Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What Next After PhD? Decoding Your Life After a PhD

Acquiring a doctoral degree is undoubtedly a momentous occasion worthy of celebrations—students can relax, unwind, and let go of the many stresses associated with the past few years of hard work. But soon, these celebrations are followed by questions on the steps needed to grow professionally after a PhD. In this post, I hope to guide you toward finding an answer to the question “What comes after a PhD?”
So what does life after a PhD look like? It is inevitable that your PhD will leave you with an array of skills that are transferable across different sectors. These could be technical skills that are domain-specific and, more importantly, broad skills such as project management, data analysis, and effective communication. Often, it takes a while after a PhD for students to acknowledge that they are indeed equipped with these skills. Hence, it is a good idea to create a portfolio, mapping different skills to the projects and tasks that were undertaken during and after your PhD.
Choosing the next step in your career and life after PhD would then trickle down to your personal preferences and leveraging your skills tactfully. If you’ve felt stuck with the question of what to do after a PhD, here are some career options to consider:
- Postdoctoral fellowship. After a PhD, if you are keen to continue doing research, you can pursue a postdoctoral fellowship in an academic institution and then work toward securing a tenure-track professorship. And while this path surely has its perks, especially if you want to set up your own research lab, it may be helpful to know that this is not the only worthwhile career path in life after a PhD.
- Industry research. If you are not keen on research in academia after a PhD, you can opt to join the industry directly or after a few years of academic or industrial postdoctoral fellowship. If you choose this life after a PhD, you may need to invest additional time and energy in understanding the differences in work ethic and culture between industry and academia. However, orientation to these aspects is usually part of the training that you might receive as a new employee. Upon entering the industry, you can expand your portfolio by exploring sales and marketing, product development, and business development options.
- Publication support. If you envision your life after PhD to be closely associated with research, but not directly involved in it, you can opt for careers in publication support, and work with publishers/journals or organizations specializing in scholarly communications.
- Science journalism and social outreach. If after a PhD, you are keen to explore your communication skills and contribute to filling the gap between science and society, you can opt for a career in science journalism/communication and can look for organizations that are involved in science outreach and social engagement.

If you have wondered about your career after a PhD, by now it may be clear that what comes after PhD is not a question you should stress about as there is no dearth of career options. However, here are a few additional points to consider helping you shape your life after PhD and to ensure that your career choice aligns well with your personal preferences.
- Financial aspirations. Financial perks vary drastically across the above-mentioned career options, and it is important to understand your personal financial goals before deciding what to do after PhD. Choosing an option that will help you grow both professionally and financially will keep you happier in the long run.
- Working in a team vs. working solo. As a PhD student, you may be used to working on your own and taking complete ownership of your projects and ideas. You may not always have this option in your life after PhD. It is important to acknowledge your preference regarding the change that might occur in an organization where you are expected to engage in teamwork and share credit for your ideas.
- Fixed work hours vs. flexible work hours . The doctoral journey is filled with unpredictability and you might have started getting used to the flexible work hours. However, after a PhD if you are planning to work in an organization where fixed work hours are a norm, then you might want to relook at your preferences and reconsider what to do after a PhD.
- Hierarchical vs. non-hierarchical work environment. This can be an important point to consider when assessing where you can thrive the most in your life after a PhD. A structured work environment, like an established company with a defined hierarchy may provide you security, stability, and opportunities for a steady rise up the career ladder. On the other hand, working in a non-hierarchical or non-structured environment like a start-up may require you to perform a variety of roles simultaneously, give you the flexibility and chance to explore new domains and acquire new skills regularly, and could be rewarding in its own way after a PhD.
Through this article, we hope you found an answer to the common conundrum of what’s next after a PhD. Ultimately, for a happy and satisfying life after PhD, adopting a growth mindset will take you far in your career, no matter which direction you choose.
Related Posts

What is Inductive Reasoning? Definition, Types and Examples

Independent vs Dependent Variables: Definitions & Examples
View the latest institution tables
View the latest country/territory tables
Finished your PhD? Six questions to ask yourself about what’s next
There is no single path to success, so here's a plan to help you choose.
Natalie Parletta

Credit: z_wei/Getty Images
13 October 2020

z_wei/Getty Images
Early career researchers can find it challenging to decide what to do next after dedicating years to their PhD.
There are many different paths that can lead to a successful career, from increasing your publication numbers or transitioning to a different lab or institution to acknowledging that what you really need is a break.
Nature Index asked five researchers for their insights on what to do after completing a PhD.
1. Pursue your passion project – even if it’s niche
“I can’t emphasise enough that science has to be something you love doing,” says biologist Aaron MacNeil from Dalhousie University in Canada, who studies marine conservation, focussing on species such as reef sharks and monkfish.

Aaron MacNeil
But what if you’ve been researching a niche topic that will only ever have small amounts of funding and a small pool of collaborators?
To balance passion and productivity, geneticist Marguerite Evans-Galea from Australia’s Murdoch Children’s Research Institute suggests running two projects in parallel, even if one is an offshoot of the other. She notes, for example, that some of the greatest techniques in conservation were borrowed from economics.
Pursuing a research area that’s more advanced and can garner more funding gives you the opportunity to continue working on your niche area where time permits.
Ask yourself : Now that you no longer have the structure of a PhD program in place to support your passion project, do you have the right collaborators to help keep the momentum up?

Alessandro Ossola
2. Move to a different lab or institution
“To grow academically and personally, you need exposure to new ideas, people and places,” says Alessandro Ossola, an urban ecology researcher at Macquarie University in Sydney, Australia.
Ossola made several unsuccessful postdoc applications towards the end of his PhD before winning a fellowship with the United States’ National Research Council (NRC). Ossola says his experience working with the NRC gave him a better understanding of government procedures, which has helped him pursue research that can make a tangible difference to people’s lives.
Moving cities or even countries can be an excellent career decision to gain new skills and a wider network of collaborators.
While the pandemic may prevent such moves just now, Terry Ord, an evolutionary ecologist at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, recommends that new PhD graduates use this time to research the labs and institutes that interest them, connecting with their researchers via Zoom.
Ask yourself : What preparation work can I do now to ensure that I’m in a good place to make a move once travel restrictions are lifted?

Trisha Atwood. Credit: Edd Hammill
3. Switch fields and work your way up again
Some researchers may consider switching fields. The competitive research environment can make it difficult to catch up, but not impossible.
After completing her PhD, Trisha Atwood, assistant professor in the Department of Watershed Sciences and the Ecology Center at Utah State University in Logan, Utah, left the US to do a postdoc on an unfamiliar research topic (carbon storage in marine systems) at Australia’s University of Queensland.
“That opportunity reshaped my research and catapulted my career,” she says. “I got to work with some of the most productive, creative, and nicest people I’ve ever met in research.”
Although working your way back up in a new field may be daunting, Atwood says there are advantages. “If you can integrate aspects of your past field with your current one, you may be able to do something truly transformational.”
Ask yourself : Are you ready to ‘start again’ in a new field and work your way up, and do you have a supportive environment to get you through the initial challenges?
4. Stay the course and focus on publishing
Publications are important, but it’s not just a numbers game, says Evans-Galea. “To compete on the international stage, you need to be publishing quality over quantity, driving change and making a difference.”
Evans-Galea recommends reading often , which can deepen and broaden your knowledge base and make you a better and more productive writer.

Marguerite Evans-Galea
And while you can’t always be publishing ground-breaking work, Ord recommends that young researchers challenge themselves to turn an average paper into something better, by packaging it with a meta-analysis, for instance, or using a null finding to challenge an accepted paradigm.
Ask yourself: Which papers do I truly admire, and what elements can I take from those to improve my own manuscripts?
5. Consider an industry role
A PhD can be a distinct advantage when pursuing an industry role. If this appeals to you, investigate what industries relevant to you are looking for, as corporate organizations tend to value expertise differently to academic institutions.
Some industries value communication and teamwork skills more highly than individual achievement, for example.
Networking can be the key to gaining a good position with industry. Isaiah Hankel , a business consultant and author, contacted employers on LinkedIn after completing his PhD in anatomy and cell biology at the University of Iowa. He attended networking events and organized chats and site visits with prospective employers before being hired as an application scientist at biosciences company FlowJo.
Ask yourself : Am I comfortable leaving academia for at least the next few years, to further my career?
6. Take time off, but keep up your connections
If you’re not ready to make a decision on next steps, you may be able to step away for a while.
This can be especially useful if you’re yet to publish a paper. MacNeil suggests taking on a part-time job if possible and using your spare time to write up and publish papers based on your thesis work.
It’s important to treat your break as a breather – not a holiday – so you don’t feel too far behind once you’re ready to return to research. Keep up connections and volunteer at conferences while working on publications. You could also take writing courses or create an academic blog.
Ask yourself : Are you ready to jump straight into another high-pressure environment, or would you be better off taking some time to recoup, publish, and explore your options?
Career paths after a PhD
Research Retold

Have you completed your PhD? Congratulations! This is a great achievement. You are part of the world’s 1% of the population with a PhD (Coldron, 2022).
If not, maybe, you are thinking about doing a PhD and are considering if it is the right step for you. If you are looking into your future career, asking yourself what you want to do afterwards is important.
So… what happens after a PhD? What could your next adventure be? Would you like to stay in academia? Would you like to try other paths?
Although the most common direction for PhD graduates is academia, it is not the only one.
- Only 30% of PhD graduates end up in academia three years on ( HEPI, 2020 )
- Other graduates transition into industry, the public or charity sectors, education or become entrepreneurs ( University of Toronto, 2016 ).
It is up to your interests and the opportunities you take to make your talents shine. In this blog, we touch on three paths: a postdoc, working in industry and becoming an entrepreneur. Consider these options if the next stage of your career is still unclear.
What is it?
The most common milestone in an academic career after a PhD is doing a postdoc. This is a period in which you are expected to manage your own career development. In what sense? Well, you should be proactive and take steps to become an independent researcher ( KU Leuven, 2022 ). This includes:
- setting up and managing a research project to achieve certain objectives
- sharing your expertise with others through teaching, supervising and outreach activities
- taking part in effective collaborations
Research During a postdoc you can develop the skills to design, develop, implement and adapt an extensive research project. This can be a project proposed by you or you can support an existing project or research group. The project can be small or large-scale, in which case you will also gain coordination skills.
Networking You are encouraged to create and extend a network of researchers and industrial partners. A way to do this is by participating in (international) multi-stakeholder projects or research stays abroad. Besides travelling, staying abroad can enhance your professional profile and enrich the scientific community you are part of. Other tasks you should be mindful of, if you choose to stay in academia, are writing papers as well as editing and submitting grant or funding applications.
Teaching The teaching requirements during the postdoc will vary depending on the institution you are working at. In some cases, teaching is not compulsory. In other cases, you are expected to teach a certain number of hours and balance it with your research time. Whichever the case, it is always advisable to carry out some teaching, grading or tutoring; this will enhance your CV, build up your experience and reinforce your knowledge.
Existing support As a postdoc, you should get support from a senior academic who will play the role of “host” and offer guidance. Be mindful of who you choose to work with. Is that person an expert in your field of interest? Are they interested in your project? Are you interested in their project or research group? Are your working styles compatible? As in the case of the PhD, having a good relationship with your supervisor can boost your research and even your career.
Is a Postdoc for you?
Go for it if you want to stay in academia and if you want to become an independent scientist.
How do you know if you want to be a scientist? Well, getting involved in academia can occur in different ways. For example, some people use the PhD or the postdoc as means to advance their career since they can move to different countries and meet different networks where they find better opportunities. In other situations, good students working closely with a professor or research group can be offered the opportunity to stay for longer projects doing a postdoc.
Alternatively, there are people who have always wanted to do research. In this case, a postdoc might be the best course of action since it allows you to consolidate your research skills and gain more experience. Just remember that a postdoc is for a short period of time, usually a couple of years, and afterwards, you might be competing for funding often. If financial stability is a priority for you, consider your options carefully.
During the postdoc, you become aware of your capabilities and you realise how you can employ the skills you learned during the PhD for a personal project. Dr Jonathan J Huerta y Munive, Postdoc at the University of Copenhagen
Transition to Industry

What are the options for a PhD graduate in the industry?
Positions for PhDs in the industry largely depend on the field of the PhD, and what skills and interests you cultivated. For example, PhDs in arts and humanities can be a good fit for the publishing industry, digital marketing, NGOs, charities or civil services. Moreover, STEM PhDs can find a place in pharmaceuticals, data science, consultancy, industrial chemistry, aeronautics, finance, or even software engineering, among others ( Bennett, 2022 ).
Is a path in industry for you?
The industry has a faster pace and is a different environment than academia. If you want a change of lifestyle, then working in industry might be for you. Another advantage is that in industry, contracts tend to be longer than a postdoc, which provides more financial stability.
How can I transition to industry?
If you want to make the change from academia to the industry you must focus on your strengths. During the PhD, you gained many skills that are highly transferable to the industry. Here are some of the top transferable skills you gain from a PhD ( Lantsoght, 2022 ):
- Writing: After writing a thesis (and possibly journal papers or even blogs), your writing skills have been trained to be clear and concise. This comes in handy when reporting to someone, managing a team or for written communication in general.
- Presenting: If during the PhD you presented your research to many audiences, you now have practice in translating complex information and insights into accessible language and format. Use this skill to express your thoughts clearly according to your audience and influence others, for example when building relationships with stakeholders.
- Visualising information: Depending on your research, it is likely that you employed different visualisation techniques for your thesis and presentations. This experience to create and use clear visualisations is useful for reporting, presenting and management.
- Time management: During the PhD, you learn to manage your time and prioritise tasks. You become capable of organising yourself and meeting deadlines. This is very useful for project management and supervising.
- Analytical thinking : Being able to critically analyse a situation and solve complex problems is crucial in research, but also in businesses. Comparing solutions, deciding the best course of action and being able to see the big picture can provide a competitive edge to organisations.
- Autonomy: During the PhD, you learn to be independent and proactive. You do not need someone to tell you what to do next or to give you a set to-do list. Many organisations appreciate it if you do not require a lot of supervision.
- Teamwork: Depending on the nature of your research project, you might have come across teams that required your collaboration. For example, PhDs working in a laboratory or research group need to adapt to different opinions and working habits. These collaborations make you open-minded towards others and capable of creating productive relationships.
- Resilience: The PhD is full of challenges (the lab equipment is not working, the participants of your study are not complying with the activities, your code does not run, your draft is rejected… you name it). As you overcome them, you persist in achieving your goals. Being able to recover from setbacks and coming up with new solutions is useful for business development.
These skills are valued by commercial employers and organisations who look for skilled staff (including the public and charitable sectors). They also set you apart from bachelor’s and master’s students, so make sure you take advantage of them.
Additionally, be mindful of your interests and look for matching positions. Research your potential employers and think about what they are looking for. Is this something you have or need to develop? Do the daily activities appeal to you? Do you like the working culture? You can find useful information about companies on LinkedIn, so we recommend you create and maintain your profile. Here are some tips for optimising your LinkedIn profile .
Entrepreneurship

Self-employed PhD
As a PhD graduate, you become an expert in your field. It might not feel that way since you also become more aware of all you ignore. Yet, you still have more knowledge than most people. You can use this knowledge as a consultant within an organisation or independently. Alternatively, you can create your own business. It can be totally unrelated to your PhD or it can be the result of your research.
Creating a science spin-off company
It might be the case that your PhD research project can be employed to create new technology/drugs/methodologies with potential for commercialisation. In this case, creating a spin-off company might be something you can become interested in. Here is a list of 44 examples of spin-off companies in case you are looking for inspiration.
Is entrepreneurship for you?
Having a PhD does not necessarily mean you have an entrepreneurial profile. Although resilience, patience and the ability to work in teams are traits you can develop, entrepreneurs have to go the extra mile to influence and inspire others, while raising money and building trust and relationships ( Domayne-Hayman, 2020 ). If this is something you enjoy, then it can be a good path for you.
Things to consider
If you are thinking about creating a spin-off company from your research, consider the following points ( Domayne-Hayman, 2020 ):
- Is your idea fit to work in the real world? How can you make it appropriate for fulfilling a market need? Remember to get feedback from potential users in the early stages.
- How are you going to protect your idea? This will help you reassure investors that they will have a competitive advantage.
- Is there any support at your institution for startups? Many universities have hubs or incubation centres.
- Do you have any intellectual property obligations towards your institution? There are many cases in which the University has the intellectual property of research carried out within its boundaries. Revise your conditions.
- Who will be your team? What is your leadership style? Make sure you are compatible with your team.
- Who will fund your enterprise? Do research on the available kinds of investment (from venture capital to angel investors and supporting programmes at your institution)
In summary:
What do you think? Are any of these three options appealing to you? What do you want to do after your PhD? Let us know in the comments!
Many thanks to our Research Communicator, Phebe Bonilla, for writing this blog post.
- Bennett, Mark (2022) Non-Academic Careers – Jobs for PhD Graduates . Consulted 20th June 2022.
- Coldron, Alice (2022) How Rare (or Common) is it to have a PhD? Consulted 20th June 2022
- Higher Education Policy Institute (HEPI) (2020) New report shows 67% of PhD students want a career in academic research but only 30% stay in academia three years on . Consulted 21st June 2022.
- KU Leuven (2022) Charter of the postdoctoral researcher and the senior academic host . Consulted 16th June 2022.
- Lantsoght, Eva (2022) Transferable skills from your PhD . Consulted 20th June.
- University of Toronto (2016) 10,000 PhDs Project , School of Graduate Studies. Consulted 21st June 2022.
- Domayne-Hayman, Barbara (2020) The four pillars of a successful science spin-off company , Nature. Career column. Consulted 21st June 2022.
- 44 firms highlighted in The Spinoff Prize 2020 , Nature . Consulted 21st June 2022.
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
What to do after getting your phd: 5 next steps, published by steve tippins on february 11, 2019 february 11, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:47 am
What to do after finishing your PhD is a surprisingly common challenge for students who have recently graduated. So if you’re asking this question, you’re not alone.
After years of hard work and passing on enjoyable opportunities to get your writing done, you have finished your dissertation. This is quite an accomplishment. But what do you do now that you’ve finished?
This is something that few doctoral programs prepare you for. How do you take what you have learned and capitalize on it? How do you start your new career or use your PhD to take the next step in your existing one?
What to Do After Getting Your PhD
Based on my own experience and my experience coaching countless recent graduates, I’ve come up with an answer. Here is what to do after PhD is officially part of your title.
Step 1: Take a Breath
It may be tempting to rush right into the next thing. You finally have your PhD, now you get to use it! Apply for a thousand jobs, become a postdoctoral fellow, take a research trip to Indonesia with your favorite professor, launch a consulting firm, and publish a Nobel-Prize-worthy paper in an academic journal. All before breakfast.
Or not. In fact, my advice is to slow down. Not for too long–of course you have to take the next steps in your career. But once you start your career, it’s that much more difficult to take a break. Relax for a moment, and then take a good long deep breath. You are at the summit of one of the largest (proverbial) mountains you’ve ever climbed. Take a moment to appreciate the view. Then, get back to work.
Step 2: Set your Goals

After taking a break, the first thing you need to do is figure out what your goals are . You employed a great deal of discipline to get to this point. Use that skill to determine how you want to move forward. Your doctoral degree is an asset, so try to maximize the return that you get. Getting clear on your goals will determine your next steps and provide a map of what to do after completing your PhD.
When setting your career goals, it’s important to remember your life goals. Remember why you started this journey in the first place. How have you changed? How have your goals changed? What is most important in your life, and how will your next steps support this? Considering how your career fits into your life as a whole will help you make decisions about how to move forward.
Here are some of your options:
Do you want to publish? Think hard about this. You are now an expert on your topic, it would be great if you shared that expertise with the world. Think about your goal in publishing. Is your goal to see your name in print so that your mother can brag about her child being a published author? Do you want to spread the findings of your dissertation across the world to help humanity? Different goals will lead you in different publishing directions.
What a noble profession. Many people want to use their degree to help shape the future by teaching. If this is a path for you, think about the following questions: Do you want to teach full time or part time? Would you prefer to teach online or in a traditional classroom setting? Are you bound to one geographic location or are you willing to go anywhere? Do you want to prioritize teaching over research or vice-versa? Each choice offers various, but different, opportunities.
Outside of Academia
Are there non-academic alternatives available to you? Are you looking for a promotion at your current job? Do you want to speak at conferences? How about a new job? Maybe consulting is the path that you want to take. Your degree puts you in a very small group outside of academia; use it as best you can, remembering that you will be seen as the expert in most settings.
There are many things that you might want to do with your degree. Stop and take the time to determine your goals and then you can see how all of the hard work that you put in to get your degree can get you there. If you find yourself stuck, or want support realizing your full potential, career coaching can help.
Step 3: Prepare your Material
No matter what you choose to do after getting your PhD, you will have to put together a package of material that represents you. This is true whether you want to apply for academic jobs, work outside academia, or start your own business as a consultant. This is the first thing that most employers or potential clients will see of you, so make sure it represents the best of who you are.
You will need a resume and to be ready to answer all kinds of questions. It’s important to update your resume after finishing your PhD, adding relevant accomplishments and experience besides your new degree.
Prepare to answer common questions (for example, “Why did you get a PhD?” “Can you tell me about a situation where you worked well with others?” and “Can you tell me about a situation where you were able to work with someone who was difficult to work with?”).
Also, remember to highlight the unique strengths and skills that you have as a newly minted PhD. Having spent the past few years in the company of other people who either already have PhDs or are trying to get them, it’s easy to lose sight of your uniqueness. Remember the grit and persistence you’ve shown, the critical thinking skills you’ve had to cultivate, and the balanced ability to simultaneously take direction from committee members and forge your own unique research path.
Remember that you are a member of a small group of people with an exceptionally useful skill set, and a degree to prove it. You have proven your capacity to innovate, learn, and work with others. Take a look at Catherine Sorbara’s excellent article on this subject.
Inside of Academia
Work on creating a CV (curriculum vitae) that fits the standards of your discipline. You will probably need to submit documents that cover your teaching philosophy, a list of references, a research agenda, and copies of teaching evaluations, if available.
If you get a campus visit interview, you will need to prepare a presentation about your research and may be asked to teach a class or give a seminar to interested students. Do not take these two steps lightly, as the search committee will get feedback from everyone who participates in these sessions about your suitability for the position.
Find research interest connections at prospective universities. Look within the department you are applying for professors who share your research interests, but also look more widely — to the college and to other colleges within the university — for others doing related studies that may dovetail with your work. The potential for collaborative research and interdisciplinary studies will catch the attention of university administrators and may well give you an edge.
Seek advice. Make sure you are prepared for all of this and get well-acquainted with norms. Your professors and advisors are an excellent resource to help you prepare for this, as are my career coaching services .
Step 4: Search for a Job

When people ask what to do after PhD completion, they’re usually trying to skip ahead to this step–but it’s vital to take the time to set your goals and prepare your material before looking for a job . Now that you’ve done that, you can set your sights on your new (or improved) career. Many people use their PhD as a springboard to an exciting new career path. Here are some insights to help you do that.
The Chronicle of Higher Education is a great place to start. The Chronicle posts jobs daily online for most disciplines. You can also look at HigherEdJobs which tends to have jobs that may not make it to the chronicle.
Conferences within your discipline are a very good place to find out about jobs. Also, the professors within your program may be a good source of contacts who may know about jobs. Remember, most academic jobs start in August/September and postings may come out as much as 11 months before a job starts.
Some professions specifically recruit PhDs. If you are in the sciences this may be the case. Consultancy firms also seek PhDs. Outside of these areas the job search may include networking, sending out resumes, and using the services of recruiters. Your committee chair may be able to connect you with former students in your field who would be willing to make introductions. Most universities have career centers that offer assistance with networking and other job-seeking skills.
Step 5: Stay on Track
Periodically reevaluate your goals–both whether you’re meeting them and whether the goals themselves need to change. Perhaps you started out wanting to pursue research but have fallen in love with teaching. Or maybe you started off teaching but found that consulting is much more enjoyable. Whatever your goals are, they’re subject to change as you learn and grow.
However, if your goal was to teach but you find yourself getting bogged down in research projects due to the pressure to publish, take some time to reflect on how you can better achieve the goals that are most fulfilling to you. Would you prefer an instructor’s position? Or perhaps looking at universities that emphasize teaching over research would be your solution.
What to Do After PhD Completion: A Summary

Getting your PhD is a huge accomplishment. However, if you’re wondering what to do after your PhD is complete, you’re not alone. Once you finish your PhD, take a breath and allow some space in your life. Next, determine your goals and create a plan for how to proceed. Once you are clear on your goals, prepare your materials and apply for jobs. Finally, periodically re-evaluate your goals to see whether you’re meeting them and whether they’re still relevant.
Many recent graduates use a career coach to help them in this process. If you are interested in this kind of coaching, feel free to take a look at my services page or get in touch.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Academic Career
Bipoc academics matter: diversity in academia is long overdue.
We at Beyond PhD Coaching firmly believe that diversifying academia is both necessary and important – and well past overdue. There’s no denying that higher education equals more power in society. This power has been Read more…

Academic Arrogance: Dismantling a Culture of Harm
Academics are like polar bears. We live alone; we hibernate. If you walk down the halls of academic offices, you’ll find that almost all of the doors are shut. We live a solitary existence, occasionally Read more…

How to Be a Good PhD Student
If you’re curious about how to be a good PhD student, this article is a good place to start. As a professor for over 30 years, much of that as a Dissertation Committee Chair, I’ve Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
Hack Your Dissertation
5-Day Mini Course: How to Finish Faster With Less Stress
Interested in more helpful tips about improving your dissertation experience? Join our 5-day mini course by email!
- Communications
- Computer Science
- Criminal Justice
- Environmental Management
- Forensic Psychology
- Healthcare Admin
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Social work
- Special Education
- Sports Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Adult Education
- Business Intelligence
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- Homeland Security
- Information Systems Security
- Information Technology
- International Business
- Management Information Systems
- Nonprofit Management
- School Counseling
- Academic Publishing Guide
- Building a Graduate School Resume or CV
- Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
- Expert Guide to Studying Abroad
- FAQ: Online Master's Degrees
- Grad School Guide Book
- Graduate School for Students with Disabilities
- Green Graduate Degrees
- How to Be a Successful Grad Student
- How to Choose the Right Graduate Program
- How to Get a Master's Degree in an Unrelated Field
- How to Transfer College Credits in Grad School
- How to Write a Winning Personal Statement
- Inside Graduate Admissions
- Ivy League Grad Schools
- Master's Degrees for Veterans
- Master's Degree for Women
- Mental Health in Grad School
- Progressive LGBTQ Graduate Degrees
- Should You Apply for a Graduate School Assistantship?
- Surviving Grad School with a Family
- Taking a Gap Year Before Grad School
- Women in STEM Graduate Resources
- Writing a Successful Statement of Purpose
- Alternative Ways to Pay for School
- The Best Part-Time Jobs During Grad School
- Company Funded Graduate School
- FAFSA For Grad Students
- Financial Aid Resources
- Graduate Student Loans
- Paying for Your Master's Degree
- Paying Off Student Loans
- Paying for Your PhD
- Fellowship Opportunities
- LGBTQ Scholarships
- MBA Scholarships
- Scholarship Resources
- Scholarships for Veterans
- Scholarships for Women
- Crushing the GRE Guidebook
- GMAT Guidebook
- Guide to the LSAT
- MCAT Prep for Medical School
- Study Guide: Exam Resources
- TOEFL Prep for Non-Native English Speakers
- Resources What to do After Grad School: All Your Questions Answered
What to do After Grad School: All Your Questions Answered
Finishing graduate school and moving toward a professional career can be complex for some new grads. Many aspects of our lives change during these transitions and, for many, it’s challenging to keep a positive attitude, stay focused on our goals, and face the competitive job market. From job hunting and professional development to managing student debt and networking strategies, the following guide offers some tips and resources for new graduates getting ready to tackle life beyond grad school.
Adjusting to Life After Grad School
The five tips listed below offer links to helpful resources and methods of preparing for the stresses of the job search, life after school, and how to cope with inevitable emotional and professional challenges.
Make time for yourself: According to a Harvard study, by the time students enter their final years of graduate school, up to 25 percent experience moderate or severe symptoms of depression. Upon graduation, these symptoms don't necessarily disappear. In her article “ The Grief of Graduation ,” Anne Guarnera discusses graduate students' feelings of loss upon finishing their programs. For the most part, she considers these feelings to be a loss of student identity and all the social and spatial connections that one develops while spending three to six years in a town, city or campus environment. When we graduate, many of us move elsewhere. We leave the area in search of a new job, to find a fresh landscape to begin the next chapter or even move in with family or friends to save money. Whatever the scenario, Guarnera suggests that we all need to practice emotional self-care as a means of dealing with these transitions. To do so, she urges us to schedule time to organize our thoughts and process the changes in our lives.
Prepare early: While you’re still in school, take advantage of career-focused resources available through your program. These resources include career planning and coaching, interview workshops, job fairs and networking opportunities. If your department or school doesn’t have free services readily available, you can reach out to professors for help in this area. Many of them will be glad to offer advice on how to prepare for the job market and help you avoid any mistakes they may have made.
Change your perspective on graduate school: Many students, especially first-generation graduate degree seekers, approach graduate school as an extension of their undergraduate program. Nathaniel Lambert argues that students should treat their post-baccalaureate training as more of an apprenticeship instead of “school” as they’ve traditionally conceptualized it. This concept comes from the middle ages when craftspeople would study with masters of a trade and learn by imitating their techniques and processes. Lambert suggests that graduate learning should be no different and, whenever possible, we should learn by doing, “not simply by reading about it and talking about it in classes.” As a result, we may be better prepared for the transition into our careers upon graduation.
Remember: Your thesis or dissertation doesn’t guarantee you a job: While creating a well-formulated, written document based on original research that contributes in some way to your field is important, it’s best to keep that work in perspective. Whether you pursue a career in academia, at a Fortune 500 company or in a research laboratory, there’s little chance that anyone wants to hear about your thesis or dissertation in detail. That said, it’s still essential that you create a thorough and meaningful project. Bear in mind, however, most employers want to know how your knowledge and expertise makes you a good fit for a position. At this point in your career, they want to know what makes you a good problem-solver, teacher, researcher, etc. You need to tell them how you can meet and exceed these expectations and not simply show them what you’ve written in the past.
Cultivate a support system and friendship: Our expert, Rebecca Newman, urges professionals after graduate school to find trusted individuals outside of work with whom they can share their personal, academic or professional frustrations. “Have a strong support network when entering a new field after graduate school. This can take the form of family, friends, a partner or a mentor. They can offer you support that will keep your ’dirty laundry’ out of your workplace,” Newman says. “You might think you’re venting to a friend in the form of a colleague, but it can be more professionally advantageous to look at work as being ’on stage.’ If you have a valid concern, you should absolutely bring it up at work in a thoughtful, constructive manner.”
Landing a Job after Grad School
Now that you’ve completed your degree and you’re on the job market, where do you start? There are an overwhelming number of job search engines and, depending on your area, just as many jobs to consider. While all of these jobs may not be a good fit, you still end up spending time reading job descriptions, researching companies, locating salary information in certain geographical areas and more. It’s time consuming, no doubt. Here’s some tips to help you streamline your search and save some time. We’ll offer more advice on this topic throughout the guide as well.
Where and how should I look?
TheCollegeInvestor.com suggests that job seekers leverage both their personal network and online search engines or job aggregators. In addition to asking colleagues, professors, friends and family for leads on open positions, job aggregators such as LinkedIn, Glassdoor, ZipRecruiter, Indeed and HigherEdJobs can alert you to positions as soon as they’re posted. Additionally, most of these websites allow job seekers to post their resumes or CVs. This feature allows employers to search for candidates using keywords. Dora Farkas of FinishYourThesis.com , argues that it’s a common and fatal mistake to avoid using LinkedIn and related sites as part of your front-facing, public image, as many of your prospective employers use these sites to find out more about job candidates.
Should I only look for dream jobs?
Truth be told, many graduate students don’t land their dream job immediately after graduation. For Ph.D.’s interested in teaching at the college level, most don’t secure a tenure-track position until after they’ve acquired solo teaching experience in community colleges, adjunct positions or visiting professorships. (That’s not to say that one teaching job is necessarily “better” than another. Many scholars dream of the tenure-track position, however, because of the job security and various freedoms that come with it.) Whatever your field, you may need to find some stepping stones before landing the perfect position.
“To land your dream job, take every responsibility at every job seriously, and prioritize your relationships,” Newman says. “When I was once grumbling about an unrelated task we were doing as interns, the senior intern said to me, ’Sometimes, social work is doing the hustling that no one else wants to do.’ That stuck with me, and I tried to be thoughtful about what I expressed on the job while venting my frustrations elsewhere when I needed that support. Based on having a strong ethic at a past job that was very challenging, my former director cold-called me to ask if I wanted to come back to the organization in a different capacity, in what is now my dream job.”
Should I apply for jobs I’m overqualified for?
While it depends on whom you ask, most professionals will tell you to avoid applying for jobs for which are you overqualified. Some employers might be interested in having someone like you on staff because you may already know the ropes or can act as a leader. More often than not, however, they will see you as someone who will probably get bored and move on to another job before too long. They may also see you as a threat or internal competitor who could take their place later on. On the other hand, if you are unemployed, you are probably in need of a job immediately or in the very near future. In that case, cast a wide net and apply for jobs even if you appear overqualified.
Once You’ve Got the Job, Ask Yourself These Questions
After all of your hard work, applications, and interviews, you finally land a job you’re excited about. As with most positions, you won’t get a full picture of the position, your tasks, the work environment and other details until you’ve had a chance to settle in and take on some responsibilities. Scott Webb, an academic adviser at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey, suggests that we ask ourselves a series of questions after several weeks on the job, then after several months and finally at the end of a year. Newman echos Webb’s techniques for checking in with ourselves, making the most of a job and planning ahead.
What are the pros and cons of this job? How do I make it work?
Both Newman and Webb suggest that in the first several weeks of a job we identify those aspects of the position that are the most fulfilling and the most challenging. Acknowledging these positives and negatives helps us get a clearer picture of what we need out of a job and helps us identify our strengths. As Webb points out, during these early stages it’s important to keep an open mind and be willing to embrace unexpected challenges and difficult tasks. These challenges can help us grow as individuals, allow us to do well and advance in our current role, and teach us something about ourselves that may have otherwise gone unrealized.
Is this job a good fit for now, or could I see myself here for longer, perhaps in a different capacity? If/when I leave this job, what are things I would want to be different in my next role?
Newman advises us to plan ahead and think about our next career move, if that’s something we anticipate. This certainly depends on the individual and career path. Professionals with a Ph.D. or master’s degree working in academia, for example, may be content with their current teaching position. If they’re on the lookout for a tenure-track job, then they need to consider if their current role helps make them a stronger competitor when the opportunity presents itself.
What do I like about this job: the camaraderie, content of work or both? Which of those is more important to me?
Of course, we all want to be happy with our work responsibilities, work environment and our coworkers. In a perfect world, we would be satisfied with all three. In addition to planning ahead, Newman suggests that we weigh the quality of the work environment and camaraderie versus how much we enjoy the actual tasks of the job. Which aspect is more important to you?
Licensing and Credentials
Licensure and certifications are required by law for many professions across the U.S. License-based credentials ensure that professionals meet a high standard of practice and are up-to-date on relevant research or advancements in their field. Certifications are usually voluntary credentials, which professionals earn through a professional society or educational institute. The terminology and requirements vary per field.
Licensure requirements vary by state. In psychology, some professionals with a master’s degree can obtain licensure to be professional counselors. More often than not, most states require a Ph.D. All states require supervised training, a written examination and/or oral examination for practicing psychologists. Similarly, those graduate students in criminal justice who wish to become lawyers must complete law school and pass the bar exam. Other roles in the criminal justice system, such as holding a position as a judge, require extra credentials. They also must pass a written exam administered by the U.S. Office of Personnel Management .
While most certifications are voluntary, they help you secure higher-level positions in various professions. Advanced positions in public administration, for example, sometimes require professionals to obtain a Certified Public Manager credential. Prospective recipients must have a bachelor’s degree or higher and complete the required 300 hours of study through a program accredited by the National Certified Public Manager Consortium . Comparatively, the National Board of Public Health Examiners offers the Certified Public Health exam. Professionals who wish to obtain some of the higher-paying jobs in public health must meet the certification standards of their state, along with obtaining a graduate degree.
Professional Development and Continuing Education
Professional development and continuing education are opportunities for students and professionals to enhance their current skill set, learn new techniques and methods in their field, and keep up with the latest advancements and research. In general, we can organize these opportunities into categories: teaching, mentorship, research, networking, workshops, professional conferences, certificates and volunteer work. While some of these categories apply more to some professions than others, they help us locate possibilities for bolstering our resumes, improving our skills and, in some cases, keeping us eligible to work in our fields.
If teaching is part of your profession, you’re required by most states to participate in continuing education classes to keep your teaching license. It’s easiest to think about these opportunities by separating them into categories. Consider looking into professional development courses in behavioral, classroom technology, Common Core, English and reading, mathematics, science and special needs, as well as taking online courses for credit.
This is a great chance for experienced professionals to share their knowledge with the future leaders of their fields. Mentors motivate and empower individuals, businesses and communities to achieve their goals. Mentees must be willing to take advice, change their habits and further develop a body of knowledge that supports their efforts with short- and long-term plans. Both mentors and mentees benefit from these encounters, and you should experience both roles.
Research opportunities for master’s and doctoral degree holders come in many shapes and sizes. For the most part, keep an eye out for post-doctorate positions, fellowships and research assistantships. All of these opportunities depend on your field. For example, in the area of the humanities, it’s rare to seek out post-doctorate positions. Researchers in the hard sciences, however, often spend a lot of time and energy trying locate those research opportunities. These research positions look good on your resume or CV, and many of them offer job security for a couple years at a time with a steady paycheck.
You may not be a "people person" or enjoy getting to know new faces. Unfortunately, the tired and old-fashioned saying, “It’s not what you know, but who you know,” rings true to some degree. Making the most out of every networking opportunity is essential to your success after graduate school. From informal gatherings to organized meetings at professional conferences, you need to cast a wide net and actively expand your professional and personal networks.
Practical and theoretical training workshops benefit professionals in virtually any specialty area. These hands-on meetings are often taught by leading academics or highly experienced practitioners. Workshops are available both online and in-person. They can be as short as one day or last the duration of a summer semester.
Professional conferences
You may not be a "people person" or enjoy getting to know new faces. Unfortunately, the tired and old-fashioned saying, "It’s not what you know, but who you know," rings true to some degree. Making the most out of every networking opportunity is essential to your success after graduate school. From informal gatherings to organized meetings at professional conferences, you need to cast a wide net and actively expand your professional and personal networks.
Certificates
Certificates are typically voluntary in most fields and offer additional training to boost your marketability in a competitive job market. They can also help you climb the ladder at your current job. You can easily access on-demand courses in widely useful topics through popular sites such as LinkedIn’s certification and continuing education programs page.
Volunteer work
Improving your skill set and bolstering your resume can also come in the form of volunteer work. In some professions, substantial volunteer work in one area can count as documented work experience. At the same time, many volunteer opportunities allow you to help those in need. You can also gain exposure to new ideas, organizations and connect with a new network of people through this type of work.
Managing Grad School Student Debt
Some colleges and universities offer graduate students some type of funding, maybe even a full tuition waiver plus a stipend, to defray the cost of their education. In other cases, MA and Ph.D. students may receive no funding at all. Unless they are fortunate enough to receive a tuition waiver and a stipend, many graduate students still take out student loans to cover tuition and living expenses. In fact, about 40 percent of the $1.5 trillion in student loan debt comes from graduate students and professional degree seekers. GoGrad offers 10 helpful strategies for paying off student loan debt.
From the Expert
Advice from a psychiatric social worker.

Rebecca Newman is a psychiatric social worker at the Thomas Jefferson University Physicians Department of Psychiatry and Human Behavior, where she provides individual psychotherapy in Philadelphia. She specializes in working with eating disorders, anxiety, depression, substance abuse, grief and loss, LGBTQIA+ topics, trauma and adjustment to life changes.
What’s one tip for current graduate students or new graduates to manage student debt?
Don’t avoid dealing with your loans or repayment out of anxiety. Your student loan servicer can and wants to help you make your payments. You can work with them on an income-based repayment plan, which can then inform your budget about other expenses. Do your best to develop a budget and stick to it when you’re adjusting to making loan payments.
What are some benefits of participating in professional development or continuing education programs and workshops?
Continuing education programs are a great opportunity to meet other professionals who are a few years ahead of you in your career and can perhaps support you moving forward in your trajectory. Additionally, staying current in your field is important. Think about whether you had a professor or instructor in graduate school who felt out-of-touch. They might not be engaging with continuing education in a thoughtful way, or staying in a lane that is comfortable for them. Professional development requires a certain degree of humility to acknowledge that you don’t know everything, and placing yourself back in the position of a learner can ultimately make you more effective in a role or on a team.
What was your licensing process/timeline to become a licensed social worker?
In my field, licensing is an essential and somewhat lengthy process. Upon graduation (or in your last semester of graduate school, if you’re in good standing), social workers are eligible to take an exam to become a licensed social worker. For this exam, some preparation is necessary -- it is a combination of theoretical knowledge that is a direct reflection of the program curriculum and clinical vignettes. Following passing this exam, in order to move forward, you must accrue 3,000 hours of supervised work experience over no less than two years. With a full-time job this is manageable, as long as your responsibilities at work are relevant to the profession. In conjunction with those hours, you must accumulate 150 hours of clinical supervision, half of which must be individual and with another licensed professional in the field with years of experience. The other half can be in a group, with another mental health professional or a combination of the two. Once you have accumulated 150 hours of supervision, worked 3,000 hours in your job and two years have elapsed, you can apply to take the clinical licensure exam. Upon passing, you are a licensed clinical social worker and can function independently as a clinician and become credentialed with private insurance carriers.
Additional Resources
For those who might feel overwhelmed by the results of a follow-up query into criminal justice or for the experts who want a refresher, here’s a list of industry-leading agencies, institutes, universities and opportunities.
- AcademicLadder.com's "Depression in Grad School and Beyond" : Symptoms of depression among graduate students, how to make sense of it and practice self-care.
- Chemical and Engineering News' "How to Prepare for Life After Graduate School" : Helpful column with career advice for graduate students in the hard sciences.
- Dorsa Amir's "Modest Advice for New Graduate Students" : An excellent list of wise and calming advice for all graduate students.
- Finding Brave's Podcast: "How to Land a Dream Job at the Salary You Deserve" : Advice from Austin Belcak on confidence, networking and going the extra mile.
- Finish Your Thesis Blog : A collection of articles that help graduates handle the stresses of writing a thesis or dissertation as well as job hunting advice.
- Kathy Caprino's "Preparing for Life After Graduation: How to Land a Great Job Your First Time Out" : Interview with Austin Belcak, founder of Cultivated Culture, that offers unconventional strategies to obtain employment after graduate school.
- Northeastern University's "How To Be a Successful Graduate Student" : The large Boston institution's take on getting ahead and making the most of your resources in graduate school.
- Peterson's "A Guide for Potential Grad Students: Should You Go To Graduate School?" : A numbered list, broken into convenient sections, with dozens of salient points to consider before taking the plunge into graduate school.
- StudyBreaks.com's "Tips for Life After College Graduation" : Practical advice and pep talks for graduates from all walks of life.

After a PhD
Learn about life after a PhD, from employability statistics to career prospects. Find out the skills you’ll gain, how to apply these to a range of professions and how to continue enhancing your profile as a researcher.
Key Resources

Postdocs: The Definitive Guide
A postdoc can be a crucial stepping stone to a successful career after completing a PhD. Find out what they are, what they involve and much more.

Transferable PhD Skills You Can Use in Any Career
From communication to time management, you will gain a large variety of transferable skills from completing a PhD. Learn what these are and how to use them in your CV.

Life After a PhD: What Can You Do?
Find out the most common career paths for doctorates both within and outside of the academic world.
Supporting Resources

What is a Research Assistant?
Research assistants are employed by research institutes to assist with academic or private research. Find out all you need to know about the role.

Lecturer and Professor Salaries – Explained
Thinking about becoming a University Lecturer? If so, you’re going to want to learn all about the teaching and researching life, including the salary you can expect!


The Journal Peer Review Process
The journal peer review process to publish a research paper can take several months to complete. Learn more about all the different steps involved here.

What You Can Expect as a New University Lecturer
Starting a career as a university lecturer can be one of the most rewarding highlights of your academic journey. Learn more about what to expect in this demanding role.

What Can You Do with A PhD in Public Health?
Studying public health is a wonderful choice for those who wish to dedicate their career to advancing healthcare delivery and improving the health and wellbeing of the public.

What Can You Do With A PhD In Sociology?
A PhD in sociology provides insight into social concepts and requires a strong understanding of statistics and data; learn more about career options afterwards.

Turn Your PhD Thesis Into a Paper
There may be opportunities to convert your thesis into a form ready for peer-review. Here’re a few tips to help you on your paper writing journey.
Gain valuable insight from our collection of exclusive interviews with both current and past PhD students. Learn from their best advice, personal challenges and career path after completing their doctorate.

Fig 1. Comparative analysis of the population in 2013 vs. 2003. Above solid line. The PhD population increased by ~26% = 35,541 PhDs. Below solid line. Percentage of the new population dedicated to the indicated categories. Data obtained from the NSF Scientists and Engineers Statistical Data System (13). The percent for each category out of the total PhD population in 2013 is indicated on the right. See text for 2013 PhD population numbers for each category.
To further extend these reports, I compared census data on graduate and postgraduate employment between the years 2003 and 2013 (Fig 1).
In the last decade, total number of PhDs increased by ~26% (35,541 PhDs) to a total of 172,139 PhDs (13). If employment increases were to follow the rate of population growth, then all employment sectors should see a ~26% increase. Indeed this was the case for two categories: out of the workforce PhDs (stay at home parents and part time employees) with a ~24% increase to a total of ~19,500 PhDs; and management and administration with a ~27% increase to a total of ~27,000 PhDs. The only positive change in PhD employment was a ~30% increase in teaching to a total of ~25,000 PhDs (including K-12 on up, but excluding research-intensive universities). Troubling changes in PhD employment include a ~50% increase in non-science related occupations (e.g., transportation, culinary field, or construction) to a total of ~22,000 PhDs; and a significant ~1.6 fold increase in unemployment to a total of ~4,000 PhDs (Fig 1) .
Importantly, the total number of PhDs engaged in research and development (R&D; all positions in both industry and academia) increased only by ~19% to a total of 72,409 PhDs; which reflects a continued trend in decline (see paragraph preceding Fig 1). Moreover, when looking more in depth at the 2010-2013 transition ) (13) , I observed that the number of biological and medical PhDs in science careers decreased by ~4%. These positions include jobs in academia (both faculty and staff scientist) and industry; and the categories include medical scientists, biochemists, biophysicists and biological scientists (e.g., botanists, ecologists, zoologists). This indicates that in recent years PhDs are moving away from research and development positions (Fig 1) .
Indeed, this has been also shown in a couple of recent survey-driven studies examining the career preferences of junior biomedical scientists in more detail. One study followed students during training in the 2007-2012 period (2), and the other study collected all data in 2009 (6). In both studies, the authors found that the career pathway interests of graduate students changed significantly between starting and finishing their degree. Important changes were observed for a decrease of interest in both teaching-intensive faculty positions (small change), and research-intensive faculty positions (large change). The opposite was found for interest in non-academic research positions (including industry, pharma, biotech, government or startup), and non-research careers (including consulting, policy, scientific writing, technology transfer or business (2,6).
Current estimates indicate that there is approximately only one tenure-track position in the US for every 6.3 PhD graduates (1). This means that 84% of today’s PhD graduates need to pursue careers other than tenure-track faculty positions at research-intensive institutions. Having said that, the employment perspective does not appear to be so gloomy:
A recent study reports a decrease in the biomedical postdoctoral population of ~5% between 2010 and 2013, indicating that PhDs are exploring positions outside of academia, and suggesting we may be reaching the end of the exponential period of biomedical PhD/postdoctoral population expansion (14). However, this could also reflect a decrease in availability of postdoctoral positions due to reduced NIH funding across the board.
And the Bureau of Labor Statistics expects a ~20% increase in total employment in the biomedical sciences for the 2010-2020 decade (15). If the current trends in PhD employment continue, this suggests that by the end of the decade the vast majority of the PhD population would be employed outside of academic/industry research institutions (it was ~40% on 2013).
Clearly the real “alternative career” is pursuing tenure-track faculty positions at research-intensive institutions.
All in all, these statistics are enlightening about the reality PhDs are encountering when trying to find their next position. The challenge we face is to prevent an increase in the unemployment rate and to reduce the shift to non-science related careers paths (e.g., construction, …). Both goals should be attainable in the near future: we should dedicate resources to advertise the reality of employment and remuneration for PhDs in biomedical sciences, we should expose graduate students and postdocs to all employment opportunities beyond academia, and encourage them to engage in internships and make timely and informed employment decisions. Also discussed in (16) and (17) .
As graduate students and postdocs, we should periodically pry ourselves away from the bench, papers and presentations to also attend career development seminars to learn which are other available career paths, and then incorporate this knowledge with our own progress, goals, skills, interests and values when deciding on our next career step (see Skill Inventory Matrix and My IDP in following two sections). Engaging in these activities should also benefit those wishing to remain in science. For example, preparing for a career in consulting will give students/postdocs new tools to tackle scientific problems and write better grants (anecdotal).
On transferable skills and self-marketing
Whether you are staying in academia or not, it is very useful to determine what your skill set is. This can also help you identify skills you should improve on or acquire, e.g., management skills to effectively run a laboratory (including conflict resolution and budget managing among many).
Because we are immersed in our research, we often do not realize the valuable skills we have developed. In the book Networking for Nerds (18), Alaina Levine describes the use of the Skill Inventory Matrix to identify strengths and weaknesses, as well as its use to help define which career path to pursue. To help identify what these seemly intangible transferable skills are, below I assembled a list to help guide you to identify your own set. The credit goes to the sources I used (18-22).
- experience:
- jobs, research/teaching assistantships, committee assignments,
- College and University academic societies, competitions,
- extracurricular activities: fund raising/management, newspapers, policy, family commitments
- computer literacy: office packages, presentation software, programming skills (e.g., C++, java, perl, mySQL)
- personal characteristics that define how you operate:
- your values
- detail-oriented vs. results-driven
- disciplined and self-reliant
- ability to work effectively under pressure to meet deadlines
- ability to quickly learn/acquire new skills (quick study)
- ability to work with limited supervision (independence)
- technical skills:
- scientific: research methodologies; experimental design; data collection, management and analysis; …
- use of laboratory equipment: confocal microscopy, analytical centrifugation, …
- knowledge of statistics
- specialized packages for data management: SPSS, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis, FiJi, Imaris, …
- analysis and problem solving skills:
- critical appraisal of literature, critical thinker
- problem solver: define a problem, postulate and test hypotheses, and summarize conclusions
- identify sources of information/experiments to address problems
- design, apply and analyze surveys
- ability to manage large datasets, including sorting and evaluating data
- ability to defend independent conclusions
- application of basic principles in a wider context
- business skills:
- project management: manage (a) project(s) from beginning to end, ability to maintain flexibility
- identify and prioritize tasks, determine realistic timeline for completion of tasks
- teamwork, ability to delegate, negotiation skills, and diplomacy
- inventory control, risk management and safety assessment
- effective grant writing
- event planning and management (e.g., Gordon Research Conference/Seminar, local scientific meeting)
- leadership:
- conduct meetings or facilitate group discussions, motivate others to complete projects
- collaborate on projects, mentor and train lab-mates, respond well to feedback
- conflict resolution, creative problem solving, team building, strategic thinking
- soft skills:
- organize and orally communicate ideas clearly and to peers and lay people
- ability to prepare concise and logically-written materials: specify the length (abstract, book,…)
- ability to debate issues in a collegiate manner with peers and supervisors
- ability to use logical argument to persuade others
- ability to speak/translate other languages (e.g., careers in law, education, or mass communication)
The next thing to do is to assign love/hate qualifiers to each one (18-22). This is crucial when tailoring your resume and cover letter, and when preparing for job interviews. These tools will help effectively market yourself as the best possible job candidate, as well as help categorize (from best to worst match) all potential job opportunities. Once you have defined the position(s) you are interested in you have to market and sell yourself. For most of us PhDs, self-marketing is distressing; yet, you should become comfortable talking about yourself and asking/accepting networking favors that may push your applications to the top of the pile.
When applying, it is important to research the position(s) you are interested in, not just reading the original posting(s). This also applies to when you are planning to create your own job. You have to read about the company, its financial data (especially when going into finance or consulting), its history (if relevant), its values, the people in the work group you might join, any videos published on YouTube or elsewhere (e.g., interviews with CEOs, TED talks), and any publication coming out from the group and company. Also, rely on your network, LinkedIn, Facebook and Google.
In addition, you have to research the market and identify the competition. This is easier when applied to a product, but a bit harder when applied to your vision. For example, I am interested in commercialization of science. Briefly my options are: 1) offices of technology development; 2) family office, angel network, or venture capital firm needing expertise in biomedical field to make informed decisions; 3) officer at a US Patent and Trademark Office; 4) law firm working on patenting and intellectual property; or 5) create my own job. I lean toward options 1, 2 and 5. Not many options are open in family offices, angel network/venture capital firms and the competition is fierce. There are 5 offices of technology development in the area and I need an internship to support my application (working on it) and there are few openings.
I decided that creating a consulting service to aid university technology transfer offices, private investment offices and startups would be the way to go. This idea is not novel(3), but has not been put into effect in the area, there is a clear demand (determined during many networking interactions), and we have a trained/in-training group that should deliver. Also, this idea is very appealing to me for many reasons: it includes what I want to do, it allows me to be involved in student and postdoc training, and gives me experience in creating and leading a new organization. Still, I keep looking and categorizing options using my Skill Inventory Matrix (18).
And finally, when applying make sure to include keywords related to the posting, look at your Skill Inventory Matrix and pull the relevant information out. And in your cover letter be sure to briefly describe examples. This is best done by intentionally leaving questions for the interviewer to ask you. In short, sell your best qualities and experiences fitting the job.
Learning about other career paths
I think this could be divided in three subsections: know yourself, do your research, and plan your path.
To get to know yourself I have three suggestions. The first one I read on LinkedIn and lost the reference (sorry); the author suggested asking different people to describe you in 20 words. The second one is to take the Gallup Strengths and Myers-Briggs Type Indicator® (MBTI®) assessments. And the last one is to use the My IDP website (see below). Together these tools should help identify abilities, qualities, strengths and weaknesses to populate the Skill Inventory Matrix (18). There is plenty of information on both tests online so I will not further describe them or their outputs. The 20 questions approach is self explanatory and both insightful and humbling.
Next, the research. This part should come easy to us PhDs, it involves reading A LOT about different career paths. There are plenty of websites and books published on the subject. I enjoyed the book Career Options for Biomedical Scientists (23), and I have also extensively used LinkedIn’s PhD Careers Outside of Academia, The Versatile PhD , Inside Higher Ed , BioCareers blog , My IDP website (see below), and –of course– Google. What matters is to compare the employment paths you think you may like with your values, the lifestyle you expect to lead, and with your Skill Inventory Matrix .
The last part in this section is planning your trajectory. Here, the best advice I have is to follow an IDP, Individual Development Plan (24), and I suggest using the Science Careers My IDP website . This great resource takes into consideration your skills, your interests, your values, and your expected-lifestyle to suggest a list of options categorized by probability match, along with several links to informational resources. In addition, the website helps you set goals, implement your plan, and encourages you to go out and gain first hand experience at suggested jobs to sort them into “ good idea ” or “ bad idea .” The problem is, however, that the website does not help find where and how to gain such experience. This is why mentors and networking are so important.
Network, network and network to find new opportunities and mentors
We do not accomplish anything in a void. We need to assemble our job-search team. Mine is composed of:
- my wife and family, who provide support, guidance and encouragement;
- my postdoctoral mentor, who has been supportive and helpful both at the bench and away from it;
- my contact at the Graduate Career Development office who helped me focus on my goals and interests, inspired me to network to find/create my dream position, and pointed out new opportunities;
- and my business mentor whom I met through networking and has been helping me by pointing out opportunities, introducing me to new contacts and being a sounding board for ideas.
Why is networking important? It can open the door to unknown opportunities both in making new contacts and finding positions. Alaina Levine, author of Networking for Nerds (a suggested read), estimates that about 90% of the “ job market is clandestine,” meaning that “it is accessed only through networking and reputation management activities ” (18).
So, what is networking? In Levine’s words: “ Networking entails providing authentic and genuine information for and between both parties so that you both can contribute value to each other’s projects and interests […] you have to tell people about what you do and the value you can provide them so they understand how an alliance could be mutually beneficial […] Remember, everyone has problems that need solutions .“ You should “ offer to be of assistance even if you don’t immediately see a potential return on investment ” (18). Such assistance could be a collaboration, direct contribution, suggest a contact they do not know or have not thought of, introducing people, other… This strategy should also be useful when you are applying/interviewing for a position: ask yourself “what can I bring to the company” and emphasize it. In other words, demonstrate value and knowledge about the company while marketing your relevant qualities.
The initial mistake most people make (I made) is to approach people in a one-sided manner. The communication cannot be only about your interests. “ If you approach networking expecting your contact to offer you a job, you will likely be disappointed—most contacts will not know of current or planned openings “ (25). In addition, this may cause potential contacts to shy away from interacting with you again because you are only interested in yourself. “ Instead, try to meet people who can offer advice for your search, answer questions about career choices and provide you with the names of more contacts who may be able to help you get further along in the process of finding a job. They can give you a closer look at the practical aspects of their own jobs and provide details that you may find critical when deciding where to apply “ (25). Once you make a close contact, you may ask for suggestions on how to improve your resume, how to fill any voids your application, and who else to contact to further pursue your interests. Among these close contacts you may find new mentors.
How to network? This is the topic covered by whole books (18), and several online blog posts and articles. I will summarize what I understand to be most important, but caution the reader that I am by no means an expert.
Craft brief and powerful introductions
The elevator pitch is used to effectively and concisely introduce yourself (26-28). Crafting one requires self-evaluation and concisely writing and practicing (over and over) how to deliver this speech in a short period of time (typically 30 seconds), and to do it in a way that interests people and avoids jargon. This pitch should stick to the big picture and hopefully contain a memorable story.
Most times, however, pitches are not appropriate. Therefore, it is important to craft different versions of your introductions to match different audiences , CEO vs. CFO vs. Nobel Laureate), different situations (e.g., elevator, airplane, dinning table, church, playground), different individuals (depending background and common interests), or to fit available time (elevator vs. networking event vs. airplane).
I do not have an elevator pitch; I am wordy (have you noticed?). I wrote the following examples on the fly based on past networking experiences. They need perfecting; yet, I hope they provide an idea of how to tailor introductions depending on your target audience.
When introducing myself to scientists at Conferences I would say: “ Hi, my name is Andrés Lorente, and I am a postdoctoral fellow in the laboratory of Dr. Melanie Cobb, where we study protein signaling networks. I work on elucidating the crosstalk between calcium and with no lysine [K] WNK signaling pathways, and the role of the WNK pathway in non-canonical pathways, namely cancer. To this end, I am also characterizing novel WNK kinase inhibitors for use in the clinic. What you mentioned in your talk about [ add here ] interests me because [ add here ] “… and then go from there. This introduction did not explain my findings, leading to an easy question. This can be shortened to fit context, time, common research goals, …
When addressing middle-school students at an outreach event, I would say: “ Hi, my name is Andrés Lorente, and I am a scientist at UT Southwestern Medical Center. My goal here today is to show you how important lipids are for life. Lipids are fatty molecules that cells use to define themselves: what is in and what is out, it is like your skin. But lipids do much more than that, and understanding [ briefly go into disease, lab findings and drug discovery ].” Here, my goal is to go to task, not spend much time on myself.
When addressing adults at family events or at the playground , I would say: [begin here chatting about the kids, easy in, then] “ Hi, my name is Andrés Lorente, and I am a cell biologist. My research goal is to gain a better understanding of how cells operate in health and disease. Currently, I am working on identifying the role of a molecular switch, called kinases, in progression of different cancer phenotypes. At present, I am also characterizing kinase inhibitors, one of which shows promise for potential use in the clinic. ” Again, I tailor to fit my audience.
And lastly, when addressing a CEO at a networking event I would say: “ Hi, my name is Andrés Lorente, and I am a cancer biologist at UT Southwestern Medical Center. I am currently involved in the characterization of novel kinase inhibitors, some of which have shown promise for potential use in the clinic. Toward the future, however, I am looking to transition to the business of science because I want to have a more direct/immediate impact on human health. To this effect I am currently leading the foundation of a new graduate student and postdoc driven consulting group to provide low cost consulting services to universities and the startup community in the Dallas / Fort Worth area. I approached you because [option 1: I am interested in learning how you got to be where you are; option 2: I believe our consulting group could bring value to your company], [ and then add more here ].“ Here I have two hooks: what I am doing in research and my involvement with this new consulting group. Again, there are variations that depend on whether the CEO has scientific background, whether the company is working on cancer drug development, or whether instead of a CEO I am approaching an Angel Investor. Tailoring is always necessary.
- Identify people you are interested in meeting and who may either provide relevant information on your job search or refer you to others who can. Look at your inner circle first: family, outside friends, church and career development offices; and use LinkedIn to identify people in universities and societies you belong to.
- Ask your network for help reaching out to people: introductions work better than sending cold emails.
- Research the background of the people you are interested in meeting. This helps in many ways: it provides an easier way to establish initial contact and shows both knowledge of their environment and sincere interest in who they are and what they do. Not surprisingly, people respond really well to this approach.
- Be honest about who you are and what your value is: “ Your productivity in your field and profession must be sustained at high levels in order to “ (18) be valuable to your contacts.
- When making connections be sure to show “ sincere interest in his or her work and advice ” (24). Here a listener may do better than a talker, but participating in monologues does not lead to establishment of connections.
- Questions to ask. Again, the credit goes to the sources I used (18, 29-30).
- What do you like/dislike most about your work?
- What are your primary job responsibilities?
- What are the toughest problems and decisions you handle?
- Can you tell me about your career path and how it led you where you are?
- What experience did you have to gain in order to get your job?
- What do you wish you had known about your position/field before you started?
- What type of professional and personal skills does it take to succeed at this type of work?
Just as importantly as making new contacts, you should nurture your network by sending thank you notes (better if handwritten), following up with your contacts to update them on your progress, and continually showing sincere interest in their work and advice.
In conclusion
Get to know yourself through 20 questions and/or Gallup Strengths and/or MBTI® assessments; identify your transferable skills using a Skill Inventory Matrix (18) or similar tool; self-evaluate using tools like the Science Careers My IDP website ; and keep learning about different career paths by reading books/online resources and attending career development seminars.
Whether your goal is to stay in academia to pursue a tenure track position, become a (staff) research scientist in academia or industry, or branch out into a non-academic career, these tools should help identify where you are and what you need to learn or improve, trace a path to follow, and help market yourself effectively to a prospective employer. Also irrespective of the path you want to follow, network, network, and network. The more you network, the better off you will be in terms of available options and mentoring relationships.
And most importantly, persevere, keep plugging away, do not give up, and always, like at the bench, have a backup plan in place.
- N. Ghaffarzadegan, J. Hawley, R. Larson, Y. Xue, A Note on PhD Population Growth in Biomedical Sciences. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 23, 402–405 (2015).
- K. D. Gibbs, M. John, J. C. Bennett, G. Kimberly, Biomedical Science Ph.D. Career Interest Patterns by Race/Ethnicity and Gender. PLoS One. 9, e114736 (2014).
- M. Schillebeeckx, S. Maximiliaan, M. Brett, L. Cory, The missing piece to changing the university culture. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 938–941 (2013).
- G. S. McDowell et al., Shaping the Future of Research: a perspective from junior scientists. F1000Res. 3, 291 (2014).
- G. Jacobs, From science PhD to careers outside academia: what might help? Sciblogs , ( http://goo.gl/6XhQez ).
- H. Sauermann, S. Henry, R. Michael, Science PhD Career Preferences: Levels, Changes, and Advisor Encouragement. PLoS One. 7, e36307 (2012).
- D. Lametti, Why You Should Go to Graduate School in Science. Slate Magazine (2012) , ( http://goo.gl/G8fEpn ).
- D. Cyranoski, N. Gilbert, H. Ledford, A. Nayar, M. Yahia, Education: The PhD factory. Nature. 472, 276–279 (2011).
- P. E. Stephan, Chapter 10: The Biomedical Workforce in the US: An Example of Positive Feedbacks in Handbook on the Economic Complexity of Technological Change, C. Antonelli, Ed. (Edward Elgar Publishing, 2012).
- J. Weissmann, The Ph.D Bust: America’s Awful Market for Young Scientists—in 7 Charts. The Atlantic (2013) , ( http://goo.gl/XoIc33 ).
- P. E. Stephan, 2012 slideshow for “How Economics Shapes Science,” (http://goo.gl/UmpNLf).
- nsf.gov – S&E Indicators 2014 – Chapter 3. Science and Engineering Labor Force – Sidebars – US National Science Foundation (NSF) , ( http://goo.gl/SpbfOa ).
- SESTAT DATA TOOL v1.6.0; Years: 2003, 2006, 2008, 2010, 2013; Tables generated by filtering for Field of major for most recent degree (recoded for public use), showing the variables: Labor force status; Summarized primary work activity; Summarized secondary work activity; and Extent that principal job is related to highest degree ( https://ncsesdata.nsf.gov/sestat/sestat.html ).
- H. H. Garrison, L. B. Justement, S. A. Gerbi, Biomedical science postdocs: an end to the era of expansion. FASEB J. (2015), doi:10.1096/fj.15-280552.
- nsf.gov – S&E Indicators 2014 – Table 3A – US National Science Foundation (NSF) , ( http://goo.gl/LQNRV5 ).
- The Postdoctoral Experience Revisited (National Academies Press (US), Washington (DC), 2015).
- M. J. Mulvany, Biomedical PhD education–an international perspective. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 112, 289–295 (2013).
- A. G. Levine, Networking for Nerds: Find, Access and Land Hidden Game-Changing Career Opportunities Everywhere (John Wiley & Sons, 2015).
- I. Hankel, How Smart PhDs Use Their Transferable Skills To Get High-Paying Jobs | Industry Training For Intelligent People. Cheeky Scientist® (2014), ( http://goo.gl/y4fNxo ).
- L. Celano, How to Evaluate, Build, and Highlight Transferable and Career Relevant Skills. Bio Careers , ( http://goo.gl/KnW8ZT ).
- PhD transferable skills. University of Michigan: The career center , ( https://goo.gl/0wSpVQ ).
- Key transferable skills. Cambridge University Skills Portal , (http://goo.gl/QoFoZB).
- K. A. Sever R Janssen, Career Options for Biomedical Scientists (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2014).
- J. A. Hobin, P. S. Clifford, B. M. Dunn, S. Rich, L. B. Justement, Putting PhDs to Work: Career Planning for Today’s Scientist. Cell Biol. Educ. 13, 49–53 (2014).
- Networking Tips. Harvard Law School , (http://goo.gl/R44JP1).
- N. Collamer, The Perfect Elevator Pitch To Land A Job. Forbes , ( http://goo.gl/A0C3gA ).
- The Mind Tools Editorial Team, Crafting an Elevator Pitch: Introducing Your Company Quickly and Compellingly. Mind Tools , ( https://goo.gl/czNTsF ).
- C. O’Leary, Elevator Pitch 101, ( http://goo.gl/Aw6kKs ).
- J. Barber, How to sound knowledgeable about a career field you’ve never actually worked in. Inside Higher Ed , ( https://goo.gl/tE26vZ ).
- Networking: Questions to Ask. Harvard Law School , (http://goo.gl/RZj3Gx).
About the Author:
Recommended articles.

- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Is a PhD?
A PhD is often the highest possible academic degree you can get in a subject. Learn more about whether earning a PhD could benefit your career.
![what is next degree after phd [Featured image] Two PhD students in caps and gowns celebrate their new degrees on a video call.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6s5qn9Bv4nySJetkmsaOGj/baea54b21625b8601d4debf8589775cb/GettyImages-1307766599.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years , some graduate students may take longer as they balance the responsibilities of coursework, original research, and other degree requirements with raising families or working full time.
With a PhD, you may find opportunities to work as a university professor, a researcher in a commercial or government laboratory, a consultant, or a subject matter expert (SME). If you have the intellectual curiosity and dedication, earning a PhD can be a rewarding experience. In this article, we’ll go over what it takes to earn a PhD, the requirements to apply for a PhD program, and other factors worth considering.
Learn more: What Does ‘PhD’ Stand For?
PhD: Key facts
Generally, students begin their PhD after earning a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree . However, some doctoral programs may offer you the chance to earn your master’s while pursuing your PhD, so that may not be an admissions requirement.
What can you get a PhD in?
It’s possible to earn your PhD in a number of academic disciplines, including the natural sciences , humanities , arts, and social sciences . The 2021 Survey of Earned Doctorates, from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics, offers a numerical breakdown of actual degrees earned in broad academic fields [ 1 ]:
Engineering: 10,240
Biological and biomedical sciences: 8,149
Social sciences: 4,878
Physical sciences: 4,693
Psychology: 3,797
Computer and information sciences: 2,361
Health sciences: 2,331
Mathematics and statistics: 2,012
Agricultural sciences and natural resources: 1,334
Geosciences, atmospheric sciences, and ocean sciences: 1,064
Education: 4,252
Humanities and arts: 4,137
Business: 1,392
Other fields: 1,610
Depending on the university you attend, you may find that the broad academic fields above break down into more specific disciplines. For example, within a physical science department, you might get a PhD in physics or chemistry. Within an engineering department, you might get a PhD in electrical or mechanical engineering. Philosophy, theology, history, or English might fall within a humanities department, while economics or social work could fall within a social sciences department. Marketing could be a specific PhD major within a business department.
In terms of your PhD coursework and research, you will likely be expected to concentrate in some area of your larger subject. For example, PhDs in biology may focus on biochemistry or biostatistics, whereas a PhD in English may concentrate on twentieth-century American literature.
Requirements to get a PhD
PhD programs typically require at least two years of advanced coursework, as well as comprehensive exams, and the successful completion of a dissertation. Let’s break that down on a year-by-year basis:
Years 1 and 2: Take classes to develop advanced knowledge in your subject area.
Year 3: Study for and successfully pass your comprehensive exams.
Years 4 and 5: Research, write, and defend your dissertation.
Once you have successfully passed your comprehensive exams, you’re typically considered “All But Dissertation” or ABD, which signals that you’ve finished everything in your doctoral program except your dissertation.
Research supervisor
PhD students often choose a faculty member who specializes in their area of interest to serve as the research supervisor. It can help to identify professors or programs that will support your research endeavors before applying, so you can establish a relationship with your potential research advisor early.
The average cost of a PhD program in the US is $106,860, though that figure can differ based on the type of institution you attend and what you study [ 2 ].
Reasons to get a PhD
Earning your PhD can be an immensely rewarding experience, but the degree can be a big commitment, requiring significant time, money, and work.
Here are some more reasons you may want to pursue a PhD:
Become a subject matter expert in a particular field.
Conduct the research you are passionate about.
Develop transferable skills that can help in your professional life.
Make a difference in the world with new research.
Make connections with scholars in your academic community.
Open up career avenues in academic and research work.
Completing a PhD can reveal to employers that you possess a wide range of competencies that are valued in both academic and non-academic settings.
PhD salaries
PhD holders earn a median weekly income of $1,909 compared to master’s degree holders, who earn a median weekly income of $1,574, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) [ 3 ]. They may also experience lower percentages of unemployment. The unemployment rate for PhD graduates is 1.5 percent compared to master’s degree holders at 2.6 percent [ 3 ].
Requirements to apply to a PhD program
PhD programs expect you to meet several requirements before enrolling. Here are some examples of common requirements:
Have an undergraduate degree, usually with at least a 3.0 overall GPA.
Have a master's degree, though some programs may not require it.
Take the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) and achieve a minimum score.
Submit a sample of your academic writing.
Submit your CV .
Provide letters of recommendation , which should ideally come from academic faculty members who can speak to your research or intellectual abilities.
Requirements differ by program and school, so take time to become familiar with the entry requirements of universities where you’re interested in applying. Admissions staff or departmental staff should be able to give you specific information about their admissions requirements.
If a program is interested in you, based on your application, you may have to complete an interview. The university representatives that interview you will look at your motivation, how prepared you are, and how suitable you are for acceptance into the doctoral degree program.
PhD vs. other terminal degrees
Terminal degrees are the highest degree available in a field of study. While the PhD is the highest academic degree you can earn in a field of study, a Juris Doctor (JD) is the highest degree you can earn in law, and a professional degree , such as a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) , is the highest degree you can earn in these medical professions.
Learn more: What is a Terminal Degree and Do You Need One?
Professional doctorates are a different category of doctorate degree. They are usually intended for professionals already working in a field who want to pursue advanced training in their area. The main difference between a professional doctorate and an academic doctorate has to do with subject matter and research. While PhDs are interested in conducting new research, professional degree students take existing models and knowledge and apply them to solve problems. Professional doctorates are also designed to prepare learners for careers in a certain industry rather than academia.
Examples of professional doctorates include:
DBA (Doctor of Business Administration)
DNP (Doctor of Nursing Practice)
EdD (Doctor of Education)
DPH (Doctor of Public Health)
Is someone with a PhD a doctor?
You can use the salutation "Dr" to address people who hold doctorates, including PhDs and other professional degrees. The word "doctor" comes from the Latin word for "teacher," and PhDs are often professors at universities. While it has become more common to refer to medical doctors as “Dr,” some professors use the honorific when addressing students and in professional settings.
Explore career and education options with Coursera
Learning online can be a great way to explore a field you're interested in, discover career paths , and even decide whether a PhD is for you. Consider one of Coursera's Professional Certificates , available from Google, Meta, IBM, Salesforce, and other industry leaders, and gain job-ready skills that employers are looking for.
Ready to get a Master's degree ? Coursera partners with universities to offer online Master's degrees in a range of fields like data science, public health, and business.
Article sources
NCSES. " 2021 Survey of Earned Doctorates , https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsf23300/report/field-of-doctorate." Accessed August 1, 2023.
Education Data Initiative. “Average Cost of a Doctorate Degree , https://educationdata.org/average-cost-of-a-doctorate-degree.” Accessed August 1, 2023.
US Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Earnings and Unemployment rates by educational attainment, 2021 , https://www.bls.gov/emp/chart-unemployment-earnings-education.htm." Accessed August 1, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

You Have a PhD! What Next?
A PhD is the highest qualification you can have and is essential for a career in academia. However, there are many challenges to getting academic jobs as some PhDs have interest in non-academic careers. You should have a plan for your career after your PhD. What path will you take? What can you expect from life after your PhD?
Difficult Job Climate
The job market information is not encouraging. A recent report by the National Science Foundation on PhDs found that a PhD takes about eight years to complete. PhD graduates have significant debt and more than 12% of graduates owe $70,000 in student loans. They often do not have a job soon after graduation. Almost 40% of 2014, PhD graduates did not have a job offer.
The ones who get a tenure-track job will earn about $60,000 a year. About 39% of PhDs will do a post-doc where the average salary is $40,000 a year. This is less than the median entry-level salary for a B.A. graduate, which is $45,478. Some of the PhD graduates with academic jobs are part-time or adjunct professors. These positions comprise 76% of the academic labor force . They pay less than $3,000 per class, and offer neither benefits nor job security.
Are There Too Many PhDs?
Despite these depressing statistics, more people are doing PhDs. In 2014 alone, 54,070 PhDs were awarded. This is 12,000 more graduates than in 2004. Every field had more graduates in 2014 than 2004 except for education. Science and engineering had the biggest increases. However, what are all these graduates to do?
The majority of these people will not find work in academia. A recent study has found that there is a definite bias to those who become a professor. Just 25% of universities produce 71-86% of tenure-track faculty. Graduates of more prestigious universities have a much better chance of getting tenure. For example, history graduates from the top 10 universities produce triple the number of professors as the universities ranked 11 through 20.
It is possible to become a professor without graduating from an Ivy League school; however, this is extremely difficult. This requires a lot of hard work. Landing a postdoctoral fellowship where you can show your skills helps as does having an influential mentor. This incredible bias also means that important discoveries from lower ranked universities can end up being ignored.
The difficulty in getting an academic job may not be a bad thing. Only 56% of economics PhDs stayed in academia in 2011. Regardless of field, PhD programs teach some invaluable skills. Doing a PhD teaches you to be self-motivated and helps in understanding complex ideas. PhD programs also help in learning to communicate complex ideas clearly and force students to come up with innovative solutions to problems. These are valuable skills outside of academia as well.
The labor market is changing. The most successful people will be those with advanced skills who can work alongside machines. This will require thinking and technical skills and such advanced skills are acquired during a PhD. The days when doing a PhD guaranteed a comfortable academic job is now behind us.
What Should a PhD Graduate Do?
For starters, learn how to transition. PhD programs generally do not teach students how to market themselves for non-academic jobs. A few mistakes are common during job search. Networking is essential and important to make connections with people who will not be competing for the same jobs. An interview is not a chance for you to get as many questions right as possible. it is important to treat every job interview as your chance to see if the company is a good fit for you. You should also know your worth.
You could start your career after your PhD by investigating the possible jobs relevant to you. Once you know what the options are, you can decide to which non-academic position you wish to apply. There are many different niches that you could fit into.
If you want a career in academia, there are a few things you can do to get a job . Publications are critical. Being able to show a clear plan for your future research can’t hurt. Above all, you will have to be persistent. Do not give up when your applications are rejected. It is also important to have an alternative job plan. As you have seen, this is a difficult path and very few succeed in getting tenure.
A career in academia can be very fulfilling as academic jobs offer intellectual freedom and allow you to pursue research ideas that interest you. You can also tailor your life after PhD. There is the option of either choosing a research-intensive academic job or a position with a greater emphasis on teaching. You could also be interested in non-academic jobs, which could mean working in industry. Your career after PhD could also mean working in a job that is close to academia . Although getting a job in academia is difficult, the good news is that academia is not the only place where your PhD is valuable.
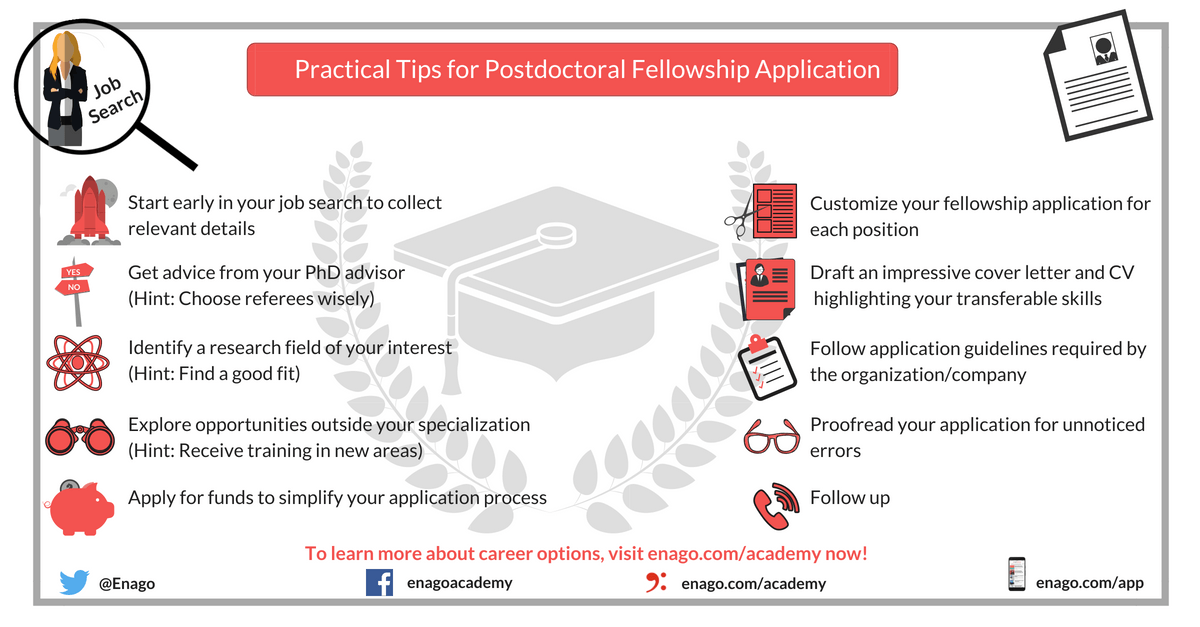
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

- AI in Academia
- Reporting Research
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without AI-assistance
Imagine you’re a scientist who just made a ground-breaking discovery! You want to share your…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia…
7 Steps of Writing an Excellent Academic Book Chapter
When Your Thesis Advisor Asks You to Quit
Virtual Defense: Top 5 Online Thesis Defense Tips

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
What Comes After a Master's Degree?
Know Your Graduate School Options Beyond a Master's
- Choosing a Graduate Program
- Tips & Advice
- Admissions Essays
- Recommendation Letters
- Medical School Admissions
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
- M.A., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
After receiving your master's degree, there are still more options to study in graduate school, including an additional master's degree, doctorate programs (Ph.D., Ed.D., and others) and certificate programs to consider. These degree and certificate programs all vary in level, time to complete, and more.
Additional Master's Degrees
If you have already earned a master's degree and wish to continue your studies, you might consider a second master's degree. Since master's degrees tend to be specialized degrees, as you grow within your career you may find that a new specialty is required or that two specialties will make you an even more desirable candidate when job hunting. In education, for example, many teachers earn a Master's of Arts in Teaching degree but may return to the classroom to study for a degree in the field in which they are teaching, such as English or mathematics. They may also wish to pursue a degree in organizational leadership, especially if they are looking to grow into an administrative role in the school.
Master's degrees generally take two, sometimes three, years to complete (after earning a bachelor's degree), but pursuing a second degree in a similar discipline might allow you to carry over some credits and complete the program sooner. There are also some accelerated master's programs that can earn you a degree in less than a year; just be prepared for a lot of hard work. All master's programs entail coursework and exams , and, depending on the field, possibly an internship or other applied experience (for example, in some fields of psychology ). Whether a thesis is required to obtain a master's degree depends on the program. Some programs require a written thesis; others offer an option between a thesis and a comprehensive exam . Some programs provide capstone courses, which are usually semester-long courses that provide a comprehensive overview of everything learned within the program and ask students to complete several small thesis statements to demonstrate mastery.
A meaningful way in which master's programs differ from many, but not all, doctoral programs is in the level of financial aid available to students. Most programs do not offer as much assistance to master's students as they do for doctoral students, and so students often pay most if not all of their tuition. Many top institutions even offer full scholarships for doctoral students, but a doctoral program is usually a much more comprehensive and time-consuming educational program, requiring a full-time commitment, versus the possibility of working your full-time job while going for a master's degree.
The value of the master's degree varies by field. In some areas such as business, a master's is the unstated norm and necessary for advancement. Other fields do not require advanced degrees for career advancement. In some cases, a master's degree may hold advantages over a doctoral degree. For example, a master's degree in social work (MSW) may be more cost-effective than a doctoral degree, given the time and funds required to earn the degree and the pay differential. The admission offices at the schools you're applying to can often help you determine which program is best for you.
Ph.D. and Other Doctoral Degrees
A doctoral degree is a more advanced degree and takes more time (often a great deal more time). Depending on the program, a Ph.D. could take four to eight years to complete. Typically, a Ph.D. in North American programs entails two to three years of coursework and a dissertation — an independent research project designed to uncover new knowledge in your field that must be of publishable quality. A dissertation can take a year or more to complete, with most averaging about 18 months. Some fields, like applied psychology, may also require an internship of one year or more.
Most doctorate programs offer various forms of financial aid , from assistantships to scholarships to loans. The availability and types of support vary by discipline (e.g., those in which faculty conduct research sponsored by large grants are more likely to hire students in exchange for tuition) and by the institution. Students in some doctoral programs also earn master's degrees along the way.
Certificate Programs
Certificates can usually be earned in less than a year and are often significantly less expensive than going after additional degrees. If you're wondering what should come after your master's degree and you're not sure if a doctoral program is right for you, this could be the way to go. Certificates range in scope greatly and can allow you to hyperfocus on the areas in which you wish to excel. Some schools even offer certificate programs that are of a masters degree caliber, so you can walk away better prepared for your career and without breaking the bank. Employers who offer tuition assistance may look favorably on a less expensive certificate program as well.
Which Is the Best?
There is no easy answer. It depends on your interests, field, motivation, and career goals. Read more about your field and consult faculty advisers to learn more about which option best fits your career goals. Some final considerations are as follows:
- What types of jobs do a master's degree, doctoral degree, and certificate holders have? Do they differ? How?
- How much will each degree cost? How much will you earn after obtaining each degree? Is the outcome worth the cost? What can you afford?
- How much time do you have to invest in additional schooling?
- Are you interested enough to pursue many years of schooling?
- Will earning a doctoral degree offer a substantial benefit in your employment and advancement opportunities?
Only you know which is the right degree for you. Take your time and ask questions, then carefully weigh what you learn about each, its opportunities, as well as your own needs, interests, and competencies. What comes after a master's degree is up to you.
- A Note About Masters and Doctoral Comprehensive Exams
- Pros and Cons of Earning a Master's Degree Before a PhD
- How to Earn a Doctorate Degree Online
- What Does It Take to Earn a Master's Degree?
- A Doctor of Philosophy or Doctorate
- Business Administration Education and Careers
- Should I Earn a Human Resources Degree?
- Should I Earn a Management Degree?
- Should I Earn an Entrepreneurship Degree?
- Should I Earn an Operations Management Degree?
- Should I Earn a Project Management Degree?
- Should I Earn a Doctorate Degree?
- Degree Requirements for Therapists
- Abbreviations and Titles All College Students Should Know
- 6 Tips Applying to Grad School for a Different Major
- How to Decide Between a Ph.D. or Psy.D. in Psychology
- QUICK LINKS
- How to enroll
- Career services
Comparing the differences between MD vs. PhD vs. professional doctorate
By Michael Feder
This article has been vetted by University of Phoenix's editorial advisory committee. Read more about our editorial process.
Reviewed by Marc Booker, PhD, Vice Provost, Strategy
At a glance
- MD is the abbreviation for Doctor of Medicine and PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. These are two types of doctoral degrees in addition to professional doctorates.
- An MD is a doctoral degree for medical professionals, while a PhD is an academic degree focused on original research. Somewhat similar to a PhD are professional doctorates, which focus on applying practical research to problems in workplaces or communities.
- A professional or practice-based doctorate (EdD, DBA, etc.) can be medical, and others are for scholar-practitioners in disciplines like education, business or psychology.
- University of Phoenix does not offer MD or PhD programs, but students can earn a doctorate in business, nursing, education or healthcare that allows them to build upon their industry expertise. Learn more about the differences between these degree programs and if one of the five doctoral programs at University of Phoenix is right for you !
What is a doctorate? Breaking down the three types
Some people might confuse an MD (Doctor of Medicine) with a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) , and vice versa. While both an MD and a PhD are prestigious degrees near the top of the academic ladder , they each have a different meaning and come with very different requirements .
Different still from both of those degrees are professional doctorates, which allow industry professionals to translate their education and experience into credibility and leadership through research. Professional doctorates have similar requirements to PhDs, such as a dissertation and residency, but focus on the application of research and professional growth over original research.
Upon graduation, those who have earned any of these three degrees can call themselves a “doctor,” but the path to a degree, the purpose behind it and its applications vary based on the choice. MD graduates want to work in medicine and healthcare. PhDs want to bring new knowledge and research to the world. A practice-based doctoral graduate wants to grow in their professional expertise. (If the last one sounds like you, University of Phoenix can help!)
Keep reading to learn more about these doctoral programs and which is right for you.
What does MD stand for?
MD is an abbreviation for Doctor of Medicine and identifies a medical practitioner who has completed undergraduate studies and four years of medical school. An MD program teaches medical students about the human body and diseases through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on clinical labs.
Several types of physicians might have this degree, depending on their area of study. For example, medical practitioners with an MD degree might become a medical doctor and potentially specialize in dermatology, cardiovascular disease, family medicine, oncology, pediatrics, neurology or preventive medicine. As you can see, this degree can lead to a variety of career paths , depending on which specialty interests you and what your medical education is.
Learn more about online doctoral degrees at University of Phoenix.
How to earn an MD
Becoming a Doctor of Medicine requires a significant investment of time and money, but the reward can be well worth it. Before medical school, you’ll need to take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT ® ) and earn a passing score. You’ll also need to build a portfolio of coursework and experience to help you gain admittance to medical school.
Medical school typically takes students four years to complete. You’ll learn the latest techniques and approaches for patient assessment, diagnosis and treatment. Medical schools commonly provide a combination of classroom, research and clinical experience . You’ll work alongside peers and healthcare professionals as you develop skills in general medicine.
You’ll choose a field to specialize in during your final year of medical school. Students have more than 120 options to choose from when specializing, including primary care, pediatrics, geriatrics, emergency medicine and family medicine .
After graduating, you’ll complete residency training to further develop skills in your specialty. Residency typically lasts three to seven years, depending on the field you’ve selected. During the residency portion of your education, you’ll treat patients under the supervision of more experienced physicians.
Even after you begin to practice as an MD, the educational portion of your career never stops . As practices change, patient needs evolve and research continues, MDs benefit from ongoing education to stay current.
What does PhD stand for?
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy , is a doctoral degree that recognizes graduates who have completed a full postsecondary program. Students can earn a PhD in more fields than philosophy. After completing the necessary coursework, original research and hands-on experience, you can earn a PhD in fields like science, the humanities and engineering.
Earning a PhD can help unlock a wide range of potential career opportunities. Computer engineers, research scientists, statisticians, healthcare administrators, professors, chemists and other careers commonly require a PhD degree, in addition to appropriate undergraduate study.
How to earn a PhD
Becoming a PhD is also a serious commitment that requires an investment of time, money and energy .
Here is what’s typically required to become a PhD:
- Complete a bachelor’s degree in your field
- Complete a master’s degree in an appropriate field
- Pass any program entrance exams
- Fulfill coursework, research and hands-on lab requirements in your program
- Finalize and defend your dissertation as a doctoral candidate (unless your program specifies otherwise)
It’s important to note that many PhD programs have different requirements , prerequisites and parameters for students. Check with your preferred institution for a more detailed explanation of these requirements.
What is a professional doctorate?
While some professional or practice-based doctorate programs are medical, others are designed for professionals in other fields . These programs are meant for scholar-practitioners in disciplines like education, business or psychology. One of the key differences between this degree and a PhD is the focus on applying research to a professional setting rather than conducting theoretical and research-focused studies. Often, programs are differentiated as academic versus professional.
Examples of doctoral degrees are Doctor of Education, Doctor of Nursing Practice and Doctor of Business Administration. Each of these programs focuses on a specific discipline and applying research in those areas to a professional setting.
How to earn a doctorate
While practitioner doctoral programs teach different skills, they all share common requirements. You’ll need to complete a bachelor’s degree in your field and sometimes a master’s degree, depending on program requirements.
After completing the necessary coursework and research, students also typically need to finish a supervised thesis and defend their dissertation or capstone project-specific coursework, research and hands-on labs alongside other students in the same field. However, this will depend on the specific program and its requirements.
What does the title “Dr.” really mean?
The term “doctor” or “Dr.” is commonly used today to describe a wide variety of occupations. Students who complete a doctoral degree can earn the title of “Dr.” even though they earned their credentials in a non-medical field like education or business management.
While a variety of professionals can earn a doctorate, the term is often still reserved for medical practitioners . In conventional use, doctors typically refer to medical physicians . However, it is appropriate to use “Dr.” if you graduated from any of the three programs discussed above.
read similar articles

What is doctoral candidacy?
Practitioner doctoral degree programs at university of phoenix.
While University of Phoenix (UOPX) does not have MD or PhD programs, it does offer several professional doctoral degrees that can be earned completely online. Students might choose the UOPX programs because classes are flexible and offered online, and because of the University’s unique “ Scholar-Practitioner-Leader model .”
If you are curious about a doctoral degree, the following programs are available at UOPX:
- Doctor of Business Administration — This doctorate can help you gain strategic vision and skills to position yourself as a business leader. It explores how to solve organizational problems, how to design and conduct research studies, how to introduce innovative business ideas to the industry and more.
- Doctor of Management — This doctorate equips you with critical thinking skills to find creative solutions to complex problems.
- Doctor of Education — This doctoral program prepares you to use analytical, critical and innovative thinking to improve performance and solve complex problems in education.
- Doctor of Health Administration — If you’re a health professional who is seeking greater responsibility in shaping the future of the health sector, this doctorate can help you meet the challenges inherent to today’s healthcare landscape, including economic fluctuations, burgeoning patient needs and industry-changing legislation.
- Doctor of Nursing Practice — This doctorate is designed for working nurses who require a doctorate for advanced practice or nurses who desire their terminal degree. It does not prepare students for professional certification or state licensure as a nurse or as an advanced practice nurse.
These doctoral studies are only some of the many options for professionals who want to gain the highest academic credentials in their fields. Doctoral programs offer significant benefits to program graduates, including newly developed skills , insight into field trends, hands-on research opportunities and leadership capabilities .
Completing a doctoral program is also a strong indication to employers that you’re serious about your career and your field. With so many options for advanced study, these programs are available for most major fields. Even if you have already completed a bachelor’s or master’s degree in your discipline, a doctorate lends further credibility to your reputation and can help prepare you for a leadership position .

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Michael Feder is a content marketing specialist at University of Phoenix, where he researches and writes on a variety of topics, ranging from healthcare to IT. He is a graduate of the Johns Hopkins University Writing Seminars program and a New Jersey native!

want to read more like this?

Careers With a Doctor of Education Degree
Online degrees.
April 28, 2021 • 4 minute read

Should I get a Doctor of Education (EdD) Degree?
September 08, 2022 • 9 minutes

3 Reasons You Should Get a Graduate Degree
September 15, 2021 • 7 minute read
Top 7 Career Opportunities in India after PhD in 2024

A PhD or Doctor of Philosophy is the highest academic qualification offered to an individual following a course of study. The term PhD originates from the Latin term ‘Philosophiae Doctor’ and represents competition of individual research in a field of interest. The doctoral research degree paves the path for a wide range of opportunities. It is a 3 to 8 years course that helps you become competent at presenting your thesis based on independent research of a topic.
There is a breadth of skills students acquire while pursuing a PhD. It elevates your ability to critically analyse a subject, display intellectual maturity, gain in-depth knowledge of a specific field and publish a valid thesis.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the best job opportunities after PhD that are available to students in different industries—academia, government sector, entrepreneurship, consultancy, and so on. If you are looking for PhD admission for 2024, please read further.
What is the career outlook for PhD holders in 2024?
Based on my experience and insights, job opportunities after phd in india appear promising in 2024. Their advanced research and analytical skills are in high demand across various sectors. In academia, opportunities abound as they can pursue careers as professors or researchers. The corporate sector offers avenues for success in roles related to research and development, data science, and consulting. Government agencies value their expertise in policy analysis and implementation. Additionally, for those inclined towards entrepreneurship and innovation, there are opportunities to venture into new territories. Overall, the year 2024 presents an encouraging landscape for PhD holders in India, offering diverse career paths and the potential to make meaningful contributions in their respective fields.

Top Job Opportunities after PhD
1. academics, a. faculty position.
One of the most commonly opted choices after a PhD is teaching, primarily due to the uncanny similarity between academia and what an individual must do to acquire the degree. The degree practice and teaching involve teaching, researching, and nurturing your acquired knowledge.
If you are interested in landing a faculty position or taking up the teaching path, plenty of institutions are keen on having a PhD holder in their faculty, especially in developing countries.
The PhD holders have a niche of their own in the domain or topic they have spent time researching about. They have made a good number of contributions to the field of study, so they have a firm hold on the subject.
So the PhD holders as faculty seem to be a natural fit, as they can impart the knowledge mentioned in the curriculum and much beyond that. They can open their students’ minds to concepts they would not usually be exposed to and thus help them develop a frame of mind that is inquisitive and has a strong foundation.
Some of the skills that the faculty must possess to impart the education smoothly are an excellent hold of the subject, communication skills, analytical skills, people management, understanding of human behavior, assessment skills, empathy, etc.
The profession of teaching is considered one of the best, high paying and most successful one. The compensation varies according to the subject, institution, experience, etc. On average, after PhD salary in India of a faculty is 12.0 lakhs per annum. The average salary bracket ranges from 1.3 lakhs per annum to 30.0 lakhs per annum (Source).
b. Post Doctorate
You can also choose to stay in the same university for varying periods (from one to four years) and get an extended project based on the one you did earlier. You might also work on publishing your erstwhile researched product.
The significance of a post-doctorate is many. They take on individual or group research projects that are impactful. Their research and findings help society, government education, industries, etc.
A post-doc has the autonomy of their day. Some of the skills that are required from a post-doc are the nature of being inquisitive, research skills, documentation, verbal and written communication, a good hold of the subject matter, people skills, team management, etc.
The salary for a post-doc may vary depending on factors such as the institution, domain, research topic, experience, etc. On average, a postdoctoral researcher procures the compensation of 10.0 lakhs per annum. The salary ranges from 3.0 lakhs per annum to 40.0 lakhs per annum (Source). People have apprehension about “ What comes after PhD ?” Post-doctorate can be considered an option.
c. Adjunct Position
An adjunct position is a non-tenure position in universities; they are professionals who don’t carry the title of a professor but make valuable contributions to the faculty. In some universities, professionals in Adjunct positions work overtime and bear numerous educational responsibilities.
d. Teaching
PhD holders can teach at institutions offering undergraduate courses where they are looking for staff with a PhD who can carry out practical research.
PhD candidates can be assistant professors by teaching undergraduate courses or being a part of committees that help form academic and organisational policies and perform research to achieve tenure.
There exists a myth that PhD courses are designed to PAVE the path for individuals to become professors at the university level. However, the horizons of a PhD degree spread farther than simply academia, so it’s wrong to assume so.
Here’s looking at the different verticals where PhD holders can chart a rewarding career.
2. Government Jobs
The government job sector is ideal for patriotic and passionate people who want to serve the country. Since the government is always on the lookout for creative and skilled people, professionals who love researching and put their skills to good use can rely on the government sector.
PhD holders carry a unique, innovative perspective that allows them to view complex problems, understand them and make practical, diplomatic choices.
There are several opportunities here, starting from the military sector (e.g. military research). If you are interested in politics, you can opt for a policymaker position in state and central government. You can also be a minister if you can work your way up with innovative diplomatic ideas.
First, the PhD holders are eligible to sit in the government exam. They are highly qualified professionals who give a learned and deeper perspective to the government professionals that helps in better decision-making. They can work in various departments of the government, such as policy making, rural development, transportation, scientific research, military, international relations, etc. One can procure various PhD jobs in India in the government sector.
3. Entrepreneur
In today’s world, the entrepreneurship sector is growing exponentially. Since information and technology are accessible to everyone, there’s a growing shift towards startups, self-employment, and innovation. PhDs holders carry the potential to be first-grade innovators/entrepreneurs.
Research shows that PhDs and entrepreneurial journeys are way more similar than they seem, and hence, students who have PhD degrees are very likely to thrive when they get into entrepreneurship.
Apart from various similarities between the entrepreneurs and PhDs, there is one common similarity between these two, and that is innovation and research skills. Both of these professionals identify a problem persisting in society and develop a model that solves it. So naturally, the PhD holders seem as a fit progression to entrepreneurship.
Some of the skills required for a successful entrepreneur are identifying problems, critical thinking, problem-solving, business management, creativity, team management, self-starter attitude, communication skills, networking, etc.
4. Consultancy
The skillset required to be a consultant includes maintaining large amounts of data. Plenty of companies rely on MBA professionals and PhD holders for consultancy due to the increasing influence of technology in the real world.
Large consultancy firms hire PhD holders from all different fields. The idea is to leverage valuable data and glean helpful insights to empower business decision-making.
PhD and other advanced degrees help students shine in consultancy since there is a massive requirement for specialised expertise in today’s age. Therefore, if you have a PhD, consultancy is a very prominent job opportunity that can be highly rewarding.
There are various reasons for being a consultant professional as a PhD holder, as they have a high capacity for critical thinking. They are skillful for effectively and scientifically solving problems. The PhD holders can effectively analyse the data and come to conclusions. The companies hire the PhD holders for the level of expertise they bring. Usually, they are hired at the same level as MBA professionals. This may vary depending on the companies, level of skill sets, location, and other factors.
5. Digital Media Company
The job description is to prepare reports providing a comprehensive analysis and context on various topics. It also includes preparing reports on artistic and cultural events. A PhD course equips you to be an individual with excellent writing and research skills. These are extremely handy when pursuing a writing job opportunity at media company.
Unlike a regular digital marketing professional a PhD holder would come up with a much deeper perspective and understanding. They would be having the in depth knowledge of the funcitonings.
There is an option available to do PhD in digital marketing, these professionals would come up with understanding on the culture, society, ethnicities, human behaviour and many more. There are various options available fo r phd jobs as there are various firms and companies that employe the professionals.
6. Research Associate
As the word suggests, a research associate job position requires you to gather data to determine whether consumers or companies find a product or service desirable or appealing.
For this job position, the skills you acquire during your PhD study (presentation and research skills) prove to be highly influential; these are the skills that help you excel in research.
Switching from academic research to corporate research, where the information acquired via research is used well, is a choice most professionals make these days since academic research can get monotonous and underwhelming at times.
The research associates are responsible for various tasks such as gathering of data, preparing data, analysing, reporting, research and may more. They identify the problem and then go about their workf to find solutions for the problem.
It is considered as one of the most sought- after jobs one can go for. There are various industries and fields one can go ahead to make a career fro themselves. These researches make a positive contribution to the society in various fields such as history, science, art and culture, society, policy making, etc.
Usually there is no degree after PhD is required to become a research associate a PhD suffices. Moreover, the profession as a research associate is high paying and is a stable career.
7. Product Manager
The job profile of a product manager includes overseeing every aspect of the development, growth, maintenance, and improvement of a product.
Companies prefer PhD holders over other UG PG holders for positions that require overseeing or handling end-to-end tasks since a PhD equips you to handle multitasking effortlessly.
The role of a product manager doesn’t stop after product formulation and release. It extends to maintenance, improving product performance, devising marketing strategies, and enhancing product efficiency by bringing in new methods that can replace older ways. Online PhD programs offer you offer flexibility to manage your work and other commitments.
A product manager is required to be aware of the customer’s needs and manage to address the gap by innovating the product. They are responsible for making the product better that helps in taking the business forward.
In order to all of that, they are required to be equipped with certain skill sets that understands th ehuman behavioru, mindsets of people coming from different geographies and age groups. And according to various factors, inculcate the innovations in such a way that the product feels relatable to the target audience. But most importantly, they should also be having the business acumen that helps them in aking decisions that benefits the business.
The profession as a product manager is considered as high paying and on average the salary goes up to 16.3 lakhs per annum. The average salary ranges from 6.0 lakhs per annum to 35.0 lakhs per annum (Source). This salary bracket may differ due to various factors such as geographical location, skill sets, experience, type of company, etc.
Check out upGrad’s Global Doctor of Business Administration from the ACBSP-accredited Swiss School of Business and Management. The 36-months program caters to 75+ nationalities and provides 12+ specialisations and 70+ faculty industry collaborations to help you succeed. There are 1:1 thesis supervisions to ensure you exploit your potential in your domain of choice.
The minimum requirement to pursue this degree is a Master’s Degree (or equivalent) or 5+ years of work experience. Don’t wait, sign up and book your seat today!
Is it easier to find a career opportunity with a PhD degree?
Based on my own experience and observations, pursuing a PhD, although demanding in terms of time and effort, can significantly broaden your career horizons. PhD holders are highly esteemed for their specialized knowledge, exceptional research skills, and critical thinking abilities. They find ample opportunities in academia, securing coveted positions as professors and researchers. Moreover, industries such as healthcare, finance, and technology highly value PhDs, often offering them lucrative roles in research and development, data analysis, and leadership.
However, the ease of finding suitable job opportunities after phd in india can vary based on factors like your field of study and location. In India, PhD graduates can unlock diverse and rewarding career paths with the right set of skills and effective networking. The investment in higher education pays off in the form of fulfilling and promising professional opportunities.
T he landscape of job opportunities after a PhD in India in 2024 appears promising and diverse. The demand for highly skilled and specialized professionals continues to grow across various sectors. Whether you aspire to excel in academia, contribute to cutting-edg e research, or significantly impac t the corporate world, a PhD opens doors to numerou s avenues. The key lies in leveragin g your unique expertis e , networking effectively, and staying attuned to emerging trends in your field. With the right strategy and dedication, you can embark on a fulfilling and rewarding career journey, making your investment in a Ph .D. an asset in the dynamic Indian job market.
Something went wrong
Our Most Popular DBA Course

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Communication skills can effectively drive career potential since PhD holders are expected to deliver out-of-the-box thinking, management, and creative ways of solving problems via critical thinking. Developing communication skills is crucial in showcasing and presenting your ideas to technical and non-tech teams convincingly.
PhD holders have the upper hand over Master’s or Bachelors's students across industries due to their high-end skill sets that include critical thinking, problem-solving, and effective decision making. In addition, their unmatched research skills and data management abilities make them an obvious choice for a host of high-profile roles across industries.
The average salary of PhD holders ranges between ₹ 6,00,000 and ₹ 12,00,000 per year, depending on the field of choice, experience, and skillsets. The average base salary for a PhD holder working as a professor is ₹16,73,000 per year, approximately ₹90k per month).
Related Programs View All
ACBSP and HLC Accredited Program
View Program

IACBE Membership

WES Recognized

Offline Campus Experience

ACBSP Accredited & EduQua Certified
Rushford Alumni Status
icon-degree
Explore Free Courses
Learn more about the education system, top universities, entrance tests, course information, and employment opportunities in Canada through this course.
Advance your career in the field of marketing with Industry relevant free courses
Build your foundation in one of the hottest industry of the 21st century
Master industry-relevant skills that are required to become a leader and drive organizational success
Build essential technical skills to move forward in your career in these evolving times
Get insights from industry leaders and career counselors and learn how to stay ahead in your career
Kickstart your career in law by building a solid foundation with these relevant free courses.
Stay ahead of the curve and upskill yourself on Generative AI and ChatGPT
Build your confidence by learning essential soft skills to help you become an Industry ready professional.
Learn more about the education system, top universities, entrance tests, course information, and employment opportunities in USA through this course.
Suggested Blogs
![what is next degree after phd DBA Salary in India: For Freshers & Experienced [2023]](https://www.upgrad.com/__khugblog-next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd14b9ctw0m6fid.cloudfront.net%2Fugblog%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2020%2F05%2F517-DBA-Salary-in-India.png&w=3840&q=75)
18 Feb 2024

08 Apr 2023

06 Apr 2023

04 Apr 2023

28 Mar 2023

27 Feb 2023
![what is next degree after phd Business Management Job Description [in 2024]](https://www.upgrad.com/__khugblog-next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd14b9ctw0m6fid.cloudfront.net%2Fugblog%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2019%2F07%2FBlog_FI_July_upGrads-Knowledge-base.png&w=3840&q=75)
26 Feb 2023

25 Feb 2023

24 Feb 2023

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Often, it takes a while after a PhD for students to acknowledge that they are indeed equipped with these skills. Hence, it is a good idea to create a portfolio, mapping different skills to the projects and tasks that were undertaken during and after your PhD. Choosing the next step in your career and life after PhD would then trickle down to ...
Having a Ph.D. means you are not only a general master of the field but that you also have a specific study that you understand completely. Students with master's degrees have mastery in a subject, but a Ph.D. takes this mastery further. Such mastery can help you become a leading member of academia or the author of a book on the subject.
Cons of Pursuing Postdoc. Despite the impressive benefits, considering the flip side of pursuing a postdoc position is imperative before taking the big decision. 1. No Tenure-track Guarantee. The uncertain career prospects in academia does not guarantee a tenure-track position even after completing your postdoc.
A postdoc is, in fact, a job, and as someone in a postdoc position, you will be considered an 'employee'. And just like any other job, the position will come with its own salary, responsibilities, training and employers. Most postdocs are awarded by universities or research institutes as temporary contracts. However, they can also be ...
Jobs Outside of Academia. There may be alternatives to teaching or working in academia. Speaking at conferences, consulting, and getting a promotion or a new job all may be options you want to pursue. Having a PhD means you are part of a small and coveted group outside of academia-use this to your advantage.
Postgraduate degrees fall into three main categories: Master's, professional, and doctoral. Let's take a closer look at each: 1. Master's degree. For many students, a master's degree is typically the next degree pursued after earning a bachelor's degree.
In general, a PhD is the highest degree you can get. A postdoc is simply a research position that is not permanent, i.e. no fixed contract or tenure. There are some exceptions, for example in the German system where you can get your Habilitation, which is a degree after you get your PhD. But in most systems there is nothing beyond a PhD in ...
There are many different paths that can lead to a successful career, from increasing your publication numbers or transitioning to a different lab or institution to acknowledging that what you ...
A PhD in Maths and Computing could benefit jobs in Finance, Investment or Web Development, complimenting skills in logic, problem solving and data. A PhD in the Physical Sciences demonstrates experience with software and data. This could set graduates up to work in Software Engineering, Data Science or even Sound Engineering.
This experience to create and use clear visualisations is useful for reporting, presenting and management. Time management: During the PhD, you learn to manage your time and prioritise tasks. You become capable of organising yourself and meeting deadlines. This is very useful for project management and supervising.
Step 2: Set your Goals. After taking a break, the first thing you need to do is figure out what your goals are. You employed a great deal of discipline to get to this point. Use that skill to determine how you want to move forward. Your doctoral degree is an asset, so try to maximize the return that you get.
Career after PhD: Options and scope Postdoctoral Position: The postdoctoral position is a prevalent trajectory pursued by many PhD graduates as a natural progression beyond their doctoral studies.
The five tips listed below offer links to helpful resources and methods of preparing for the stresses of the job search, life after school, and how to cope with inevitable emotional and professional challenges. Make time for yourself: According to a Harvard study, by the time students enter their final years of graduate school, up to 25 percent ...
What is the next level of education after PhD? A doctorate in philosophy (PhD) is the highest degree obtainable. After earning your degree, you can keep your knowledge current and make yourself more employable by pursuing industry certificates. If you plan on entering academia or research, consider a post-doctoral research position.
Gain valuable insight from our collection of exclusive interviews with both current and past PhD students. Learn from their best advice, personal challenges and career path after completing their doctorate. Learn about life after a PhD, from employability statistics to career prospects. Learn the skills you'll gain and how to apply these to a ...
This is often an overwhelming question for freshly minted doctorates. After so many years of tedious laboratory work, your next step seems more crucial than ever. It could determine the direction in which your career heads! Frankly, fresh doctorates in Singapore today have many more choices than ever before. During my own time--I got my PhD a ...
Troubling changes in PhD employment include a ~50% increase in non-science related occupations (e.g., transportation, culinary field, or construction) to a total of ~22,000 PhDs; and a significant ~1.6 fold increase in unemployment to a total of ~4,000 PhDs (Fig 1) .
Learn more about whether earning a PhD could benefit your career. A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as ...
They often do not have a job soon after graduation. Almost 40% of 2014, PhD graduates did not have a job offer. The ones who get a tenure-track job will earn about $60,000 a year. About 39% of PhDs will do a post-doc where the average salary is $40,000 a year. This is less than the median entry-level salary for a B.A. graduate, which is $45,478.
Najim M.M.M. After the PhD, the holder of it should get more qualified through research. The list of a PhD holders publications, their impacts, citations and relevance in his/her field of ...
Other fields do not require advanced degrees for career advancement. In some cases, a master's degree may hold advantages over a doctoral degree. For example, a master's degree in social work (MSW) may be more cost-effective than a doctoral degree, given the time and funds required to earn the degree and the pay differential.
10 weeks after submission: Usually the viva will take place within 10 weeks of the examiners receiving your thesis. 3-6 months after viva: Most PhD students pass with corrections and are given a period to edit the thesis. The length of time given will depend on whether you pass with major or minor corrections. After editing period
What is a doctorate? Breaking down the three types. Some people might confuse an MD (Doctor of Medicine) with a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy), and vice versa.While both an MD and a PhD are prestigious degrees near the top of the academic ladder, they each have a different meaning and come with very different requirements. Different still from both of those degrees are professional doctorates ...
The degree requires 54 to 66 credits, and students can graduate within three years. All students must also complete a dissertation and an oral defense of their work. The program costs $950 per ...
1. Academics. a. Faculty Position. One of the most commonly opted choices after a PhD is teaching, primarily due to the uncanny similarity between academia and what an individual must do to acquire the degree. The degree practice and teaching involve teaching, researching, and nurturing your acquired knowledge.
A PhD in USA is a 3 to 6 year full time program offered in popular specialisations such as Engineering, Applied Sciences, Computer Science, and Management. To get admission to the PhD program, you need a bachelor's degree with a GPA of 2.7 to 3.9 on a 4.0 scale or a Master's degree in the relevant stream. What distinguishes PhD in America from other countries is that you don't necessarily ...