

How to Write an Email in English With Examples (Formal and Informal)

Writing emails in English is a skill and a craft that can be as tricky as small talk or networking. If you’re learning English, you might feel that your language barrier adds an extra level of difficulty in learning how to write emails in English.
But if you break down English emails into smaller parts and master the basic structures, you’ll be able to write better emails in English in no time.
So, today, we’re going to take a look at how to write formal and informal emails in English. We’ll explore:
How to write a formal email in English
How to write an informal email in english, differences between formal and informal emails in english.
If you’re ready to learn and practice writing emails in English, let’s get into it!

Teaching English Just Got Easier!
Save hours of time with an organized collection of high quality , easy-prep ESL lesson plans and worksheets right at your fingertips.
Writing Emails in English
Write a clear subject line.
The subject line of an email is the line of text that your recipient will see in their inbox before opening the email. So, you want to write the subject line in a way that quickly communicates what you want them to do or why they should open the email.
First, place the most important words at the beginning:
Request for more information
Action needed: contract attached below
Strategy meeting this Tuesday?
Invitation to apply: Outreach Intern
Event Coordinator Job Application
Met at Networking Event: Resume Attached
As you can see, there are no strict grammar or punctuation rules that you need to follow in the subject line of an email. Just make sure it looks consistent, and your spelling is correct.
One thing you shouldn’t do, though: Don’t use all caps. It looks like you’re shouting at people, and people in the professional world usually don’t like it.
Start your formal email with a greeting
The greeting is the first line in the actual text of the email. If you can, make sure it’s always addressed to an actual person. Remember that, with a greeting, we have to capitalize every word in the line. So, you can write,
Hello [Name],
We don’t insert a comma between “Hello” and the name, even though we do in all other cases (“Hello, Danny!”).
“Hi” or “hello” might sound informal, but both greetings are actually standard in a formal or business setting. If you feel like that’s too informal, though, you can write:
Dear [Name],
If you don’t have a name, here are a few other options,
Hello there,
Dear Hiring Manager,
Dear Recruiting Director,
Dear [Company Name] Team,
If you do know the name of the person you’re writing to, but you don’t know them well, you can use an honorific like Ms., Mr., or Dr. if you’re sure about their gender.
But be sure to avoid “Mrs.” for a woman if you don’t know her marital status. So, you can write:
Hello Ms. Johnson,
Dear Dr. Sanchez,
If you aren’t sure about their gender, it’s perfectly okay to use a first name and last name.
Write an opening line
The opening line is probably one of the hardest things to write in an email.
But, as a polite gesture, it's an important way to set the tone of the email and show that you want to establish a relationship on good terms.
You can use a phrase like, “I hope you are doing well,” or “I hope you had a good weekend ” but it’s better if you can personalize it a bit more, like:
I hope things in Tokyo are going well.
I hope you have been enjoying the warm weather we’re having.
I hope you had a smooth trip back from Thailand.
I hope you’re surviving tax season.
Another way to start an email is to ask a polite question, like:
How are you?
Have you been able to get settled in?
How are things going in Dallas?
Write the body of the formal email
You’ll probably find that most of the time, you write formal emails in English to people you don’t know very well. And, of course, you’re writing to give them a good impression of your professionalism and abilities.
You can ask yourself: Do I need to remind them of who I am? Do I need to give them context for my request? Do I need to give them background information on the ideas I will propose or suggestions I make?
1. SHARE THE REASON FOR THE EMAIL
I’m reaching out because…
As you may know, our department is currently looking for someone to…
A colleague of mine recently informed me about a job opening in your company, and so…
You mentioned in our last meeting that you wanted to focus on content strategy, so I suggest that…
2. MENTION THE ACTION NEEDED
Most emails that you send in a professional setting require some action. It’s important to be as clear as you can about what action or actions you need the reader to take:
Let me know what you think about my ideas/suggestions.
Let me know when you would be available to meet next week.
Please review the following attachments before our next meeting.
Can you please review the agenda for the meeting and let me know if you have any suggestions?
3. WRITE YOUR CLOSING STATEMENT
Before you end the email, take a sentence or two to make sure that you allow your reader to ask questions or reply:
Feel free to reach out if you have any questions.
Let me know if you need any clarification.
Please let me know if you have any feedback or suggestions.
Don’t hesitate to let me know if you need more time.
How to end a formal email in English
The closing, or sign-off, should reflect your professionalism and how familiar you are with the reader. But don’t spend too much time worrying about the perfect sign-off. If you’re ever in doubt, it’s better to be a bit more formal than informal. When it comes to the closing, you only need to capitalize the first word of the line.
Here are a few examples:
Warm regards,
Kind regards,
Formal email example
Here’s an example of a formal email to give you a picture of how all the pieces come together. This is an example of a follow-up email after a meeting.
Subject: [Strategy meeting follow up]
Hello everyone,
Thank you all again for attending our most recent strategy meeting. I was really impressed by the participation and ideas of everyone present.
As promised, I’ve attached a copy of everything we discussed and some action items and goals that I’d like us all to think about in the upcoming months.
Please review the attachment and discuss them with your respective teams. Then, I’d like an email update on how each of your departments intends to implement those goals by the end of the day next Friday. If you have any questions, or if, for any reason, you need more time, don’t hesitate to reach out before Friday.
Anya Jensen
We usually write informal emails to friends, family, or people we know really well. We also write informal emails to quickly communicate a piece of information or share things with our coworkers.
Write a friendly subject line
The subject line still matters in an informal email, but you can use a friendlier tone:
Here’s the schedule
Here’s the video you asked about
Check out this article!
Start with a casual greeting
When we’re greeting someone in an informal email, we don’t need to worry so much about what we say. We can use a casual “hey,” or “hi,” or we can just address them by name. We can also use more exclamation points or emoticons to express excitement and friendliness:
Hey [Name],
Write the body of the informal email
When it comes to the body of an informal email in English, we can write as much or as little as we want. But, in terms of practicality, think about your reader. You still want to save them time, so it’s best to be as brief as you can.
Here’s the schedule you asked for.
Here’s the video. Hope you enjoy it!
The meeting’s at 5:00 pm. See you there!
Can you send me that file again? Thanks!
How to end an informal email
In an informal email, don’t worry too much about the closing! You can use these friendly sign-offs:
See you later,
See you soon,
Happy Friday,
Have a good weekend!
Informal email example 1
Thanks for the notes. You’re the best!
Informal email example 2
We loved seeing you at the conference. Let’s catch up sometime soon. When are you free?
So, now that we’ve broken down how to write formal and informal emails, let’s take a look at some of the major differences between the two and some of the mistakes you should avoid.
Ask: Who is the reader of the email?
Let the reader help you decide how to write your email in English.
If you need to ask for a favor or set up a meeting, it’s okay if you get to the point pretty quickly.
But if, for example, you’re pitching an idea to someone new or trying to make a new network connection, it’s okay to take a little more time to make a personal connection first so that they feel they can trust you and get to know your personality a little. Then, present your ideas, and ask them to take some kind of action.
The truth is that many of the emails you write in English mix the formal and the informal.
With an informal email, rambling and talking about how things are going is okay!
But with a formal email: Stick to the point as much as you can.
Grammar tips for emails in English
In a formal English email, you should avoid:
Incomplete sentences
Run-on sentences
Long, complicated sentences
Grammatical errors
The last bullet point sounds obvious, of course, but grammatical errors in a formal email can make you look like you didn’t put enough time or attention into your writing.
Figure out which English grammar structures or tenses that you struggle with, and practice them. Here are some grammar structures that will help you write better emails in English:
Conditional structures
The passive voice
Will vs. would
Double-object verbs
Transitional words and phrases
The present perfect vs. past simple
Prepositions
Write down this list if you need to, and take your time to work through each of these structures and practice them in your writing and emails.
And, if you’re in doubt, use a correction software like Grammarly to help you double-check your grammar in emails.
Content tips for emails in English
I’m sure you’ve seen the viral meme with a man holding a sign that says, “That meeting could have been an email.”

But, the reverse can be true, too. So, make sure that your English email doesn’t need to be a meeting.
Keep it concise and direct. You want to make sure that everything in your email belongs there.
You should avoid:
stories or anecdotes
inspirational quotes, unless they’re essential
long, unbroken paragraphs of more than three lines.
If you’re writing a follow-up email after a meeting, break your content into small paragraphs, or use numbers or bullets to make your content more digestible.
Choosing the tone of your email
Formal does not mean cold. It’s okay to be warm and friendly in a formal email.
Here are some things to avoid:
Emojis or emoticons
Jokes, slang, or idioms you’re not very familiar with
Words like “gonna” or “wanna.”
Too many (or any) exclamation points
It would be best if you were warm and friendly in your email. But it doesn’t mean that you should be overly polite or apologetic, as in,
Sorry to bother you, but could you…?
In fact, directness is much more effective if you want to get things done. Take it from me, someone who apologizes too much.
If your tone is too apologetic, and if you don’t make it clear that you want someone to do something, they may not do it. They may think you are only making a suggestion instead of asking for them to do something.
Take a look at the examples below to see what I mean. The first sentences are a little too polite and indirect:
I have attached a contract below.
Please read and sign the contract before sending it back to me.
When are you available for a meeting?
Let me know when you’re available to meet.
It might be good if you reached out to Barbara.
Can you please reach out to Barbara?
If that still feels too direct to you, you can always soften it a bit with:
If you let me know when you can meet, I’d appreciate it.
If you wouldn’t mind reaching out to Barbara, that would be great.
We’re still asking for them to do something, but we’re using some indirect language.
Trust your judgment on this. If you’re writing to someone you don’t know, or if you’re writing to someone who prefers a more indirect style, it’s okay to write that way. But it’s also perfectly fine to be fairly direct.

How can I practice writing emails in English?
If you know that your English emails need work and want to improve, the best place to start is to look at your old emails.
Take a look at what you’ve done right and the areas where you should improve.
Then, get an English-speaking friend, language partner, or English teacher to look over your old emails. They can give you feedback about where you need to focus your practice.
Next, practice writing sample emails! The great thing about emails is that they should be short, so commit to writing one or two emails in English every week. Send it to your teacher or a friend for feedback.
Finally, if you can, commit to writing more English emails at work! Take any opportunity you can write formal or informal emails to your coworkers or other people. Not only will it impress your managers or colleagues, it will boost your confidence, too!
Join Our Community
Be the first to know about new lessons, posts or worksheets!
We respect your privacy.
About the Writer
Marta is an online ESL teacher who works with students from around the world. As a writer, language nerd, and content contributor for In English With Love, her mission is to empower English learners with knowledge and positivity.
More English Writing Tips

A Quick Guide to Reported Speech
How to use the future continuous in english.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
How to Write an Email in English: Our 18 Favorite Tips [+ Example Emails]
Emails have been hugely important to the internet for decades, as most people read and send emails almost every day.
That’s why being able to write a strong, clear email in English is a really important skill—on top of the fact that it can help you get a job , make friends, get into a university and much more.
If it’s your first time writing an email in English, check out this guide for beginners , but if not, continue reading this post for useful tips about email writing and email culture (dos and don’ts).
You’ll get comfortable with the format of email writing in English and you’ll see full samples of different types of emails written in English.
Our Favorite English Email Tips
1. be sure an email is necessary, 2. use separate business and personal email addresses, 3. be clear, brief and polite, 4. don’t write emails when you’re angry, 5. use short sentences, 6. avoid forwarding emails and replying to all, 7. use a spell checker, 8. watch out for signatures, 9. have a native speaker proofread your email, if possible, 10. read your email personally before sending it, 11. double-check email addresses for all recipients, 12. use the subject line, 13. start with an appropriate greeting, 14. pay attention to punctuation, 15. consider where to put “small talk”, 16. start with the end in mind, 17. put spaces between paragraphs, 18. use an appropriate closing, english email examples, how to introduce yourself in an email, how to request an appointment or meeting, how to write a formal email, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Like most of the email writing tips in this section, this may seem obvious. But sometimes we forget obvious things.
So ask yourself, “Is there a better or faster way to take care of this situation?” Many people get dozens or even hundreds of emails a day, so be sure that email is the fastest, clearest and most efficient way to communicate in your situation .
For example, if you’re writing to a coworker or a friend that you often see, you can probably just talk to him or her in person. Or you could also send a text message or call on the phone.
If you’ve decided that an email is the best option, then check the following tips before you click “Send.”
This may not apply to everyone, but if you can do it, it can help you in many ways.
Many jobs automatically give you an email address that you have to use. If that’s the case, then the problem is solved. Use the business email address for work and your personal email address for personal emails.
If you have a business email address, it can make an email look more professional. That’s good if you’re writing a formal email, but it might not be as nice if you’re writing to a friend. So that’s why having two can be useful.
Also, if you have separate accounts, it can help you balance your personal and professional life.
Again, many people receive so many emails each day. If your email is confusing, angry or really long, the recipient may not respond right away. Eventually they may forget to answer or even just delete it.
So be sure to get to the point quickly, but not in a rude way.
Treat an email similarly to an essay , only much shorter, and you will probably have good results. In an essay, you have to introduce the topic, explain the different points and then conclude the topic.
Honestly, this is something I have difficulty doing myself. I’m not (usually) rude in email, but I do have problems with the “brief” part. So when I’m done writing an email, I check it and try to eliminate about 20% of the content, since it was probably unnecessary.
It can be very tempting to write a mean email when you’re frustrated or angry at something. But it’s not worth it.
If you’re angry, wait until you’ve calmed down before writing your email. It’s better to wait a day than to lose a job or destroy a friendship because you said something stupid when you were angry.
Like #3, this is a problem that I have myself. I like to write long, complicated sentences, but often those are very confusing for the reader. That’s especially true if the reader is not a native English speaker.
I teach English in Costa Rica, and in Spanish it seems to be more common to have really long sentences with many commas. That’s very confusing, especially if you translate those ideas into English.
So here’s a tip: Write short sentences. It’s not bad style in English if you write short, clear sentences. Some authors, like Ernest Hemingway, are famous for doing it. (There’s even an online tool called Hemingway App that can help you write more like him!)
If you’re very comfortable writing in English, you can use long, more complicated sentences. But then again, if you’re very comfortable writing in English, then you probably don’t need these email writing tips!
The “Forward” option on email is a blessing (a good thing) and a curse (a bad thing). It can be good to quickly pass on important information to a new person. However, it can also be annoying for the recipient if it’s not used correctly. (The same thing is true about the “Reply All” option.)
If you need to forward an email, check carefully what information you’re forwarding. In some cases, it may be personal, confidential or just plain excessive (unnecessary). If so, cut those parts out.
Also, some email programs filter out emails marked with “Fwd” (forward) at the beginning of the subject line, and may even put them in the Spam filter or refuse to deliver them.
And if you click on “Reply All,” look closely at all of the recipients who will receive your email. Some people may not need to see your message. It’s frustrating to receive emails about subjects that aren’t relevant to you.
Most email programs have this option, so make sure you use it before sending the email.
Or if your email program doesn’t offer English spell checking , you can add an extension like Grammarly to your browser and use it anytime you’re writing anything.
To get the most accurate version of Grammarly, you’ll need to make sure you have Grammarly Premium , which highlights and offers corrections for more advanced English issues.
Many people put “cool” or “funny” signatures at the bottom of emails. They often include contact information, like email addresses or phone numbers. That can be useful, but if your emails get forwarded (see #5), that information may get to people you don’t know, or even people you wouldn’t want to have that information.
Additionally, if you send multiple emails back and forth with another person, it may include your signature every time, and the email chain just gets longer and longer. So consider not including your signature in some emails.
Or if you do want an email signature, try to keep it simple, without including your personal information.
If you know any native speakers or have friends who speak English very well, you may want to ask them to review your email before you send it. That’s especially true if it’s about something important.
If you’re taking an English class, you might even be able to ask your teacher to review the email—just be sure to ask nicely and say “please”!
It might not always be possible to find a native speaker to check your email. In those cases, it’s still useful to read your email yourself. It can help your English, too.
Try to read the text of your email out loud. First of all, that will help you work on your pronunciation, which is always nice. Second, it can help you see and hear mistakes in grammar.
It also helps you understand how your email “flows.” If it’s too long or complicated to read out loud, then you should probably make it shorter and clearer.
As I mentioned before, I live in Costa Rica. People here often have the same last name as many other people. It’s basically like “Smith” or “Johnson” in the U.S., but about 10 times worse.
I’ve even had multiple students at the same time who had the exact same first and last names. And I’ve mistakenly sent emails to people who had very similar names.
So just check those email addresses twice to be safe.
After you’ve followed the general email writing tips in the previous section, you need to actually write the email. So how do you do that?
There’s a specific structure and format of email writing in English, shown in the following tips.
It’s surprising how many people don’t do this. Be specific in your subject line, as well.
For example, don’t just write “Question.” Instead, be more specific, like “Question About Schedule for Friday’s Meeting.” That way, the recipient will know immediately what your email is about, even before opening it.
It’s most polite to begin with some type of greeting. If you know the person well and it’s an informal email, you can just say “Hey [First Name].”
You can also use “Hi [First Name]” or “Hello [First Name],” to be a little less casual.
If you don’t know the name of the person (like if you’re writing to customer service), you can use “To Whom It May Concern.”
Notice that after greetings, you should generally use a comma. According to many sites like Business Writing , you should use a comma after a greeting in personal emails and letters, and use a colon after a greeting in business or formal emails/letters.
But in reality, a comma will probably always be fine if you can’t remember the rule.
Start each sentence with a capital letter. Be sure to put periods or other appropriate punctuation at the end of each sentence.
It’s a small detail, but it can really help to make a positive impression.
If you know the person you’re writing an email to, you might want to include a bit of “small talk.” That could be something like asking about the person’s family, a mutual friend or an activity that you have in common. But where and how can you include this?
Personally, I actually prefer to include this information after the “business” part of an email. If I’m asking for a favor, I prefer to ask first, and then to make small talk after.
Other people or cultures may prefer to have the small talk first, so you may want to adjust it if you know the reader’s personality well.
Get to know how to use small talk in English by seeing it in use through a program like FluentU .
As you write, focus on the purpose and the goal of your email. If you’re asking a question, that should be the main focus of your email. If you need a favor, then it should be very clear what favor you need and exactly how the reader can help you.
Imagine you are the recipient: Would you understand immediately what you needed to do in response to the email?
If you don’t do this, you’ll end up with a giant block of text. Just hit the “Return/Enter” key twice between paragraphs. It’s much easier to read and less overwhelming.
You can find some examples below, but be sure that it’s a goodbye that’s appropriate for the purpose of your email . In other words, don’t sign an email with “Love, Ryan” if you’re writing to your boss.
Similarly, don’t sign it “Sincerely, Ryan Sitzman” if you’re writing to your grandma to thank her for the birthday present she gave you. (And definitely don’t sign your emails as “Ryan Sitzman” if that’s not your name! And if it is your name, let me know. I’d like to start a Ryan Sitzmans Club!)
Here are some more closings you can use to say goodbye at the end of your email. Now, let’s put all of these tips into practice!
For this example, let’s imagine that you’re going to travel to the U.S., Canada or another English-speaking country. When you get there, you’ll stay with a host family. So the organization has matched you with a family and you need to introduce yourselves before you meet in person.
Here’s what you might send:
Dear Smith Family,
Hello, my name is John. I received a confirmation letter from the exchange organization today. It said I’ll be staying with you for two months later this year. I wanted to introduce myself so you can know a bit more about me.
I’m 18 years old. I like listening to rock music, playing basketball and reading comic books. I will graduate from high school later this year, and I hope to go to college next year. I’ve never traveled outside of my country, so meeting you and visiting your country will be an exciting, new experience for me!
I’d also like to know more about you, so if you have a chance, please write back at this email address. If you have any questions for me, I’d be happy to answer them.
Thanks again for agreeing to host me—I’m very excited to meet you in person!
Dear Professor Smith,
I really enjoyed your Introduction to Writing Course, and I was interested in continuing by taking the Advanced Writing Course next semester. I’d like to meet with you to ask a few questions about the course, and also to get more information about the scholarship for international students.
Would it be possible to meet with you at your office sometime next week? I’m available during your regular office hours on Monday and Wednesday (2-5 p.m.), but if you’re busy on those days, I could also meet any time on Tuesday or on Friday afternoon. Please let me know what day and time would work best for you.
Thanks very much for your time and help!
John Johnson
I have to write emails like this pretty often, unfortunately. I say “unfortunately” because it’s frustrating to have a problem with a product. Dealing with a company’s customer service representatives can be difficult at times. But a clear, polite email should help you resolve your problems faster.
To Whom It May Concern,
I recently bought a toaster from your company, but unfortunately it appears that the heating element isn’t working correctly.
For reference, the model number is TOS-577, and I bought it on May 1, 2016 at the Toaster Emporium in New York City. I returned the toaster to the store, but they said I should contact you because the model had been an “open-box” discontinued model. Because of that, they weren’t able to offer a refund or exchange.
I can understand the Toaster Emporium’s position, but the toaster shouldn’t have broken so soon. It is still covered under your company’s one-year warranty, so I would like to exchange the toaster for a working model. If that isn’t possible I would like to receive a refund. Please let me know what steps I need to take for this to happen.
Thanks very much for your help with this situation.
Sincerely, John Johnson
So, there you have it! If you keep these tips in mind while writing emails in English, you can become an email expert.
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

Our products
- Email signature generator
Create a stunning email signature for yourself within a few clicks
- Email signature manager
Manage your teams email signatures and gain control over your brand
- Gmail signature
- Google Workspace
- Outlook signature
- Outlook 365 signatures
- Exchange signatures
- See all platforms
- Education facilities
- Real Estate agencies
- SaaS companies
- Health care
- Finance & insurance
- See all industries
- CEOs & executive
- Realtors & brokers
- Legal & lawyers
- Marketing & sales
- All signature examples
- Email signature examples
- Email signature templates
- Email signature design
- Email sign offs
- Email signature banners
- Handwritten signatures
- Disclaimer templates
- Cool signature templates
- Minimalist templates
- Animated templates
- Banner templates
- Signature generator
- Banner maker
- Email disclaimer generator
- How to add signature in Outlook
- Add a signature in Outlook 365
- Add signatures in Exchange
- How to add signature in Gmail
- Add multiple Gmail signatures
- Google Workspace signatures
- See all guides
- Email marketing updates
- Digital marketing hub
- Branding & PR
- Business updates
- Tech & IT
- Product updates
- Our features
- Help center
- 24/6 support
- Contact sales
- User reviews
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Security and compliance
- Trust center
Users stories

See how companies save time & money automating their email signatures
Home / Formal email writing examples & tips
25 formal email writing format examples & best practices
Get professional email writing formats proven to work in real life. See top formal email examples and learn professional email best practices.

Email writing is an art and doing it well takes know-how and practice. But you don’t have to make all the mistakes for yourself in order to write professional emails.
We assembled for you the essential tips for creating highly effective formal emails with a deep dive into formal email formats, structure, and best practices. We also gathered some real-life examples and templates you can use right away with a few tweaks.
What’s in this article
- Basic formal email structure
- 25 top professional formal email examples you can use today
Aesthetics of a formal email
- How to improve your email writing skills
Formal vs. informal email writing
Formal email writing is usually in a B2B or B2C scenario or a professional email between colleagues, businesses, or partners. Informal email writing is something you might send a friend, or family member, or sometimes even a quick email you’re firing off to a colleague.
When you’re emailing a friend there is not much risk of getting your words or meaning wrong, and there is little risk of hurting your reputation or wrecking an incredible business opportunity. But when writing a business email there is much at stake and many things that can go horribly wrong. This is why our article will deal mostly with formal email writing and how to get it right every time.
Here, we’ll go over all the ins and outs of what goes into an email structure, different email formats you can use, as well as short email templates that you can use in various scenarios. Keep reading to learn how to write the perfect email.

Basic formal & professional email structure
Before we get into different email templates, it’s important to know how to build an email yourself. For the most part, every email, regardless of its contents, will follow the same structure with the same basic elements. You should get to know these elements in order to ensure proper and effective email writing as a whole.
The basic elements of professional email writing:
- Your email address
- Subject line
Email Opening
Email ending.
- Email Sign off
Email signature/footer
Now let’s break these down, one by one.
Professional email address
Your email address is oftentimes out of your control. If you’re working for a company or operate under the umbrella of a brand your email address will likely include the company or brand name domain.
For example, the emails in WiseStamp are all in the following format: [employee_name]@wisestamp.com. This ensures that we all have a professional business email address. Since only the owner of wisestamp.com can issue email addresses under that domain name, this ensures our emails appear legitimate.
Imagine if each employee had a random Gmail address like [name][email protected], which anyone can create, that would be a bit suspicious. Email open rates are first and foremost dependent on trust, so make sure you have a trustworthy email address or suffer very low open rates.
If you are a freelancer professional, working separately from an established brand, consider buying a domain name for your personal brand. You can look up available domains on Google domain registrar .
Subject lines
Your subject line will be the single most important element in your formal email writing. It is the first thing your recipient will see and unless you convince her then and there that your email is a safe, relevant, and high priority (in that order) it may never be opened. If this happens, any effort you put into the rest of the email elements will go to waste.
Your subject line will depend on the purpose or content of your email, but overall, you want it to be something engaging enough for a recipient to click on.
Email subject line guidelines:
- Be clear and specific – avoid using generic or clickbait subject lines that say nothing or make unrealistic promises, like “find out how to double your business in a week”.
- Be original – avoid using those all too common subject line templates you find on the internet. Instead make original subject lines that are relevant, personal, and concise.
- Add relevancy – address something that the recipient will recognize, like an acquaintance’s name or an article/ show/ book they appeared on.
Studies have shown that personalized subject lines are 26% more likely to be opened . You also want to tailor your email subject line to your email goal, whether it’s a sales email, a personal email, a newsletter, or something else. I advise that you take the time to think of 3-4 refined options then consider which of them will likely be most appropriate.

The next most important way to hook a recipient into your email is by writing a strong email opening line . Like your subject line, the email opening is mostly used as another filtering stage for most people. If it fails to meet the promise made in the subject line, your readers will ditch it.
Therefore, it’s extremely important to define your main point in 1 or 2 paragraphs tops. If you clearly convey your request or question and your reader feels it’s relevant and interesting, then they’ll continue reading your email. If you manage to get them to stay after this point, in most cases, they’ll return your email. Good for you.

Email opening guidelines:
- Address your recipient by their preferred name – look up an article they’ve written or their LinkedIn page and see what name they use. Some people will use their full name or their nickname accordingly (for example David vs. Dave, or Anastasia vs. Ana).
- Establish a connection – connect your email to a personal experience that involves the recipient, like an article or a news piece you’ve read about them, or a conversation you had with an acquaintance.
- Match the opening with the subject line – your opening message has to mirror the promise made in the subject line because this is how the reader validates relevancy. If you don’t connect the subject line to the opening, readers will be confused and even assume clickbait.
- Get to the point fast – tell your reader why you contacted her and what’s in it for her.

The body of your email is where you get into your main message. Whether you’re composing an email to establish a new business connection or just following up on a meeting, the body of your email should be detailed enough that the reader isn’t confused, but also brief and to the point. No one wants to sit and read a long-winded email when they have dozens of other unattended messages in their inbox.
Email body writing guidelines:
- Be concise – detail only what’s needed to get your point across.
- Use words that convey (authentic) positive personal emotions – words like “glad”, “excited”, “intrigued”, and “confident”.
- Use the word “because ” when asking for something – it’s been scientifically shown that people are more easily convinced to do something if told why, and more so if the reason is important to them.
- Show don’t tell – if you can’t explain something in a few words, see if you can add a screenshot, a video, or a link that explains it better.
- Use headings to split long content into sub-topics – if you can’t avoid writing a long email, make sure to break it up into subsections with headings. This will help your time-scarce readers to scan and find their points of interest.
- Add your concrete request or question in bold text – to ensure your readers do not miss the most important piece of content (your request or question) – set it in a separate line and put it in bold. You can also use some color. If you do avoid light shades (you want high contrast between the text and the white background. Once you pick a color – stick with it.
After you’ve addressed all your main points in the body of your email, you’ll want to end it with a respectful and brief salutation. You can either invite your recipient to reach out for more questions, wish them success, or ask a question. It all depends on the motive for your email. If it was a long email it could also be a good idea to gently reiterate your main request, question, or motivation.
Email sign-off
When closing your email, you’ll want to choose a suitable email sign-off . There are different sign-offs you can use for each occasion, such as “best regards,” “sincerely,” or “with love,” but you obviously wouldn’t want to send the last one to your manager. Make sure your signoff is appropriate to your email content and your recipient.
A cool tip you can apply is to add a handwritten signature sign off. A handwritten signature give your recipient the feeling that you gave the email special attention and a personal touch. You can create one here .
Your email signature (or footer) is your wave of goodbye. The way you do this can affect the impression you’ve made up to this point. If you make this moment memorable, organized, and aesthetic you can get some extra credit and a positive attitude from your reader. On the other hand, if you mess this up, your entire message or offer may be put in doubt. So, make sure your email signature looks visually appealing and well organized.
Consider creating a professional email signature to nail a positive lasting impression. Use the simple text email signature we all used back when email started at your discretion. Whichever you choose, be sure to include all your professional and contact information. It would also be a good idea to add links to your website, social media sites you are most active in, or a landing page.
Professional formal email examples: specific formats for specific goals & uses
In order to get a better understanding of how all the elements of an email work together in different types of emails, it’s helpful to look at some templates. Here, we’ll cover a number of email scenarios and provide you with an example for each one. Each of these letters refers to a specific situation, but you can always tweak the content to make it more relevant to your needs.
Our examples of the most common email formats:
Thank you email
Formal letter of appreciation, letter of complaint, cover letter, reminder email.
Apology letters samples:
Letter of apology for a client
Apology letter from boss.
- Apology mail for the manager
Sample business emails (B2B and B2C):
- Introduction email to client (outreach)
- Sample email for proposal submission
Proposal submission email
- Quotation email
Email asking for feedback
Information inquiry letter samples:
Email of inquiry requesting information
Email asking for a status update.
Request email samples – professional email asking for something:
Sick leave mail format
Letter asking for a discount from the supplier, ask for a raise, email your boss about a problem (asking for help), email to schedule a meeting.
Work update email samples:
- Email to the client sharing the status of project
- Email to the boss about work progress
Confirmation vs rejection email samples :
Acceptance email
“this is to inform you that” letter, job rejection email.
A thank you email is usually one that you’ll send after previous communication with someone. You might want to thank them for their help on a project, for fulfilling your personal request that you previously sent, for a job interview, or even for something as simple as taking a phone call or a meeting.
When composing a thank you email, you don’t want it to be too long, so get straight to the point. Additionally, they aren’t necessary 100% of the time and can sometimes just clog up the inbox of someone who might be really busy, so consider whether or not it will be useful for you before you click send on a “thank you” email.
Thank you email for work done or service rendered
Thank you so much for [action they did] It was such a pleasure to work with you, and I’m very excited about the next opportunity to work together again.
Please don’t hesitate to contact me if I can provide any additional information.
Best regards, [name and job title]
Thank you email for a job interview
Dear [name of hiring manager],
I enjoyed speaking with you the other day at the interview for the [job name]. The job appears to be an ideal match for my skills, ambitions, and interests.
The innovative approach to the corporate culture within the [job field] world confirmed my wish to work at your firm.
I will bring my engineering skills, assertiveness, and ability to engage others to work in a cooperative way within the [name of department] department.
Thank you for taking the time to interview me for the [position title] at [company]. I have a high level of interest in working for your firm and look forward to hearing from you.
Best Regards,

Dear Mr./Mrs. [name],
I would like to formally recognize all the hard work and dedication you’ve put into completing [project/task]. Due to your consistent efforts, the project is what it is today and that led to the positive results we were hoping for.
On behalf of [company name, board members, etc.], we would like to formally thank you for your hard work and we would like to let you know that we highly value your contribution and your continued dedication to your job.
We are very grateful to have you as a member of our team and we wish to continue to see you thrive within our organization.
Best regards,
[Name and job title]
Dear [name],
On January 30th, 2020, I made a reservation at your restaurant located at 1234 Mulberry Lane for a birthday dinner for four people. This letter is intended to bring certain issues to your attention.
Unfortunately, we did not enjoy our dinner due to the fact that the food was very slow to arrive and we received the wrong dishes. It’s understandable that it was a busy time at your restaurant, but the quality of the service was not as expected.
To resolve this problem, I would appreciate it if you could provide compensation in the form of a gift voucher or discount on a future meal.
I’m looking forward to your reply.
With regards,
[Your name]
It used to be common to send your cover letter and CV as an attachment to your email. However, it’s becoming a lot more accepted to use the email itself as your cover letter and simply attach your CV.
When sending a cover letter email, make sure you’re using formal language, addressing the right person such as HR or the hiring manager, you use a relevant subject and opening line, and the body of your email demonstrates why you’d be a perfect fit for the job and company. Since hiring managers likely receive dozens of email cover letters, be sure to make sure yours stands out and doesn’t drag on too long.
Cover letter example
Dear hiring manager [name],
I was very interested while reading the job posting for the position of [job title]. I believe that the experience I have strongly match the responsibilities of this position. I am enthusiastic about submitting my application for the position.
My most recent position was at [company name], where I was a [job title name ]. Additionally, I recently participated in a [mention an accomplishment in your last job that is relevent]
I have attached my resume to this email. Thanks to it, I believe you will learn more about my experience, education, and achievements.
Looking forward to hearing from you,
If it’s your first time reaching out to someone or a second or even third, the format of your email should be different. A first contact email has to include certain details that provide context.
when writing a reminder email or follow-up email you don’t need to provide a broad context. Instead, you should just briefly and lightly remind your recipients of what you already agreed on (assume that it simply may have been forgotten or placed low in their backlog).
This little push can go a long way in shortening your timetables and making sure you’re items are prioritized. Most people appreciate the reminder and respect you for being steadfast.
Reminder email sample
I’m sure your schedule is very busy, so this email is simply to remind you of your upcoming interview with [name] who is a candidate for [name of position].
The interview will be at [time] on [date] in [location].
Please let me know if there’s anything I can help you with to prepare to interview this candidate.
Apology letters samples
From time to time we all make mistakes, and we all get something wrong. Sometimes our mistakes hurt others, cause them discomfort, or make them frustrated. In these situations, it’s usually the right call to simply apologize.
Apologizing is something that must be sincere or you risk offending the person further. It’s always the best approach to express genuine regret.
But regardless of whatever you truly feel, be very careful to only use words that express empathy for whomever it is you’re apologizing to. Do not lay any responsibility on them, and do not give excuses.
Dear [client’s name],
Please accept my deepest apologies on behalf of [company or business name] for the poor experience you had at our restaurant.
I want to thank you for bringing these issues to my attention and please know that we are making every effort to correct our mistakes so events like these don’t happen in the future.
As a token of our apology, please accept a gift card in the amount of $50.00 that can be used at our restaurant in the future.
I hope to greet you again soon at [company or business name].
Yours sincerely,
[Your name and job title]
Dear Mr./Mrs. [boss’s family name],
I’m writing to you to express my regret for my behavior on [date] in regard to [event]. I would like to apologize for my words and actions and reassure you that such an event will not happen again.
On the date in question, I got into a verbal altercation with the head waiter about the scheduling, and this led to my inexcusable behavior. I have already apologized to [name of colleague], and I wanted to assure you that I will work to improve my reactions and behavior in the future.
I’d be happy to meet with you to speak about the incident further if you have any outstanding concerns.
I am sorry again.
Apology mail for manager
Dear [manager’s name],
I owe you an apology for providing you with the wrong information on [date] regarding [event]. It was not my intention to provide inaccurate information and I apologize for any inconvenience it may have caused you.
It wasn’t my intention to mislead you, and it seems the false information was a result of a careless mistake. I will be sure to be more thoughtful in the future and learn from this incident.
Please do not hesitate to share any thoughts or concerns with me and I’d be glad to discuss this further.
Business emai l sample s
Introduction email to a client (sample email to approach a new client).
Dear [Sir/Madame/Name],
I would like to take a moment to introduce myself and my company. My name is [name] and I am a [job title] at [company name]. Our company provides customers with cutting-edge technology for all their email signature needs.
At [company name], there are a number of services we can offer, such as [short list of services]. Our employees are also highly dedicated and are willing to help you with your every need.
I’d love the opportunity to speak or meet with you to discuss your needs further and to tell you more about how [company name] can help you succeed. You can contact me at [phone number] with any questions you may have.
Dear [Name],
Please find enclosed to this email the proposal you requested regarding your website audit.
We hope that you will find this proposal helpful and insightful and that it meets your expectations. Of course, if you would like to make any adjustments or go in a different direction, feel free to let us know and we’d be happy to discuss with you.
Thank you for entrusting [your company name] with your website audit, and we hope to hear back from you soon.
Sending quotation email
Dear [customer name],
We’d like to thank you for sending in your inquiry on [date] regarding a quotation for auditing your website.
Based on an initial estimation, we are happy to offer you a quotation based on your requests. Please find the official pricing quote attached to this email. Note that this quotation includes [list of services], but should you want additional services, we’d be happy to discuss it further with you and provide another quotation.
Please do not hesitate to get back to us with any questions about the quotation or our services.
Hi [customer name],
We really appreciate you using our services on [date] and we’d like to get your feedback on your experience.
Please follow the link [insert link] to complete a short survey regarding your experience. This survey shouldn’t take any longer than 2 minutes and it will help us improve our products and services in the future.
We want to thank you in advance for your time and hope that you enjoyed your experience with [company name].
[Name and/or company name]
Inquiry letter samples
This email is to inquire about the website audit services you posted on your website.
As I understand, you offer services to audit businesses’ websites and provide personalized insight into what improvements can be made. I’d like to request further information with regard to your pricing as well as the scope of the work that will be performed, including specific services that can be expected.
I look forward to receiving your response.
I wanted to check in and check on the status of the website audit project that is due on [date].
Please let me know where you’re at with the project and don’t hesitate to let me know if you require any assistance from my end.
Request email samples – professional email asking for something
A personal request email is usually straight to the point and involves a sender asking a recipient for something. It could be anything from connecting on a professional network, asking to set up a meeting, or even requesting a professional introduction. Following a personal request email, a recipient may decide to either accept or reject what the sender is asking for. In this type of email, it’s important to be very clear with what you’re asking for.
Hi [Name of manager/supervisor],
I am writing to request sick leave from [date range]. I will be undergoing surgery and at the recommendation of my doctor, I need to be off of work for 2 weeks in order to recover. I hope to be back at work on [date].
Please let me know if you have any questions.
Dear [name of the supplier],
Thank you for sending over your catalog of goods. We are very much interested in purchasing [name of the product(s)] from you and would like to get a quote for these items.
Additionally, we are hoping that this will lead to a prolonged partnership between the two of us. Therefore, we are kindly requesting that you provide us with your best possible price since we would like to use your goods on a permanent basis.
Thank you for your understanding.
Dear [Name of Manager/supervisor],
I have greatly enjoyed working for [company name] over the last 3 years. During these years, I feel that I have become a valuable member of your team and I have contributed to projects in a significant way.
Since working here, I have accomplished: [list accomplishments].
As an employee, I think I have outperformed the goals set for me. As a result, I would like to have the opportunity to discuss increasing my salary so that it matches my current performance. Please let me know when is a good time for you to meet so that we can discuss this further.
Once again, I am grateful to be part of an organization that provides me with unique challenges and opportunities to continuously learn and grow.
Dear Mr./Mrs. [name of boss],
I would like to bring to your attention the incident that occurred at [location] on [date] at [time].
I was deeply upset by the actions of [coworker/event]. I tried to speak with them, but this did not lead to any sort of resolution and now I feel as if our professional relationship at work is strained as a result.
I am turning to you for assistance with the matter and I hope that you are able to come up with a solution that neither of us has thought of yet.
Thank you for taking the matter seriously and please let me know if you have any questions or concerns.
Thanks for getting in touch with us about our product. I’d be glad to set up a meeting in order to give you more information, answer your questions, and show you how it can work for your business. Does [date] at [time] work for you?
I look forward to meeting with you soon!
Work update email
Email to the client sharing the status of the project.
Dear [name of client],
We’d like to keep you updated regarding the progress we’ve made on our project. Please have a look at the tasks we’ve accomplished below and do not hesitate to get back to me with any questions or concerns you may have.
Key highlights and updates:
- [list them]
Tasks accomplished this week:
Tasks to do next week :
Email the boss about work progress
Hi [name of boss],
I am happy to let you know that the project [name of project] that was assigned to me on [date] is now nearing completion. Due to the hard work of our team, the project is expected to be completed on time. Based on the pace of our work, I expect to have the entire project completed by [date].
The remaining elements of this project to be completed are as follows:
- [List them 1]
- [List them 2]
- [List them n]
Thank you for your continued support and guidance and please do not hesitate to get in touch with any questions.
Confirmation vs rejection email samples
You might get an email confirmation after you purchase something online, or you can also reply to a formal email confirming receipt of an email attachment, a meeting time, or a company update. A rejection email is similar in that it might reject the item that was proposed in an email, in which case you’d let the sender know.
It is my great pleasure to inform you that I will be accepting your offer for employment as [job title] with [company name]. The goals for this role that you described are in line with my personal career aspirations, and I hope to be able to learn and grow in this role.
As discussed in our previous meeting, my salary will be [salary] and I will be starting on [date].
I appreciate all the time you took to make the interviews as seamless as they were, and I look forward to working with you soon.
This is to inform you that your business proposal [title of the proposal] has unfortunately been rejected by our committee. While we did like your idea, unfortunately, the costs involved reach well beyond our budget for this quarter.
We wish you the best of luck in your future endeavors and encourage you to submit additional proposals if you have others that are aligned with our goals.
Best of luck,
This is to inform you that I will not be proceeding in the interview process for [job title] with [company name]. I would like to formally withdraw my candidacy.
At this time, I have accepted a position with another company, so I am no longer in search of employment. However, I would like to sincerely thank you for taking the time to meet with me and for being attentive to my questions about the role.
It was a pleasure meeting with you and I wish you luck in finding the right candidate for the job.
Before you even get started on the content of your email, you want to make sure the aesthetic is appealing and not too out of the ordinary. Of course, you want to capture the attention of your recipient, but you also want to appear professional, so keep the Comic Sans font out of the equation. What sort of aesthetics should you pay attention to in a formal email? Let’s take a look.
Choice of Font
Don’t start reinventing the wheel here. It’s better to go with a safe bet instead of a creative option when selecting a font. Choose a font that’s easy to read and skim, since if you’re sending a longer email it’s possible your recipient will just skim its contents. Therefore, you want to font to be clear and the letters to be far enough apart. We suggest going with fonts like Georgia, Verdana, Arial, or Times New Roman

You don’t want your recipient to have to squint to read your email, but your text also shouldn’t appear as if it’s yelling either. Depending on the font you go with you might need to tweak the sizing a little, but in general, font size 12 is what you should be using. You can use size 10 or 11 as well, just make sure it doesn’t look too small before sending your email.
How do I improve my email writing skills?
There are a number of ways you can make your emails shine, and you don’t need to be a professional writer to do it. In fact, there are a few small areas you can focus on to make your emails clearer and more well-received. Here are a few things you should keep in mind when composing an email.
1. Practice optimizing your subject lines
Your subject line is the first thing a recipient sees when they receive your email. Therefore, it’s important that it’s optimized as much as possible. Keep these tips in mind when coming up with your subject line:
- Keep it short, no more than 40 characters is ideal
- Make it personal, use the recipient’s name if you have it
- Use a call to action, like “let’s set up a meeting today”
- Create a sense of urgency, such as “offer to expire soon”
2. Practice summarizing your main point for your email openings
Once you get your recipient to open your email, you don’t want to bore them right away. You have to keep things interesting, relevant, and straight to the point. That’s why it’s crucial to put your main point somewhere in the first sentence, or at least the first paragraph.
While your opening line can be something general like “thank you for taking the time to meet with me,” the very next line should be something more powerful. Whether you ask for the results of a meeting, make a proposal, or initiate a follow-up meeting, this first sentence sets the tone of the rest of the email so the reader knows exactly what the subject is and what to expect from the rest of your message.
3. Research the correct email etiquette to use for your most common scenarios
When sending emails, especially formal or professional emails for work, it’s important to maintain email etiquette . Since many of us answer our emails on our phones while on the go, it’s tempting to reply to emails as we would a text message, but that’s not good practice.
4. Proofread grammar
Finally, before you click send, always give your email a once-over. Make sure your email is free of types, the punctuation makes sense (avoid using too many exclamation points), and that your syntax is correct.
Don’t always rely on spell-checkers, you want to read through your email before sending, especially if it’s an important message to a superior or a client since emails with grammar mistakes can potentially have a negative impact.
There are countless reasons for sending an email, and even if we didn’t cover every single scenario here, you should at least have a better idea of what constitutes a good email. Using our tips and examples, you’ll be able to compose better emails that get you the results you want.
- An Interview with Chatgpt: Can AI think outside of the box for email marketing?
- Email closings: The definitive guide
- Email blast marketing: Learn how to effectively promote your brand
- Email management: : Proven Tips for Boosting Productivity
- Various best regards alternatives for email closing
- Ultimate guide on how to end an email
- How to get a professional email address
- How does BCC work: complete guide
- How to craft an introduction email to a new team
- Email etiquette explained: rules and examples in business and in the workplace
Flow through your inbox
Flowrite turns your instructions into ready-to-send emails and messages across your browser.
.png)
For companies
Jan 18, 2022
How to write emails in English with examples
Want to learn how to write emails in English? Email English can be tricky, but our English email examples and guide on format, etiquette, phrases, greeting and closings will help you in writing emails in English and improve your email writing skills in English.

Lawrie Jones
Table of contents
Writing emails in English isn't easy especially for non-native English speakers, but it is an essential skill that can benefit you both personally and professionally.
So, how to write emails in English? First of all, you need to learn many rules and conventions of email English. You must familiarize yourself with the English email format including English email greetings and closing phrases.
When you know how to start and end an email in English, you must have the common email phrases English in your back pocket and understand the English email etiquette in order to always come off as polite and professional.
To help you improve your email writing skills in English further we will provide you with English email examples covering how to write formal, professional, and informal email in English language.
This in-depth guide on email writing will be topped off by an example how Flowrite's AI writing tool can assist you to deliver your message effectively with grammatically correct, perfect English, like this:
How to write emails in English
To get your started we will unbundle the English email format covering email greetings , body, email closing phrases and signature.
English email format
English language emails are what academics describe as a "highly prescriptive form of written communication." Simply put, there are strong and established rules dictating the format of English language emails.
Most of these rules emerged in the Victorian age, so it's no surprise that the English language email format closely follows that of a formal letter. Typically an English language email has five elements:
- Subject Line
- Formal or informal greeting
- Closing phrase
This article walks you through each part and provides examples of email structures that illustrate our points. By the end, you should understand how to format emails in English.
Why should I format my emails?
From the outside, the English email letter format may seem strange. Still, once you understand the rules, it makes creating effective emails simpler and quicker for everyone, as this study into letter-writing found .
But why bother formatting emails in English? Here are five reasons:
- It's professional: The rules and conventions of formal email English are accepted professional practice. While you're free to write however you want, your choice of email style, tone of voice, and format convey a message to the recipient.
- It's more effective: Every email should have a purpose, in most cases, to elicit an action. Using the established English-language format provides a simple and clear structure to convey your message that's likely to get the response or the result you want.
- It reduces stress and anxiety: "If a user can understand a letter, they're less likely to get in touch to ask questions via another channel and more likely to do the thing the letter is asking them to do," says the UK Government . Clearly stating what you want and why means the reader doesn't need to fill gaps or make assumptions.
- It's easier: Understanding how to format English language emails makes writing them more manageable. There's no stress worrying about how to address someone or sign-off; it's already decided for you. It leaves you time to focus on the core of your message.
- It's quicker: Once you understand the fundamental building blocks of a formal email, writing them is easy and quick. This could save you hours if you're anything like the average worker who spends half their working day writing emails . Tools such as Flowrite can save you even more time, creating perfectly formatted, free-flowing emails that get results in seconds.
Understanding how to format an English language email provides the fundamental basis for all correspondence. But, of course, you're free to change, adapt or ignore any part of this, should the situation or circumstances demand it.
Language changes and evolves, giving you the freedom and flexibility to shape correspondence for each audience. For example, language "laws" aren't set in stone, say academics . Instead, readers want to be able to access information quickly, which has "impacted the structure and the function of emails," researchers have said. Essentially, if there's a better way to communicate your message than sticking to the rules, then feel free to use it.
How to start an email in English
The traditional way to start an email in English is by using the word 'Dear'. In the past, you would be advised to use a title (Mr, Mrs, etc.) in the past, but things have moved on. Gendered terms such as Mr and Mrs can now cause offence, so we need to find another way of introducing ourselves to email recipients.
The different email greetings in English depend on whether you are addressing an individual you know, a person you don't know, or a collective (an organization, team, or anonymous email address, for example).
Here are some of the ways to write formal email greetings in English.
If you know a person's full name, you should use it. So, instead of "Dear Mrs. Roberts", you would write:
- Dear Sarah Roberts
Many old formal English email writing blogs and articles suggest using "Dear Sir" or "Dear Madam" if you don't know the person you're writing to. However, we disagree. This is outdated and unnecessary. If you can't find a person's full name (LinkedIn is your friend here), find another way to address them.
Here are a few examples of addressing a person who's name you don't know:
- Dear Marketing Manager
- Dear Team Leader
If you're addressing a group, find a way of engaging them that's suitable, such as:
- Dear Marketing Directorate
- Dear Complaints Team
Lots of people wonder whether you can use 'Hi' as a greeting in a formal email, and you can. If you know the person or aren't writing in a formal context or capacity, it's your choice.
The body of an email is where you explain what the message is all about. There are no hard and fast rules because each email is slightly different. Still, there is a natural flow for information in a formal English email :
- Introduce yourself – a name, job title, and organization are pretty much essential
- Explain why you are emailing – describe why are you contacting someone
- Say what you want – if you want something in return (a response, document, image, etc.), then ask for it
- Next steps – describe what happens now, providing a timeframe. If you're expecting a reply, be clear when you expect one. Never leave your reader confused
It's easier to see this on the page, so be sure to check out the examples below to see how we've used this format to create effective English-language emails.
English email closing phrases
The type of closing phrase you use in an English language email depends on whether you're writing a formal or an informal email. Let's look at both types of email closing messages below.
How to end a formal email in English
There are only two things you need to know about finishing a formal email in English:
- If you know the person's name, you use the ending "Yours sincerely".
- If you don't know the person (or are writing to an organization or collective email address), you use "yours faithfully".
How to end an informal email in English
By their very nature, informal emails aren't governed by rules, so you're free to write whatever you want. Nevertheless, some familiar phrases that you may find are commonly used when ending informal email messages.
Some email sign-offs you may choose to use include:
- Kind regards
- Best regards
- I look forward to hearing from you
- Please contact me for additional help
Email signature
A professional email signature provides the essential information a reader needs to know about you, including:
- Organization
- Contact details
Every English email signature should include the following, but you have the freedom to add more, including:
- Details of qualifications
- Chosen pronouns
- Social media links
Common English email phrases
You could write a whole book on English language email phrases, but we need to keep things brief for the purposes of this blog (and to stop you from getting bored). Here are some helpful business English phrases that you may want to include in your English language emails:
- I am writing to tell you about
- I'm contacting you to confirm that
- This is just a short email to explain that
- Just a quick reminder that
- This email is to let you know that
- I'm getting back in touch with you with some additional information
- Attached is the information you requested
- I'd welcome your thoughts on
There are some informal email English phrases that you may read and choose to use yourself:
- Great to catch up
- I hope you had a great weekend
- I hope you are well
- I hope all is well with you
- It's lovely to hear from you
- I was delighted to receive your message
English email etiquette
The formal rules of English language rules dictate how an email should be structured, including greetings, the flow of information, and suitable sign-offs. Email etiquette describes the unwritten rules that help you craft and shape better messages.
Here are 10 email etiquette rules and tips that all English email writers need to know.
- Write a professional subject line – Provide as much information you can about your message in the subject line
- Keep messages short and to the point – Sharpen your messages and remove information that isn't essential
- Don't' try to be funny – Jokes are acceptable among friends, but humor doesn't always travel way, so don't bother
- Limit caps – Limit the number of capitals you use and write in sentence case where possible
- Avoid exclamation marks – Exclamation marks are popular on social media but should be used sparingly in formal and informal English-language emails
- Respect cultural differences – When writing to anyone, be respectful of cultural differences in your messages
- Avoid gendered terms – It's not suitable anymore to use terms such as Mr, Mrs, and Ms, so avoid them
- Use standards fonts – Don't use a crazy or confusing font; stick to professional fonts for all messages
- Always proof every message – Check your messages before sending them (and check again to be sure!)
- Limit attachment sizes – Email inboxes can become cluttered, and large email attachments won't help, so don't send large files
Following email etiquette can be a challenge for us all, which is why we've created a detailed guide to some of the unwritten rules that govern English-language emails .
Grammar rules for email writing
The English language is governed by grammar rules that can be confusing for everyone at times. While you don't need to have a fluent grasp of the English language to write effective emails, understanding the basics is essential.
Here are 10 things you need to write better English-language emails:
- Always use capital letters for names
- Follow the email format outlined above
- Start sentences with a capital letter, break up sentences with commas, and end every sentence with a full stop
- Keep sentences short
- Every sentence should have a subject (John), verb (reads) object (books)
- Use the active voice to engage the reader. Tools such as Flowrite can help you engage users directly and clearly
- Don't use emoticons
- Break up lists into bullet points to make information easy for readers to understand
- Explain acronyms when you use them
- Never use swear words
English email examples
We've provided a comprehensive guide on how to structure and write effective emails in English. Now, let's put some of these rules into practice and illustrate them with some examples of how to write a formal email in English, a professional email in English, and an informal email in English.
How to write a formal email in English
We've covered the fundamentals of writing a formal emai l in English above; here's how it works. In this English language email example, we're requesting products from individuals and businesses we already know.
How to write a professional email in English
In business, time is money, so the perfect professional email in English is short, clear, and straight to the point. So here's an example of how to write a professional email in English.
How to write an informal email in English
When writing an informal email, you're not as constrained by the rules and can be freer with how you communicate and correspond. So here's an example of a warm and friendly email to someone you know.
Improving your email writing skills in English
The best way to learn how to write English language emails is to read (and write) as many emails as possible. Check out samples online, sign-up to mailing lists, or read back through your inbox to identify English email examples you like.
To improve your email writing skills in English, one great approach is to keep a list of phrases you like and want to use. Over time, you'll find this helps you understand the building blocks of perfect English emails and improves your vocabulary as well as grammar skills.
You can also build a bank of email templates that you can use to save time when writing emails in English language. This resource can help you identify successful (and unsuccessful) emails, helping you develop your own style of writing formal email English.
Lastly, we must tooth our own horn. Flowrite's blog features dozens and dozens of articles on how to write formal and professional emails in English. They cover all the aspects of daily communication needed in various jobs and can help you become more productive at work and your personal life.
However, that's not all. Our AI writing assistant can help you to communicate with confidence by turning short instruction into ready-to-send emails in perfect English. If you don't believe us, check out the example of Flowrite in action below. As you can see it can be as easy as click of a button.
We hope that this blog post has helped you to learn how to write emails in English. If you found it helpful, we suggest that you bookmark this page to refresh your memory in case you ever have doubts about grammar, etiquette, phrases or format of email English. To relief yourself from any doubts make sure to try Flowrite and start to supercharge your daily communications.
Supercharge your communication with Flowrite
Write emails and messages faster across Google Chrome.
Explore Flowrite
.png)
Start using Flowrite today
Try it yourself
General template
Reply to: "
Received message
introduce flowrite short instruction to ready to send emails we finish email
Generate a reply
Generate an outreach

Business inquiry
about to update our office supplies could you send 2022 catalog to me? currently speaking to a range of suppliers looking to make an order in the next two weeks
Share this article
Related articles

How to write a professional email – 5 easy steps & 5 best practices
Learning how to write a professional email is an investment in your career and these simple steps, best practices, and examples will help you get started.

Best AI email assistants to increase your productivity
Learn about the AI email assistants that can help you cope with email overload that hurts your productivity.

Write any email quickly with these 3 easy steps
Want to learn how to write emails faster? This blog post will teach you an easy process and give you actionable tips on how to write emails quickly starting today.

We use cookies to analyze site performance and deliver a better experience for visitors.
%20(1).png)
Product updates
Read the latest →
%20(1).png)
About Flowrite
Get to know us →
Productivity

© 2023 Flowrite
- Facebook Profile
Learning English with Oxford
The latest language learning tips, resources, and content from oxford university press., how to write the perfect email in english.
- by Oxford University Press ELT
- Posted on March 18, 2021 March 22, 2021

It’s also common in many English tests to have to write an email. That includes computer-based exams such as the Oxford Test of English , where you have to write an 80-130 word email in 20 minutes, for the Part 1 Writing task.
In this guide, we’ll teach you how to write informal and formal emails to use in your day-to-day life or in your Oxford Test of English exam.
Use the right register
First things first, you need to think about who you’re writing to. Maybe it’s a friend, someone you don’t know that well, or a complete stranger. Establishing your audience will help you decide if you need to use a formal, neutral or informal register.
As a general rule, only write an informal email when you know the reader well, such as a friend or classmate. Formal emails are much more appropriate in a business setting. You might send a formal email to a public official, customer services or a company you’re working with. If you’re unsure, it’s always better to write a formal or neutral email.
Think about why you’re writing
Thinking about the purpose of your email can also help decide on the correct level of formality. If you’re planning a day out with friends, keep it friendly and lighthearted. If you’re requesting information from a company you want to sound professional and polite. Keep in mind your reasons for writing and make sure that’s reflected in the tone.
Keep it organised
English works well with short, simple sentences. It’s also a good idea to break your email into paragraphs. And if it’s really complex, don’t be afraid to use bullet points. Although there is some variation between an informal and formal email, one thing is clear – a good one always follows the same six-step structure:
1. Subject line
People are busy, and your email is one of many in their inbox. That means you want to keep the subject line meaningful and concise so they don’t hit the delete button before they’ve even opened it. Think about one clear sentence that conveys the main idea of your email.
Some good examples include:
2. Greeting
Greetings are important in any email. Some people believe the word ‘Dear’ should only be used in a handwritten letter. However, it is perfectly acceptable to use in an email as well. Especially if your email is very formal, like for a job application or an email of complaint.
We normally use a comma after the opening phrase, and then begin a new line after the person we’re writing to. Take a look at these different ways to begin your email:
3. Opening
Often after the greeting we write an opening line. This is normally a polite gesture to establish a good relationship with the reader. It could be to wish someone well, introduce who you are, or state why you’re writing. Here are some examples:
4. Main body
When writing an email, it is important to get the level of detail correct. If it’s a quick internal email to a colleague it can be quite brief. However, if you’re writing for an exam, like the Oxford Test of English , you want to show what you can do. We recommend following the acronym RED ( R easons, E xamples, D etails) to help bulk out your answers.
The main body of your email should also have a clear and specific purpose. This could be anything from suggesting a birthday present for a friend or giving feedback on an event you attended. Here’s some useful language you could use:
For more informal and formal language to use in the exam, take a look at our Oxford Test of English Writing Tips .
5. Closing
Before signing off at the end of your email, it’s a good idea to finish with a closing statement. In a formal email this might be requesting some form of action. In an informal email it might be just to send some good wishes. Either way it’s best to end on a high note!
6. Signing-off
Saying goodbye is the last thing you do at the end of an email, so you want to get it right. It should reflect your professionalism, and mimic how close you are to the recipient. Again, you must use a comma after the closing phrase and capitalise the first letter. These are some of the most common ways to end an email.
Once you’ve written your email, it’s time to check it and make sure it really is perfect. Give it a quick review, and look for any typos, spelling or grammatical errors. This is especially important if English is not your first language.
Last but not least: Practise
Any kind of writing skill comes with trying and trying again. At Learning English with Oxford we have lots of resources to help you prepare for the Oxford Test of English.
- Find lots of useful tips for passing the exam
- See the test specification s for more information on the email question.
- You can also download a sample test
- And try our online demo to put what you’ve learned into practice!
The Oxford Test of English is an online test, certified by the University of Oxford, and recognised all over the world. Find out more about it on our website .
Share this:
Author: Oxford University Press ELT
Every year we help millions of people around the world to learn English. As a department of the University of Oxford, we further the University’s objective of excellence in education by publishing proven and tested language learning books, eBooks, learning materials, and educational technologies. View all posts by Oxford University Press ELT
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from learning english with oxford.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
elttguide.com
- Premium Content
- Publications
- Lesson Plans

Quick Tips to Write a Great Email & Essay in English

Writing a great essay and a perfect email can be a challenge, especially in a foreign language. You have to think about many things such as the tone, formality, and organization. Not to mention check over all those little errors you may have made.
In this article, you will learn some tips to write a great essay and email to use in your day-to-day life or in any of your English exams.
Writing a Great Email
Adapted from https://learningenglishwithoxford.com/2021/03/18/write-perfect-email-english/
1. Think about who you’re writing to
Maybe it’s a friend, someone you don’t know well, or a complete stranger.
Knowing your target audience will help you decide if you need to use a formal, neutral, or informal register.
As a general rule, only write an informal email when you know the reader well, such as a friend or classmate.
Formal emails are much more appropriate in a business setting. You might send a formal email to a public official, customer service, or a company you’re working with.
If you’re unsure, it’s always better to write a formal or neutral email.
2. Think about why you’re writing
Thinking about the purpose of your email can also help decide on the correct level of formality. If you’re planning a day out with friends, keep it friendly and lighthearted.
If you’re requesting information from a company, you should sound professional and polite.
Keep in mind that the reasons for writing should be reflected in the tone.
3. Keep it organized
English works well with short, simple sentences. It’s also a good idea to break your email into paragraphs. And if it’s really complex, don’t be afraid to use bullet points.
The six-step structure of a great email
A good email always follows the following six-step structure:
1. Subject line
Keep it meaningful and concise so people don’t hit the delete button before they’ve even opened it. Think about one clear sentence that conveys the main idea of your email.
Some good examples include:
- Introducing our new school magazine.
- End-of-year assessment!
- Meeting arranged for Tuesday.
- Proposal for TESOL Conference.
2. Greeting
Greetings are important in any email. Some people believe the word ‘Dear’ should only be used in a handwritten letter. However, it is perfectly acceptable to use it in an email as well. Especially if your email is very formal, like for a job application or an email of complaint. When you write to a friend you can use “Hi” or “Hello”
We normally use a comma after the opening phrase, and then begin a new line after the person we’re writing to. Take a look at these different ways to begin your email:
Often after the greeting we write an opening line. This is normally a polite gesture to establish a good relationship with the reader. It could be to wish someone well, introduce who you are, or state why you’re writing.
Here are some examples:
4. Main body
If your email is a quick internal email to a colleague it should be quite brief.
However, if you’re writing for an exam, the acronym RED is recommended; ( R easons, E xamples, D etails) to help bulk out your answers.
The main body of your email should also have a clear and specific purpose. This could be anything from suggesting a birthday present for a friend or giving feedback on an event you attended.
Here’s some useful language you could use:
Before signing off at the end of your email, it’s a good idea to finish with a closing statement. In a formal email, this might be requesting some form of action. In an informal email, it might be just to send some good wishes.
6. Signing-off
Saying goodbye is the last thing you do at the end of an email, so you want to get it right. It should reflect your professionalism, and mimic how close you are to the recipient.
Again, you must use a comma after the closing phrase and capitalize the first letter.
These are some of the most common ways to end an email.
4. Proofread
Once you’ve written your email, it’s time to check it and make sure it really is perfect. Give it a quick review, and look for any typos, spelling, or grammatical errors.
This is especially important if English is not your first language.
Last but not least: Practise. Any kind of writing skill comes with trying and trying again.
Writing a Great Essay
- Leave a space in the first line only and at the beginning of each paragraph.
- Write short sentences to avoid mistakes.
- Write correct sentences in terms of sentence order and tense.
- Write the subject in the present simple tense if it is a general topic and the simple past tense if it is a story or a journey.
- Use interrogative words (Wh) to help in deducing ideas and writing quick sentences.
- Write ideas on the side, and when an idea comes to you, write it down immediately.
- Use punctuation marks well; capital letters, the stop sign, commas, question marks, and exclamation marks.
- Start the topic with a main sentence indicating that you will write on a specific topic.
- The opening has a positive effect on the reader, so try not to make mistakes.
- If you are not sure about writing a certain word, search for another because spelling errors have a bad effect.
- Be careful not to use incorrect tenses because they have the same bad impression.
- Use the active voice and avoid the unknown for ease of the sentence.
You can use the following links and phrases to give more ideas:
- We all agree that ……..
- First of all, I believe that ………
- On the other hand, ………
- On the contrary, …….
- Moreover, ……..
- Above all ………….. / Important still, ………..
- In summary, ……
- We should do our best to realize ……
- We look forward to a better future.
- We are indebted much to modern inventions.
- …………plays an important role in our life.
- Finally, we have to admit that ………
- To sum up, one can say that ……
- For the prosperity of our country, we must…….
- We must stand hand in hand against…….
- The government has taken practical steps …..
- Illiteracy leads to unemployment and crime …
- To sum up, (To summarize,) (In brief,) (In short,) ……….
- Last but not least, ………..
- Finally, we can say that ……..
- From what I have mentioned in the above lines, it’s obvious that …………
Simple Guide To Writing A Basic Essay – Part 1
Simple Guide To Writing A Basic Essay – Part 2
The Most Important Book for EFL Teachers is Now Available!
Want to develop the essential skills in tefl.
Claim your copy from this book: TEFL Essential Skills
It is a valuable book giving you everything you need to develop professionally in TEFL.
When completing it, you will master the skills that are essential for every EFL teacher.
Get it from here, and you won’t regret it!
If you like it, share it on:
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Subscribe to My Newsletter
Affiliate disclosure.
This website might have affiliate links, and if you buy something by clicking on them, the website owner could earn some money. To learn more, read the full disclosure.

Study TEFL/TESOL Online

Get 15% Discount

Visit My Video Channel

Articles Categories
- Back To School
- Brain-based ELT
- Classroom Management
- CLT Communicative Language Teaching
- Correcting Mistakes
- Develop Students' Speaking Skills
- Developing Critical Thinking
- Developing Life Skills
- ELT Snippets
- ELTT Questions & Answers
- For IELTS Exam
- Guest Posts
- Job Interview Preparation
- Lanaguage Teaching Approaches
- Learning How to Learn
- Lesson Planning
- Low Achiever Students
- Online Courses
- Printables Library
- Professional Development
- Talk on Supervision
- Teach Conversations
- Teach Grammar
- Teach Language Functions
- Teach Listening Activities
- Teach Pronunciation
- Teach Reading
- Teach Vocabulary
- Teach Writing
- Teacher Wellness
- Teaching Aids
- TEFL Essential Skills
- TEFL to Young Learners
- Testing and Assessment
- The ELT Insider
- Uncategorized
- Using Technology in EFL Classes

Choose a region
How to Write Formal Emails in English
19 Aug 2019
This article will help you to communicate better and to write formal emails in English.
Emails are among the most commonly used means of communication in the world. They’re fast, immediate, and allow you to interact with all kinds of businesses within and beyond the national boundaries. At work above all, writing formal emails in English in the right way requires certain skills, and being a professional situation, it’s essential not to commit mistakes in order to make a good impression of yourself and your company.
In this article you’ll find:
The rules for writing formal emails in English
- The right format to use
Examples of formal emails in English
To write an email in English in the right way, don’t improvise! Read the following advice to avoid making serious mistakes that could compromise the success of the email from the moment it is received.
The subject is the first piece of information that the recipients of an email see, and if it’s written incorrectly or unclearly, it could push the reader to delete it without even opening it! So it’s important to give a clear and precise message, right from the start, indicating the content or reason for writing in two or three words that grabs the attention of the recipient.
Unlike many other languages which require long complex sentences in a formal written context, English is very concise and favors short sentences and a simple structure. Make sure you break up the text into two or three paragraphs – this enables the reader to quickly see the key points.
Courtesy formulas
When you write an email in English, you’re not only using another language but you’re also entering another culture with different habits. The Anglo-Saxons in general pay a lot of attention to forms of courtesy and gratitude, therefore never forget to add them.
Check the email
Never send an email in English without having re-read what you wrote. Grammatical or typing mistakes are very common even in your own language, so in English you can make errors much more easily. Double-checking what you’ve written is a simple step to take that can prevent you from appearing unprofessional and above all careless.
Be sure to have set your emails to end with all the important information about you, including:
- name and surname
- relative details about your company (name, address..)
- link to the company website
The format of a formal email in English
Introduction
Body of the text
Depending on the type of relationship you have with the person you’re writing to, there are different ways of starting an email, but any email should always start with a greeting. In our specific case being formal, the most appropriate options are:
- Dear Mr/Mrs/Ms (surname of the recipient, e.g. Mr Black)
- Dear Sir/Madam (if you don’t know the name of the recipient) or more generally ‘To whom it may concern’
After the initial greeting you need an introductory sentence that indicates clearly the reason for writing and is consistent with the subject of the email. Introduce yourself briefly (long texts often discourage people from reading them), then follow on with:
- I am writing with regard to… (email subject)
- I am writing in connection with… (email subject)
- I am writing in reference to…
If you’re writing an email to send information, you can start with one of the following sentences:
- I am writing to let you know…
- I am delighted to tell you… (if you’re communicating good news)
- I regret to inform you that… (if you’re communicating bad news)
If instead you’re replying to an email you received, you can say:
- I am writing in response to…
- I am writing in reply to…
- I am writing to thank you for… (if you need to thank the recipient)
There are no conventional formulas for writing the body of the text because this varies according to the function of what you need to communicate. It’s useful to prepare an initial draft and then proceed with any corrections.
The general rules are that the text should be divided into short paragraphs that avoid abbreviations and acronyms, both of which you can use, on the contrary, when you write an informal email to family and friends.
Based on the type of message you’re sending, there are various ways to write a final invitation before ending the email, such as:
- I look forward to hearing from you soon
- Thank you in advance
- For further information, please do not hesitate to contact me
- Please let me know if you have any questions
- Thanks for your attention
The most common way to end an email are:
- Best regards
- Kind regards
- Yours faithfully (if you began the email with ‘Dear Sir/Madam’ because you don’t know the name of the recipient)
- Yours sincerely (if you began the email with ‘Dear Mr/Mrs/Ms + surname)
Let’s see how all of this works in practice.
Example 1: Delay with the delivery of an order
Subject: Delivery delay
Dear Mr Pascal,
We regret to inform you that we will not be able to respect the deadline previously agreed for the delivery of your order. Our supplier has warned us today that they are experiencing supply problems, which will result in a delay in our production chain. We count on your understanding and thank you for your patience.
Please accept our apologies.
Best regards,
Example 2: Replying to a job advertisement
Subject: Web Content Editor position
Dear Sir/Madam,
With reference to your job ad in xxx, I would like to submit my application for the position of Web Content Editor in your company.
I graduated in Communication Sciences at the University of xxx and worked for several years in a Digital Agency as Content Specialist. I believe my skills and experience are in line with the requirements for the job position. I will be glad to introduce myself in an interview, that will allow you to better evaluate my possible recruitment.
Please find attached a copy of my resume. I look forward to hearing from you.
Yours faithfully,
Example 3: Sending a product catalogue
Subject: New product catalogue
Dear Ms.Chapman,
Following your request, we have recently sent you our new catalogue. We are convinced that it will enable you to see the quality of our products. Our local agent will contact you soon to arrange a meeting on a day and time that suits you in order to discuss in detail how our products can be of benefit to your company’s needs.
For further information, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Yours sincerely,
If you want to improve your English and get better at writing emails, find an English course that suits your needs.
This post has been adapted from the WSE Italy blog: Come Scrivere Email In Inglese Esempi
Learning and improving your knowledge of business vocabulary is a must. Read on to find out more.
Do you want to improve your writing skills? Read on to find out our tips on how to become a better writer in English!
Get in touch
Ready to chat to a member of the Wall Street English team? We’re here to help you.
Log In 0 The website uses cookies for functionality and the collection of anonymised analytics data. We do not set cookies for marketing or advertising purposes. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies and our privacy policy . We're sorry, but you cannot use our site without agreeing to our cookie usage and privacy policy . You can change your mind and continue to use our site by clicking the button below. This confirms that you accept our cookie usage and privacy policy.
Free English Lessons
How to write emails in english – video.
Download PDF

In this lesson, you can learn how to write an email in English.
Do you need to write emails at work are you worried that your emails aren’t clear, or that you make mistakes in english in this lesson, you can see a how to write clear, natural-sounding emails easily and quickly., we’ll show you how to write emails in english from beginning to end, in simple, clear steps that you can follow right now, let’s start at the beginning., quiz: how to write emails in english.
Test how well you remember the ideas from this lesson by trying this short quiz.
There are 20 questions. When you have finished, press ‘Finish Quiz’ to see your score. You can then have another go (press ‘Restart Quiz’) or click ‘View Questions’ to see what you got right.
When you’re happy with your score, put it on the leaderboard!
Quiz Summary
0 of 20 Questions completed
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 20 Questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 ) 0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
- Not categorized 0%
Well done! You’ve finished!
That’s an excellent score! Congratulations!
A perfect score! Congratulations!
1 . Question
Which word is not used in an email greeting?
2 . Question
Write the missing word from this formal email greeting.
“Dear Sir/ “
3 . Question
If you’re writing a professional email to someone you know well, who is not senior to you, you can start by writing just their name and then a comma.
4 . Question
Write one contraction in the gap, to complete this common opening line from an email.
I hope well.
The contraction is a pronoun + a verb; write five letters and an apostrophe.
5 . Question
In what situation is it not necessary to write a greeting?
- When you write an email and send it to everyone who works at your company.
- When you do not know the name of the person you’re writing to.
- When you are having an email ‘conversation’, involving a lot of short messages, and you are sending another one.
6 . Question
“I’m writing _________ the company’s public liability insurance, which is due for renewal soon.”
Which word can go in the gap?
7 . Question
“I need to bring something to your ________.”
- information
8 . Question
“As a matter of urgently , you need to contact the supplier and change the order.”
The highlighted word is incorrect. Write is correctly in the gap below.
“As a matter of , you need to contact the supplier and change the order.”
9 . Question
“Could you _________ give me a call as soon as you get this?”
Which words can go in the gap? Choose two options.
10 . Question
“Let’s arrange a quick video call to discuss this, shall we?”
Who is the reader of this email?
- a colleague you have worked with for a while
- a customer you have never met
- a senior manager from your company’s head office
11 . Question
Write one word in the gap.
“This doesn’t require any immediate response, but please keep an on the situation.”
12 . Question
Which version of this request is the most indirect – i.e. the best ‘call to action’ to put in an email to your line manager?
- Can I ask you to keep me informed of what is decided?
- Tell me when you’ve made your decision!
- Please don’t forget to let me know what you decide.
‘Indirect’ or polite language includes passive verbs, modal verbs and avoiding ‘you’ as the subject.

13 . Question
“There’s one more thing I’d like to discuss.”
In which section of an email would you write this?
- a central paragraph about details
- a call to action
14 . Question
“Best Regards,”
In what type of email can you say this as a sign-off?
- a very formal email to a senior colleague
- a fairly formal email to a customer you’ve never met
- an informal email to someone who works in your office
- any of the above
This might sound too formal in a message to a good friend that you speak to all the time, but apart from that, it’s fine in most situations.
15 . Question
“I wanted to touch base with you about the Smith-Thomas case, because a slight issue with it has come to my attention.”
What section of an email is this?
- an explanation of why you’re writing
- a paragraph explaining details
16 . Question
“This is just to keep you updated.”
What is the purpose of this sentence?
- It’s the title of an email.
- It’s a greeting.
- It’s used instead of a call-to-action, when no action is required.
- It’s a sign-off.
It’s quite unusual to have a full sentence as the title of an email.
17 . Question
For the next three questions, put the parts of the emails in the right order, following the framework from the lesson – you can see this framework if you press ‘Hint’.
- About the refurb we were discussing with Abigail yesterday.
- Cheers, Davina
- All three builders looked fine, but I forgot to note down the prices.
- Can you remind me what each one quoted, please?
View Answers:
‘Refurb’ is an informal abbreviation for ‘refurbishment’, meaning when you redecorate a building, often when transforming it for a new use. The email order should be as follows: One: use an appropriate greeting. Two: introduce your topic in a single sentence. Three: add details to your topic in a short paragraph. Four: add a call-to-action to explain what you need the other person to do. Five: use an appropriate sign-off.
18 . Question
Put the sections in order.
- Kind Regards, Eamonn Accountant
- I see that some of your entries for travel expenses do not match the amounts shown on your receipts for the same. In some cases the difference is small enough to be overlooked, but there are one or two to the tune of hundreds of pounds. This may raise a query at the Revenue.
- I wanted to bring to your attention a discrepancy that I discovered when reviewing your accounts.
- Dear Mr Jefferson, I trust you’re well.
- Would you review the information highlighted in the attached file and advise me why it does not appear to correlate?
‘discrepancy’ = when two figures (or facts) do not show the same thing, but should ‘the revenue’ = an abbreviation for Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs – the UK tax office ‘correlate’ = match The email order should be as follows: One: use an appropriate greeting. Two: introduce your topic in a single sentence. Three: add details to your topic in a short paragraph. Four: add a call-to-action to explain what you need the other person to do. Five: use an appropriate sign-off.
19 . Question
- I realise you are busy with a different client this week, but I hope you’ll be able to get to the bottom of this as soon as possible.
- Many thanks, Philippa
- Several customers have flagged up that they have booked a membership package and now have full access to the site, in spite of the fact that when they tried to make the payment, it was declined. I suspect there may be other users who have had this ‘problem’ but didn’t bother to tell us – it’s not a problem for them, but it could be for us!
- I wondered if you would have time this afternoon to take a look at the settings in our booking system.
- Hello Sanjay,
‘flag up’ = tell somebody some information, particularly about something problematic ‘get to the bottom of’ something = identify what is causing a problem The email order should be as follows: One: use an appropriate greeting. Two: introduce your topic in a single sentence. Three: add details to your topic in a short paragraph. Four: add a call-to-action to explain what you need the other person to do. Five: use an appropriate sign-off.
20 . Question
Finally, look at the emails from the last three questions, then sort the letters into the correct categories below.
Sort elements
A freelance contractor is self-employed and works for many different people.
1. How to Write Email Greetings

With emails, you can start like a letter. For example:
- Dear Sir/Madam,
- Dear Mr Hill,
However, emails are generally much less formal than letters. Use a greeting with dear only if you’re writing something formal.
So, what else can you use?
Many emails in English start with hello , or hi plus the person’s name. For example,
In many business emails, you’ll follow the greeting with something like:
- I hope you’re well.
- How are you?
In business emails, these are simply polite phrases, and they don’t generally need an answer.
For more informal emails, you can start with just the word hi or hey , plus a comma:
You can also just write the person’s name plus a comma. This is a more professional style, even though it’s more informal. It’s best with people you already know.
For a very informal email, you might not use a greeting at all. This is also true if you’re sending several emails to the same person in a short time: you don’t need to write a greeting every time.
Let’s review quickly:
For very formal emails, use a greeting with dear plus a name, like a letter.
For most everyday emails, use either hello or hi plus a name.
For less formal emails, use hi or hey without a name, or don’t use a greeting at all.
Okay, but what next?
2. Explaining Why You’re Writing
After your greeting, you should explain why you’re writing. Make this as short as possible.
If you’re writing to someone who receives hundreds of emails every day, you need to make your purpose clear quickly. Someone who’s very busy won’t spend a lot of time trying to work out what you’re trying to say!
How can you do this?
Start with a simple phrase, like:
- I’m writing regarding…
- I wanted to follow up on…
- I would like to ask about…
These phrases are slightly more formal. Let’s see how you could use them:
- I’m writing regarding the issues we’ve been having with our database system.
- I wanted to follow up on our meeting last week and confirm our plans for this month.
- I would like to ask about the new budget and whether this will affect our department.
In a more informal email, you wouldn’t use a phrase like this. You might ask a more direct question or make a direct statement, like this:
- Do you know when the database issues will be fixed?
- Let’s confirm our plans for this month.
- How will the new budget affect our department?
If you’re writing because you want to find a solution to a problem, here are some useful phrases:
- I’m concerned about…
- I need to bring something to your attention: …
Again, these are more formal phrases.
Let’s see how you can use them:
- I’m concerned about the number of sick days staff have been taking recently.
- I need to bring something to your attention: using outdated software puts us at risk of malware infections and data loss.
Now it’s your turn. Imagine that you’re writing an email to your manager, colleague, or client. You need to write an appropriate greeting, then write one or two sentences to explain why you’re writing.
Pause the video and do it now! Start again when you’ve finished.
Ready? Let’s move on.
3. Adding Details to Your Email
After you introduce why you’re writing, you need to add details and supporting information, so that your reader understands the situation you’re describing.
Put this information in a new paragraph. This will make your email clear and easy to follow.
First, ask yourself what the person you’re writing to needs to know.
With emails in English, less is more. No one wants to read a very long email, and it’s hard to make yourself clear if you write too much.
So, try to limit yourself to two to three sentences. Put your most important point first.
Let’s look at some examples:
- I’m writing regarding the issues we’ve been having with our database
- Both clients and staff have been experiencing severe problems for several days now. We are unable to update records or access information on customer interactions. This is costing us large amounts of money, both in time spent trying to fix the problem, and in lost sales.
Here’s one more:
- Staff in the IT department have taken a total of 44 sick days so far this month, compared to a total of 23 for last month, and just 18 for the previous month. This is affecting productivity, and also placing a lot of stress on the employees who do come to work.
In both cases, you’re writing to describe a problem. Your first sentence introduces the problem, and then your next paragraph gives more details.
You can see that in both examples, we use just two sentences, but you can include a lot of useful information in two sentences.
If you have more than one point to make in your email, you can repeat this pattern: first put a short sentence to introduce your point, then add a paragraph with two to three sentences to add details.
You can move from one point to another using a phrase like:
- There’s one more thing I’d like to discuss with you.
- I’d also like to ask you about…
Use one of these phrases to change the topic, and then introduce your next point.
For example:
- There’s one more thing I’d like to discuss with you. It seems like the number of customer complaints has been increasing for three months…
Now, you can practice. Take the email you started before. Add a new paragraph, which should be two to three sentences long. Add details to the point you introduced before.
Pause the video and do it now. If you want extra practice, add another topic to your email, using one of the linking phrases you just saw.
After you explain all the points you want to make, what should you do next?
4. Adding a Call to Action to Your Email
When learning how to write emails in English, it’s important to make it clear what you expect from the person you’re sending it to.
Even if you’re writing just to give the other person some information, it’s a good idea to make that clear.
Put your call to action in a new paragraph. Again, putting each thing in its own paragraph makes your email structured and easy to follow.
So, what can you write here?
First, let’s consider situations where you need the other person to do something urgently. You could say:
- Please … by tomorrow at the latest.
- As a matter of urgency, you need to…
- Please arrange a meeting of all department heads by tomorrow at the latest.
- As a matter of urgency, you need to contact all the clients who may have been affected by this data breach.
If your request is less urgent, you could use phrases such as:
- Could you please…?
- I would like you to…
- Could you please talk to Matt in the HR department and clarify our options on this?
- I would like you to design a poster to inform staff about the new policies.
With calls to action, you should think about your relationship with the person you’re writing to.
For example, saying something like, you need to… or I would like you to… is relatively direct. That’s fine if you’re a manager writing to one of your team, but it might sound inappropriate if you write that to your manager.
This also depends on the corporate culture where you work. Generally, if you aren’t sure, it’s better to be less direct.
- I suggest that you contact all clients who may have been affected by the data breach.
- Can I ask you to design a poster to inform staff about the new policies?
But, be careful! Don’t be so indirect that the other person doesn’t understand what you need.
If you don’t need a response from the other person, say something like:
- This is just to keep you updated.
- This doesn’t require any immediate response, but please keep an eye on the situation.
Now, it’s your turn! Pause the video and add a call to action to the end of your email. Think about who you’re writing to, and make your call-to-action appropriately direct or indirect.
So, now you’re nearly finished. What’s left?
5. Adding a Sign-off to Your Email
Finish your email with a sign-off and your name.
You can use a lot of the same sign-offs you can use in a paper letter, such as:
- Best Wishes,
- Kind Regards,
Like with greetings, you wouldn’t generally use very formal sign-offs like Yours Sincerely in an email. You might see it sometimes, but only in very formal emails.
Don’t forget to write each word of your sign-off with a capital letter, and put a comma at the end.
The sign-offs you’ve just seen are neutral and can be used in almost any situation.
If you’re writing something more informal, you might use a sign-off like:
In this case, you wouldn’t capitalise each word, which is why care in take care has a small ‘c’.
Like with greetings, you might not need a sign-off at all in an informal email. Just write your name at the bottom, or don’t write anything at all!
After you put your sign-off, add your name, and you’ve finished! For example,
- Regards, Vijay
- Cheers, Katya
Now you know how to write a clear, effective email in English.
Let’s put everything you’ve learned together.
6. How to Write an Email in English
To write an effective email in English, you need to:
- Use an appropriate greeting.
- Introduce your topic in a single sentence.
- Add details to your topic in a short paragraph.
- Add a call-to-action to explain what you need the other person to do.
- Use an appropriate signoff.
Let’s do a longer example together:
- I need to bring something to your attention: many staff are using very weak passwords on their laptops and for database access.
- Our work depends on keeping our clients’ personal financial information safe. If we lose our clients’ trust on this issue, it will not be easy to recover. I trust that you can see that it is better to take action now, rather than after something goes wrong.
- I suggest we make a rule that passwords must be a specific length, and that staff must change their passwords at least once a month. Please let me know what you think about this.
- Regards,Vijay
What do you think: could you write an email like this?
Try it! Use words and phrases from the lesson. Remember to organise your email into paragraphs, like we showed you. This will make it easier to keep your ideas structured and clear.
Thanks for watching this business English lesson from Oxford Online English!
We Offer Video Licensing and Production
Use our videos in your own materials or corporate training, videos edited to your specifications, scripts written to reflect your training needs, bulk pricing available.
Interested?
More English Lessons
Business english lessons.

English Writing Lessons

- Facebook 136
- Odnoklassniki icon Odnoklassniki 0
- VKontakte 25
- Pinterest 0
- LinkedIn 44
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Online Communications
- Writing Emails
How to Write an Email
Last Updated: October 5, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Tami Claytor and by wikiHow staff writer, Rain Kengly . Tami Claytor is an Etiquette Coach, Image Consultant, and the Owner of Always Appropriate Image and Etiquette Consulting in New York, New York. With over 20 years of experience, Tami specializes in teaching etiquette classes to individuals, students, companies, and community organizations. Tami has spent decades studying cultures through her extensive travels across five continents and has created cultural diversity workshops to promote social justice and cross-cultural awareness. She holds a BA in Economics with a concentration in International Relations from Clark University. Tami studied at the Ophelia DeVore School of Charm and the Fashion Institute of Technology, where she earned her Image Consultant Certification. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 514,296 times.
Do you want to know how to write an email? It can be intimidating if you don't know where to start. When sending emails, there is a general format you should keep in mind. Be sure to know your recipient and the differences between informal and formal email messages. This wikiHow guide will teach you how to write friendly, formal, and professional emails for every occasion.
Things You Should Know
- You must choose between a formal or informal tone when writing an email.
- Using the wrong tone in an email can cause issues with the recipient.
- When writing emails, you'll need an email account from a trusted service.
Email Essentials

- If you are uncertain about how to create a new message, check the help pages for your email service to learn more about it in greater detail.

- A space is often enough to separate multiple email addresses, but some services do request that you separate multiple addresses with a comma or some other form of punctuation. If this is the case, these instructions should be specified by your specific email provider.
- Type the email address of the main receiver or receivers in the “To:” field. The main receiver usually refers to anyone whom the email is directly meant for or addressed to in the body of the email.
- Type other email addresses in the “CC:” field. This is the “copy” field. A receiver should be listed in the “CC:” field if the email does not directly mention them but does refer to something that individual should be aware of.
- Use the “BCC:” field to hide email addresses. If you do not want the receivers of an email to see a list of email addresses the message went to, you should type those email addresses in the “blind copy” field.

- For example, a casual email to a friend could simply say “What's Up?” If you are emailing with a question about an assignment, though, the subject line might read something like “Math homework.”
- Similarly, a question to a supervisor or professor could be labeled with a subject line like “Question” or “Question about...” followed by a brief label describing the topic in question.
- Note that a message without a subject will appear in a recipient's inbox with the label of “(no subject).”

- The nature of email is fast, so you should generally keep the length of your message fairly short.

Writing a Friendly Email

- The only time you would not send a friendly email to a family or friend would be if you are sending a group email of an official nature, like a plea for donations or sale advertisement. Since these emails will likely be sent to people who you are not on casual terms with, as well, you must gear the email toward them.

- If you are just writing an email to catch up with a friend, you could include a humorous subject line or one as simple as "Long time no see!"
- If you are writing with a purpose, mention what that purpose is. For example, if you decide to write an email about a group outing, label the email with a subject that specifically mentions that outing.

- "Morning Bob!"

- Read your email and ask yourself if the content of the email sounds like the way you speak in person. If so, then you've achieved a good tone for a friendly email.
- Use contractions. Contractions are not a part of formal writing, but they are a common part of everyday conversation, making them appropriate for a friendly email.
- Feel free to use slang. If desired, you can include Internet slang: "thx" instead of "thanks," "4" instead of "for," "l8r" instead of "later," etc.
- Also use emoticons when appropriate. :)

- "Later! Jen"
- "This email will self-destruct in 3...2...1..."
Writing a Formal Email

- The tone of your message can be a little more conversational but you should stay away from Internet slang.
- You should still include your signature, but you may not need to provide all of your contact information below your name.

- "Essay question" (when writing an email to a professor asking for details about an essay assignment)
- "Application for Management Job Ad" (when sending an email in response to a job ad)
- "Problem with Part #00000" (when typing an email to request customer service or to report a technical problem)

- "Dear Mr. Smith:"
- "Dear Ms. Jones:"
- "Dear Dr. Evans:"

- Avoid the use of contractions.
- Do not use Internet slang or emoticons.

- Yours faithfully
- Best regards
- Best wishes

- Your title, if you have one, should include your position and the name of the company or institution you are a part of.
- Include your telephone number, fax number, and email address, at minimum. You may also wish to include your mailing address and website URL.
Specific Types of Friendly Emails

- While it's a pretty risky move, you can also use email to tell a guy you like him.

- Similarly, write a flirty email to someone on an dating website. For an email like this, though, you need to be both flirty and informative so that the recipient gets a good idea of who you are.

Specific Types of Formal Emails

- Similarly, you can also write an email applying for an internship . Describe what sort of internship you are looking for and how it will help you meet your career goals. Also provide reasons why you should be selected for the internship.
- Send a follow-up email if you have not yet received a reply about the position you applied for.

- If your professor knows you well enough, you can also email your professor when asking for a letter of recommendation .

Sample Professional Emails

Community Q&A

- Never provide usernames, passwords, or personal information like credit card numbers and social security numbers via email. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/gmail/sending-email/1/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-start-an-email/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-end-an-email/
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/format-for-formal-email
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/finding-a-job/sending-applications
- ↑ https://www.purdue.edu/advisors/students/professor.php
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/email-hr
About This Article

To write a formal email, start with a formal salutation followed by the recipient's last name and appropriate title, like "Dear Mr. Smith." Then, when you're finished writing the body of your email, conclude with a formal closing, like "Sincerely," "Best regards," or "Thank you." Next, include your full name below the closing of your email, followed by your title and the name of your company, if you have one. Finally, underneath your name, add your phone number and email address. To learn how to write a friendly, casual email, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Is this article up to date?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
An informal email to a friend

Learn how to write an informal email to a friend.
Do the preparation task first. Then read the text and tips and do the exercises.
Preparation
Grouping_MjMwNDc=
How's it going?
Sorry I haven't been in touch for such a long time but I've had exams so I've been studying every free minute. Anyway, I'd love to hear all your news and I'm hoping we can get together soon to catch up. We just moved to a bigger flat so maybe you can come and visit one weekend?
How's the new job?
Looking forward to hearing from you!
I've been meaning to write to you for ages now so don't worry! How did your exams go? When will you know your results? I'm sure you did brilliantly as always!
As for me, I'll have been in the new job three months by the end of next week so I'm feeling more settled in. At first I felt like I had no idea what I was doing but now I realise it's normal to feel like that. There was a lot to learn – there still is actually – and I soon had to get used to the idea that I can't know everything. I used to work late a lot and at weekends but I'm slowly getting into a normal routine.
Which means I'd love to come and visit! We really need a good catch up! I can't believe we haven't seen each other since Carl's wedding. How does next month sound?
Anyway, I'd better get back to work.
Congratulations on the new flat! Can't wait to see you!
TrueOrFalse_MjMwNTA=.xml
Matching_MjMwNTE=.xml
GapFillTyping_MjMwNTI=.xml
What's the best way to stay in touch with friends you don't see often?
Language level
Well, I think the best way to stay in touch with my friends is call them or write them e-mails. Another way is by visiting their social networks, comments their publications or putting Likes on their photos. They love that.
- Log in or register to post comments
The best way to keep in touch is to go and see them!
I was pulling your leg! It was the best way before the internet was invented.
After the advent of the Internet, nobody can complain about not being aware of your friends and family. There are a lot of ways we can choose according to our situation.
In my view, video and voice calls make a more tangible connection. I usually reach out to them on special occasions like their birthday. But at other times, send a text and voice message.
If I would like to catch my friend on the hop, on her birthday, I will write a letter. This sounds old-fashioned but, in this era, receiving a letter is an unusual and exciting way to hear from someone.
I prefer to stay in touch with my friends by using instant messaging apps like WhatsApp or Facebook Messenger.
I agree, but i think THE BEST WAY IS TO see one anotHer . I know i'm old school
the best way to stay in touch with my friends i don't see often is texting them since we are occupied with our study and we also don't have much free time to meet in person.
I use Facebook and other social media to see what my friends are doing on daily basis. But if I want to know what is really happen I have to call them. The best way to know what's going on and how someone is feeling is to meet him and talk
I think so in all things that you right Sanja.
I think the most important is offline meetings. The best way is go to interesting place and after all speak about most interesting events in life. For example, I can go to cinema and then walk in park with guitar and ice cream and speak about everything!
What's your assement about this email ? thank you for advance.
Dear Bob I Hope this letter will find you and your entire family in good health. It's been a while! I'm writing to tell you about my recent relocation to a new house. As I told you the last time we spoke on the phone that I've got a new job, so it saves money, avoids traffic and it requires less effort to get to my office. My new house is close to Victoria métro station and it's located in the town's center. It's a second floor apartement with two bedrooms, a leavingroom, a small dining room, a bathroom and of corse a kitchen, it's rather roomy for that reason why I'm grateful for it. Besides the neighborhood is serene and beautiful as well. Would you like to visit us for a few days during the next holiday, I'm sure you'll enjoy the area, so we are waiting for you. I look forward to seeing you in my new home Take care Warm wishes Adil.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
How to Write an Email - Best Examples and Top 5 Dos and Don’ts

Want to know how to write an email? Need some guidance on what goes where and why? Well, whether this is the first email you’ve ever composed, or you just want to refresh your memory, here go through everything you need on the subject of how to write email properly! For more advanced email writing techniques, check out our how to write a professional email article .
Formatting and Components
Learning how to write a basic email is simple, and every email you ever write will feature the same format that requires you to address each of these components:
To, CC, BCC
Attachments.
- Subject Line
Here, we go into each of these components in more detail so you know exactly what makes a great email.
These fields, found at the top of your email, are where you will place the email addresses of the people you wish to contact. Each has a different function:
Discover More:
- What’s The Difference Between CC and BCC In Email? Your Complete Guide!
- The Best Email Providers That Don’t Need a Phone Number
- Want iMessage for PC? We’ve got the Solution for You
The attachment function in your email allows you to attach supporting documents that can be downloaded or previewed within your message. Most formats are supported, and in most cases, you can include text, images, videos, audio, and GIFs. It’s worth remembering, however, that there is usually a limit to the size of the file you can send.
The subject line of your email is all-important , spelling out the intention of your email and what it contains.
They’re often forgotten but this is bad news as they not only help the recipient understand what the body of your message contains, but they also ensure your email doesn’t end up in the trash folder .
Always start your email with a greeting.
Learning how to write an email introduction and greeting is important as it allows you to be polite and let the recipient know the purpose of your message .
Formal emails, such as for a job application or sales email , require a formal greeting. When considering personal emails or those between close colleagues, it’s usually fine to use a more casual greeting. You should keep this in mind in you’re using any email templates or AI writing tools.
Naturally, the body of your message is an important element when writing an email. The ideal email body has to be focused, structured, with a clear purpose and to the point .
Remember that story telling qualities aren’t appreciated in an email and people tend to lose focus and interest if you don’t keep your email short and to the point.
Always state what your email is about early in your message, and layout your information so it is easily accessible when skim reading .
Signing off your email correctly is just as important as starting it correctly, and ensuring you use the right kind of closing for your intended recipient ensures they know the message is finished.
Tailor your closing on a per-message basis and, if you are unsure about how to sign off, always default on the side of formality.
Sending and Writing an Email – Dos and Don’ts
There are many dos and don’ts when learning to write an email:
How To Write An Email – The Basics
When learning how to write an email, once you have added the recipients email address to the correct field, you’ll need to focus on three main areas. These are:
Here, we provide some examples of how you should approach each of these elements so that you can compose your email.
How to Write an Email Subject Line — Examples
Your subject line should be concise and to the point and include any relevant information that the recipient needs in order to identify the purpose of the message. When learning how to write an email subject line, you can use the following examples to guide you:
How to Write Email Introduction – Examples
Your greeting, salutation, or introduction should be tailored to your intended recipient. In many cases, your email introduction will be familiar to you from letter writing practices.
How to Write the Email Body – Examples
The body of your email will need to contain all the information you want to convey, without being overly long or complicated. Here are a few tips:
How to Write an Email Signature or Sign Off – Examples
Signing off your email is simple, and you can choose how you do it depending on who you are writing to. Here are a few ideas:
How To Write Email Like A Boss – Full Examples
Here, we look at some common examples of email writing to help you combine the elements above and rock your email technique.
How to Write an Email to a Friend or Family Member
When writing an email to a friend or family member, you don’t have to have as detailed of a subject line as you would for a more professional environment. Something along the lines of “Catching Up” will suffice. With your introduction, you can take a more conversational tone with them. You can use an informal introduction like “Hi Sam” when starting a conversation with them.
Since you are talking to someone close to you in a non-business setting, you can treat it as would you a text message conversation. You’ll want to use a friendly tone, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t be concise and clear, though. Don’t ramble as they’ll likely skim past your information if so. When closing your message, salutations like “Love”, “From”, etc. are acceptable depending on the nature of your relationship.
Example
I just wanted to check you’d received my invite for Thanksgiving? Please let me know if you’re coming so I know how much turkey to cook!
Love,
How to Write an Email to a Teacher or Professor
When emailing a teacher or a professor, you’ll want to use a much more clear tone than you would normally. In this setting, this person is an academic, so formality is required. Your introduction should be very formal. In our example below, we use “Dear” as the best option. When emailing a professor, be very concise and use bullet points when possible to make your point clear. When closing your email, use a formal salutation like “ Best Regards ”.
Dear Professor Smith,
Unfortunately, due to sickness, I would like to request an extension to the deadline of our current project. If possible, I would like an extension until Monday. Please let me know if this works for if you.
Kind Regards,
How to Write an Email for a Job Application
When sending an email for a job application, formality will be required. Your subject line should include “Application – JOB TITLE”. In your introduction, use a formal option like “Dear”. In your body, clearly state that your resume and cover letter are attached (don’t forget to attach them!).
Dear Sir/Madam,
Please find attached my introductory letter and resume in application for the position of Marketing Associate as advertised on your website. You will find all the information you need in these documents, however, if you require anything further, you can reach me on my mobile or through email.
Best Regards,
Lorraine Lister
How to Write a Thank You Email After an Interview
Getting a job interview is hard enough, so do something to set yourself apart from the rest of the applicants and send a thank you letter after the interview. In the subject line, state that you are thanking the interviewer for their time and attention. In the introduction, use the opening of “Dear NAME”. In the body, thank them for their time and let them know you are available to meet again if needed. “ Kindest regards ” is a great closing to use as your salutation.
Dear Jan,
Thanks for giving me the time to speak with you and learn more about the role available. It was a pleasure to connect with you and discuss and how I might fill the position of Marketing Associate.
Please feel free to contact me if you would like any more information or if you would like to arrange another meeting to discuss how we can proceed. I look forward to hearing from you in the near future.
Kindest Regards,
How to Write an Email for Business Purposes
Email is the communication language of business, so it’s important to know how to learn ace email skills to further your career. “Hi Team” or “Hi All” is an ideal opening when sending to a group of people, but for a single person, use “Hi NAME” . Clearly state the purpose of the email, the intended outcome (meeting scheduled, documents reviewed, etc.), and then communicate the timeline. When closing, use “ Thanks ” or “ Best Regards ” .
Hi Team,
Attached you’ll find the latest sales figures from the last quarter. If you have any comments, please get in touch with me directly.
Best,
Emma Watson
Sales Manager
ABC Company

How to Write an Email – FAQs
Email is the number one method of digital communication in the world, and its simplicity and ease of use mean it’s still popular even though it’s pretty old. You can write an email for a number of reasons, including keeping in touch with friends or family, applying for jobs, communicating with colleagues, or even just requesting information.
Anyone with an email app and an email address can write an email, and it remains one of the most popular methods of communication thanks to its availability and ease of use.
Your email address will be made up of three of four components. These are: your name (or other handle), the @ sign, and the domain of your email provider. This is usually a .com or .net domain, however this will depend on your email service.
The subject line is usually found at the very top of your email, just below the To, CC , and BCC fields where you enter the email addresses of your contacts. Don’t forget to write a short and snappy subject line so your recipients know what your email is about.
Depending on the email app you use, you may find the attachment button at the top or bottom of the screen. It is usually indicated with a paperclip icon and a click will allow you to attach files from a computer or the cloud.
The send button may be at the top or bottom of the screen depending on the app you use. It may be a simple arrow icon, or it could be a button with the word “send”. Usually, one click is all it takes to send your message, so make sure you check it properly first.
Gain Communication Clarity with Spike

Email Writing

Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to the future of letter writing– electronic mail writing. Gone are the days where people have to wait for weeks to receive a letter from a friend or a significant other. The concept of pen pals is no longer applicable when everyone from any part of the world can be contacted almost immediately– depending on your Internet speed and the kind of social media site you are using. If there are certain laws in your country that prevent you from accessing Google-related sites or even Facebook-owned sites, (e.g. China) then you would have to find another way to contact your fellow peers and colleagues using whatever mobile apps they have (e.g. WeChat). You may also see formal writings .
- Free Writing Examples
- Essay Writing Examples
Regardless, almost all forms of communication (except face-to-face talking) is already done through the use of modern technology that is able to fill the gap between the distance among people. The use of electronic mail writing these days are for more semi-formal and formal purposes (e.g. submitting a resume, asking your college instructor for some clarifications, making a business transaction) than casual purposes (e.g. chatting with a friend). You may also see some email examples by clicking here. For newbies who do not know the first thing about email writing, here are a few tips for you. You may also see application writings .
Sample Email Writing Example
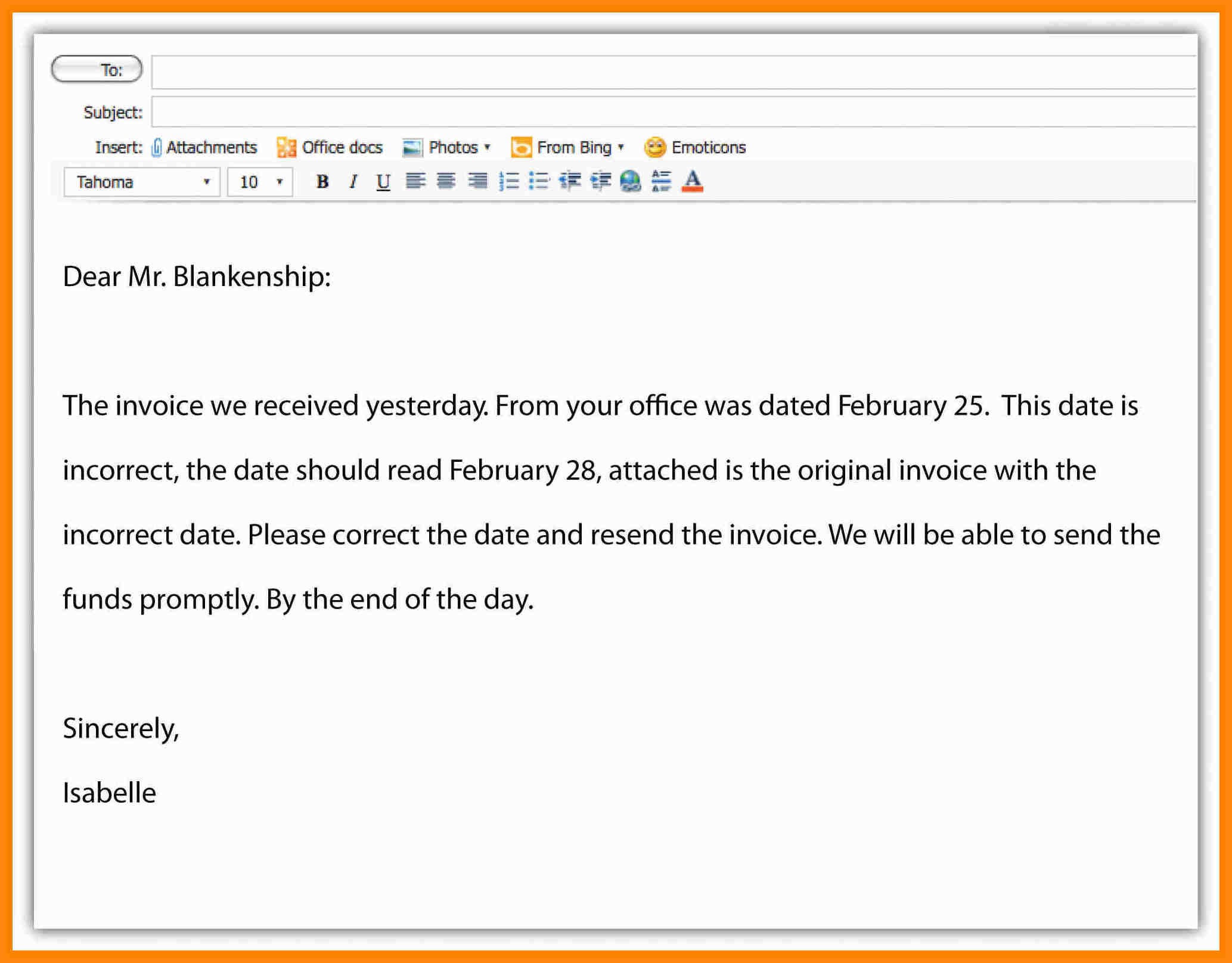
Size: 65 KB
General Tips for Writing Emails in English
1. be sure an email is necessary.
Ask yourself if sending an email is really the best option to use in addressing the query or issue to the concerned party. Because if the matter at hand is something not so important or confidential, it can always be dealt directly with the aforementioned party. But then again, it is entirely up to your discretion. If you’ve decided that an email is the best option, then write your email and click “send”. You may also see article writings .
2. Use separate business and personal email addresses
Many jobs will normally give you an email address that you have to use, in case you have concerns or questions that you would want to raise to your boss or supervisor. Make sure that you strictly use your work email for work matters and personal email address for personal matters. Having a work email can look and sound more professional. That’s good if you’re writing a formal email, but it might not be as nice if you’re writing to a friend. You may also see memo writings .
3. Be clear, brief and polite
Everyone in the office is usually bombarded with emails every single day. That is why it is always best to keep the content of the message short, simple and concise enough so that they may be able to understand the gist of the letter without straining so much effort and time. Go straight to the point, but not in a rude and condescending way. Write your email just like you would in an essay. Similar to an essay, you have to introduce the topic, explain the different points, and then conclude the topic. You may also see summary writings .
4. Don’t write emails when you’re angry
They say that there is a right time for everything– which includes expressing that rage and anger towards the person. But never in an email. Keep in mind that you have to be respectful and courteous to the one you are sending that letter to.
5. Use short sentences
Just as it is important to keep the content of your message short and simple, it is also essential to keep the sentences simple and easy to read in order to keep your thoughts cohesive and understandable. Try your best not to use very lengthy sentences in your letter. Instead, learn to break down each separate thought with a ‘period’. You may also see minutes writings .
6. Be careful with “forward” and “reply to all”
The “forward” button is considered a lifesaver especially when you do not have the files you need to send to your boss or colleague, and you realize you sent that specific file to someone else who needed it before they did. So, you simply use that forward button in order to save time and effort. But make sure that the content of the forwarded message is meant for that specific person. Otherwise, it is best you delete the rest and to just retain the file that is needed to be sent. The same can be said for the “reply to all” option. If your supervisor has sent a joint message to recipients A, B, and C, make sure you only reply to your supervisor and not reply to all the concerned parties mentioned, especially if it is not really “need to know” information by the others. You may also see narrative writings
7. Read your email personally before sending it
Since you are the one composing the email, it would be best if you took the time to proofread the letter just to make sure that the grammar is in tact and that the thoughts are coherent enough for your letter to be organized and understandable. This will prevent the email recipient from struggling to understand your email.
8. Double-check email addresses for all recipients
Make sure that the recipient’s email address is correct. Be careful as there are times that email addresses are structured in a similar way. You may also see argumentative writings .
Sports Email Writing Example
Size: 498 KB
The 3 Common Types of Emails
1. a personal email – introducing yourself for the first time.
As mentioned before, most people do not write personal emails to each another anymore. They would mostly communicate through texting, calling, or via any social media applications that do not really need much formality (e.g. Facebook Messenger, Viber, WeChat). But if ever you are the conservative type of person, then here are a few guidelines that you would need to follow.
General rules for personal emails:
- Politeness: You don’t need to be too formal, but you would want to appear polite and friendly when you address the recipient. If you have any requests that you would need to ask from your friends, make sure that you are polite in doing so. Instead of saying “Write me back,” for example, try something like “If you have a chance, I’d love to hear back from you,” or even “Please write back when you have a chance.”
- Greetings: For greetings, people would normally use the first name after the word “Dear”.
- Closings: To say goodbye, use something like “Thank you”, “See you soon!” or even a brief sentence like “I’m really looking forward to meeting you in person.” Be sure to write/type your name, even if it will be included in your signature.
- Casualness: With these types of emails, you can probably include more jokes or informal comments. However, still be careful about the tone of your email, especially if you don’t know the recipient well.
Example of a personal email:
For this example, let’s imagine that you are going abroad for the summer, say the United States or Canada. When you get there, you’ll be staying with a host family. There is a great chance that you will need to introduce yourself via email. Listed below is a sample:
Dear Smith Family,
My name is Mark. I received a confirmation letter from the exchange organization today. It said I’ll be staying with you for three months later this year. I wanted to introduce myself so you can know a bit more about me.
I’m currently 17 years old. I like listening to classical music, playing football and reading comic books. I will graduate from high school later this year, and I hope to go to college in the next year. I’ve never traveled outside of my country, so meeting you and visiting your country will be an exciting, new experience!
I’d also like to know more about you, so if you have a chance, please write back at this email address. If you have any questions for me, I’d be happy to answer them.
Thanks again for agreeing to host me—I’m very excited to meet you in person!
2. A Semi-Formal Email – Writing to request an appointment or meeting
This is a very common type of email, especially when you need to write to your teacher to request a meeting.
General rules for semi-formal emails:
- Length: Follow the K.I.S.S. (keep it short and simple). Remember that you are talking to a professional. These types of people do not have the luxury of time to thoroughly go through your letter, sentence per sentence. So, go straight to the point on what you want to discuss. After all, other concerns can be resolved during the meeting.
- Respect: Remember that you’re requesting a favor from the recipient, so be respectful and not too demanding.
- Greetings: Use formal or semi-formal greetings. You can still use “Dear ~,” but instead of including the recipient’s first name, use their title (Mr., Mrs., Ms., Dr., Prof. etc.) and last name.
- Closings: Depending on the purpose, you can probably use a semi-formal goodbye, such as “Thanks,” “Hope to hear from you soon” or “Thanks in advance.” If it’s someone you have talked to before in person, you can maybe use something less formal, like “Have a great weekend.”
- Clarity: If you’re requesting for a specific day, that day/date and time should be set. Try to give multiple options. That way, if your first option doesn’t work out, your recipient has other dates/times to choose from.
Example of a semi-formal email:
Dear Professor Constantine,
I really enjoyed your Introduction to Witchcraft Course, and I was interested in continuing by taking the Advanced Demonology Course next semester. I’d like to meet with you to ask a few questions about the course, and also to get more information about the scholarship for international students.
Would it be possible to meet with you at your office sometime next week? I’m available during your regular office hours on Tuesday and Wednesday (1-4 p.m.), but if you’re busy on those days, I could also meet any time on Monday or on Friday afternoon. Please let me know what day and time would work best for you.
Thanks very much for your time and help!
Gary Oldman
3. A Formal Email – Writing about a problem with a product
General rules for formal emails:.
- Politeness: Follow Confucius’ Golden Rule which is, “Do not do unto others want you others to do unto you.”
- Formality: Avoid making jokes and using slang words.
- Clarity: Be clear by including any relevant details.
- Requests: State the result or response that you want or expect. This is also called making your email “actionable.”
- Greetings: For greetings, use a common phrase like “To Whom It May Concern,” since you probably won’t know the name of the person who will be receiving the email. But if you do know the name, you can use “Dear [Title] [Last Name],” like the one in the semi-formal email example.
If those seem too formal, you may want to try something like “Good Morning/Afternoon/Evening.” It could make you seem friendly and make the recipient more receptive to your complaint or questions.
- Closings: For goodbyes, a simple “Sincerely Yours” is best. But if it’s a more casual company or an organization that you’ve already interacted with, you can always say “Thanks”.
Example of a formal email:
To Whom It May Concern,
I recently bought a magic wand from Hogwarts, but unfortunately it appears that the wand is not working correctly.
For reference, the model number is TOS-577, and I bought it on May 1, 2016 from Dumbledore at Hogwarts. I returned the magic wand to the store, but they said I should contact you since you would have an idea on how to fix the wand. Because of that, they weren’t able to offer a refund or exchange.
I can understand Hogwarts’ position, but the magic wand shouldn’t have broken so soon. It is still covered under the school’s warranty, so I would like to exchange the magic wand for a working model. Please let me know what steps I need to take for this to happen.
Thanks very much for your help with this situation.
Sincerely, Voldemort
Business Conference Call Email Writing Example
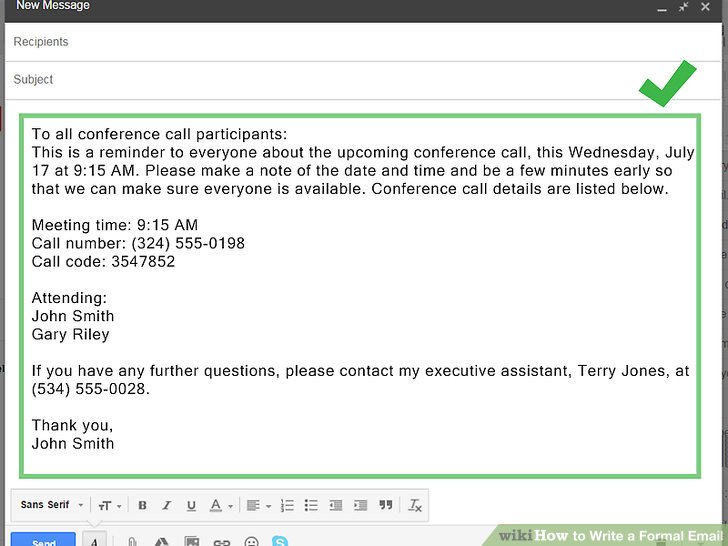
Size: 524 KB
Just remember these steps in writing an email and you’ll be able to get it in no time.
Email Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an email to parents about an upcoming school event
Compose an email to students reminding them of homework due dates.
Search form
A more formal email.
Look at the exam question and answer and do the exercises to improve your writing skills.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then read the text and do the other exercises.
Preparation

Check your writing: gap fill - indirect questions
Check your writing: gap fill - useful phrases, worksheets and downloads.
Would you like to study in a different country?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
- Email Writing
Email Writing - Format and Samples
Emails are modern-age letters. This article explains the format of email writing and also gives you sample emails for students of Class 8 to Class 12 and working professionals.
How to Write an Email?
Email expressing your appreciation, email about your trip.
- Email on Seeking Information about Course Details
Email on Introducing a New Employee to Your Team
Email on official intimation of your resignation, email informing your employees about the change in work timings, faqs on email writing format.
Email writing is an essential part of professional communication. It is not easy to get people to respond to your emails if they do not feel interested in your message or proposal. This is exactly the reason why you should learn to write good emails. Be bold. Get to the point right away. The best email communication is the one that is simple and clear.
There are a few tips you have to keep in mind when you sit down to write emails. Emails can be casual or professional, just like informal and formal letters. The format of the email changes according to the kind of email you are writing. However, accurate grammar and spelling are aspects that are to be taken seriously.
When you start writing an email,
- Make sure you type in the right email ID. Always check with the receiver for the exact email address because even a full stop that is not part of the email address can land your email with the wrong person, or the mail would simply bounce.
- The Subject line is the next most important factor you should carefully consider because that is the first thing anyone receiving the email would see. It also determines if the receiver would want to open the mail. ‘The from line is what recipients use to determine whether to delete an email. The subject line is what motivates people to actually open the email.’ said Loren McDonald. Spend double the time you spend on drafting the body to draft the subject.
- See to it that your Salutation or Greeting is appropriate to the receiver/s. The greeting builds a rapport.
- The Body of the email states what the email is about. Be clear with what you want your receiver to know. Make sure you have everything you want to convey drafted in simple terms. Do not use colloquial language or long unwinding sentences. Try not to repeat words or use cliched terms. Make your message positive, even if you’re turning down an offer. If you have to follow, do it before they remind you to. Keep it short. Use standard font style and size. Do a final spelling/grammar check/proofread.
- Finally, Sign off the email on a polite note and proofread it before hitting send. The closing should feel genuine; only then will the receiver want to respond.
Email Writing Format Samples
Here are some sample emails that will help you understand how to write an email in the best possible way.
Informal Email Writing Format Samples
To: Recipient’s email address
Subject: Congratulations!
Dear (Name),
My heartfelt congratulations to you. I was glad to see your name on the merit list. All your efforts were definitely not in vain. I bet everyone at home is so proud of you.
You have truly honoured the family name, and I am happy that you would get to take up the course in architecture that you had been waiting for. I am waiting to meet you in person to convey all my love and appreciation.
Convey my regards to uncle, aunty and grandpa.
To: Recipient’s email ID
Subject: About my trip
My dear (Name),
I am very excited to write to you about the long tour I will be going on along with my parents. We will be leaving on the 25 th .
We will be away for three months. We are going to San Francisco for an official meeting my father has to attend. We would then be travelling to New York to visit our cousins. We would stay there for a month. After that, we will be going to Paris. It has always been my dream to visit Paris at least once in my lifetime, and my parents have finally agreed to take me there. I will definitely write to you all about my trip – all the different places we visit, the variety of food we eat and the people we meet.
It would have been even more special if you had come along with me. We will make sure we plan out a trip once I am back home.
With best wishes,
Formal Email Writing Format Samples
Email on seeking information regarding course details.
Subject: Regarding Course Details
I have passed the B.Sc. degree examination with Electronics as the main subject. I intend to have a course in Computer Science and would like to know the details of the courses taught at your institution. Could you please send me a copy of your prospectus?
Yours faithfully,
Subject: Meet the New Customer Service Representative
I am pleased to introduce you to (Name), who is starting today as our Customer Service Representative. She will be providing technical support and assistance to our users and making sure they enjoy the best experience with our products.
Feel free to greet (Name) in person and congratulate her on the new role!
Best regards,
Designation
Subject: Resignation
Dear Sir/Ma’am,
I am planning to pursue my higher studies in the coming academic year, and hence I would like to inform you of my intention to resign from the post of (Designation) at (Name of the Institution), effective three months from now.
I appreciate the opportunities for growth and development you have provided during my association with (Name of the Institution). It was indeed a privilege working here, and it was a valuable work experience which has helped me grow personally and professionally to a great extent.
Please accept this letter as the formal intimation of my resignation.
Thank you for your guidance and support.
Yours sincerely,
Subject: Revised Working Hours
Our company is growing, and there is a good inflow of projects every week. This has been possible with your dedicated and timely teamwork. In order to keep up with this, we have decided that the working hours would be advanced by 30 minutes. The revised time would be 8:30 am to 5 pm. This will be in effect from July 5, 2021 (Monday). It would be appreciated if all of you keep up with the timing and abide by it.
Feel free to come up with suggestions, if any.
Warm regards,
What should I put as the subject in an email?
The subject in an email should state what your email is about. Do not use long sentences when writing the subject. Use simple vocabulary and place the most important words at the very beginning of the subject.
What is the format of email writing?
Be sure to type in the exact email address of the recipient. Keep the subject as short as possible. Use it only to convey what the mail is about. No explanation about the matter should be included in the subject line. The body of the email should explain the purpose of the email. However, add only the necessary details. Keep it simple. End the email with a complimentary close and sign off with just your name in informal emails and with your name and destination in a formal email.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Effective communication
- How to Start an Email | 10 Greetings & Opening Lines
How to Start an Email | 10 Greetings & Opening Lines
Published on December 22, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on June 26, 2023.
Sending good emails is an important skill in academic and professional contexts. It’s essential to start your emails on the right foot with an appropriate greeting and an engaging opening line .
Below, we explore how to start an email, providing five professional greetings and five strong opening lines that you can use in your correspondence. We also explain the contexts where each one would be an appropriate choice.
Fix common mistakes for free
Fix mistakes for free
Table of contents
5 strong greetings (salutations), 5 good opening lines, how not to start an email, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
For your email’s greeting (also called a salutation ), you don’t need to do anything fancy. Keep it simple and choose one of the tried and tested greetings below based on the context and the level of formality you’re aiming for.
1. Dear [full name],
Greeting the recipient by their full name is best when you haven’t previously interacted with them.
Use “Dear,” not the less formal greetings “Hello” and “Hi,” alongside someone’s full name to avoid creating a jarring combination of different levels of formality. Also avoid using this option if you’ve interacted with the person previously, as it comes across as overly stiff.
2. Dear [title and last name],
Using an abbreviated title (such as “Ms.” or “Dr.”) followed by the person’s last name is another way of greeting someone formally. This can be a good option to show respect to a superior in some context—for example, when writing to your professor at university. It’s also a formal way of addressing someone you’ve never interacted with before.
Use of titles like this is often considered somewhat old-fashioned, though. As such, it’s best saved for contexts in which you haven’t interacted with the person before or want to show a special level of respect.
3. Hi [first name],
People sometimes assume that all emails sent in a professional context need to be formal in tone, but this isn’t the case in most workplaces today. If you’ve had some previous interaction with a person, it’s normally fine to just greet them by their first name, preceded by “Hi,” “Hello,” or the slightly more formal “Dear.”
This kind of informal greeting is not appropriate in all contexts. If you’re applying for a job or contacting someone you don’t know, it’s best to go for something more formal. This kind of greeting is sometimes used in marketing emails, but some might find it presumptuous —always consider your target audience.
4. Dear [team, department, or job title],
When your email is addressed to someone whose name you don’t know, to a group of people, or to an organization or department, using alternative names is an appropriate choice: the person’s job title, the name of the team, or (in a more familiar context) something more generic like “team” or “everyone.”
Do this only when you have a good reason to. If you’re writing to an individual whose name you know or can reasonably find out, it’s better to use their name than something generic like a job title.
Sometimes a simple “Hello” or “Hi” is all you need. It’s a good, straightforward choice for a quick message to someone you communicate with frequently and don’t need to show any particular formality with. It lets you get straight to the point.
Though people sometimes choose this greeting when they’re not sure whom they’re writing to, it’s not a good choice in that context, as it can come across as overly blunt. In that situation, try using a job title or department name instead, as suggested above.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
The opening line of the email itself is where you can catch the reader’s attention, build a rapport, or quickly communicate what you need from them.
1. I’m reaching out …
If you want to get straight to the point but don’t want to sound overly blunt (e.g., “I need you to do x for me by Tuesday”), a phrasing using “I’m reaching out” is a good choice. It avoids wasting your or the reader’s time but still comes across as polite and thoughtful.
However, this opening only really makes sense to begin or resume a conversation, not to continue an ongoing discussion. Use this expression for an unsolicited email, not a direct reply to a previous message.
I’m reaching out to let you know that I won’t be available for any assignments in April.
2. How are you?
A straightforward way too add a friendly personal touch to your email is to simply ask the recipient how they’re doing, how their week is going, what they did at the weekend, or something more specific if you know something about their interests. A generic “How are you?” is good enough but can seem formulaic—try emphasizing it with another sentence.
This kind of question is appropriate in an email to someone you know or work with regularly, but it will appear overfamiliar if sent to someone you’ve had no previous interaction with. Don’t open with this in your first email to someone.
How’s your week going? I took a couple of days off, so I’m still catching up.
3. Thanks for …
If you’re replying to someone directly, or following up on a previous discussion, one way to build a positive interaction is to thank them for their previous contribution. This could be for some information they gave you, something they did for you, or just taking the time to talk to you.
This opening obviously only makes sense if the person has done something for you. You could try thanking someone for opening your email in the first place, but it’s likely to come across as patronizing.
I appreciate your quick response. Regarding the invoice, …
4. I hope you …
Simply wishing the recipient well is a good way to start an email in a friendly way. Rather than the generic “ Hope you’re doing well ” or the slightly stiff “ I hope this email finds you well ,” try a more specific phrasing to emphasize the sincerity of your wishes.
Hope you had a good time on vacation!
5. We met at …
When writing to someone you don’t know well but with whom you’ve had some previous interaction, or with whom you have a mutual connection, it’s a good idea to start by explaining that connection or reminding them where you’ve previously met.
If that introduction involves mentioning a mutual connection, make sure you have their permission to do so.
Maybe you remember me from your first weekly meeting, but we didn’t get the chance to speak much at the time. I’m reaching out to …
There are many valid ways to start an email, but there are also a few common pitfalls to avoid.
Overly impersonal greeting
Greetings like “ Dear Sir or Madam ” and “ To Whom It May Concern ” are best avoided whenever possible. Besides sounding quite old-fashioned, they show the recipient that you’re not sure exactly whom you’re contacting. Always address the recipient by name if you can find it out; use something like a job title if not.
No greeting at all
Starting an email without any sort of greeting line is rarely appropriate in a professional context. While you might sometimes skip the greeting in personal emails to someone you know well, in a work email you should always have some kind of greeting, whether formal (e.g., “Dear Ms. Aoki”) or casual (e.g., “Hi John”).
Redundant opening
Consider whether your opening really adds anything of value or just wastes the reader’s time. Statements announcing what you’re going to do next in the email are usually unnecessary. Try cutting them out entirely.
- Let me introduce myself. My name is …
- I know you’re very busy, but do you have time to help me with something? I was wondering …
- Could you possibly do me a favor? I’d like to …
If you want to know more about commonly confused words , definitions , and differences between US and UK spellings , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Confused words
- Affect vs effect
- Further vs farther
- Loose vs lose
- Whose vs who’s
Definitions
- Bear with me
- Presumptuous
US vs. UK spellings
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
You should start a professional email with a greeting and the name and title of the recipient (e.g., “Dear Mr. Walken”). Then, you should include an introductory line like I hope this email finds you well , followed by the body of the email.
For less formal emails, you can use a more casual introductory line like I hope you’re doing well .
Miss is a title for an unmarried woman or girl, especially one under the age of about 30 (e.g., “Miss Jones”). It cannot be used for a married woman. It is sometimes seen as slightly old-fashioned, since it defines the woman by her marital status.
Ms. is a title for a woman whose marital status is unknown, for an older unmarried woman, or for any woman in a context where you don’t want to emphasize the woman’s marital status. It’s intended to be neutral, in that it can be used for married and unmarried women alike—much like “Mr.” can be used for married and unmarried men.
Some synonyms and phrases related to I hope this email finds you well include:
- It is a pleasure connecting with you again
- I hope you are doing well
- I hope you are having a productive week
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, June 26). How to Start an Email | 10 Greetings & Opening Lines. Scribbr. Retrieved April 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/effective-communication/start-an-email/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, dear sir or madam | alternatives & when to use, 7 alternatives to “i hope this email finds you well”, better alternatives to “hope you’re doing well”, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
10 Example Email/Letter Topics (Writing) (PDF) | B2 First (FCE)
How to write B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter?
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter: Writing Topics
B2 first (fce) email/letter topic 1.
You have received this email from an English-speaking boy called Simon.
Hello, I would like to get to know someone from your country and a friend has told me that you would like to practise your English. Perhaps we could email each other: Could you tell me a bit about yourself and your family? Could you suggest how we might meet sometime in the future?
Thanks, Simon
Write your email in 140-190 words in an appropriate style.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 2
You have received this email from your English-speaking friend. Jean.
I hear you organised a surprise birthday party for your mother: I’d love to hear about it. What kind of party did you organise? Who did you invite? How did it go?
Do tell me. Love, Jean
Write your email in 140-190 words in an appropriate style.”
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 3
You recently helped organise a college ski trip and you have received this email from a parent of one of the students who went.
I understand you were one of the organisers of our son’s ski trip. I have to say my husband and I were extremely dissatisfied with the arrangements. My son has informed us that the ski slopes were poor, the lessons were fewer than promised and the accommodation was inadequate.
Can you please give us a satisfactory explanation?
Yours sincerely, Nora White
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 4
You see this advertisement in a student newspaper.
Lifeguard assistants wanted
We are looking for someone in August to assist our lifeguards, provide supervision during beach activities and observe swimmers.
Write to the Lifeguard Manager, saying what your experience and qualifications are and stating the reasons why you are suitable for the job.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 5
You see this announcement in an English-language college prospectus.
Scholarships
Every year, two scholarships are offered to candidates from overseas who can show how our one-year course in English and American studies would help their careers. Scholarships cover fees, accommodation and food, but not transport or personal spending money.
To apply, write a letter explaining why you think you deserve a scholarship.
Write your letter in 140-190 words in an appropriate style. .
Get Your (FCE) Email/Letter Checked!
B2 first (fce) email/letter topic 6.
Your Italian pen friend, Antonia, wrote and asked about your lifestyle in England.
Read part of Antonia’s letter and reply.
I think I have a very healthy lifestyle. I eat a lot of fruit and I get a lot of fresh air. My family lives near the mountains, so we ofien go walking. Last weekend, we went rock climbing. I saw a lot of wildlife and I took a lot of photos. What kind of lifestyle do you have?
Write your letter in 140-190 words in an appropriate style.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 7
This is part of a letter you receive from an English friend.
In your last letter, you said you were organising a surprise party for a friend. Was it diffjcult to organise? What did your friend say? I love to hear how it went.
Write your letter , answering your friend’s questions and giving relevant details.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 8
You have seen the following advertisement in a newspaper:
VOLUNTEERS NEEDED!
We are the National Diabetes Organisation and we are organising a camp for diabetic children. We need volunteers to work with us during the camp.
Your responsibilities will include:
- Teaching children about diabetes
- Playing games with them
Also, you should speak several languages because it’s an international camp
Write a letter applying to become a volunteer.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 9
You have come across the following advertisement online:
FITNESS SUMMER CAMP
Do you need to get fit in a short period of time? Do you have the experience exercising but want to learn even more? Come and join our fitness summer camp. It will be a great experience and you will return home feeling better than ever and knowing much more about healthy lifestyles.
Write an email to find out more about the camp.
In your email, you should:
- explain why you would benefit from this camp
- ask for more information about the diet and accommodation
Write a letter.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter Topic 10
You have received this email from your English-speaking friend David.
From : David Subject : touring holiday Some college friends of mine are visiting your area soon for a week’s touring holiday.
They would like to travel around and learn about your local area and its history. Can you tell me about some of the places they could visit? What’s the best way to travel around – car, bike or coach?
Thanks, David
Write your email.
B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter: Writing Topics (PDF)
Download B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter: Writing Topics (PDF)
FCE, CAE, CPE
Practice tests online, would you pass b2 first (fce).
Writing an Email (Form 1 Unit 1 Non-Textbook Lesson - English)
Loading ad...
AmandaNavaratnam
Write an email based on technology
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF
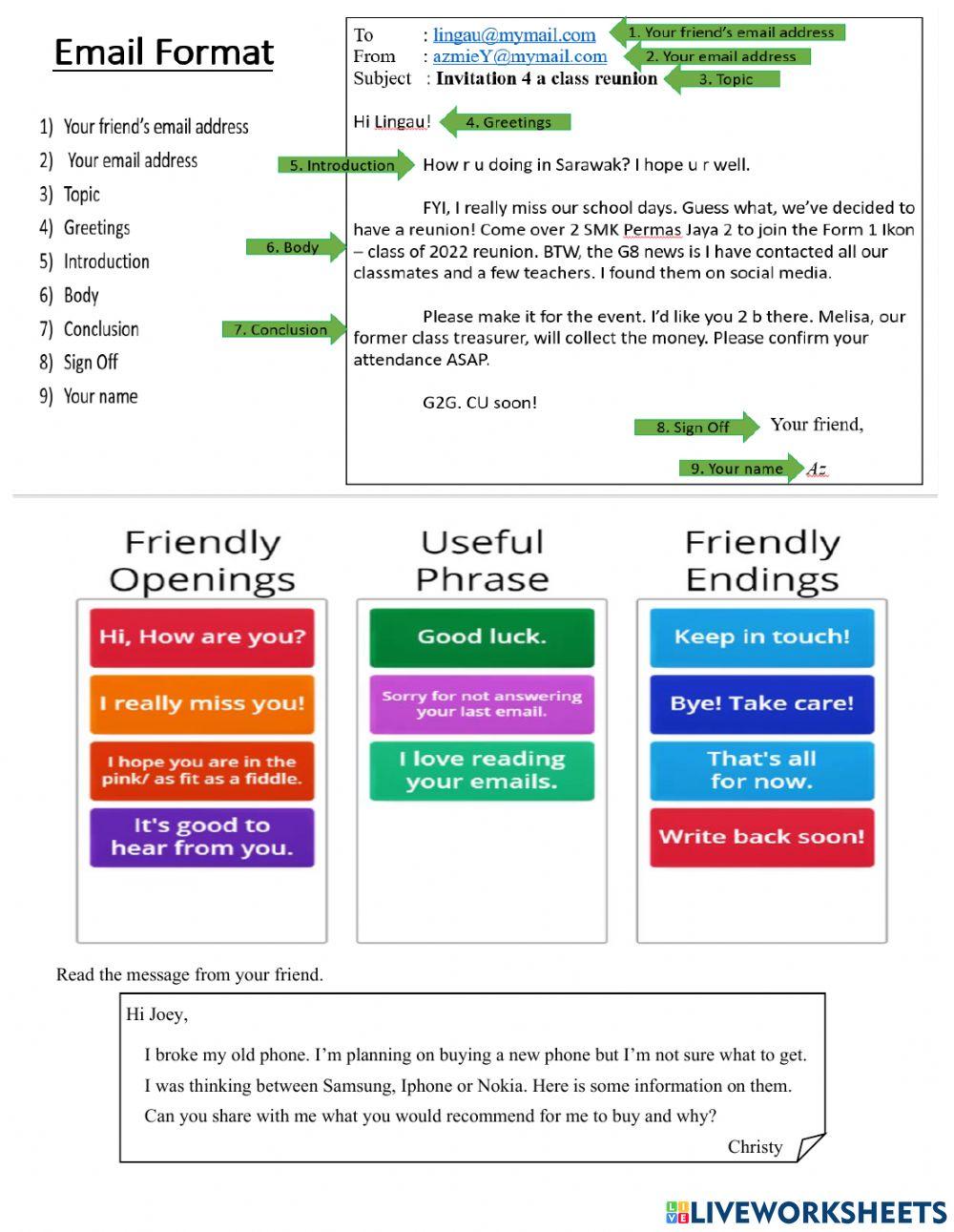
Dennis G. Zill
Travel, Money, Pets Et Cetera
5 Email Essay Spm example – Informal Email
Informal emails are suitable for communicating with acquaintances, friends, or colleagues you share a close relationship with, allowing you to express yourself more freely and naturally compared to formal or business communication. However, it’s essential to be mindful of the context and the nature of your relationship with the recipient to ensure that the tone and content of your email are appropriate. Certainly, here is an example of an email essay for the SPM (Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia) examination:

Subject: Activities during free time
Dear Ahmad,
It’s great to hear from you.
I agree, watching TV is tiresome. These days, I’m into gardening. My sister and I tried planting a flowering plant a few months ago. Seeing it grow made me feel delighted. Since then, we turned the empty lawn into a garden. Why don’t you try it as well?
If you want something to di indoor, you could try playing online games. My brother loves it. He said it’s fun and exciting.
I hope this will be of help. Write to me as soon as you can and tell me what to do.
- 5 Example of Article Essay for Student
- 10 Tanda – Cara Nak Tahu Hamil Tanpa Pregnancy Test
- Example Article Essay SPM: The Impact of Social Media on Society
- What is the best introduction for a SPM email?
- Email Format Essay: How Do You Start a Formal Email Essay?
- 5 Short Essays for High School Students (150 – 250 words)
Subject: Ways to take care of the environment, let’s go green.
Hi Sonali Bendre,
It’s good to hear that your family has jumped on the recycling bandwagon.
There are few things you can do to take care of the environment. You should switch off and unplug any electrical appliances when not use. When you leave a room, make sure to swich off the lights and fans. This can help to reduce carbon emission.
Additionally, you should use a green bag instead of a plastic bag when shopping. Keep away from using straws too. Both of these cannot be recycled.
Hope this has helped.
Sincerely, Raju Chandran
Subject: The best way to go to Kuala Terengganu – by Car or flight
Dear Monalisa
In my opinion, going to Kota Bharu by car is better than taking a flight. Although it will take longer hours, it is economical. Your parents only need to pay for the toll and fuel which are cheaper compared to the flight tickets. Moreover, your family won’t have to worry about renting a car once you have arrived in Kuala Terengganu.
As for me, my family do not have any plans yet for the holidays. But I do hope we will get to go to the beach.
I hope I have helped you.
Love, Rashidah
Subject: Malaysia Day Celebration: Singing and Dancing Activities
Hello Melissa Saila,
My suggestion for the Malaysia Day celebration would be Dancing dan Singing competition. This activity will help the students know the patriotic songs besides showing off their hidden talents. Over and above that, the students will also get the opportunity to show their creativity in composing songs and delivering them to the audience. They can dress up as freedom fighters or national leaders. I am pretty sure the students will enjoy it.
I hope this suggestion will help you to organise the day. See you later.
Nationalist Latifah Omar
Email Essay Spm example Email Essay Spm example
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)

- Publications
- Virtual Health Library
- Virtual Campus for Public Health
- PAHO/WHO Collaborating Centres
- Track your shipment
- Regional Revolving Funds
- The Decade of Healthy Aging
- Elimination Initiative
- Migration and Health in the Americas
- HEARTS in the Americas
- Sustainable Health Agenda for the Americas 2018-2030
- Alerts and Epidemiologic Updates
- Technical and Scientific Products
- Resources for Journalists
- News Releases
- Country News
- Technical Unit News
- Infographics
- Champions of Health
- Public Health Heroes
- Collaborators
- Past campaigns
- PAHO/WHO Newsletters
- PAHO Calendars
- History of PAHO
- PAHO's Former Directors
- Organizational Chart
- Statement of Assessed Contributions due from Member States
- Communicable Disease Prevention, Control, and Elimination
- Comprehensive Immunization
- Evidence and Intelligence for Action in Health
- Innovation, Access to Medicines and Health Technologies
Social and Environmental Determinants for Health Equity
- Health Emergencies
- Health Systems and Services
- Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health
- Pan American Sanitary Conference
- Directing Council
- Executive Committee
- Subcommittee on Program, Budget and Administration
- Internships
- Partnerships
- Office of Internal Audit
World Health Day 2024 - 'My health, my right’

April 7, 2024
Around the world, the right to health of millions is increasingly coming under threat.
Diseases and disasters loom large as causes of death and disability.
Conflicts are devastating lives, causing death, pain, hunger and psychological distress.
The burning of fossil fuels is simultaneously driving the climate crisis and taking away our right to breathe clean air, with indoor and outdoor air pollution claiming a life every 5 seconds.
The WHO Council on the Economics of Health for All has found that at least 140 countries recognize health as a human right in their constitution. Yet countries are not passing and putting into practice laws to ensure their populations are entitled to access health services. This underpins the fact that at least 4.5 billion people — more than half of the world’s population — were not fully covered by essential health services in 2021.
To address these types of challenges, the theme for World Health Day 2024 is 'My health, my right’.
This year’s theme was chosen to champion the right of everyone, everywhere to have access to quality health services, education, and information, as well as safe drinking water, clean air, good nutrition, quality housing, decent working and environmental conditions, and freedom from discrimination.
Key messages
Human rights factsheet (WHO)
Communication material - PAHO | WHO

Human Rights and Health

Universal Health

Air Quality

Health Equity
Find anything you save across the site in your account
What Have Fourteen Years of Conservative Rule Done to Britain?
By Sam Knight

Listen to this article.
My life divides, evenly enough, into three political eras. I was born in 1980, a year after Margaret Thatcher entered Downing Street with the prayer of St. Francis of Assisi on her lips: “Where there is doubt, may we bring faith. And where there is despair, may we bring hope.” The Conservative-run Britain of the eighties was not harmonious. Life beyond the North London square where my family lived often seemed to be in the grip of one confrontation or another. The news was always showing police on horseback. There were strikes, protests, the I.R.A., and George Michael on the radio. My father, who was a lawyer in the City, travelled to Germany to buy a Mercedes and drove it back, elated. Until Thatcher resigned, when I was ten, her steeply back-combed hair and deep, impossible voice played an outsized role in my imagination—a more interesting, more dangerous version of the Queen.
I was nearly seventeen when the Tories finally lost power, to Tony Blair and “New Labour,” an updated, market-friendly version of the Party. Before he moved to Downing Street, Blair lived in Islington, the gentrifying borough I was from. Boris Johnson, an amusing right-wing columnist, who was getting his start on television, also lived nearby. Our local Member of Parliament was an out-of-touch leftist named Jeremy Corbyn.
New Labour believed in the responsibility of the state to look after its citizens, and in capitalism to make them prosper. Blair was convincing, even when he was wrong. He won three general elections in ten years and walked out of the House of Commons to a standing ovation, undefeated in his eyes. I was turning thirty when Labour eventually ran out of road, undone by the Iraq War, the global financial crisis, and the grim temper of Gordon Brown, Blair’s successor. He was caught in a hot-mike moment describing an ordinary voter, who was complaining about taxes and immigration, as a bigot.
Since then, it’s been the Conservatives again. In 2010, the Party returned to government in a coalition with the Liberal Democrats. Since 2015, it has held power alone. Last May, the Tories surpassed the thirteen years and nine days that New Labour had held office. But the third political era of my lifetime has been nothing like the previous two. There has been no dominant figure or overt political project, no Thatcherism, no Blairism. Instead, there has been a quickening, lowering churn: five Prime Ministers, three general elections, two financial emergencies, a once-in-a-century constitutional crisis, and an atmosphere of tired, almost constant drama.
The period is bisected by the United Kingdom’s decision, in 2016, to leave the European Union, a Conservative fantasy, or nightmare, depending on whom you talk to. Brexit catalyzed some of the worst tendencies in British politics—its superficiality, nostalgia, and love of game play—and exhausted the country’s political class, leaving it ill prepared for the pandemic and the twin economic shocks of the war in Ukraine and the forty-nine-day experimental premiership of Liz Truss. Covering British politics during this period has been like trying to remember, and explain, a very convoluted and ultimately boring dream. If you really concentrate, you can recall a lot of the details, but that doesn’t lead you closer to any meaning.
Last year, I started interviewing Conservatives to try to make sense of these years. “One always starts with disclaimers now—I didn’t start this car crash,” Julian Glover, a former speechwriter for David Cameron, the longest-serving Prime Minister of the period, told me. I spoke to M.P.s and former Cabinet ministers; political advisers who helped to make major decisions; and civil servants, local-government officials, and frontline workers hundreds of miles from London who had to deal with the consequences.
Some people insisted that the past decade and a half of British politics resists satisfying explanation. The only way to think about it is as a psychodrama enacted, for the most part, by a small group of middle-aged men who went to élite private schools, studied at the University of Oxford, and have been climbing and chucking one another off the ladder of British public life—the cursus honorum , as Johnson once called it—ever since. The Conservative Party, whose history goes back some three hundred and fifty years, aids this theory by not having anything as vulgar as an ideology. “They’re not on a mission to do X, Y, or Z,” as a former senior adviser explained. “You win and you govern because we are better at it, right?”
Another way to think about these years is to consider them in psychological, or theoretical, terms. In “Heroic Failure,” the Irish journalist Fintan O’Toole explains Brexit by describing Britain’s fall from imperial nation to “occupied colony” of the E.U., and the rise of a powerful English nationalism as a result. Last year, Abby Innes, a scholar at the London School of Economics, published “Late Soviet Britain: Why Materialist Utopias Fail,” which argues that, since Thatcher, Britain’s political mainstream has become as devoted to particular ideas about running the state—a default commitment to competition, markets, and forms of privatization—as Brezhnev’s U.S.S.R. ever was. “The resulting regime,” Innes writes, “has proved anything but stable.”
These observations are surely right, but I worry that they obscure two basic truths about Britain’s experience since 2010. The first is that the country has suffered grievously. These have been years of loss and waste. The U.K. has yet to recover from the financial crisis that began in 2008. According to one estimate, the average worker is now fourteen thousand pounds worse off per year than if earnings had continued to rise at pre-crisis rates—it is the worst period for wage growth since the Napoleonic Wars. “Nobody who’s alive and working in the British economy today has ever seen anything like this,” Torsten Bell, the chief executive of the Resolution Foundation, which published the analysis, told the BBC last year. “This is what failure looks like.”

Link copied
High levels of employment and immigration, coupled with the enduring dynamism of London, mask a national reality of low pay, precarious jobs, and chronic underinvestment. The trains are late. The traffic is bad. The housing market is a joke. “The core problem is easy to observe, but it’s tough to live with,” Mark Carney, the former governor of the Bank of England, told me. “It’s just not that productive an economy anymore.”
With stagnant wages, people’s living standards have fallen. In 2008, Brown’s Labour government commissioned Michael Marmot, a renowned epidemiologist, to come up with ways to reduce England’s health inequalities. Marmot made suggestions in six policy areas, including better access to child care, walking and cycling programs, social-security reforms, and measures to improve people’s sense of agency at work. In 2010, he presented his ideas to the incoming Conservative-led coalition, which accepted his findings. “I thought, Wow, this is great. . . . I was pretty bullish about the whole thing,” Marmot told me. “The problem was they then didn’t do it.”
Ten years later, Marmot led a follow-up study, in which he documented stalling life expectancy, particularly among women in England’s poorest communities—and widening inequalities. “For men and women everywhere the time spent in poor health is increasing,” he wrote. “This is shocking.” According to Marmot, the U.K.’s health performance since 2010, which includes rising infant mortality, slowing growth in children, and the return of rickets, makes it an outlier among comparable European nations. “The damage to the nation’s health need not have happened,” Marmot concluded in 2020. He told me, “It was a political choice.”
And that is the second, all too obvious, fact of British life throughout this period: a single party has been responsible. You cannot say that the country has been ruled against its will. Since 2010, the Tories have emerged as the winner of the popular vote and as the largest party in Parliament in three elections. In December, 2019, Boris Johnson won an eighty-seat majority in the House of Commons, the Conservatives’ biggest electoral success since the heyday of Thatcherism.
How is this possible? The opposition has been underwhelming. For years, Labour drifted and squabbled under two unconvincing leaders: Ed Miliband and Corbyn, my old Islington M.P. It is telling that, since Labour elected Keir Starmer, an unimaginative former prosecutor with a rigidly centrist program, the Party is competitive again. But the Conservatives have not survived by default. Their party has excelled at diminishing Britain’s political landscape and shrinking the sense of what is possible. It has governed and skirmished, never settling for long. “It’s all about constantly drawing dividing lines,” a former Party strategist told me. “That’s all you need. It’s not about big ideological debates or policies or anything.” In many ways, the two momentous decisions of this period—what came to be known as austerity and Brexit—are now widely accepted as events that happened, rather than as choices that were made. Starmer’s Labour Party does not seek to reverse them.
If you live in an old country, it can be easy to succumb to a narrative of decline. The state withers. The charlatans take over. You give up on progress, to some extent, and simply pray that this particular chapter of British nonsense will come to an end. It will. Rishi Sunak, the fifth, and presumably final, Conservative Prime Minister of the era, faces an election later this year, which he will almost certainly lose. But Britain cannot move on from the Tories without properly facing up to the harm that they have caused.
The Conservative Party manifesto for the 2010 election was a plain blue hardback book titled “Invitation to Join the British Government.” After the Party’s longest spell out of power in more than a century, its pitch to voters was “the Big Society,” a call for civic volunteering and private enterprise after the statism of Labour. “There was a feeling that it must be possible to be positive about a better future in a way that wasn’t socialist,” Glover, the former speechwriter, said. “And that wasn’t an ignoble thing to try.”
Beginning in 2005, Cameron and George Osborne, the shadow Chancellor, had modernized the Tories. The duo represented a new generation of Conservatives: deft and urbane, easy in their privilege. Osborne was the heir to a baronetcy; Cameron’s family descended from a mistress of William IV. Cameron embraced centrist causes, including the environment and prison reform. There was talk of a “post-bureaucratic age.” But the main aim was simpler. “Above all, it was trying to win,” Osborne told me recently.
In the spring of 2009, Cameron told a gathering of Party members in Gloucestershire, “The age of irresponsibility is giving way to the age of austerity.” The speech was part of a successful campaign to associate Labour’s public spending with the global financial crash, to which Britain had been badly exposed. “The word ‘austerity’ was deliberately introduced into the lexicon by myself and David Cameron,” Osborne said. “Austerity” evoked the country’s sober rebuilding after the Second World War. “The word didn’t have the connotations then that it does now,” Osborne recalled. “It was, you know, a bit like prudence.”
In 2010, the Conservatives fell short of a majority in the House of Commons and formed, with the Liberal Democrats, Britain’s first coalition government in almost seventy years. The state was running a deficit of a hundred and fifty-seven billion pounds—about one and a half times the budget of the National Health Service. Any incoming administration would have had to find ways to balance the books, but, under Cameron and Osborne’s leadership, austerity was a moral as well as an economic mission. “We allowed it to become the defining thing,” the former senior adviser reflected.
“Austerity” is now a contested term. Plenty of Conservatives question whether it really happened. So it is worth being clear: between 2010 and 2019, British public spending fell from about forty-one per cent of G.D.P. to thirty-five per cent. The Office of Budget Responsibility, the equivalent of the American Congressional Budget Office, describes what came to be known as Plan A as “one of the biggest deficit reduction programmes seen in any advanced economy since World War II.” Governments across Europe pursued fiscal consolidation, but the British version was distinct for its emphasis on shrinking the state rather than raising taxes.
Like the choice of the word itself, austerity was politically calculated. Huge areas of public spending—on the N.H.S. and education—were nominally maintained. Pensions and international aid became more generous, to show that British compassion was not dead. But protecting some parts of the state meant sacrificing the rest: the courts, the prisons, police budgets, wildlife departments, rural buses, care for the elderly, youth programs, road maintenance, public health, the diplomatic corps.
Plan A spooked economists because of the risk to economic growth. But, in 2013, the British economy grew by 1.8 per cent. The government claimed victory. Around that time, Osborne declared that the nation could win “the global race” and become the richest major economy in the world by 2030. “We were in complete command of the political landscape,” he recalled. “The U.K. is the country that is seen to have got its act together after the crash. London has become the kind of global capital. So it has worked—there’s a bit of a dénouement coming—but it had worked.” At the general election in 2015, the Conservatives won a majority in the House of Commons, with proposals to make a further thirty-seven billion pounds’ worth of cuts.
“It was devastatingly politically effective,” Osborne told me, of austerity. It’s just that the effects were so horrendous. Between 2010 and 2018, funding for police forces in England fell by up to a quarter. Officers stopped investigating burglaries. Only four per cent now end in prosecution. In 2021, the median time between a rape offense and the completion of a trial reached more than two and a half years. Last fall, hundreds of school buildings had to be closed for emergency repairs, because the country’s school-construction budget had been cut by forty-six per cent between 2009 and 2022.
In October, I talked with Tony Durcan, a retired local-government employee who was responsible for libraries and other cultural programs in the city of Newcastle during the twenty-tens. Durcan told me that he’d had “a good war,” all things considered. There were moments, he said, when the sheer extremity of the crisis was exciting. Between 2010 and 2020, central-government funding for local authorities fell by forty per cent. At one point, it looked as if sixteen of Newcastle’s eighteen libraries would close. The city’s parks budget was cut by ninety-one per cent. The situation forced some creative reforms: Newcastle City Library now hosts the Citizens Advice bureau, where residents can apply for benefits and seek other forms of financial guidance. (The library is featured in “I, Daniel Blake,” Ken Loach’s anti-austerity film of 2016.) But other parts of the city government fell apart. “Youth services and a lot of community-support services, they just disappeared completely,” Durcan said. Child poverty rose sharply. (About forty per cent of children in Newcastle currently live below the poverty line.) But after a while Durcan and his colleagues stopped talking about the cuts, even though their budgets continued to fall. “There was a view—was it helpful? Were you risking losing confidence in the city?”
Over time, Durcan came to question the official reasoning for the savings. “You can make a mistake, even when you’re acting for the best,” he explained. “I don’t think that’s what happened in austerity.” Newcastle was a Labour stronghold, as was the rest of the northeast. Until 2019, the Tories held only three out of twenty-nine parliamentary seats in the region. A similar pattern was repeated across England. Poorer communities, particularly in urban areas, which tended to vote Labour, suffered disproportionately.
In Liverpool, where the Conservatives have not won a Parliamentary seat for forty years, spending, per head, fell more than in any other city in the country. Public-health spending in Blackpool, one of the poorest local authorities in England, was cut almost five times more, per person, than in the affluent county of Surrey, just south of London, whose eleven M.P.s are all Tories. Durcan and his colleagues noted the discrepancies between Labour- and Conservative-supporting regions. “And so there was cynicism,” he said, “and also great disappointment, a sense of injustice.”
Osborne denies that austerity was ever targeted in this way. “It’s not like we ministers just sit there and go, We’re not going to cut Kensington Council. We’re going to cut Liverpool Council. That is a lampoonish way of thinking about British politics,” he said. But some of his colleagues were more willing to acknowledge that electoral thinking was at play. One former Cabinet minister conceded that there were “big strategic moves” to favor older voters, who were more likely to vote Conservative, in the form of pension increases and interventions to raise property prices. David Gauke, a Treasury minister from 2010 to 2017, agreed that the parts of the country that had benefitted most under Labour had seen their budgets cut under the Conservatives. “There was a rebalancing that went on,” he said. “Did it go too far? Maybe it did.”
What was less forgivable, in the end, was the cuts’ unthinking nature, their lack of reason. In the fall of 2013, a staffer named Giles Wilkes, who worked for a senior Liberal Democrat minister in the coalition, became alarmed by projections that showed ever-reducing government budgets. “I don’t wish to paint the picture of the British state as too chaotic and heedless and amateur. But I was wandering around in 2013 and 2014, saying to people, Does anyone know what this means for the Home Office or the court system, for local authorities and the social-care budget?” Wilkes said. “Nobody was curious .” Wilkes is now a fellow at the Institute for Government, a nonpartisan think tank. “It was very obvious in real time,” he told me. “There wasn’t a central function going, Hold on a mo. Have we made sure that we can provide a decent prison estate, a decent sort of police system?”
And so stupid things happened. Since 2010, forty-three per cent of the courts in England and Wales have closed. No one thinks that this was a good idea. For years, the Conservatives cut prison funding and staffing while encouraging longer jail times. “You kind of had a mismatch,” Gauke, who later served as the Justice Secretary, admitted. The number of adults sentenced to more than ten years in prison more than doubled—until the system caved in, overrun by violence, self-harm, drug use, and staff shortages. In 2023, the government activated what it called Operation Safeguard, in which hundreds of jail cells in police stations were requisitioned to hold convicted offenders, because the prisons were full. In September, a terrorism suspect escaped from Wandsworth Prison, in South London, by clinging to the underside of a food-delivery truck. Eighty of the prison’s two hundred and five officers had not shown up for work that day.
The long-term effects of austerity are still playing out. A 2019 paper by Thiemo Fetzer, an economist at the University of Warwick, asked, “Did Austerity Cause Brexit?” Fetzer found that, beginning in 2010, the parts of the country most affected by welfare cuts were more likely to support Nigel Farage’s U.K. Independence Party, which campaigned against immigration and the E.U. The withdrawal of the social safety net in communities already negatively hit by globalization exacerbated the sense of a nation going awry. Public-health experts, including Marmot, argue that a decade of frozen health-care spending undermined the country’s response to the pandemic. More broadly, austerity has contributed to an atmosphere of fatalism, an aversion to thinking about the future. “It is a mood,” Johnna Montgomerie, a professor at the University of British Columbia who studies debt and inequality, has written. “A depression, a chronic case of financial melancholia.”
Since leaving politics, in 2017, Osborne has enjoyed a lucrative career, serving simultaneously as an adviser at BlackRock, the asset-management firm, and as the editor of the Evening Standard newspaper; more recently, he has been a partner at an investment bank and a podcaster. He insists that the cuts, ultimately, enabled the U.K.’s public finances to withstand the pandemic and the energy crisis that followed Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. “There’s no counterfactual,” he told me. Osborne likes to accuse his critics of living in a parallel reality, in which the financial crisis and Britain’s deficit never existed: “It’s, like, Apart from the assassination, Mrs. Lincoln, did you enjoy the play?”
But that does not mean the Tories made good choices. British social-security payments are at their lowest levels, relative to wages, in half a century. Under a steady downward ratchet, started by Osborne and continued by his successors, household payments have been capped and income thresholds effectively lowered. In 2017, a “two child” limit was placed on benefits for poor families. In November, 2018, Philip Alston, the U.N.’s special rapporteur on extreme poverty, toured the U.K. When we spoke, he recalled a strong sense of denial, or ignorance, among British politicians about the consequences of their decisions. “There was a disconnect between the world and what senior ministers wanted to believe,” he said.
The fall in Britain’s living standards isn’t easy for anyone to talk about, least of all Conservatives. The Resolution Foundation, which studies the lives of people with low and middle incomes, is chaired by David Willetts, a former minister in Cameron’s government. Willetts is a tall, genial man, who worked for Margaret Thatcher’s policy unit in the eighties. His nickname in the Party was Two Brains. “What I say to Tories now is, Look, we are behind for various reasons,” Willetts said, carefully. “You can argue about it. But our household incomes are clearly lower than France or Germany or the Netherlands.” Part of the problem, Willetts explained, was that Britain’s richest twenty per cent had largely been spared the effects of the past fourteen years—and that made it genuinely difficult for them to comprehend the damage. “We are all O.K.,” he said. “The burden of adjustment has almost entirely been borne by the less affluent half of the British population.”
In late November, I took a train to Worcester, a cathedral city south of Birmingham, on the River Severn. It was a raw, washed-out morning. Floodwater shone in the meadows. The city is famous as the home of Lea & Perrins Worcestershire sauce—a dark, sweet yet sour, almost indescribably English condiment, first sold by a pair of chemists in 1837—which has been doused on two centuries’ worth of shepherd’s pie and other stodgy lunches. Worcester used to be a den of political corruption: in 1906, men willing to sell their votes to the Tories could collect payment in the rest rooms of the Duke of York, a pub in the middle of town. More recently, it has been a bellwether. In the nineties, Conservative strategists described “Worcester Woman,” a median female voter—politically aware, married, with two children. (Since 1979, the city’s M.P.s have belonged to the party in power.) I was on my way to Citizens Advice Worcester—part of a charitable network that offers free counselling on debt relief and legal matters—behind a restored Victorian hotel.
Shakira was playing on the radio in the reception and a sign read “If You Are Frightened of Your Partner, Call Us.” Geraint Thomas, a Welsh lawyer who runs the center, was in his office, worrying about a heating bill. A few years ago, it was some four thousand pounds a year, but after recent price hikes it was now about fourteen thousand. In 2017, the charity had started running services in Herefordshire as well. Now funding was tight, and various Covid emergency funds were coming to an end. “Next year, we have got a bit of a hole,” Thomas said. The clock on his wall had stopped.
Since 2019, the number of people seeking help at the center had risen by thirty per cent. Two years of high inflation and rising interest rates meant that the caseworkers were now seeing homeowners and people working two jobs, along with the unemployed and families on benefits. “It’s like a black hole, dragging more and more people in,” Colin Stuart, who manages volunteers, said. Anne Limbert, who oversees the advice team, explained that, until a few years ago, it was usually possible to make a recovery plan for clients. “It used to be that we could help people, you know, and make a difference,” she said. “Now it’s just kind of depressing.” Increasingly, Limbert was sending clients to food banks.
The caseworkers said that they had mostly tuned out politics. Gwen Fraser, a volunteer manager in Herefordshire, which has some of England’s most deprived rural communities, had met a visiting M.P. a few months earlier. “I thought, You’re not in the real world, mate,” she said. Not long ago, a seventy-seven-year-old man, behind on his mortgage, had told Fraser that he was suicidal. The proportion of people coming to the center with a long-term health condition had risen by twenty per cent since 2019. (N.H.S. prescriptions for antidepressants in England almost doubled between 2011 and 2023.) Fraser had recently settled on a phrase that she found useful in her paperwork: “Overwhelming distress.”
Worcester Woman voted for Brexit. In 2016, the city chose to leave the European Union by a margin of fifty-four per cent to forty-six per cent. The perception of the Brexit vote as a cry of anguish from deindustrialized northern towns or from faded seaside resorts isn’t wrong—it just leaves out the rest of England. Two weeks after the referendum, Danny Dorling, a geography professor at the University of Oxford, published an article in the British Medical Journal showing that Leave voters weren’t defined neatly either by geography or by income. Fifty-nine per cent identified as middle class, and most lived in the South. “People wouldn’t believe me for years,” Dorling told me. “This was Hampshire voted to leave.”
Dorling’s politics are on the left. He opposed Brexit and often describes Britain as a failing state. During the summer of 2018, Dorling gave dozens of public talks across the country reflecting on the referendum. He noticed that places that had voted Remain invariably had better rail connections than those that voted Leave. A lot of Brexit supporters were older and economically secure but had a keen sense of the country going downhill. “Something was falling apart,” Dorling said. “They had got a house in their twenties. They’d had full employment. Their children were in their forties and they might be renting. . . . It was an almost entirely unselfish vote by the old for their grandchildren—let’s try it, or let’s at least show we’re angry.”
How you interpret the Brexit vote informs, to a great extent, how you make sense of the past fourteen years of British politics. It is not just a watershed—a before and after. It is also a prism that clarifies or scrambles the picture entirely. One perspective sees the whole saga as a woeful mistake. In this view, Cameron decided to settle, once and for all, an internal Tory argument about Britain’s place in an integrating E.U., a question that had haunted the Party since the last days of Thatcher. In the process, he turned what was an abstruse obsession on the right wing of British politics into a much simpler, terrifyingly binary choice for the population on how they felt their life was going.
In the accident theory of Brexit, leaving the E.U. has turned out to be a puncture rather than a catastrophe: a falloff in trade; a return of forgotten bureaucracy with our near neighbors; an exodus of financial jobs from London; a misalignment in the world. “There is a sort of problem for the British state, including Labour as well as all these Tory governments since 2016, which is that they are having to live a lie,” as Osborne, who voted Remain, said. “It’s a bit like tractor-production figures in the Soviet Union. You have to sort of pretend that this thing is working, and everyone in the system knows it isn’t.”
The other view sees Brexit as an unfinished revolution. Regardless of its origins, the vote in 2016 was a repudiation of how Britain had been governed for a generation or more. In the B . M . J . article, Dorling observed that younger voters—who chose overwhelmingly to remain in the E.U.—were angry with their elders. “They will feel newly betrayed . . . but their real betrayal has been a long time in the making,” he wrote. For a highly centralized country that is smaller than Wyoming, the U.K. is lopsided beyond belief. It contains regional inequalities greater than those between the east and the west of Germany, or the north and the south of Italy—inequalities that have been allowed by successive governments to grow to shameful extremes. On average, people in Nottingham earn about a quarter of what people make in Kensington and Chelsea, in West London, which is some two hours away by train.
During the Brexit campaign, the E.U. came to represent not just a supranational monolith across the English Channel but profound distances within the U.K. itself. And the politicians who defended the E.U. looked and sounded, for the most part, as if they spent more time in Tuscany each summer than they had spent on Teesside in their lives. “The kind of globalism, the internationalism, the liberal élite view, was seized on by people who thought that they’d been spoken down to for decades,” John Hayes, a Tory M.P. and a Brexiteer, told me. “And the more they wheeled out the establishment figures, the more it was, Yeah, that’s them. Those are the ones who don’t get it. They don’t understand us.”
Almost eight years after the vote, what stays with me is how unimagined Brexit was. Overnight, and against the will of its leaders, the country abandoned its economic model—as the Anglo-Saxon gateway to the world’s largest trading bloc—and replaced it with nothing at all. “I can’t think of another occasion when a party has so radically changed direction while in office,” Willetts said. Thatcher was an architect of the E.U.’s single market, which in time became a heresy.
You can marvel at the recklessness of Brexiteers such as Farage, or of Johnson, who spearheaded the Vote Leave campaign. (“He is not a Brexiteer,” Osborne said. “I really would go to my grave saying, deep down, Boris Johnson did not want to leave the E.U.”) But the real dereliction ran deeper. Sensible Britain failed. The Civil Service did not plan for Brexit. Ivan Rogers was the U.K.’s permanent representative to the E.U. from 2013 to 2017. He started warning about the likelihood of Brexit about five years before the vote. “It was difficult to get the attention of the system,” he said. Beyond a briefing paper, demanded by the House of Lords, there was only some “confidential thinking,” in the words of Jeremy Heywood, the former head of the Civil Service. (Heywood died in 2018.) “The mandarins have a lot to answer for on this,” Rogers said. “We were very badly prepared in 2016.”
“I didn’t think it was very wise,” Carney, the former governor of the Bank of England, said, of the official refusal to consider the referendum going wrong. “We did a ton of planning.” After the vote, the Bank stabilized the markets while British politics imploded. Cameron resigned and was replaced by Theresa May, a former Home Secretary with limited experience of the economy or of international affairs. In the second half of 2016, May worked with a small group of advisers to formulate a Brexit strategy that ultimately satisfied nobody. “It was incredibly poor statecraft,” a former Cabinet colleague said. “Absolute shit. Abominable.” The abiding image of the Brexit talks was a photo of Michel Barnier, the E.U.’s chief negotiator, with his colleagues and their neat piles of paper on one side of a table, while their British counterparts, led by David Davis, a bluff former special-forces reservist, sat on the other side with a single notebook among them.
One Friday lunchtime, a couple of months ago, I met Dominic Cummings at a pub not far from his house in London. A light snow was in the air. Cummings, who is fifty-two, worked on education policy in the coalition government before becoming the campaign director of Vote Leave. (He coined its notorious slogan, “Take Back Control.”) Cummings is a Savonarola figure in British politics, an ascetic and a technocrat, who wants to save the state by burning it down. He refers to Elon Musk by his first name and writes Substack essays with titles such as “On Complexity, ‘fog and moonlight,’ prediction, and politics VII: why social science is so bad at prediction & what is to be done.”
Cummings reveres the Apollo space program and takes a dim view of almost all Britain’s elected officials. “Where they are not malicious they are moronic,” he told me once. He talks rapidly, with a slight Northern rasp. (He is from Durham, near Newcastle.) Next to our table in the pub, a woodstove emitted a sudden, enveloping cloud of smoke, which dissipated while we talked. Cummings appeared to be wearing two hats, against the cold. He apologized if it seemed as if he were staring at me. He had recently undergone retinal surgery.
Cummings, unsurprisingly, saw Brexit in revolutionary terms—as a chance to break with the country’s ruling orthodoxy. “The Vote Leave campaign was not of the Tory Party,” he said. “It was not a conservative—big ‘C’ or little ‘c’—effort. But none of them wanted to confront the reasons why we did it in the first place. . . . For us, this was an attempt to wrench us off the Cameron, establishment, Blairite line.” Cummings believes that Britain must rediscover its ability to build things—roads, railways, houses, research institutes, products that people want to buy—in order to prosper again. He argues that it is America’s ecosystem of universities, entrepreneurs, and government procurement departments that have helped maintain its economic and technological edge, not just lower taxes or a freer form of capitalism. “When you start talking about this to Tories, they go, Oh, Dominic, you sound like a terrible central planner,” Cummings said. “And you go, That’s America. This is not weird left-wing shit.”
No one would accuse Cummings of having a popular platform. His jam is A.I. and Nietzsche. But, after the Brexit vote, he kept waiting for May’s government to act on what was, to him, its obvious implications: to restrict immigration, reform the state, and explore dramatic economic policies, in order to diverge from the E.U. and to boost the country’s productivity. “I kept thinking, month after month, God, like, it’s weird the way they are just thrashing around and not facing it,” Cummings said. In his view, the election of Trump, that November, provided a perfect excuse for Remainers not to take the Brexit vote seriously. “They just lumped it all in with, Oh, it’s a global tide of populism. It’s mad, irrational, evil. It’s partly funded by Putin,” he said. “They didn’t have to reëvaluate and go, Maybe the establishment in general has been, like, fucking up for twenty-plus years. ”
In July, 2019, May resigned as Prime Minister and was replaced by Johnson, who hired Cummings as a senior adviser. Cummings thought that Johnson would probably screw it up. At the same time, he saw an opportunity to advance what he considered the true Vote Leave agenda. “In some sense,” he said, “the risk was worth taking.”
That fall was the most kinetic, breathtaking period of Britain’s fourteen years of Tory rule. With Cummings at his side, along with Lee Cain, another former Vote Leave official, who became his director of communications, Johnson broke the deadlock that had existed since the referendum. He asked the Queen to prorogue, or suspend, Parliament. He expelled twenty-one Conservative M.P.s—including eight former Cabinet ministers and Nicholas Soames, the grandson of Winston Churchill—for attempting to stop the country from leaving the E.U. with no deal at all.
On a Tuesday in late September, the Supreme Court ruled that Johnson’s suspension of Parliament had been unlawful. “The effect upon the fundamentals of our democracy was extreme,” the Justices found. I stood outside the court in the rain, and it felt as though the thousand-year-old timbers of the state were moving beneath our feet. Someone in the crowd was wearing a prison jumpsuit and an enlarged Johnson head. A woman was dressed as a suffragist. Anna Soubry, a former Tory M.P. who quit the party to fight for a second referendum, shook her head in wonder. “Astonishing,” she said. But Johnson prevailed. Before the year was out, he had cobbled together a new, hard-line Brexit deal and thumped Corbyn at a general election on another three-word Cummings-approved slogan: “Get Brexit Done.”
Johnson was, briefly, unassailable. In the election that December, the Conservatives won seats in places such as Bishop Auckland, in Cummings’s home county of Durham, which they had not held for more than a hundred years. The Party gathered a new, loose coalition of pro-Brexit voters—many of whom were from formerly Labour-voting English towns—to go with its traditionally older, fiscally conservative base. Johnson’s celebrity (the hair, the mess, the faux Churchillian vibes, the ridiculous Latin) was the glue that held it all together. He sensed the public mood. (With Johnson, that was not the same as doing something about it.) He disavowed austerity—promising more money for the N.H.S., new hospitals, and more police—and described a mighty program to redress the country’s economic imbalances, which he called Levelling Up.
Johnson’s premiership collapsed under the pressure of the pandemic and of his own proclivities. According to Cummings, the alignment between the goals of Vote Leave and Johnson’s ambitions as Prime Minister decoupled in January, 2020, just a few weeks after the election. Cummings wanted to overhaul the civil service and Britain’s planning laws. Johnson, for his part, wanted a rest. “He was, like, What the fuck are you talking about? Why would I want to do that?” Cummings recalled. (Johnson did not reply to a request for comment.) “It’s basically cake-ism, right?,” Cummings said, referring to Johnson’s political lodestar: having his cake and eating it, too. “I want to do all the things you want to do, and I want everyone to love me,” Cummings recalled. “I was, like, Yeah, that’s not happening.”
Britain’s first cases of the coronavirus were announced on January 31, 2020, the day the country left the European Union. In March, Johnson ordered the first national lockdown, caught COVID , and later spent three nights in the I.C.U. For months, the country staggered from one set of restrictions to the next—a reflection of Johnson’s inconstant attitude toward the virus. In texts, Cummings used a shopping-cart emoji to indicate the Prime Minister veering from one half-formed idea to the next. Levelling Up became a pork-barrel exercise: of seven hundred and twenty-five million pounds earmarked in June, 2021, about eighty per cent was for Conservative constituencies.
Johnson’s Downing Street was operatically dysfunctional. A rift opened between Cummings and his team and a faction centered on Carrie Symonds, Johnson’s then fiancée, a former Conservative Party communications director. In November, 2020, Cummings accused the Prime Minister of betraying the Vote Leave program and resigned. “I said, Listen, we had a deal. And if you end up breaking our deal there is going to be hell to pay,” Cummings recalled. Cain left as well. A little more than a year later, the Daily Mirror , a left-wing tabloid, broke the news that Johnson and his staff had organized parties while the rest of the country was under lockdown—beginning with the party for Cain’s departure, the previous November. Johnson resigned six months later.
The pandemic bore out truths about the British state. There were bright spots: the vaccines and their rollout by the N.H.S.; the intervention of the Treasury, under Rishi Sunak, the Chancellor, whose furlough plan protected millions of jobs. More generally, though, the virus revealed tired public services, a population in poor health, and a government that was less competent than it thought it was. “It’s very convenient for everyone to blame Boris,” Cummings said. “But the truth is, in January, February, of 2020, it was the civil service saying‚ We’re the best-prepared country in the world. We’re brilliant at pandemics. The reality is, everything was crumbling.”
In October, 2023, Cummings testified at the U.K.’s Covid inquiry, an investigation of the government’s handling of the pandemic led by a retired judge. His written evidence was a hundred and fifteen pages long and began with an epigraph from “War and Peace”: “Nothing was ready for the war which everybody expected.”
The hearings took place in an office building around the corner from Paddington Station. I sat next to a row of bereaved family members, who were holding photographs of their loved ones. Cummings wore a white linen shirt, which came untucked, a tweed jacket with elbow patches, and black boots. He is such a contentious figure—an agent of these disordered times—that people often don’t really listen to what he says. A great deal of the media coverage of Cummings’s testimony focussed on his texting style. In messages during the pandemic, he referred to ministers as “useless fuckpigs,” “morons,” and “cunts.” The inquiry’s lawyer asked Cummings if he thought his language had been too strong. “I would say, if anything, it understated the position,” he replied.
In written testimony, Cummings implored the Covid inquiry to address a wider crisis in Britain’s political class. “Our political parties and the civil service are extremely closed institutions with little place for people who can think and build,” he wrote. Cummings believes that the war in Iraq, the financial crisis, the pandemic, and the invasion of Ukraine all, in their ways, exposed serious shortcomings in the British state that have yet to be addressed.
Brexit, too. When we met, Cummings observed that the country has still failed to confront the full implications of the vote, either domestically or abroad: “You can just treat it as, like, a weird thing, like a witch trial in a medieval village. Now the witch has been burnt, and now the community is getting back to normal. Or you can think of it as part of big structural changes in Western politics, society, and the economy. And if the establishment thinks that you can treat it like a sort of episode of witchcraft mania, then they’re just going to walk straight into recurring shocks.”
I was at Heathrow Airport, refreshing the BBC’s Web site on my phone, when the screen changed to a black-and-white commemorative portrait of the Queen. On February 6, 1952, when Elizabeth’s father, George VI, died, the Prime Minister was Winston Churchill. “We cannot at this moment do more than record a spontaneous expression of our grief,” he told the House of Commons that afternoon. Seventy years later, in September, 2022, Britain was seized again by deference, tenderness, and other, more inchoate, emotions. You could not escape the ritual. Hats, horses, artillery in London’s parks. In her later years, the Queen’s aura of permanence had been enhanced by the recklessness at work in other parts of Britain’s public life. Her survival helped to contain a sense of crisis.
The Queen died on Liz Truss’s second full day in office. When the country’s brand-new Prime Minister and her husband, Hugh O’Leary, arrived at Westminster Abbey for the state funeral, Australian television identified them as “maybe minor royals.” Four days later, Truss launched the Growth Plan 2022, a Thatcher-inspired, forty-five-billion-pound package of tax cuts intended to reignite the British economy. The bond markets didn’t like it. The pound fell to a record low against the dollar. The International Monetary Fund asked Truss to “re-evaluate.” Her approval rating dropped by almost thirty points in a week. Ashen, Truss fired her Chancellor, Kwasi Kwarteng, then left office herself, on October 25th, serving seventy-one days fewer than Britain’s previous shortest-serving Prime Minister, George Canning, who died suddenly of pneumonia in 1827.
It made sense to pretend that Truss and her Growth Plan had been a rogue mission, inflicted on an unsuspecting nation. Truss was depicted as mad, or ideologically unreliable, or both. She had been a Liberal Democrat at Oxford who once opposed the monarchy. She was strangely besotted with mental arithmetic. But the truth is that Truss was neither an outlier nor a secret radical, but a representative spirit of the Conservative Party and its years in power. She was one of the first M.P.s of her intake to be promoted to the Cabinet, brought on by Cameron, before serving both May and Johnson in a hectic and haphazard series of important jobs: running departments for the environment, justice, international trade, and a large part of the Treasury.
In all these positions, Truss was the same: spiky, dynamic, considered skillful on TV. In 2012, she and Kwarteng contributed to “Britannia Unchained,” an ode to tax cutting and deregulation that described the British as “among the worst idlers in the world.” I asked one of Truss’s contemporaries, the former Cabinet minister, if anyone took the ideas seriously at the time. It was hard to catch the attention of the Party’s base under the coalition, he complained. “The easiest way was to show a bit of leg,” he said. “It used to be hanging.” Truss campaigned for Remain before becoming a Brexiteer. As Foreign Secretary, she posed on top of a tank—pure Thatcher cosplay—and dominated the government’s Flickr account, with pictures of herself jogging across the Brooklyn Bridge and standing, ruminatively, in Red Square, in Moscow.

“It’s silliness,” Rory Stewart told me. Stewart became a Conservative M.P. on the same day as Truss, in 2010, after working for the British government in Iraq, running an N.G.O. in Afghanistan, and teaching at Harvard. He was ejected from the Party during the Johnson purge of 2019. Last year, he published “How Not to Be a Politician,” a compulsive, depressing memoir of his career during this period. “It’s clever, silly people. It’s a lack of seriousness,” he said, of Truss and many of his peers.
In 2015, Stewart was sent to work under Truss at Britain’s department for the environment. Truss challenged him to come up with a strategy for England’s national parks in three days. “She said, Come on, Rory, how difficult can this be?” he recalled. Truss started firing off suggestions. “Get young people into nature. Blah blah blah blah.” (The plan was announced on time; Truss declined to speak to me.) “I felt with Liz Truss slight affection but above all profound pity,” Stewart said. “Because she’s approaching these big conversations as though she’s sort of performing as an underprepared undergraduate at a seminar.”
On a cloudless summer’s morning, in the dog days of Theresa May’s government, I travelled to Scunthorpe, in North Lincolnshire. In the sixties, Scunthorpe was a growing steel town with four blast furnaces named after English queens. In 2016, the population voted overwhelmingly for Brexit; three years later, the steelworks was at risk of closure, in part because of trade uncertainties caused by the vote. British Steel, which ran the plant, had been sold to private-equity investors for a pound. Four thousand jobs were on the line.
In the afternoon, I sat down with Simon Green, the deputy chief executive of the local council. Green was in his early fifties, angular and forthright. He grew up in Grimsby, a fishing town on the coast, and spent his career in local government—in Boston and New York, as well as in Nottingham and Sheffield—before taking the job in North Lincolnshire, in 2017. Green was sick of reporters, like me, coming up to Scunthorpe from London for the day, to gawk at its predicament and wonder why people could have believed that Brexit would improve their situation. “No disrespect, but we do get a level of poverty porn,” he said. “A lot of doom and gloom.”
Green assured me that the Brexit-related anxiety around the steelworks was a blip. “We’re actually on a bit of a comeback roll,” he said. He was excited about the region’s potential for green technology and the construction of HS2, a new Y-shaped high-speed railway that was going to transform connections between London and cities in the northeast and the northwest. “Rail track, ballast, concrete, cement—you name anything to do with trains, infrastructure, it’s an engineering, Midlands, Northern thing,” he said. Green ascribed the Brexit vote in Scunthorpe to “values and culture” rather than to economics—a sense of dislocation and of feeling disdained by politicians in London.
Recently, I wondered how Green was getting on. In 2019, Scunthorpe was part of the “Red Wall” of Labour constituencies that flipped for the Tories. British Steel had changed hands once more. Now Chinese investors were planning to install new furnaces, which required fewer workers and were fed with scrap metal. For the first time since 1890, the plant would no longer produce virgin steel from ore. I met Green a couple of weeks before Christmas. He had left his job a few days before. He seemed relieved to be done. Seven local authorities in England have gone bust since 2020, including the one serving Birmingham, Britain’s second-largest city. In North Lincolnshire, the council now spends about three-quarters of its budget on services for vulnerable children and adults—roughly double the proportion of a decade ago. “We’re still here,” Green said, ruefully. The saga of the steelworks continued. “It’s endless,” he went on. “Is it closing? Isn’t it closing?” Britain has had eleven different economic programs in the past thirteen years.
We were in a teaching room at the University Campus North Lincolnshire, which opened a few years ago in the former local-authority offices. The old council chamber, built in the shape of a blast furnace, was now a lecture hall. The average student age was twenty-nine. Green was proud of the project. It reminded him of mechanics’ institutes in the nineteenth century. “People are using their own judgment to better themselves,” he said. “If you want a job in this area, you can get a job. We need more quality opportunity.” Green had had a clear strategy for Scunthorpe and the nearby Humber estuary, built around green technology and education. “I asked a question to my colleagues and politicians as well,” he said. “What sort of town do you want this to be in ten, fifteen, twenty years?”
Britain has no equivalent strategy for itself. In September, Sunak weakened several of the country’s key climate-change targets. A few weeks later, he cancelled what was left of HS2, the new rail network. Only the stem of the Y will now be built, from London to Birmingham, at a cost of some four hundred and seventy million pounds per mile , with little or no benefit to the North. “I can get quite excited, agitated by that,” Green said. “It makes us look a laughingstock.” Green was studiously apolitical when we talked. I had no sense of which way he voted. But he despaired of the shallowness and contingency now at the heart of British politics, and the lack of narrative coherence—or shared purpose—about what these years of struggle had been intended to achieve. I asked if he ever worried that the country was in a permanent state of decline. “I think, at the moment, we are at the crossroads,” he replied.
When will it end? Sunak says that he will call a general election in the second half of the year. The gossip in Westminster says that probably that means mid-November: a British encore, to follow the main event in the U.S. But it could come as soon as May. The Prime Minister began preparing the ground last fall, after his first year in office, by presenting himself as a change candidate—a big claim, considering the circumstances.
In October, I went to Manchester to watch Sunak address the Conservative Party’s annual conference. He was introduced onstage by his wife, Akshata Murty, the daughter of N. R. Narayana Murthy, a founder of Infosys, the Indian I.T. conglomerate. (According to the London Sunday Times , Sunak and Murty have an estimated net worth of about five hundred million pounds.) Murty wore an orange pants suit, and she addressed Britain’s most successful political organization as if it were a local gardening society. “Please know that Rishi is working hard,” she said. “He shares your values and he knows how much you care about the future of the U.K.”
Sunak has a quietly imploring tone. British politics was in a bad way, he explained. People were fed up. “It isn’t anger,” Sunak said. “It’s an exhaustion with politics, in particular politicians saying things and then nothing ever changing.” Sunak dated the rot back thirty years without explaining why, but, presumably, to indicate the fall of Thatcher. (Thatcher was everywhere in Manchester; she is the modern Party’s only ghost.) Having positioned himself as the country’s next, truly transformative, leader, Sunak offered his party a weirdly pallid program: the dismantling of HS2, plus two long-range, complex policies, to abolish smoking and to reform the A-levels—England’s standard end-of-school exams. “We will be bold. We will be radical,” Sunak promised. “We will face resistance and we will meet it.”
Increasingly, Sunak has been pulled between the Party’s diverging instincts: to retreat to the dry, liberal competence of the Cameron-Osborne regime or to head off in a more explicitly protectionist, anti-immigrant, anti-woke direction. In Manchester, the energy was unmistakably on the Party’s right. Suella Braverman, then the Home Secretary, magnetized delegates with a speech warning of a “hurricane” of mass migration. Truss staged a growth rally, and Nigel Farage cruised the conference hall, posing for selfies. (There is talk of Farage standing as a Conservative M.P.) Back in London, I had lunch with David Frost, an influential Conservative peer. “Rishi, I feel for him, in a way,” Frost said. “He’s just trying to keep the show on the road and not upset all these different wings of the Party. But the consequence of that is you end up with a sort of agenda which is not politically meaningful at all.”
On January 14th, a poll of fourteen thousand people, which Frost facilitated, suggested that the Party is on course for a huge defeat later this year. The question is what kind of haunted political realm it will leave behind. Under Starmer, Labour has been tactical in the extreme, exorcising Corbyn’s left-wing policies (Corbyn has been blocked from standing for the Party at the election), while making vague noises about everything else. It has nothing new to say about Brexit and equivocates about its own tax and spending plans, if it wins power. The Party recently scaled back a plan to invest twenty-eight billion pounds a year in green projects. There is no rescue on the way for Britain’s welfare state.
Osborne noted all this with satisfaction. “The underlying economic arguments have basically been accepted,” he said, of austerity. “It’s rather like the Thatcher period. Everyone complained that Thatcher did deindustrialization, and yet no one wants to unpick it.” By contrast, Cummings sees the two cautious, hedging leaders in charge of Britain’s main political parties—and the relief among some centrists that the candidates are not so different from each other—in rather darker terms. “They are deluded when they think it’s great that Sunak and Starmer are in. It’s just like they’re arguing over trivia,” he said. “The politics of it are insane.”
I am afraid that I agree. It is unnerving to be heading into an election year in Britain with the political conversation so small, next to questions that can feel immeasurable. I put this to Hayes, the Tory M.P., when I went to see him in the House of Commons. “You’re arguing we have very vanilla-flavor politics, in a richly colored world. There’s something in that,” he said. Then he surprised me. “I think the key thing for the Conservatives now is to be more conservative,” he said. We were sitting in a bay window, overlooking the Thames. A waiter poured tea. Hayes seemed to relish the coming election. It was as if, after almost fourteen years of tortuous experiment, real conservatism might finally be at hand. “Outside metropolitan Britain and the university towns, it’s all up for grabs,” Hayes assured me. “Toryism must have its day again.” ♦
New Yorker Favorites
Searching for the cause of a catastrophic plane crash .
The man who spent forty-two years at the Beverly Hills Hotel pool .
Gloria Steinem’s life on the feminist frontier .
Where the Amish go on vacation .
How Colonel Sanders built his Kentucky-fried fortune .
What does procrastination tell us about ourselves ?
Fiction by Patricia Highsmith: “The Trouble with Mrs. Blynn, the Trouble with the World”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .

By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Gideon Lewis-Kraus

By Adam Gopnik

By Joshua Yaffa

By Alex Ross
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

- IMF at a Glance
- Surveillance
- Capacity Development
- IMF Factsheets List
- IMF Members
- IMF Timeline
- Senior Officials
- Job Opportunities
- Archives of the IMF
- Climate Change
- Fiscal Policies
- Income Inequality
Flagship Publications
Other publications.
- World Economic Outlook
- Global Financial Stability Report
- Fiscal Monitor
- External Sector Report
- Staff Discussion Notes
- Working Papers
- IMF Research Perspectives
- Economic Review
- Global Housing Watch
- Commodity Prices
- Commodities Data Portal
- IMF Researchers
- Annual Research Conference
- Other IMF Events
IMF reports and publications by country
Regional offices.
- IMF Resident Representative Offices
- IMF Regional Reports
- IMF and Europe
- IMF Members' Quotas and Voting Power, and Board of Governors
- IMF Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific
- IMF Capacity Development Office in Thailand (CDOT)
- IMF Regional Office in Central America, Panama, and the Dominican Republic
- Eastern Caribbean Currency Union (ECCU)
- IMF Europe Office in Paris and Brussels
- IMF Office in the Pacific Islands
- How We Work
- IMF Training
- Digital Training Catalog
- Online Learning
- Our Partners
- Country Stories
- Technical Assistance Reports
- High-Level Summary Technical Assistance Reports
- Strategy and Policies
For Journalists
- Country Focus
- Chart of the Week
- Communiqués
- Mission Concluding Statements
- Press Releases
- Statements at Donor Meetings
- Transcripts
- Views & Commentaries
- Article IV Consultations
- Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP)
- Seminars, Conferences, & Other Events
- E-mail Notification
Press Center
The IMF Press Center is a password-protected site for working journalists.
- Login or Register
- Information of interest
- About the IMF
- Conferences
- Press briefings
- Special Features
- Middle East and Central Asia
- Economic Outlook
- Annual and spring meetings
- Most Recent
- Most Popular
- IMF Finances
- Additional Data Sources
- World Economic Outlook Databases
- Climate Change Indicators Dashboard
- IMF eLibrary-Data
- International Financial Statistics
- G20 Data Gaps Initiative
- Public Sector Debt Statistics Online Centralized Database
- Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Financial Access Survey
- Government Finance Statistics
- Publications Advanced Search
- IMF eLibrary
- IMF Bookstore
- Publications Newsletter
- Essential Reading Guides
- Regional Economic Reports
- Country Reports
- Departmental Papers
- Policy Papers
- Selected Issues Papers
- All Staff Notes Series
- Analytical Notes
- Fintech Notes
- How-To Notes
Staff Climate Notes
Key challenges faced by fossil fuel exporters during the energy transition.
Author/Editor:
Diego Mesa Puyo ; Augustus J Panton ; Tarun Sridhar ; Martin Stuermer ; Christoph Ungerer ; Alice Tianbo Zhang
Publication Date:
March 27, 2024
Electronic Access:
Free Download . Use the free Adobe Acrobat Reader to view this PDF file
The global energy transition is affecting fossil fuel exporters from multiple angles. It is adding to longstanding uncertainties on relative movements of fossil fuel demand and supply—which impact fossil fuel-related exports, fiscal flows, investment and subsequently external and fiscal accounts, economic growth, and employment. While policymakers are very familiar with these challenges, they now also face expectations of a permanent decline in the long-run global demand for fossil fuels. Key factors that could determine country-level impacts include (i) the type of fossil fuel a country exports (ii) extraction costs and (iii) country characteristics. The monitoring and mitigation of fiscal risks will need to be stepped up. Fiscal policy also has a role in reducing domestic emissions, encouraging adoption of low-carbon technologies, and helping those most vulnerable to changes from the transition. Broader macroeconomic risks can be reduced by accelerating ongoing structural reforms that support alternative engines of growth. Low- or zero-carbon emission energy industries could offer new avenues that build on existing fossil fuel knowledge and infrastructure. Concurrently, improved financial regulation and supervision could reduce financial sector exposures. Finally, international coordination on the design and implementation of climate policy as well as international transfer schemes (financing and capacity development) could reduce uncertainties surrounding the transition path and associated adverse economic consequences.
Staff Climate Note No 2024/001
Commodities Economic sectors Environment Exports Financial crises International trade Non-renewable resources Oil Renewable energy
9798400270147/2789-0600
CLNEA2024001
Please address any questions about this title to [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you can, make sure it's always addressed to an actual person. Remember that, with a greeting, we have to capitalize every word in the line. So, you can write, Hello [Name], Hi [Name], We don't insert a comma between "Hello" and the name, even though we do in all other cases ("Hello, Danny!").
If you know the person well and it's an informal email, you can just say "Hey [First Name].". You can also use "Hi [First Name]" or "Hello [First Name]," to be a little less casual. If you don't know the name of the person (like if you're writing to customer service), you can use "To Whom It May Concern.".
Email writing is an art and doing it well takes know-how and practice. But you don't have to make all the mistakes for yourself in order to write professional emails.. We assembled for you the essential tips for creating highly effective formal emails with a deep dive into formal email formats, structure, and best practices. We also gathered some real-life examples and templates you can use ...
How to write emails in English. To get your started we will unbundle the English email format covering email greetings, body, email closing phrases and signature.. English email format. English language emails are what academics describe as a "highly prescriptive form of written communication." Simply put, there are strong and established rules dictating the format of English language emails.
For more informal and formal language to use in the exam, take a look at our Oxford Test of English Writing Tips. 5. Closing. Before signing off at the end of your email, it's a good idea to finish with a closing statement. In a formal email this might be requesting some form of action.
4. Main body. If your email is a quick internal email to a colleague it should be quite brief. However, if you're writing for an exam, the acronym RED is recommended; (Reasons, Examples, Details) to help bulk out your answers.The main body of your email should also have a clear and specific purpose.
Dear Mr/Mrs/Ms (surname of the recipient, e.g. Mr Black) Dear Sir/Madam (if you don't know the name of the recipient) or more generally 'To whom it may concern'. After the initial greeting you need an introductory sentence that indicates clearly the reason for writing and is consistent with the subject of the email.
4. Hi. Write the missing word from this formal email greeting. If you're writing a professional email to someone you know well, who is not senior to you, you can start by writing just their name and then a comma. True. False. Write one contraction in the gap, to complete this common opening line from an email.
2. Click on "Compose" or "New." Before you can write an email, you will need to open a new, blank message box to write your email in. The exact method varies depending on the service you use, but there will usually be a button toward the top of the page with a label like "Compose," "New," or "New Message.".
In this section, follow our series of lessons for pre-intermediate (CEFR level A2) or intermediate (CEFR level B1) learners and improve your email writing skills in English. You will learn useful language and techniques for writing, organising and checking emails. Each unit has interactive exercises to help you understand and use the language.
Do you want to improve your writing skills and communicate better with your friends? In this lesson, you will learn how to write an informal email to a friend, using appropriate language, tone and format. You will also see some examples of informal emails and practice your own writing. Join the LearnEnglish - British Council community and start writing today!
Here are 10 etiquette tips to follow when writing an email in English: Keep subject lines to 5 or 7 words (or risk being ignored or unread!) Use a greeting suitable for 2023 (Hi), not 1823 (Dear Sir/Madam). Learn what are some common opening sentences for an English email. Start every email with a (virtual) smile, express gratitude and ...
When emailing a professor, be very concise and use bullet points when possible to make your point clear. When closing your email, use a formal salutation like "Best Regards". Example. Dear Professor Smith, Unfortunately, due to sickness, I would like to request an extension to the deadline of our current project.
General Tips for Writing Emails in English 1. Be sure an email is necessary. ... Write your email just like you would in an essay. Similar to an essay, you have to introduce the topic, explain the different points, and then conclude the topic. You may also see summary writings. 4. Don't write emails when you're angry.
Worksheets and downloads. A more formal email - exercises 460.02 KB. A more formal email - answers 138.35 KB. A more formal email - email 533.13 KB. A more formal email - writing practice 373.17 KB.
Informal Email Writing Format Samples. Email Expressing Your Appreciation. Email about Your Trip. Formal Email Writing Format Samples. Email on Seeking Information about Course Details. Email on Introducing a New Employee to Your Team. Email on Official Intimation of Your Resignation. Email Informing Your Employees about the Change in Work Timings.
4. I hope you …. Simply wishing the recipient well is a good way to start an email in a friendly way. Rather than the generic " Hope you're doing well " or the slightly stiff " I hope this email finds you well ," try a more specific phrasing to emphasize the sincerity of your wishes. Examples: Wishing them well.
Article navigation: B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter: Writing Topics B2 First (FCE) Email/Letter: Writing Topics (PDF) A Email/Letter is usually written for an English-language magazine, newspaper or website.The main purpose is to describe and express a personal opinion about something which the writer has experienced (e.g. a film, a holiday, a product, a website etc.) and to give the reader a ...
School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Writing (2013230) Write an email based on technology. Other contents: Writing an email.
5 Email Essay Spm example - Informal Email. Informal emails are suitable for communicating with acquaintances, friends, or colleagues you share a close relationship with, allowing you to express yourself more freely and naturally compared to formal or business communication. However, it's essential to be mindful of the context and the ...
World Health Day 2024 is 'My health, my right'. This year's theme was chosen to champion the right of everyone, everywhere to have access to quality health services, education, and information, as well as safe drinking water, clean air, good nutrition, quality housing, decent working and environmental conditions, and freedom from discrimination.
The Conservative-run Britain of the eighties was not harmonious. Life beyond the North London square where my family lived often seemed to be in the grip of one confrontation or another. The news ...
The global energy transition is affecting fossil fuel exporters from multiple angles. It is adding to longstanding uncertainties on relative movements of fossil fuel demand and supply—which impact fossil fuel-related exports, fiscal flows, investment and subsequently external and fiscal accounts, economic growth, and employment. While policymakers are very familiar with these challenges ...