Speech Writing
Speech Format

Understanding the Speech Format - Detailed Guide & Examples
People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
How to Write a Special Occasion Speech: Types, Tips, and Examples
Introduction Speech - A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Write the Best Acceptance Speech for Your Audience?
Presentation Speech - An Ultimate Writing Guide
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech - Writing Tips & Examples
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting the Perfect Graduation Speech: A Guide with Examples
Are you looking for the optimal speech format that will help you leave a lasting impact on your listeners?
Well, some speakers can’t deliver a speech without a well-written script in their hand. Whereas, some avoid using a written speech because they believe that reading makes them feel uncomfortable and stiff.
A successful speech depends on both careful preparation and effective presentation. Hence, speech writing is very important.
Writing a speech should not be a nail-biting or anxiety-provoking experience. If you learn the basic speech format, you can excel in speech writing !
Having said that, this step-by-step guide on speech format can make the nerve-racking task of speech delivery simple and straightforward.
Let’s get started!
- 1. How to Write a Speech Format?
- 2. How to Rehearse a Speech
- 3. Speech Format Examples for Different Academic Levels
- 4. Speech Format Examples for Different Occasions
How to Write a Speech Format?
Speech writing gives you a chance to leave an everlasting and meaningful impression on the audience. You might have always believed that you are not good with words. And speech writing may bring you out in cold sweats, but this is different.
Let’s see how one should write a great speech that impresses the audience.
1. Decide the Purpose of Your Speech
To understand the purpose of your speech, consider these queries:
- What is the main motive behind it?
- Is it to inform or persuade? Is it to entertain or demonstrate? Or is it a combination of these?
- What do you want to achieve with your speech?
- Do you want your audience to act upon something, or do you want to convince them to believe what you are saying?
Your answer to all of these questions will decide the organizational structure, type of speech, tone, and content as well.
Identify your listeners and decide which type of speech is suitable for your targeted audience. If you are going to deliver a speech at a wedding, write a special occasion speech . Similarly, if your motive is to persuade the audience, you’ll have to write a persuasive speech .
2. Choose a Speech Topic
Choose an effective speech topic that catches the audience’s attention immediately. A good speech topic is your first step to impress the audience.
You can select any topic according to the type of speech you need to deliver. Pick a motivational speech topic if you want to get the audience to act upon your message. If you want to make your audience laugh, decide on an entertaining speech topic .
3. Do the Research
Conduct thorough research on your particular subject to collect relevant material. Finding credible and updated material is crucial, as good research is the backbone of sound speech.
Before you write your speech, you need to know what your speech will be about exactly. And how long it needs to be, i.e., 5 minutes or 30 minutes long. So, always collect the data according to the time limit.
For a 5-minute speech, you only need a brief material. Your speech should revolve around the central idea. If your speech is 30 minutes long, you need to collect enough details to cover in 30 minutes.
4. Craft the Outline
Now that you have the material for your speech, craft an outline to organize your material. Drafting an outline at first always saves precious time.
Write keywords in the outline that prompt you to remember what you’ll include in your speech. Having an outline for your speech is like having a road map that guides you throughout the speech delivery.
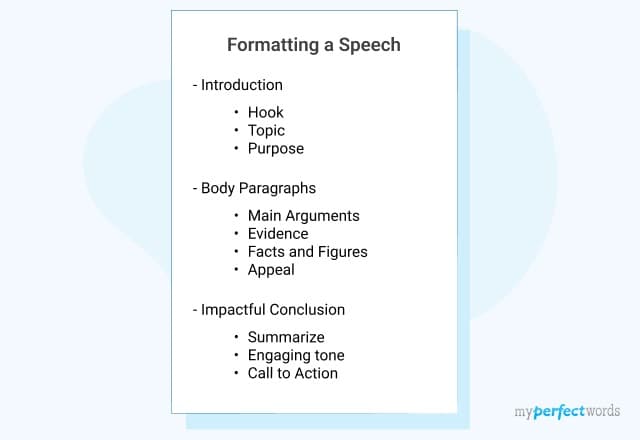
As mentioned before, the basic speech outline format consists of three things:
- Introduction
Here is a speech outline template that you can use while crafting an outline for your speech.
Speech Format Outline
5. Write an Effective Introduction
An introduction will give a brief overview of what you are going to tell your audience. Here are the five things that you should include in your introduction paragraph.
- Greetings and Your Introduction
Decide how you are going to greet your audience and how you will introduce yourself to the audience. You can start with a fact, a quotation, posing a rhetorical question, or even with one-liner humor.
Keep in mind that whatever you start with, must be related to your topic and suitable for your audience.
- A Precise Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a brief summary of your speech, and it provides the main message of your speech.
- Your Credibility
You need to establish your credibility to make your speech effective. Cite your expertise and qualification that gives you the right to speak about your speech topic.
- Brief Overview
Briefly tell your audience what you are going to share so that they have an idea of what to expect from your speech.
- Benefits of Listening to Your Speech
Convince your audience why they should listen to you. Tell them what's in your speech for them and why should they pay attention. Give them reasons and be specific about the benefits.
6. Write a Detailed Body
The body is where you write the details of what you want to share with your audience. Generally, the body section has three main points, but it can have more than 3 points.
It is always a good idea to be specific and inform the audience of only essential things.
Quite frankly, if you introduce the audience to an abundance of ideas or topics, they might not remember them all! To leave a lasting impact, decide on 2 or 3 ideas, so the crowd remembers them all!
While crafting the body section of your speech, you should keep the following things in mind:
- Choose the three strongest points that describe your topic efficiently.
- Always provide supporting examples. Make sure that the evidence you provide matches the type of speech you are going to write.
- Use transition phrases to make a logical connection between the details.
- Use visual aids like images, graphs, or tables to help your audience understand your topic better.
- Keep the sentence structures in check. Make sure there are no grammatical errors and follow an engaging tone.
7. Craft a Compelling Conclusion
The final section is the conclusion that sums up the whole speech. Here is how you can write an effective speech conclusion that summarizes and draws all the details together:
- Summarize all the main points
- Restate the thesis statement to reinforce your message
- Remind the audience about the benefits they’ll get if they carry out what you have proposed.
- Provide a call to action at the end of your speech
8. Do the Formatting
After the final draft, the next step is editing and formatting. Read your speech aloud and check the flow and organization of the information. Refine the draft by removing unnecessary things and correcting any grammatical mistakes.
Proofread your speech to make sure it contains all the vital information. Correct the structure if needed, and ensure that your speech is free from all kinds of mistakes. Revise your speech as many times as possible.
How to Rehearse a Speech
Rehearsal plays an important role in delivering an effective presentation. You need to practice a lot to be confident with your speech and deliver it perfectly. Here is how you can do it efficiently:
- Set the time on the stopwatch that is going to be allocated to you. You need to finish your speech within the allocated time.
- Read your speech out loud. Hearing yourself will help you familiarize yourself with the flow of your speech quickly. Remove or change the phrases that sound awkward, and fix the organization of information.
- Your habitual unconscious gestures
- Irregular breathing because of long sentences
- Taking breaks or pauses at the wrong places
- The body posture
- Raising or dropping the voice
- Repeated fillers, i.e., umm, err, uhh, etc
- Lack of smiling and eye contact
- Tone variation
- If you experience any problems, stop and fix the problem before starting again from where you left off.
- Make notes of where you need to remember to do something. It will help you improve your speech delivery.
- If possible, do a proper dress rehearsal at the actual venue in front of a bunch of friends. It will help you to get comfortable with the dress, stage, and actual presentation situation.
If you’ve plenty of time, rehearse at least three times or more, before the final presentation. The more you do the rehearsals, the more you build up your confidence and the easier it becomes to deliver your speech.
Now, let’s take a look at some comprehensive speech format examples for multiple academic levels and various occasions.
Speech Format Examples for Different Academic Levels
Follow these speech format samples to learn how to properly format a speech and easily get through the speech writing process.
Speech Format for Class 8
Speech Format for Class 9
Speech Format for Class 10
Speech Format for Class 11
Speech Format for Class 12
O Levels Speech Format
Speech Format Examples for Different Occasions
Best Man Speech Format
College Speech Format
Debate Speech Format
Impromptu Speech Format
Formal Speech Format
Welcome Speech Format in English
Persuasive Speech Format
Public Speech Format
Informative Speech Format
Extemporaneous Speech Format
Want to see some outstanding speech examples ? Head over to our detailed blog!
Wrapping it up, if you came up with a speech after following the guide, you should be able to grab the attention of the audience within seconds!
This guide contains all the essentials to crafting a compelling speech and presenting it in a meaningful way!
However, if you still need some help, you can hire a professional writer. Our speech writing service provides top-notch speeches at cheap prices.
Order now and get expertly crafted speeches to impress your audience. Hire our reliable essay writing service and let our experts handle your speech writing needs!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


Formatting a speech for smooth delivery: 12 steps
Oct 17, 2013

This time of year is usually speechwriting season for me, and 2013 has been no exception. I really enjoy every step of the speechwriting process including the very last step, the icing on the cake: formatting. Once I’m completely happy with a speech (and so is my client and the nonprofit leader delivering the remarks), it’s time to format the document in a way that supports smooth and successful delivery.
If the remarks you have written are anything over five minutes (and sometimes, even if under), there is a good chance your speaker will need to read from notes. These points will help ensure that they don’t look like they are doing so!
Here are twelve steps to formatting a speech for smooth delivery:
1. Use 16-20 pt font: This will help ensure the remarks are legible from the podium.
2. Double-space the document: F or readability and to help make the speech easy to skim through.
3. Use sub-headings: Include subheadings in square brackets to guide your speaker through the structure of the speech. Knowing the subject area of a sub-section will help the speaker to understand the themes and structure you have pulled together as well as possibly adjust pace, tone and body language to suit the subject matter.
4. Create extra paragraph breaks: Along with sub-headings, put a little extra breathing room around certain paragraphs to encourage pauses and to indicate shifts in topic.
5. Italicize, bold and underline key words or phrases: Help your reader to find points of emphasis by highlighting them.
6. Include incomplete sentences: Writing and formatting for speaking is very different, so you’ll have to be willing to break more than one grammar rule. Break sentences into fragments to slow down delivery and give the speaker time for meaningful pauses.
7. Use ellipses to highlight pauses: You will inevitably come across sentences that are just too long to deliver in one straight go…break them up and give your speaker room to breathe using ellipses.
8. Insert bullets: Visually guide and alert your speaker that a list is coming up within a speech by breaking it into bullets.
9. Use contractions: There will be exceptions, but most speakers will sound more natural when delivering remarks in which contractions are used liberally.
10. Insert pages numbers: The last thing you want is for the pages to get out of order and not be easily reassembled!
11. Remove broken sentences or paragraphs at the bottom of pages: Use page breaks to prevent your speaker from having to turn pages mid-sentence. Word of caution: if you won’t be printing the speech yourself, make sure that you are using a widely available font like Arial. These page breaks won’t translate if the person printing doesn’t have the same font you’ve used on their machine.
12. Paperclip, don’t staple: This point refers, of course, to the physical, printed document. Make sure to use paperclips to collate the speech so that it’s easy for your speaker to move through the pages in a way that works for him or her.
Usually, the easiest way to incorporate this formatting is to read the finished speech aloud and format changes as you go along. Once you’ve done that and if it’s an option, have the speaker read the speech aloud for you in order to fine tune further.
How do you format speeches? Do you have any tips or tricks to share?
Related Posts
![speech paper format Internal copy review pet peeves – and help with getting useful feedback [includes swipe copy]](https://moflow.ca/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/sharable-boxes-3-400x250.png)
Internal copy review pet peeves – and help with getting useful feedback [includes swipe copy]
Feb 19, 2021
When you request internal copy review, how often do you get the subject matter guidance and input you’re seeking? How often do you get a mess of unhelpful revisions that you have to sort through? Last year, I worked on a big copy project for a client at a large,...

Website copywriting package for nonprofit organizations
Jan 12, 2021
Are you ready for strong web copy that works for your nonprofit? Learn about my “Core content web copy package” for nonprofit organizations. And then contact me to get started.

Building a copywriting project timeline: three steps you can’t forget
May 28, 2020
Are you building a project plan for a copywriting assignment? Do you know how to estimate how long it will take? Be careful - especially when you're assigning the work to someone else - not to underestimate your copywriting project timeline. For example, if you need...
Pin It on Pinterest
- Print Friendly
Speech And Debate
Speech Writing
Last updated on: Feb 9, 2023
How to Write a Speech - Outline With Example
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Sep 8, 2020

Giving a speech for a class, event or work can be nerve-wracking. However, writing an effective speech can boost your confidence level.
A speech is an effective medium to communicate your message and speech writing is a skill that has its advantages even if you are a student or a professional.
With careful planning and paying attention to small details, you can write a speech that will inform, persuade, entertain or motivate the people you are writing for.
If this is your first speech. Take all the time you need.
Like other skills, you can learn speech writing too.
Give yourself enough time to write and practice it several times for the best possible results.

On this Page
You have a message that you want people to hear or you are preparing a speech for a particular situation such as a commemorative speech.
No matter what the case, it is important to ensure that the speech is well structured or else you will fail to deliver your effective message. And you don’t want that, do you?
You can also explore our complete guide to write a commemorative speech . Make sure to give the article a thorough read.
How to Create a Speech Outline?
Want to write a speech your audience will remember? A speech outline is a thing you should start with.
‘How to write a speech outline?’
A speech outline is very important in helping you sound more authoritative and in control. As you write your speech outline you will have to focus on how you will introduce yourself, your topic, and the points that you will be going to cover.
A speech outline will save a lot of your time and will help you organize your thoughts. It will make sure the speech is following a proper structure and format.
Before you start writing your own speech you need to know:
- WHO you are writing the speech for
- WHAT the speech will be going to cover
- HOW long it needs to be e.g if it is a 5-minute speech (then how many words in a 5-minute speech)
These speech tips will help you get on the right track from the start. Here is an example of how you can craft a speech outline.
Preparation
- Choose your topic and the main points that your speech will cover. Know your audience and get to know what they are looking for. Pay attention to their needs
- Define the purpose of the speech and properly organize it
Introduction
- A strong statement to grab the reader’s attention
- Refine the thesis statement
- State something that establishes credibility
- Provide your main idea and include some supporting statements.
- Examples and further details (if needed)
- Summarize the main points of the speech
- Closing statement
- Call to action

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Write an Effective Speech?
‘How to write a graduation speech?’
‘How to write a speech for school?’
‘How to write a speech about yourself?’
Get your answers in the below sections.
Just like essays, the speech also follows three sections: Introduction, the main body, and conclusion.
However, unlike essays, a speech must be written to be heard as opposed to just being read. It is important to write a speech in a way that can grab the reader’s attention and helps in painting a mental image.
It is the opening statement of a speech. It is important to know how to start a speech that can grab the attention of the audience.
‘How to write a speech introduction?’
It should include a hook-grabber statement about your topic. It should end with a strong transition from a big idea of the introduction to the main body of the essay. Some great ways to begin your speech are, to begin with, a rhetorical question, a quote, or another strong statement.
Make sure the introduction is not more than one paragraph. This will ensure you do not spend much time on the background before getting to the main idea of the topic.
The introduction is a great chance to make sure your opening is memorable as this is the point when your audience will make up their mind about you.
The Main body
The majority of the speech should be spent presenting your thesis statement and supporting ideas in an organized way.
Avoid rambling as it will immediately lose your audience’s attention. No need to share everything, instead pick some points and stick to them throughout your speech.
Organize your points in a logical manner so they support and build on each other. Add as many points as needed to support the overall message of your speech.
State each point clearly and provide all the required information, facts, statistics, and evidence, to clarify each of your points.
It is a good idea to include your personal experiences to make your speech more interesting and memorable.
Another important thing to be kept in mind is the use of transition. The purpose of adding transition words is to improve the overall flow of the information and help the reader to understand the speech structure. Words like next, then, after, before, at that moment, etc. are the most commonly used transition words to make the whole writing less choppy and more interesting.
The conclusion should restate and summarize all the main points of the speech. Because the audience will most likely remember what they have heard last. Beautifully wrap up the whole speech and give something for the audience to think about.
For an extra element, close your speech by restating the introduction statement so it feels like a complete package.
A good approach to conclude your speech is to introduce a call to action. Encourage your audience to participate in the solution to the problem that you are discussing. Give your audience some direction on how they can participate.
Practice and more practice is key to a great speech so it is important that you read your speech and listen to yourself. When writing, take care of the required length also.
Speech Topics - Engaging Topics to Choose From
You feel relief when your teacher says you are free to choose your speech topic. Feel free to write about anything you want. The problem is students still feel stuck in choosing an effective speech topic. If you are one of them, here is a list of the best speech ideas to help you get through the process.
- What role do cats play in human’s lives
- How to improve communication disorders
- World’s fastest-growing country
- Today’s world pollution rate
- How to improve interpersonal skills
- Are paper books better than e-books
- Should the death penalty be abolished
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote
- Should voting be made compulsory
- Is it better to live together before marriage
These are some of the interesting topics that you can consider. However, if you are still not sure about the topic of your speech, you can explore our article on informative speech topics and pick any of your choices.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Speech Example
Stressing over on how to write a good speech? Speech examples are sure to be your best friend for effective speech writing and its effortless delivery.
Here is a sample speech example to help you get through your own speech writing process. Explore this example and get the answer on how to give a good speech.
Get Professional Help for Your Speech
If you are good at public speaking but lack writing skills or you do not have enough time to follow the mentioned points and write a speech, don't worry.
You can always contact us at 5StarEssays.com.
We have a highly qualified and amazing team of expert writers who can help you if you want to buy speeches online with high-quality content.
Contact our " write my essay " service with your requirements. Our essay writer will provide you with quality material that your audience will remember for a long time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best introduction for a speech.
The best way to open a speech’s introduction is, to begin with, a story. Tell an inspiring story to your audience and connect it with your personal narrative.
What is the first step of speech writing?
The first step of writing a speech is to choose a topic. Choosing a good topic is important to have an engaging and great speech.
What are the five steps in speech writing?
Here are the five steps involved in writing a speech.
- Choose a topic.
- Investigate your audience.
- Built an outline.
- Rehearse the speech.
- Revise and finalize.
What are the types of speech delivery?
Here are the types of speech delivery.
- Extemporaneous
What are the two P’s required for good speech delivery?
The two P’s required for proper speech delivery are Preparation and Practice.

Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Informative Speech Topics - Interesting Ideas By Experts

- Commemorative Speech: Guide to Craft an Engaging Speech

- Persuasive Speech Topics - 150+ Topics for Students

- 50+ Demonstration Speech Ideas for Your Next Great Speech

- Impromptu Speech Topics - 150+ Interesting Ideas

- Debate Topics (2024) - Top 200+ Compelling Topics

- 100+ Motivational Speech Topics for an Inspirational Speech

- Extemporaneous Speech - How to Write One Successfully?

- Graduation Speech - Write Your Best Graduation Speech

People Also Read
- speech writing
- argumentative essay outline
- writing an analytical essay
- how to write a bio
- solve math problems
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
- The Buckley Experience
- Our Clients
- Registration
- Finding Our School
- On-Site Training
- Writing and Organizing
- Business Etiquette
- Private Coaching
- Virtual Training
- Course Calendar
- Media Training
- Writing & Editing
- Presentation Development
- Company Retreats
- Video Reviews
September 7, 2018
How to: Format a speech text

Some speakers avoid using written scripts, because they say "reading" makes them feel stiff or uncomfortable.
Others rely on having the speech in front of them word for word.
And some situations require that a speaker use a script—because precise language is important or because the speech will live on, part of a permanent record.
Wherever you fall in this picture, you can be more successful with a written script by doing something incredibly simple and obvious: formatting the words on the page for easy reading.
Here’s how:

1. Make the font size larger
This seems obvious, but you might be surprised to learn that even veteran speakers don’t do this.
Go up to 14 point, to start—then don’t be shy about making it even larger if that makes it easier for you to read.

2. Break lines where you’d naturally pause, rather than have large blocks of continuous text.
The goal when delivering from a text is that you can look down, grab the line, then look up and deliver it, holding eye contact with the audience through the last word.
Speakers are tempted to look down on that last word, though, because they’re afraid they won’t be able to find the next word.
By breaking the lines deliberately, where you’d naturally pause, you make it easy to get through the final word, then look back to grab the next line or phrase where a pause would naturally occur.
So don’t default to running paragraphs. Use the return key to break lines where it makes the most sense to you.

3. Bold key words, not for emphasis, but to prompt your memory.
As you practice and become more familiar with your script, you’ll find this especially helpful. Those key words will prompt you to remember the entire line.
We do not use bold type to indicate emphasis and suggest you might mark up your text with a pen or highlighters to indicate HOW you want to deliver. But that’s just our suggestion. Whatever makes the most sense to you is what you should do.

4. Add extra space and insert page breaks to cue pace and timing.
Extra space can remind you that you’ve completed one thought and should pause for a beat before moving on to the next one.
Managing page breaks lets you move from page to page naturally and not have a page change in the middle of an idea or sentence.
And be sure to number your pages!
Other tips and tricks that work for some speakers:
- Only use the top two-thirds of the page. Some speakers feel this keeps them from having to look so far down to see the script, thus improving eye contact.
- Print your script on card stock instead of paper, so it’s easier to handle.
- Put your script in a notebook and arrange pages so that you can see two pages at one time (book style) before you have to flip the page.
- Keep pages loose and slide them across the top of the lectern, rather than turning them, so the pages are less noticeable.
The only thing that matters in all of this is what works for you. Your preferences will evolve, and trivial as it might seem, these experiments are worth conducting. We’ve seen speakers dramatically improve their delivery, instantly, when we change the way we format their scripts.
- Executive Seminar
- Open Enrollment
Share this article
Buckley Speaking
Our online magazine with tips, news, and instruction for you

- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- How to outline a speech
Sample speech outline template
Get a printable. Learn how to outline a speech effectively.
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 02-20-2023
There's a printable sample speech outline template below for you to download and use.
Why? Because a well-completed outline becomes the backbone of your speech. You'll use it to guide you logically, and carefully, through ALL the aspects you need to consider before you actually write the speech itself.
It will help you clarify what material you want to cover to fit your audience, and speech purpose, as well as help to effectively organize it.
What you'll find on this page:
- t he reasons for using a speech outline
- how to outline a speech : the 4 essentials steps involved in writing an outline - detailed sequential help, with examples, covering: 1. choosing a topic, 2. audience analysis, 3. choosing the best organizational pattern to fit your speech purpose, 4. what to put in each part of your speech: introduction, body and conclusion
- a printable speech outline template to download
- links to 2 completed examples of speech outlines (a demonstration and a persuasive speech. Both with printable outlines to download.)
- a link to 7 completed examples of impromptu speech outlines , each with printable speech outline templates
- links to more resources for preparing an effective speech
Why bother writing a speech outline?
Because completing a speech outline is the first vital step toward preparing a successful speech.

It is often overlooked in a misguided attempt to get on with what is considered the real work: writing the speech, or the words you're going to say.
Despite what many people think, time spent completing an outline is not wasted. Instead, it helps you save it. A nd sidestep any anxiety caused by inadequate preparation.
The process might appear daunting and horrifically time consuming but prepare a speech outline all the same.☺
What you'll learn about speech structure, matching content to your speech purpose and your audience's needs will pay you back over and over again. I promise you, having an outline will make giving a speech easier and less stressful.
How to best use this page
Read the page all the way through to familiarize yourself with the terms and the process. When you're done, click the link at the foot of the page to download and print the blank sample speech outline template for your own use.
How to outline a speech: 4 essential steps
The process of outlining a speech is broken down into 4 essential steps.
(Click a heading to find out more about each one)
- deciding on your topic
- considering the audience and refining your topic to suit them
- deciding on the purpose of the speech
- choosing an organizational method to support your speech purpose
- opening greeting and attention getter
- defining your thesis statement (a summary of what your speech is about)
- establishing your credibility
- an overview and the benefit to the audience
- transition or link between introduction and body
- main ideas with supporting ideas
- examples and details
- summary of main points
- closer or call to action
Remember this old saying?
First: tell them what you're going to tell them. Second: tell them. Third: tell them what you told them.
A simple, or basic, speech outline follows that advice.
- 'Tell them what you're going to tell them' becomes your introduction
- 'Tell them' forms the body
- 'Tell them what you told them' is your conclusion
Step 1 - Preparation for writing a speech outline
You need to complete this step before you do anything else. It is made up of five smaller steps, each of them an important part of the overall process. The decisions you make at this point will have a major impact on the final outcome of your speech.
By the time you are finished step 1 you will have:
- decided on your topic
- analyzed your audience
- refined your topic to meet the needs of your audience
- decided on the specific purpose of your speech
- chosen the best fitting of six organizational patterns to use - one matching your purpose and your material

Start with choosing a topic
The place to begin is deciding what you are going to talk about.
For example, if you are a realtor (real estate agent) who has been asked to talk to a suburban community group residential real estate seems like a good logical topic to pick.
(If you don't have a topic in mind, go to speech topics . You'll find 100s of them ordered by speech type and theme.)
Put yourself to one side & focus on your audience
However, before you make a final decision considering more closely who will be listening to you makes better sense than assuming whatever you come up with will be right!
How do you really know what aspects of your topic are best suited to meet your audience's needs? Or what would be of real benefit for them to hear about?
The scope of the topic 'residential real estate' is huge.
Your speech could cover any number of sub-topics like: financial advice for first home buyers, how to thoroughly check a house before purchase, the rise of mortgagee default sales, the collapse of property development schemes, how to purchase properties for makeovers...
Analyze your audience
So before you settle on the exact topic of your speech analyze your audience .
Without analysis you are 'guessing' what would be interesting and relevant for them to hear.
Refine your topic
Using what you found out about your audience, decide on an aspect of your topic that will be of benefit to them and the angle you will take on it. Take care with this. One size does not fit all!
For example a speech on housing affordability which includes a step by step plan toward buying a first home will likely interest an audience of youngish, (late 20s- early 40s), people with steady professional incomes.
But for another audience, (e.g. one that is older, less financially secure, or younger and not ready to consider settling yet...), it could be completely inappropriate.
Minimize the risk of getting it wrong by finding out as much as you can about your audience.
Deciding on the purpose of your speech
What is the purpose of this speech? Why are you giving it?
Is it to persuade or inform? Is it to demonstrate, entertain, or welcome? Or is it a combination of these?
What do you want your speech to achieve? Is there a particular action you want people to take as a result of listening to you?
Your answers to all of these questions will dictate what organizational pattern you'll use for your speech, its content and tone.
Return to Top
Choosing an organizational pattern or method

There are 6 basic organizational patterns or methods of arranging the body (main points) of your material. Choose the one most appropriate for your need.
1. Cause - Effect
Because event 'A' happened, event 'B' occurred.
- Because the driver was speeding, they crashed the car.
- Because of the earthquake, the city was destroyed.
- Because the minimum wage is low, families can not afford good health care.
2. Problem - Solution
The problem is 'X'. The answer is 'Y'.
- The problem is unaffordable housing. The solution is community funded housing complexes.
- The problem is unemployment. The solution is meaningful, sustainable education and employment programs.
- The problem is poor food choices. The solution is practical community outreach programs to teach people about nutrition, food buying, storage and preparation, along side living wages, educational and employment programs.
This pattern suits a broad topic which can be broken down into naturally occurring sub-topics.
- The broad topic is 'Vocal Variety'. Its sub-topics include rate of speech, use of pausing, voice tone, volume, articulation...
- The broad topic is 'Organizational speech patterns'. Sub-topics could be problem-solution, cause- effect, logical...
- The broad topic is 'Residential real estate'. Its sub-topics could include houses for first-home buyers, how to apply for a mortgage, how to select the right neighborhood to buy in, the impact of high-density housing...
4. Spatial or geographic
Use this pattern for topics dealing with physical spaces.
- The 10 most popular tourist attractions in New Zealand.
- The European migration patterns of the 19th century.
- The population shift from country to town in USA.
5. Time or chronological/sequential
These are either historical topics or demonstration speeches. The foundation of both is an ordered sequence of events.
For example:
- The history of women's suffrage in USA, the abolition of slavery
- How to bake a cake, how to mend a puncture in a bicycle tire, or how to knot a tie
6. Advantage - disadvantage
Use this pattern to examine the range of positive and negative aspects of an idea or event.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of private schooling?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of lowering the voting age?
- What is good about supporting local industry? What is negative about supporting local industry?
Step Two - Outlining the introduction

The 5 parts of preparing an introduction
1. greeting & attention getter.
How are you going to greet your audience, grab their attention and compel them to listen?
You could use a rhetorical question, a startling statistic, a quotation or a humorous one-liner. To be effective it must be related to your topic and apt for your audience.
- Rhetorical question How many of you really are more afraid of public speaking than death?
- A startling statistic Apparently in USA 75% of the population experiences public speaking anxiety. Some just a little. And some a lot.
- A quotation Mark Twain famously said, there are only two types of speakers in the world: the nervous and the liars.
- Humorous Speaker of United States House of Representatives, Nancy Pelosi set a record for the longest speech on the House floor: 8 hours and 7 minutes. Relax. I only plan on taking 15 minutes of your valuable time. * * Be careful with humor. It will only work if it's appropriate; that is fitting for the occasion, and understood by the majority of your audience. For more about Nancy's record: Nancy Pelosi's all-day marathon speech sets record as longest continuous speech since at least 1909.
For more on effective speech openings see: How to write a speech introduction - 12 of the best ways to start a speech
2. Thesis statement
This is a short summary of your speech topic and your point of view or angle.
Example:
Green politics is no longer a fanciful fringe fad. It is a necessity.
3. Credibility
This segment establishes your right to speak on the topic. It cites your qualification or expertise.
Using myself as an example, I can speak about preparing speeches because I've written many over the past twenty or so years. Prior to becoming a professional speech writer , I taught high school level English and drama and I also belonged to the global public speaking club Toastmasters for a long time.
4. Summative overview
This is a brief outline of the main points you are going to cover.
Today I am going to share with you three effective ways to lessen public speaking fear.
The first and second cover aspects of preparation: writing and rehearsal or practice: actually doing the work, rather than being frightened of it. ☺ The third is about the benefits of public speaking.
5. Benefit(s)
What's in your speech for your audience? Why will they want to hear what you've got to tell them? Be specific. Tell them.
When you make a decision to speak up in public you also gain: confidence, the ability to take on leadership roles, a growing collection of presentation skills like story telling, how to use your voice, the ability to use props well, how to listen, how to craft a speech to meet the needs of specific audiences... In short, you release the potential to become a bigger and better you * .
( * For more see 14 benefits of public speaking .)
Step Three - Outlining the body of your speech
This is the heart of your speech, the place where you lay out what you want to share with your audience.
Generally three main ideas, along with supporting examples, work more effectively than four or five or more. If you have a number of them to choose from, go with your three strongest points. And if one of your final three is noticeably weaker sandwich it between the other two.
If you intend to use visual aids (slides showing graphs, tables or images), or actual props, mark them in too.

Note: If you're unsure about the exact nature of links or transitions and how they work or what they are, you'll find more about them, with examples, on my page how to write a speech
- Main Idea 3 - Supporting ideas - Details and examples - Visuals or props - Transition to...
Step Four - Outlining the conclusion of your speech
There are four parts to preparing an effective conclusion to your speech. Use them to draw together and summarize all the material from your introduction and the body of your speech, and end with a clincher!

- Summary of main ideas These are the main points you covered in the body of your speech.
- Re-statement of thesis statement Use the statement from your introduction to reinforce your message.
- Re-statement of benefit to audience Remind the audience of the benefits they'll receive through carrying out whatever your propose. Again this comes from your introduction.
- Closer, Clincher or Call to Action This is your final sentence. To ensure your speech ends with a bang rather than a whimper check out this page on how to end a speech memorably. You'll find options and examples.
Get your printable sample speech outline template
This is a simple four page PDF of all four steps and their sub- headings with spaces for you to write your notes. Click to download and print your sample speech outline now.

2 completed examples of speech outlines
Use these links to go to a fully completed:
- demonstration speech outline example on how to leave an effective voice mail message (with a free printable sequential demonstration speech outline template)
- persuasive speech topic outline example on overcoming public speaking fear using Monroe's Motivated Sequence (with a free printable MMS persuasive speech outline template)
Example impromptu speech outline patterns
Impromptu speech outline patterns - seven different structural formats, each with completed examples and a free blank printable outline for you to download and use.

Other resources for preparing successful speeches
Planning and writing, rehearsing a speech.
Once you're done with planning, completing your sample speech outline and writing find out how to rehearse. A speech is a live performance. Rehearsal helps you expose and iron out glitches before you find them out the hard way - in front of your audience.
Speech evaluation
And if your speech is being assessed check out this standard speech evaluation form to see what aspects are likely to be judged and how a rating scale works.
- Return to the top
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Speech and Essay Samples
Don’t know where to start? Get inspired by our FREE speech and essay examples .
Use them to get the creative juices flowing . Don’t copy any of these examples! Since these speeches are available for anyone to download, you can never be sure that another student has not used them, and that they will pass plagiarism evaluation tools, such as Turnitin or Plagscan.
Whether you find a sample that is on your given topic or a closely related discussion, all of the speeches can help you get organized and focused.
Review multiple speeches to learn:
- How the presenter laid out the talking points and the number of points used
- What references and statistics they used to solidify their arguments
- How long the speech was for a given topic
- How the topic was introduced and summarized
- How the speaker engaged and interacted with the audience
By using these speech examples as an outline, you’ll have a fully formed presentation in no time ! We also have this page with gun control speech examples , in case you’d like to see different examples on the same topic.
Persuasive Speeches
- Birth Control Persuasive Speech
- We should stand up for our gun rights
- The truth about gun control
- The controversy over gun control
- Speech against stricter gun control
- It’s up to society to solve gun problems
- Guns don’t kill people
- Does banning firearms help prevent homicides
- Criminals will be criminals
- What to do about Deadbeat Parents
- Why state aid applicants need to be drug tested
- Subculture is Mainstream
- Eating Healthy
- Teachers should be paid more
- Digital Piracy
- Minimum Wage
- Drug Testing for State Aid
- Drug testing welfare
- Why snakes make good pets
- Why you need to quit drinking soda
- Why Everyone Should Learn to Play an Instrument
- Why Android is better then IOS 2
- Why Android is better then IOS 1
- Video Games Do Not Cause Violence
- Soda and Obesity
- Plastic Surgery 2
- Plastic Surgery
- Maintaining A Healthy Lifestyle
- Human development depends primarily on environmental factors
- Donating Blood
- Birth Control Persuasive Speech Example with Outline
- Social Media Persuasive Speech Example with Outline
- Texting and Driving Persuasive Speech Example with Outline
- Persuasive Speech on Sleep
- Persuasive Speech about Bullying
- Persuasive Speech on Organ Donation
Informative Speeches
- Guns and gun control - Texas
- Gun violence and control
- Gun control on campuses
- Wind Energy
- About Serial Killers
- Eating Disorder
- Robin Williams 2
- Dream Types
- Separation of Powers of the Federal Government
- Memory Loss
- Internet Black Market
- Blood Donation
- Alcohol in Winter
- About Guitar
- Social Media Informative Speech Example with Outline
- Texting and Driving Informative Speech Example with Outline
- Informative Speech on Sleep
- Informative Speech about Bullying
- Free Organ Donation Informative Speech
- Free Informative Speech on Caffeine and Its Effects
- Five Side Effects of Global Warming
- Global Warming Is Real
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- How to Write a Letter of Complaint

How to Write an Effective Speech Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Speaker Lab
- March 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Mastering the art of speaking starts with crafting a stellar speech outline. A well-structured outline not only clarifies your message but also keeps your audience locked in.
In this article, you’ll learn how to mold outlines for various speech types, weaving in research that resonates and transitions that keep listeners on track. We’ll also show you ways to spotlight crucial points and manage the clock so every second counts. When it’s time for final prep, we’ve got smart tips for fine-tuning your work before stepping into the spotlight.
Understanding the Structure of a Speech Outline
An effective speech outline is like a map for your journey as a speaker, guiding you from start to finish. Think of it as the blueprint that gives shape to your message and ensures you hit all the right notes along the way.
Tailoring Your Outline for Different Speech Types
Different speeches have different goals: some aim to persuade, others inform or celebrate. Each type demands its own structure in an outline. For instance, a persuasive speech might highlight compelling evidence while an informative one focuses on clear explanations. Crafting your outline with precision means adapting it to fit these distinct objectives.
Incorporating Research and Supporting Data
Your credibility hinges on solid research and data that back up your claims. When writing your outline, mark the places where you’ll incorporate certain pieces of research or data. Every stat you choose should serve a purpose in supporting your narrative arc. And remember to balance others’ research with your own unique insights. After all, you want your work to stand out, not sound like someone else’s.
The Role of Transitions in Speech Flow
Slick transitions are what turn choppy ideas into smooth storytelling—think about how bridges connect disparate land masses seamlessly. They’re not just filler; they carry listeners from one thought to another while maintaining momentum.
Incorporate transitions that feel natural yet keep people hooked. To keep things smooth, outline these transitions ahead of time so nothing feels left up to chance during delivery.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Outline
To make certain points pop off the page—and stage—you’ll need strategies beyond bolding text or speaking louder. Use repetition wisely or pause strategically after delivering something significant. Rather than go impromptu, plan out what points you want to emphasize before you hit the stage.

Timing Your Speech Through Your Outline
A watchful eye on timing ensures you don’t overstay—or undercut—your moment under the spotlight. The rhythm set by pacing can be pre-determined through practice runs timed against sections marked clearly in outlines. Practice will help ensure that your grand finale isn’t cut short by surprise.
What Type Of Speaker Are You?
Click below to discover your Speaker Archetype and how to start getting booked and paid to speak!
Depending on the type of speech you’re giving, your speech outline will vary. The key ingredients—introduction, body, and conclusion—are always there, but nuances like tone or message will change with each speaking occasion.
Persuasive Speeches: Convincing With Clarity
When outlining a persuasive speech, arrange your arguments from strong to strongest. The primacy effect works wonders here, so make sure to start off with a strong point. And just when they think they’ve heard it all, hit them with an emotional story that clinches the deal.
You might start by sharing startling statistics about plastic pollution before pivoting to how individuals can make a difference. Back this up with data on successful recycling programs which demonstrate tangible impact, a technique that turns facts into fuel for action.
Informative Speeches: Educating Without Overwhelming
An informative speech shouldn’t feel like drinking from a fire hose of facts and figures. Instead, lay out clear subtopics in your outline and tie them together with succinct explanations—not unlike stepping stones across a stream of knowledge.
If you’re talking about breakthroughs in renewable energy technology, use bullet points to highlight different innovations then expand upon their potential implications one at a time so the audience can follow along without getting lost in technical jargon or complexity.
Ceremonial Speeches: Creating Moments That Matter
In a ceremonial speech you want to capture emotion. Accordingly, your outline should feature personal anecdotes and quotes that resonate on an emotional level. However, make sure to maintain brevity because sometimes less really is more when celebrating milestones or honoring achievements.
Instead of just going through a hero’s whole life story, share the powerful tales of how they stepped up in tough times. This approach hits home for listeners, letting them feel the impact these heroes have had on their communities and sparking an emotional bond.
Incorporating Research in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting a speech, the backbone of your credibility lies in solid research and data. But remember, it’s not just about piling on the facts. It’s how you weave them into your narrative that makes listeners sit up and take notice.
Selecting Credible Sources
Finding trustworthy sources is like going on a treasure hunt where not all that glitters is gold. To strike real gold, aim for academic journals or publications known for their rigorous standards. Google Scholar or industry-specific databases are great places to start your search. Be picky. Your audience can tell when you’ve done your homework versus when you’ve settled for less-than-stellar intel.
You want to arm yourself with evidence so compelling that even skeptics start nodding along. A well-chosen statistic from a reputable study does more than decorate your point—it gives it an ironclad suit of armor.
Organizing Information Effectively
Your outline isn’t just a roadmap; think of it as scaffolding that holds up your argument piece by piece. Start strong with an eye-opening factoid to hook your audience right off the bat because first impressions matter—even in speeches.
To keep things digestible, group related ideas together under clear subheadings within your outline. Stick to presenting data that backs up each key idea without wandering down tangential paths. That way, everyone stays on track.
Making Data Relatable
Sure, numbers don’t lie but they can be hard to connect to. If you plan on using stats in your speech, make them meaningful by connecting them to relatable scenarios or outcomes people care about deeply. For instance, if you’re talking health statistics, relate them back to someone’s loved ones or local hospitals. By making the personal connection for your audience, you’ll get their attention.
The trick is using these nuggets strategically throughout your talk, not dumping them all at once but rather placing each one carefully where its impact will be greatest.
Imagine your speech as a road trip. Without smooth roads and clear signs, the journey gets bumpy, and passengers might miss the scenery along the way. That’s where transitions come in. They’re like your speech’s traffic signals guiding listeners from one point to another.
Crafting Seamless Bridges Between Ideas
Transitions are more than just linguistic filler. They’re strategic connectors that carry an audience smoothly through your narrative. Start by using phrases like “on top of this” or “let’s consider,” which help you pivot naturally between points without losing momentum.
To weave these seamlessly into your outline, map out each major turn beforehand to ensure no idea is left stranded on a tangent.
Making Use of Transitional Phrases Wisely
Be cautious: overusing transitional phrases can clutter up your speech faster than rush hour traffic. Striking a balance is key—think about how often you’d want to see signposts on a highway. Enough to keep you confident but not so many that it feels overwhelming.
Pick pivotal moments for transitions when shifting gears from one major topic to another or introducing contrasting information. A little direction at critical junctures keeps everyone onboard and attentive.
Leveraging Pauses as Transition Tools
Sometimes silence speaks louder than words, and pauses are powerful tools for transitioning thoughts. A well-timed pause lets ideas resonate and gives audiences time to digest complex information before moving forward again.
This approach also allows speakers some breathing room themselves—the chance to regroup mentally before diving into their next point with renewed vigor.
Connecting Emotional Threads Throughout Your Speech
Last but not least, don’t forget emotional continuity, that intangible thread pulling heartstrings from start-to-finish. Even if topics shift drastically, maintaining an underlying emotional connection ensures everything flows together cohesively within the larger tapestry of your message.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting your speech outline, shine a spotlight on what matters most so that your audience doesn’t miss your key points.
Bold and Italicize for Impact
You wouldn’t whisper your punchline in a crowded room. Similarly, why let your main ideas get lost in a sea of text? Use bold or italics to give those lines extra weight. This visual cue signals importance, so when you glance at your notes during delivery, you’ll know to emphasize those main ideas.
Analogies That Stick
A good analogy is like super glue—it makes anything stick. Weave them into your outline and watch as complex concepts become crystal clear. But remember: choose analogies that resonate with your target audience’s experiences or interests. The closer home it hits, the longer it lingers.
The Power of Repetition
If something’s important say it again. And maybe even once more after that—with flair. Repetition can feel redundant on paper, but audiences often need to hear critical messages several times before they take root.
Keep these strategies in mind when you’re ready to dive into your outline. You’ll transform those core ideas into memorable insights before you know it.
Picture this: you’re delivering a speech, and just as you’re about to reach the end, your time’s up. Ouch! Let’s make sure that never happens. Crafting an outline is not only about what to say but also how long to say it.
Finding Balance in Section Lengths
An outline isn’t just bullet points; it’s a roadmap for pacing. When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you’d like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part’s duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
The Magic of Mini Milestones
To stay on track, a savvy speaker will mark time stamps or “mini milestones” on their outline. These time stamps give the speaker an idea of where should be in their speech by the time, say, 15 minutes has passed. If by checkpoint three you should be 15 minutes deep and instead you’re hitting 20 minutes, it’s time to pick up the pace or trim some fat from earlier sections. This approach helps you stay on track without having to glance at the clock after every sentence.
Utilizing Visual Aids and Multimedia in Your Outline
Pictures speak louder than words, especially when you’re on stage. Think about it: How many times have you sat through a presentation that felt like an eternity of endless bullet points? Now imagine if instead, there was a vibrant image or a short video clip to break up the monotony—it’s game-changing. That’s why integrating visual aids and multimedia into your speech outline isn’t just smart. It’s crucial for keeping your audience locked in.
Choosing Effective Visuals
Selecting the right visuals is not about flooding your slides with random images but finding those that truly amplify your message. Say you’re talking about climate change. In this case, a graph showing rising global temperatures can hit hard and illustrate your chosen statistic clearly. Remember, simplicity reigns supreme; one powerful image will always trump a cluttered collage.
Multimedia Magic
Videos are another ace up your sleeve. They can deliver testimonials more powerfully than quotes or transport viewers to places mere descriptions cannot reach. But be warned—timing is everything. Keep clips short and sweet because no one came to watch a movie—they came to hear you . You might highlight innovations using short video snippets, ensuring these moments serve as compelling punctuations rather than pauses in your narrative.
The Power of Sound
We often forget audio when we think multimedia, yet sound can evoke emotions and set tones subtly yet effectively. Think striking chords for dramatic effect or nature sounds for storytelling depth during environmental talks.
Audiences crave experiences they’ll remember long after they leave their seats. With well-chosen visuals and gripping multimedia elements woven thoughtfully into every section of your speech outline, you’ll give them exactly that.
Rehearsing with Your Speech Outline
When you’re gearing up to take the stage, your speech outline is a great tool to practice with. With a little preparation, you’ll give a performance that feels both natural and engaging.
Familiarizing Yourself with Content
To start off strong, get cozy with your outline’s content. Read through your outline aloud multiple times until the flow of words feels smooth. This will help make sure that when showtime comes around, you can deliver those lines without tripping over tough transitions or complex concepts.
Beyond mere memorization, understanding the heart behind each point allows you to speak from a place of confidence. You know this stuff—you wrote it. Now let’s bring that knowledge front and center in an authentic way.
Mimicking Presentation Conditions
Rehearsing under conditions similar to those expected during the actual presentation pays off big time. Are you going to stand or roam about? Will there be a podium? Think about these details and simulate them during rehearsal because comfort breeds confidence—and we’re all about boosting confidence.
If technology plays its part in your talk, don’t leave them out of rehearsals either. The last thing anyone needs is tech trouble during their talk.
Perfecting Pace Through Practice
Pacing matters big time when speaking. Use timed rehearsals to nail down timing. Adjust speed as needed but remember: clarity trumps velocity every single time.
You want people hanging onto every word, which is hard to do if you’re talking so fast they can barely make out what you’re saying. During rehearsals, find balance between pacing and comprehension; they should go hand-in-hand.
Finalizing Your Speech Outline for Presentation
You’ve poured hours into crafting your speech, shaping each word and idea with precision. Now, it’s time to tighten the nuts and bolts. Finalizing your outline isn’t just about dotting the i’s and crossing the t’s. It’s about making sure your message sticks like a perfectly thrown dart.
Reviewing Your Content for Clarity
Your first task is to strip away any fluff that might cloud your core message. Read through every point in your outline with a critical eye. Think of yourself as an editor on a mission to cut out anything that doesn’t serve a purpose. Ask yourself if you can explain each concept clearly without needing extra words or complex jargon. If not, simplify.
Strengthening Your Argument
The meat of any good presentation lies in its argument, the why behind what you’re saying. Strengthen yours by ensuring every claim has iron-clad backing—a stat here, an expert quote there. Let this be more than just facts tossed at an audience; weave them into stories they’ll remember long after they leave their seats.
Crafting Memorable Takeaways
Audiences may forget details but never how you made them feel—or think. Embed memorable takeaways throughout your outline so when folks step out into fresh air post-talk, they carry bits of wisdom with them.
This could mean distilling complex ideas down to pithy phrases or ending sections with punchy lines that resonate. It’s these golden nuggets people will mine for later reflection.
FAQs on Speech Outlines
How do you write a speech outline.
To craft an outline, jot down your main ideas, arrange them logically, and add supporting points beneath each.
What are the 3 main parts of a speech outline?
An effective speech has three core parts: an engaging introduction, a content-rich body, and a memorable conclusion.
What are the three features of a good speech outline?
A strong outline is clear, concise, and structured in logical sequence to maximize impact on listeners.
What is a working outline for a speech?
A working outline serves as your blueprint while preparing. It’s detailed but flexible enough to adjust as needed.
Crafting a speech outline is like drawing your map before the journey. It starts with structure and flows into customization for different types of talks. Remember, research and evidence are your compass—they guide you to credibility. Transitions act as bridges, connecting one idea to another smoothly. Key points? They’re landmarks so make them shine.
When delivering your speech, keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself so that every word counts.
Multimedia turns a good talk into a great show. Rehearsing polishes that gem of a presentation until it sparkles.
Last up: fine-tuning your speech outline means you step out confident, ready to deliver something memorable because this isn’t just any roadmap—it’s yours.
- Last Updated: March 5, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Speech Outline
Last Updated: January 3, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 504,538 times.
A speech outline can increase your confidence and help you keep your place so you sound authoritative and in control. As you write your speech outline, focus on how you'll introduce yourself and your topic, the points you'll cover, and the interests of your audience.
Sample Outline and Writing Help

Crafting Your Introduction

- Keep in mind you may be nervous when you start your speech. Include this in your outline so you won't forget.
- If there's anything about you that relates you to your audience, or to the group that organized the event, you want to include that in your brief greeting as well – especially if you didn't have the benefit of an introduction from someone else.
- For example, you might say "Good afternoon. I'm Sally Sunshine, and I've been a volunteer with the Springfield Animal Society for five years. I'm honored they've invited me to speak here today about the importance of spaying or neutering your pets."

- When choosing your attention-getter, keep your audience in mind. Think about what would grab their attention – not necessarily what you personally find interesting or humorous.
- If you're not sure whether your attention-getter will work, try practicing it in front of friends or family members who are similar in age and interests to the people who will be in the audience when you give your speech.
- For example, if you're giving a speech on spaying and neutering pets to a group of suburban families, you might open with a humorous reference to the Disney movie "101 Dalmatians."

- Briefly explain the importance of the topic or issue you'll be discussing in your speech.
- If your speech is an informative one, explain why the information is important or relevant to your audience.
- For argumentative speeches, explain what might happen if action isn't taken on the issue.
- For example, you might say "Every year, our local animal shelter has to put down 500 unwanted cats and dogs. If all pets were spayed and neutered, it's estimated this number would decrease to under 100."

- If you're giving an argumentative speech, your thesis statement will be a statement of the ultimate point you hope to prove through the information and evidence you lay out in your speech.
- For example, the thesis statement for a speech arguing that all pet owners should spay or neuter their pets might be "Our entire community would benefit if all pets were spayed or neutered."
- The thesis statement for a more informative speech will simply summarize the type of information you're going to provide the audience through your speech.
- For a more scientific speech, your thesis statement will reflect the hypothesis of the scientific study you're presenting in your speech.

- If you're giving a speech for a class in school, your "credibility" may be as simple as the fact that you took the class and researched the topic.
- However, if you have a more personalized interest in the topic of your speech, this is a good time to mention that.
- For an argumentative speech, a personal connection to the subject matter can enhance your credibility. For example, maybe you're giving a speech about local urban housing policy and you became interested in the topic when you learned your family was facing eviction. A personal connection often can mean more to members of your audience than extensive professional experience in the area.

- There's no hard and fast rule, but speeches typically have three main points. You should list them in your introduction in the order you plan to present them in your speech. The order in which you discuss your points depends on the type of speech you're giving.
- For example, your speech on spaying or neutering pets might address the benefits to the pet first, then the benefit to the pet's family, then the benefit to the community at large. This starts small and moves outward.
- For an argumentative speech, you typically want to lead with your strongest argument and work down in order of strength.
- If you're giving an informative speech based on a historical event, you may want to provide your points chronologically. Other informative speeches may be better served by starting with the broadest point and moving to more narrow points.
- Ultimately, you want to order your points in a way that feels natural to you and will enable you to easily transition from one point to another.
Building the Body of Your Speech

- Your first point will be a top-level entry on your outline, typically noted by a Roman numeral.
- Beneath that top-level, you will have a number of sub-points which are comments, statistics, or other evidence supporting that point. Depending on how your outline is formatted, these typically will be letters or bullet points.

- As with the points themselves, with your evidence you typically want to start with the strongest or most important sub-point or piece of evidence and move down. This way, if you start running short on time, you can easily cut the last points without worrying that you're leaving out something important.
- The type of evidence or sub-points you'll want to include will depend on the type of speech you're giving.
- Try to avoid pounding your audience with long series of numbers or statistics – they typically won't retain the information. If you have a significant amount of numerical data or statistics, creating an infographic you can project during your presentation may be more useful.
- Keep in mind that additional personal stories or anecdotes can be particularly effective to get your point across in a speech.
- For example, if your first point in your speech about spaying or neutering pets is that the procedure benefits the pets themselves, you might point out that pets that are spayed or neutered live longer, are at a decreased risk for certain types of cancer, and are generally more healthy than pets who aren't spayed or neutered.

- Avoid over-thinking your transition. It really doesn't need to be incredibly sophisticated. If you can't come up with anything specific, using a simple transitional phrase will work fine.
- For example, you might say "Now that I've discussed how spaying and neutering has a positive effect on your pet's health, I want to move to the effect that spaying and neutering has on your family."
- Some of the most effective transitions turn on a particular word or phrase, such as the word "effect" in the example above.

- When choosing your sub-points or the facts that you want to emphasize in your speech, keep your audience in mind as well as the overall point. Think about what's important to them, or what they potentially would find most surprising or most interesting.
Creating Your Closing

- This transition doesn't need to be fancy – it doesn't even have to be a whole sentence. You can simply say "In conclusion," and then launch into your summary.

- You don't need to go into detail here – you're just reinforcing what you've already told your audience.
- Make sure you don't introduce any new information in your closing summary.
- For example, you might say "As you've seen, spaying or neutering your pet has substantial benefits not only for you and your pet, but also for the community at large."

- If your speech went well, you have fully proven your thesis and demonstrated its importance. This statement should relate back to the summary of your points and present a strong statement.
- Particularly for brief speeches, you can even combine your summary of points with your thesis statement in a single sentence that wraps up your speech.
- For example, you might say "Given the benefits to your pet's health, to your family, and to the overall well-being of your community, it is clear that spaying or neutering pets should be a top priority for all pet owners."

- You may want to think of a way to bring the entire speech back around to that story you initially told to grab your audience's attention.
- If you have an argumentative or similar speech, your closing lines typically will include a call to action. Give your audience an example of how important the subject of your speech is, and implore them to act on the information you gave them in a specific way.
- When making a call to action, make sure you include specific details, such as where to go, who to contact, and when to act.
- For example, you might say "For the next week, the Springfield Animal Society will be spaying and neutering pets for free at their clinic on 123 Main Street. Call 555-555-5555 to make an appointment for your furry friend today!"

- Particularly if your speech was longer or if you went over the time allotted, be sure to tell them that you appreciate their time.
- As with your initial greeting, including this in your outline ensures you won't forget it in the moment. That doesn't mean you should try to write something verbatim. Rather, you should focus on your thanks being more off-the-cuff and sincere.

- If you want to establish parameters for the questions, be sure to list these in your outline so you can mention them when you announce that you're open for questions.
- Anticipate questions that may be asked dependent on your speech topic. Preemptively answer those questions and include them in your outline.
- You also should note if you only have a specified period of time for questions, or if you're only taking a set number of questions.
Community Q&A
- Outlines can vary in how formal or informal you make them. You could either make it a full script or use shorthand with highlighted main points. Use the outline that works best for you. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 0
- Use a large font that you can easily read by glancing down. Print your outline and place it on a desk, then stand and look down at the paper. If it's too small or you find yourself leaning over to read it, increase the font size. Thanks Helpful 15 Not Helpful 3
- If you're giving the speech for a class, you may need to turn in an outline of your speech that follows particular content or format requirements. Review your assignment carefully and turn in an outline that follows your instructor's requirements, even if you decide to use a slightly different outline when you give your speech. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/speech-introductions
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ https://lewisu.edu/writingcenter/pdf/final-developing-a-speech-outline.pdf
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/speech-evidence
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/10-2-keeping-your-speech-moving/
About This Article

The best way to write a speech outline is to write the main points of your greeting and introduction in the first section, including your name and what you’ll be talking about. Then, make a second section with bullet points of all the important details you want to mention in the body of your speech. Make sure to include facts and evidence to back your argument up. Finish your outline with a section that summarizes your points concisely. To learn how to keep your audience's attention throughout your speech, keep reading below! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ren Solomon
Oct 1, 2018
Did this article help you?
Erick Villegas
Sep 21, 2017
Fernando Patino
Nov 19, 2018
Tristan Doell
Oct 12, 2017
Nov 23, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Speech Writing
- Updated on
- Jan 16, 2024

The power of good, inspiring, motivating, and thought-provoking speeches can never be overlooked. If we retrospect, a good speech has not only won people’s hearts but also has been a verbal tool to conquer nations. For centuries, many leaders have used this instrument to charm audiences with their powerful speeches. Apart from vocalizing your speech perfectly, the words you choose in a speech carry immense weight, and practising speech writing begins with our school life. Speech writing is an important part of the English syllabus for Class 12th, Class 11th, and Class 8th to 10th. This blog brings you the Speech Writing format, samples, examples, tips, and tricks!
This Blog Includes:
What is speech writing, speech in english language writing, how do you begin an english-language speech, introduction, how to write a speech, speech writing samples, example of a great speech, english speech topics, practice time.
Must Read: Story Writing Format for Class 9 & 10
Speech writing is the art of using proper grammar and expression to convey a thought or message to a reader. Speech writing isn’t all that distinct from other types of narrative writing. However, students should be aware of certain distinct punctuation and writing style techniques. While writing the ideal speech might be challenging, sticking to the appropriate speech writing structure will ensure that you never fall short.
“There are three things to aim at in public speaking: first, to get into your subject, then to get your subject into yourself, and lastly, to get your subject into the heart of your audience.”- Alexander Gregg
The English language includes eight parts of speech i.e. nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives 410 , adverbs , prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
- Noun- A noun is a word that describes anything, such as an animal, a person, a place, or an emotion. Nouns are the building blocks for most sentences.
- Pronoun – Pronouns are words that can be used in place of nouns. They are used so that we don’t have to repeat words. This makes our writing and speaking much more natural.
- Verb – A verb is a term that implies activity or ‘doing.’ These are very vital for your children’s grammar studies, as a sentence cannot be complete without a verb.
- Adjective – An adjective is a term that describes something. An adjective is frequently used before a noun to add extra information or description.
- Prepositions- A preposition is a term that expresses the location or timing of something in relation to something else.
- Conjunction- Because every language has its own set of conjunctions, English conjunctions differ from those found in other languages. They’re typically used as a connecting word between two statements, concepts, or ideas.
- Interjections- Interjections are words that are used to describe a strong emotion or a sudden feeling.
Relevant Read: Speech on the Importance of English
The way you start your English speech can set the tone for the remainder of it. This semester, there are a variety of options for you to begin presentations in your classes. For example, try some of these engaging speech in English language starters.
- Rhetorical questions : A rhetorical question is a figure of speech that uses a question to convey a point rather than asking for a response. The answer to a rhetorical question may be clear, yet the questioner asks it to emphasize the point. Rhetorical questions may be a good method for students to start their English speeches. This method of introducing your material might be appealing to the viewers and encourage them to consider how they personally relate to your issue.
- Statistics: When making an instructive or persuasive speech in an English class, statistics can help to strengthen the speaker’s authority and understanding of the subject. To get your point over quickly and create an emotional response, try using an unexpected statistic or fact that will resonate with the audience.
- Set up an imaginary scene: Create an imaginary situation in your audience’s thoughts if you want to persuade them to agree with you with your speech. This method of starting your speech assists each member of the audience in visualizing a fantastic scenario that you wish to see come true.
Relevant Read: Reported Speech Rules With Exercises
Format of Speech Writing
Here is the format of Speech Writing:
- Introduction : Greet the audience, tell them about yourself and further introduce the topic.
- Body : Present the topic in an elaborate way, explaining its key features, pros and cons, if any and the like.
- Conclusion : Summary of your speech, wrap up the topic and leave your audience with a compelling reminder to think about!
Let’s further understand each element of the format of Speech Writing in further detail:
After the greetings, the Introduction has to be attention-getting. Quickly get people’s attention. The goal of a speech is to engage the audience and persuade them to think or act in your favour. The introduction must effectively include:
- A brief preview of your topic.
- Define the outlines of your speech. (For example, I’ll be talking about…First..Second…Third)
- Begin with a story, quote, fact, joke, or observation in the room. It shouldn’t be longer than 3-4 lines. (For Example: “Mahatma Gandhi said once…”, or “This topic reminds me of an incident/story…”)
This part is also important because that’s when your audience decides if the speech is worth their time. Keep your introduction factual, interesting, and convincing.
It is the most important part of any speech. You should provide a number of reasons and arguments to convince the audience to agree with you.
Handling objections is an important aspect of speech composition. There is no time for questions or concerns since a speech is a monologue. Any concerns that may occur during the speech will be addressed by a powerful speech. As a result, you’ll be able to respond to questions as they come in from the crowd. To make speech simpler you can prepare a flow chart of the details in a systematic way.
For example: If your speech is about waste management; distribute information and arrange it according to subparagraphs for your reference. It could include:
- What is Waste Management?
- Major techniques used to manage waste
- Advantages of Waste Management
- Importance of Waste Management
The conclusion should be something that the audience takes with them. It could be a reminder, a collective call to action, a summary of your speech, or a story. For example: “It is upon us to choose the fate of our home, the earth by choosing to begin waste management at our personal spaces.”
After concluding, add a few lines of gratitude to the audience for their time.
For example: “Thank you for being a wonderful audience and lending me your time. Hope this speech gave you something to take away.”

Practice Your Speech Writing with these English Speech topics for students !
A good speech is well-timed, informative, and thought-provoking. Here are the tips for writing a good school speech:
Speech Sandwich of Public Speaking
The introduction and conclusion must be crisp. People psychologically follow the primacy effect (tendency to remember the first part of the list/speech) and recency effect (tendency to recall the last part of the list/speech).
Use Concrete Facts
Make sure you thoroughly research your topic. Including facts appeals to the audience and makes your speech stronger. How much waste is managed? Give names of organisations and provide numerical data in one line.
Use Rhetorical Strategies and Humour
Include one or two open-ended or thought-provoking questions. For Example: “Would we want our future generation to face trouble due to global warming?” Also, make good use of humour and convenient jokes that engages your audience and keeps them listening.
Check Out: Message Writing
Know your Audience and Plan Accordingly
This is essential before writing your speech. To whom is it directed? The categorised audience on the basis of –
- Knowledge of the Topic (familiar or unfamiliar)
Use the information to formulate the speech accordingly, use information that they will understand, and a sentence that they can retain.
Timing Yourself is Important
An important aspect of your speech is to time yourself. Don’t write a speech that exceeds your word limit. Here’s how can decide the right timing for your speech writing:
- A one-minute speech roughly requires around 130-150 words
- A two-minute speech requires roughly around 250-300 words
Recommended Read: Letter Writing
Speech Writing Examples
Here are some examples to help you understand how to write a good speech. Read these to prepare for your next speech:
Write a speech to be delivered in the school assembly as Rahul/ Rubaina of Delhi Public School emphasises the importance of cleanliness, implying that the level of cleanliness represents the character of its residents. (150-200 words)
“Cleanliness is next to godliness,” said the great John Wesley. Hello, respected principal, instructors, and good friends. Today, I, Rahul/Rubaina, stand in front of you all to emphasise the significance of cleanliness.
Cleanliness is the condition or attribute of being or remaining clean. Everyone must learn about cleaning, hygiene, sanitation, and the different diseases that are produced by unsanitary circumstances. It is essential for physical well-being and the maintenance of a healthy atmosphere at home and at school. A filthy atmosphere invites a large number of mosquitos to grow and spread dangerous diseases. On the other side, poor personal cleanliness causes a variety of skin disorders as well as lowered immunity.
Habits formed at a young age become ingrained in one’s personality. Even if we teach our children to wash their hands before and after meals, brush their teeth and bathe on a regular basis, we are unconcerned about keeping public places clean. On October 2, 2014, the Indian Prime Minister began the “Swachh Bharat” programme to offer sanitation amenities to every family, including toilets, solid and liquid waste disposal systems, village cleanliness, and safe and appropriate drinking water supplies. Teachers and children in schools are actively participating in the ‘Clean India Campaign’ with zeal and excitement.
Good health ensures a healthy mind, which leads to better overall productivity, higher living standards, and economic development. It will improve India’s international standing. As a result, a clean environment is a green environment with fewer illnesses. Thus, cleanliness is defined as a symbol of mental purity.
Thank you very much.
Relevant Read: Speech on Corruption
You are Sahil/Sanya, the school’s Head Girl/Head Boy. You are greatly troubled by the increasing instances of aggressive behaviour among your students. You decide to speak about it during the morning assembly. Create a speech about “School Discipline.” (150 – 200 words)
INDISCIPLINE IN SCHOOLS,
It has been reported that the frequency of fights and incidences of bullying in our school has increased dramatically in the previous several months. Good morning to everyone present. Today, I, Sahil/Sanya, your head boy/girl, am here to shed light on the serious topic of “Increased Indiscipline in Schools.”
It has come to light that instructor disobedience, bullying, confrontations with students, truancy, and insults are becoming more widespread. Furthermore, there have been reports of parents noticing a shift in their children’s attitudes. As a result, many children are suffering emotionally, psychologically, and physically. The impact of this mindset on children at a young age is devastating and irreversible.
Not to mention the harm done to the school’s property. Theft of chalk, scribbling on desks, walls and lavatory doors, destruction of CCTV cameras and so forth. We are merely depriving ourselves of the comforts granted to us by doing so.
Following numerous meetings, it was determined that the main reasons for the problem were a lack of sufficient guidance, excessive use of social media, and peer pressure. The council is working to make things better. Everyone is required to take life skills classes. Counselling, motivating, and instilling friendly ideals will be part of the curriculum. Seminars for parents and students will be held on a regular basis.
A counsellor is being made available to help you all discuss your sentiments, grudges, and personal problems. We are doing everything we can and expect you to do the same.
So, let us work together to create an environment in which we encourage, motivate, assist, and be nice to one another because we are good and civilised humans capable of a great deal of love.
Relevant Read: How to Write a Speech on Discipline?
The current increase in incidences of violent student misbehaviour is cause for alarm for everyone. Students who learn how to manage their anger can help to alleviate the situation. Write a 150-200-word speech about the topic to be delivered at the school’s morning assembly. (10)
HOW TO CONTROL ANGER
Honourable Principal, Respected Teachers, and Dear Friends, I’d like to share a few “Ways to Manage Anger” with you today.
The growing intolerance among the younger generation, which is resulting in violence against teachers, is cause for severe concern. The guru-shishya parampara is losing its lustre. Aggressive behaviour in students can be provoked by a variety of factors, including self-defence, stressful circumstance, over-stimulation, or a lack of adult supervision.
It has become imperative to address the situation. Life skills workshops will be included in the curriculum. Teachers should be trained to deal with such stubborn and confrontational behaviours. Meditation and deep breathing are very beneficial and should be practised every morning. Students should be taught to count to ten before reacting angrily. Sessions on anger control and its importance must also be held.
Remember that Anger is one letter away from danger. It becomes much more crucial to be able to control one’s rage. It’s never too late to start, as a wise man once said.
“Every minute you stay angry, you lose sixty seconds of peace of mind.”
Relevant Read: English Speech Topics for Students
Martin Luther King Jr’s ‘I Have A Dream’ is one of his most famous speeches. Its impact has lasted through generations. The speech is written by utilising the techniques above. Here are some examples:
“still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination” – emotive Language
“In a sense, we’ve come to our nation’s capital to cash a check” – personalising the speech
“to stand up for freedom together” – a call to action.
Importantly, this is an example of how the listener comes first while drafting a speech. The language chosen appeals to a specific sort of audience and was widely utilised in 1963 when the speech was delivered.
- The Best Day of My Life
- Social Media: Bane or Boon?
- Pros and Cons of Online Learning
- Benefits of Yoga
- If I had a Superpower
- I wish I were ______
- Environment Conservation
- Women Should Rule the World!
- The Best Lesson I Have Learned
- Paperbacks vs E-books
- How to Tackle a Bad Habit?
- My Favorite Pastime/Hobby
- Understanding Feminism
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Is it real or not?
- Importance of Reading
- Importance of Books in Our Life
- My Favorite Fictional Character
- Introverts vs Extroverts
- Lessons to Learn from Sports
- Beauty is in the eye of the beholder
Also Read: How to Ace IELTS Writing Section?
Ans. Speech writing is the process of communicating a notion or message to a reader by employing proper punctuation and expression. Speech writing is similar to other types of narrative writing. However, students should be aware of some different punctuation and writing structure techniques.
Ans. Before beginning with the speech, choose an important topic. Create an outline; rehearse your speech, and adjust the outline based on comments from the rehearsal. This five-step strategy for speech planning serves as the foundation for both lessons and learning activities.
Ans. Writing down a speech is vital since it helps you better comprehend the issue, organises your thoughts, prevents errors in your speech, allows you to get more comfortable with it, and improves its overall quality.
Speech writing and public speaking are effective and influential. Hope this blog helped you know the various tips for writing the speech people would want to hear. If you need help in making the right career choices at any phase of your academic and professional journey, our Leverage Edu experts are here to guide you. Sign up for a free session now!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
14 comments
This site has been very helpful to me
Wow i have gained more knowledge
lt’s a nice One and l have loved it
Thank you for your feedback! Happy that you loved it.
Thank you for your feedback!
Very educating.
thanks for your valuable feedback
This is indeed very helpful
Thanks for your valuable feedback!
I have learned alot thank you
Hi, Thanks for your feedback!
Wow so reliable, thanks.

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Writing Guide
- Assignment Writing
How to Write a Speech
efore you are able to write a great speech, it is necessary to first learn a little bit about the different types of speeches and how one is made up. Not surprisingly, there are various types of speeches, and each will contain specific characteristics depending on their nature.
Tips for Beginners – How to write a speech
Similar to essays, every speech has three primary sections: The beginning (the introduction), the middle (the body) and the end (the conclusion.) Contrary to essays, speeches are designed to be heard rather than read. The best speeches are written in a manner that not only engages with the audience, but also holds their attention from start to finish. This, of course, necessitates that your speech must have ‘flair’ or ‘pizzazz’ something that draws the listener in.
The various types of speeches are:
- Informative
- Instructional
- Entertaining
- Special Occasion
Some Ideas How to start a speech
How you start your speech will depend largely on the reason you are delivering the speech. For example, the most powerful speeches that also happen to be informative in nature, often contain an introductory statement that not only introduces the topic being discussed but also piques the interest of the audience. It must be followed up by a strong transition into the main body of the speech.
Think of the attention grabbing portion of the introduction as the ‘hook’, it must be something that not only compels the audience to remain open-minded, but also encourages them to want to listen to everything you have to say. How long is your introduction or speech supposed to be? That will depend specifically on the amount of time that you’ve been allotted to deliver your speech and whether or not there is a question and answer forum afterwards.
Speech Format – Is There Any?
As mentioned earlier, speech writing follow the same basic format as a traditional essay. There must be an introduction, a body and a conclusion. We discussed the introduction earlier.
There is no ‘set in stone’ rule when it comes to how the body of a speech must be organized. However there are a few speech tips to keep in mind.
- Keep in chronological – this provides a more accurate order for the timeline of events
- Present one key piece of information at a time
- Follow a cause and effect pattern
- Offer a full overview of the design or physical arrangement
Most speeches will have the body divided into three topic sections.
Lastly you would move on to the conclusion. More on that below.
A Short Guide How to write a speech outline
Writing an outline is one of the most crucial success factors for writing the best speeches, and often one of the most overlooked items.
Having an outline will not only save you time in the long run, it will help you to keep your thoughts organized and ensure that you are following proper structure and formatting.
Here is an example of how to make a speech outline you might use for reference purposes
- Determine your topic
- Get to know your audience
- Determine the purpose of the speech
- Decide how you will organize the speech
- Jot down an attention grabbing intro statement
- Redefine your thesis statement (summarize what the speech is about)
- State something that establishes credibility
- Transition from the intro to the body
- Offer your main idea and supporting information
- Provide examples and as much detail as needed
- Offer a summary of the body and the main points
- Jot down a strong call to action or closing statement
Ways How to end a speech
Ending your speech properly requires that you not only restate your main points, but also leave the audience with something to think about. Some people choose to do this by prompting listeners to consider a statement or by reciting a quote. Ideally, you are looking for something that neatly wraps up the entire speech, but also offers a bit of a twist or call to action.
Regardless of the nature of your speech, there are certain things that you will want to consider including. They are:
- Witty or relevant quotes
- Funny stories or anecdotes that have a purpose
- Strong transitions that are meaningful and make sense
- A solid ending
The most important thing to consider when writing a speech comes from knowing who you are writing it for. You need to be able to convey passion and eagerness, but you also want your audience to share in your eagerness with their own enthusiasm. This means you need to be able to write attention-grabbing statements that pique their interest and not just your own.
Some of Speech Examples You May Find Useful
When preparing to write (or deliver) a speech, there is merit in reading or listening to famous speeches to pick up on little things like transitions, body language, openers and how strong conclusions are delivered.
Here are a few world-famous great speeches that you can refer to:
- I have a dream by Martin Luther King
- The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
- T he Infamy Speech by Franklin Roosevelt
- Barak Obama’s Election Speech
- Checkers Speech by Richard Nixon
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

Forget about ChatGPT and get quality content right away.

COMM 101: Fundamentals of Public Speaking - Valparaiso
- Delivery Skills
- Stage Fright
- Body Language / Non-Verbal Communication
- Listening Skills
- Quotation Resources
- Speech Outline Examples
- Speech Examples
- More Speech Examples
- Presentation Options
- Citation Resources This link opens in a new window
A basic speech outline should include three main sections:
- The Introduction -- This is where you tell them what you're going to tell them.
- The Body -- This is where you tell them.
- The Conclusion -- This is where you tell them what you've told them.
- Speech Outline Formatting Guide The outline for a public speech, according to COMM 101 online textbook The Public Speaking Project , p.p. 8-9.
Use these samples to help prepare your speech outlines and bibliographies:
- Sample Speech Preparation Outline This type of outline is very detailed with all the main points and subpoints written in complete sentences. Your bibliography should be included with this outline.
- Sample Speech Speaking Outline This type of outline is very brief and uses phrases or key words for the main points and subpoints. This outline is used by the speaker during the speech.
- << Previous: Quotation Resources
- Next: Informative Speeches >>
- Last Updated: Sep 22, 2023 4:37 PM
- URL: https://library.ivytech.edu/Valpo_COMM101
- Ask-a-Librarian
- [email protected]
- (219) 464-8514 x 3021
- Library staff | Find people
- Library Guides
- Student Life & Activities
- Testing Services
- B&N Bookstore
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- How to cite a speech in APA Style
How to Cite a Speech in APA Style | Format & Examples
Published on December 10, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on December 27, 2023.
How you cite a speech in APA Style depends on the format in which you heard it.
For an audio recording of a speech found online, list the speaker, the date when the speech took place, the title in italics, “Speech audio recording” in square brackets, the website, and the URL. You can use a timestamp to specify a location in the in-text citation.
Scribbr’s free APA Citation Generator can help you cite a speech correctly.
Table of contents
Citing a paper presentation, citing speeches as personal communications.
To cite a paper presentation from an academic conference, use the following format. List the date as the range of dates across which the conference took place.
However, if you’re citing a published conference paper from a journal or book , use the format of that source type.
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

Speeches that cannot be accessed by the reader in some sort of recording or transcript and were not part of a conference are cited as personal communications .
This is the format used in APA Style for sources the reader won’t be able to access themselves. Because they are not retrievable, personal communications don’t appear in the reference list; they’re just cited in the text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, December 27). How to Cite a Speech in APA Style | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-examples/speech/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite a ted talk in apa style, how to cite a podcast in apa style, citing personal communications in apa style, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

University Interscholastic League

This is the main content.
- Oral Interpretation
Preparing Your Manuscript
Speech & debate.
- Extemporaneous Speaking
- Tournaments
- New Coach Information
Speech & Debate Contact Info
Speech & Debate Director: Jana Riggins
Department Phone: 512-471-5883
State Champions
View State Champions
Preparing the Manuscript
Since UIL prose and poetry contests are reading events, a manuscript should be used for competition. Preparation of that manuscript is a vital part of the process as a whole. Rules of the contest state that “The contestant should perform the selections using manuscripts or copies of the selections that are in a binder. Students shall not read from books or magazines.” Contest rules also state the manuscript or copies of the selection should be available to the contest director, if needed at the contest, to aid in addressing question or concerns.
Most competitors use a black stiff-backed 3-ring binder, approximately 9” x 6” in size, as their manuscript folder for several reasons:
- Black is less obtrusive than other colors. You want the focus of the audience and judge on your performance, not your binder.
- 3-ring binders make page turning easier. Avoid binders with back-mounted rings because they make the binder unwieldy to hold open properly for performance. Rings should be mounted in the spine. Also avoid binders with plastic see-through covers.
- 3-ring binders allow greater flexibility in arranging your manuscript.
- 3- ring binders easily accommodate “slicks” (plastic sheet covers).
- The 9” x 6” size is easy to handle and less obtrusive than other sizes.
- Most binders have pockets to accommodate documentation. (Before standing in front of the audience, be sure to empty the binder of everything but the selection you are about to perform.)

Type the manuscript in Landscape format. Use a clean, plain font that is easy to read. Arial is an example of a clean font. Increase the font size to 16 or larger, and double space the lines, so there’s room to add scoring notes. Break the selection down into “beats”, which are edited units of time or thought. Print only on one side.
Many competitors have turned to the 9” x 6” binder with the plastic sheets because it facilitates the handling of the manuscript. Not only do the “slicks” keep the manuscript intact and prevent it from falling out of the folder, but they also add a stiffness that allows you to turn pages smoothly, one page at a time. Slicks and binders can be ordered from office supply stores or The Black Book Depot (www.blackbookdepot.com).Mounting your manuscript on black construction paper or black card stock before insertion into the slick is advantageous because it provides some rigidity for the page and it allows the eye to focus more readily on the page.
The binder is meant to serve as a constant visual reminder that the words you relay to the audience are not your own but those of the author of the literary work.
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Political typology quiz.
Notice: Beginning April 18th community groups will be temporarily unavailable for extended maintenance. Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.
Where do you fit in the political typology?
Are you a faith and flag conservative progressive left or somewhere in between.

Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That’s OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if it isn’t exactly right.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For a 5-minute speech, you only need a brief material. Your speech should revolve around the central idea. If your speech is 30 minutes long, you need to collect enough details to cover in 30 minutes. 4. Craft the Outline. Now that you have the material for your speech, craft an outline to organize your material.
Step 3: Edit and polish what you've written until you have a cohesive first draft of your speech. Step 4: Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your speech the more you'll discover which sections need reworked, which transitions should be improved, and which sentences are hard to say. You'll also find out how you're doing ...
Ethos refers to an appeal to your audience by establishing your authenticity and trustworthiness as a speaker. If you employ pathos, you appeal to your audience's emotions. Using logos includes the support of hard facts, statistics, and logical argumentation. The most effective speeches usually present a combination these rhetorical strategies.
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
You need to write a speech in a way that keeps the attention of an audience and helps paint a mental image at the same time. This means that your speech should contain some color, drama, or humor. It should have "flair.". Make your speech memorable by using attention-grabbing anecdotes and examples.
Here are twelve steps to formatting a speech for smooth delivery: 1. Use 16-20 pt font: This will help ensure the remarks are legible from the podium. 2. Double-space the document: F or readability and to help make the speech easy to skim through. 3. Use sub-headings: Include subheadings in square brackets to guide your speaker through the ...
Choose your topic and the main points that your speech will cover. Know your audience and get to know what they are looking for. Pay attention to their needs. Define the purpose of the speech and properly organize it. Introduction. A strong statement to grab the reader's attention. Refine the thesis statement.
Here's how: 1. Make the font size larger. This seems obvious, but you might be surprised to learn that even veteran speakers don't do this. Go up to 14 point, to start—then don't be shy about making it even larger if that makes it easier for you to read. 2.
When writing an essay, the style and organization is often determined by the purpose of the specific writing. Similarly, speeches are also designed around a purpose and crafted for a ... Sample Speech Outline Speech Topic: Type of Speech: Goals and Strategies for Preparing a Speech, Fall 2021. 5 of 6 Specific Purpose: Audience: I. Opening
how to outline a speech: the 4 essentials steps involved in writing an outline - detailed sequential help, with examples, covering: 1. choosing a topic, 2. audience analysis, 3. choosing the best organizational pattern to fit your speech purpose, 4. what to put in each part of your speech: introduction, body and conclusion. a printable speech ...
Get inspired by our FREE speech and essay examples. Use them to get the creative juices flowing. Don't copy any of these examples! Since these speeches are available for anyone to download, you can never be sure that another student has not used them, and that they will pass plagiarism evaluation tools, such as Turnitin or Plagscan.
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you'd like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part's duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
1. State your first point. The outline of the body of your speech will begin with the first point you intend to make in your speech. Write out a smooth transition from your introduction into the body of your speech. Your first point will be a top-level entry on your outline, typically noted by a Roman numeral.
YouTube: Nihir Shah. Must Read: Story Writing Format for Class 9 & 10 Speech writing is the art of using proper grammar and expression to convey a thought or message to a reader. Speech writing isn't all that distinct from other types of narrative writing.
As mentioned earlier, speech writing follow the same basic format as a traditional essay. There must be an introduction, a body and a conclusion. We discussed the introduction earlier. There is no 'set in stone' rule when it comes to how the body of a speech must be organized. However there are a few speech tips to keep in mind.
speech or to use the actual paper as notes. You will sound like you are reading a paper. Make an outline or bullet points. Practice until you can deliver the speech extemporaneously (i.e. looking at the audience more than your notes). Written by Dr. Marcia Berry, Ph.D., Department of Communication Studies Turning a paper into a speech
The outline for a public speech, according to COMM 101 online textbook The Public Speaking Project, p.p. 8-9. Use these samples to help prepare your speech outlines and bibliographies: Sample Speech Preparation Outline
you would in a research paper for a course. Moving from the intro into the body of the speech quickly will help keep your audience interested. You may be tempted to create suspense by keeping the audience guessing about your thesis until the end, then springing the implications of your discussion on them.
Speech Analysis Example Essay [Author's note: To listen to the speech analyzed in this essay and read the official transcript, visit Elie Wiesel Buchenwald's Speech at American Rhetoric. Citations in this essay follow MLA format.] Introduction. The following paragraph is the introduction to the analysis.
To cite a paper presentation from an academic conference, use the following format. List the date as the range of dates across which the conference took place. APA format. Author name, Initials. ( Year, Month Day - Day ). Paper title [Paper presentation]. Conference Name, City, State, Country. URL.
Type the manuscript in Landscape format. Use a clean, plain font that is easy to read. Arial is an example of a clean font. Increase the font size to 16 or larger, and double space the lines, so there's room to add scoring notes. Break the selection down into "beats", which are edited units of time or thought. Print only on one side.
Rhetorical Analysis: Paper Sample. Rhetorical prowess has long been celebrated as a formidable instrument in the arsenal of influential communicators. Barack Obama's "A More Perfect Union" speech stands as a testament to the enduring power of rhetoric in shaping public discourse and galvanizing collective action.
The upcoming May 29th elections will feature three ballot papers and an unprecedented number of candidates. South African voters to receive three ballots in the 2024 election - what you need to know
The Writing Manual is the Ohio authority in legal practice for the structure, style, and format of opinions from all courts. It is also widely used as the standard for drafting briefs and pleadings filed with the courts. More than a decade since the last edition was released, legal research is conducted, and briefs and opinions are read ...
Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That's OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if ...
CEO speech rate is a unique characteristic of company conference calls and online videos. We analyze a hand-collected sample of 60 earnings call transcripts from S&P 500 companies and find that CEO speech rate varies significantly across companies. We also find that CEOs tend to speak more quickly when discussing financial restatements.