framing, screenwriting), “social commentary” (treatment of women), and “performance” (acting).
- Alternatively, you could organize your critique by “strengths” and “weaknesses.” The aim of a critique is not merely to criticize, but to point out what the creator or author has done well and what s/he has not.

- For example, if you are critiquing a song, you could consider how the beat or tone of the music supports or detracts from the lyrics.
- For a research article or a media item, you may want to consider questions such as how the data was gathered in an experiment, or what method a journalist used to discover information.

- Does the author use primary sources (e.g., historical documents, interviews, etc.)? Secondary sources? Quantitative data? Qualitative data? Are these sources appropriate for the argument?
- Has evidence been presented fairly, without distortion or selectivity?
- Does the argument proceed logically from the evidence used?

- If the work is a creative work, consider whether it presents its ideas in an original or interesting way. You can also consider whether it engages with key concepts or ideas in popular culture or society.
- If the work is a research article, you can consider whether the work enhances your understanding of a particular theory or idea in its discipline. Research articles often include a section on “further research” where they discuss the contributions their research has made and what future contributions they hope to make.

Writing the Conclusion Paragraph and References

Sample Critiques

Community Q&A
- Before you begin writing, take notes while you are watching or reading the subject of your critique. Keep to mind certain aspects such as how it made you feel. What was your first impression? With deeper examination, what is your overall opinion? How did you come to this opinion? Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- While the 5-paragraph form can work very well to help you organize your ideas, some instructors do not allow this type of essay. Be sure that you understand the assignment. If you’re not sure whether a 5-paragraph format is acceptable to your teacher, ask! Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid using first and second person pronouns such as, “you”, “your”, “I”, “my”, or “mine.” State your opinion objectively for a more credible approach. Thanks Helpful 39 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-critique
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-article-critique
- ↑ https://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/writing-well/critique.html
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/book-review
- ↑ https://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/invention/Writing-a-Critique
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/esl/resources/writing-critiques/
About This Article

To write a 5-paragraph critique, provide the basic information about the work you're critiquing in the first paragraph, including the author, when it was published, and what its key themes are. Then, conclude this paragraph with a statement of your opinion of the work. Next, identify 3 central positive or negative issues in the work and write a paragraph about each one. For example, you could focus on the color, light, and composition of a painting. In the final paragraph, state your overall assessment of the work, and give reasons to back it up. For tips on how to take notes on the piece your critiquing, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lura Norton
Feb 7, 2017
Did this article help you?
Ahmed Misry
Sep 30, 2017
Celia Seecharan
Feb 11, 2017
Sep 23, 2017
Lusady Taylor
Jul 28, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Undergraduate Programs
- Majors & Minors
- Academic Catalog & Courses
- Goshen Core
- Global Education
- Adult & Continuing Studies
- Nursing (RN to BSN)
- Business Management (BS)
- Communication (BS)
- Social Work (BS)
- Transition to Interpreting
- Transition to Teaching
- English Learners License
- Graduate Programs
- Business Administration (MBA)
- Environmental Education (MA)
- Nursing (MS, FNP Track)
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP)
- Online Programs
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Scholarships
- Net Price Calculator
- International Students
- Transfer Students
- Admitted Students
- Committed Students
- Financial Aid
- Student Life
- Health & Safety
- Dining Services
- Clubs & Activities
- Spiritual Life
- Mission, Vision & Values
- Quick Facts
- Leadership & Governance
- Faith Identity
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Sustainability
- Community Engagement
- Where We Are
- Map & Directions
- City of Goshen
- Virtual Visit
- Alumni Directory
- Transcripts
- The Bulletin
- Homecoming Weekend
- Parents of Prospective Students
- Parents of Current Students
- Current Students
- Registrar's Office
- Accounting Office
- Faculty & Staff
- Human Resources
- Department Forms
- Quick Links
- Event Calendar
- News & Events
- Events Calendar
- Latest News
- GC in the News
- Social Media Directory
- Alumni Magazine
- Photo Albums
- Current Blogs
- President's
- Ecuador SST
- Tanzania SST
- Music Center
- E-Subscribe
- Live Streams
- Cross Country
- Track and Field
- GoLeafs.net
- Live Stream
- Online Store
- Rec-Fitness Center
- Intramurals

Essay Critique Guidelines

Whenever you read an essay, use the following questions to guide your response.
First, keep in mind that, although you may not be a writing expert, you are THE reader of this essay and your response is a valid one . I have found that almost every reader, regardless of experience, can identify the primary strength and weakness in an essay, although their method of describing those issues may be different. The author will welcome your response and your ability to explain your reaction in a new way. Although the author is not required to, and really shouldn’t, respond to everything you say, he or she will take your comments seriously and consider how the essays has enlightened or confused you. Therefore, comment freely, although respectfully. Keep in mind that it is better to begin by noting the strengths of the essay before pointing out the areas that need improvement. I would always include a personal response to questions like the following: What about the essay most connects with your experience? Moves you? Provokes you? Entertains you?
So that is how to respond. So how do you critique? For every essay, regardless of the mode, consider the broad categories of content, organization, style, and correctness.
- Content : Consider the topic (its appropriateness and interest for the assignment as well as a clear focus suitable to essay length) and the way the topic is developed (clarity sufficiency of its argument, its scope, subcategories, amount and type of examples, anecdotes, evidence, etc.).
- Organization : Consider how the essay is introduced and concluded (especially looking for a “frame” to the essay, where the intro and conclusion refer to the same idea), whether the thesis is located in the most helpful place (direct or implied), how the essay is structured, whether the order or extent of development is successful, as well as how individual paragraphs are organized (clear topic sentences, appropriate and concrete evidence, logical organization of evidence).
- Style : Style can refer to the overall style of an essay: whether the tone is appropriate (humorous, serious, reflective, satirical, etc.), whether you use sufficient and appropriate variety (factual, analytical, evaluative, reflective), whether you use sufficient creativity. Style can also refer to the style of individual sentences: whether you use a variety of sentences styles and lengths, whether sentences are worded clearly, and whether word choice is interesting and appropriate.
Rolling around in the bottom of the drawer, Tim found the missing earring. [certainly the earring was rolling, not Tim!]
You could also easily tell that the following sentence actually contains two sentences that need punctuation between them:
The new manager instituted several new procedures some were impractical. [You need to add punctuation (period) after “procedures” and capitalize “some.”]
Further Directions for Specific Assignments
Below are more detailed questions to consider when responding to individual types of essays. First, make sure that you have reviewed the description of the essay mode in the Essay Assignment Guidelines. Use at least one or two of these when responding to an essay. Do not simply answer yes or no; offer specific evidence from the text and elaborate on the reasons behind your answer.
Personal Essay Critique:
- Does the writer have a clear but understated purpose to the essay?
- Does it avoid being overly moralistic or heavy-handed?
- Does the essay contain suspense or tension that is resolved in some way?
- Do you have any suggestions for organizing the essay, such as focusing in on one event rather than many, providing more background, turning explanation into action, etc.?
- Does the essay make good use of concrete description, anecdote, and dialogue?
- Does the essay help you to feel the emotions rather than just describe the emotions of the author?
- Does the essay reveal a significant aspect of the writer’s personality?
- Does the writer seem authentic?
- Is this a passionate piece? Is it creative?
Critical Review Critique
- Does a direct thesis convey both the subject and the reviewer’s value judgment?
- Does the review provide a summary or description to help you experience the film, music, event, etc.? Note places where the author provides too much or too little detail.
- Does the essay clearly identify relevant criteria for evaluation? Are they appropriate, believable, and consistent?
- Are any important features of the reviewed subject omitted?
- Logos (logic, content) : Does the essay provide sufficient, relevant, and interesting details and examples to adequately inform and entertain?
- Ethos (author) : Does the author’s judgment seem sound and convincing?
- Pathos (emotional appeals) : Does the author responsibly and effectively utilize emotional appeals to the audience?
- Does the author include adequate reference to the opposition and respond to that opposition appropriately?
Information Essay Critique : The questions posed about an informative essay will vary, depending on the purpose and strategy of the essay. The SMGW suggests evaluating for the following issues:
- Is topic clearly explained and sufficiently focused?
- Does the content fit the audience?
- Is it organized effectively?
- Are definitions clear?
- Are other strategies (classification, comparison/contrast, analysis) used effectively?
- Are sources used sufficiently, effectively, and appropriately?
You might also assess the following criteria:
- Does the author utilize vivid detail, interesting examples, and lively language?
- Does the essay avoid emphasizing judgment over explanation?
- Does the essay have a clear focus or implied thesis?
Comparison/Contrast Essay Critique
- Is the purpose for a comparison or contrast evident and convincing?
- Does the essay identify significant and parallel characteristics for comparison?
- Does the author adequately explain, analyze, or reflect on the comparison or contrast?
- Does the author provide appropriate transitions words to indicate comparison and contrast?
- Is the treatment of each side of the comparison or contrast in balance?
- Does the essay provide sufficient, relevant, and interesting details?
Feature Article Critique
- Does this article interest you? Do you think it will interest the intended audience? Can you suggest ways to increase interest?
- Can you tell what the “angle” or implied thesis is? Does the author avoid editorial judgment on the subject while still keeping the purpose clear?
- Has the writer done sufficient research? What questions have gone unasked or unanswered? Whose point of view or what information would add further to the completeness of the feature?
- Is the subject presented vividly with sensory images, graphic detail, and figurative language? Do you have suggestions of details or images to include?
- Does the writer use an appropriate mixture of anecdote, quotation, description, and explanation? Would more or less of one of these improve the essay?
- Are the beginning and ending paragraphs interesting and appropriate for the specific audience? Consider the need for a “lead sentence” if intended for a newspaper.
Documented Argument Critique
- Is the thesis clear, argumentative, and effective? Why or why not?
- Are the topic and thesis are reasonable for the assignment, audience, and context of the essay?
- Does the author define his or her terms and provide sufficient background information? What ideas or terms are undefined or inadequately explained?
- Is the thesis supported by clear reasons? Are the reasons clearly worded and supported sufficiently?
- Do the reasons fit logically together and are they placed in the right order?
- Does the author adequately address the opposition? What is another opposing argument he/she should or could have addressed?
- Has the author done adequate research?
- Are the works cited adequately introduced and explained before citing from them?
- Does the paper contain an appropriate blend of well-placed quotations within a context of the author’s own words and paraphrases from other sources?
- Is the writer clearly in charge, naturally introducing and interacting with sources rather than merely reporting on them?
- Do you find the argument convincing? What might you add or omit?
Business Writing Critique
- Does the memo begin with the most important information?
- Does the memo build rapport by involving the reader in opening paragraph?
- Does the memo provide sufficient, relevant, and interesting details? Is it focused and brief?
- Does the memo focus each paragraph on one idea?
- Is the memo informed, accurate, demonstrating the author’s grasp of the situation?
- Is the final paragraph calling for a specific action? Is it brief? Does it build good will?
- Is the memo form correct, with concise subject line, initialed name, correct spacing?
- Is the information arranged (indentations and numbering) in a way that makes it easy to skim and still get central information?
Cover letter
- Does the first paragraph identify who the author is, briefly state why he/she is writing, and refer to how he/she found out about the job?
- Does the second paragraph highlight specific strengths, special abilities, or features of the résumé to be noted?
- Does the third paragraph make a specific request of the reader or address what action is to be taken?
- Does the letter provide sufficient, relevant, and interesting details to make the request convincing?
- Is the letter brief and focused? What elements could be eliminated?
- Does the writer achieve his or her purpose? Does it make you want to consider the résumé more carefully?
- Is the tone of the letter courteous without being too formal, relaxed without being too familiar?
- Is the letter’s form appropriate (heading, spacing, greeting, salutation)? Is the letter addressed to a specific person rather than a general “Dear Madam/Sir”?
- Does the résumé contain the necessary features for the position (name/address, position desired, education, work experience, achievements, relevant personal information, references)?
- Does the résumé contain only essential, relevant information for the position required?
- Does the résumé emphasize the applicant’s strengths?
- Does the résumé emphasize what is unique about this person’s experience? Does it demonstrate a common interest or ability (leadership, teaching experience, dedication, creativity, etc.)?
- What additional information might you like to have about this applicant?
- If you were leading an interview based on this résumé, what are two questions you might ask?
- Does the résumé look neat (appropriate spacing, clear headings, good quality paper)?
- Is the résumé easy to read?
- Is the information presented as concisely as possible?
- Are the elements of each section of the résumé presented in a parallel format and style (begin w/ active verbs, put date in consistent place, use of parallelism for elements, consistent underlining or italics)?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This critique essay type examines texts and other written papers. It usually focuses on specific characteristics of a piece. Sometimes, a work can be compared to other examples in its genre. Descriptive essays often provide detailed insight into the examined works. Evaluative: These essays estimate the value of a work.
A critique is a response to a body of work, be it a performance, concept, argument, scholarly article, poem or book. If you write a critique, you can present your opinion of the work or provide an alternative opinion. Critiques typically include the following: Description of the work, including its purpose, the creator and the intention
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work-deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole. Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain ...
A critical essay is a form of academic writing that analyzes, interprets, and/or evaluates a text. In a critical essay, an author makes a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, then supports that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources. In casual conversation, we often associate the word "critical ...
Example of Critique Essay On Articles An article-related critique essay is a paper that evaluates an article to determine its effectiveness in attaining a goal. An article could comprise opinions, personal experiences, and external research.
A critical essay is written in the third-person and ensures the reader is presented with an objective analysis. Discuss whether the author was able to achieve their goals and adequately get their point across. It is important not to confuse facts and opinions. An opinion is a personal thought and requires confirmation, whereas a fact is ...
Writing Critiques. Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people's work in their academic area.
A critique evaluates a resource. It requires both critical reading and analysis in order to present the strengths and weaknesses of a particular resource for readers.The critique includes your opinion of the work. Because of the analytics involved, a critique and a summary are not the same. For quick reference, you can use the following chart in order to determine if your paper is a critique ...
A critique may include a brief summary, but the main focus should be on your evaluation and analysis of the research itself. What steps need to be taken to write an article critique? Before you start writing, you will need to take some steps to get ready for your critique: Choose an article that meets the criteria outlined by your instructor.
When you hear that your writing assignment is a "critique," here's what you do: instantly substitute the word "evaluation." You see, essentially, that's what a critique is—an e-value-ation. ... Let's take a look at the typical parts of a critique or evaluation essay and get to know what should be done in each one: Introduction ...
The critique is your evaluation of the resource. A strong critique: Discusses the strengths of the resource. Discusses the weaknesses of the resource. Provides specific examples (direct quotes, with proper citation) as needed to support your evaluation. Discusses anything else pertinent to your evaluation, including.
The structure of a typical critique essay example includes an introduction, a summary, an analysis, and a conclusion. The paper format is a crucial element. Just like when you write your research papers, a critique benefits from a clear one to guide the reader. Therefore, work on defining the critique essay outline before starting the writing ...
Writing a Critique. A critique (or critical review) is not to be mistaken for a literature review. A 'critical review', or 'critique', is a complete type of text (or genre), discussing one particular article or book in detail. In some instances, you may be asked to write a critique of two or three articles (e.g. a comparative critical review).
Writing a Critique. To critique a piece of writing is to do the following: describe: give the reader a sense of the writer's overall purpose and intent. analyze: examine how the structure and language of the text convey its meaning. interpret: state the significance or importance of each part of the text. assess: make a judgment of the work ...
Describe Author and Work. Describe the work and its creator in the first paragraph. Do not assume that readers know the work or author prior to reading the critique. It is necessary to place the work in context so the reader has a sense of what is happening. Determine if the text is a first outing for the author or the latest in a long series.
What is a Critique? An overview of the standard critique essay. Getting Started Tips to set yourself up for success when writing a critique Components of a Critique Essay The components of a critique essay and how to write them; Examples Example critique articles; Get Help Provides links to additional resources that were not otherwise mentioned.
8.5: Assignment- Writing a Critique Essay. If you have been doing the exercises and following through the process I've outlined in this chapter then you should be well on your way in the process of writing an effective critique. As you work on the writing assignment for this chapter, put to work your new knowledge of the process of critiquing.
Critiques evaluate and analyze a wide variety of things (texts, images, performances, etc.) based on reasons or criteria. Sometimes, people equate the notion of "critique" to "criticism," which usually suggests a negative interpretation. These terms are easy to confuse, but I want to be clear that critique and criticize don't mean the ...
A critique, also known as a review, an assessment, or an evaluation, is much less personal than a response paper, although it does entail responding to a text. In a critique, you evaluate the quality or merit of a text, based on a set of clearly defined criteria. These criteria will vary depending on the type of text you are evaluating.
A critique is different from an expository essay which is, as you have learned, a discussion revolving around a topic with multiple sources to support the discussion points. As you can see in Self-Practice Exercise 8.1, depending on the type of critique you are writing, your reference page could include one source only.
A critique is a formal analysis and evaluation of a text, production, or performance—either one's own (a self-critique) or someone else's. In composition, a critique is sometimes called a response paper. When written by another expert in the field, a critique can also be called a peer review. Peer reviews are done to decide whether to accept ...
An essay critique is an analysis of a work in the context of its intent. It is more than simply a review, a set of likes and dislikes. It is designed to determine if a written work has fulfilled ...
Critique is a literary technique that means to critically evaluate a piece of literary work, or a political or philosophical theory in detail. A critique could be a critical essay, an article evaluating a literary piece, or a review. It may be just like a summary that identifies the central issue, raises questions, takes notice of theoretical ...
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Critical analysis essays can be a daunting form of academic writing, but crafting a good critical analysis paper can be straightforward if you have the right approach.
2) Format of the Critique Paper. First, you will need to know the procedure that will guide you in evaluating a paper. Second, the format of the critique paper refers to how you present it so that it becomes logical and scholarly in tone. The Four Steps in Writing a Critique Paper. Here are the four steps in writing a critique paper:
Agreeing with, defending or confirming a particular point of view. Proposing a new point of view. Conceding to an existing point of view, but qualifying certain points. Reformulating an existing idea for a better explanation. Dismissing a point of view through an evaluation of its criteria. Reconciling two seemingly different points of view.
The Critique Essay It's your first essay in ENG 112, and, of course, you want to do well. This handout offers some helpful hints for writing the first essay—The Critique. Remember the author! The critique essay is not about concerned with the content of the article - but whether or
When we critique a text, we evaluate it, asking it questions. Critique shares a root with the word "criticize.". Most of us tend to think of criticism as being negative or mean, but in the academic sense, doing a critique is a constructive way to better explore and understand the material we're working with. The word critique's origin ...
1. Give the basic information about the work. The first paragraph is your introduction to the work, and you should give the basic information about it in this paragraph. This information will include the author's or creator's name (s), the title of the work, and the date of its creation.
Study English at Goshen College. Whenever you read an essay, use the following questions to guide your response. First, keep in mind that, although you may not be a writing expert, you are THE reader of this essay and your response is a valid one. I have found that almost every reader, regardless of experience, can identify the primary strength ...