

25 Useful Presentation Topics for Science
By: Author Shrot Katewa

We are mostly asked questions about Presentation Design. But, sometimes, we do have our patrons reaching out to us to seek help with the “content” that needs to be created even before we begin with the design of the presentation.
So, today we are sharing a few really easy-to-cover super useful presentation topics for Science. This is especially helpful for all those teachers and parents who are looking to increase the curiosity of aspiring students and children.
So, let’s dive right into it –
A Quick Note Before We Begin – if you want to make jaw-dropping presentations, I would recommend using one of these Presentation Designs . The best part is – it is only $16.5 a month, but you get to download and use as many presentation designs as you like! I personally use it from time-to-time, and it makes my task of making beautiful presentations really quick and easy!
1. Big Bang Theory – Origin of Our Universe
As a kid, I was always curious about how we came into existence! How the planet Earth was created? How did it all start? This is a great topic to really generate and at times, even quench the curiosity of your students or children. While it is a great topic for presentation in class, it is also an equally good topic for a dinner conversation with your kids.
2. DNA structure
Our DNA is the very core of our life. If the Big Bang Theory is how the universe came into being, DNA is where our personal journey begins. While the structure of DNA is quite fascinating, the impact it has on our lives and how it affects our characteristics is mind-boggling!
It is another great topic for a Science Presentation. Do keep in mind, use of visual aids will most likely improve comprehension and retention among your audience.
3. Gene Editing & Its Uses
In case you choose to go with the previous topic of DNA, Gene Editing serves as a perfect extension of that topic even though it can be a great topic in itself. Sharing insights on Gene Editing and how it works, can showcase the capacity of human endeavors and its resolve to make things better.
4. Important Discoveries of Science
Okay, so this can really be a fun topic. As a kid, it was always fascinating to know about some of the world’s greatest discoveries and inventions.
Be it Penicillium or the first flight by the Wright Brothers, such topics allow you to take your audience on a journey and relive the times in which these discoveries and inventions were made. The thing that I like the most about this topic is that it doesn’t have to be completed in one session.
In fact, this can be turned into a knowledge series of multiple sessions as the list of discoveries is endless.
5. Aerodynamics
Most kids and students are really fascinated with planes. But, only a few really understand the basic principles of how a plane works. Explaining Aerodynamics can be an interesting topic.
It also allows you to introduce props such as a plane and practical exercises such as creating your own plane and analyzing its aerodynamics. The introduction of visuals for such a topic can greatly enhance the learning experience.
So this is a topic that most of the kids and students would have at least heard of, most might know about it a little. But very few would really understand how gravity truly changed our concepts not just on Earth, but also beyond our Planet in our Solar System.
Gravity alone is responsible for the tectonic shift of mindset that the Earth was the center of our Solar System to the fact that the Sun is the center of our Solar System around which the rest of the planets revolve. That and much more!
Explaining the stories of Galileo who first challenged this assumption and how Newton turned everything we knew upside down (almost literally!)
7. Photosynthesis
Another interesting Science topic for a presentation.
How do non-moving organisms produce and consume food? How Photosynthesis is not just limited to trees but virtually drives all lifeforms on Earth through the transfer of energy.
Also, touching upon the fact how Photosynthesis has led to the revolutionary discovery of Solar cells and how it is potentially going to be powering our future.
8. Artificial Intelligence – Boon or Bane
When it comes to Artificial Intelligence, there is a lot that we can do to engage the curiosity of our kids and students. It is an evolving part of Science as we haven’t fully applied and utilized AI.
One of the reasons this can be a great topic is because it engages your students or kids to really think. You may consider forming 2 teams and allowing an open debate on how AI could be a boon or a bane – a great way to promote cross-learning.
9. Ocean – The Unknown World
Our Ocean is what sets our planet Earth apart from the other planets in our solar planet. It is not only one of the main factors contributing to life on earth, the Ocean holds a world of its own with hidden creatures which have only recently been explored.
There is a lot to cover when it comes to the Ocean. Don’t limit your imagination to just lifeforms as you can even talk about treasures troves contained in the ships that sank!
10. Astronomy
So I have a confession to make. Which is this – Astronomy astonished me as a kid, and it amazes me even now! There have been countless nights that I gazed at the stars in the sky in amazement trying to locate a planet, and falling stars and other man-made satellites in the sky.
This is not just an amazing topic for a presentation, but if you could get hold of a telescope for a practical session, it will make a night to remember for the kids and the students!
11. Light and its effects
This is another topic that can turn into a great practical session!
Presentations can be accompanied by a trip to the physics lab or even using equipment like a prism to take the session experience of your audience to a totally different level! Experiencing the various colors that form light is one thing, but understanding how it impacts almost every single thing in our day-to-day activities makes us admire it.
12. Atoms – Building Blocks of Matter
While there is a whole universe outside of our Planet, there is a completely different world that exists when we go granular inside any matter.
There are literally billions and billions of atoms inside just our human body. Each atom has its own world making it as diverse as you can imagine.
How these atoms interact with each other and what makes an atom can be a really engaging topic to bubble the curiosity of the students or your kids!
13. Sound & Waves
Another super interesting presentation topic for Science for kids and students is to understand how Sound works.
There are several things to cover as part of this ranging from simple waves to frequency and resonance experiments. Sound is not just a good topic for a presentation but also for experiments and physical demos.
14. Technology
Technology as a topic has a lot to cover. As we all know that technology touches each of our lives on a daily basis, students can find this topic relatable quite easily. The canvas for exploration and presentation is quite broad giving you a wide range of technology topics to present from.
15. Human Brain
Many believe that we only use 10% of the capacity of our human brain. We have to date only barely managed to understand how our brain works.
Even the parts that we have gathered an understanding about, we don’t quite fully understand. The human brain has remained a topic of astonishment for scientists for a long time. It is only logical to conclude that if presented effectively, this can be a good presentation topic on science.
16. Evolution
When Charles Darwin presented his Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection in his book “The Origin of Species”, it took the world of science by storm.
How the species have evolved over a period of millions of years is quite interesting. There were quite a few interesting learnings that Darwin had and he shared that as a summary. This is something that has been also covered in the TV series Cosmos by Neil Degrasse Tyson.
I highly recommend giving this TV series a watch to get inspiration for some topics for presentation.
17. Magnetism
The majority of the kids have handled and spent hours in awe playing with a magnet. Many try to understand how a magnet really works! But, only a few are able to really understand the science behind it.
Magnetism can be a really fun topic to give a presentation on. Additionally, this topic also allows enough space to display, experiment, and have fun with real magnet and iron filings to showcase the effect of magnetism.
18. Electricity
Electricity is pretty much everywhere.
Today, if there is no electricity, the region is considered underdeveloped or backward. The discovery and the use of electricity is probably one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century.
It has been single-handedly responsible for industrialization, powering growth, and the development of the human race.
19. Steam Engine
Steam Engine was the first step of the human race towards powered locomotives.
From the discovery of the steam engine to how it was responsible for creating a time standard and time zones along with the stories related to it, can all be very fascinating and take you back in time to relive history!
A perfect presentation topic for science students.
20. Science of Medicine
No list of presentation topics for Science would be complete without mentioning medicine and its benefits.
The discovery of medicines and drugs has been responsible for nearly doubling the average human age. The impact is far-reaching with several pros and cons that constitute an interesting topic for presentation.
21. Periodic Table
Students often find this topic very dull. However, if you can help them understand the beauty and significance of this periodic table, it can be an amazing topic.
To really understand how Mendeleev could predict the existence of various elements even before they were discovered, is mind-boggling!
The periodic table is such a perfect table that explains how the elements are arranged in a well-structured manner in nature. This topic can be turned into a very interesting topic but a bit of effort and some out-of-the-box thinking may be required.
22. Buoyancy
Okay, so we all may have heard the story of Archimedes in a bathtub and how he shouted “Eureka” when he managed to solve the problem that was tasked to him. He did this using the Buoyancy principle.
While this story is something we relate to buoyancy the most, there is a lot more than we can truly learn and apply using this principle. This can be a very helpful topic for a presentation as well as a practical science experiment.
23. Health & Nutrition
Health & Nutrition is a very important aspect of our life. Its importance is often not completely understood by kids and students alike. Presenting about Health & Nutrition can go a long way to benefit the students to maintain a very healthy life!
24. Our Solar System
Our Solar System is a topic that is mostly taught since you join the school.
However, while most of us know about our solar system, there are enough mysteries about it to capture and captivate the attention of your audience. Questions like – why is Pluto not a planet anymore?
Or other questions such as – are we alone in this universe or even topics around the Sun as a star or even the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter can all lead to great engaging presentations and discussions.
25. Stem Cell
Stem cell research has become cutting-edge medical research. Thus, it is often a hot topic for discussion but is often not completely understood.
This topic will also provide you an opportunity to engage your audience in a debate that could be centered around the ethics of stem cells and their application.
This is a perfect topic as this allows your students or kids to learn and share their opinion with others.
Science is a vast world. Even though there are several other topics that can be covered, we decided to list topics that are relatively common such that it widely applies to a large set of people. If you have shortlisted your presentation topic and are looking for help to create a visually appealing presentation that captures the attention of your audience, be sure to reach out to us!
Our goal on this blog is to create content that helps YOU create fantastic presentations; especially if you have never been a designer. We’ve started our blog with non-designers in mind, and we have got some amazing content on our site to help YOU design better.
If you have any topics in mind that you would want us to write about, be sure to drop us a comment below. In case you need us to work with you and improve the design of your presentation, write to us on [email protected] . Our team will be happy to help you with your requirements.
Lastly, your contribution can make this world a better place for presentations . All you have to do is simply share this blog in your network and help other fellow non-designers with their designs!
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to make a scientific presentation

Scientific presentation outlines
Questions to ask yourself before you write your talk, 1. how much time do you have, 2. who will you speak to, 3. what do you want the audience to learn from your talk, step 1: outline your presentation, step 2: plan your presentation slides, step 3: make the presentation slides, slide design, text elements, animations and transitions, step 4: practice your presentation, final thoughts, frequently asked questions about preparing scientific presentations, related articles.
A good scientific presentation achieves three things: you communicate the science clearly, your research leaves a lasting impression on your audience, and you enhance your reputation as a scientist.
But, what is the best way to prepare for a scientific presentation? How do you start writing a talk? What details do you include, and what do you leave out?
It’s tempting to launch into making lots of slides. But, starting with the slides can mean you neglect the narrative of your presentation, resulting in an overly detailed, boring talk.
The key to making an engaging scientific presentation is to prepare the narrative of your talk before beginning to construct your presentation slides. Planning your talk will ensure that you tell a clear, compelling scientific story that will engage the audience.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to make a good oral scientific presentation, including:
- The different types of oral scientific presentations and how they are delivered;
- How to outline a scientific presentation;
- How to make slides for a scientific presentation.
Our advice results from delving into the literature on writing scientific talks and from our own experiences as scientists in giving and listening to presentations. We provide tips and best practices for giving scientific talks in a separate post.
There are two main types of scientific talks:
- Your talk focuses on a single study . Typically, you tell the story of a single scientific paper. This format is common for short talks at contributed sessions in conferences.
- Your talk describes multiple studies. You tell the story of multiple scientific papers. It is crucial to have a theme that unites the studies, for example, an overarching question or problem statement, with each study representing specific but different variations of the same theme. Typically, PhD defenses, invited seminars, lectures, or talks for a prospective employer (i.e., “job talks”) fall into this category.
➡️ Learn how to prepare an excellent thesis defense
The length of time you are allotted for your talk will determine whether you will discuss a single study or multiple studies, and which details to include in your story.
The background and interests of your audience will determine the narrative direction of your talk, and what devices you will use to get their attention. Will you be speaking to people specializing in your field, or will the audience also contain people from disciplines other than your own? To reach non-specialists, you will need to discuss the broader implications of your study outside your field.
The needs of the audience will also determine what technical details you will include, and the language you will use. For example, an undergraduate audience will have different needs than an audience of seasoned academics. Students will require a more comprehensive overview of background information and explanations of jargon but will need less technical methodological details.
Your goal is to speak to the majority. But, make your talk accessible to the least knowledgeable person in the room.
This is called the thesis statement, or simply the “take-home message”. Having listened to your talk, what message do you want the audience to take away from your presentation? Describe the main idea in one or two sentences. You want this theme to be present throughout your presentation. Again, the thesis statement will depend on the audience and the type of talk you are giving.
Your thesis statement will drive the narrative for your talk. By deciding the take-home message you want to convince the audience of as a result of listening to your talk, you decide how the story of your talk will flow and how you will navigate its twists and turns. The thesis statement tells you the results you need to show, which subsequently tells you the methods or studies you need to describe, which decides the angle you take in your introduction.
➡️ Learn how to write a thesis statement
The goal of your talk is that the audience leaves afterward with a clear understanding of the key take-away message of your research. To achieve that goal, you need to tell a coherent, logical story that conveys your thesis statement throughout the presentation. You can tell your story through careful preparation of your talk.
Preparation of a scientific presentation involves three separate stages: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slides, and practicing your delivery. Making the slides of your talk without first planning what you are going to say is inefficient.
Here, we provide a 4 step guide to writing your scientific presentation:
- Outline your presentation
- Plan your presentation slides
- Make the presentation slides
- Practice your presentation

Writing an outline helps you consider the key pieces of your talk and how they fit together from the beginning, preventing you from forgetting any important details. It also means you avoid changing the order of your slides multiple times, saving you time.
Plan your talk as discrete sections. In the table below, we describe the sections for a single study talk vs. a talk discussing multiple studies:
The following tips apply when writing the outline of a single study talk. You can easily adapt this framework if you are writing a talk discussing multiple studies.
Introduction: Writing the introduction can be the hardest part of writing a talk. And when giving it, it’s the point where you might be at your most nervous. But preparing a good, concise introduction will settle your nerves.
The introduction tells the audience the story of why you studied your topic. A good introduction succinctly achieves four things, in the following order.
- It gives a broad perspective on the problem or topic for people in the audience who may be outside your discipline (i.e., it explains the big-picture problem motivating your study).
- It describes why you did the study, and why the audience should care.
- It gives a brief indication of how your study addressed the problem and provides the necessary background information that the audience needs to understand your work.
- It indicates what the audience will learn from the talk, and prepares them for what will come next.
A good introduction not only gives the big picture and motivations behind your study but also concisely sets the stage for what the audience will learn from the talk (e.g., the questions your work answers, and/or the hypotheses that your work tests). The end of the introduction will lead to a natural transition to the methods.
Give a broad perspective on the problem. The easiest way to start with the big picture is to think of a hook for the first slide of your presentation. A hook is an opening that gets the audience’s attention and gets them interested in your story. In science, this might take the form of a why, or a how question, or it could be a statement about a major problem or open question in your field. Other examples of hooks include quotes, short anecdotes, or interesting statistics.
Why should the audience care? Next, decide on the angle you are going to take on your hook that links to the thesis of your talk. In other words, you need to set the context, i.e., explain why the audience should care. For example, you may introduce an observation from nature, a pattern in experimental data, or a theory that you want to test. The audience must understand your motivations for the study.
Supplementary details. Once you have established the hook and angle, you need to include supplementary details to support them. For example, you might state your hypothesis. Then go into previous work and the current state of knowledge. Include citations of these studies. If you need to introduce some technical methodological details, theory, or jargon, do it here.
Conclude your introduction. The motivation for the work and background information should set the stage for the conclusion of the introduction, where you describe the goals of your study, and any hypotheses or predictions. Let the audience know what they are going to learn.
Methods: The audience will use your description of the methods to assess the approach you took in your study and to decide whether your findings are credible. Tell the story of your methods in chronological order. Use visuals to describe your methods as much as possible. If you have equations, make sure to take the time to explain them. Decide what methods to include and how you will show them. You need enough detail so that your audience will understand what you did and therefore can evaluate your approach, but avoid including superfluous details that do not support your main idea. You want to avoid the common mistake of including too much data, as the audience can read the paper(s) later.
Results: This is the evidence you present for your thesis. The audience will use the results to evaluate the support for your main idea. Choose the most important and interesting results—those that support your thesis. You don’t need to present all the results from your study (indeed, you most likely won’t have time to present them all). Break down complex results into digestible pieces, e.g., comparisons over multiple slides (more tips in the next section).
Summary: Summarize your main findings. Displaying your main findings through visuals can be effective. Emphasize the new contributions to scientific knowledge that your work makes.
Conclusion: Complete the circle by relating your conclusions to the big picture topic in your introduction—and your hook, if possible. It’s important to describe any alternative explanations for your findings. You might also speculate on future directions arising from your research. The slides that comprise your conclusion do not need to state “conclusion”. Rather, the concluding slide title should be a declarative sentence linking back to the big picture problem and your main idea.
It’s important to end well by planning a strong closure to your talk, after which you will thank the audience. Your closing statement should relate to your thesis, perhaps by stating it differently or memorably. Avoid ending awkwardly by memorizing your closing sentence.
By now, you have an outline of the story of your talk, which you can use to plan your slides. Your slides should complement and enhance what you will say. Use the following steps to prepare your slides.
- Write the slide titles to match your talk outline. These should be clear and informative declarative sentences that succinctly give the main idea of the slide (e.g., don’t use “Methods” as a slide title). Have one major idea per slide. In a YouTube talk on designing effective slides , researcher Michael Alley shows examples of instructive slide titles.
- Decide how you will convey the main idea of the slide (e.g., what figures, photographs, equations, statistics, references, or other elements you will need). The body of the slide should support the slide’s main idea.
- Under each slide title, outline what you want to say, in bullet points.
In sum, for each slide, prepare a title that summarizes its major idea, a list of visual elements, and a summary of the points you will make. Ensure each slide connects to your thesis. If it doesn’t, then you don’t need the slide.
Slides for scientific presentations have three major components: text (including labels and legends), graphics, and equations. Here, we give tips on how to present each of these components.
- Have an informative title slide. Include the names of all coauthors and their affiliations. Include an attractive image relating to your study.
- Make the foreground content of your slides “pop” by using an appropriate background. Slides that have white backgrounds with black text work well for small rooms, whereas slides with black backgrounds and white text are suitable for large rooms.
- The layout of your slides should be simple. Pay attention to how and where you lay the visual and text elements on each slide. It’s tempting to cram information, but you need lots of empty space. Retain space at the sides and bottom of your slides.
- Use sans serif fonts with a font size of at least 20 for text, and up to 40 for slide titles. Citations can be in 14 font and should be included at the bottom of the slide.
- Use bold or italics to emphasize words, not underlines or caps. Keep these effects to a minimum.
- Use concise text . You don’t need full sentences. Convey the essence of your message in as few words as possible. Write down what you’d like to say, and then shorten it for the slide. Remove unnecessary filler words.
- Text blocks should be limited to two lines. This will prevent you from crowding too much information on the slide.
- Include names of technical terms in your talk slides, especially if they are not familiar to everyone in the audience.
- Proofread your slides. Typos and grammatical errors are distracting for your audience.
- Include citations for the hypotheses or observations of other scientists.
- Good figures and graphics are essential to sustain audience interest. Use graphics and photographs to show the experiment or study system in action and to explain abstract concepts.
- Don’t use figures straight from your paper as they may be too detailed for your talk, and details like axes may be too small. Make new versions if necessary. Make them large enough to be visible from the back of the room.
- Use graphs to show your results, not tables. Tables are difficult for your audience to digest! If you must present a table, keep it simple.
- Label the axes of graphs and indicate the units. Label important components of graphics and photographs and include captions. Include sources for graphics that are not your own.
- Explain all the elements of a graph. This includes the axes, what the colors and markers mean, and patterns in the data.
- Use colors in figures and text in a meaningful, not random, way. For example, contrasting colors can be effective for pointing out comparisons and/or differences. Don’t use neon colors or pastels.
- Use thick lines in figures, and use color to create contrasts in the figures you present. Don’t use red/green or red/blue combinations, as color-blind audience members can’t distinguish between them.
- Arrows or circles can be effective for drawing attention to key details in graphs and equations. Add some text annotations along with them.
- Write your summary and conclusion slides using graphics, rather than showing a slide with a list of bullet points. Showing some of your results again can be helpful to remind the audience of your message.
- If your talk has equations, take time to explain them. Include text boxes to explain variables and mathematical terms, and put them under each term in the equation.
- Combine equations with a graphic that shows the scientific principle, or include a diagram of the mathematical model.
- Use animations judiciously. They are helpful to reveal complex ideas gradually, for example, if you need to make a comparison or contrast or to build a complicated argument or figure. For lists, reveal one bullet point at a time. New ideas appearing sequentially will help your audience follow your logic.
- Slide transitions should be simple. Silly ones distract from your message.
- Decide how you will make the transition as you move from one section of your talk to the next. For example, if you spend time talking through details, provide a summary afterward, especially in a long talk. Another common tactic is to have a “home slide” that you return to multiple times during the talk that reinforces your main idea or message. In her YouTube talk on designing effective scientific presentations , Stanford biologist Susan McConnell suggests using the approach of home slides to build a cohesive narrative.
To deliver a polished presentation, it is essential to practice it. Here are some tips.
- For your first run-through, practice alone. Pay attention to your narrative. Does your story flow naturally? Do you know how you will start and end? Are there any awkward transitions? Do animations help you tell your story? Do your slides help to convey what you are saying or are they missing components?
- Next, practice in front of your advisor, and/or your peers (e.g., your lab group). Ask someone to time your talk. Take note of their feedback and the questions that they ask you (you might be asked similar questions during your real talk).
- Edit your talk, taking into account the feedback you’ve received. Eliminate superfluous slides that don’t contribute to your takeaway message.
- Practice as many times as needed to memorize the order of your slides and the key transition points of your talk. However, don’t try to learn your talk word for word. Instead, memorize opening and closing statements, and sentences at key junctures in the presentation. Your presentation should resemble a serious but spontaneous conversation with the audience.
- Practicing multiple times also helps you hone the delivery of your talk. While rehearsing, pay attention to your vocal intonations and speed. Make sure to take pauses while you speak, and make eye contact with your imaginary audience.
- Make sure your talk finishes within the allotted time, and remember to leave time for questions. Conferences are particularly strict on run time.
- Anticipate questions and challenges from the audience, and clarify ambiguities within your slides and/or speech in response.
- If you anticipate that you could be asked questions about details but you don’t have time to include them, or they detract from the main message of your talk, you can prepare slides that address these questions and place them after the final slide of your talk.
➡️ More tips for giving scientific presentations
An organized presentation with a clear narrative will help you communicate your ideas effectively, which is essential for engaging your audience and conveying the importance of your work. Taking time to plan and outline your scientific presentation before writing the slides will help you manage your nerves and feel more confident during the presentation, which will improve your overall performance.
A good scientific presentation has an engaging scientific narrative with a memorable take-home message. It has clear, informative slides that enhance what the speaker says. You need to practice your talk many times to ensure you deliver a polished presentation.
First, consider who will attend your presentation, and what you want the audience to learn about your research. Tailor your content to their level of knowledge and interests. Second, create an outline for your presentation, including the key points you want to make and the evidence you will use to support those points. Finally, practice your presentation several times to ensure that it flows smoothly and that you are comfortable with the material.
Prepare an opening that immediately gets the audience’s attention. A common device is a why or a how question, or a statement of a major open problem in your field, but you could also start with a quote, interesting statistic, or case study from your field.
Scientific presentations typically either focus on a single study (e.g., a 15-minute conference presentation) or tell the story of multiple studies (e.g., a PhD defense or 50-minute conference keynote talk). For a single study talk, the structure follows the scientific paper format: Introduction, Methods, Results, Summary, and Conclusion, whereas the format of a talk discussing multiple studies is more complex, but a theme unifies the studies.
Ensure you have one major idea per slide, and convey that idea clearly (through images, equations, statistics, citations, video, etc.). The slide should include a title that summarizes the major point of the slide, should not contain too much text or too many graphics, and color should be used meaningfully.

Get in touch
555-555-5555

Limited time offer: 20% off all templates ➞

Scientific Presentation Guide: How to Create an Engaging Research Talk
Creating an effective scientific presentation requires developing clear talking points and slide designs that highlight your most important research results..
Scientific presentations are detailed talks that showcase a research project or analysis results. This comprehensive guide reviews everything you need to know to give an engaging presentation for scientific conferences, lab meetings, and PhD thesis talks. From creating your presentation outline to designing effective slides, the tips in this article will give you the tools you need to impress your scientific peers and superiors.

Step 1. Create a Presentation Outline
The first step to giving a good scientific talk is to create a presentation outline that engages the audience at the start of the talk, highlights only 3-5 main points of your research, and then ends with a clear take-home message. Creating an outline ensures that the overall talk storyline is clear and will save you time when you start to design your slides.
Engage Your Audience
The first part of your presentation outline should contain slide ideas that will gain your audience's attention. Below are a few recommendations for slides that engage your audience at the start of the talk:
- Create a slide that makes connects your data or presentation information to a shared purpose, such as relevance to solving a medical problem or fundamental question in your field of research
- Create slides that ask and invite questions
- Use humor or entertainment

Identify Clear Main Points
After writing down your engagement ideas, the next step is to list the main points that will become the outline slide for your presentation. A great way to accomplish this is to set a timer for five minutes and write down all of the main points and results or your research that you want to discuss in the talk. When the time is up, review the points and select no more than three to five main points that create your talk outline. Limiting the amount of information you share goes a long way in maintaining audience engagement and understanding.

Create a Take-Home Message
And finally, you should brainstorm a single take-home message that makes the most important main point stand out. This is the one idea that you want people to remember or to take action on after your talk. This can be your core research discovery or the next steps that will move the project forward.
Step 2. Choose a Professional Slide Theme
After you have a good presentation outline, the next step is to choose your slide colors and create a theme. Good slide themes use between two to four main colors that are accessible to people with color vision deficiencies. Read this article to learn more about choosing the best scientific color palettes .
You can also choose templates that already have an accessible color scheme. However, be aware that many PowerPoint templates that are available online are too cheesy for a scientific audience. Below options to download professional scientific slide templates that are designed specifically for academic conferences, research talks, and graduate thesis defenses.
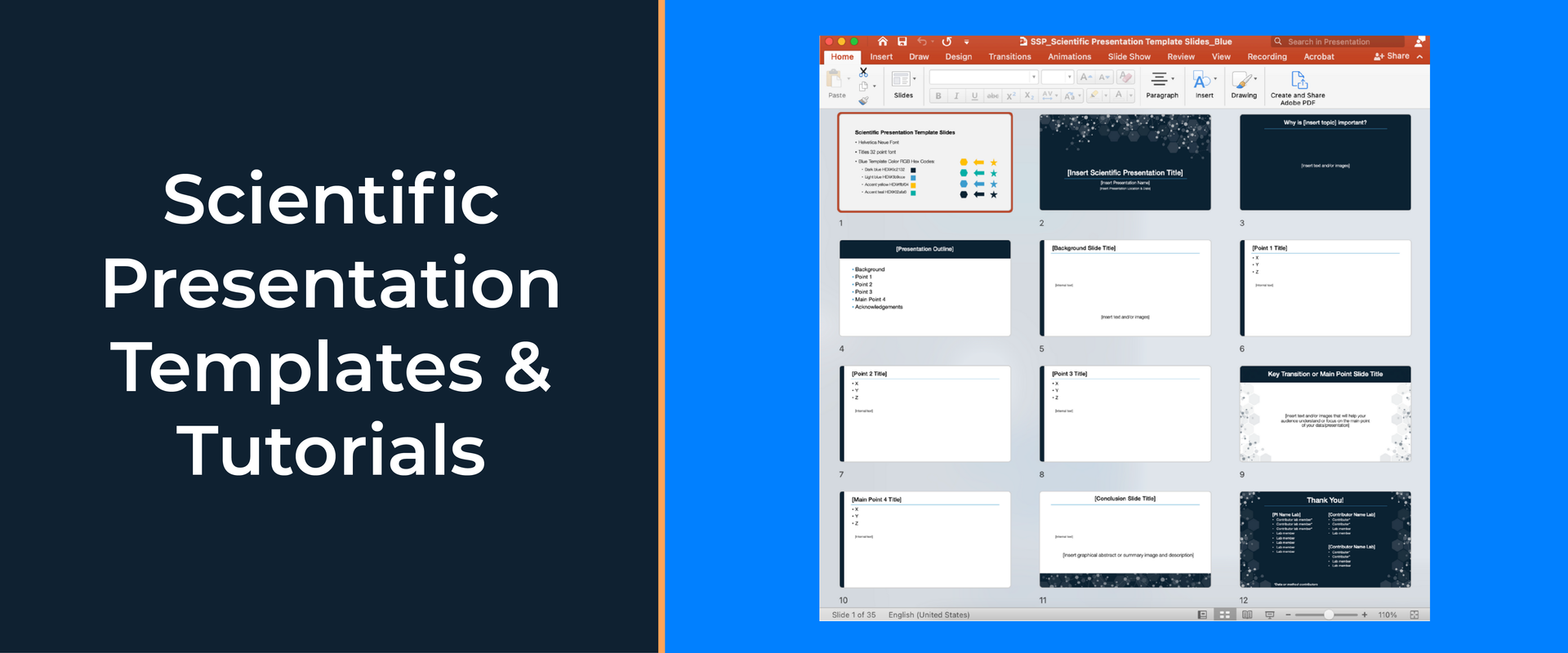
Step 3. Design Your Slides
Designing good slides is essential to maintaining audience interest during your scientific talk. Follow these four best practices for designing your slides:
- Keep it simple: limit the amount of information you show on each slide
- Use images and illustrations that clearly show the main points with very little text.
- Read this article to see research slide example designs for inspiration
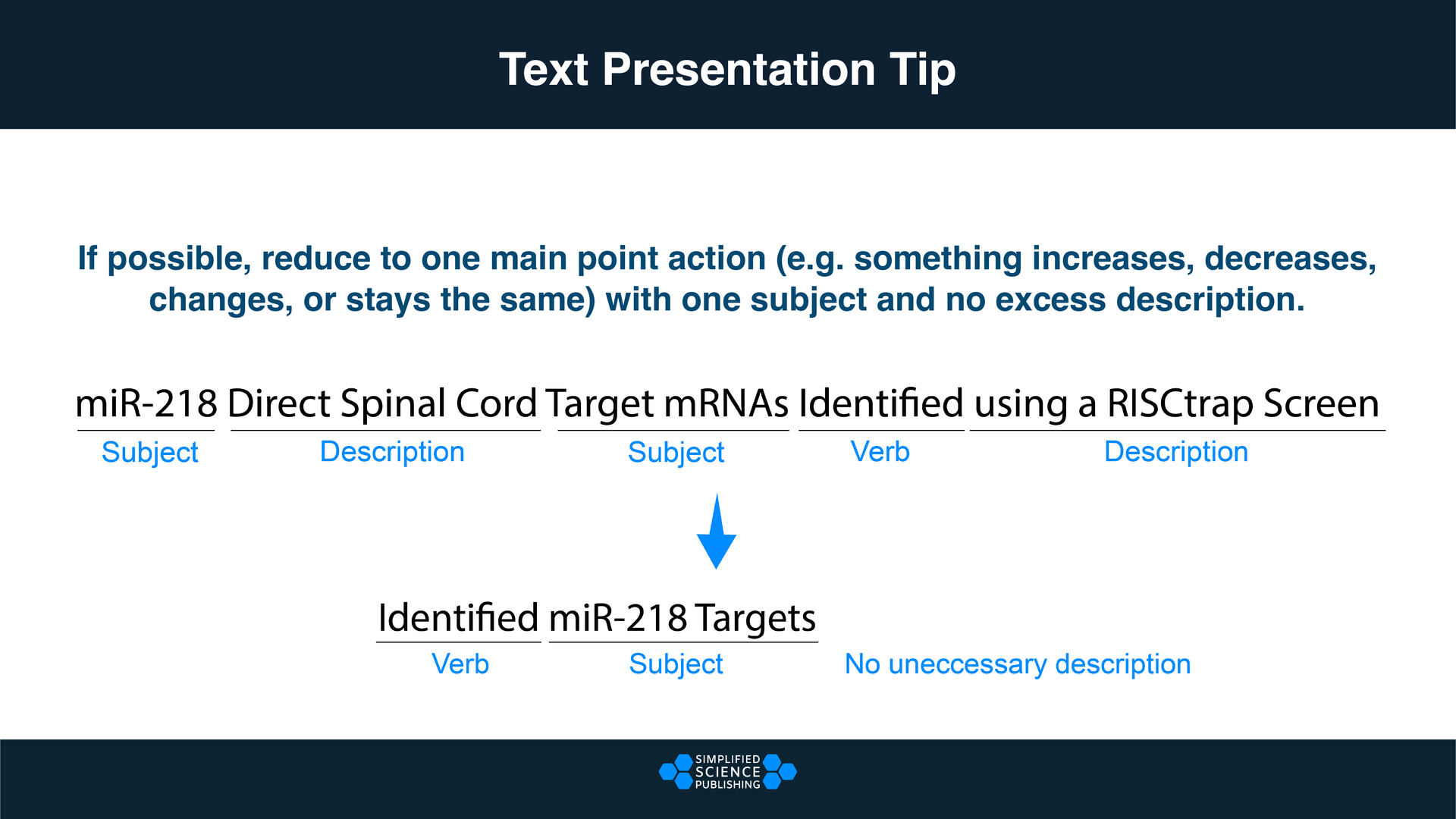
- When you are using text, try to reduce the scientific jargon that is unnecessary. Text on research talk slides needs to be much more simple than the text used in scientific publications (see example below).
- Use appear/disappear animations to break up the details into smaller digestible bites
- Sign up for the free presentation design course to learn PowerPoint animation tricks
Scientific Presentation Design Summary
All of the examples and tips described in this article will help you create impressive scientific presentations. Below is the summary of how to give an engaging talk that will earn respect from your scientific community.
Step 1. Draft Presentation Outline. Create a presentation outline that clearly highlights the main point of your research. Make sure to start your talk outline with ideas to engage your audience and end your talk with a clear take-home message.
Step 2. Choose Slide Theme. Use a slide template or theme that looks professional, best represents your data, and matches your audience's expectations. Do not use slides that are too plain or too cheesy.
Step 3. Design Engaging Slides. Effective presentation slide designs use clear data visualizations and limits the amount of information that is added to each slide.
And a final tip is to practice your presentation so that you can refine your talking points. This way you will also know how long it will take you to cover the most essential information on your slides. Thank you for choosing Simplified Science Publishing as your science communication resource and good luck with your presentations!
Interested in free design templates and training?
Explore scientific illustration templates and courses by creating a Simplified Science Publishing Log In. Whether you are new to data visualization design or have some experience, these resources will improve your ability to use both basic and advanced design tools.
Interested in reading more articles on scientific design? Learn more below:

Data Storytelling Techniques: How to Tell a Great Data Story in 4 Steps

Best Science PowerPoint Templates and Slide Design Examples

Free Research Poster Templates and Tutorials
Content is protected by Copyright license. Website visitors are welcome to share images and articles, however they must include the Simplified Science Publishing URL source link when shared. Thank you!
Online Courses
Stay up-to-date for new simplified science courses, subscribe to our newsletter.
Thank you for signing up!
You have been added to the emailing list and will only recieve updates when there are new courses or templates added to the website.
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience and we do not sell data. By using this website, you are giving your consent for us to set cookies: View Privacy Policy
Simplified Science Publishing, LLC
- Program Design
- Peer Mentors
- Excelling in Graduate School
- Oral Communication
- Written communication
- About Climb
Creating a 10-15 Minute Scientific Presentation
In the course of your career as a scientist, you will be asked to give brief presentations -- to colleagues, lab groups, and in other venues. We have put together a series of short videos to help you organize and deliver a crisp 10-15 minute scientific presentation.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation.
Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation
Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions
Two additional videos should prove useful:
Designing PowerPoint Slides for a Scientific Presentation walks you through the key principles in designing powerful, easy to read slides.
Delivering a Presentation provides tips and approaches to help you put your best foot forward when you stand up in front of a group.
Other resources include:
Quick Links
Northwestern bioscience programs.
- Biomedical Engineering (BME)
- Chemical and Biological Engineering (ChBE)
- Driskill Graduate Program in the Life Sciences (DGP)
- Interdepartmental Biological Sciences (IBiS)
- Northwestern University Interdepartmental Neuroscience (NUIN)
- Campus Emergency Information
- Contact Northwestern University
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- University Policies
- Northwestern Home
- Northwestern Calendar: PlanIt Purple
- Northwestern Search
Chicago: 420 East Superior Street, Rubloff 6-644, Chicago, IL 60611 312-503-8286
- Enterprise Custom Courses
- Build Your Own Courses
- Help Center
- Clinical Trial Recruitment
- Pharmaceutical Marketing
- Health Department Resources
- Patient Education
- Research Presentation
- Remote Monitoring
- Health Literacy & SciComm
- Student Education & Higher Ed
- Individual Learning
- Member Directory
- Community Chats on Slack
- SciComm Program
- The Story-Driven Method
- The Instructional Method
How to Create an Engaging Science Presentation: A Quick Guide
We’ve all been there – rushing to put slides together for an upcoming talk, filling them with bullet points and text that we want to remember to cover. We aren’t sure exactly what the audience will want to know or how much detail to include, so we default to putting ALL the details in that might be needed. But such efforts often result in presentations that are too long, too confusing, and difficult for both ourselves and our audiences to navigate.
Today I gave a workshop to public health graduate students about how to create more engaging science presentations and talks. I’ve summarized the main takeaways below. I hope this quick guide will be useful to you as you prepare for your next science talk or presentation!

The best science talks start with a process of simplifying – peeling back the layers of information and detail to get at the one core idea that you want to communicate. Over the course of your talk, you may present 2-3 key messages that relate to, demonstrate, provide examples of or underpin this idea. (Three is a nice round number of messages or takeaways that your audience will be able to remember!) But stick to one big idea. Trying to communicate too much in a presentation or talk will overwhelm your audience, and they may walk away without a good memory of any of the ideas you presented.
Once you’ve settled on your one big idea, you can develop a theme that will pervade every aspect of your talk. This theme might be a defining element of your big idea and something that can tie all of your data or talking points together. Your theme should inform the examples, anecdotes and analogies that you use to make the science concepts you present more accessible. It should also inform your slides’ very design – the colors, visuals, layout and content flow.
If you have trouble identifying your big idea and your theme, you can try using what scientist and science author Randy Olson calls the “Dobzhansky Template.” Fill in the blanks of this statement: “ Nothing in [your talk topic, research topic or big idea] makes sense, except in the light of [your theme!] .”
Here’s an example for you: “Nothing in the creation of engaging science talks makes sense except in the light of people’s need for personal connection .” With this statement, I’m identifying a key aspect, a unifying theme, for my talk (or blog post) on how to create engaging science talks. We all crave personal connection. Yes, even to the speakers of science talks we listen to! What does this mean in terms of what we want or expect from these speakers? It means we want storytelling . We want to hear their stories, know their background, hear about their struggles and triumphs! We want to be able to step into their shoes and see what they saw. We want to interact with them.

Tell a Story
Narratives engage more than facts. By telling a story , using suspense and characters to pull people through your presentation, you will capture and keep their attention for longer. People also remember information presented in a story format better than they do information presented as disparate facts or bullet points.
“Story is a pull strategy. If your story is good enough, people—of their own free will—come to the conclusion they can trust you and the message you bring.” – Annette Simmons
Storytelling is a powerful science communication tool. In storytelling, both the storyteller and the listener or reader contribute to the story’s meaning through their interpretations, feelings and emotions. Liz Neeley, former executive director of The Story Collider, once said: “Science communicators frequently fail to understand that a feeling is almost never conquered with a fact.”
Stories are exciting. They elicit emotions. They help foster a personal connection between the storyteller and the listener, and a connection between the listener and the topic, characters or ideas presented in the story.
But what IS a story? As humans, we excel at recognizing a story when we hear one, but defining a story’s key characteristics is more difficult than you might think. If you ask anyone to explain what makes for a good story, they likely will have a hard time explaining it.
In her fantastic book Wired for Story , Lisa Cron starts by explaining what a story is NOT.
It is not plot – that is just what happens in the story.
It is not characters , although characters are critical components of storytelling, even if they are not human or even alive. Cells and molecules could be the characters of your next science talk!
It is not suspense or conflict , although these elements get us closer to what defines a good story. But just because your talk builds suspense does not necessarily make it an engaging story. What if we don’t identify with your characters?
The truth is that the key defining element of story is internal change . Think of how every Aesop’s fable communicates a moral or lesson that the main character learned from some journey. As Lisa Cron writes, “A story is how what happens affects someone who is trying to achieve what turns out to be a difficult goal, and how he or she changes as a result.” The key here is the part about “how he or she changes.” A great story calls characters to a great adventure, but the adventure doesn’t leave them just as they were before. The adventure – like a scientific discovery that took years of experimentation (and failure) in the lab – leads to an internal change, in perspective or knowledge or behavior, as a result of conflicts overcome.
This is the secret of storytelling. A story asks characters to change and grow, and so the scientists in our stories must change and grow, discover new things about themselves and overcome challenges that force them to adopt new perspectives. So if you are giving a science talk about your own research, this might look like telling stories about your own struggles, growths and changes in perspective as you made your journey to discovery!
How can you bring a story of internal change to your next science presentation or talk?
What is one of the most common mistakes people make when creating slides to accompany a science talk? They use WAY too much text, and they use visuals as an afterthought. Worse yet, they use visuals that are copyrighted without attribution. They use stock imagery that reinforces stereotypes. They use visuals pasted from a Google search that don’t help the viewer understand or interpret what is said or written on the slides.
Visuals can be a powerful tool to advance audience learning or engagement during your science talks. You can use visuals to provide concrete examples of concepts you are talking about. You can use imagery that sparks thought or emotion. You can use visuals that reinforce your BIG idea or the theme of your talk, in a way that will make your talk more memorable for them. Yes, you might need to use a scientific figure, graph, chart or data visualization here and there if you are giving a more technical scientific talk, and that’s ok as long as you also talk the audience through this visual. Don’t assume they can listen to you talk about something different while also taking the time to interpret the message in this graphic or visualization – they can’t.
The same goes for text. You are demanding way too much brainpower of your audience to expect them to listen to you while also reading your slides. And if you are saying the same things as are written on your slides, they will grow bored. Simple visual aids used the right way, however, can delight your audience and help them better understand what you are saying.
Consider working with a professional artist or designer to create visuals for the slides of your next science talk! They excel at creating visuals that capture people’s attention, curiosity and emotions. And if you do this, your visuals will perfectly match what you are trying to communicate in words, boosting learning and understanding.
Foster Interaction
A good science talk or presentation gives the audience opportunities to interact with you! This could be through questions, activities, discussions or thought experiments. Let the audience explore your data or interpretations with you. They will be more engaged and likely trust you more as a result, because they felt heard .
Personalize!
Most great science speakers make themselves vulnerable in a way – they tell personal stories of struggles, growth and discovery. Personal stories are engaging. They also help the audience care about what the speaker has to say.
It can be scary to talk about yourself, especially for a scientist who has been trained to focus solely on the data. But the humans listening to your talk or presentation crave human connection. They will also grab hold of anything that helps them better relate to you. Give them that in the form of personal stories of obstacles overcome, of personal lessons learned, of work-life balance, of your fears and passions. Better yet, tell personal stories that reinforce your theme and show the power of your big idea!

Do you have other strategies for how you make your science talks and presentations more engaging? Let me know in the comments below!
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
About the author: paige jarreau.

Related Posts

Una actividad práctica para ayudarte a comunicar la ciencia de forma culturalmente relevante

The Power of SciComm in Combatting Mental Health Stigma
Make your scicomm more culturally relevant: a practice activity.

Communicating About Postpartum Depression

Science Communication and Genetic Counselling
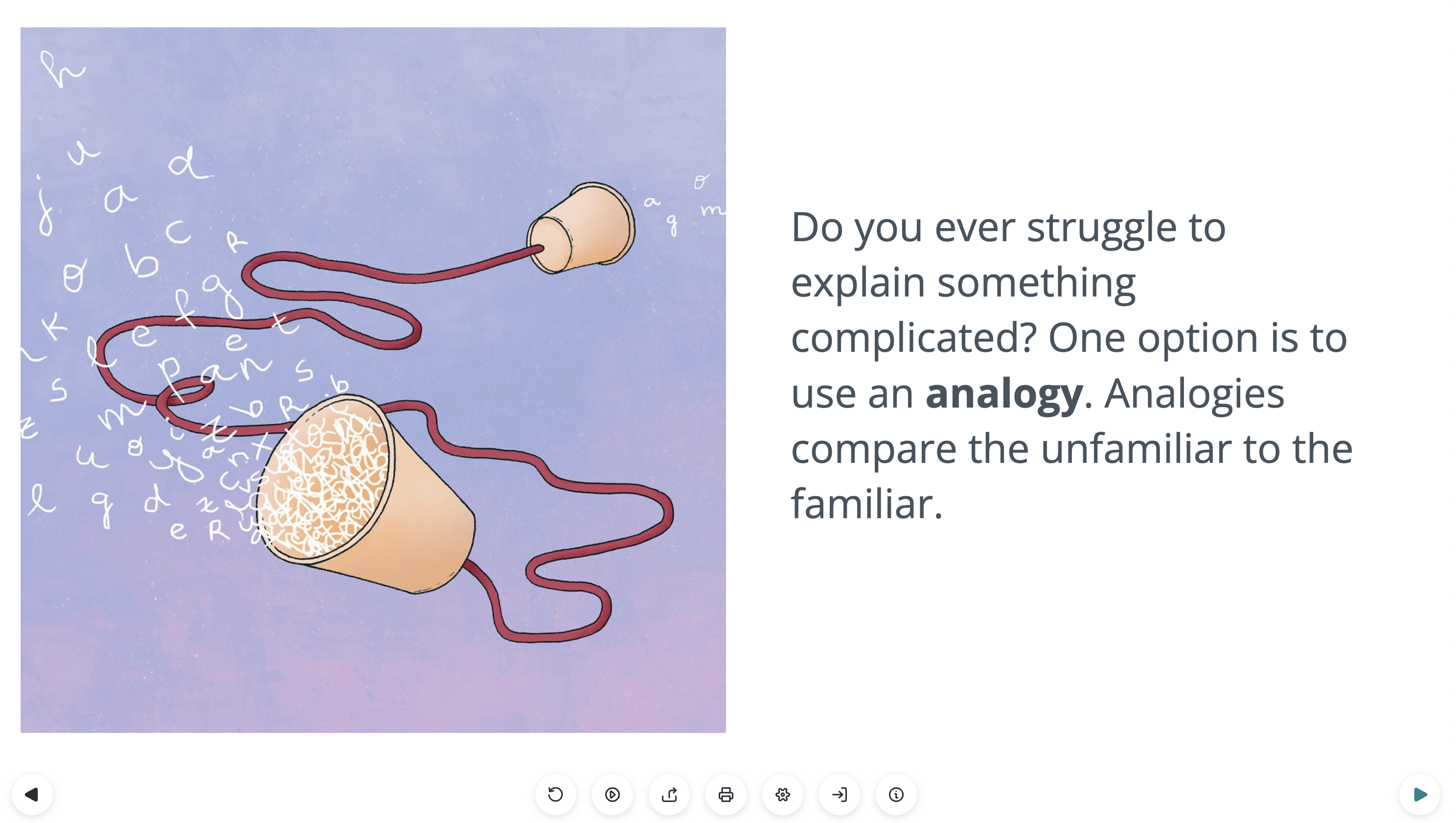
Creating Analogies: Elevate Your Science with a Lifeology Course
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER GUIDE
- 01 December 2021
How to tell a compelling story in scientific presentations
- Bruce Kirchoff 0
Bruce Kirchoff is a botanist and storyteller at the University of North Carolina at Greensboro in North Carolina, USA. His new book is Presenting Science Concisely .
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Structuring your presentations with care can help you to clearly communicate to your audience. Credit: Getty
Scientific presentations are too often boring and ineffective. Their focus on techniques and data do not make it easy for the audience to understand the main point of the research.
If you want to reach beyond the narrow group of scientists who work in your specific area, you need to tell your audience members why they should be interested. Three things can help you to be engaging and convey the importance of your research to a wide audience. I had been teaching scientific communication for several years when I was approached to write a book about improving scientific presentations 1 . These are my three most important tips.
State your main finding in your title
The best titles get straight to the point. They tell the audience what you found, and they let them know what your talk will be about. Throughout this article, I will use titles from Nature papers published in the past two years as examples that will stand in for presentation titles. This is because Nature articles have a similar goal of attempting to make discipline-specific research available to a broader audience of scientists. Take, for example: ‘Supply chain diversity buffers cities against food shocks’ 2 .
A great title tells the reader exactly what’s new and precisely conveys the main result, as this one demonstrates. A more conventional title would have been ‘Effect of supply chain diversity on food shocks’, which omits the direction of the effect — so mainly scientists who are interested in your research area will be attracted to the talk. Others will wonder whether the talk will be a waste of time: maybe there was no effect at all.

Collection: Careers toolkit
Another example of a good title is: ‘Organic management promotes natural pest control through altered plant resistance to insects’ 3 .
This title ensures that the audience members know that the talk will be about the beneficial effects of organic crop management before they hear it. They also know that organic management increases plant resistance to insects. This title is much better than one such as: ‘Effects of organic pest management on plant insect resistance’. This title tells the audience the general area of the talk but does not give them the main result.
Finally, look at: ‘A highly magnetized and rapidly rotating white dwarf as small as the Moon’ 4 .
Good titles can just as easily be written for descriptive work as for experimental results. All you need to do is tell your audience what you found. Be as specific as possible. Compare this title with a more conventional one for the same work: ‘Use of the Zwicky Transient Facility to search for short period objects below the main white dwarf cooling sequence’. This title might be of interest to astronomers interested in using this facility, but is unlikely to attract anyone beyond them.
‘But’ is good — use it for dramatic effect
The contradiction implied by the word ‘but’ is one of the most powerful tools a scientist can use 5 . Contradictions introduce problems and provide dramatic effect, tension and a reason to keep listening.
Without such contradictions, the talk will consist of a bunch of results strung together in a seemingly endless and mind-numbing list. We can think of this list as a series of ‘and’ statements: “We did this and this and ran this experiment and found this result and . . . and . . . and.”
Contrast this with a structure that begins with a few important facts, tethered by ands, and then introduces the problem to be solved. Finally, ‘therefore’ can introduce results or subsequent actions. That structure would look like this: ‘X is the current state of knowledge, and we know Y. But Z problem remains. Therefore, we carried out ABC research.’ The introduction of even one contradiction wakes up people in the audience and helps them to focus on the results.

Collection: Conferences
A paper published earlier this year on SARS-CoV-2 and host protein synthesis provides an excellent example of the narrative form using ‘and’, ‘but’ and ‘therefore’ 6 . In the example below, I have shortened the abstract and simplified the transitions, but maintained the authors’ original structure 6 . Although they did not use ‘but’ or ‘therefore’ in their abstract, the existence of these terms is clearly implied. I have made them explicit in the following rendition.
“Coronaviruses have developed a variety of mechanisms to repress host messenger RNA translation and to allow the translation of viral mRNA and block the cellular immune response. But a comprehensive picture of the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on cellular gene expression is lacking. Therefore, we combine RNA sequencing, ribosome profiling and metabolic labelling of newly synthesized RNA to comprehensively define the mechanisms that are used by SARS-CoV-2 to shut off cellular protein synthesis.”
In this example, background information is given in the first sentence, linked by a series of conjunctions. Then the problem is introduced — this is the contradiction that comes with ‘but’. The solution to this problem is given in the next sentence (and introduced by using ‘therefore’). This structure makes the text interesting. It will do the same for your presentations.
Use repeated problems and solutions to create a story
Use the power of contradiction to maintain audience engagement throughout your talk. You can string together a series of problems and solutions (buts and therefores) to create a story that leads to your main result. The result highlighted in your title will help you to focus your talk so that the solutions you present lead to this overarching result.
Here is the general pattern:
1. Present the first part of your results.
2. Introduce a problem that remains.
3. Provide a solution to this problem by presenting more results.
4. Introduce the next problem.
5. Present the results that address this problem.
6. Continue this ‘problem and solution’ process through your presentation.
7. End by restating your main finding and summarize how it arises from your intermediate results.
The SARS-CoV-2 abstract 6 uses this pattern of repeated problems (buts) and solutions (therefores). I have modified the wording to clarify these sections.
1. Result 1: SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to a global reduction in translation, but we found that viral transcripts are not preferentially translated.
2. Problem 1: How then does viral mRNA comes to dominate the mRNA pool?
3. Solution 1: Accelerated degradation of cytosolic cellular mRNAs facilitates viral takeover of the mRNA pool in infected cells.
4. Problem 2: How is the translation of induced transcripts affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection?
5. Solution 2: The translation of induced transcripts (including innate immune genes) is impaired.
6. Problem 3: How is translation impaired? What is the mechanism?
7. Solution 3: Impairment is probably mediated by inhibiting the export of nuclear mRNA from the nucleus, which prevents newly transcribed cellular mRNA from accessing ribosomes.
8. Final summary: Our results demonstrate a multipronged strategy used by SARS-CoV-2 to take over the translation machinery and suppress host defences.
Using these three basic tips, you can create engaging presentations that will hold the attention of your audience and help them to remember you. For young scientists, especially, that is the most important thing the audience can take away from your talk.
Nature 600 , S88-S89 (2021)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03603-2
This article is part of Nature Events Guide , an editorially independent supplement. Advertisers have no influence over the content.
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged .
Kirchoff, B. Presenting Science Concisely (CABI, 2021).
Google Scholar
Gomez, M., Mejia, A., Ruddell, B. L. & Rushforth, R. R. Nature 595 , 250–254 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Blundell, R. et al. Nature Plants 6 , 483–491 (2020).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Caiazzo, I. et al. Nature 595 , 39–42 (2021).
Olson, R. The Narrative Gym (Prairie Starfish Press, 2020).
Finkel, Y. et al. Nature 594 , 240–245 (2021).
Download references
Competing Interests
B.K. receives royalties for his book, which this article is based on.
Related Articles

Partner content: Scientific Conferences to fuel new ideas and the next generation of scientists
Partner content: Wellcome Connecting Science: A global provider of genomics learning and training
- Conferences and meetings

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
Career News 18 APR 24
Deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how I found my niche in virology research
Spotlight 17 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships

I dive for fish in the longest freshwater lake in the world
Female academics need more support — in China as elsewhere
Correspondence 16 APR 24

China promises more money for science in 2024
News 08 MAR 24

One-third of Indian STEM conferences have no women
News 15 NOV 23

How remote conferencing broadened my horizons and opened career paths
Career Column 04 AUG 23
Qiushi Chair Professor
Distinguished scholars with notable achievements and extensive international influence.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Zhejiang University
ZJU 100 Young Professor
Promising young scholars who can independently establish and develop a research direction.
Head of the Thrust of Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Reporting to the Dean of Systems Hub, the Head of ROAS is an executive assuming overall responsibility for the academic, student, human resources...
Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
Head of Biology, Bio-island
Head of Biology to lead the discovery biology group.
BeiGene Ltd.
Research Postdoctoral Fellow - MD (Cardiac Surgery)
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Home Blog Education How to Prepare Your Scientific Presentation
How to Prepare Your Scientific Presentation

Since the dawn of time, humans were eager to find explanations for the world around them. At first, our scientific method was very simplistic and somewhat naive. We observed and reflected. But with the progressive evolution of research methods and thinking paradigms, we arrived into the modern era of enlightenment and science. So what represents the modern scientific method and how can you accurately share and present your research findings to others? These are the two fundamental questions we attempt to answer in this post.
What is the Scientific Method?
To better understand the concept, let’s start with this scientific method definition from the International Encyclopedia of Human Geography :
The scientific method is a way of conducting research, based on theory construction, the generation of testable hypotheses, their empirical testing, and the revision of theory if the hypothesis is rejected.
Essentially, a scientific method is a cumulative term, used to describe the process any scientist uses to objectively interpret the world (and specific phenomenon) around them.
The scientific method is the opposite of beliefs and cognitive biases — mostly irrational, often unconscious, interpretations of different occurrences that we lean on as a mental shortcut.
The scientific method in research, on the contrary, forces the thinker to holistically assess and test our approaches to interpreting data. So that they could gain consistent and non-arbitrary results.
The common scientific method examples are:
- Systematic observation
- Experimentation
- Inductive and deductive reasoning
- Formation and testing of hypotheses and theories
All of the above are used by both scientists and businesses to make better sense of the data and/or phenomenon at hand.
The Evolution of the Scientific Method
According to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , ancient thinkers such as Plato and Aristotle are believed to be the forefathers of the scientific method. They were among the first to try to justify and refine their thought process using the scientific method experiments and deductive reasoning.
Both developed specific systems for knowledge acquisition and processing. For example, the Platonic way of knowledge emphasized reasoning as the main method for learning but downplayed the importance of observation. The Aristotelian corpus of knowledge, on the contrary, said that we must carefully observe the natural world to discover its fundamental principles.
In medieval times, thinkers such as Thomas Aquinas, Roger Bacon, and Andreas Vesalius among many others worked on further clarifying how we can obtain proven knowledge through observation and induction.
The 16th–18th centuries are believed to have given the greatest advances in terms of scientific method application. We, humans, learned to better interpret the world around us from mechanical, biological, economic, political, and medical perspectives. Thinkers such as Galileo Galilei, Francis Bacon, and their followers also increasingly switched to a tradition of explaining everything through mathematics, geometry, and numbers.
Up till today, mathematical and mechanical explanations remain the core parts of the scientific method.
Why is the Scientific Method Important Today?
Because our ancestors didn’t have as much data as we do. We now live in the era of paramount data accessibility and connectivity, where over 2.5 quintillions of data are produced each day. This has tremendously accelerated knowledge creation.
But, at the same time, such overwhelming exposure to data made us more prone to external influences, biases, and false beliefs. These can jeopardize the objectivity of any research you are conducting.
Scientific findings need to remain objective, verifiable, accurate, and consistent. Diligent usage of scientific methods in modern business and science helps ensure proper data interpretation, results replication, and undisputable validity.
6 Steps of the Scientific Method
Over the course of history, the scientific method underwent many interactions. Yet, it still carries some of the integral steps our ancestors used to analyze the world such as observation and inductive reasoning. However, the modern scientific method steps differ a bit.
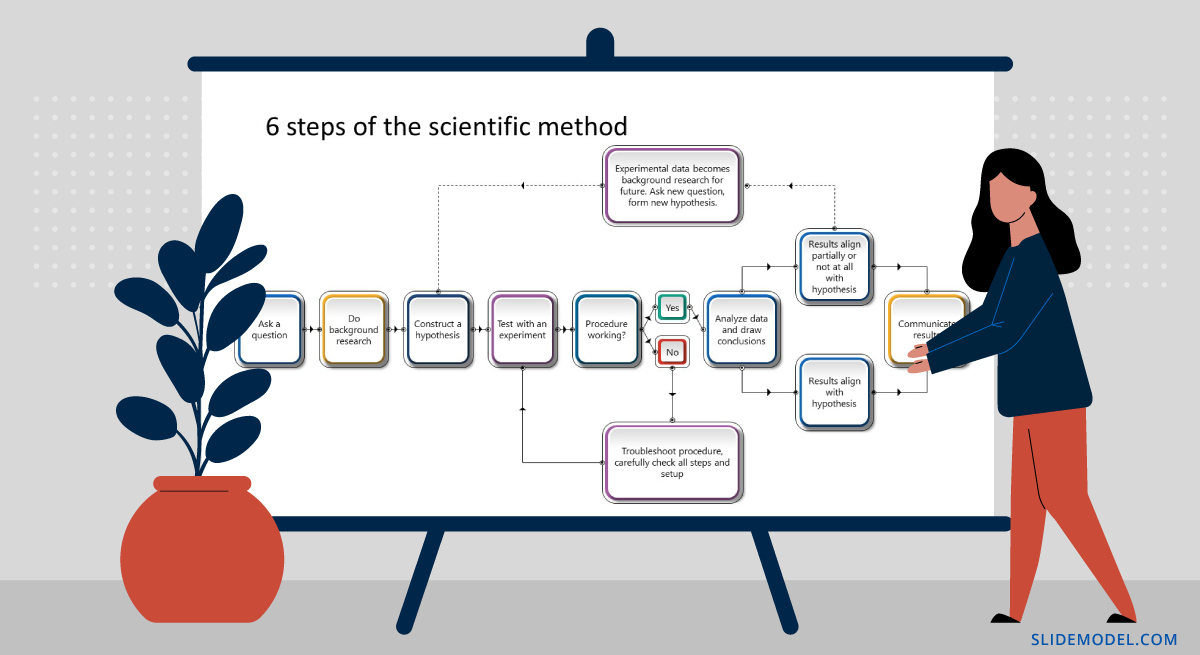
1. Make an Observation
An observation serves as a baseline for your research. There are two important characteristics for a good research observation:
- It must be objective, not subjective.
- It must be verifiable, meaning others can say it’s true or false with this.
For example, This apple is red (objective/verifiable observation). This apple is delicious (subjective, harder-to-verify observation).
2. Develop a Hypothesis
Observations tell us about the present or past. But the goal of science is to glean in the future. A scientific hypothesis is based on prior knowledge and produced through reasoning as an attempt to descriptive a future event.
Here are characteristics of a good scientific hypothesis:
- General and tentative idea
- Agrees with all available observations
- Testable and potentially falsifiable
Remember: If we state our hypothesis to indicate there is no effect, our hypothesis is a cause-and-effect relationship . A hypothesis, which asserts no effect, is called a null hypothesis.
3. Make a Prediction
A hypothesis is a mental “launchpad” for predicting the existence of other phenomena or quantitative results of new observations.
Going back to an earlier example here’s how to turn it into a hypothesis and a potential prediction for proving it. For example: If this apple is red, other apples of this type should be red too.
Your goal is then to decide which variables can help you prove or disprove your hypothesis and prepare to test these.
4. Perform an Experiment
Collect all the information around variables that will help you prove or disprove your prediction. According to the scientific method, a hypothesis has to be discarded or modified if its predictions are clearly and repeatedly incompatible with experimental results.

Yes, you may come up with an elegant theory. However, if your hypothetical predictions cannot be backed by experimental results, you cannot use them as a valid explanation of the phenomenon.
5. Analyze the Results of the Experiment
To come up with proof for your hypothesis, use different statistical analysis methods to interpret the meaning behind your data.
Remember to stay objective and emotionally unattached to your results. If 95 apples turned red, but 5 were yellow, does it disprove your hypothesis? Not entirely. It may mean that you didn’t account for all variables and must adapt the parameters of your experiment.
Here are some common data analysis techniques, used as a part of a scientific method:
- Statistical analysis
- Cause and effect analysis (see cause and effect analysis slides )
- Regression analysis
- Factor analysis
- Cluster analysis
- Time series analysis
- Diagnostic analysis
- Root cause analysis (see root cause analysis slides )
6. Draw a Conclusion
Every experiment has two possible outcomes:
- The results correspond to the prediction
- The results disprove the prediction
If that’s the latter, as a scientist you must discard the prediction then and most likely also rework the hypothesis based on it.
How to Give a Scientific Presentation to Showcase Your Methods
Whether you are doing a poster session, conference talk, or follow-up presentation on a recently published journal article, most of your peers need to know how you’ve arrived at the presented conclusions.
In other words, they will probe your scientific method for gaps to ensure that your results are fair and possible to replicate. So that they could incorporate your theories in their research too. Thus your scientific presentation must be sharp, on-point, and focus clearly on your research approaches.
Below we propose a quick framework for creating a compelling scientific presentation in PowerPoint (+ some helpful templates!).
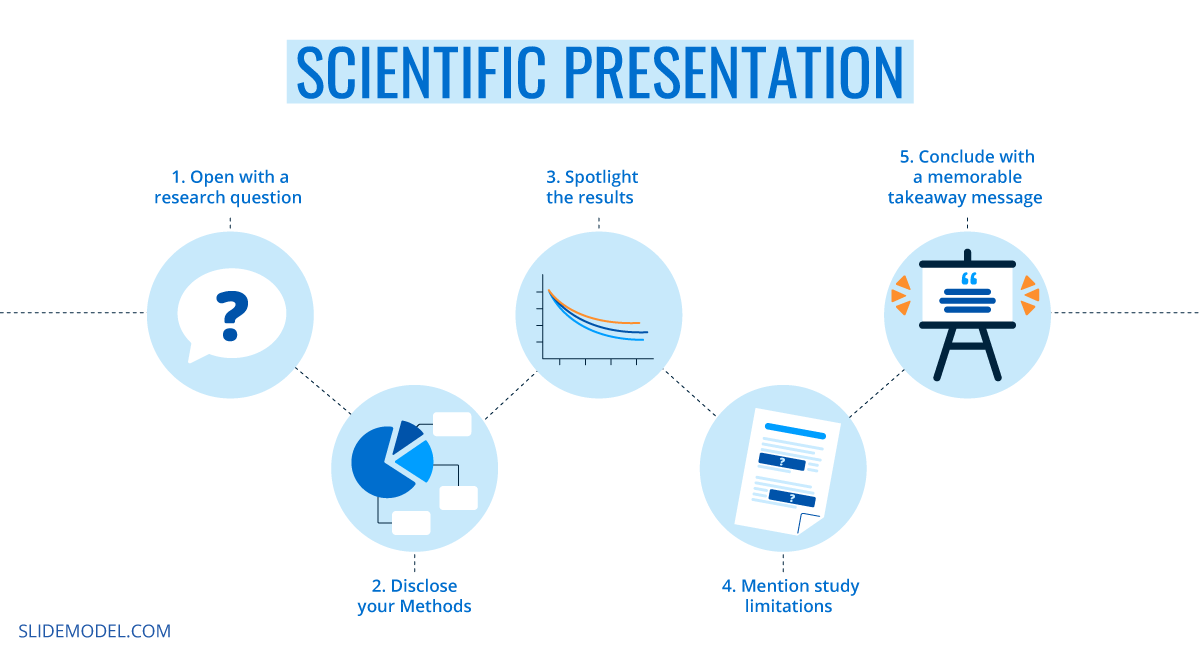
1. Open with a Research Question
Here’s how to start a scientific presentation with ease: share your research question. On the first slide, briefly recap how your thought process went. Briefly state what was the underlying aim of your research: Share your main hypothesis, mention if you could prove or disprove them.
It might be tempting to pack a lot of ideas into your first slide but don’t. Keep the opening of your presentation short to pique the audience’s initial interest and set the stage for the follow-up narrative.

2. Disclose Your Methods
Whether you are doing a science poster presentation or conference talk, many audience members would be curious to understand how you arrived at your results. Deliver this information at the beginning of your presentation to avoid any ambiguities.
Here’s how to organize your science methods on a presentation:
- Do not use bullet points or full sentences. Use diagrams and structured images to list the methods
- Use visuals and iconography to use metaphors where possible.
- Organize your methods by groups e.g. quantifiable and non-quantifiable
Finally, when you work on visuals for your presentation — charts, graphs, illustrations, etc. — think from the perspective of a subject novice. Does the image really convey the key information around the subject? Does it help break down complex ideas?

3. Spotlight the Results
Obviously, the research results will be your biggest bragging right. However, don’t over-pack your presentation with a long-winded discussion of your findings and how revolutionary these may be for the community.
Rather than writing a wall of text, do this instead:
- Use graphs with large axis values/numbers to showcase the findings in great detail
- Prioritize formats that are known to everybody (e.g. odds ratios, Kaplan Meier curves, etc.)
- Do not include more than 5 lines of plain text per slide
Overall, when you feel that the results slide gets too cramped, it’s best to move the data to a new one.
Also, as you work on organizing data on your scientific presentation PowerPoint template , think if there are obvious limitations and gaps. If yes, make sure you acknowledge them during your speech.
4. Mention Study Limitations
The scientific method mandates objectivity. That’s why every researcher must clearly state what was excluded from their study. Remember: no piece of scientific research is truly universal and has certain boundaries. However, when you fail to personally state those, others might struggle to draw the line themselves and replicate your results. Then, if they fail to do so, they’d question the viability of your research.
5. Conclude with a Memorable Takeaway Message
Every experienced speaker will tell you that the audience best retains the information they hear first and last. Most people will attend more than one scientific presentation during the day.
So if you want the audience to better remember your talk, brainstorm a take-home message for the last slide of your presentation. Think of your last slide texts as an elevator pitch — a short, concluding message, summarizing your research.
To Conclude
Today we have no shortage of research and scientific methods for testing and proving our hypothesis. However, unlike our ancestors, most scientists experience deeper scrutiny when it comes to presenting and explaining their findings to others. That’s why it’s important to ensure that your scientific presentation clearly relays the aim, vector, and thought process behind your research.

Like this article? Please share
Education, Presentation Ideas, Presentation Skills, Presentation Tips Filed under Education
Related Articles

Filed under Business • April 10th, 2024
Discovering Coaching Presentation Tools
Discover the best PPT templates to use as coaching presentation tools with this article. Tools explained + examples.
Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • March 22nd, 2024
How to Share a Google Slides Presentation
Optimize your presentation delivery as we explore how to share a Google Slides presentation. A must-read for traveling presenters.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.
Leave a Reply
A Nature Research Service

- On-demand Courses
- Share & disseminate
Advancing your Scientific Presentations
For researchers in the natural sciences who want to improve the quality of their peer-to-peer scientific presentations with both virtual and face-to-face audiences
10 experts who excel at presenting their work, including renowned presentation designers, and trainers and experts in narrative tools
10 hours of learning
15-minute lessons
4-module course with course certificate
About this course
'Advancing Your Scientific Presentations' teaches you how to create more memorable and engaging presentations to your scientific peers. In the course, you will discover how you can develop your research story - the foundation of your presentation - using narrative tools, how to build a slide deck that supports and enhances your presentation, and how to prepare to deliver your presentation on the day.
What you'll learn
- To identify techniques that can help to overcome the challenges that researchers commonly face when creating and delivering oral presentations
- To build compelling research stories to use as the foundation for your presentations
- To create professional slide decks that effectively communicate your research findings to your audience
- To apply strategies to help you deliver your presentation effectively on the day, in both virtual and face-to-face environments
Free Sample Overcoming your research presentation challenges
5 lessons 2h

Free Sample Developing the story behind your talk
7 lessons 2h 30m
Free Sample Building an engaging slide deck
Free sample preparing and navigating your talk.
7 lessons 3h
Free Sample Advancing Your Scientific Presentations: Free Sample - section
No subscription yet? Try this free sample to preview lessons from the course
4 lessons 1h
Start this module
Developed with expert academics and professionals
This course benefits from the insights of experts with a wide range of experience, including:
- Delivering compelling presentations to audiences of scientific peers
- Using narrative techniques when communicating research
- Designing slide decks to support and enhance presentations
- Training researchers how to deliver scientific presentations in a clear and engaging manner
Meet the expert panel that have helped shape and refine the content of the course:
Michael Alley
Teaching Professor of Engineering Communications, Penn State
Shohini Ghose
Professor of Physics and Computer Science, Wilfrid Laurier University
Nolan Haims
Principal, Nolan Haims Creative
Magdalena Skipper
Editor in Chief, Nature and Chief Editorial Advisor, Nature Portfolio
Michael White
Senior Editor, Nature
Advice from experienced researchers
The course has additional insights through video interviews from:
Beatrice Chiew
Postdoctoral Researcher, University of Newcastle, Australia
Jean-luc Doumont
Founding Partner, Principiae
Michael Dahlstrom
LAS Dean's Professor and Director, Greenlee School of Journalism, Iowa State University
Richard Goring
Director, Bright Carbon
Samuel Ramsey
Entomologist, USDA-ARS Bee Research Laboratory
Feedback from course users
I was reluctant to see my research results as a "story" to be told to others. But now I understand it's what makes my results stick. Postdoctoral student, United States
I found it really helpful to have a clear process that I could apply to develop my talk, from the core message to the design details of the slides. Research scientist, India
Discover related courses
Networking for researchers.
Create and nurture professional relationships for mutual benefit
Narrative Tools for Researchers
Examine the best ways you can share your research story persuasively with your peers
Access options
For researchers.
- Register and complete our free course offering , or try a free sample of any of our paid-for courses
- Recommend our courses to your institution, so that we can contact them to discuss becoming a subscriber
For institutions, departments and labs
Find out which of our subscription plans best suits your needs See our subscription plans
Does my institution provide full course access?
When registering, you’ll be asked to select your institution first. If your institution is listed, it has subscribed and provides full access to our on-demand courses catalogue.
My institution isn’t listed!
Select „other“ and register with an individual account. This allows you to access all our free sample course modules, and our entirely free course on peer review. You might also want to recommend our courses to your institution.
I am in charge of purchasing training materials for our lab / department / institution. Buy a subscription
Start this course
Full course access via institutional subscription only. More info
Institutions, departments and labs: Give your research full access to our entire course catalogue
Image Credits
This website uses cookies to improve your user experience. By continuing to use the site, you are accepting our use of cookies. Read the ACS privacy policy.
- ACS Publications
10 Keys to an Engaging Scientific Presentation
- May 31, 2018
What makes an engaging scientific presentation? Georgia Tech Professor Will Ratcliff uses a method based on the style of nature documentary presenter David Attenborough. Ratcliff’s approach looks to capture an audience’s natural curiosity by using engaging visuals and simple storytelling techniques. Here are his 10 keys to an engaging scientific presentation: 1) Be an Entertainer First: […]

What makes an engaging scientific presentation? Georgia Tech Professor Will Ratcliff uses a method based on the style of nature documentary presenter David Attenborough. Ratcliff’s approach looks to capture an audience’s natural curiosity by using engaging visuals and simple storytelling techniques.
Here are his 10 keys to an engaging scientific presentation:
1) Be an Entertainer First : Before your science can wow your audience, they have to understand it. Before they can understand it, you must engage them with what you’re saying. Look at your presentation from your audience’s perspective and think about how they’ll relate to your material. Focus on presenting your science in a way that engages and entertains as it explains.
2) Be a Storyteller, Not a Lecturer : Don’t assume that your audience knows your field. Tell the story of your science: identify the big picture backdrop, your specific research questions, how you answer those questions, and how it affects the way we now think about the big picture.
3) Prioritize Clarity : If the audience doesn’t understand every word you use, they’ll stop paying attention, and you may never win them back. Your goal is to never lose their attention in the first place, so make an effort to be clear and have a simple narrative arc to your talk.
4) Mind Your Transitions: The easiest place to lose your audience’s focus is when you move from one slide to another. Practice the transitions in your talk to make sure the link between the ideas of one slide and the next remains clear.
5) Keep Complete Sentences Out of Your Slides: Keep the text in your slides to a minimum. Instead, use compelling visual to hold your audience’s attention while you speak.
6) Animations Are Your Friend: You can use animations to reveal new details on your slide as they become relevant to what you are saying. That way you get to control what your audience is seeing, minimizing distraction and putting laser pointers out of a job. Note: never use silly and unnecessary animations, like spinning or scrolling text, this will just annoy your audience.
7) Get Excited: If you’re not excited and energetic about your work, your audience won’t be either.
8) Look at the Audience: Don’t stare at the floor, the ceiling, or your slides while you’re presenting. Look directly at your audience, or if you’re nervous, toward the back of the lecture hall. This will help you connect with your audience.
9) Be Wary of Jokes: Scientific talks are serious by nature and you have more to lose than to gain. If a joke is poorly timed or if you misjudge an audience, you risk alienating them. Play it safe and find other ways to be entertaining unless you know your audience well.
10) Leave the Laser Pointer at Home: Laser pointers are distracting. If you feel you need one to guide your audience through a slide, that’s a sign your slide is too cluttered.
Want More Tips on Giving an Engaging Scientific Presentation? Check Out: 3 Elements of a Great Scientific Talk
Want the latest stories delivered to your inbox each month.
A collection of TED Talks (and more) on the topic of Science.
Video playlists about Science

The most popular TED Talks of 2022

The most popular TED Talks of 2021

Harnessing the future of data

The most popular talks of 2020
Talks about science.

The program that brought Nazis to America

Can cannabis help you sleep? Here's the science

What happens to sex in midlife? A look at the "bedroom gap"

What causes addiction, and why is it so hard to treat?

3 mysteries of the universe — and a new force that might explain them

How poop turns into forests

Can nanoparticles help fight hunger?

Is climate change slowing down the ocean?

Why can't you put metal in a microwave?

The aboriginal knowledge stored in the stars

The climate solutions worth funding — now

Why does this flower smell like a dead body?

How babies think about danger

How does alcohol cause blackouts?

The real reason dodo birds went extinct

A reframing of masculinity, rooted in empathy
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Present a Science Project
Last Updated: August 17, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Meredith Juncker, PhD . Meredith Juncker is a PhD candidate in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center. Her studies are focused on proteins and neurodegenerative diseases. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 53,303 times.
After creating a science project , you’ll likely have to present your work to your class or at a science fair. Try to give yourself a few weeks to plan and put together your presentation. Outline your main points, make note cards, and practice ahead of time. Make a clear, neat display board or PowerPoint presentation. When it comes time to present, relax, speak clearly and loudly, and avoid reading your presentation word for word.
Putting Together Your Presentation

- Finish up your experiment, research, and other aspects of your project.
- Get the materials you’ll need for your display board.
- Start to imagine how you’ll organize your information.

- An introduction to your topic or the problem you’ve addressed.
- How the problem impacts the real world (such as how a better understanding of the issue can impact humans).
- Your hypothesis, or what you expected to learn about through your experiment.
- The research you did to learn more about your topic.
- The Materials that you used in your project.
- Each step of your experiment’s procedure.
- The results of your experiment.
- Your conclusion, including what you learned and whether your data supports your hypothesis.

- When writing your speech, try to keep it simple, and avoid using phrases that are more complicated than necessary. Try to tailor the presentation to your audience: will you be presenting to your class, judges, a higher grade than yours, or to an honors class?
- Writing out your presentation can also help you manage your time. For example, if you’re supposed to talk for less than five minutes, shoot for less than two pages.

- For example, if you've made a volcano, make sure you know the exact mix of chemicals that will create the eruption.

Creating Your Display Board

- When you purchase your board, you should also acquire other materials, like a glue stick, construction paper, a pencil, markers, and a ruler.

- Consider using the top left corner for your topic introduction, the section under that for your hypothesis, and the bottom left section to discuss your research.
- Use the top right corner to outline your experiment’s procedure. List your results underneath, and finally, put the section with your conclusion under the results.

- Be sure to use a dark font color that’s easy to see from a distance.
- You can also write everything out by hand. Draft your lettering in pencil before using a pen or marker, and use a ruler to make sure everything is straight.

- Before gluing anything, make sure you plan out each section’s position and are sure everything will fit without looking cluttered. Use rulers to make sure everything is positioned evenly.

- Consider including 1 slide for each section, like 1 for the title of your project, 1 for your hypothesis, and 1 that outlines each main point of your research. If a slide becomes too dense, break it down by concept.
- Limit the text to 1 line and include a visual aid, like an image or a graph, that demonstrates the concept or explains the data. [6] X Research source
Giving a Great Presentation

- Take the time to iron your clothes and tuck your shirt in to avoid looking sloppy.

- It’s a good idea to use the restroom before you have to present your project.

- It can be really hard to resist, but try to avoid saying “um” or “uh” during your presentation.
- Speaking when you have a dry mouth can be difficult, so it’s a good idea to keep a water bottle handy.

- Remember it’s better to be honest if you don't know how to answer a question instead of making something up. Ask the person who asked the question to repeat or rephrase it, or say something like, "That's certainly an area I can explore in more detail in the future."
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.opencolleges.edu.au/informed/teacher-resources/science-fair-projects/#sciencefairpresentation
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4KVTLT6QeTE
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NHXidlH-dBw
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g3hT6Ocf39w
- ↑ https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/science-fair/judging-tips-to-prepare-science-fair
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Shruti Choudhary
Dec 17, 2017
Did this article help you?

Dec 11, 2017
Dec 5, 2016
Feb 5, 2017
Oct 13, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Pete’s PowerPoint Station
Science Index
- Math/Maths Index
- Language Arts/Literature Index
- Social Studies Index
- Holidays Index
- Art, Music, and Many More, A-Z
- Meteorology
- Four Seasons
- Pre-Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Pre-Calculus & Calculus
- Language Arts
- Punctuation
- Social Studies
- World Religions
- US Government
- Criminal Justice
- Famous People
- American History
- World History
- Ancient History
- The Middle Ages
- Architecture
- All Topics, A–Z
- Privacy & Cookie Policy
- Presentations
Free Presentations in PowerPoint Format & Free Games for Kids
- Biogeochemical Cycles
- General Science
- Environment
- Natural Hazards
- Nanoscience
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

49 templates

18 templates

32 templates

42 templates

40 templates

16 templates
Science Lesson
Science lesson presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Revolutionize the education sector and take your students to another galaxy with this new Slidesgo template, where your science lessons will display a colorful universe of creative design.
Surround yourself with a space full of color and space patterns with this new SlidesGo template. Learning concepts will be a thrilling experience for your audience. There’s not only room for your lesson, but also for any exercise or assignment that you consider proper. Every slide has illustrations and galactic motifs to stay on topic at all times. You and your audience will feel like you’re on space, and this feeling is reinforced by a sans-serif font, providing maximum readability. The color palette is composed of warm tones, conveying energy and happiness. Learning in a fun way is possible, so are you ready for takeoff?
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 17 different slides
- Contains editable graphics and maps
- Includes 1000+ icons divided into 11 different themes for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


- Search Search Search …
Free Science Templates for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Make your presentations and lessons stand out with these free templates for Science .
Download them to use with PowerPoint or edit them in Google Slides and start creating!

Geometrical shapes and volume formulas free PowerPoint Template and Google Slides Theme Ready to dive into geometry and volume? This template is perfect for this type of Math. Paper like backgrounds, highlighters, pen, ruler and a compass are featured in this free theme, along with some geometric shapes and their […]
Geometrical Shapes and Volume, free school template.

Modern with neon accents Free PowerPoint Template and Google Slides Theme Jackson is a modern template with neon color accents and can be used for presentations abut technology – a new product launch, software development, or any other tech-related topic -, for a presentation about a new modern art exhibit, […]
Jackson Modern Neon free slideshow template.

World Oceans Day Free PowerPoint Template and Google Slides Theme Celebrate World Oceans Day with this free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme! This template features a beautiful blue color scheme and ocean-themed images, making it the perfect way to create presentations about the importance of our oceans. The template […]
World Oceans Day free PowerPoint template.

Free Earth Day animated template for Google Slides and PowerPoint. You can use this PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme to raise awareness of environmental issues. It features beautiful visuals and resources of planet Earth, which you can customize freely to make the presentation your own. Earth Day is an […]
Earth Day free ppt and Google Slides template.

Free interactive choice board and mini theme + morning meeting / daily agenda slide for Google Slides and PowerPoint. This free interactive choice board and mini theme with morning meeting / daily agenda slide is perfect for the little ones. Let’s learn about the importance of bees with this black […]
Bees are awesome. Interactive choice board and mini theme.

Free education templates for Google Slides and PowerPoint. 17 different layouts. Utilize them in PowerPoint or Google Slides. Or customize them, save them as JPEG and use them in Google Jamboard or Microsoft Whiteboard. – Or print them out! – This bundle includes: – Frayer model– Weekly planner– Station rotation– […]
School Bundle 06. Templates for education.

Free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme. Microscope template with interactive slides. If you are teaching about cells, bacteria or anything microscopic, this template might work! I’ve included a couple of slides with activities for elementary students: drag the names of the parts of a flower or a plant to […]
Biology free presentation template.

Free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme. Cardiovascular research and risk factors thesis presentation template. A free medical template to present about the circulatory system, medication treatments, coronary or cardiovascular diseases or to talk about the importance of donating blood. It’s also a great template for pharmaceutical presentations. DOWNLOAD POWERPOINT […]
Free medical slides theme.

Free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme. Weather template with animated icons. Sometimes I receive some special requests that immediately light a sparkle in my head. This template was one of those! And it was really fun to make! If you are teaching about meteorology, well, this is perfect! Even […]
Animated weather forecast slides backgrounds.

Free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme. Unbox your lesson with this template! It comes with an agenda slide. Are you ready to unbox your ideas? This template is perfect to get them out of your head and share them with your colleagues or classmates! And not only you can […]
Unbox your ideas presentation template.

Free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme. Under the sea slides backgrounds. A while back someone asked me for an “under the sea” template, and little by little I’m trying to catch up. Stingrays, whales and fishes along with some algae and corals set the scene for this template. I […]
Sebastian, ocean slides theme.

Free PowerPoint template and Google Slides theme. Jungle theme for presentations. I received a lot of requests for a jungle theme, so here it’s Bravestone. It has lots of green, leaves, a swamp, monkeys, hippos, and snakes. Also, an old piece of paper (I stained a sheet of paper with […]
Bravestone, jungle backgrounds presentation template.

Free Fun Template for PowerPoint or Google Slides Presentations Koch Koch is a fun template to motivate, achieving goals, conquering worlds, setting records and going beyond. Also works for presentations or school lessons about space, planets, astronauts, NASA missions, a spaceship launch, Apollos’ missions or the moon landing. A free pptx […]
Koch Free Template for Google Slides or PowerPoint Presentations

Free Template for PowerPoint or Google Slides Presentations Carlina Carlina is specially made for presentations about clean energy, environmental stewardship, renewable energies, recycling, ecology, nature or sustainable economy. Go green with this free presentation template for Google Slides or PowerPoint. – Thank you Carlina for letting me name it after […]
Carlina Free Environmental Template for Google Slides or PowerPoint.

Free Template for PowerPoint and Google Slides Presentations Starman Starman is a fun theme featuring astronauts in space. Perfect for presentations about galaxies, NASA missions, the universe or if your next lecture is out of this world! DOWNLOAD POWERPOINT OPEN IN GOOGLE SLIDES
Starman Free Space template for Google Slides or PowerPoint

Maven Overview Presentation
Download the PDF or PPT of the MAVEN Overview Presentation.
Maven Overview PDF Presentation
(pdf?emrc=6621f34807410) (6.32 MB)
The support of your Internet Explorer has already ended so that correct displays and behaviors are not guaranteed. The old Internet Exproler is strongly recommended to update the new browsers from the videwpoint of security. A new Internet Exproler , Edge Chrome or Firefox should be used.

- Greeting from Dean of Graduate School
- Idea of the School
- Administrating Organization
- Facility Map
- International Relations
- Gender Equality Initiatives
- Admission Information
- IESC Masters Program
- IESC Doctoral Program
- Admission Documentation
- Admission FAQ
- Research Student
- Socio-Environmental Energy Science Dept.
- Fundamental Energy Science Dept.
- Energy Conversion Science Dept.
- Energy Science and Technology Dept.
- Sharing Space
- Sharing Equipment
- News Letter and Evaluation Report
- IAESREC Science Cafe
- Education Policy
- Course Overview of IESC
- Academic Calendar
- Event guides
- News Topics
- HOME »
- News »
- 未分類 »
The 2nd-Year Presentation of the Master’s program (IESC), Department of Socio-Environmental Energy Science, was held.
The 2nd-Year Presentation of the Master’s program (International Energy Science Course), Department of Socio-Environmental Energy Science, was held on April 11th. Jules Lanneluc won the Best Presentation Award.

- Course Event
- Energy Conversion Dept.
- Event report
- International Advanced Energy Science Research and Education Center (IAESREC)
- Professor transfer
- Socio-environmental Energy Science Dept.

Language selection
- Français fr
CSA astronaut Joshua Kutryk to give virtual presentation to schools across Canada
From: Canadian Space Agency
Media advisory
Tomorrow, Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut Joshua Kutryk will give a virtual presentation to nearly 4,000 Canadian students in grades 5 to 12 to talk about space exploration, his astronaut career and Starliner-1, his first mission aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Longueuil , Quebec, April 18, 2024 — Tomorrow, Canadian Space Agency ( CSA ) astronaut Joshua Kutryk will give a virtual presentation to nearly 4,000 Canadian students in grades 5 to 12 to talk about space exploration, his astronaut career and Starliner-1 , his first mission aboard the International Space Station ( ISS ).
Joshua will be the fourth CSA astronaut to take part in a long-duration mission on the ISS and the first one to fly under NASA 's Commercial Crew Program.
Media who wish to attend the virtual presentation or interview Joshua Kutryk must contact CSA Media Relations Office. Please note that there will be no question period for media during the webinar.
Contact information
Canadian Space Agency Media Relations Office Telephone: 450-926-4370 Email: [email protected] Website: www.asc-csa.gc.ca Follow us on social media !
Page details

Public presentation on the Bluestone Dam renovation held at Concord University
ATHENS, WV (WVNS) — A presentation about the Bluestone Dam was held at Concord University on Tuesday, April 16, 2024.
The presentation was hosted by Concord University’s Environmental Geosciences program in room 400 of the science building on Tuesday, April 16, 2024 at 12:00 p.m.
The event was also open to the public, and people could participate through Zoom as well. Classroom teachers were welcome to use the Zoom link to show the presentation in schools.
Topics that were discussed during the presentation included what it is like to have a career as a geologist working for the Army Corps of Engineers, an introduction to the history and purpose of the Bluestone Dam, and the ongoing geological engineering work to assess the bedrock foundations of the dam.
Staff with the Army Corps of Engineers, Aidan Hodge, John Vaught, and Kelli Gagnon, were involved in the presentation. Both Vaught and Hodge are Concord University Environmental Geosciences program alumni.
The Bluestone Dam, located near Hinton in Summers County, is a major flood-control installation located on the New River. The dam is 2,048 feet long, 165 feet tall, and controls water flow from a 4,620 square mile drainage area.
Out of all the dams in the Mountain State, the Bluestone Dam has the largest flood storage capacity. It also gives flood protection, not only for Hinton, but also for other areas that are in the Kanawha Valley and have thousands of houses, businesses, and industries such as Charleston, West Virginia.
The Bluestone Dam, which is more than 70 years old and had its 50th anniversary in 1999, was believed to have prevented more than $1.6 billion in flood damages as of its anniversary. However the amount of flood damages prevented because of the dam have only went up through the years.
Improvements were made to the dam since 2000 to increase safety and the stability of the dam’s foundations. Some improvements include using concrete to reinforce the toe of the dam, decrease bedrock erosion by covering the dam’s spillway with concrete, and better anchoring the dam to bedrock.
Thorough geological work is needed to focus on details in the bedrock that the dam is built on. Throughout the year, multiple samples of sandstone will be examined in labs at Concord University to evaluate properties of the bedrock.
The electron microprobe in Concord University’s developing Materials and Rare Earth Element Analysis Center will be one of the labs included in examining the bedrock of the dam.
For the latest news, weather, sports, and streaming video, head to WVNS.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
While this story is something we relate to buoyancy the most, there is a lot more than we can truly learn and apply using this principle. This can be a very helpful topic for a presentation as well as a practical science experiment. 23. Health & Nutrition. Health & Nutrition is a very important aspect of our life.
Related Articles. This guide provides a 4-step process for making a good scientific presentation: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slide outlines, constructing slides, and practicing the talk. We give advice on how to make effective slides, including tips for text, graphics, and equations, and how to use rehearsals of your talk to ...
Below is the summary of how to give an engaging talk that will earn respect from your scientific community. Step 1. Draft Presentation Outline. Create a presentation outline that clearly highlights the main point of your research. Make sure to start your talk outline with ideas to engage your audience and end your talk with a clear take-home ...
Here are 10 tips to help you present your scientific work and leave the audience wanting more. 1. Set the stage. Get your equipment ready and run through your slides if possible (use the "speaker ready" room if one is available). If you've never been in the venue, try getting there early and walk the room.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation. Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation. Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions. Two additional videos should prove useful: Designing PowerPoint Slides for a ...
The best science talks start with a process of simplifying - peeling back the layers of information and detail to get at the one core idea that you want to communicate. Over the course of your talk, you may present 2-3 key messages that relate to, demonstrate, provide examples of or underpin this idea. (Three is a nice round number of ...
The result highlighted in your title will help you to focus your talk so that the solutions you present lead to this overarching result. Here is the general pattern: 1. Present the first part of ...
Example opening a Scientific presentation with a Research Question - Source: using Invictus PowerPoint template by SlideModel 2. Disclose Your Methods. Whether you are doing a science poster presentation or conference talk, many audience members would be curious to understand how you arrived at your results.
Advancing your Scientific Presentations. For researchers in the natural sciences who want to improve the quality of their peer-to-peer scientific presentations with both virtual and face-to-face audiences. 10 experts who excel at presenting their work, including renowned presentation designers, and trainers and experts in narrative tools.
Here are his 10 keys to an engaging scientific presentation: 1) Be an Entertainer First: Before your science can wow your audience, they have to understand it. Before they can understand it, you must engage them with what you're saying. Look at your presentation from your audience's perspective and think about how they'll relate to your ...
Scientific Presentations. Presenting science to an audience of peers is among the most fundamental of job skills. Yet, few scientists receive training in how to present, beyond the occasional ad hoc critique during the weekly lab meeting, or the odd rehearsal leading up to a thesis defense.
Practice a 1- to 2-minute pitch until you feel comfortable. The poster and your pitch must be aimed at the audience that will be present. The clearer and more rational your poster layout, the easier it will then be for you to make a strong pitch. —Srinivas.
Some basic tips on Presenting Science - See Communicating with non-Scientists for even more fun tips! Know your audience: Tailor your presentation based on the expertise and interests of the audience. Use visuals: Ensure that each slide has at least one visual and explain why you are using that visual. Be enthusiastic: Don't let the audience ...
Here are the talks that intrigued and inspired in 2021. 8 talks. Harnessing the future of data. Mind-blowing tech is right around the corner -- and the data to power it is here and now. Get an awe-inspiring look at the future that awaits with visionaries already predicting, embracing and innovating on the potential of tomorrow. 20 talks.
6. Practice making your presentation. First, practice by yourself or in a mirror. If you have a time limit, time yourself to make sure your presentation isn't too long or short. Ask your parents or a friend if you can present your project to them, and ask if they have any pointers. 7.
Download the "Science Subject for High School - 9th Grade: The Building Blocks of Life Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover this set of editable infographics for education presentations. These resources, from graphs to tables, can be combined with other presentations or used independently.
If designing isn't your strength, let Canva's science presentation templates serve as your guide. Featuring a wide array of themes, color stories, and aesthetics, this collection of creative science presentation ideas will help you demonstrate your research and analysis skills in the best light. You can take a serious and scholarly approach ...
Pete's PowerPoint Station is your destination for free PowerPoint presentations for kids and teachers about Science, and so much more. Free PowerPoint Presentations about Science for Kids & Teachers (K-12)
2. WHAT IS SCIENCE? Some definitions. "Science (from the Latin scientia, meaning „knowledge‟ or „knowing‟) is the effort to discover, and increase human understanding of how the physical world works." (from Wikipedia) "Any system of knowledge that is concerned with the physical world and its phenomena and that entails unbiased observations and systematic experimentation." (from ...
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Revolutionize the education sector and take your students to another galaxy with this new Slidesgo template, where your science lessons will display a colorful universe of creative design. Surround yourself with a space full of color and space patterns with this new SlidesGo template. Learning ...
Free Fun Template for PowerPoint or Google Slides Presentations Koch Koch is a fun template to motivate, achieving goals, conquering worlds, setting records and going beyond. Also works for presentations or school lessons about space, planets, astronauts, NASA missions, a spaceship launch, Apollos' missions or the moon landing. A free pptx […]
Presentation skills based on the science of learning. No matter what kind of presentation you need to deliver, you do it for a reason. You do it to move your audience; to help them understand what they didn't understand, to help them do what they couldn't do, to energize them to act more vigorously, more effectively, more productively, more ...
Free Science Project Slide Templates for an Engaging Slideshow. Make your science project stand out with this science project presentation template. Whether you're a student, teacher, or scientist, these templates will help you deliver your message with clarity and style. With a range of customizable slides, you can easily manage your project ...
Download the PDF or PPT of the MAVEN Overview Presentation.
The 2nd-Year Presentation of the Master's program (International Energy Science Course), Department of Socio-Environmental Energy Science, was held on April 11th. Jules Lanneluc won the Best Presentation Award.
Media advisory. Longueuil, Quebec, April 18, 2024 — Tomorrow, Canadian Space Agency ( CSA) astronaut Joshua Kutryk will give a virtual presentation to nearly 4,000 Canadian students in grades 5 to 12 to talk about space exploration, his astronaut career and Starliner-1, his first mission aboard the International Space Station ( ISS ).
The presentation, titled, "PrimeC, An Oral Candidate for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Meets Primary and Secondary Endpoints in the Phase 2b PARADIGM Trial," was presented yesterday as an ...
article.main-content table{display: table !important; overflow-x: initial !important; width: 100%; h-align:center;} .research_headline{text-align:center;} .th {v-align:center; width:100%; .img { width:3000px; height:654px; object-fit: contain; } February 29, 2024 Minuets Topic Speaker Presentation Welcome and FES Introduction JP Allain PDF PFR Agenda, Program Elements and Charge Discussion ...
The presentation, titled, "PrimeC, An Oral Candidate for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Meets Primary and Secondary Endpoints in the Phase 2b PARADIGM Trial," was presented yesterday as an Emerging Science presentation by Merit Cudkowicz, M.D., M.Sc., chair of neurology and Director of the Sean M. Healey & AMG Center for ALS at Massachusetts General Hospital.
The presentation was hosted by Concord University's Environmental Geosciences program in room 400 of the science building on Tuesday, April 16, 2024 at 12:00 p.m.