

How to Write a Complete Literature Review for Your Thesis/Dissertation

A literature review critically evaluates and synthesizes existing research and scholarly publications on a specific topic or research question. Its goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on the topic, identify gaps in the literature, and highlight areas for future research. A well-conducted literature review is an essential component of research because it helps to establish the research context, justify the need for the study, and guide the development of research questions or hypotheses.
The literature review of your thesis/dissertation is a very significant part of your paper. It provides readers with an understanding of previously published research in relation to your topic. It also highlights where your research fits into the existing literature. In other words, it provides valuable context for your readers about the field as a whole and the specific topic you have chosen to cover in your thesis/dissertation.
Literature reviews: An overview
A literature review does not only summarize what has been written about a topic already: it also offers a critical analysis of the existing literature.
Literature reviews can take different forms depending on what type of research you are doing and what your field of research is about. Literature reviews are a key part of the majority of academic articles or theses, and can even be written as articles all on their own. A literature review does not only summarize what has been written about a topic already: it also offers a critical analysis of the existing literature. In other words, you, the author, offer your analysis or critique on what has been written already. A literature review, however, should not just be a description of what has been written or a set of summaries.
The idea of reviewing and analyzing all the research that has been done on a topic can sound overwhelming; however, the task is easier than it sounds. This is also a vital step in performing the work necessary to write a good thesis. As you prepare and write your literature review, you will select and filter which sources are relevant to your work and which are not. As you review the literature, you will develop a clear understanding of the work that has come before you. This will enable you to write about it in such a way that you clearly demonstrate how you arrived at your own thesis statement or hypothesis.
A literature review can be quite short (5% of a paper) or quite long (30% of a paper) depending on the type of paper. For a thesis/dissertation, a literature review may be a full chapter, and is usually at least 10-20% of your paper.
Types of literature reviews
There are different types of literature reviews and the type you choose will be determined by the topic you are researching. Four common types of literature reviews are summarized below, but there are also other types that may be preferable depending on your thesis topic.
Chronological
This type of literature review organizes sources and their ideas by the date of publication. For example, if you are writing about chronic Lyme disease, you would start with articles describing and identifying Lyme disease (1970s), then describe initial treatments and discoveries (1980s), increased prevalence of Lyme disease and rise of people with chronic Lyme disease (2000s), and finally discuss the current controversies and treatments (2010s).
This type is often used in social science papers such as political science or public policy. They focus on specific trends in a field and can still include a chronological component. For example, you could write about changes in approaches to early childhood education by discussing the rise and fall in popularity of public preschool, highlighting relevant case studies, and presenting arguments that there is no need for schooling so early. This is often used to highlight competing schools of thought in a field.
Methodological
This focuses less on what is said in different sources and more on how previous research has been performed. For example, a methodological review of the treatment of chronic Lyme disease might reveal that previous studies which relied solely on laboratory tests dismissed persistent Lyme symptoms as “all in the patients’ heads,” while studies that focused on interviewing patients as well as doctors classified the disease as an unidentified syndrome. Methodological studies can highlight how approaches to research have changed over time and how the approaches used in research influence the results.
Theoretical
Theoretical literature reviews are often found in fields like philosophy or humanities, but are also prevalent in social sciences. They review existing theories and their relationships, as well as what has been tested and what has not. This kind of review is quite useful in demonstrating where existing theories fall short in describing a particular phenomenon in the field.
Structuring your literature review
A literature review is usually a chapter in your thesis/dissertation and as such generally includes an introduction, main body, and conclusion. The introduction will explain:
- The type of literature review you have performed
- Why you have chosen to perform that type of literature review
- Your criteria for selecting sources
Your main body will be the actual literature review, which we will discuss further in the next section. In your conclusion, you will summarize the major arguments that you have highlighted in your literature review and center your own research among them. The conclusion of the literature review should explain why your research study is necessary (what gap in the literature it fulfils) to lead smoothly into your next thesis chapter.
How do I review the literature?
An easy way to find relevant sources is to look at the citations of papers you find that are on the topic you want to research.
Before you write a literature review, you need to:
- Become familiar with the literature
- Select which sources are relevant to your thesis topic
- Organize your sources
- Choose the type of literature review you will write
- Arrange your notes to reflect the type of literature review
How do you become familiar with the literature?
If you aren’t sure where to start, try going to Google Scholar and typing in some keywords about your topic. For example, if you’re researching chronic Lyme disease, you could type in keywords such as “chronic Lyme” “post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome” and “Lyme disease treatment” to see what results show up. As you search, you will be able to identify more keywords that are relevant to what you want to search. Making a list of these keywords can help you as you engage in this task. When you find an article that looks promising, copy the citation information from Google Scholar and save it in a file or use a reference manager like Mendeley . You will thank yourself for this later. You can then search your academic institution’s online library to download the article.
An easy way to find relevant sources is to look at the citations of papers you find that are on the topic you want to research. If you aren’t sure whether an article or paper you are reading is reputable , you can check its citation metrics using Google Scholar, which can tell you how many other people cited a particular source. Generally, it holds true that the more highly cited a source is, the more reliable and useful it is. Of course, your citation sources don’t need to be limited to journal articles. Books , news articles , interviews, and other sources are all acceptable .
Finally, as you read through sources and organize them, you will want to take notes. Don’t just save an article and hope you’ll remember why you did. Jot down a few sentences about the main argument of this source and why/how it is relevant to your research study. Once you have done this, you will want to go ahead and organize your sources in an order that reflects the type of literature review you have chosen to do. For example, if you are doing a thematic review, you should organize sources by a theme or type of argument. If you are doing a historical review, you would organize them in chronological order.
Writing the literature review
As you write your literature review, you will want to walk the reader through what has happened in the literature review and offer your analysis of it.
Now that you’ve reviewed the literature, taken notes, organized your sources and your notes, you are ready to begin! As we mentioned above, a literature review needs an introduction and a conclusion. As you write your literature review, you will want to walk the reader through what has happened in the literature review and offer your analysis of it. For example, you could say “while Yue and Xu argue that Lyme disease is a bacterial infection and should not result in symptoms resembling post-viral syndromes, others such as Scott and Zebrowski have noted the strong similarities between patients with chronic Lyme disease and the newly emerging group of COVID long-haulers. Scott and Zebrowski appear to be at the forefront of the changing perspective on chronic Lyme disease as newer evidence supports their position.”
Your literature review will include the ideas of many other people, but it should not be a lengthy chapter directly quoting other papers. You should instead paraphrase what others say. Of course you can use some quotes! They are not off limits. Short quotes like “Marx said ‘religion is the opiate of the masses’ while Mao Zedong said ‘religion is poison’” is fine. Longer blocks of text should be used only when necessary and properly indicated within the text .
Now you are ready to write your thesis literature review! Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis, where to find the best thesis editing services, and more about thesis editing and proofreading services .
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Checklist for writing a literature review
Below is a list of points to remember when writing your literature review. These will help you make sure that your literature review is thorough and properly structured.
Do a thorough review of the sources in your field that are relevant to your thesis topic.
Make sure your sources are reliable and high-quality.
Take detailed notes and maintain an organized list of your sources.
Cover a wide variety of viewpoints, not just those that support or agree with your argument. Make it clear what controversies and unsettled point of views exist.
Make sure your literature review chapter has a clear introduction, main body, and conclusion.
Use quotes sparingly.
What is a literature review? +
A literature review is a summary of the major studies and sources related to your topic that already exist and provides critical analysis of these sources. A literature review is not a bibliography or a list of sources. It is written in a narrative format.
e.g. “Clowes and McKnight (2002) argue that chronic Lyme disease is analogous to post-viral syndrome.”
What kinds of sources can be included in a literature review? +
Anything you can cite in an academic paper can be included in a literature review. This includes journal articles, books, news sources, interviews, and so on. You should not include Wikipedia or your Uncle Bob as a source in the literature review (unless your Uncle Bob is a recognized expert in your topic!).
Do I really have to write a literature review? +
A literature review is part of most social science or natural science theses/dissertations. your institutional requirements inform you to, then you have to write a literature review. If you are writing a thesis/dissertation in humanities or in another field where the structure does not mandate a literature review, you may be able to skip it. Always check with your advisor and your institution about the requirements of your thesis/dissertation structure.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a literature review in 6 steps

What is a literature review?
How to write a literature review, 1. determine the purpose of your literature review, 2. do an extensive search, 3. evaluate and select literature, 4. analyze the literature, 5. plan the structure of your literature review, 6. write your literature review, other resources to help you write a successful literature review, frequently asked questions about writing a literature review, related articles.
A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research.
A good literature review does not just summarize sources. It analyzes the state of the field on a given topic and creates a scholarly foundation for you to make your own intervention. It demonstrates to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.
In a thesis, a literature review is part of the introduction, but it can also be a separate section. In research papers, a literature review may have its own section or it may be integrated into the introduction, depending on the field.
➡️ Our guide on what is a literature review covers additional basics about literature reviews.
- Identify the main purpose of the literature review.
- Do extensive research.
- Evaluate and select relevant sources.
- Analyze the sources.
- Plan a structure.
- Write the review.
In this section, we review each step of the process of creating a literature review.
In the first step, make sure you know specifically what the assignment is and what form your literature review should take. Read your assignment carefully and seek clarification from your professor or instructor if needed. You should be able to answer the following questions:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What types of sources should I review?
- Should I evaluate the sources?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or critique sources?
- Do I need to provide any definitions or background information?
In addition to that, be aware that the narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good overview of the topic.
Now you need to find out what has been written on the topic and search for literature related to your research topic. Make sure to select appropriate source material, which means using academic or scholarly sources , including books, reports, journal articles , government documents and web resources.
➡️ If you’re unsure about how to tell if a source is scholarly, take a look at our guide on how to identify a scholarly source .
Come up with a list of relevant keywords and then start your search with your institution's library catalog, and extend it to other useful databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Science.gov
➡️ Our guide on how to collect data for your thesis might be helpful at this stage of your research as well as the top list of academic search engines .
Once you find a useful article, check out the reference list. It should provide you with even more relevant sources. Also, keep a note of the:
- authors' names
- page numbers
Keeping track of the bibliographic information for each source will save you time when you’re ready to create citations. You could also use a reference manager like Paperpile to automatically save, manage, and cite your references.
Read the literature. You will most likely not be able to read absolutely everything that is out there on the topic. Therefore, read the abstract first to determine whether the rest of the source is worth your time. If the source is relevant for your topic:
- Read it critically.
- Look for the main arguments.
- Take notes as you read.
- Organize your notes using a table, mind map, or other technique.
Now you are ready to analyze the literature you have gathered. While your are working on your analysis, you should ask the following questions:
- What are the key terms, concepts and problems addressed by the author?
- How is this source relevant for my specific topic?
- How is the article structured? What are the major trends and findings?
- What are the conclusions of the study?
- How are the results presented? Is the source credible?
- When comparing different sources, how do they relate to each other? What are the similarities, what are the differences?
- Does the study help me understand the topic better?
- Are there any gaps in the research that need to be filled? How can I further my research as a result of the review?
Tip: Decide on the structure of your literature review before you start writing.
There are various ways to organize your literature review:
- Chronological method : Writing in the chronological method means you are presenting the materials according to when they were published. Follow this approach only if a clear path of research can be identified.
- Thematic review : A thematic review of literature is organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time.
- Publication-based : You can order your sources by publication, if the way you present the order of your sources demonstrates a more important trend. This is the case when a progression revealed from study to study and the practices of researchers have changed and adapted due to the new revelations.
- Methodological approach : A methodological approach focuses on the methods used by the researcher. If you have used sources from different disciplines that use a variety of research methods, you might want to compare the results in light of the different methods and discuss how the topic has been approached from different sides.
Regardless of the structure you chose, a review should always include the following three sections:
- An introduction, which should give the reader an outline of why you are writing the review and explain the relevance of the topic.
- A body, which divides your literature review into different sections. Write in well-structured paragraphs, use transitions and topic sentences and critically analyze each source for how it contributes to the themes you are researching.
- A conclusion , which summarizes the key findings, the main agreements and disagreements in the literature, your overall perspective, and any gaps or areas for further research.
➡️ If your literature review is part of a longer paper, visit our guide on what is a research paper for additional tips.
➡️ UNC writing center: Literature reviews
➡️ How to write a literature review in 3 steps
➡️ How to write a literature review in 30 minutes or less
The goal of a literature review is to asses the state of the field on a given topic in preparation for making an intervention.
A literature review should have its own independent section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where it can be found, and address this section as “Literature Review.”
There is no set amount of words for a literature review; the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, then it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, then it will be short.
Most research papers include a literature review. By assessing the available sources in your field of research, you will be able to make a more confident argument about the topic.
Literature reviews are most commonly found in theses and dissertations. However, you find them in research papers as well.

- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Make a Literature Review in Research (RRL Example)
What is an RRL in a research paper?
A relevant review of the literature (RRL) is an objective, concise, critical summary of published research literature relevant to a topic being researched in an article. In an RRL, you discuss knowledge and findings from existing literature relevant to your study topic. If there are conflicts or gaps in existing literature, you can also discuss these in your review, as well as how you will confront these missing elements or resolve these issues in your study.
To complete an RRL, you first need to collect relevant literature; this can include online and offline sources. Save all of your applicable resources as you will need to include them in your paper. When looking through these sources, take notes and identify concepts of each source to describe in the review of the literature.
A good RRL does NOT:
A literature review does not simply reference and list all of the material you have cited in your paper.
- Presenting material that is not directly relevant to your study will distract and frustrate the reader and make them lose sight of the purpose of your study.
- Starting a literature review with “A number of scholars have studied the relationship between X and Y” and simply listing who has studied the topic and what each scholar concluded is not going to strengthen your paper.
A good RRL DOES:
- Present a brief typology that orders articles and books into groups to help readers focus on unresolved debates, inconsistencies, tensions, and new questions about a research topic.
- Summarize the most relevant and important aspects of the scientific literature related to your area of research
- Synthesize what has been done in this area of research and by whom, highlight what previous research indicates about a topic, and identify potential gaps and areas of disagreement in the field
- Give the reader an understanding of the background of the field and show which studies are important—and highlight errors in previous studies
How long is a review of the literature for a research paper?
The length of a review of the literature depends on its purpose and target readership and can vary significantly in scope and depth. In a dissertation, thesis, or standalone review of literature, it is usually a full chapter of the text (at least 20 pages). Whereas, a standard research article or school assignment literature review section could only be a few paragraphs in the Introduction section .
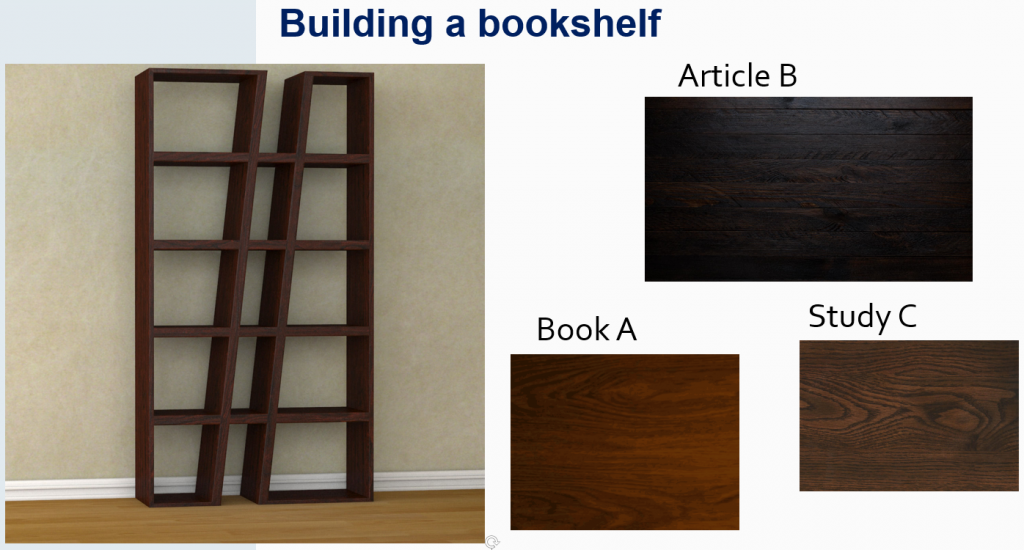
Building Your Literature Review Bookshelf
One way to conceive of a literature review is to think about writing it as you would build a bookshelf. You don’t need to cut each piece by yourself from scratch. Rather, you can take the pieces that other researchers have cut out and put them together to build a framework on which to hang your own “books”—that is, your own study methods, results, and conclusions.
What Makes a Good Literature Review?
The contents of a literature review (RRL) are determined by many factors, including its precise purpose in the article, the degree of consensus with a given theory or tension between competing theories, the length of the article, the number of previous studies existing in the given field, etc. The following are some of the most important elements that a literature review provides.
Historical background for your research
Analyze what has been written about your field of research to highlight what is new and significant in your study—or how the analysis itself contributes to the understanding of this field, even in a small way. Providing a historical background also demonstrates to other researchers and journal editors your competency in discussing theoretical concepts. You should also make sure to understand how to paraphrase scientific literature to avoid plagiarism in your work.
The current context of your research
Discuss central (or peripheral) questions, issues, and debates in the field. Because a field is constantly being updated by new work, you can show where your research fits into this context and explain developments and trends in research.
A discussion of relevant theories and concepts
Theories and concepts should provide the foundation for your research. For example, if you are researching the relationship between ecological environments and human populations, provide models and theories that focus on specific aspects of this connection to contextualize your study. If your study asks a question concerning sustainability, mention a theory or model that underpins this concept. If it concerns invasive species, choose material that is focused in this direction.
Definitions of relevant terminology
In the natural sciences, the meaning of terms is relatively straightforward and consistent. But if you present a term that is obscure or context-specific, you should define the meaning of the term in the Introduction section (if you are introducing a study) or in the summary of the literature being reviewed.
Description of related relevant research
Include a description of related research that shows how your work expands or challenges earlier studies or fills in gaps in previous work. You can use your literature review as evidence of what works, what doesn’t, and what is missing in the field.
Supporting evidence for a practical problem or issue your research is addressing that demonstrates its importance: Referencing related research establishes your area of research as reputable and shows you are building upon previous work that other researchers have deemed significant.
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews can differ in structure, length, amount, and breadth of content included. They can range from selective (a very narrow area of research or only a single work) to comprehensive (a larger amount or range of works). They can also be part of a larger work or stand on their own.
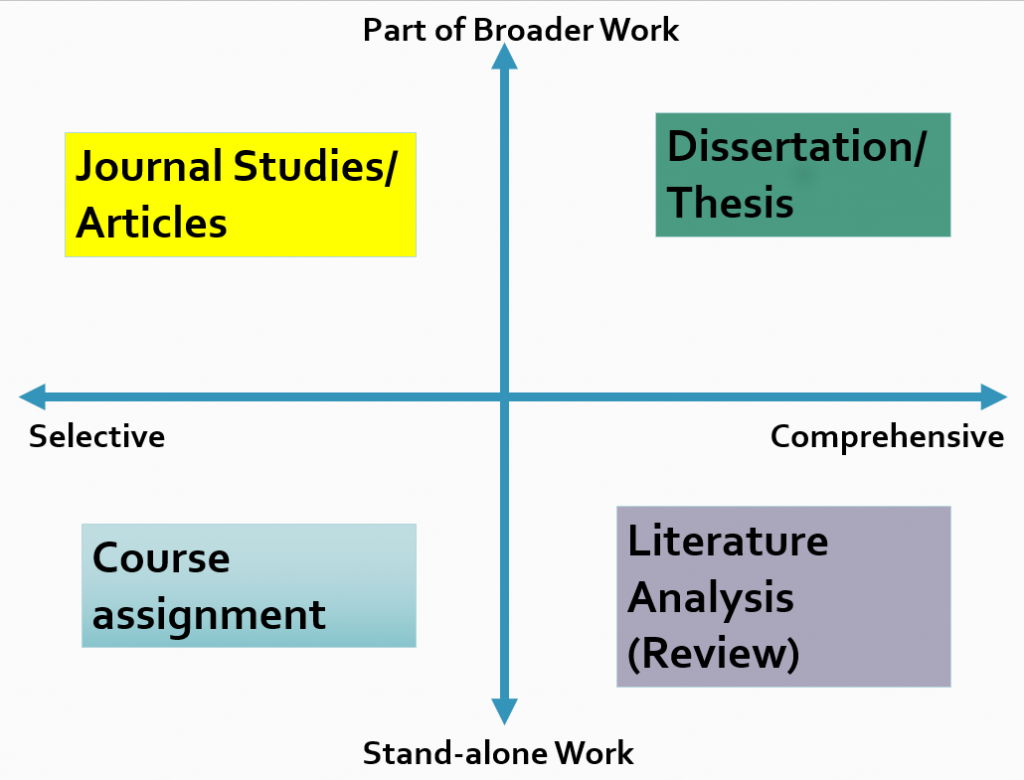
- A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work. It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own.
- The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.
- A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the study; such a literature review is usually included in the Introduction section (but it can also follow the presentation of the results in the Discussion section ).
- Some literature reviews are both comprehensive and stand as a separate work—in this case, the entire article analyzes the literature on a given topic.
Literature Reviews Found in Academic Journals
The two types of literature reviews commonly found in journals are those introducing research articles (studies and surveys) and stand-alone literature analyses. They can differ in their scope, length, and specific purpose.
Literature reviews introducing research articles
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, usually near the end. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must be limited to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to the current study. Its purpose is to set research precedence and provide support for the study’s theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles contain an explicit review of the literature, but most do, whether it is a discrete section or indistinguishable from the rest of the Introduction.
How to structure a literature review for an article
When writing a literature review as part of an introduction to a study, simply follow the structure of the Introduction and move from the general to the specific—presenting the broadest background information about a topic first and then moving to specific studies that support your rationale , finally leading to your hypothesis statement. Such a literature review is often indistinguishable from the Introduction itself—the literature is INTRODUCING the background and defining the gaps your study aims to fill.
The stand-alone literature review
The literature review published as a stand-alone article presents and analyzes as many of the important publications in an area of study as possible to provide background information and context for a current area of research or a study. Stand-alone reviews are an excellent resource for researchers when they are first searching for the most relevant information on an area of study.
Such literature reviews are generally a bit broader in scope and can extend further back in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all sections of such a “review article” refer to existing literature rather than describing the results of the authors’ own study.
In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study. At the end of the review follows a conclusion that once again explicitly ties all of the cited works together to show how this analysis is itself a contribution to the literature. While not absolutely necessary, such articles often include the terms “Literature Review” or “Review of the Literature” in the title. Whether or not that is necessary or appropriate can also depend on the specific author instructions of the target journal. Have a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field.

How to Write a Literature Review in 6 Steps
So how do authors turn a network of articles into a coherent review of relevant literature?
Writing a literature review is not usually a linear process—authors often go back and check the literature while reformulating their ideas or making adjustments to their study. Sometimes new findings are published before a study is completed and need to be incorporated into the current work. This also means you will not be writing the literature review at any one time, but constantly working on it before, during, and after your study is complete.
Here are some steps that will help you begin and follow through on your literature review.
Step 1: Choose a topic to write about—focus on and explore this topic.
Choose a topic that you are familiar with and highly interested in analyzing; a topic your intended readers and researchers will find interesting and useful; and a topic that is current, well-established in the field, and about which there has been sufficient research conducted for a review. This will help you find the “sweet spot” for what to focus on.
Step 2: Research and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study.
This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations, and theses—these and any other academic work related to your area of study is called “the literature.”
Step 3: Analyze the network of information that extends or responds to the major works in your area; select the material that is most useful.
Use thought maps and charts to identify intersections in the research and to outline important categories; select the material that will be most useful to your review.
Step 4: Describe and summarize each article—provide the essential information of the article that pertains to your study.
Determine 2-3 important concepts (depending on the length of your article) that are discussed in the literature; take notes about all of the important aspects of this study relevant to the topic being reviewed.
For example, in a given study, perhaps some of the main concepts are X, Y, and Z. Note these concepts and then write a brief summary about how the article incorporates them. In reviews that introduce a study, these can be relatively short. In stand-alone reviews, there may be significantly more texts and more concepts.
Step 5: Demonstrate how these concepts in the literature relate to what you discovered in your study or how the literature connects the concepts or topics being discussed.
In a literature review intro for an article, this information might include a summary of the results or methods of previous studies that correspond to and/or confirm those sections in your own study. For a stand-alone literature review, this may mean highlighting the concepts in each article and showing how they strengthen a hypothesis or show a pattern.
Discuss unaddressed issues in previous studies. These studies that are missing something you address are important to include in your literature review. In addition, those works whose theories and conclusions directly support your findings will be valuable to review here.
Step 6: Identify relationships in the literature and develop and connect your own ideas to them.
This is essentially the same as step 5 but focused on the connections between the literature and the current study or guiding concepts or arguments of the paper, not only on the connections between the works themselves.
Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the “golden thread” that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn’t have before reading your literature review. Make sure you know where to put the research question , hypothesis, or statement of the problem in your research paper so that you guide your readers logically and naturally from your introduction of earlier work and evidence to the conclusions you want them to draw from the bigger picture.
Your literature review will not only cover publications on your topics but will include your own ideas and contributions. By following these steps you will be telling the specific story that sets the background and shows the significance of your research and you can turn a network of related works into a focused review of the literature.

Literature Review (RRL) Examples
Because creating sample literature reviews would take too long and not properly capture the nuances and detailed information needed for a good review, we have included some links to different types of literature reviews below. You can find links to more literature reviews in these categories by visiting the TUS Library’s website . Sample literature reviews as part of an article, dissertation, or thesis:
- Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
- Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience Based Approach in a Tourism Context (Martina Donnelly)
Sample stand-alone literature reviews
- Literature Review on Attitudes towards Disability (National Disability Authority)
- The Effects of Communication Styles on Marital Satisfaction (Hannah Yager)
Additional Literature Review Format Guidelines
In addition to the content guidelines above, authors also need to check which style guidelines to use ( APA , Chicago, MLA, etc.) and what specific rules the target journal might have for how to structure such articles or how many studies to include—such information can usually be found on the journals’ “Guide for Authors” pages. Additionally, use one of the four Wordvice citation generators below, choosing the citation style needed for your paper:
Wordvice Writing and Academic Editing Resources
Finally, after you have finished drafting your literature review, be sure to receive professional proofreading services , including paper editing for your academic work. A competent proofreader who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by academic journals will ensure that your paper is ready for publication in your target journal.
See our academic resources for further advice on references in your paper , how to write an abstract , how to write a research paper title, how to impress the editor of your target journal with a perfect cover letter , and dozens of other research writing and publication topics.
Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
How To Write Literature Review For Thesis? Read On To Find Out!

Table of Contents
- 1. What is a literature review?
- 2. Thesis literature review example
- 3. Importance of the thesis literature review
- 4. Literature review structure
- 4.1. Step 1: Look for the Relevant Scholarly Resources
- 4.2. Step 2: Evaluate the Resources
- 4.3. Step 3: Identify Gaps in Current Resources
- 4.4. Step 4: Develop the Outline of the Master Thesis Literature Review
Types Of Literature Review
- 4.5. Write Your Literature Review
- 4.6. Step 7: Write Your Bibliography
What Is A Literature Review
A thesis literature review is a complete analysis of scholarly sources on a selected topic of study. It is crafted to give an overview of the current knowledge, to help the researcher know the methods, theories, and gaps that exist in research.
Thesis Literature Review Example

Why is Literature Review for Thesis Important?
When you are working on your graduate thesis, one of the core components needed to make it complete is a literature review. Here is a demonstration of the main benefits of carrying a literature review for your thesis.
- Allows you to show how familiar you are with the topic of study.
- Offers you an opportunity to develop a comprehensive methodology.
- Demonstrate how your research will address the existing gap in your topic of study.
- Make your contribution to your area of the study felt.
Doing a literature review requires you to collect and analyze scholarly resources that are related to your topic. When conducting a literature review, the process can be broken down into five key stages.
Literature Review Structure
- Look for relevant scholarly resources . This is checking for different resources, such as journals and books, which are related to your study.
- Evaluate the resources. This is careful sorting of the different resources to identify the most relevant ones.
- Identify debates and gaps in these resources . This is further analysis of the scholarly resources to establish the main arguments and possible gaps in research.
- Develop your outline. This is the format of the literature review that tells you what you are supposed to discuss at different points.
- Write the literature review . This is the final step that involves putting down the findings that you found after analyzing different resources.
To help you craft a good literature review for thesis, here are the main steps that you should follow.
Step 1: Look for the Relevant Scholarly Resources
By the time you get to writing the thesis for your literature, you will have worked on chapter one (introduction) that clearly defines the topic. But you can still relook at it before setting off to look for the relevant resources. By defining the problem, you will be able to look at the resources that are closely related to the study questions and problems.
Another method of looking for relevant studies is searching using the keyword. Consider using the main databases for the latest journals, books and articles. Some of these databases include:
- Project Muse .
- Google Scholar .
- Your university library.
After pulling out different resources, check whether it is relevant by going through the abstract. If the resource is relevant, peruse to the last section, the bibliography, for additional resources. When you find a specific resource recurring in the resources, it means it is very relevant.
Step 2: Evaluate the Resources
Once you have gathered an assortment of resources, the chances are that not all of them will be used during the study. So you will need to evaluate them further to determine which ones to use in the study. So here is how to evaluate every resource:
- What problem is addressed in the resource?
- How has the author defined the main concepts?
- What theories and methods are used in the resource?
- What is the conclusion of the resource?
- What is the relationship between the resource and other resources?
- How does the resource contribute to knowledge about the topic?
You should only pick the most relevant resources. Also, it is important to appreciate that if you are in the sciences, the review has to be focused on the latest resources. But if your thesis is in humanities, it might be necessary to check older resources to bring out the historical perspectives. As you read through, keep track of the resources by taking notes, capturing the pages, and citing them properly.
Step 3: Identify Gaps in Current Resources
Before you can organize the arguments in the literature, it is prudent to comprehend how the resources are related. So what should you look for?
- Patterns and trends, especially in theories, methods, and results.
- Debates, major conflicts, and contradictions.
- Gaps on what is missing in the literature.
- Pivotal publications.
Step 4: Develop the Outline of the Master Thesis Literature Review
The outline of your literature provides you with a breakdown of what you should discuss at what different stages. There are a number of strategies that you can use to prepare your literature review.
- Chronological . This approach involves tracing the development based on the topic occurrence over time. It is the simplest strategy.
- Thematic . This strategy involves presenting the review based on different themes.
- Methodological . If the resources you use for the review have varying methods, a methodological presentation can helps you to compare the results as well as conclusions.
- Theoretical . This approach involves exploring the theories, definitions, concepts, and models used in the resources. You might also want to focus on particular theories depending on the topic of study.
Note that you can opt to use one or combine several of them to make your literature review more articulate.
Step 5: Write Your Literature Review
Like other forms of academic writing, your literature review should take this format: introduction, body, and conclusion. Here is what to include in every section:
- Introduction: This should be used to give the focus of the literature review.
- Body: In the body of the literature review, you get into the finer details of the review. Here you should do the following:
- Summarize, analyze, and interpret.
- Evaluate comprehensively.
- Write carefully in properly structured and easy to read paragraphs.
Literature Review Example
To help you craft a great literature review thesis, it is important to also have the entire project in mind. This means that although you are reviewing literature, the methods you will use should be clear the back of your mind. Here is a thesis literature review example paragraph. The paragraph is borrowed from literature review of a thesis on the effects of cyberbullying.
“ Cyberbullying gives the bully a much larger spectrum to choose from when it comes to how exactly they want to intimidate their victims, which may be why it is often easier for them to carry out the act. Of all the different ways to cyberbully Faucher et al. (2014) found the most common platforms for cyberbullying to be social media, text messaging, and email, which were used to bully students about half of the time followed up by blogs forums and chat rooms which were 25 percent. This is no surprise that social media is the most common platform for cyberbullying because it can allow for the bully to remain completely anonymous to your average victim. This allows people who may not fit the mold of your average bully to create a fake account and build their own persona in order to bully others.”
- Conclusion.
Once you have written the body of the literature review, you still need to conclude it. This is a summary of the literature review that captures the main points that you have discussed.
Step 6: Write Your Bibliography
This guide on how to write literature review for thesis cannot be complete without including a bibliography. This is a complete list of all the resources that you have used during the review. It is important to ensure that you follow the method that your supervisor recommends for formatting and referencing. See two reference examples presented below.
Abeele, M., & Cock, R. (2013). Cyberbullying by mobile phone among adolescents: The role of gender and peer group status. Communications: The European Journal of Communication Research, 38(1), 107-118. Doi:10.1515/commun-2013-0006
Arntfield, M. (2015). Toward a Cybervictimology: Cyberbullying, Routine Activities Theory, and the Anti-Sociality of Social Media. Canadian Journal Of Communication, 40(3), 371-388

Make PhD experience your own
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Literature Review Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Literature Review Template
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction . We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template . This includes:
- The literature review opening/ introduction section
- The theoretical framework (or foundation of theory)
- The empirical research
- The research gap
- The closing section
We then progress to the sample literature review (from an A-grade Master’s-level dissertation) to show how these concepts are applied in the literature review chapter. You can access the free resources mentioned in this video below.
FAQ: Literature Review Example
Literature review example: frequently asked questions, is the sample literature review real.
Yes. The literature review example is an extract from a Master’s-level dissertation for an MBA program. It has not been edited in any way.
Can I replicate this literature review for my dissertation?
As we discuss in the video, every literature review will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your literature review to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a literature review here .
Where can I find more examples of literature reviews?
The best place to find more examples of literature review chapters would be within dissertation/thesis databases. These databases include dissertations, theses and research projects that have successfully passed the assessment criteria for the respective university, meaning that you have at least some sort of quality assurance.
The Open Access Thesis Database (OATD) is a good starting point.
How do I get the literature review template?
You can access our free literature review chapter template here .
Is the template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the template and you are free to use it as you wish.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

What will it take for you to guide me in my Ph.D research work?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Thesis/Project Preliminary Format Review
With the help of our Graduate Student Assistants, the Graduate Resource Center will now begin taking appointments and walk-ins for preliminary formatting review for projects and theses. During these sessions, Graduate Student Assistants will help walk you through the process of formatting your project or thesis so that you are well-prepared for your appointment with an official Library Formatting Approver.
This preliminary formatting process serves as an important preparatory step and aims to bring your project or thesis one step closer to completing the formatting process, although you will not be given approval during this appointment.
Please keep in mind that if you are submitting a project abstract, library formatting approval is NOT required. Formatting is required only for submission of Project reports and Thesis. If you have any questions regarding the steps to completing your project or thesis , please review the steps here: https://www.cpp.edu/gradstudies/steps-towards-completing-your-thesis-or-project.shtml.
Graduate Student Assistants
Janki joshi.
Hours of availability: Mondays – 9 am to 2 pm Tuesdays - 12 pm to 5 pm Wednesdays 12 pm to 5 pm Thursdays – 10 am to 3 pm
Hours of availability: Mondays – 1:45 pm to 5:15 pm Tuesdays – 9:30 am to 1:30 pm and 2 pm to 5 pm Wednesdays – 11 am to 3:30 pm and 4 PM to 9 PM
Amir Mohideen
Hours of availability: Mondays – 1:30 pm to 3:30 pm and 5:30 pm to 9 PM Tuesdays – 12 pm to 2 pm and 4 pm to 9 pm Thursdays – 11:30 am to 2 pm and 4 pm to 9 pm
Abrar Fahim
Hours of availability: Mondays – 10 am to 1:30 pm and 2 pm to 3:30 pm Tuesdays – 10 am to 12:30 pm and 1 pm to 3:30 pm Wednesdays – 10 am to 12:30 pm and 1 pm to 4:30 pm Thursdays – 10 am to 2 pm
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

College accepts 1,937 to Class of 2028

Progress and challenges on the road to net zero

Pushing back on DEI ‘orthodoxy’
The stories behind the theses.

Photo illustration by Liz Zonarich/Harvard Staff
Eileen O’Grady, Christy DeSmith, Anne Manning
Harvard Staff Writers
Six students share their inspirations and outcomes
From African baobabs to virtual reality, here is a closer look at six thesis projects Harvard students undertook this year.
In the suburbs

Madeline Ranalli is pictured alongside a mural promoting Nonantum, one of 13 villages within her hometown of Newton, Massachusetts.
Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard Staff Photographer
In leafy suburbs across the U.S., residents have rallied to block affordable housing from their neighborhoods.
“A lot of the resistance comes in the form of people saying, ‘Look what this development is going to do to the trees,’” noted Madeline Ranalli ’23.
The government concentrator (with a secondary in energy and environment ) used her senior thesis to examine how these communities wield environmentalism in opposition to multifamily residential developments.
“There’s this misconception that the more green you see, the more environmentally friendly a place is,” Ranalli explained. “But the way a community is designed can actually undermine the environmental benefits of those natural resources.”
The thesis analyzes four car-centric suburbs in California’s Bay Area, where the shortage of affordable housing is especially stark. The region is the birthplace of mainstream American environmentalism and has a history of resistance to multifamily housing. But it’s also a place where lawmakers are passing leading-edge legislation to bolster affordability and density.
Ranalli conducted dozens of in-person interviews, and worked with the Harvard Digital Lab for the Social Sciences to survey the nationwide frequency of using environmentalism to oppose land use that would actually reduce carbon footprints.
“This is by no means unique to California,” said Ranalli, who grew up observing similar rhetoric in her hometown of Newton, Massachusetts. “It’s very much a phenomenon in affluent, Democratic suburbs.”
While conducting research, Ranalli, now a legislative intern with the U.S. Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works, discovered “The Environmental Protection Hustle” (1979) by the late MIT urban planning professor Bernard J. Frieden , which helped inform her argument that environmentalism is more than an ideology about the importance of protecting natural resources.
“It’s also a very legitimate political strategy that can be employed very successfully to achieve certain ends,” Ranalli said.
Across the savannas

Audrey “Rey” Chin in Mozambique studying baobab trees.
Courtesy photo
Last summer, Audrey “Rey” Chin ’24 hiked 125 miles across dense savanna in Mozambique, painstakingly collecting data from more than 100 trees that make up a delicate, changing ecosystem.
An Environmental Science and Public Policy program concentrator, Chin wrote her senior thesis on the distribution and vulnerability of African baobabs, the largest fruit-bearing trees on the planet, which carry both ecological and cultural significance for the region. Elephants use these iconic trees as nutrient sources, stripping their bark, extracting water, and eating them. In doing so, they spread the seeds to help the trees reproduce.

Chin wrote her senior thesis on the distribution and vulnerability of African baobabs.
Chin’s thesis integrates her field study with remote sensing data to evaluate the extent to which landscape variables, including elephants, affect the health of baobabs. Chin is conducting the research in the lab of Andrew Davies , assistant professor of organismic and evolutionary biology.
“I think [the project] is ultimately about trying to find a way to balance the conservation priorities of the two species, and understand the interaction that’s happening,” she said.
The remote Karingani Game Reserve in southern Mozambique, where Chin and classmate/labmate Hannah Adler ’25 conducted the field work, is a test bed for understanding the current level of elephant utilization of the trees, and how that relationship could inform stewardship and conservation practices for years to come. The area came under official protection in 2017. Since then, migration from nearby Kruger National Park as well as anti-poaching and landscape restoration measures have led to a surge in the elephant population.
“The opportunity to witness the biodiversity and interconnectivity of different species was probably the most awe-inspiring part of the project,” Chin said.
In the workshop

Francisco Marquez with his prototype bicycle.
Photos by Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard Staff Photographer
Francisco Marquez ’24 had always ridden bicycles, but it was pandemic-fueled restlessness during his freshman year that led the mechanical engineering concentrator to learn how to build them.
Now the de facto bike mechanic of his friend group, Marquez pursued a senior capstone project that tackled a perennial problem for two-wheeled enthusiasts like him: size.
“Because I’m a fairly large person, most bikes don’t fit me,” said Marquez, who is 6 foot 4. “I also have a bunch of friends who are very small, and they also can’t find a bike that really fits them. I decided to try to make a bike that could fit everybody.”

Marquez designed and built a modular bicycle frame with a shape and size that can be adjusted to fit very short people, very tall people, and everyone in between. It also allows children to grow into their wheels.
“It could even be something that you buy for a teenager, that they can then use as they grow into adulthood,” he said.
Simplifying the frame into standard components such as top tube, down tube, and fork, Marquez redesigned each piece with unlocking mechanisms using joints and pins, allowing for rotating, loosening, and retightening. Manufacturing was no simple task; it took a year’s worth of testing to find the right materials and configuration for a bike that could be adjusted easily yet remain reliably rigid during use. He settled upon a retrofit of a vintage steel-framed bicycle and created his own custom parts. Throughout the process, Marquez picked up skills like welding and spent many hours in the Science and Engineering Complex machine shop , working with tools like a lathe and a mill.
Testing it for the first time in its tallest configuration, Marquez smiled when it fit like a glove. He said it was gratifying to be able to see his own design come to life.
“I’ve never ridden a bike that feels like this,” he said.
In the gardens

Rivers Sheehan in her studio space on Linden Street.
In the southern colonies of 18th-century America, the science of botany was used for economic purposes but also for aesthetics, using beautiful gardens and cultivated landscapes to mask a brutal plantation economy.
Rivers Sheehan ’23, a joint concentrator in art, film, and visual studies and history of science , completed a thesis project that combined historical research with an art exhibit, examining how botany, considered a gentlemanly European science in the 18th century, found new roots in the U.S.
“I looked at how that epistemology got applied in the South, in the frontier lands where people were both setting up really profitable and violent plantations using botanical knowledge and also setting up estate gardens that were inspired by French and English landscape design, often on the same properties,” said Sheehan, who wrote a 90-page paper detailing her findings.
For the art element, the December 2023 graduate created a multimedia exhibit of paintings, photographs, prints, and drawings inspired by her research at the plantations and also her own relationship to the natural world. Some of the pieces use paper dyed with natural indigo, birch bark, rabbit skin glue, leaves, and wild mushrooms. Sheehan worked in a variety of media, each representative of a different modality she learned during her time at Harvard.
“The studio project is a way of bringing this niche research into the contemporary moment and offering another way for an audience to come into it who isn’t necessarily an academic historian of science, which is the audience for the written part of it,” Sheehan explained.

Stepping back in time

Cindy Tian created a virtual reality program.
Virtual reality can facilitate all manner of educational experiences — like bringing visitors inside the Pyramids of Giza . Cindy Tian ’23, a joint concentrator in computer science and archaeology , wondered how the technology would fare with more complicated lessons.
“I wanted to see if VR can show archaeological processes that are harder for the general public to understand,” she said. “Would the technology improve the transfer of information from archaeologists and museum staff?”
Her thesis took the form of an exhibit for the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnography , still on view near the third-floor stairwell. Tian first created a display featuring artifacts that illuminate flintknapping — or fashioning blades, points, and other tools from a stone core. On view are everything from hammerstones to chipping tools.

Tian, a December grad, also created a virtual reality program that allowed visitors to simulate making their own tools with objects like the ones on display.
“Flintknapping is a reductive process where you basically remove pieces of rock,” said Tian, who will soon start a full-time role with a music analytics startup. “It’s just one of the things where it’s better to learn by doing rather than reading or hearing someone talk about it.”
Finally, Tian tested who learned best about flintknapping — those who took in the exhibit, those who used the VR program, or those who encountered both.
“Are we integrating VR because it’s cool? Or is it actually helpful ?” she wondered.
Those who experienced both the exhibit and the VR scored highest on Tian’s post-visit content quiz. The same group emerged with more positive opinions of the flintknapping lesson.
“They essentially got to do it without doing it,” Tian said. “I found that the virtual reality is definitely beneficial for helping people learn about archaeological processes.”
Working in the studio

Five large abstract paintings are included in Isabel Haro’s thesis, which is titled “Taking Refuge.”
Abstract art has long served as a vessel for artists — think Hilma af Klint or Wassily Kandinsky — to explore religion and spirituality.
Isabel Haro ’24, a concentrator in art, film, and visual studies with a secondary in music , was inspired to pursue a thesis that explored this topic after taking the course “Spiritual Paths to Abstract Art” with Professor Ann Braude at Harvard Divinity School . Haro, who practices Buddhism, wanted to create a collection of work inspired by her own experiences.
“It’s very hard to talk about spirituality in the contemporary art world. It’s something that a lot of people are not interested in, or actively shy away from,” said Haro. “My intention was to be really diligent and responsible with how I was bringing Buddhism into the art conversation.”
To prepare, she studied other artists and paintings, read Buddhist scripture and poetry, meditated, and sketched. Inspired by color field style and the techniques of abstract painter Morris Louis, Haro played with gravity, standing on a stool to pour ink down the canvas, and laid canvas on the floor to let the paint move in rivulets.
The thesis, titled “Taking Refuge,” includes five large abstract paintings done in paint on muslin and canvas. One is painted with black Sumi ink — the kind used for Zen calligraphy — and uses salt and soap to create textures.
“I spent so much time preparing for this final set of paintings and all of that work prepared me to let these paintings emerge in a natural way,” Haro said. “I learned how valuable it is to work on a project over an extended period of time.”
Share this article

You might like
Students represent 94 countries, all 50 states

New reporting requirement for public companies ‘a meaningful step forward,’ says director of sustainable investing at HMC

Panelists support diversity efforts but worry that current model is too narrow, denying institutions the benefit of other voices, ideas
So what exactly makes Taylor Swift so great?
Experts weigh in on pop superstar's cultural and financial impact as her tours and albums continue to break records.
Terrain Gallery fundraiser offers community chance to fund art, artists
It takes a lot to sustain art in the community. You need artists, of course, but you also need spaces for them to show their work, events where people can view and purchase art and organizations who help bring artists and patrons together.
For years, Terrain has provided all of that and more, championing artists of all mediums through gallery shows, where art purchases are split 70/30, with 70% of the profit going to the artist. There is also the retail store From Here and events like Bazaar, Brrrzaar and the Terrain flagship event, which is held every October.
But how do you sustain the sustainers?
Terrain executive director and co-founder Ginger Ewing said the gallery costs more than $80,000 a year to operate.
Rent comes to $44,400 a year, with gas and electricity ringing in at $2,160 a year. There’s internet ($1,200 a year), wall vinyls announcing the title of each month’s gallery show ($1,500 a year), artist handbills ($600 a year), insurance ($3,000 a year), wine at First Friday events ($1,200 a year), graphic design ($4,200 a year), and paint and other supplies ($1,800 a year).
That $80,000 price tag doesn’t include staff time, the exhibit preparator or gallery sitters, or marketing throughout the year.
To help cover the annual cost, the organization is hosting a Terrain Gallery fundraiser on Friday at, of course, Terrain Gallery.
The fundraiser began after artists Carl Richardson and Mardis Nenno approached Ewing and told her they wanted to do something to give back to Terrain. She didn’t anticipate the event becoming so popular so quickly, but last year, people were lined up for two blocks before doors opened.
“It speaks to the desire of our community to consume local art and to support organizations like Terrain,” she said. “We’ve been really taken aback and grateful for the enthusiasm that has been surrounding this event so far.”
The fundraiser will feature 82 pieces by 80 artists, all of whom have donated their work to the event, ensuring all profits go to Terrain.
“One of the things that we’re trying to be really cognizant of is that we’re only asking artists who have some sort of relationship with Terrain, so Terrain has supported them in some way,” Ewing said. “It’s this synergistic exchange, and there’s reciprocity in that exchange versus us blindly asking any artists in this community to donate work.”
Each piece is $200. The pieces in this year’s fundraiser won’t be revealed until doors open, but Ewing said in past years, a majority of the work has been two-dimensional. There is no bidding required at the fundraiser; simply find a piece of work that you love and purchase it.
“We are trying to create and grow the customer base, the patronage of the arts, by creating relationships between artists and art buyers,” Ewing said. “The hope is that people see an artist’s work, they fall in love with that artist’s work and therefore that artist and it’s the beginning of creating a long-term relationship between them, all while also being accessible and equitable and raising money for our organization.”
Ewing said in the past, most of the artwork sold in the first 30 minutes, so patrons should get there early for the best chance of going home with a new piece of art. The event will also feature music from rosethrow, a no-host bar and a chance to check out Terrain’s newest venture, the Annex.
“It’s acting like a retail wing of the gallery where we have around 30 artists who are selling out of there year round,” Ewing said. “The concept there is immediate gratification. You buy artwork off the wall.”
The artwork in the Annex will be priced at market rate, not the $200 price of the pieces in the fundraiser.
Outside of the Terrain Gallery fundraiser, art fans can continue to expect monthly exhibits at the gallery, including work from Dustin Brinkman in April and Jiemei Lin in May. Some of the upcoming artists will host a workshop or talk during their time in the gallery, offering another chance to build the artist-patron relationship Ewing hopes this fundraiser will jumpstart.
It’s free for artists to show in the gallery and free for visitors to see the exhibits, something Ewing is proud of. But that brings it all back to how to sustain the sustainers. This fundraiser helps, as does applying for grants and receiving individual donations, but Ewing wants to stress that a monetary donation isn’t the only way someone can support Terrain.
“We always are looking at accessibility and equity so if you can’t financially support us, then you can volunteer or if you can’t volunteer, you can help us spread the word,” Ewing said. “We always want everything we do, even in our fundraising efforts, to be as equitable and as successful as possible.”
An earlier version of this story misstated the cost of running the gallery.
Unleashing the power of career readiness programs
As the new school year begins, local juniors and seniors in the Greater Spokane area find themselves standing at the precipice of their future.
We couldn’t find any results matching your search.
Please try using other words for your search or explore other sections of the website for relevant information.
We’re sorry, we are currently experiencing some issues, please try again later.
Our team is working diligently to resolve the issue. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
News & Insights

‘Load Up,’ Says Raymond James About These 2 Buy-rated Stocks
March 31, 2024 — 05:26 am EDT
Written by Michael Marcus for TipRanks ->
The good feelings engendered by last year’s bull market are still with us, and are helping to power more gains. Since their October low points, the S&P 500 is up 27.5% and the NASDAQ is up 29.5%. The gains put stocks well into bull market territory, and mark the latest installment of a secular bullish trend that has lasted more than a decade so far.
It’s clearly a positive environment for stock investors; the chief difficulty being how to locate the right stocks to buy. Last year, the gains were driven by Big Tech corporations. This year, those gains are finding a broader footing. In a recent note, Raymond James’ Chief Investment Officer Larry Adam looks at the current market strength and adds some context: “The S&P 500 is off its best start to the year since 2019, climbing ~10% and hitting its 20th record high YTD… Resilient economic data, strong earnings (2024 earnings have bucked the typical downward revision trend), AI optimism and increased investor optimism have been the key drivers. Historically, a strong start has been a positive signal for the market, with the S&P 500 up an additional ~7% on average the rest of year when Q1 performance is greater than 10%. While we remain optimistic longer term, caution is warranted in the near term.”
While Adam advocates a careful approach right now, that’s not to say there aren’t good opportunities available. Going forward, Raymond James’ analysts are selecting Buy-rated stocks where they see solid potential for gains. The firm advises investors to ‘load up’ now – and we’ve opened up the databanks at TipRanks to get a better picture of two of their picks. Let’s take a closer look.
Weave Communications ( WEAV )
The first stock we’ll look at is Weave Communications. This tech company provides a software platform optimized to streamline the way that small- and mid-sized healthcare businesses locate, contact, and interact with their patients and customers. The company operates in the US healthcare sector, and its platform can support office phone lines, messaging systems, digital forms and online assistants, email marketing and patient scheduling, and data analysis and customer insights.
The company boasts that its platform helps ensure that users – mainly medical and dental clinics – miss fewer phone calls, save work hours, and operate with greater efficiency. Smoother office communications can have a ripple effect into other areas of operations – medical clinics using Weave report better patient compliance with scheduling and billing due to text message reminders, a feature that can be automated through the system.
On the financial front, both revenues and earnings have been trending upwards for the past couple of years. This was clearly visible in the last reported quarter, Q4 2023. Weave showed a top line of $45.7 million, for a year-over-year increase of 21% and beating the forecast by $1.5 million. Like many emerging tech firms, Weave operates at a net loss; in the last quarter of 2023, that loss came to $0.8 million, or 1 cent per share. This was a strong improvement from the 6-cent EPS loss recorded in Q4 2022, and it beat the forecast by two cents per share.
Over the last 12 months, the shares are up by 131% although they have retreated a bit since the print. As such, Raymond James analyst Alexander Sklar thinks investors should take advantage. He writes up an upbeat reaction to the company’s recent earnings and its prospects: “We believe recent momentum in the business will continue in 2024 and the pullback in shares following its 4Q23 report… creates an even more favorable risk/reward setup. Our positive fundamental thesis is centered around the belief that its growth acceleration exiting 2023 can be maintained in 2024 (with a medium-term compounding opportunity) that is not reflected in shares that trade at ~4x our 2024E revenue.”
Getting into some details, Sklar adds his outline of where Weave is going, and how it will benefit investors, saying , “We see several contributors to support higher growth in 2024 including: 1) Higher take rates of its largest bundle (ARPU up); 2) Improved rep tenure/ productivity and growth in reps; 3) A broader lead-gen motion (digital, live events, partners, etc.); 4) A formal focus on large specialty medical vertical (now its 3rd largest customer base); 5) Continued product enhancements (integrations, multi-office functionality, new offerings). With an improving profitability profile, an attractive beat and raise setup, and the potential for a ~20% growth profile to continue into 2024, we believe a Strong Buy rating is warranted.”
That Strong Buy rating is backed by a $15 price target that shows his confidence in a 30.5% upside potential on the one-year time horizon. (To watch Sklar’s track record, click here .)
Overall, WEAV shares get a Moderate Buy rating from the Street consensus, based on 7 recent analyst reviews that include 5 Buys and 2 Holds. The shares are trading for $11.48 and their $14.57 average target price implies a one-year upside of 27%. (See Weave’s stock forecast .)
GoDaddy, Inc. ( GDDY )
Next up, GoDaddy, is an internet company, a firm offering web domain and hosting services. GoDaddy is based in Arizona, and its services include web hosting and domain registration for a wide-ranging customer base of private individuals and corporate entities. The company stands among the top web hosting firms by market share and hosts more than 84 million domain names with over 21 million entrepreneurs among its customer base.
Among the services domain registrants can access are free installs for up to 150 apps, an easy-to-use management dashboard, 24/7 customer service, and a guarantee of 99.9% uptime reliability. The company will give its customers one free domain name during the first year of the paid hosting subscription, and plenty of choices in monthly subscription service and payment options. It’s all designed to make GoDaddy the one-stop shop for web domain hosting.
The online world is changing rapidly, as AI makes inroads into virtually every digital activity – and GoDaddy is adapting to the new circumstances. The company has introduced a suite of tools, GoDaddy Airo, designed to harness AI technology and capabilities for website domain maintenance, site construction, email marketing, and more. The tools aim to make AI-based automation available to site builders and managers, in the interest of streamlining online operations.
Turning to the financials, we find that GoDaddy’s revenue has been consistently strong for the past several years, at or near $1 billion per quarter. In the last quarterly report, covering 4Q23, the company reported a result in line with expectations, at $1.1 billion for the period. This figure was up nearly 6% year-over-year. The bottom-line result, GoDaddy’s $7.85 GAAP EPS, came in $6.80 above the forecast – this was reportedly due to a one-time ‘release of valuation allowance on U.S. and state deferred tax assets.’
In other metrics, the company reported total bookings, a measure of future business, at $1.1 billion, up 7% y/y, and a free cash flow of $305.1 million, up 51% y/y.
This company’s solid performance and smart moves into AI have caught the attention of Josh Beck, one of Raymond James’ 5-star analysts. Beck, who ranks in the top 2% of Street stock pros, writes of GoDaddy, “Our ‘SMB GenAI Tailwind’ thesis is based on GoDaddy leveraging the innovative Airo GenAI stack to effectively lower adoption hurdles from products beyond core domains such as logo creation, presence, commerce/GPV that should lead to a rising mix of 2+ product customers (>50% currently). Over time, we believe GoDaddy could effectively ‘outsource’ customer care expertise and deep data set (20M+ customers and 14M interactions including a unique Conversations corpus across SMB email, messages, and social media accounts) to produce a more autonomous SMB agent to help respond to customer requests and generate a meaningfully autonomous SaaS component.”
Quantifying his stance, Beck rates the shares as a Strong Buy, with a $150 price target that implies a solid upside of 26% for the next 12 months. (To watch Beck’s track record, click here .)
This stock also gets a Moderate Buy rating from the Street’s consensus, resting it on 16 analyst recommendations that break down to 11 Buys and 5 Holds. The current trading price of $118.68 and the average target price of $130.64 together indicate a 10% share gain for the year ahead. (See GoDaddy’s stock forecast .)
To find good ideas for stocks trading at attractive valuations, visit TipRanks’ Best Stocks to Buy , a tool that unites all of TipRanks’ equity insights.
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the featured analysts. The content is intended to be used for informational purposes only. It is very important to do your own analysis before making any investment .
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.

Stocks mentioned
More related articles.
This data feed is not available at this time.
Sign up for the TradeTalks newsletter to receive your weekly dose of trading news, trends and education. Delivered Wednesdays.
To add symbols:
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to My Quotes by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
- Copy and paste multiple symbols separated by spaces.
These symbols will be available throughout the site during your session.
Your symbols have been updated
Edit watchlist.
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to Watchlist by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
Opt in to Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio is supported by our partner TipRanks. By connecting my portfolio to TipRanks Smart Portfolio I agree to their Terms of Use .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At this point in our Thesis nootropics review, it's time to turn to what customers are saying. So, we sourced testimonials from the brand's website, Reddit, and ZenMasterWellness. And spoiler alert, the Thesis nootropics reviews we came across have nothing but good things to say. On takethesis.com, the brand earns 4.4/5 stars out of 7,956 ...
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic.
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others, "standing on the shoulders of giants", as Newton put it.The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.. Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure ...
The word "literature review" can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature - i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or ...
The key here is to focus first on the literature relevant to the puzzle. In this example, the tokenism literature sets up a puzzle derived from a theory and contradictory empirical evidence. Let's consider what each of these means... The literature(s) from which you develop the theoretical/empirical puzzle that drives your research question.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
A well-conducted literature review is an essential component of research because it helps to establish the research context, justify the need for the study, and guide the development of research questions or hypotheses. The literature review of your thesis/dissertation is a very significant part of your paper.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
How To Structure Your Literature Review. Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components - an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Let's take a closer look at each of these. 1: The Introduction Section
3. Evaluate and select literature. 4. Analyze the literature. 5. Plan the structure of your literature review. 6. Write your literature review. Other resources to help you write a successful literature review.
These steps includ e; a) critical reading and note-taking, b) writing. a s ummary of the reviewed literature, c) organization of literature review, and d) the use of a synthesis matrix. The last ...
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
When you begin to write your PhD literature review, it's important to have a clear idea of its outline. Roughly speaking, the literature review structure should: Introduce your topic and explain its significance. Evaluate the existing literature with reference to your thesis. Give a conclusion that considers the implications of your research ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work.It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own. The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.; A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the ...
When you are working on your graduate thesis, one of the core components needed to make it complete is a literature review. Here is a demonstration of the main benefits of carrying a literature review for your thesis. Allows you to show how familiar you are with the topic of study. Offers you an opportunity to develop a comprehensive methodology.
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Beginning in fall 2021, faculty advisors will be asked to review and approve dissertations, theses, and reports in Digital Commons. This will replace the Approval form, and will allow faculty to see the work their student has submitted and be notified when it is published. This process is similar to reviewing a journal article. When . . .
example: thesis_rol_v1_22a pril or thesis_rol_v3_a er . review by guide. Figure 1: ... The role of the critical review article in alleviating information overload. Annu Rev 2011. [Accessed 2022 ...
If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you've come to the right place.. In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction.We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template.
Thesis Nootropics Review? Hi Everyone. Been getting these ads for Thesis Nootropics, a company that offers "personalized nootropics". Somewhat appealing to me since I really don't know where to start/what might work for me. Curious if anyone has used this company and your thoughts? Archived post. New comments cannot be posted and votes ...
Thesis/Project Preliminary Format Review. With the help of our Graduate Student Assistants, the Graduate Resource Center will now begin taking appointments and walk-ins for preliminary formatting review for projects and theses. During these sessions, Graduate Student Assistants will help walk you through the process of formatting your project ...
The thesis analyzes four car-centric suburbs in California's Bay Area, where the shortage of affordable housing is especially stark. The region is the birthplace of mainstream American environmentalism and has a history of resistance to multifamily housing. But it's also a place where lawmakers are passing leading-edge legislation to ...
Mentioning "dance" in an academic setting may feel out of place, almost as if the studio and classroom are incubators for disparate skills and experiences. However, the scholarly nature of the performing arts is found within the technique, movement quality, and performance intention. While others put pen to paper, dancers put experience and vulnerability to Marley floors.
Summary. Viatris Inc. stock has risen by 26.7% since my November 2023 bullish call, outperforming the S&P 500 Index. It's time to update my thesis - read on. Although net sales declined (as did ...
A&E; Art; Terrain Gallery fundraiser offers community chance to fund art, artists March 28, 2024 Updated Fri., March 29, 2024 at 12:20 p.m. Terrain Gallery executive director and co-founder Ginger ...
Going forward, Raymond James' analysts are selecting Buy-rated stocks where they see solid potential for gains. The firm advises investors to 'load up' now - and we've opened up the ...
301 Moved Permanently. openresty